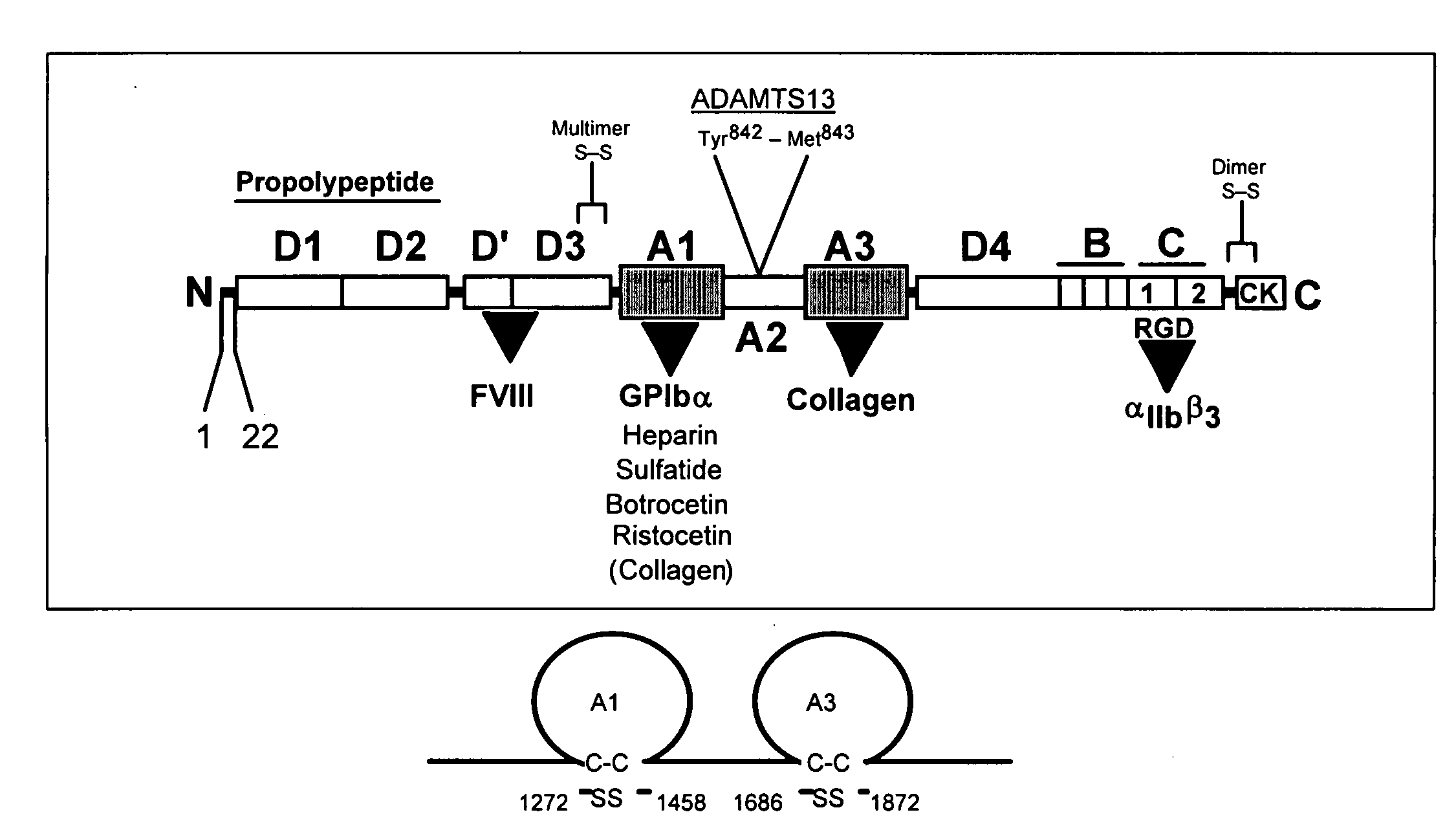
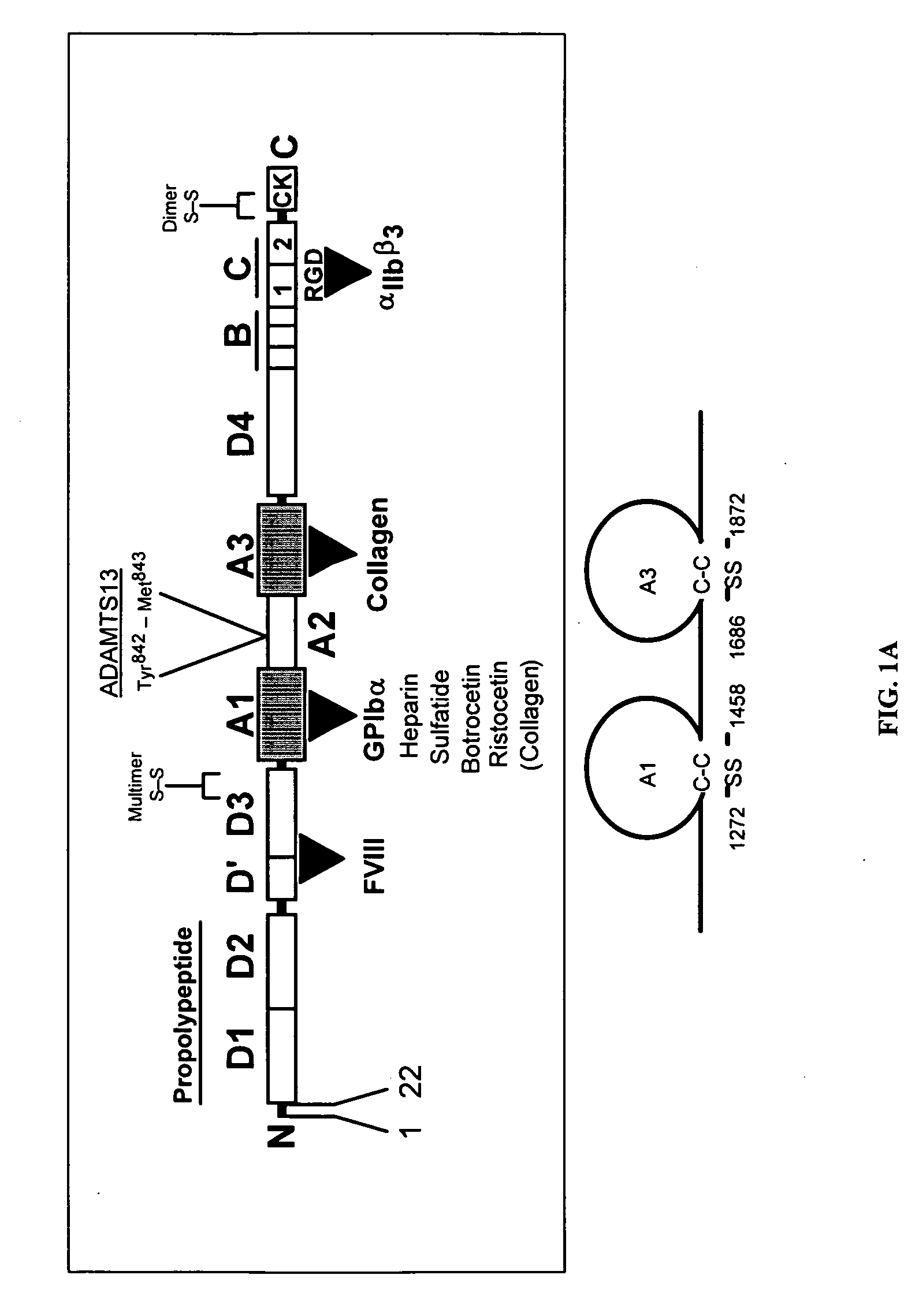
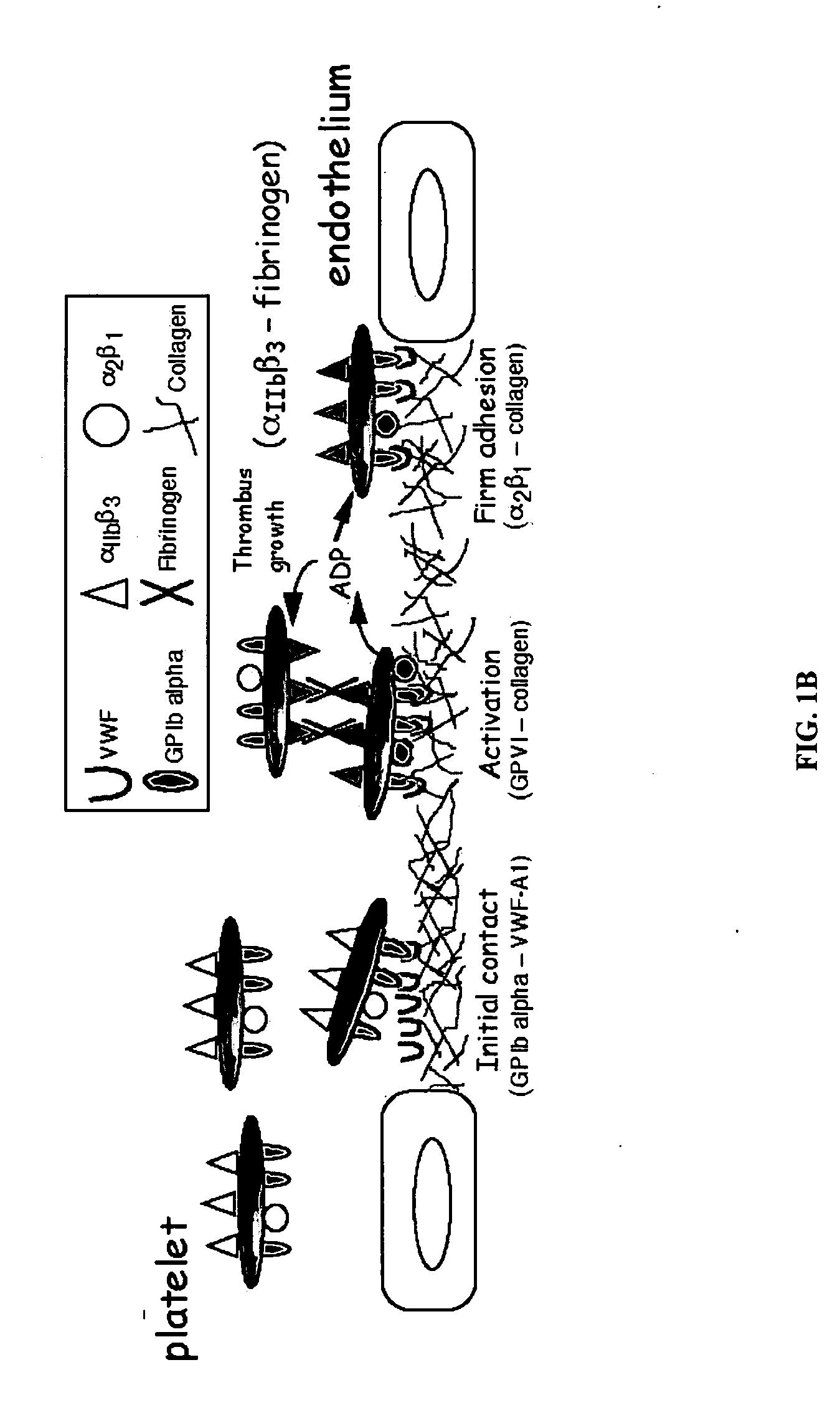
Methods for testing Anti-thrombotic agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
VWF Characterization
[0206]VWF Microsphere Studies
[0207]The association and dissociation kinetics of the GPIb alpha-VWF-A1 bond and the impact of fluid shear and particle size on these parameters can be determined by measuring the frequency and duration of transient adhesive events, known as transient tethers, that represent the smallest unit of interaction observable in a parallel-platelet flow chamber.
[0208]Production of recombinant VWF-A1 protein and coating of microspheres. The generation of recombinant VWF-A1 protein (residues 1238 to 1472 of the mature, recombinant VWF) and its subsequent coupling to microspheres is performed as previously described (Doggett, T. A. et al. (2002) Biophys. J. 83, 194-205). Proper size, purity, and disulfide bonding of all proteins is assessed by Coomasie-blue staining of SDS-PAGE gels run under reducing and non-reducing conditions. Mass spectrometry is also employed to evaluate size and disulfide bonding pattern.
[0209]The resulting recombinant pr...
example 2
VWF-A1 Mutagenesis
[0230]Preliminary results indicate that minor differences may exist between murine and human VWF that would preclude one from studying human platelet behavior in a mouse model of thrombosis. However, our findings that the estimated off-rate values and structure of these domains are similar suggest that one can investigate the role of the biophysical properties of the GPIb alpha-VWF-A1 bond in regulating platelet-VWF interactions in vivo using a mouse model. However, neither a delineation of the binding region for GPIb alpha within the murine VWF-A1 domain nor determination of the impact of mutations on the kinetics of this interaction has been performed to date. Thus, both murine and human A1 crystal structures can be exploited to 1) identify candidate residues involved in the binding site for murine GPIb alpha and to determine their impact on the kinetic properties of this receptor-ligand pair, 2) identify residues that confer species specificity, and 3) ascertain...
example 3
Genetically Modified VWF-A1 Mice
[0251]Recent kinetic evaluation of mutations associated with type 2B and platelet-type vWD suggests that the intrinsic properties of the GPIb alpha-VWF-A1 tether bond contribute to the regulation of platelet interactions with VWF. This is also supported by our preliminary studies investigating the impact of botrocetin on the biophysical properties of this receptor-ligand pair. Thus, by using the information obtained in Example 2, mutations can be incorporated into the murine A1 domain of the VWF gene that increase or decrease the intrinsic on- and off-rates by varying degrees in order to truly understand the importance of these kinetic parameters in controlling platelet adhesion. Moreover, the role of the minor binding site, where the majority of type 2B mutations have been identified, can be further delineated by combining such mutations with those that significantly shorten the lifetime of interaction between GPIb alpha and VWF-A1. Results indicate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com