Patents
Literature
41 results about "Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
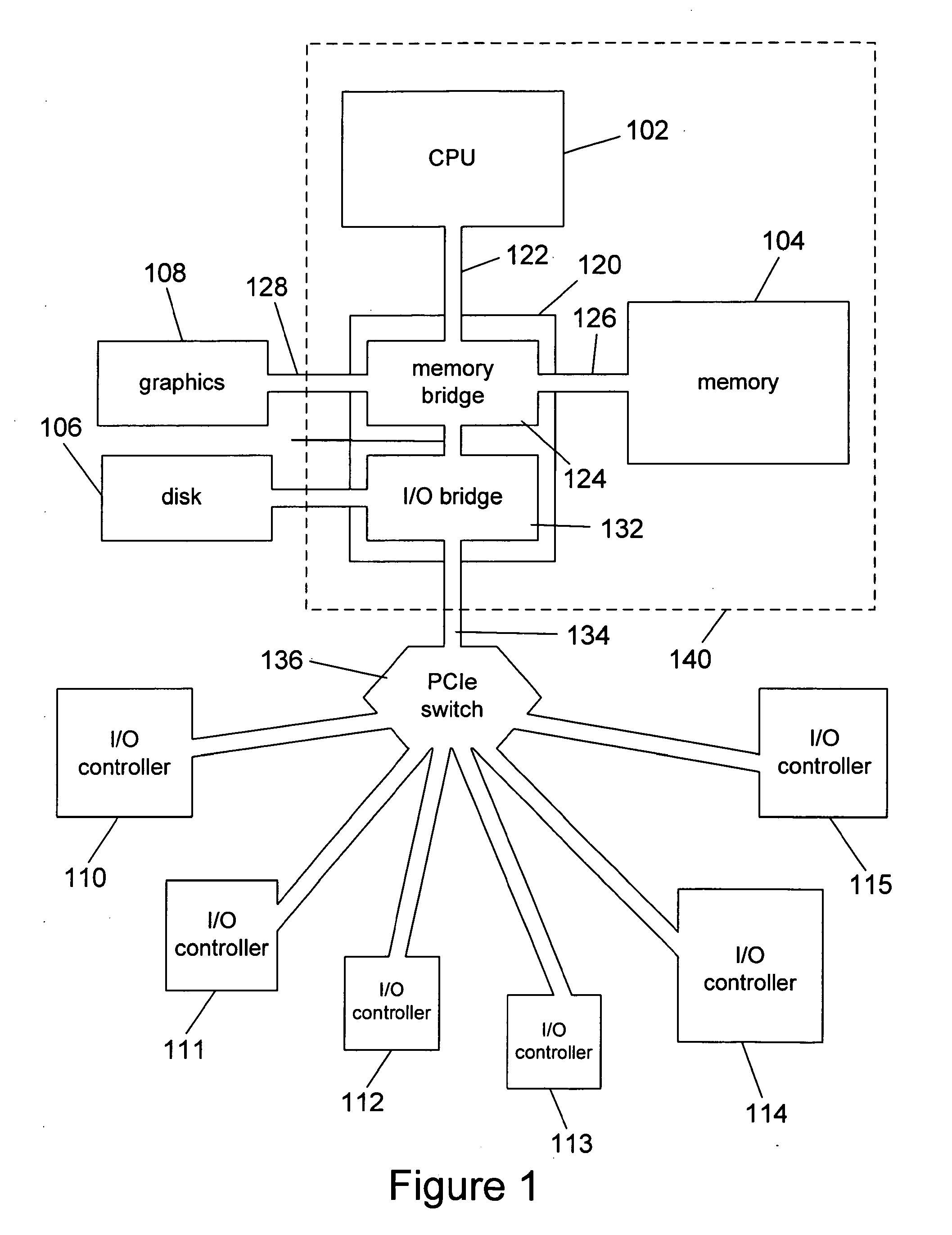
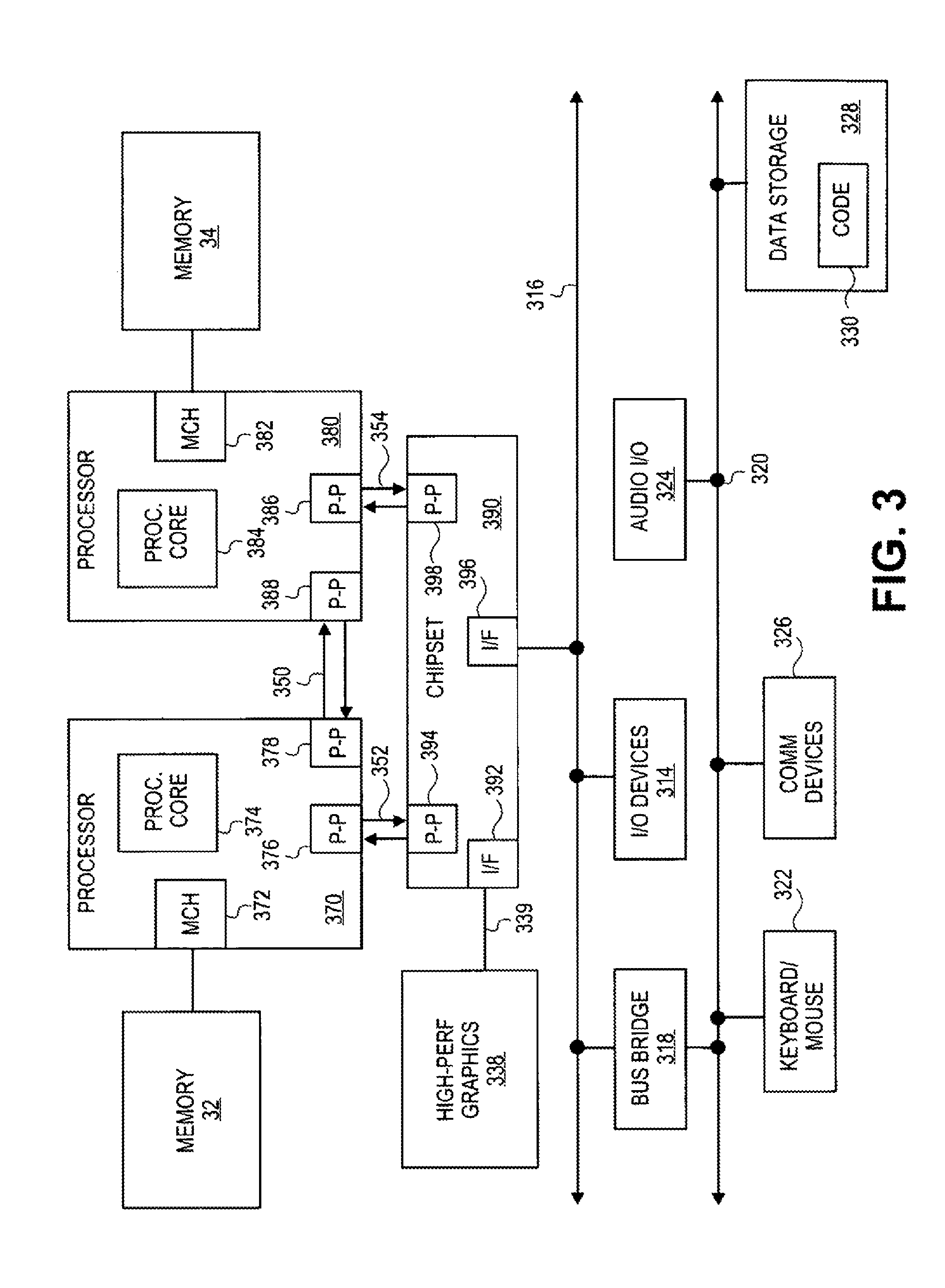
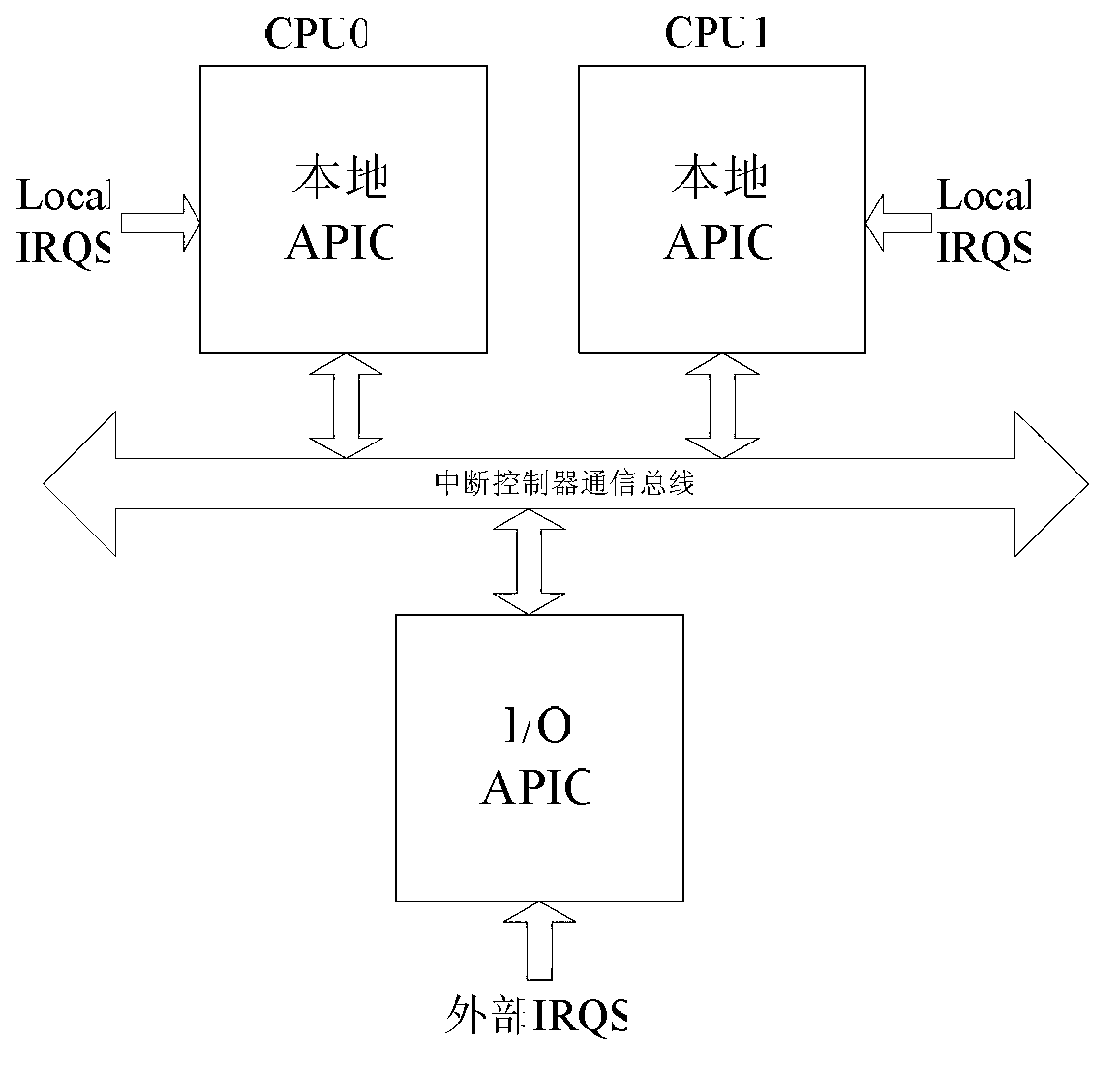
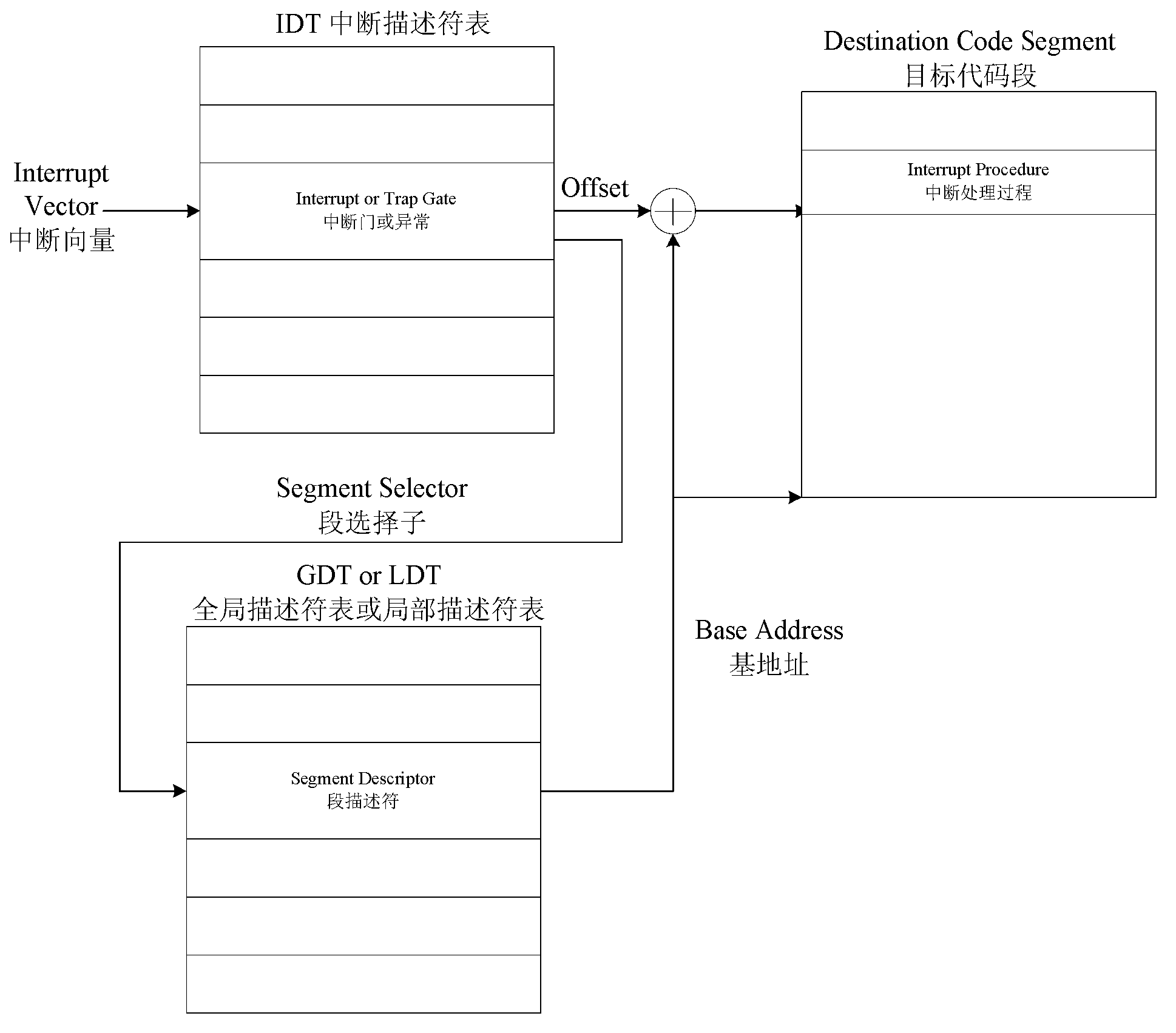
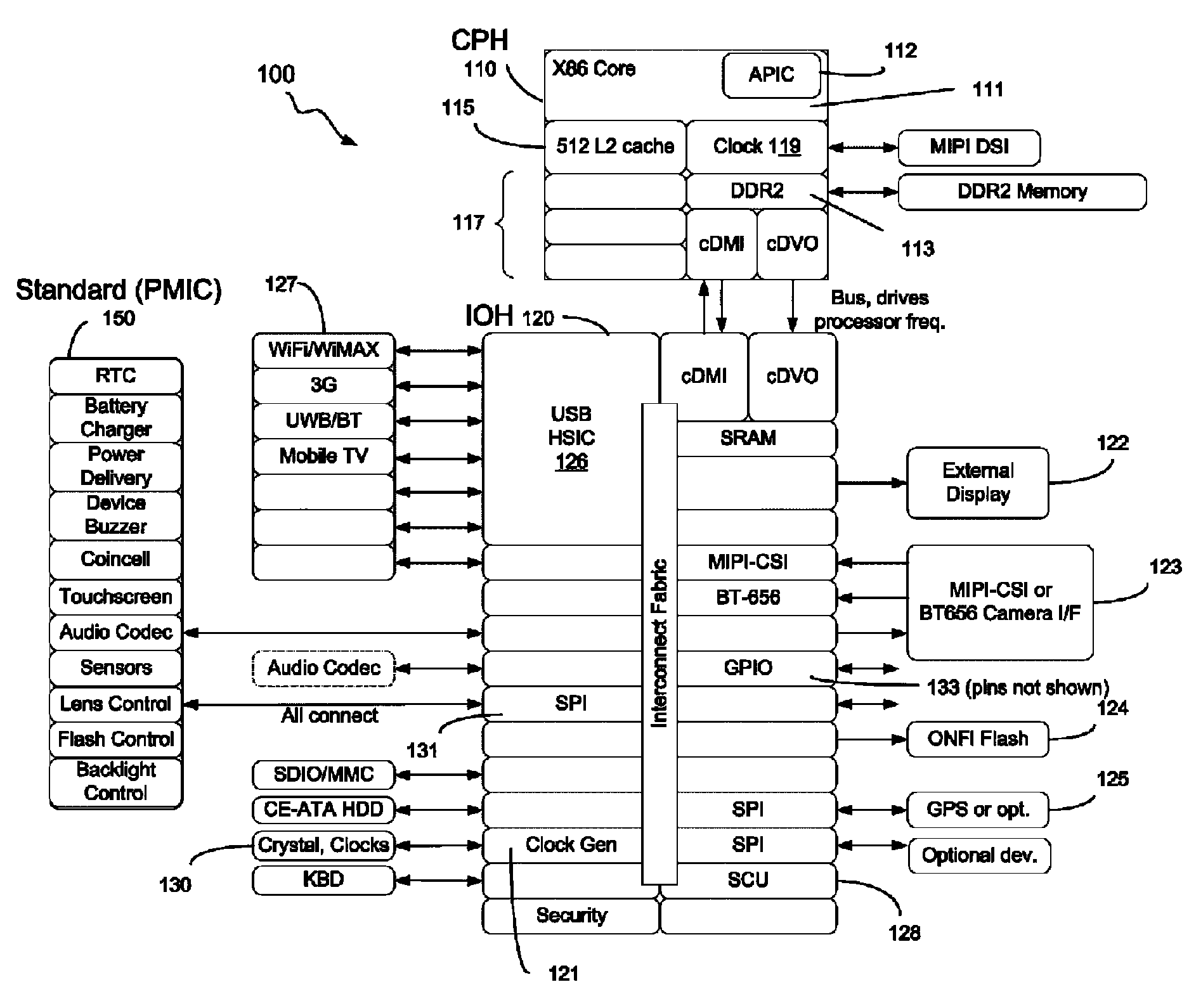
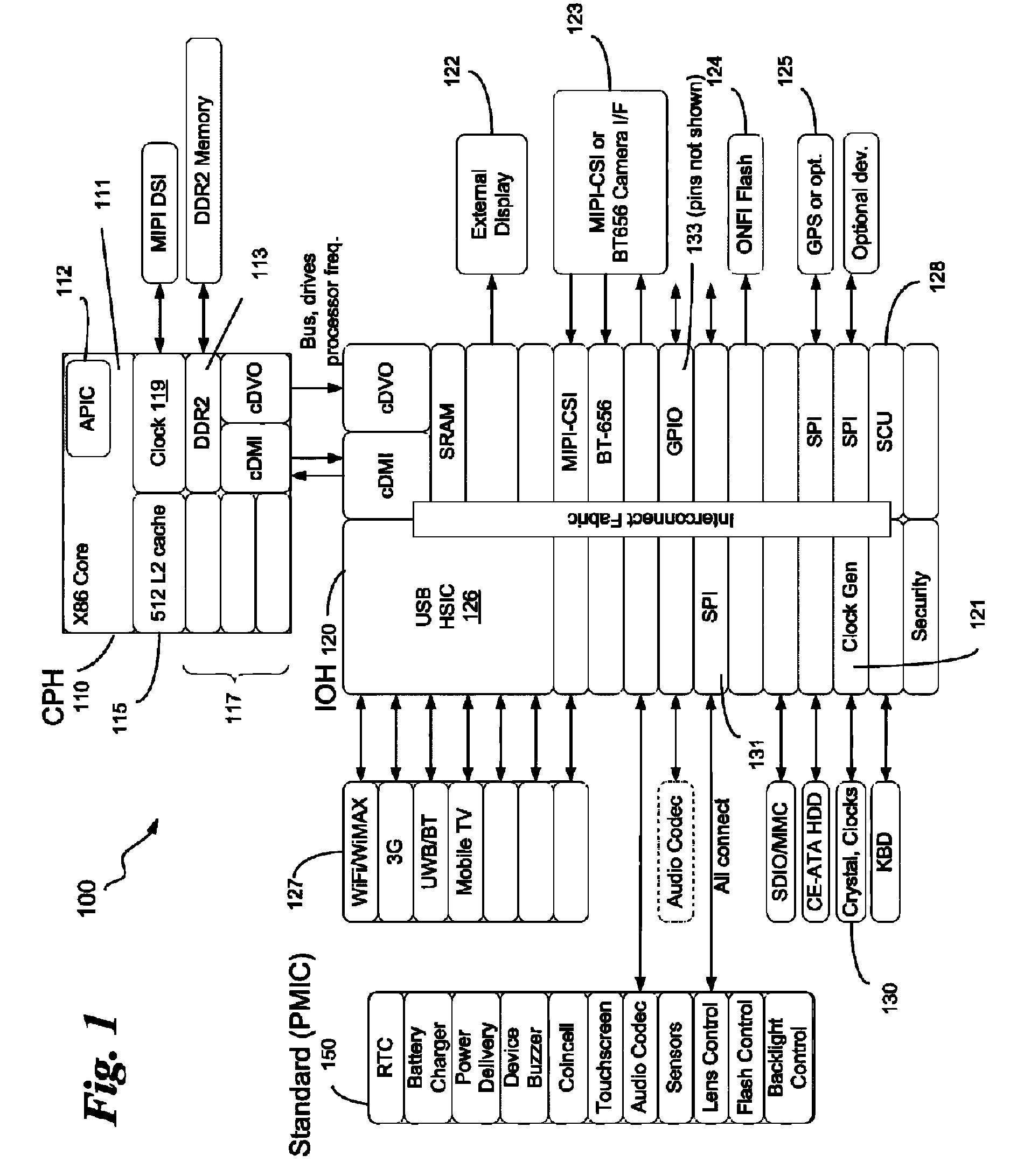
In computing, Intel's Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) is a family of interrupt controllers. As its name suggests, the APIC is more advanced than Intel's 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC), particularly enabling the construction of multiprocessor systems. It is one of several architectural designs intended to solve interrupt routing efficiency issues in multiprocessor computer systems.
Real-time scheduler
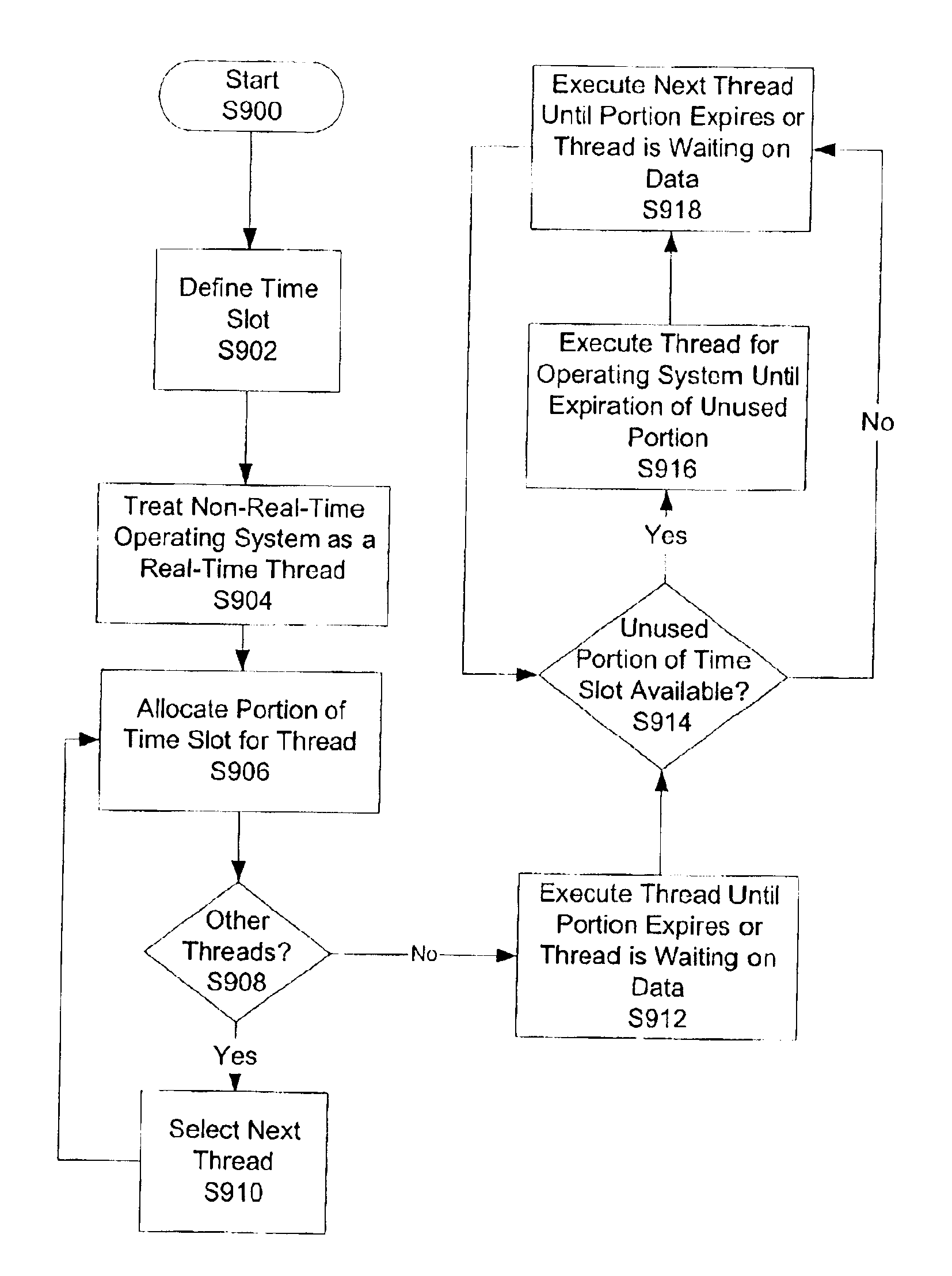
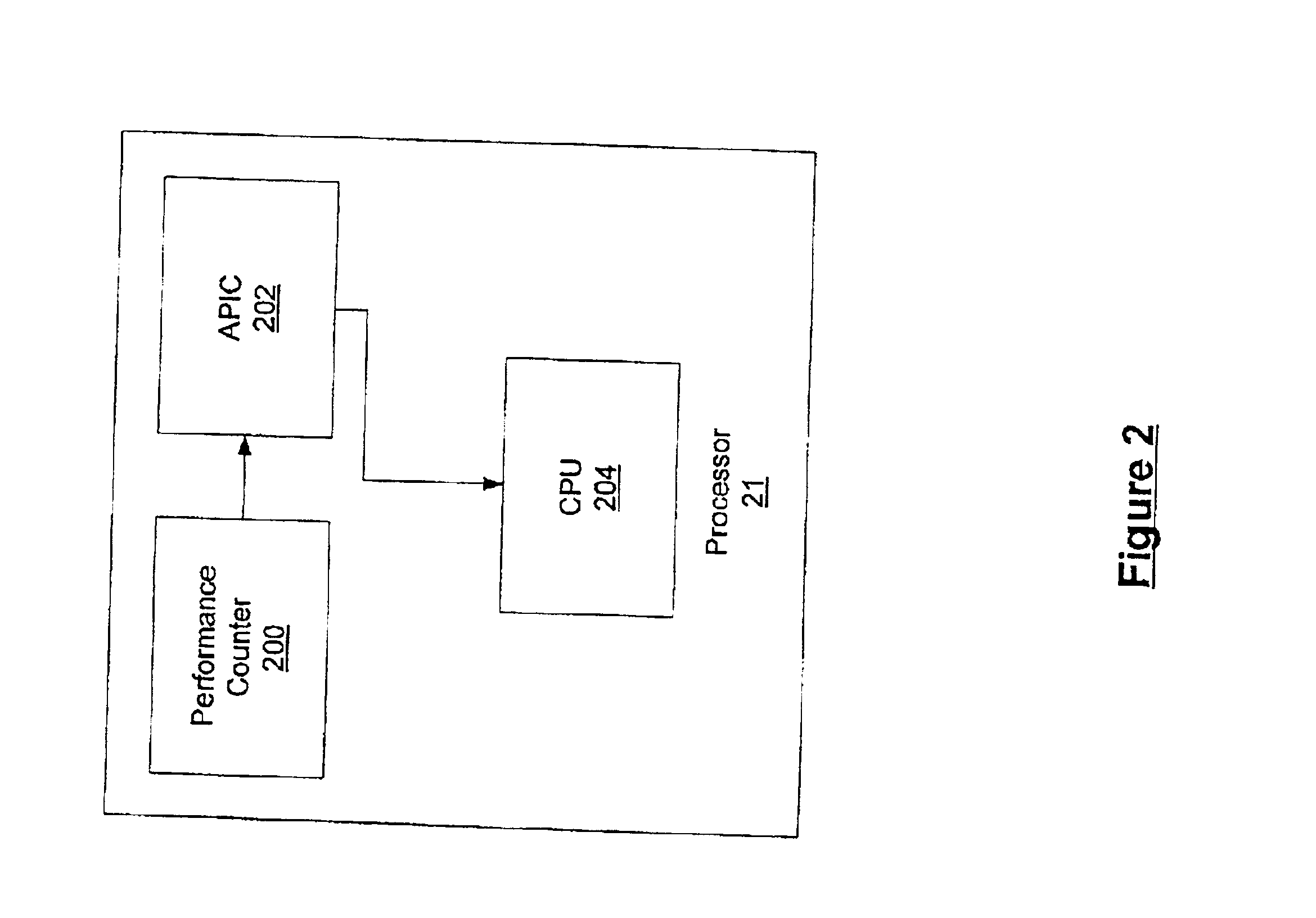
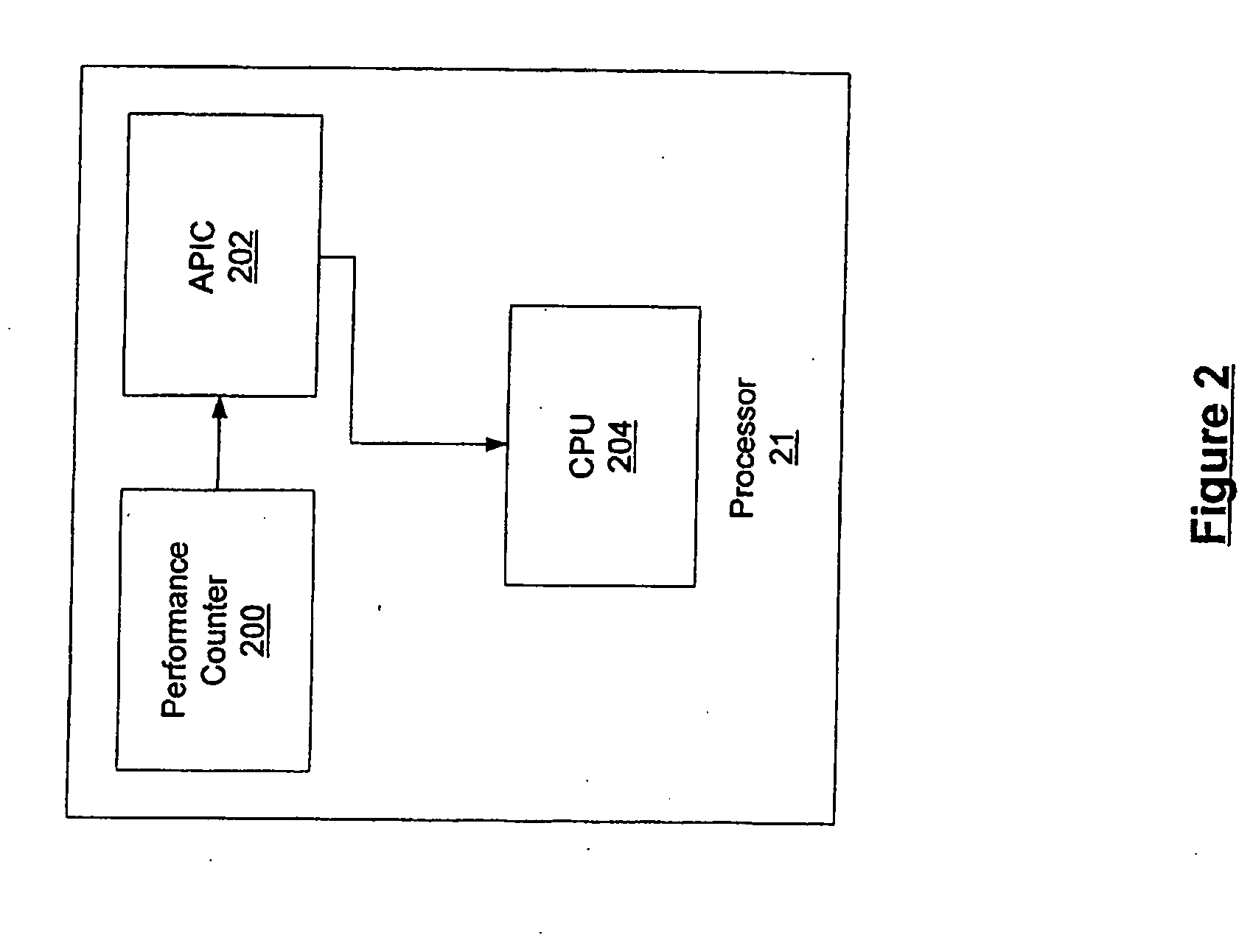
InactiveUS6957432B2Facilitates real-time schedulingSpeed of execution of operatingProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTime scheduleNon real time
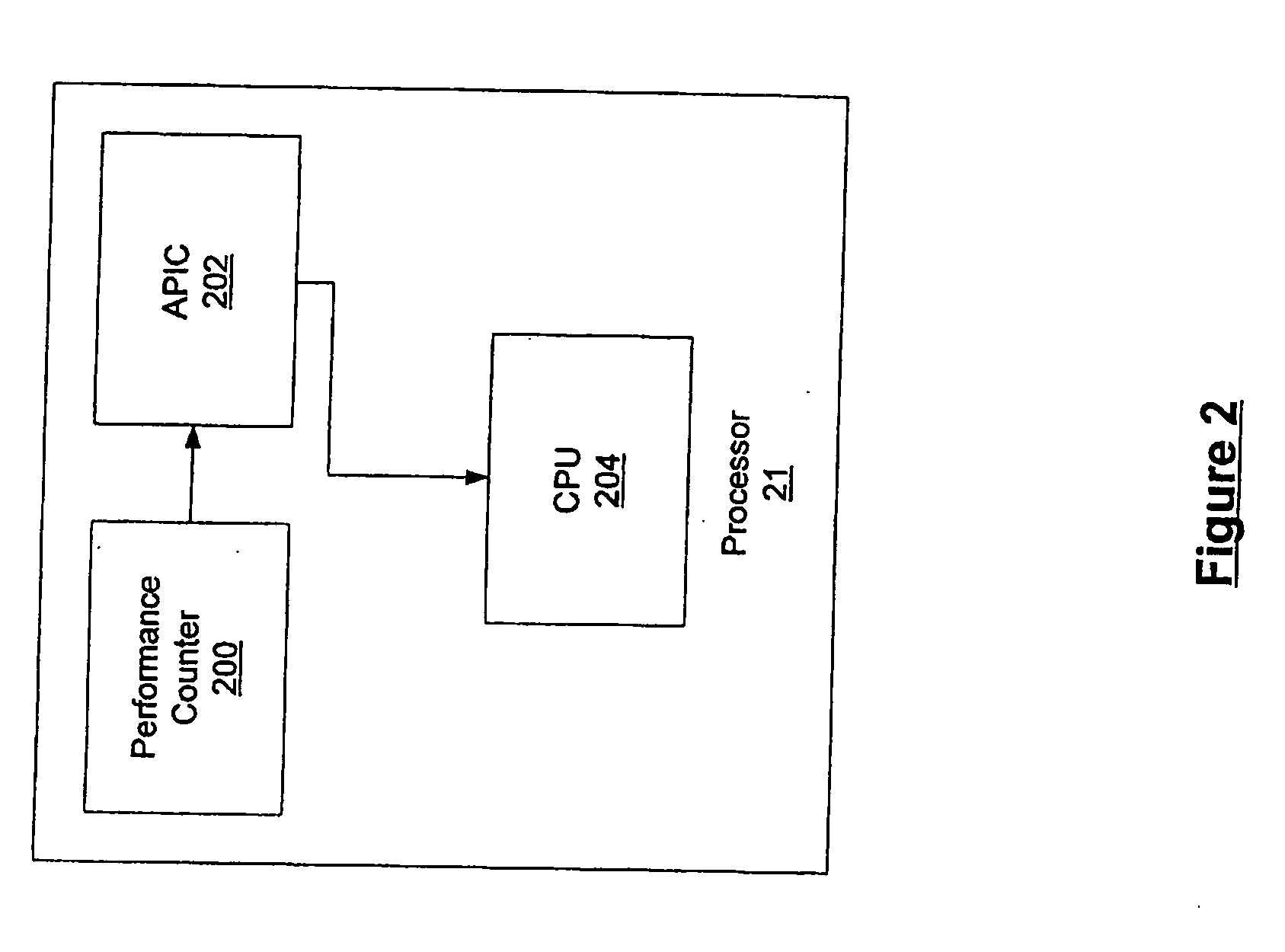
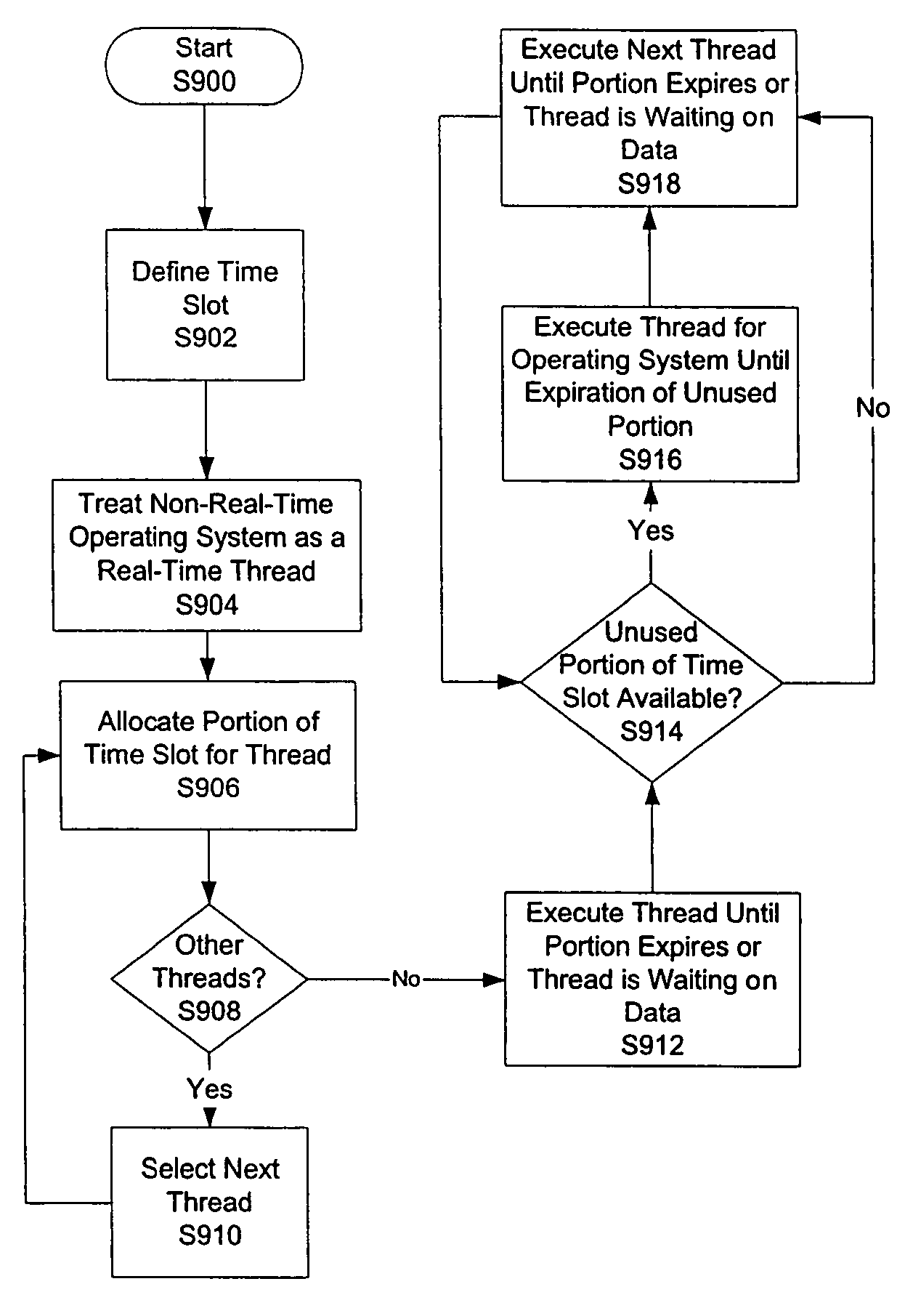
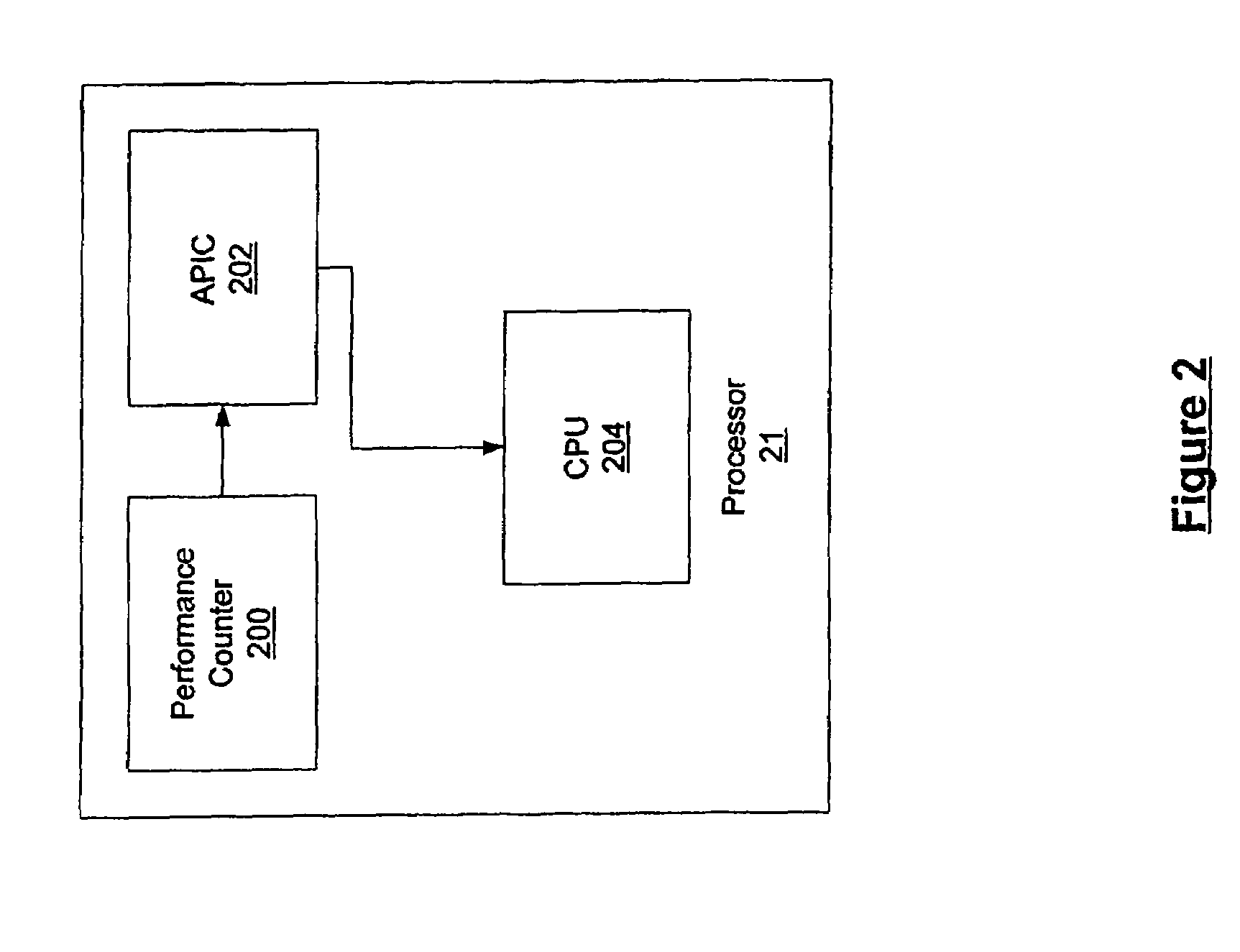
Methods and computer-executable components for real-time scheduling of CPU resources are disclosed. A performance counter determines when to allocate CPU resources to a thread. When it is time to allocate the CPU resources, the performance counter issues a maskable or non-maskable interrupt to an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC). The APIC then issues a maskable non-maskable interrupt to the CPU. In response to receiving the non-maskable interrupt, the CPU allocates resources to the thread. In addition, the disclosed methods and computer-executable components also: (a) allow scheduling of CPU resources such that real-time threads are guaranteed respective portions of time slots, (b) enable real-time scheduling on a non-real-time operating system, and (c) provide scheduling of CPU resources on a uni-processor machine such that at least first and second real-time threads dependent on one another are synchronized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
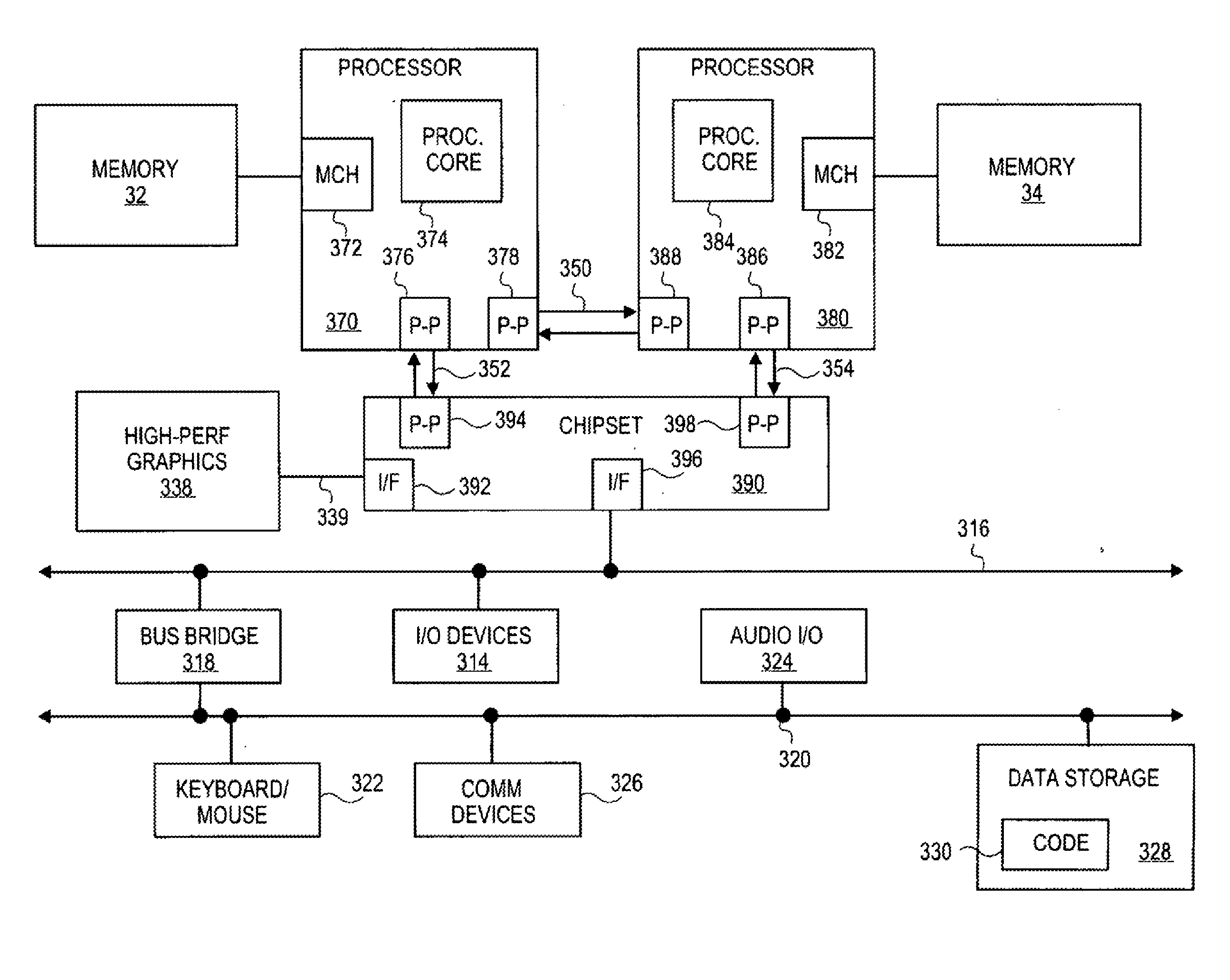
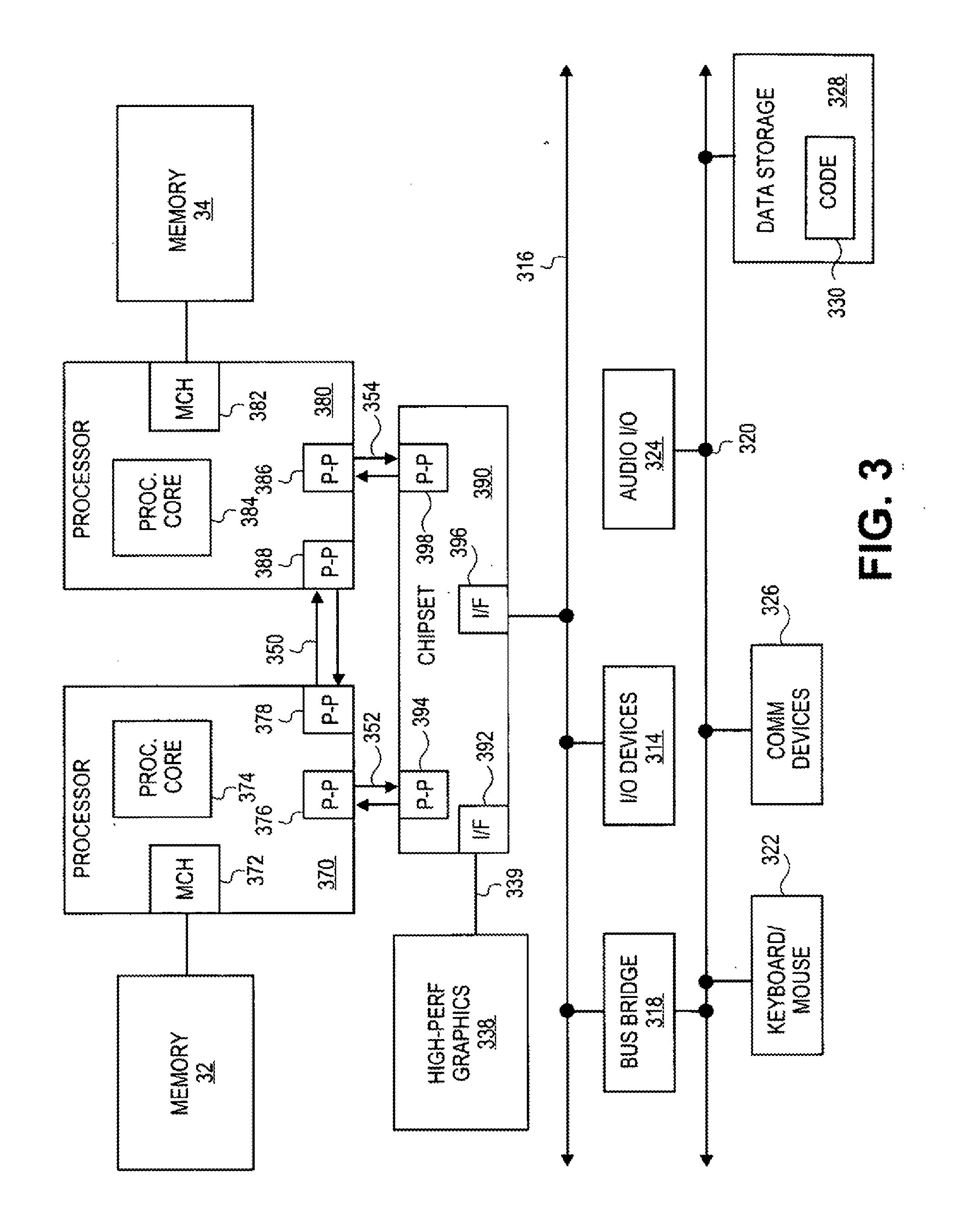
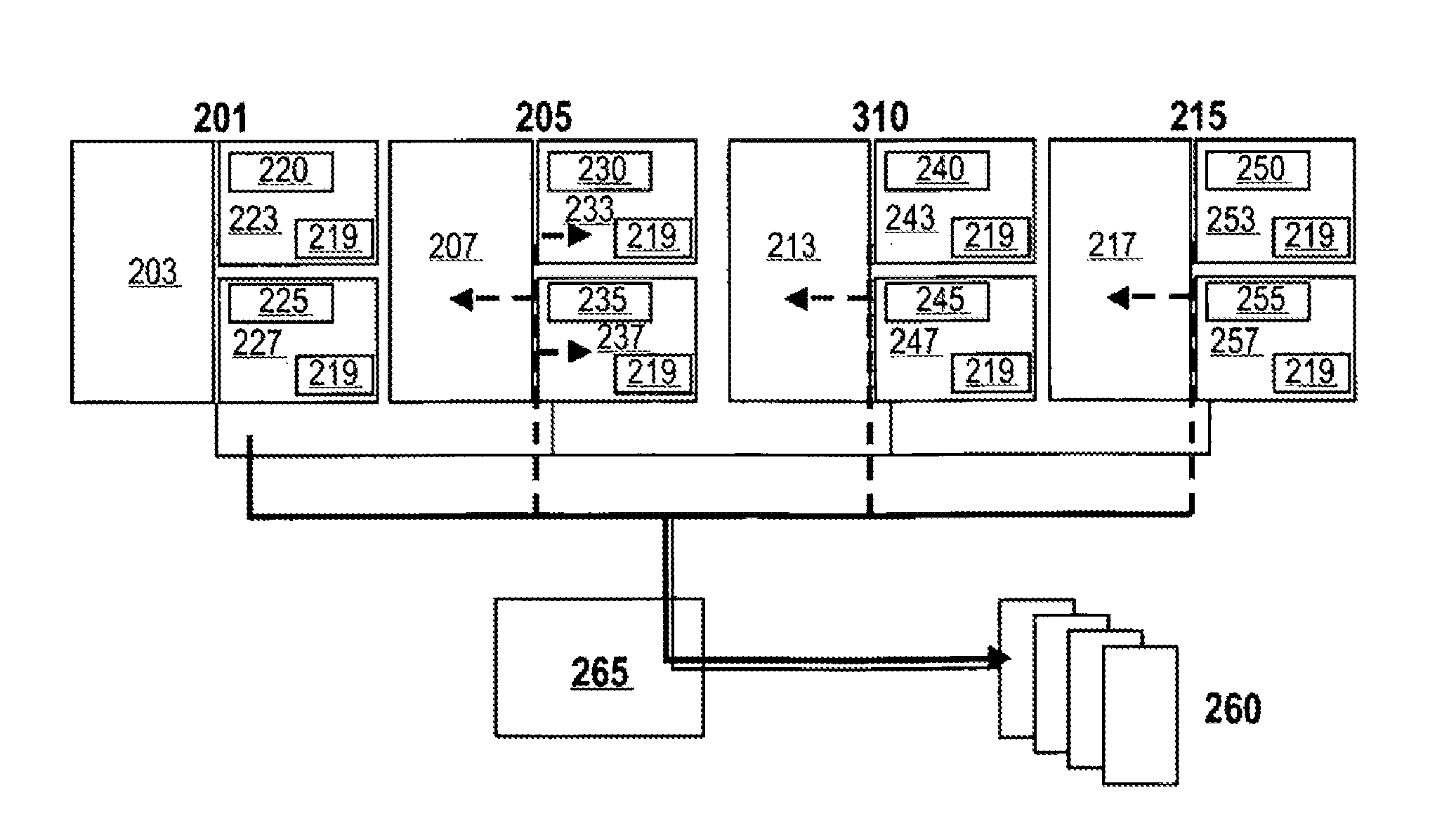
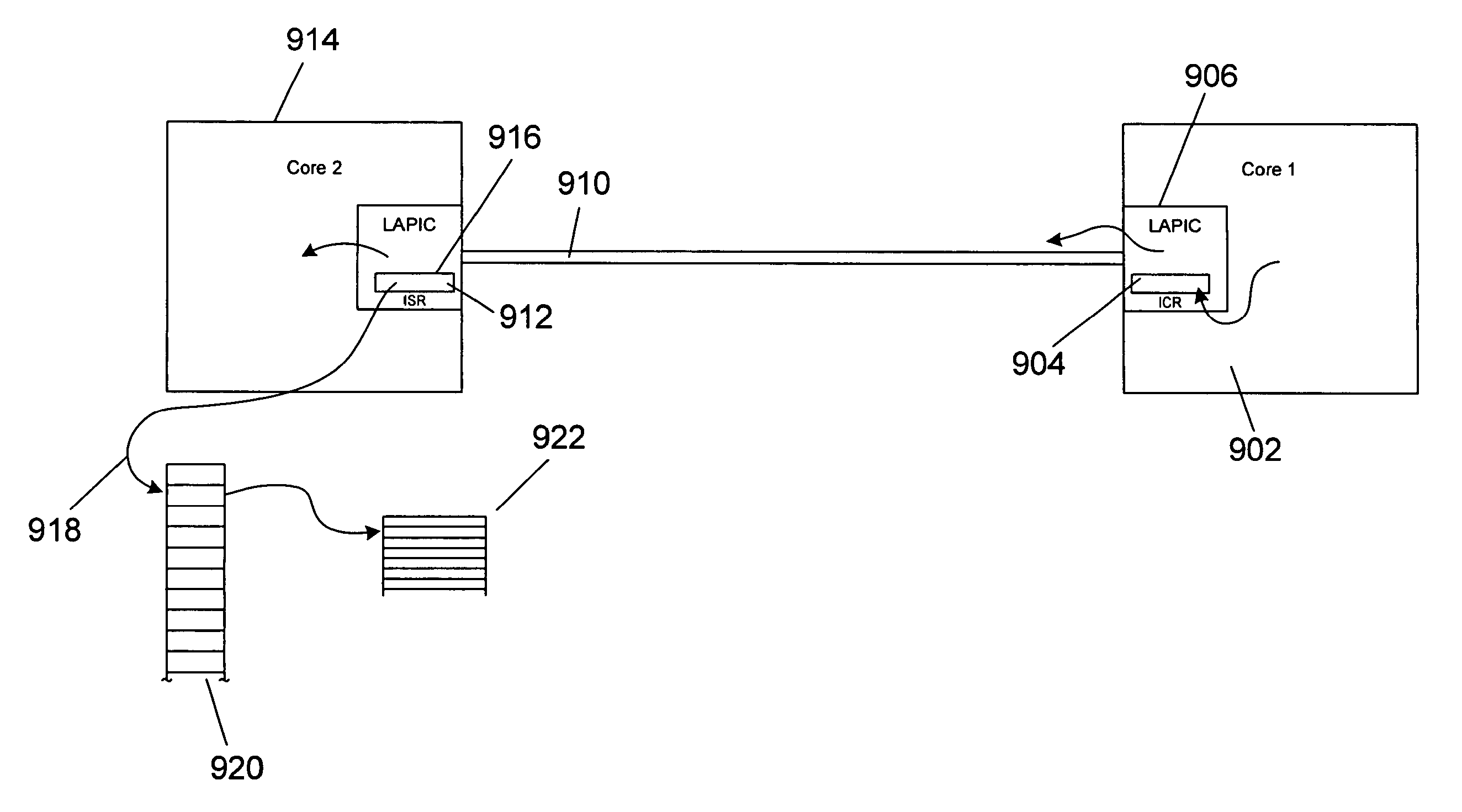
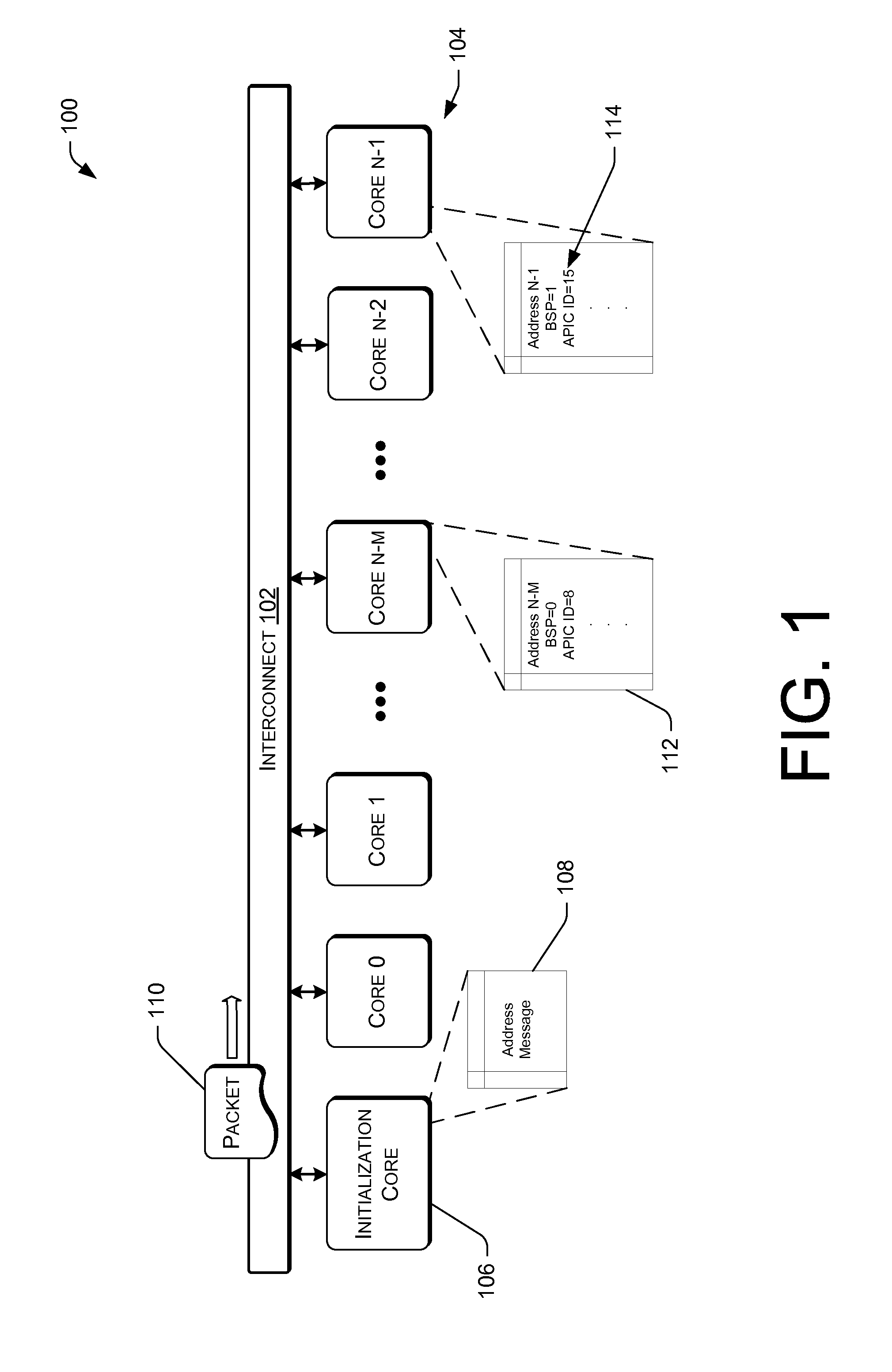
Method and System for Generating and Delivering Inter-Processor Interrupts in a Multi-Core Processor and in Ceterain Shared Memory Multi-Processor Systems
ActiveUS20110047310A1Facilitate shared-memory-based communicationEfficient use ofProgram controlMulti processorInter-processor interrupt
Certain embodiments of the present invention arc directed to providing efficient and easily-applied mechanisms for inter-core and inter-processor communications and inter-core and inter-processor signaling within multi-core microprocessors and certain multi-processor systems. In one embodiment of the present invention, local advanced programmable interrupt controllers within, or associated with, cores of a multi-core microprocessor and / or processors of a multi-processor system are enhanced so that the local advanced programmable interrupt controllers can be configured to automatically generate inter-core and inter-processor interrupts when WRITE operations are directed to particular regions of shared memory.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and system for real time scheduler
InactiveUS20050229179A1Facilitates real-time schedulingSpeed of execution of operatingProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTime scheduleNon-maskable interrupt
Methods and computer-executable components for real-time scheduling of CPU resources are disclosed. A performance counter determines when to allocate CPU resources to a thread. When it is time to allocate the CPU resources, the performance counter issues a maskable or non-maskable interrupt to an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC). The APIC then issues a maskable non-maskable interrupt to the CPU. In response to receiving the non-maskable interrupt, the CPU allocates resources to the thread. In addition, the disclosed methods and computer-executable components also: (a) allow scheduling of CPU resources such that real-time threads are guaranteed respective portions of time slots, (b) enable real-time scheduling on a non-real-time operating system, and (c) provide scheduling of CPU resources on a uni-processor machine such that at least first and second real-time threads dependent on one another are synchronized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for realtime scheduler
InactiveUS6990665B2Facilitates real-time schedulingSpeed of execution of operatingProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTime scheduleNon real time
Methods and computer-executable components for real-time scheduling of CPU resources are disclosed. A performance counter determines when to allocate CPU resources to a thread. When it is time to allocate the CPU resources, the performance counter issues a maskable or non-maskable interrupt to an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC). The APIC then issues a maskable non-maskable interrupt to the CPU. In response to receiving the non-maskable interrupt, the CPU allocates resources to the thread. In addition, the disclosed methods and computer-executable components also: (a) allow scheduling of CPU resources such that real-time threads are guaranteed respective portions of time slots, (b) enable real-time scheduling on a non-real-time operating system, and (c) provide scheduling of CPU resources on a uni-processor machine such that at least first and second real-time threads dependent on one another are synchronized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
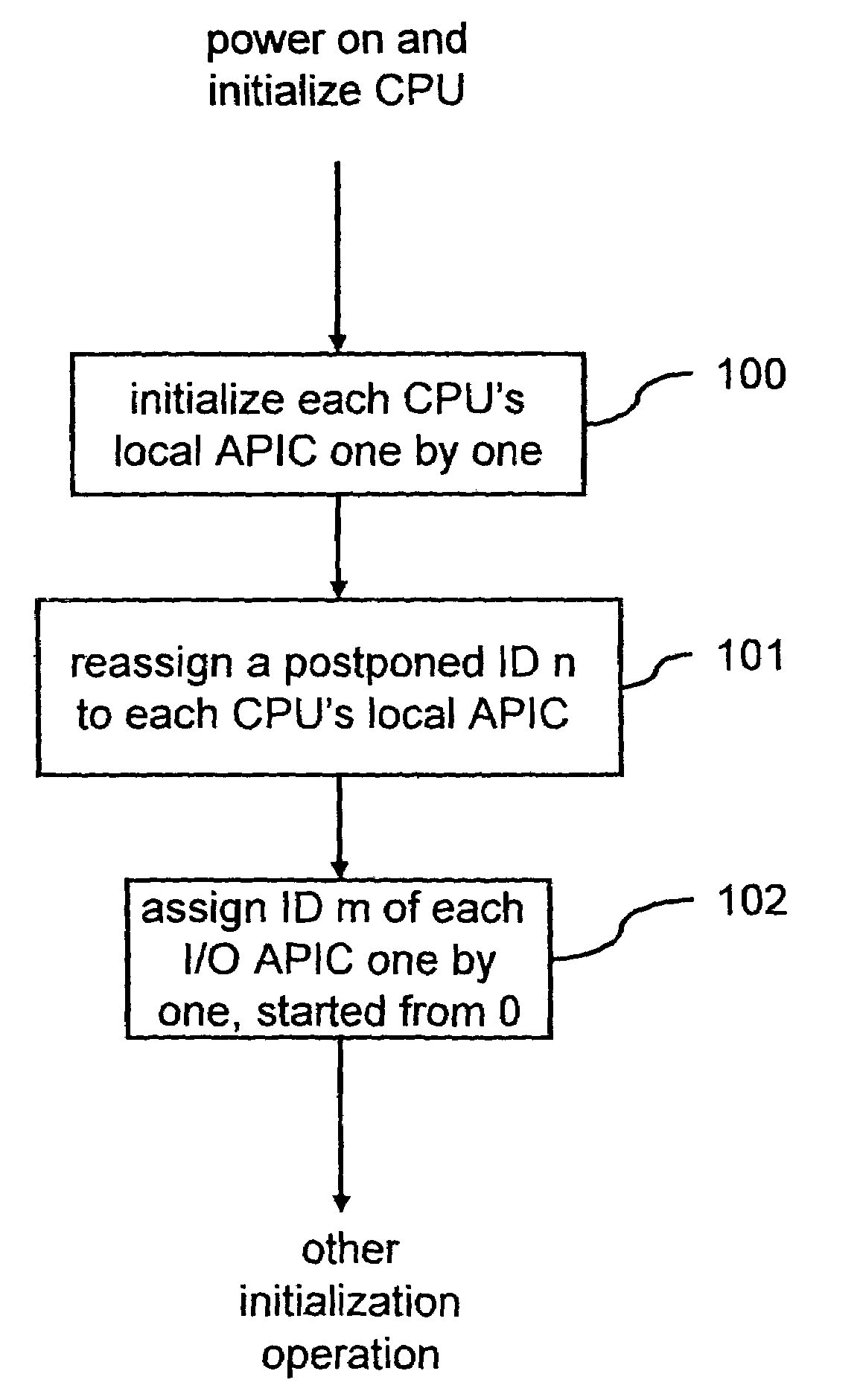
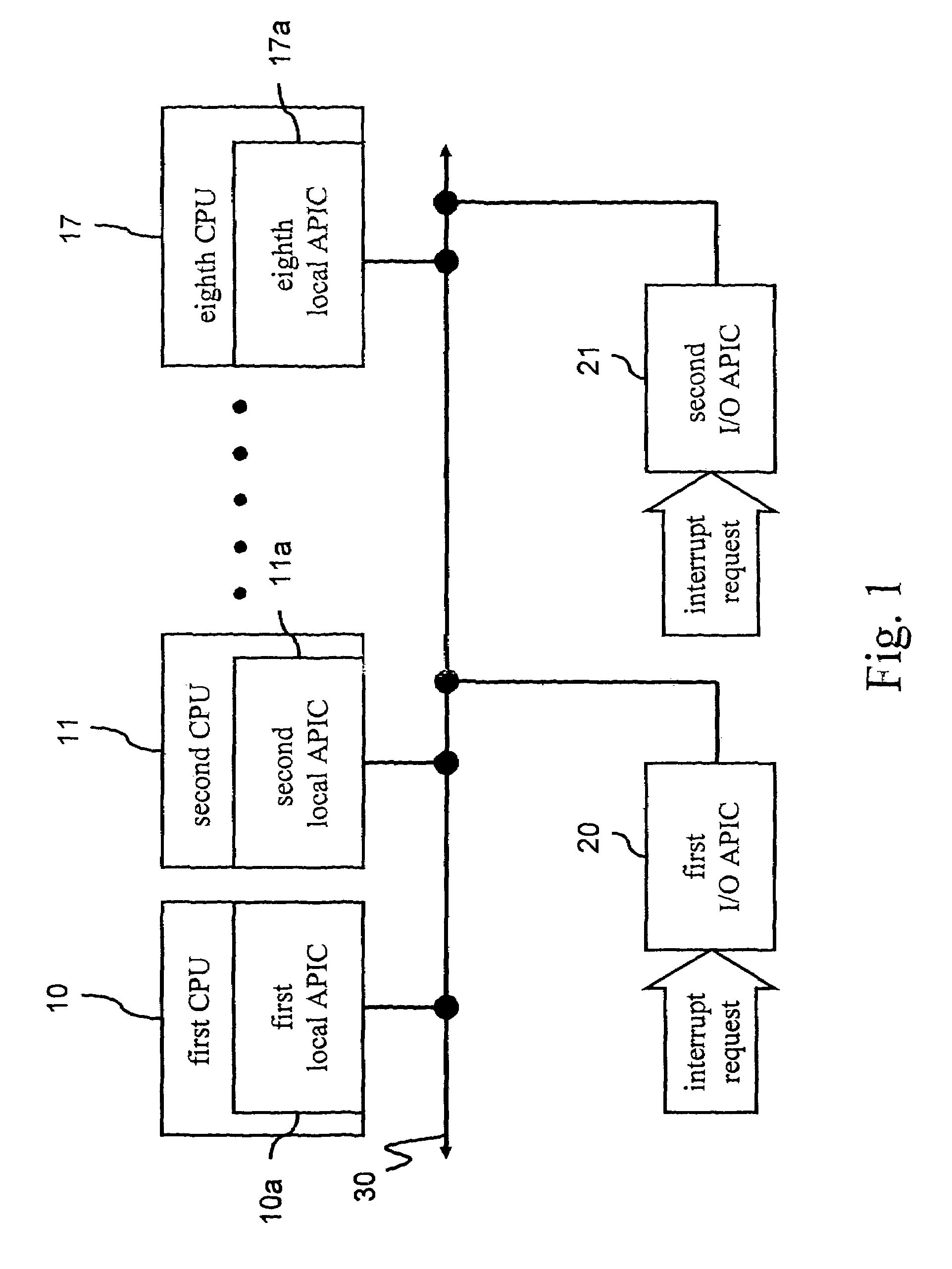
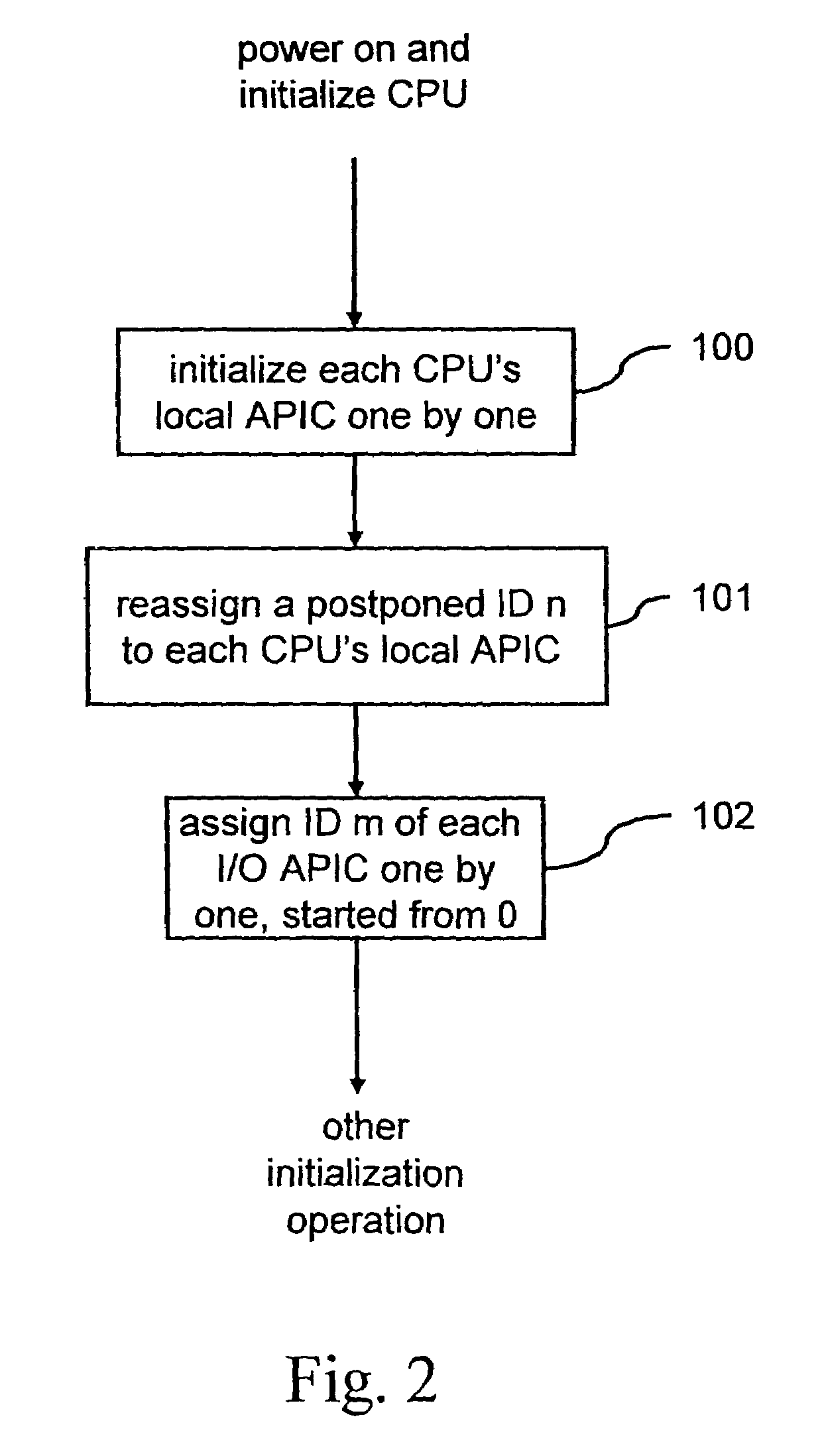
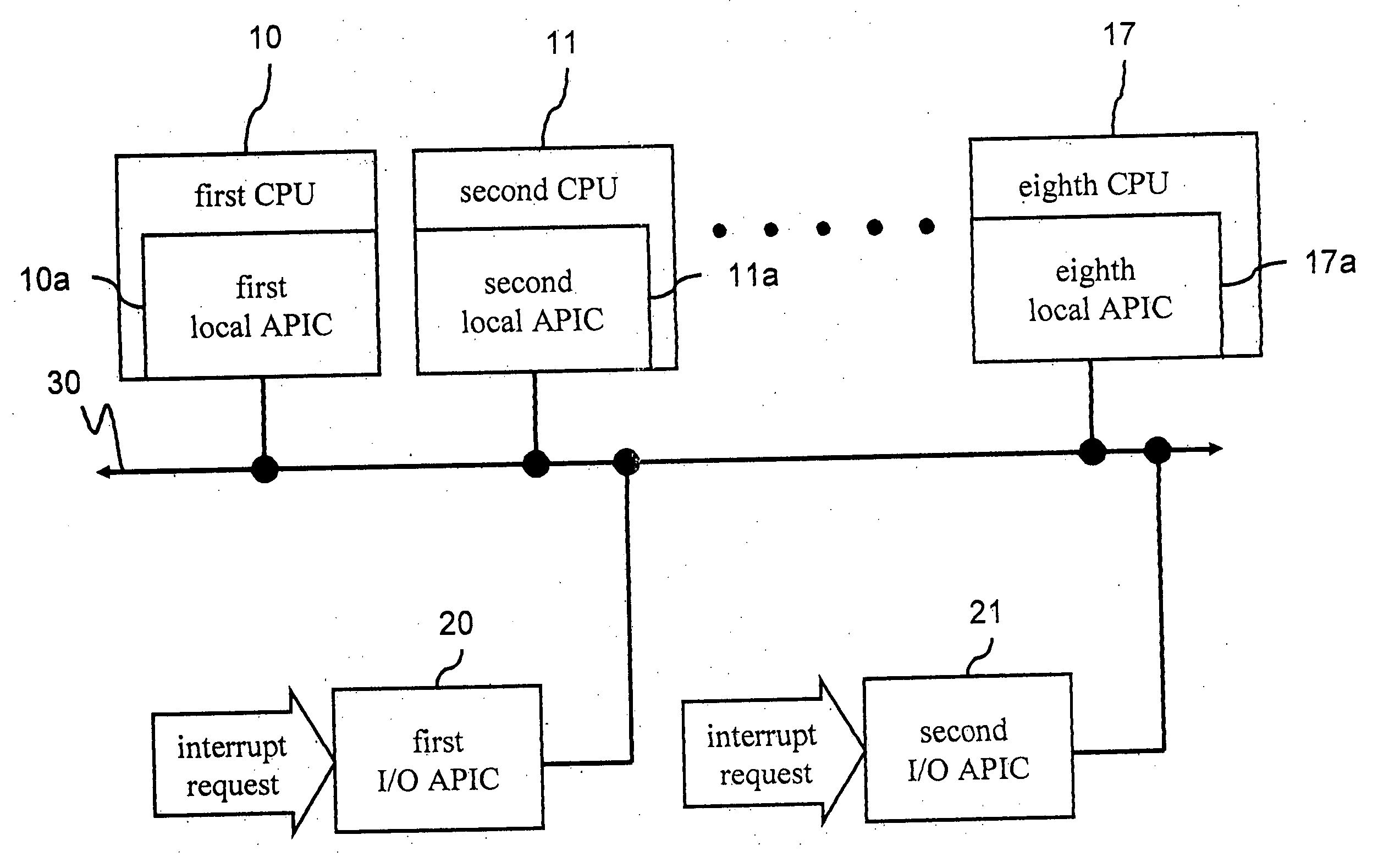
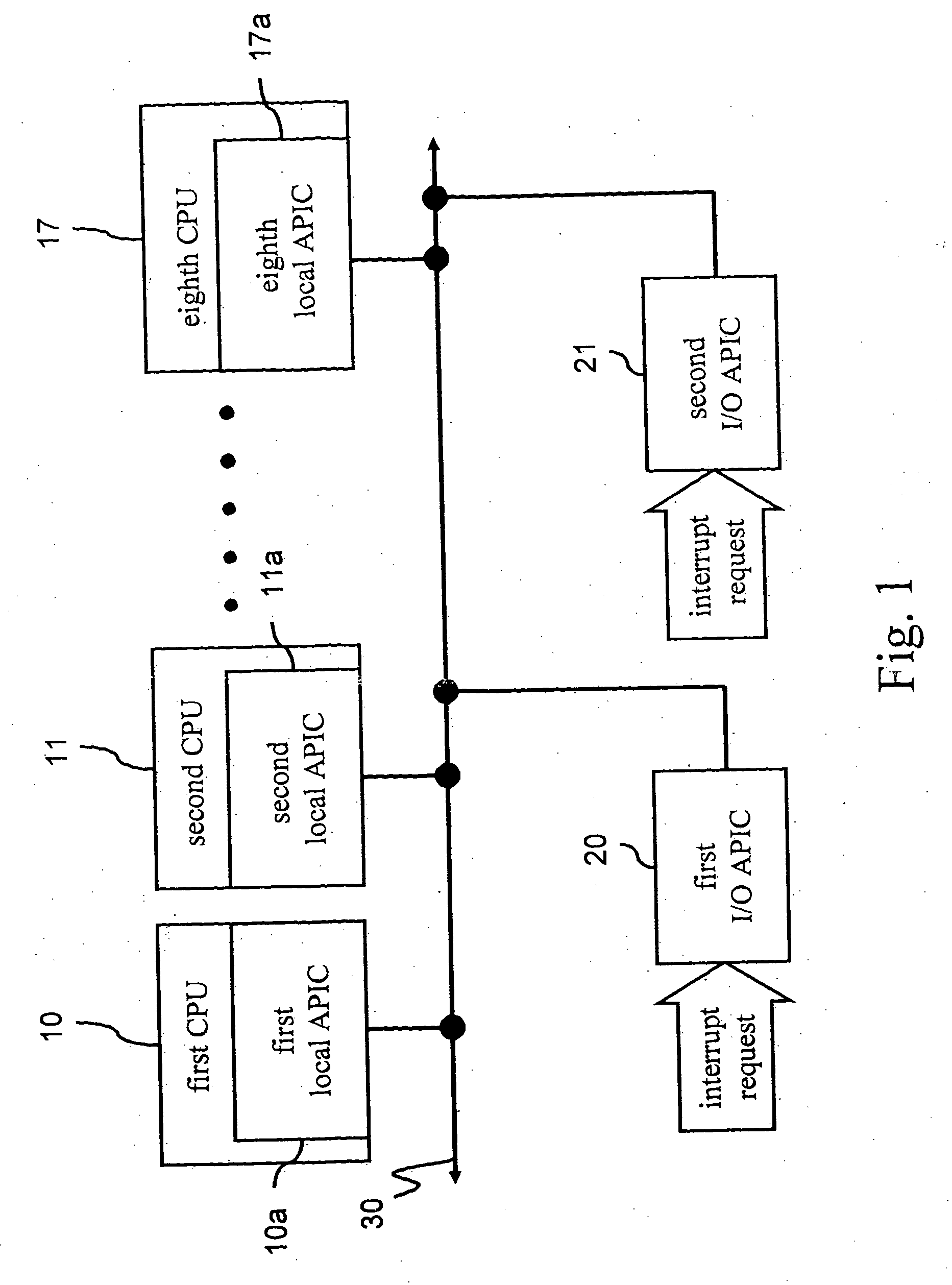
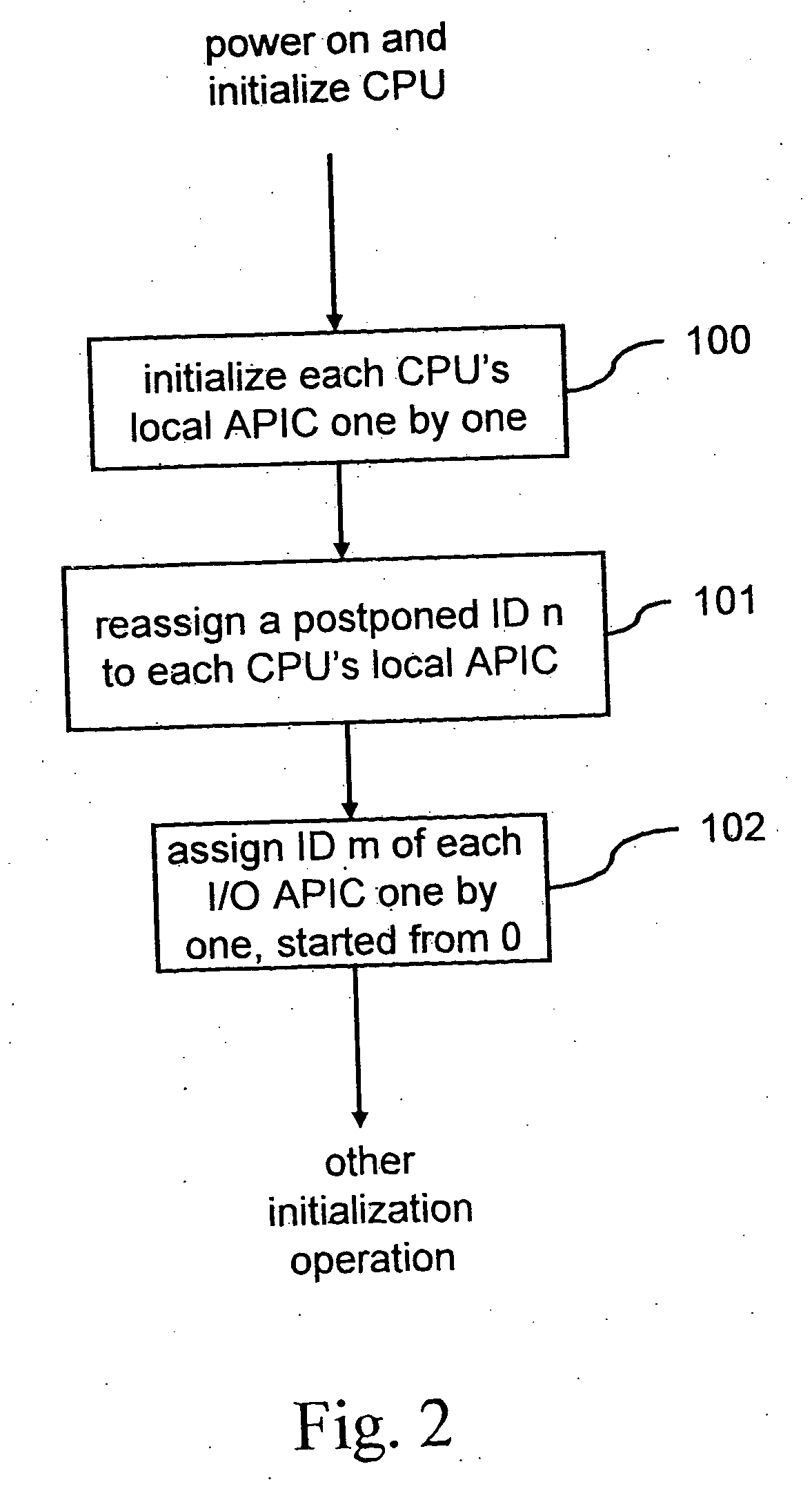
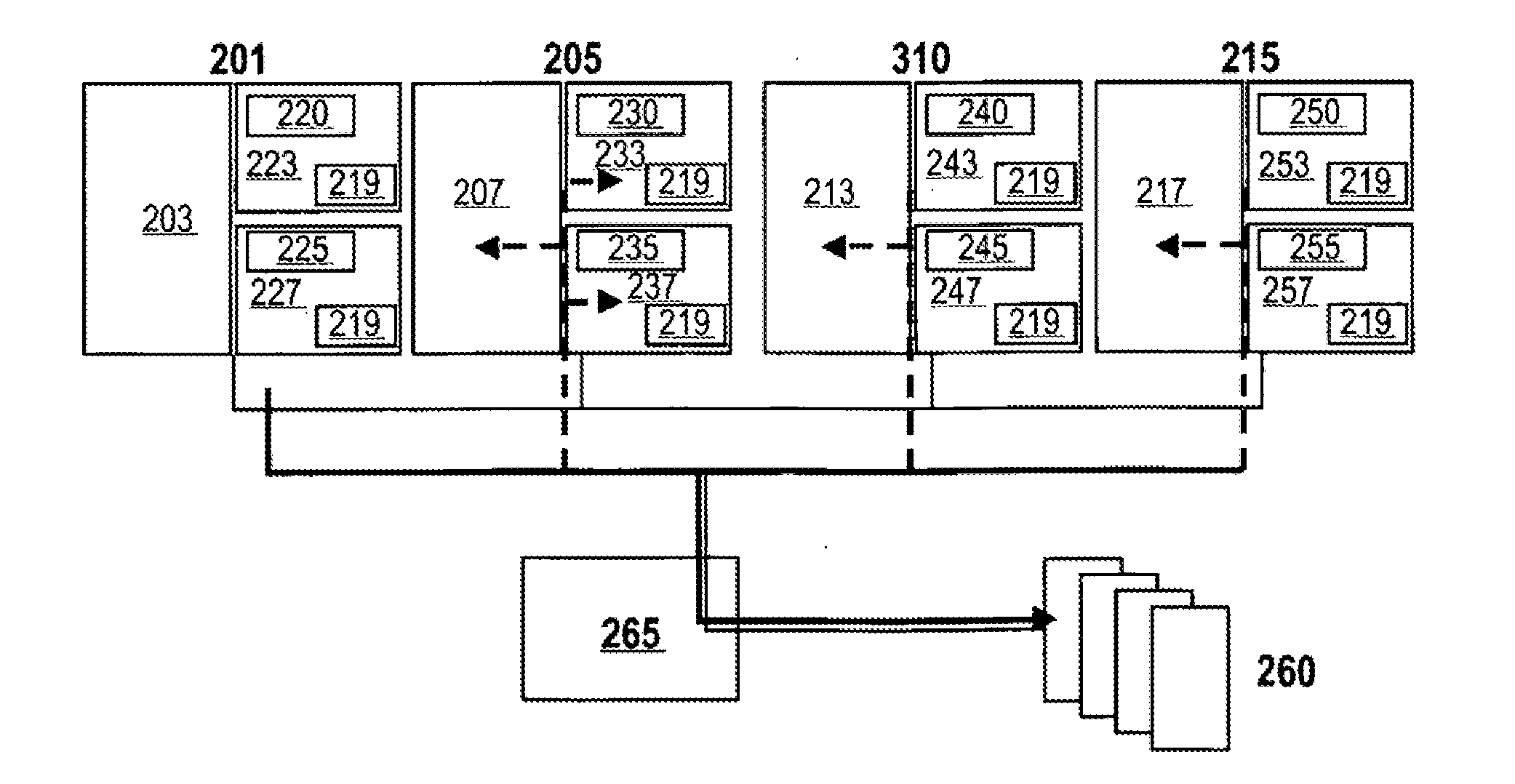
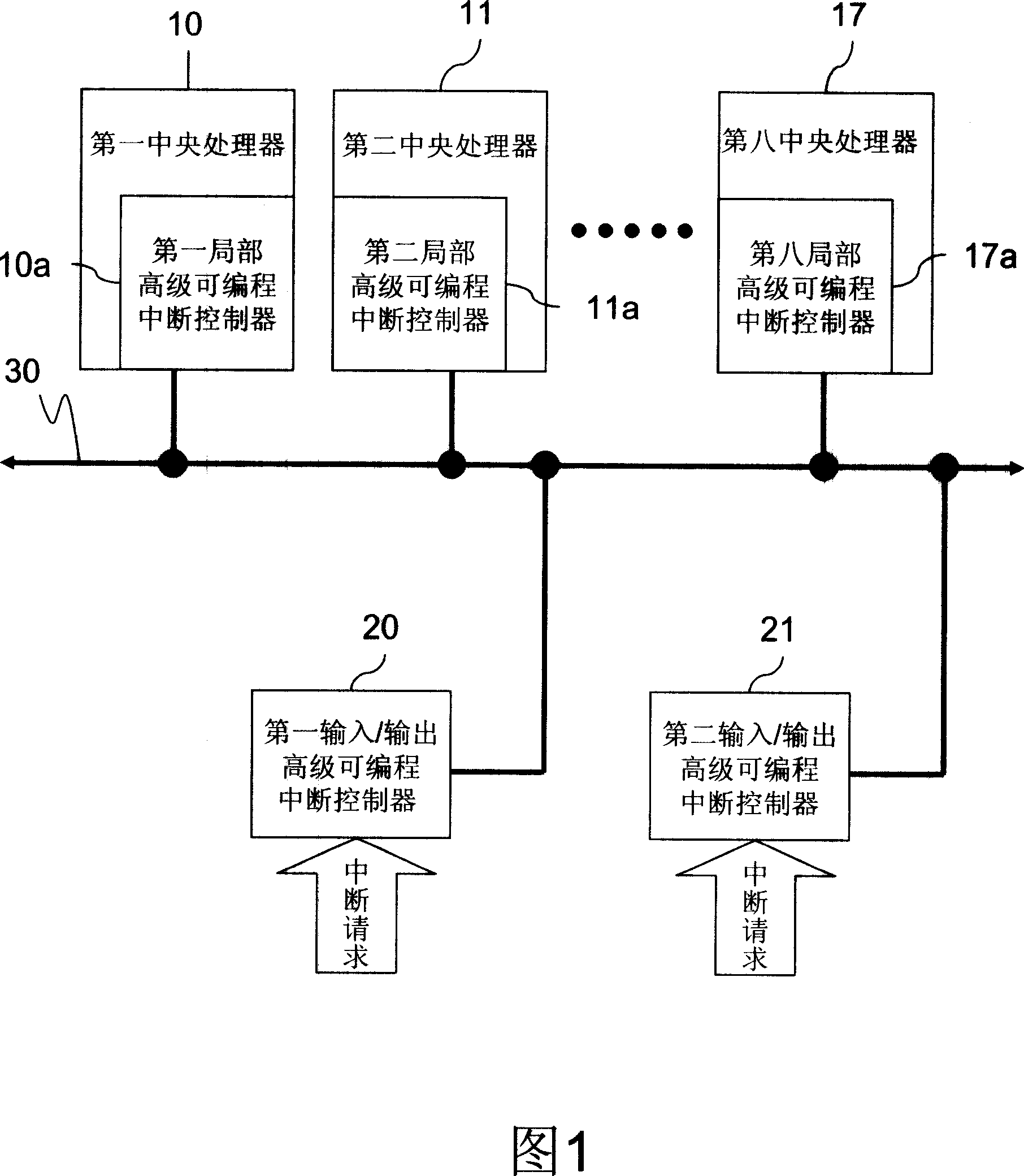
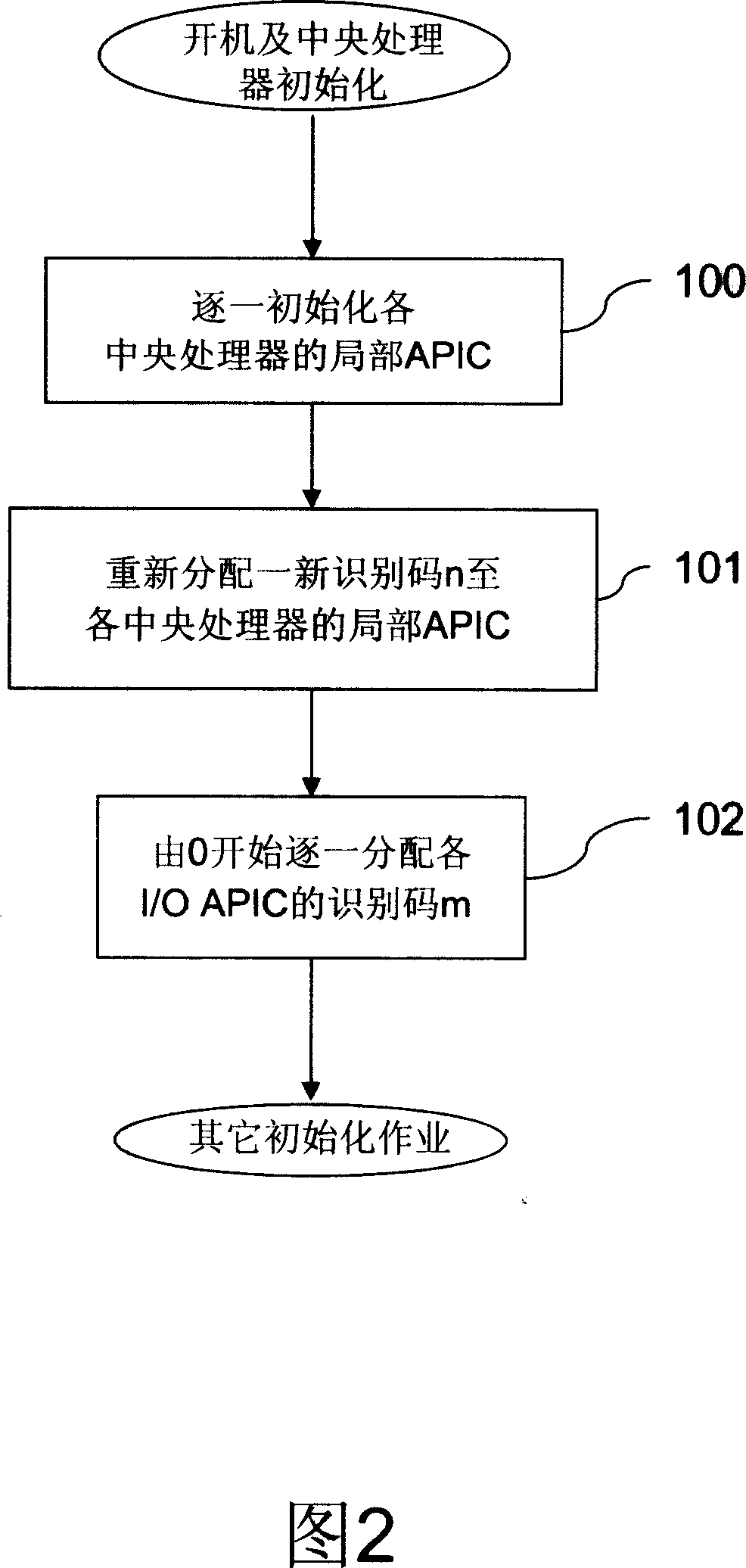
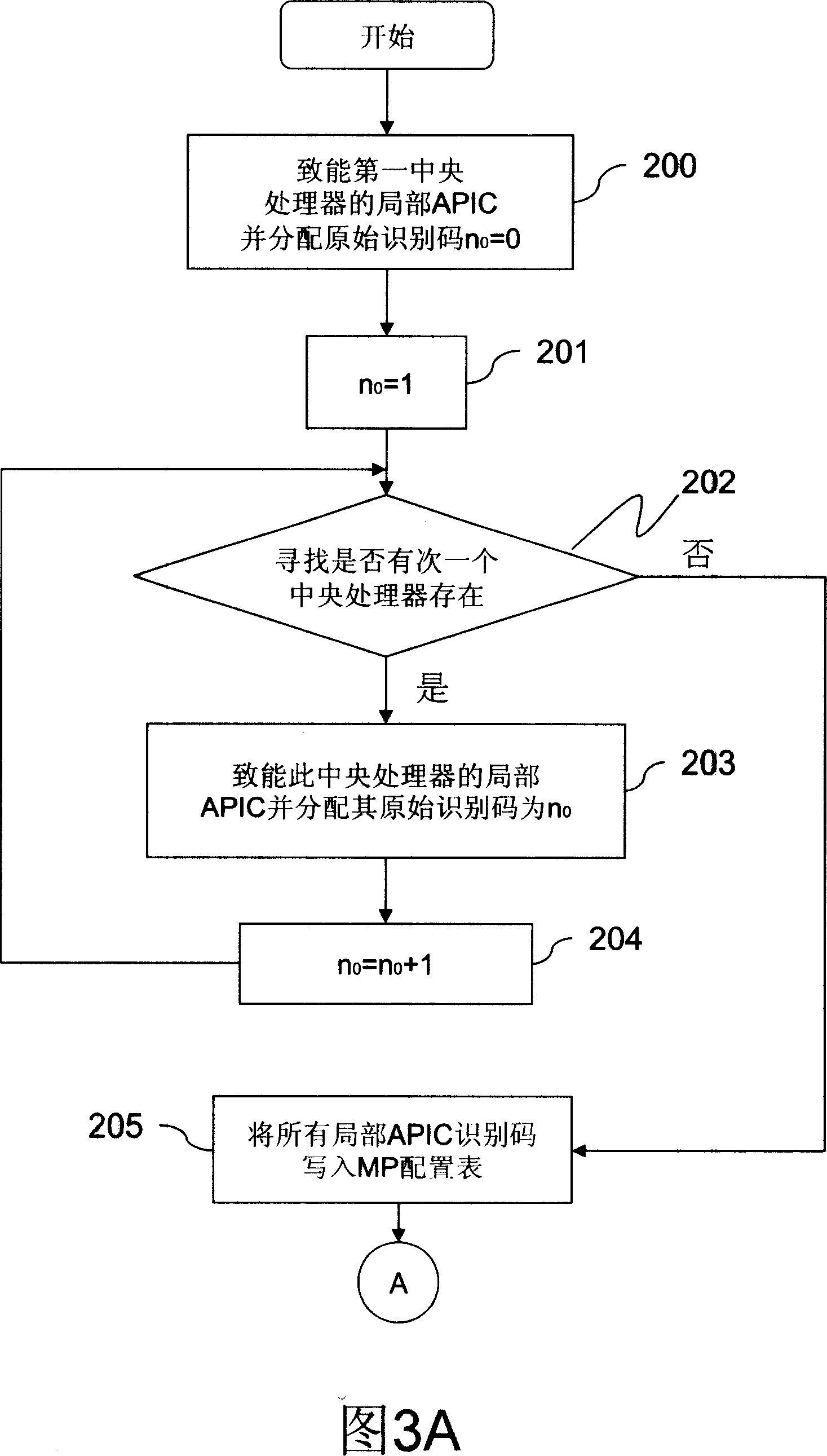
ID configuration method for advanced programmable interrupt controller
ActiveUS7363394B2Improve stabilityDigital computer detailsProgram controlMulti processorProgrammable Interrupt Controller
An advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) identification (ID) configuration method is applied to a multiprocessor computer system. The method assigns a postponed ID to each CPU's APIC IDs respectively during the initialization. Plural reserved IDs are assigned to the I / O APICs. A multiprocessor configuration table in a basic input output system (BIOS) will be updated with renewed ID configuration, to avoid an ID conflict when processing the interrupt request from the peripheral devices and raise the stability of the multiprocessor computer system.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
ID configuration method for advanced programmable interrupt controller
ActiveUS20070067521A1Improve stabilityDigital computer detailsProgram controlMulti processorProgrammable Interrupt Controller
An advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) identification (ID) configuration method is applied to a multiprocessor computer system. The method assigns a postponed ID to each CPU's APIC IDs respectively during the initialization. Plural reserved IDs are assigned to the I / O APICs. A multiprocessor configuration table in a basic input output system (BIOS) will be updated with renewed ID configuration, to avoid an ID conflict when processing the interrupt request from the peripheral devices and raise the stability of the multiprocessor computer system.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
Technique for communicating interrupts in a computer system
InactiveUS9043521B2Electric digital data processingProgrammable Interrupt ControllerComputerized system
A technique to enable efficient interrupt communication within a computer system. In one embodiment, an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) is interfaced via a set of bits within an APIC interface register using various interface instructions or operations, without using memory-mapped input / output (MMIO).
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for real time scheduler
InactiveUS20050229178A1Facilitates real-time schedulingSpeed of execution of operatingProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTime scheduleNon-maskable interrupt
Methods and computer-executable components for real-time scheduling of CPU resources are disclosed. A performance counter determines when to allocate CPU resources to a thread. When it is time to allocate the CPU resources, the performance counter issues a maskable or non-maskable interrupt to an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC). The APIC then issues a maskable non-maskable interrupt to the CPU. In response to receiving the non-maskable interrupt, the CPU allocates resources to the thread. In addition, the disclosed methods and computer-executable components also: (a) allow scheduling of CPU resources such that real-time threads are guaranteed respective portions of time slots, (b) enable real-time scheduling on a non-real-time operating system, and (c) provide scheduling of CPU resources on a uni-processor machine such that at least first and second real-time threads dependent on one another are synchronized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Interrupt realization method between virtual processors, relevant device and system
ActiveCN103559087AImprove performanceProgram initiation/switchingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAdvanced Programmable Interrupt ControllerComputer science
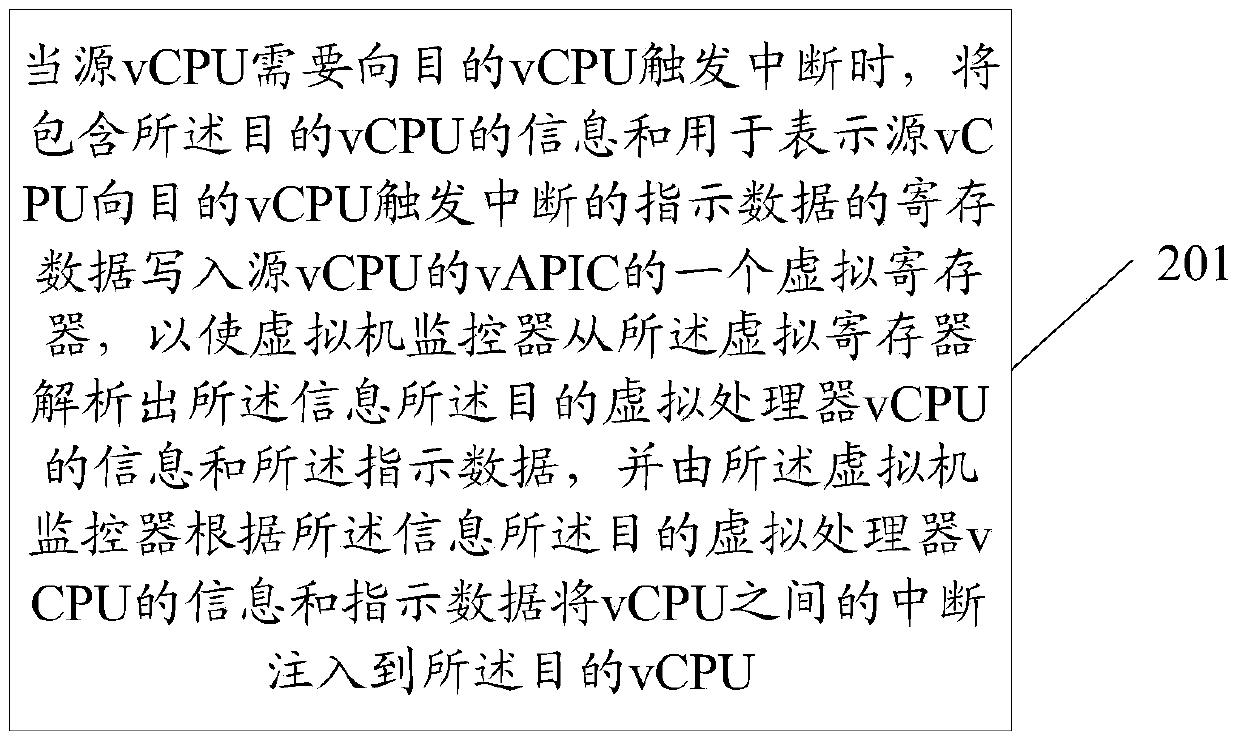
The embodiment of the invention discloses an interrupt realization method between virtual processors. The method comprises the following steps that when a source virtual processor needs to trigger the interrupt to a target virtual processor, the information comprising the target virtual processor and registering data used for expressing indication data of the interrupt triggered from the source virtual processor to the target virtual processor are written into a virtual register of a vAPIC (virtual advanced programmable interrupt controller) of the source virtual processor so that a virtual machine monitor analyzes the information of the target virtual processor and the indication data from the virtual register, and in addition, the virtual machine monitor fills the interrupt between the virtual processors into the target virtual processor according to the indication data and the information of the target virtual processor. Correspondingly, the embodiment of the invention also provides a relevant virtual machine, a virtual controller, a calculation node and a system. The performance of the virtual machine can be improved according to the embodiment of the invention.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Real-time scheduler
InactiveUS6990669B1Facilitates real-time schedulingMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsNon-maskable interruptAdvanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
Methods and computer-executable components for real-time scheduling of CPU resources are disclosed. A performance counter determines when to allocate CPU resources to a thread. When it is time to allocate the CPU resources, the performance counter issues a non-maskable interrupt to an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC). The APIC then issues a non-maskable interrupt to the CPU. In response to receiving the non-maskable interrupt, the CPU allocates resources to the thread.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Application program intercept and capture and monitoring system control break method
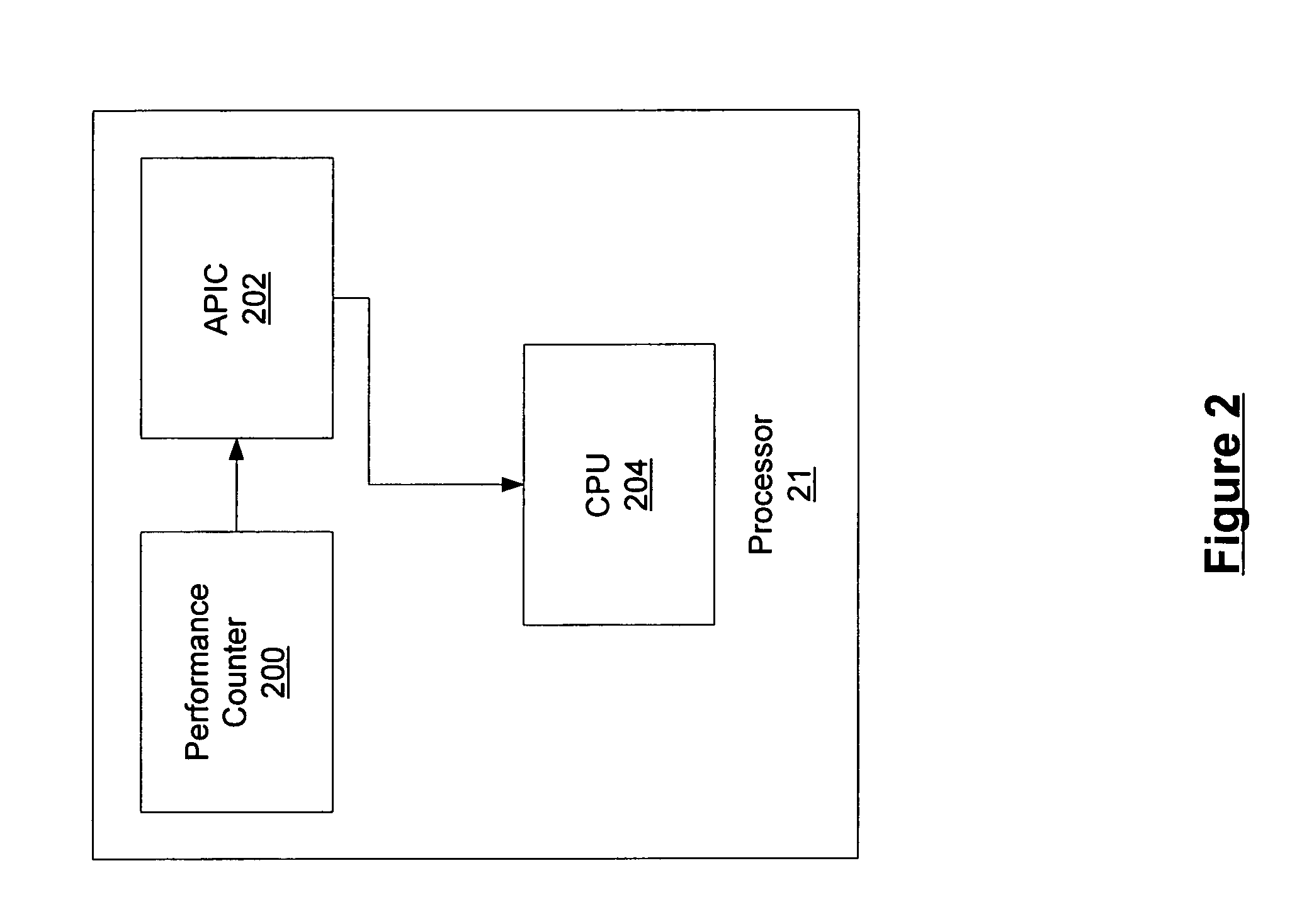
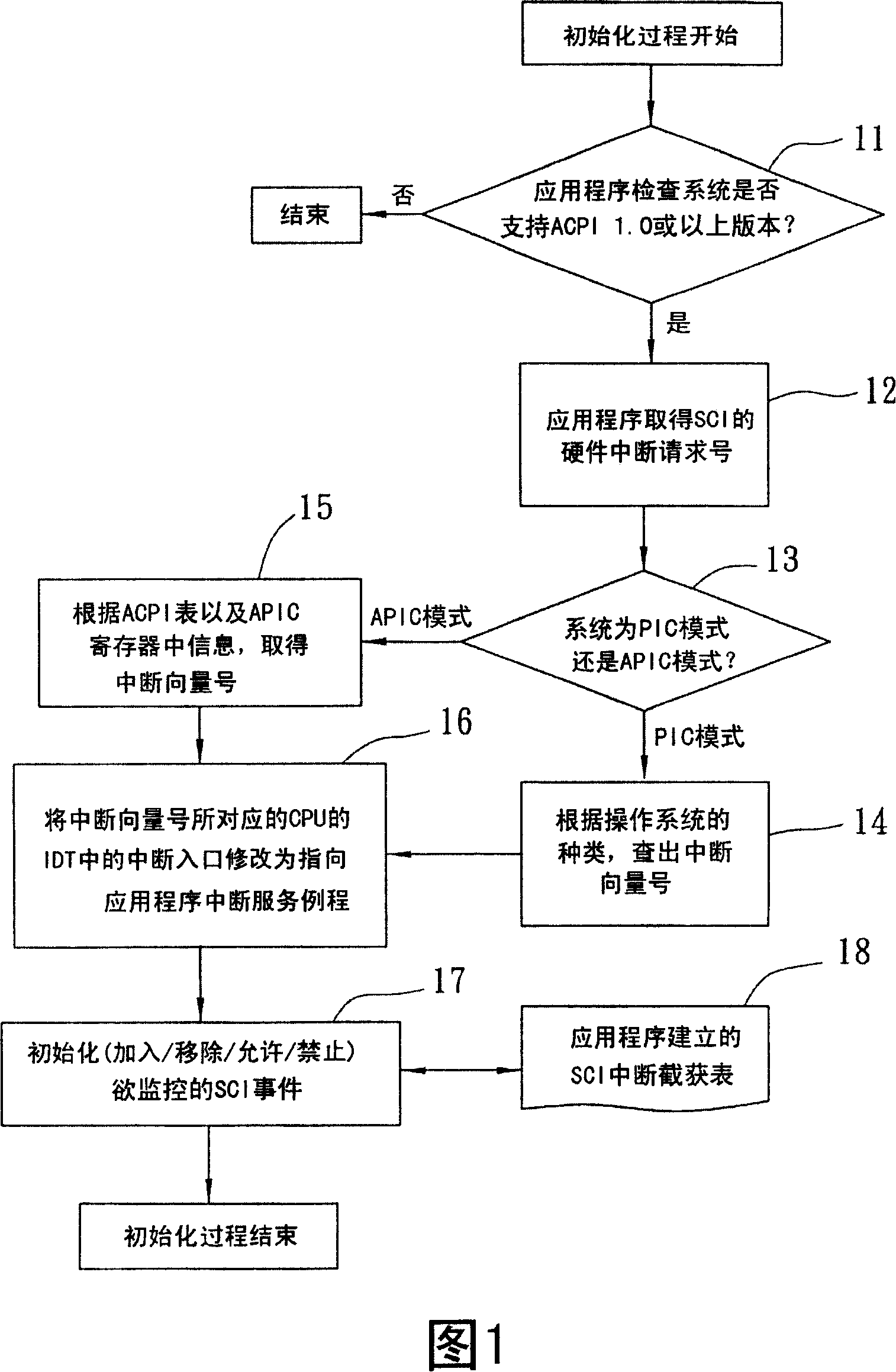
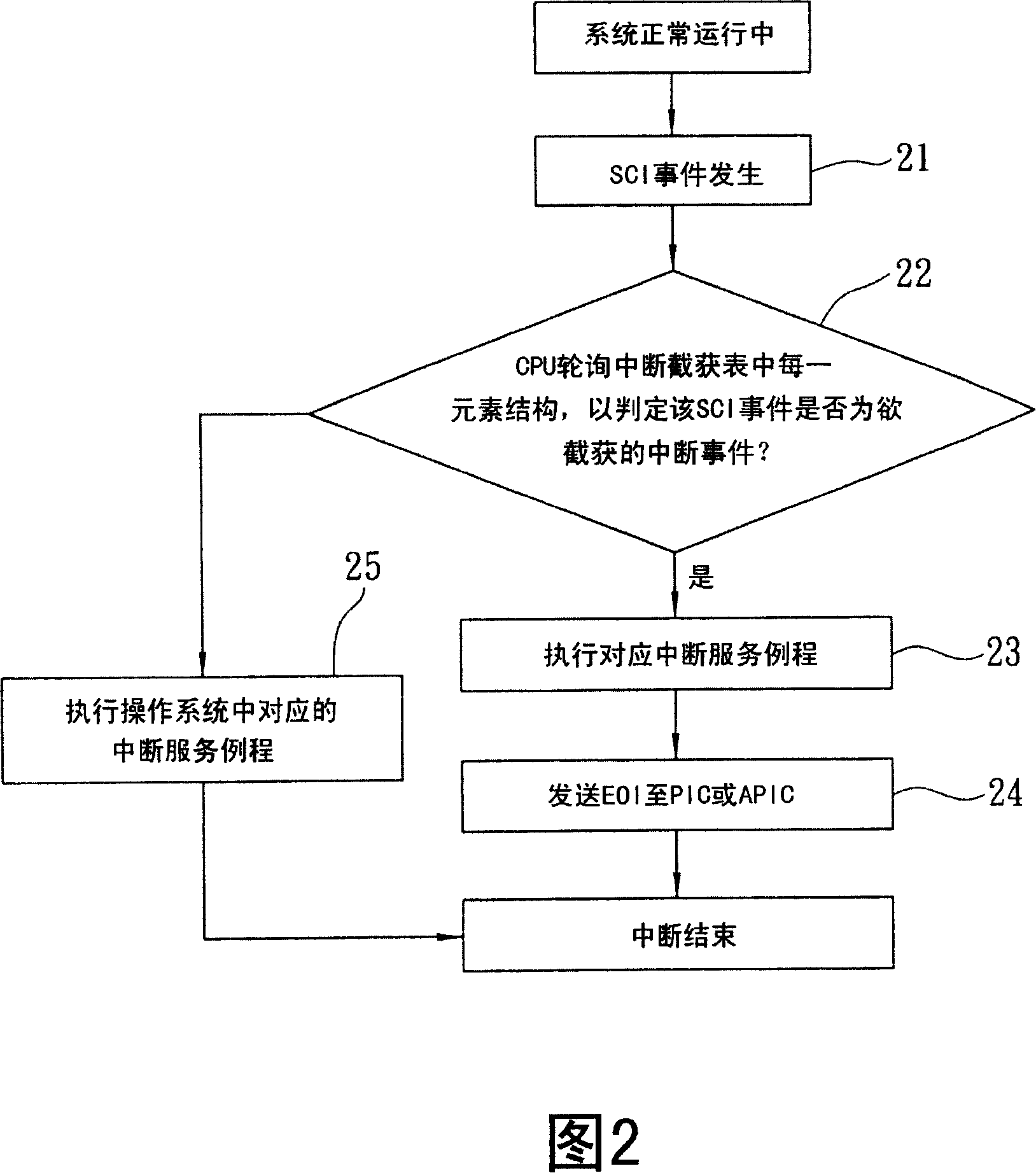
A control interruption method for application program interception and monitoring systems, comprises: A hardware interruption request number of a system control interruption that is taken by an application program from a Basic Input and Output System (BIOS); an interruption vector number that corresponds with the hardware interruption request number, and acquired by the application program in a corresponding way according to that the interruption mode is a programmable interruption controller mode, or an advanced programmable interruption controller mode; a plurality of interruption service program examples that modify interruption entrance in an interruption description symbol list in a Central Process Unit (CPU) corresponds with interruption vector number, into pointing to application programs; as well as a plurality of interruption events corresponding with initialization information that is pre-established according to an interruption and interception list in the application program, and initialization hardware interruption request number.
Owner:UNIVERSAL SCI IND CO LTD
Technique for communicating interrupts in a computer system
A technique to enable efficient interrupt communication within a computer system. In one embodiment, an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APlC) is interfaced via a set of bits within an APIC interface register using various interface instructions or operations, without using memory-mapped input / output (MMIO).
Owner:INTEL CORP
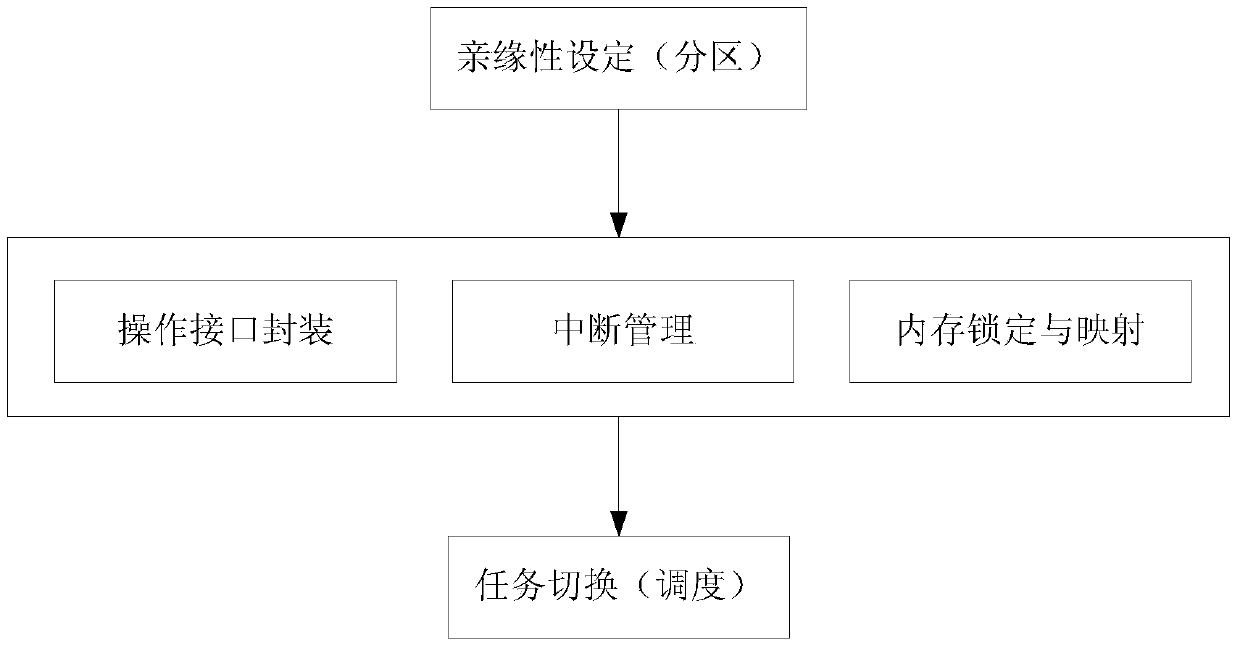
Two-stage scheduling method of real-time extension of Windows system
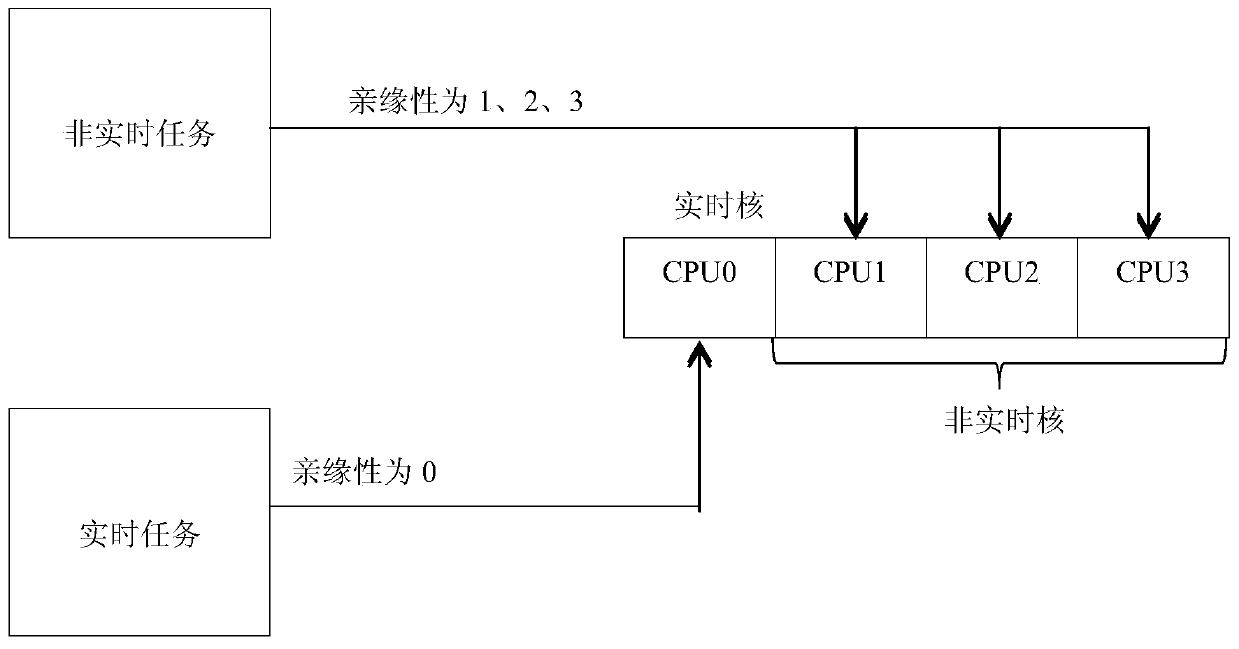
ActiveCN103744726AResolve task switchingSolve real-timeProgram initiation/switchingTime extensionAdvanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
The invention relates to a two-stage scheduling method of real-time extension of the Windows system. According to the method, by means of affinity settings of the Windows system, reallocating the CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources of the system, and specifying a running core of real-time tasks in order to ensure resources needed by the real-time tasks; setting an IOAPIC(I / O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) redirection table to enable external interrupt to point to specific core processing and to not affect the operation of real-time kernel; meanwhile, using a clock interrupt counter of Local APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) to provide task scheduling with high-precision clock signals; using WinDbg to obtain operation function entry addresses of the process and the thread of Windows from NTDLL to be packaged as DLL, and forming a basic interface of task control; locking and mapping kernel task control blocks and task queues to enable the writing and debugging of a scheduling algorithm can be performed in a user mode, and finally linking into the interrupt handling routine of the high-precision clock of the Local APIC so as to complete the real-time kernel scheduling algorithm.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for implementing high-accuracy low-CPU (central processing unit)-occupancy timer under Pentium IV architecture of Windows operating system
ActiveCN103197971AReduce occupancyImplement the callProgram initiation/switchingStructure of Management InformationChipset
The invention discloses a method for implementing a high-accuracy low-CPU (central processing unit)-occupancy timer under Pentium IV architecture of the Windows operating system, relates to the technical field of timer software development of the Windows operating system and aims to design a timer high in accuracy and low in CPU resources occupancy to solve the technical problem of failure in realizing high accuracy and low CPU resources occupancy during Windows multi-task time division operation. By adopting 8254 chips in a chip set of a PC (personal computer) under Pentium IV architecture and writing 8254 interrupt timer driving program and APIC (advanced programmable interrupt controller) program, an interrupt based clock timer is realized in the Windows. By defining an interrupt processing function, changing interrupt door structure in an interrupt descriptor table and valuating the door structure by a pointer of the self-defined interrupt processing function, calling of user-defined interrupt processing functions is realized, and applicable timer is realized. After test, timing accuracy can reach submillimeters, timing offset is smaller than 7 microseconds when timing is 100 microseconds, CPU occupancy is quite low, and most timing application requirements of the Windows system are met.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
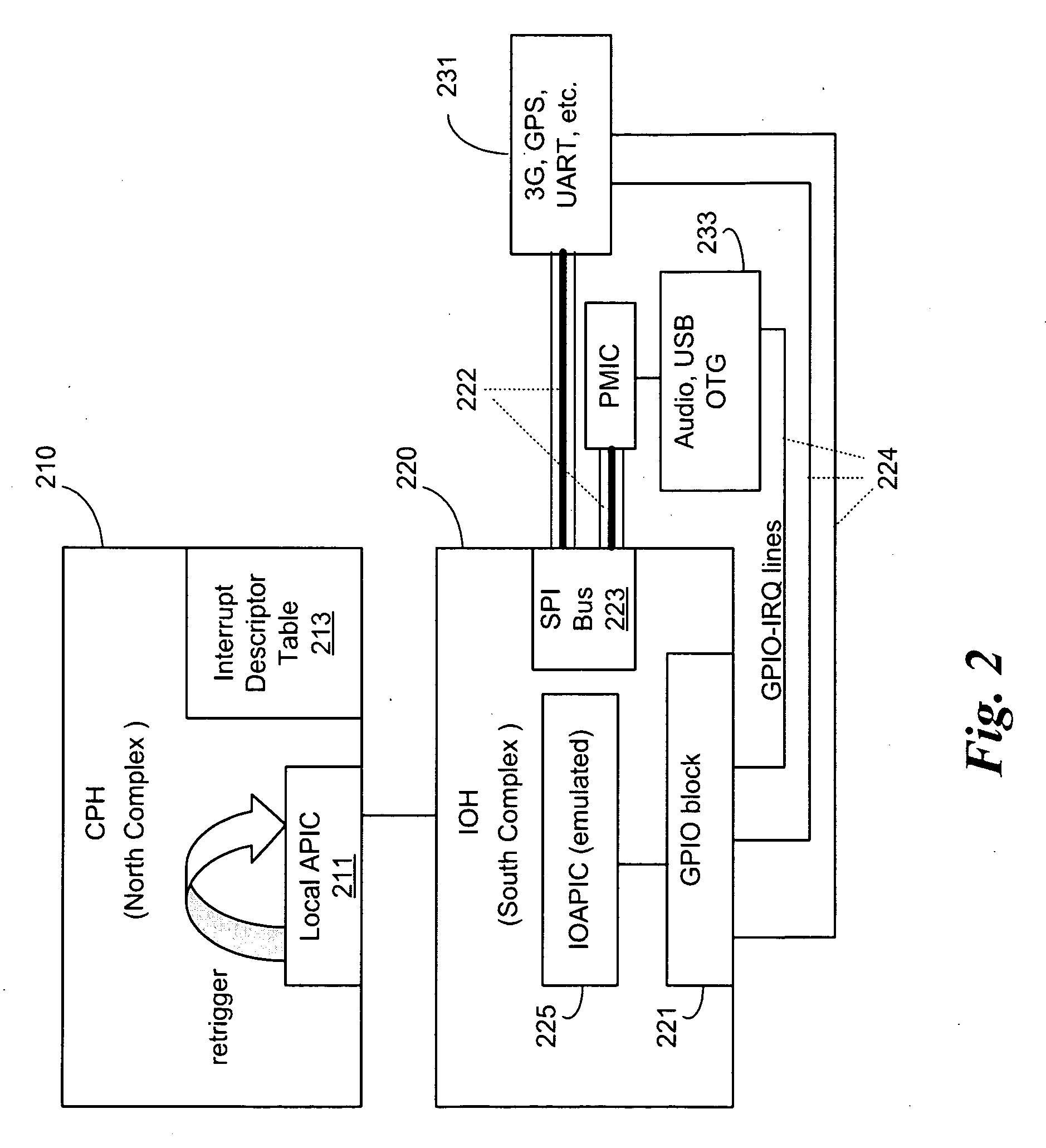
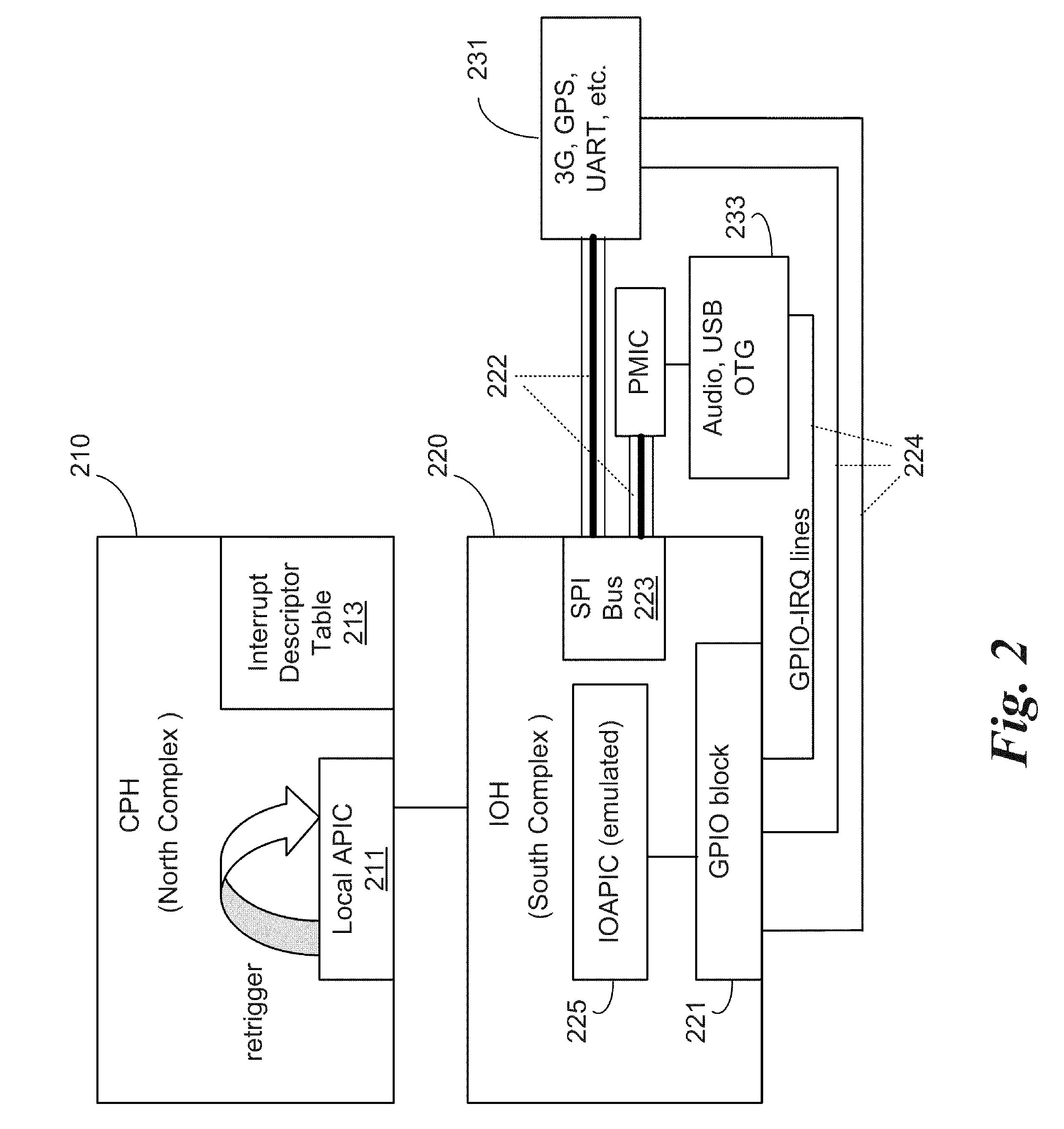
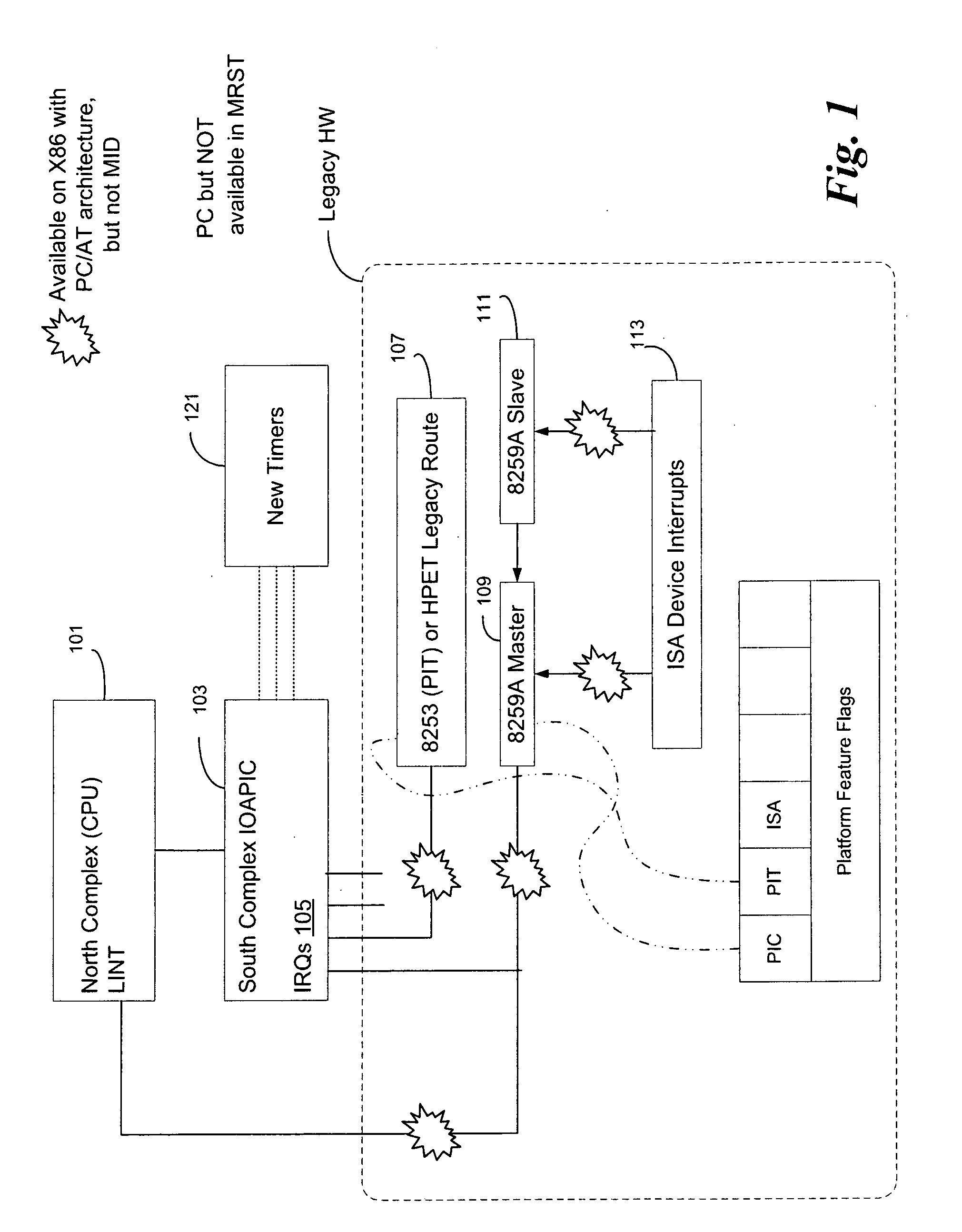
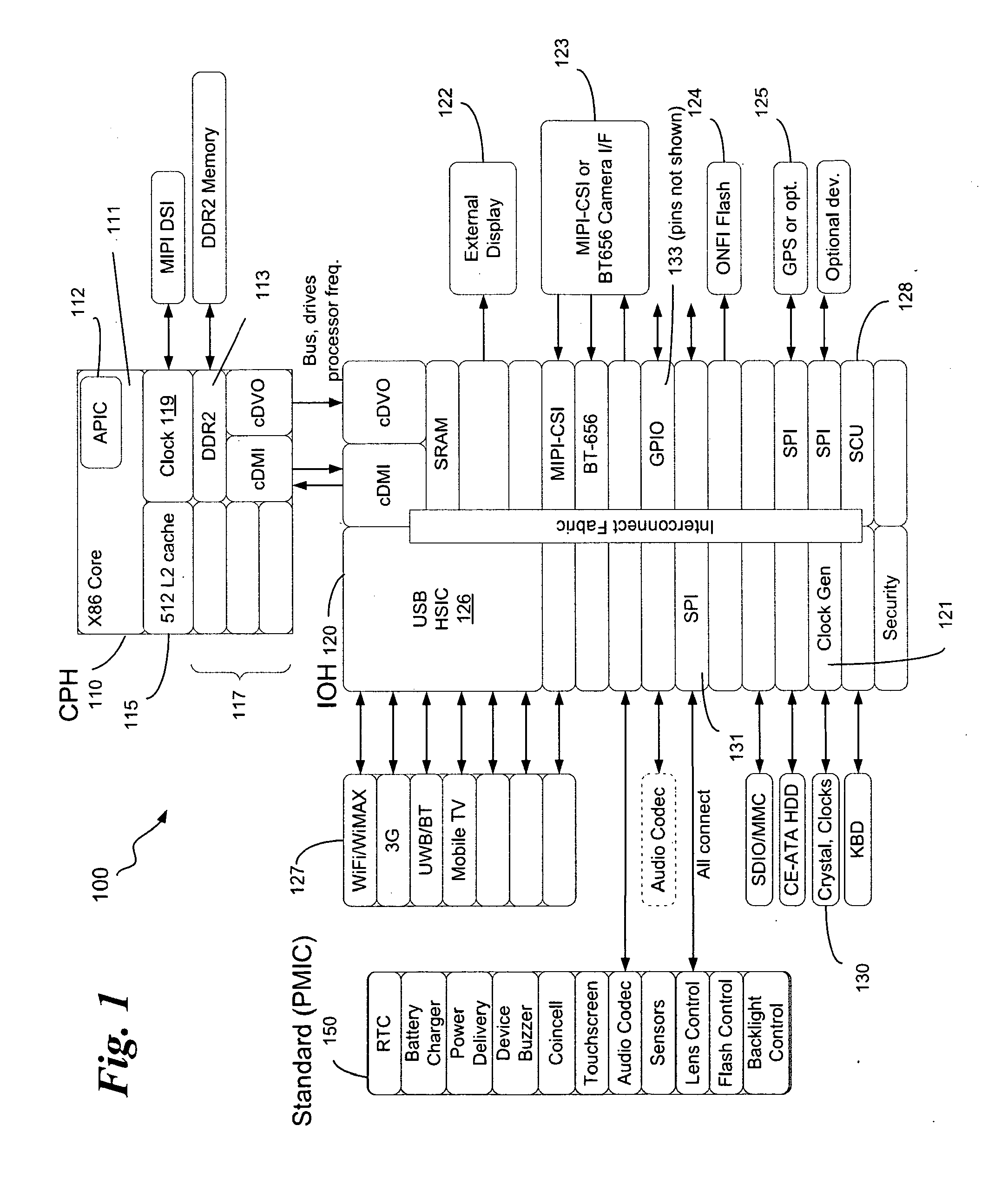
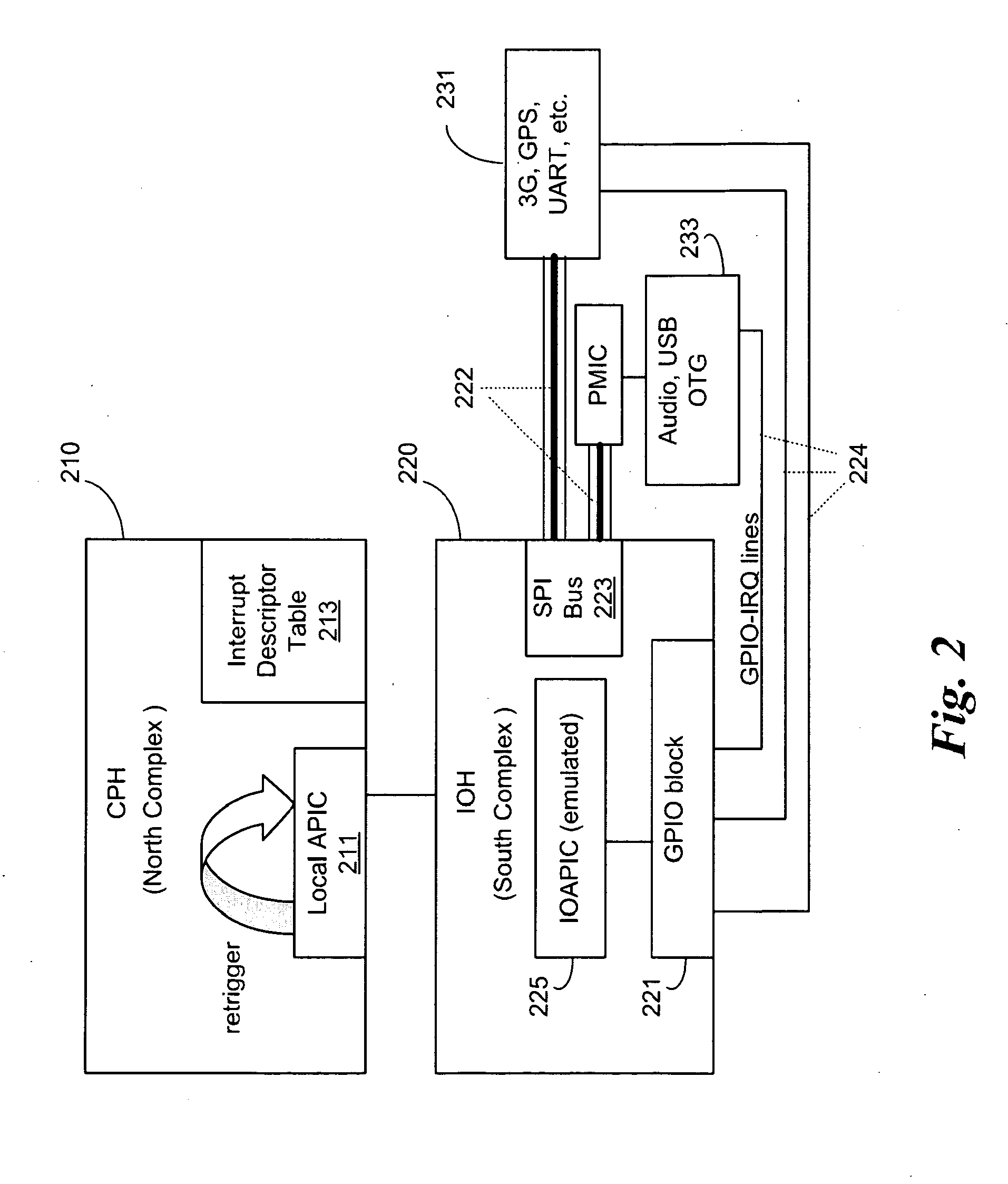
Dynamic, local retriggered interrupt routing discovery method
InactiveUS20100262737A1Reduce settingsMinimize changesElectric digital data processingAdvanced Programmable Interrupt ControllerGeneral-purpose input/output
In some embodiments, the invention involves a dynamic interrupt route discovery method with local APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) retriggering to accommodate architectures that are not PC / AT compatible. In a mobile Internet device (MID) General Purpose Input / Output (GPIO) pins are dynamically allocated and IRQs are retriggered by a GPIO driver to multiplex the requests to an appropriate device. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Technique for communicating interrupts in a computer system
A technique to enable efficient interrupt communication within a computer system. In one embodiment, an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) is interfaced via a set of bits within an APIC interface register using various interface instructions or operations, without using memory-mapped input / output (MMIO).
Owner:INTEL CORP
Interrupt controller, interrupt signal pretreating circuit and its interrupt control method
ActiveCN1858725AWake up interrupt handlingPower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingAdvanced Configuration and Power InterfaceGrating
This invention relates to an interrupt controller in conformity with the ACPI power management stanadard computer system and an interrupt signal pre-process circuit and its interrupt control method used in said interrupt controller, which can save power in ordinary work of a computer system, the control method includes: when interrupt input signals exist in a judgement system, the gating clock signal in the interrupt control process can deal with the signals properly and introduce the processed signals to an advanced programmable interrupt controller for proper process, when the process is finished, the grating clock signal is pulled to a low level.
Owner:VIA TECH CHINA
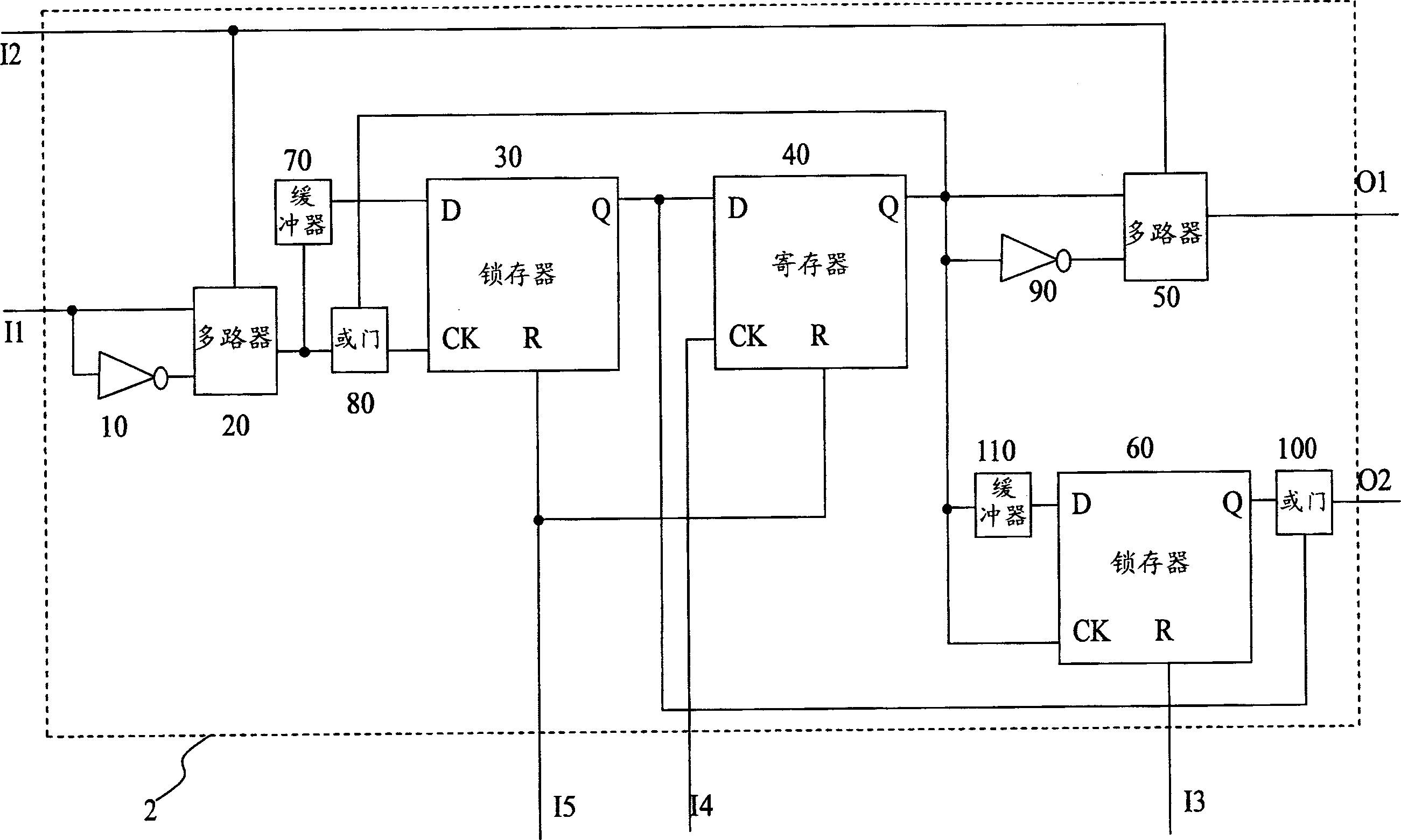
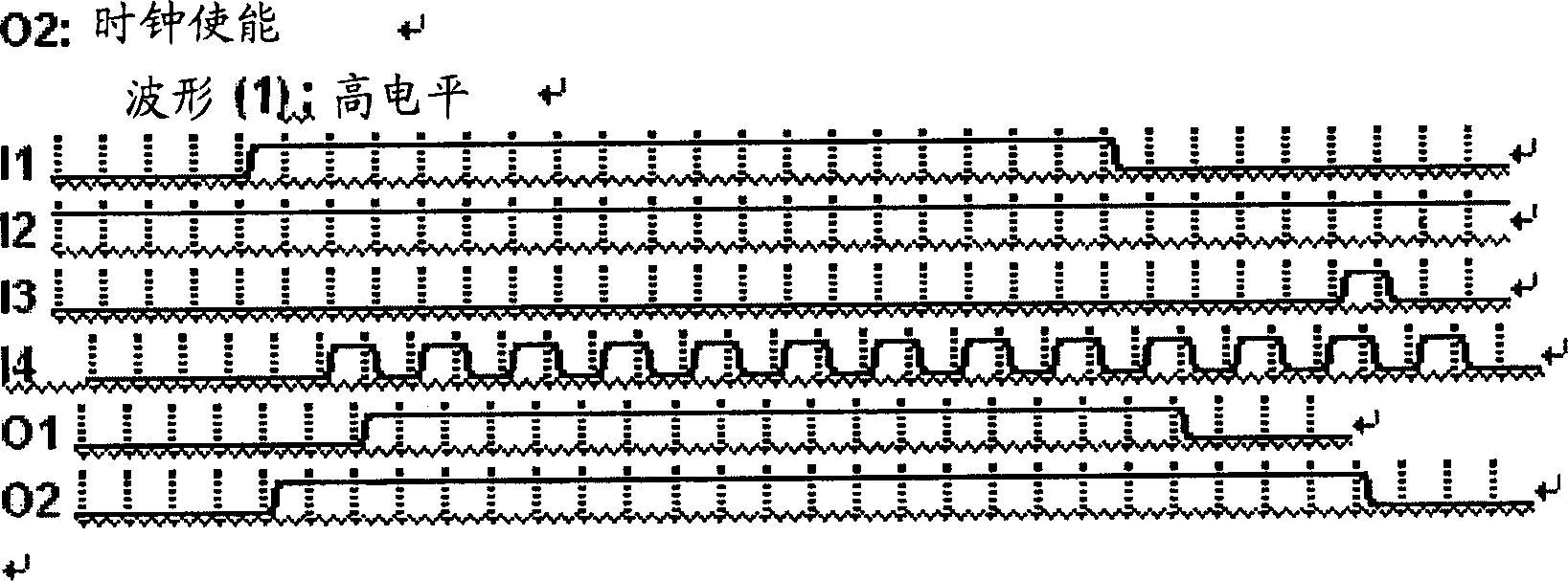
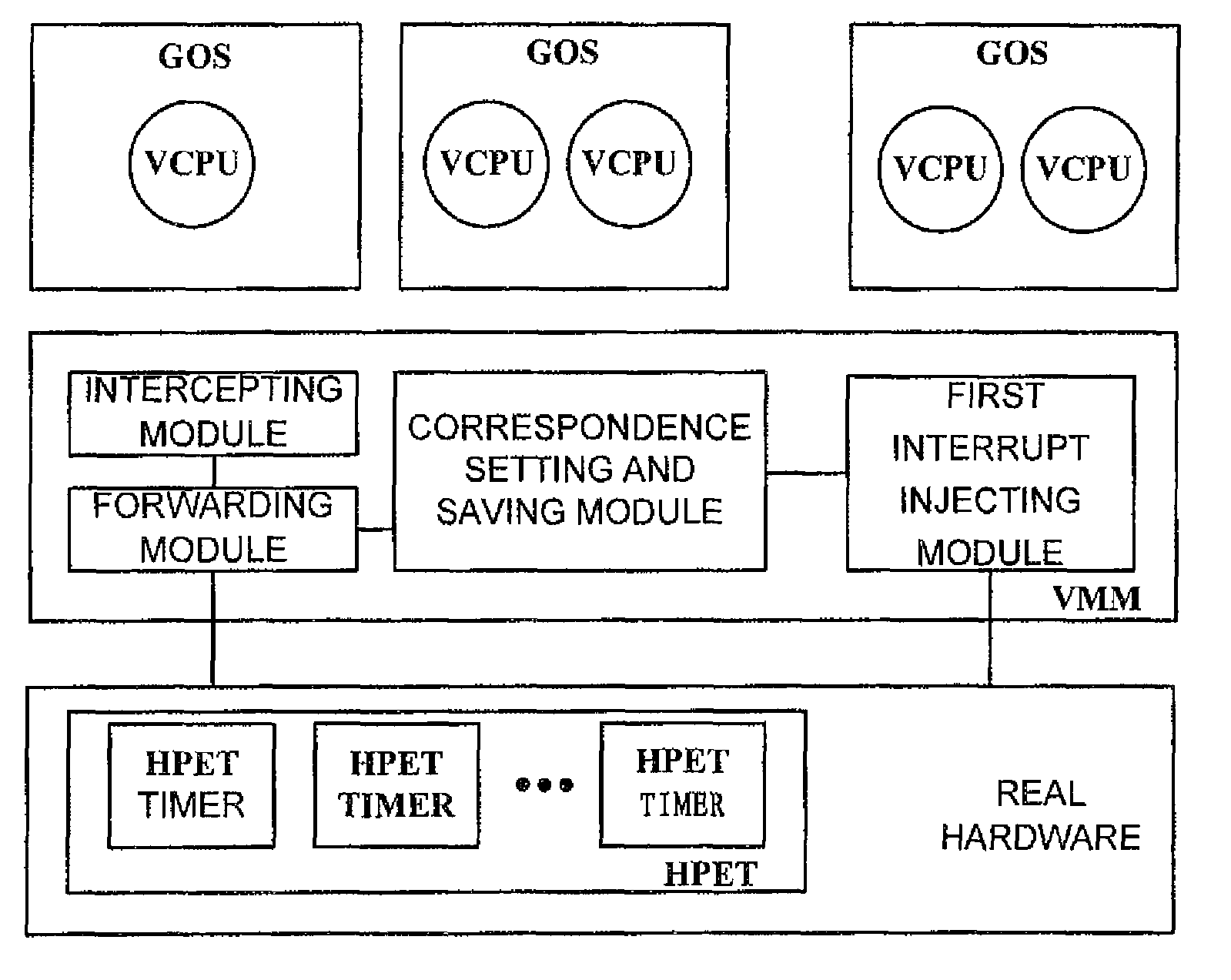
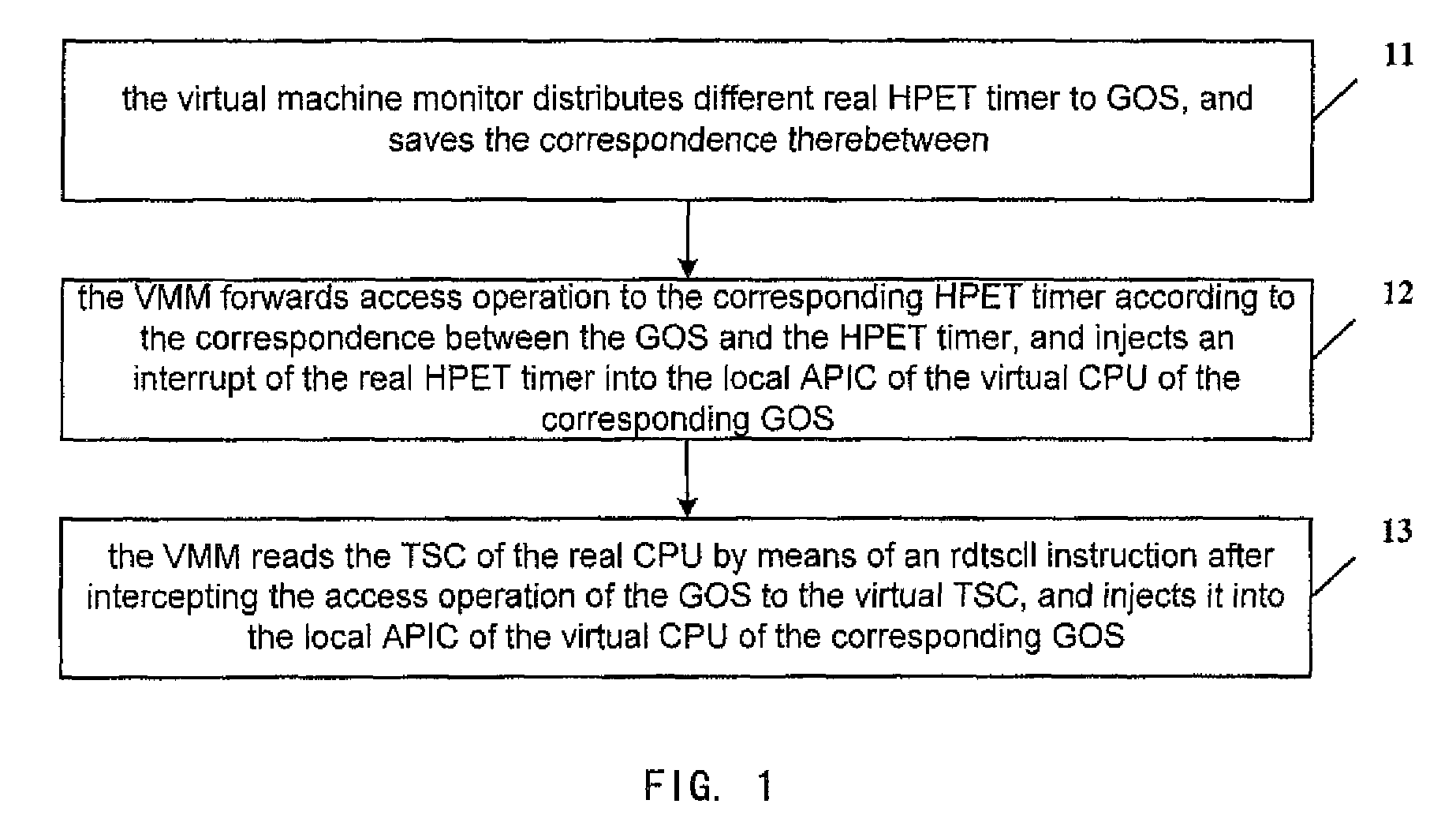
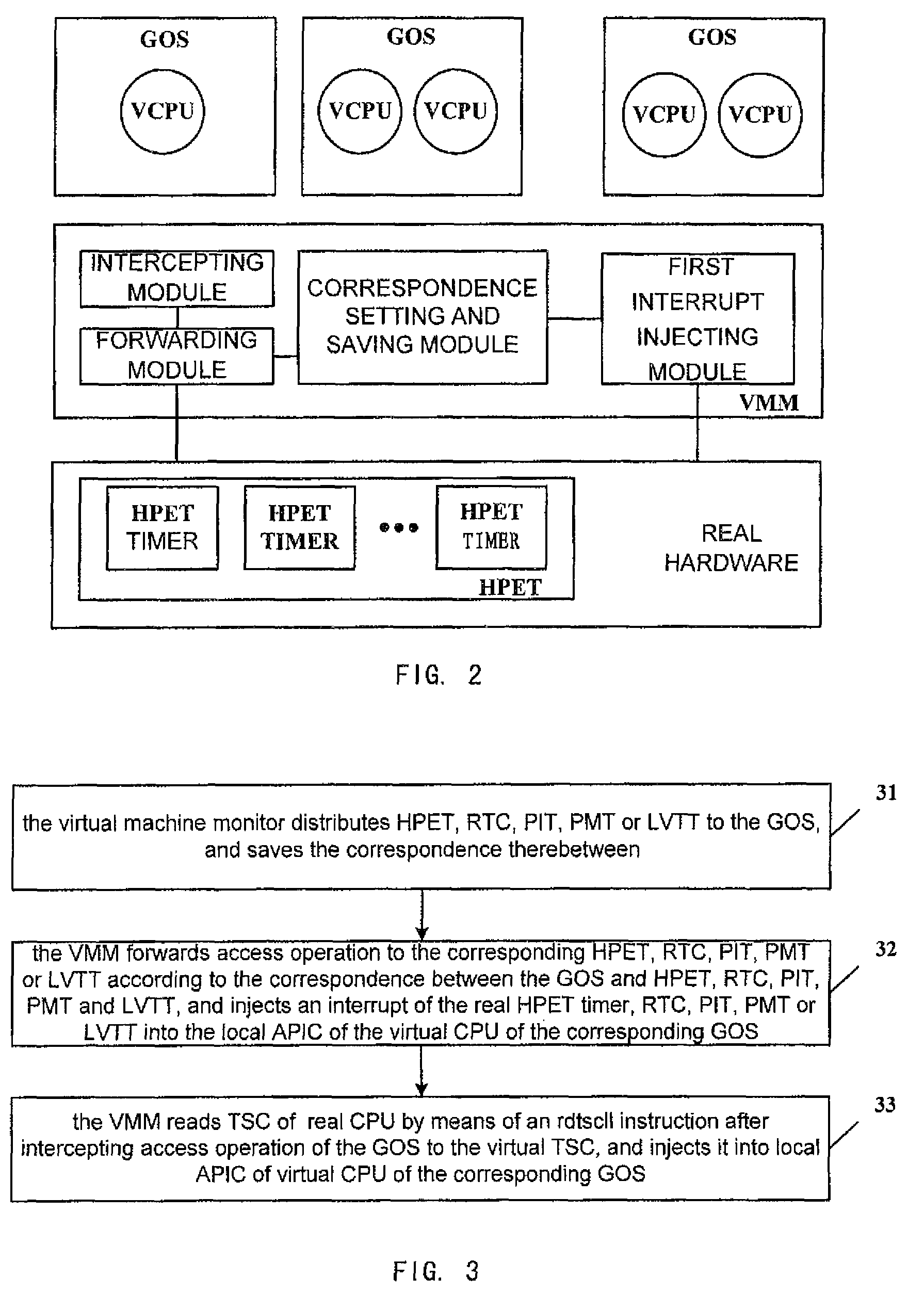
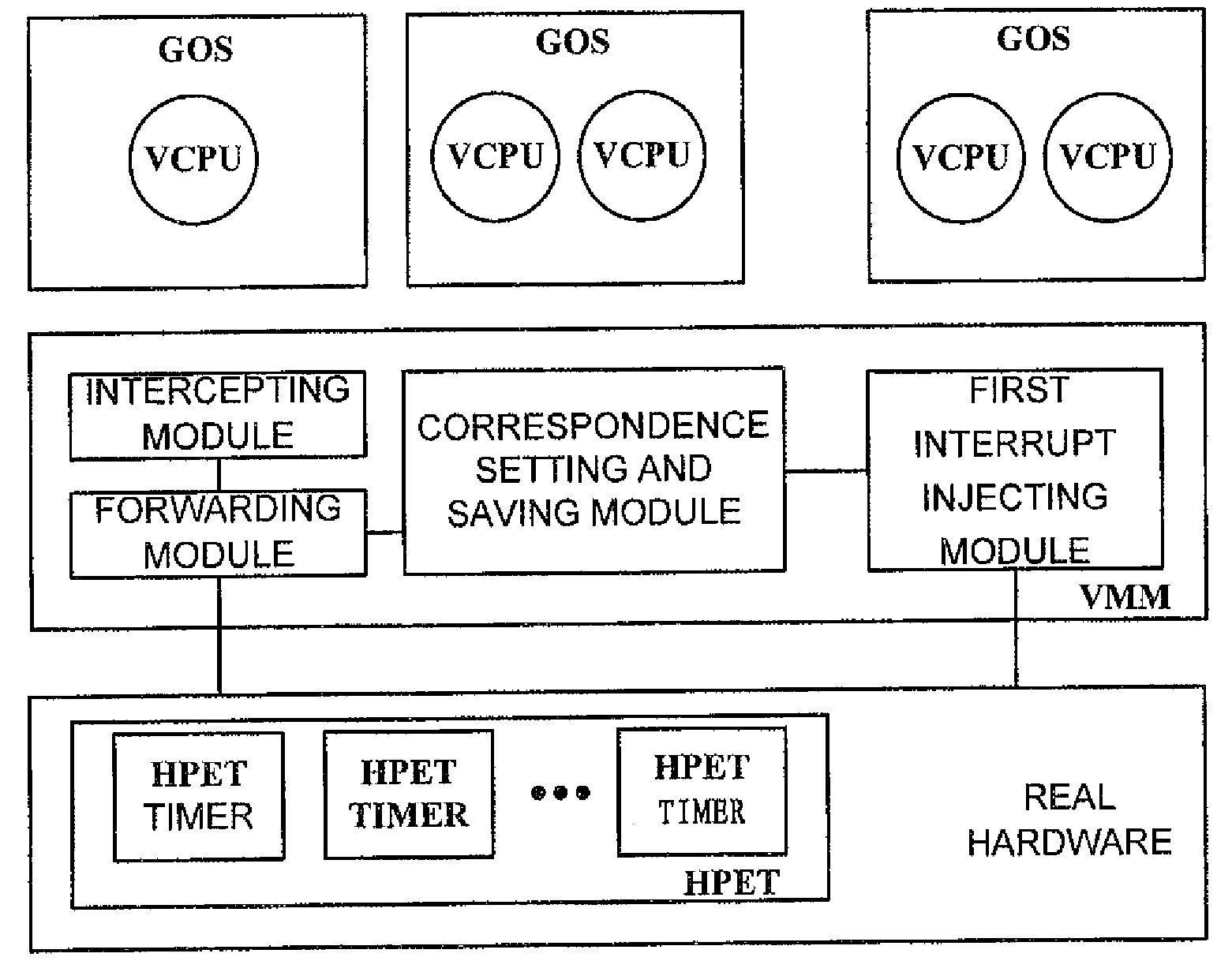
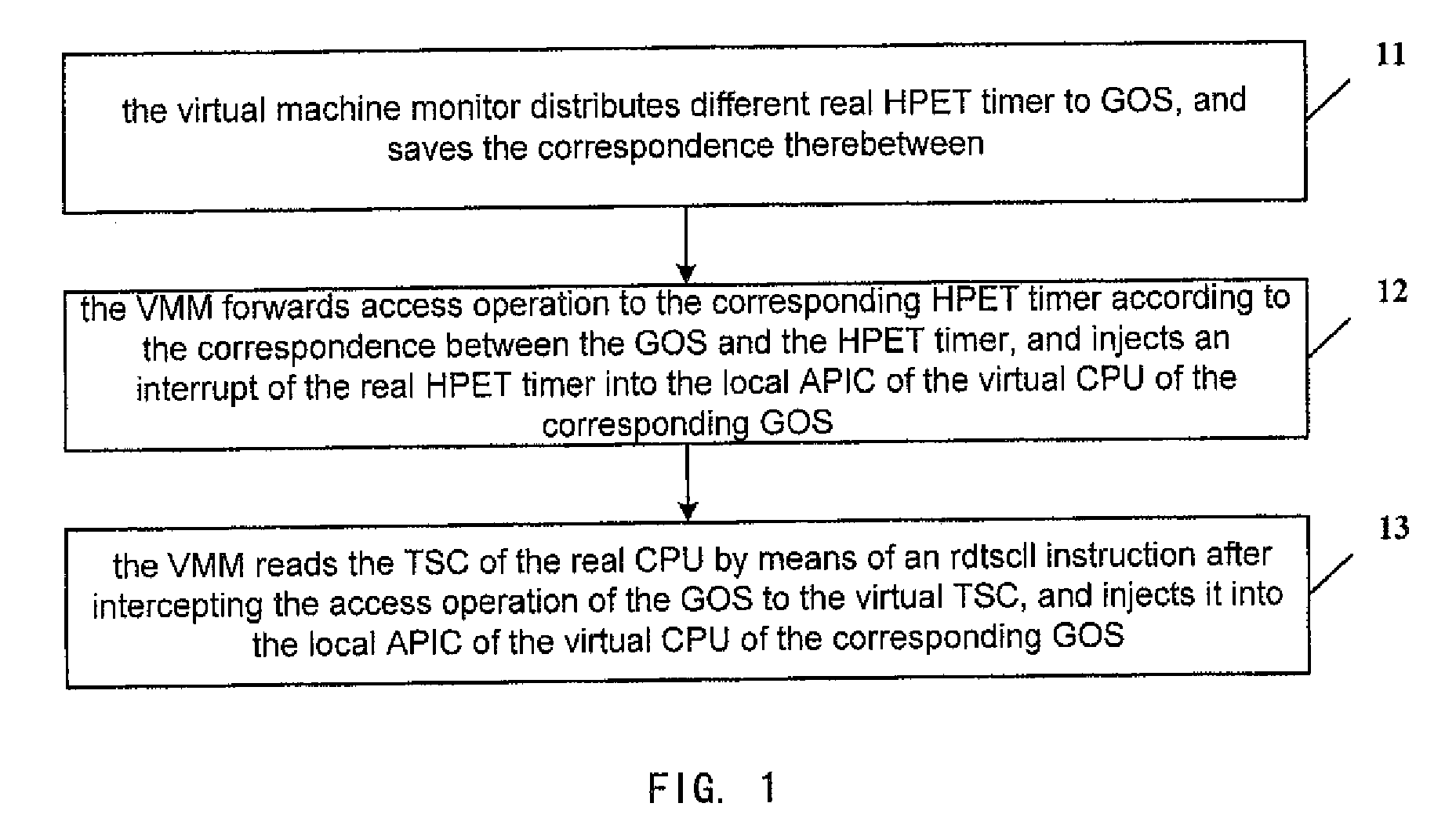
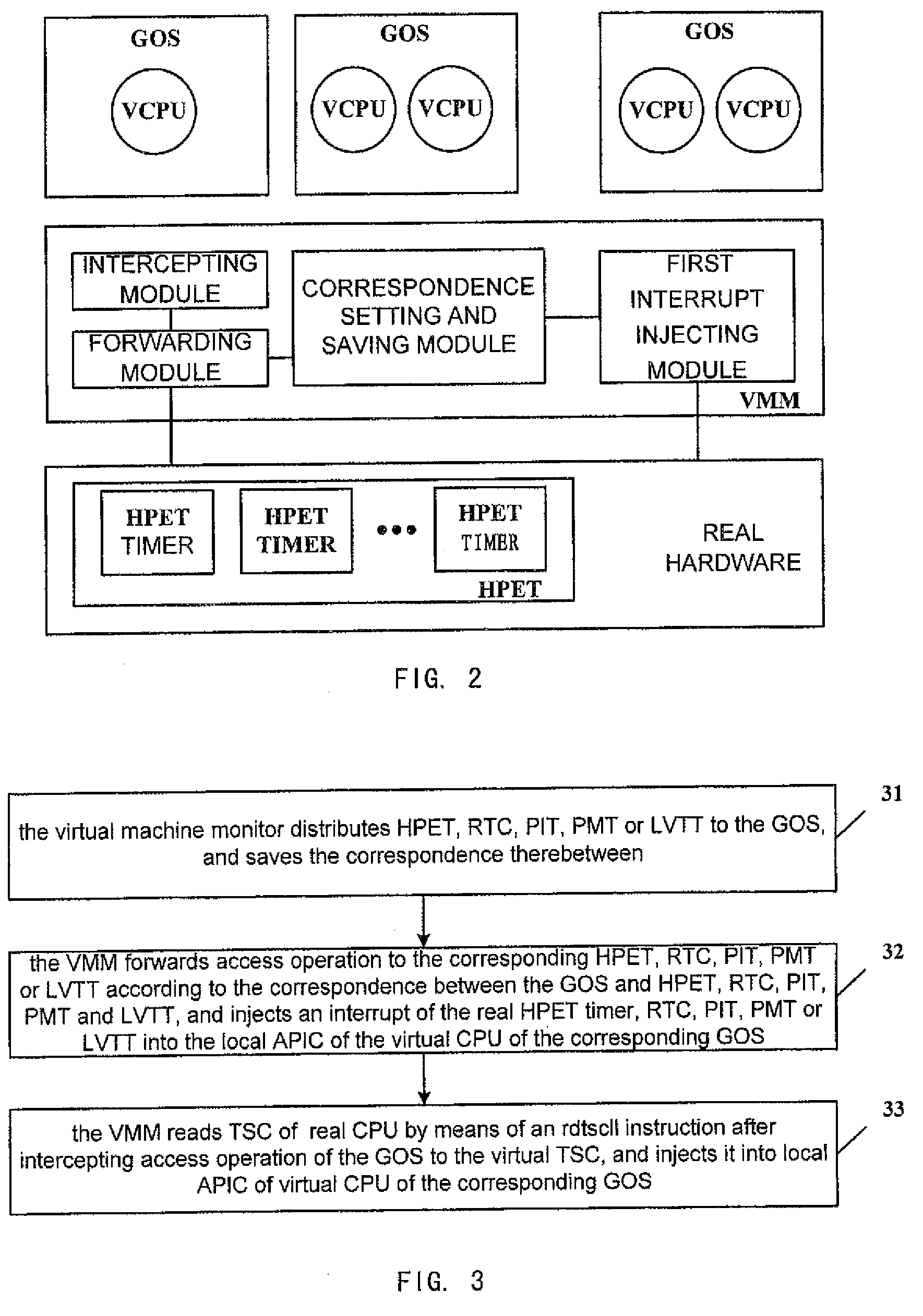
Virtual machine monitor, virtual machine system and clock distribution method thereof
ActiveUS8086890B2Accurate serviceProgram controlGenerating/distributing signalsVirtual file systemReal-time clock
A virtual machine monitor, a virtual machine system and a clock distribution method thereof. The clock distribution method includes: distributing real clock resource to a Guest Operation System (GOS), and saving correspondence between said GOS and said real clock resource; intercepting an access operation of said GOS to a virtual clock resource; sending said access operation to the corresponding real clock resource according to said correspondence, and then performing a write operation, or injecting an interrupt of said real clock resource into a local Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers (APIC) of a virtual CPU of the corresponding GOS of said GOSs.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
Virtual machine monitor, virtual machine system and clock distribution method thereof
ActiveUS20090132846A1Accurate serviceProgram controlGenerating/distributing signalsAdvanced Programmable Interrupt ControllerVirtual machine
A virtual machine monitor, a virtual machine system and a clock distribution method thereof. The clock distribution method includes: distributing real clock resource to a Guest Operation System (GOS), and saving correspondence between said GOS and said real clock resource; intercepting an access operation of said GOS to a virtual clock resource; sending said access operation to the corresponding real clock resource according to said correspondence, and then performing a write operation, or injecting an interrupt of said real clock resource into a local Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers (APIC) of a virtual CPU of the corresponding GOS of said GOSs.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Technique for communicating interrupts in a computer system
InactiveUS8312198B2Electric digital data processingProgrammable Interrupt ControllerComputerized system
A technique to enable efficient interrupt communication within a computer system. In one embodiment, an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APlC) is interfaced via a set of bits within an APIC interface register using various interface instructions or operations, without using memory-mapped input / output (MMIO).
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic, local retriggered interrupt routing discovery method
InactiveUS7953916B2Reduce settingsMinimize changesElectric digital data processingTTEthernetThe Internet
In some embodiments, the invention involves a dynamic interrupt route discovery method with local APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) retriggering to accommodate architectures that are not PC / AT compatible. In a mobile Internet device (MID) General Purpose Input / Output (GPIO) pins are dynamically allocated and IRQs are retriggered by a GPIO driver to multiplex the requests to an appropriate device. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Identifying-code configuration method of high-grade programable interruption controller
InactiveCN1979455ASolve conflictsImprove stabilityElectric digital data processingMulti processorProgrammable Interrupt Controller
The invention is an identification code configuring method for advanced programmable interrupt controllers, applied to a multiprocessor computer system, reallocating identification code of advanced programmable interrupt controller of each CPU in the initializing course, presetting partial identification codes to I / O advanced programmable interrupt controllers and updating multiprocessor configuration table in basic I / O system (BIOS) to avoid the problem of causing identification code conflict at the time of processing interrupt request of peripheral devices, and improving the stability of the multiprocessor computer system.
Owner:HUANDA COMPUTER (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
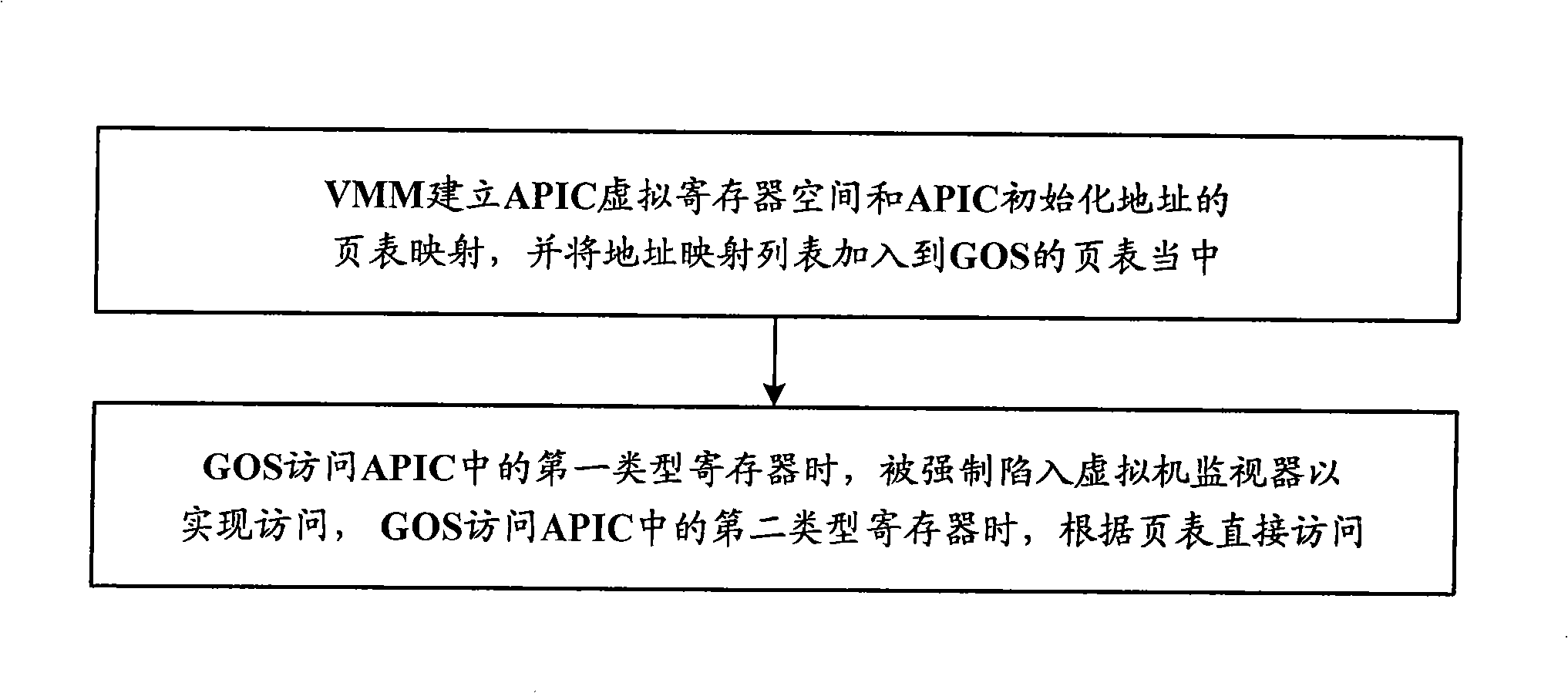
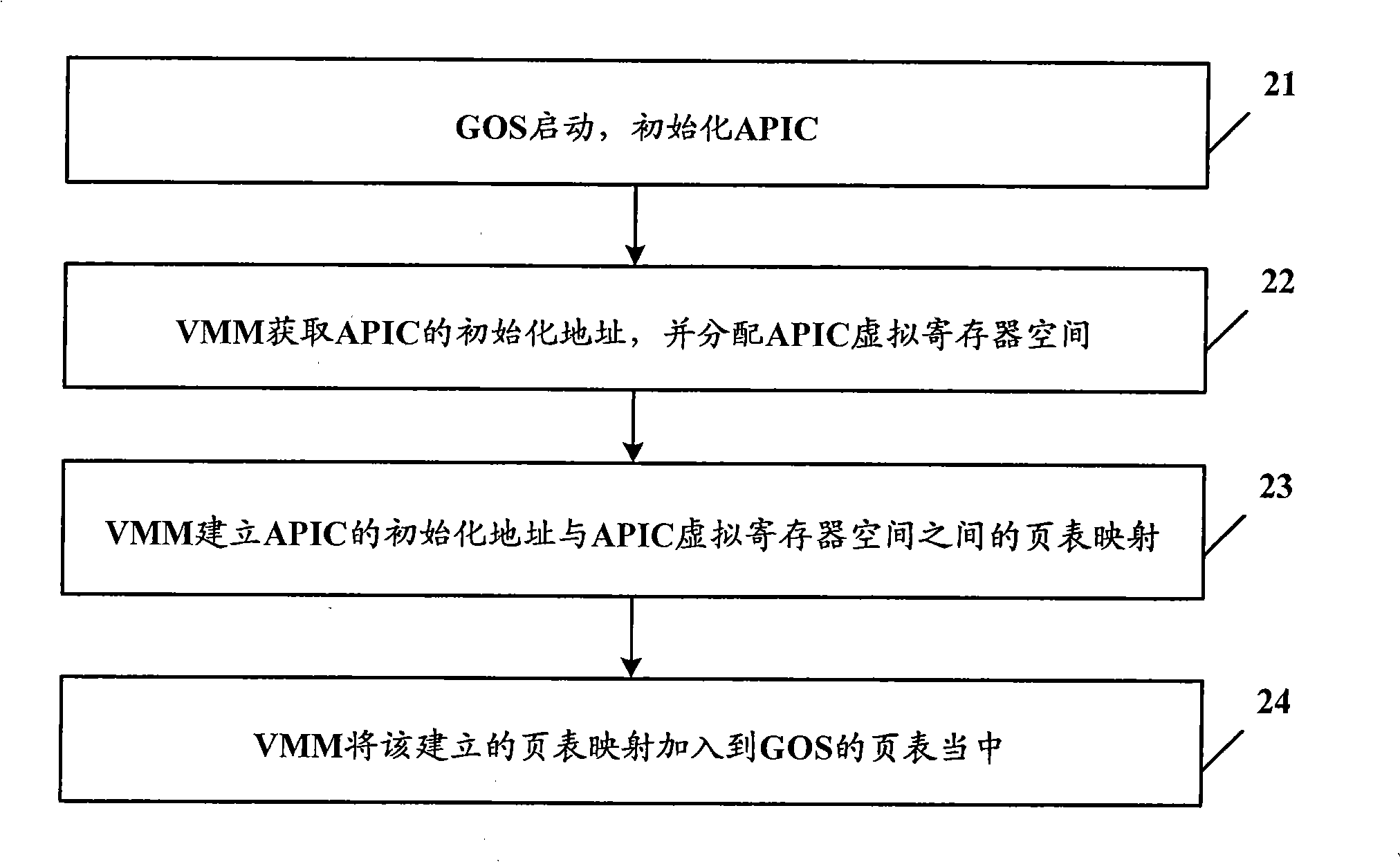
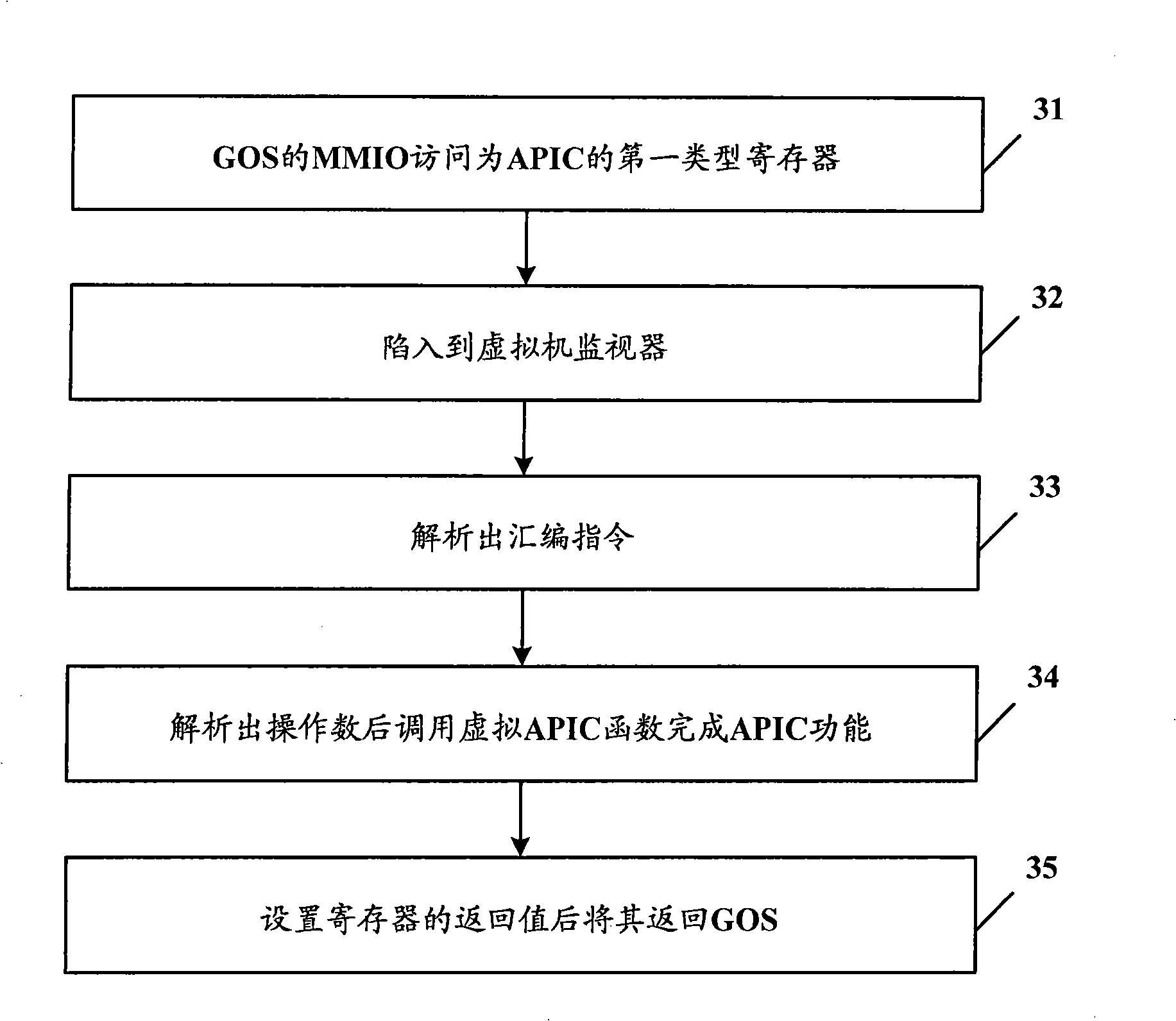
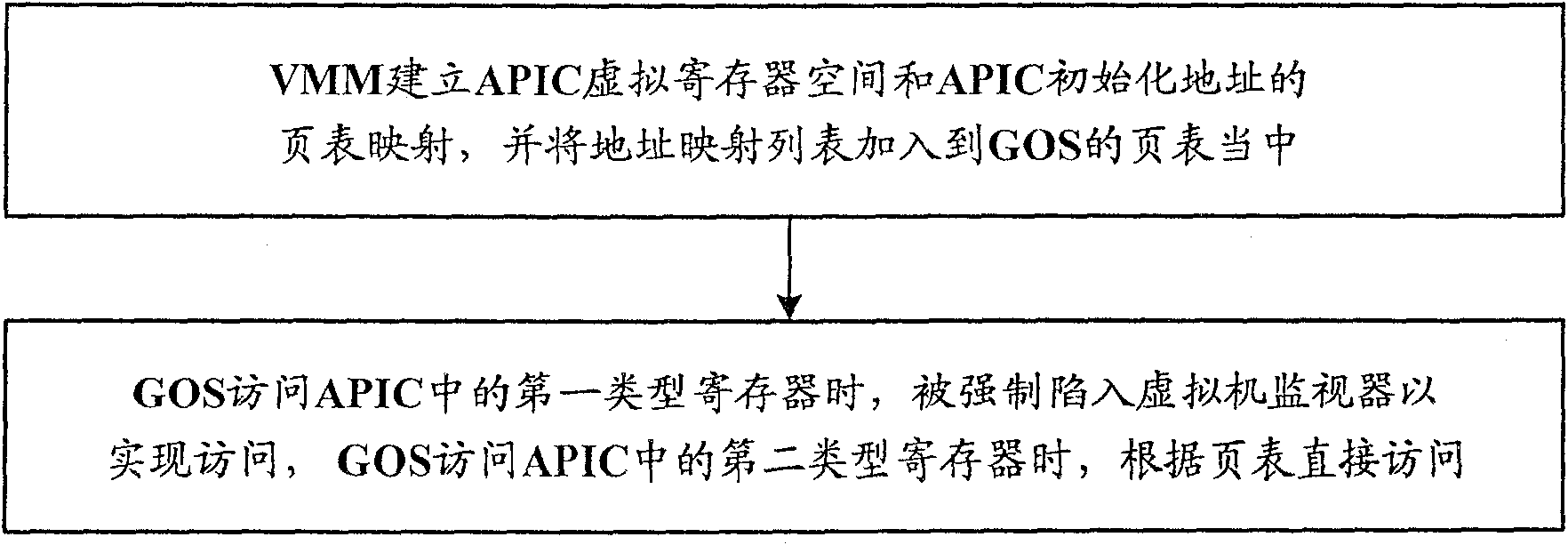
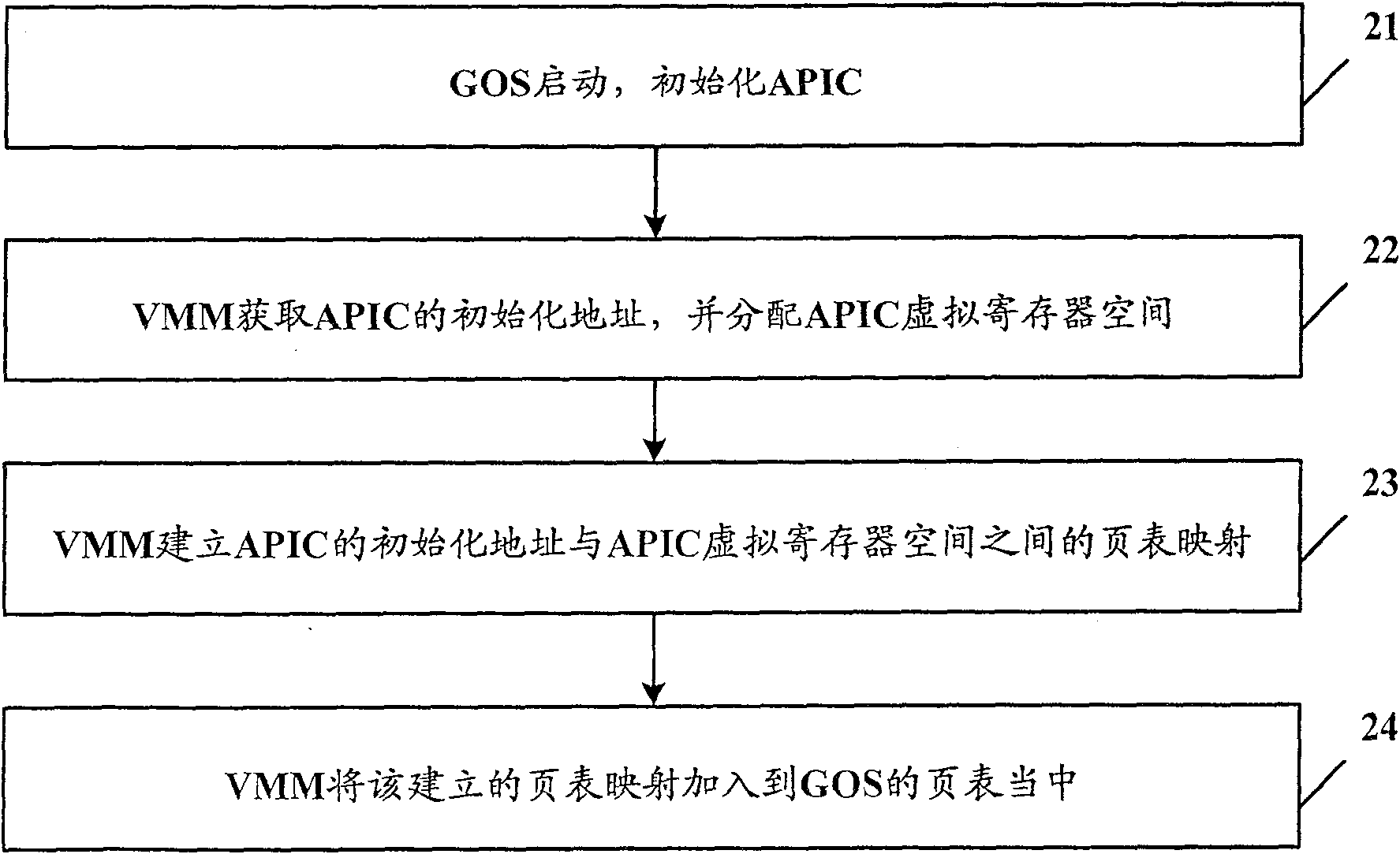
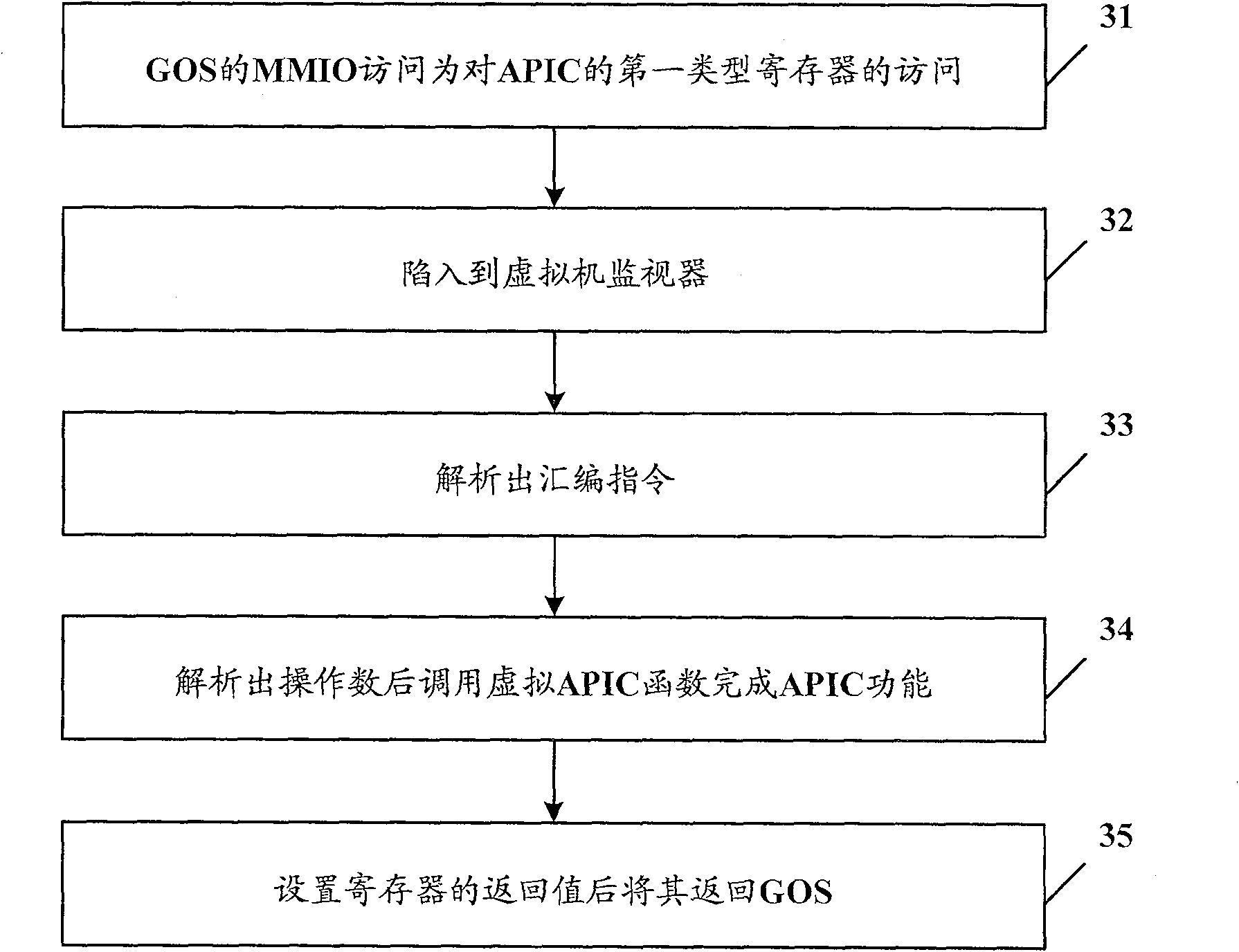
Virtual machine system and access processing method of its advanced programmable interrupt controller
ActiveCN101271436AReduce access cycleReduce stepsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAdvanced Programmable Interrupt ControllerVirtual machine
The present invention discloses a virtual machine system and a visit processing method of an advanced programmable interruption controller. The method includes an address mapping procedure in which a virtual machine monitor sets up an APIC virtual register space and a table mapping of APIC initial address and adds the address mapping table to the table of a virtual machine client operating system; an APIC visit control procedure in which the client operating system carries out the visit by compulsorily involving in the virtual machine monitor when visiting the first type register of APIC, and conducts the direct visit according to the address mapping table when visiting the second type register of APIC. The operation of the first type register can result in the change of other registers of APIC and the operation of the second type register can not affect other registers of APIC. The present invention greatly shortens the visit cycle of APIC and simplifies the operation.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Method and system for generating and delivering inter-processor interrupts in a multi-core processor and in certain shared memory multi-processor systems
ActiveUS9032128B2Facilitate shared-memory-based communicationEfficient use ofProgram initiation/switchingMulti processorInter-processor interrupt
Certain embodiments of the present invention are directed to providing efficient and easily-applied mechanisms for inter-core and inter-processor communications and inter-core and inter-processor signaling within multi-core microprocessors and certain multi-processor systems. In one embodiment of the present invention, local advanced programmable interrupt controllers within, or associated with, cores of a multi-core microprocessor and / or processors of a multi-processor system are enhanced so that the local advanced programmable interrupt controllers can be configured to automatically generate inter-core and inter-processor interrupts when WRITE operations are directed to particular regions of shared memory.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
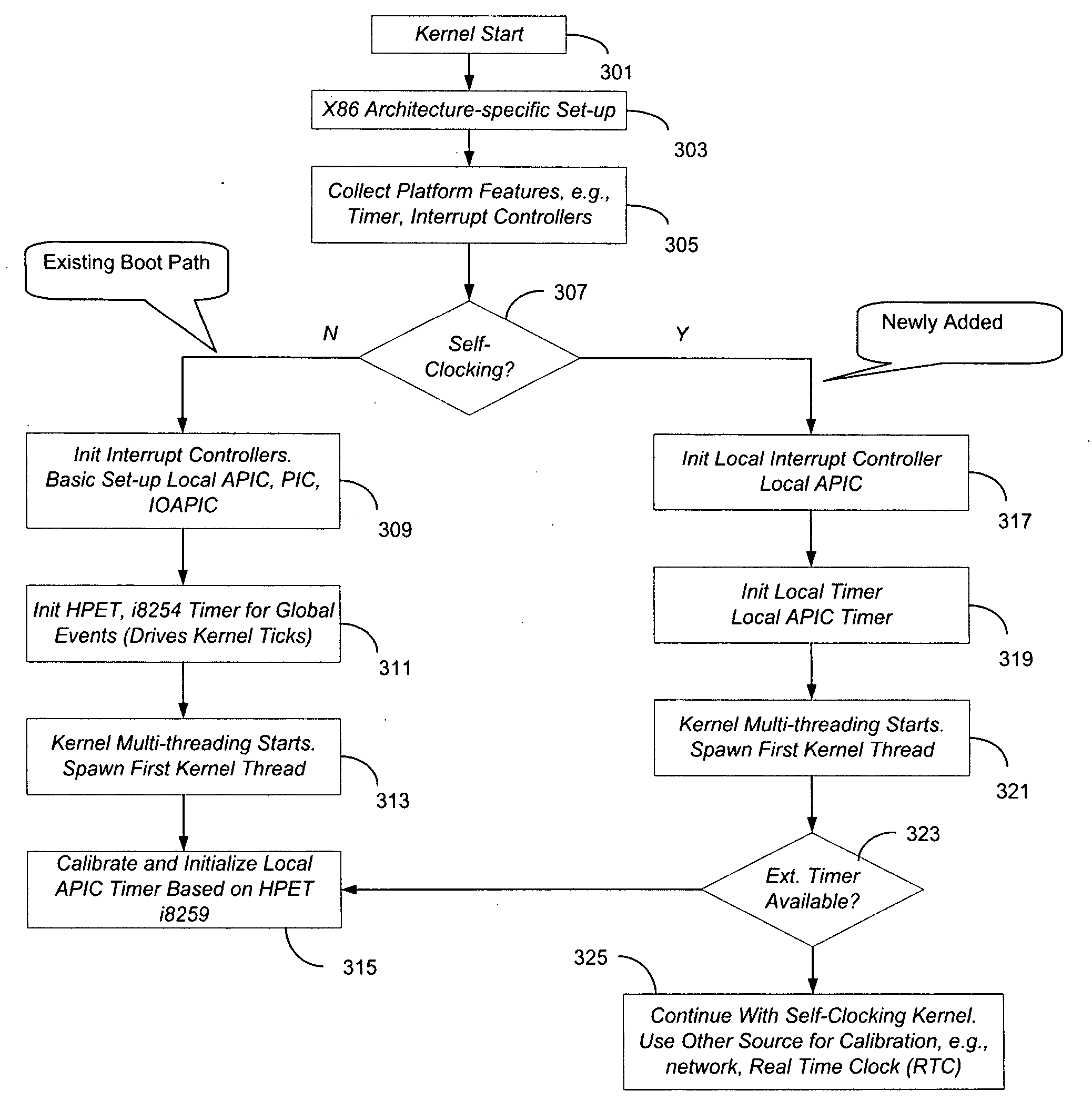
System and method for self-clocking os kernel boot
InactiveUS20100169634A1Minimal impactBoot process reliable and portableDigital computer detailsBootstrappingMobile deviceAdvanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
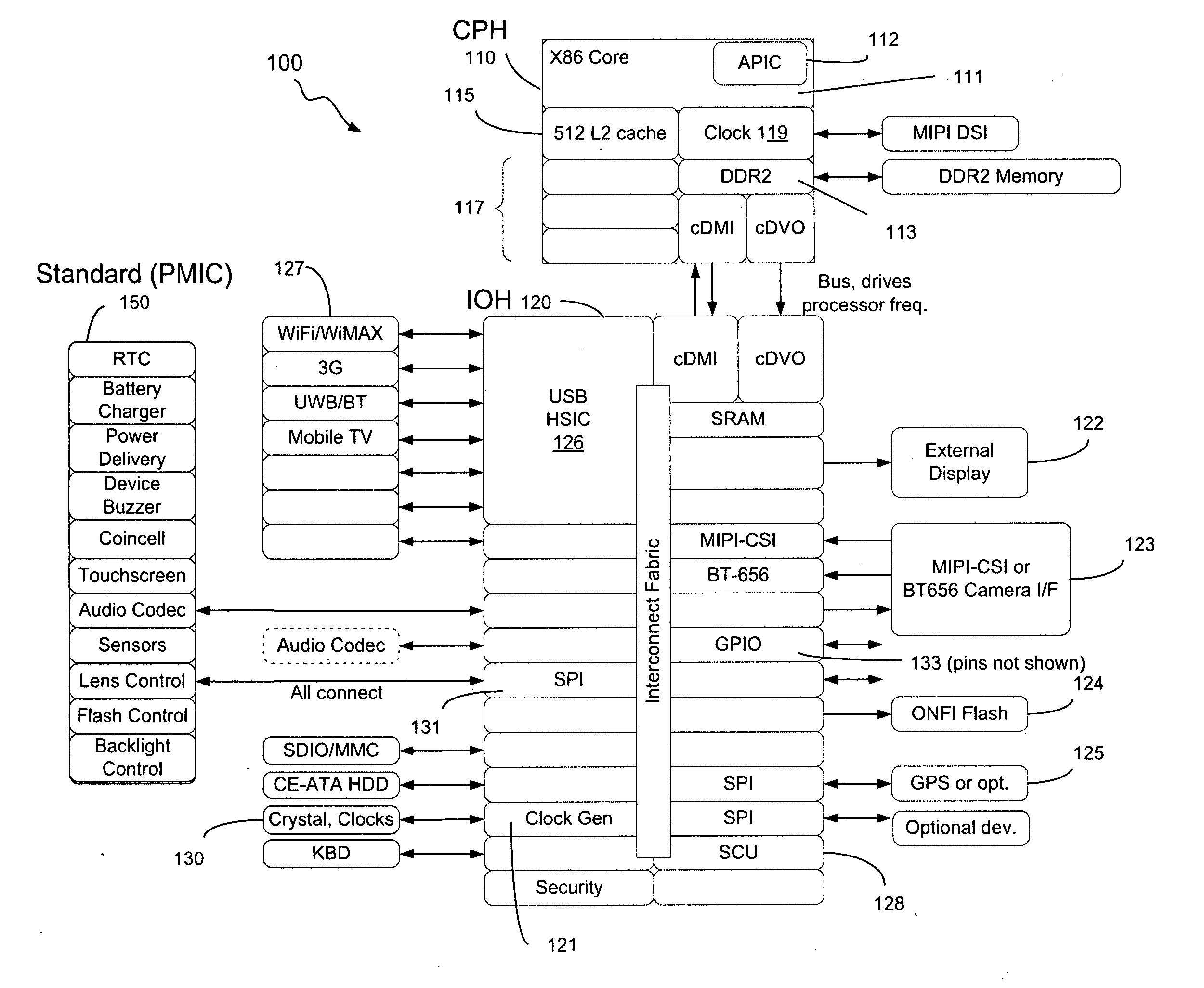
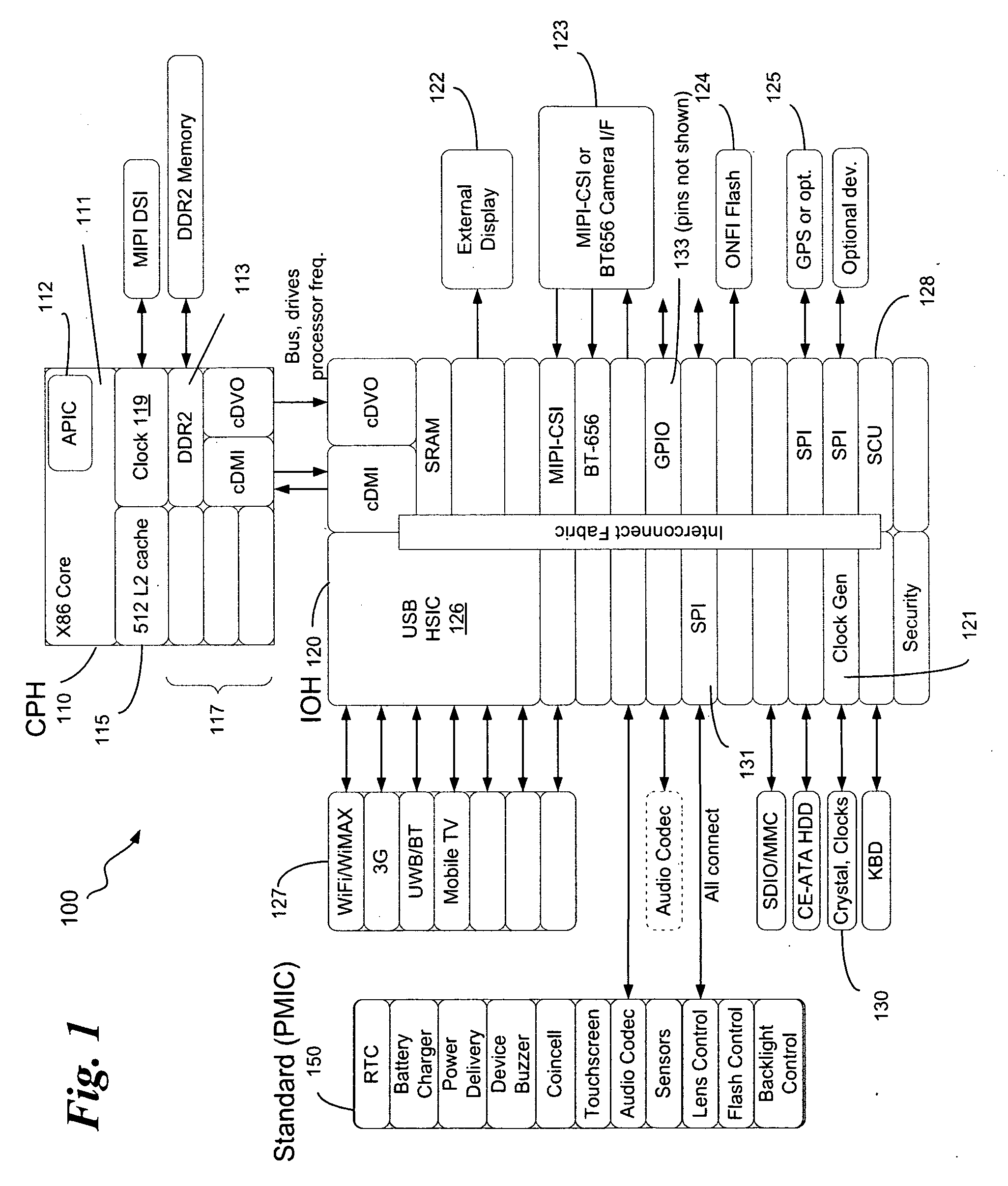
In some embodiments, the invention involves a system and method to enable a mobile device to utilize self-clocking during boot. In at least one embodiment, a platform has at least one processor core coupled to an internal timer. For an X86 processor, the internal timer may reside in an advanced programmable interrupt controller. A boot kernel executing on the platform is configured to use the internal timer early in the boot phase, when the platform is not compliant with legacy PC / AT architecture. If the platform does conform to the legacy architecture, then the boot may use an external clock for timing and clocking early in boot. In both cases, the internal timer is calibrated to the external clock before completing the boot phase. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Virtual machine system and access processing method of its advanced programmable interrupt controller
ActiveCN100570587CReduce access cycleReduce stepsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOperational systemProcessor register
The present invention discloses a virtual machine system and a visit processing method of an advanced programmable interruption controller. The method includes an address mapping procedure in which a virtual machine monitor sets up an APIC virtual register space and a table mapping of APIC initial address and adds the address mapping table to the table of a virtual machine client operating system; an APIC visit control procedure in which the client operating system carries out the visit by compulsorily involving in the virtual machine monitor when visiting the first type register of APIC, and conducts the direct visit according to the address mapping table when visiting the second type register of APIC. The operation of the first type register can result in the change of other registers of APIC and the operation of the second type register can not affect other registers of APIC. The present invention greatly shortens the visit cycle of APIC and simplifies the operation.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
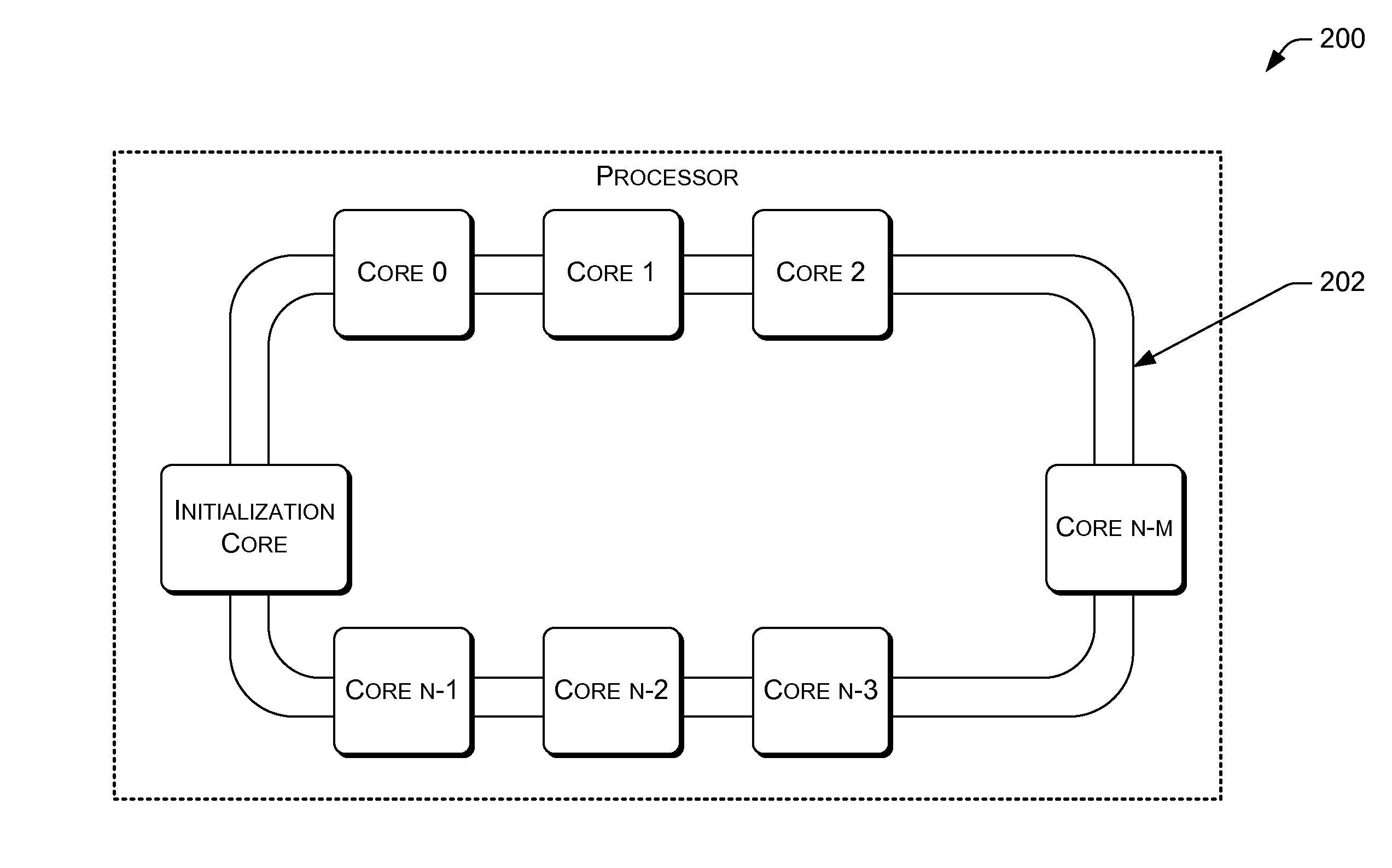
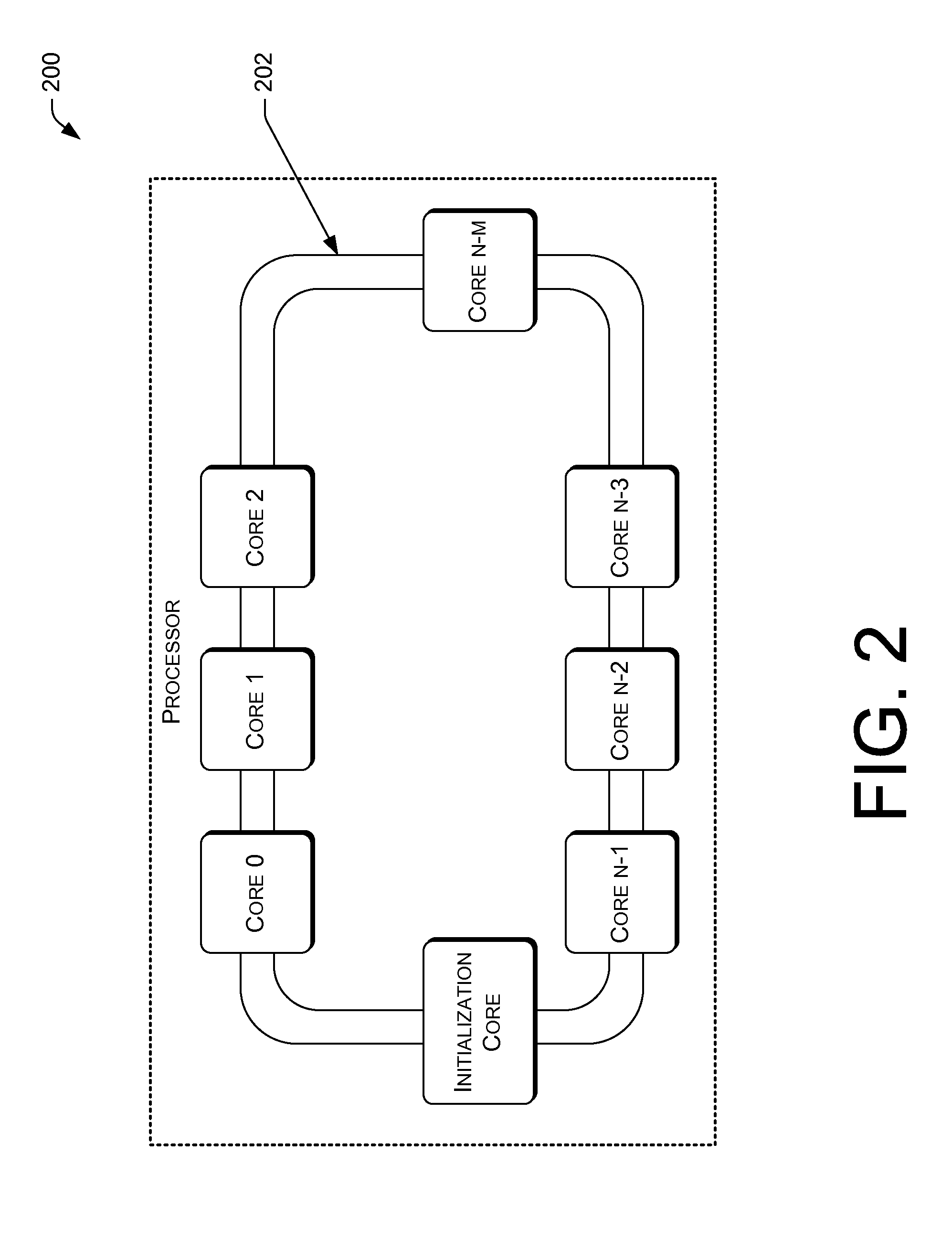
Advanced programmable interrupt controller identifier (APIC id) assignment for a multi-core processing unit
InactiveUS20140156896A1Electric digital data processingProcessing coreProgrammable Interrupt Controller
Following a restart or a reboot of a system that includes a multi-core processor, the multi-core processor may assign each active and eligible core a unique advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) identifier (ID). Initialization logic may detect a state of each of the plurality of processing cores as active or inactive. The initialization logic may detect an attribute of each of the plurality of processing cores as eligible to be assigned an APIC ID or as ineligible to be assigned the APIC ID.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Load replay precluding mechanism
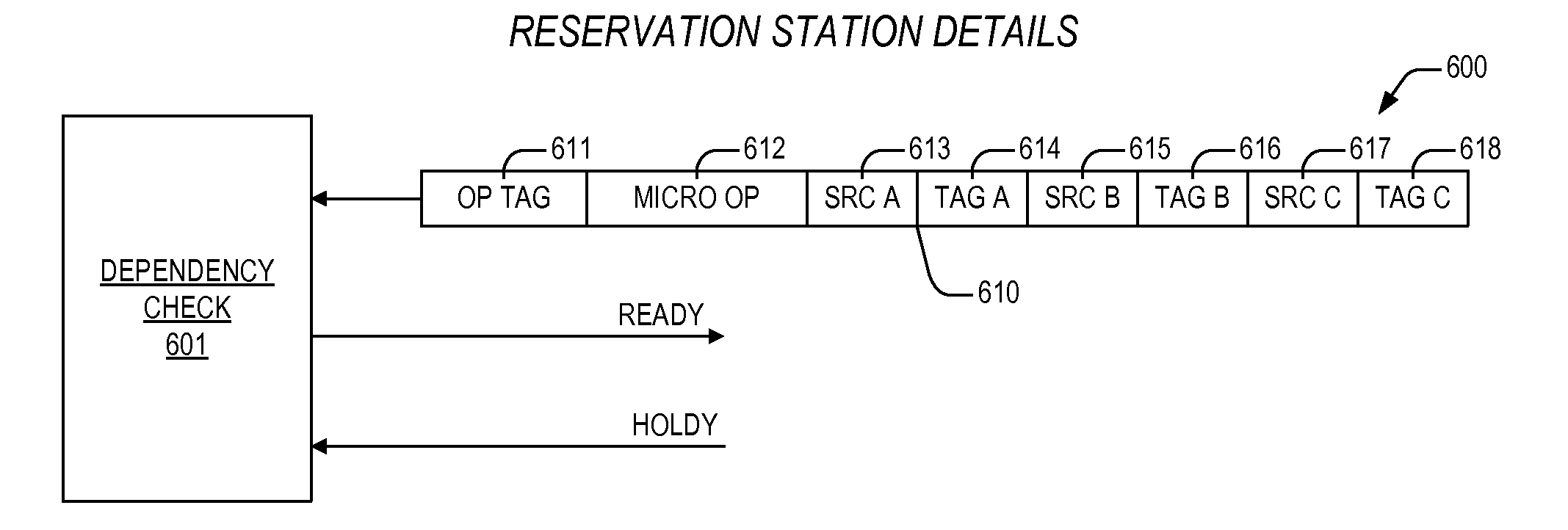
ActiveUS20160350119A1Reducing replayConcurrent instruction executionEnergy efficient computingReservation stationProgrammable Interrupt Controller
An apparatus including first and second reservation stations. The first reservation station dispatches a load micro instruction, and indicates on a hold bus if the load micro instruction is a specified load micro instruction directed to retrieve an operand from a prescribed resource other than on-core cache memory. The second reservation station is coupled to the hold bus, and dispatches one or more younger micro instructions therein that depend on the load micro instruction for execution after a number of clock cycles following dispatch of the first load micro instruction, and if it is indicated on the hold bus that the load micro instruction is the specified load micro instruction, the second reservation station is configured to stall dispatch of the one or more younger micro instructions until the load micro instruction has retrieved the operand. The resources include an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC), configured to perform interrupt operations.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
System and method for dynamic, local retriggered interrupt routing discovery
InactiveUS20110231590A1Reduce settingsMinimize changesElectric digital data processingMultiplexingProgrammable Interrupt Controller
In some embodiments, the invention involves a dynamic interrupt route discovery method with local APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) retriggering to accommodate architectures that are not PC / AT compatible. In a low power mobile device, General Purpose Input / Output (GPIO) pins are dynamically allocated and IRQs are retriggered by a GPIO driver to multiplex the requests to an appropriate device. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
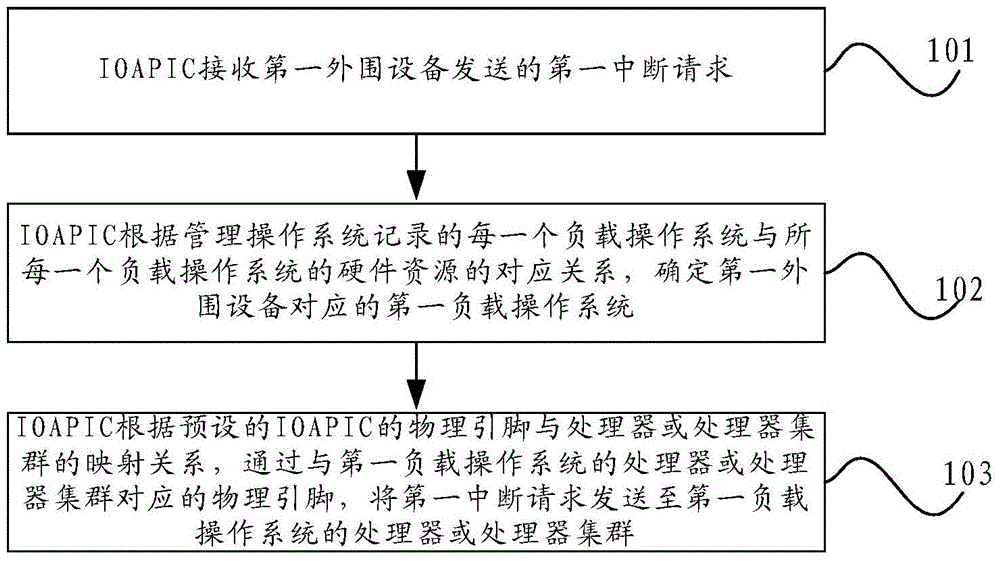
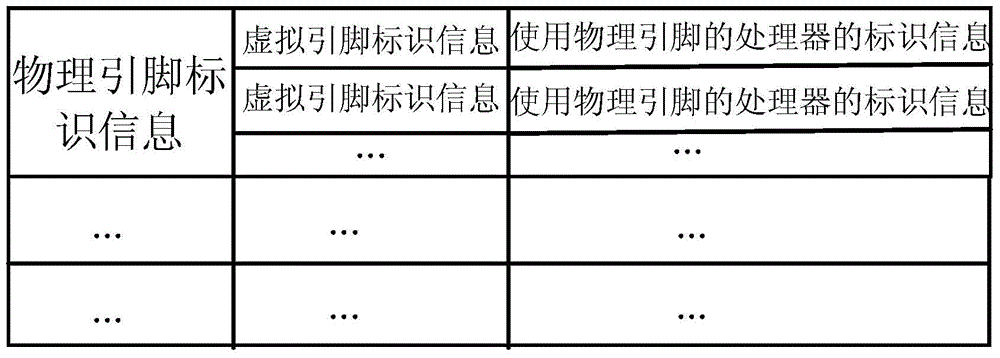
Interrupt processing method, IOAPIC (Input/ Output Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) and computer system
ActiveCN106445650AAvoiding Interrupted Forwarding ErrorsAvoid Malicious ModificationsProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationProgrammable Interrupt ControllerComputerized system
The invention provides an interrupt processing method, an IOAPIC (Input / Output Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) and a computer system, relates to the technical field of the computer and is used for the IOAPIC to accurately forward an interrupt request. According to a preset mapping relationship between an IOAPIC physical pin and a processor or a processor cluster, the IOAPIC forwards the interrupt request, and an IOAPIC interrupt forwarding error can be avoided to a certain degree. The interrupt processing method comprises the following steps of: the IOAPIC receives a first interrupt request sent from first peripheral equipment; according to a corresponding relationship, which is recorded by a management operating system, between each load operating system and the hardware resource of each load operating system, the first load operating system corresponding to the first peripheral equipment is determined; and according to the preset mapping relationship between the IOAPIC physical pin and the processor or the processor cluster, through the physical pin corresponding to the processor or the processor cluster of the first load operating system, the first interrupt request is sent to the processor or the processor cluster of the first load operating system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com