Rubber tree colletotrichum drug-resistant strain HcgHNQZ1736 and application thereof in drug resistance research
A technology of anthrax bacteria and drug resistance, applied in the direction of application, fungicides, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of increasing difficulty in anthrax control, limiting rubber anthrax bacteria compound species, and polluting the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
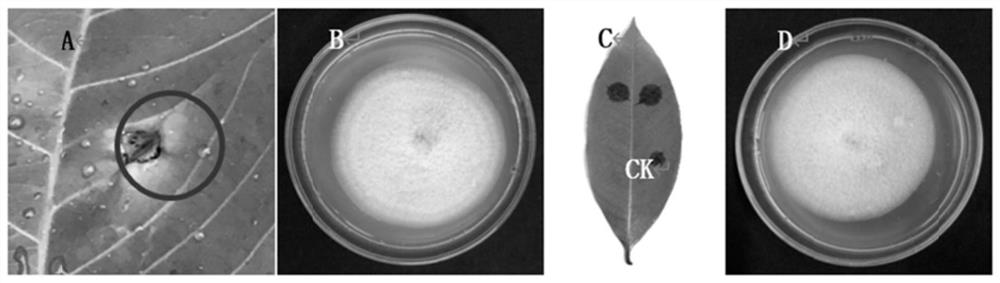
[0053] Example 1 Rubber tree anthracnose sample collection, separation, purification and preservation
[0054] From 2017 to 2018, disease samples were collected from the main rubber planting areas in Hainan Province. The collected disease samples were separated and purified indoors for pathogenic bacteria. The method is as follows: wash the collected diseased leaves with clean water and dry the surface water with filter paper. Use 75% ethanol to disinfect the leaf surface again; use sterilized scissors to cut about 3 × 3mm leaf tissue at the junction of disease and health, use 70% ethanol for 30 seconds in the workbench, and 0.1% mercuric chloride for 2 minutes. Bacterial water was treated for 3 times; dry the water with sterilized filter paper and inoculate it on a PDA plate, cultivate it in a 28°C incubator for 5 days, and then use a sterilized inoculation needle to pick a single mycelia and inoculate it on a new PDA plate above to purify the strain. Koch's law was used to ...
Embodiment 2
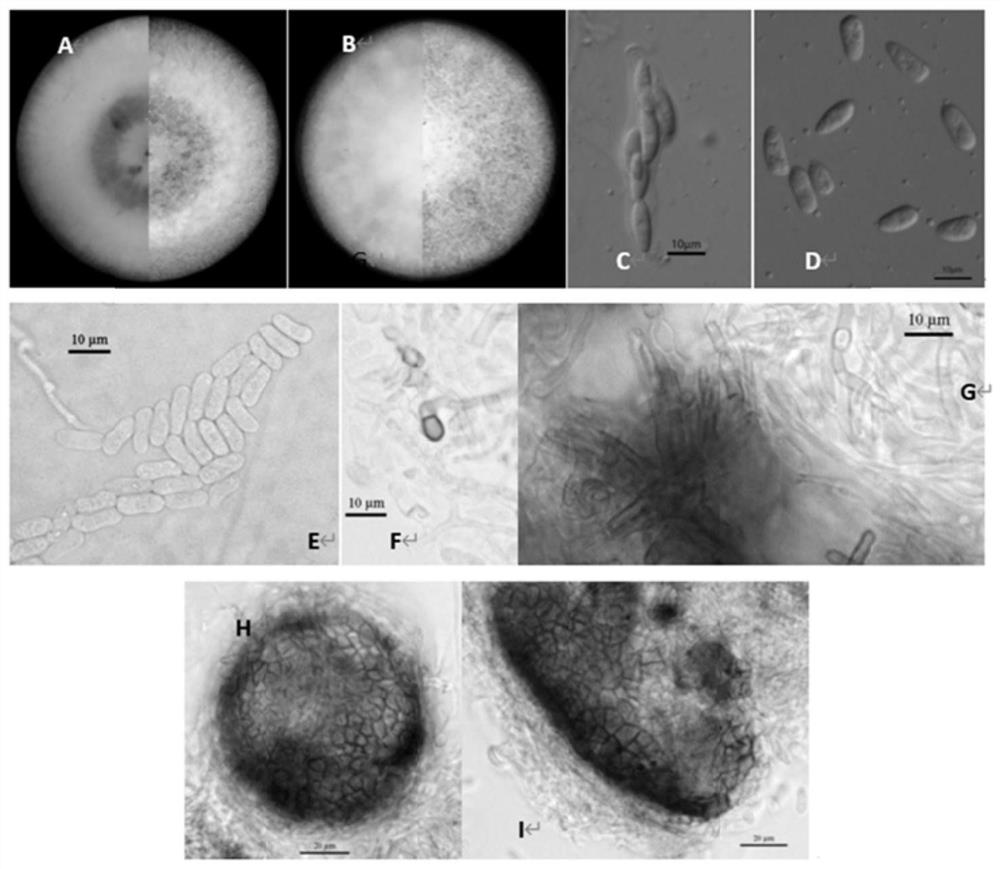
[0056] Embodiment 2 morphology observation
[0057] After the test strain was cultured on the PDA plate for 7 days, observe the colony morphology, promote the sporulation of the strain through AEA medium and SNA medium, observe the microscopic morphology of conidia, conidiophores and appresses under a microscope, and record the size; Refer to "Fungal Taxonomy" by Shao Liping, "General Phytopathology" by Xu Zhigang, etc., "Handbook of Fungal Identification" by Wei Jingchao, etc., and "Plant Pathogenic Mycology" by Zhang Zhongyi, etc. to carry out preliminary morphological classification and identification of strains .
[0058] The results of cultivation and observation of bacterial strains HcgHNQZ1736 and MeCkYN1705 showed that ( figure 2 ): The aerial hyphae on the PDA medium is felt-like, the mycelium is flat, the edges are neat, and the shape is round. The growth rate of the colony in the 28°C incubator is about 10.5±1.5mm / d. It is milky white to milky yellow, and the bac...
Embodiment 4
[0085] Example 4 Determination of basic biological characteristics
[0086] (1) Determination of suitable temperature for growth
[0087] The tested strains were inoculated on PDA plates, and cultured in the dark at 10°C, 15°C, 20°C, 25°C, 28°C, 30°C, 32°C and 35°C for 5 days, and the experiment was repeated three times. Measure and record the diameter of colony growth by cross method, and determine the suitable temperature range for the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
[0088] Table 4 below, Figure 5 and Figure 6 As shown, the growth temperature range of the tested strains HcgHNQZ1736 and MeCkYN1705 is 15-32°C; 28°C is the optimum growth temperature range of the colonies, and the colony growth rate is the fastest, about 11.7mm / d; when the temperature reaches below 10°C and 35°C Above, the colony stops growing completely.
[0089] Table 4 Mycelium growth in different temperature environments
[0090]
[0091] Note: The letters after the values in the table are the r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com