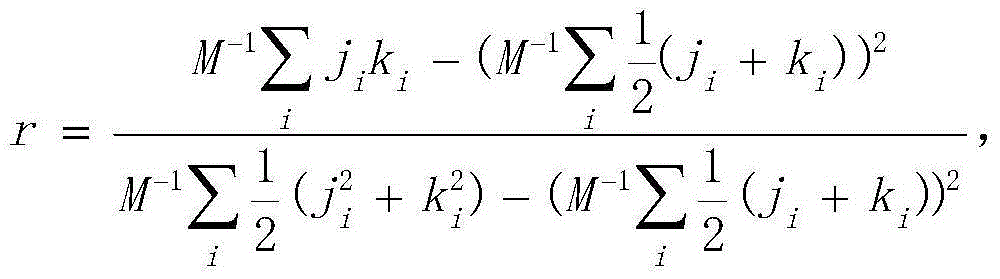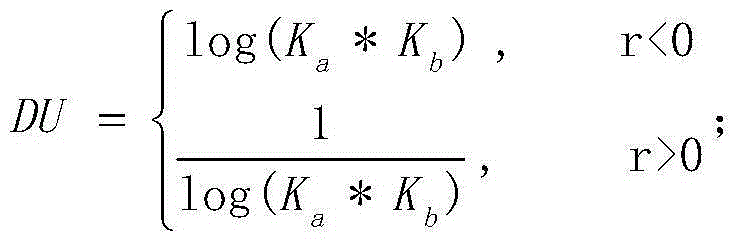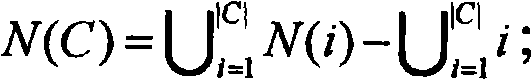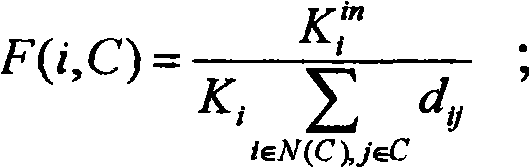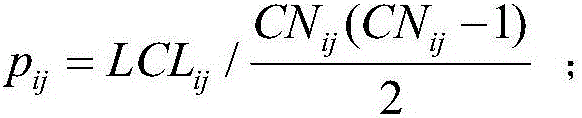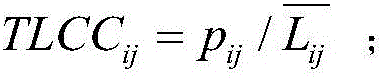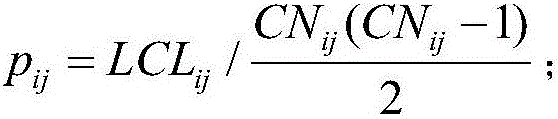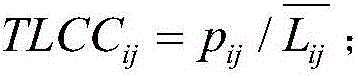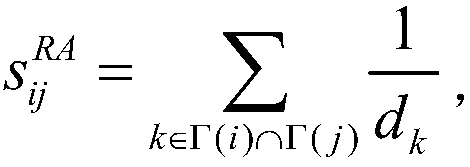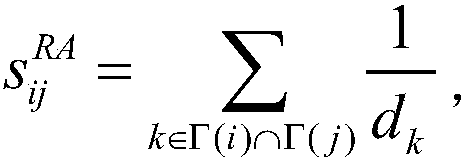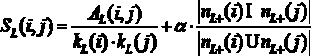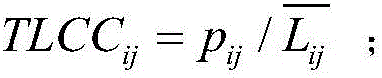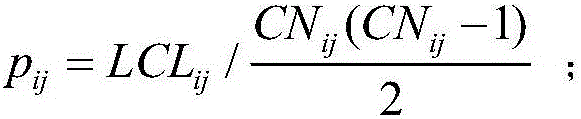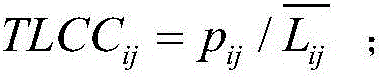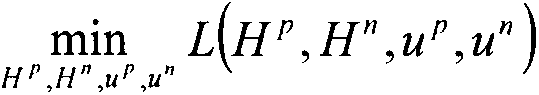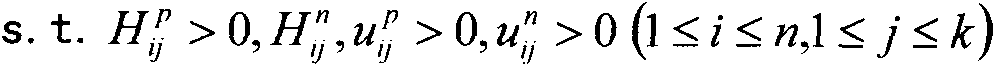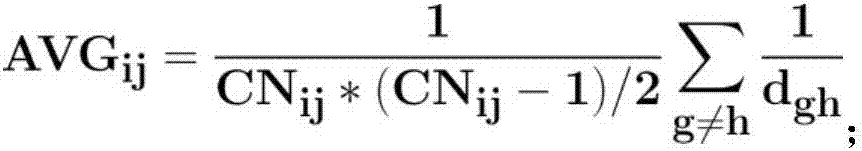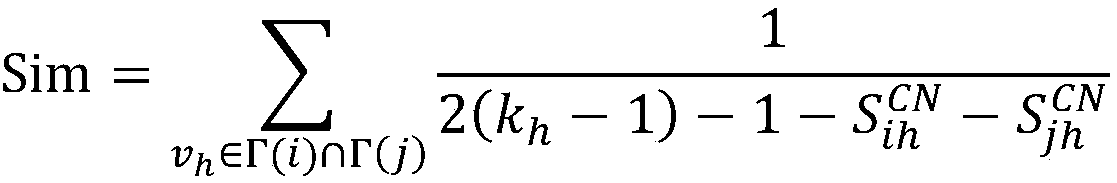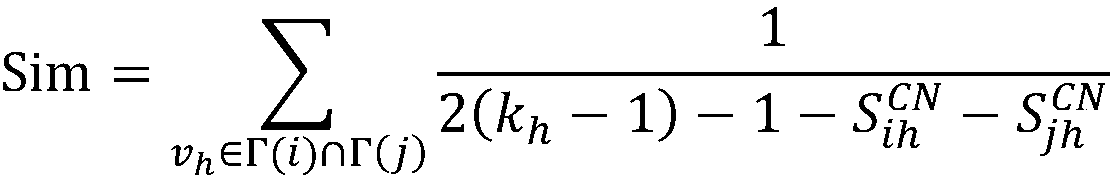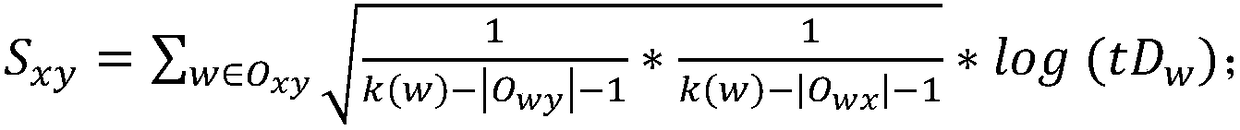Patents
Literature
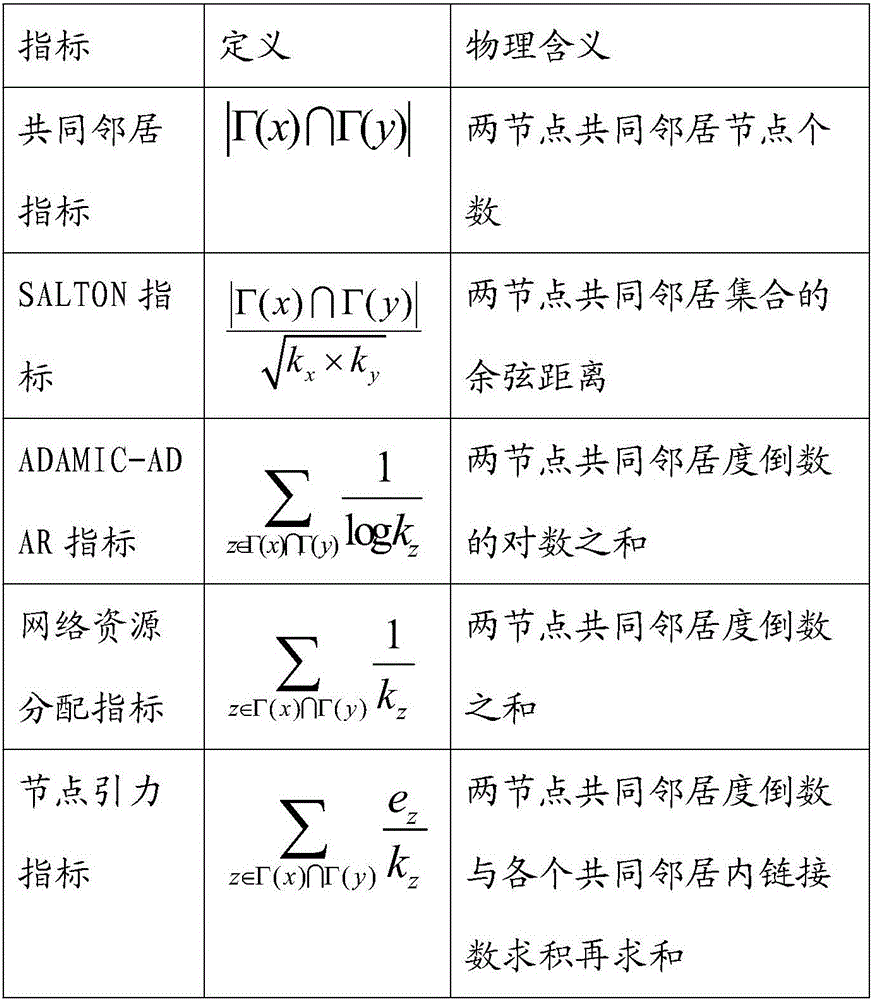
59 results about "Common neighbor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Link prediction method and device based on node similarity
ActiveCN106817251AQuick calculationReduce time complexityData switching networksNode clusteringStructure of Management Information
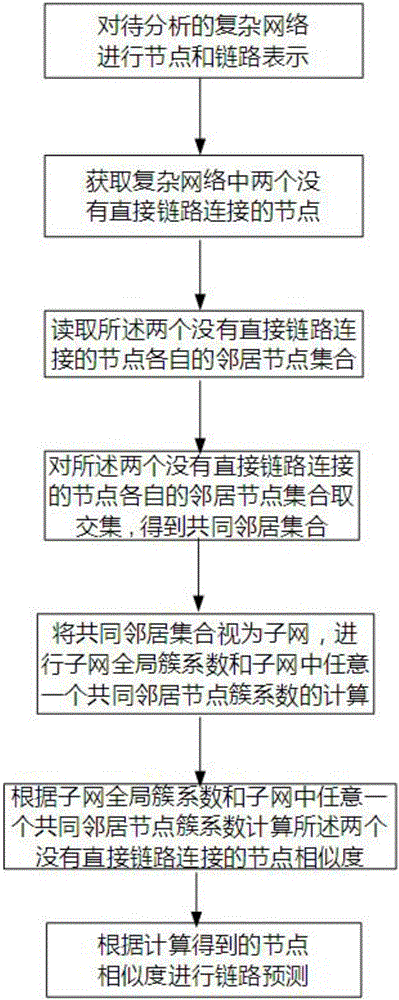
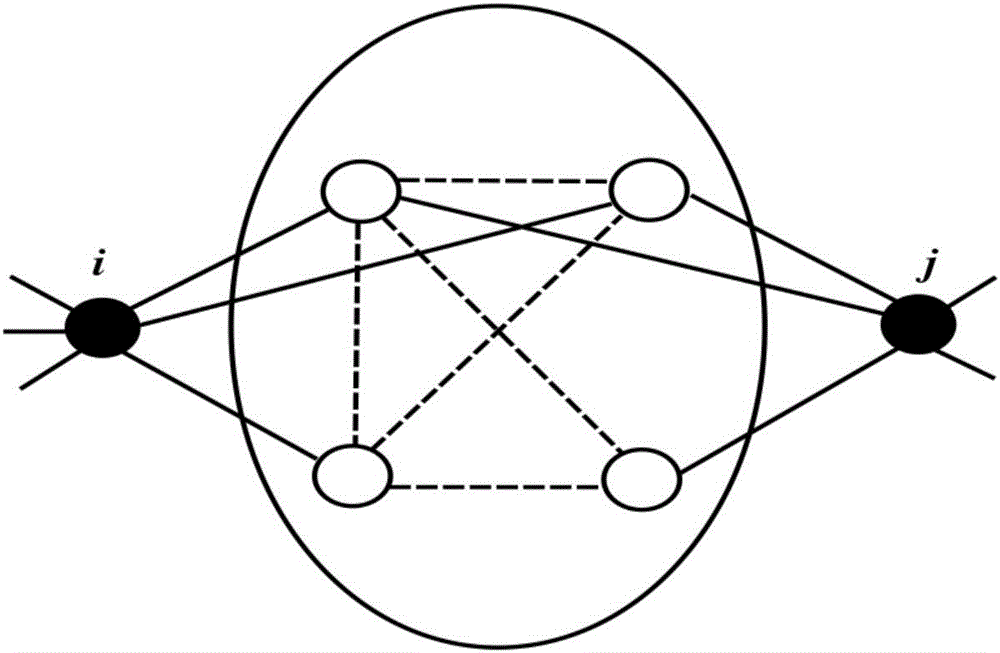
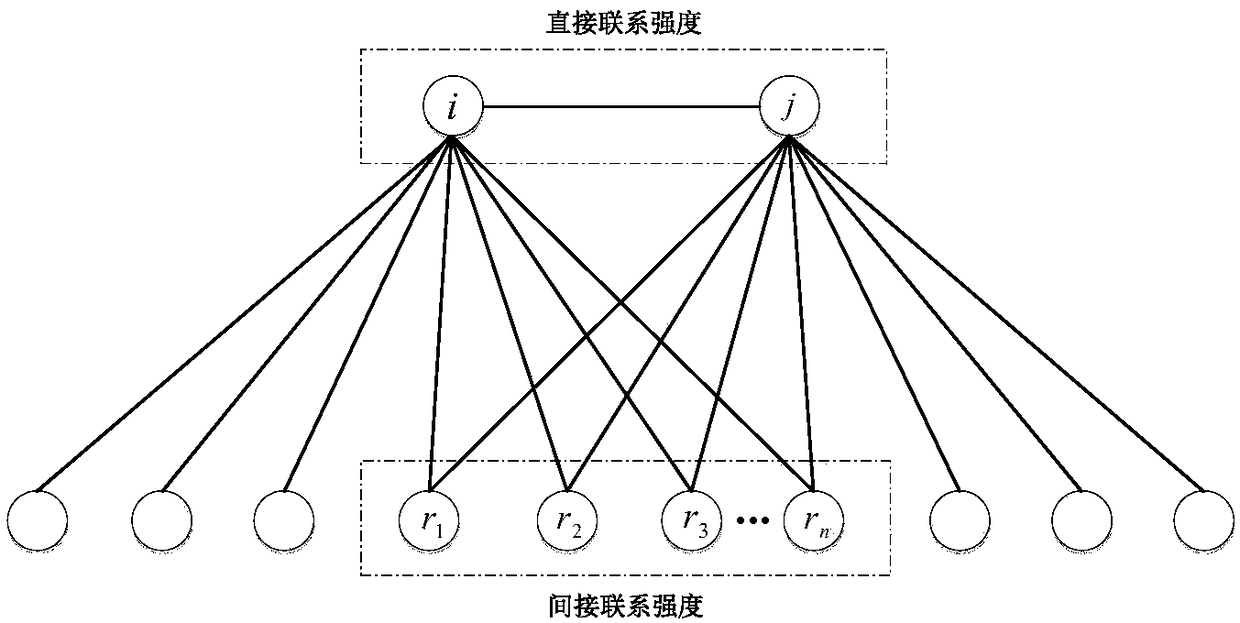
The invention relates to a link prediction method and device based on node similarities; the method comprises the following steps: carrying out node and link expression for a to-be-parsed network; obtaining two nodes having no direct link connection in the network; respectively reading a neighbor node set of the two nodes having no direct link connection; obtaining the intersection of the neighbor node sets of the two nodes having no direct link connection, thus obtaining the common neighbor set; considering the common neighbor set as a subnet, and calculating the subnet global cluster coefficient and a random common neighbor node cluster coefficient in the subnet; calculating the node similarity of the two nodes having no direct link connection according to the subnet global cluster coefficient and the random common neighbor node cluster coefficient in the subnet; carrying out link prediction according to the calculated node similarity. The method can parse the mutual relation of the nodes in the complex network local structure from the cluster coefficient angle, thus defining the node similarity calculating new index based on the local cluster coefficient.
Owner:烟台中科网络技术研究所
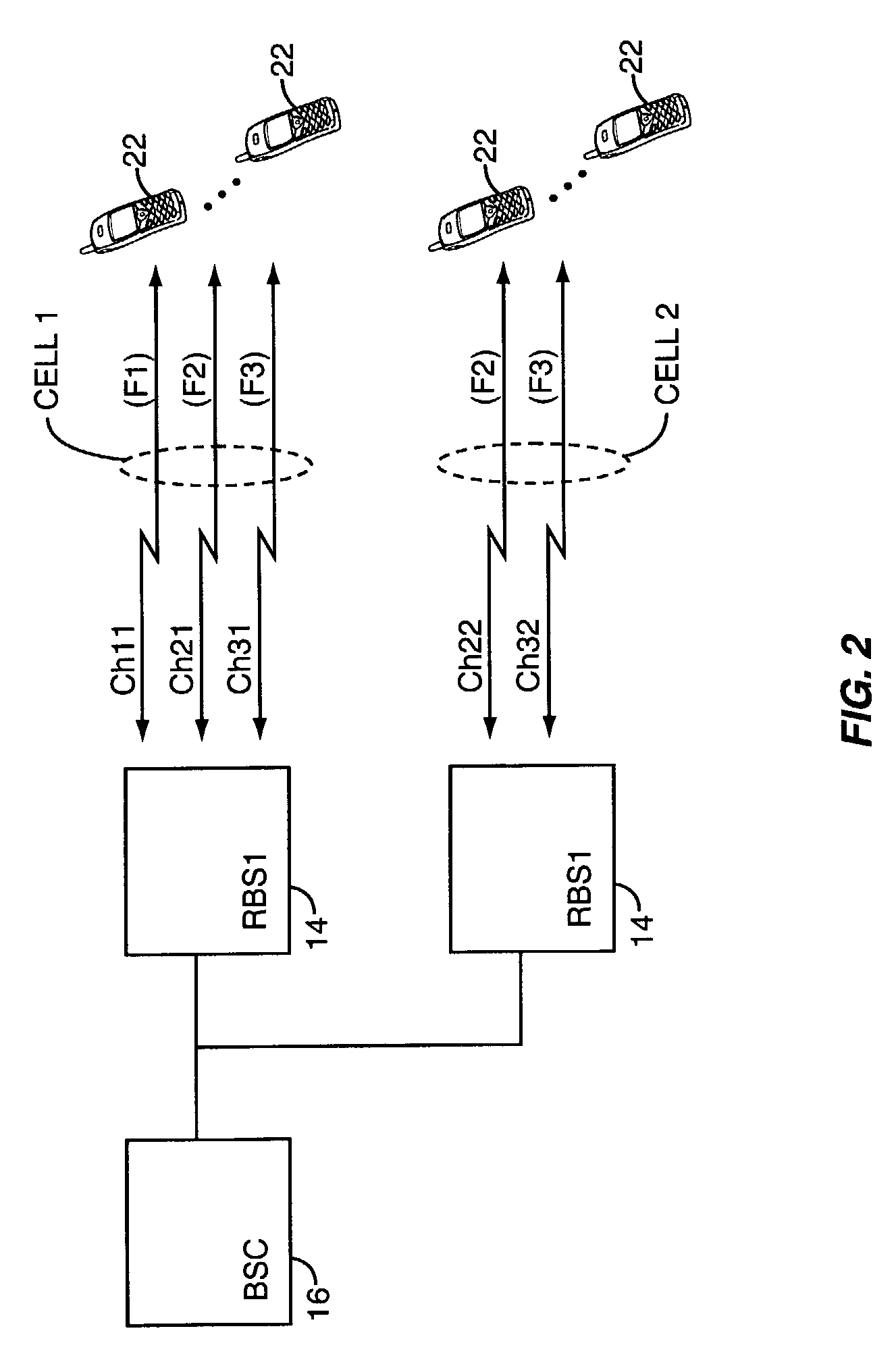
Hard handoff target generation in a multi-frequency CDMA mobile network
InactiveUS7583633B2Avoid the needLow utilization efficiencyCode division multiplexRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsMobile station
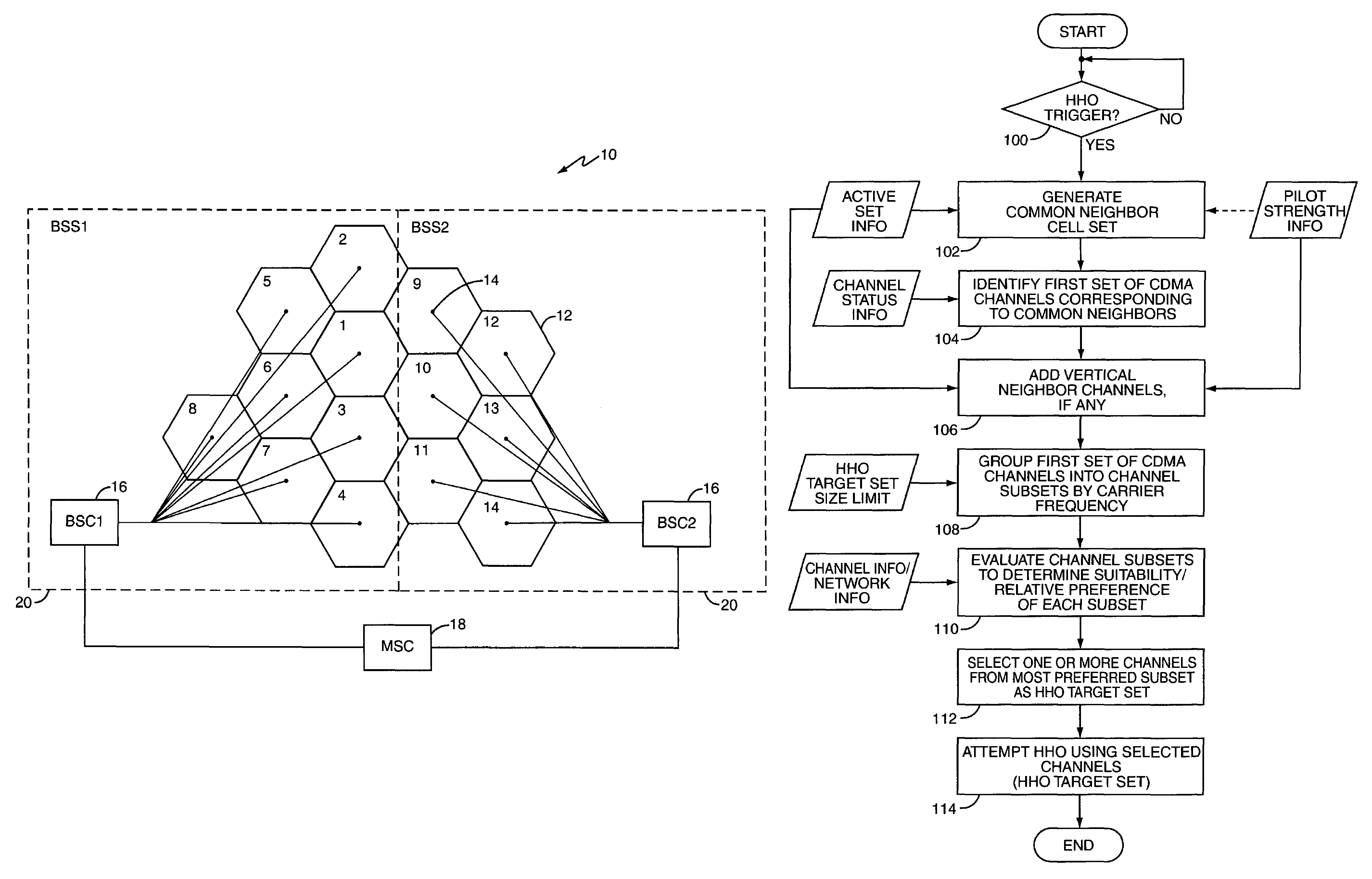
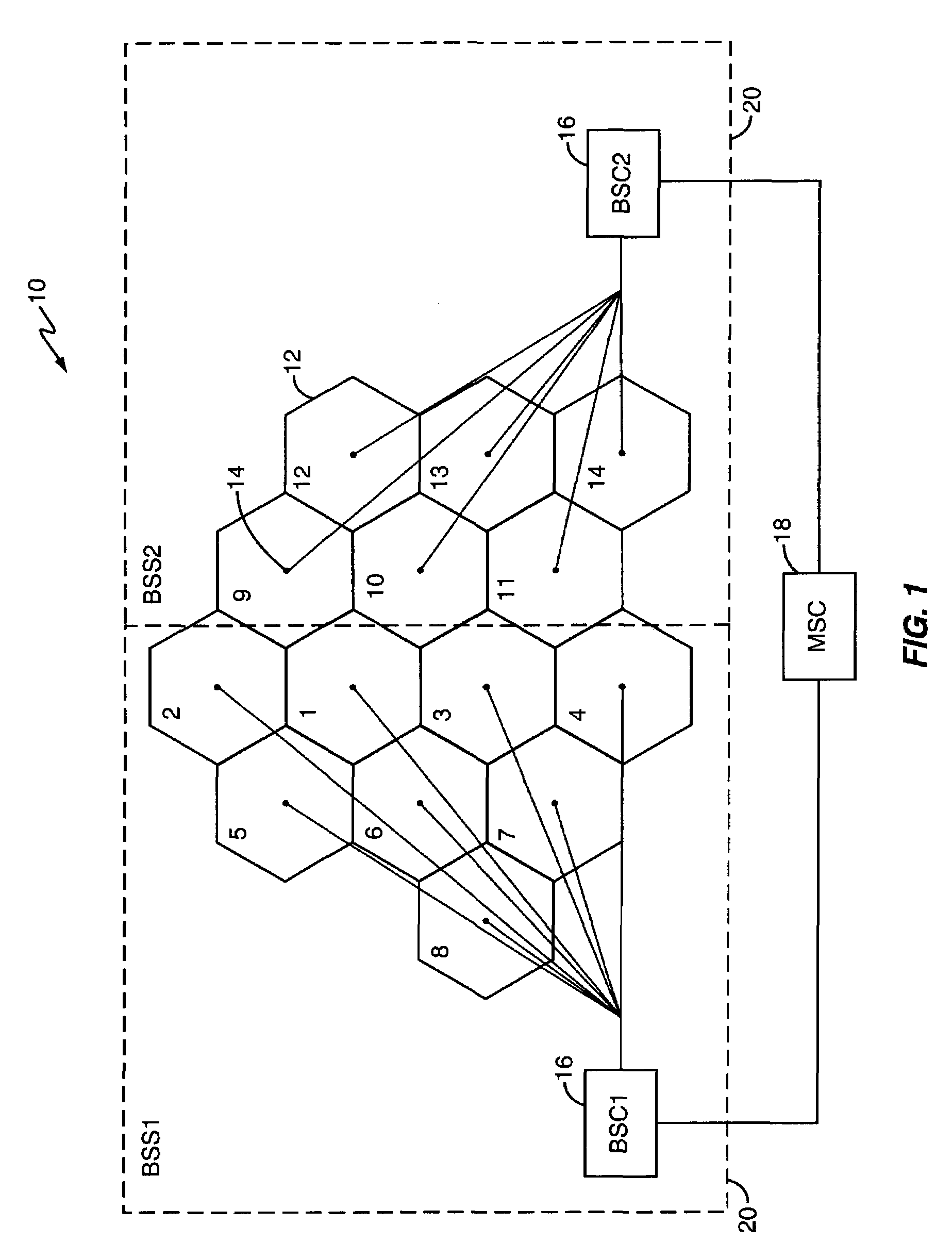
A CDMA network dynamically generates hard handoff (HHO) target sets to support mobile station HHO. Dynamically identifying CDMA channels or cells as targets for HHO eliminates the need for statically configured HHO target sets. In an exemplary embodiment, a source BSS identifies a first set of channels corresponding to common neighbor cells of the cells associated with the active set pilots and / or reported PBU pilots. This first set may be adjusted by removing any common neighbor cells that include soft handoff target channels, and by adding selected vertical neighbor channels of the active set pilots and / or reported PBU pilots. Channels in the first set may be grouped by carrier frequency and evaluated based on CDMA channel type, BSS affiliation and characteristics, and the target's relationship to the active set to identify a preferred HHO target set. Such operations permit dynamic determination of whether to perform inter- or intra-BSS HHO.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
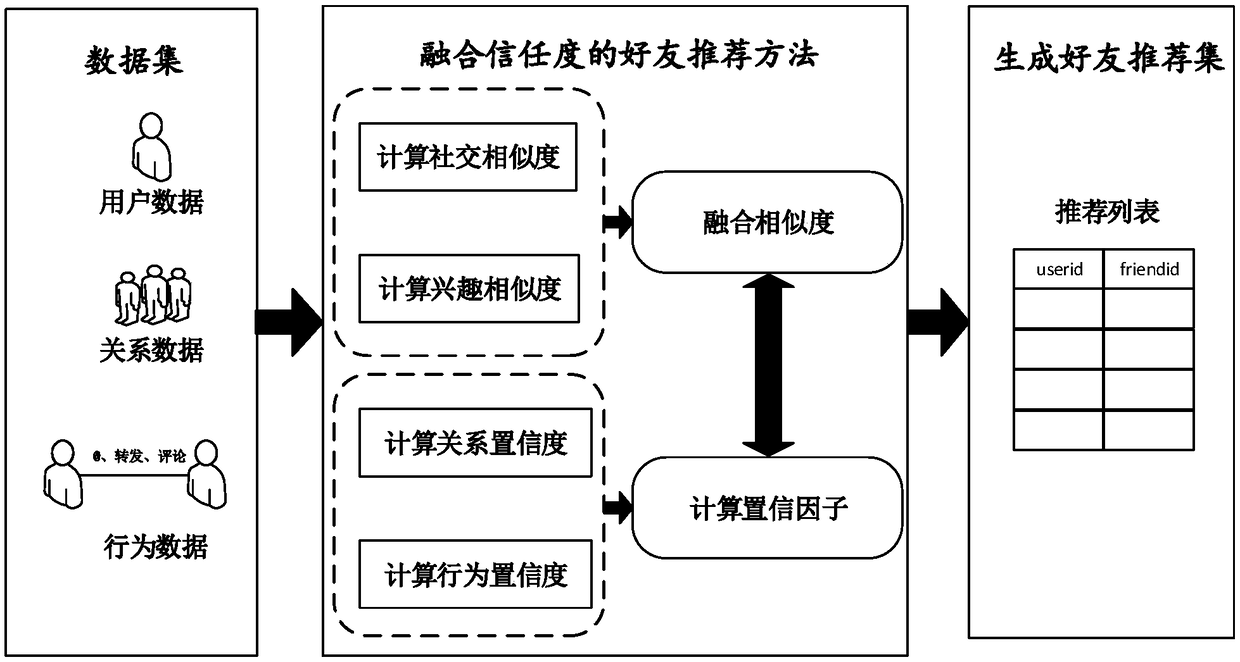
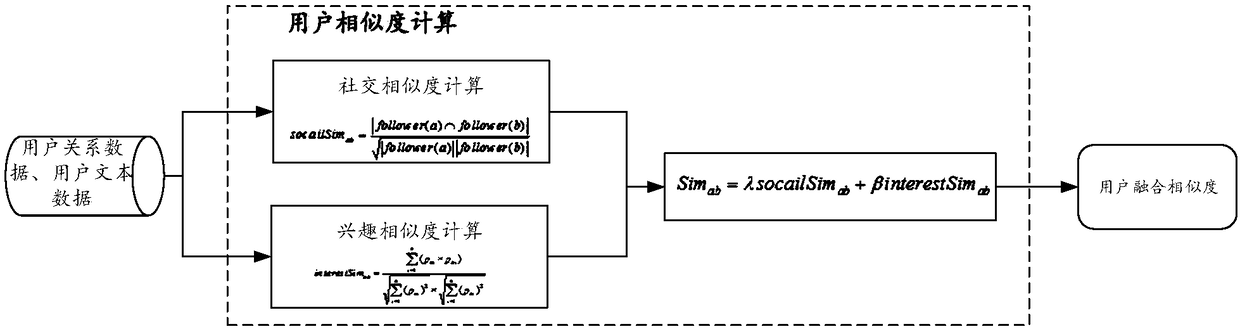
Social network friend recommendation method fusing trust degree
InactiveCN108427715ABest Fusion ParametersData processing applicationsNatural language data processingConfidence factorDependability
The invention provides a social network friend recommendation method fusing a trust degree, and relates to user similarity, confidence factor calculation and fusion. The social network topology-basedrecommendation focuses on known friends and ignores potential interested friends; the interest-based recommendation focuses on recommendation of strange users, thereby difficultly getting trust of users; and both the social network topology-based recommendation and the interest-based recommendation do not consider behaviors of the users in a social network, thereby greatly influencing the accuracy, reliability and comprehensiveness of a recommendation result. The invention provides a recommendation method comprehensively considering social network topology, user interests and social behaviors.Firstly, social similarity is calculated out according to common neighbors in the social network of the users, interest similarity is calculated according to keywords, and linear combination is performed. The social topology and the social behaviors of the users are comprehensively considered, a relationship confidence degree and a behavior confidence degree are calculated out, and fusion is performed to form a confidence factor. Finally, the similarity and the confidence factor are fused, so that the trust degree of similarity calculation is improved, and a Top-N recommendation list is generated.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A method for establishing a trust model in an underwater sensor network
ActiveCN103619009AReduce complexityImprove efficiencyNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementSensing dataNeighbor relation
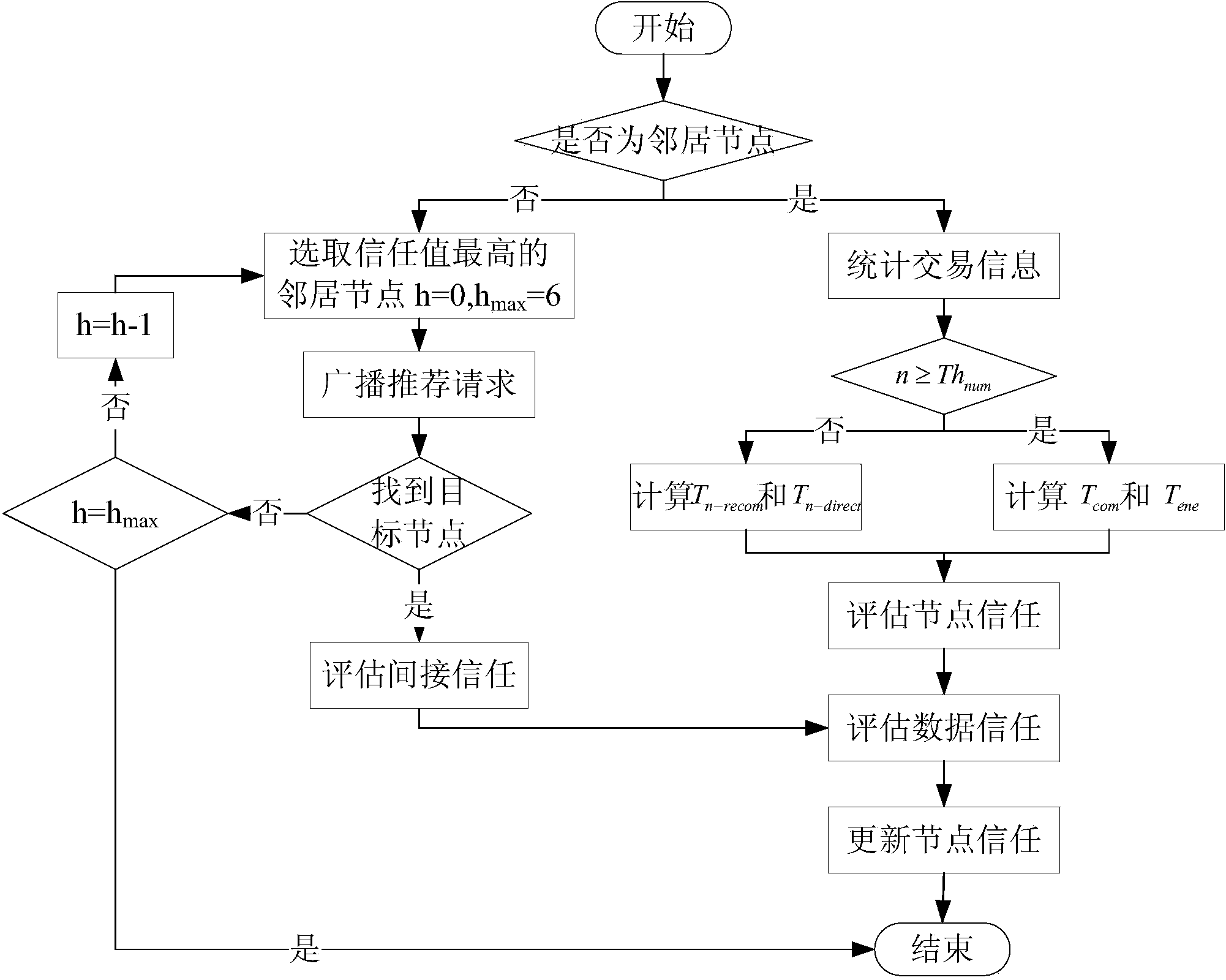
The invention relates to a method for establishing a trust model in an underwater sensor network. The method comprises steps: using a request node to perform neighbor relation determination on a target node and establishing direct trust according to data communication between the request node and the target node and the residual energy of the target node; requesting recommend trust from a common neighbor of the request node and the target node if the number of the historical communication information interaction between the request node and the target node is insufficient, and further calculating the trust value of the target node; selecting a multi-hop neighbor node to perform trust calculation if the request node and the target node are not neighbor nodes; and achieving trust assessment of the node for sensing data on the basis of node trust calculation and updating the trust value of the sensor node. The method may update the trust value of the sensor node and prevent problems of trust transmission and trust combination under the circumstance of existence of multiple recommend paths. In cooperation with sensing data trust calculation, the method achieves high precision of node trust calculation and has a wide application value.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Link prediction method based on local community information
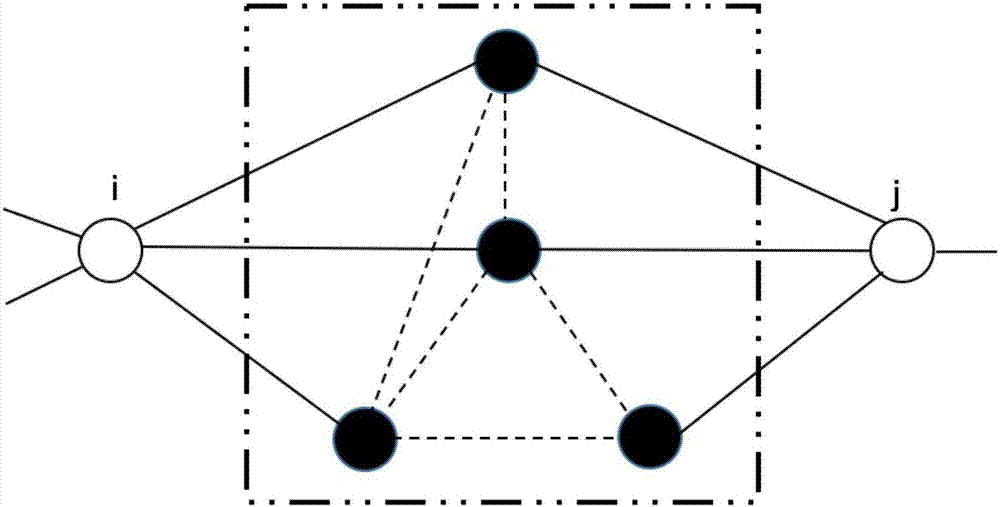
The invention provides a link prediction method based on local community information. The link prediction method comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a network model G, and calculating an assortativity coefficient of the network; step 2, using node pairs without connecting edges in the network as candidate node pairs, preparing to predict an unknown or a future link among these node pairs, and recording the node degree of two nodes; step 3, calculating DU by referring to both the assortativity coefficient and the node degrees of the node pairs without connecting edges; step 4, extracting and establishing a common neighbor network formed by the current two candidate nodes and a common neighbor node between the two candidate nodes; step 5, extracting and establishing a local community network where the common neighbor node is located, and calculating the similarity of the current two candidate nodes; step 6, establishing a similarity list of node pairs arranged in a similarity descending order; and step 7, obtaining the node pairs at the front of the similarity list to serve as the node pairs which are most likely to generate a connected edge in the future and are obtained by a link prediction algorithm. The link prediction method provided by the invention has relatively high reliability and a good prediction effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
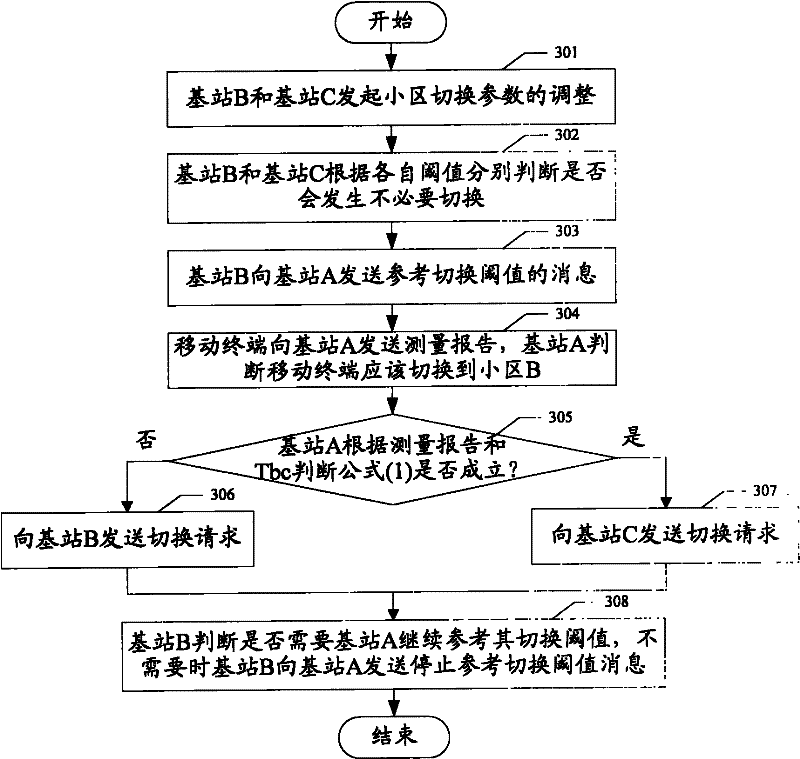
Method and system for reducing unnecessary switching in LTE (Long Term Evolution) system
ActiveCN102196485AAvoid consumptionReduce switching timesWireless communicationSwitching frequencyCommon neighbor
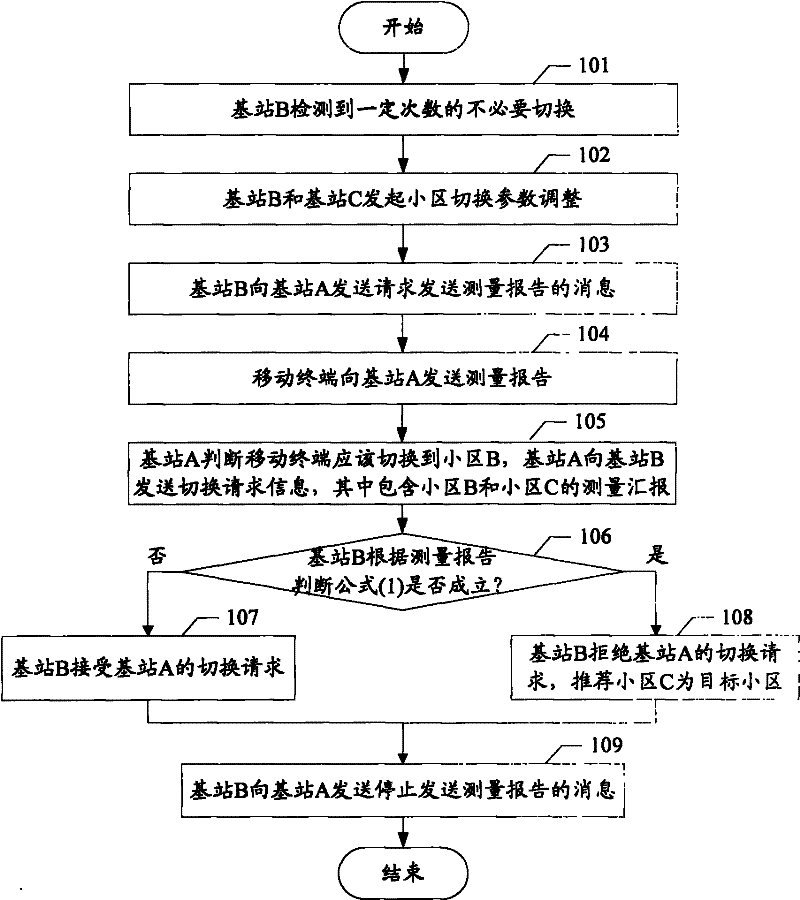
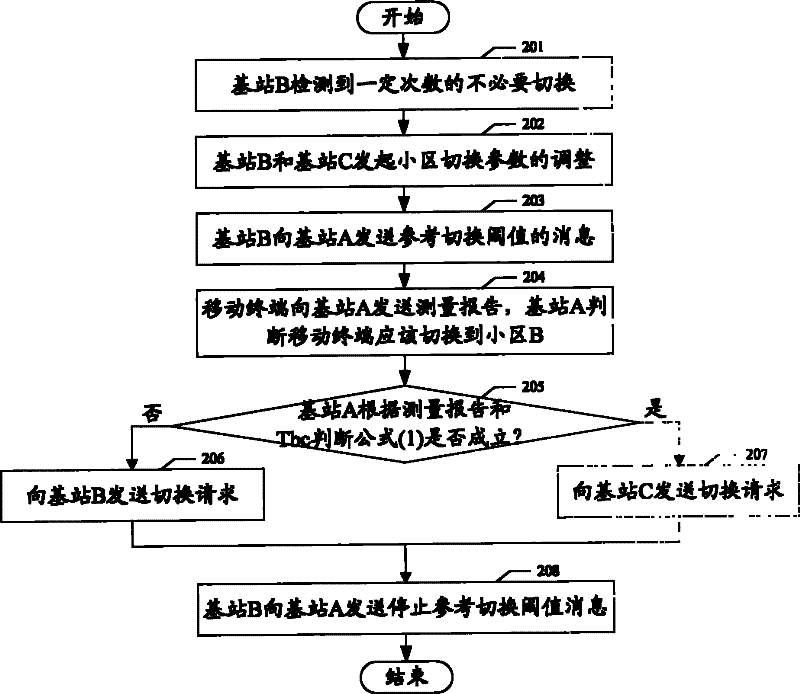
The invention discloses a method and system for reducing unnecessary switching in an LTE (Long Term Evolution) system, which are used for solving the technical problem of generating unnecessary switching between cells. In the invention, a switching request transmitted to a third base station that initiates switching to a first base station which detects the unnecessary switching carries a measuring report; the first base station judges whether the switching is accepted or not according to the measuring report and a cell switching parameter between the first base station and a second base station; and a target cell is recommended while the switching is not accepted. Or the first base station and / or the second base station judges whether the unnecessary switching is generated or not according to an adjusting direction of the cell switching parameter after the cell switching parameter of the first base station and the second base station is adjusted; and if the unnecessary switching is generated, the cell switching parameter is transmitted to a common neighbor third base station; and the third base station selects a switched target cell for a mobile terminal according to the cell switching parameter between the first base station and the second base station. According to the invention, the necessary switching frequency between the cells can be reduced and the consumption of network resources is avoided.
Owner:深圳市中兴通讯技术服务有限责任公司
Social network friend recommendation method based on community division
InactiveCN108734223AGood effectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCommunity basedNODAL
The invention discloses a social network friend recommendation method based on community division. Link prediction is to predict the connection possibility between two points according to an existingnetwork topological structure, node property information and the like. Most existing node similarity algorithms only consider information of common neighbor nodes, that is, a topological structure with path length of 2, the important information that some nodes possibly belong to the same community is ignored, and obviously the nodes in the same community are more possible to have links. Accordingto the defects of traditional link prediction methods, an improved genetic algorithm is mainly used to perform community division on all the nodes first, then link prediction is performed according to the community division result, and therefore a social network friend recommendation algorithm based on community division is proposed. By doing contrast tests among five real networks, the accuracyof the algorithm compared with the traditional node similarity algorithms is analyzed through comparison, and the availability of the algorithm is proved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining dislocation core structure based on tensor decomposition and common nearest neighbor
ActiveCN108960323ACorrect dislocation analysis resultsCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsSingular value decompositionStructure analysis
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
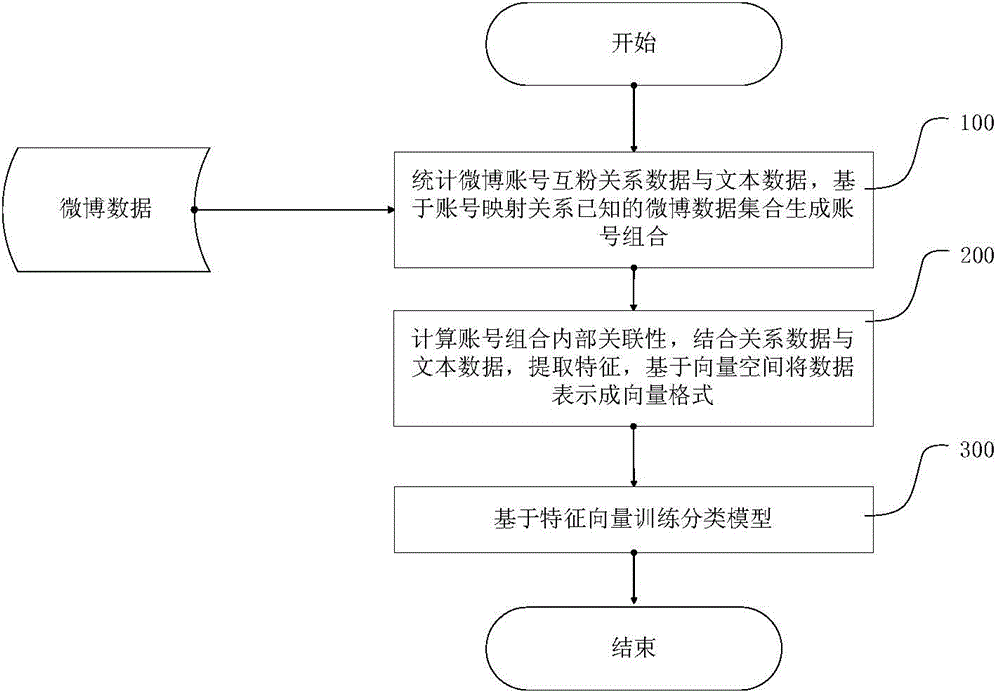
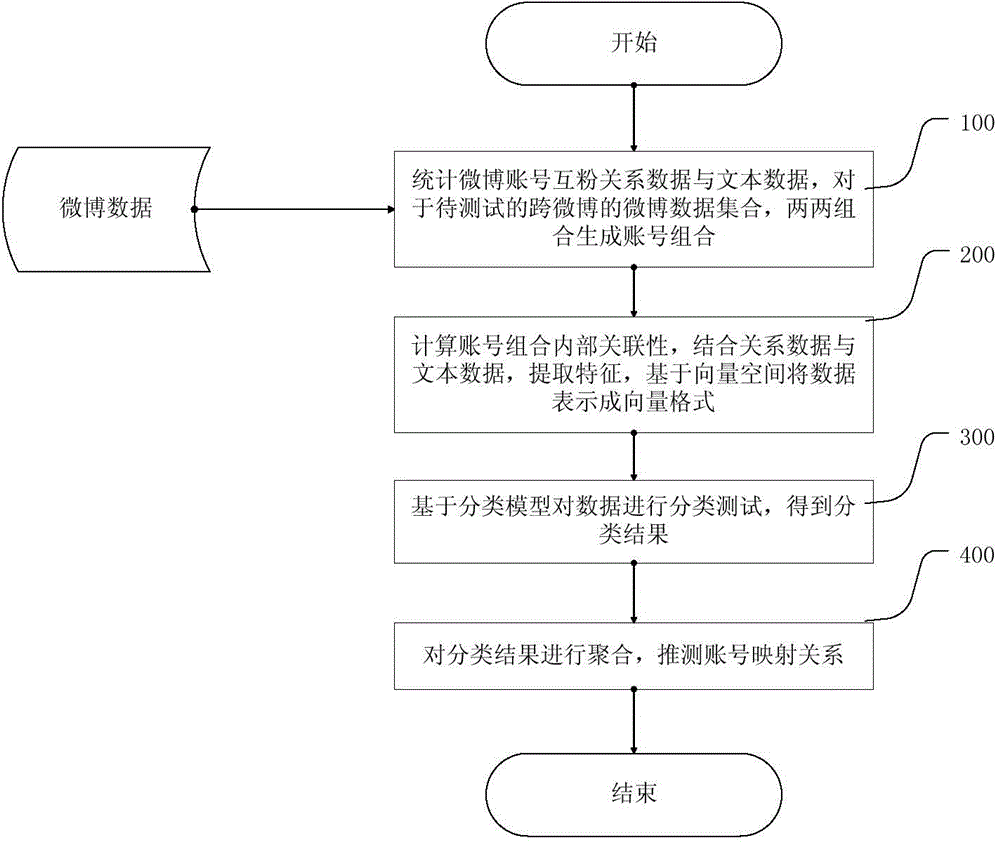
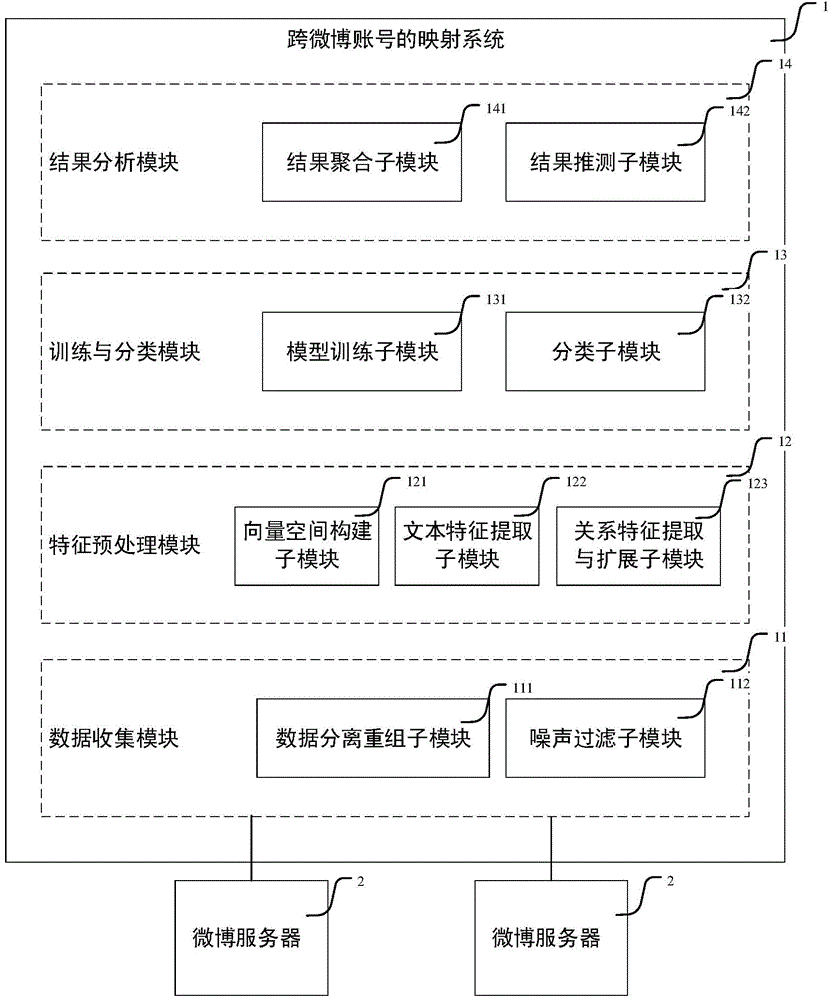
Training method of social networking account mapping model, mapping method and system
ActiveCN104866558AImprove the probability of mappingReduce missed detection rateRelational databasesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorMicroblogging
The present invention provides a training method of a social networking account mapping model. The method comprises: 1) combining any one account in a microblog account set s known in a mapping relationship and any one account in a microblog account set t known in the mapping relationship to form a training set; 2) extracting from each account combination an account combination feature vector comprising: respective text features of two accounts in the account combination, social networking relation features of the two accounts in the microblogs to which the two accounts pertain, and extended common neighbor features of the two accounts, wherein an extended common neighbor is a neighbor account pair pertaining to the same individual known in the respective neighbor accounts of the two accounts; 3) training based on the machine learning technology to obtain a social networking account mapping model. The present invention further provides a corresponding social networking account mapping method and system. According to the present invention, adverse impacts caused by sparsity of relationship data are reduced, and accuracy of social networking account mapping is effectively improved.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Local community digging method of complicated network
InactiveCN102819611AReduce time complexityImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsNODALTime complexity
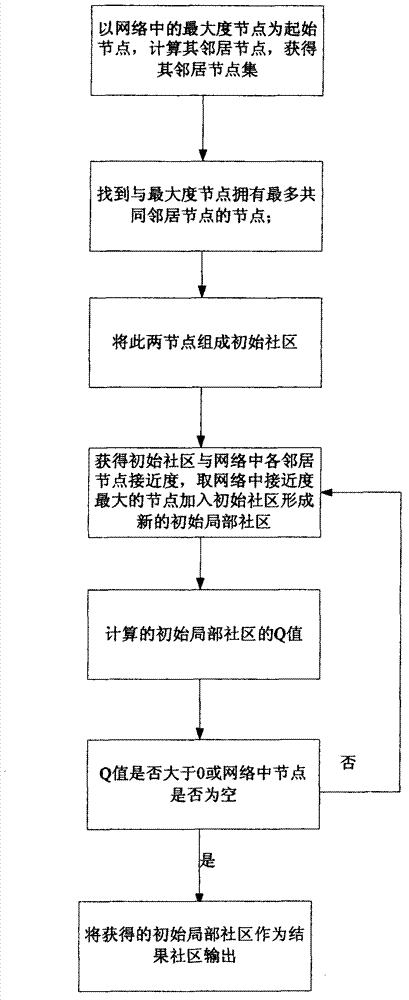
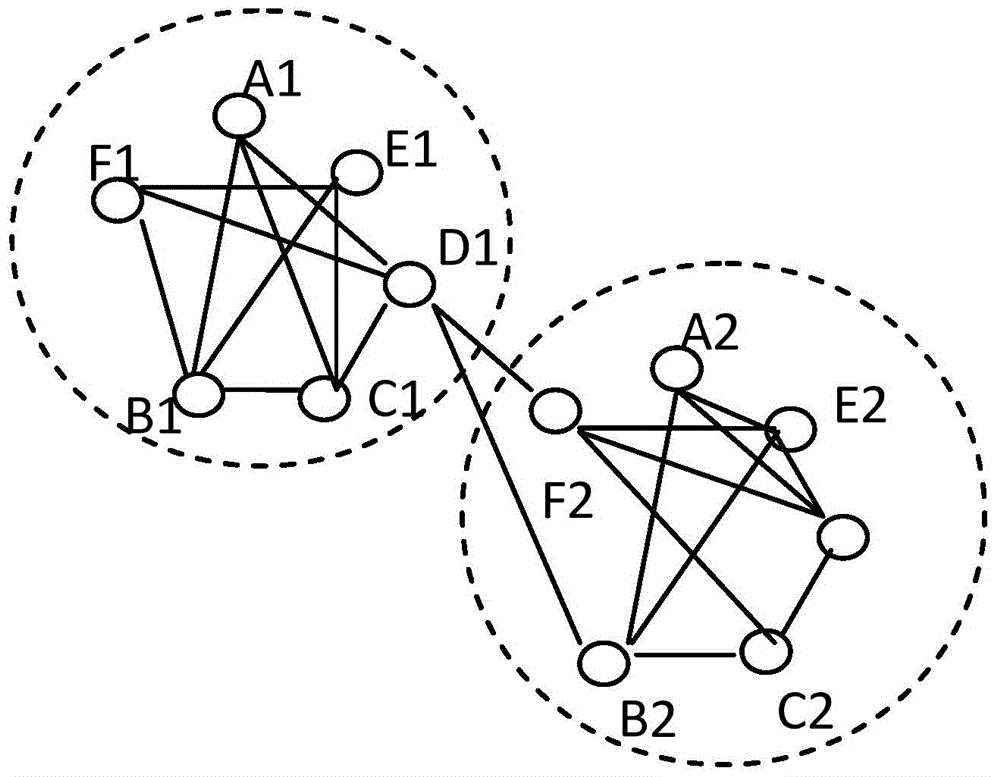
The invention relates to the technical field of a network and particularly relates to a local community digging method of a complicated network, which can effectively identify a local community structure of the complicated network, has lower time complexity, and has fewer wrongly-divided nodes. The local community digging method comprises the following steps of: taking a maximum degree node in the network as a starting node and calculating a neighbored node to obtain a neighbored node set; finding out a node which has the most common neighbored nodes with the maximum degree node; forming an initial local community by the two node sets; obtaining each neighbored node proximity of the initial local community and adding the node with the maximum proximity into the initial local community to form a new initial local community; calculating a Q value of the initial local community; and repeating the steps until the Q value of the formed new initial local community is more than 0 or the node in the network is zero.
Owner:方平
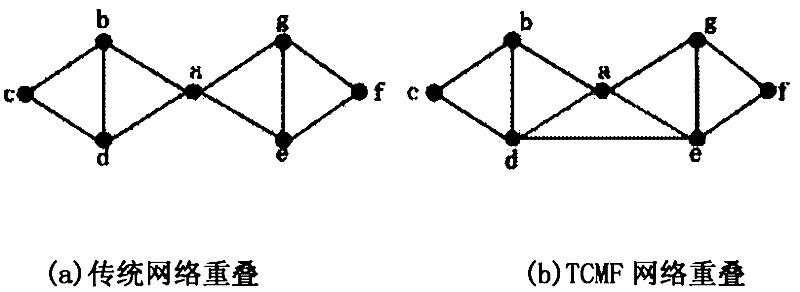
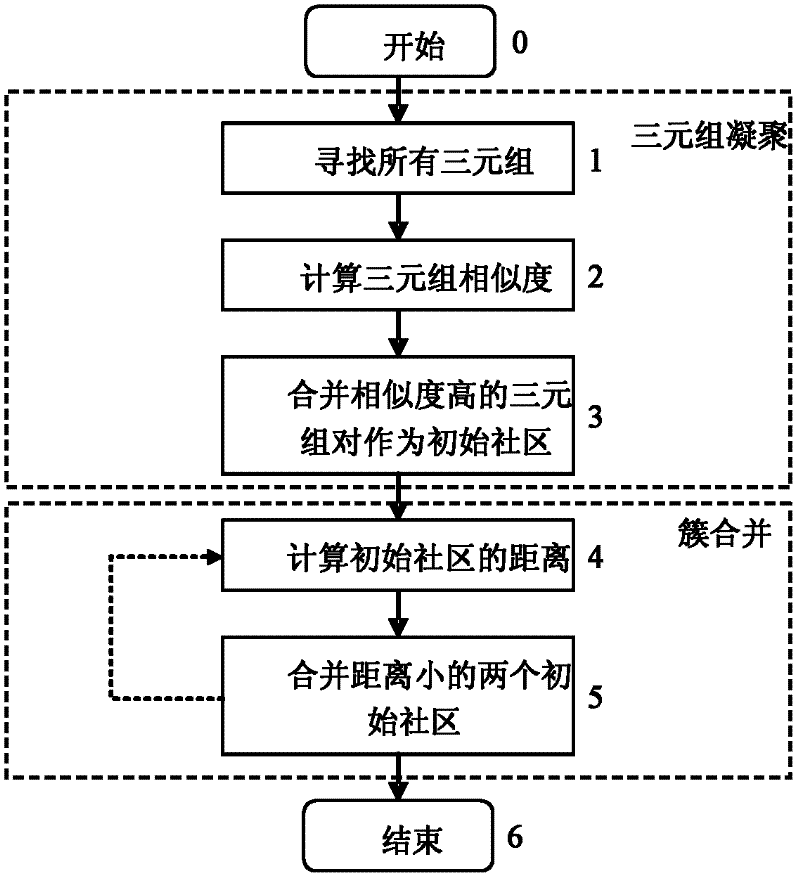
Common neighbor similar triangle agglomeration-based hierarchical and overlapping community discovery method applicable to traditional Chinese medicine herbs (TCMF) network
The invention provides a common neighbor similar triangle agglomeration-based hierarchical and overlapping community discovery method applicable to a traditional Chinese medicine herbs (TCMF) network. The method comprises the following steps: 1) common neighbor similar triad agglomeration stage a: seeking all triads; b: calculating the similarity of any two triads; c: giving a similarity threshold of the triads, and merging the triads with the similarities which are higher than the similarity threshold as initial communities; and d: ending; and 2) cluster merging stage a: calculating the distance between any two initial communities; b: setting a distance threshold of the initial communities, and merging the two initial communities with the distance which is smaller than the distance threshold; and c: ending. The TCMF network-based hierarchical and overlapping core medicine group discovery method provided by the invention provides a new method for TCMF network discovery; and by adopting the method, a high overlapping and hierarchical medicine group community structure of the TCMF network can be excavated by setting three parameters alpha, beta and gamma, and a solution is provided for core medicine group discovery in prescription compatibility.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
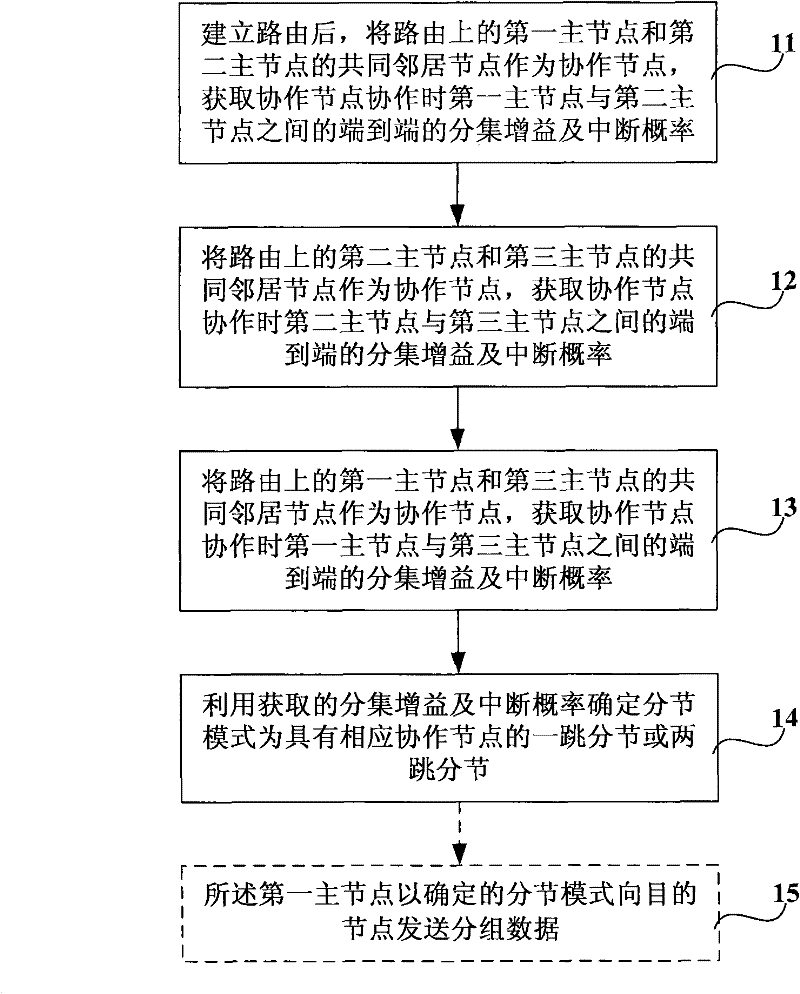
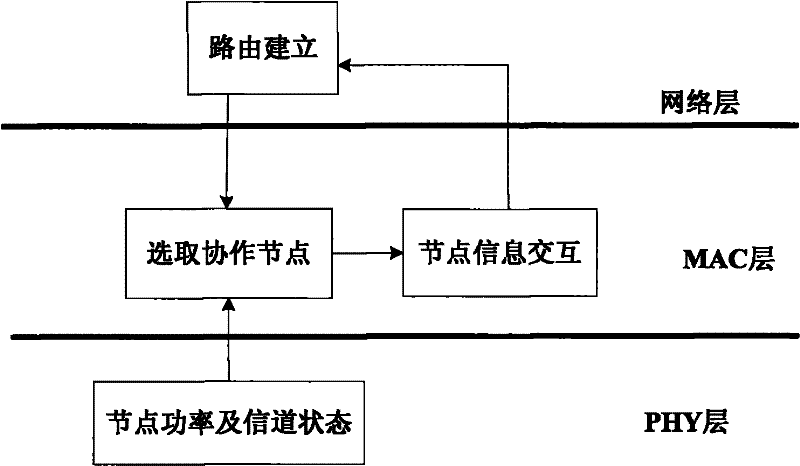
Multi-hop routing cooperation method of wireless network and realization apparatus thereof
ActiveCN102244913AImprove reception reliabilityImprove transmission capacitySite diversityNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkDiversity scheme
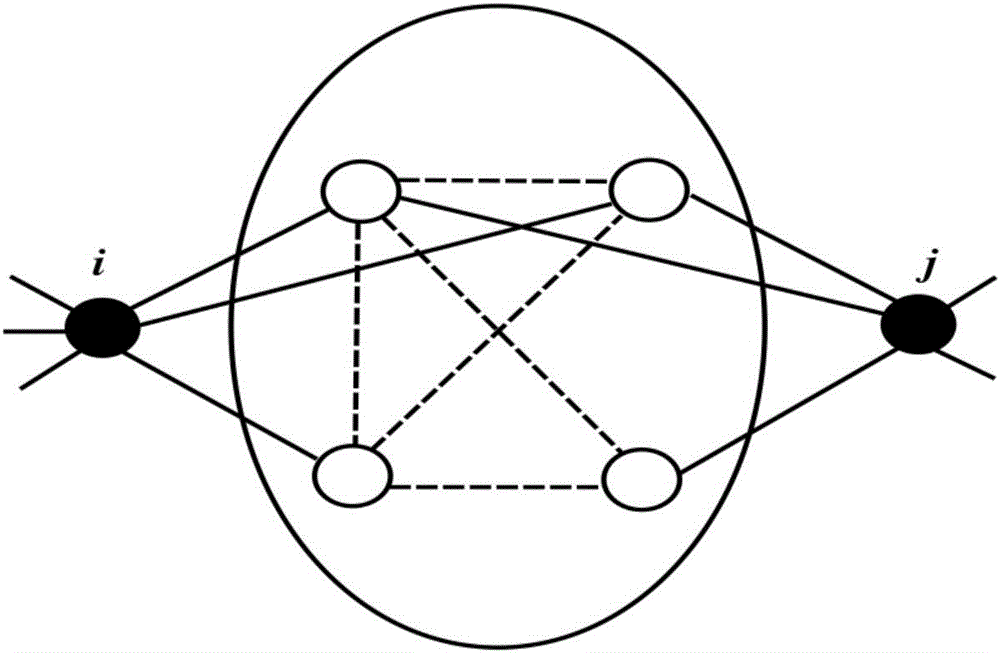
The invention relates to a multi-hop routing cooperation method of a wireless network and a realization apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: after a route is established, a common neighbor node between a first host node and a second host node on the route is taken as a cooperative node, and an end-to-end diversity gain and an end-to-end interruption probability between the first host node and the second host node are obtained during cooperation of the cooperative node; a common neighbor node between the second host node and a third host node on the route is taken as a cooperative node, and an end-to-end diversity gain and an end-to-end interruption probability between the second host node and the third host node are obtained during cooperation of the cooperative node; a common neighbor node between the first host node and the third host node on the route is taken as a cooperative node, and an end-to-end diversity gain and an end-to-end interruption probability between the first host node and the third host node are obtained during cooperation of the cooperative node; and node segmentation modes are determined as one-hop node segmentations having corresponding cooperative nodes or two-hop segmentations having corresponding cooperative nodes with utilization of the obtained diversity gains and interruption probabilities.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for cell-to-cell information interaction and base station
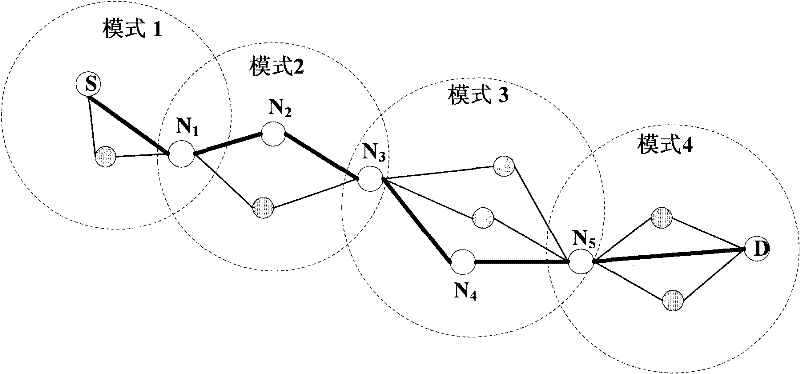
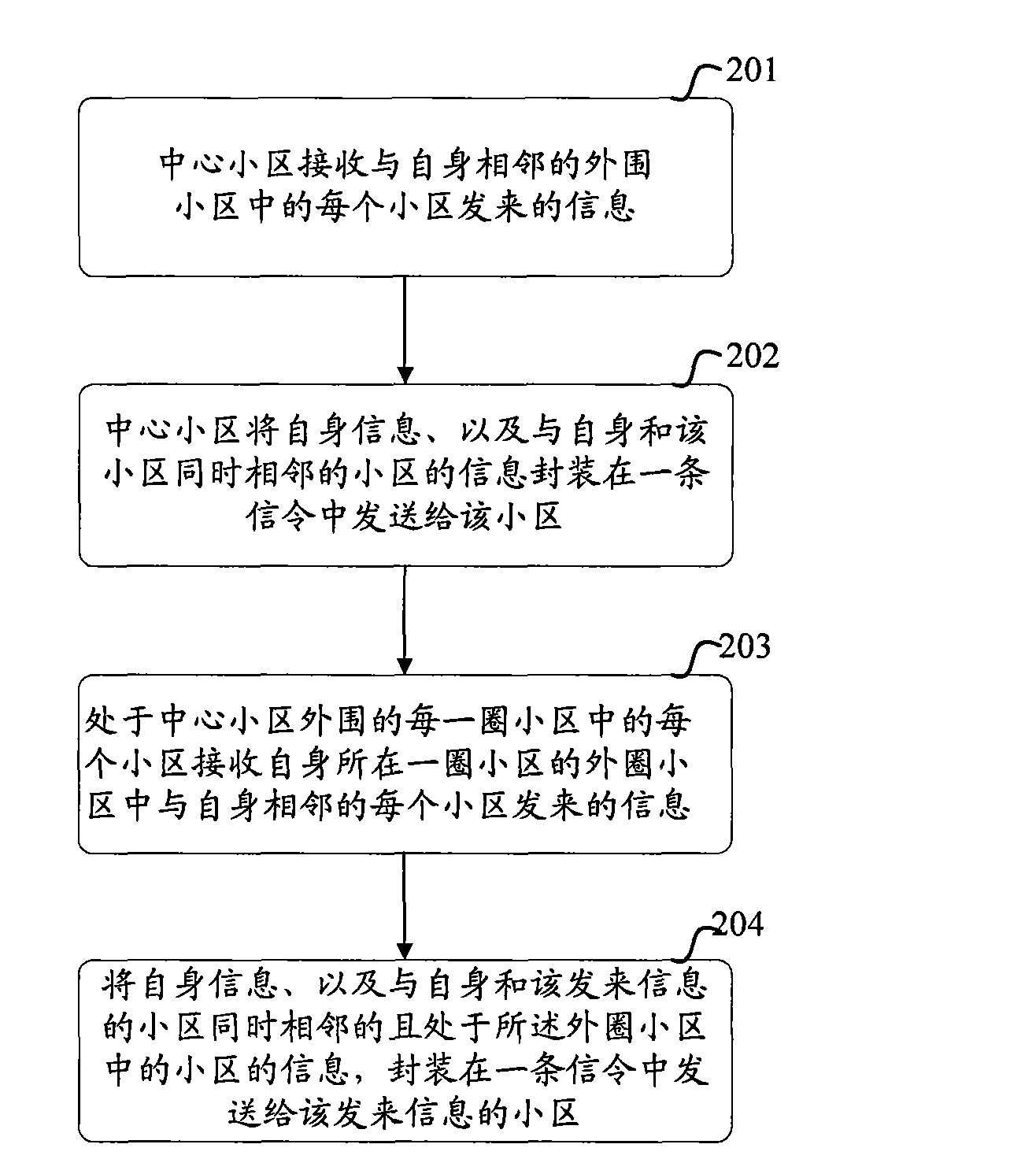
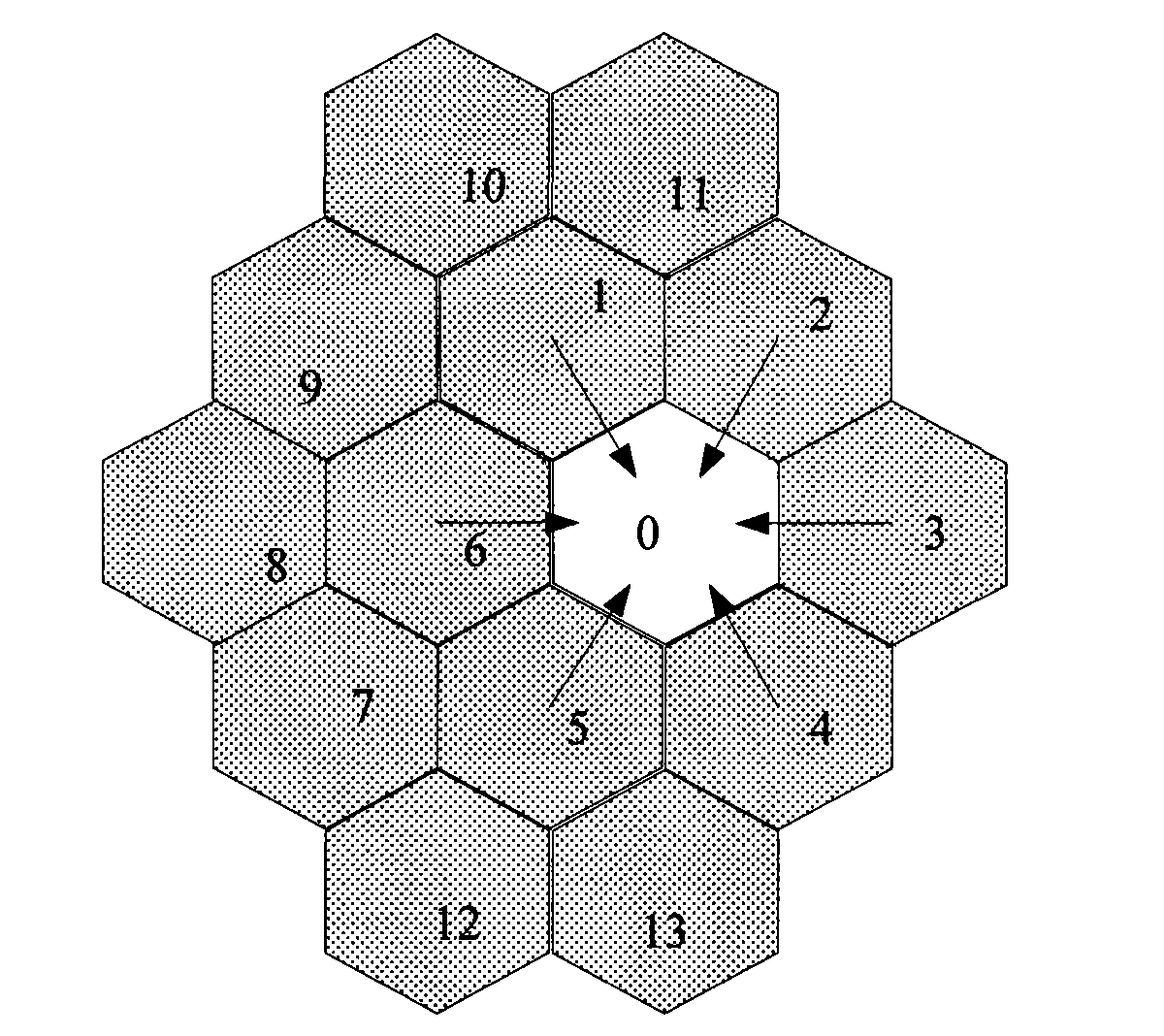
ActiveCN101583153AReduce the number of interactionsReduce loadNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemCommon neighbor
The invention discloses a method and a system for cell-to-cell information interaction and a base station. According to the technical proposal of the invention, a central cell and each cell in each cell circle surrounding the central cell receive information sent by a neighbor cell in an outer cell circle and pack self-information and information from a common neighbor cell shared with the cell of the incoming information in one signaling to be sent to the cell of the incoming information. The proposal of the invention reduces information interactions in the whole communication system and correspondingly reduces the processing tasks of eNBs and the load of the interface links between the eNBs.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Network unknown connection edge prediction method based on second-order local community and preferential attachment
The invention provides a network unknown connection edge prediction method based on a second-order local community and preferential attachment. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a network model, and obtaining first-order common neighbor nodes and second-order common neighbor nodes of a pair of unconnected nodes, wherein the nodes and the connection edges between the nodes form the second-order local community; recording the total number of the nodes and connection edges of the local community, and meanwhile, recording the number of neighbors, outside the community, of two seed nodes; calculating volume coefficient, edge-clustering coefficient and simple harmonic average distance of the community and second-order local community coefficient; calculating similarity score index between the node pair; traversing the whole network, and for any two unconnected nodes, calculating similarity score index between the corresponding node pair; and ranking similarity scores between all of the unconnected node pairs in a descending order, and taking nodes corresponding to the front m score indexes as predicted connection edges. The method takes the second-order local community and preferential attachment information of the seed nodes into consideration, and makes full utilization of information of a network local structure, and is good in prediction effect and high in accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
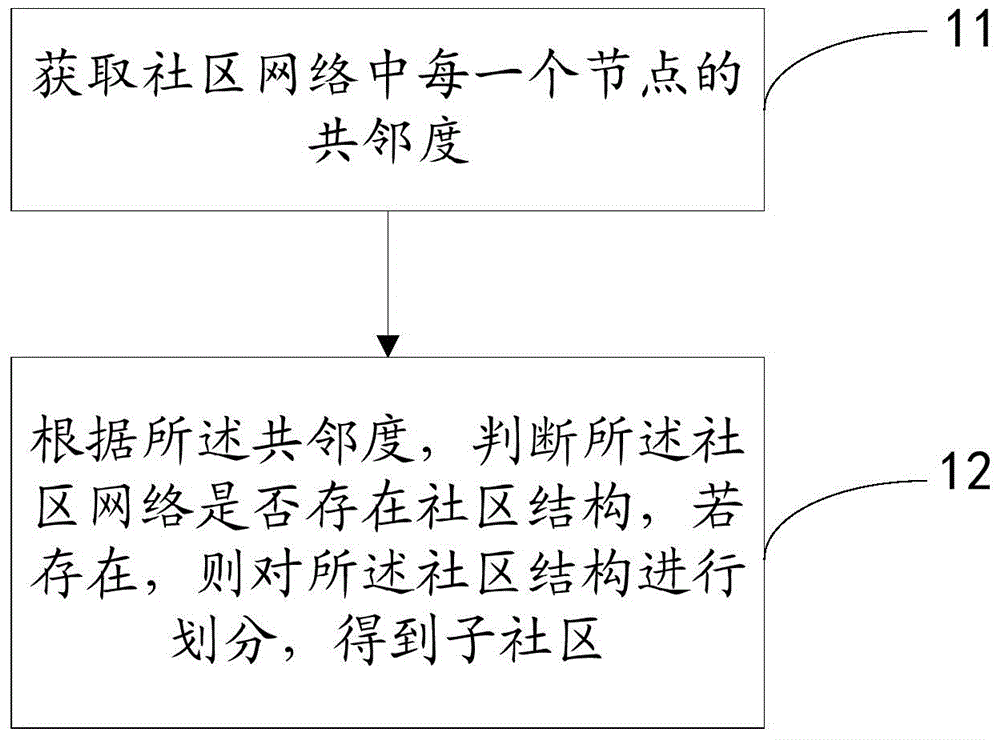
Network community dividing method and device
InactiveCN104581734AImprove division accuracyEasy to useNetwork planningCommunity structureWeb community
The invention provides a network community dividing method and device and solves problems that community core nodes are found in a limited manner, community peripheral nodes are ignored and acquired node attribute information is incomplete during community division. The network community dividing method comprises steps as follows: acquiring the common adjacency degree of each node in a community network; judging communities to which the nodes belong according to the common adjacency degrees, and dividing the community structure to acquire sub-communities. Thus, community division can be performed by the aid of common neighbors of all the nodes.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP GUANGDONG CO LTD
Prediction network unknown connection edge method based on second-order local association information
InactiveCN106295907AImprove accuracyGood forecastForecastingLocal associationStructure of Management Information
The present invention provides a prediction network unknown connection edge method based on the second-order local association information. The method comprises: constructing a network model; obtaining a pair of first-order common neighbor nodes and second-order common neighbor nodes which are not connected with nodes, wherein the connection edge between the nodes and the first-order common neighbor nodes and the second-order common neighbor nodes forms a second-order local association; recording the total number of the nodes of the association and the total number of the connection edge; calculating the edge clustering coefficient, the simple harmonic quantity mean distance of the association and the second-order association coefficients; calculating the similarity score index between the node pair; and traversing the whole network, calculating the similarity score index between the corresponding node pair aiming at two random non-connected nodes, and sorting the similarity scores among all the non-connected node pairs in the descending order to take the nodes corresponding to the front M indexes as predication connection edge. The prediction network unknown connection edge method based on the second-order local association information considers the second-order local association including the first-order common neighbor and the second-order common neighbor between two non-connected nodes to fully utilize the network local structure information, the predication effect is good, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Social relationship hiding method based on attack node similarity
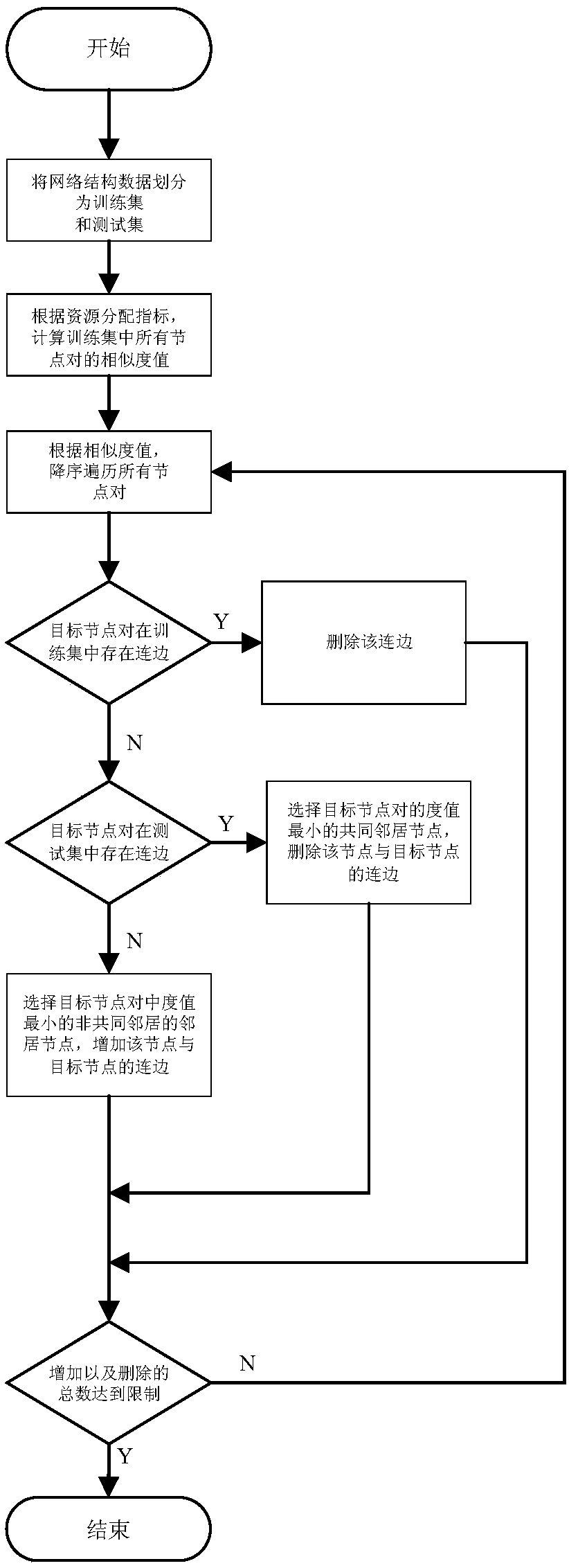
The invention provides a social relationship hiding method based on attack node similarity. The method comprises the following steps: 1) dividing network structure data into a training set and a testset; 2) calculating similarity values of all node pairs in the training set according to resource allocation indicators; 3) traversing all target node pairs in a descending order of the similarity values, and if the target node pairs have connected edges in the training set, deleting the connected edges; if the target node pairs have connected edges in the training set, selecting a common neighbornode with the smallest similarity value of the target node pairs, and deleting the connected edge of the node and the target node; if the target node pairs have no connected edges, selecting neighbornodes of a non common neighbor with the smallest median value of the target node pairs, and adding the connection edge of the node and the target node; and if the total number of adding and deletingreaches to the limitation, stopping the execution, and outputting a result. According to the social relationship hiding method provided by the invention, the connected edge disturbance of the networkis performed by using the node similarity to achieve a better hiding effect than random disturbance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Edge community discovery algorithm based on deep sparse auto-encoder
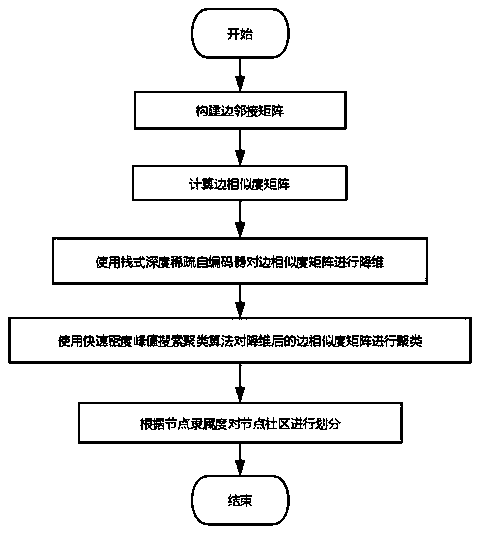
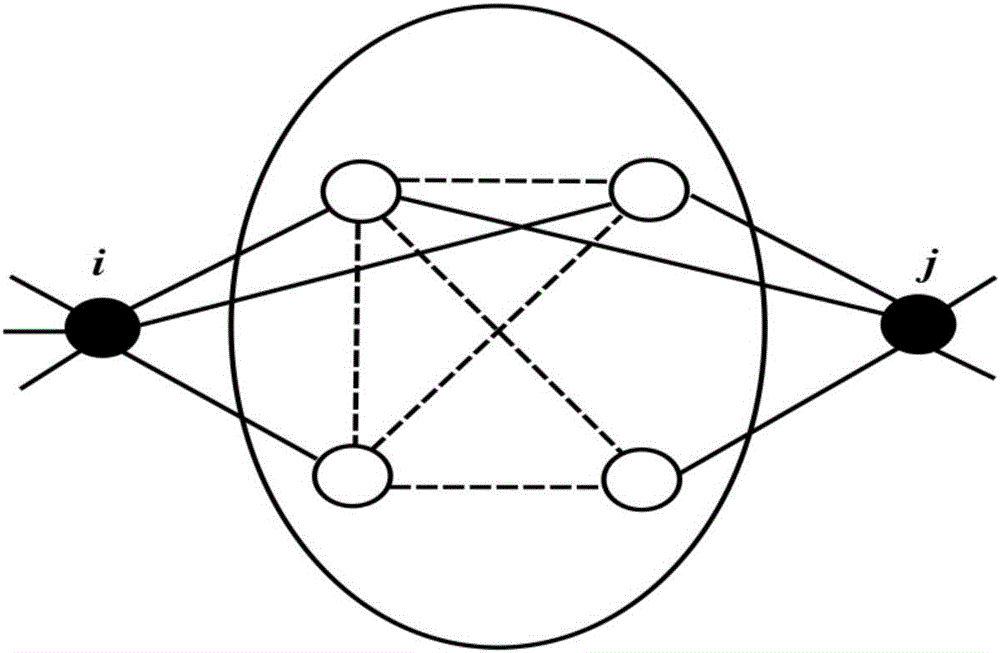
InactiveCN110533545AReduce the number of overlapping nodesData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmNODAL
The invention discloses an edge community discovery algorithm based on a deep sparse auto-encoder. The method mainly comprises the following steps: constructing an edge adjacency matrix; calculating an edge similarity matrix; carrying out dimension reduction on an edge similarity matrix based on a stack type depth sparse auto-encoder; performing edge clustering based on a fast density peak searchclustering algorithm; and carrying out node community division based on the node membership degree. According to the invention, a side community discovery algorithm based on a deep sparse auto-encoderis used, side community division and node overlapping community division are realized; a novel and efficient algorithm is provided for overlapped community discovery; compared with the existing algorithm, the method has the following advantages: (1) the algorithm considers the connection relationship between the edges and the topological structure relationship between the common neighbor edges between the edges to construct the edge similarity matrix, and uses the depth sparse auto-encoder to reduce the dimension of the edge similarity matrix, so that the complexity of the edge clustering process is reduced; and (2) the algorithm uses membership degrees to divide node communities, so that a better evaluation metric value can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Second-order local community and common neighbor proportion information-based method for predicting unknown connected edges of network
InactiveCN106372743AImprove accuracyGood forecastForecastingNODALStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses a second-order local community and common neighbor proportion information-based method for predicting unknown connected edges of a network. The method comprises the steps of building a network model, taking any pair of unconnected nodes as seed nodes, and recording total quantities of first-order and second-order neighbors of the seed nodes; obtaining first-order and second-order common neighbor nodes of the seed nodes, wherein the nodes and connected edges among the nodes form a second-order local community; recording total quantities of the nodes and the connected edges of the community; calculating a viscosity coefficient, an edge-clustering coefficient, a simple harmonic average distance and a second-order local community coefficient of the community; calculating a similarity score index between node pairs; and traversing the network, calculating a corresponding similarity score index for any two unconnected nodes, arranging similarity scores among all unconnected nodes according to a descending order, and taking the node pairs corresponding to first m indexes as predicted connected edges. According to the method, the second-order local community and the proportion of the common neighbors of the seed nodes in the neighbors are considered, and local structure information of the network is fully utilized, so that the prediction effect is good and the accuracy is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method of predicting unknown connecting sides of network based on second-order local community and seed node structure information
A method of predicting unknown connecting sides of a network based on a second-order local community and seed node structure information comprises the following steps: building a network model, randomly taking a pair of unconnected nodes as seed nodes, recording the number of neighbor nodes of the seed nodes, and acquiring first-order and second-order common neighbor nodes of the seed nodes, wherein the nodes and the connecting sides thereof constitute a second-order local community; recording the total number of nodes and connecting sides of the community; calculating the degree coefficient, side clustering coefficient, simple harmonic average distance and second-order local community coefficient of the community; calculating the similarity score index of the node pair; and traversing the whole network, and for any two unconnected nodes, calculating the similarity score index of the corresponding node pair, sorting the similarity scores of all unconnected node pairs in descending order, and taking node pairs corresponding to the first m indexes as predicted connecting sides. The method considers a second-order local community and seed node structure information, makes full use of the local structure information of a network, has a good prediction effect, and is of high accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Link prediction method based on bayes estimation and common neighbour node degree
The invention discloses a link prediction method based on bayes estimation and common neighbor node degree. The method comprises the steps of establishing a network model; taking any two nodes which are not connected directly as seed nodes and calculating a probability that a connected side exists or do not exists between the nodes; calculating the probability that the connected side is generated or is not generated between the two nodes according to degree information of an intermediate node of a path with a length of 2 or 3 between the two nodes; calculating a likelihood value of each intermediate node of the path with the length of 2 or 3 between the two nodes according to the bayes estimation and the common neighbor node degree, wherein a similarity score is the sum of the likelihood values of all intermediate nodes; and traversing a network, obtaining the similarity score between any two seed nodes through adoption of the method, sorting all seed node pairs according to the similarity scores in a descending order, and taking the node pairs corresponding to the former B score values as predicted connected sides. According to the method, on the basis of the bayes estimation and through combination of the common neighbor node degree, different intermediate nodes in the partial path between the two nodes have different importance and a prediction effect of the algorithm is good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Community discovery method based on local optimization
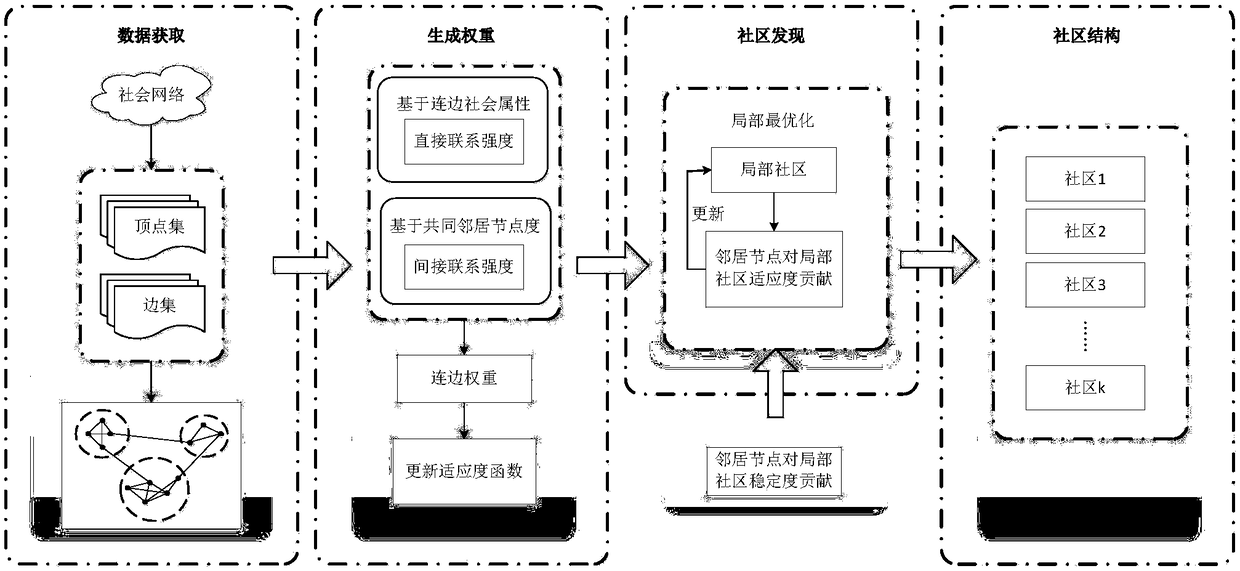
InactiveCN108400889ASlow down the expansion rateStabilize community structureData processing applicationsData switching networksLocal optimumSocial network
The invention relates to the community discovery field in a complex network, and specifically discloses a community discovery method based on local optimization. On the basis of an LFM (Local FitnessMaximum) algorithm, on the one hand, a weighting method for integrating internodal boundary social attribute with common neighbor node degree in the network is proposed, and a fitness function in theLFM algorithm is updated by using the formed boundary weight; on the other hand, the concept about the local community stability is imported into the local optimization process of the LFM algorithm, the contribution degree on the community stability by the node is judged by computing the community stability before and after the node adds in the local community, and the contribution degree is usedas the criterion whether the node is added in the community. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the appearance of the over-sized community is avoided, the more significant groupuscule structure in the network can be easily discovered, and the method is suitable for the real social network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Link deletion method for network structure privacy protection against link prediction
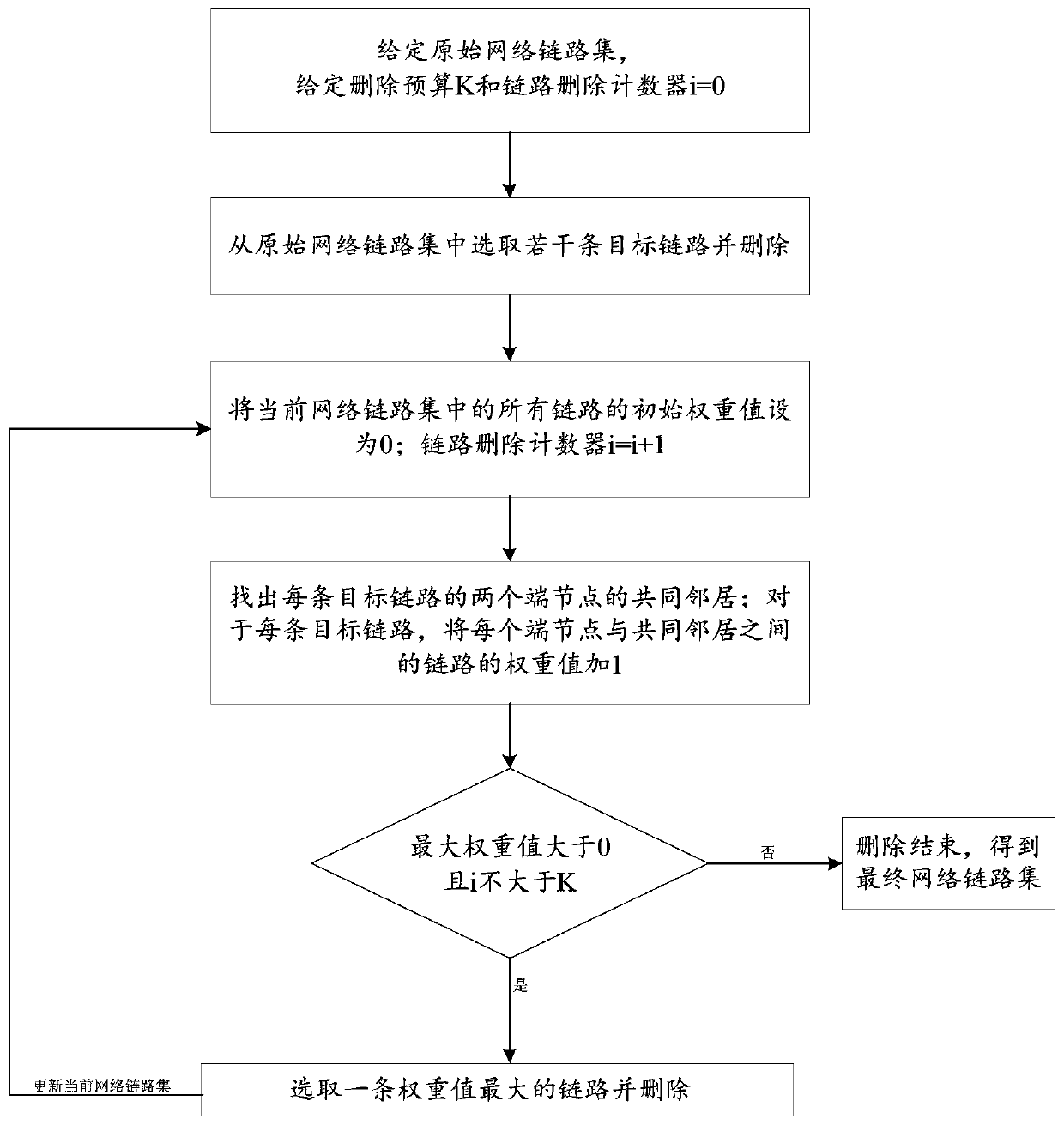
The invention discloses a link deletion method for network structure privacy protection against link prediction. The link deletion method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting a plurality of target links from an original network link set; deleting all the target links from the original network link set; giving a deletion budget K and a link deletion counter i, wherein i = 0; S2, setting theinitial weight values of all links in the current network link set as 0; wherein the link deletion counter i = i + 1; S3, finding out a common neighbor of two end nodes of each target link; for eachtarget link, adding 1 to the weight value of the link between each end node and the common neighbor; S4, when the maximum weight value is greater than 0 and i is not greater than K, performing S5, ifnot, performing S7; S5, selecting a link with the maximum weight value and deleting the link; S6, updating the current network link set in the step S2, and returning to the step S2; S7, ending. According to the method, better availability reservation of an original network can be realized, and a very good privacy protection purpose can be achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Directed network link prediction method with fusion of multimode body information
InactiveCN110493045AImprove accuracyImprove forecast accuracyData switching networksNODALPositive sample
The invention discloses a directed network link prediction method with the fusion of the multimode body information. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: S1, constructingan initial network, and obtaining a node pair list without connection edges; S2, randomly selecting 10% of connecting edges in the initial network data as positive samples of a test set, taking the remaining 90% of connecting edges as a training set, and selecting a connecting edge set as large as the positive samples of the test set as negative samples of the test set; S3, obtaining role functionvalues corresponding to individuals in the initial network; S4, obtaining a role function Rw list of a common neighbor corresponding to each node pair; S5, obtaining the number of common neighbors ofthe node pairs; S6, obtaining an r'xy list of the node pair; S7, according to the r'xy list of the single die body, obtaining a list of rxy of the double die bodies in a superposition mode; or usinga machine learning method XGBoost to obtain a new score list according to the r'xy list obtained by different single die bodies. According to the method, the structural characteristics of the directednetwork are fully applied, so that the link prediction accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Network unknown edge prediction method based on second-order local community and node degree information
The invention provides a network unknown edge prediction method based on a second-order local community and node degree information. A network model is constructed, the first-order common neighbor nodes and the second-order common neighbor nodes of a pair of unconnected nodes are acquired, and the nodes and the edges between the nodes form the second-order local community; the total number of the nodes and the edges of the community is recorded, and the degree of each node in the whole network and the degree in the community are also recorded; the degree coefficient, the edge-clustering coefficient, the harmonic average distance and the second-order local community coefficient of the community are calculated; the similarity score index between the node pairs is calculated; and the whole network is traversed, the similarity score index between the corresponding node pairs is calculated as for any two unconnected nodes, the similarity scores of all the unconnected node pairs are ordered in a descending way, and the corresponding node pairs of the previous m indexes are taken to act as the prediction edges. The second-order local community and the node degree information are considered, and network local structure information is fully utilized so that the prediction effect is great and the accuracy is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Symbolic link prediction method based on hidden space
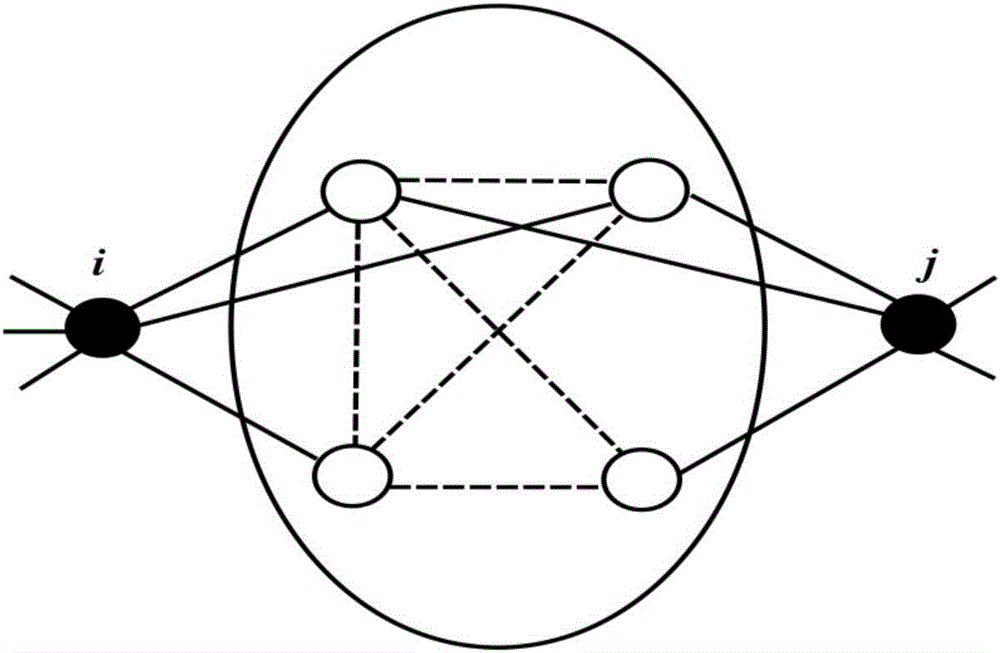
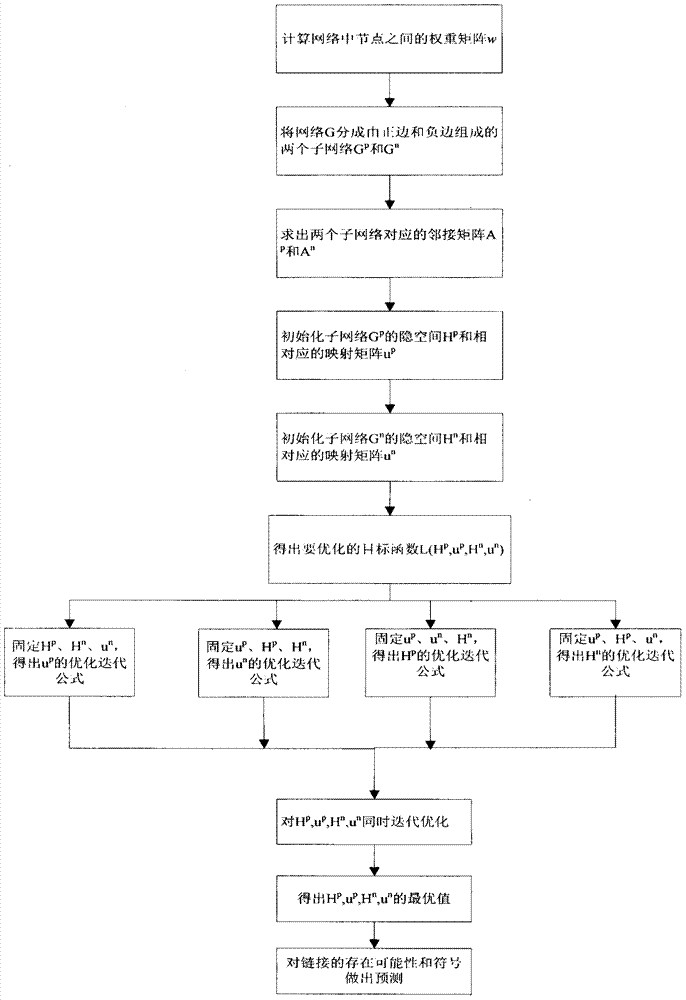
InactiveCN107358532ASolve the problem of sign predictionAvoid sign problemsData processing applicationsNODALAlgorithm
The invention relates to a symbolic link prediction method based on latent space. The present invention calculates the weight between nodes in the signed network according to the common neighbor index and the adjacency matrix of the signed network, and obtains the weight matrix w. To obtain the hidden space matrix H and the corresponding mapping matrix u that need to be optimized at the end of the method, they are respectively fixed Hp, up, Hn, un among the three items, find out the optimal iterative formula of Hp, up, Hn, un, and iteratively update Hp, up, Hn, un at the same time according to the optimized iterative formula obtained, according to the Hp after iteration , the optimal value of up, Hn, un, to make predictions on the possibility and sign of link existence. The invention overcomes the defect that previous studies only focused on linking symbols, but did not predict the possibility of the existence of the symbols. The present invention proposes a hidden space-based symbolic link prediction method for the symbolic prediction problem of a symbolic social network, which has a fast convergence speed and can make more accurate predictions about the symbol of the link and the probability of being the symbol.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Second-order local community common neighbor ratio and node correlation-based network connection edge prediction method
InactiveCN106886679AImprove forecast accuracyImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsNODALAlgorithm
The invention discloses a second-order local community common neighbor ratio and node correlation-based network connection edge prediction method. The method comprises the steps of building a network model, extracting first-order and second-order common neighbor nodes of two nodes without connection edges, and edges between the nodes to form a second-order local community, recording total numbers of the nodes and the edges of the community, and calculating an edge clustering coefficient, a simple harmonic average distance, connection edge density and a second-order local community coefficient; and calculating a Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient between the two nodes without the connection edges, calculating a common neighbor ratio, calculating a similarity index between the two nodes, calculating the similarity index between any two nodes without the connection edges in the whole network, arranging similarity scores between all node pairs without the connection edges according to a descending order, and taking the two nodes corresponding to first h indexes as predicted connection edges. According to the method, the common neighbor ratio between the nodes, the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient and internal attributes of the local community are considered, and correlation information of the network is effectively utilized, so that the accuracy is relatively high and the prediction precision is relatively high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Recommendation method based on network local structure information filtering
InactiveCN108063810AHigh precisionData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsPrediction algorithmsNetwork structure
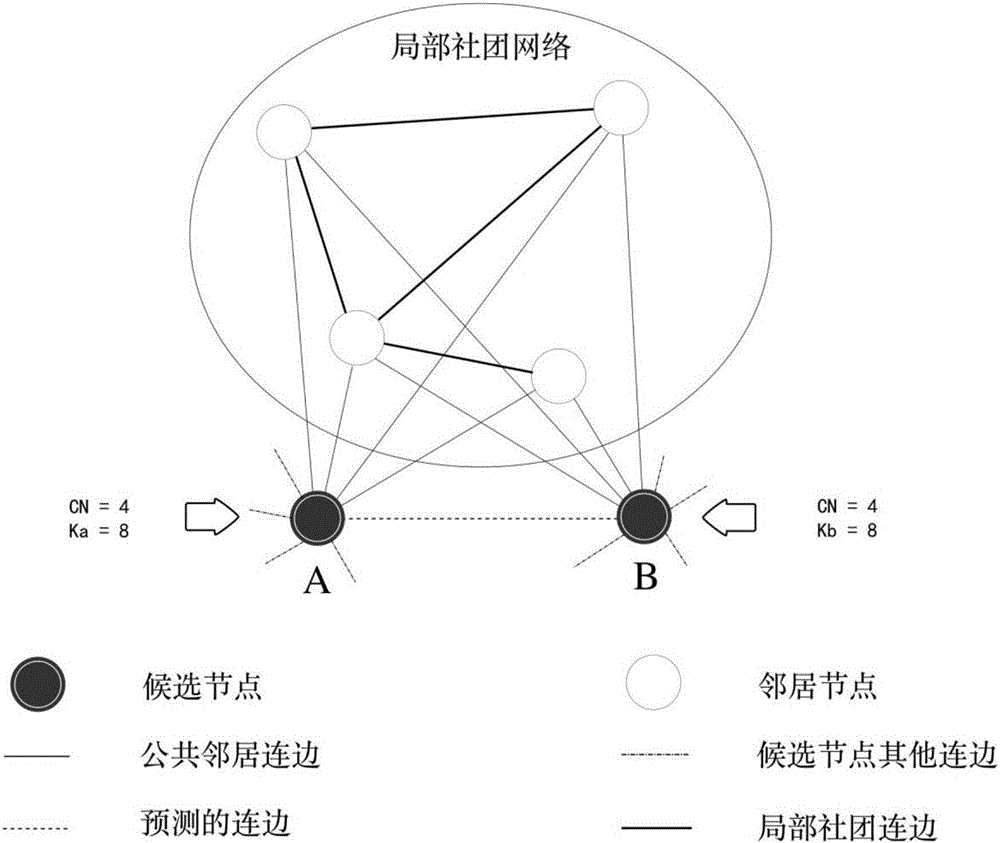
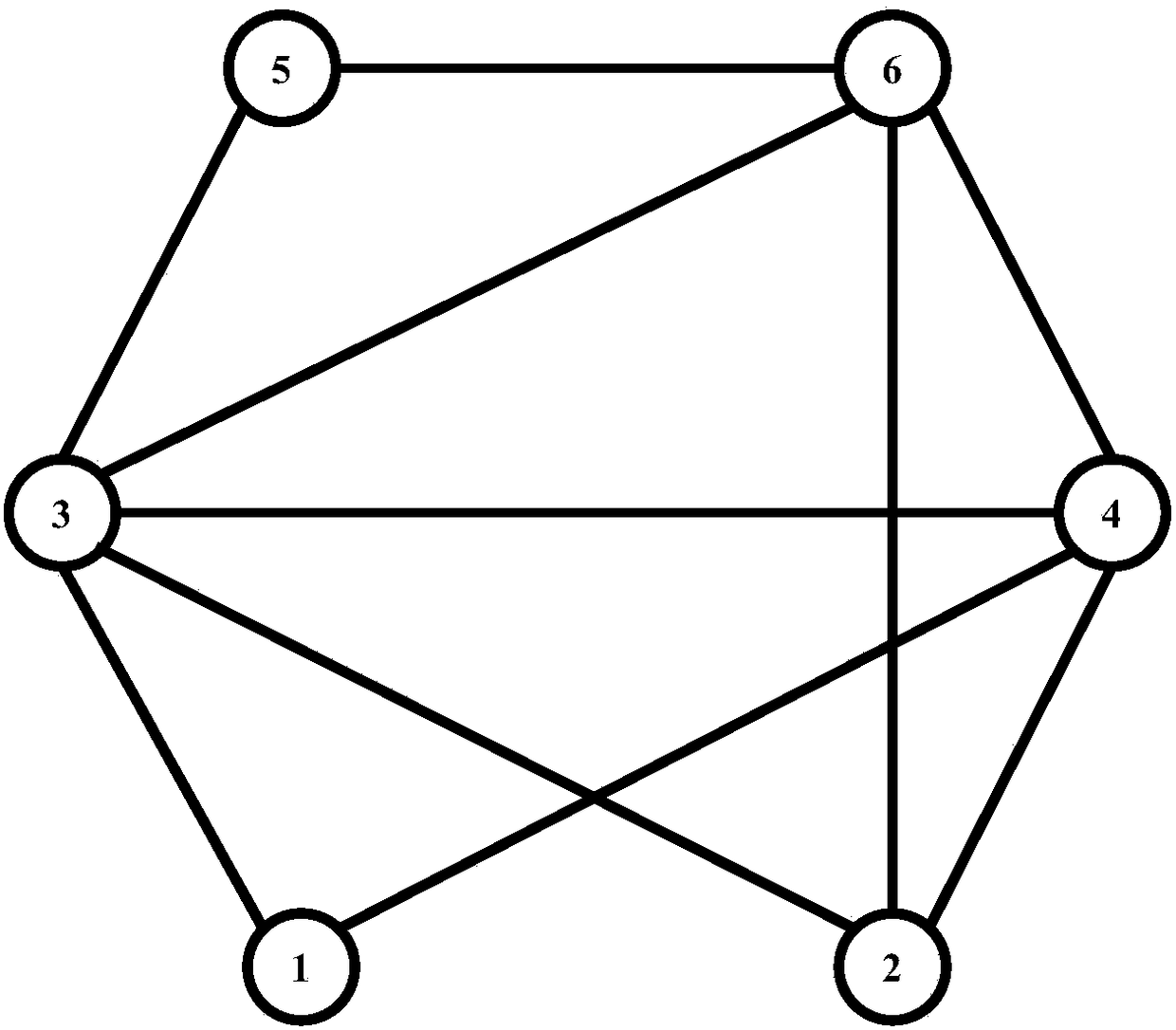
The invention discloses a recommendation method based on network local structure information filtering. The recommendation method comprises the following steps: acquiring true network structure information, and building a network model G(V,E); determining a target node v, wherein a set of all possible connection nodes to be recommended is represented with theta; optionally selecting a node v<j> from the set theta, and acquiring a common neighbor node set psi(i,j) of a node vi and the node vj; selecting a node v<h> in sequence from the set psi(i,j), calculating the degree k<h> of the node v<h>, the quantity S<ih><CN> of common neighbor nodes of the node v and the node v<h>, and the quantity S<jh><CN> of common neighbor nodes of the node v<j> and the node v<h>; calculating a similarity index of the node v<j> and the node v<j>; and calculating a similarity index between all nodes in the set theta and the node v, and selecting three nodes of which the values are greatestas three nodes of which the connection probability is highest. Through adoption of the recommendation method, the link prediction algorithm accuracy can be increased effectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A link prediction method based on common neighbor node resource allocation and naive bayesian
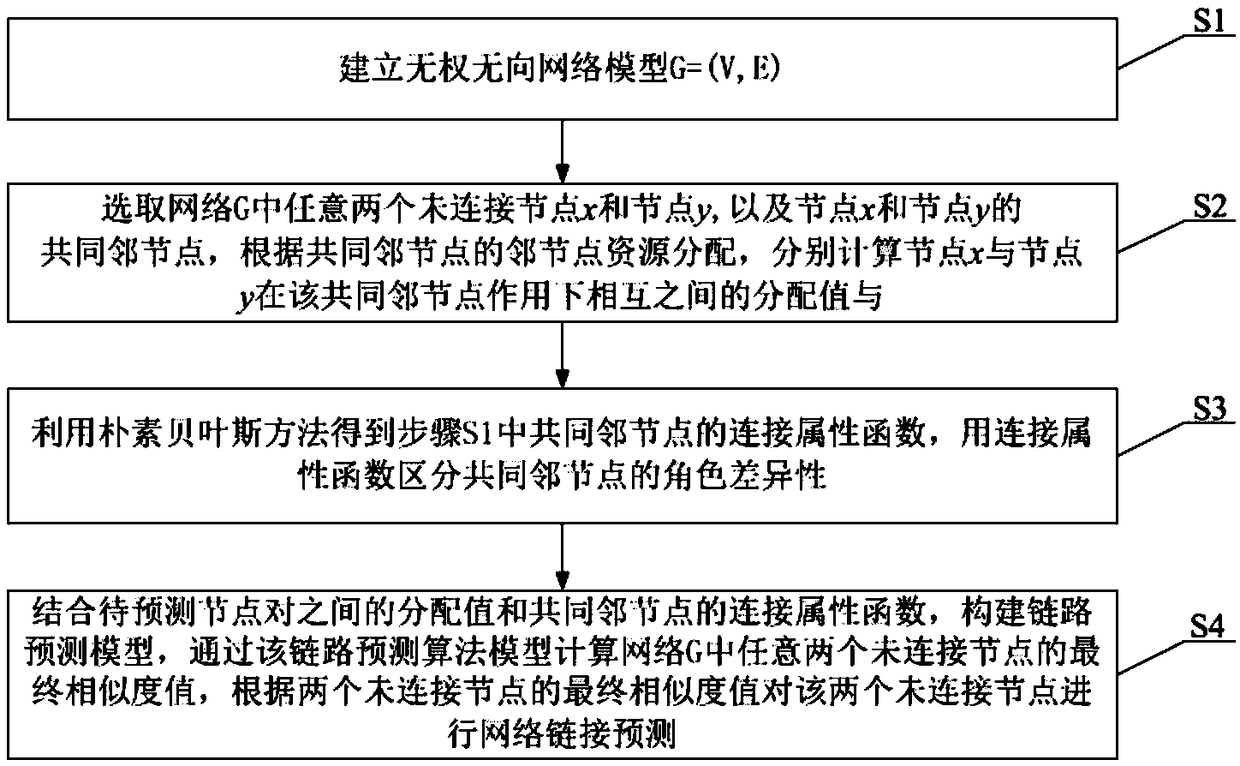
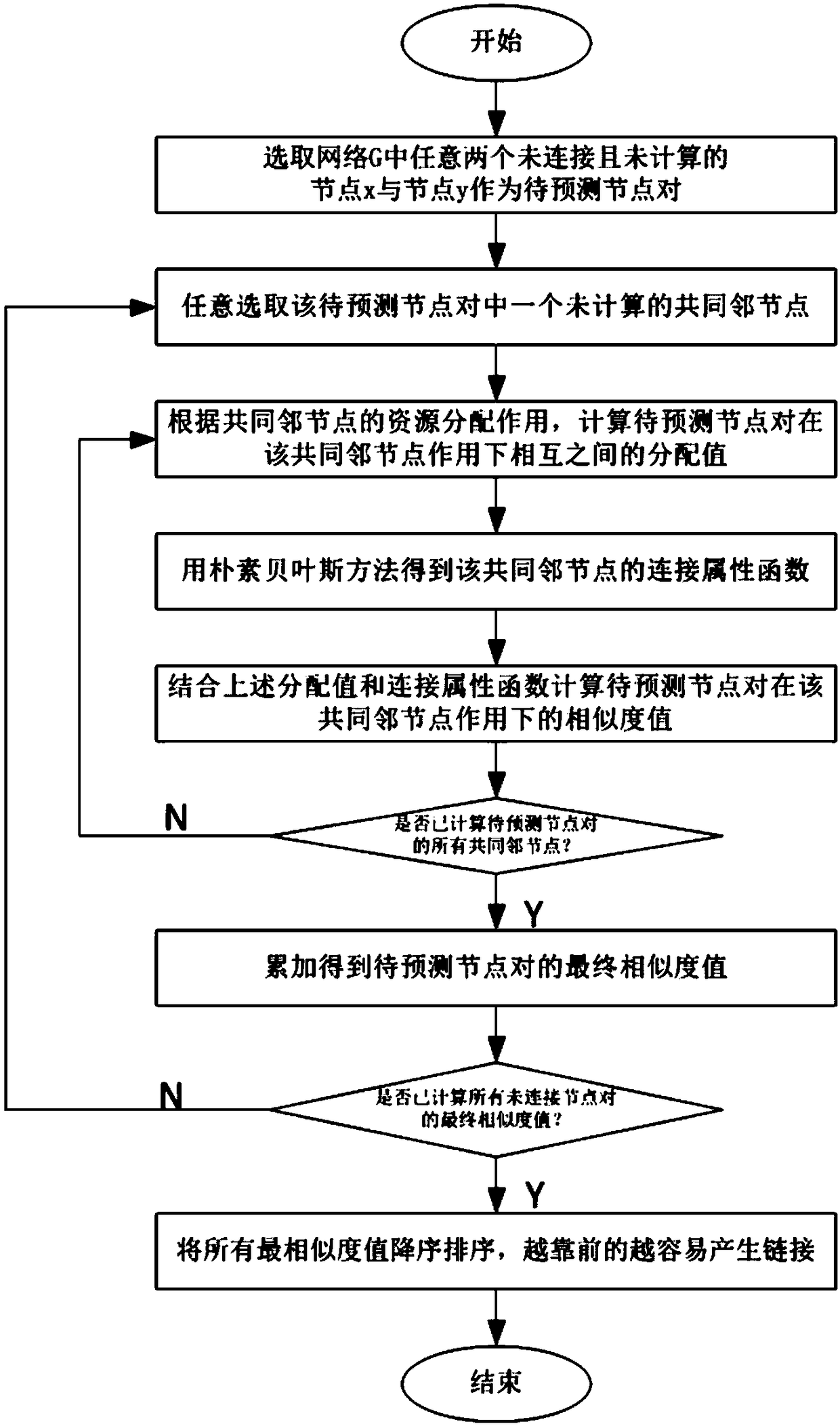
ActiveCN109039722AImprove forecast accuracyRealize deep miningData switching networksNODALNetwork link
A link prediction method base on common neighbor node resource allocation and naive Bayesian is disclosed, By establishing network model G, any two unconnected nodes x and y and the common neighbor nodes of node x and y in network G are selected to calculate the distribution value of node x and node y under the action of the common neighbor nodes. Secondly, the connection attribute function of thecommon neighbor node in step S1 is obtained by using the naive Bayesian method, and the role difference of the common neighbor node is distinguished by the connection attribute function; Finally, thefinal similarity value of any two unconnected pairs of nodes in the network G is calculated by combining the assignment value between the pairs of nodes to be predicted and the connection attribute function of the common neighboring nodes, and the network link prediction is carried out according to the final similarity value of the pairs of nodes to be predicted. The invention utilizes the naiveBayesian method to supplement the attribute differences between different nodes, so that the link prediction accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:中电科新型智慧城市研究院有限公司
Link prediction method based on local similarity
PendingCN110084423AImprove forecast accuracyFully excavatedForecastingPositive samplePredictive methods
The invention discloses a link prediction method based on local similarity. The link prediction method comprises the following specific steps: S1, obtaining original population data and constructing an initial population; s2, selecting a connection edge set with the same size as the test set positive sample from the node pair list without the connection edge as a test set negative sample; s3, obtaining community division corresponding to the population individuals by adopting an InfoMap algorithm; s4, obtaining a node pair list of the intra-community connection edge and the out-community connection edge according to the community division result; s5, starting from a first node pair in the network, according to the number of common neighbors of the node pair, sequentially calculating a common neighbor similarity index CN of each pair of nodes, and arranging all non-existing connecting edges in a descending order according to a CN value, so that the connecting edges arranged at the frontL pieces are most likely to have links. According to the method, the similarity index of the community structure information is added, so that the prediction accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com