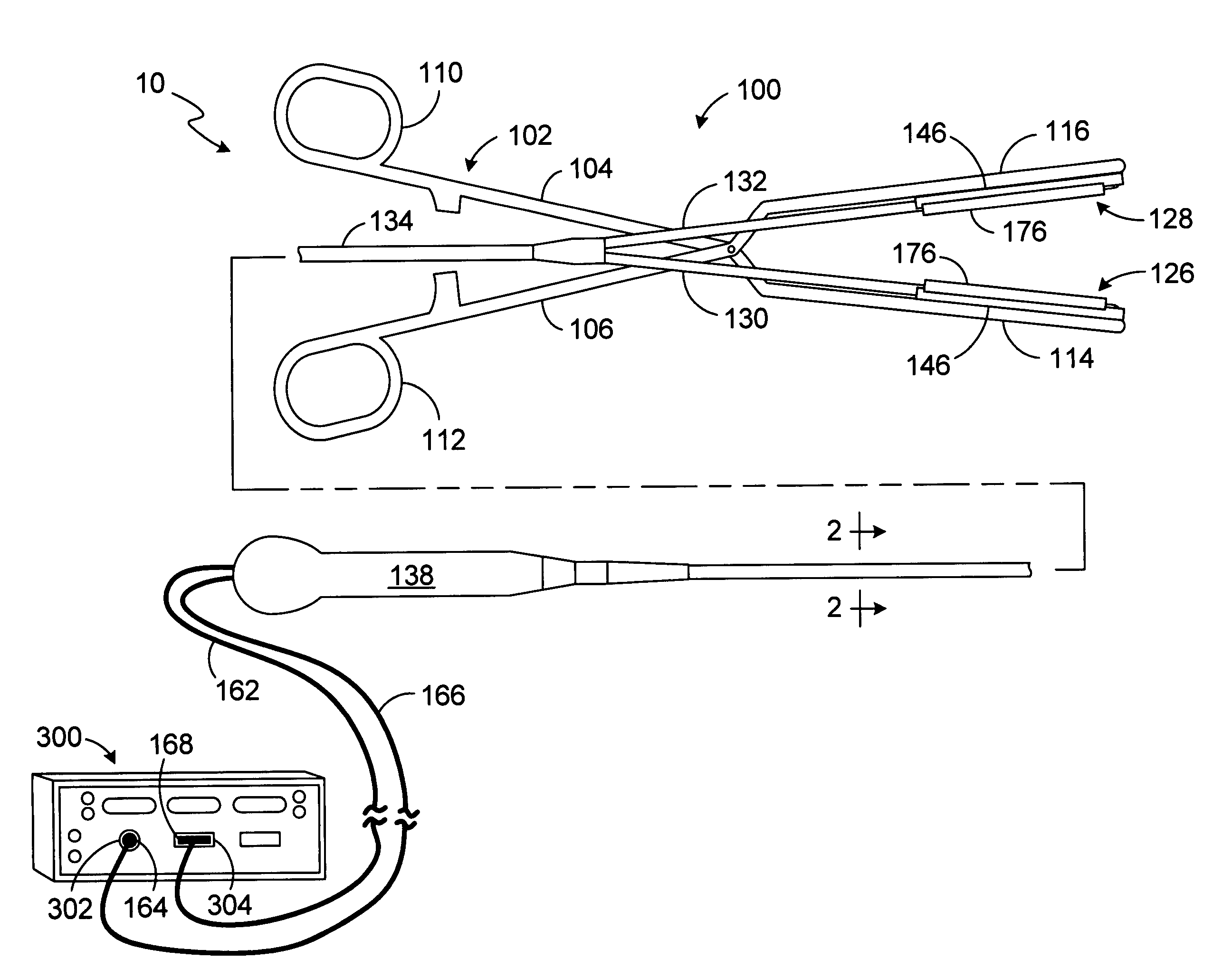
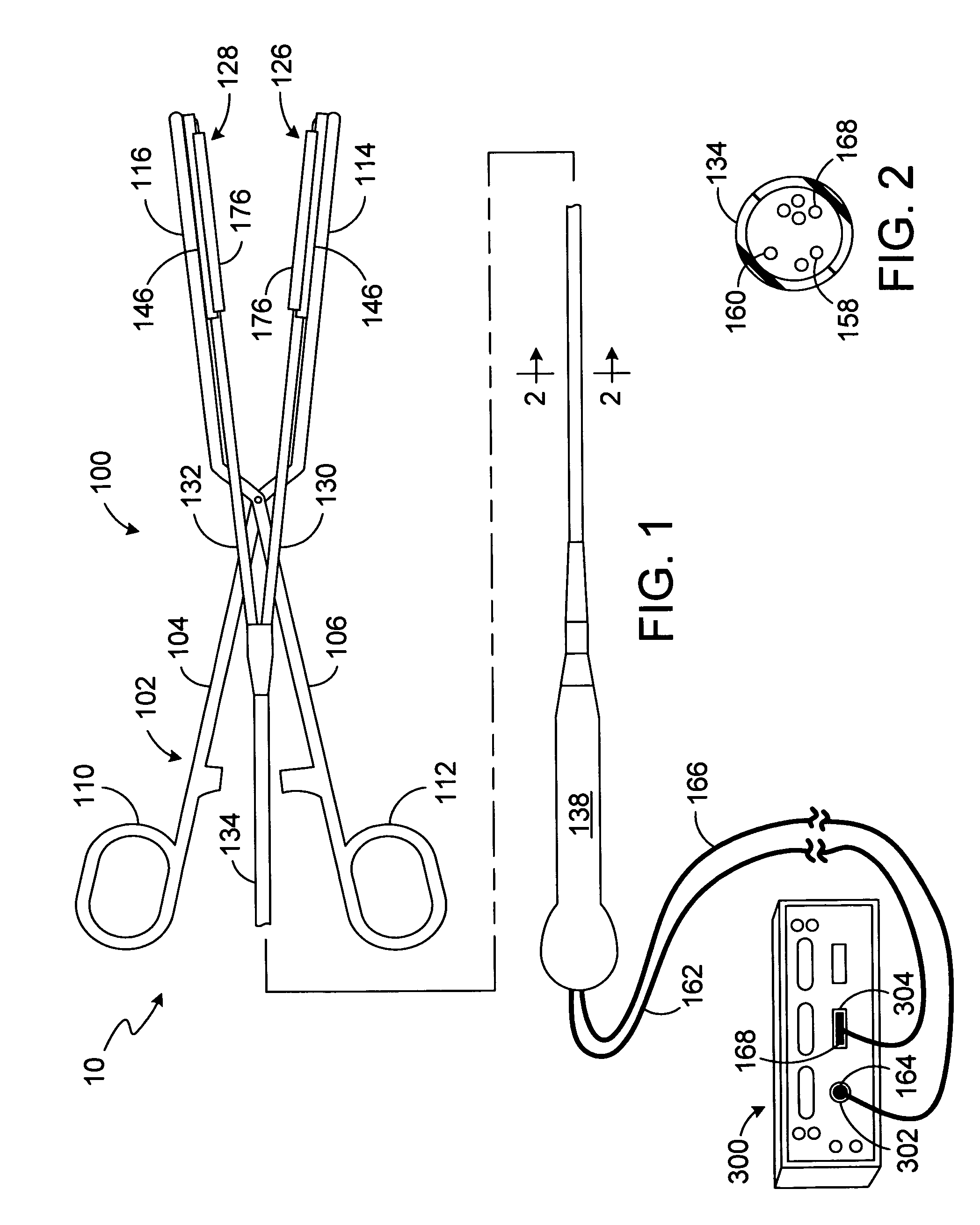
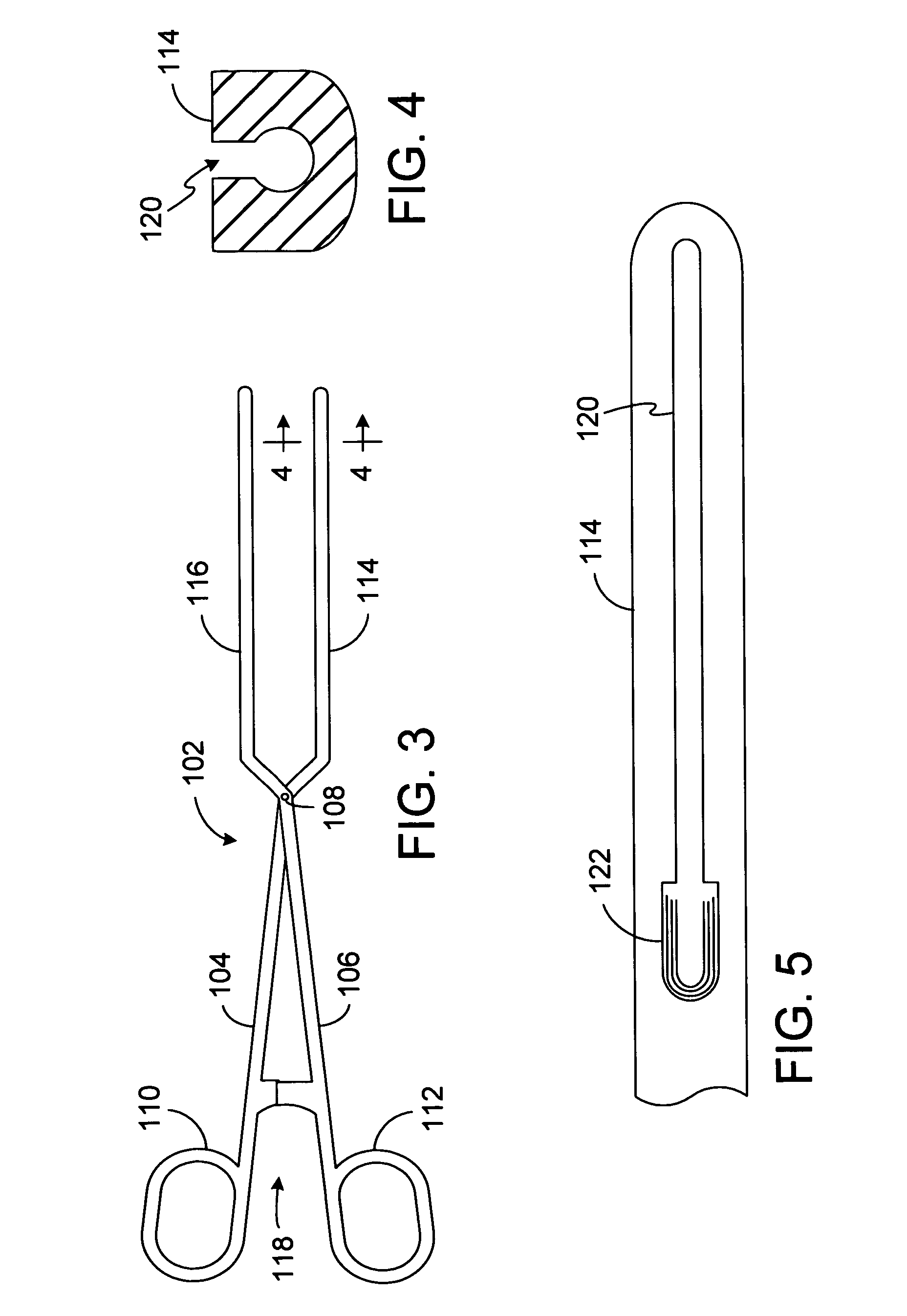
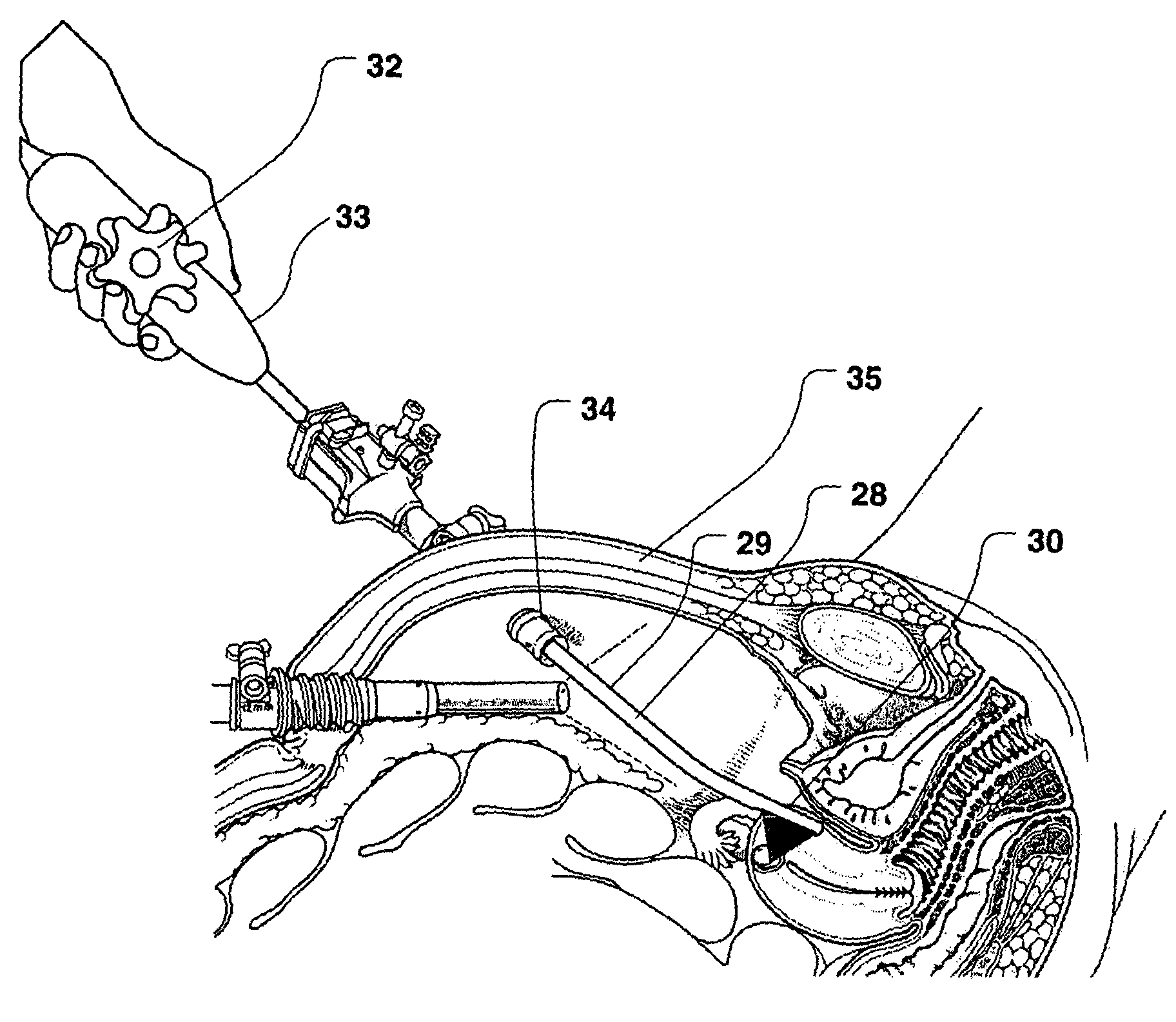
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Lesion formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
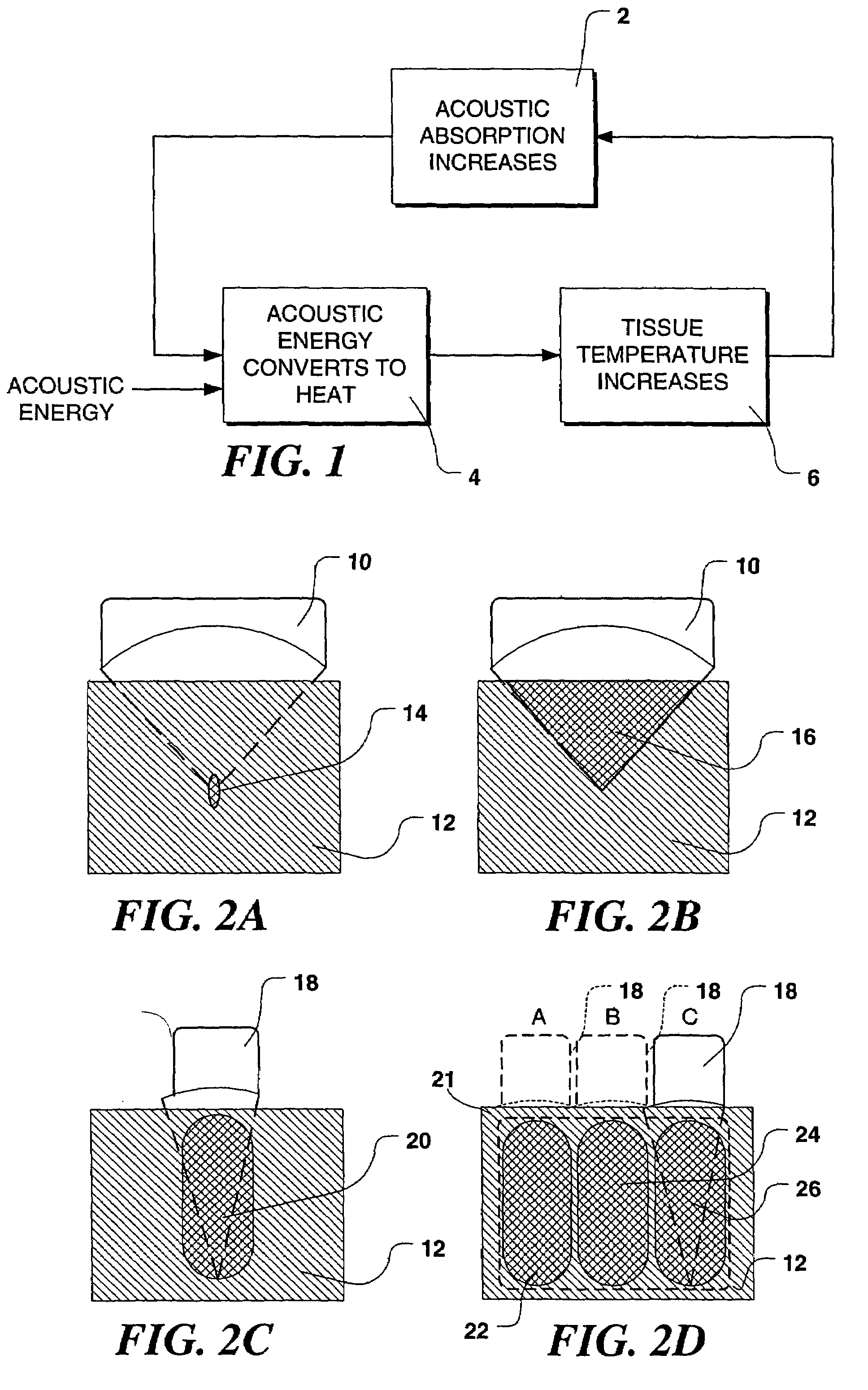
Cam lesion. A CAM lesion is the formation of extra bone on the head of the femur (ball) resulting in a ‘bump’. This extra bone can cause pain as it impinges with the acetabulum (socket) with joint movement. A Cam lesion is commonly seen in conditions such as Femoro-Acetabular Impingement (FAI) and in some cases can lead to labral tears. The evidence...
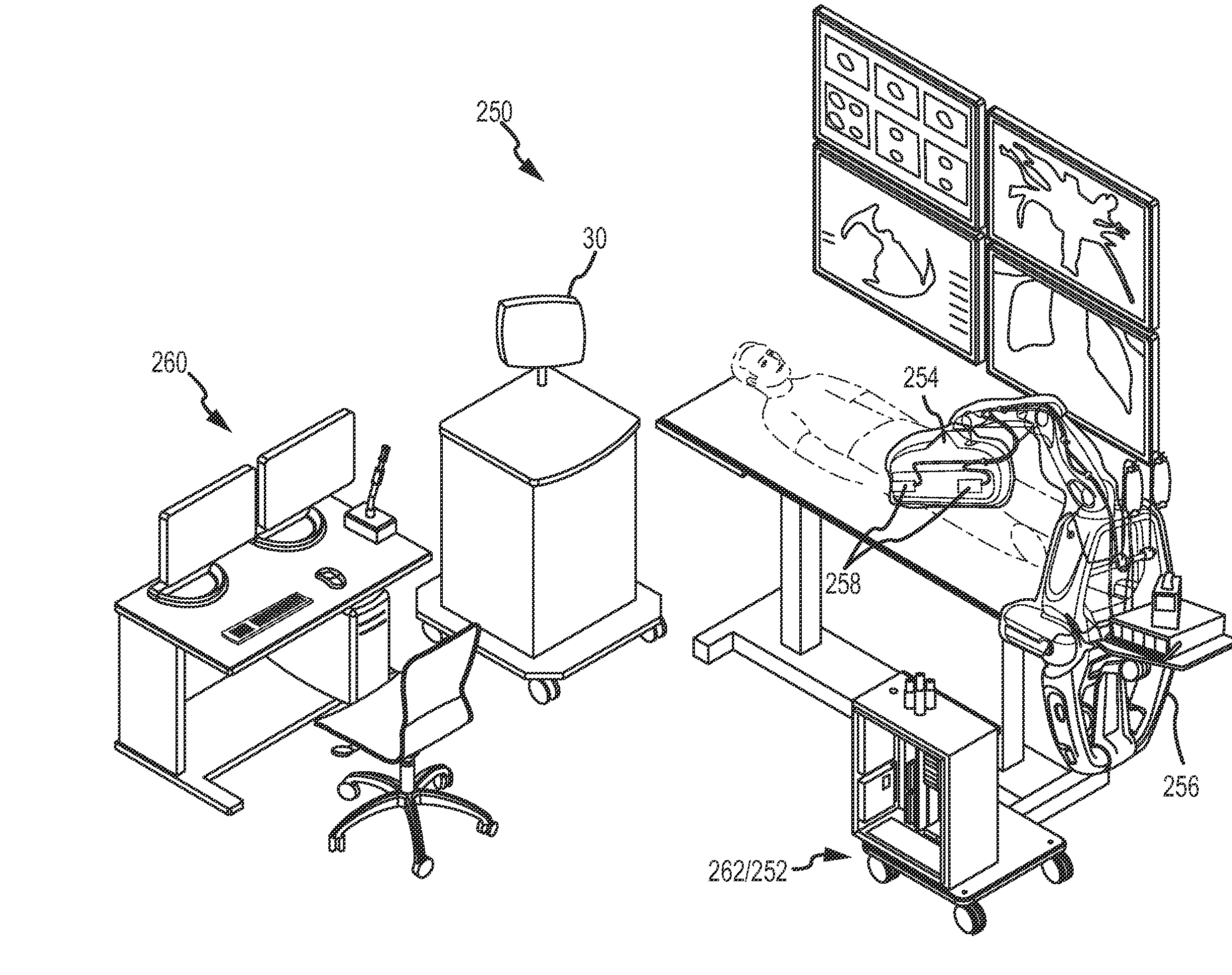
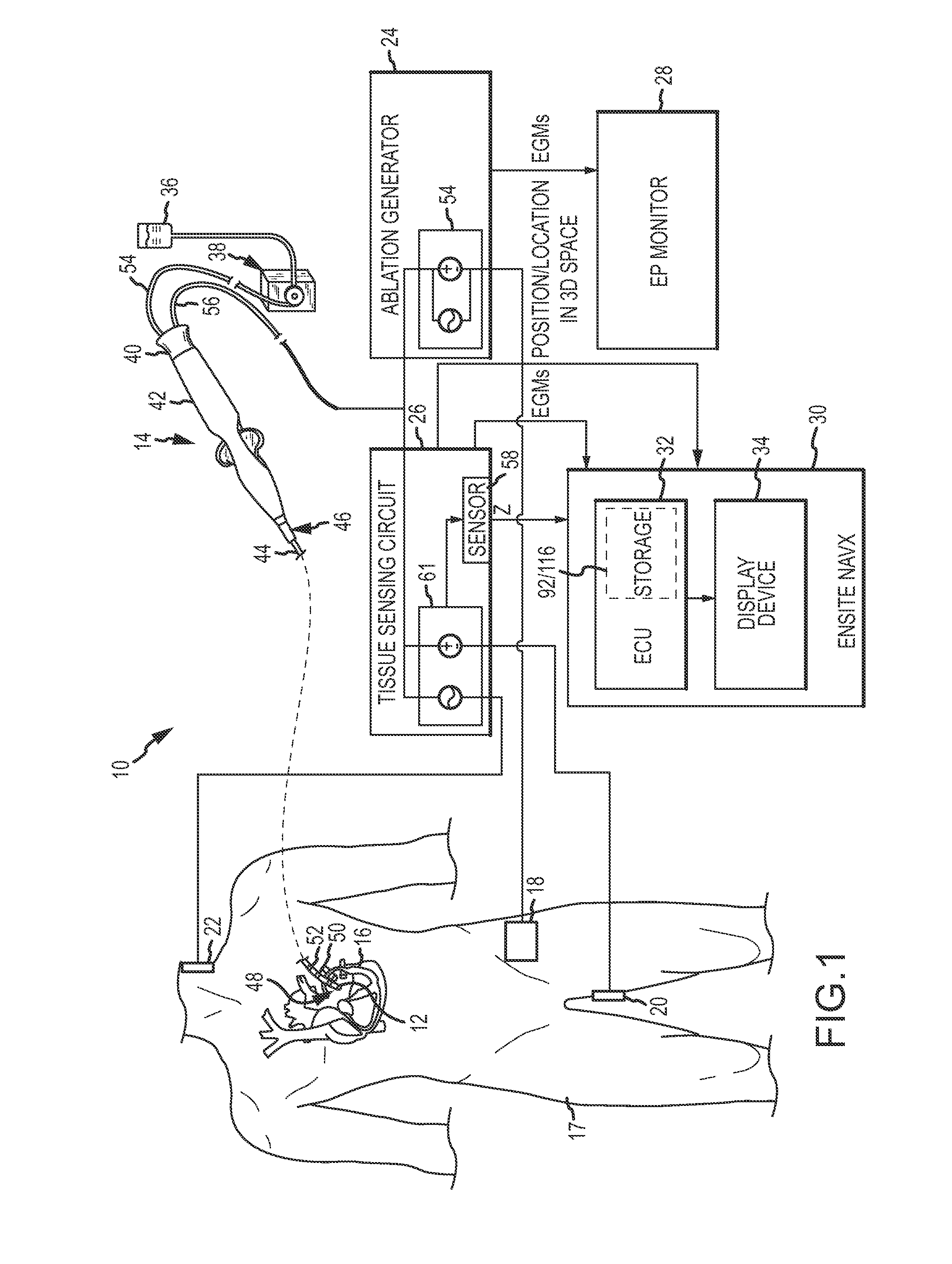
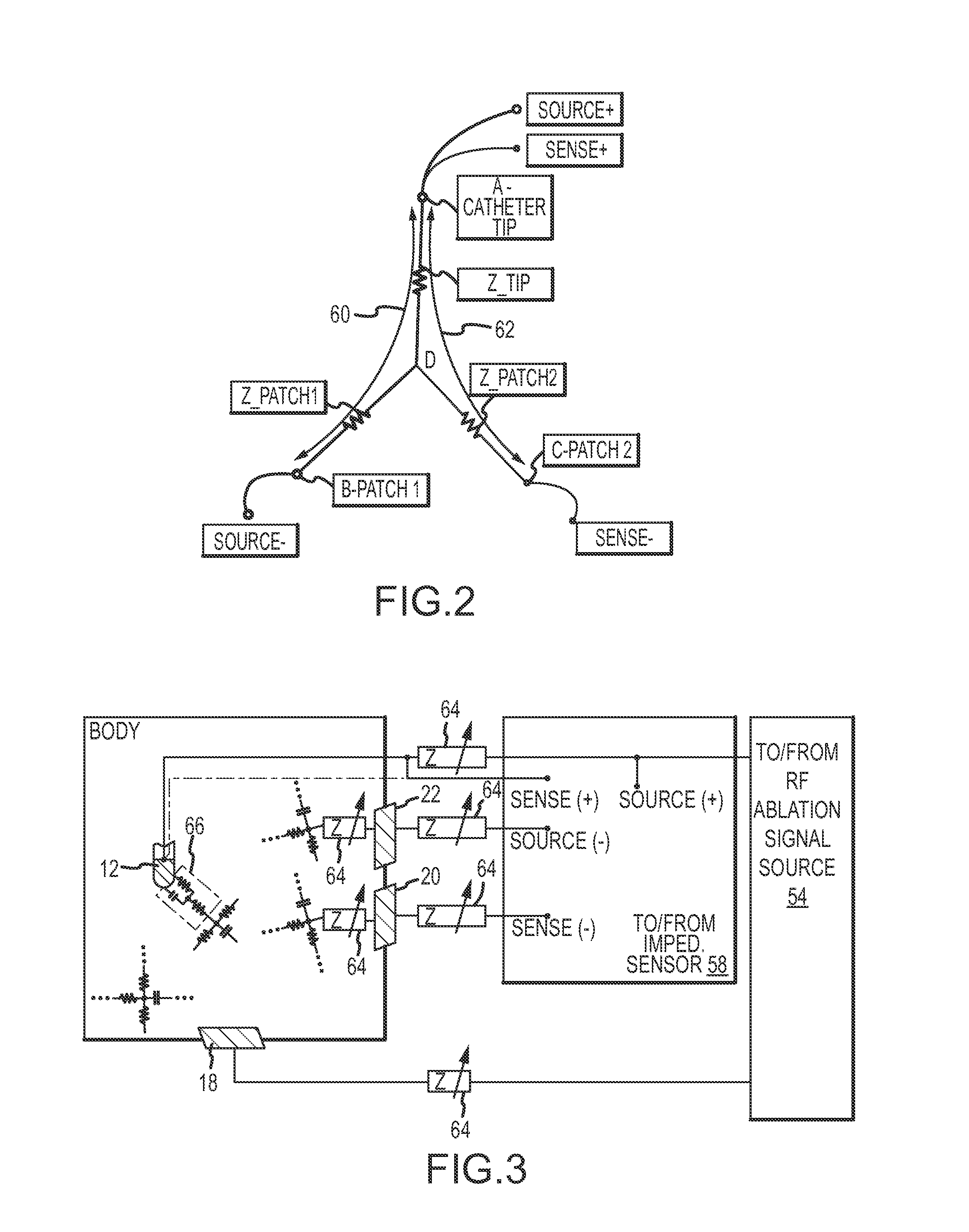
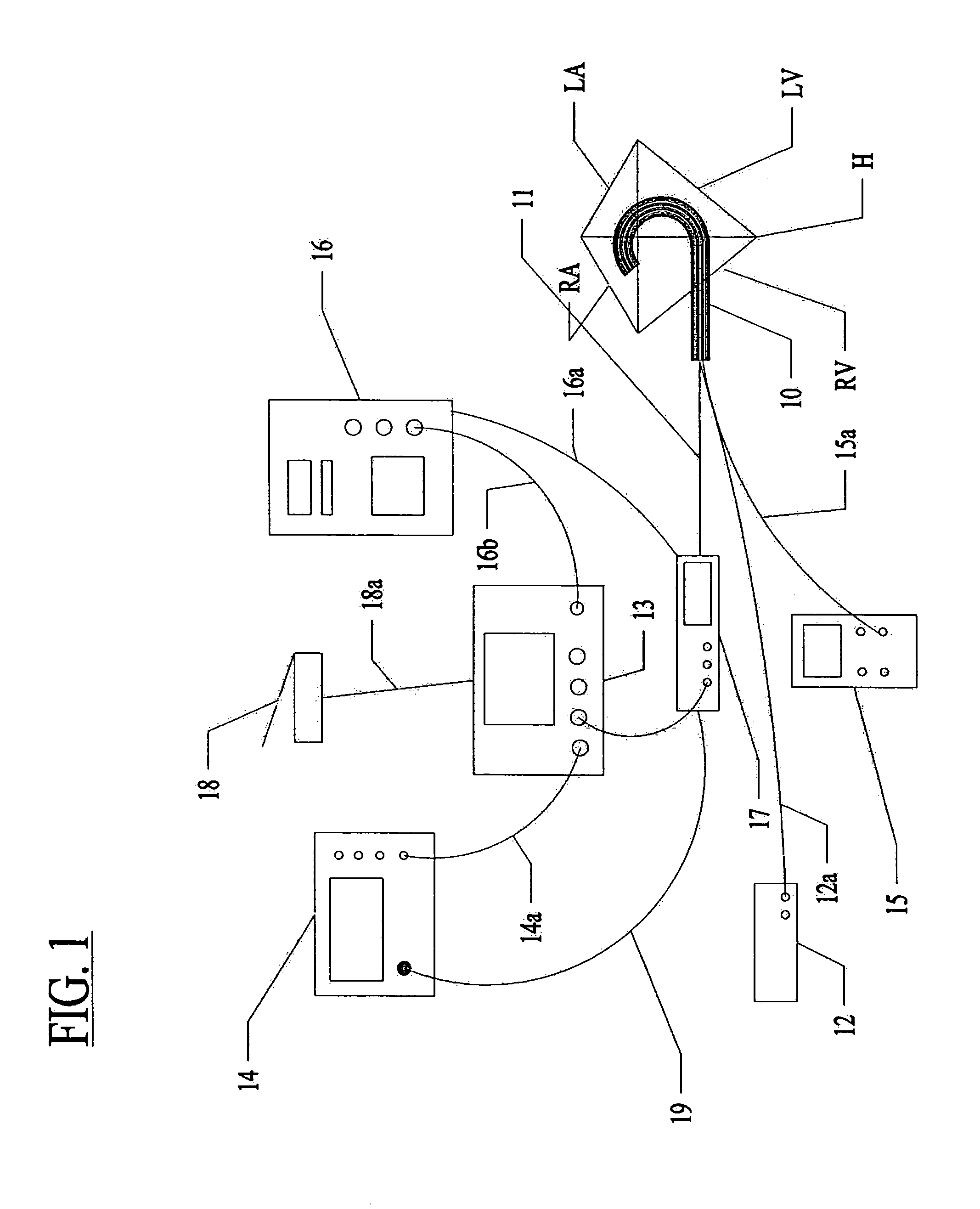
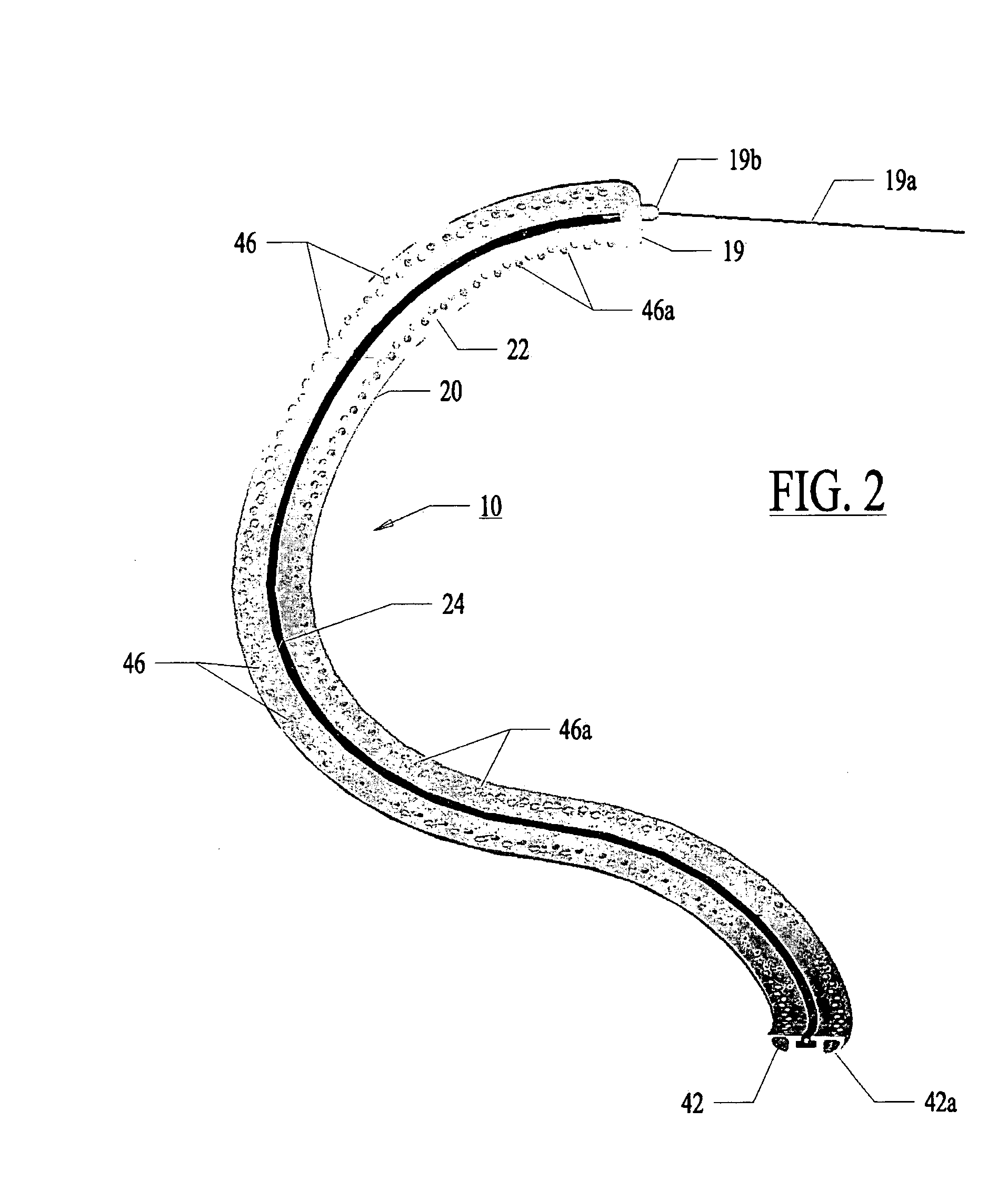
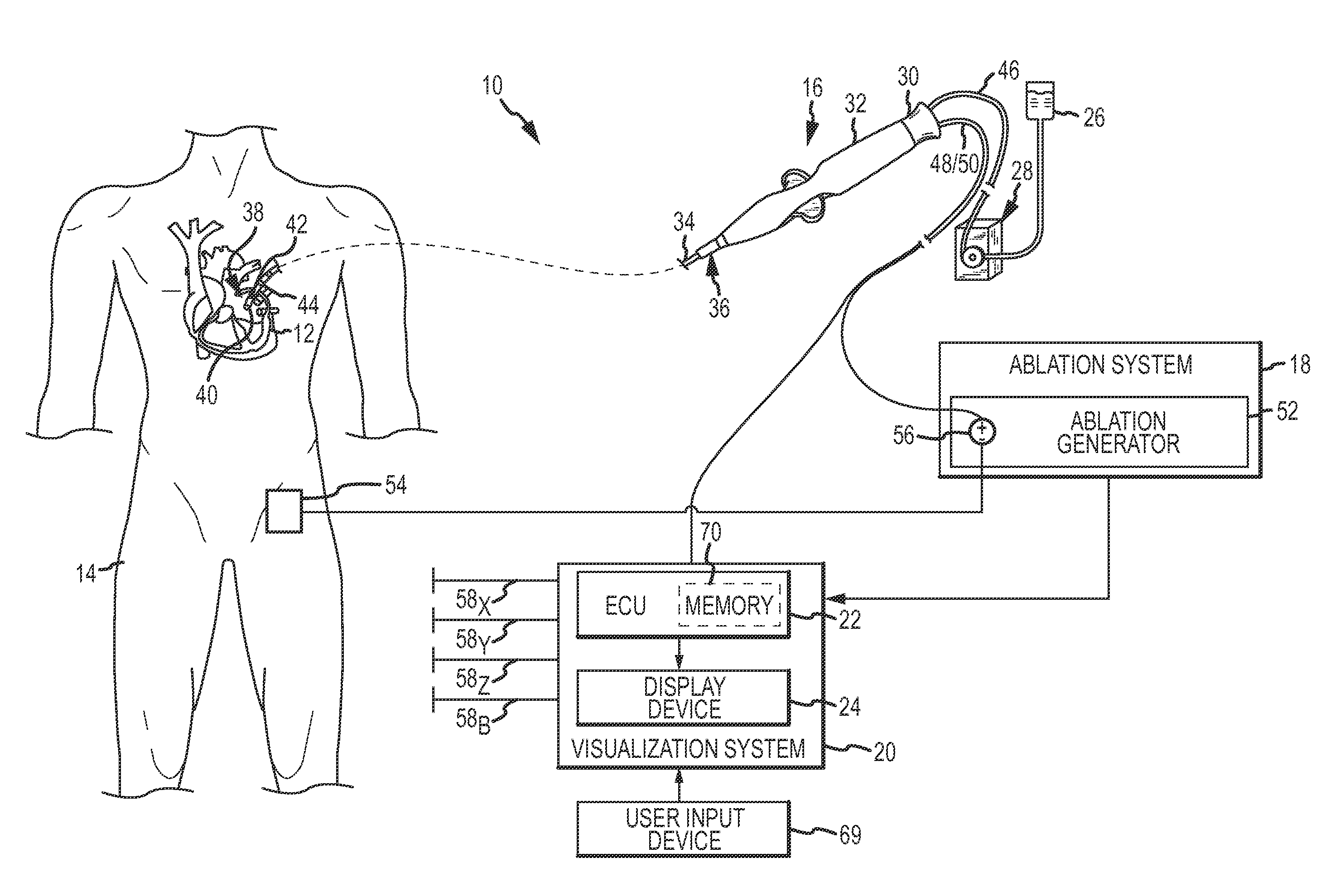
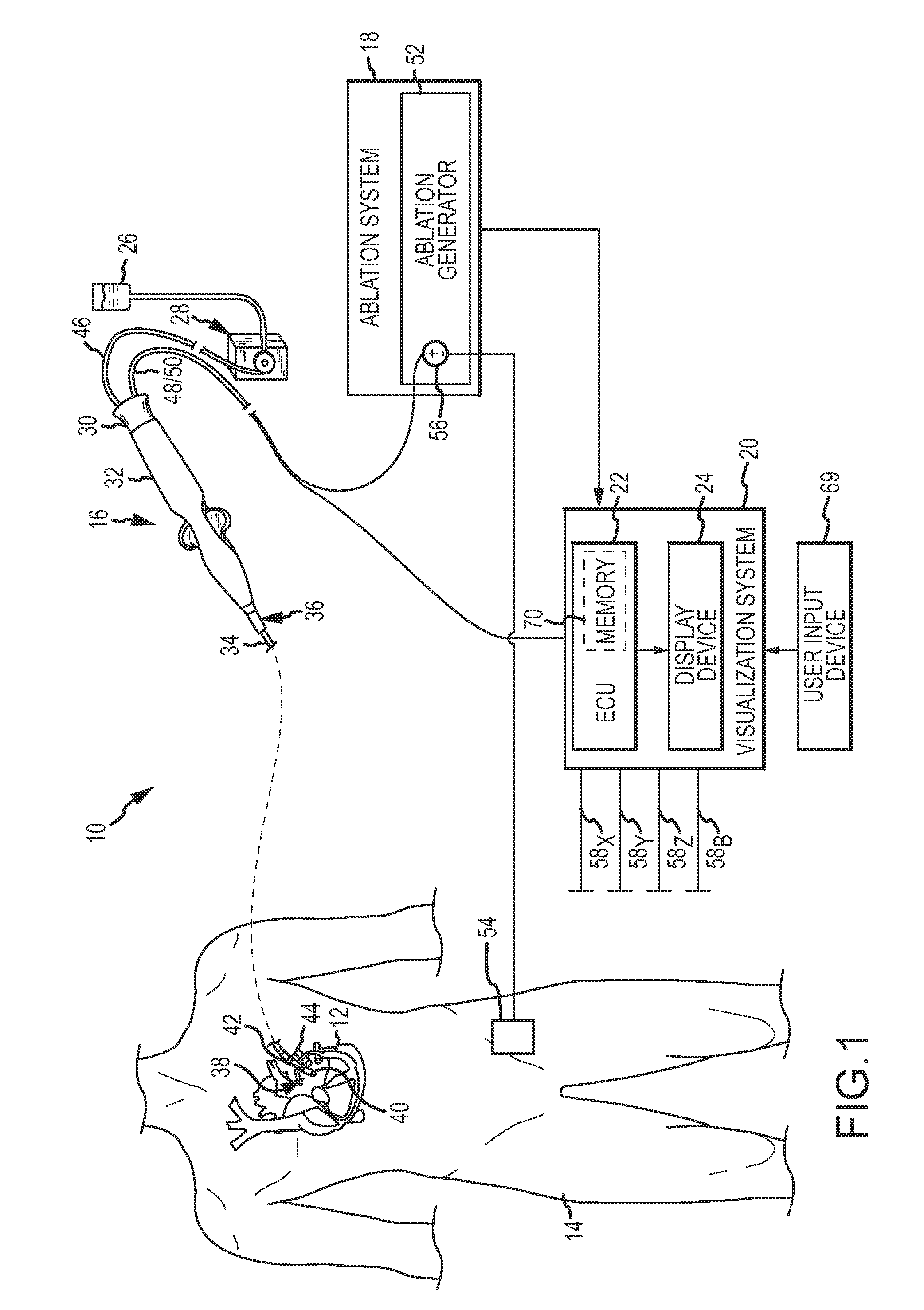
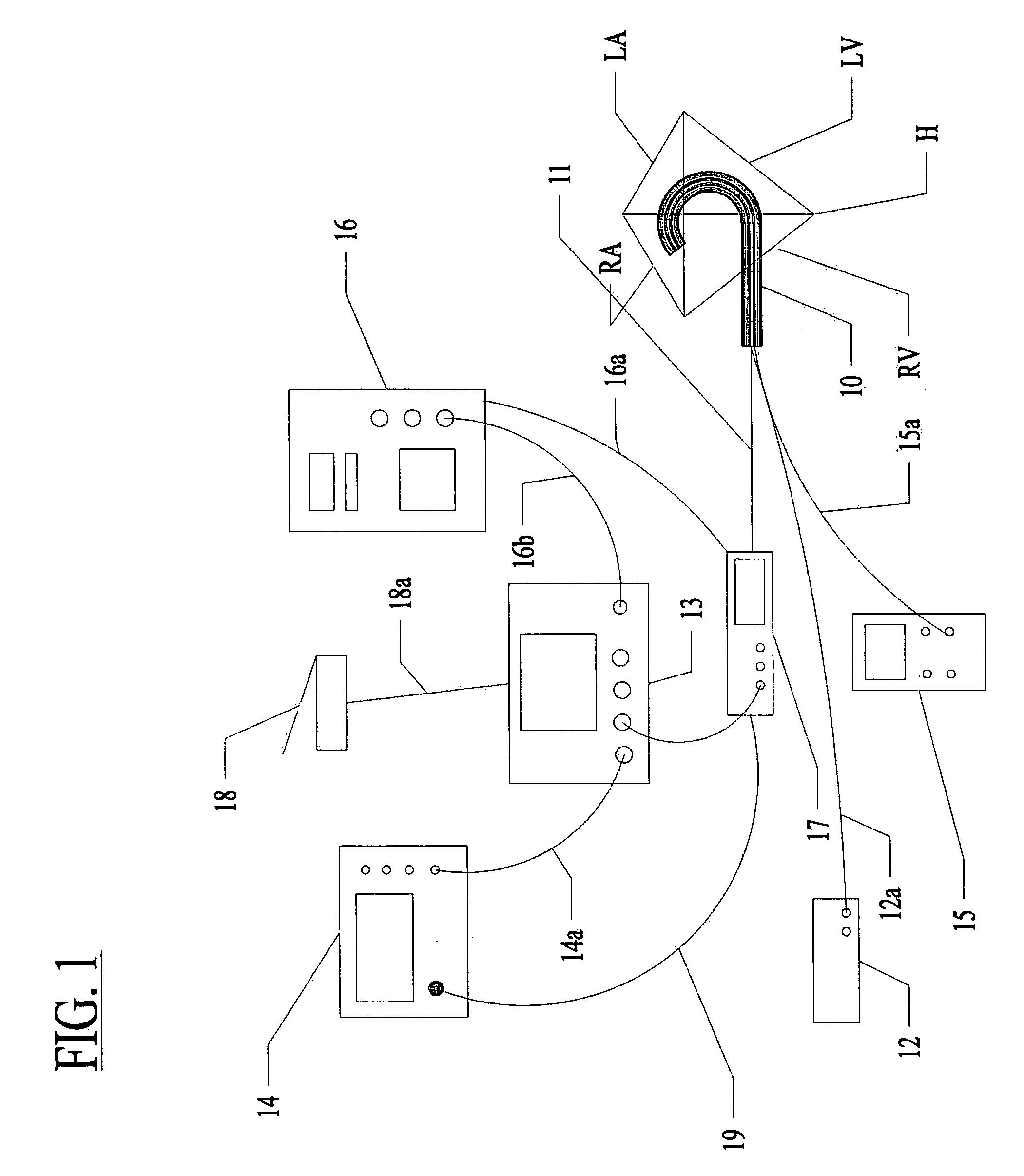
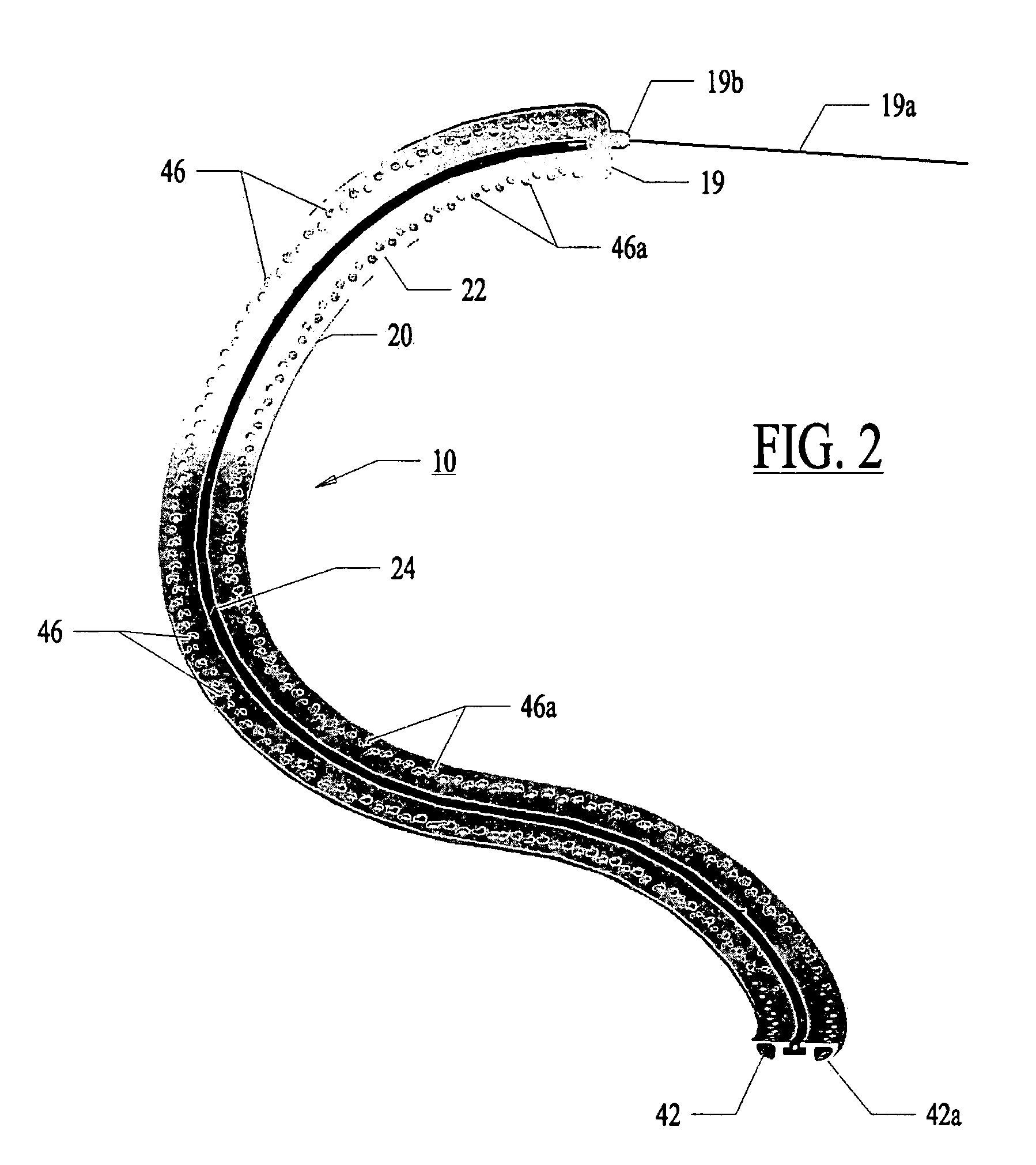
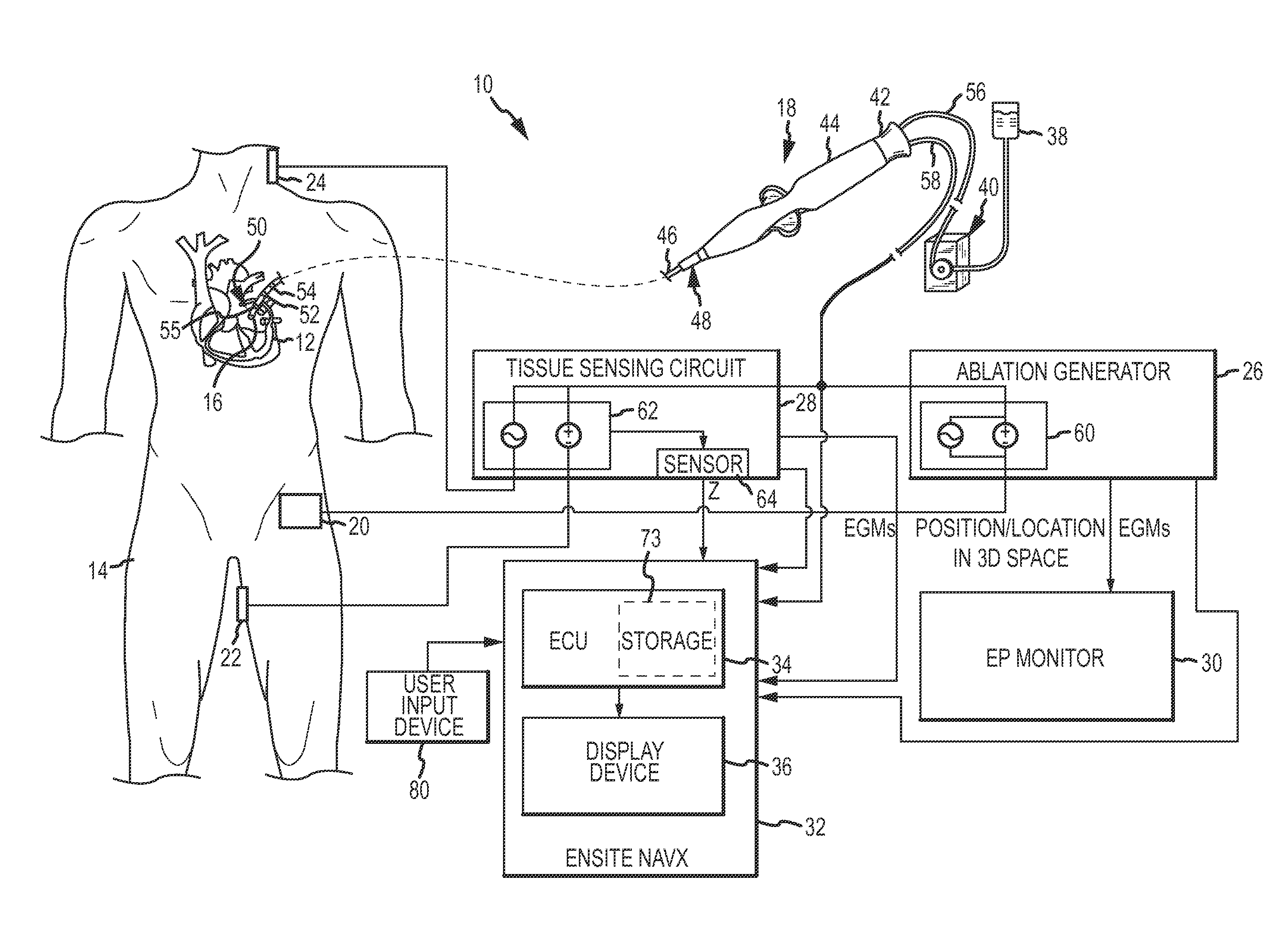
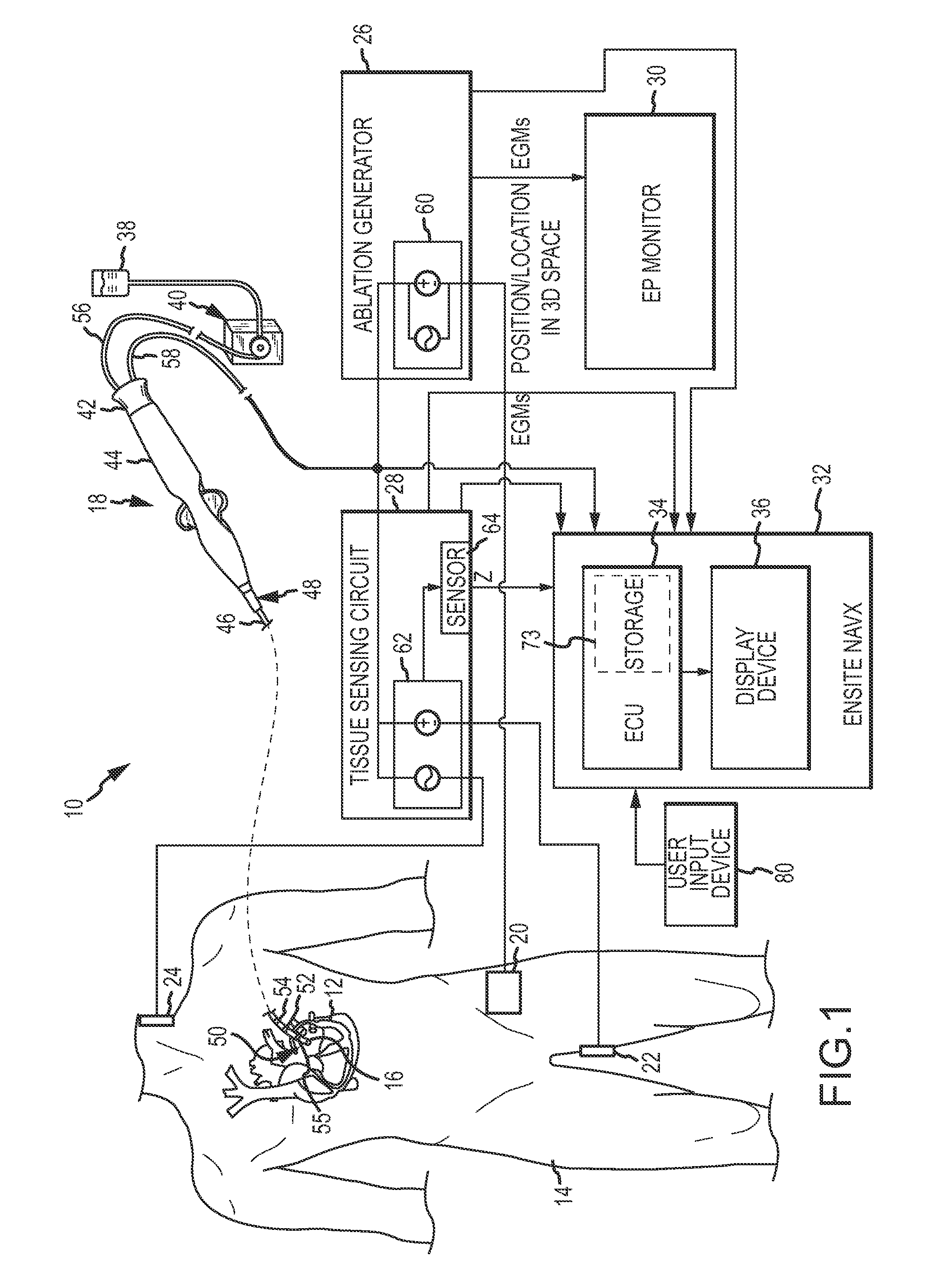
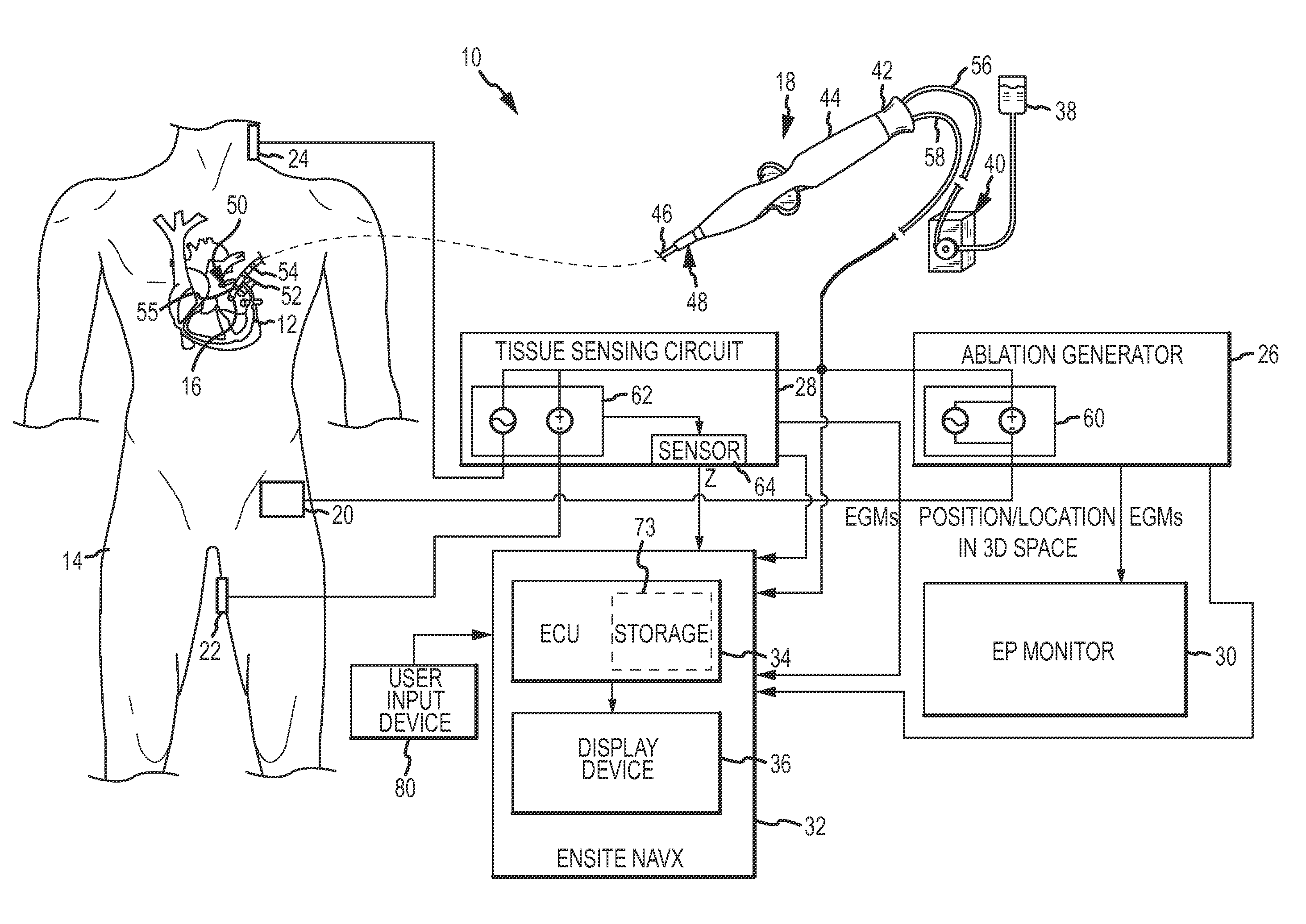
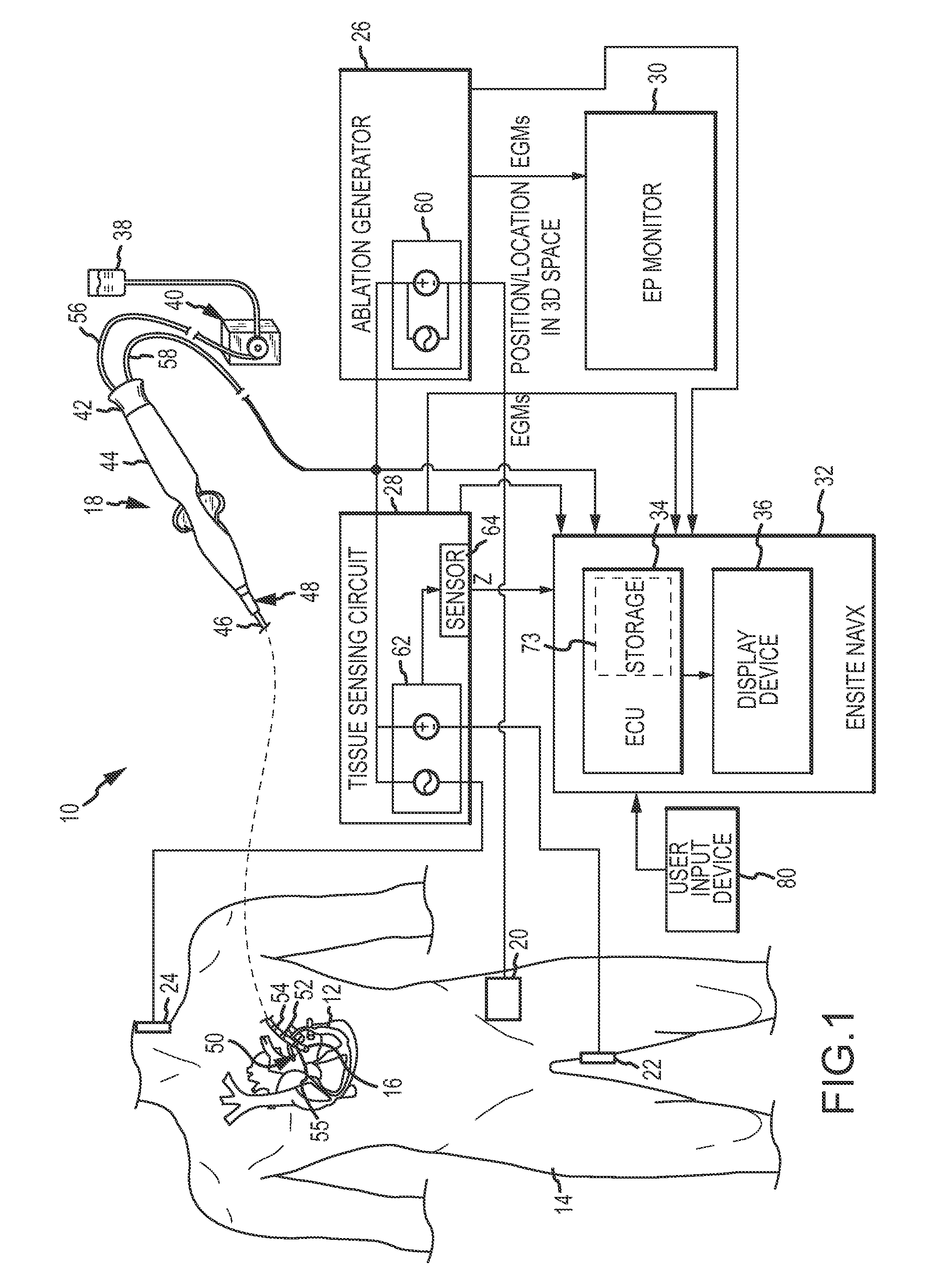
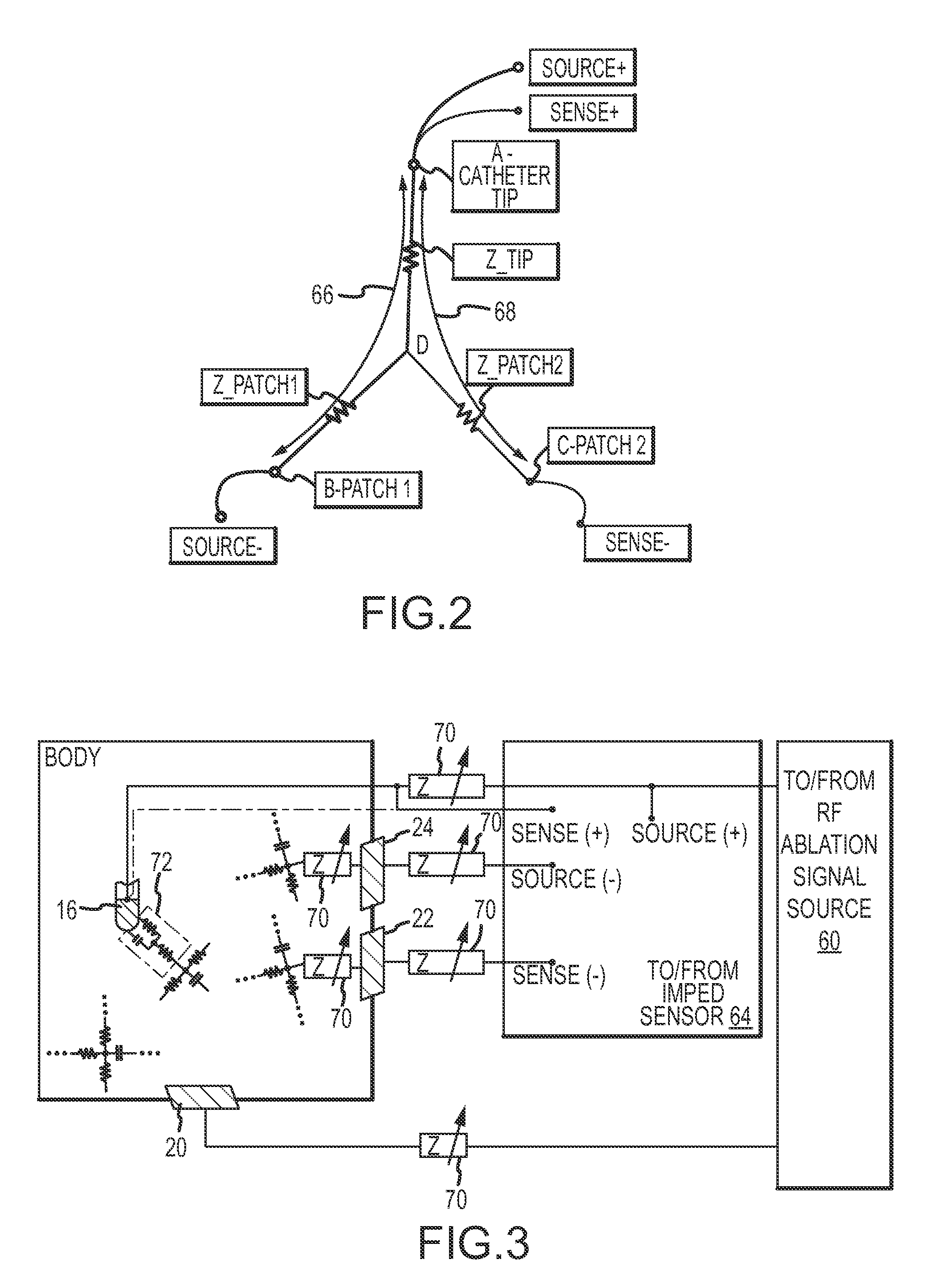
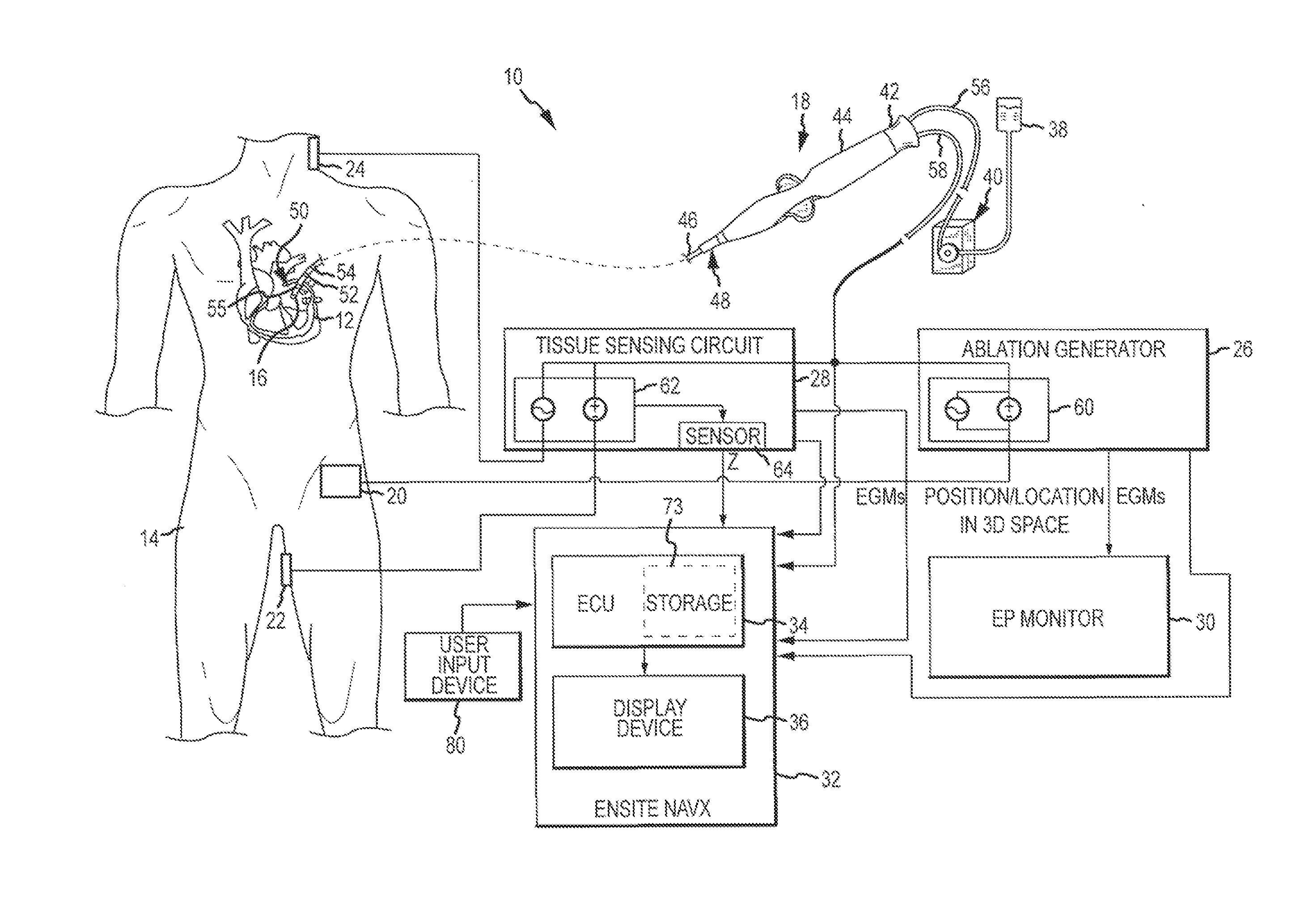
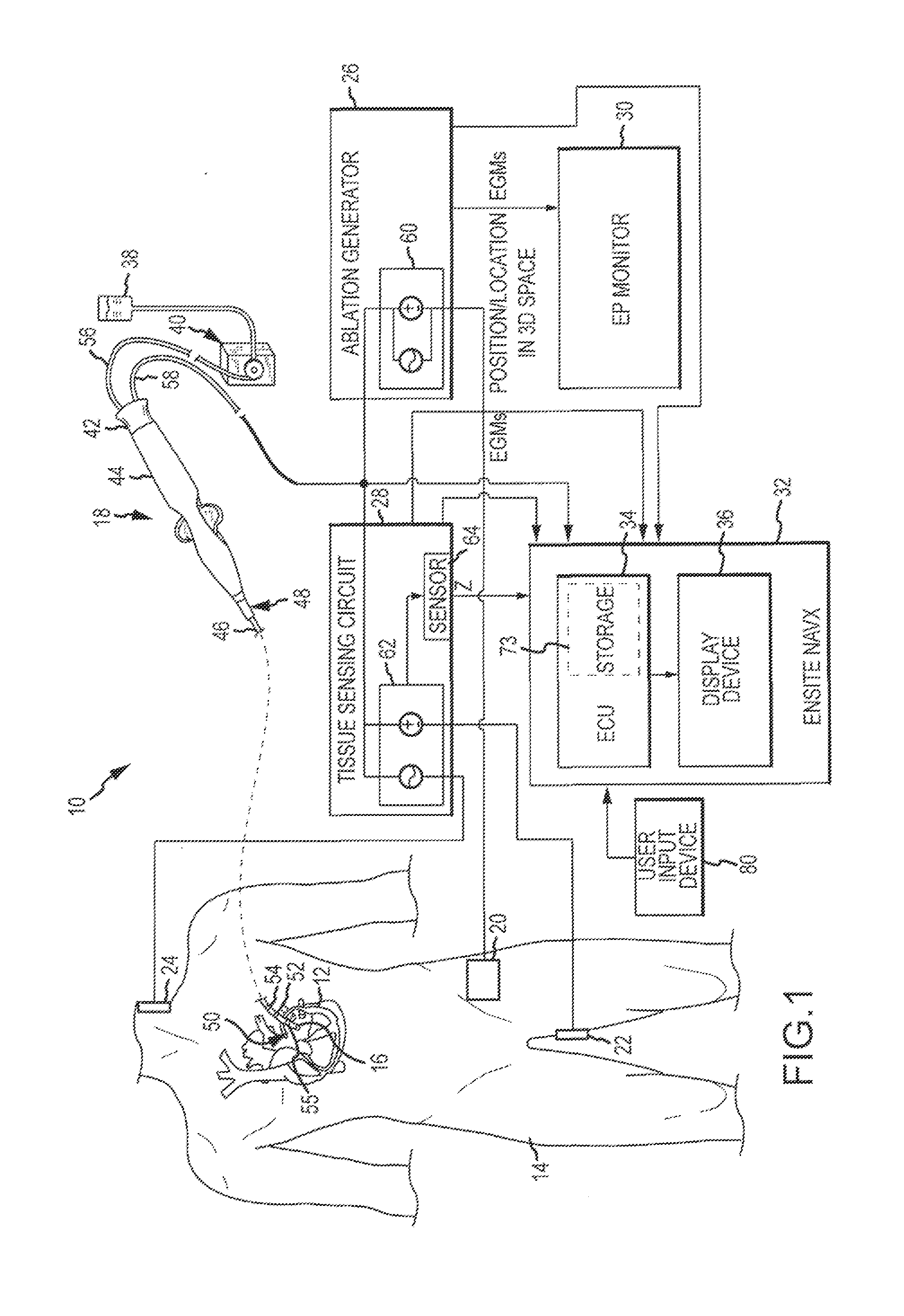
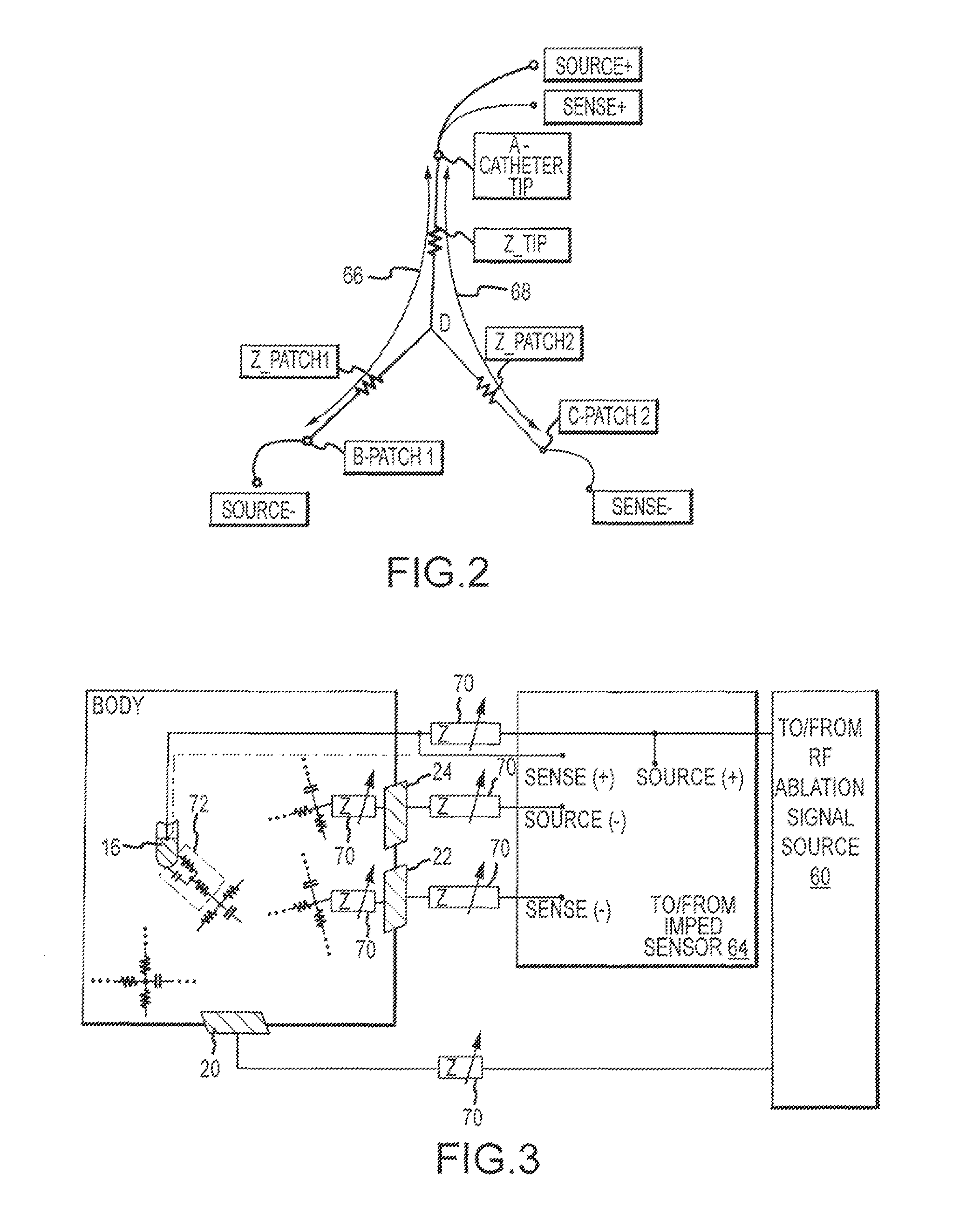
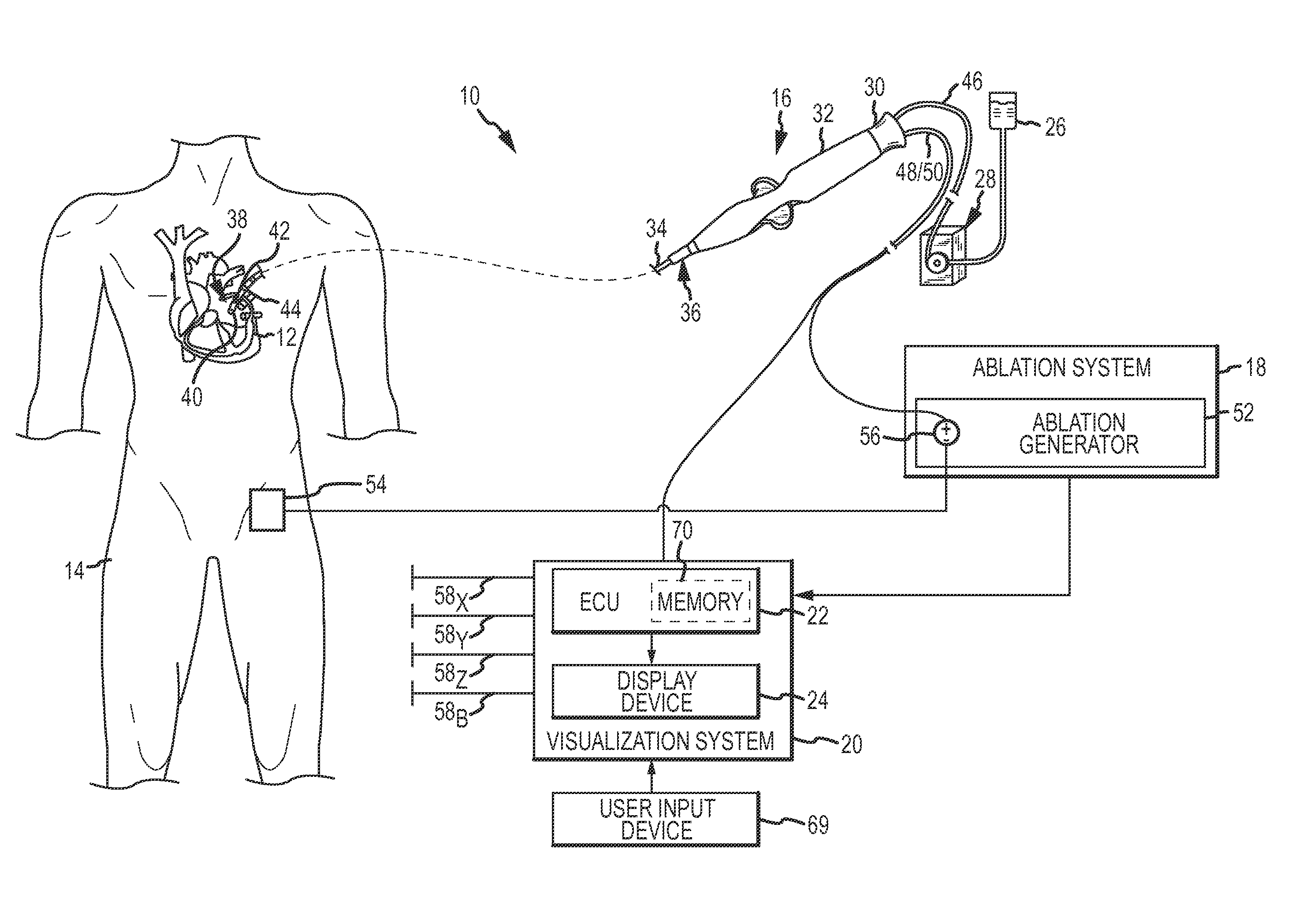
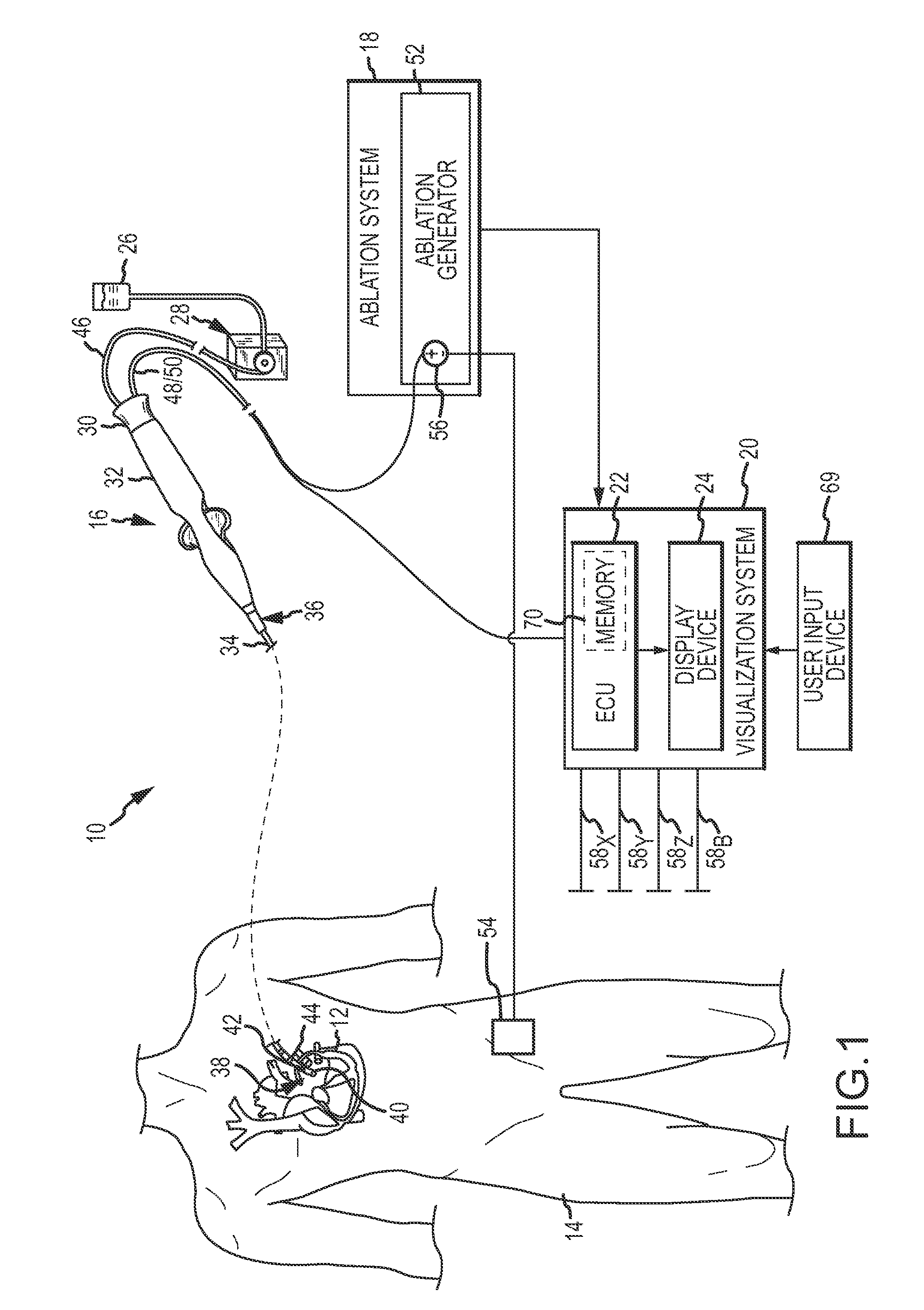
System and method for assessing lesions in tissue
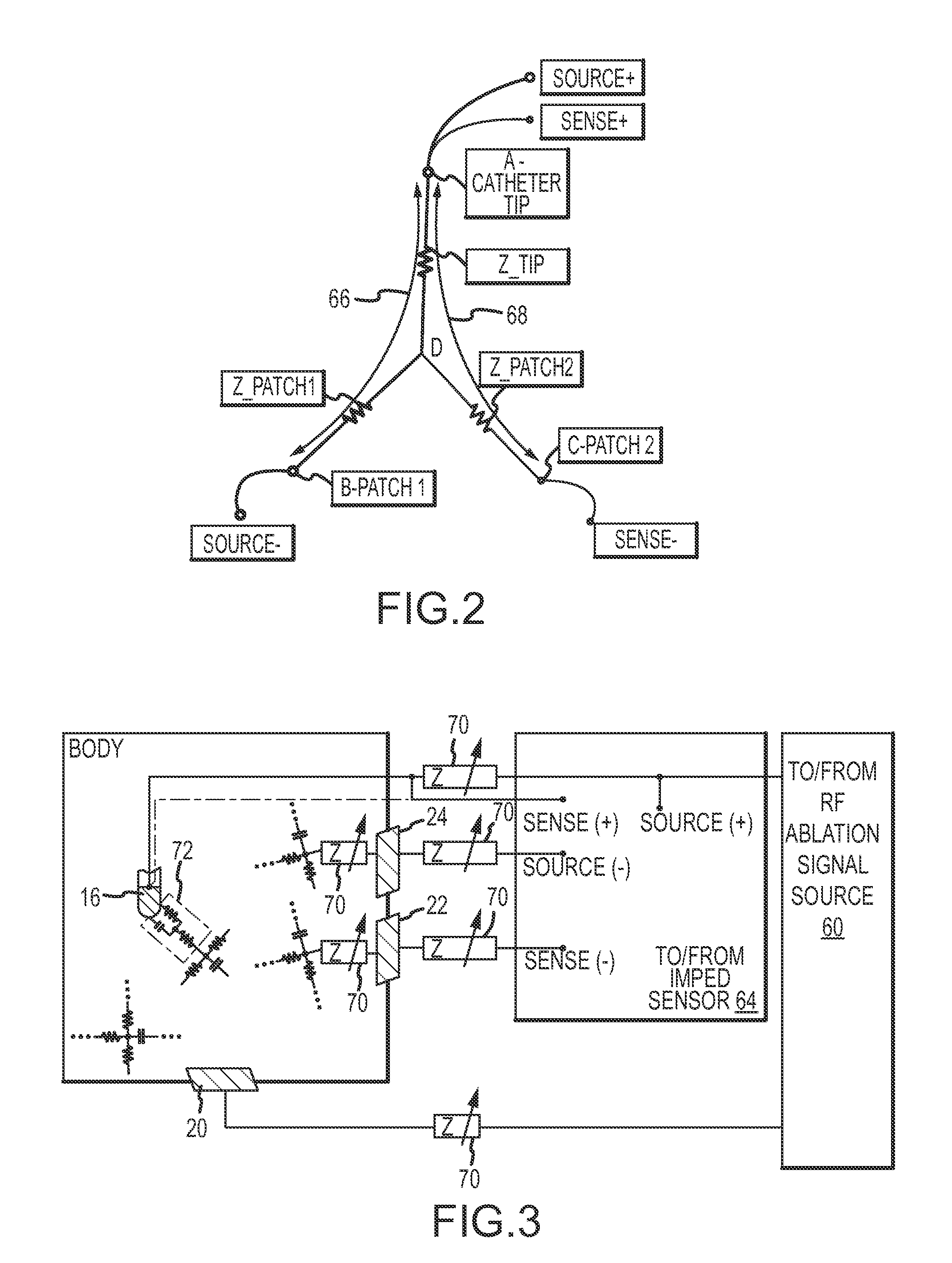
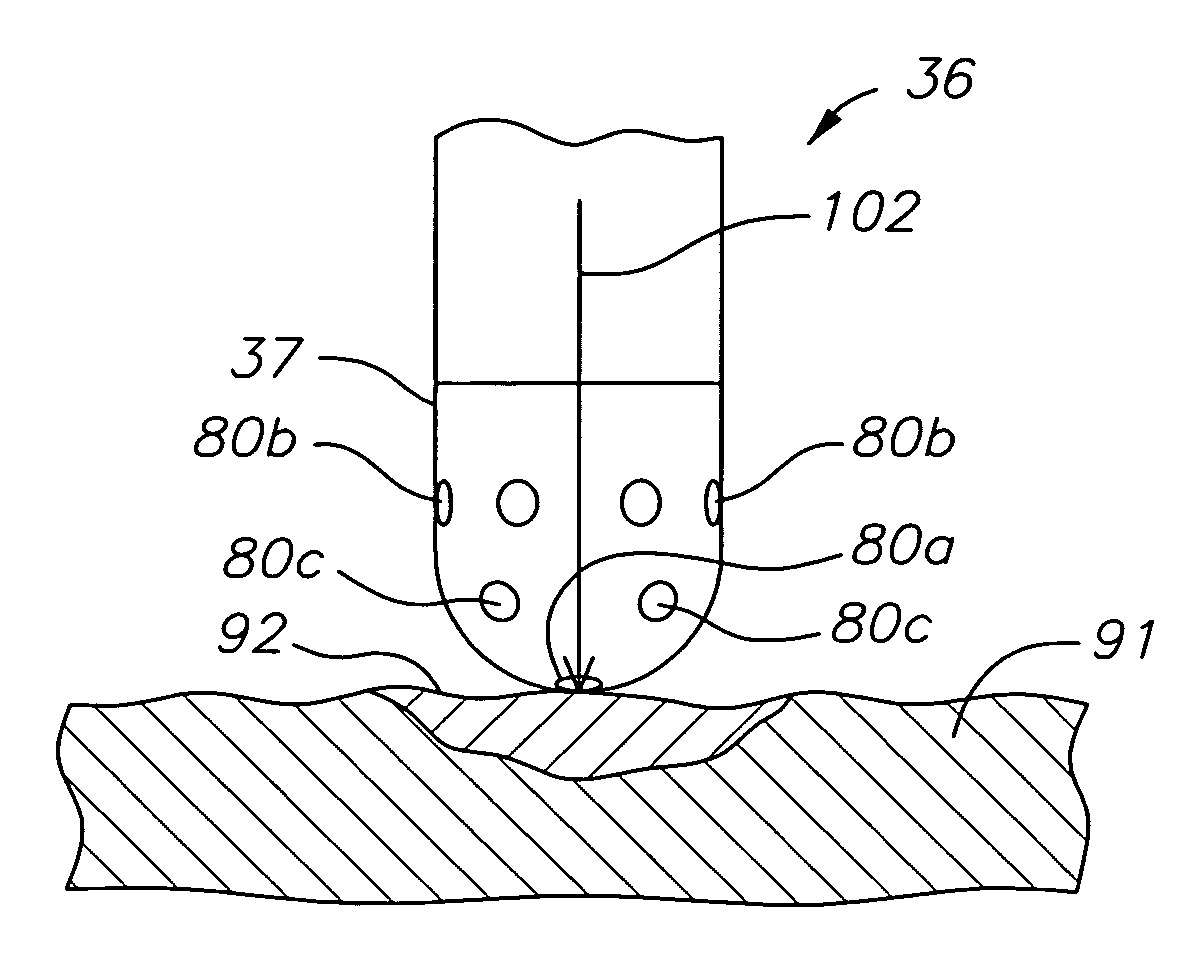
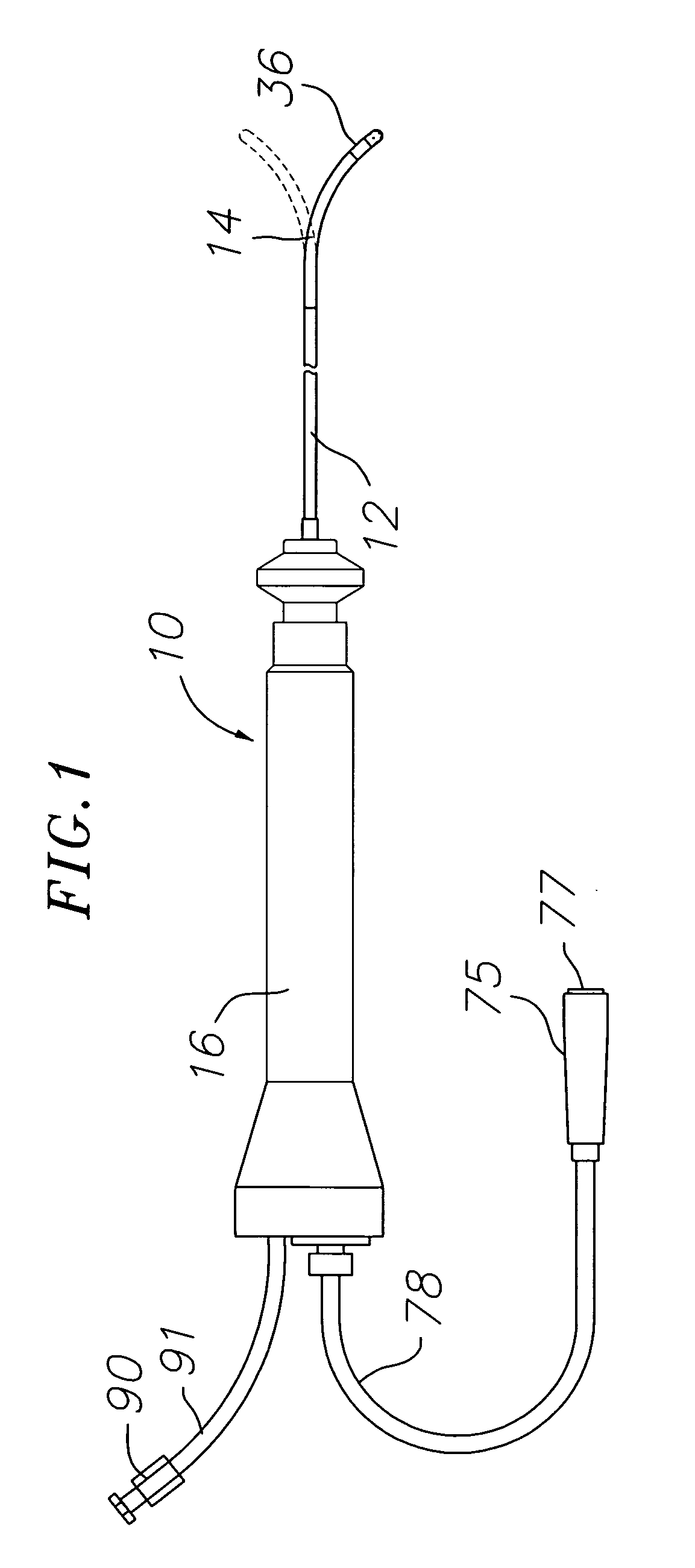
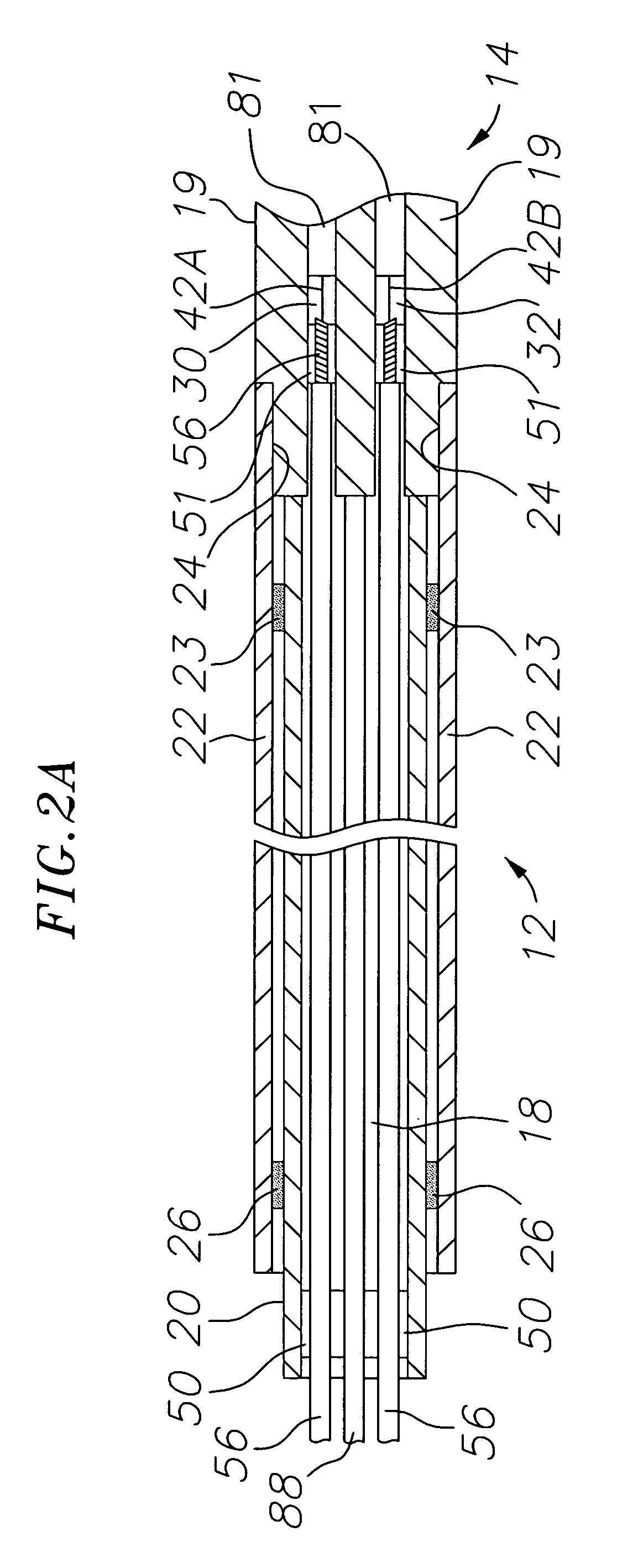
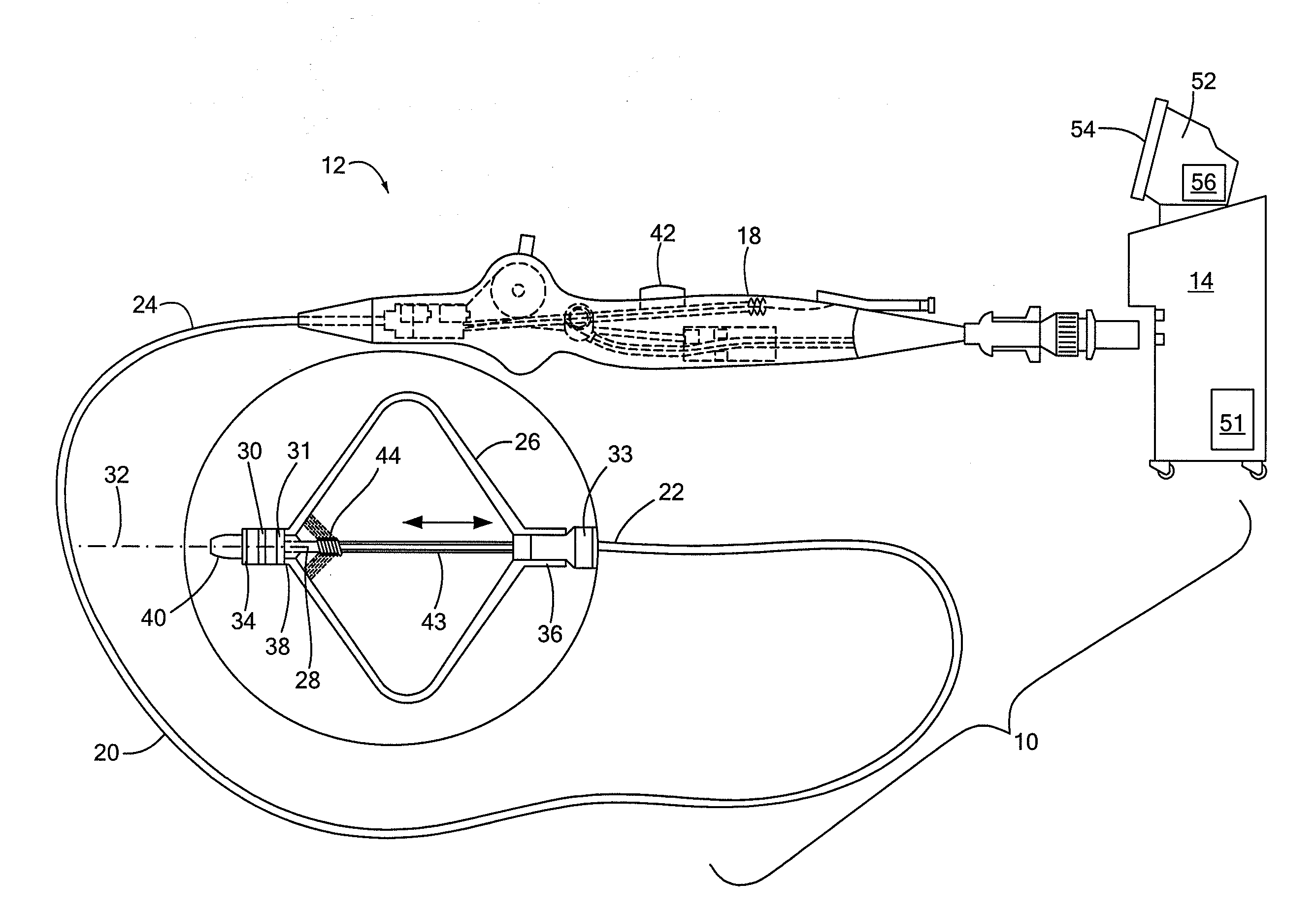
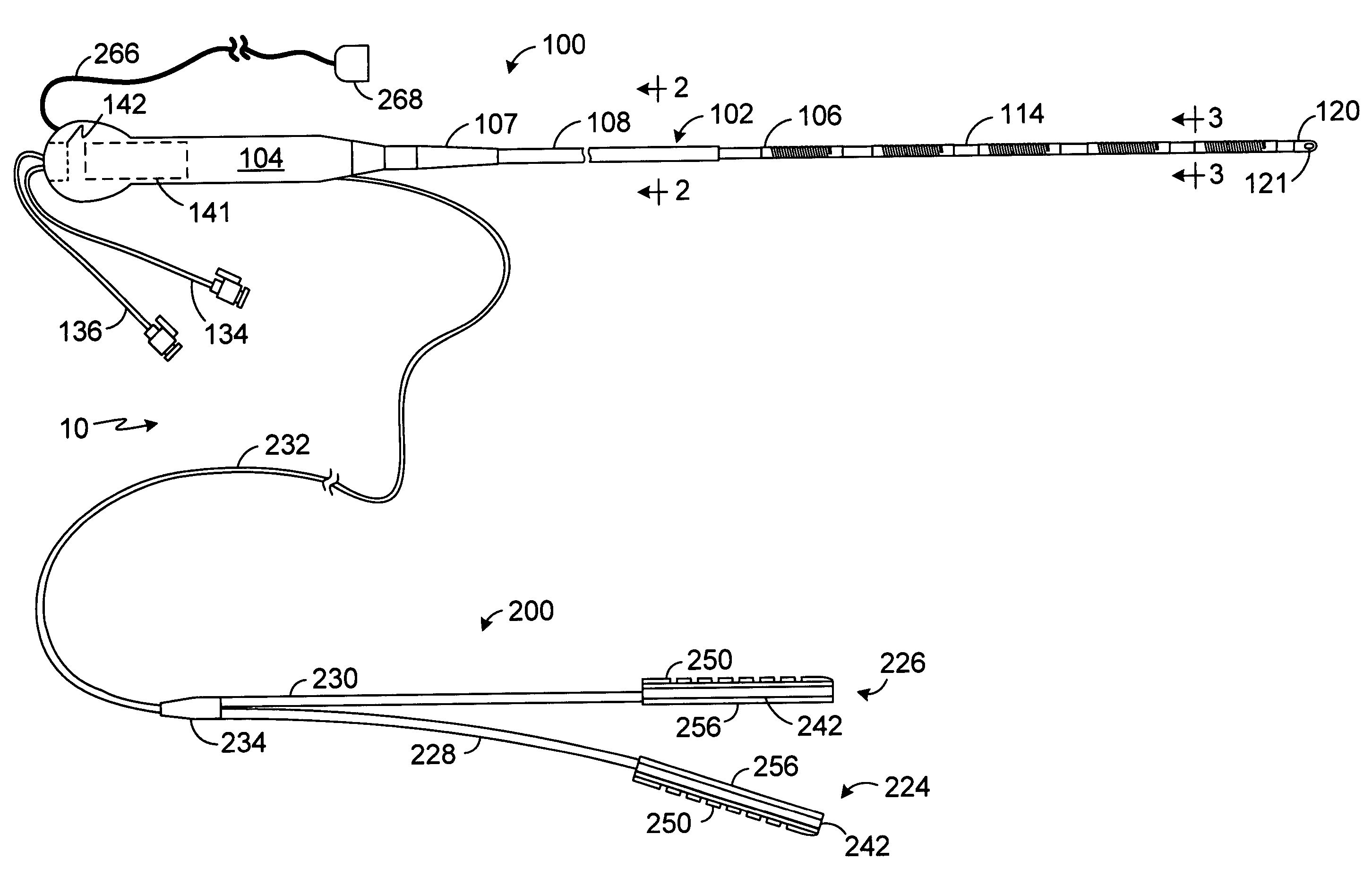
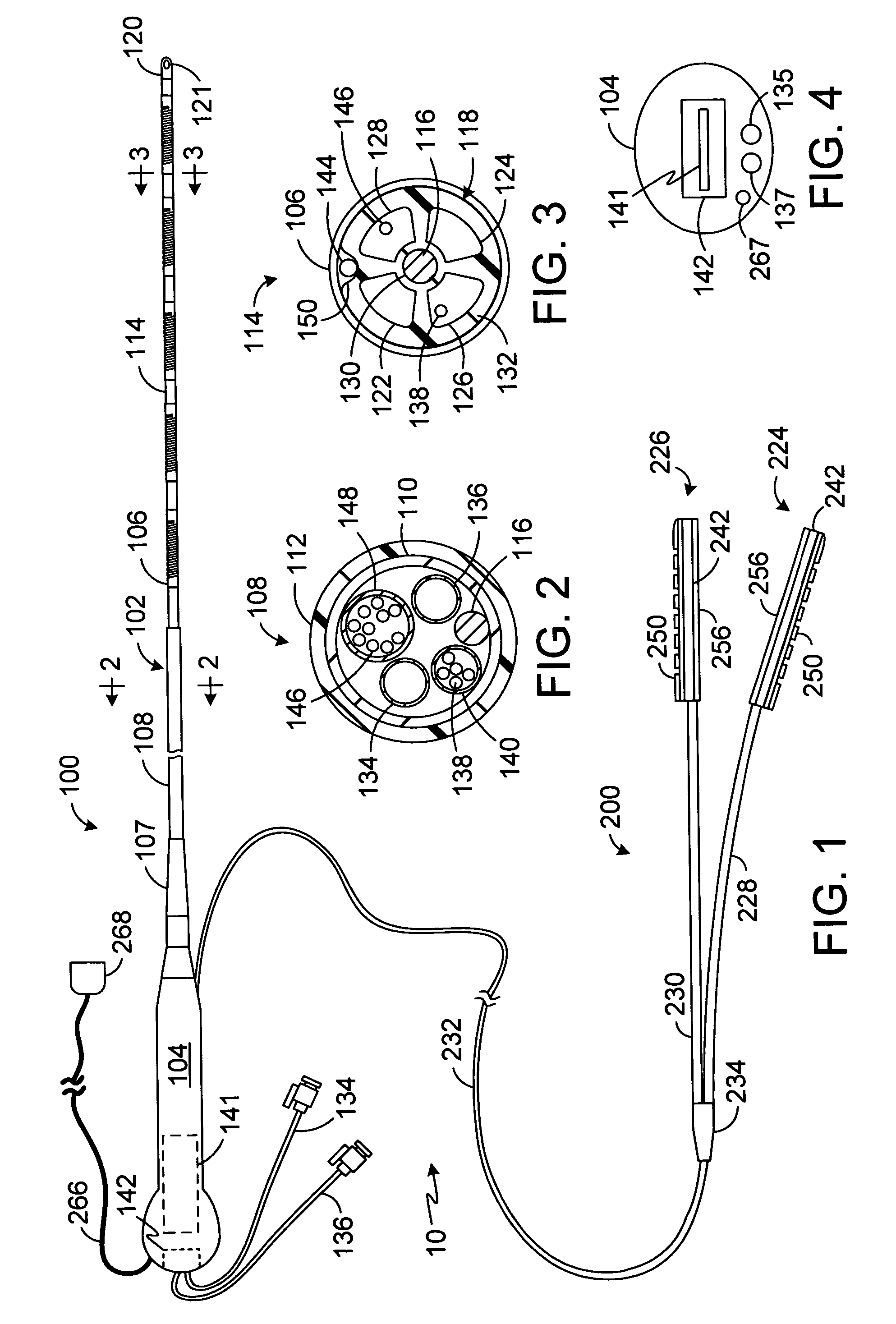
ActiveUS20100069921A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingRadiologyLesion formation
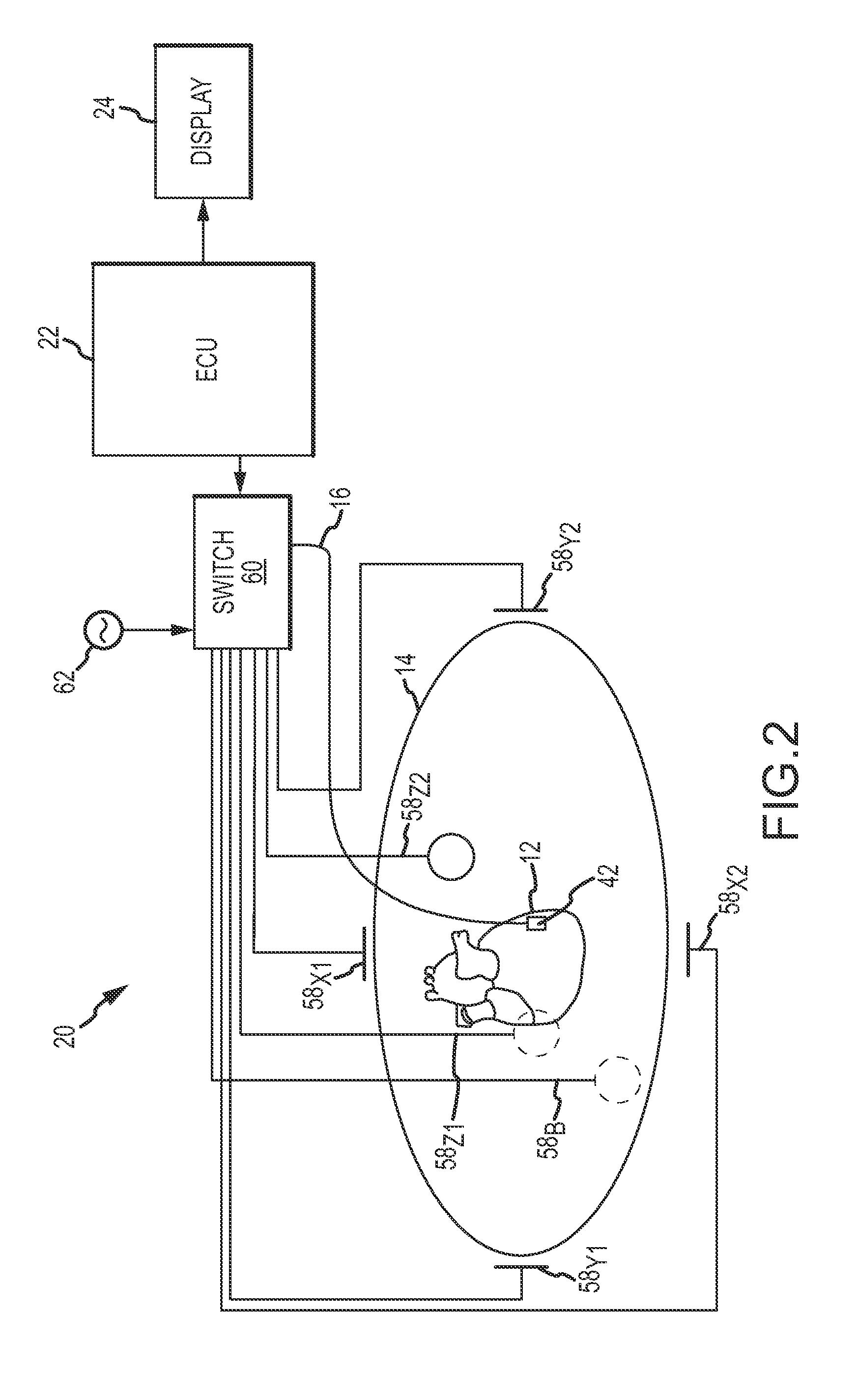
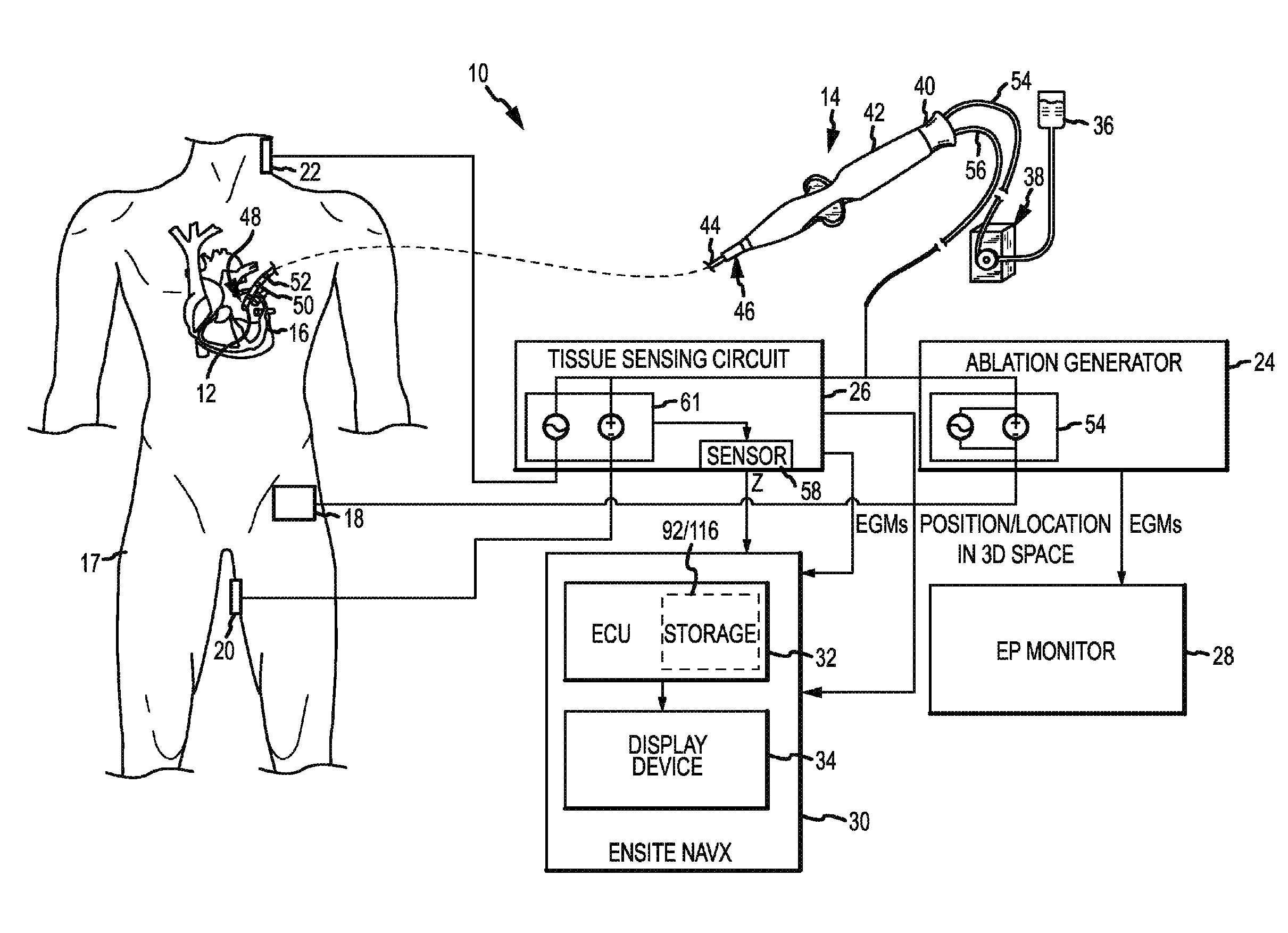
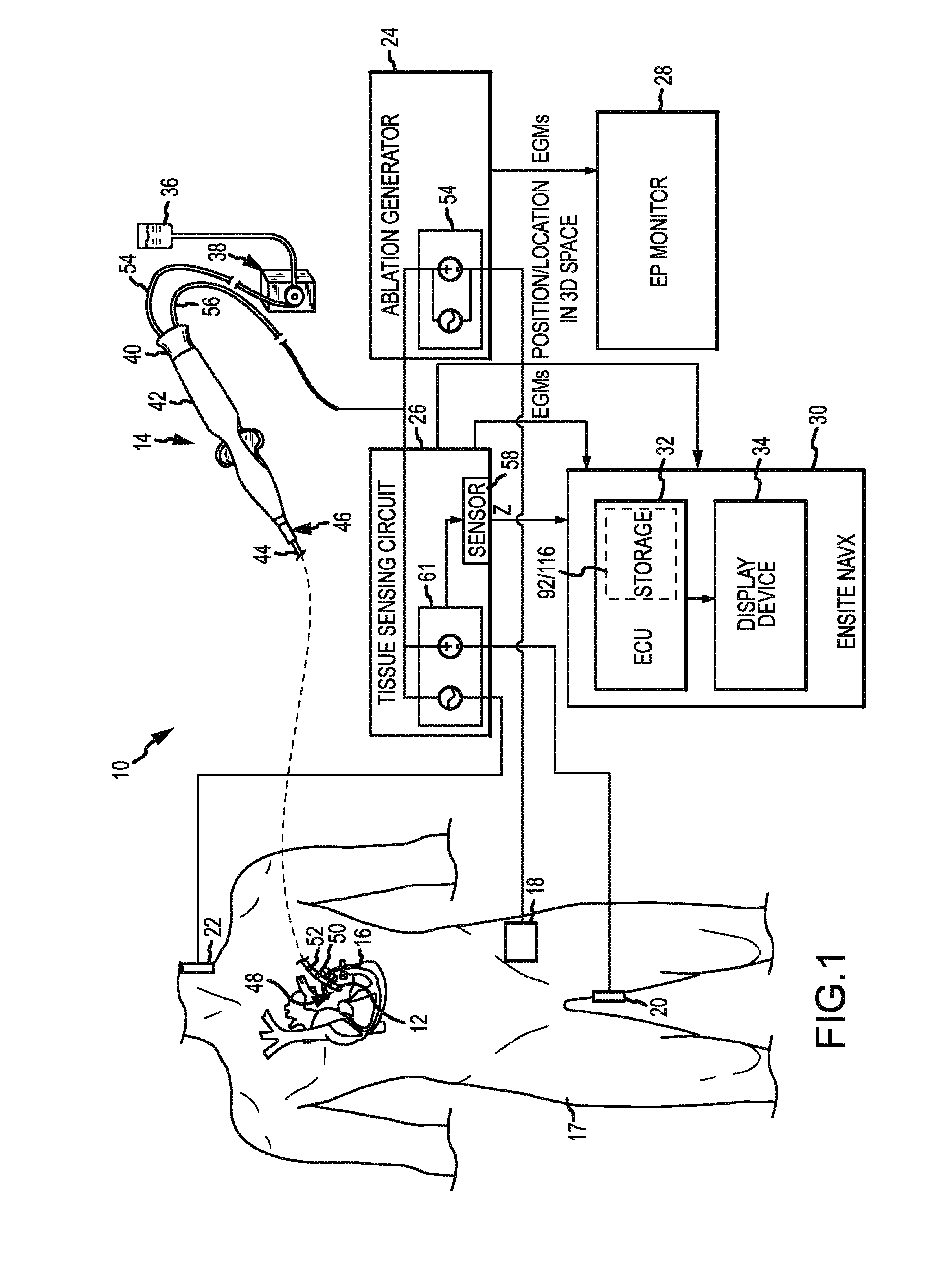
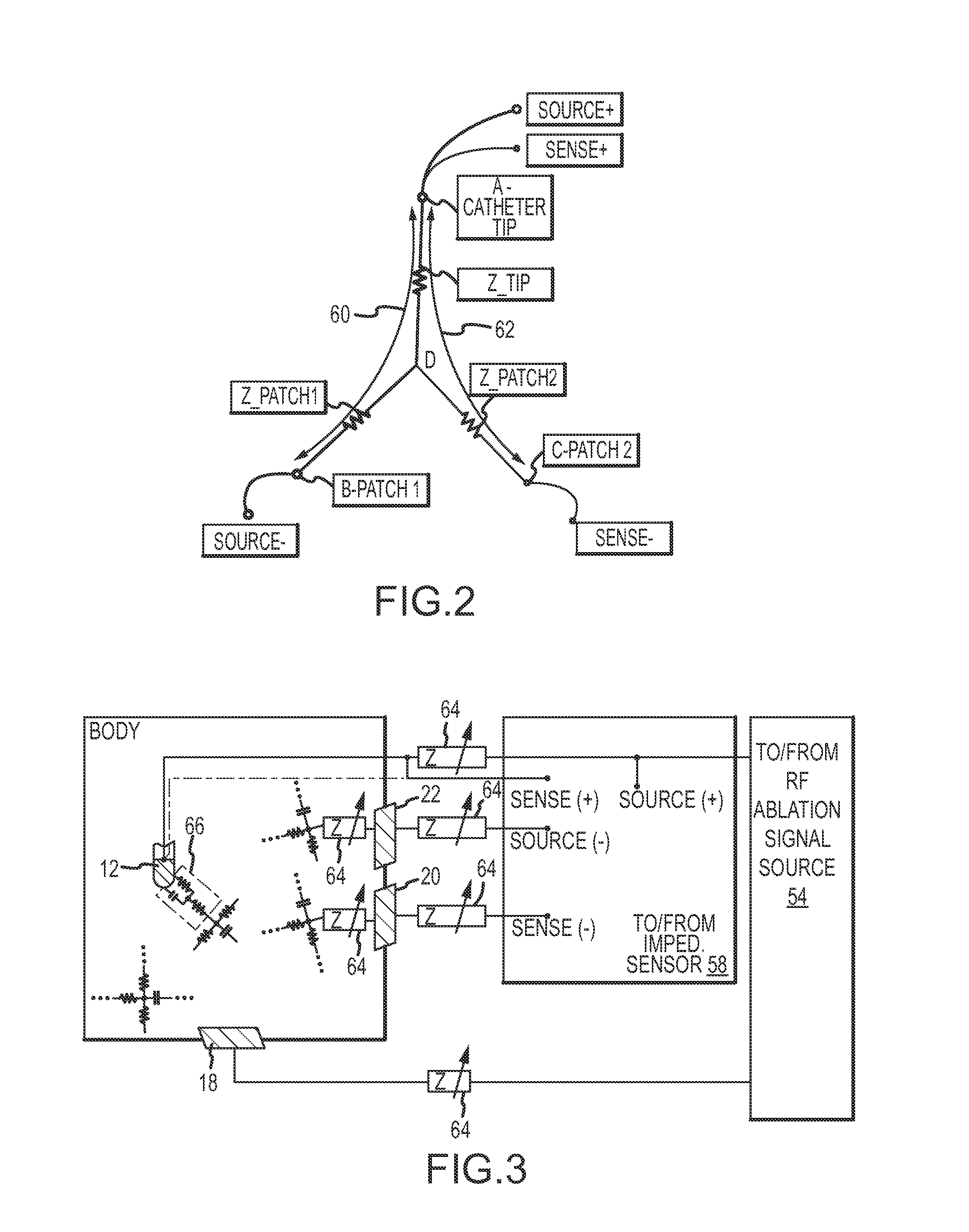
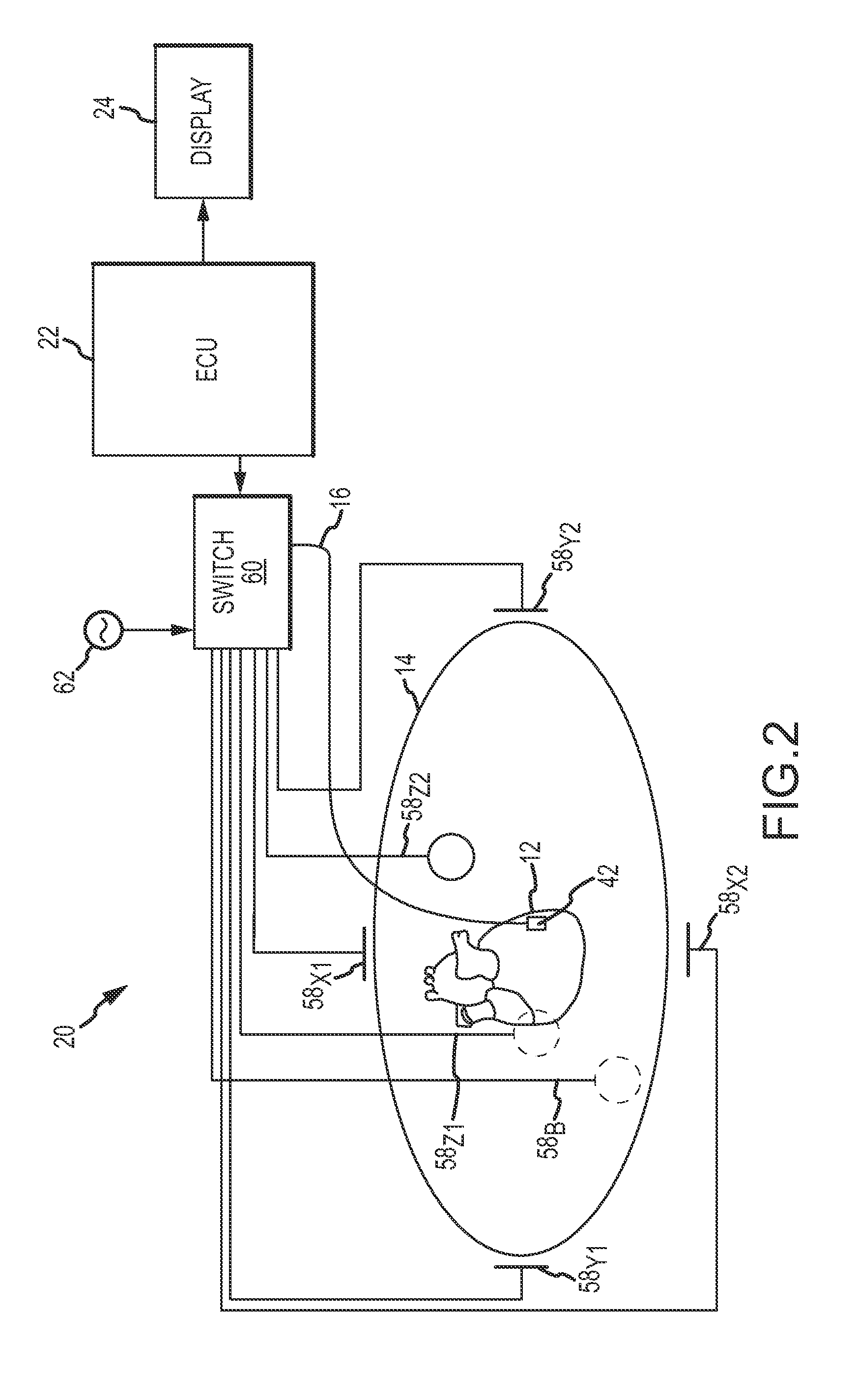
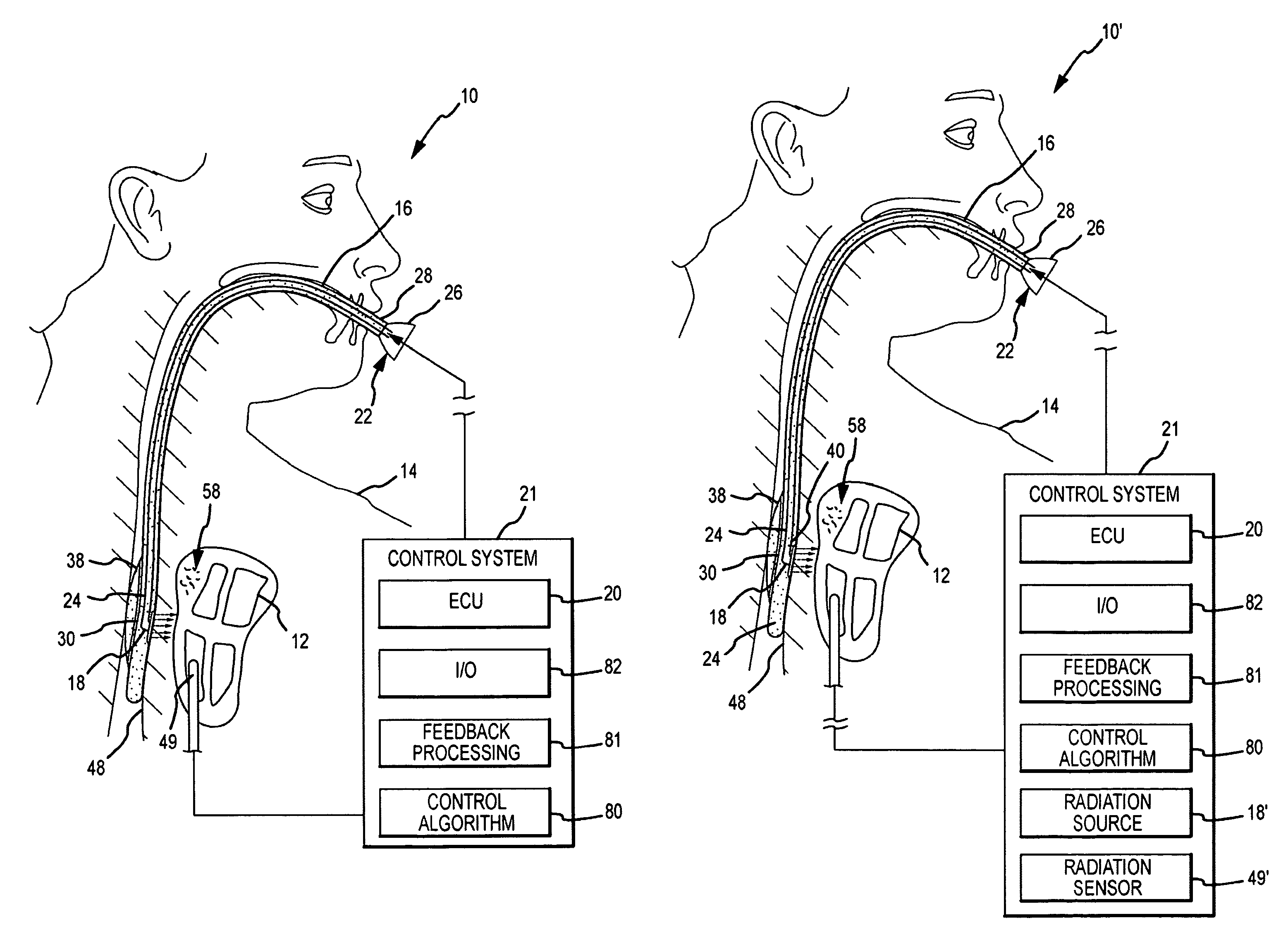
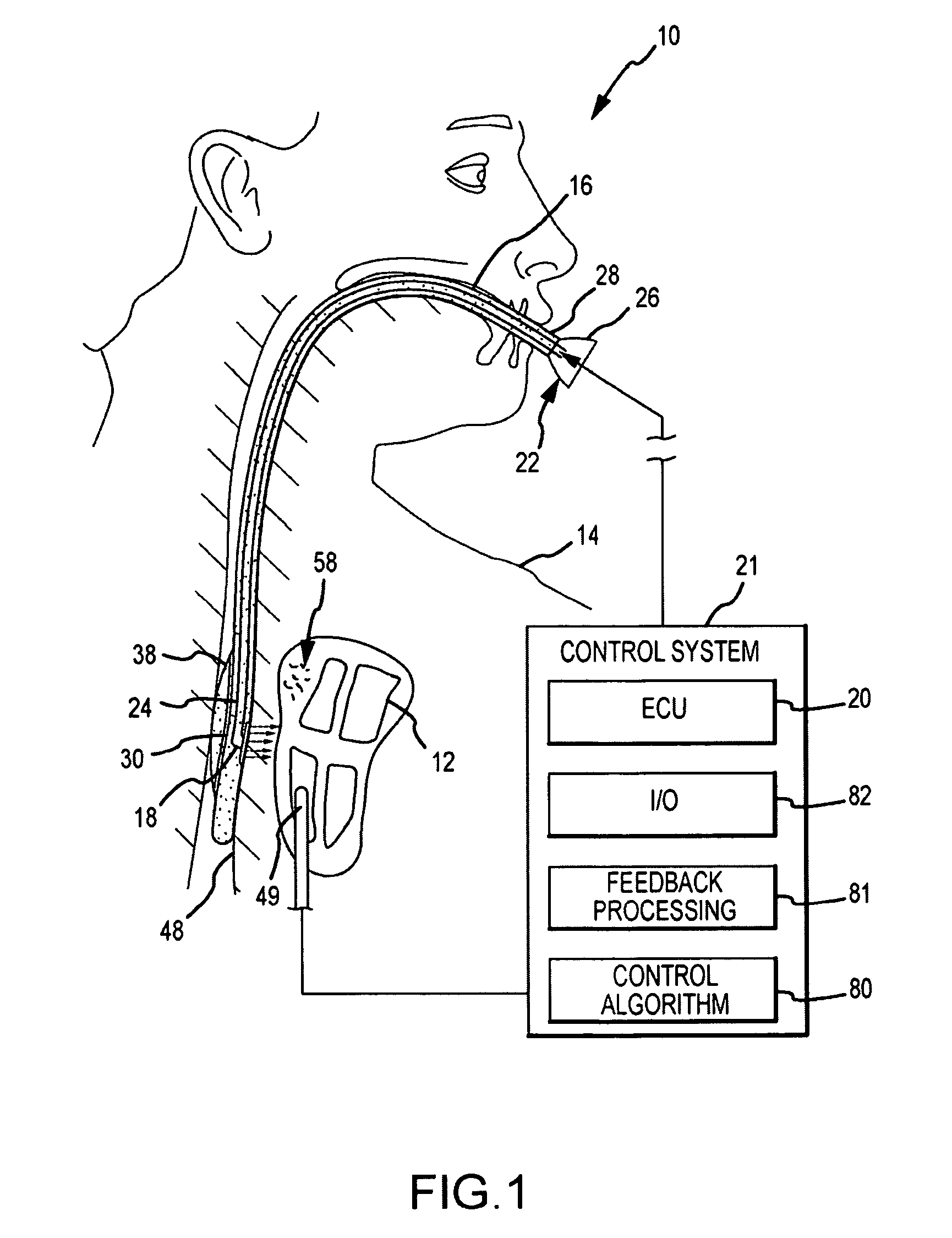
A method and system for assessing lesion formation in tissue is provided. The system includes an electronic control unit (ECU). The ECU is configured to acquire values for first and second components of a complex impedance between the electrode and the tissue, and to calculate an index responsive to the first and second values. The ECU is further configured to process the ECI to assess lesion formation in the tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Assessment of lesion transmurality
InactiveUS7232437B2Improve visualizationEvenly distributedControlling energy of instrumentCatheterCardiac surfaceLesion formation
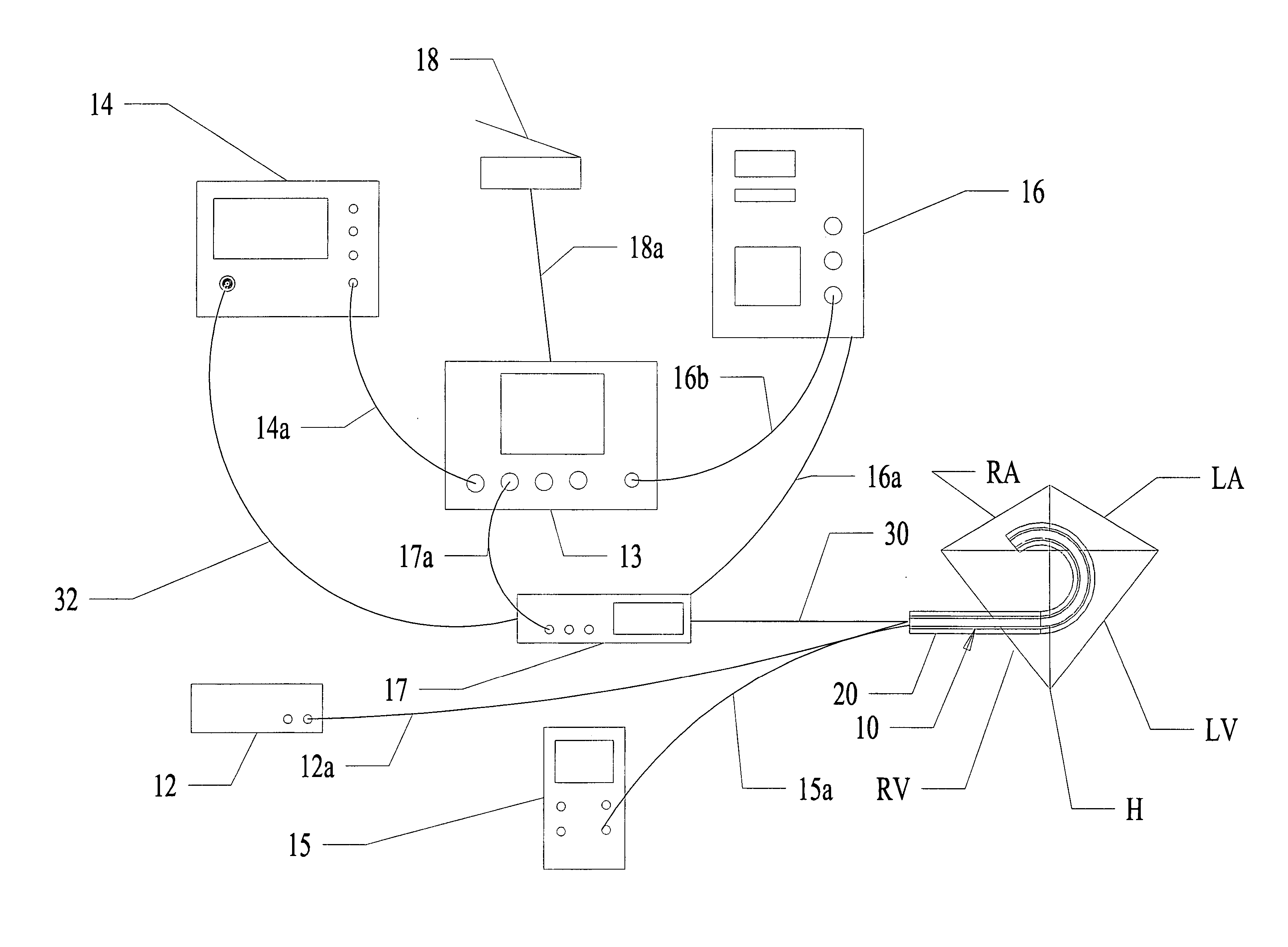
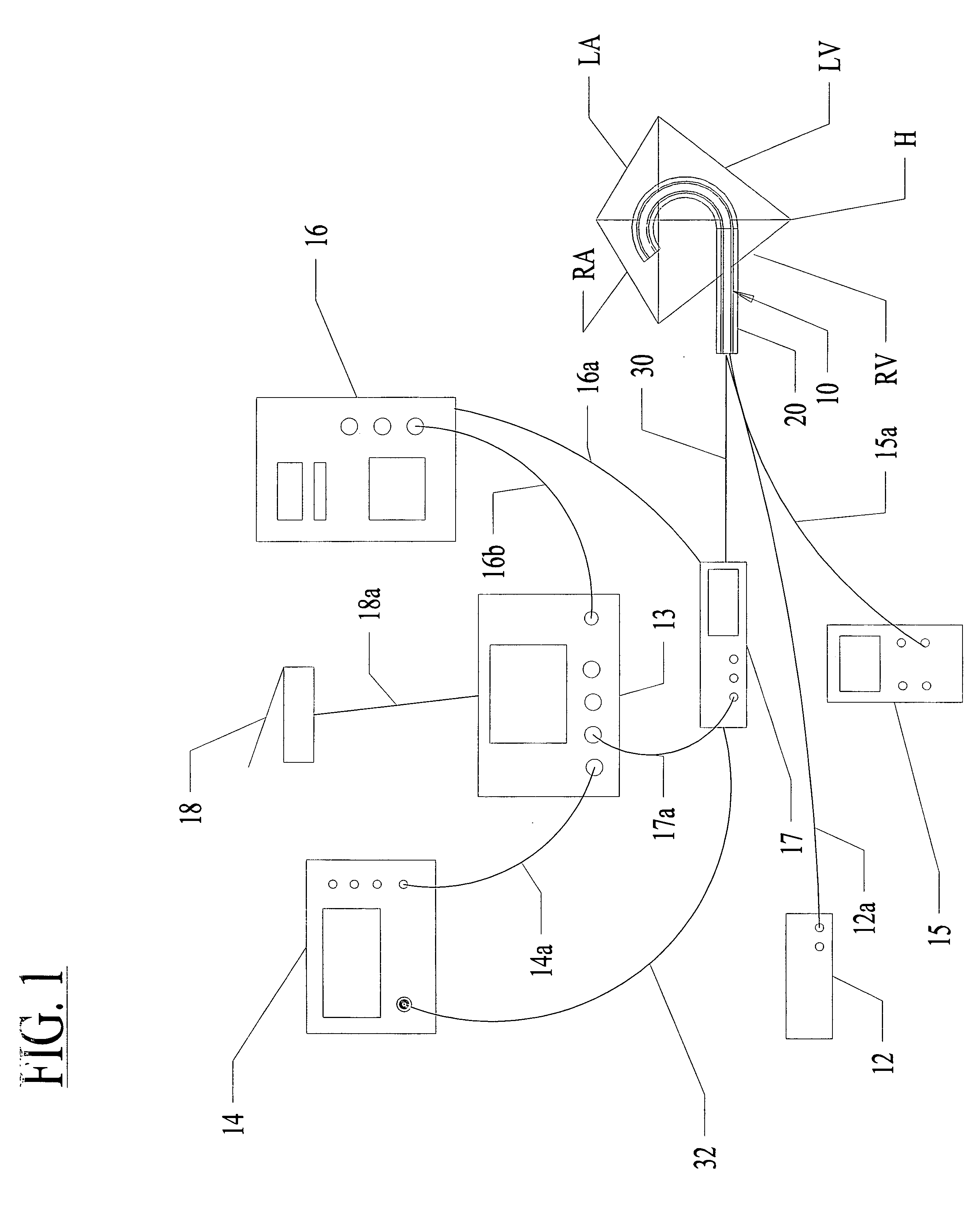
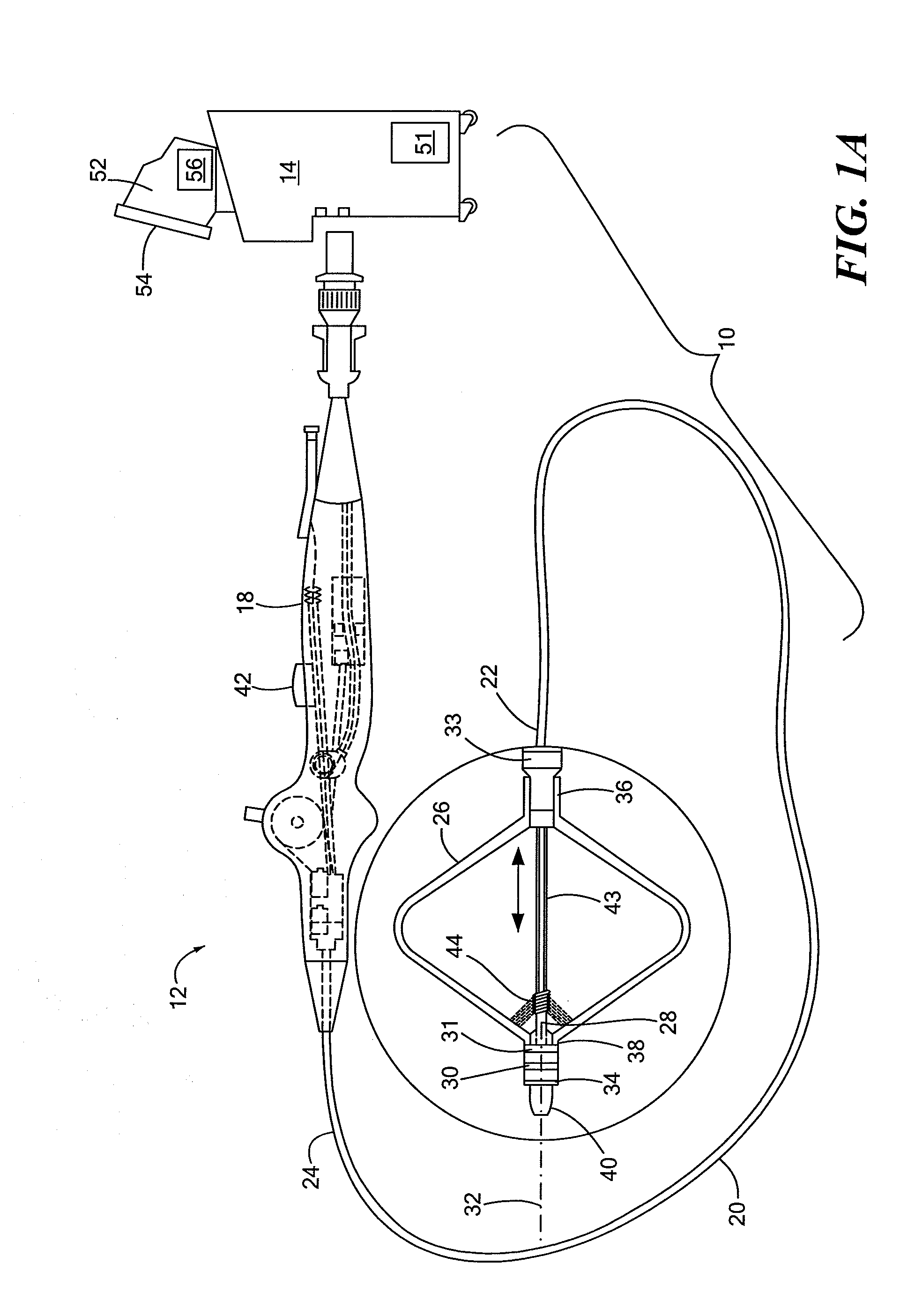
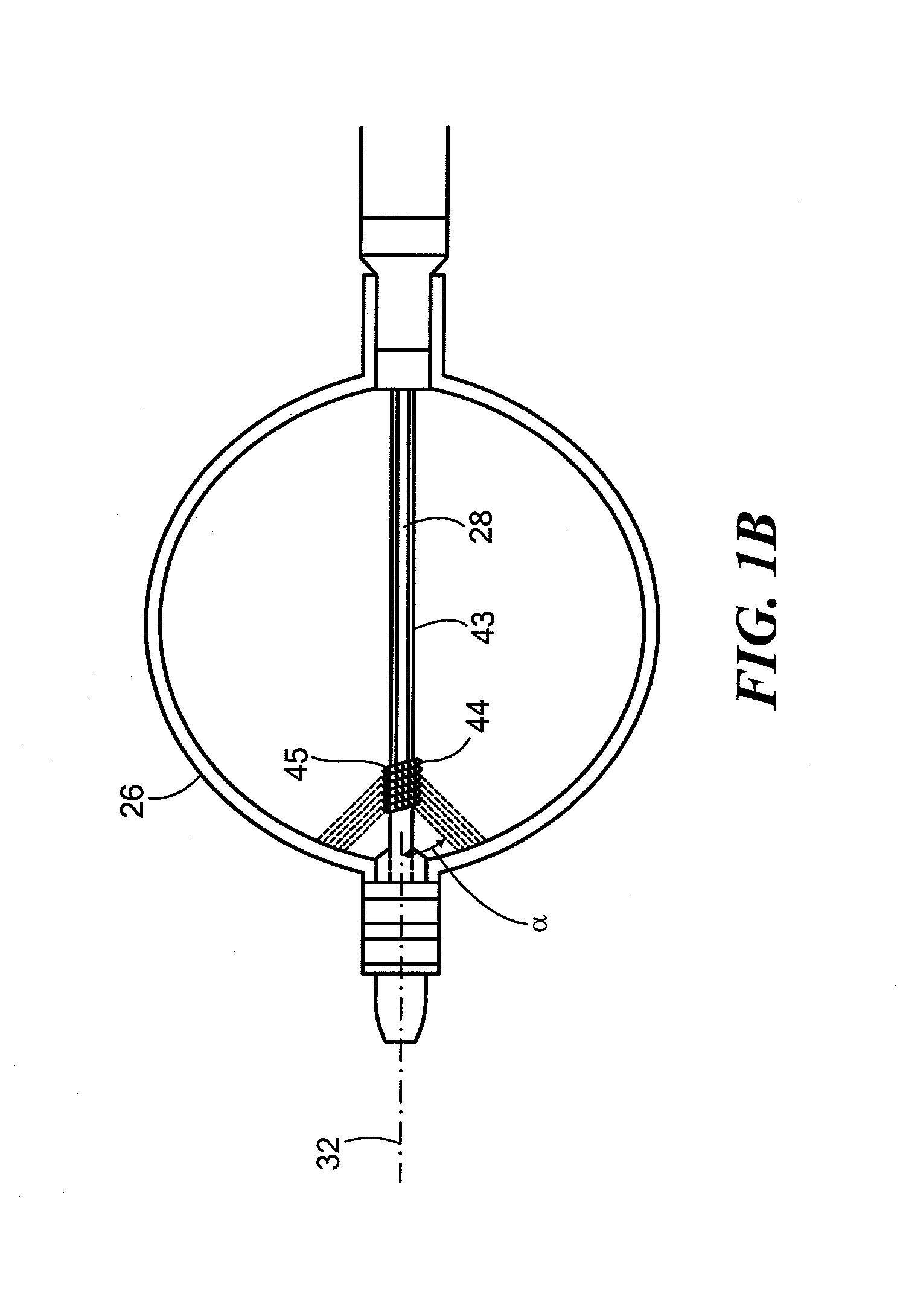
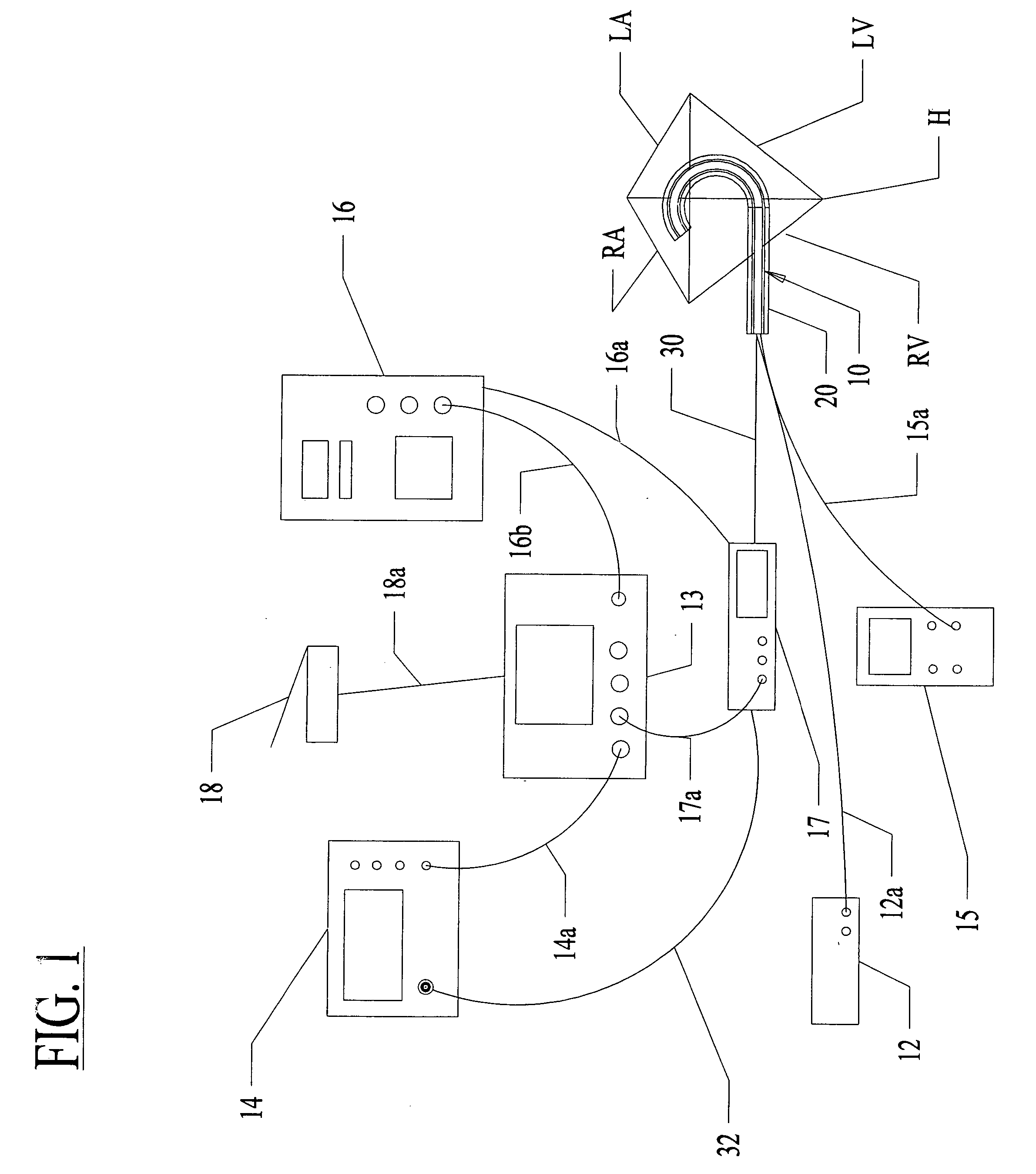
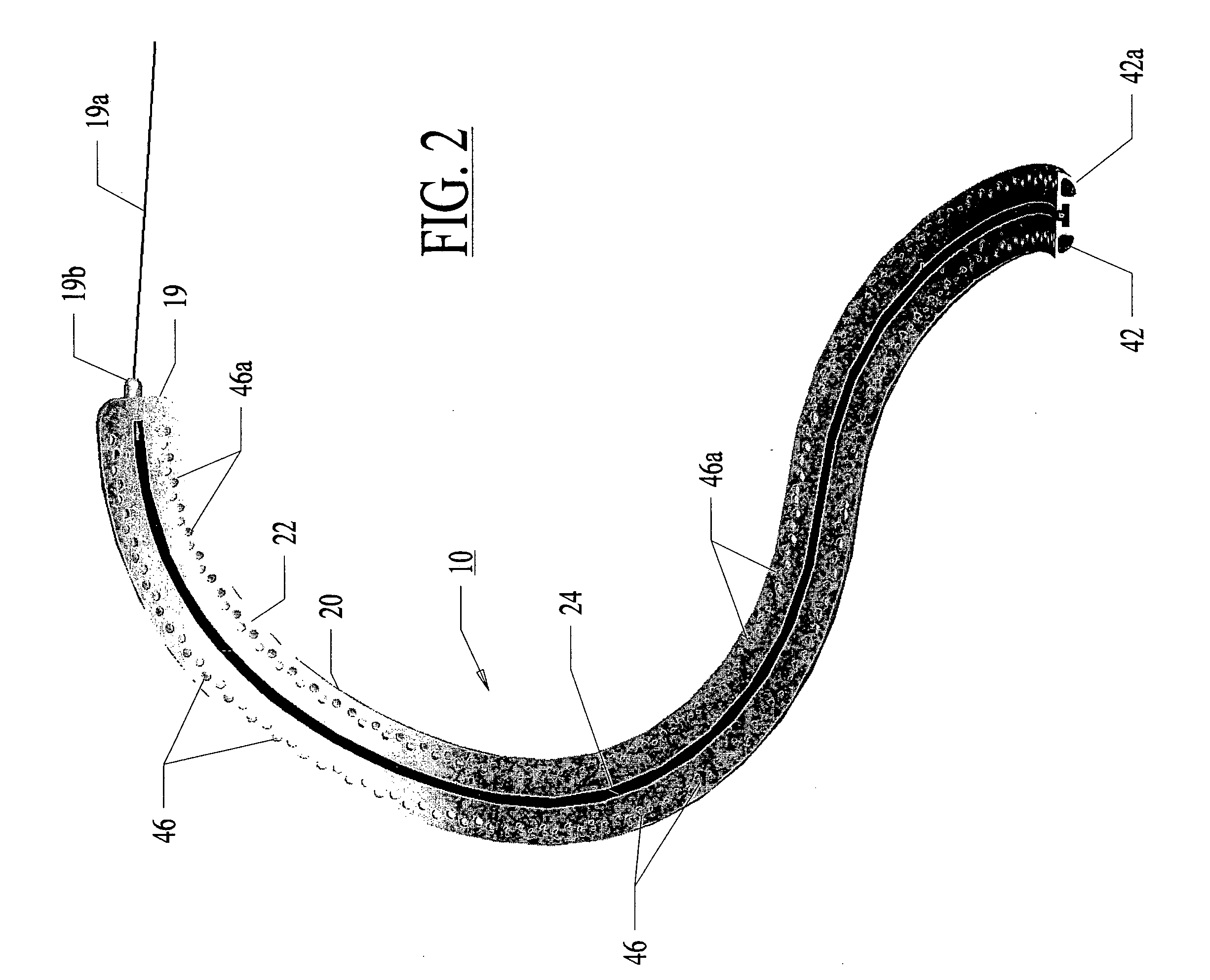
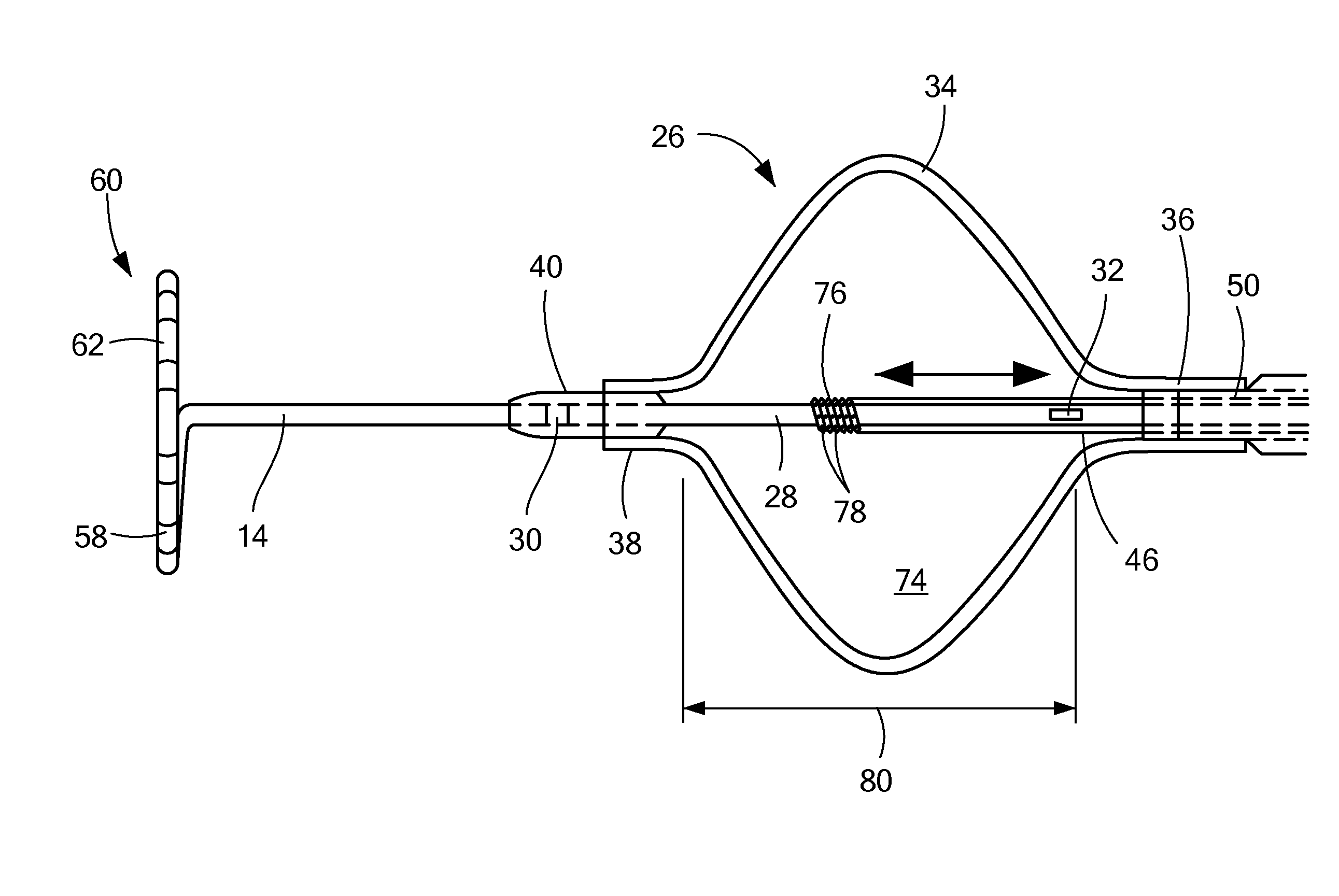
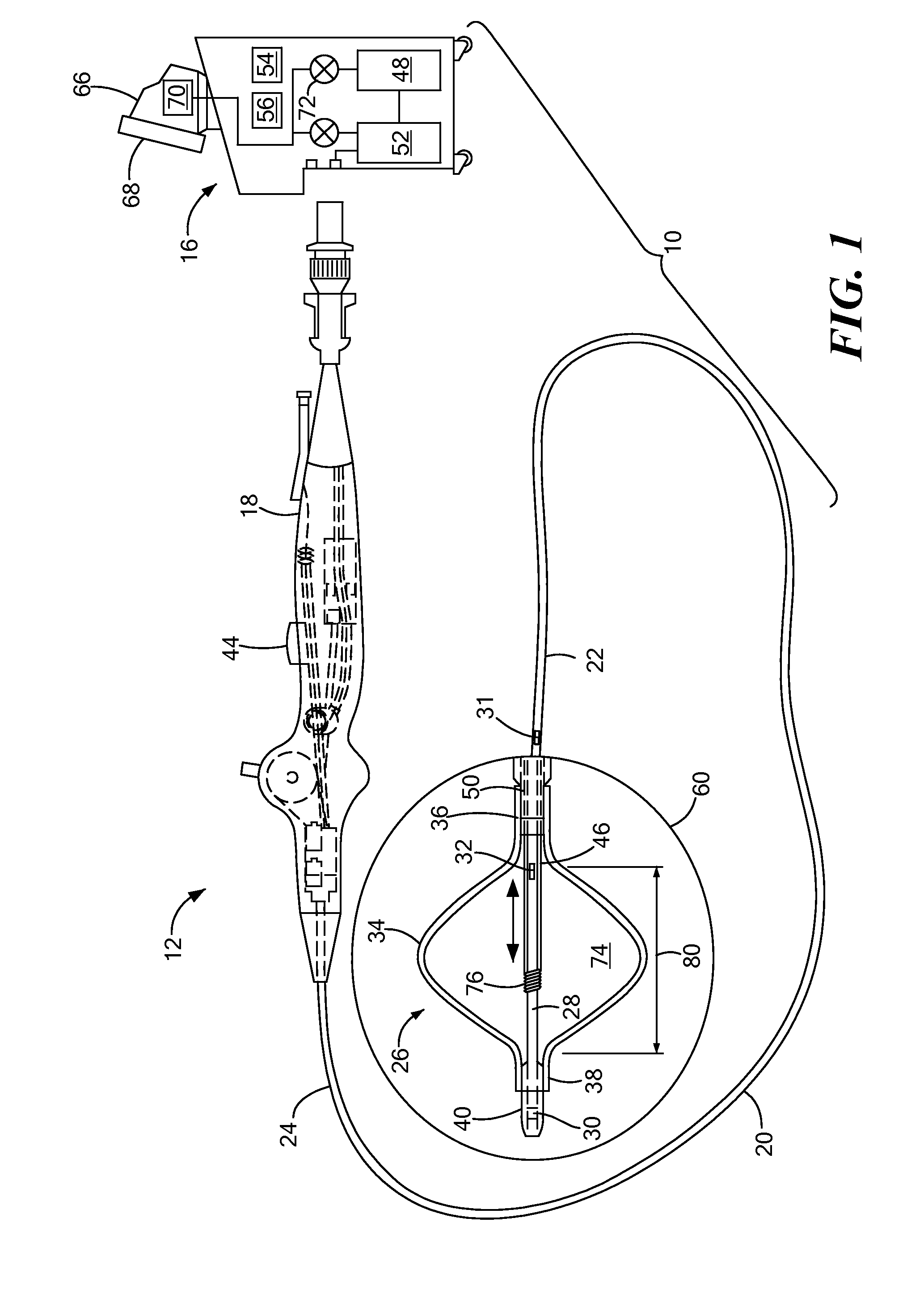
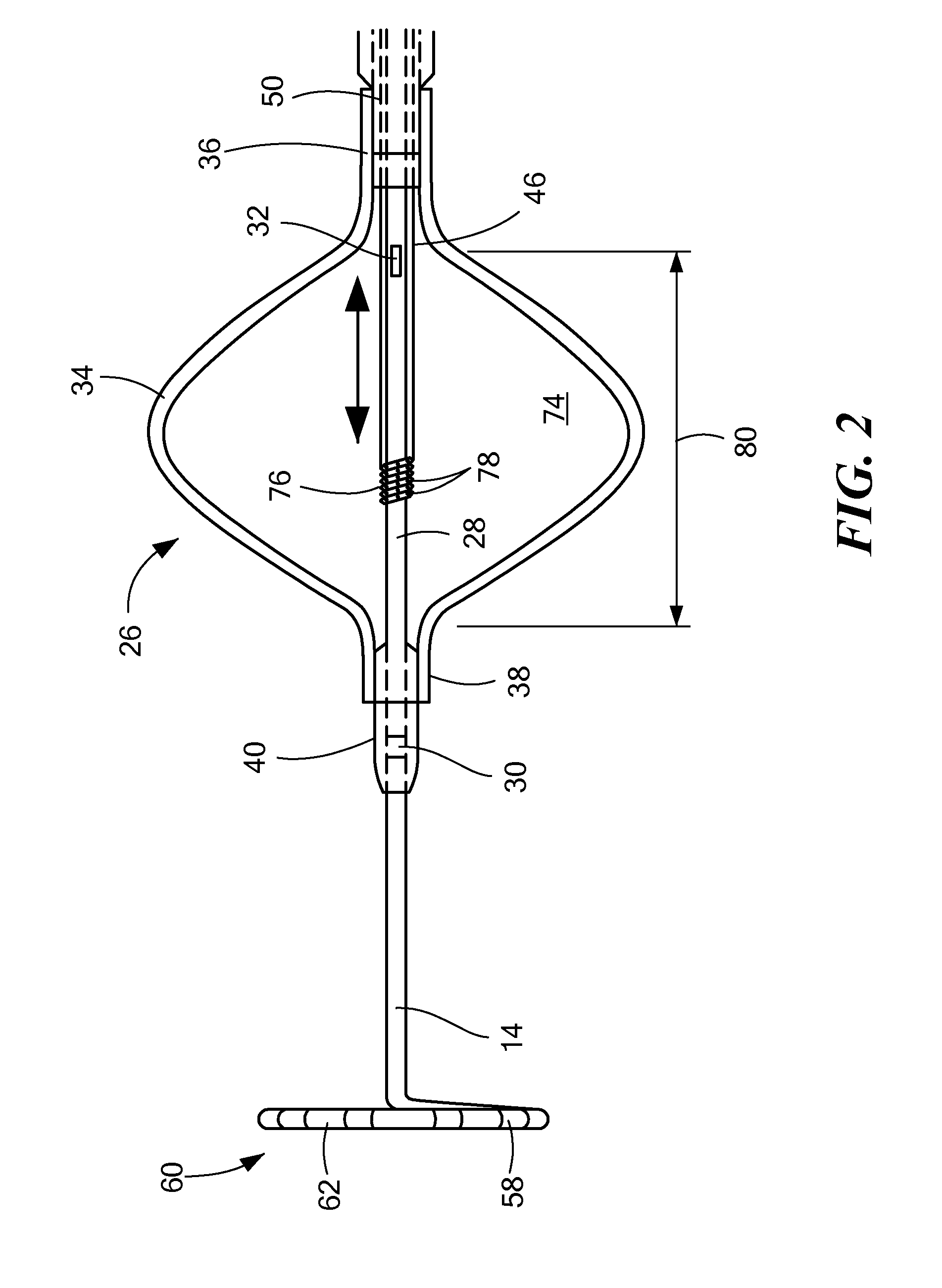
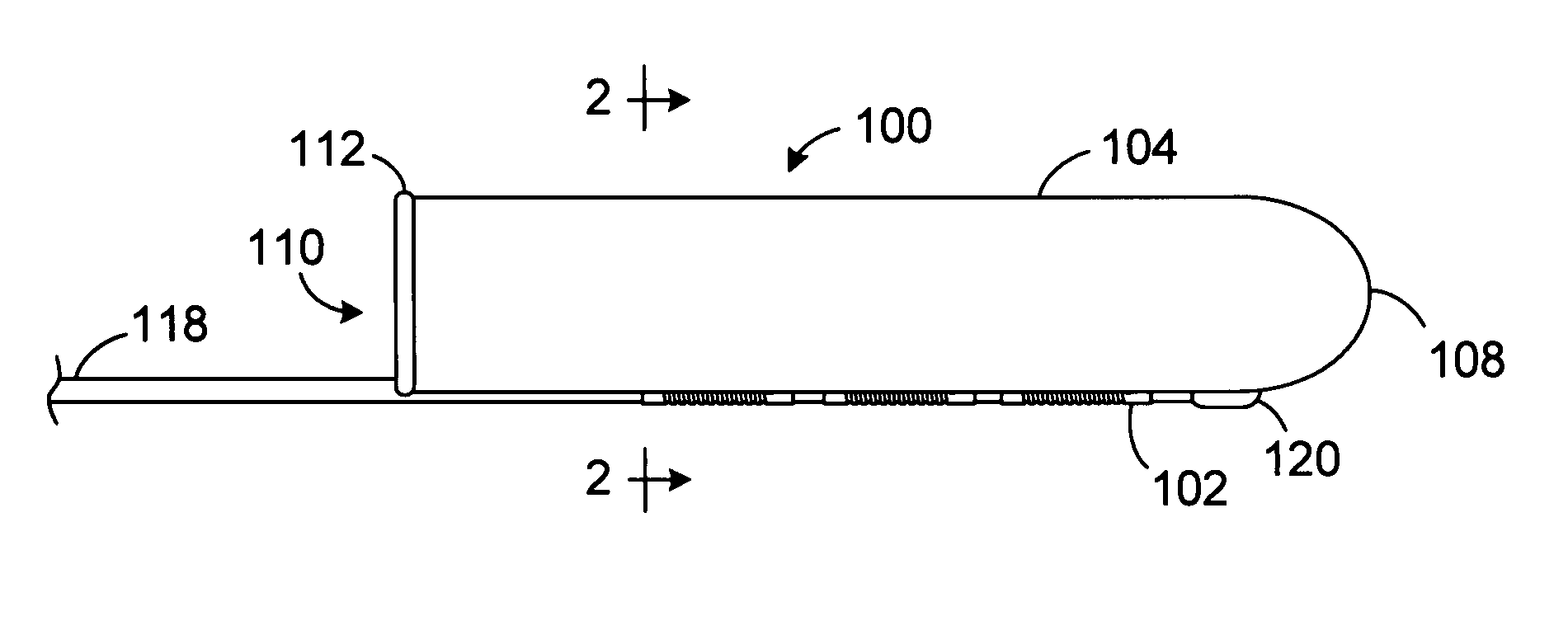
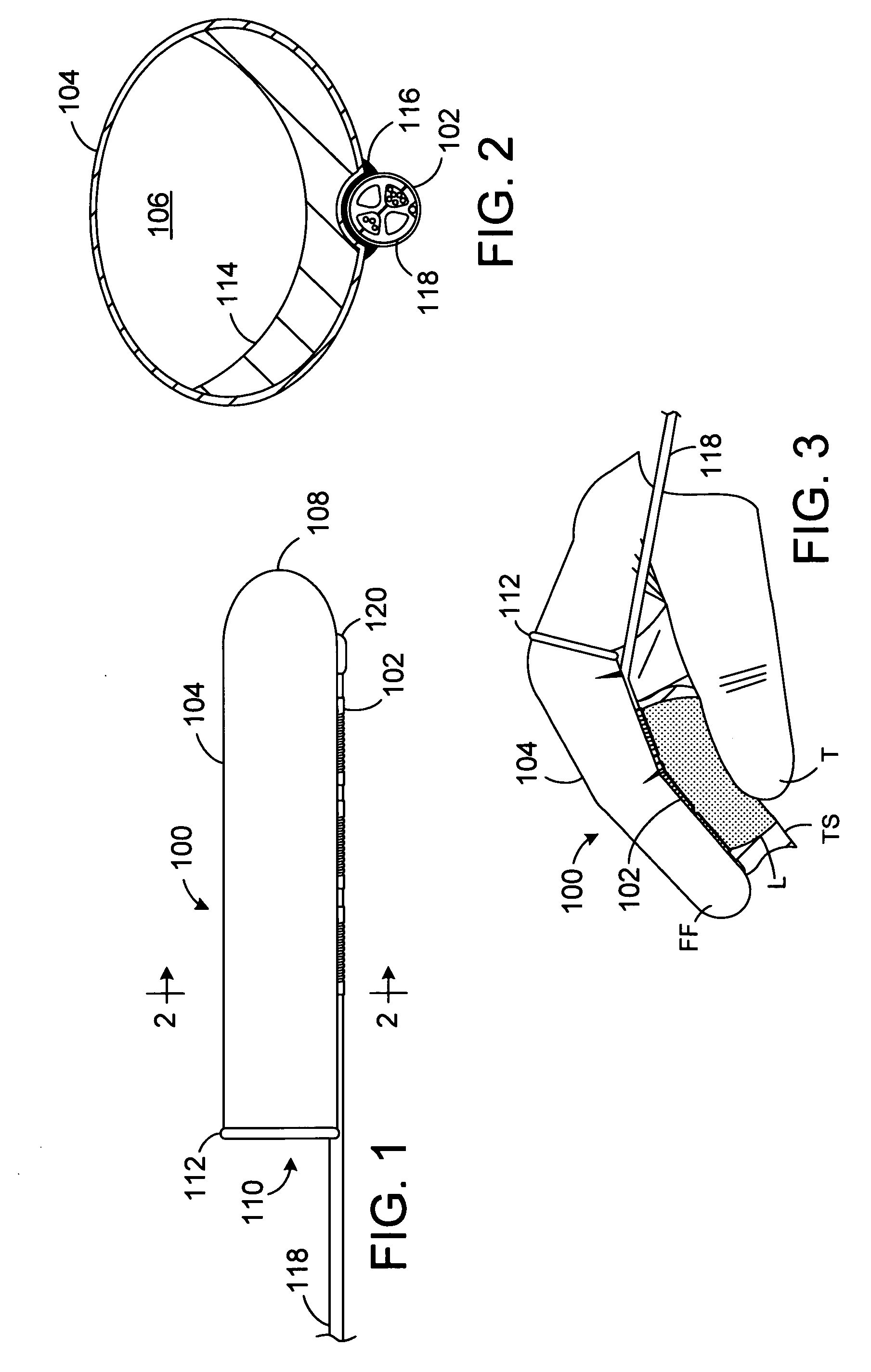
A method and apparatus for treating a body tissue in situ (e.g., an atrial tissue of a heart to treat) atrial fibrillation include a lesion formation tool is positioned against the heart surface. The lesion formation tool includes a guide member having a tissue-opposing surface for placement against a heart surface. An ablation member is coupled to the guide member to move in a longitudinal path relative to the guide member. The ablation member has an ablation element for directing ablation energy in an emitting direction away from the tissue-opposing surface. The guide member may be flexible to adjust a shape of the guide member for the longitudinal path to approximate the desired ablation path while maintaining the tissue-opposing surface against the heart surface. In one embodiment, the ablation member includes at least one radiation-emitting member disposed to travel in the longitudinal pathway. Transmurality can be assessed to approximate a location of non-transmurality in a formed lesion.
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
System and method for presenting information representative of lesion formation in tissue during an ablation procedure
A method and system for presenting information representative of lesion formation is provided. The system comprises an electronic control unit (ECU). The ECU is configured to acquire a value for an ablation description parameter and / or a position signal metric, wherein the value corresponds to a location in the tissue. The ECU is further configured to evaluate the value, assign it a visual indicator of a visualization scheme associated with the parameter / metric corresponding to the value, and generate a marker comprising the visual indicator such that the marker is indicative of the acquired value. The method comprises acquiring a value for the parameter / metric, and evaluating the value. The method further includes assigning a visual indicator of a visualization scheme associated with the parameter / metric corresponding to the value, and generating a marker comprising the visual indicator.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
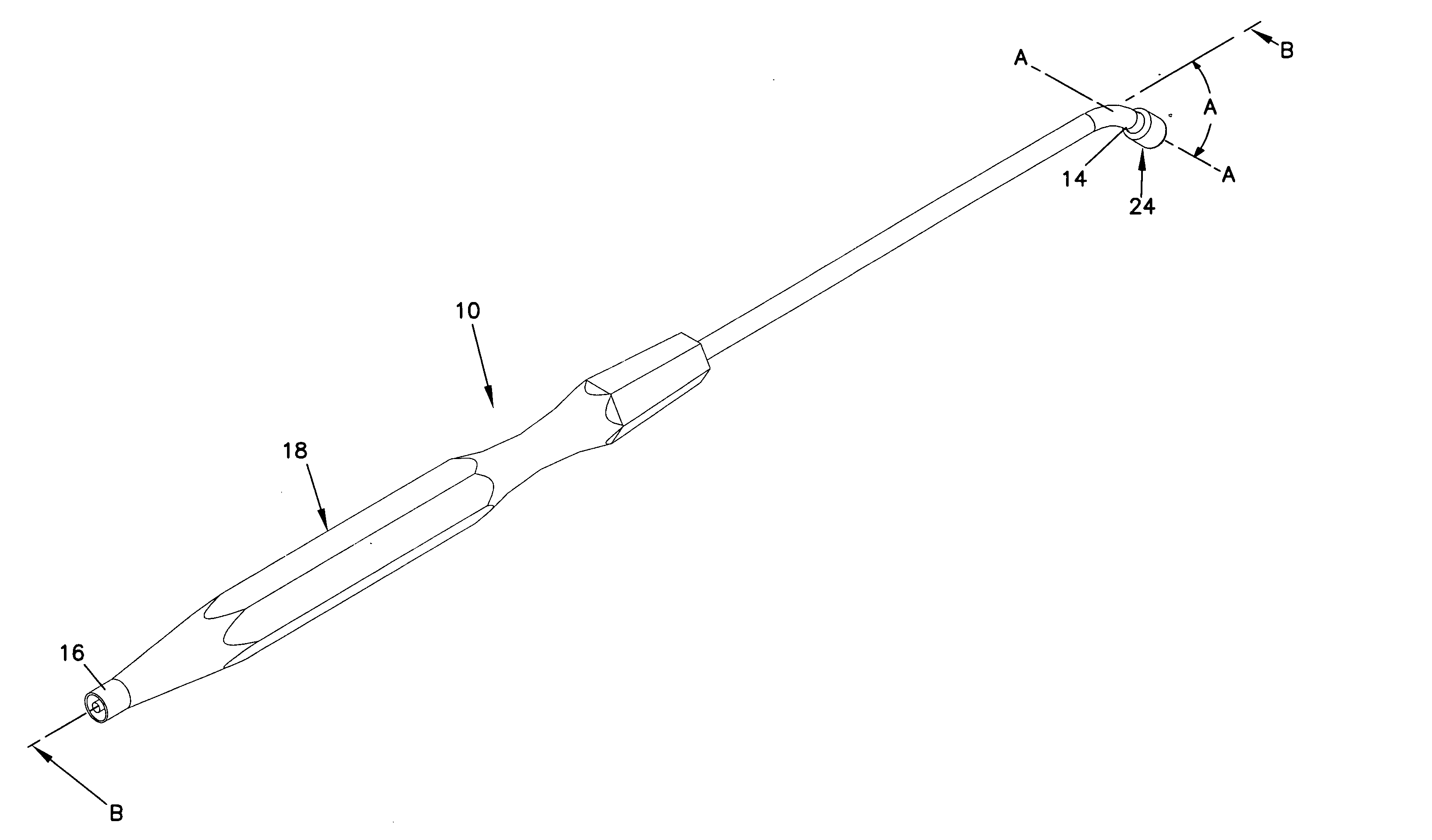
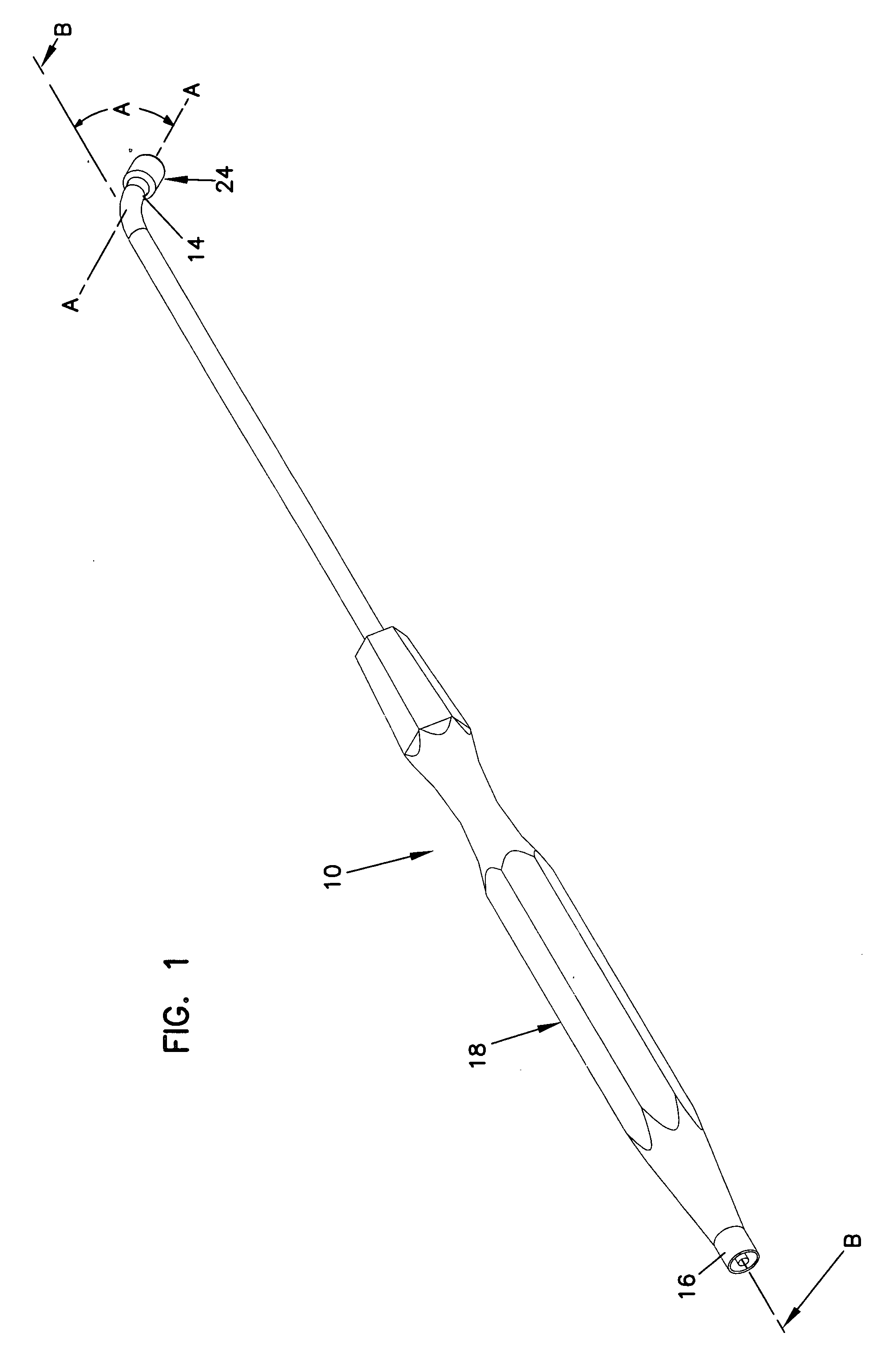
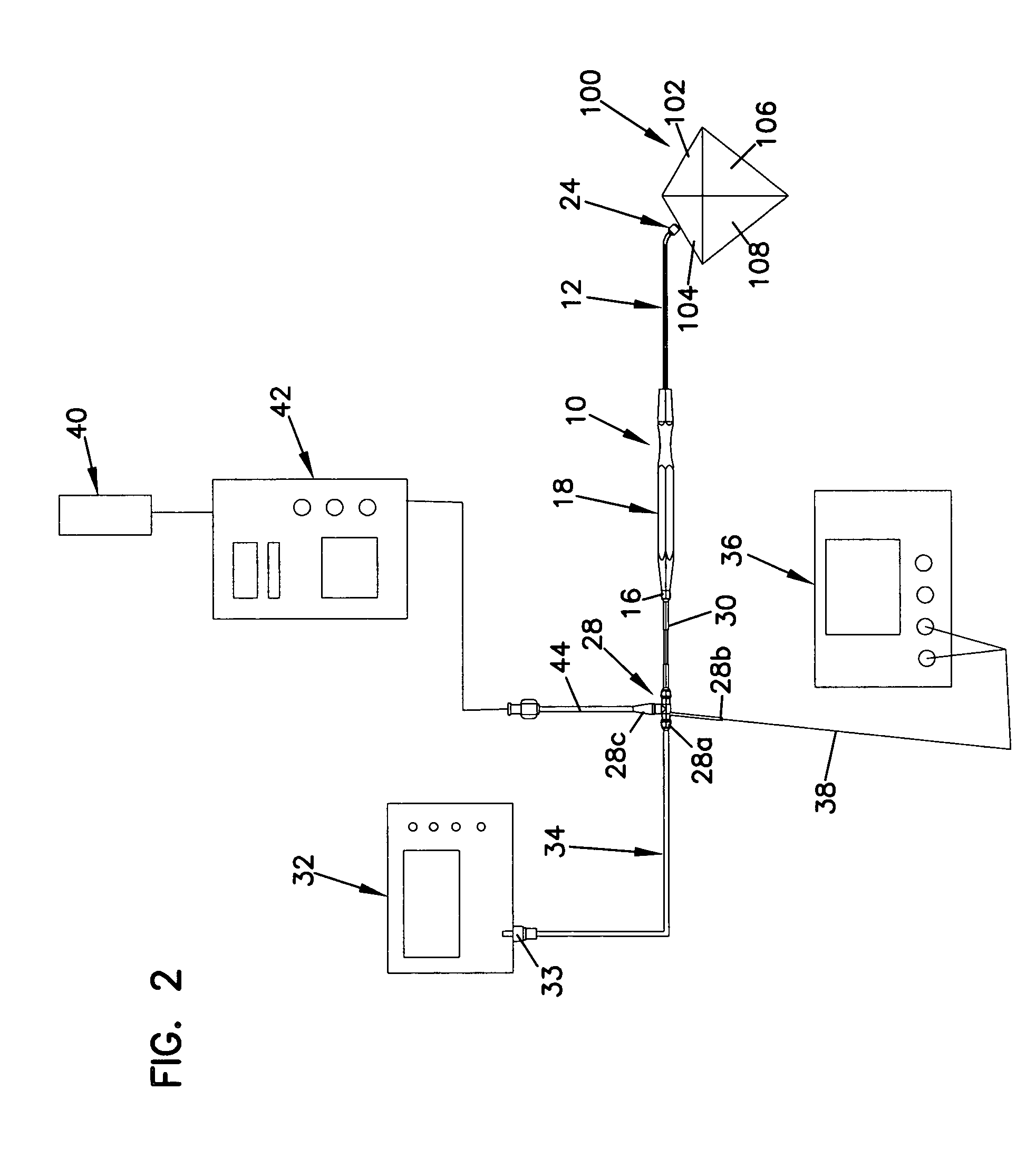
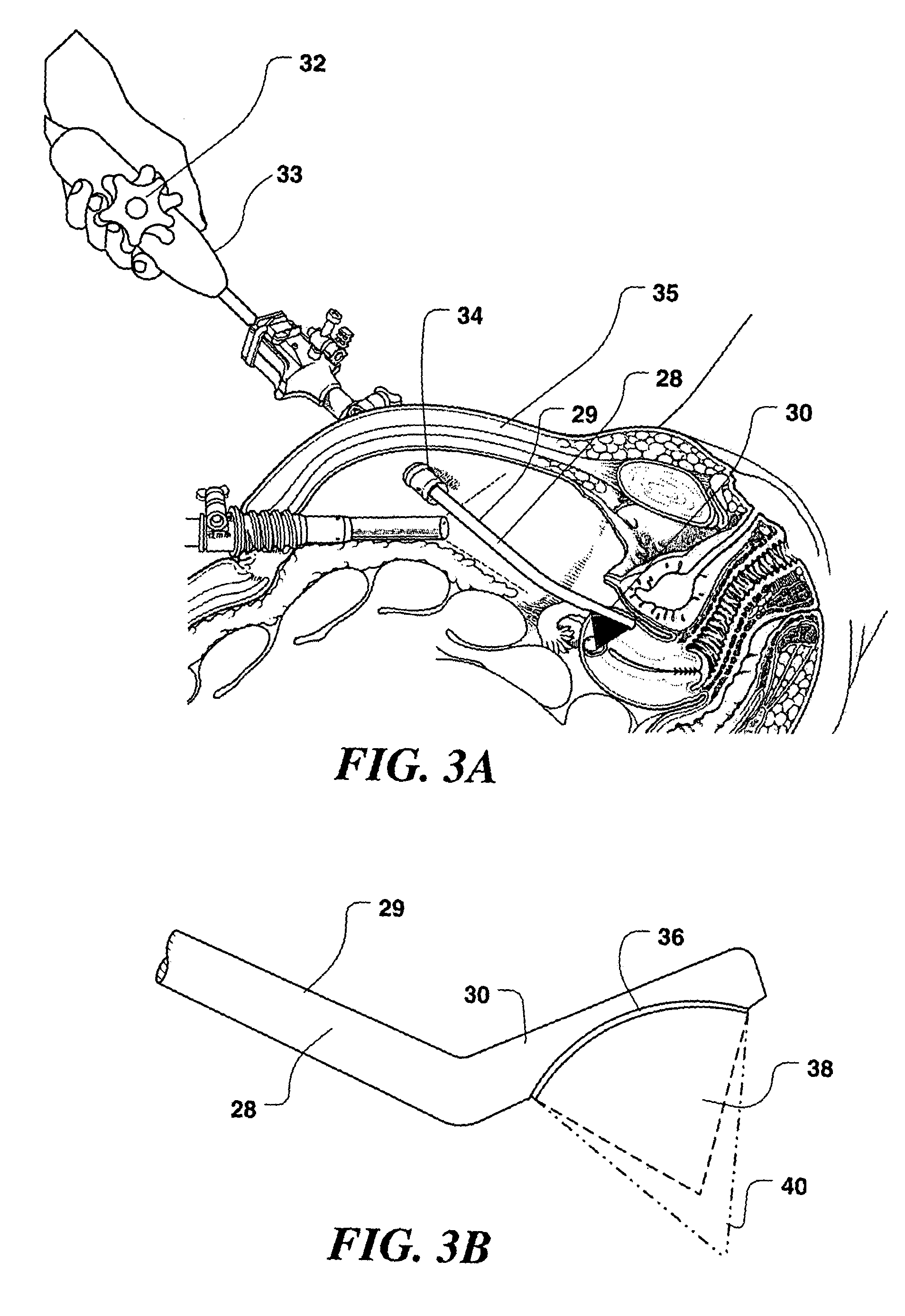
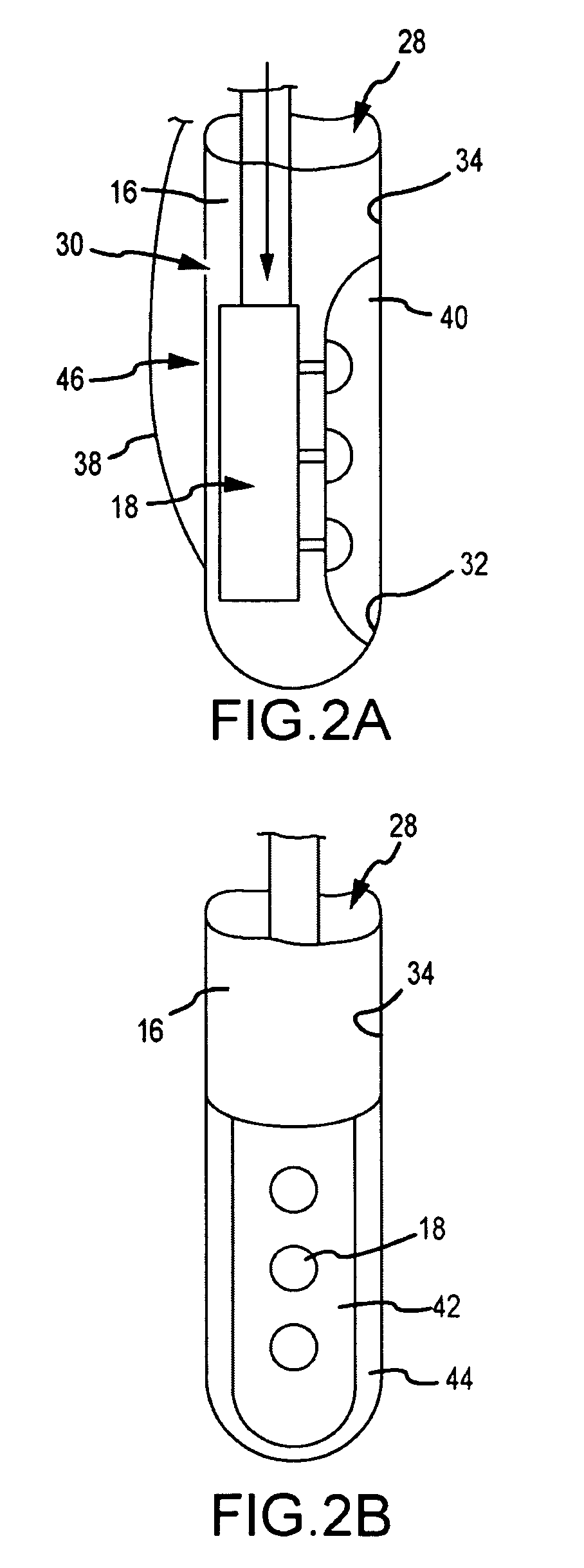
Catheter with omni-directional optical lesion evaluation
ActiveUS20090005768A1Extended service lifeMinimize damageDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsLight energyPositive pressure
A catheter is adapted to ablate tissue and provide lesion qualitative information on a real time basis, having an ablation tip section with a generally omni-directional light diffusion chamber with one openings to allow light energy in the chamber to radiate the tissue and return to the chamber. The chamber is irrigated at a positive pressure differential to continuously flush the opening with fluid. The light energy returning to the chamber from the tissue conveys a tissue parameter, including without limitation, lesion formation, depth of penetration of lesion, cross-sectional area of lesion, formation of char during ablation, recognition of char during ablation, recognition of char from non-charred tissue, formation of coagulum around the ablation site, differentiation of coagulated from non-coagulated blood, differentiation of ablated from healthy tissue, tissue proximity, and recognition of steam formation in the tissue for prevention of steam pop.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
System and method for assessing lesions in tissue
A method and system for assessing lesion formation in tissue is provided. The system includes an electronic control unit (ECU). The ECU is configured to acquire values for first and second components of a complex impedance between the electrode and the tissue, and to calculate an index responsive to the first and second values. The ECU is further configured to process the ECI to assess lesion formation in the tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Guided ablation with end-fire fiber
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
System and method for assessing the formation of a lesion in tissue
A method and system for assessing lesion formation in tissue is provided. The system includes an electronic control unit (ECU) configured to acquire magnitudes for a component of a complex impedance between an electrode and tissue, and the power applied to the tissue during lesion formation. The ECU is configured to calculate a value responsive to the complex impedance component and the power. The value is indicative of a predicted lesion depth, a likelihood the lesion has reached a predetermined depth, or a predicted tissue temperature. The method includes acquiring magnitudes for a component of a complex impedance between an electrode and tissue and the power applied during lesion formation. The method includes calculating a value responsive to the complex impedance component and the power, the value being indicative of a predicted lesion depth, a likelihood the lesion has reached a predetermined depth, and / or a predicted tissue temperature.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Apparatus and method for laser treatment
InactiveUS20050096643A1Optimize achievementEasy to moveControlling energy of instrumentCatheterLight energyLength wave
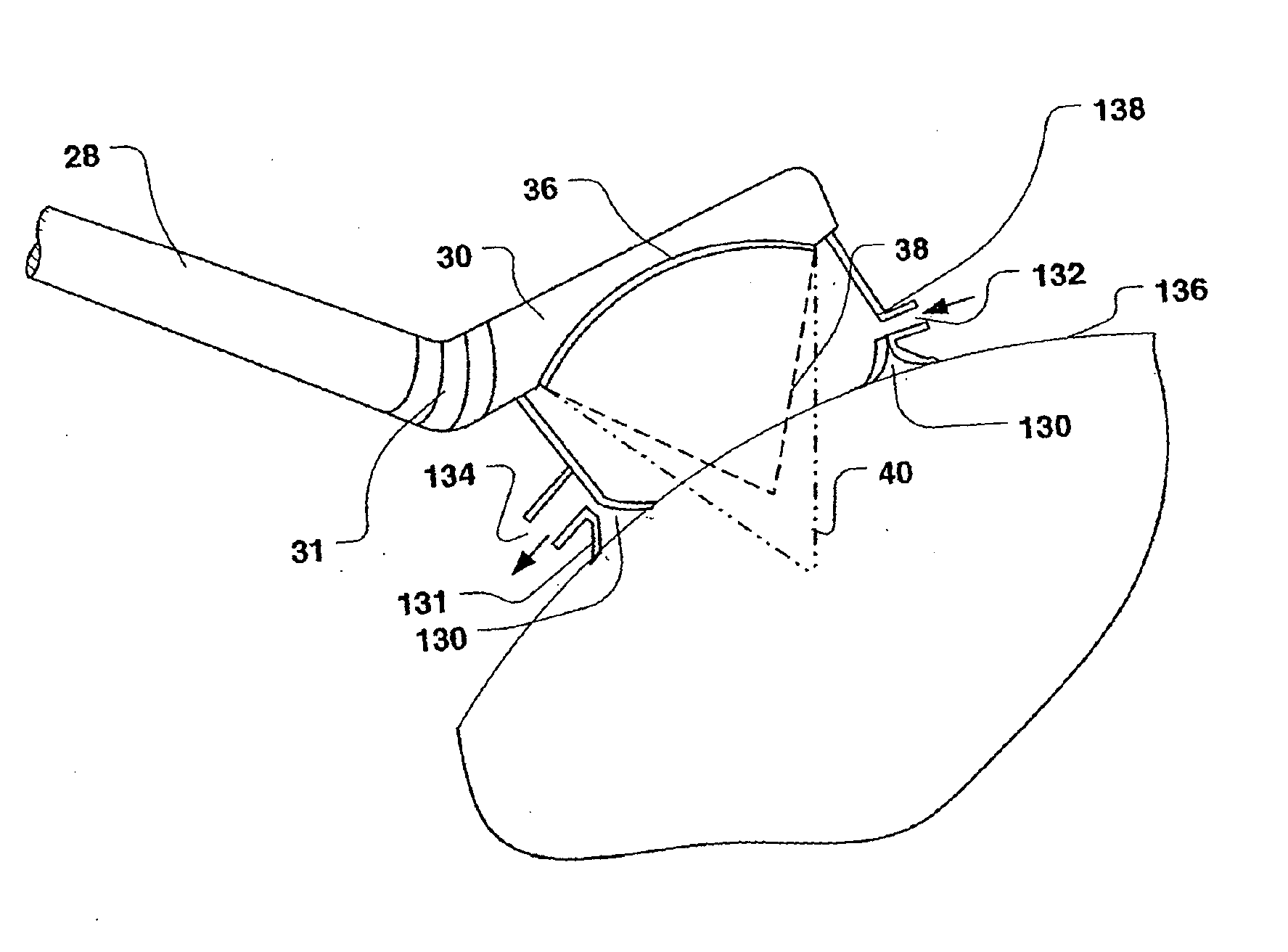
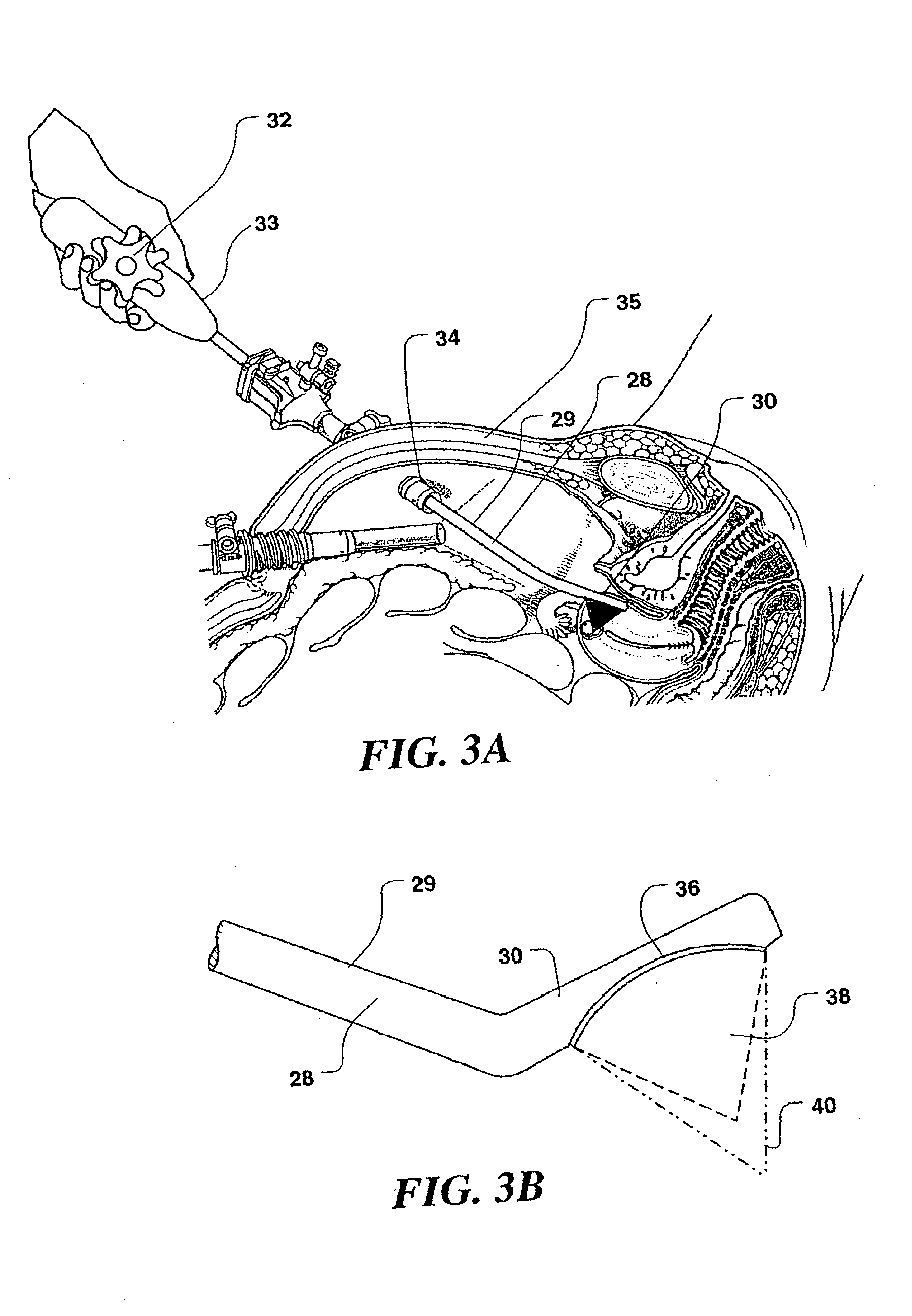
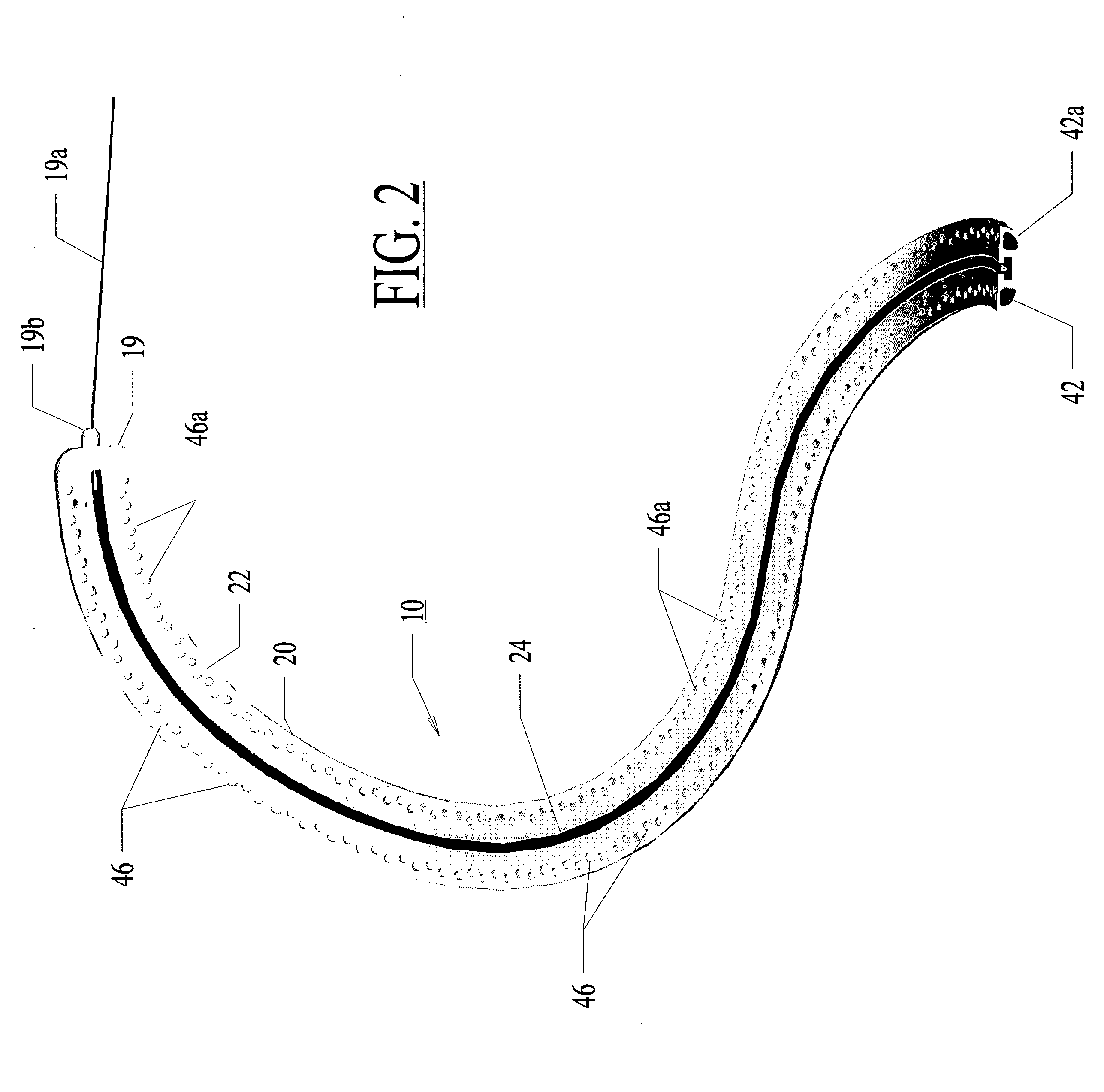
A method and apparatus for treating in situ biologic tissue include identifying a patient with a condition susceptible to treatment by forming a lesion in the tissue and accessing a surface of the tissue. A lesion formation tool is positioned against the accessed surface. The tool includes an optical fiber for guiding a coherent waveform of a selected wavelength to a fiber tip for discharge of light energy from the fiber tip. The wavelength is selected for the light energy to penetrate a full thickness of the tissue to form a volume of necrosed tissue through the thickness of the tissue. The tool further includes a guide tip coupled to the fiber tip. The guide tip is adapted to have a discharge bore aligned with the fiber tip to define an unobstructed light pathway from the fiber tip to the tissue surface. The guide tip is further adapted to be placed against the tissue surface with the guide tip slidable along the tissue surface in atraumatic sliding engagement with the discharge bore opposing the tissue surface. The lesion formation tool is manipulated to draw the guide tip over the tissue surface in a pathway while maintaining the discharge bore opposing the tissue surface to form a transmural lesion in the tissue extending a length of the pathway.
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
Clamp based lesion formation apparatus with variable spacing structures
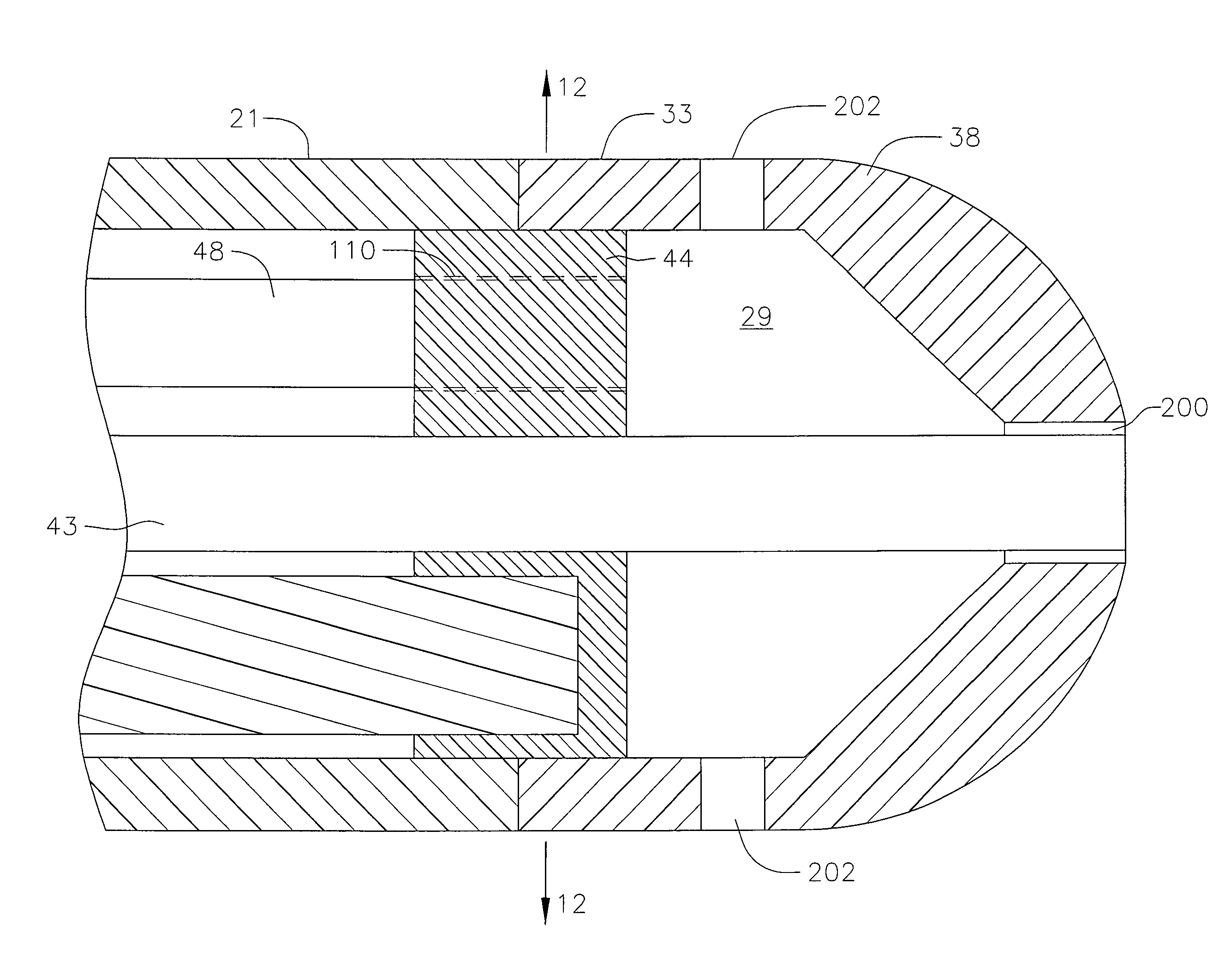
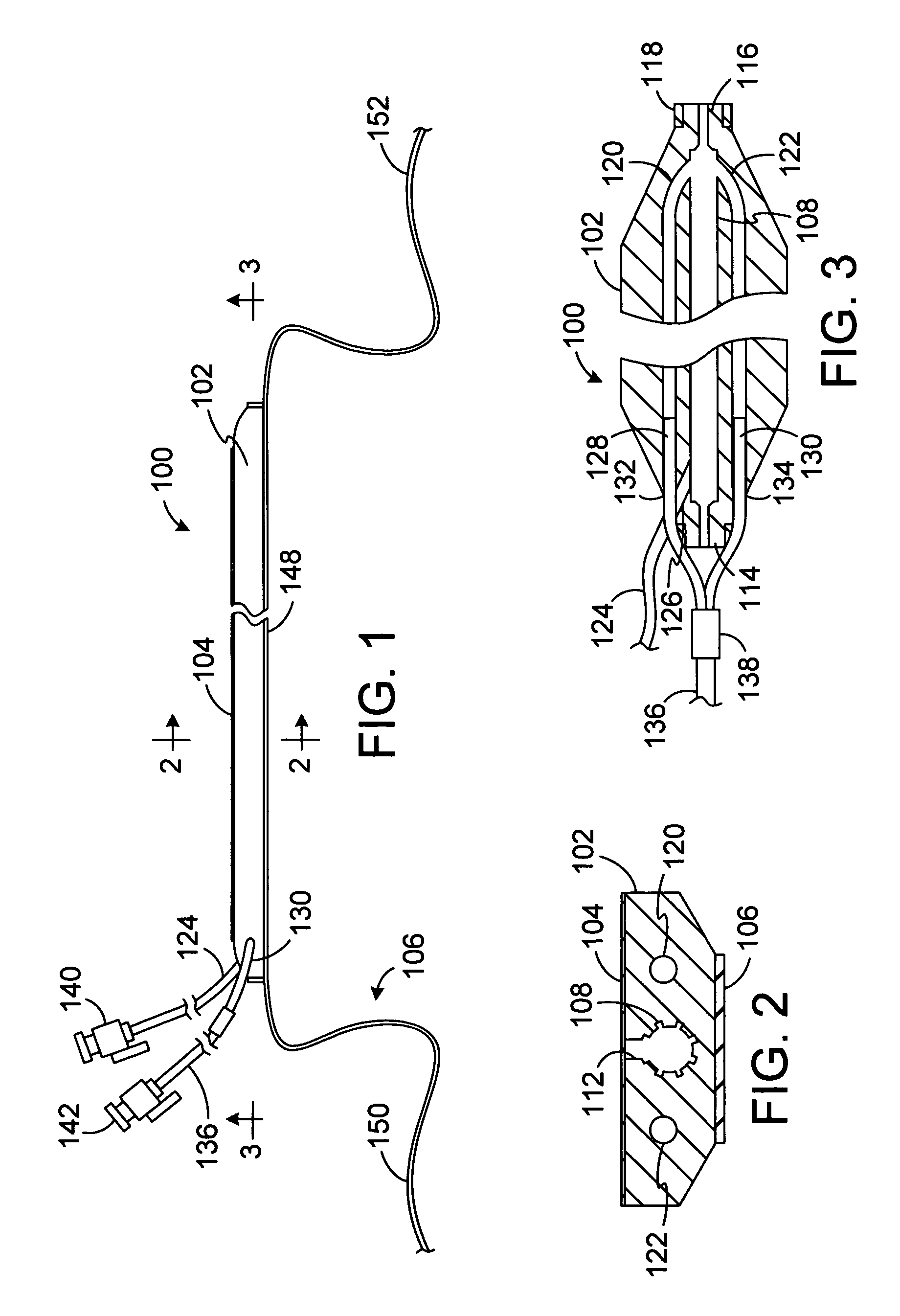
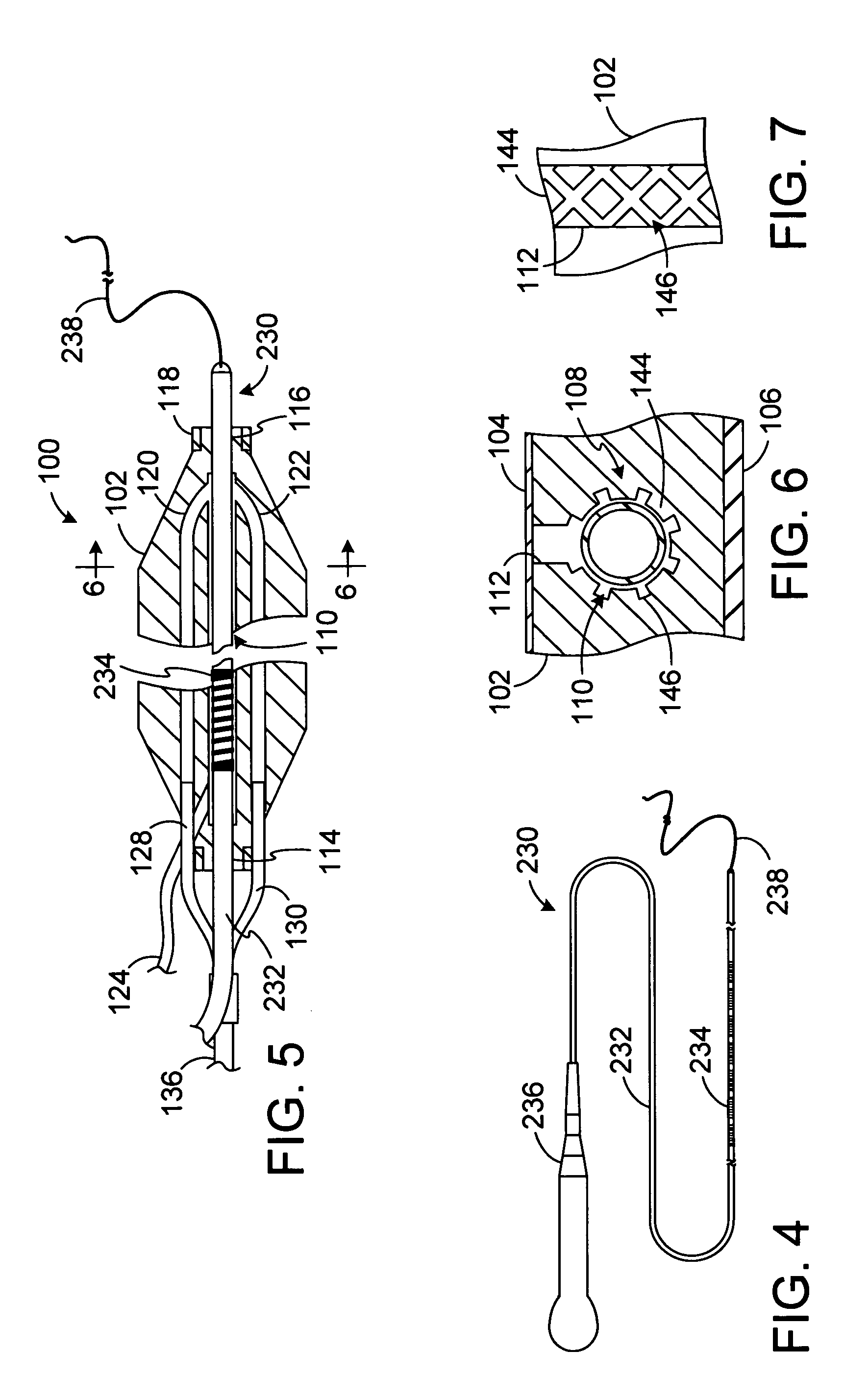
ActiveUS7862561B2Not to damageImprove conductivitySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsEngineeringLesion formation
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Controlled high efficiency lesion formation using high intensity ultrasound
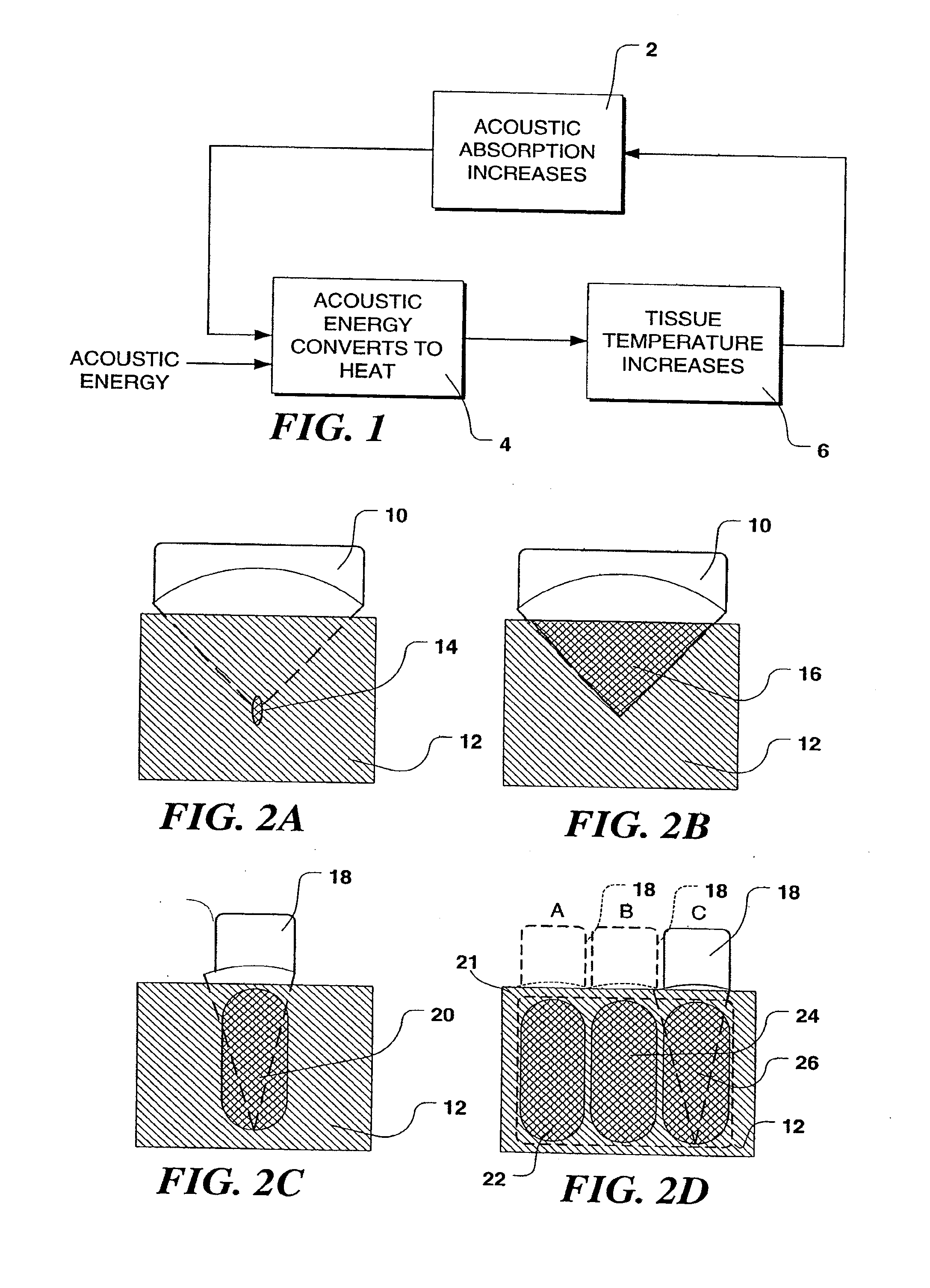
InactiveUS7470241B2Effective treatmentHigh strengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceTransducer
An ultrasound system used for both imaging and delivery high intensity ultrasound energy therapy to treatment sites and a method for treating tumors and other undesired tissue within a patient's body with an ultrasound device. The ultrasound device has an ultrasound transducer array disposed on a distal end of an elongate, relatively thin shaft. In one form of the invention, the transducer array is disposed within a liquid-filled elastomeric material that more effectively couples ultrasound energy into the tumor, that is directly contacted with the device. Using the device in a continuous wave mode, a necrotic zone of tissue having a desired size and shape (e.g., a necrotic volume selected to interrupt a blood supply to a tumor) can be created by controlling at least one of the f-number, duration, intensity, and direction of the ultrasound energy administered. This method speeds the therapy and avoids continuously pausing to enable intervening normal tissue to cool.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
System and method for assessing the formation of a lesion in tissue
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for assessing the formation of a lesion in tissue
A method and system for assessing lesion formation in tissue is provided. The system includes an electronic control unit (ECU) configured to acquire magnitudes for a component of a complex impedance between an electrode and tissue, and the power applied to the tissue during lesion formation. The ECU is configured to calculate a value responsive to the complex impedance component and the power. The value is indicative of a predicted lesion depth, a likelihood the lesion has reached a predetermined depth, or a predicted tissue temperature. The method includes acquiring magnitudes for a component of a complex impedance between an electrode and tissue and the power applied during lesion formation. The method includes calculating a value responsive to the complex impedance component and the power, the value being indicative of a predicted lesion depth, a likelihood the lesion has reached a predetermined depth, and / or a predicted tissue temperature.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
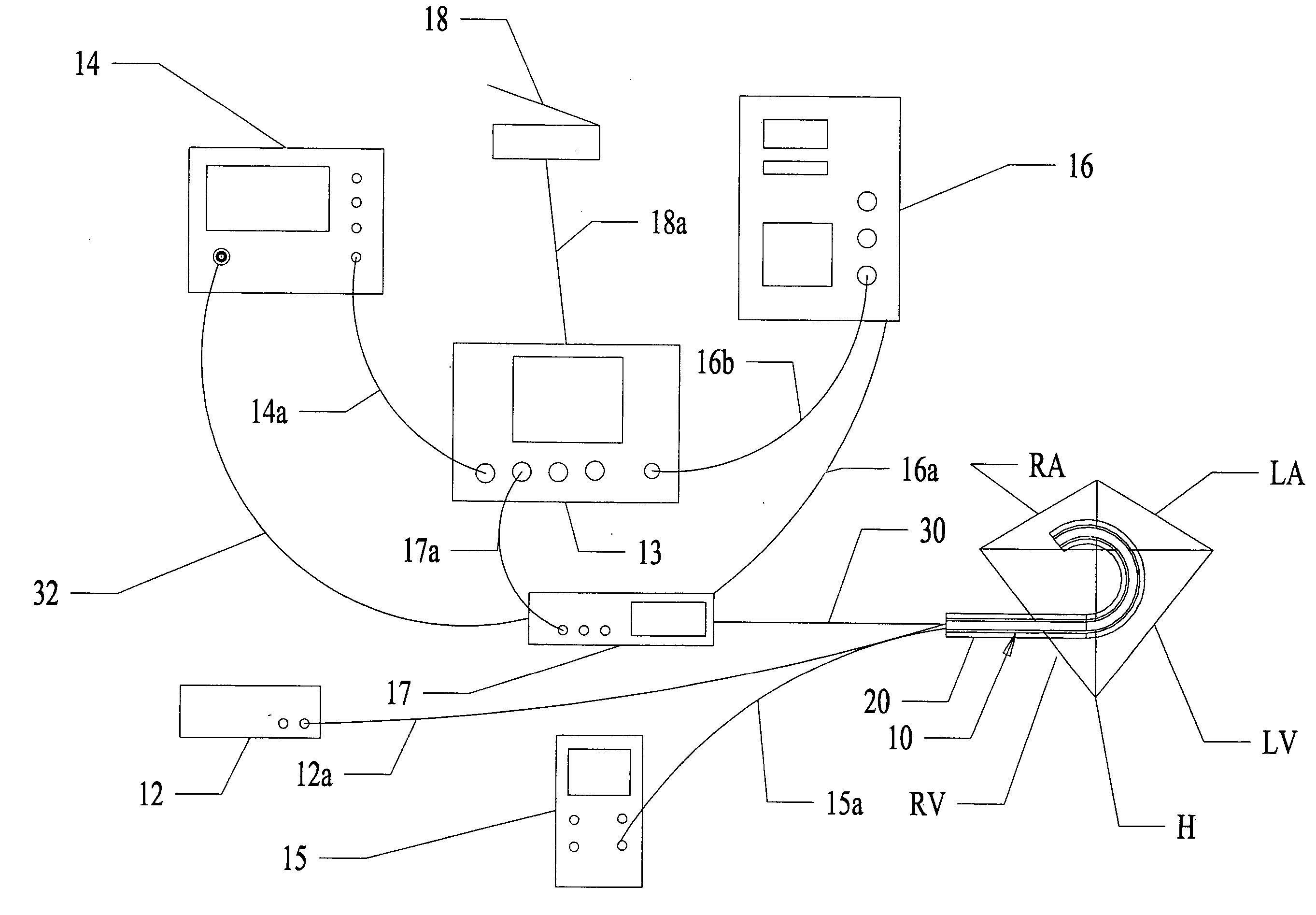
Prediction of atrial wall electrical reconnection based on contact force measured during RF ablation
ActiveUS20120209260A1Easy to predictEffective isolation lineDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingRf ablationAtrial wall
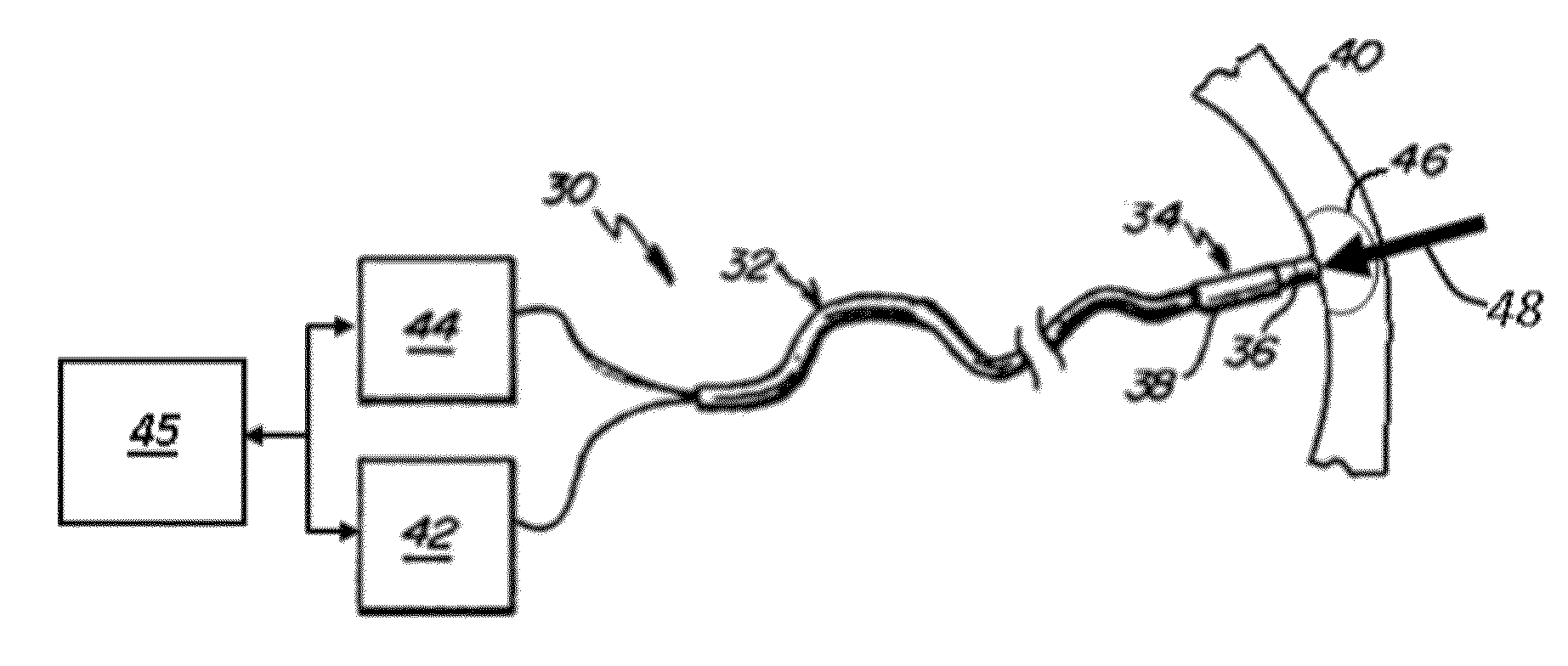
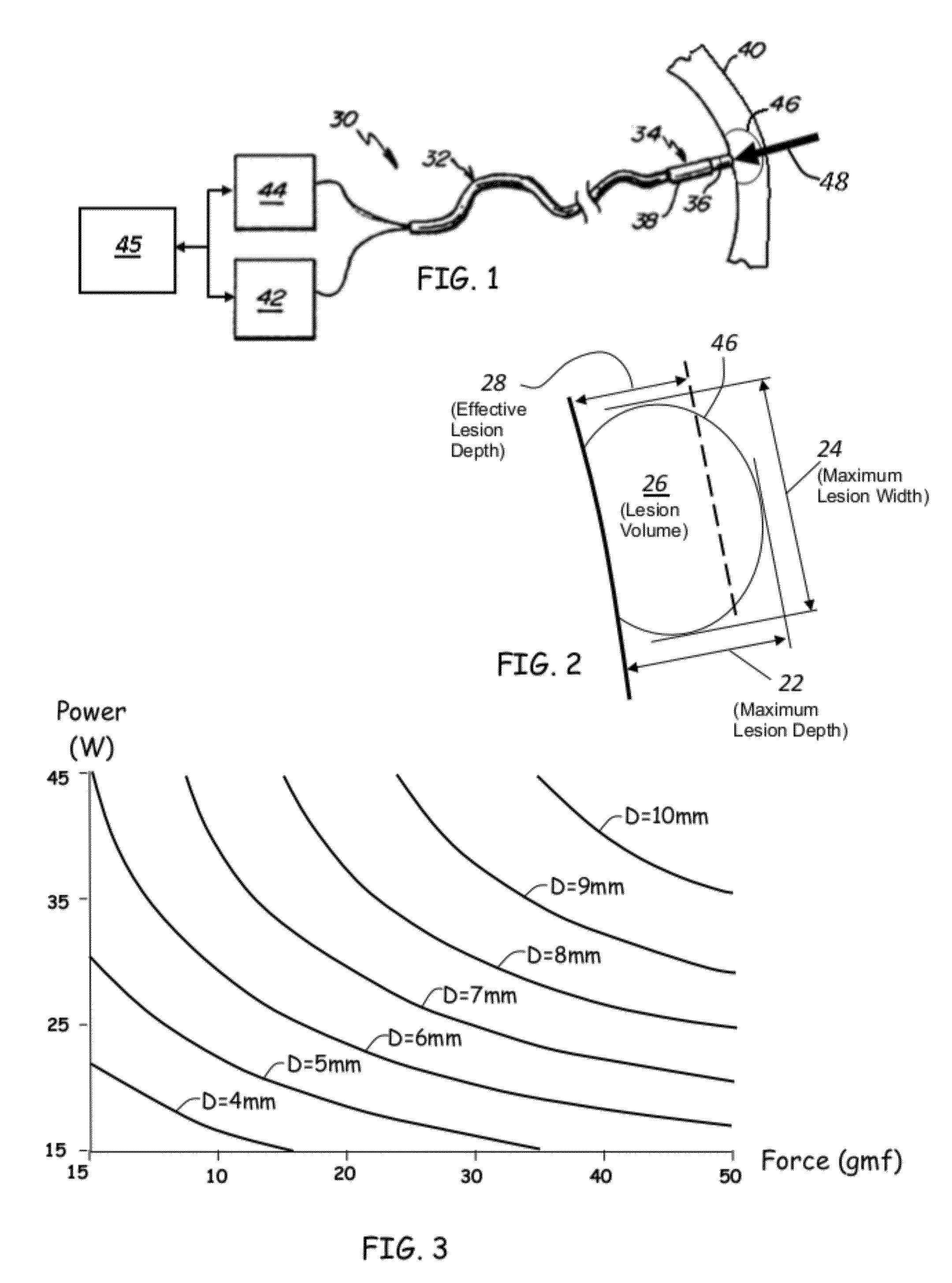
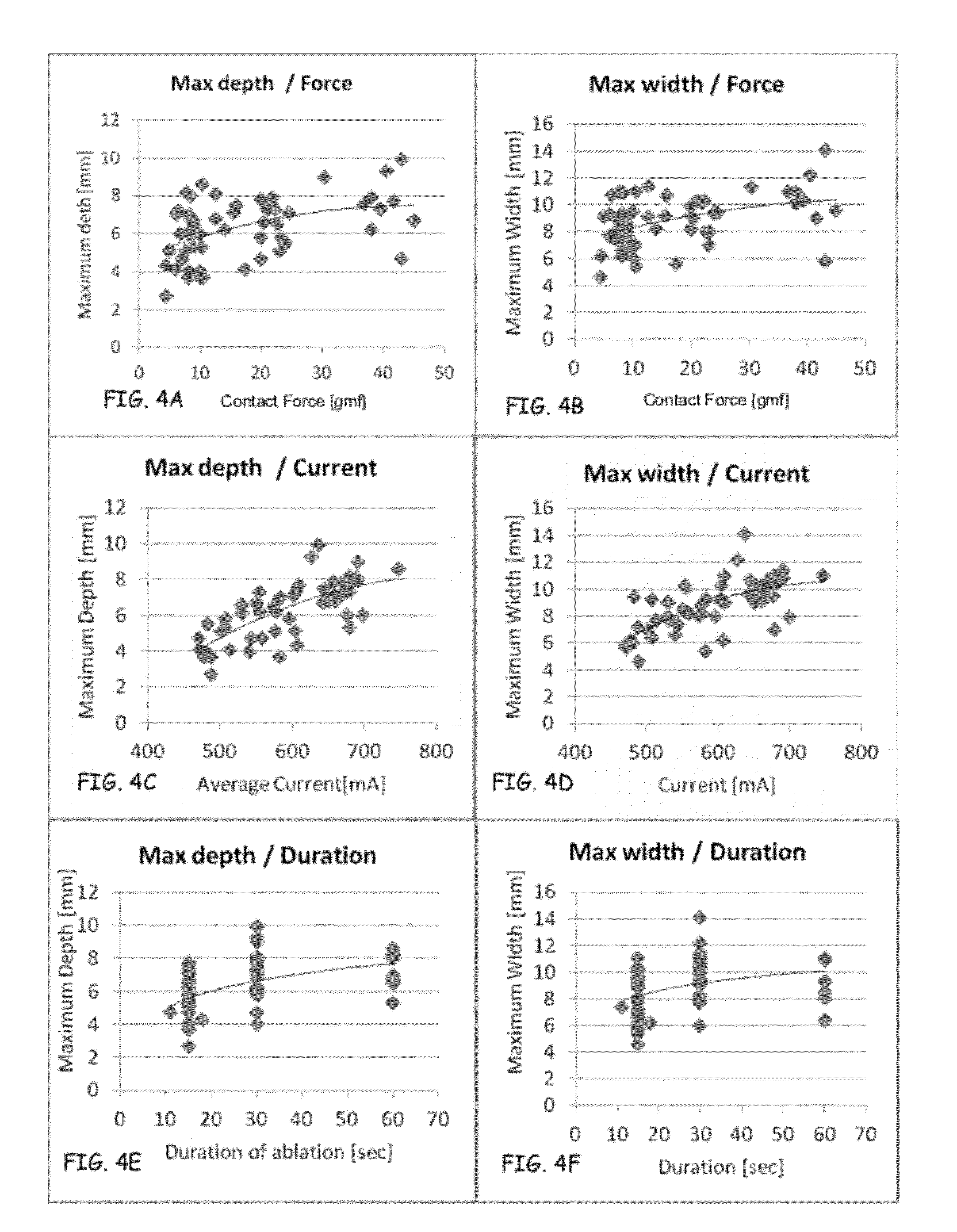
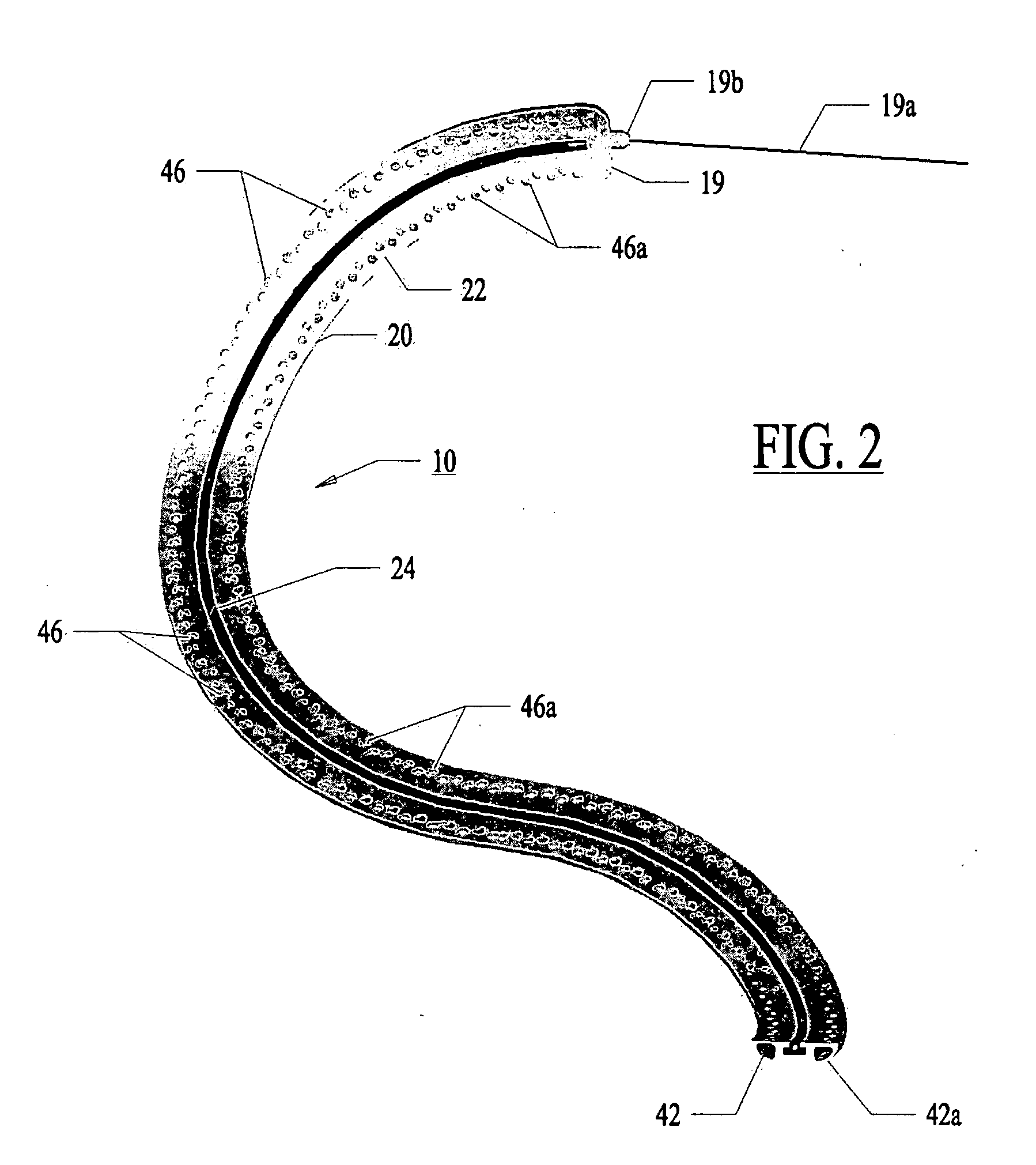
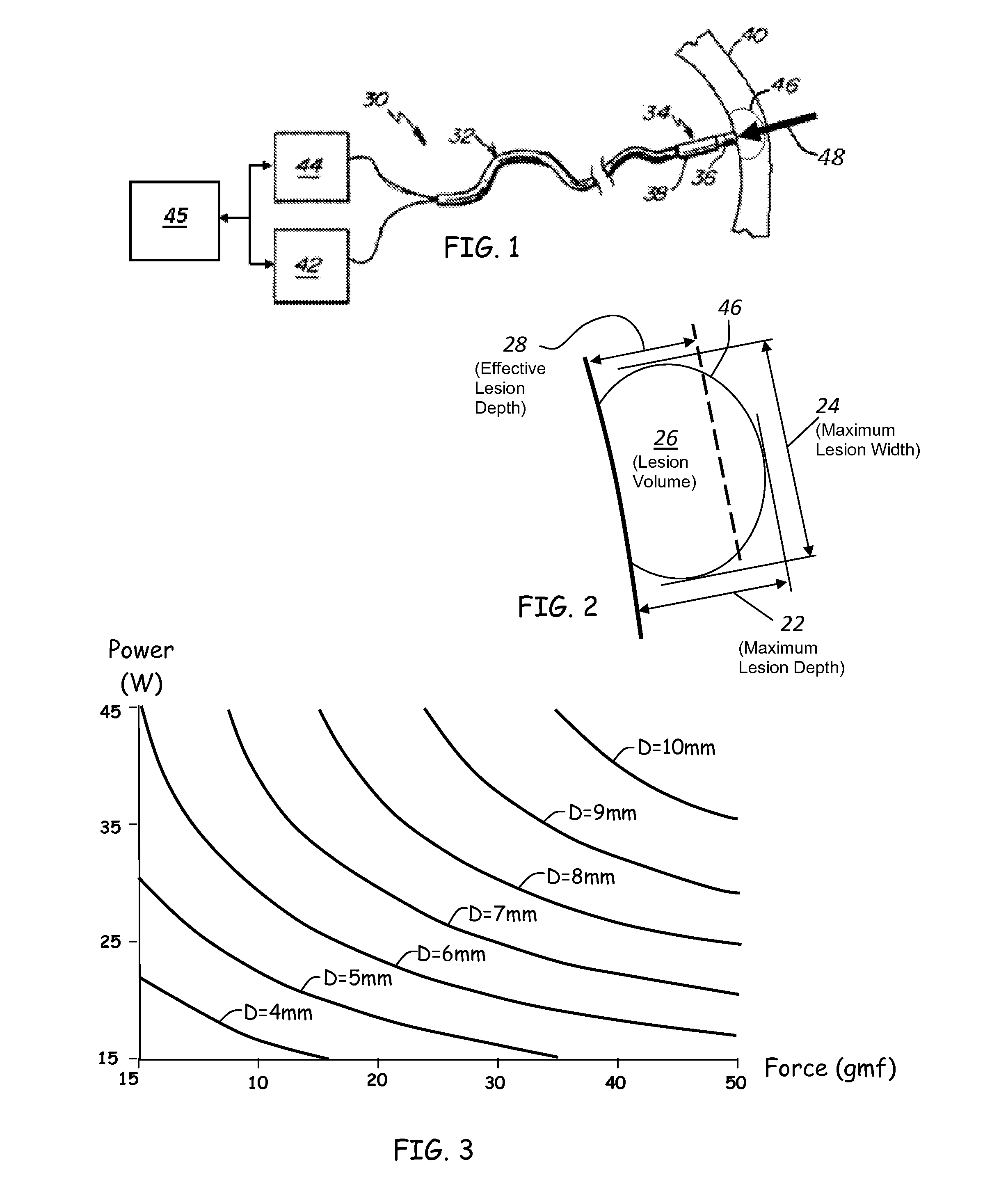
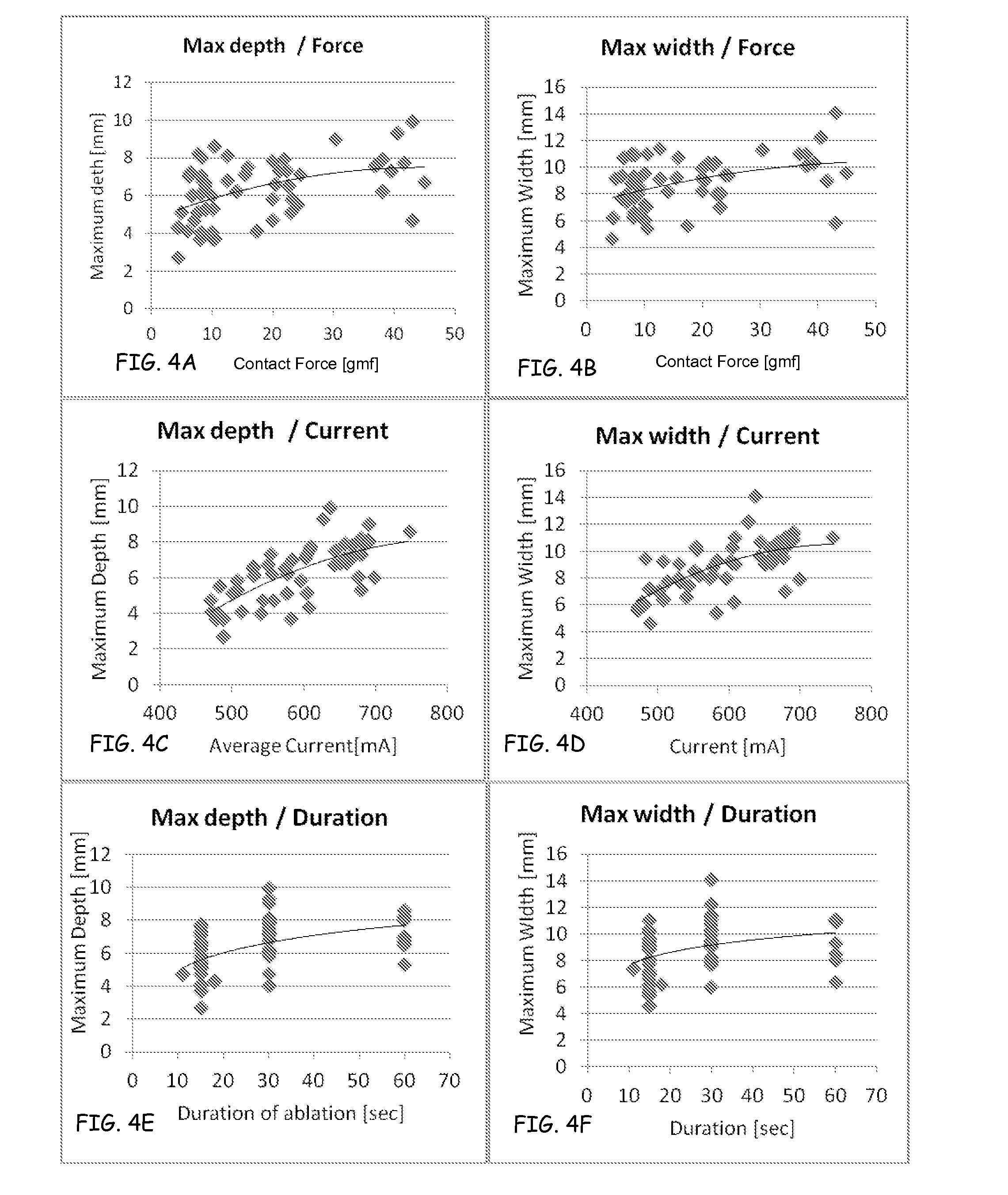
A method and device for determining the transmuriality and / or continuity of an isolation line formed by a plurality of point contact ablations. In one embodiment, a method for determining the size of a lesion (width, depth and / or volume) is disclosed, based on contact force of the ablation head with the target tissue, and an energization parameter that quantifies the energy delivered to the target tissue during the duration time of the lesion formation. In another embodiment, the sequential nature (sequence in time and space) of the ablation line formation is tracked and quantified in a quantity herein referred to as the “jump index,” and used in conjunction with the lesion size information to determine the probability of a gap later forming in the isolation line.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
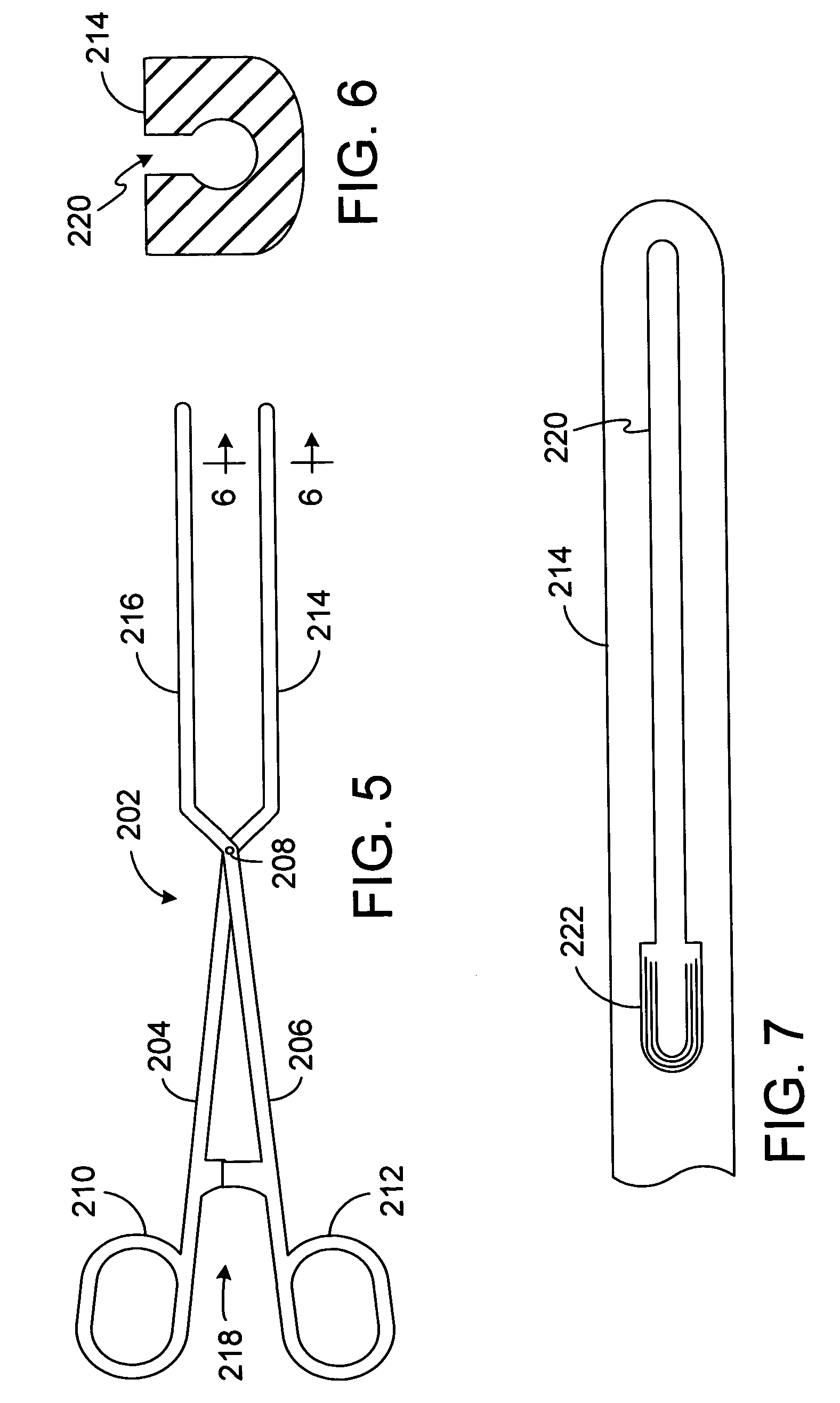
Apparatus and method for guided ablation treatment
InactiveUS7238179B2Improve visualizationEvenly distributedControlling energy of instrumentCatheterCardiac surfaceLesion formation
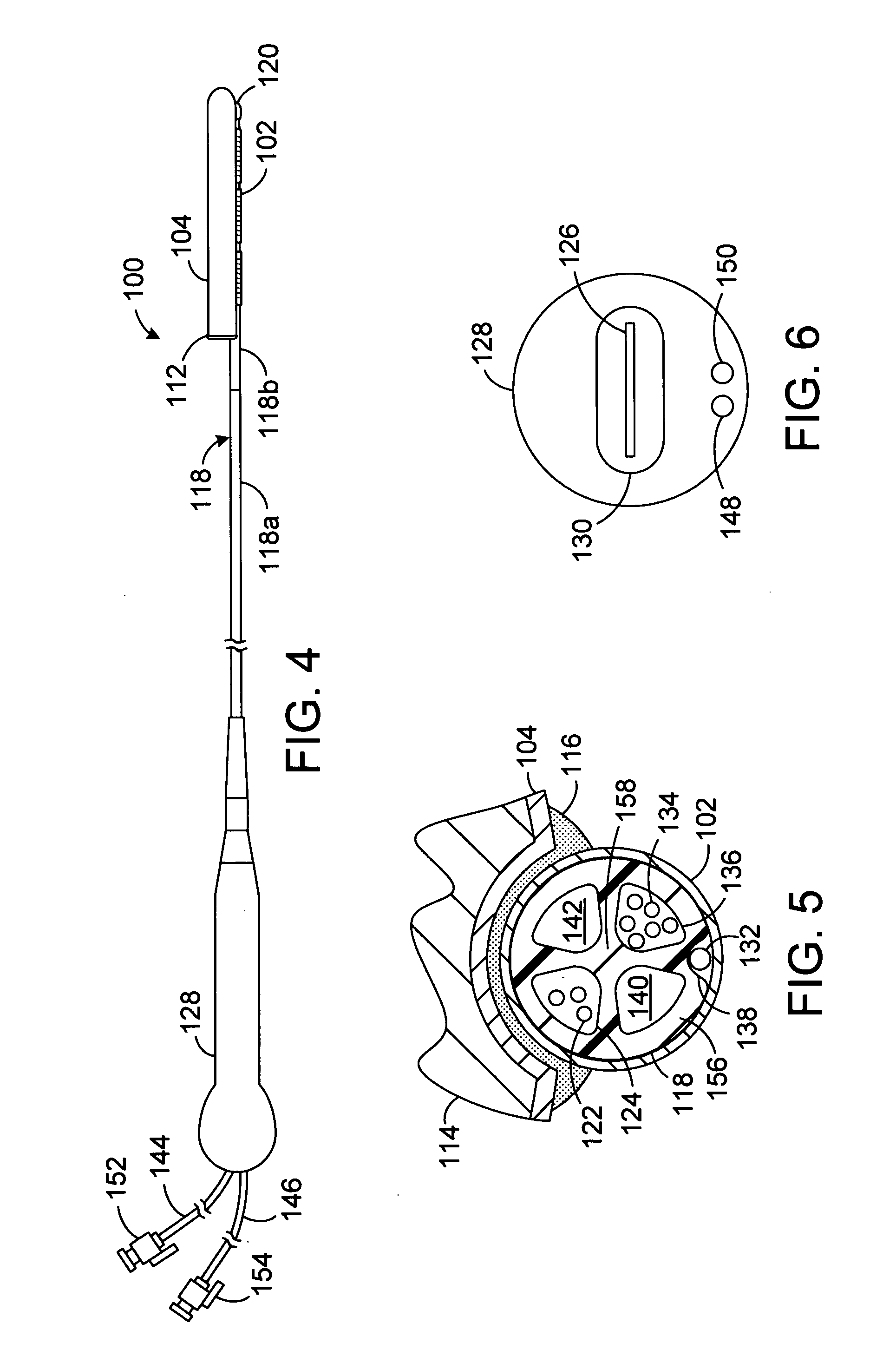
A method and apparatus for forming a lesion in tissue along a desired ablation path with treating a body tissue in situ (e.g., an atrial tissue of a heart to treat) atrial fibrillation include a lesion formation tool including is positioned against the heart surface. The lesion formation tool includes a guide member having a tissue-opposing surface for placement against a heart surface. An ablation member is coupled to the guide member to move in a longitudinal path relative to the guide member. The guide member includes a track. A carriage is slidably received with the track. The ablation member is secured to the carriage for movement therewith. The guide member includes a visualization component.
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
Guided ablation with end-fire fiber
A method and apparatus for treating a body tissue in situ (e.g., an atrial tissue of a heart to treat atrial fibrillation) include a lesion formation tool is positioned against the heart surface. The apparatus includes a guide member having a tissue-opposing surface for placement against a heart surface. The guide member also has interior surfaces and a longitudinal axis. A guide carriage is sized to be received with the guide member and moveable therein along the longitudinal axis. An optical fiber is positioned within the guide carriage with the carriage retaining the fiber. The carriage receives the fiber with an axis substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis and bends the fiber to a distal tip with an axis of said fiber at said distal tip at least 45 degrees to the longitudinal axis and aligned for discharge of laser energy through the tissue opposing surface.
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
Prediction of atrial wall electrical reconnection based on contact force measured during RF ablation
InactiveUS20160095653A1Easy to predictEffective isolation lineDiagnosticsCatheterRf ablationAtrial wall
A method and device for determining the transmurality and / or continuity of an isolation line formed by a plurality of point contact ablations. In one embodiment, a method for determining the size of a lesion (width, depth and / or volume) is disclosed, based on contact force of the ablation head with the target tissue, and an energization parameter that quantifies the energy delivered to the target tissue during the duration time of the lesion formation. In another embodiment, the sequential nature (sequence in time and space) of the ablation line formation is tracked and quantified in a quantity herein referred to as the “jump index,” and used in conjunction with the lesion size information to determine the probability of a gap later forming in the isolation line.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Controlled high efficiency lesion formation using high intensity ultrasound
InactiveUS20090036774A1Effective treatmentHigh strengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceTransducer
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
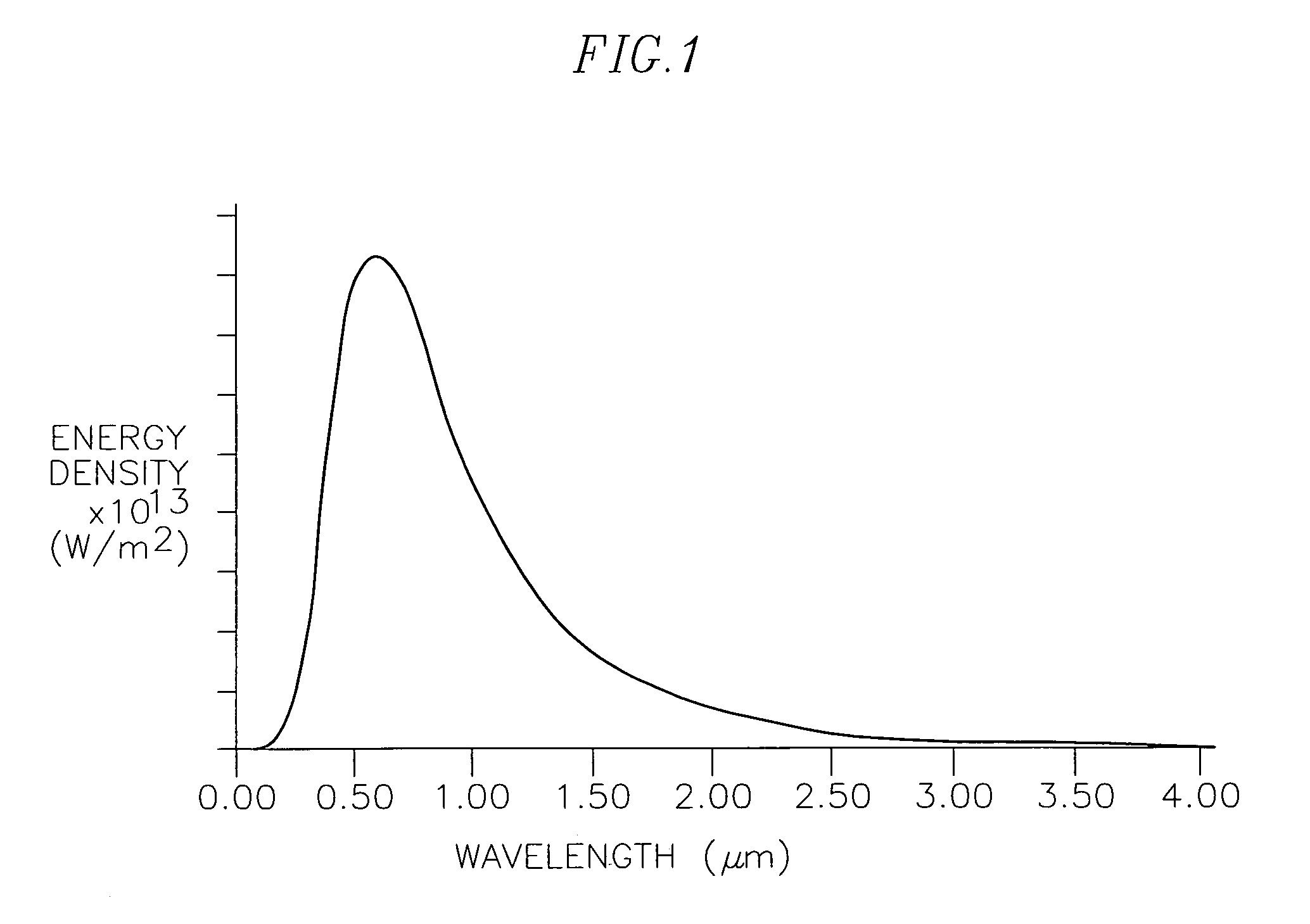
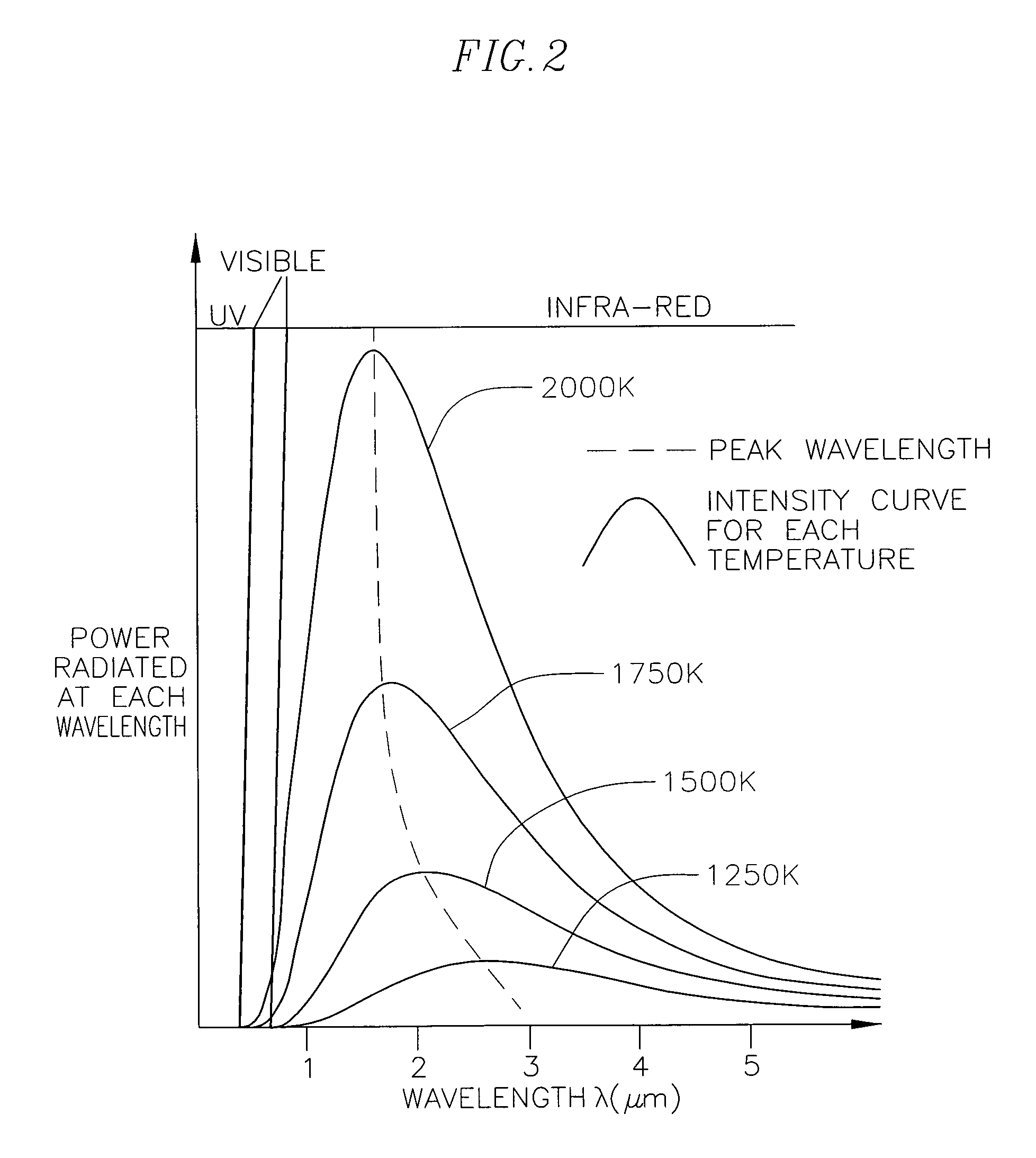
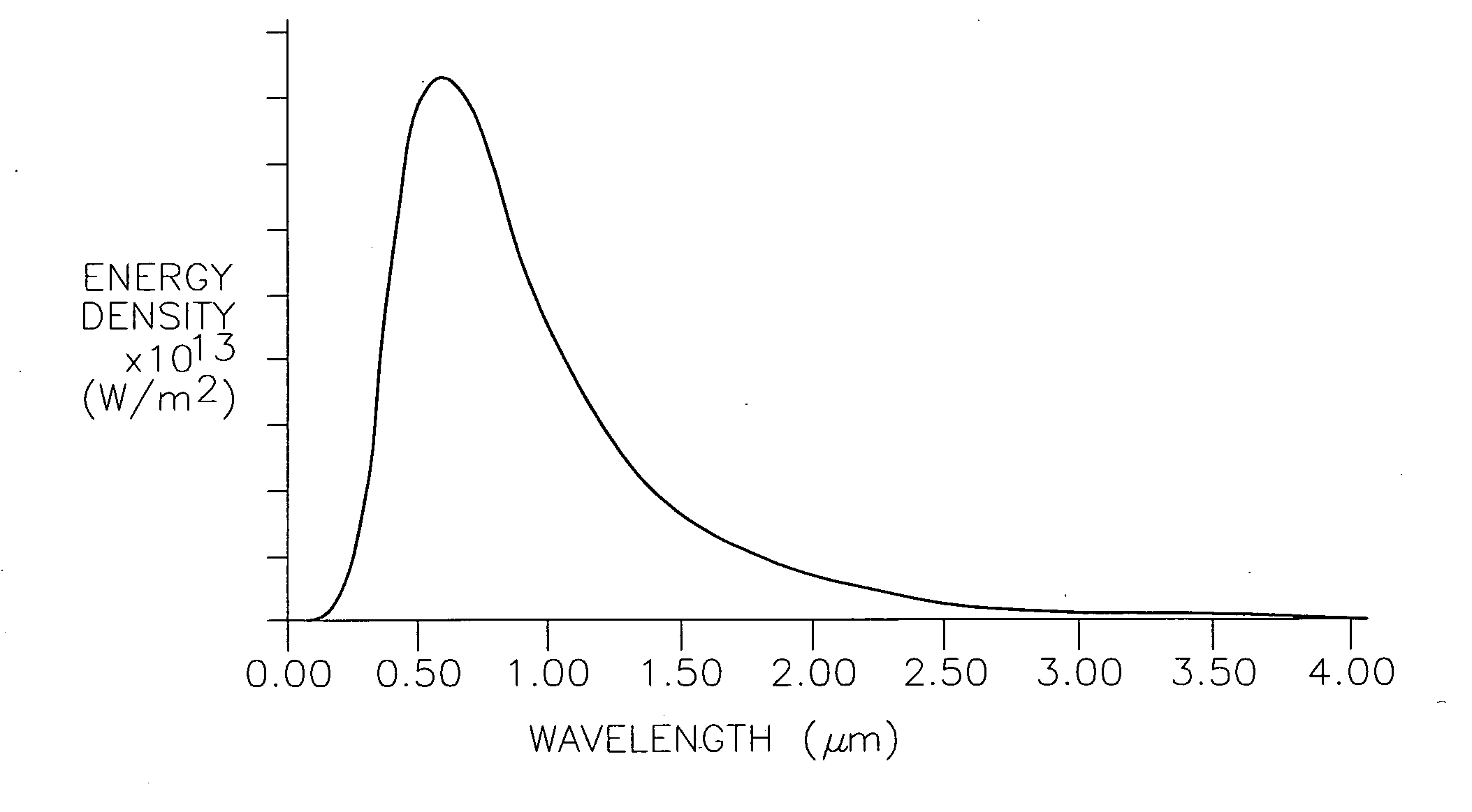
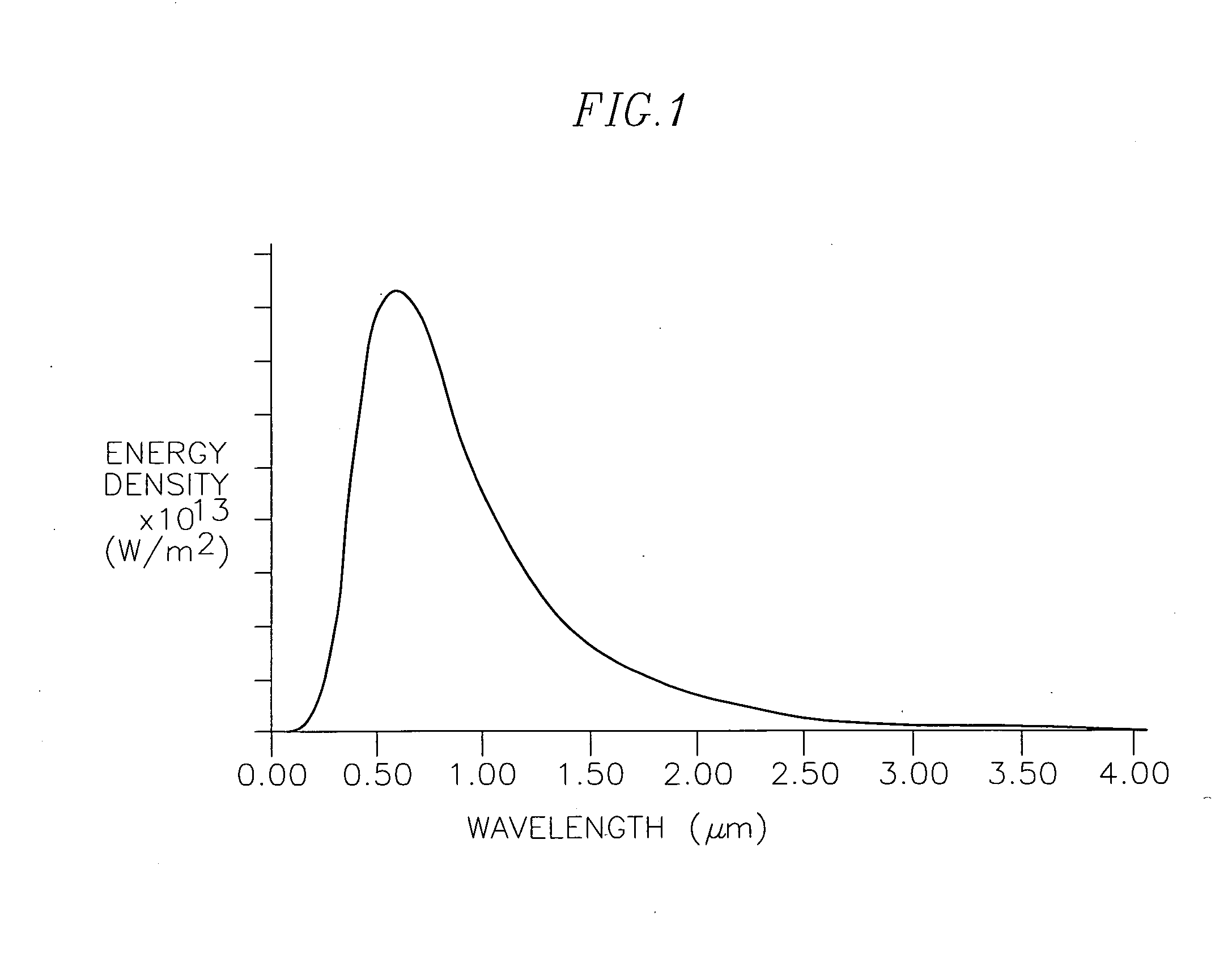
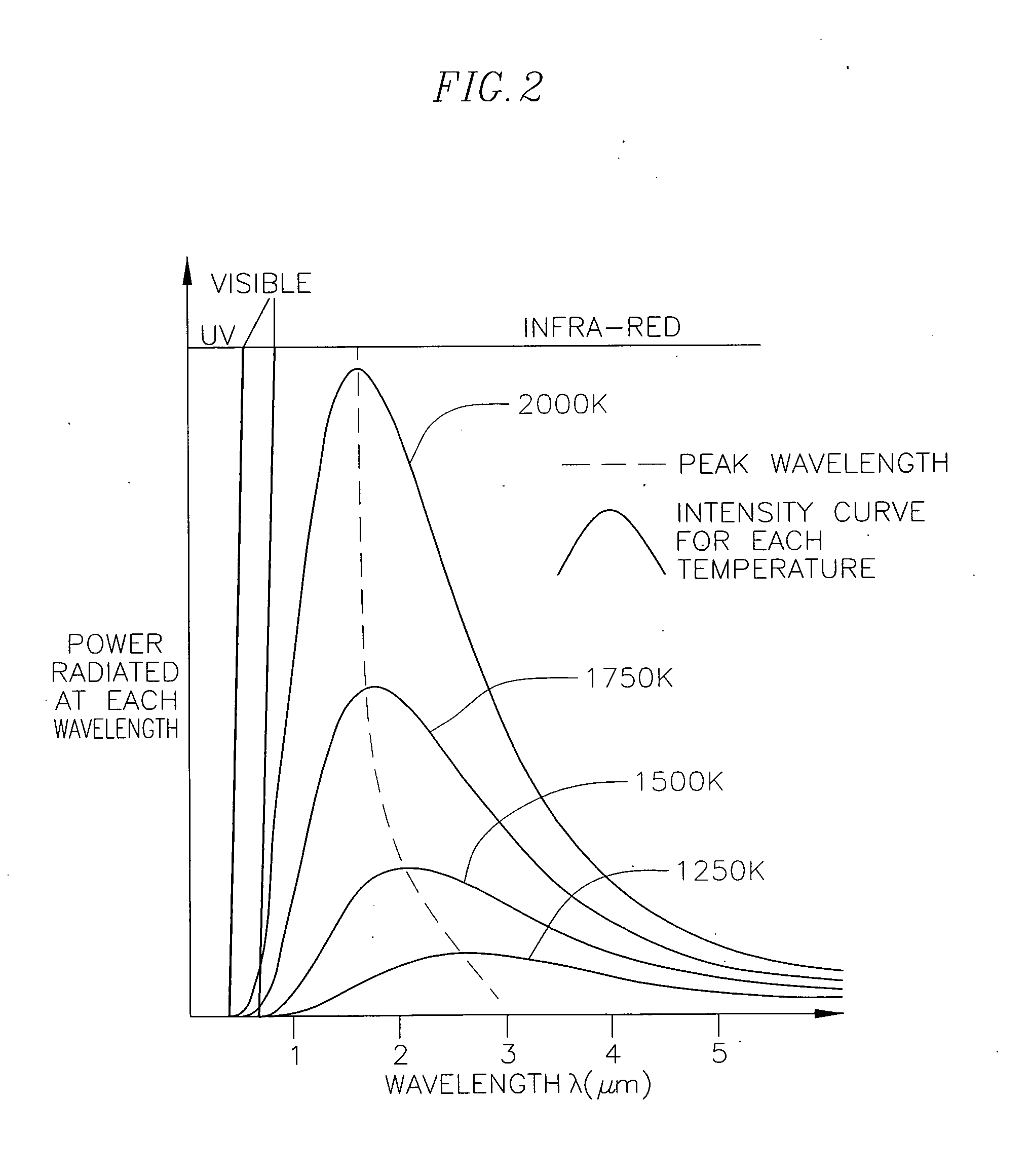
Optical pyrometric catheter for tissue temperature monitoring during cardiac ablation
A system for opto-pyrometric tissue temperature monitoring in real time. The system is adapted for cardiac ablation and tissue temperature measurement, having a catheter having a tip electrode adapted for RF ablation of cardiac tissue and an optical collector whose distal end is received in an opening formed in the tip electrode to detect black body radiation from the cardiac tissue. The system includes an optical detection system in communication with the optical collector, the optical processing system processing signals representative of a wavelength of at least a portion of the black body radiation to determine a tissue temperature. The incorporation of an optical collector within a catheter tip permits real time monitoring of tissue temperature during ablation and lesion formation to prevent critical thresholds in temperature associated with events that can damage tissue, including steam pop, thrombus, char, etc.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
System and method for presenting information representative of lesion formation in tissue during an ablation procedure
A method and system for presenting information representative of lesion formation is provided. The system comprises an electronic control unit (ECU). The ECU is configured to acquire a value for an ablation description parameter and / or a position signal metric, wherein the value corresponds to a location in the tissue. The ECU is further configured to evaluate the value, assign it a visual indicator of a visualization scheme associated with the parameter / metric corresponding to the value, and generate a marker comprising the visual indicator such that the marker is indicative of the acquired value. The method comprises acquiring a value for the parameter / metric, and evaluating the value. The method further includes assigning a visual indicator of a visualization scheme associated with the parameter / metric corresponding to the value, and generating a marker comprising the visual indicator.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Apparatus and method for guided ablation treatment
InactiveUS20050182392A1Improve visualizationEvenly distributedControlling energy of instrumentCatheterCardiac surfaceLesion formation
A method and apparatus for treating a body tissue in situ (e.g., an atrial tissue of a heart to treat) atrial fibrillation include a lesion formation tool is positioned against the heart surface. The lesion formation tool includes a guide member having a tissue-opposing surface for placement against a heart surface. An ablation member is coupled to the guide member to move in a longitudinal path relative to the guide member. The ablation member has an ablation element for directing ablation energy in an emitting direction away from the tissue-opposing surface. The guide member may be flexible to adjust a shape of the guide member for the longitudinal path to approximate the desired ablation path while maintaining the tissue-opposing surface against the heart surface. In one embodiment, the ablation member includes at least one radiation-emitting member disposed to travel in the longitudinal pathway. In another embodiment, the guide member has a plurality of longitudinally spaced apart tissue attachment locations with at least two being separately activated at the selection of an operator to be attached and unattached to an opposing tissue surface. Various means are described for the attachment including vacuum and mechanical attachment. The guide member may have a steering mechanism to remotely manipulate the shape of the guide member.
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
Catheter with omni-directional optical lesion evaluation
ActiveUS8628520B2Improve lesionExtended service lifeDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsLight energyPositive pressure
A catheter is adapted to ablate tissue and provide lesion qualitative information on a real time basis, having an ablation tip section with a generally omni-directional light diffusion chamber with one openings to allow light energy in the chamber to radiate the tissue and return to the chamber. The chamber is irrigated at a positive pressure differential to continuously flush the opening with fluid. The light energy returning to the chamber from the tissue conveys a tissue parameter, including without limitation, lesion formation, depth of penetration of lesion, cross-sectional area of lesion, formation of char during ablation, recognition of char during ablation, recognition of char from non-charred tissue, formation of coagulum around the ablation site, differentiation of coagulated from non-coagulated blood, differentiation of ablated from healthy tissue, tissue proximity, and recognition of steam formation in the tissue for prevention of steam pop.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Distal balloon impedance and temperature recording to monitor pulmonary vein ablation and occlusion
ActiveUS20150157382A1Real-time and accurate assessmentReal-time and accurate and monitoringCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingPulmonary vein ablationFar infrared
A cryoablation method, system, and device that allows for real-time and accurate assessment and monitoring of PV occlusion and lesion formation without the need for expensive imaging systems and without patient exposure to radiation. The system includes a cryoballoon catheter with a cryoballoon, a distal electrode, a proximal electrode, and a temperature sensor. Impedance measurements recorded by the electrodes may be used to predict ice formation, quality of pulmonary vein occlusion, and lesion formation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Systems and methods of photodynamic-based cardiac ablation via the esophagus
InactiveUS7996078B2Large incisionLess invasiveElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsCardiac AblationCatheter
Systems and methods for photodynamic ablation of cardiac tissue via an esophagus are disclosed. An exemplary system includes an ablation catheter having an expandable distal end for securing the ablation catheter in the esophagus. The distal end of the ablation catheter contains at least one light source operable to activate a photodynamic substance delivered to the target area of the cardiac tissue to be ablated and form a lesion. The system also includes at least one feedback device contained in the distal end of the ablation catheter. The at least one feedback device provides feedback for at least one of: positioning a distal end of an ablation catheter in a desired position in the esophagus adjacent a target area of the cardiac tissue to be ablated, forming an adequate lesion, and assessing lesion formation.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Optical Pyrometric Catheter for Tissue Temperature Monitoring During Cardiac Ablation
InactiveUS20090005771A1Avoid temperatureCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringRf ablationDamages tissue
A system for opto-pyrometric tissue temperature monitoring in real time. The system is adapted for cardiac ablation and tissue temperature measurement, having a catheter having a tip electrode adapted for RF ablation of cardiac tissue and an optical collector whose distal end is received in an opening formed in the tip electrode to detect black body radiation from the cardiac tissue. The system includes an optical detection system in communication with the optical collector, the optical processing system processing signals representative of a wavelength of at least a portion of the black body radiation to determine a tissue temperature. The incorporation of an optical collector within a catheter tip permits real time monitoring of tissue temperature during ablation and lesion formation to prevent critical thresholds in temperature associated with events that can damage tissue, including steam pop, thrombus, char, etc.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
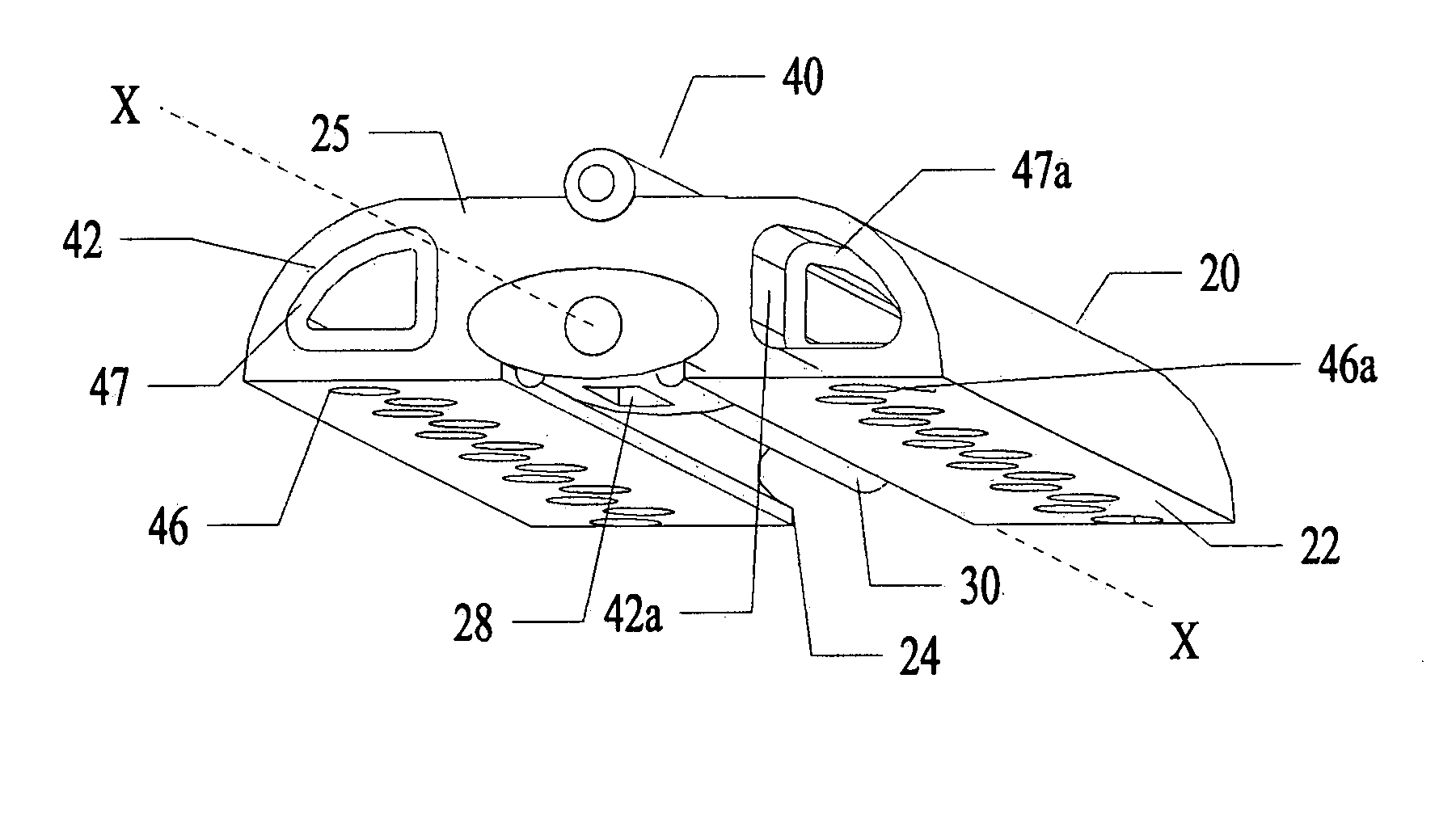
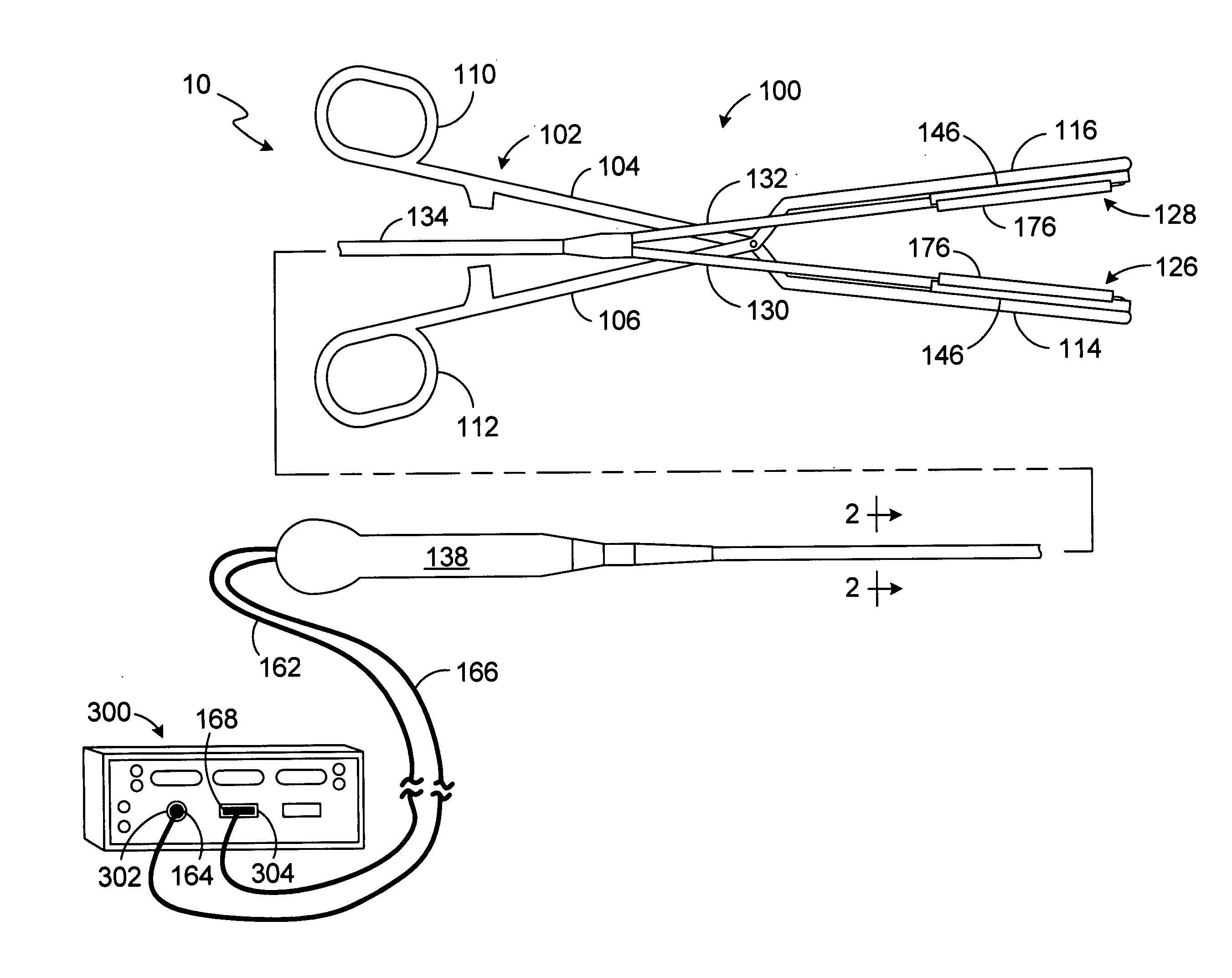
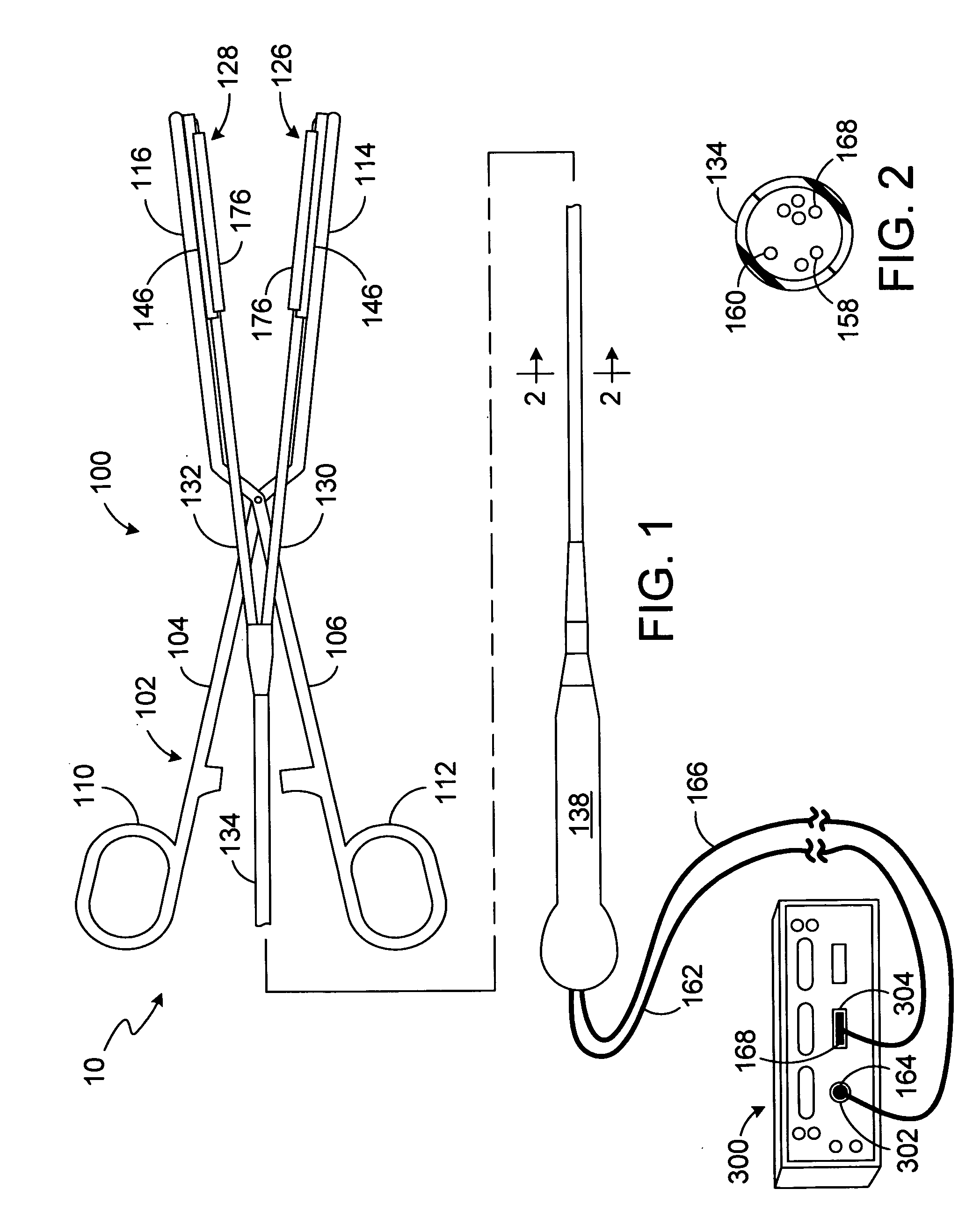
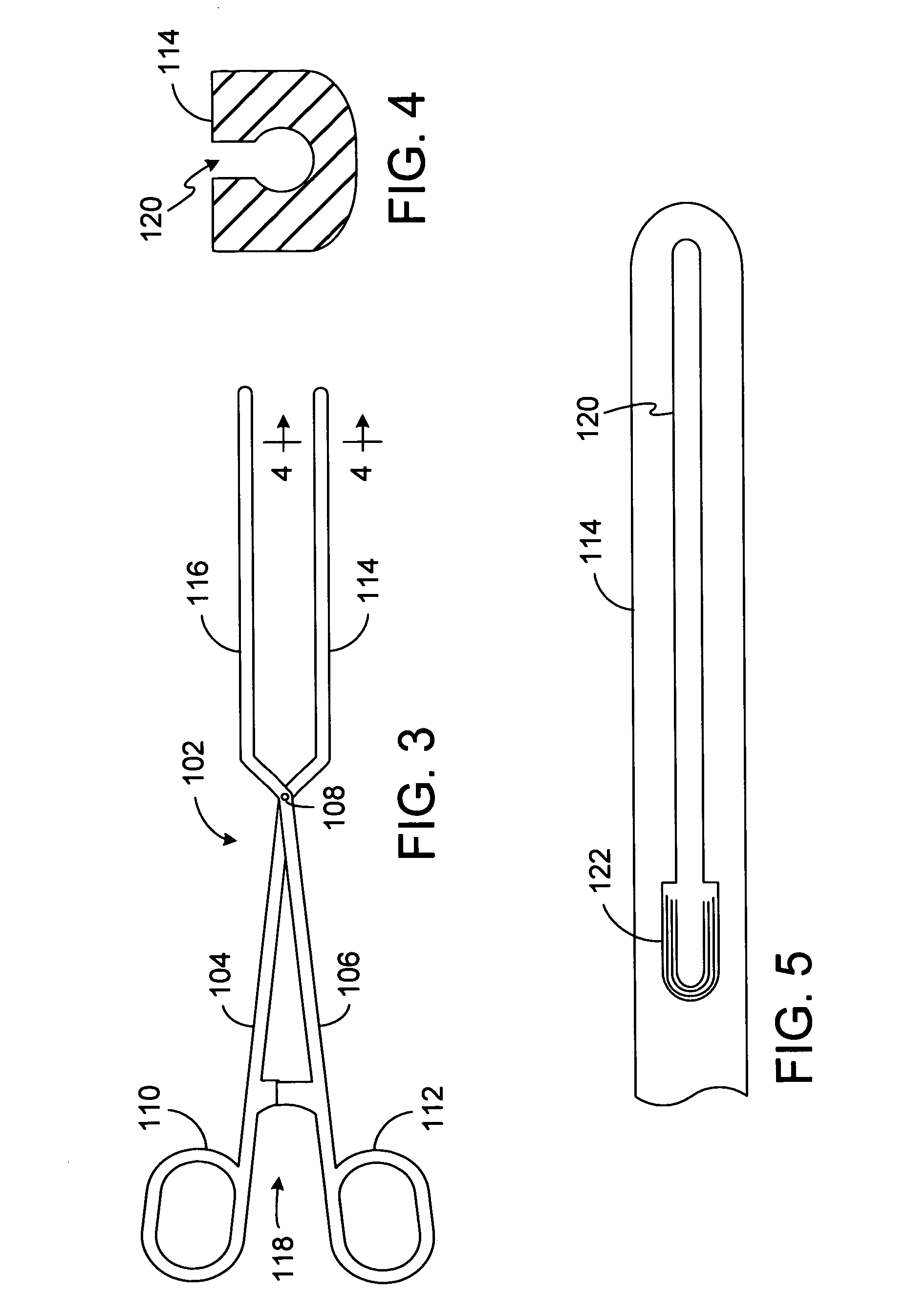
Hybrid lesion formation apparatus, systems and methods
A hybrid lesion formation apparatus including a surgical probe component and clamp component that share a common electrical connector.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Assessment of lesion transmurality
InactiveUS20050209589A1Improve visualizationEvenly distributedControlling energy of instrumentCatheterMedicineCardiac surface
A method and apparatus for treating a body tissue in situ (e.g., an atrial tissue of a heart to treat) atrial fibrillation include a lesion formation tool is positioned against the heart surface. The lesion formation tool includes a guide member having a tissue-opposing surface for placement against a heart surface. An ablation member is coupled to the guide member to move in a longitudinal path relative to the guide member. The ablation member has an ablation element for directing ablation energy in an emitting direction away from the tissue-opposing surface. The guide member may be flexible to adjust a shape of the guide member for the longitudinal path to approximate the desired ablation path while maintaining the tissue-opposing surface against the heart surface. In one embodiment, the ablation member includes at least one radiation-emitting member disposed to travel in the longitudinal pathway. Transmurality can be assessed to approximate a location of non-transmurality in a formed lesion.
Owner:ENDOPHOTONIX
Real-time lesion formation assessment
A method and system for creating permanent lesions in an area of target tissue, such as tissue at or proximate a junction between a pulmonary vein and the left atrium. The method may generally include positioning a medical device in contact with a pulmonary vein ostium, ablating the tissue, and recording a plurality of temperature measurements from one or more of three temperature sensors. The device may include an occlusion element in communication with a coolant source, a first sensor located distal of the occlusion element, a second sensor located proximal of the occlusion element, and a third sensor located in the occlusion element. One or more temperature measurements may be compared with each other to assess occlusion of the pulmonary vein, and / or may be compared with a set of reference temperatures to predict a real-time temperature within the target tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Clamp based lesion formation apparatus with variable spacing structures
ActiveUS20060155274A1Not to damageImprove conductivitySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsEngineeringLesion formation
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Clamp based lesion formation apparatus and methods configured to protect non-target tissue
ActiveUS7785324B2Avoid damageSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsLesion formationTarget tissue
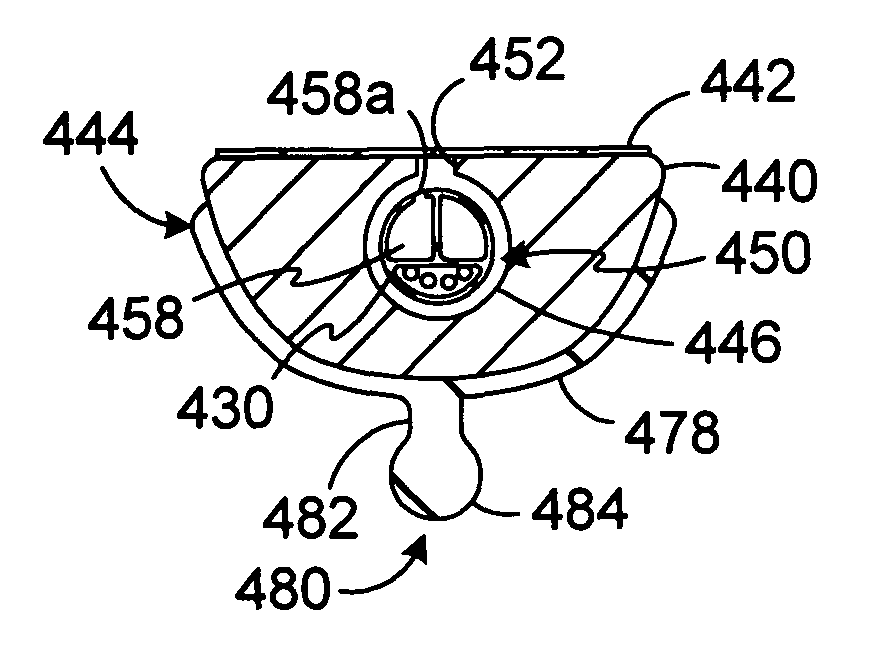
Apparatus, systems and methods for forming lesions in target tissue and positioning an insulation element adjacent to non-target tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com