Patents
Literature
35 results about "Plain old telephone system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
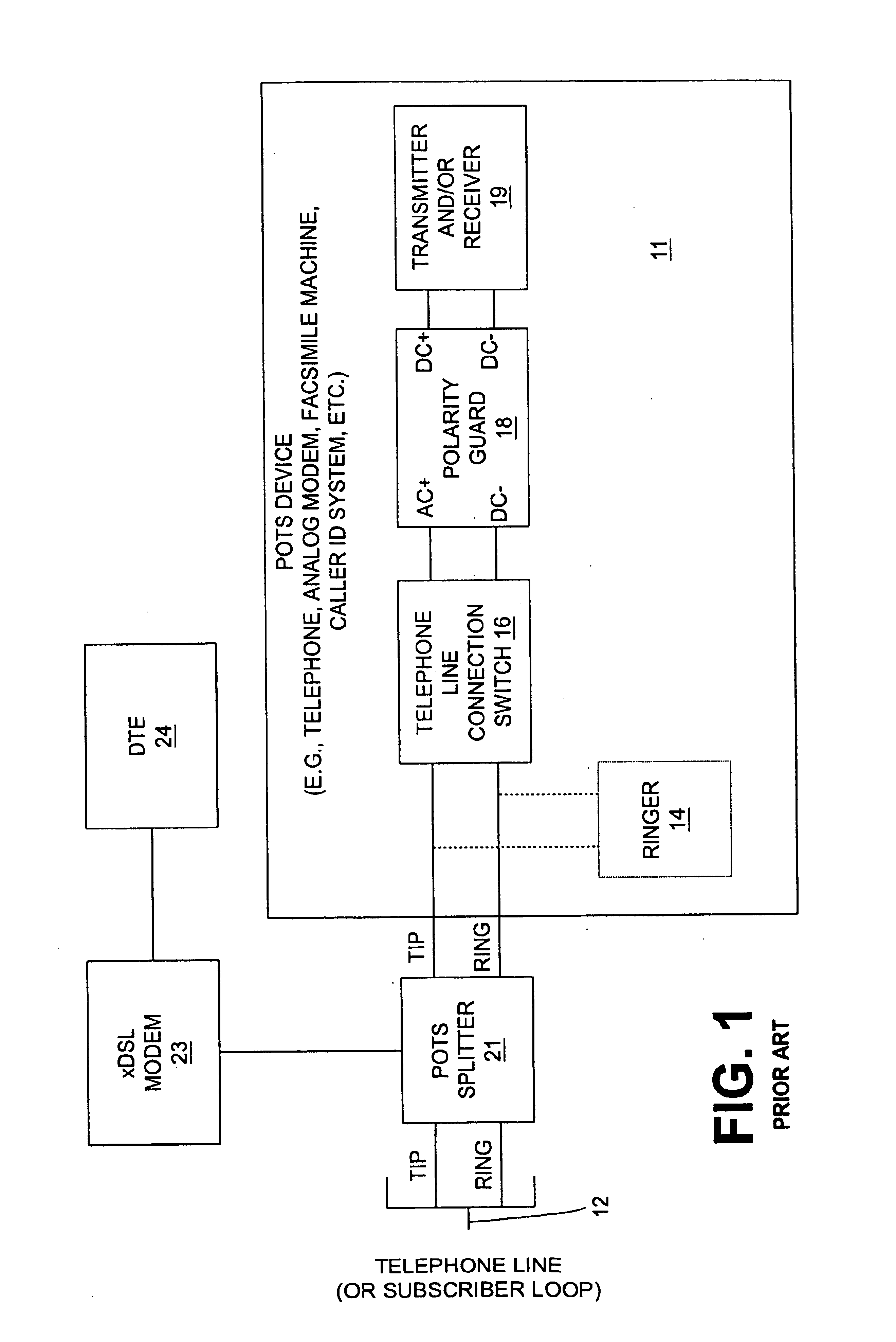
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) Definition - What does Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) mean? Plain old telephone service (POTS) is an analog telephone service implemented over copper twisted pair wires and based on the Bell Telephone system. This system connects homes and businesses to neighborhood central offices.
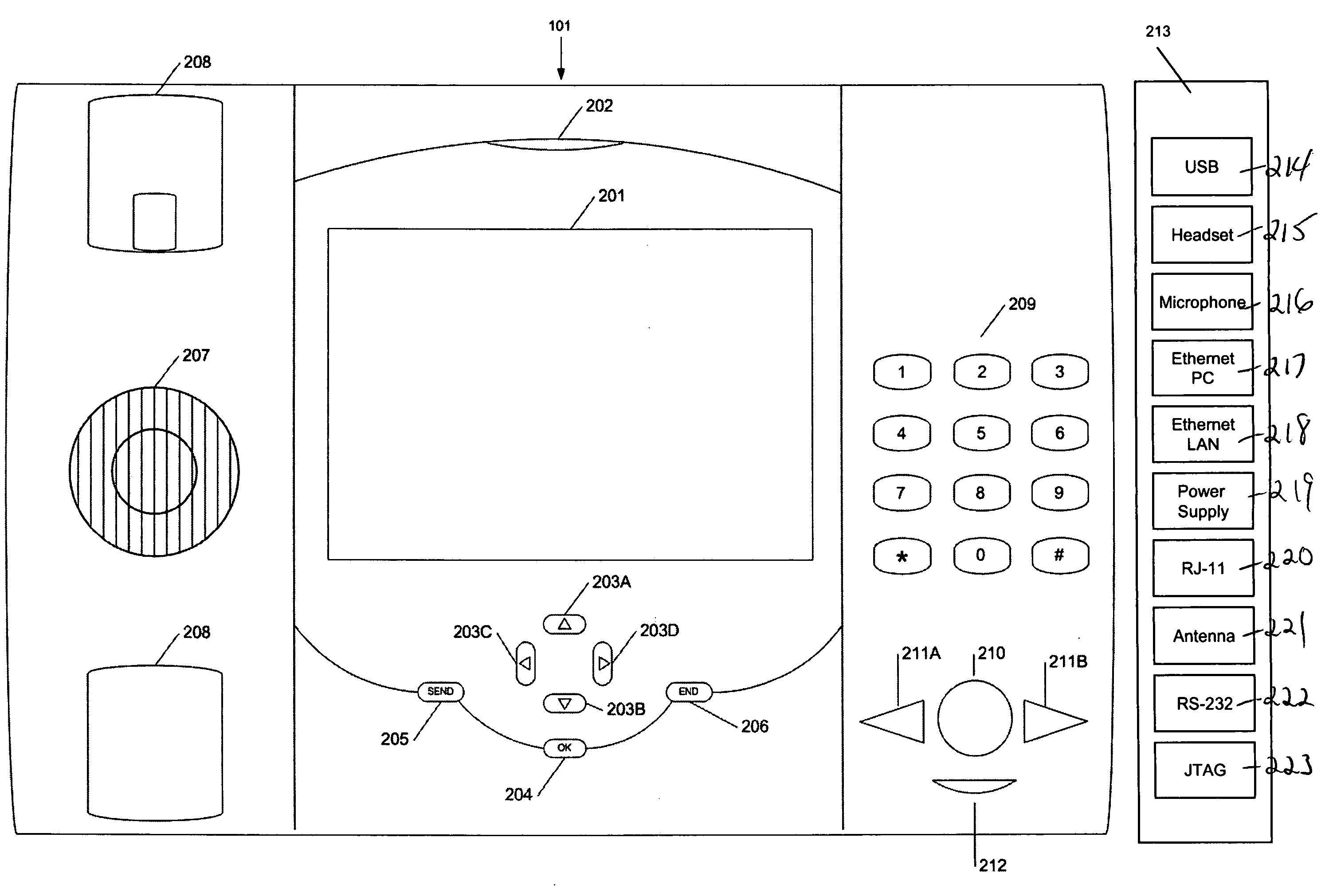
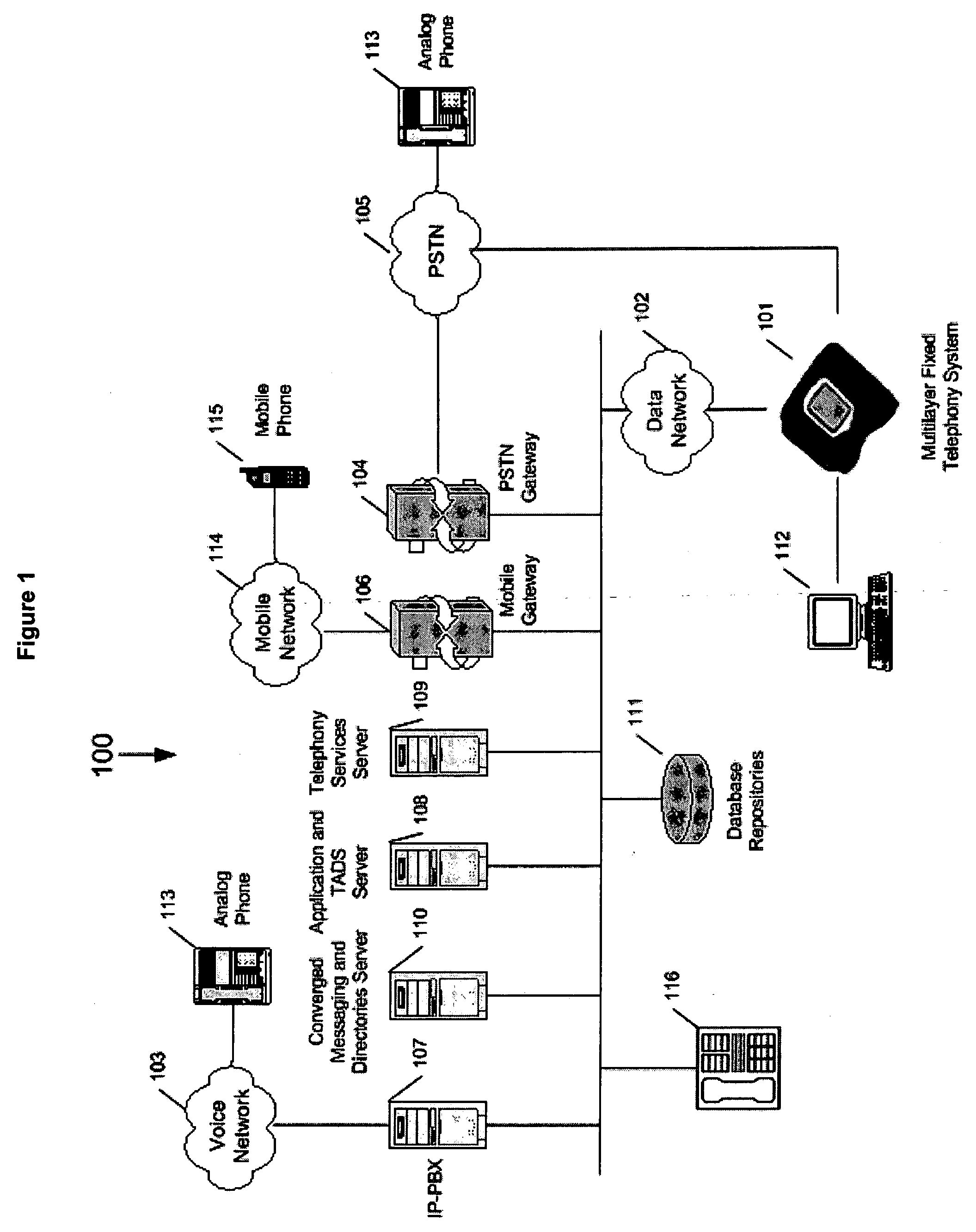
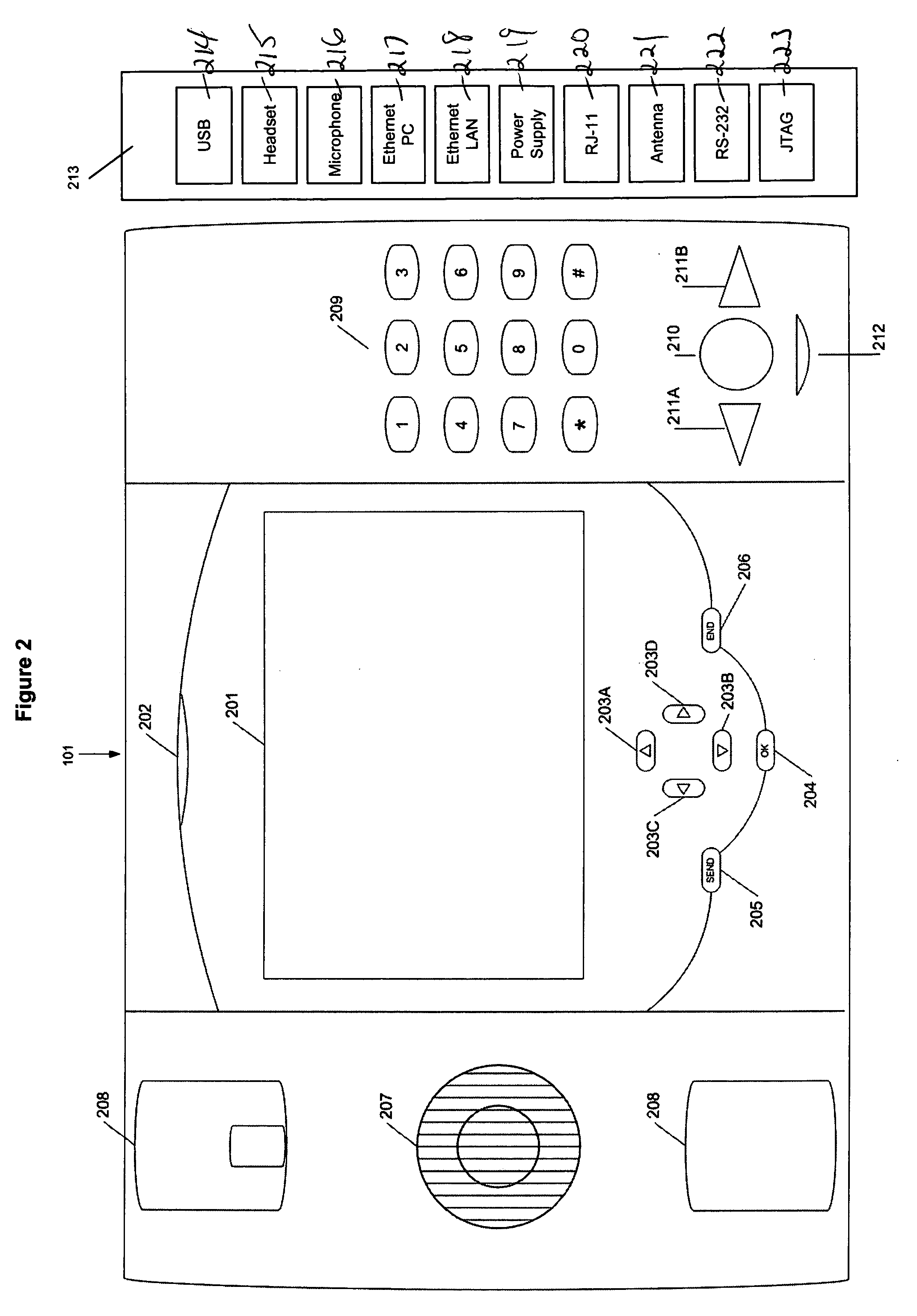
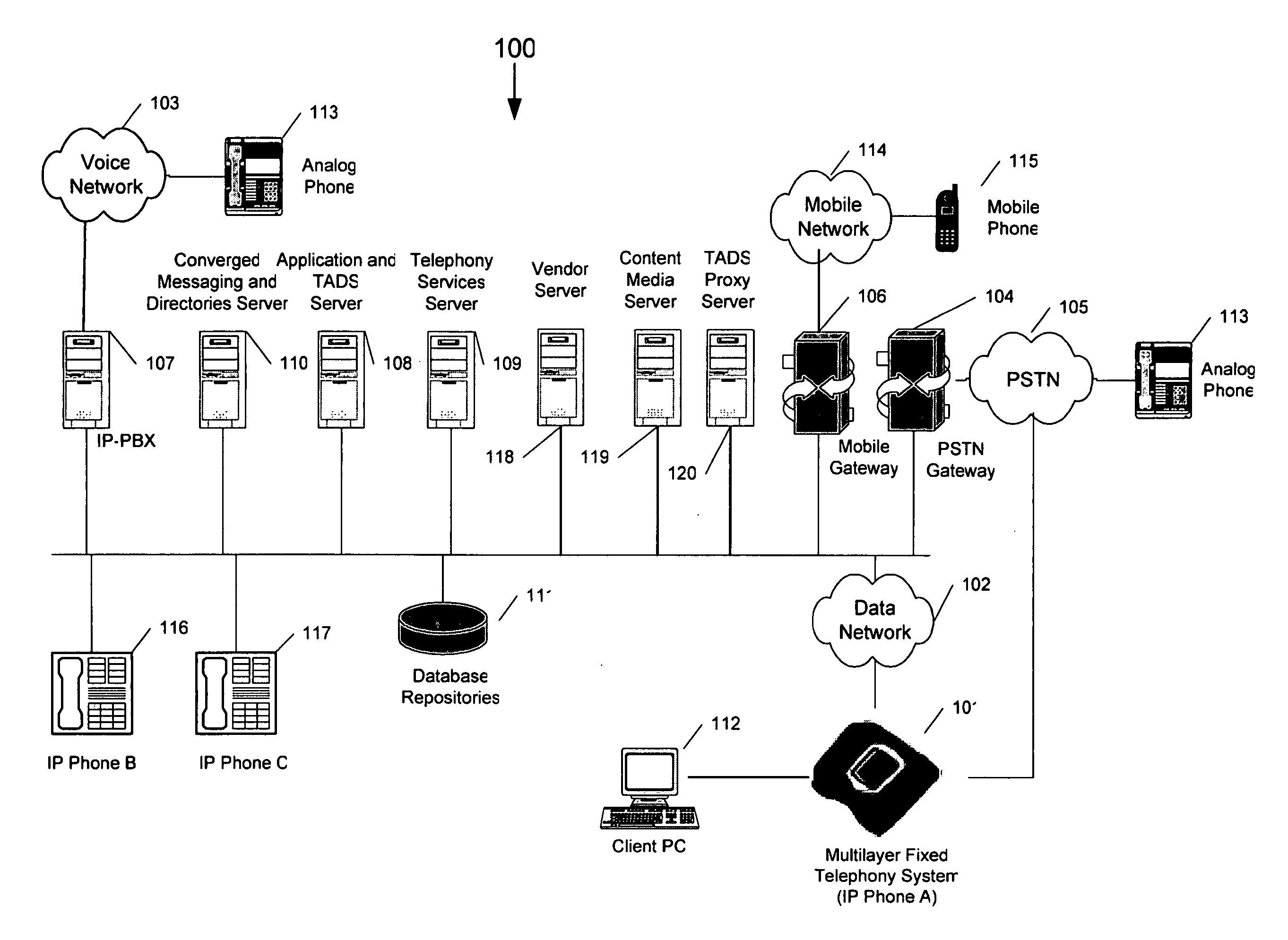
Internet protocol (IP) phone with search and advertising capability
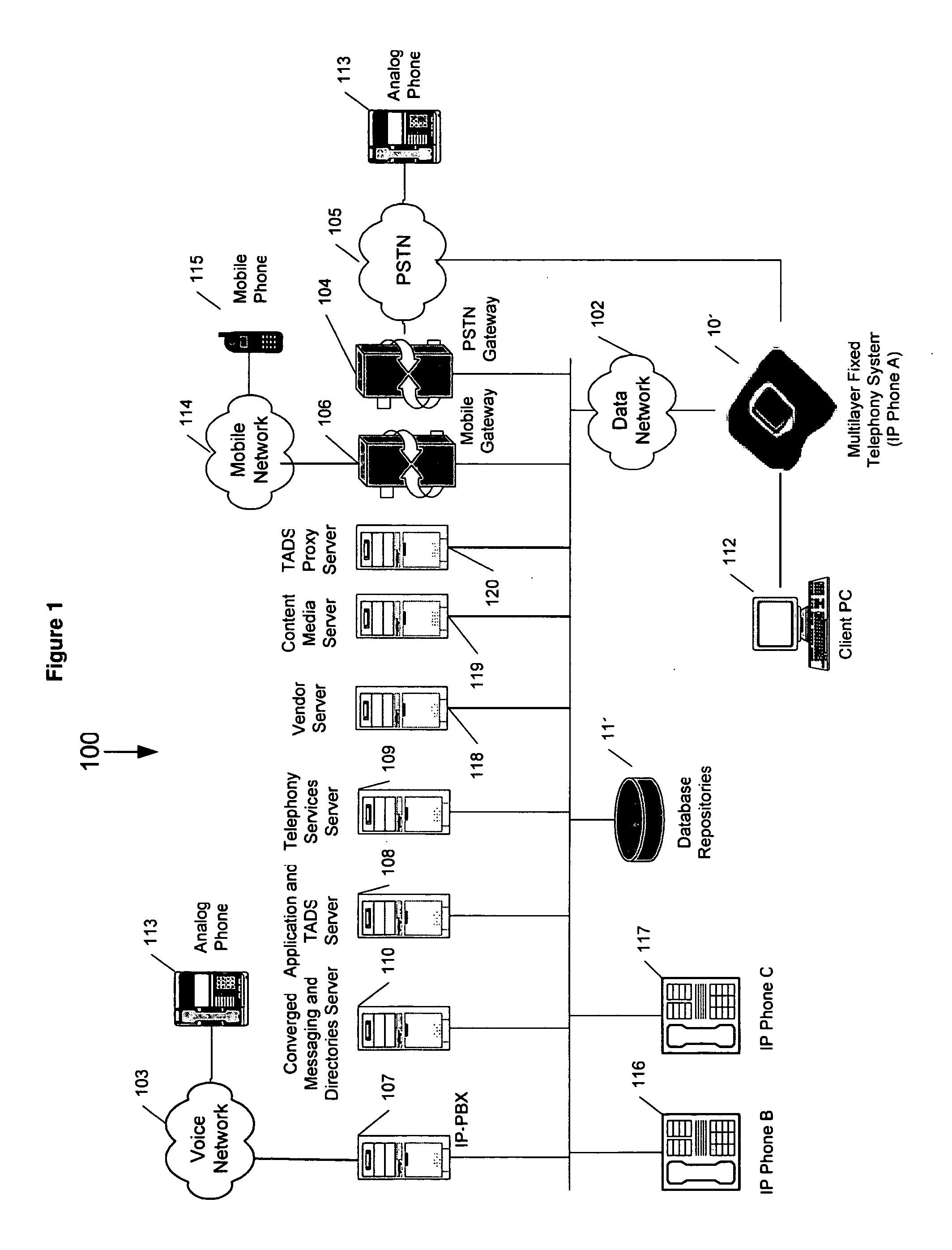
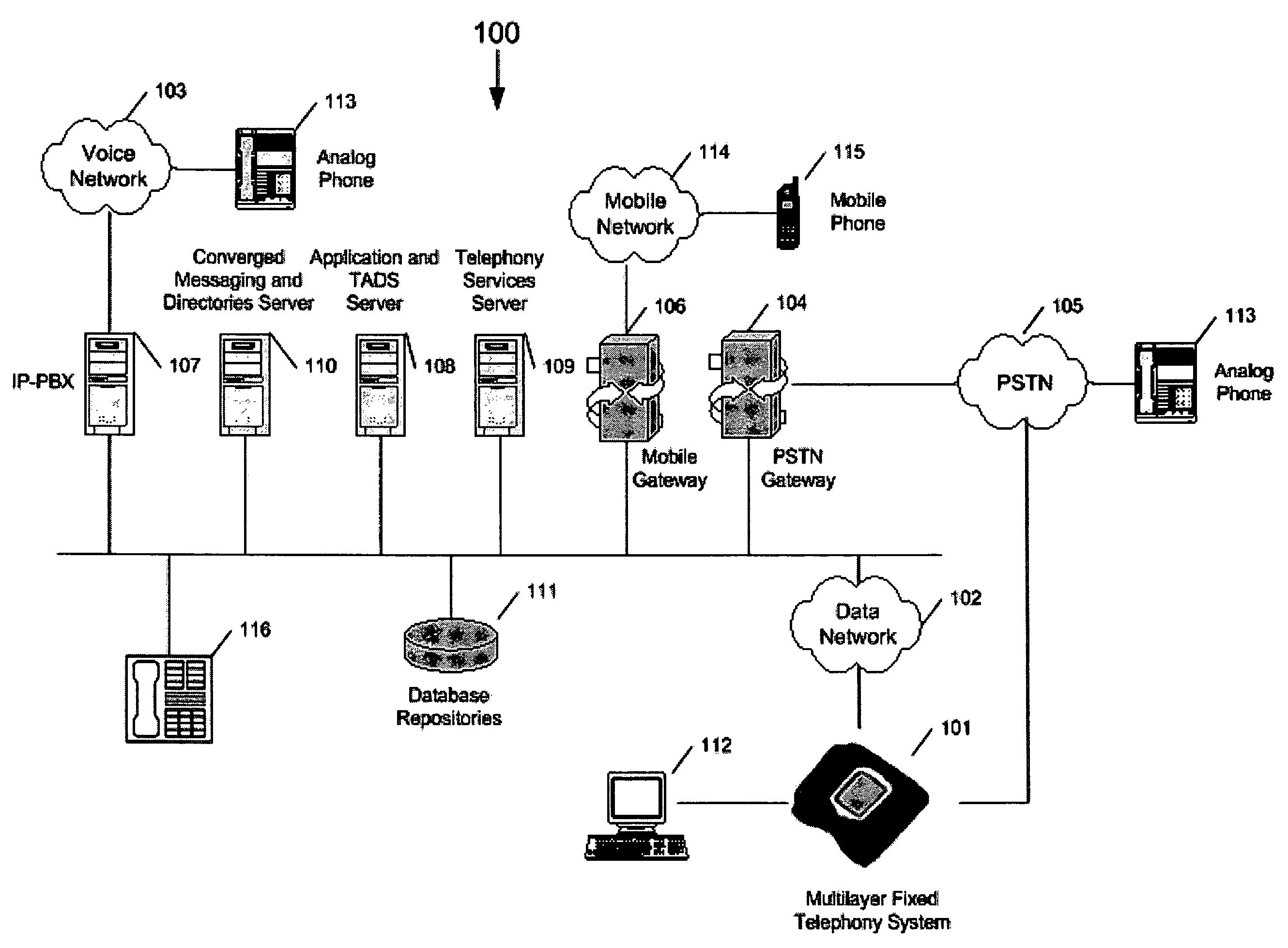
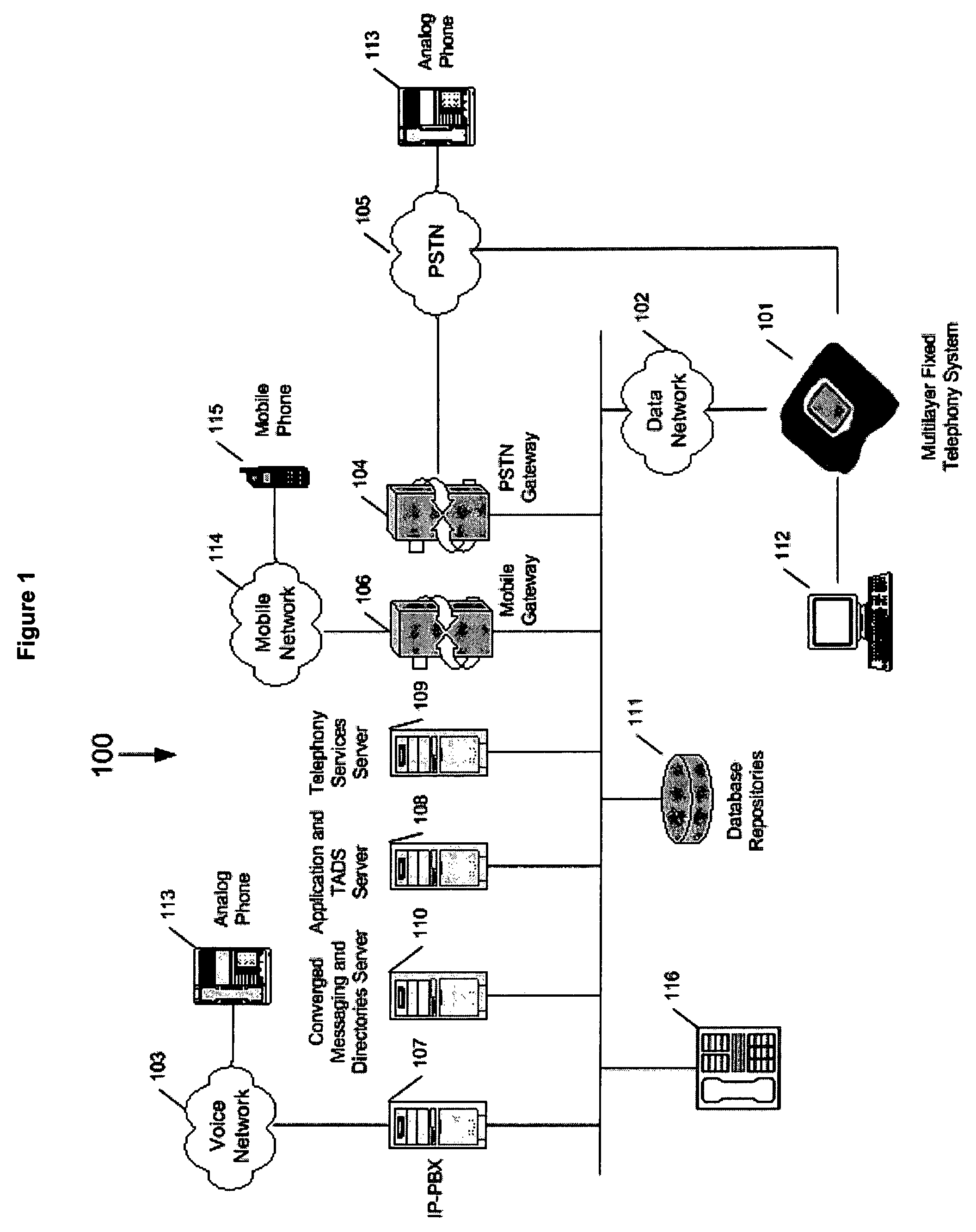
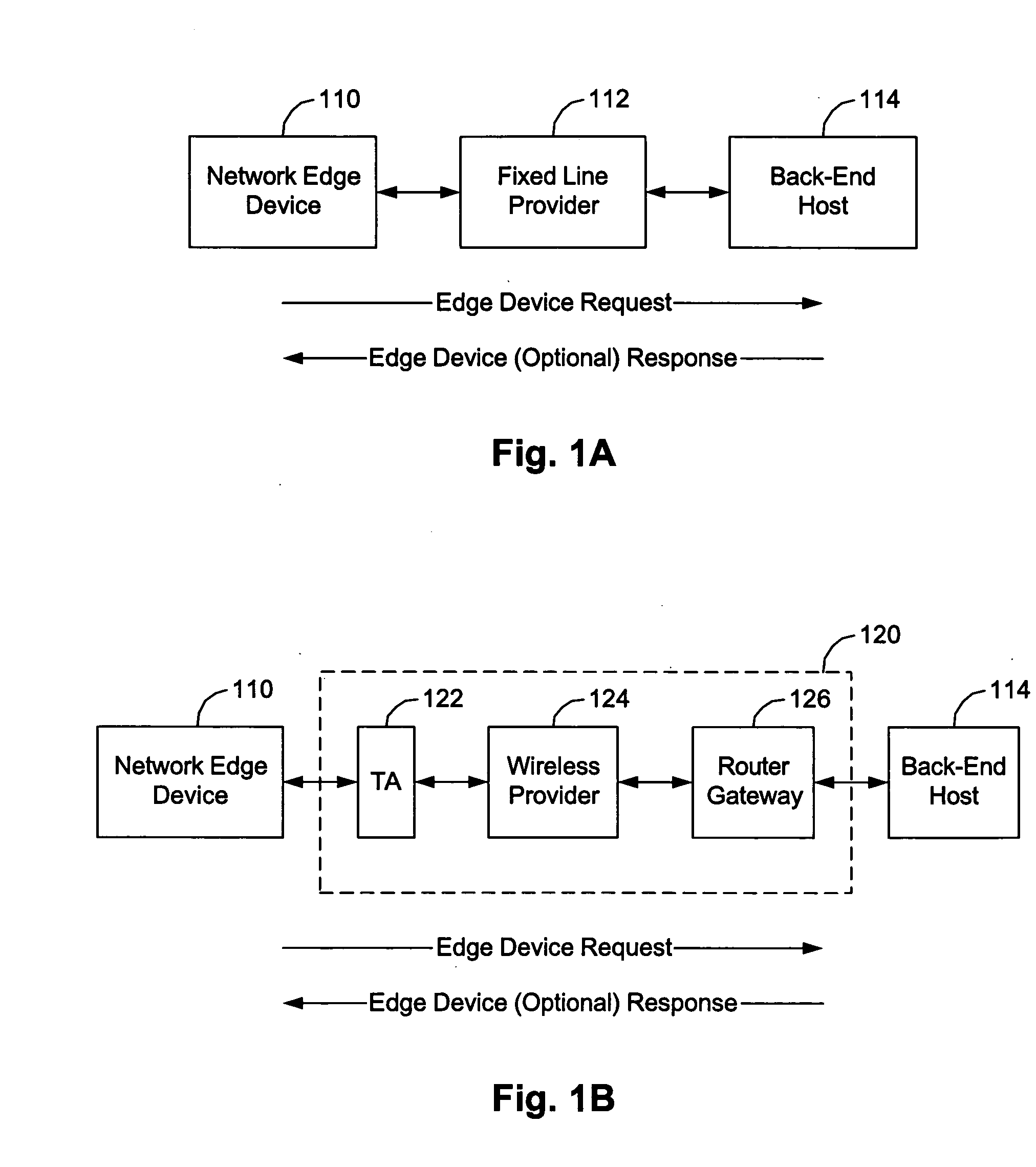
InactiveUS20050207432A1Function increaseData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsBroadbandTelephone network
A software platform in an Internet Protocol (IP) phone having the ability to be used with different communication infrastructures such as broadband, wireless communication and Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) service. Further, the software platform in the IP phone has the ability to be used with different applications operating on the IP phone. Further, the IP phone has the ability to perform additional functionality than traditional Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) phones, such as searches advertising, given its ability to converge voice and data within a single terminal.
Owner:H W TECH L C
Software platform for developing, delivering and managing data-voice applications operating on an internet protocol (IP) phone
InactiveUS20060050686A1Easy to manageSuccessful updateStore-and-forward switching systemsAutomatic exchangesCombined usePlain old telephone system
A software platform in an Internet Protocol (IP) phone having the ability to be used with different communication infrastructures such as broadband, wireless communication and Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) service. Further, the software platform in the IP phone is used in conjunction with a communication architecture, referred to herein as the Transaction Applications Delivery Services (TADS) communications architecture, that provides the ability to develop, deliver and manage data-voice applications operating on the IP phone.
Owner:COMMOCA
Internet protocol (IP) phone with search and advertising capability
InactiveUS7525955B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet protocol suitePlain old telephone system
A software platform in an Internet Protocol (IP) phone having the ability to be used with different communication infrastructures such as broadband, wireless communication and Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) service. Further, the software platform in the IP phone has the ability to be used with different applications operating on the IP phone. Further, the IP phone has the ability to perform additional functionality than traditional Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) phones, such as searches and advertising, given its ability to converge voice and data within a single terminal.
Owner:H W TECH L C
Connecting a VOIP phone call using a shared POTS line
InactiveUS20060007915A1Low costInterconnection arrangementsNetwork connectionsControl systemMediaFLO
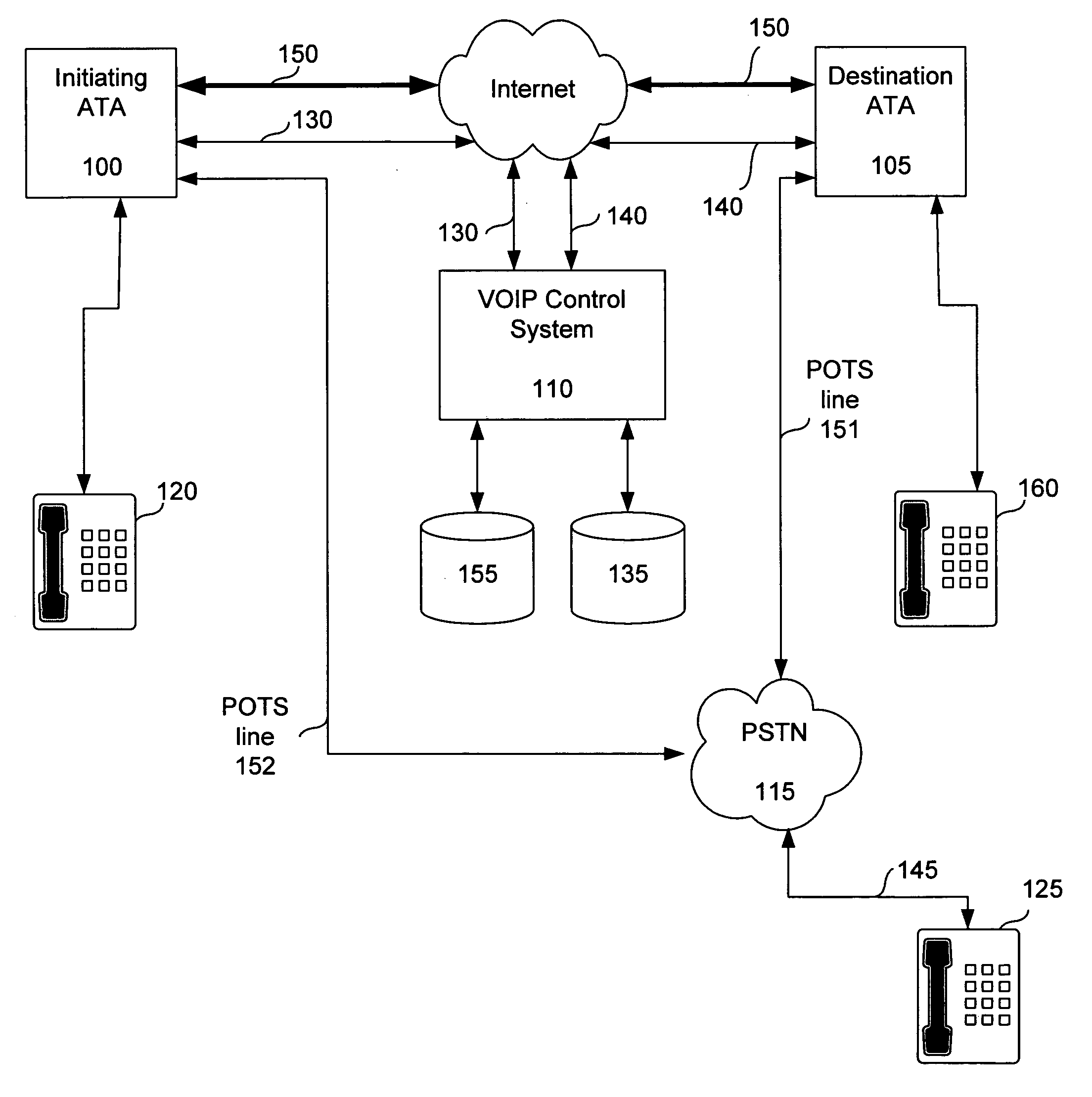
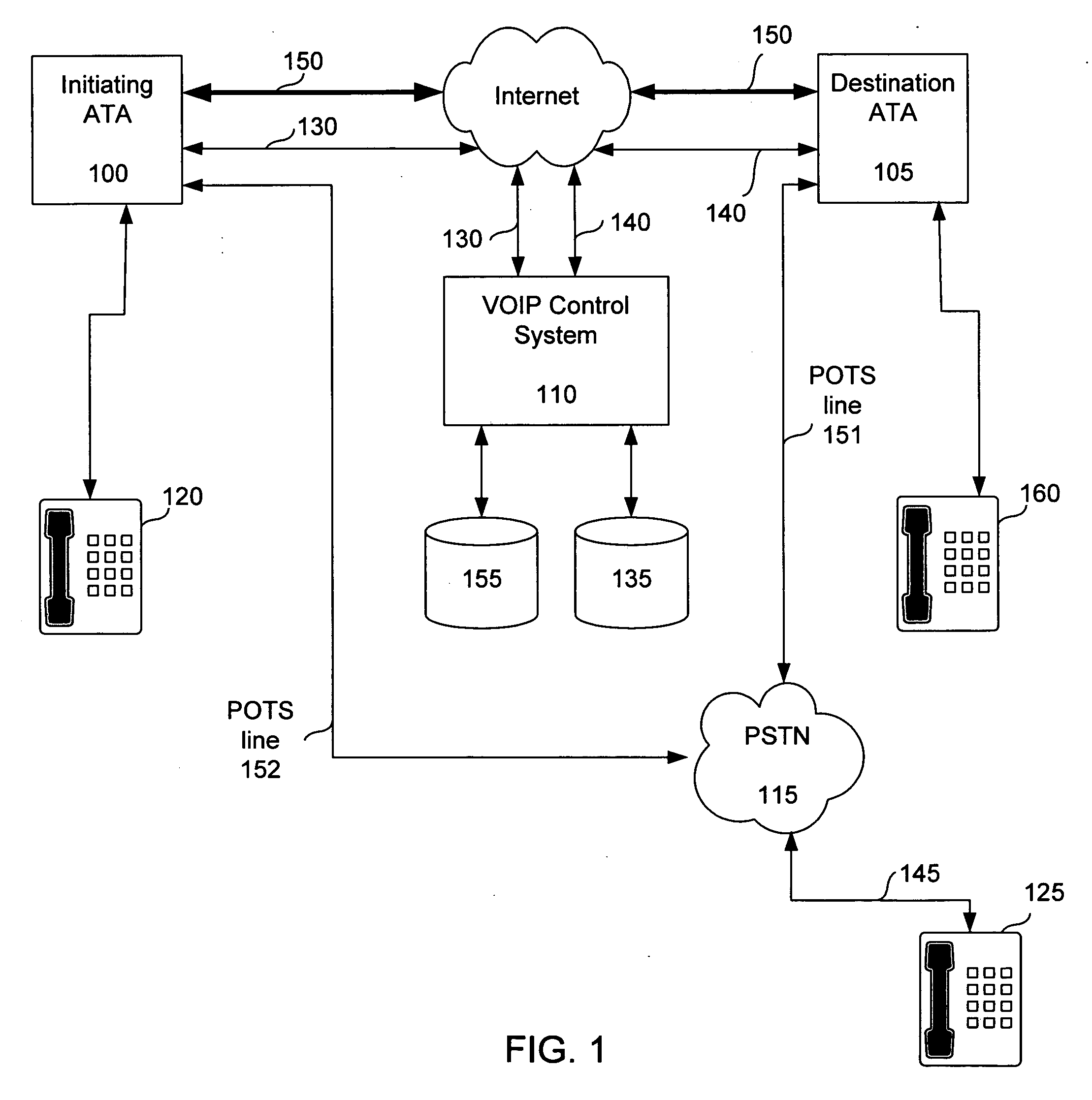
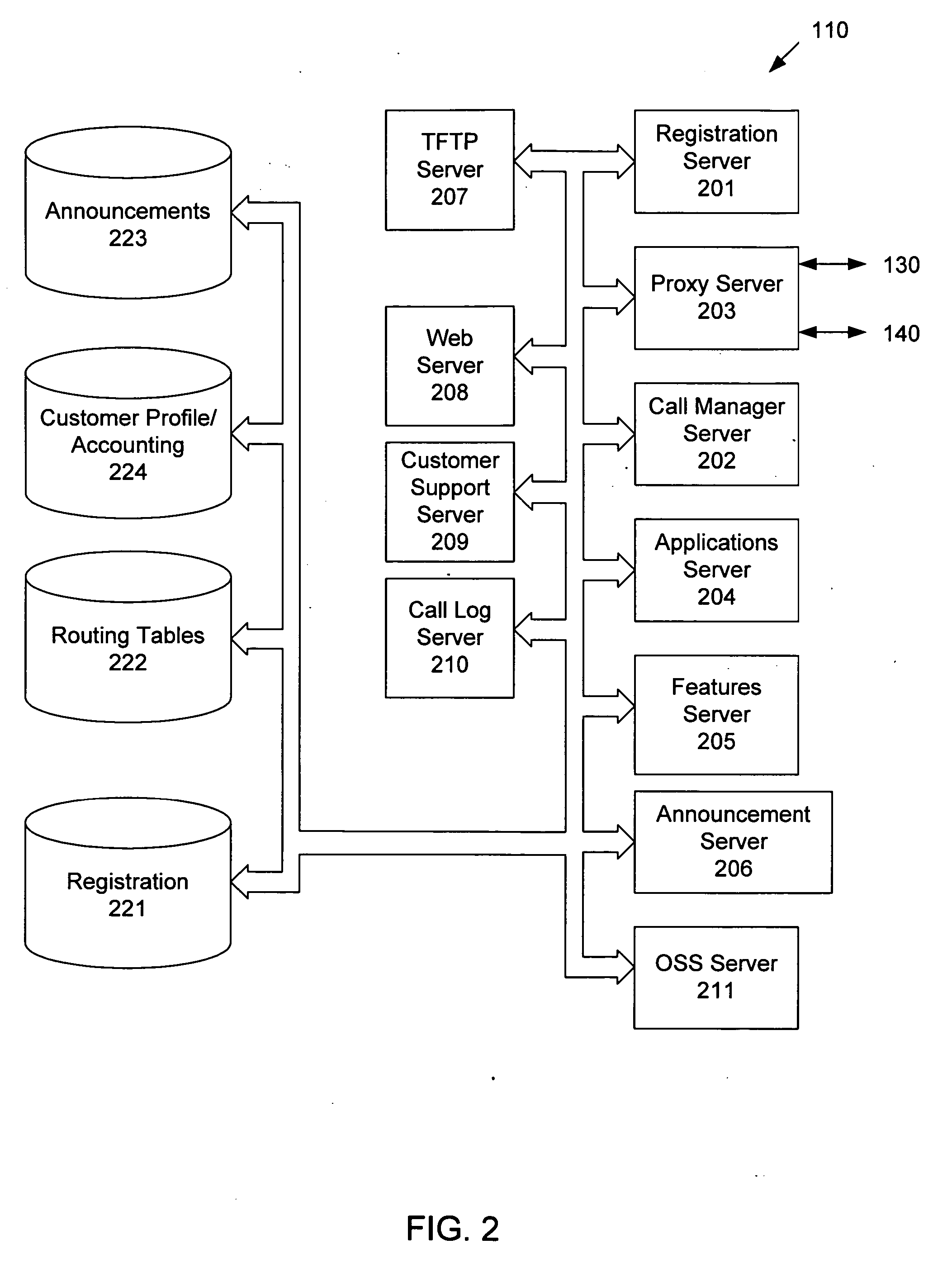
A decentralized architecture allows a plain old telephone system (POTS) line to be shared for use. Routing logic is handled by a voice over Internet protocol (VOIP) control system and by logic in an initiating analog telephone adapter (ATA). A destination ATA is selected based upon the phone number of a destination phone. Routing information for a destination ATA is communicated to the initiating ATA, and the initiating ATA communicates a media stream to the destination ATA. The system and method enables lower cost routing than currently available, relieves a caller at an initiating phone from having to select whether to use VOIP or the PSTN, and relieves the caller from dialing special phone numbers.
Owner:OOMA
Cable telephony network supporting roaming VoIP terminals
InactiveUS20070201688A1Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersEnd systemThe Internet
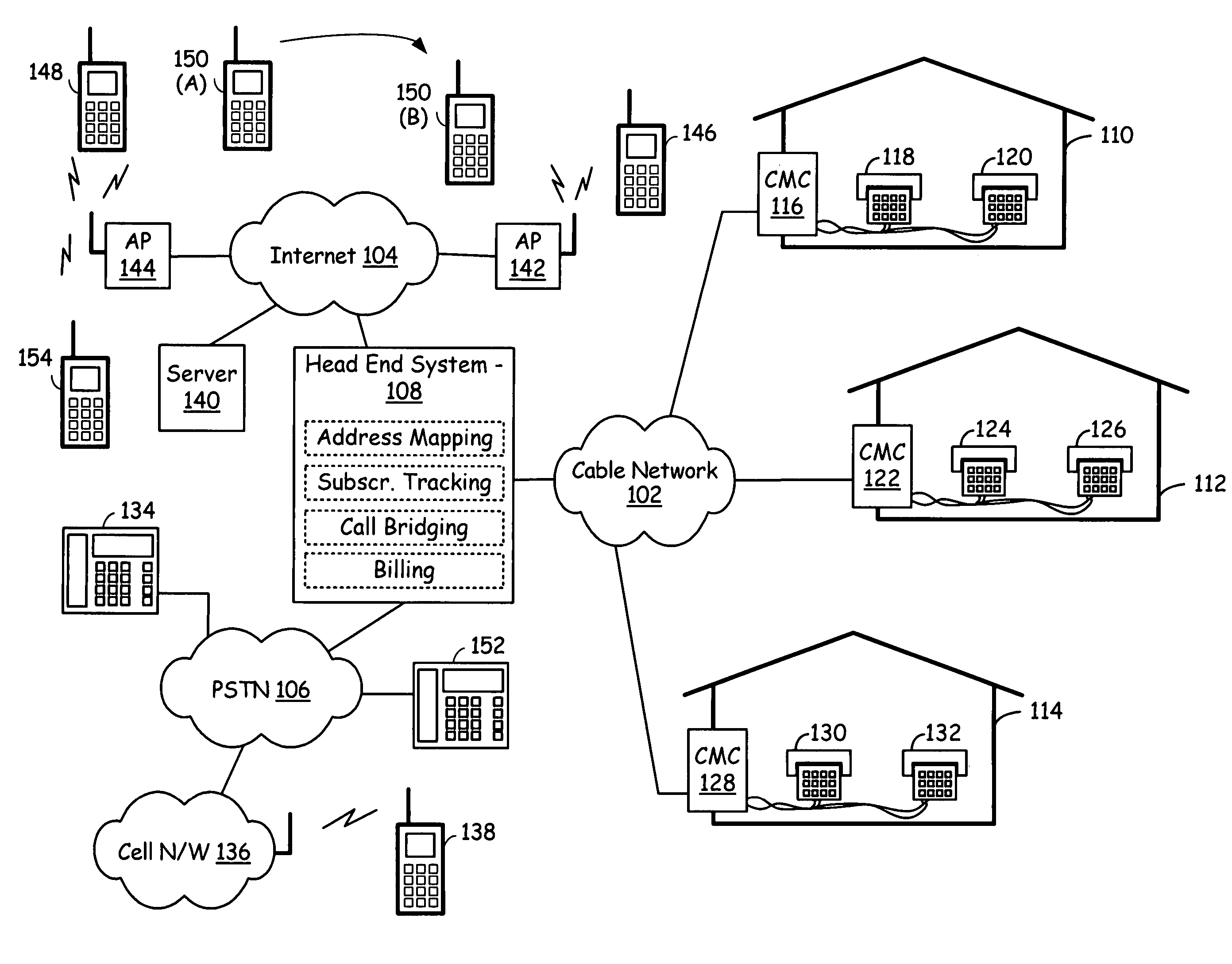
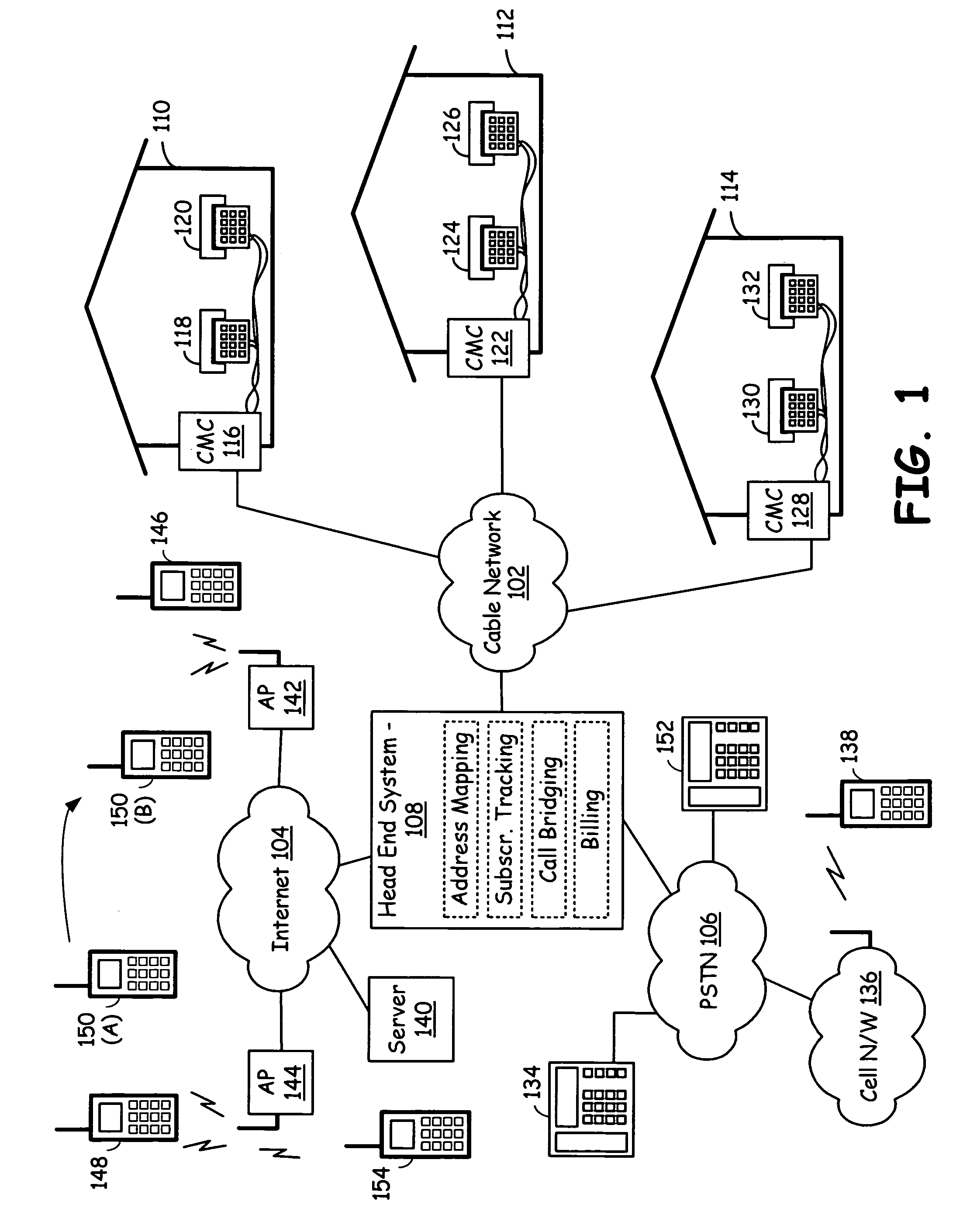
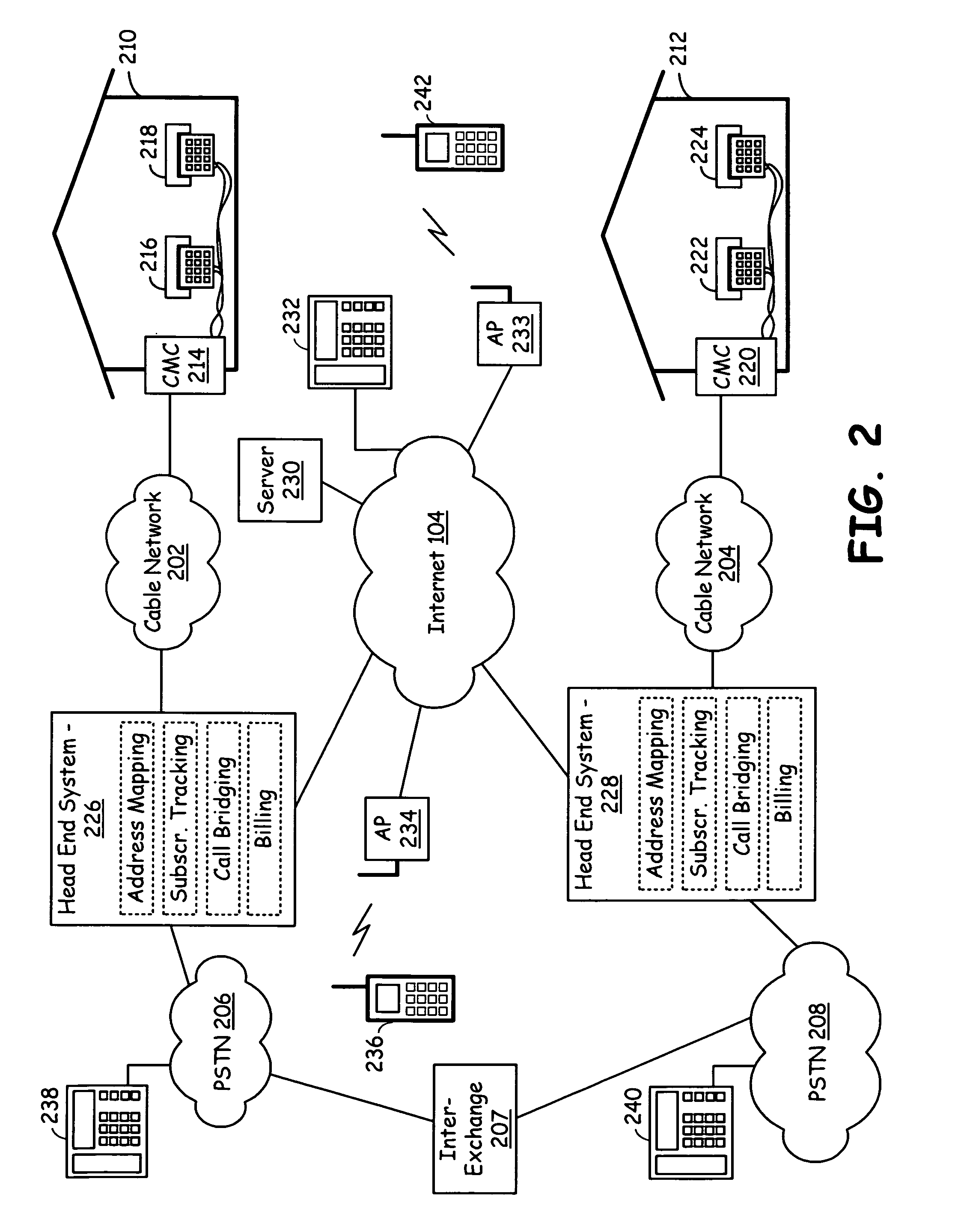
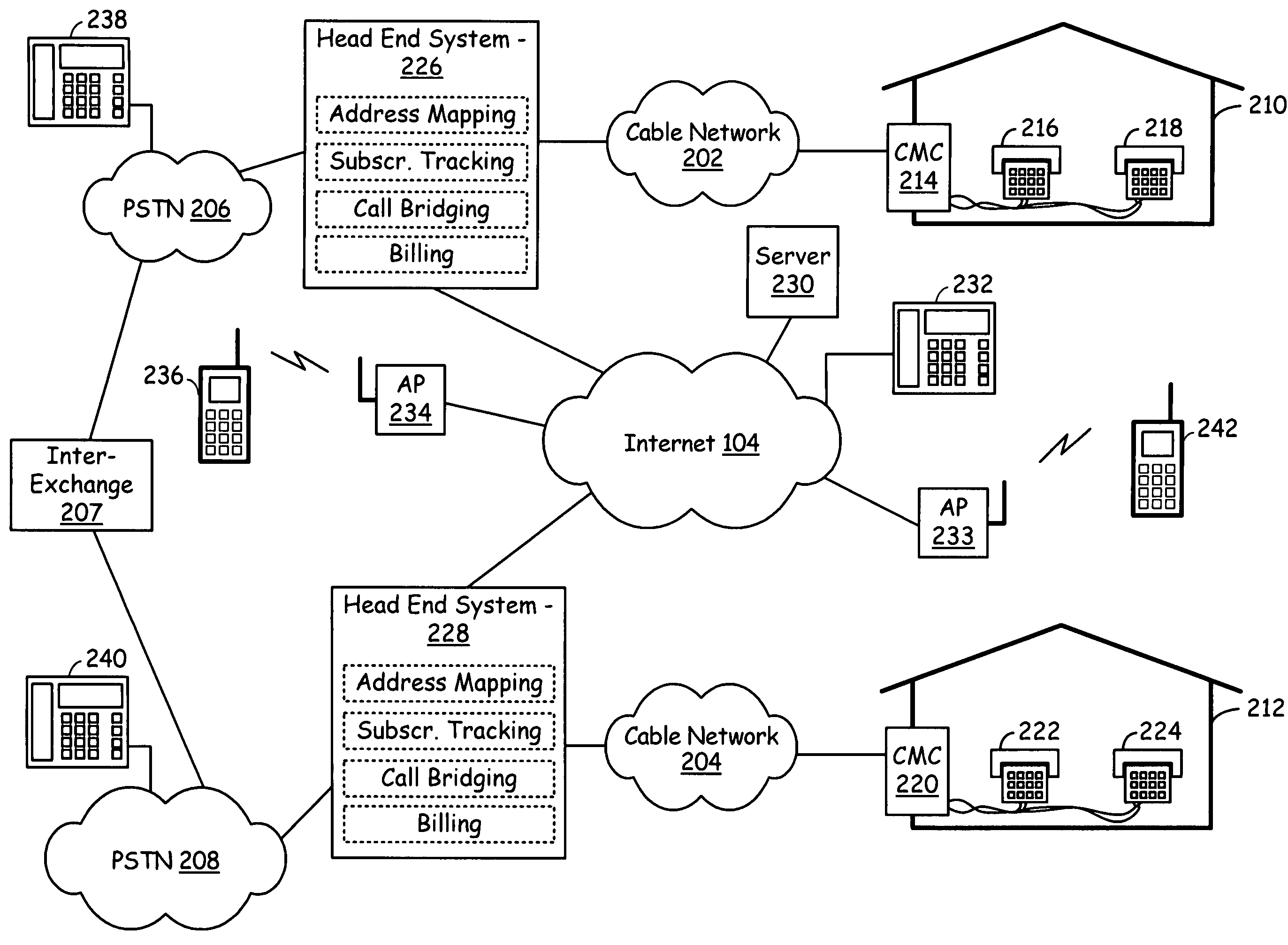
A cable infrastructure includes a plurality of cable modem circuits communicatively coupled to a cable network and associated with a corresponding one of a plurality of subscribers. Each of a plurality of telephones has both a POTS (Plain Old Telephone System) interface and a unique telephone number and associates with a corresponding one of the plurality of subscribers. Each of a plurality of interface circuits couples one of the plurality of cable modem circuits with a corresponding one of the plurality of telephones via the POTS interface. A head end system communicatively couples to the cable network, the public switched telephony network, and the Internet network and supports address mapping that enables communication exchanges between one of the plurality of telephones and an Internet telephony device. The address mapping also enables communication exchanges between telephones serviced by differing head ends via an Internet pathway that is independent of the public switched telephony network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for coupling a POTS terminal to a non-PSTN communications network
ActiveUS20050195799A1Telephonic communicationTime-division multiplexTelephone networkPlain old telephone system
The present invention relates to using a communications device to interface a plain old telephone system (POTS) terminal to a communications network. In particular, it relates to a communications device that appears to the POTS terminal to be a telephone network. Particular aspects of the present invention are described in the claims, specification and drawings.
Owner:WILINE NETWORKS
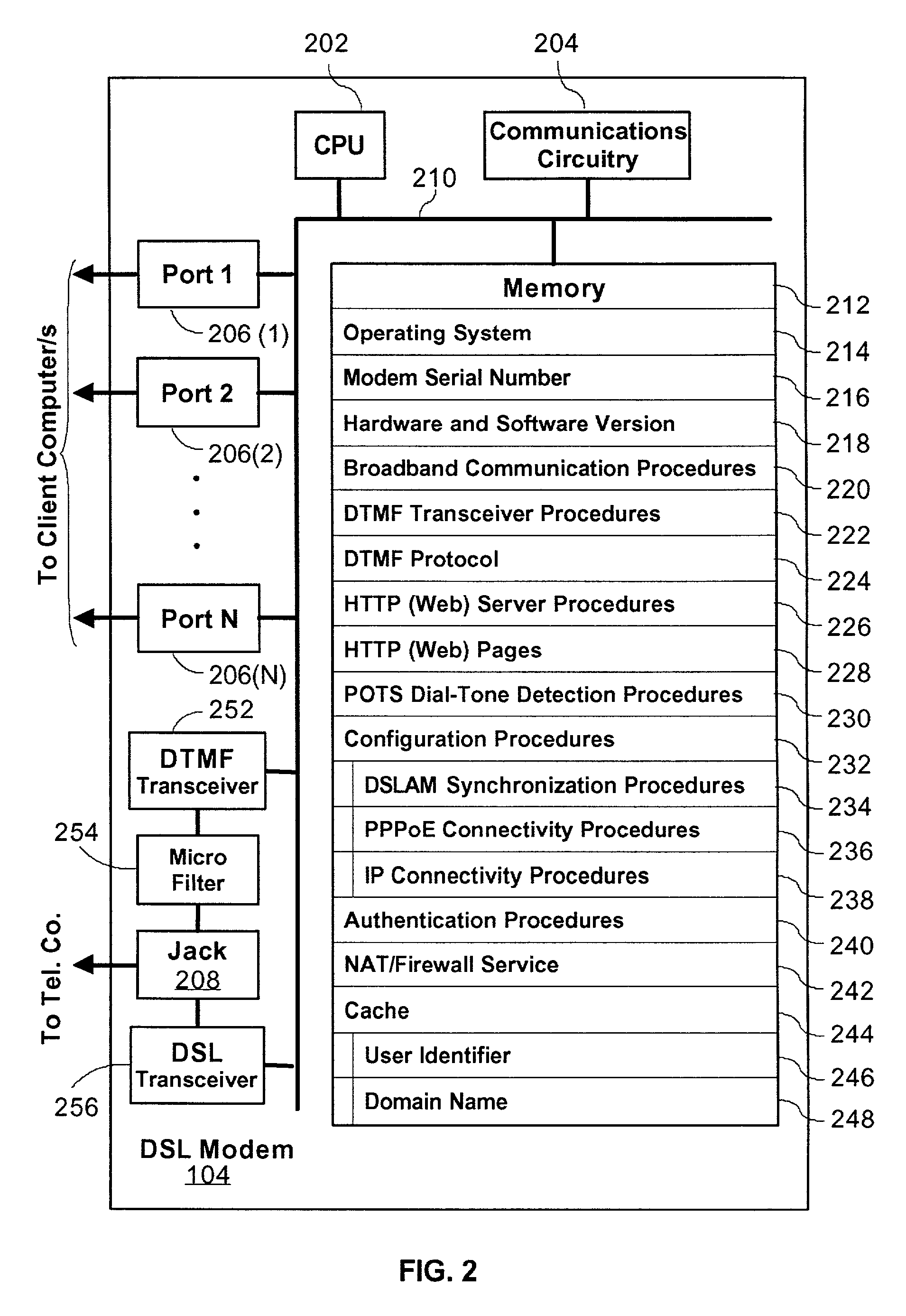
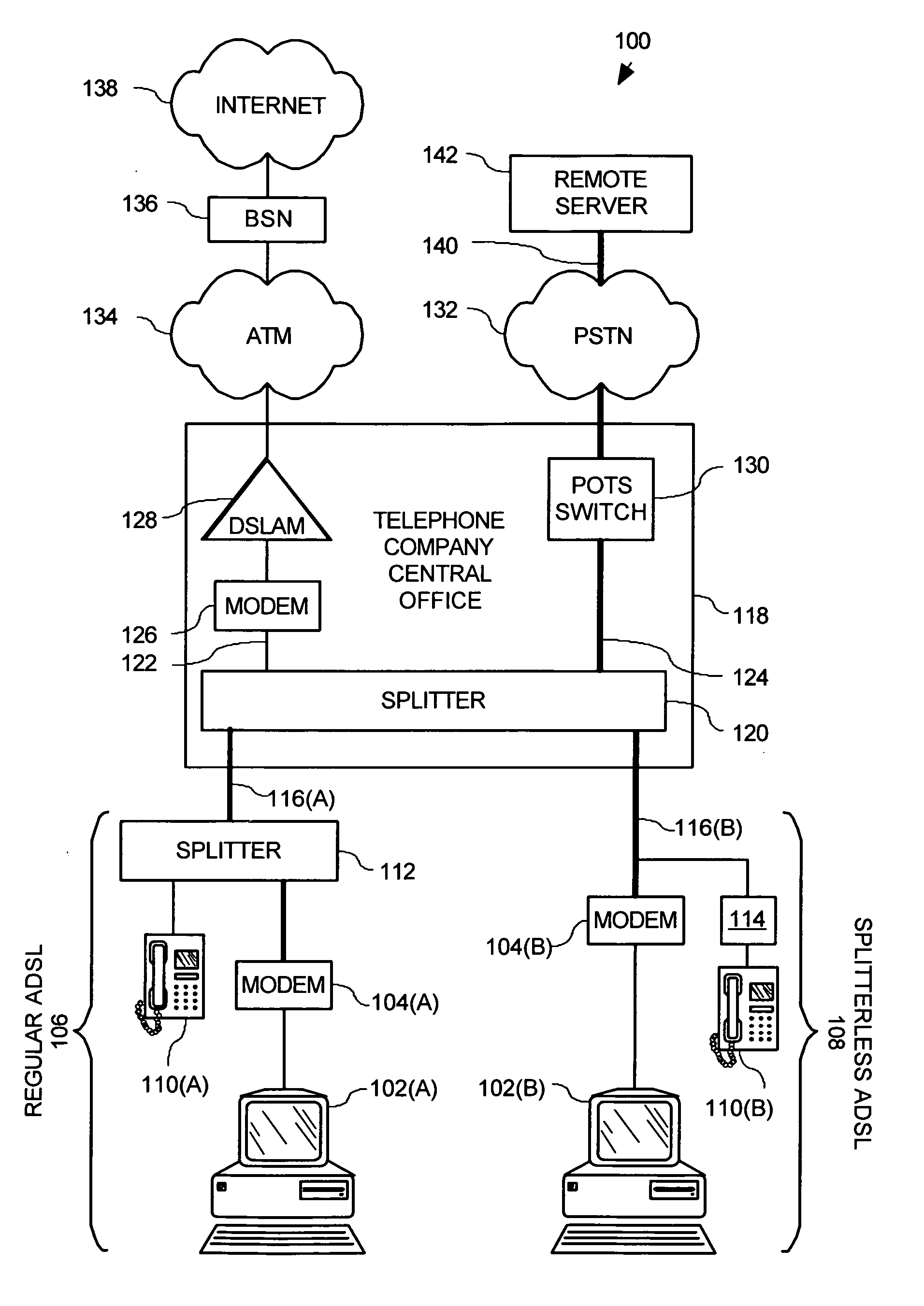
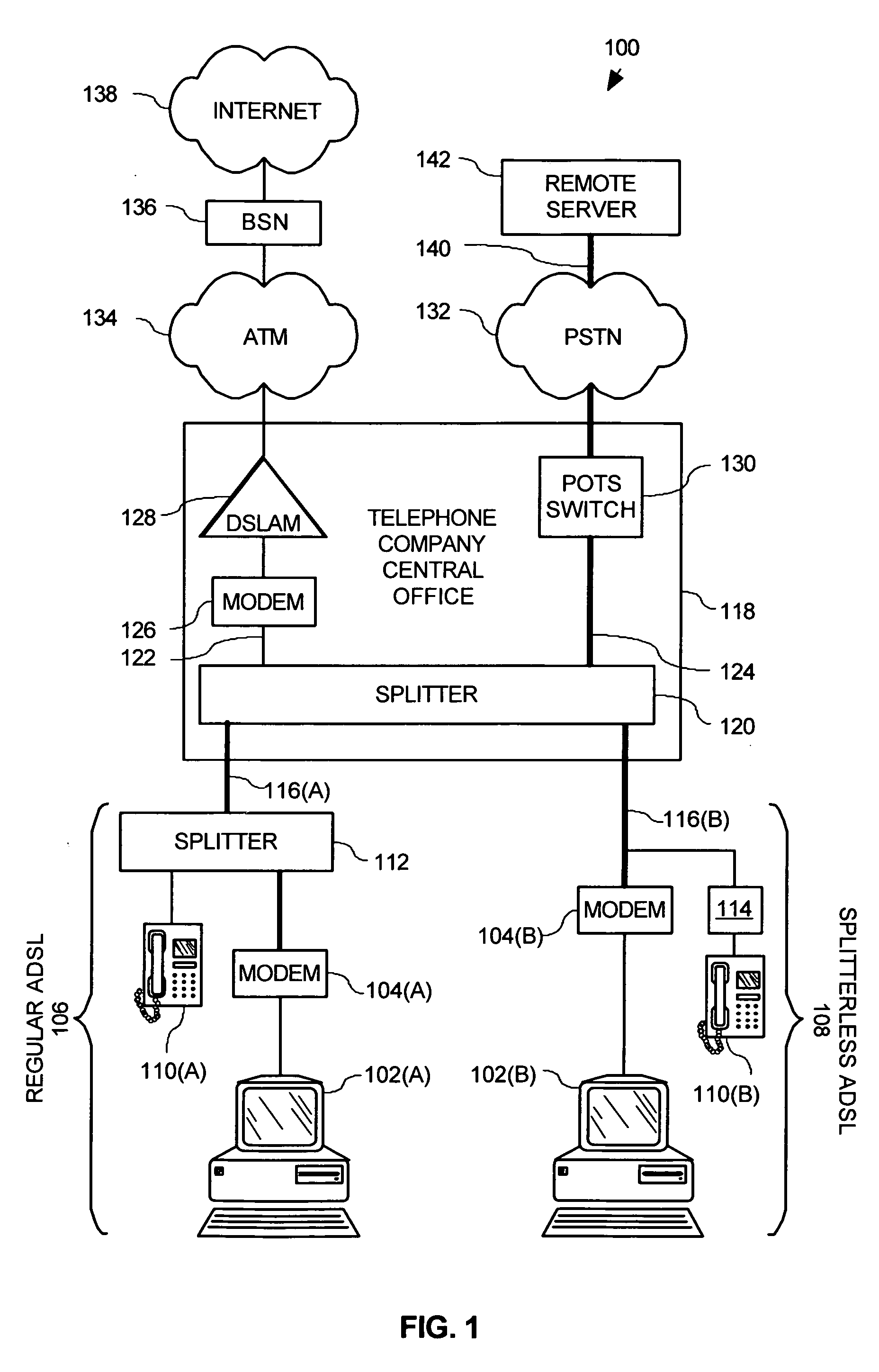
System and method for provisioning broadband service in a PPPoE network using DTMF communication
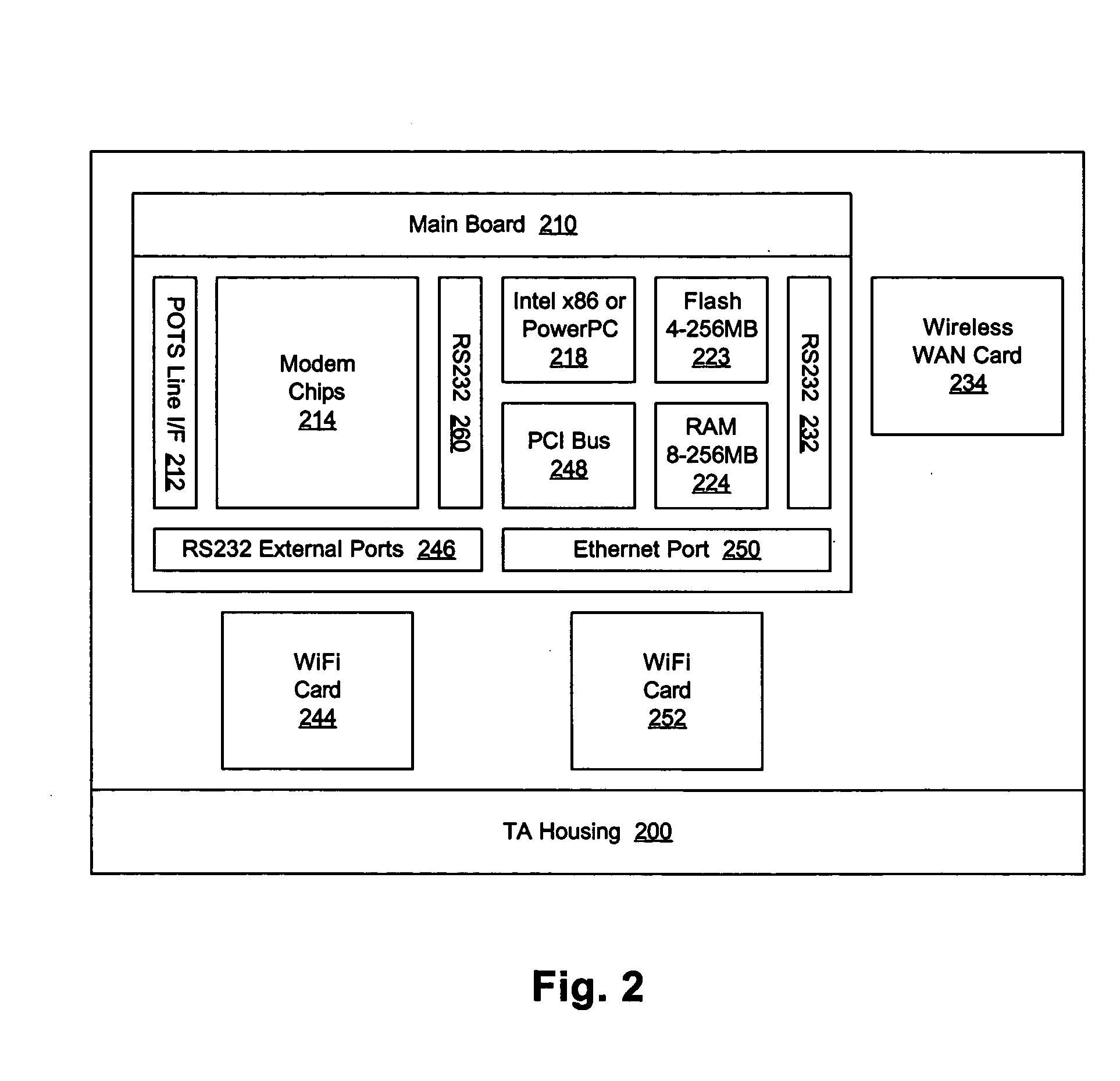
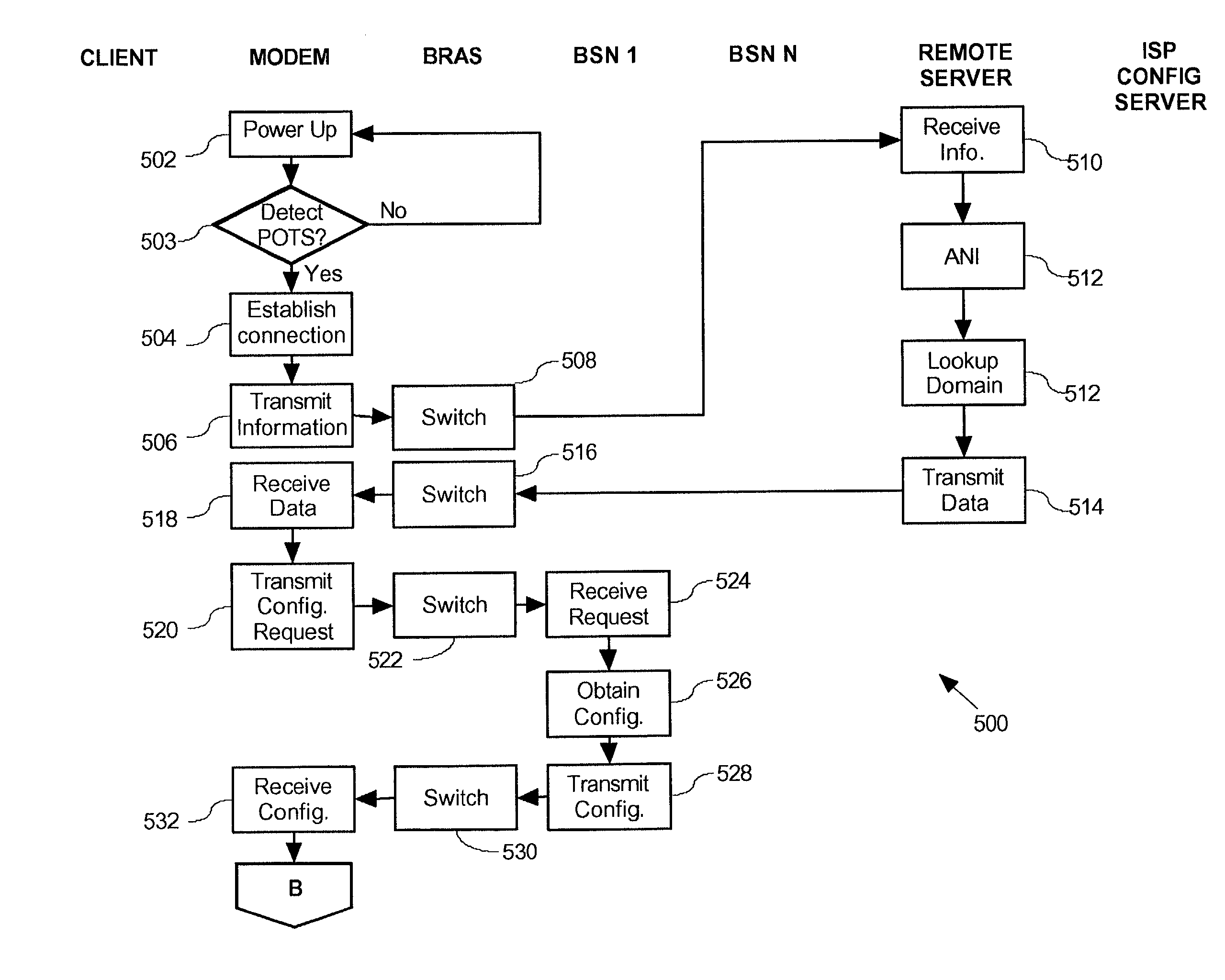
InactiveUS7079527B2Simple configurationSave precious resourcesAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingData switching by path configurationDomain nameModem device
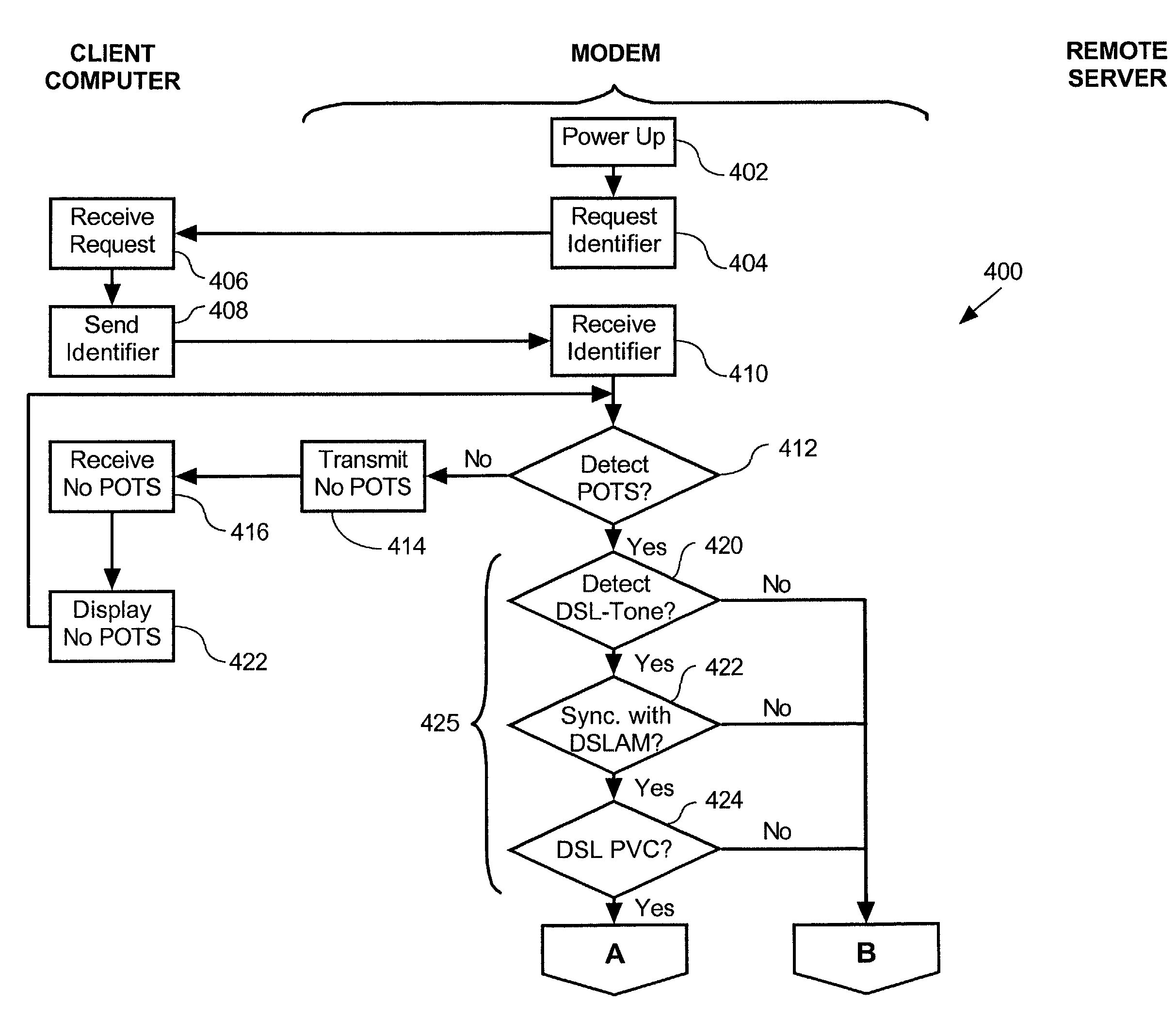
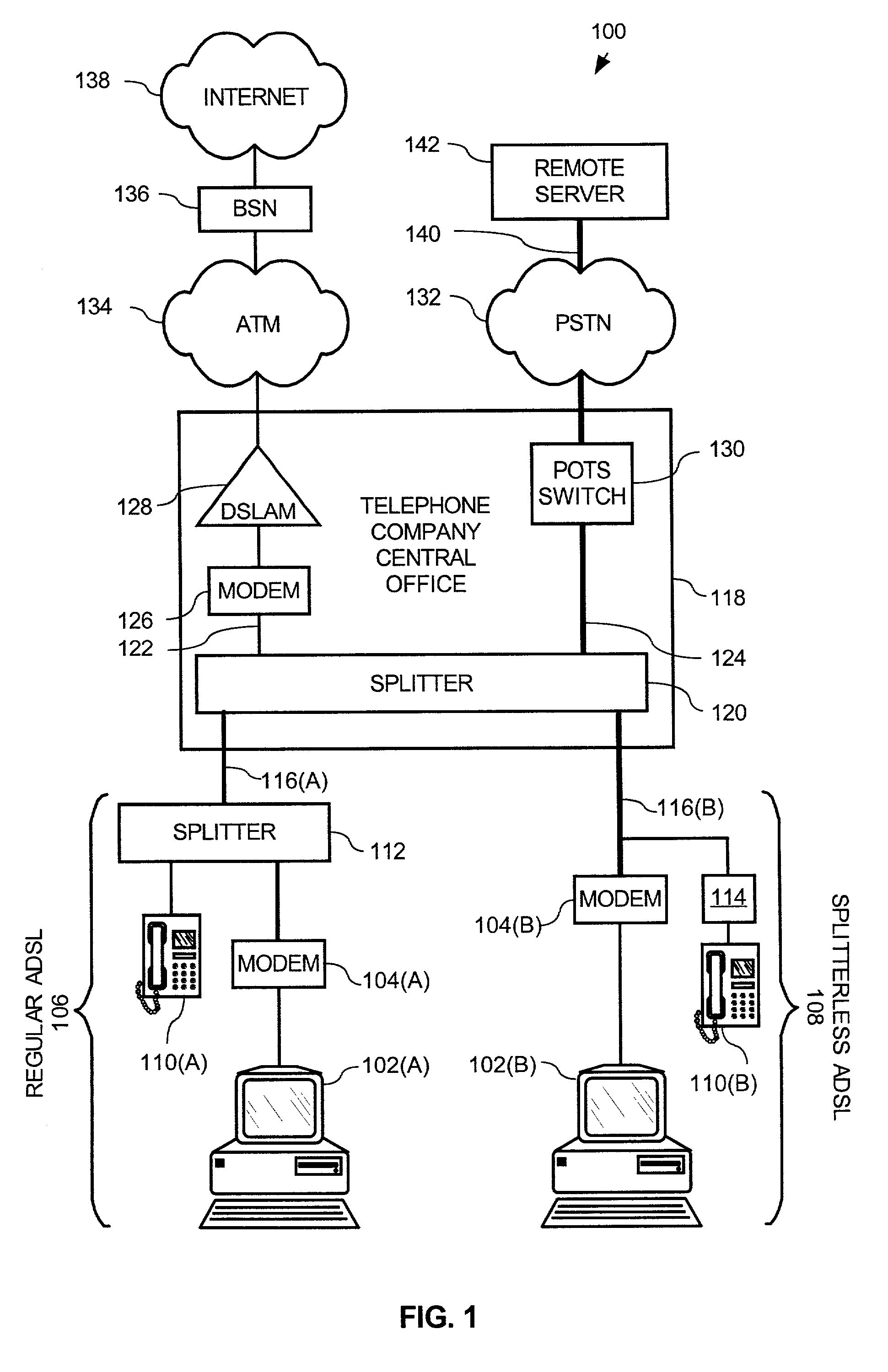
A Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) connection is established between a Broadband modem and a remote server. A configuration request is then transmitted from the Broadband modem to the remote server using DTMF tones. Subsequently a domain name associated with a Broadband Service Node (BSN) and a user identifier, such as a telephone number, is received from the remote server via the POTS connection using Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) tones. A PPPoE session is then established using the domain name, by firstly authenticating the Broadband modem for the PPPoE session and then configuring the DSL modem. This configuration is accomplished by transmitting a request for configuration details from the Broadband modem to the BSN having the domain name and then receiving configuration details from the configuration server. The Broadband modem then automatically configures itself using the configuration details.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
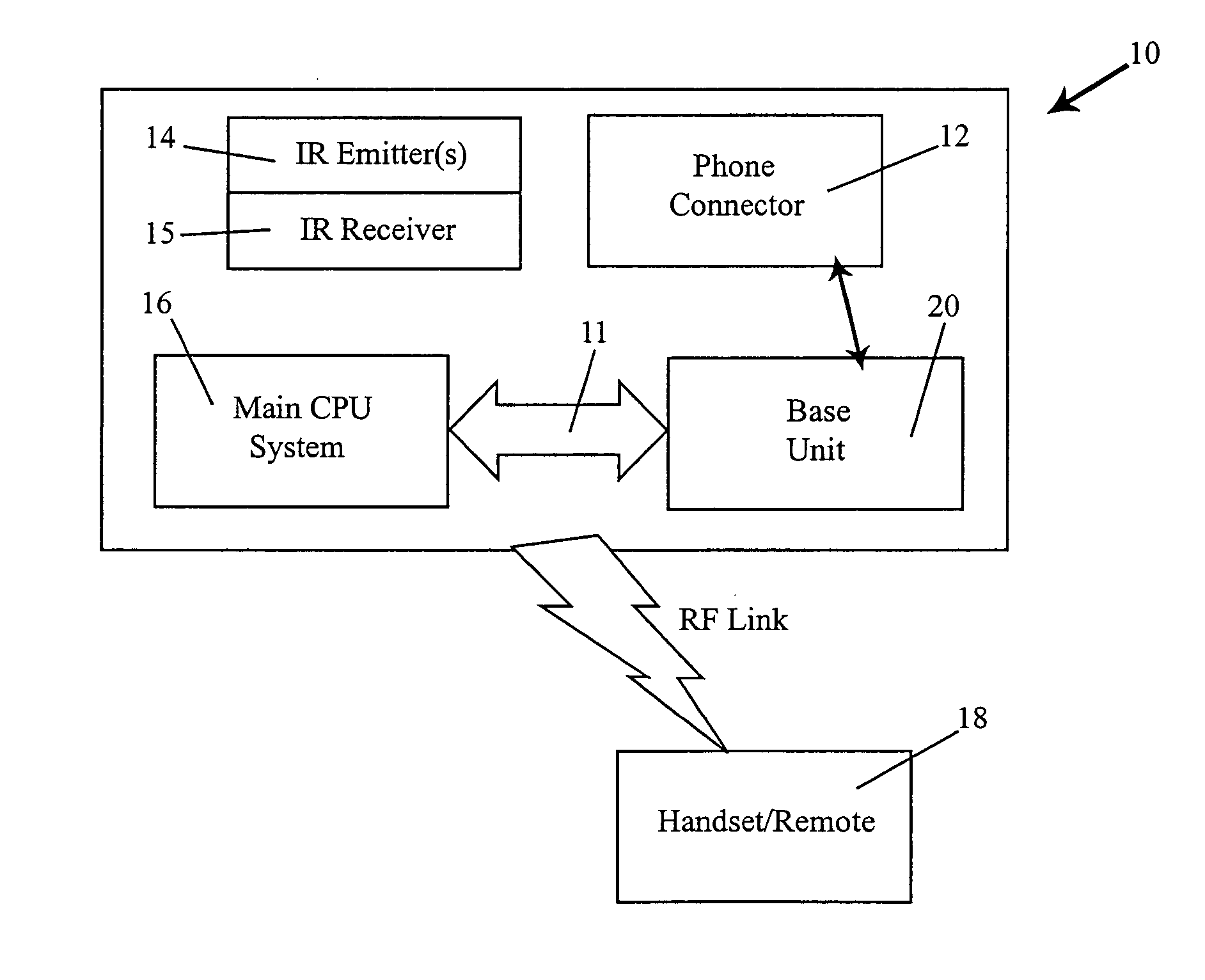
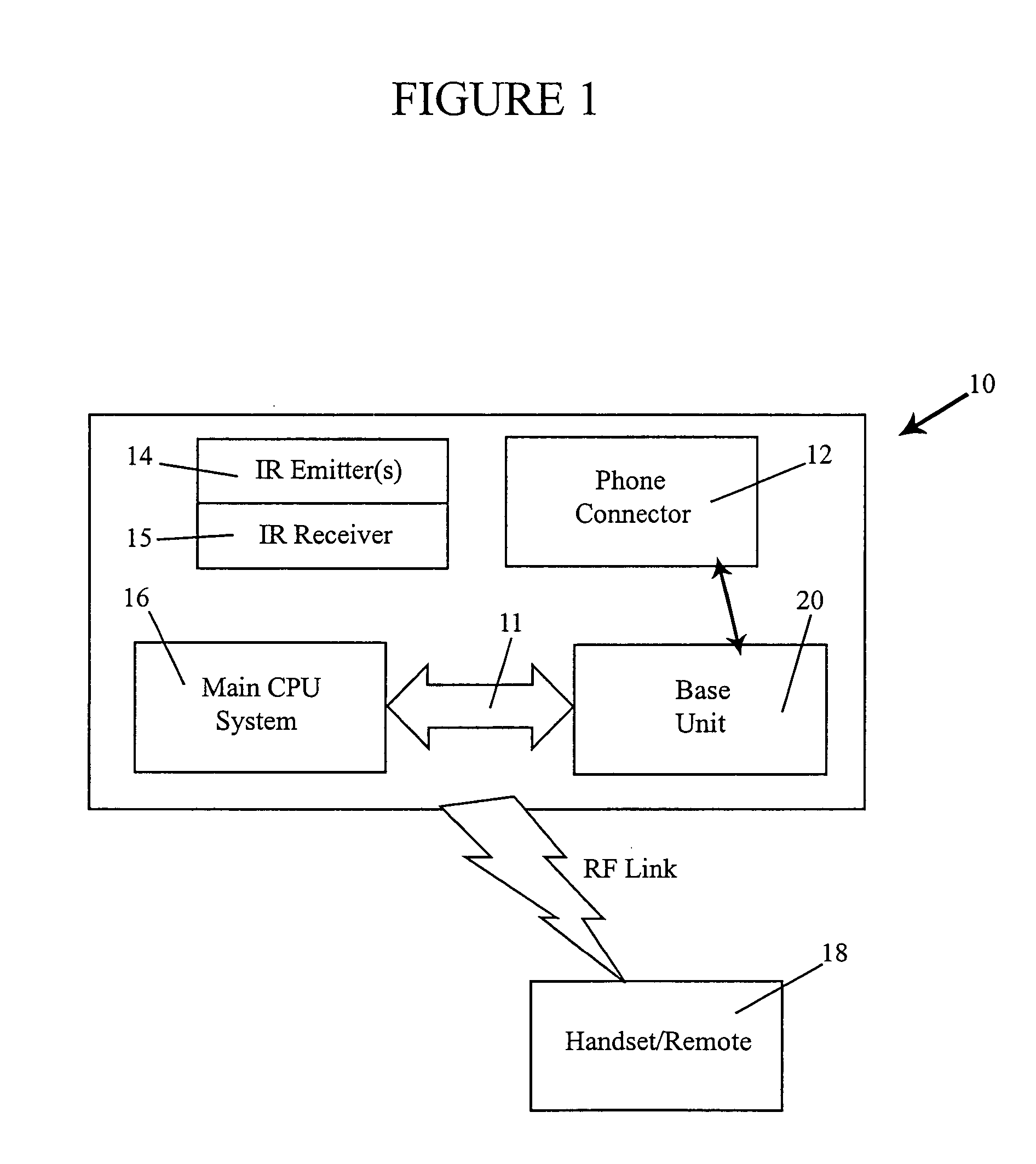
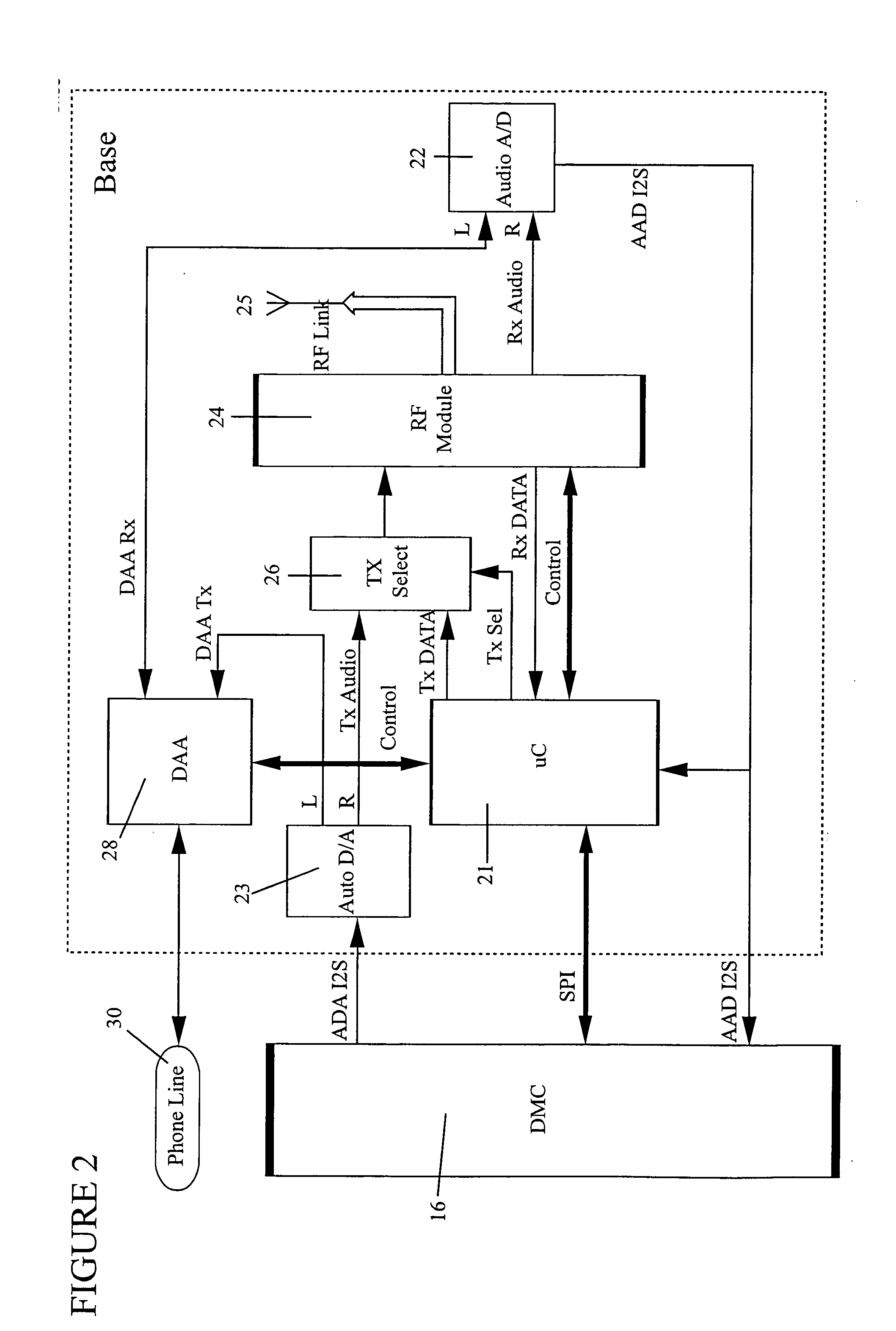
Radio frequency remote control apparatus and methodology
A remote control system includes a RF communication chipset that has a transceiver and antenna at a handset / remote and another transceiver and antenna at a base station is operable to maintain a two-way communication connection. The two-way communication connection includes the capability of uploading display data for presentation on a display located at the handset / remote, and also includes the capability of downloading keystroke codes from the handset / remote keyboard. A processor is in communication with the base station, and is operable to control an infrared emitter. Devices are controlled by infrared commands decoded from the downloaded keystrokes and provided to the infrared emitter. Full telephonic capability is supported between the handset / remote and a plain old telephone system.
Owner:NETGEAR INC
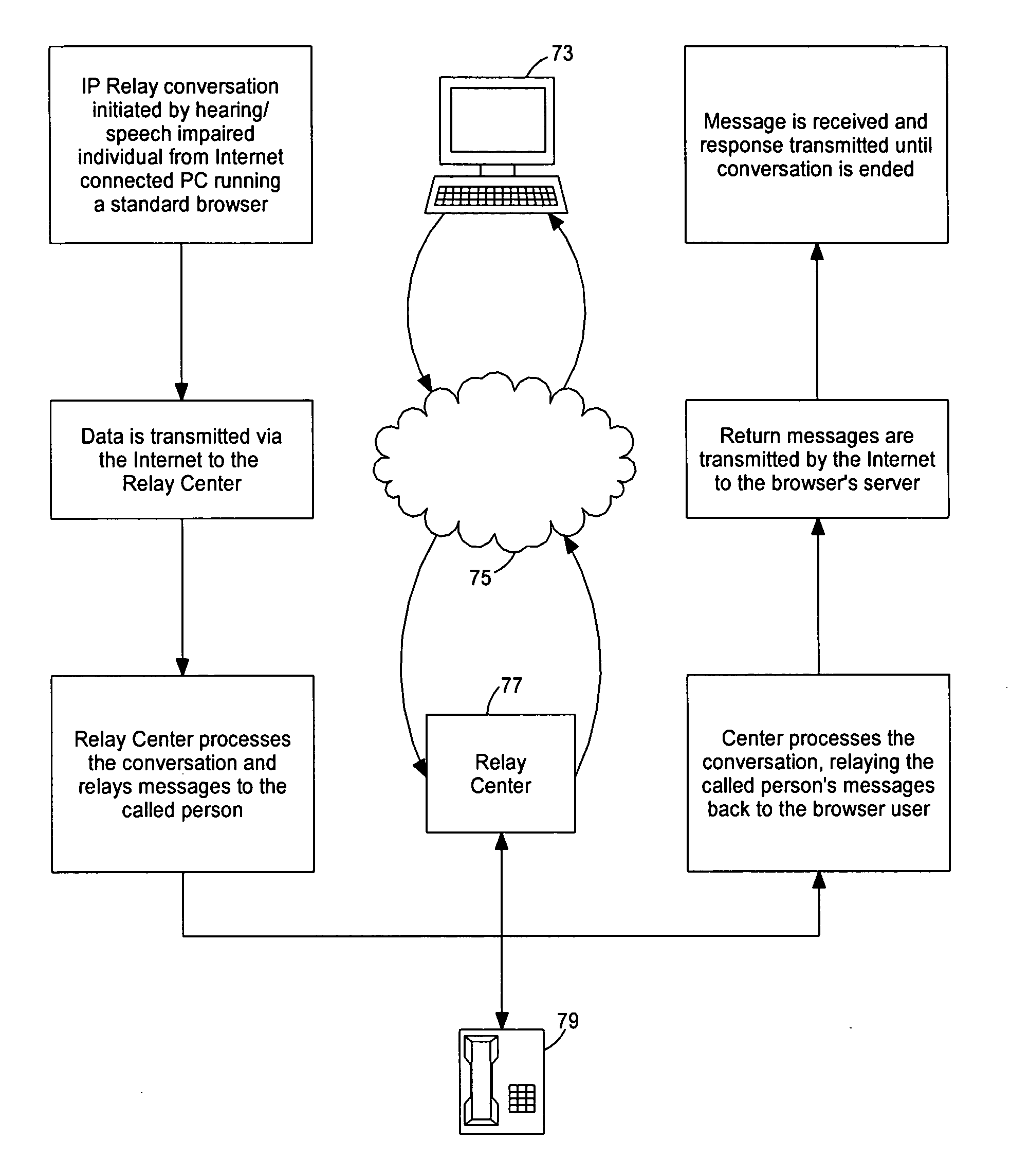
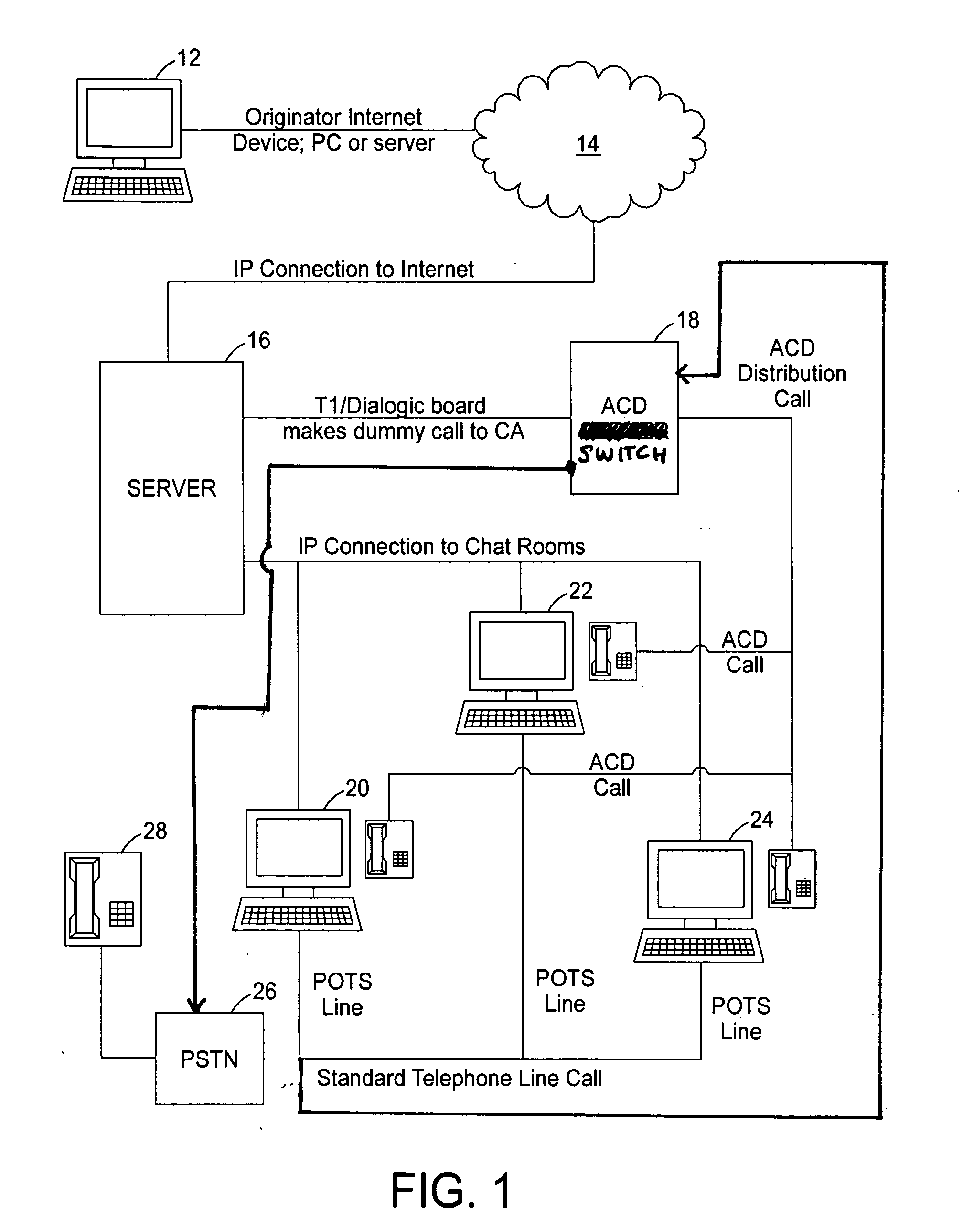
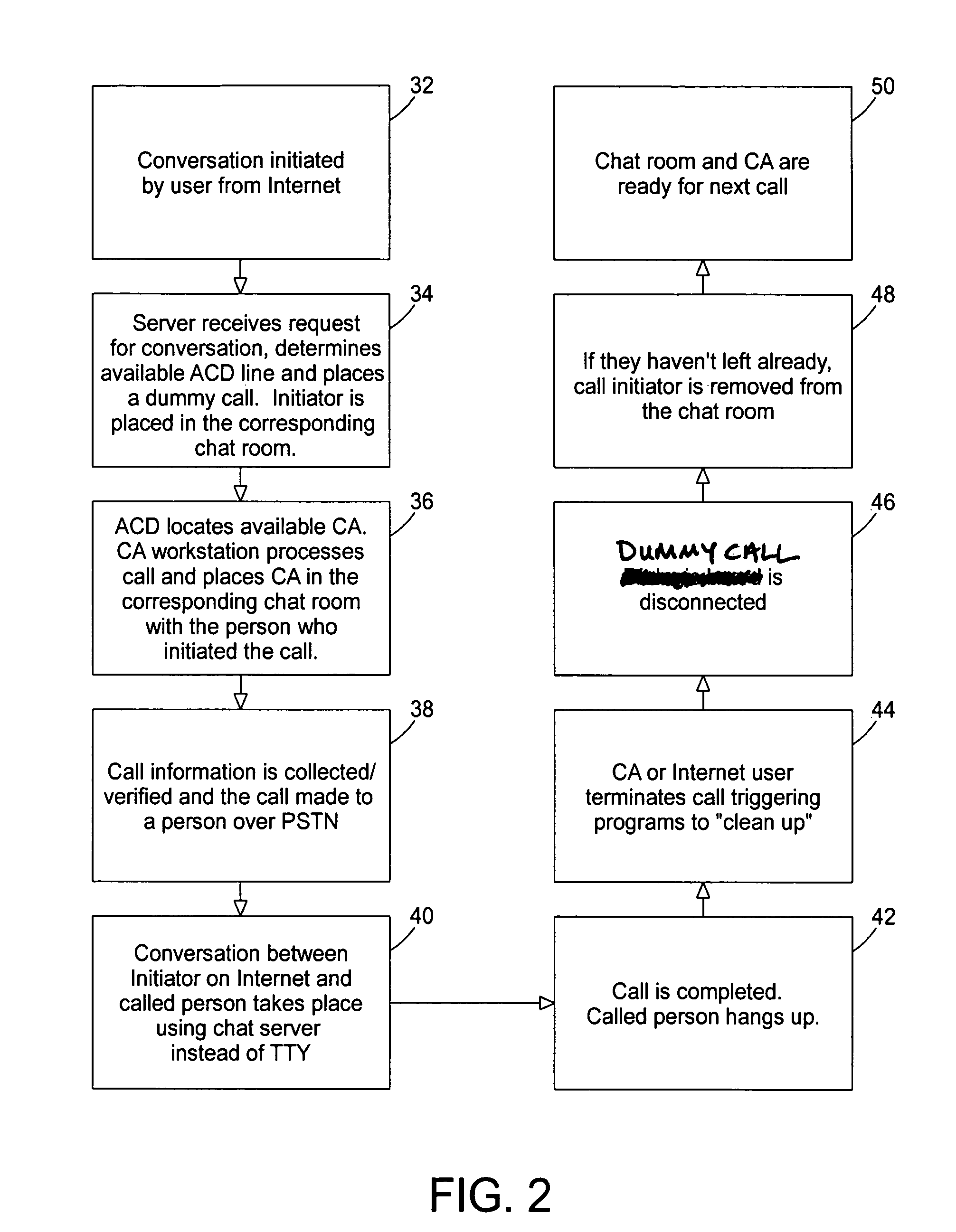
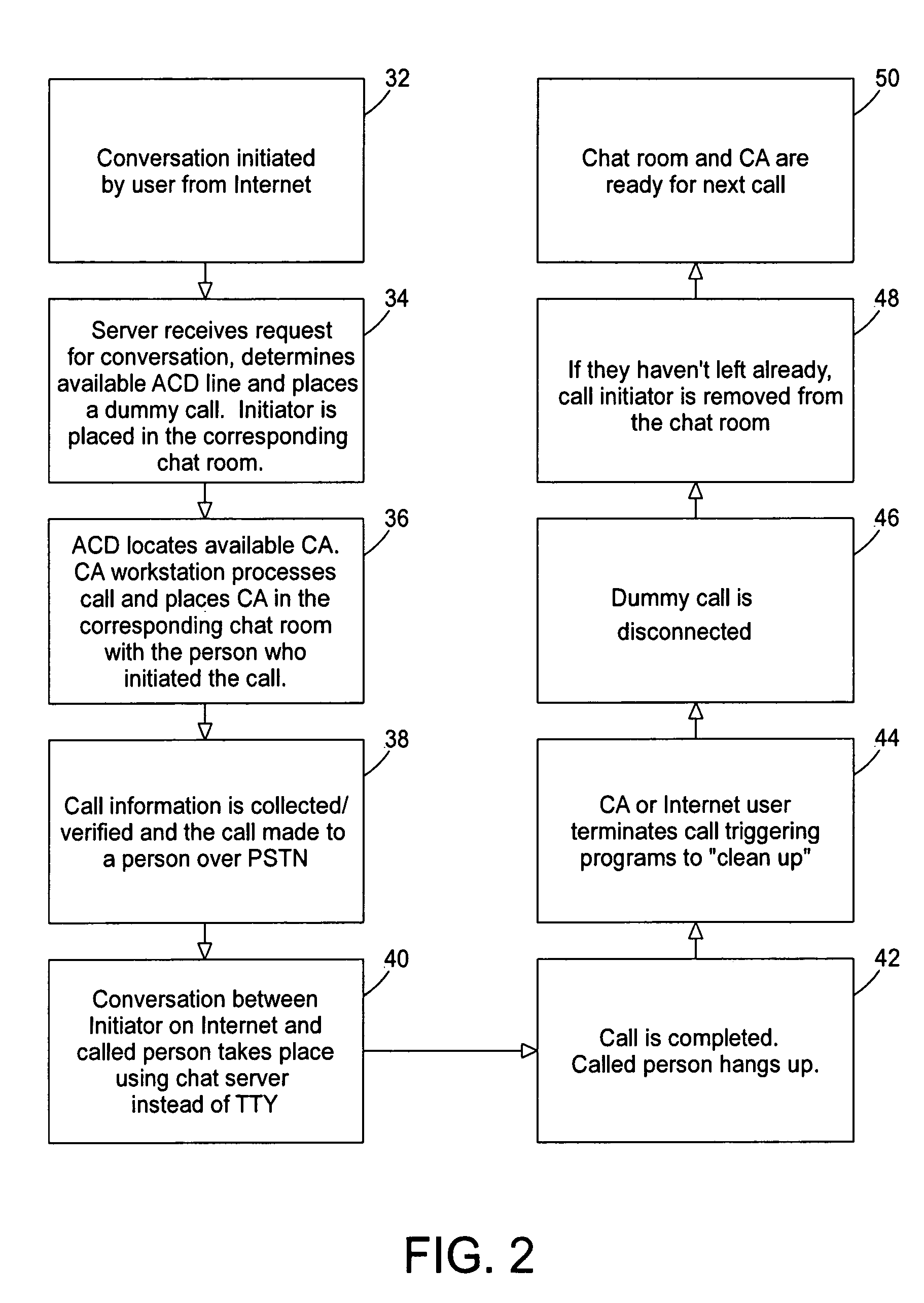
Internet protocol (IP) relay system and method
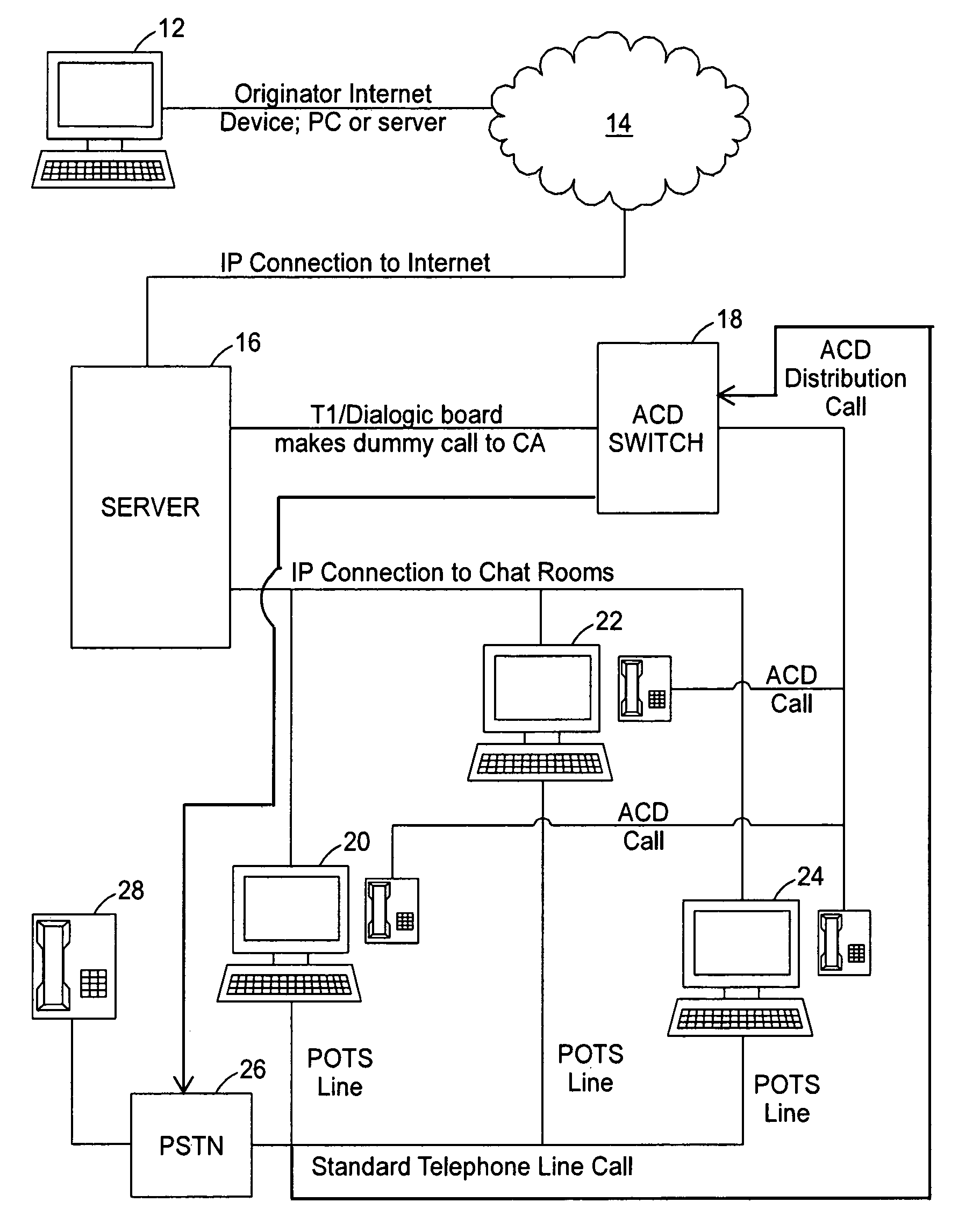
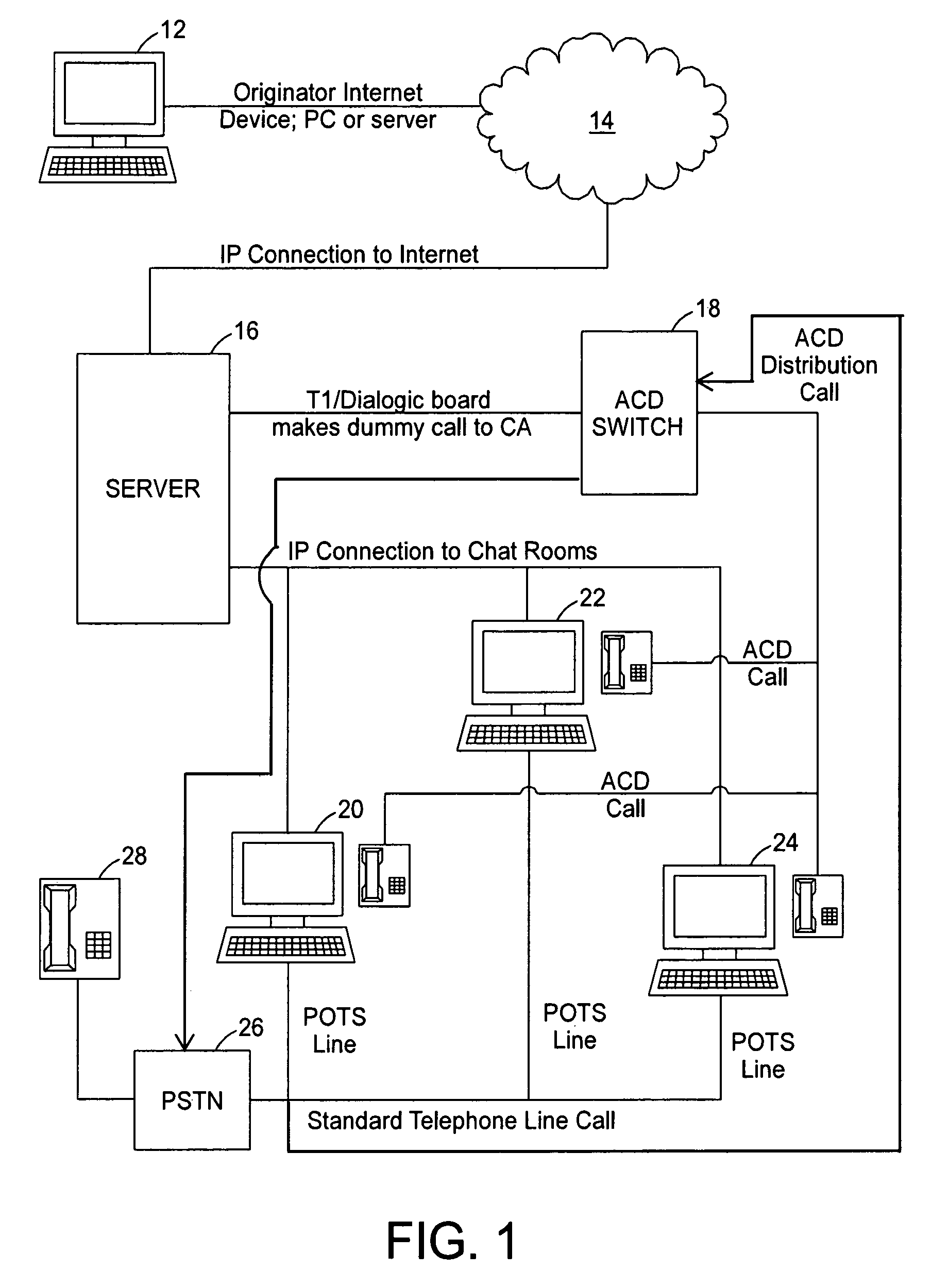
A communications system allows individuals who are deaf, hard of hearing or speech disabled to use computers and other web devices to connect to an Internet Portal in order to place a call. The system relays communications between a first device and a second device utilizing a third device as an intermediary where the second device is a telephone on a plain old telephone system network and the communications between the first device and third device involves the Internet. The system includes a first input and output communication device coupled to a network and is configured to send and receive communication messages, a server device that receives a session request from the first input and output communication device and sends a call to a call distribution device, a second input and output communication device coupled to a plain old telephone system, and a third input and communicating with the first input and output communication device using a chat room interface.
Owner:HAMILTON RELAY
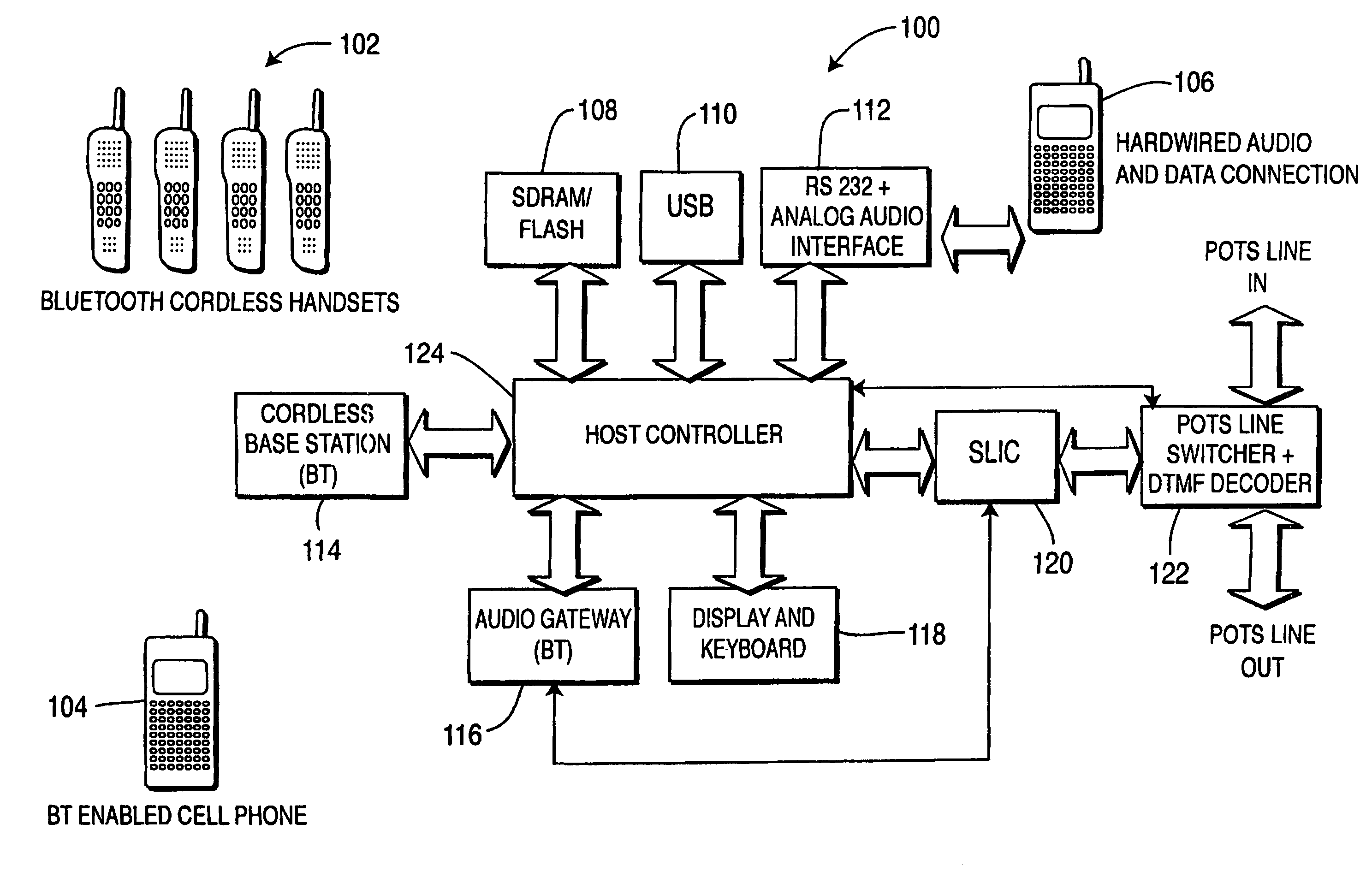
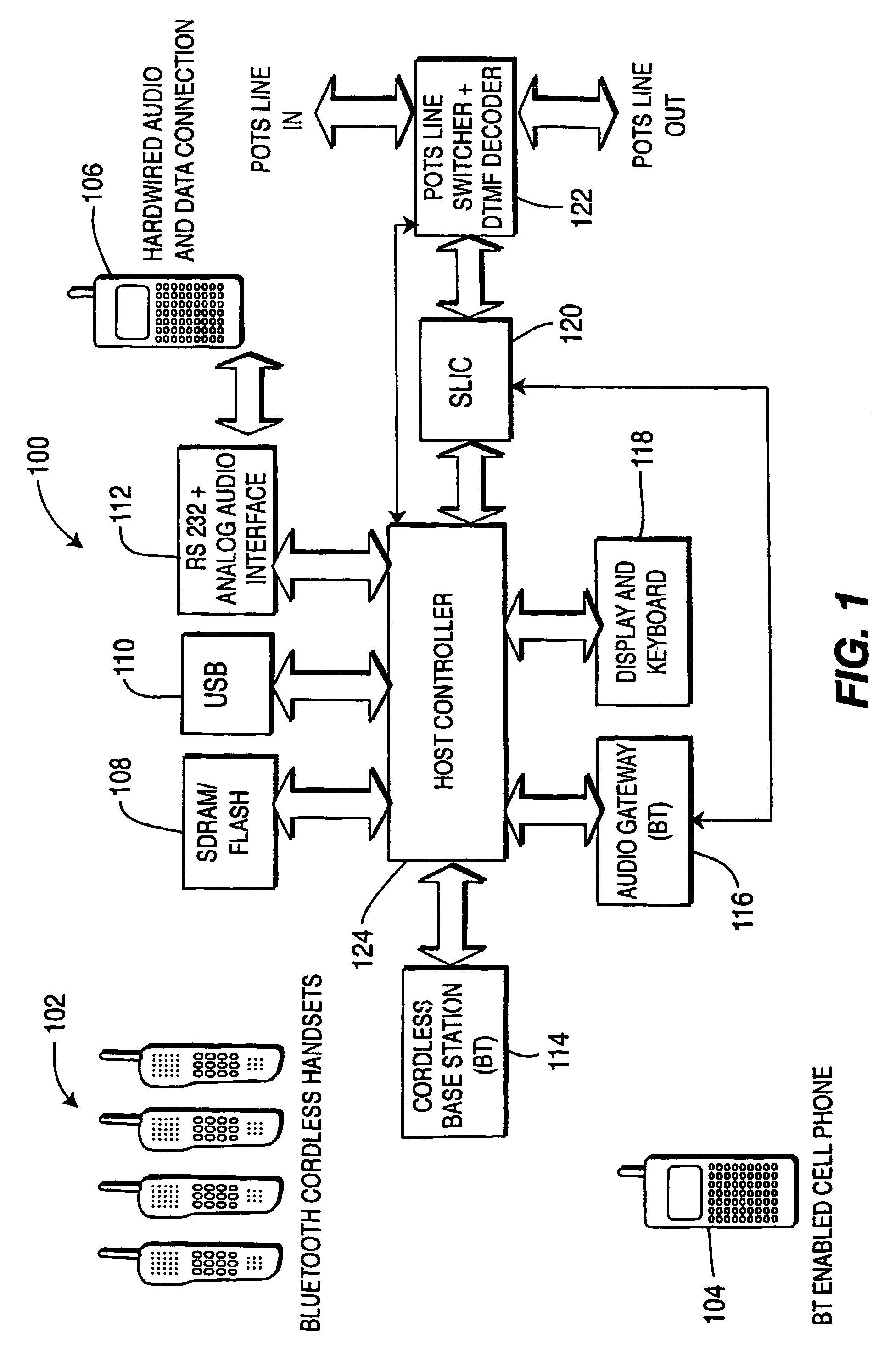
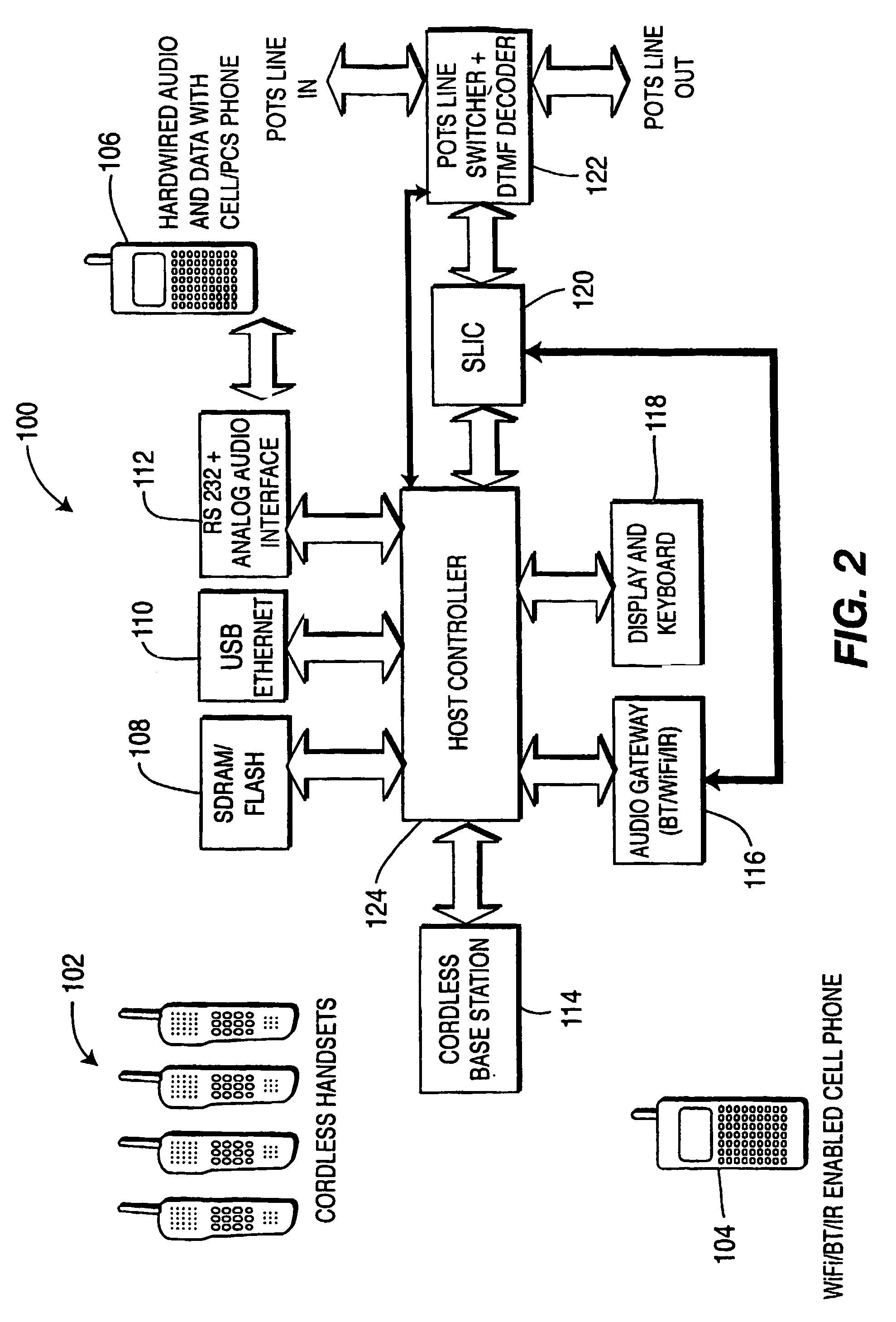
Integrated cellular/PCS-POTS communication system
ActiveUS8064594B2Interconnection arrangementsNetwork topologiesCommunications systemWireless transmission
There is provided a system for integrating at least one residential Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) phone to a cellular phone network. A Subscriber Line Interface Circuit (SLIC 120) interfaces audio from the cellular phone network to the at least one residential POTS phone. A line switcher (122), connected to the SLIC, connects the at least one residential POTS phone to any one of a POTS line or a cellular line. An audio gateway (116), connected to the SLIC, wirelessly receives the audio from a cellular phone connected to the cellular phone network for subsequent transmission to the at least one residential phone and wirelessly transmits the audio from the POTS line to the cellular phone.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
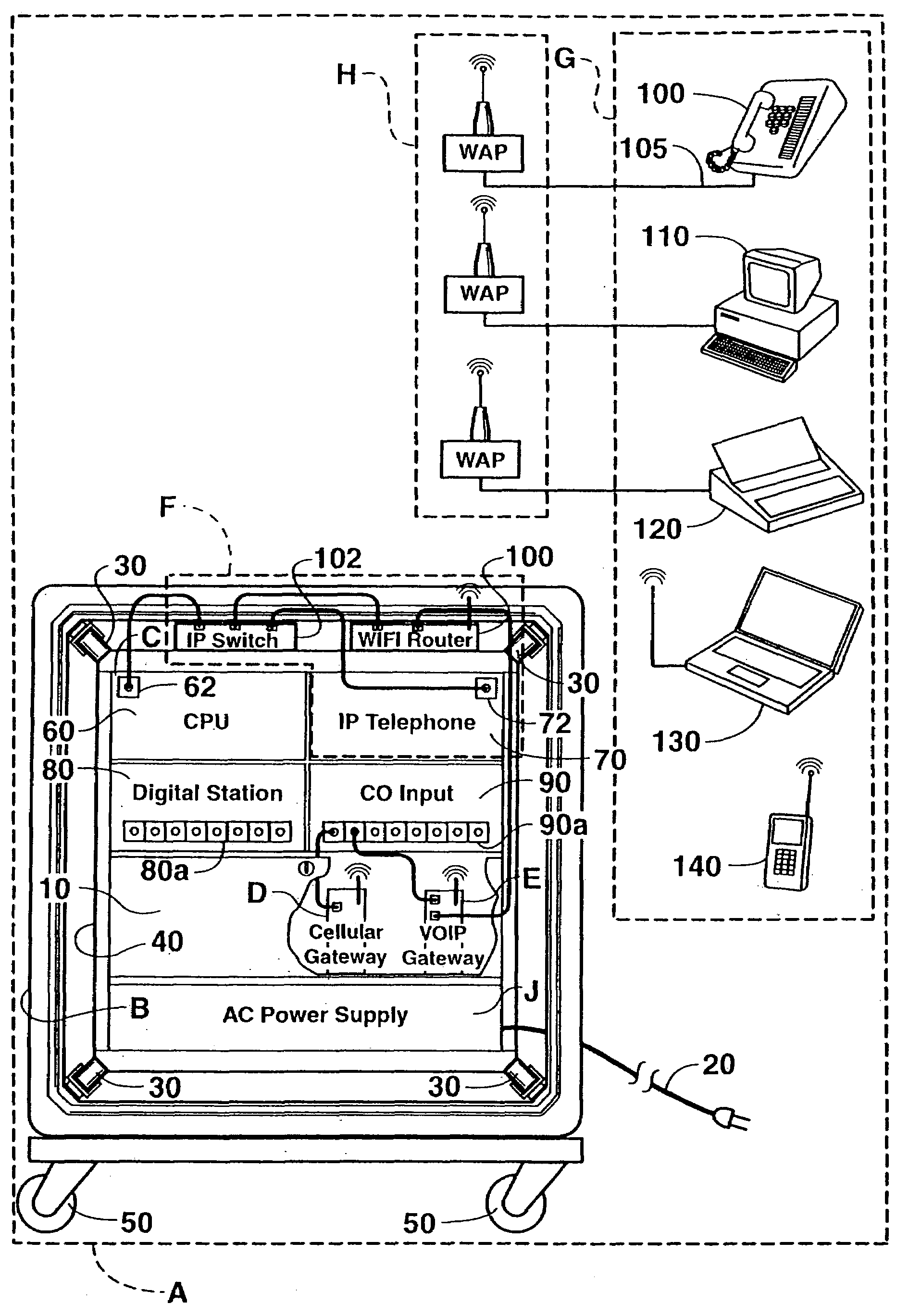
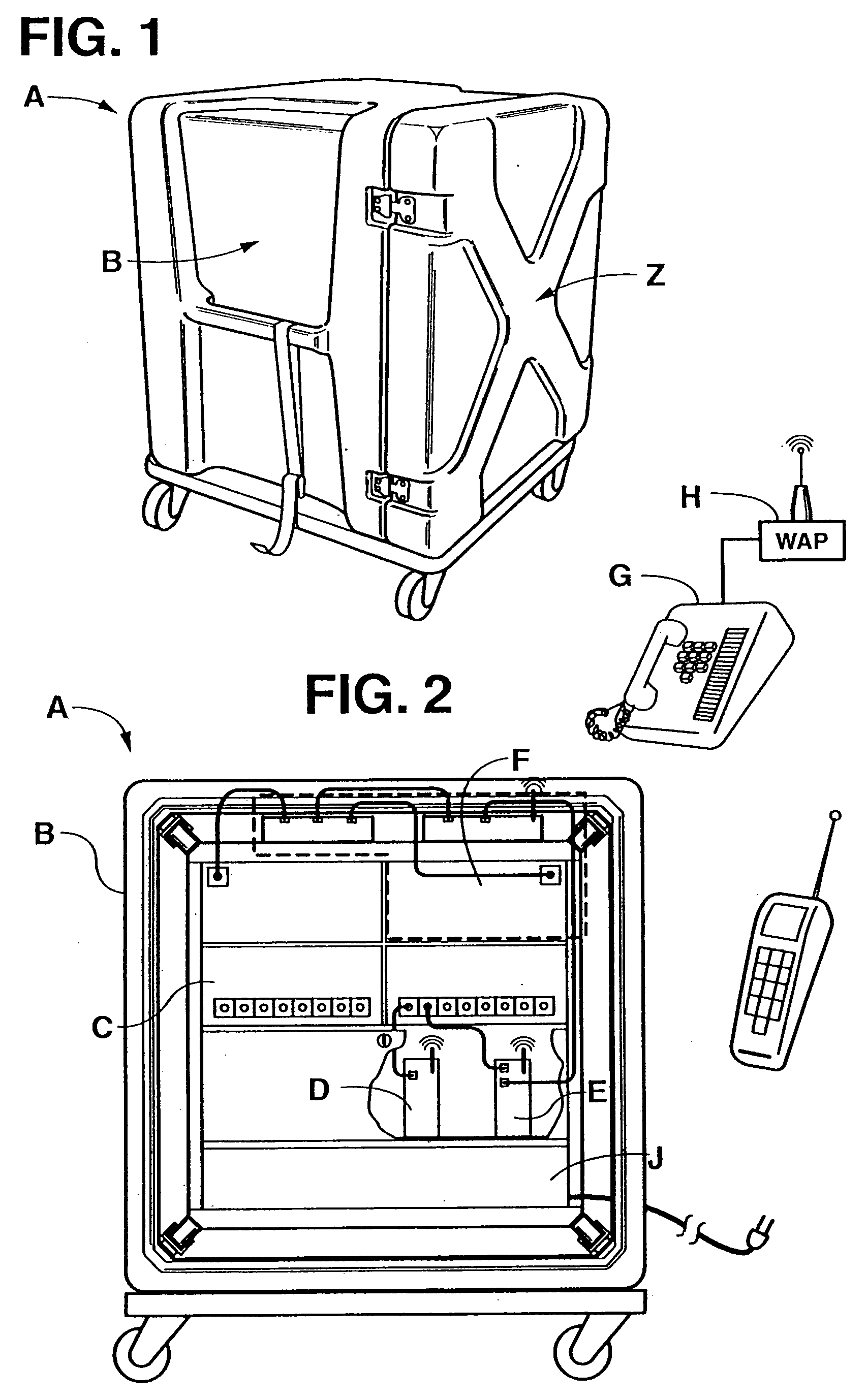
Full service mobile wireless telecommunication system and method
InactiveUS20080112339A1Overcome deficienciesMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationData systemMobile wireless
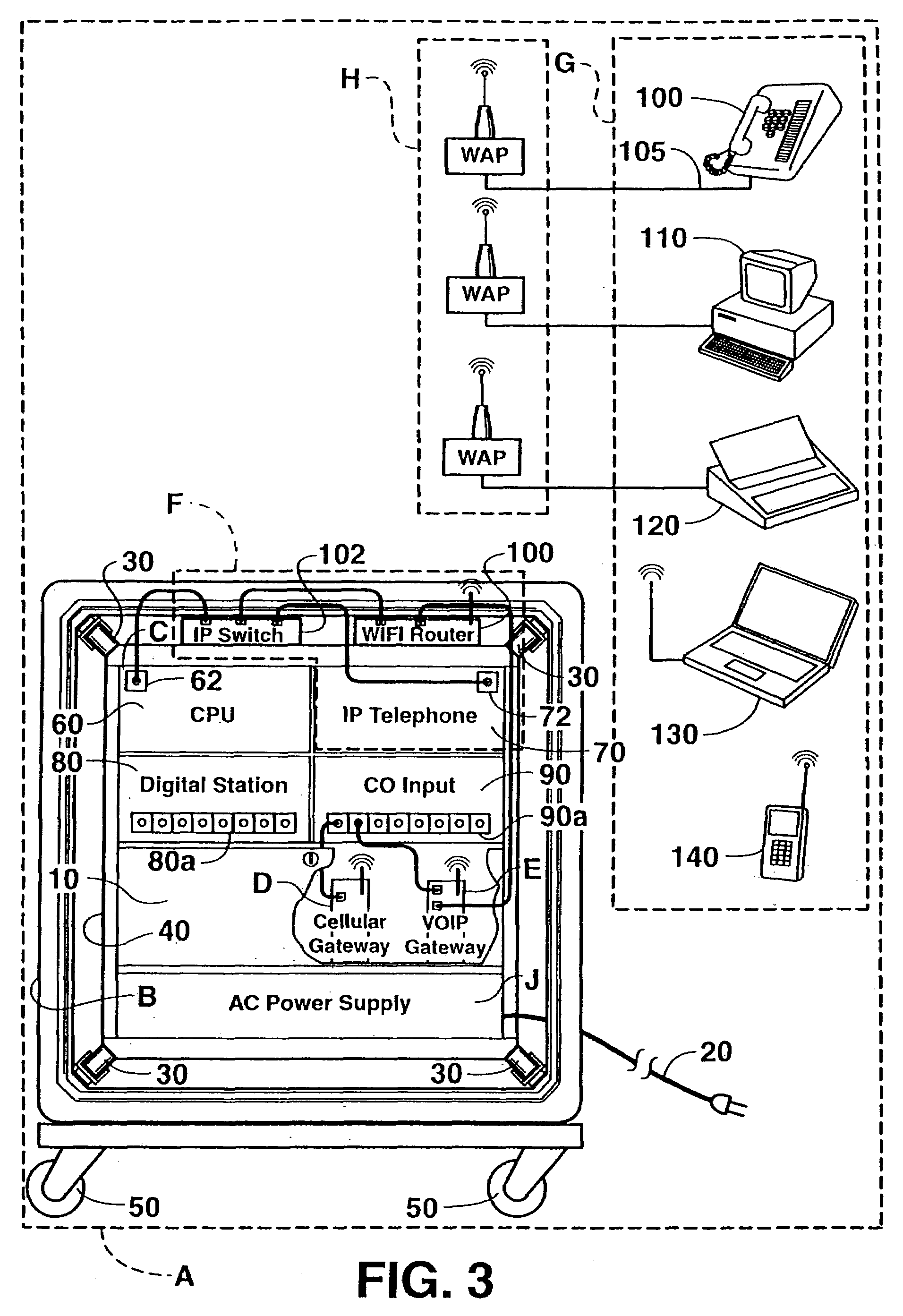
A system and method is provided to allow users in a remote location, such as a construction site, to both send and receive telephone calls, radio transmissions, and data without directly connecting to the plain old telephone system (POTS). The wireless telephone and data system is a rugged, portable, integrated system comprising an external gateway, WiFi network host, and Internet protocol-enabled telephone unit. When connected to an AC power source in the remote location, the system connects a variety of wireless devices to telephone, radio phone, cellular, and Internet access to facilitate communication of telephone calls, radio calls, and data transfer both internally and with the outside world.
Owner:TELECO
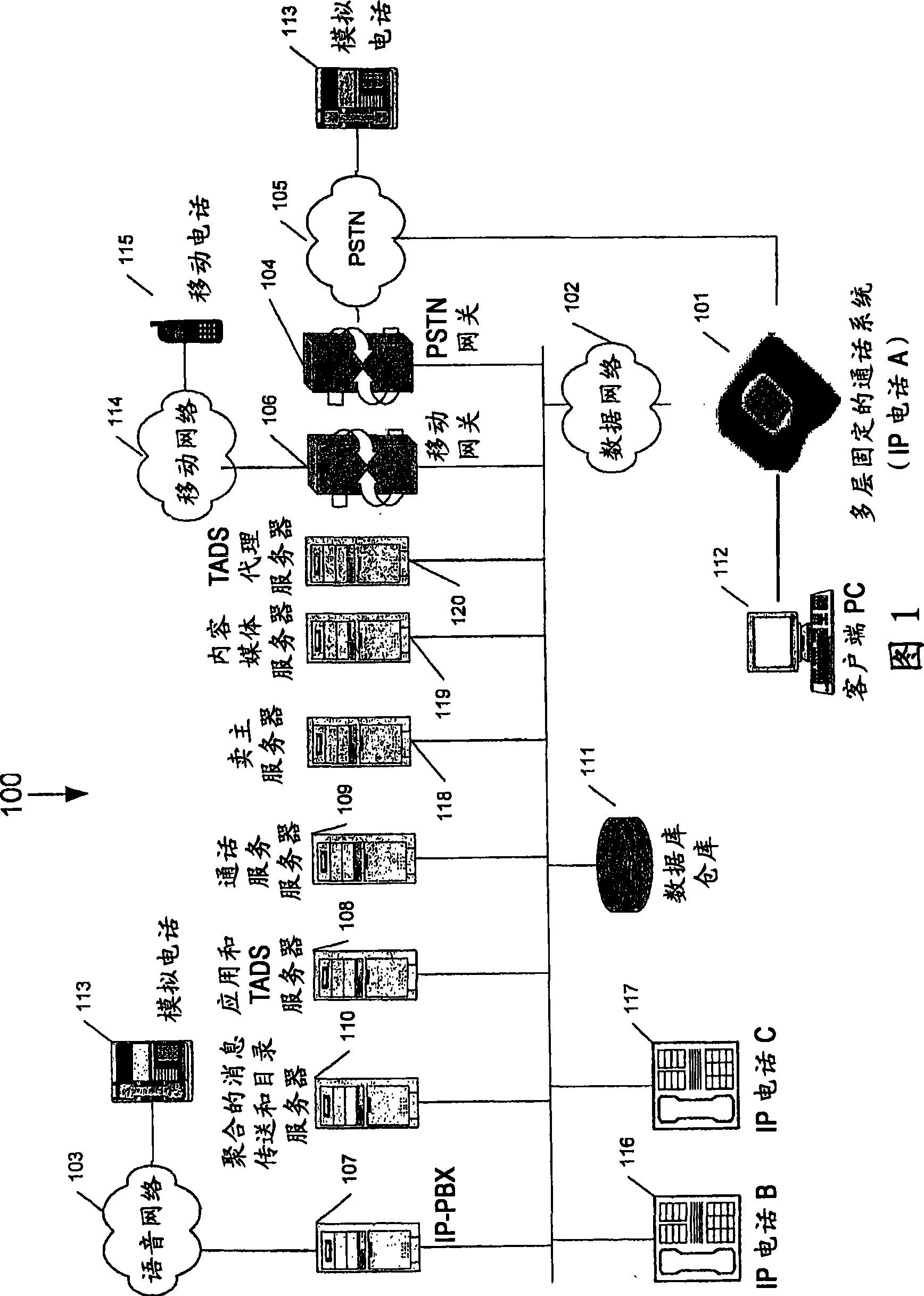
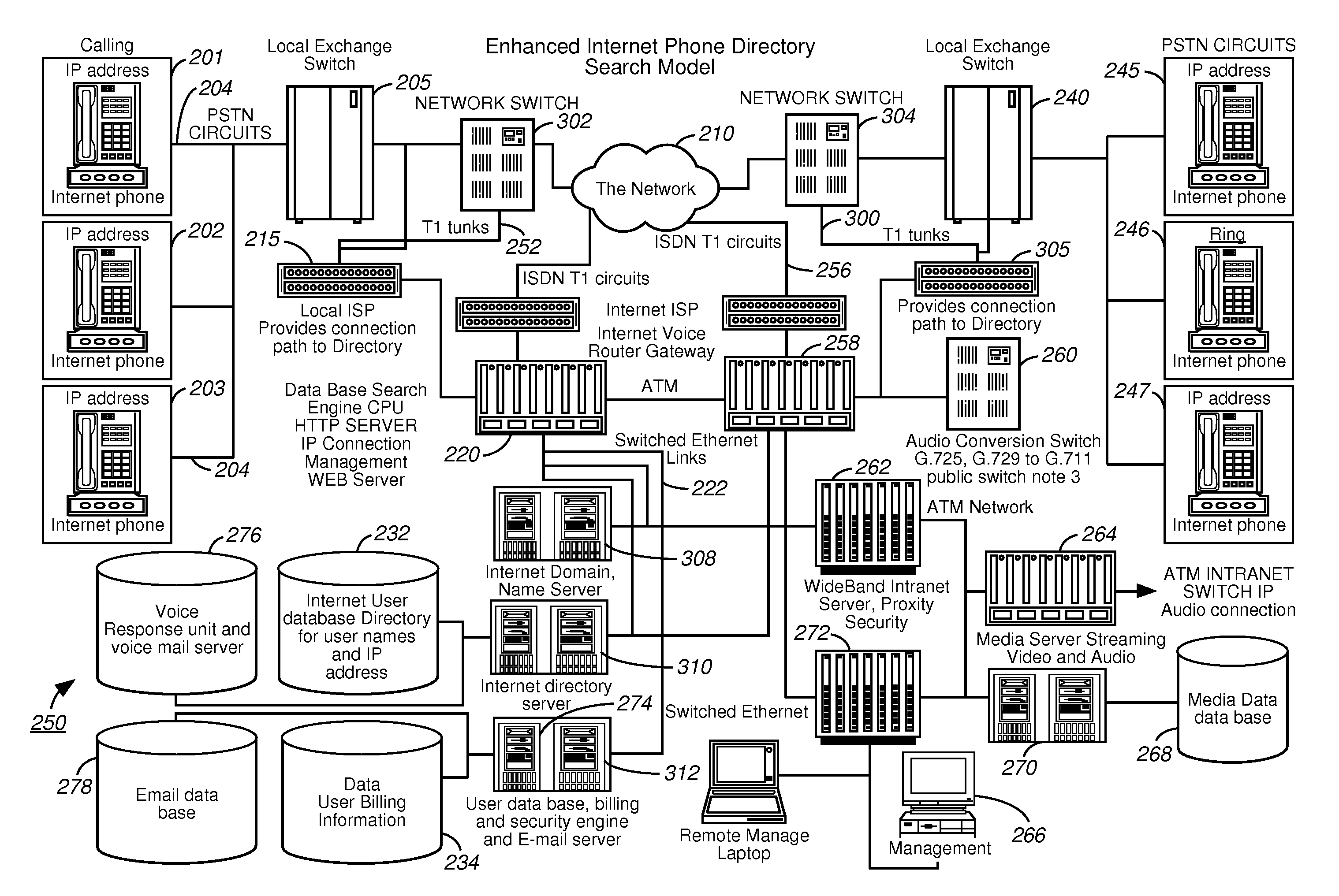
Internet phone system and directory search engine using same
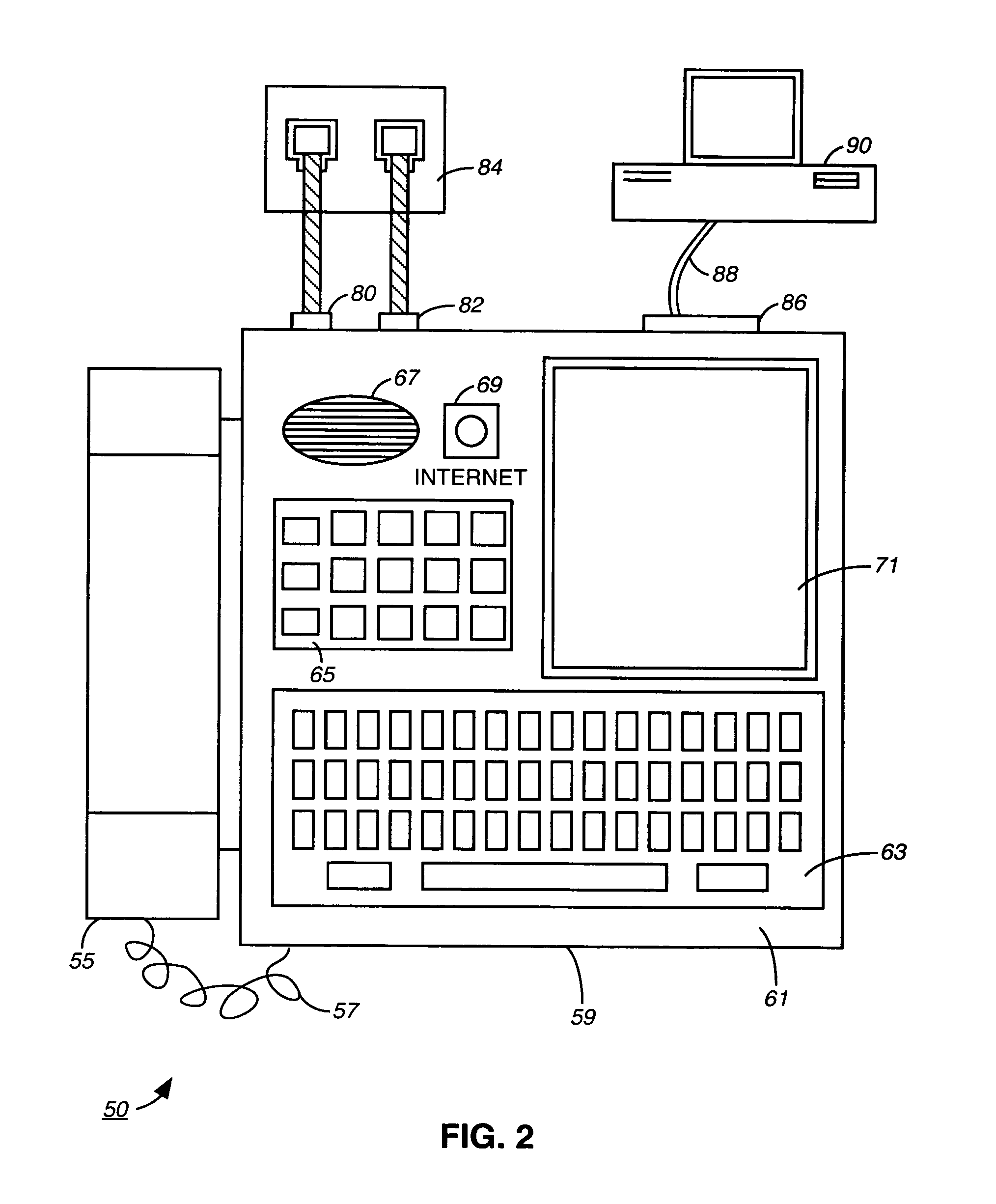
InactiveUS20050041649A1Easy to useSpecial service for subscribersNetwork connectionsDigital dataModem device
An Internet compatible dialer pad is used to dial into an Internet server to provide services similar to those found on the Plain Old Telephone System (“POTS”). The dialer pad has an integrated modem set, an extended keypad with alphanumeric entry keys and function keys, display screen and display electronics that renders visual call progress information to the user as well as other communications indicators and related information about the current Internet connection. The dialer uses the Public Switched Telephone System (“PSTN”) and standard LAN / WAN technology to give the user entry into a plurality of Internet calling functions. An Internet database is maintained and permits the dialing party to obtain callee information by entering alphanumeric characters via the dialer. Links from the PSTN to an Internet data base are not restricted to a specific digital data protocol.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
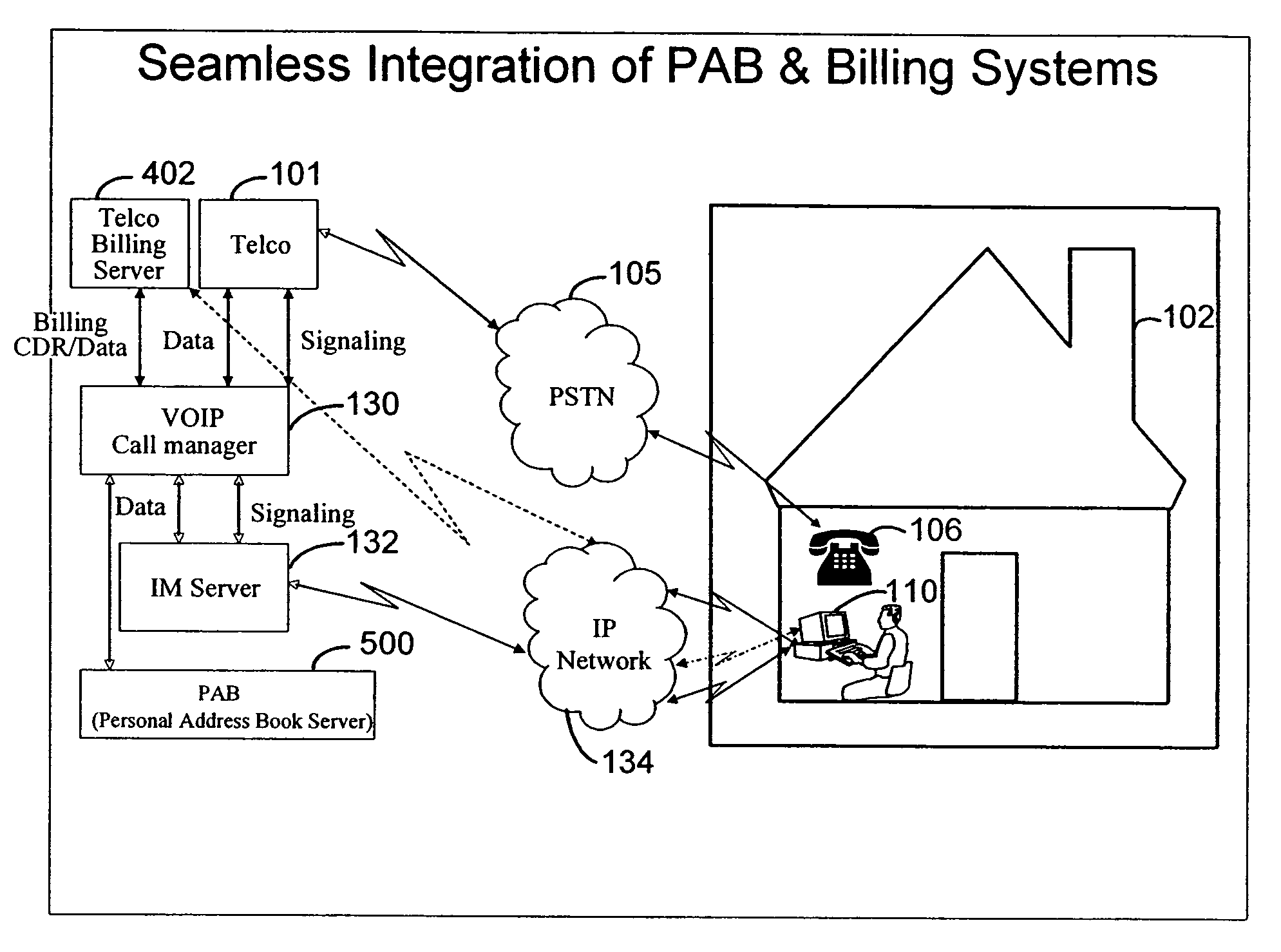
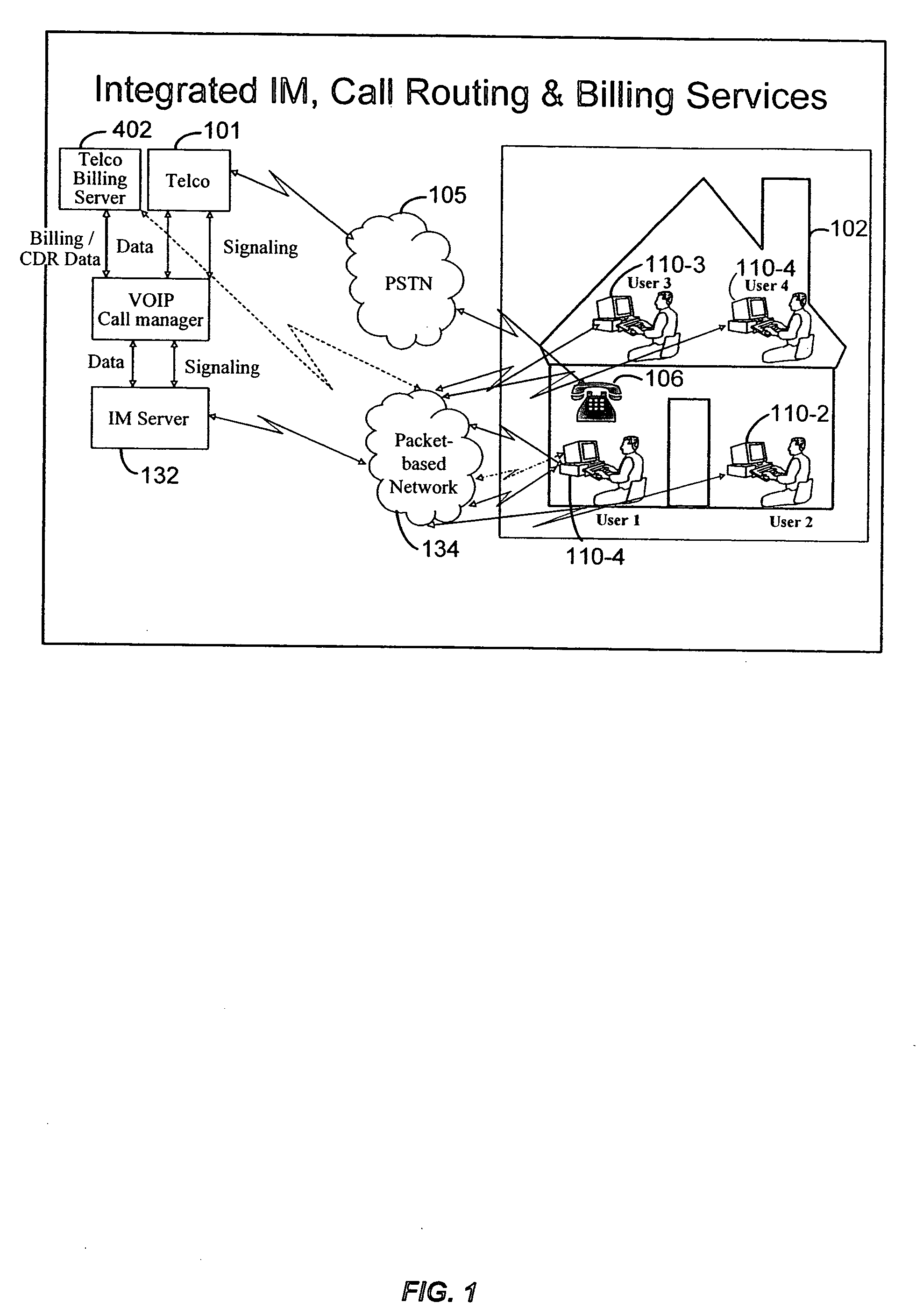
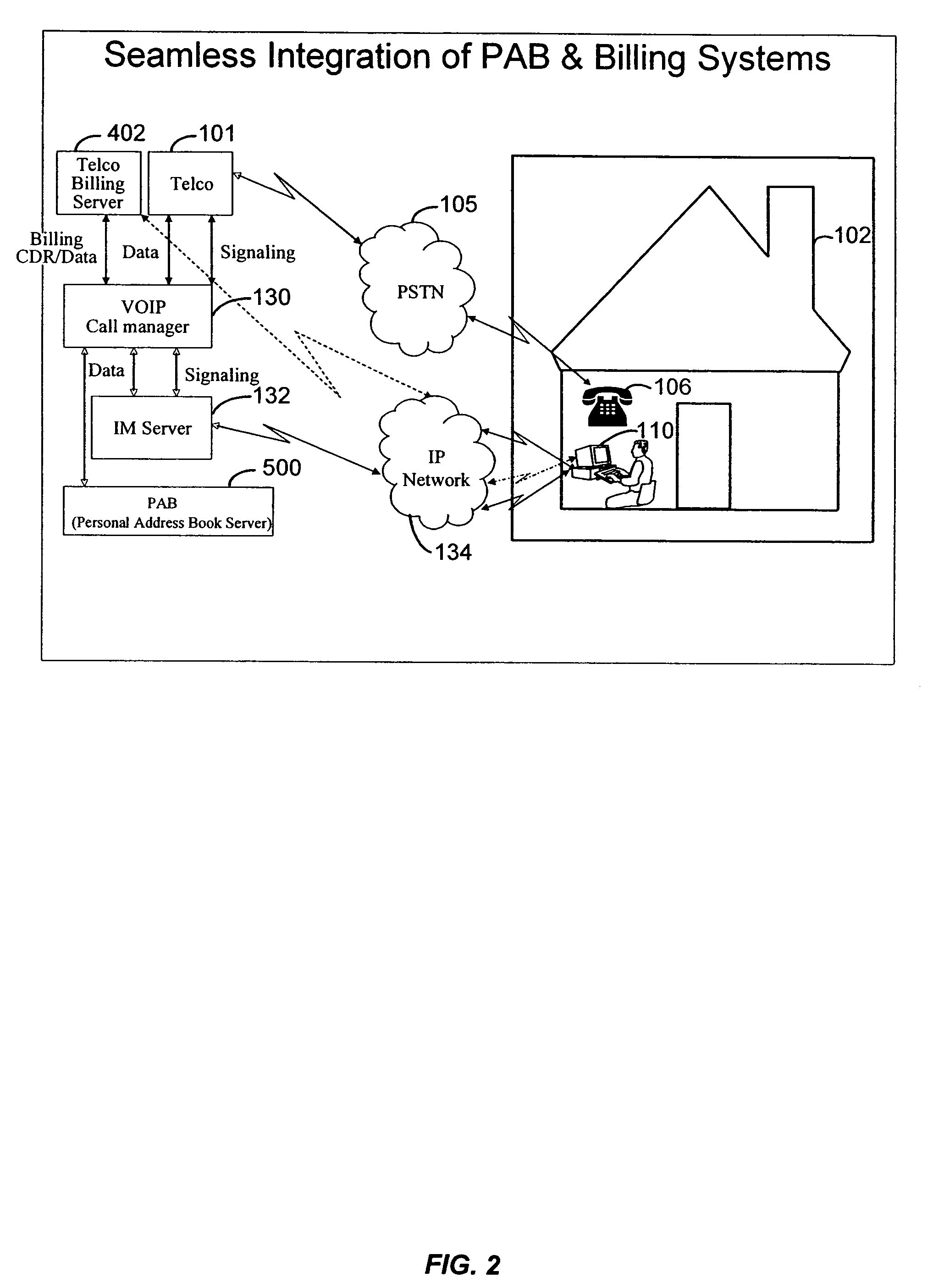
Integrated instant messaging, routing and telephone services billing system
ActiveUS20050259798A1Shorten the timeEliminate stepsMultiplex system selection arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesAddress bookPlain old telephone system
Techniques for using billing services to manage a personal address book are provided. The techniques comprise receiving a call detail record (CDR) for a plain old telephone system (POTS) or a voice-over-IP (VOIP) call by a user. The CDR is created by a telecommunication carrier that routed the call. The CDR may be stored on a telecommunications server associated with the telecommunications carrier. Address information for the call is determined from the CDR. This address information is added to the personal address book for the user. This address information may be available for the user when using an IM client.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
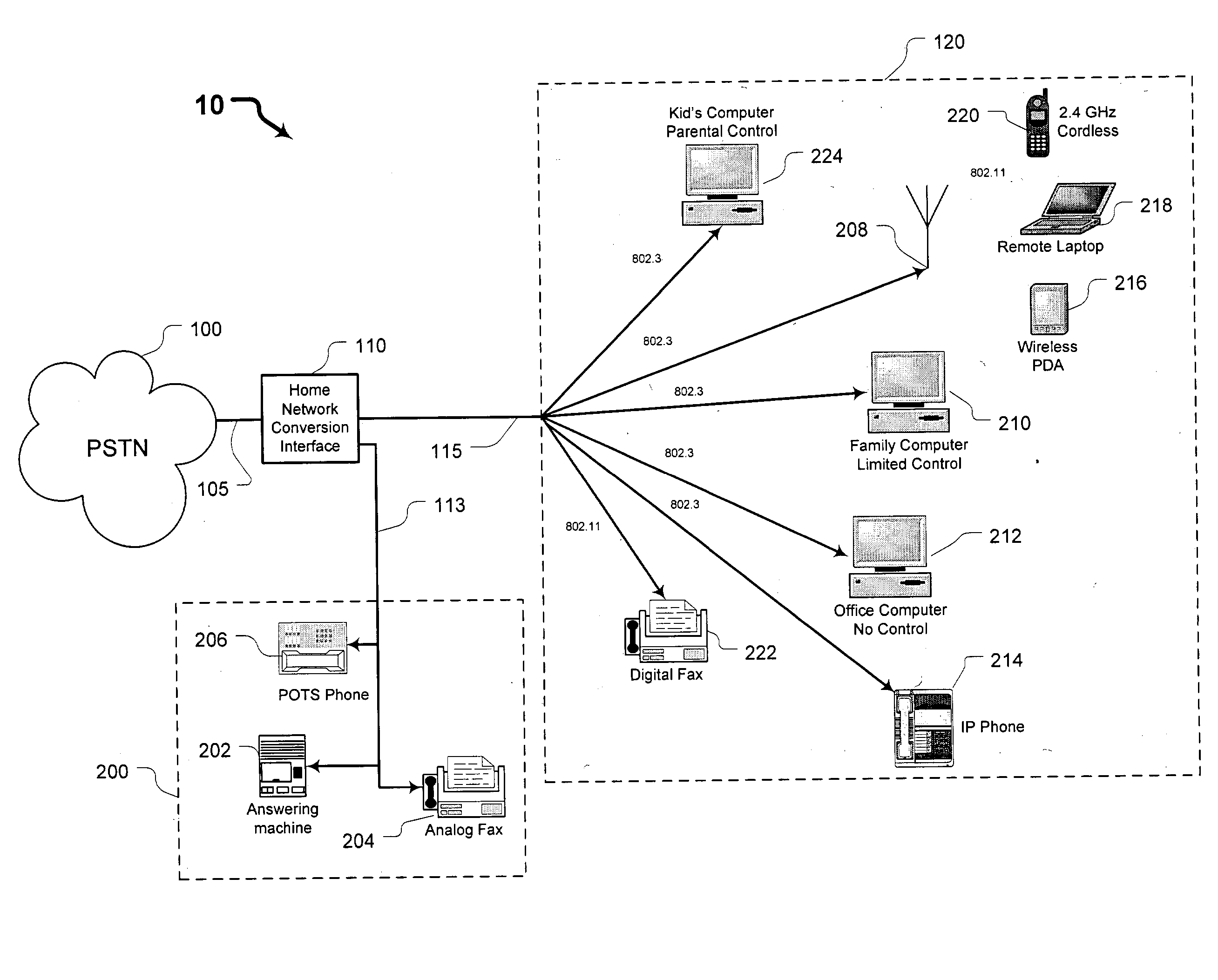
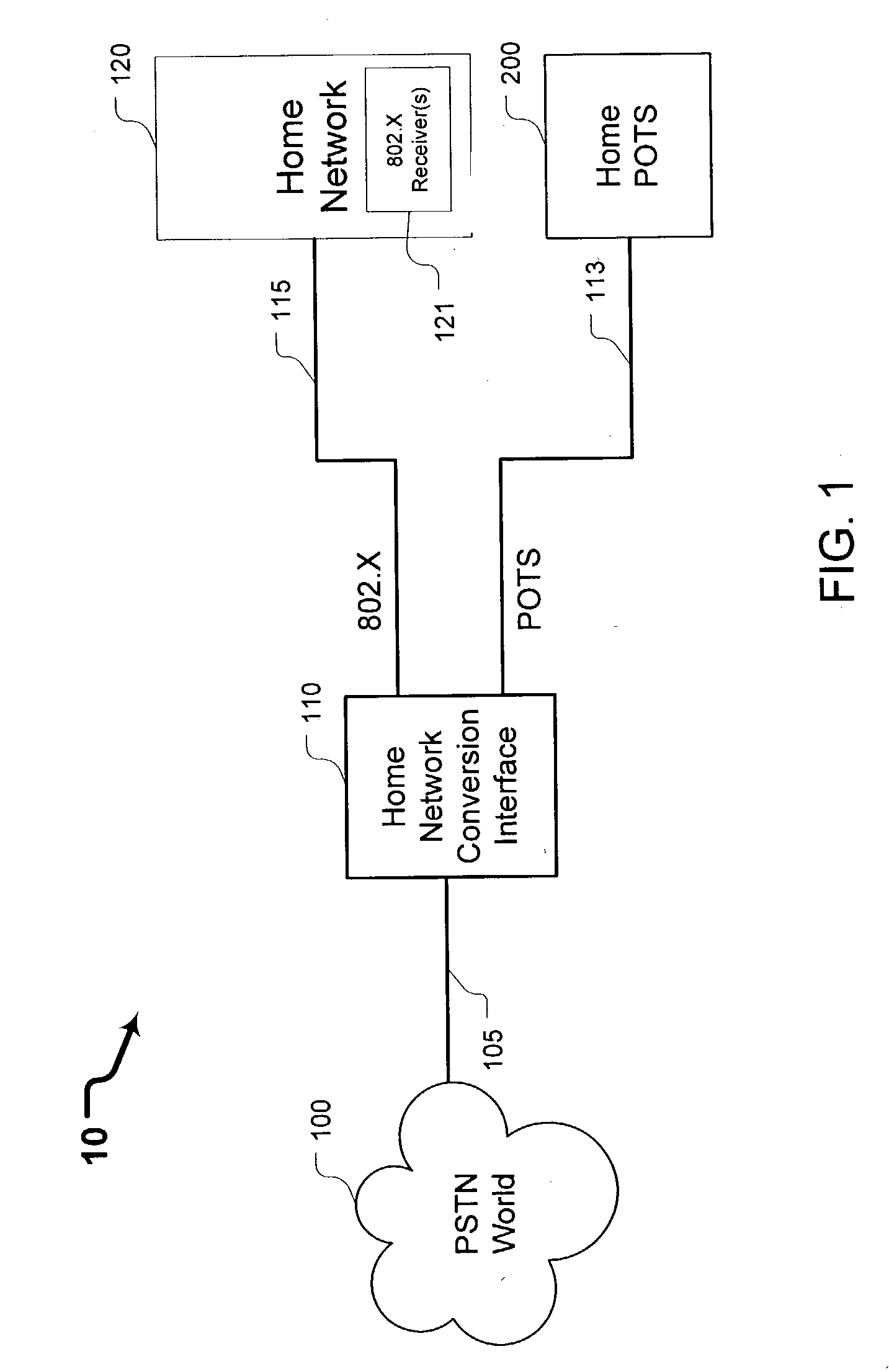
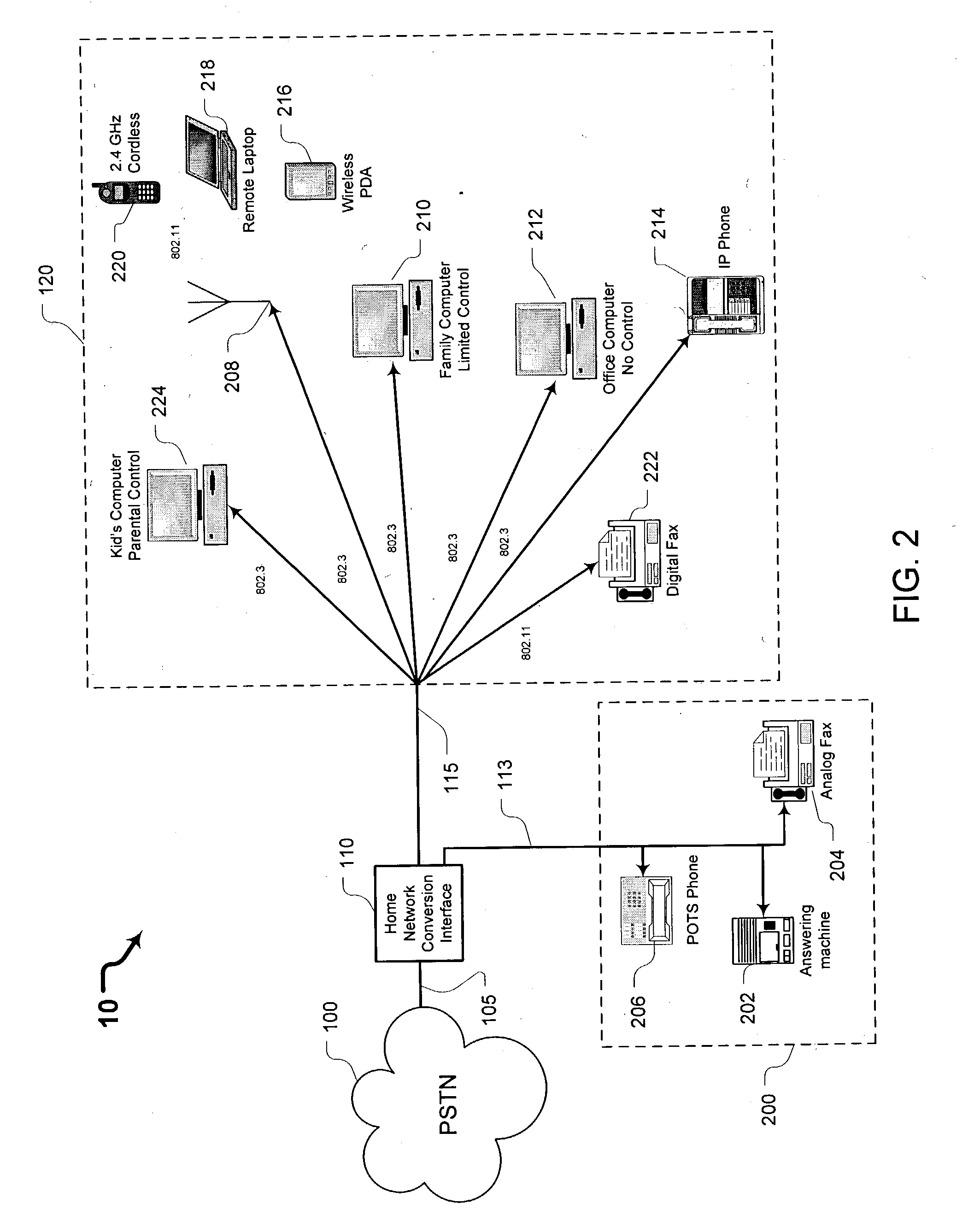
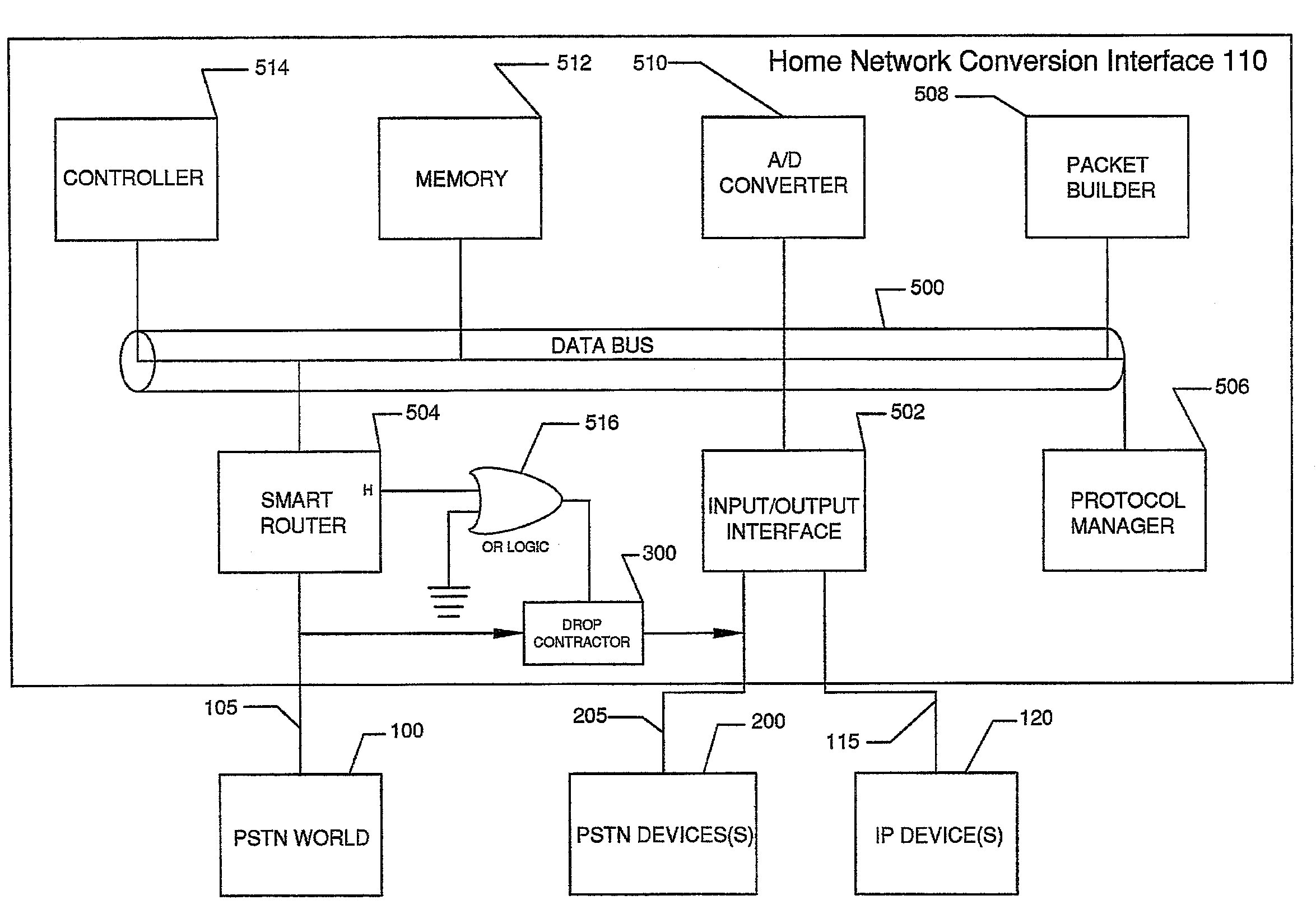
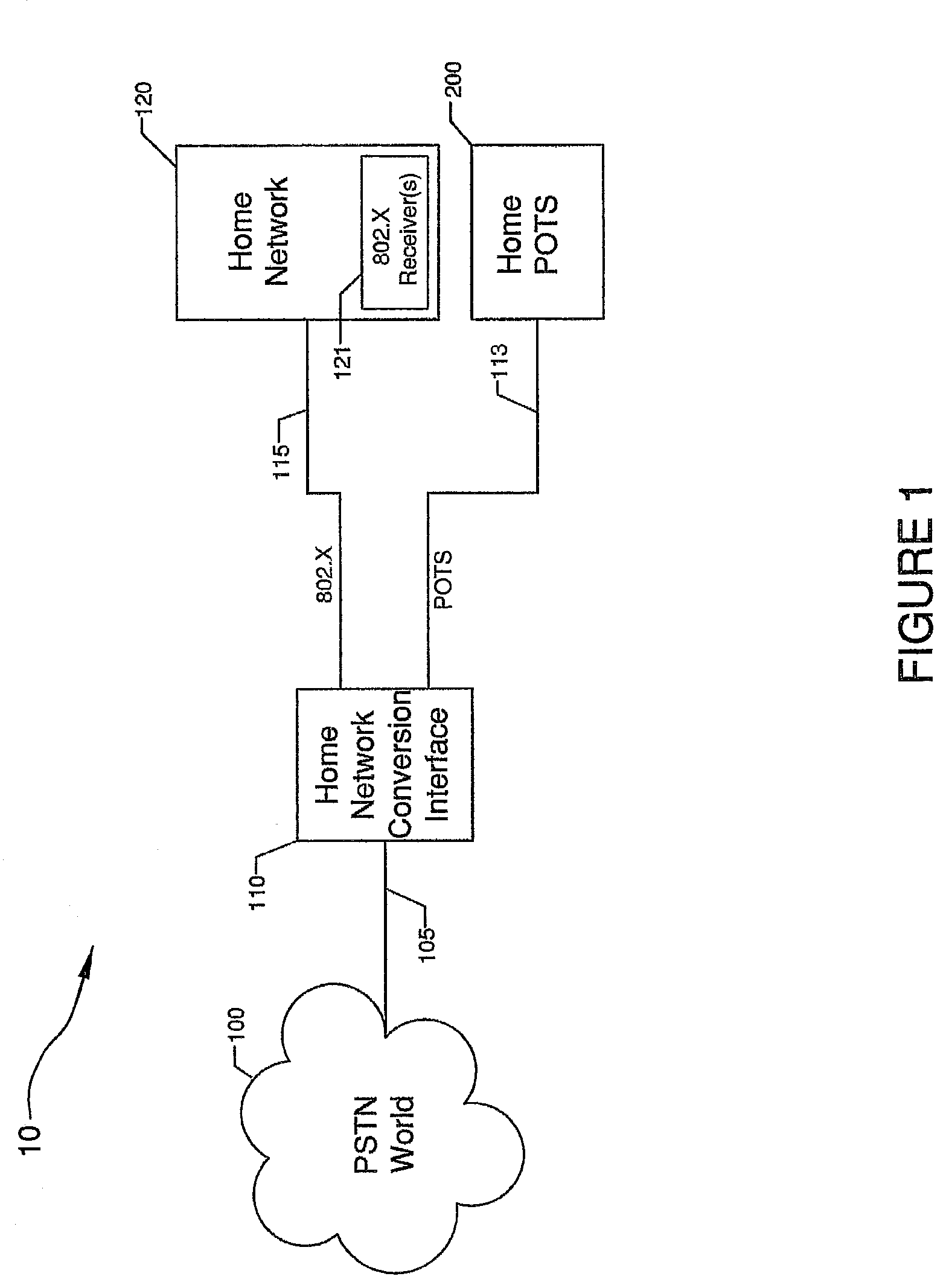
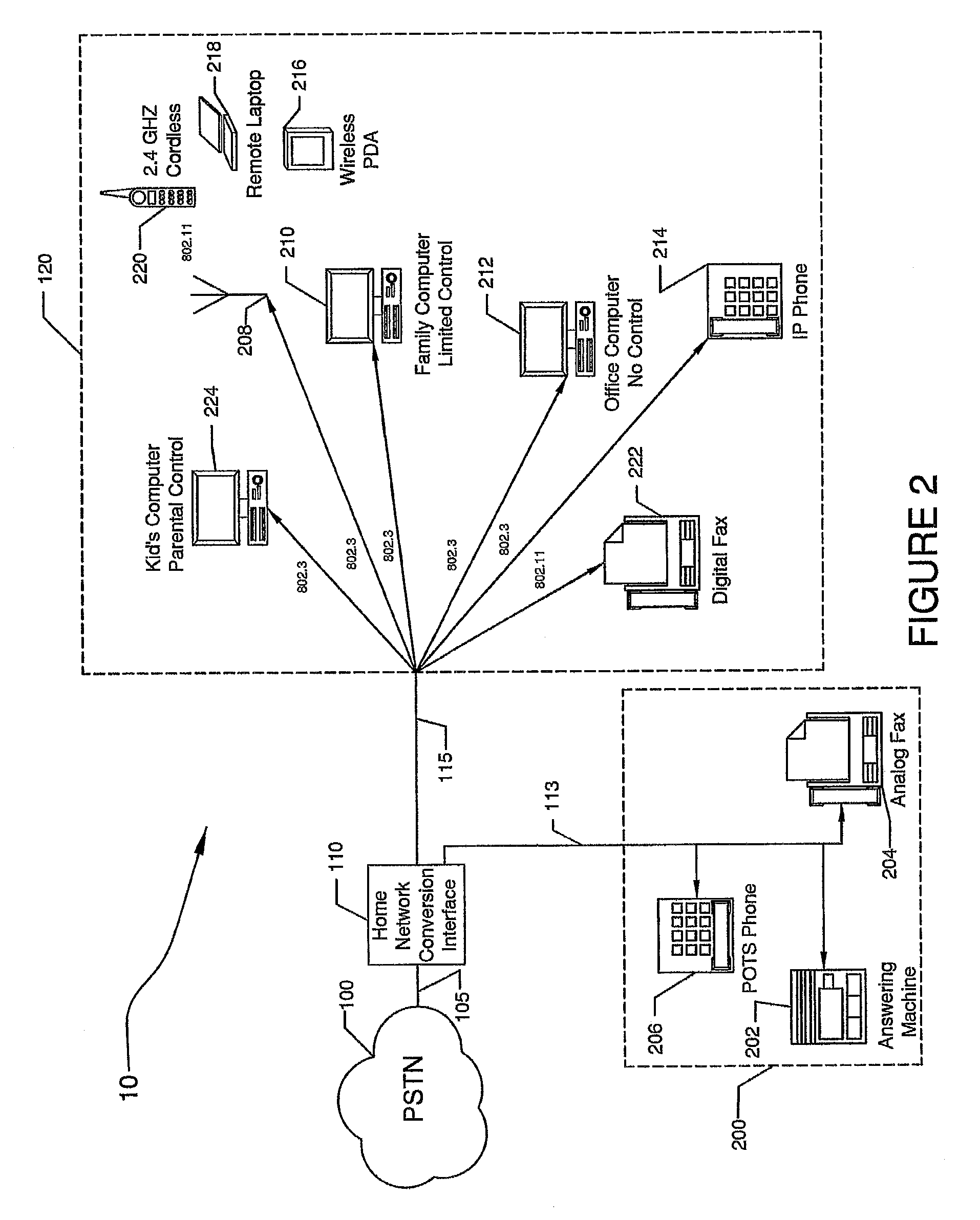
Systems and methods for providing a home network conversion interface
ActiveUS20040136398A1Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPlain old telephone systemData type
Systems and methods are provided wherein an incoming plain old telephone systems (PSTN) signal is input into a home network conversion interface. The home network conversion interface first determines the data type of the incoming signal. Next, the home network conversion interface creates a routing sequence of the incoming signal based on the determined data type. Finally, the home network conversion interface converts the incoming signal into an 802.X format and sends the signal to an appropriate IP device based on the determined signal type. Should the home network conversion interface loose electrical power, a drop contactor routes the incoming signal directly to an analog device without creating a routing sequence or performing an 802.X conversion.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P +2
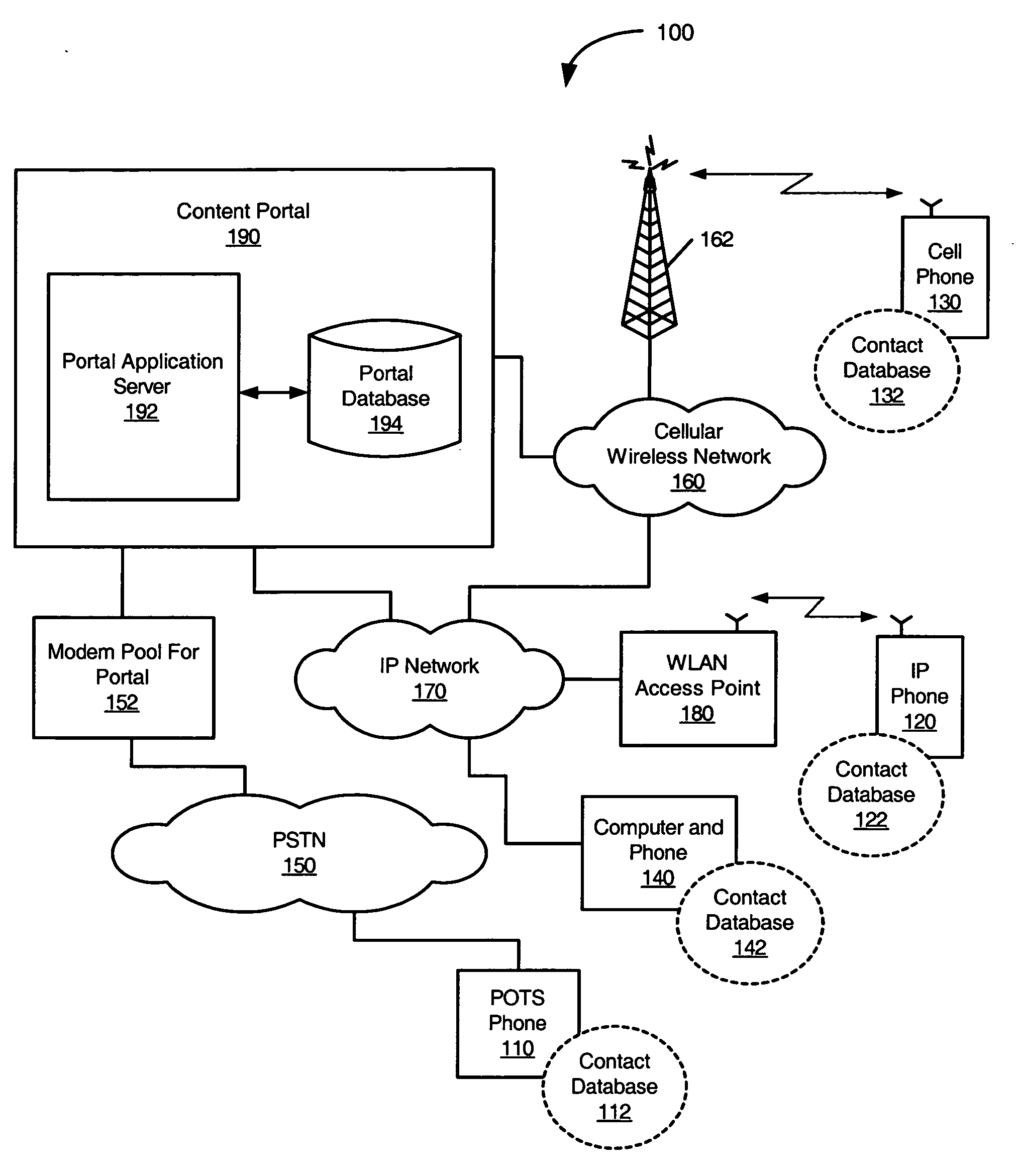
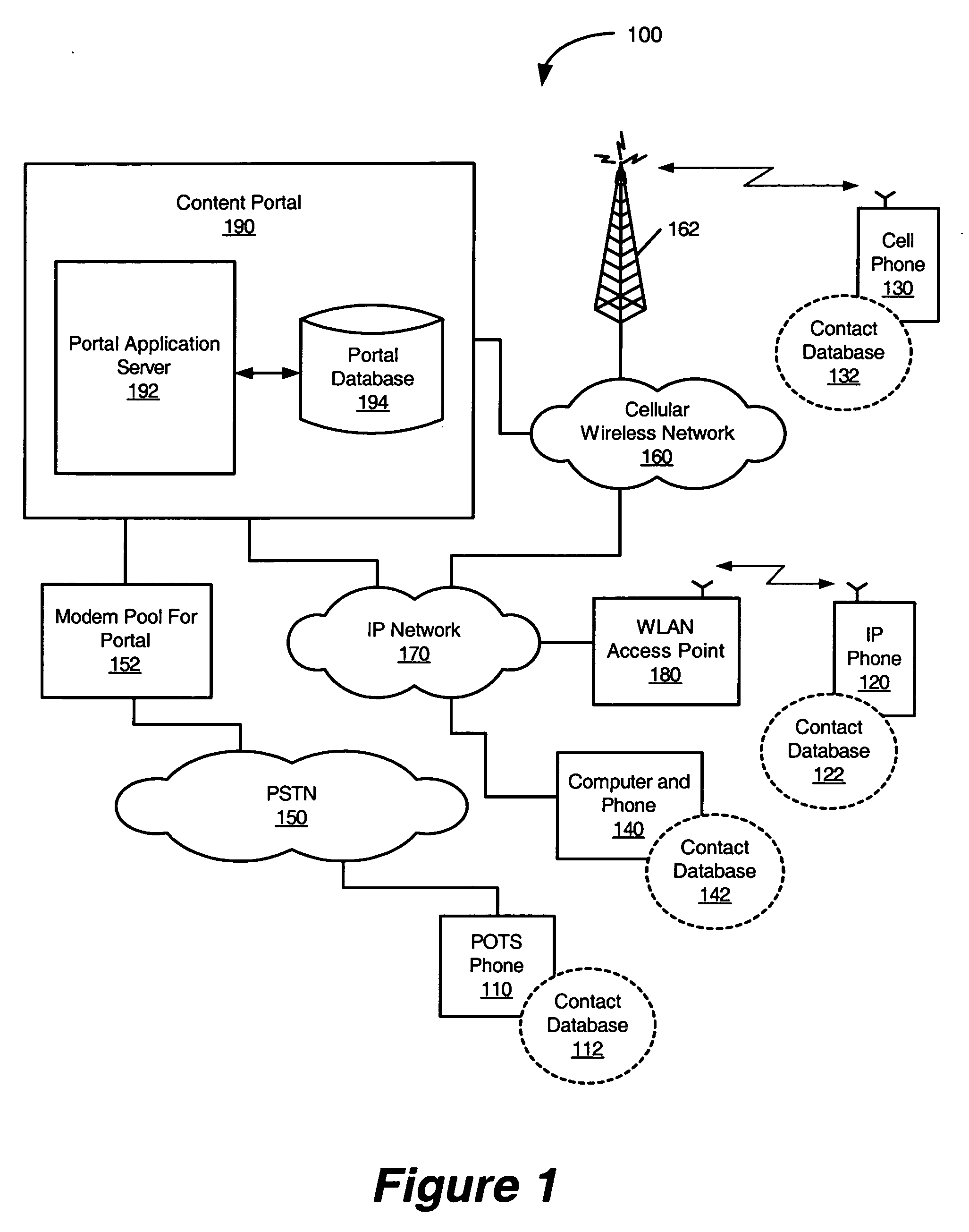
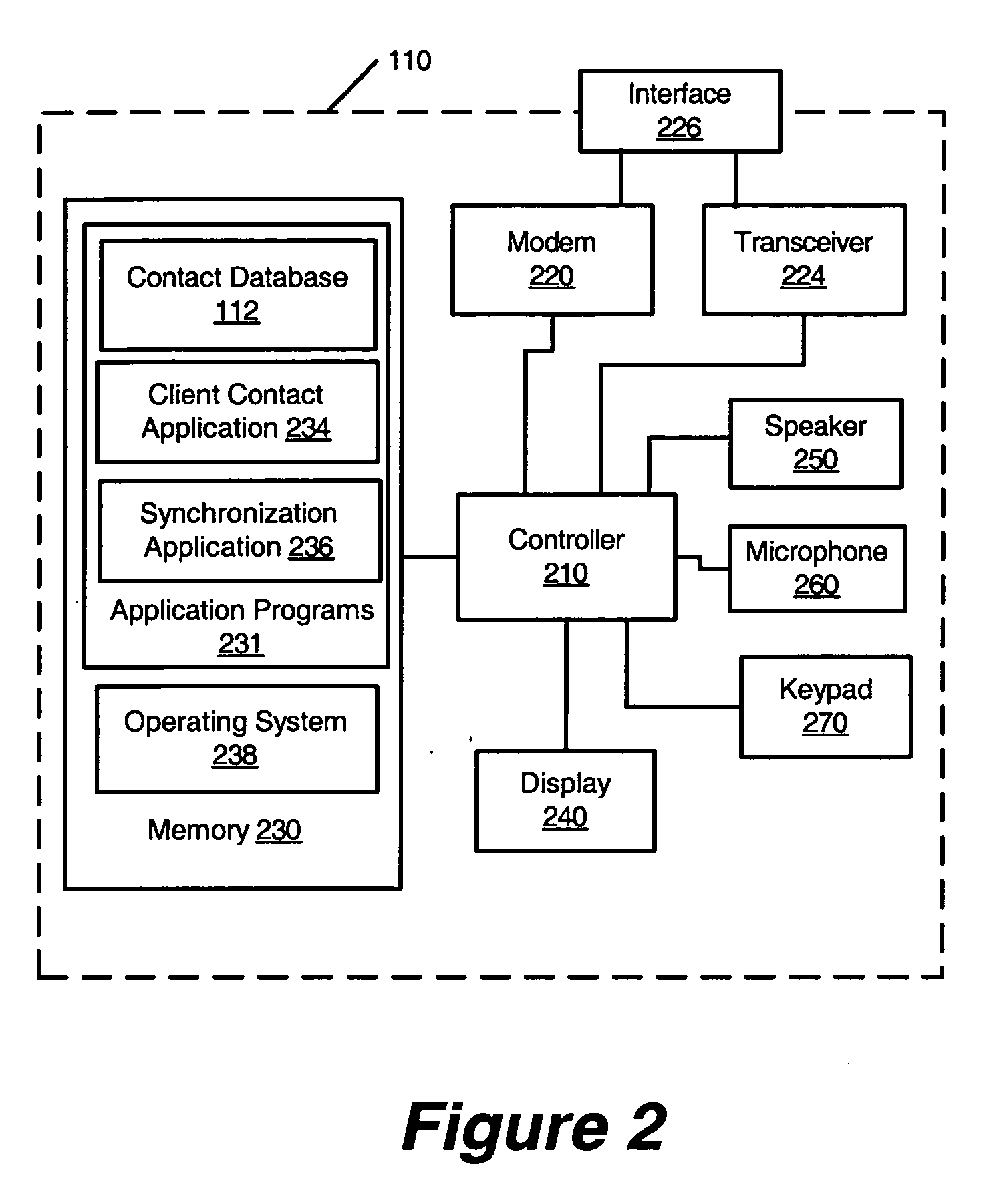
Synchronization of client application data between pots telephone and content portal through PSTN
InactiveUS20070127442A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationPlain old telephone systemTelephone network
Methods, Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) phones, and computer program products are provided for synchronizing client application data, such as names and associated telephone numbers in a phone book, between the POTS phone and a content portal through a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). A dial-up data communication connection is established between the POTS phone and the content portal through the PSTN. A determination is made at the content portal that the POTS phone is associated with client application data in the portal database of the content portal. Client application data is synchronized between the POTS phone and the portal database in response to the determined association between the POTS phone and client application data in the portal database.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Software platform for data-voice applications operating on an internet protocol (IP) phone
InactiveCN101433035AUnderstand detailed instructionsNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suitePlain old telephone system
A software platform in an Internet Protocol (IP) phone having the ability to be used with different communication infrastructures such as broadband, wireless communication and Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) service. Further, the software platform in the IP phone is used in conjunction with a communication architecture, referred to herein as the Transaction Applications Delivery Services (TADS) communications architecture, that provides the ability to develop, deliver and manage data-voice applications operating on the IP phone.
Owner:COMMOCA
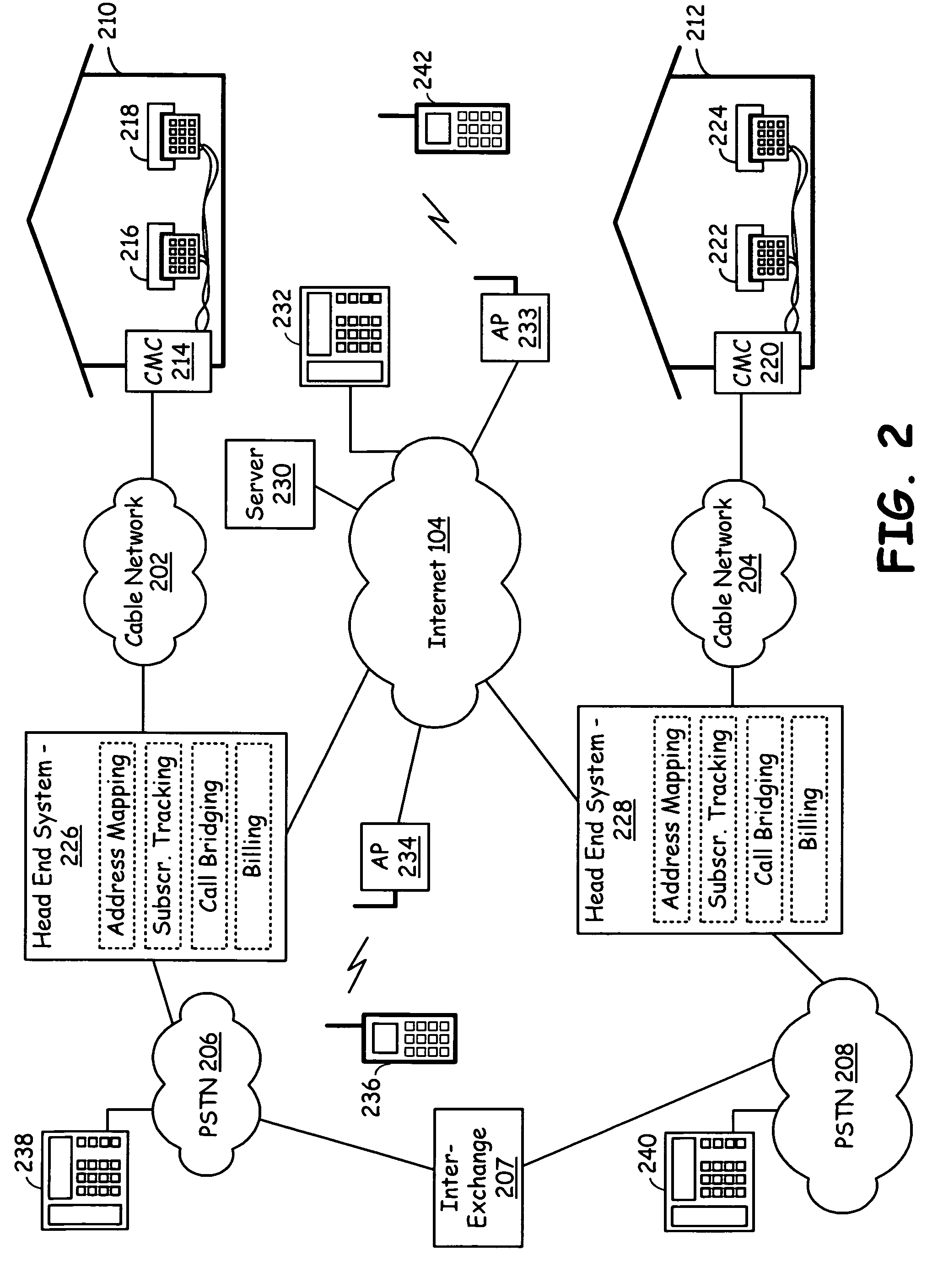
Cable telephony network supporting roaming VoIP terminals
InactiveUS7570631B2Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersEnd systemThe Internet
A cable infrastructure includes a plurality of cable modem circuits communicatively coupled to a cable network and associated with a corresponding one of a plurality of subscribers. Each of a plurality of telephones has both a POTS (Plain Old Telephone System) interface and a unique telephone number and associates with a corresponding one of the plurality of subscribers. Each of a plurality of interface circuits couples one of the plurality of cable modem circuits with a corresponding one of the plurality of telephones via the POTS interface. A head end system communicatively couples to the cable network, the public switched telephony network, and the Internet network and supports address mapping that enables communication exchanges between one of the plurality of telephones and an Internet telephony device. The address mapping also enables communication exchanges between telephones serviced by differing head ends via an Internet pathway that is independent of the public switched telephony network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
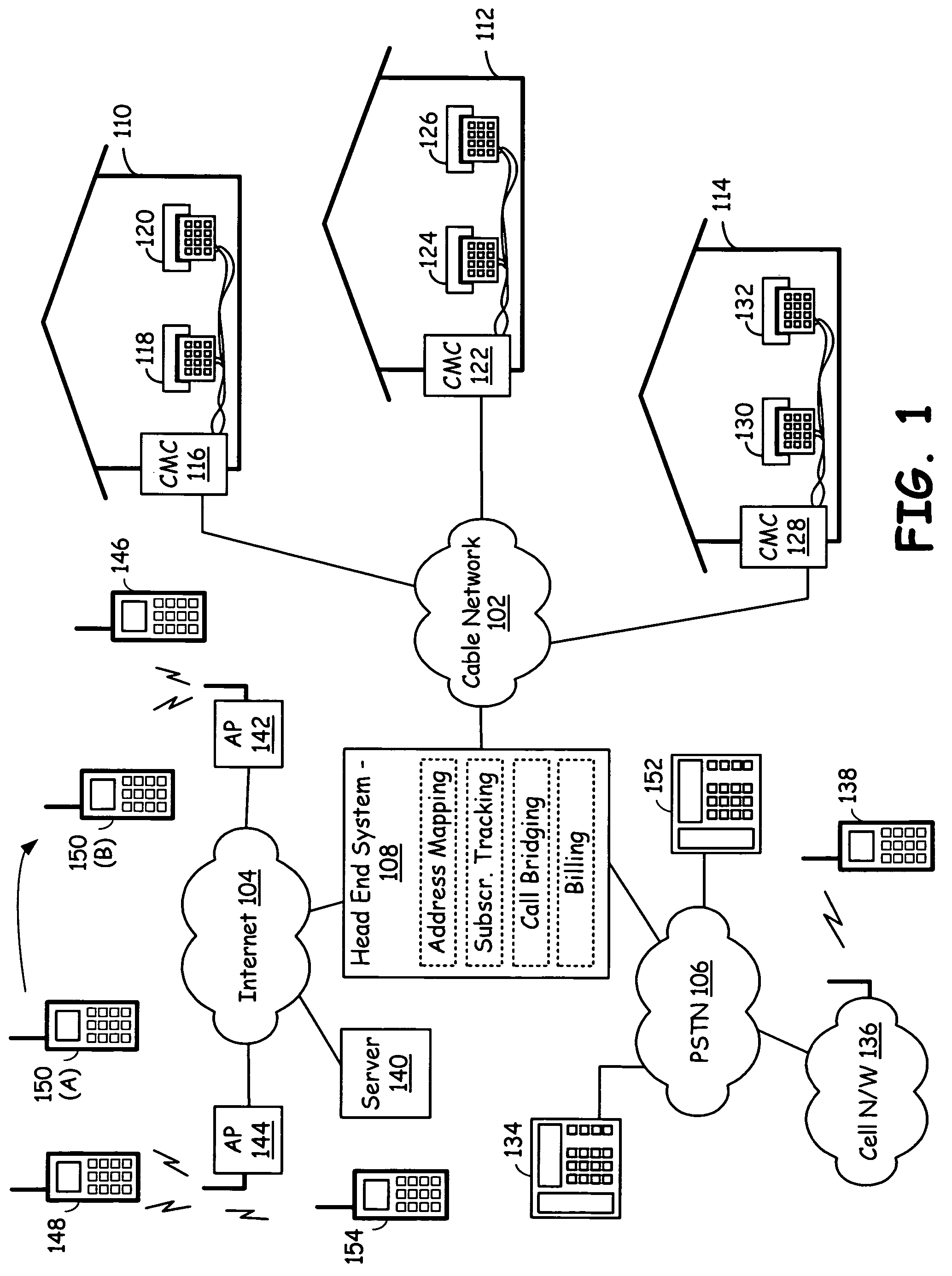
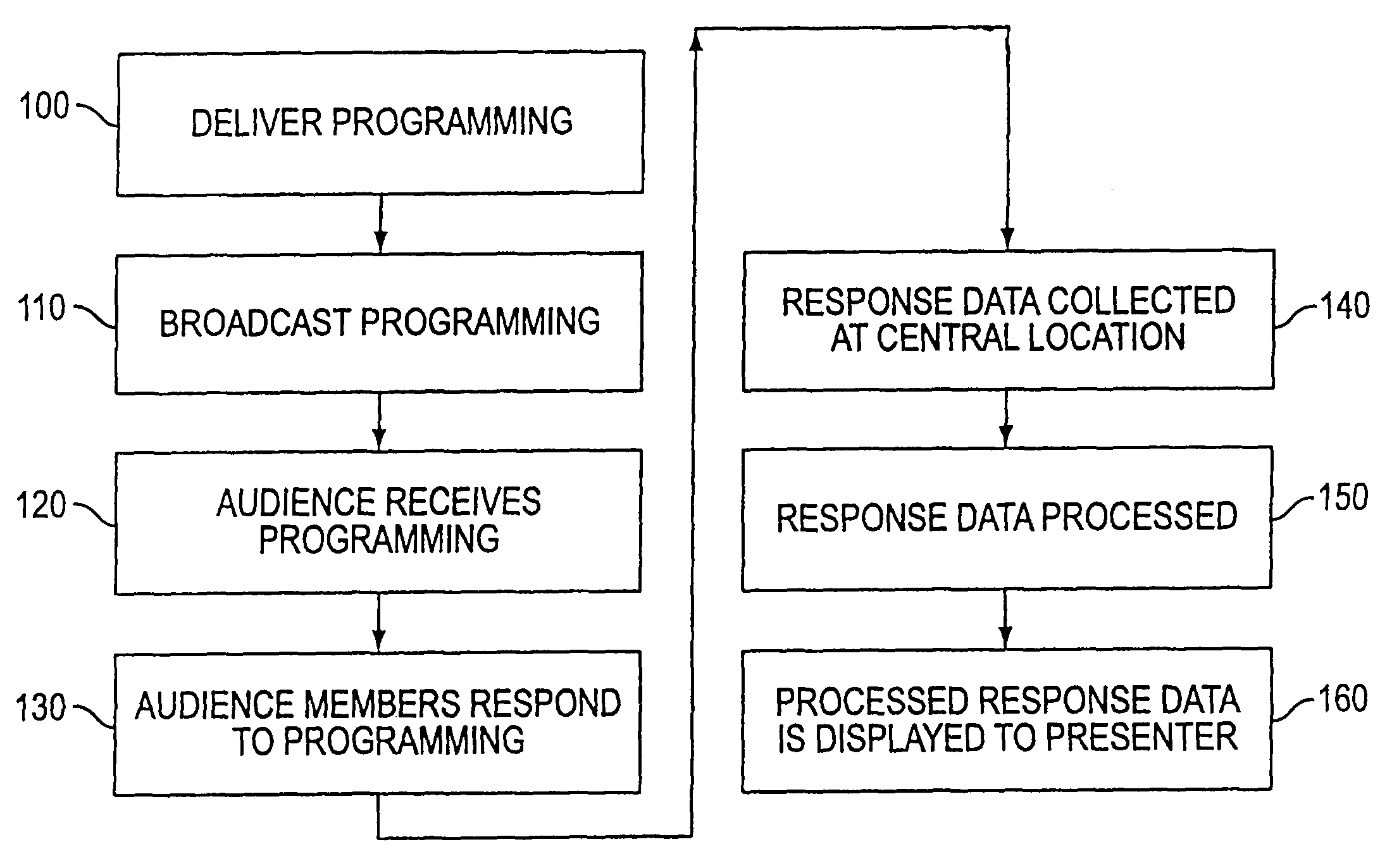
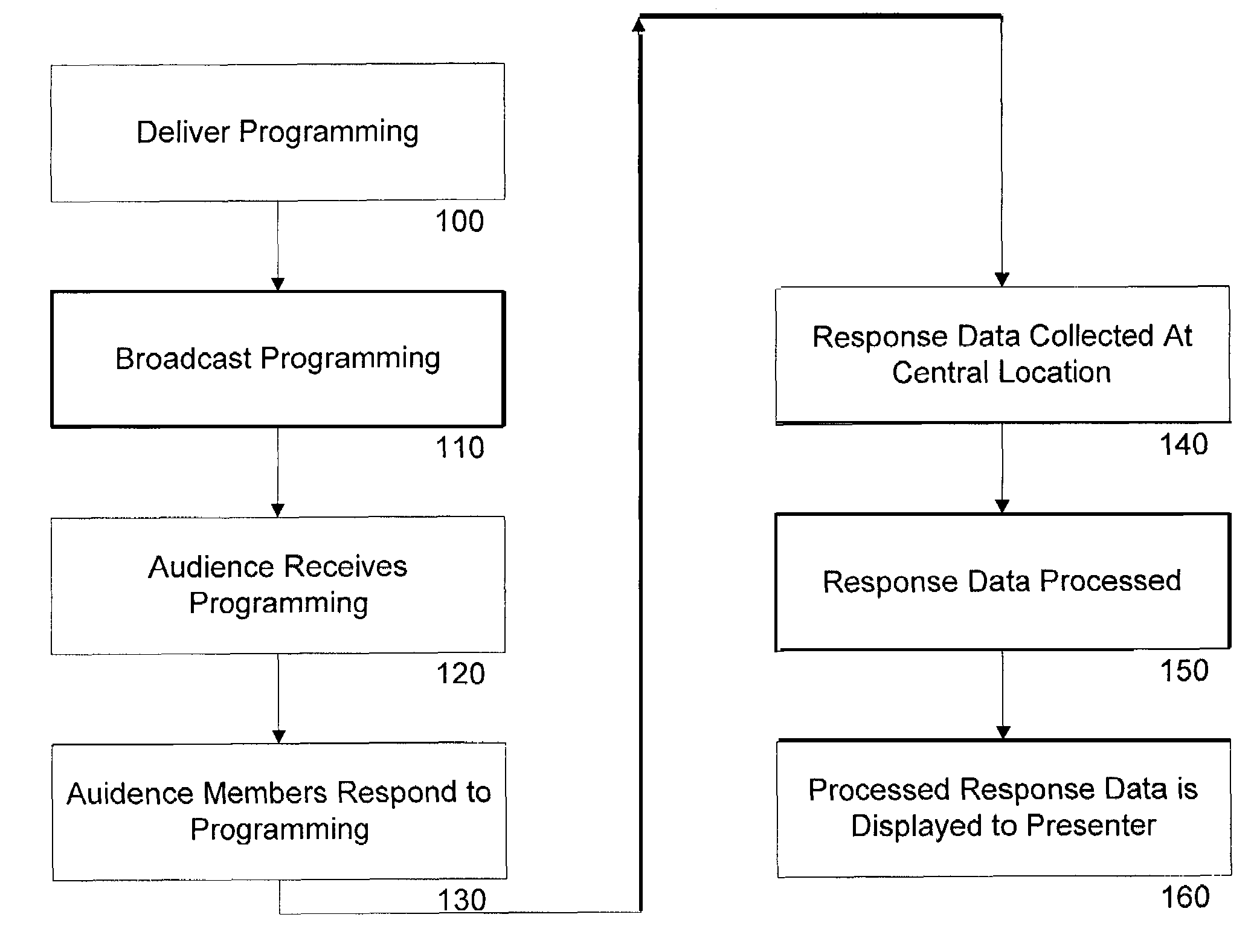
Method and apparatus for response system
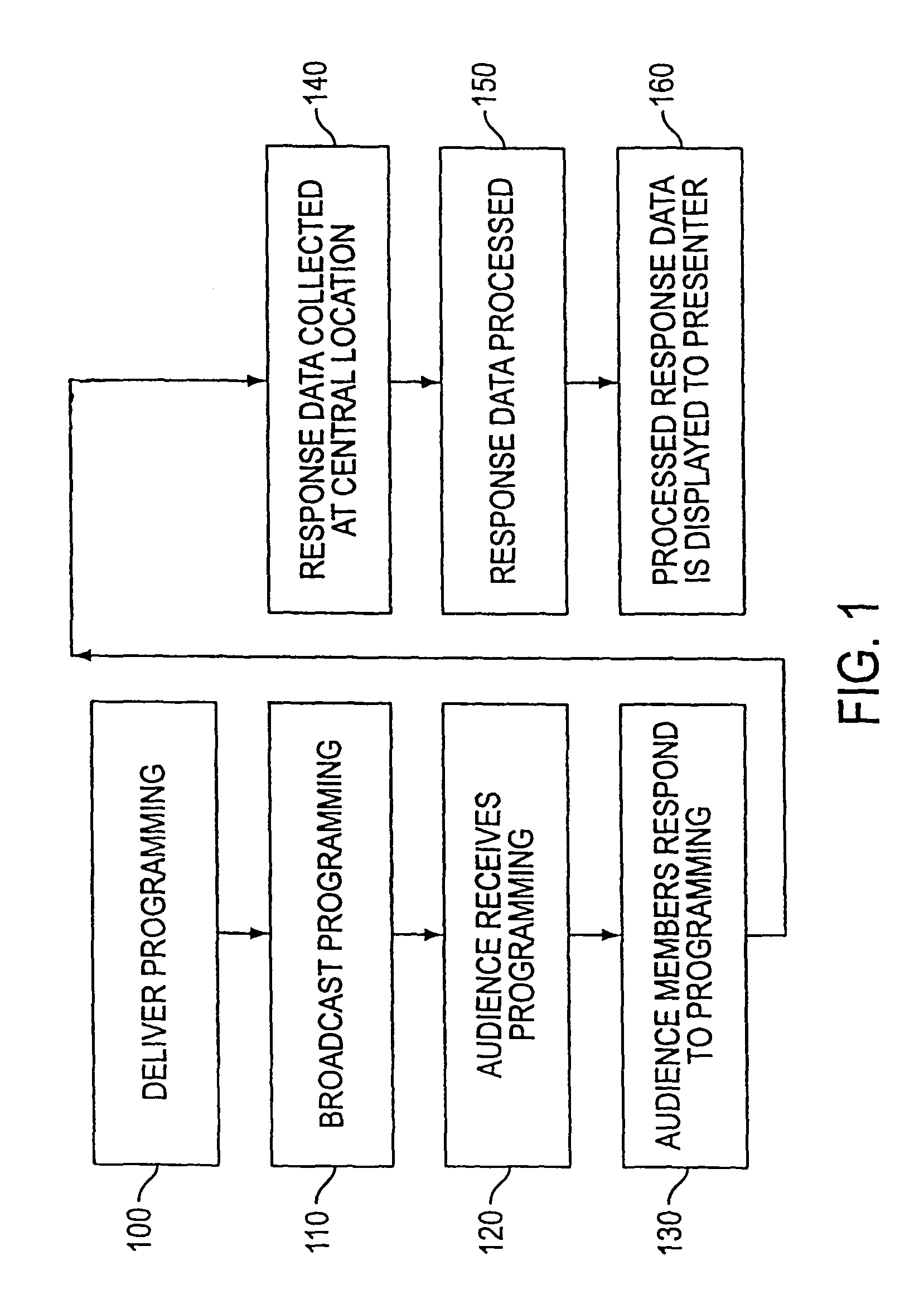
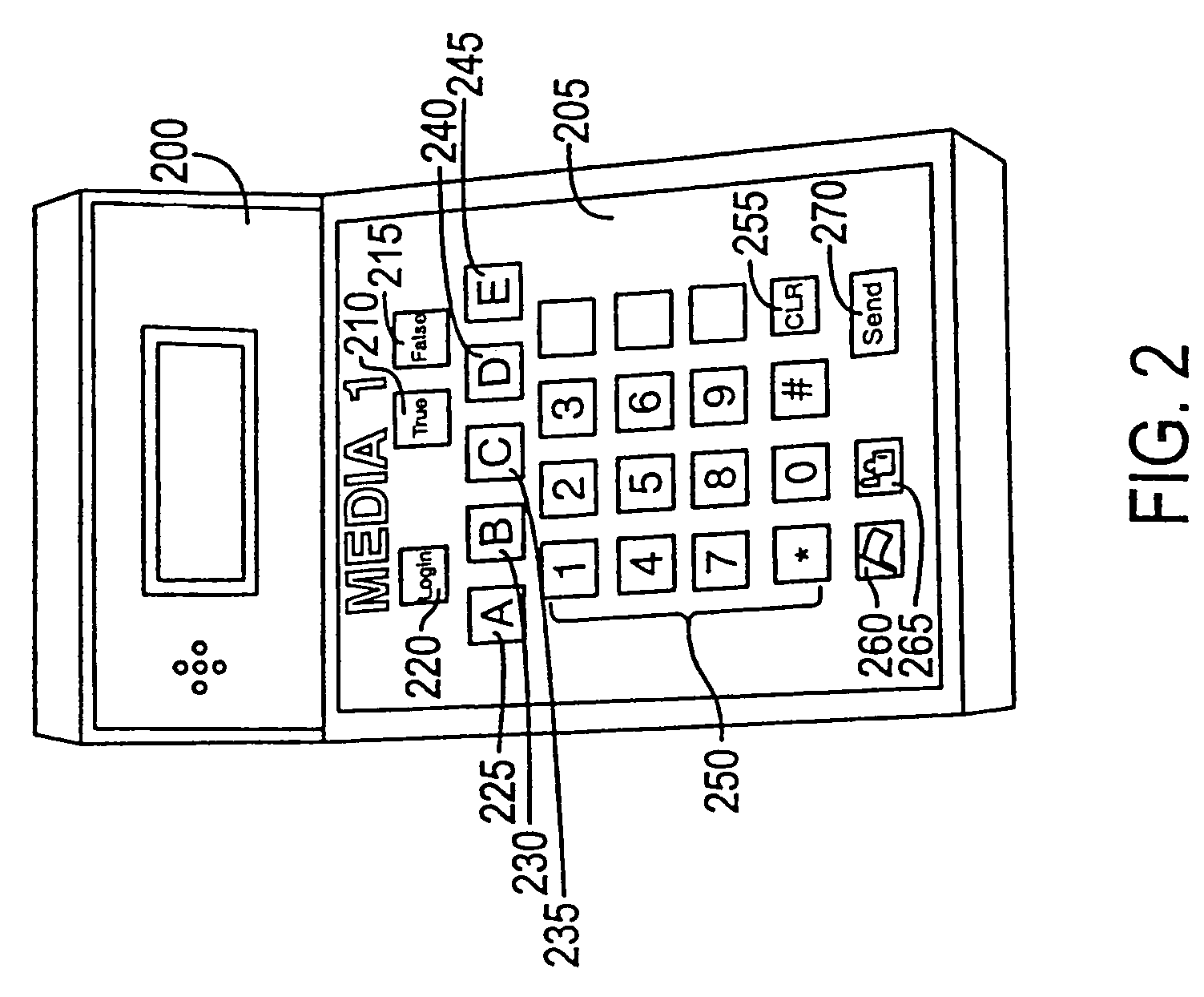
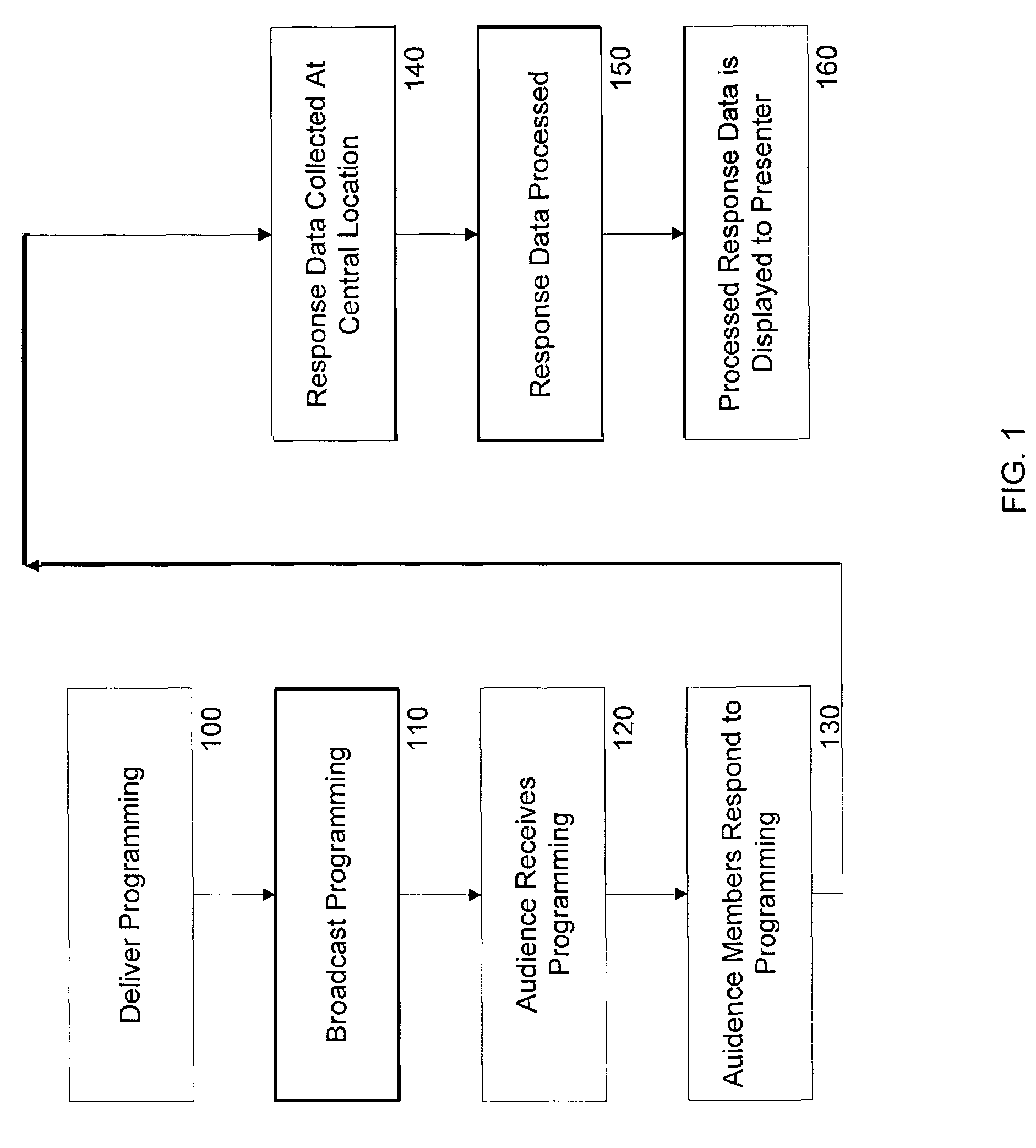
InactiveUS7730506B1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringCommunications systemUser input
A remote response system that utilizes portable response devices that require a user to input a program code and response data, which are transmitted over existing communication systems to a central location for processing. Certain response devices communicate over wireless systems, while other response devices communicate over plain old telephone systems by sending data bursts or by dialing different, pre-established telephone numbers. A user of the response device can communicate with a presenter of programming that is live or broadcast over audio / visual mediums in real time, without requiring the user to have a personal computer.
Owner:LYDA EDWIN
Method and device for coupling a POTS terminal to a non-PSTN communications network
A communications device is used to interface a plain old telephone system (POTS) terminal, which includes a dial-up modem to transmit data, to a communications network. The communications device appears to the POTS terminal to be a modem accessed via a telephone network.
Owner:WILINE NETWORKS
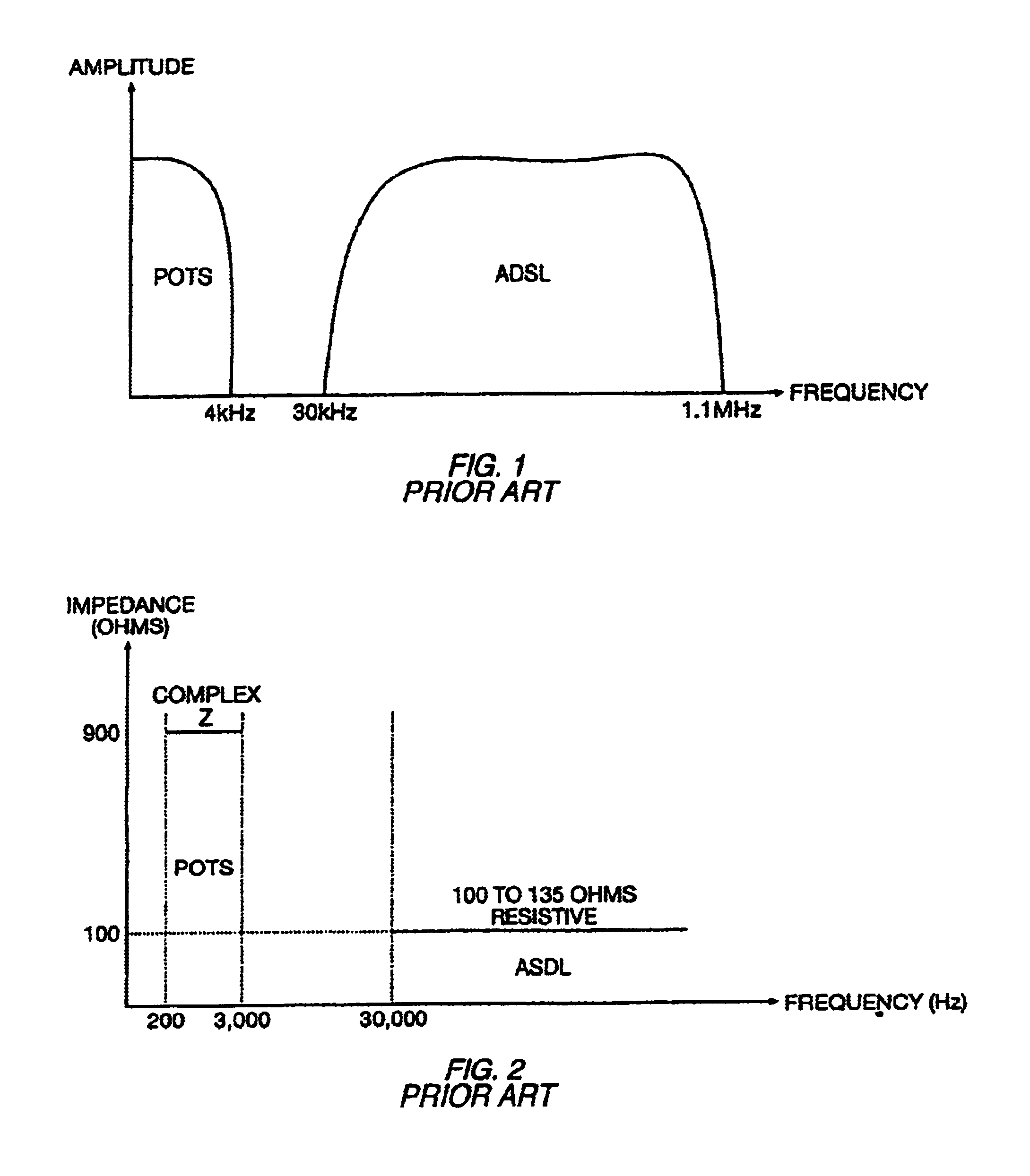
Power spectral density masks for ADSL+
InactiveUS20040057564A1Improve robustnessEnergy efficient ICTTelephonic communicationDigital subscriber lineFrequency spectrum
Disclosed herein are various power spectral density (PSD) masks for spectral shaping of an asynchronous digital subscriber line (ADSL) overlap and non-overlapped spectrums via an integrated digital services network (ISDN) or plain old telephone system (POTS).
Owner:BROOKTREE BROADBAND HLDG
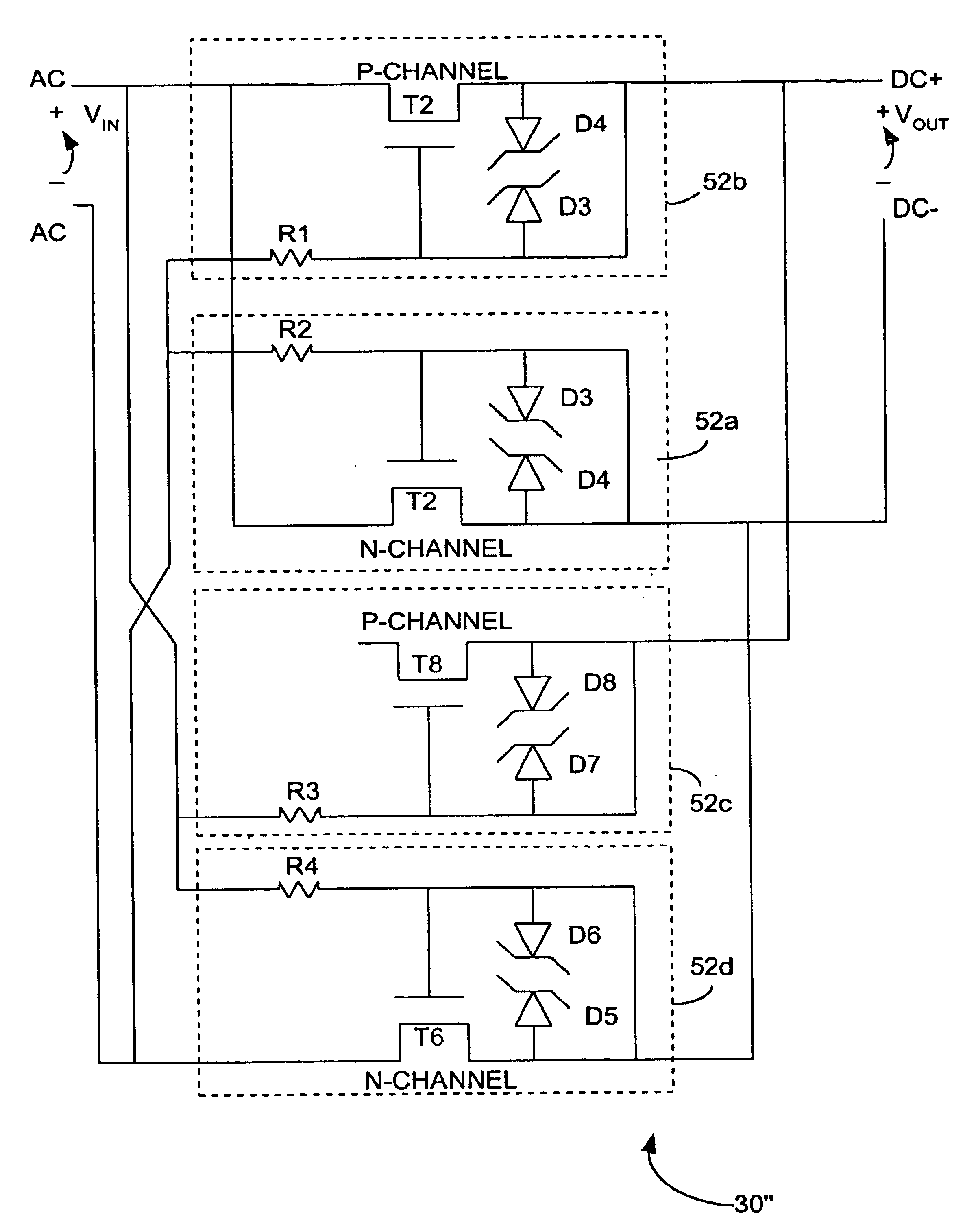
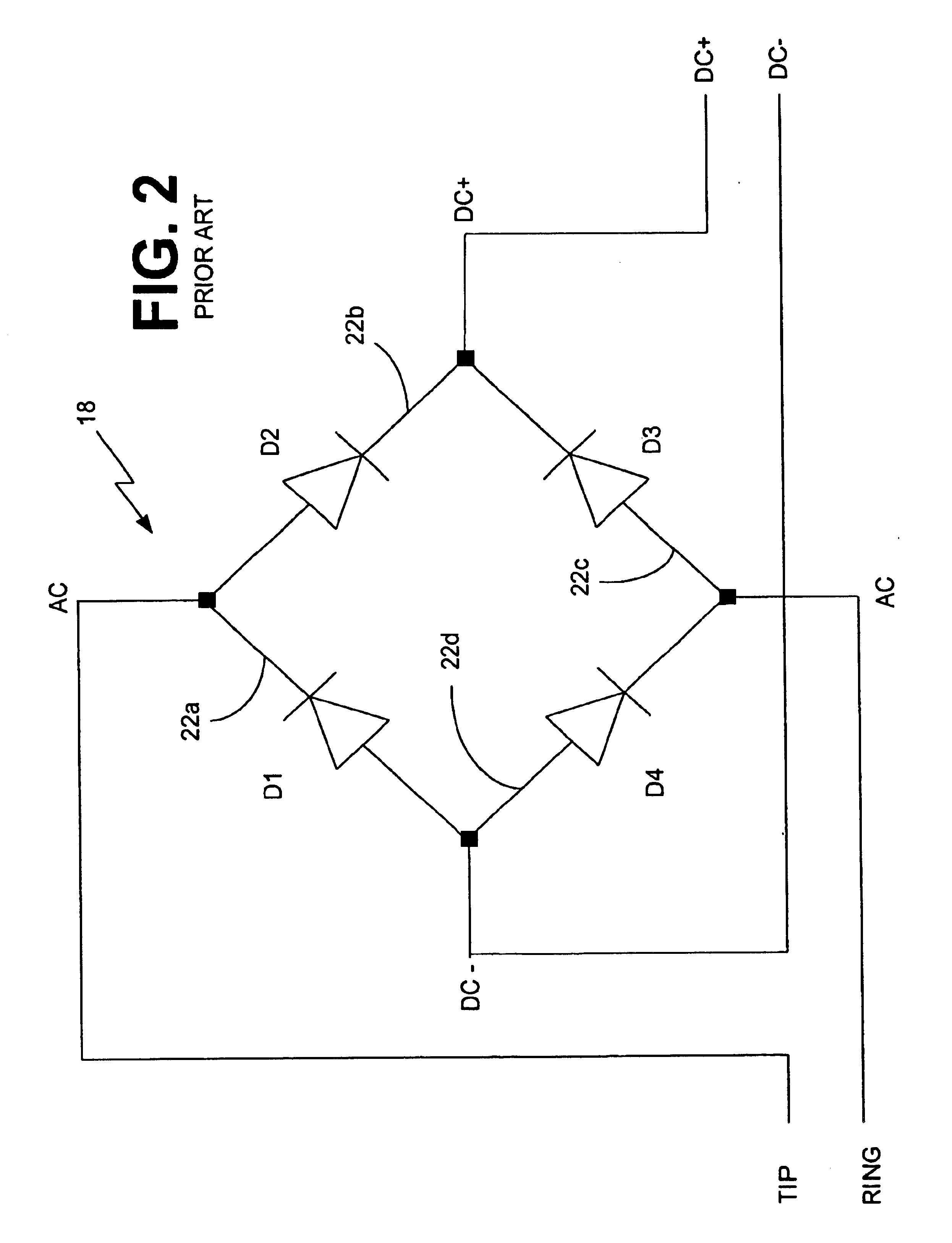
Linear polarity guard and method for DSL-ready pots devices
InactiveUS6845157B1Reduce distractionsEfficient and reliableSubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsModem deviceOn board
A plain old telephone system (POTS) device, for example but not limited to, a telephone, facsimile machine, analog modem, caller identification (ID) system, speaker phone, cordless phone, etc., employs an on-board transistor-based linear polarity guard to enable decoupling of a POTS channel from one or more xDSL channels on a telephone connection (subscriber loop associated with a public service telephone network), while reducing undesirable interference, such as intermodulation distortion imposed upon the POTS and xDSL channels. Transistors associated with the polarity guard are operated in the ohmic region, or in a nonsaturated linear mode, to achieve a substantially linear transfer function through the transistors and through the overall linear polarity guard. Current that is input to the polarity guard and the voltage drop across the transistors that conduct the current in the polarity guard exhibit a substantially linear relationship, or linear VI transfer function. Hence, the VI relationship between the overall output voltage and overall input current of the polarity guard is substantially linear in the operating region of the polarity guard.
Owner:IPR 3
Response apparatus method and system
ActiveUS7434243B2Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringCommunications systemUser input
A remote response system utilizes portable response devices that receive user input and transmit user input over existing communication systems. Certain response devices communicate over wireless systems such as paging systems, while other response devices communicate over plain old telephone systems by sending data bursts or by dialing different, established telephone numbers. A user of a remote response device can communicate with a presenter of programming that is broadcast over audio / visual mediums in real time without requiring a personal computer.
Owner:LYDA EDWIN
System and method for remotely communicating with a broadband modem
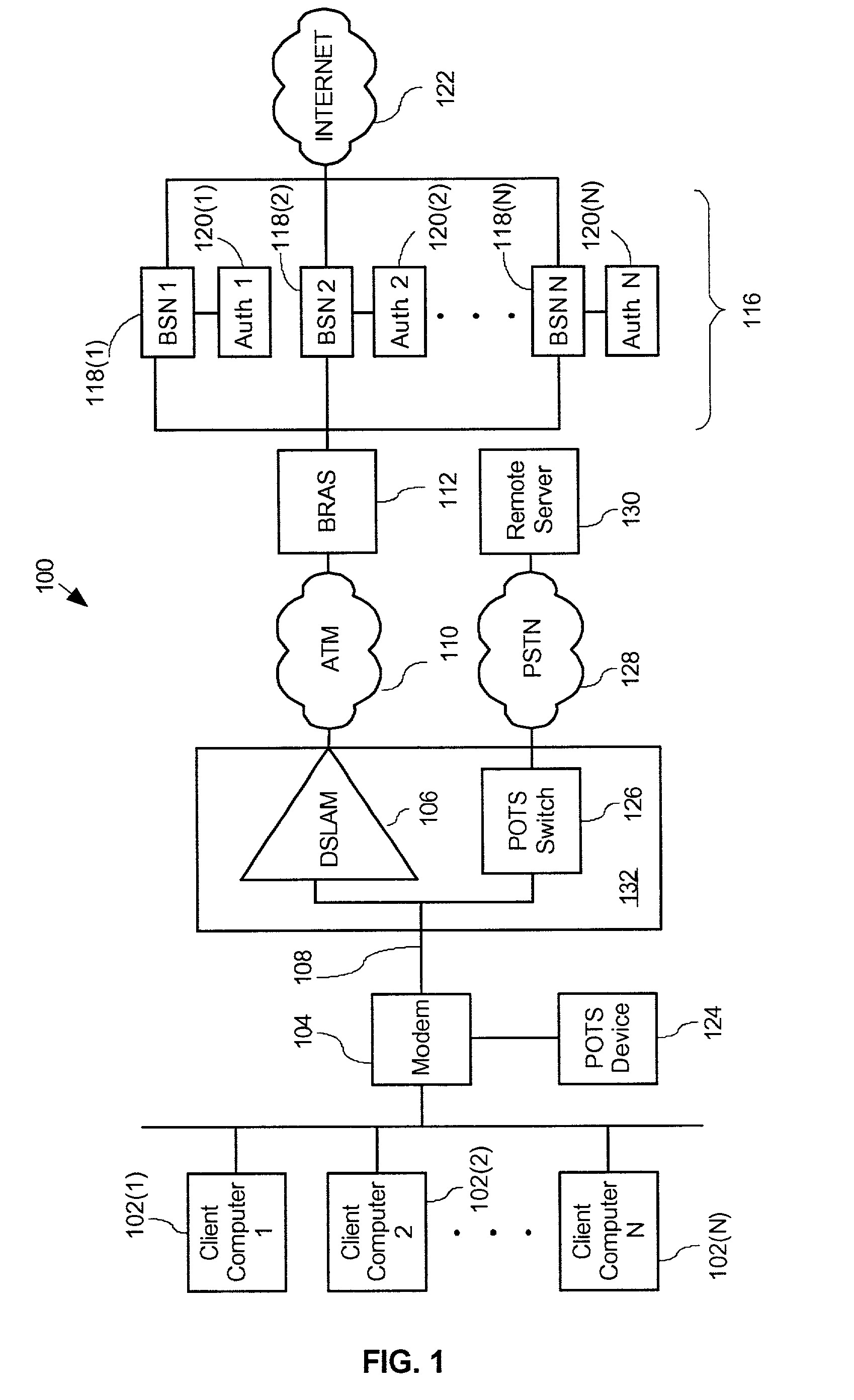
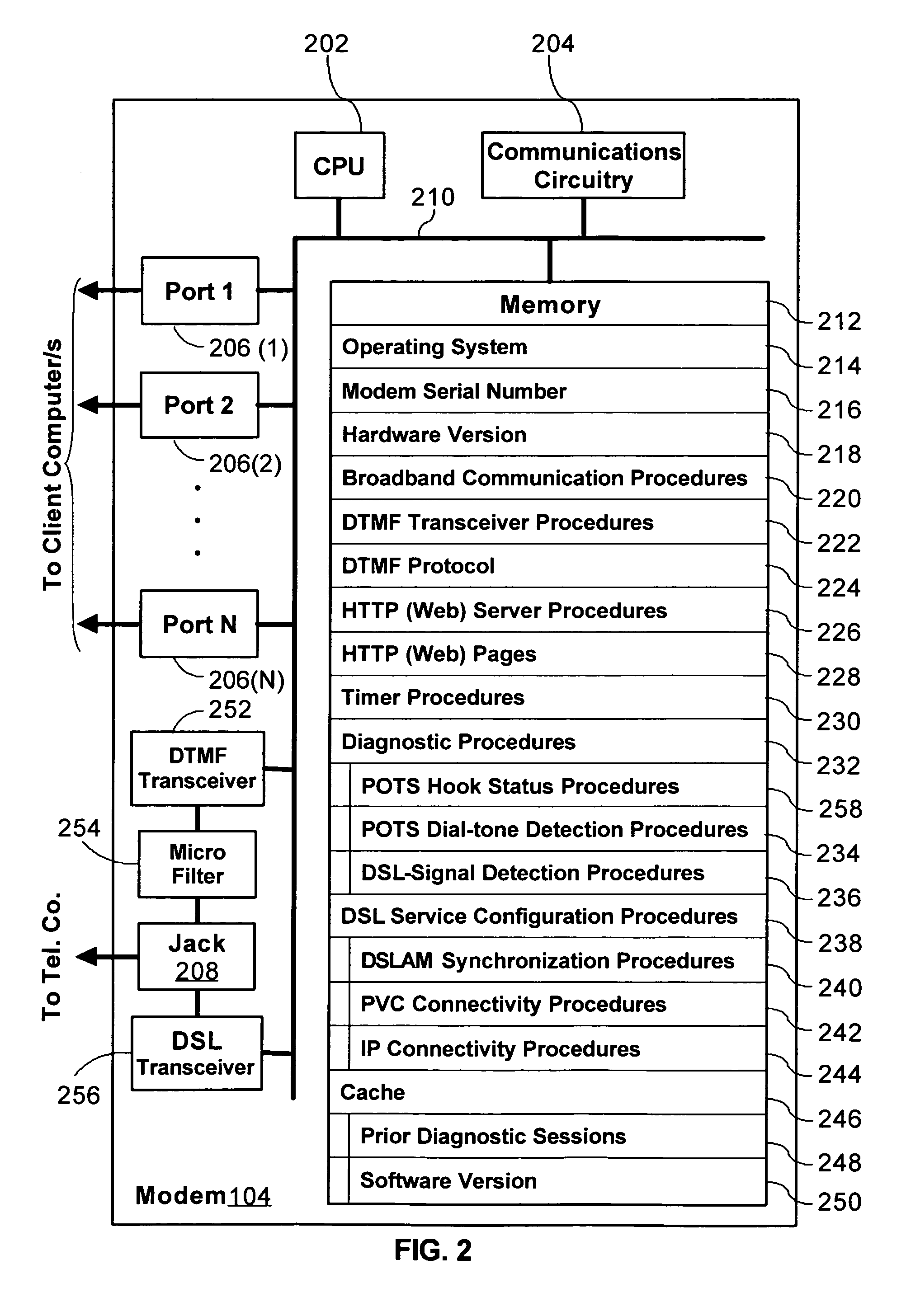
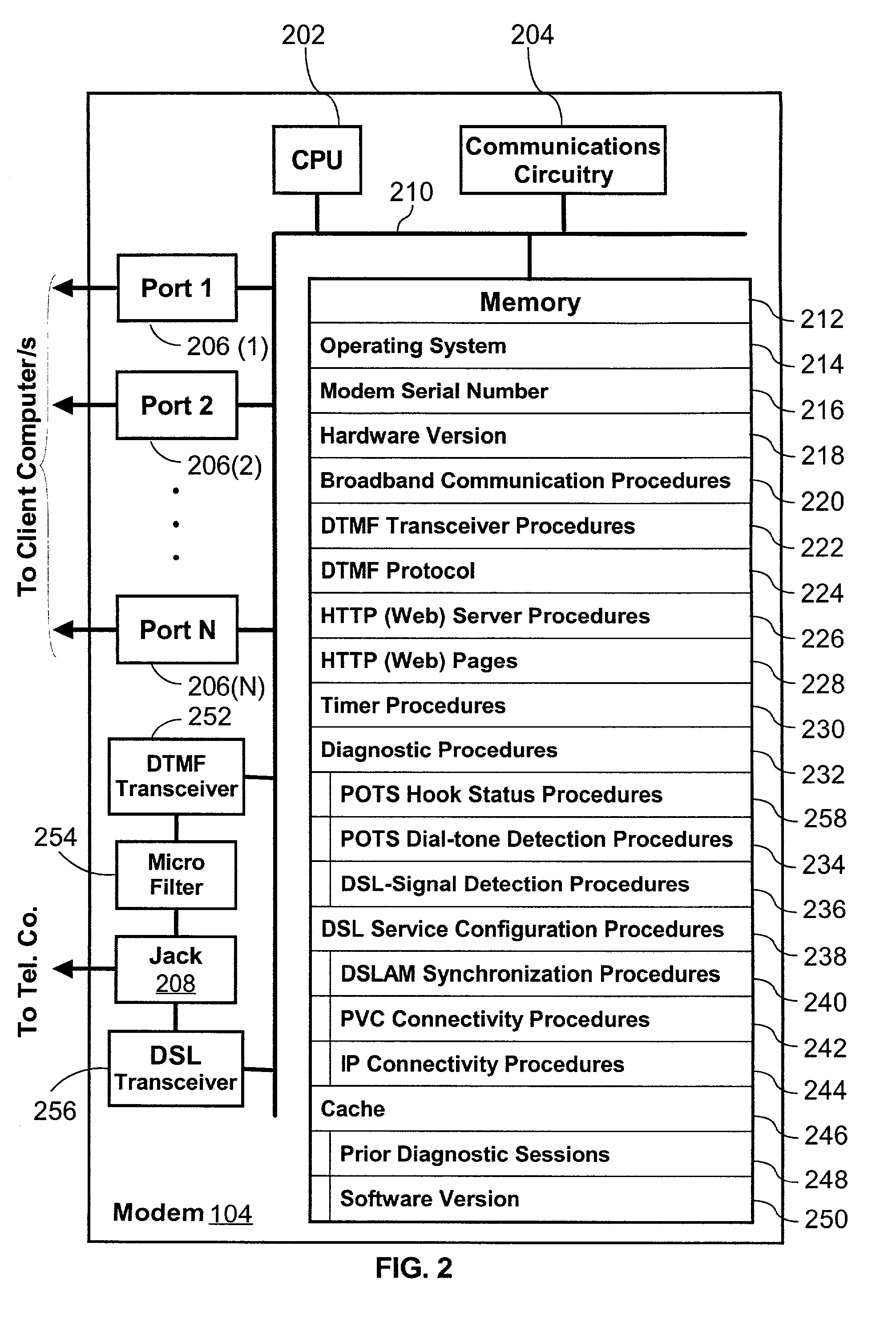
InactiveUS20060203810A1Reduce in quantityAvoid communicationData switching by path configurationHybrid transportModem deviceBroadband
A method for remotely communicating with a Broadband modem is provided. Once a communication error is detected on a Broadband modem, a Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) connection is established between the Broadband modem and a remote server. Communication then occurs with the remote server via the POTS connection using Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) tones. The communication preferably comprises transmitting information associated with the communication error to the remote server via the POTS connection using DTMF tones and receiving a diagnosis from the remote server via the POTS connection in DTMF tones. A system for remotely diagnosing a Broadband modem as well as a Broadband modem is also provided.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
System and method for remotely communicating with a broadband modem
InactiveUS7088708B2Reduce in quantityAvoid communicationAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTime-division multiplexModem deviceBroadband
A method for remotely communicating with a Broadband modem is provided. Once a communication error is detected on a Broadband modem, a Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) connection is established between the Broadband modem and a remote server. Communication then occurs with the remote server via the POTS connection using Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) tones. The communication preferably comprises transmitting information associated with the communication error to the remote server via the POTS connection using DTMF tones and receiving a diagnosis from the remote server via the POTS connection in DTMF tones. A system for remotely diagnosing a Broadband modem as well as a Broadband modem is also provided.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Internet phone system and directory search engine using same
InactiveUS20090103459A1Easy to useMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationDigital dataModem device
An Internet compatible dialer pad is used to dial into an Internet server to provide services similar to those found on the Plain Old Telephone System (“POTS”). The dialer pad has an integrated modem set, an extended keypad with alphanumeric entry keys and function keys, display screen and display electronics that renders visual call progress information to the user as well as other communications indicators and related information about the current Internet connection. The dialer uses the Public Switched Telephone System (“PSTN”) and standard LAN / WAN technology to give the user entry into a plurality of Internet calling functions. An Internet database is maintained and permits the dialing party to obtain callee information by entering alphanumeric characters via the dialer. Links from the PSTN to an Internet data base are not restricted to a specific digital data protocol.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Multifunctional electronic device
InactiveUS7340052B1Quick identificationCordless telephonesInterconnection arrangementsHandwritingThe Internet
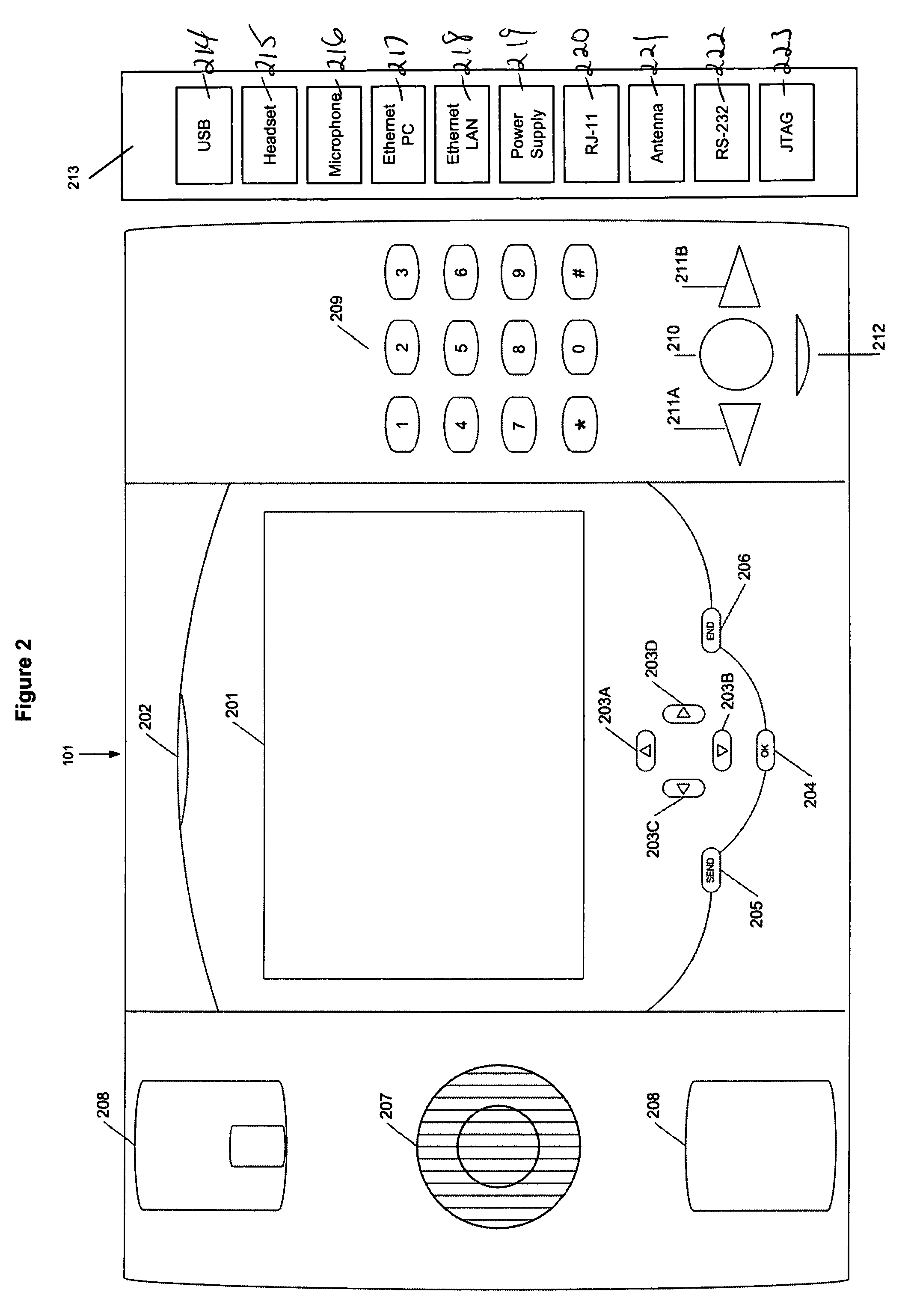
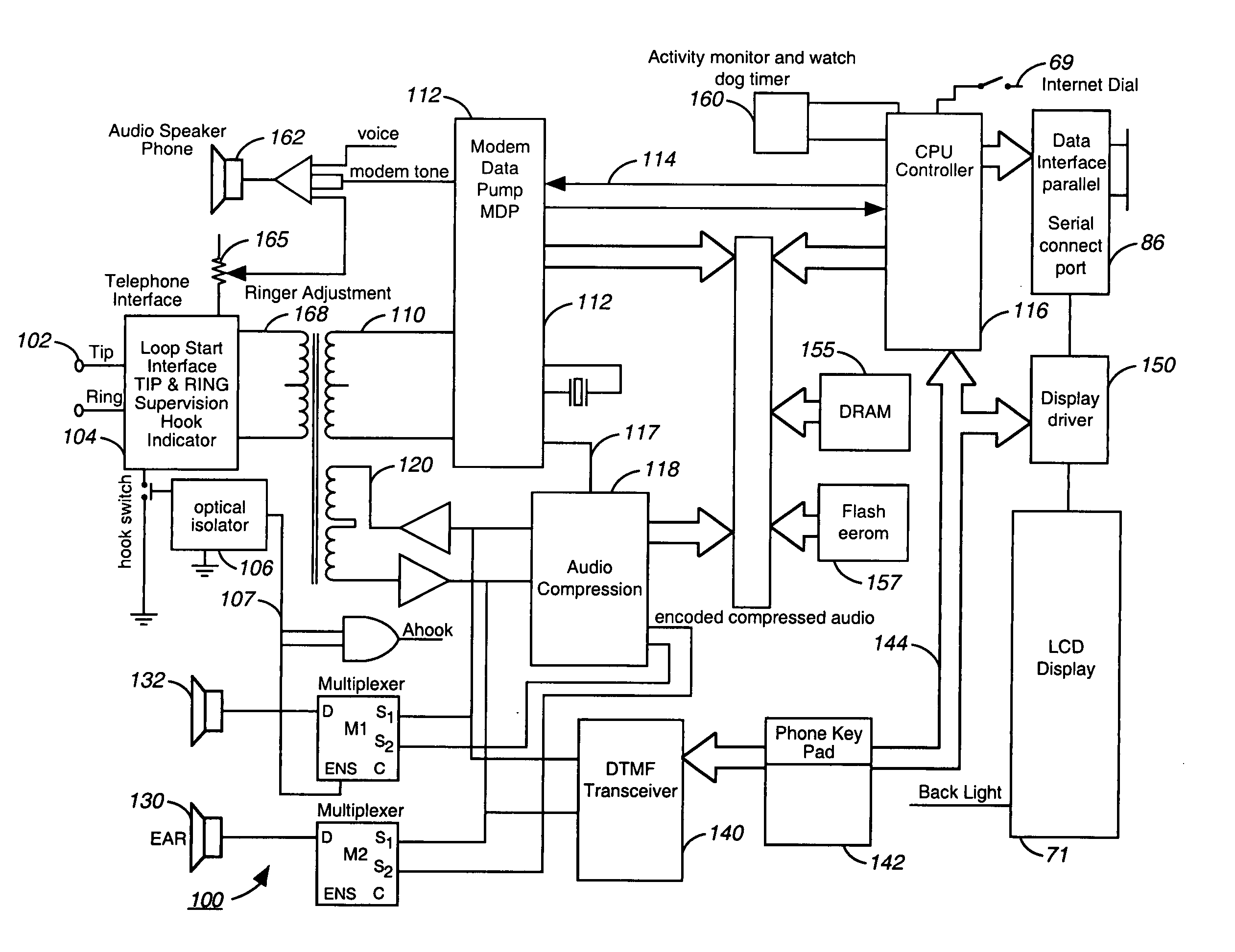
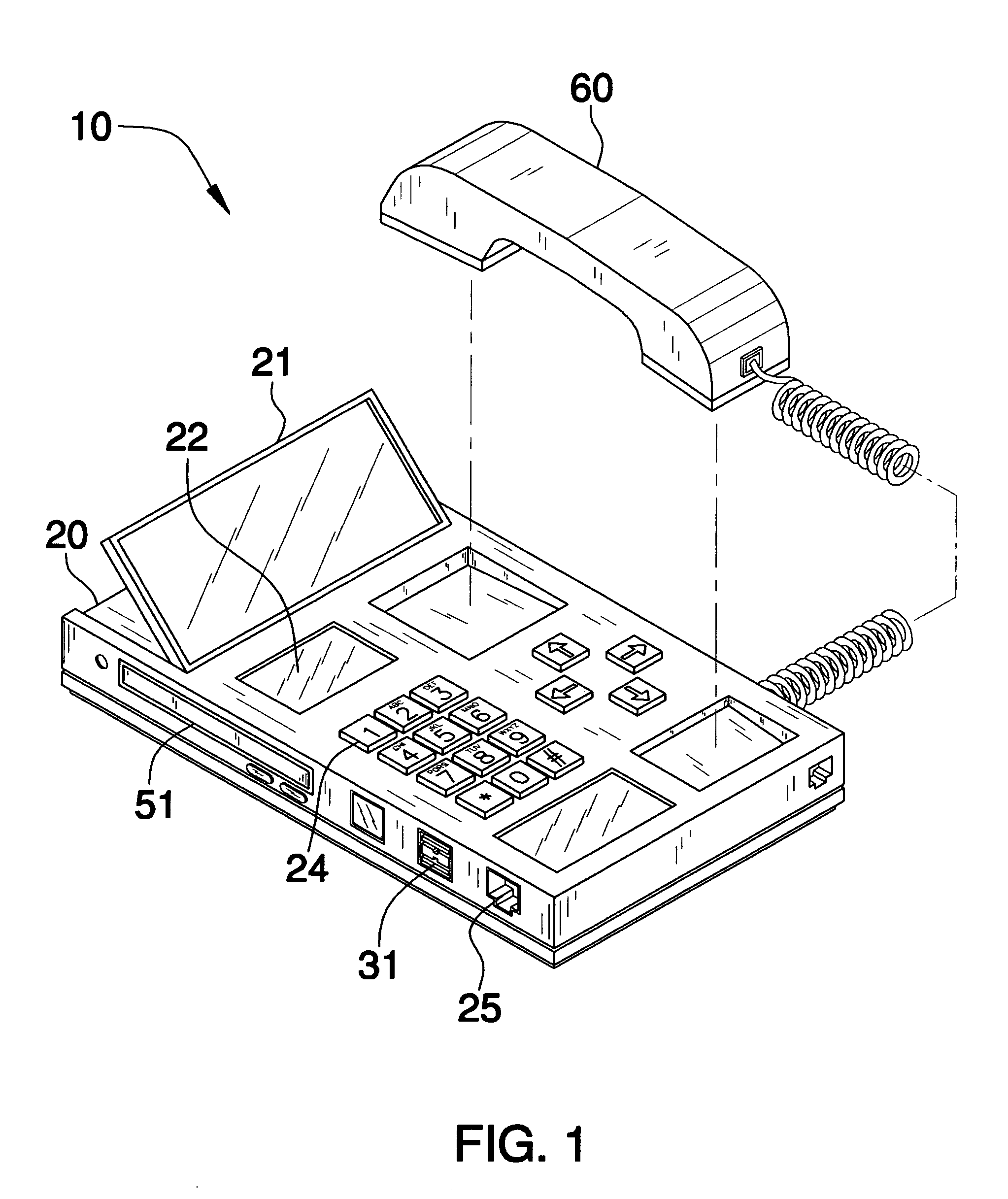
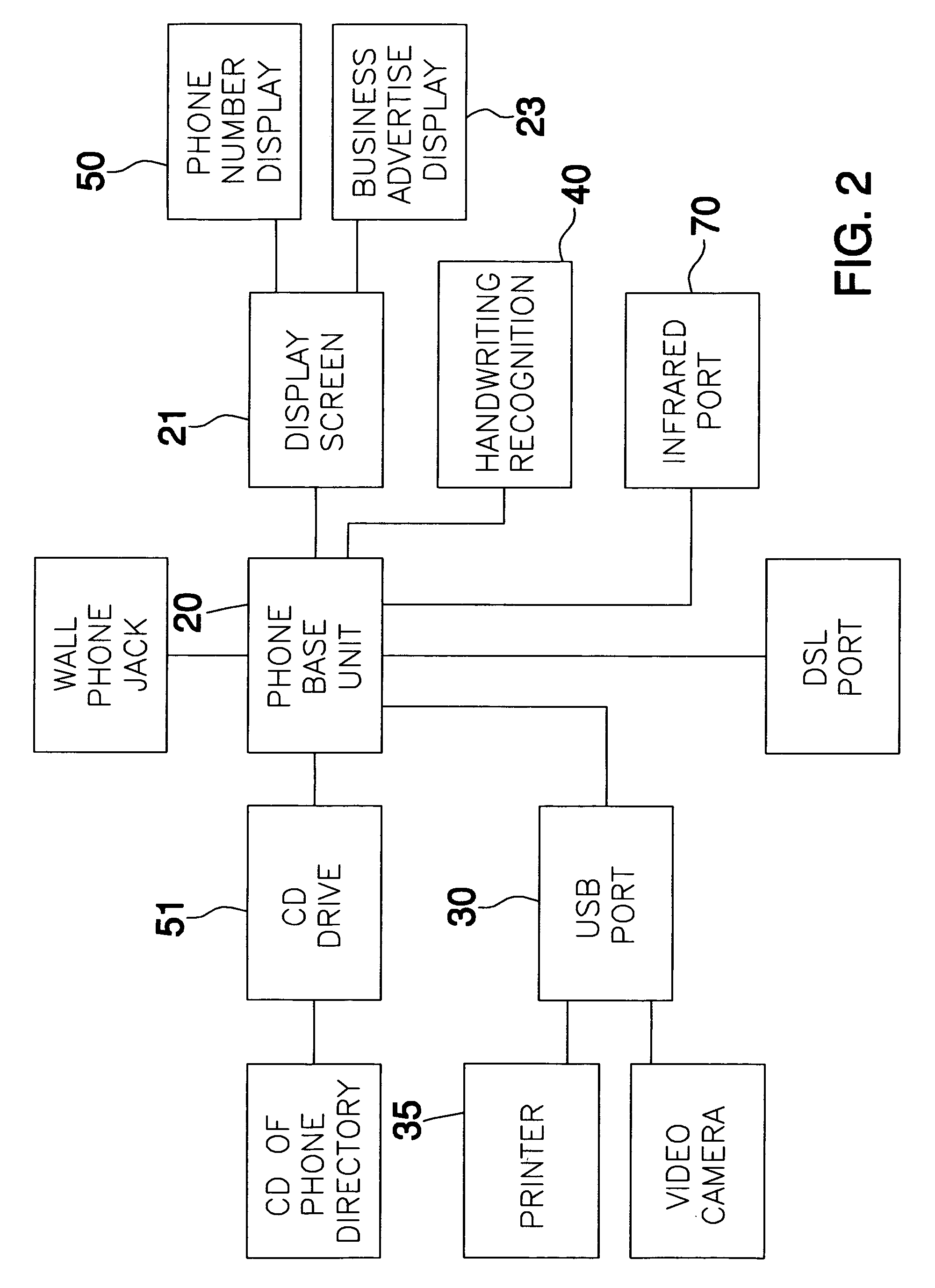
A device for providing telephone communication and data transfer includes a base unit with a display screen and means for retrieving and displaying Internet information via a DSL connection or USB line, for example. A mechanism for recognizing and verifying handwriting is included for allowing a user to sign his / her name to confirm or validate a sales transaction. A voice recognition mechanism converts and translates speech input to text wherein a hearing-impaired user can read real time text messaging. A mechanism for providing access to an electronic phone directory via a CD ROM drive is also provided. The present invention further includes a handset for allowing a user to communicate via a plain old telephone system. Advantageously, an infrared mechanism for communicating with a portable electronic device is provided wherein a variety of devices employing either infrared or fiber-optic communication technology can send and receive wireless signals to the device.
Owner:WEST MARK L
Internet protocol (IP) relay system and method
A communications system allows individuals who are deaf, hard of hearing or speech disabled to use computers and other web devices to connect to an Internet Portal in order to place a call. The system relays communications between a first device and a second device utilizing a third device as an intermediary where the second device is a telephone on a plain old telephone system network and the communications between the first device and third device involves the Internet. The system includes a first input and output communication device coupled to a network and is configured to send and receive communication messages, a server device that receives a session request from the first input and output communication device and sends a call to a call distribution device, a second input and output communication device coupled to a plain old telephone system, and a third input and communicating with the first input and output communication device using a chat room interface.
Owner:HAMILTON RELAY
Systems and methods for providing a home network conversion interface
ActiveUS7417979B2Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPlain old telephone systemData type
Systems and methods are provided wherein an incoming plain old telephone systems (PSTN) signal is input into a home network conversion interface. The home network conversion interface first determines the data type of the incoming signal. Next, the home network conversion interface creates a routing sequence of the incoming signal based on the determined data type. Finally, the home network conversion interface converts the incoming signal into an 802.X format and sends the signal to an appropriate IP device based on the determined signal type. Should the home network conversion interface loose electrical power, a drop contactor routes the incoming signal directly to an analog device without creating a routing sequence or performing an 802.X conversion.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P +2
Method and apparatus for transient suppression in an integrated POTS/DSL line card
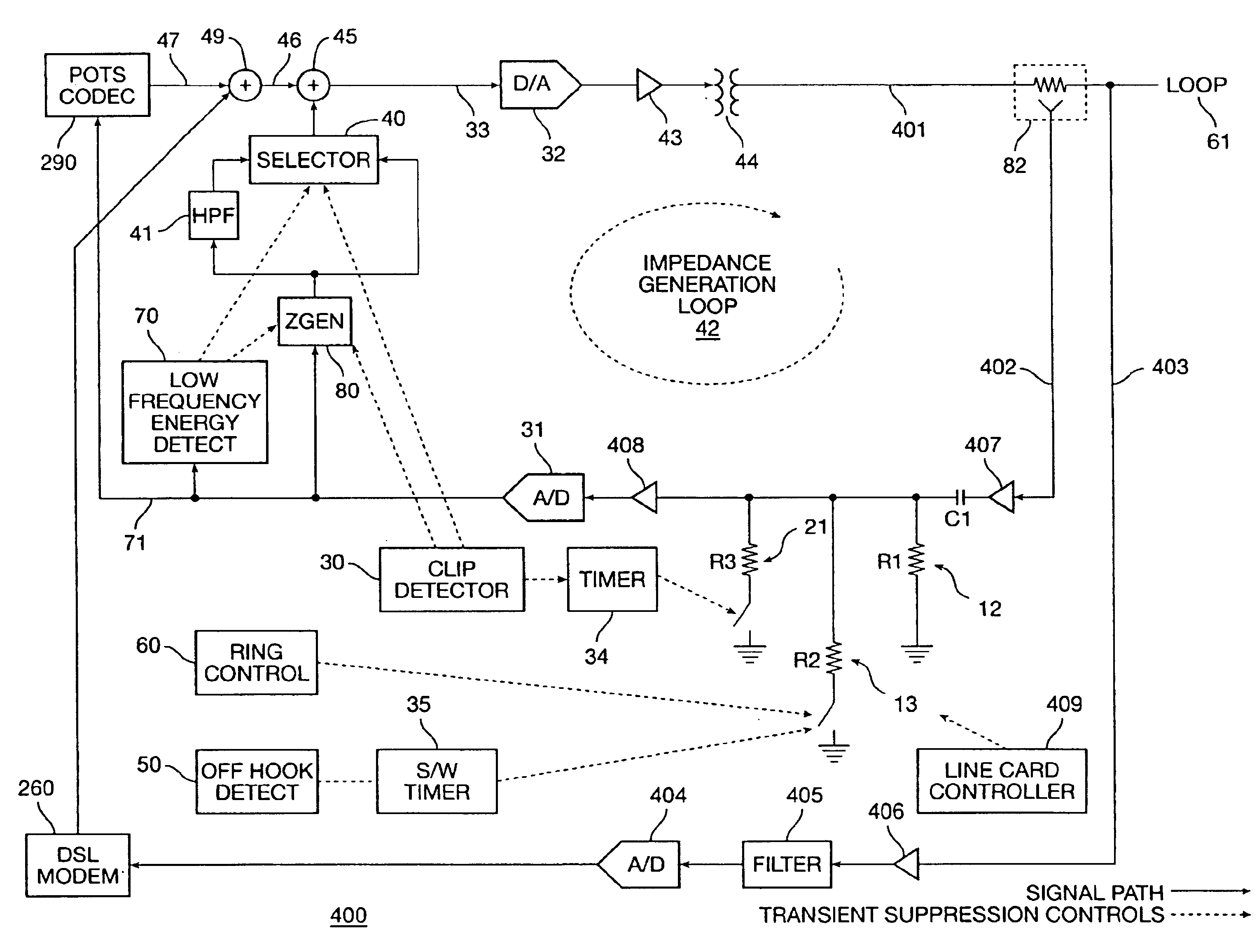
ActiveUS6920217B2Suppressing low frequency transientReduce signalingInterconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsLine cardPlain old telephone system
Combined plain old telephone system (POTS) and digital subscriber loop (DSL) line card capable of suppressing low frequency transients. The line card includes the following elements. A DSL receive path receives DSL data from a loop. A POTS receive path receives POTS data from the loop. A combined POTS and DSL transmit path transmits POTS and DSL data to the loop. An impedance generator is coupled between the POTS receive path and the combined POTS and DSL transmit path for synthesizing impedance for signals in the combined POTS and DSL transmit path. A low frequency detector selectively applies a high pass filter to an output of the impedance generator for filtering the low frequency transients. Further, a clipped signal detector and a variable pole high pass filter are provided in the POTS receive path. The clipped signal detector in the POTS receive path triggers a switch that discharges stored transient energy in the receive path. The variable pole high pass filter in the POTS receive path is modified during ringing and hook switch activity, by the line card controller, in order to attenuate transient signals.
Owner:CIENA
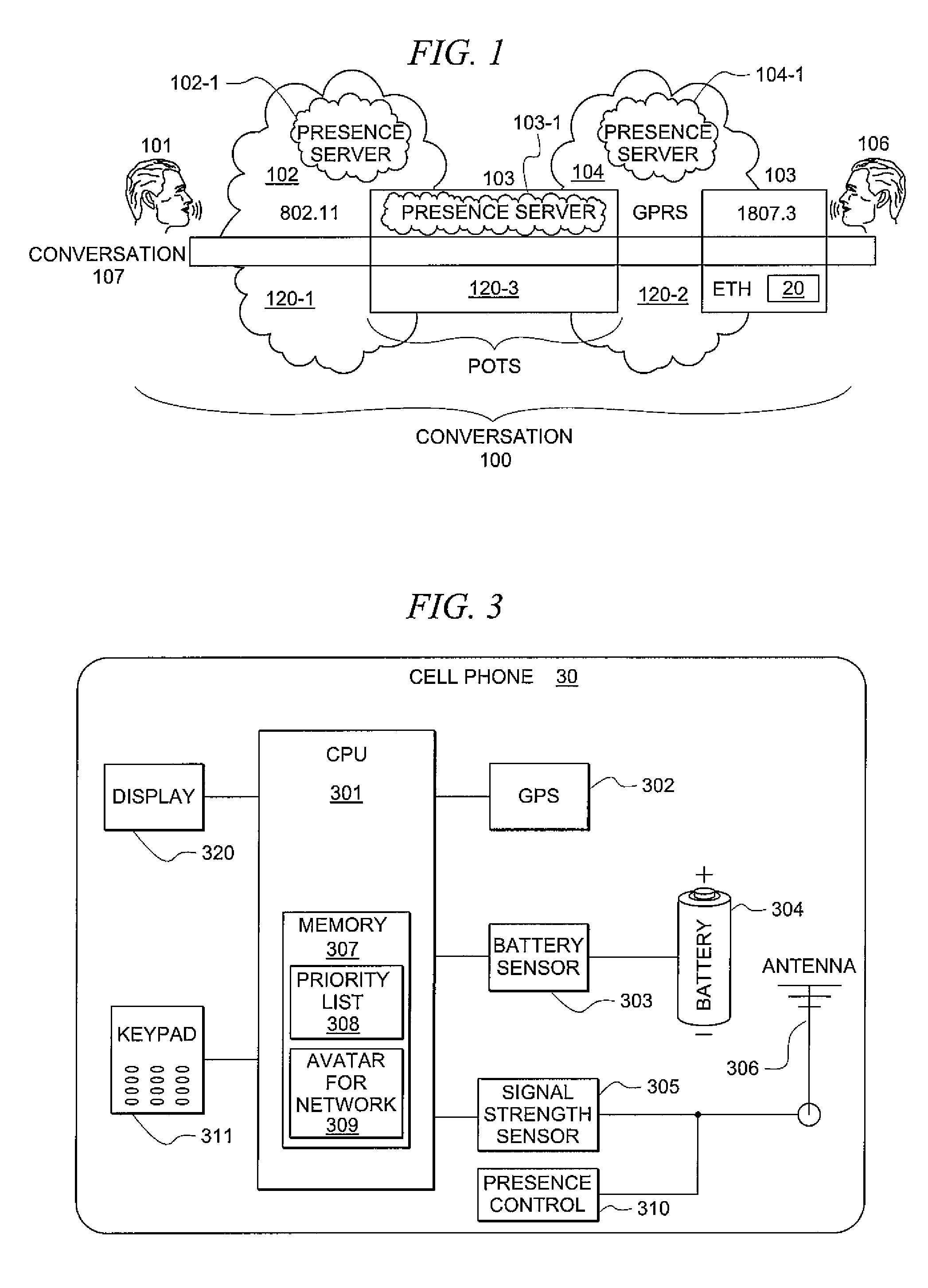
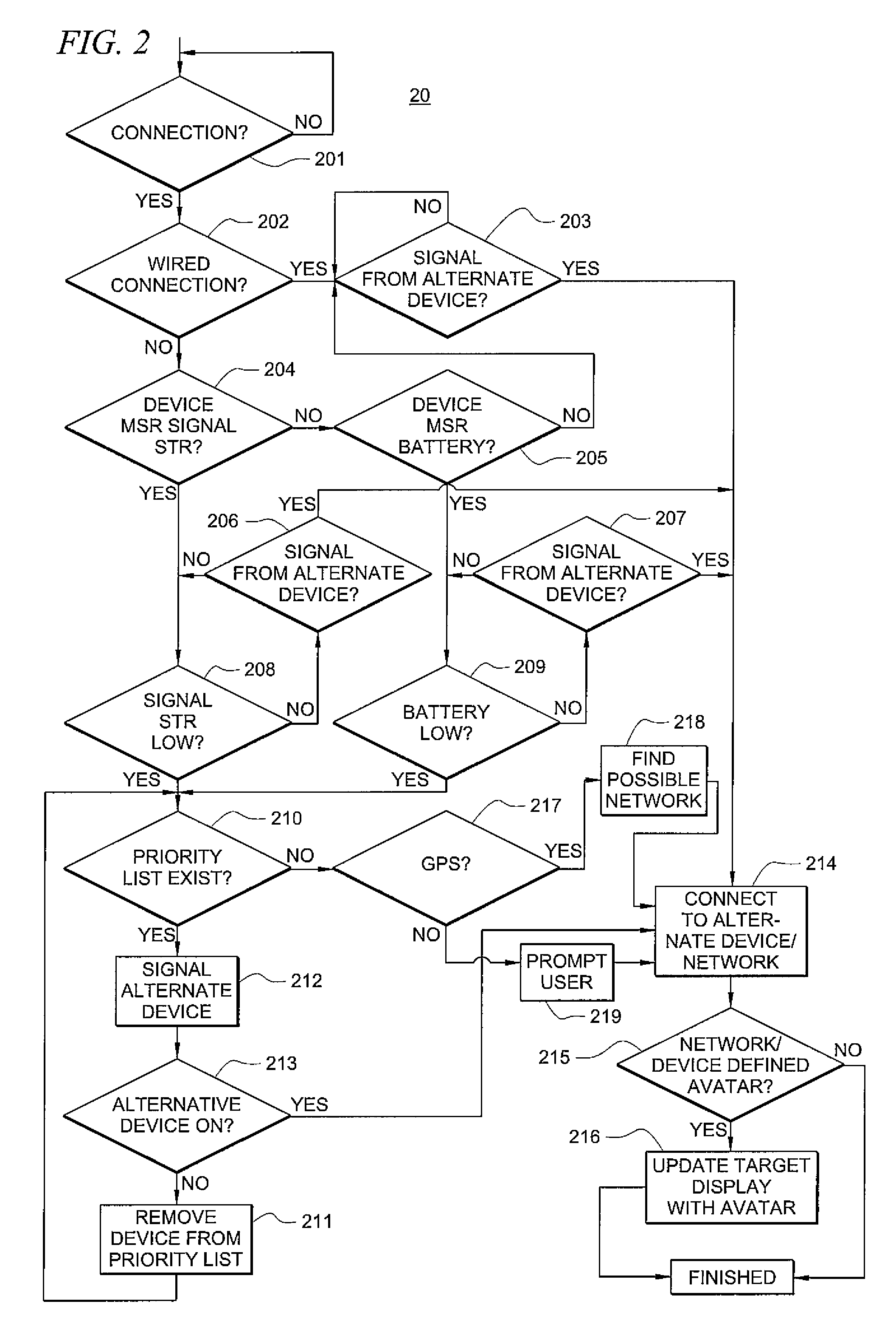
System and method for seamless communication system inter-device transition
InactiveUS7817601B1Time-division multiplexAutomatic exchangesCommunication endpointCommunications system
By modifying the communication endpoints to be presence aware and connecting them to a presence network, communication connections can be created wherein networks are added, or dropped, from the connection in order to keep the connection seamless from the perspective of the parties to the communication session. In one embodiment, an initiating user initiates a communication session on a first network (for example, a cellular network) to a target user served by a second network. During the communication session, the initiating user moves from his / her car to a landline and the communication session is transferred to a plain old telephone system (POTS) network. In one embodiment, on the target user's communication device an avatar representing the initiating user is updated to reflect that a landline network has been substituted for the cellular network.
Owner:COVERSANT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com