Patents
Literature
50results about "Counting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
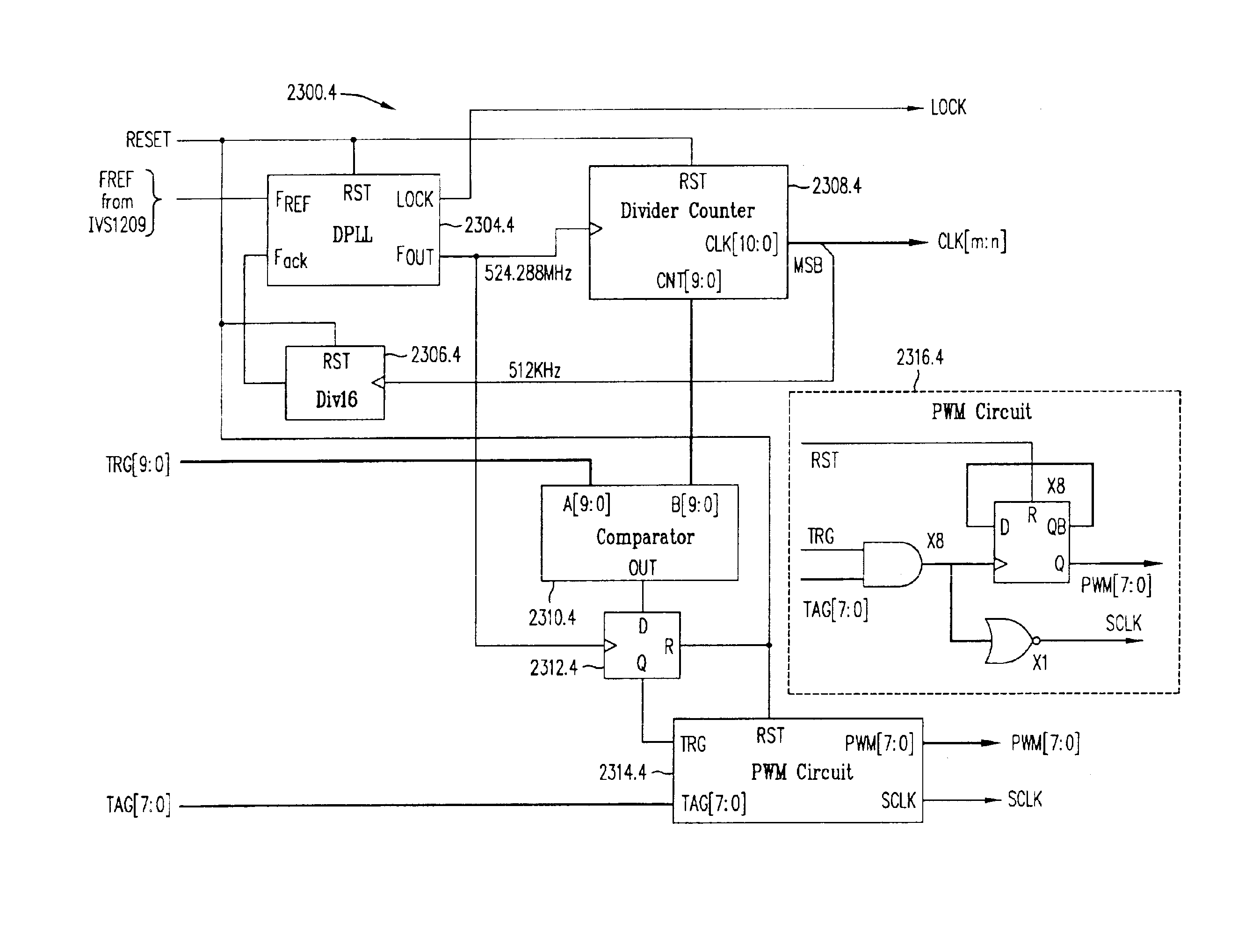
Multi-channel control methods for switched power converters
InactiveUS6912139B2Channel interference is avoided and minimizedExclusive-OR circuitsCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderVoltage pulseTransverter
Owner:EXAR CORP
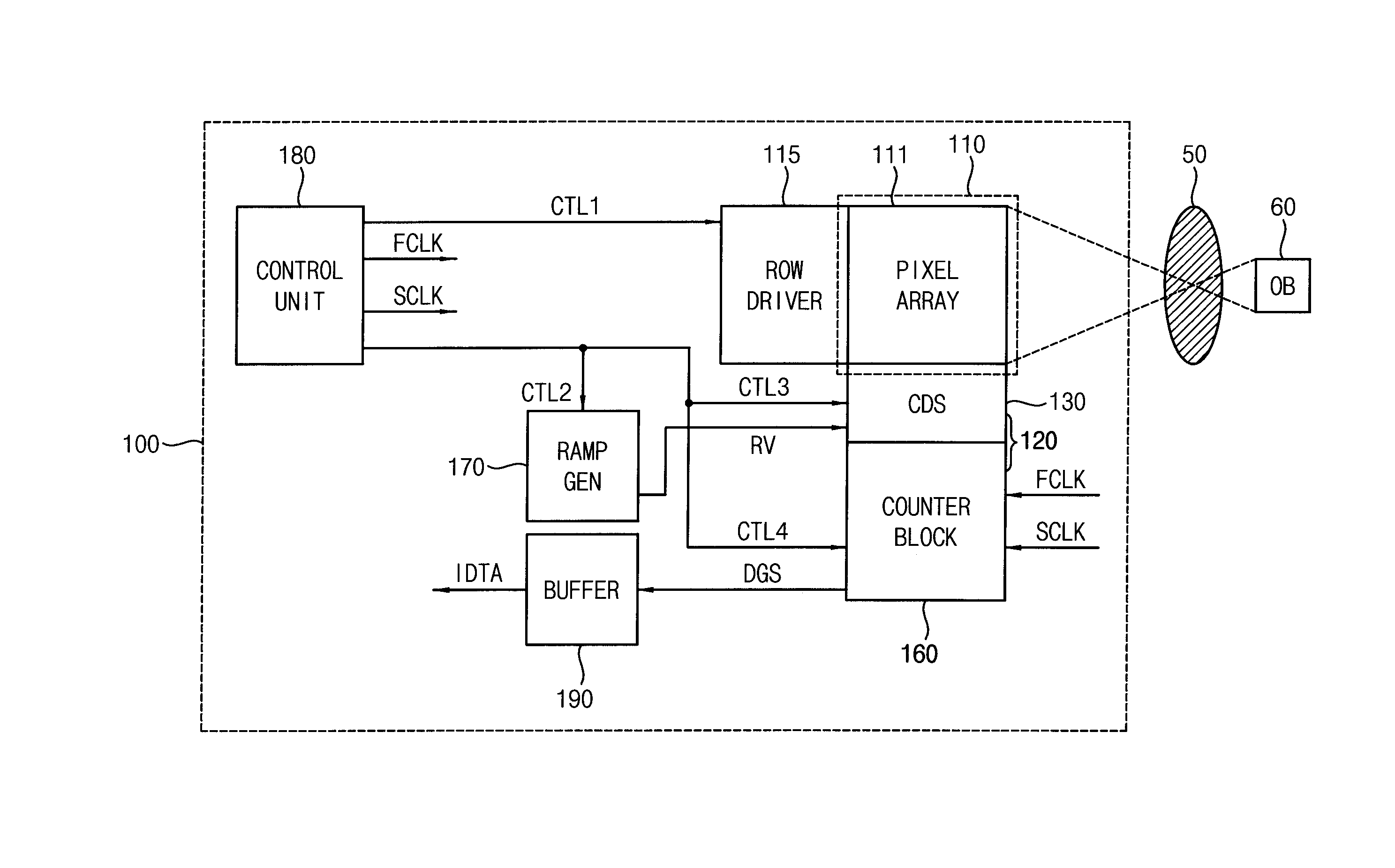
Counter circuit, analog-to-digital converter, and image sensor including the same and method of correlated double sampling
ActiveUS20150028190A1Reduce power consumptionReduce in quantityPower saving provisionsTelevision system detailsAnalog-to-digital converterComputer science
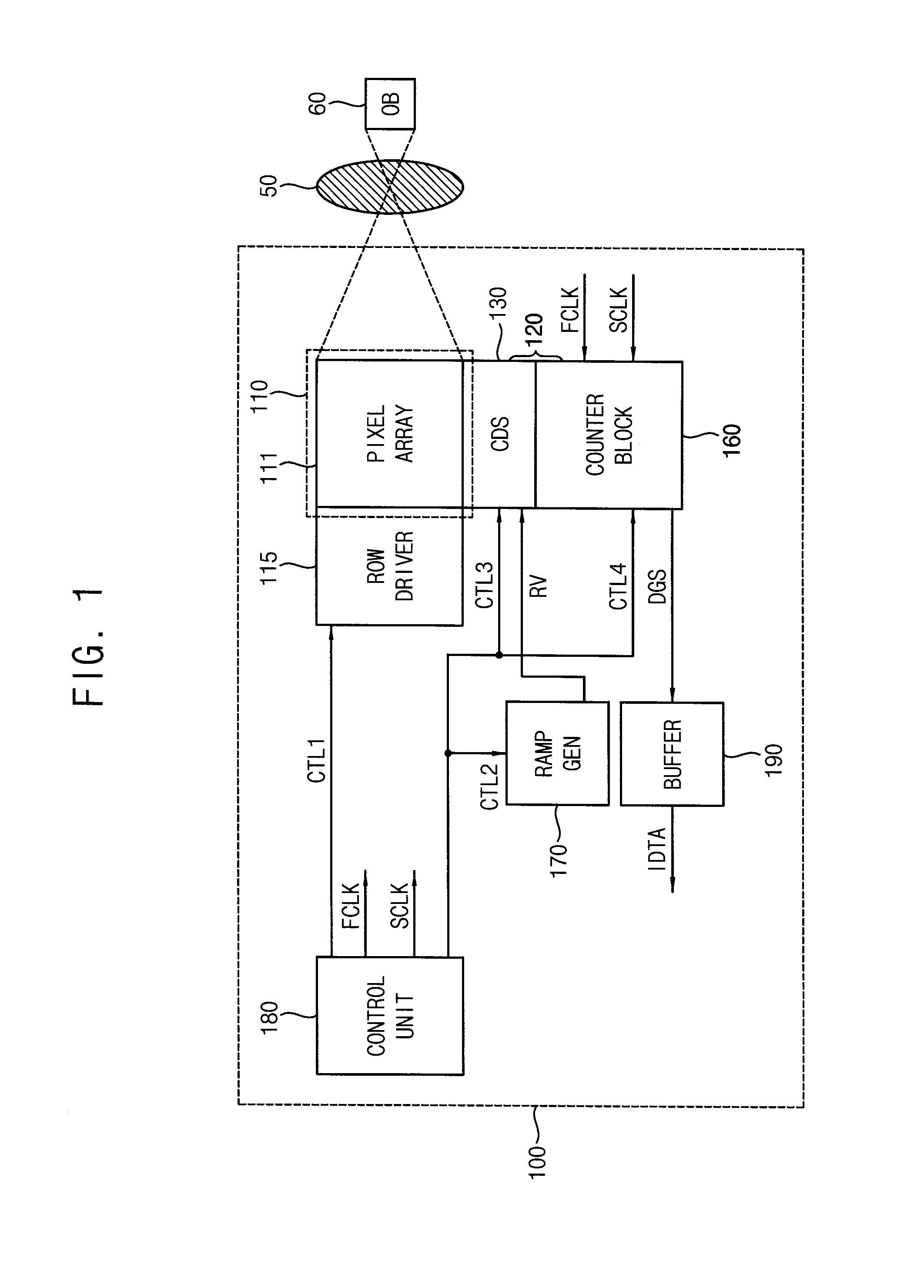
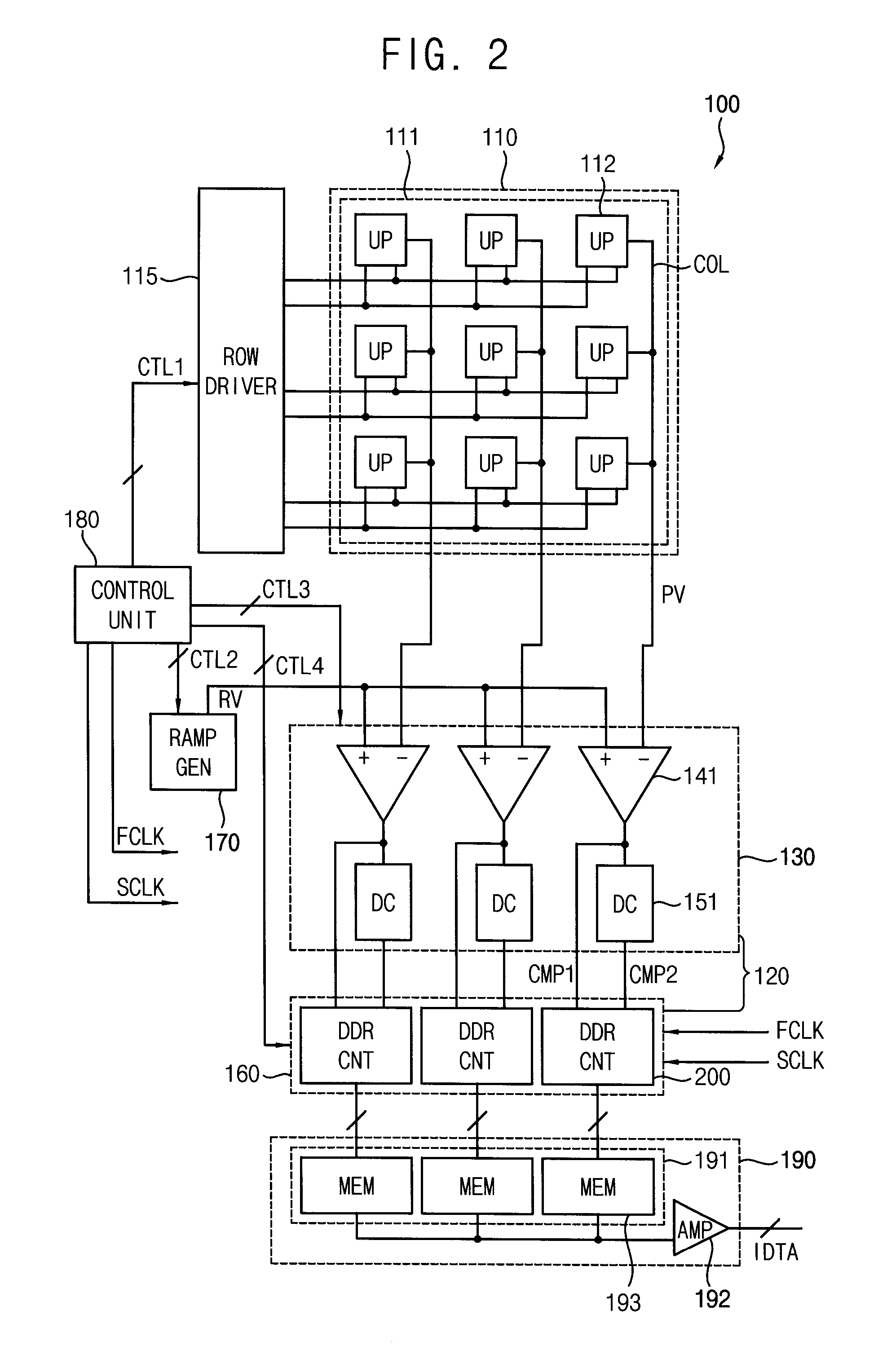
A counter circuit includes a first counter and a second counter. The first counter is configured to count a first counter clock signal which toggles with a first frequency to generate upper (N−M)-bit signals of N-bit counter output signals, in response to a first counting enable signal based on a first comparison signal during a coarse counting interval. N and M are natural numbers, N is greater than M, and M is greater than or equal to 3. The second counter is configured to count a second counter clock signal which toggles with a second frequency which is higher than the first frequency to generate lower M-bit signals of the N-bit counter output signals, in response to a second counting enable signal based on the first comparison signal and a second comparison signal during a fine counting interval which follows the coarse counting interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
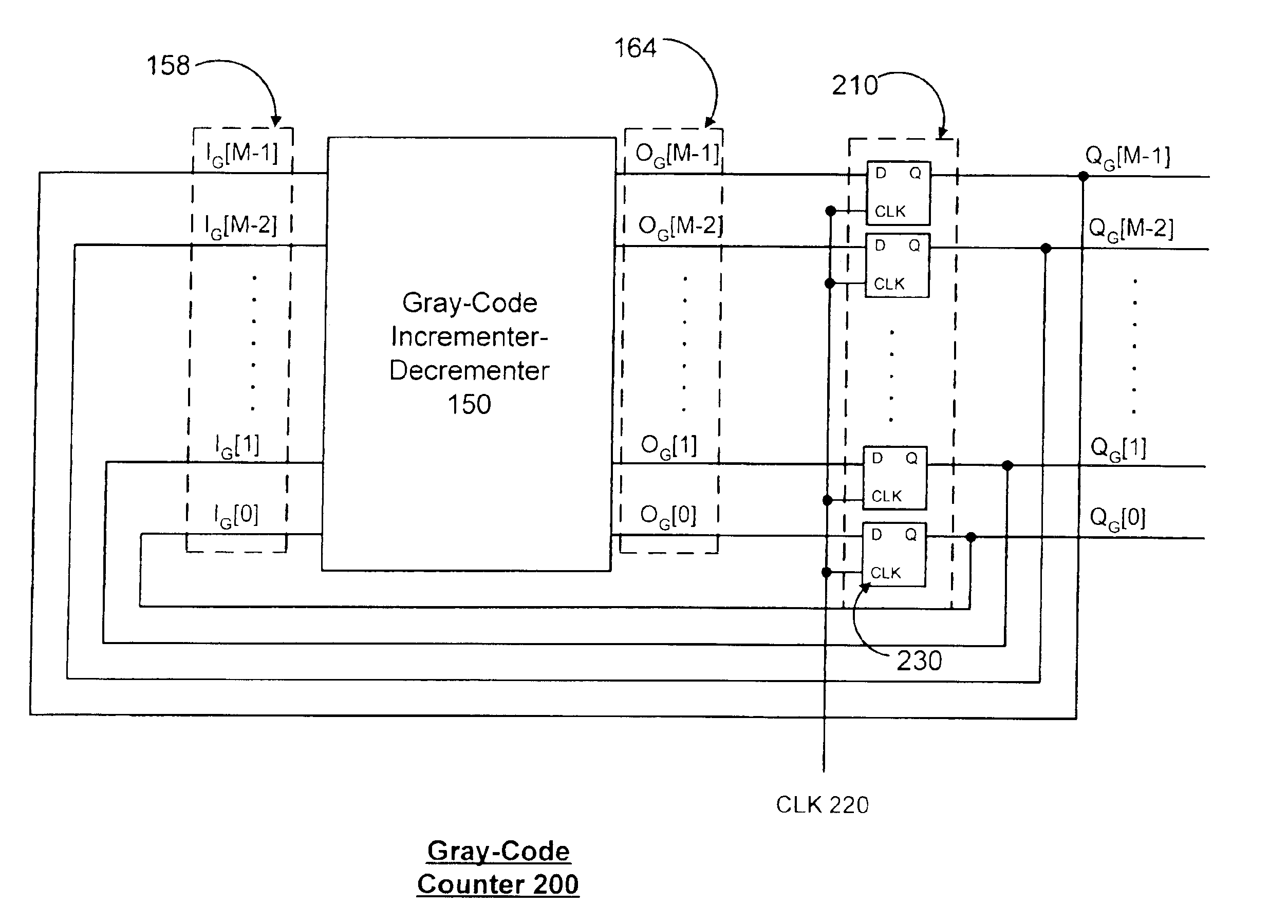
Modular low power gray code counter
InactiveUS7991104B1More area efficientEffective areaPower reduction by control/clock signalCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderModularityGray code
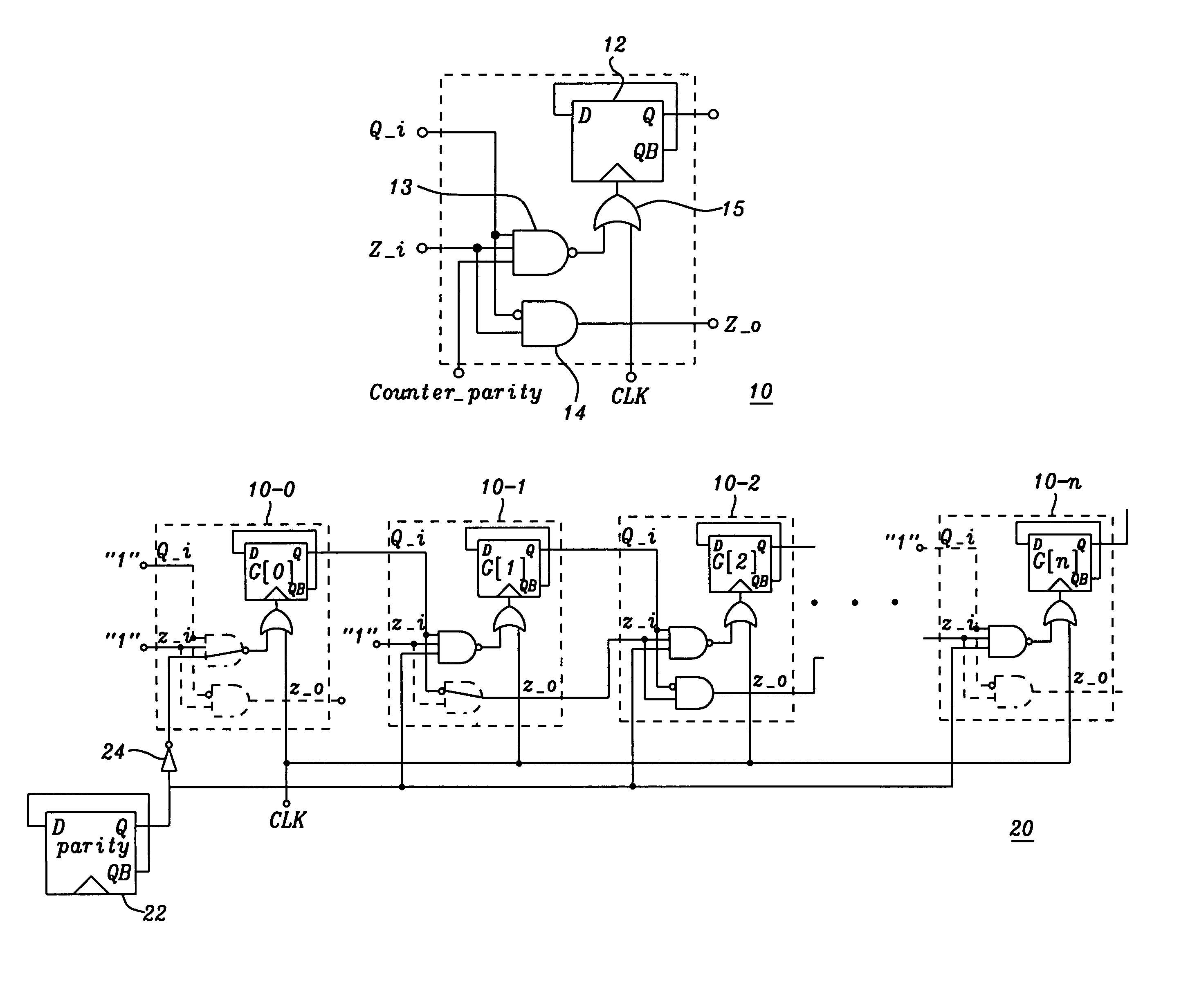
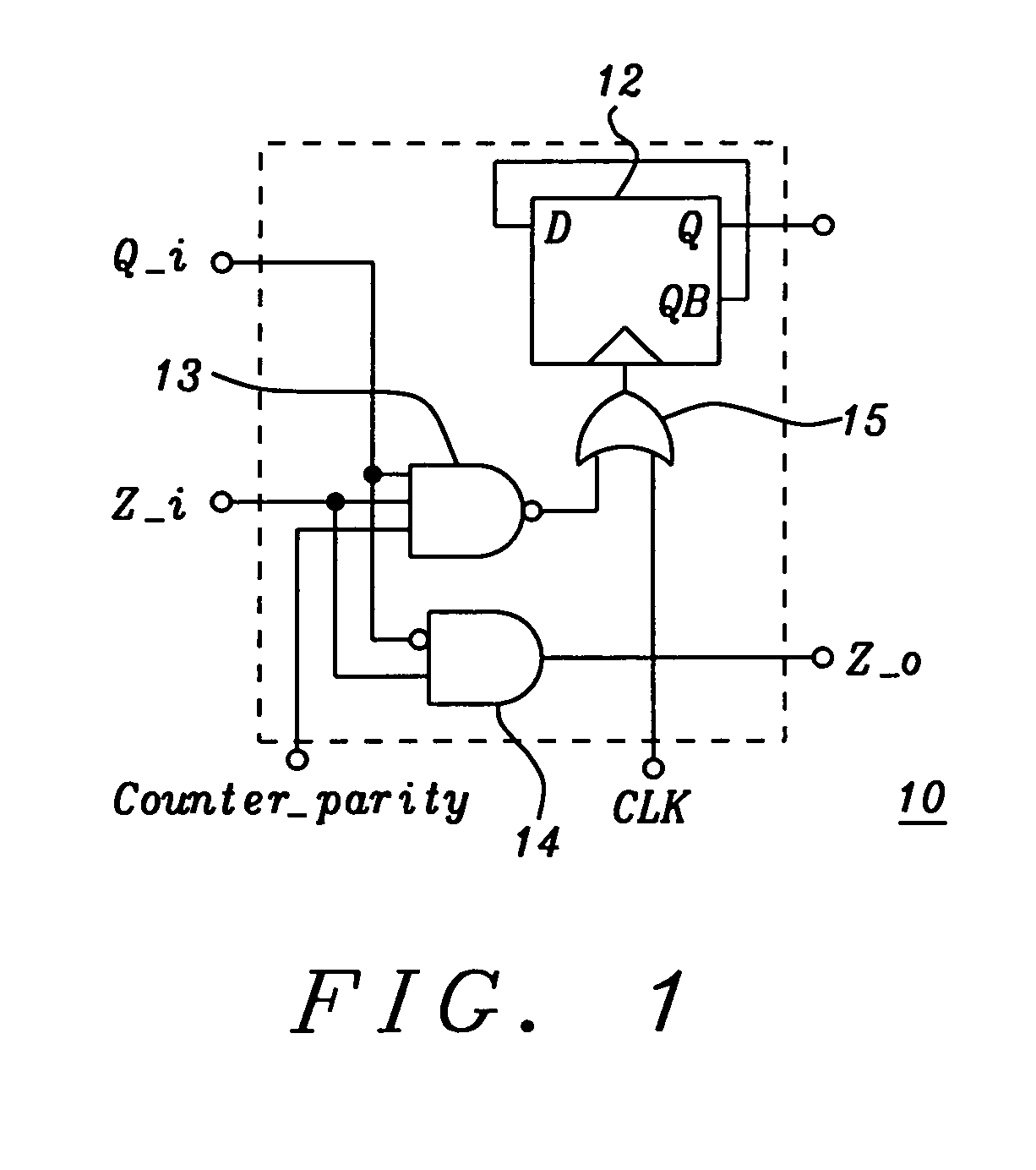
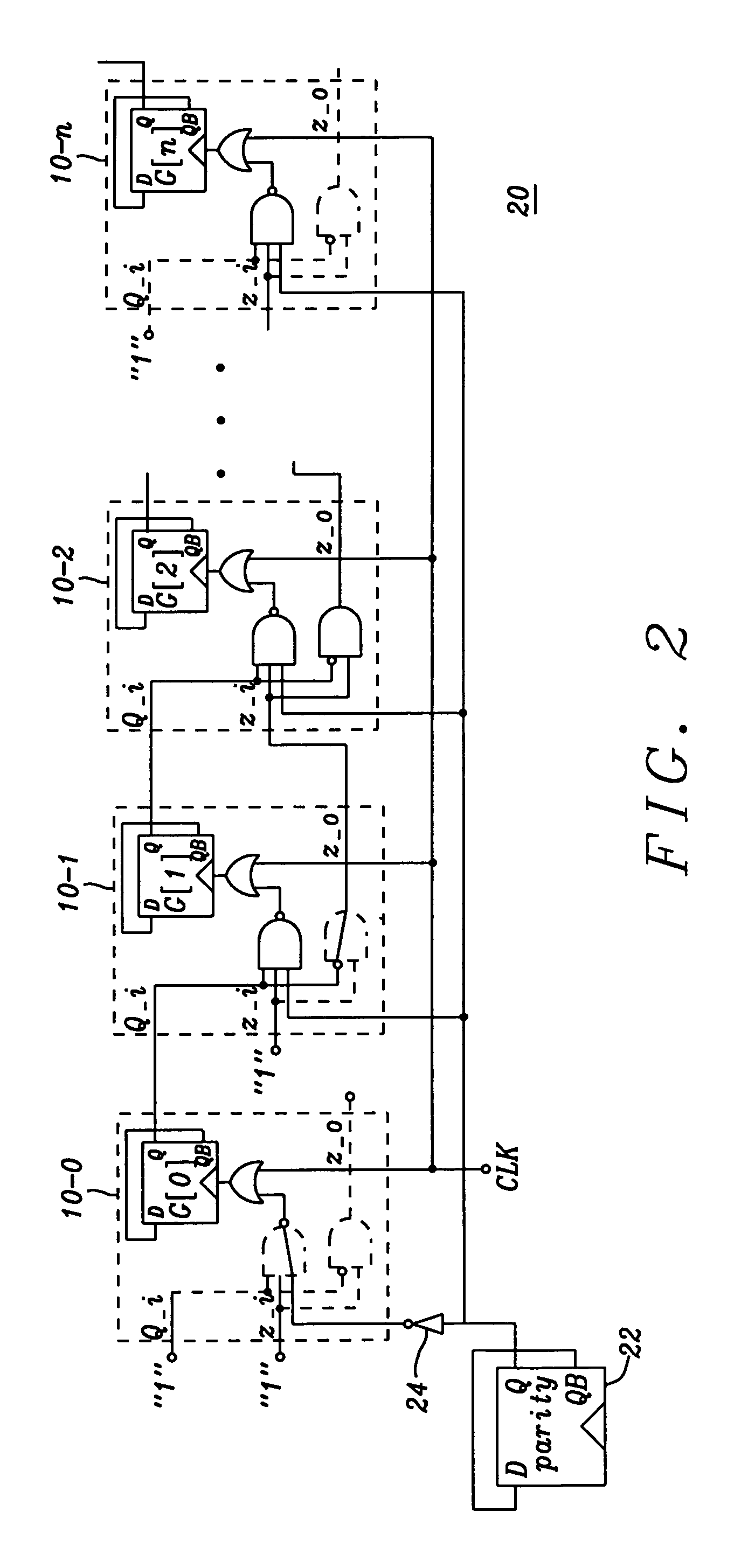
A modular Gray code counter of arbitrary bit length having identical Gray code counter cells in every bit position. Each cell comprises a Toggle Flop and logic which triggers the Toggle Flop and sets the state of the Gray code counter cell. The two outputs of a cell feed two inputs of the next more significant cell. A parity flip-flop provides odd parity, and as a third input to the cell together with the other two inputs determines the state of the cell.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
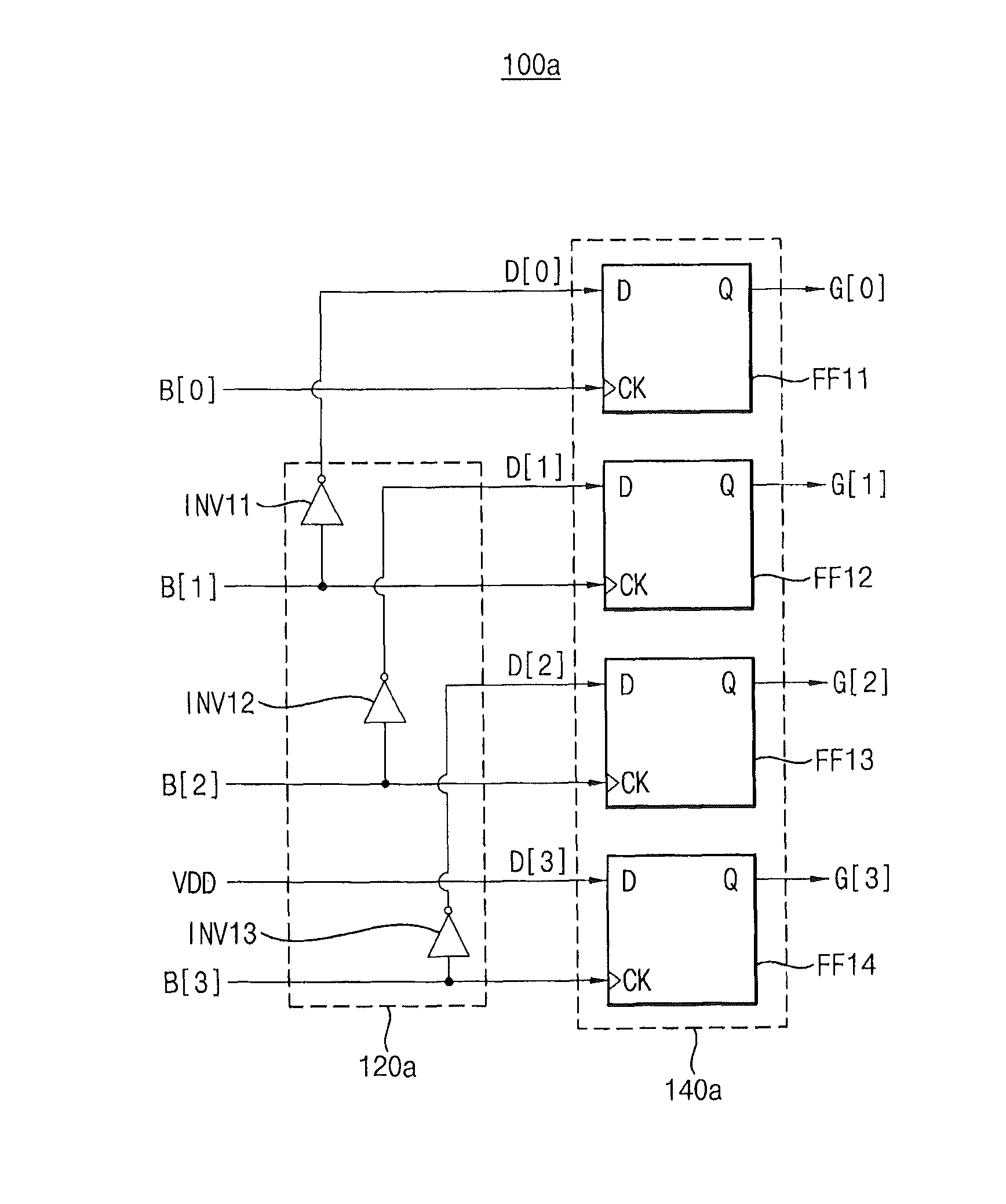
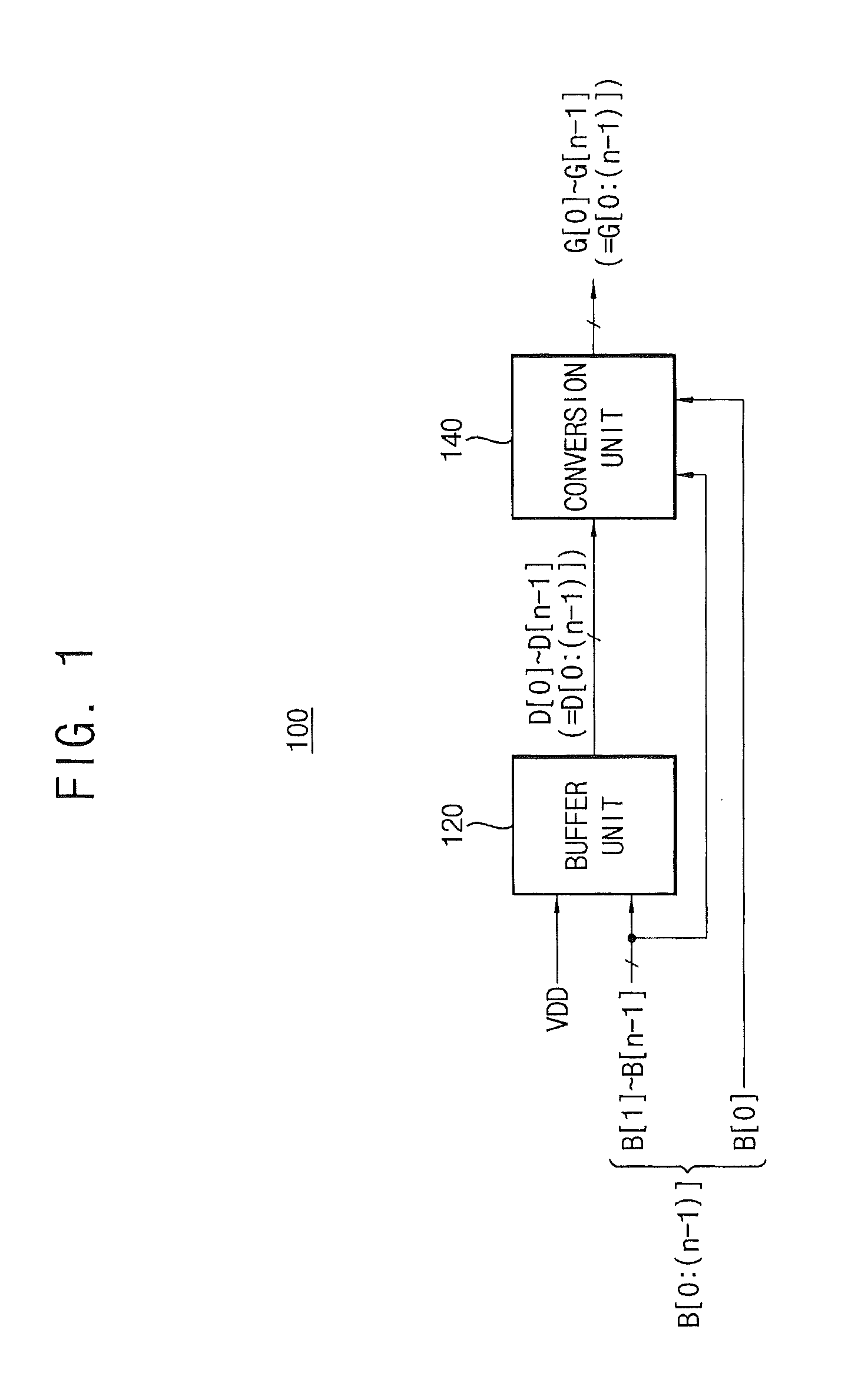
Binary-to-Gray Converting Circuits and Gray Code Counter Including the Same
ActiveUS20130278451A1Effectively generate a glitch-free Gray codePerform timing controlCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderCode conversionLeast significant bitComputer science
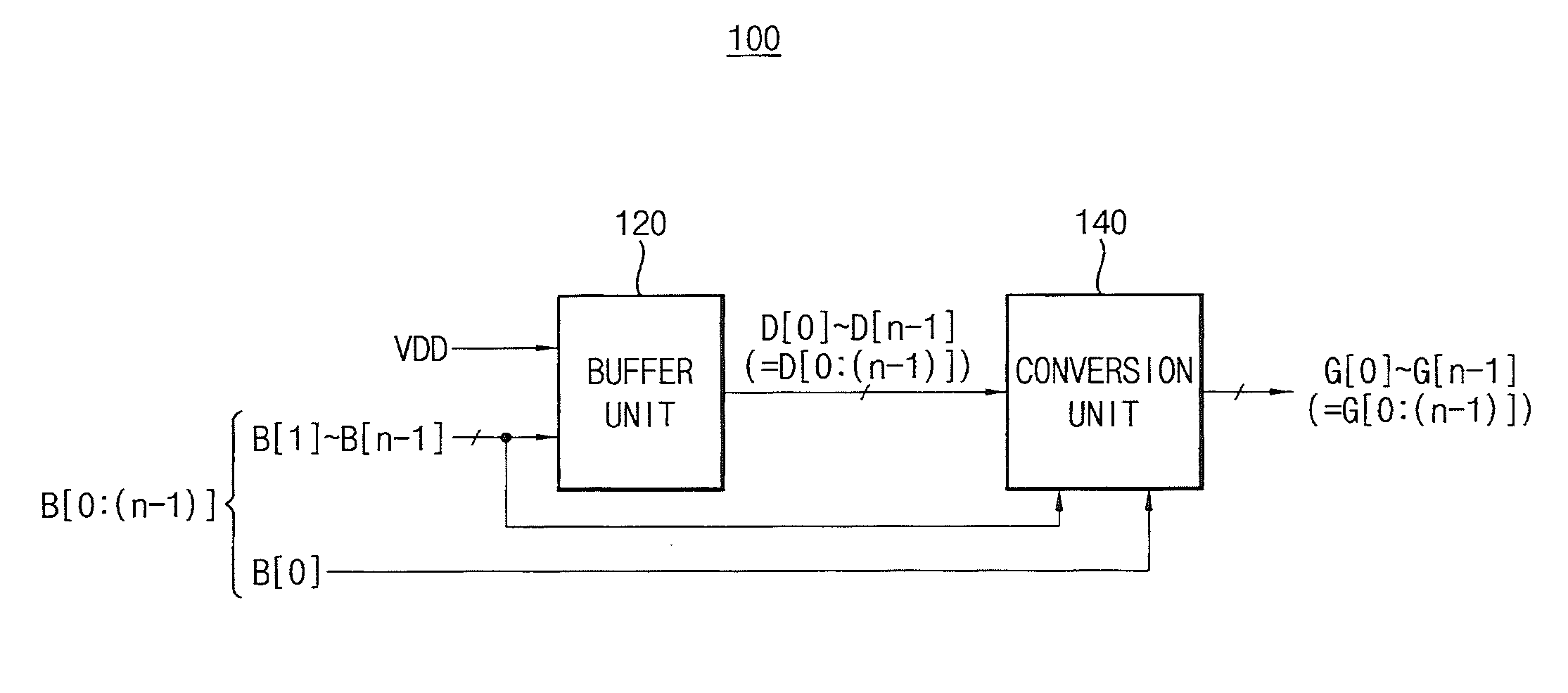
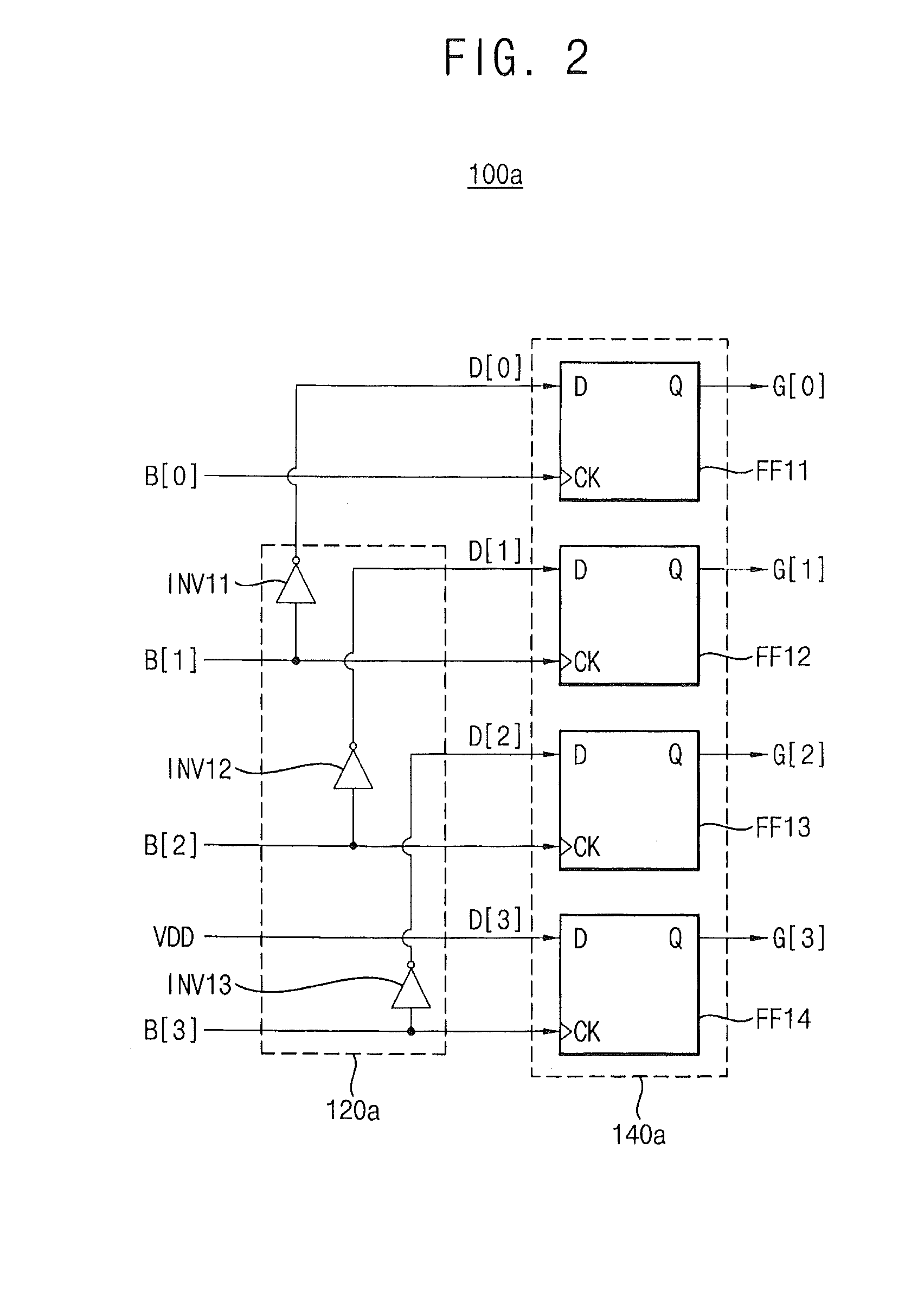
A binary-to-Gray converting circuit includes a buffer unit and a conversion unit. The buffer unit generates a data code of n bits in response to a power supply voltage and a second binary bit signal through an nth binary bit signal except for a first binary bit signal corresponding to a least significant bit of a binary code of n bits. The conversion unit generates a Gray code of n bits based on the binary code and the data code, and generates a kth Gray bit signal of the Gray code by latching a kth data bit signal of the data code in response to a kth binary bit signal of the binary code. A logic level of the kth Gray bit signal is determined corresponding to a logic level of the kth data bit signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
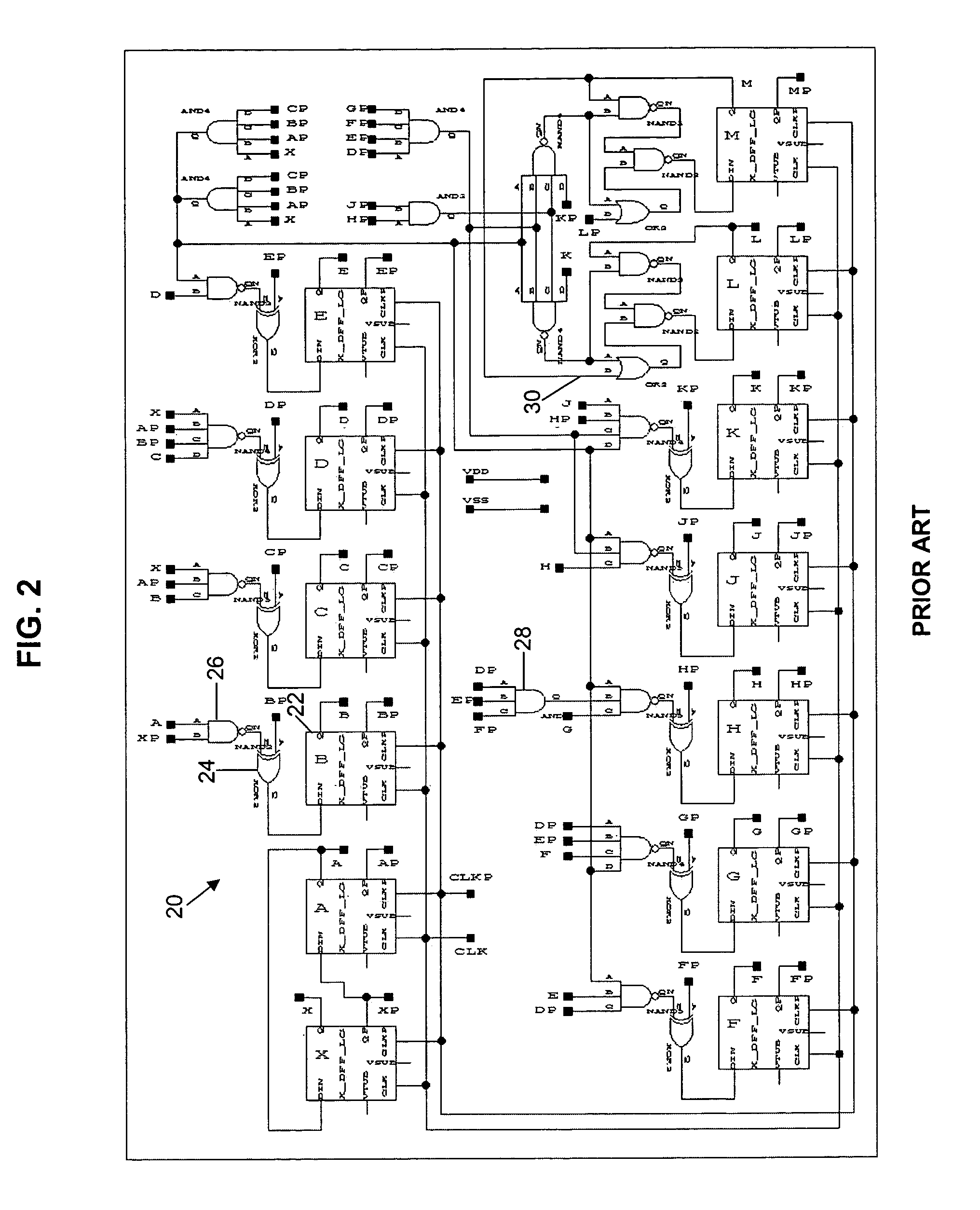
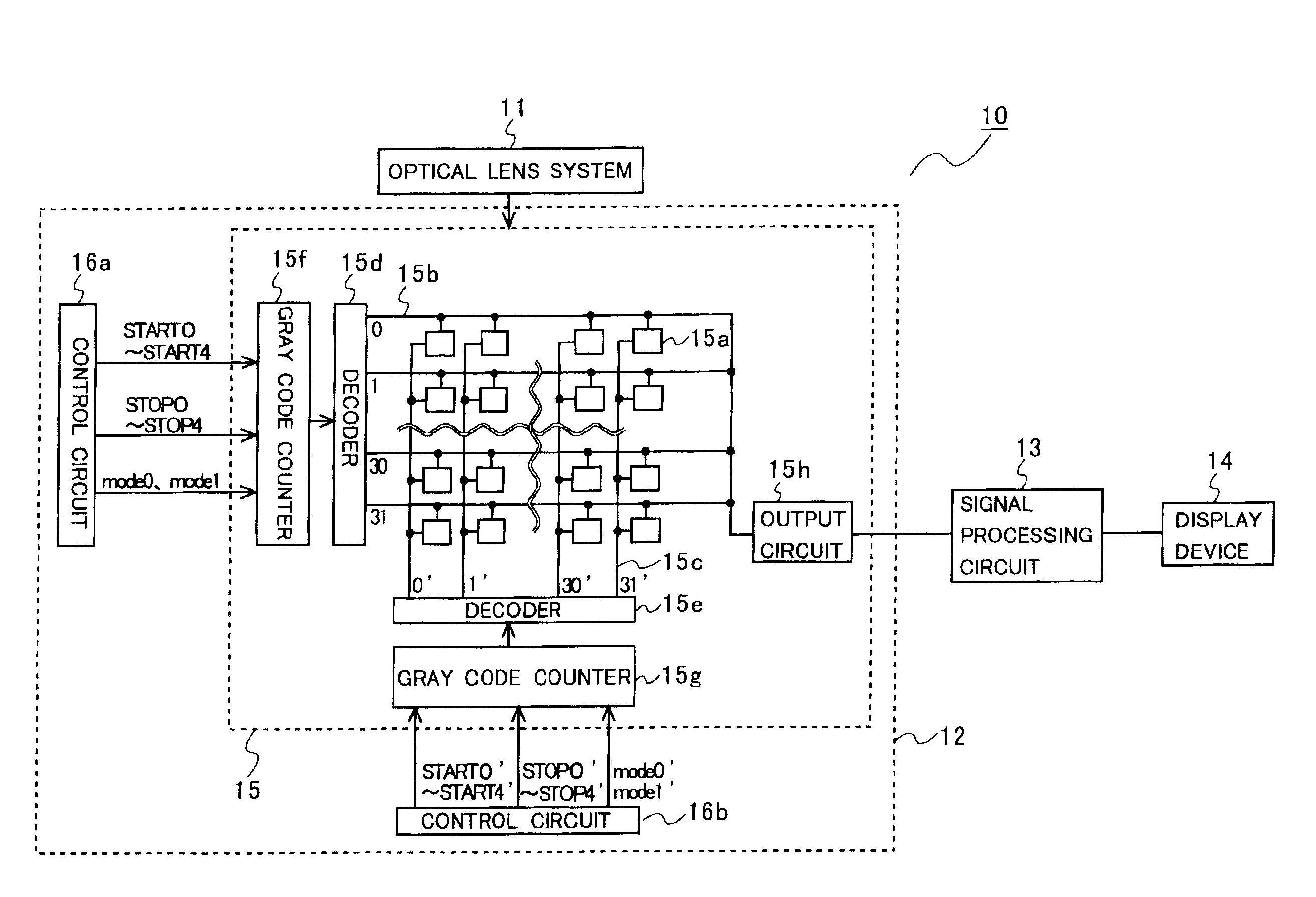
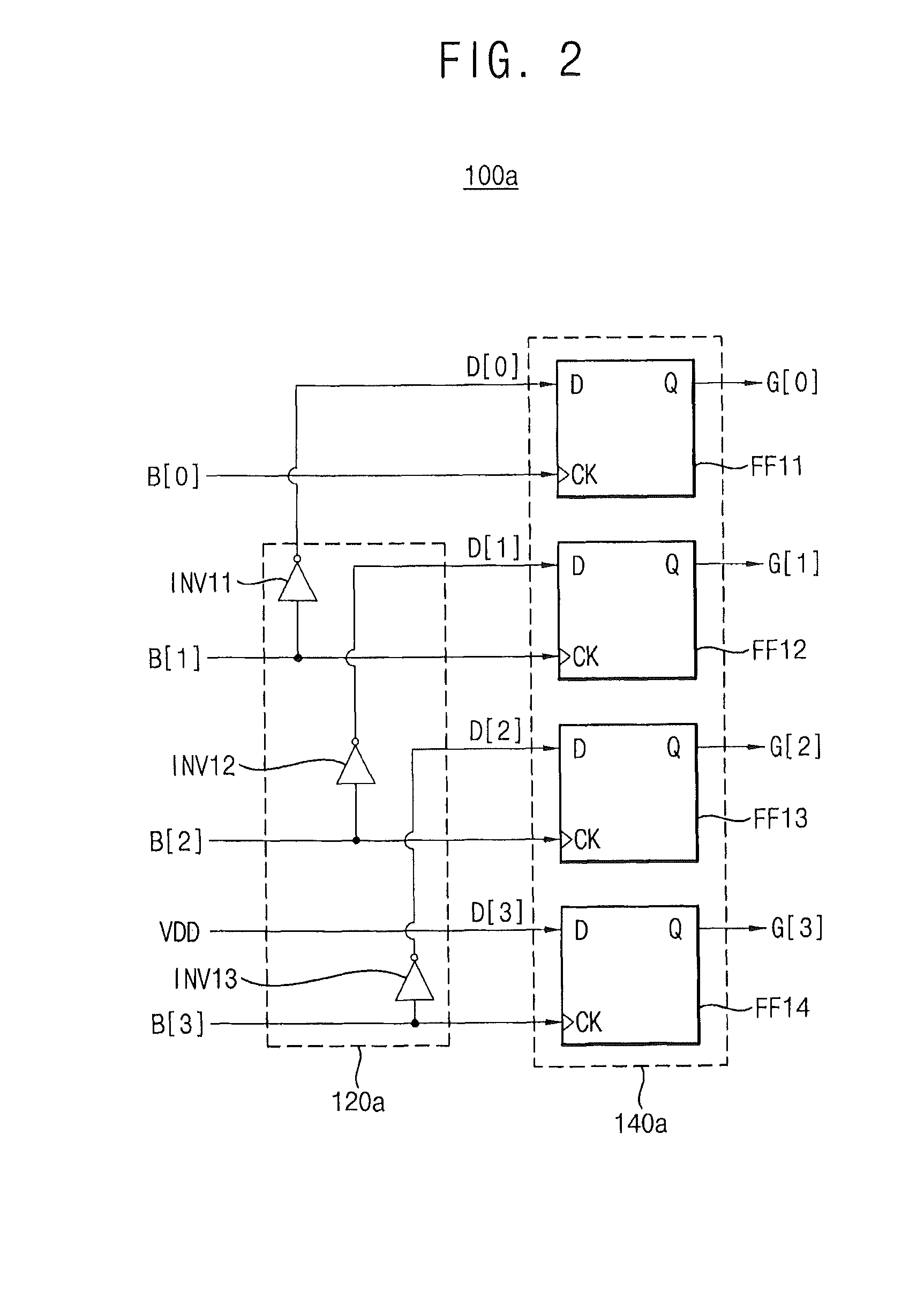
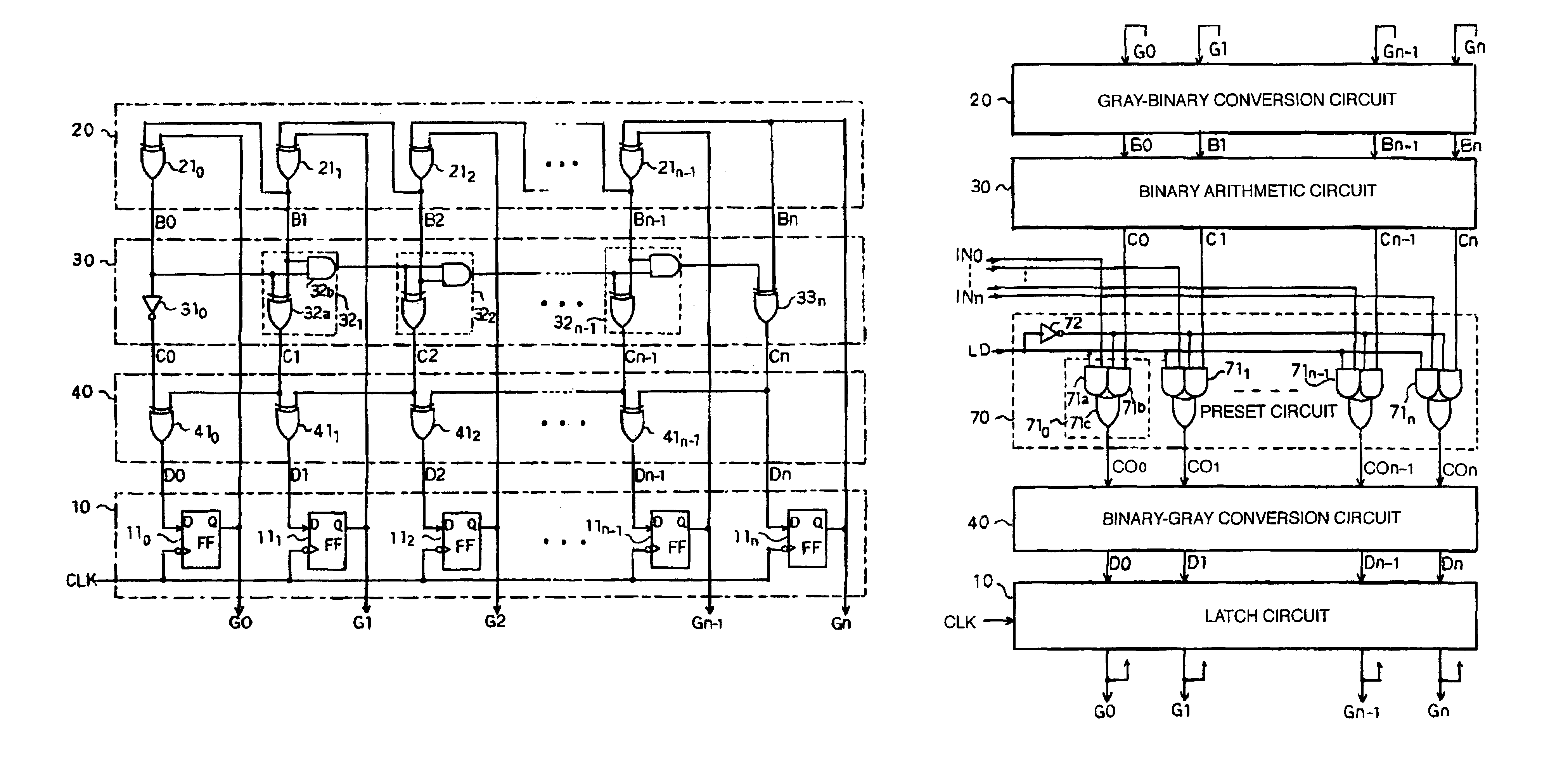
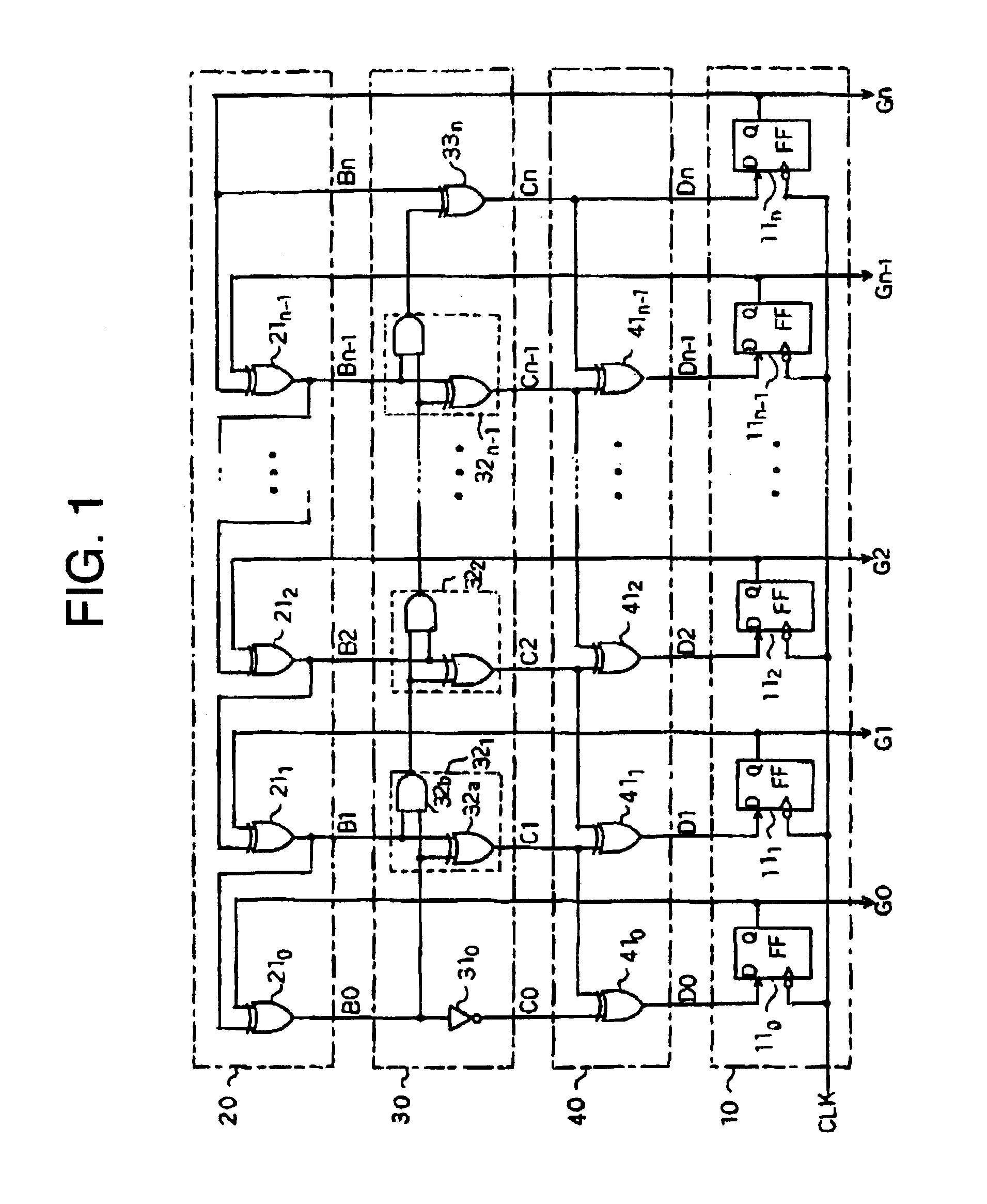
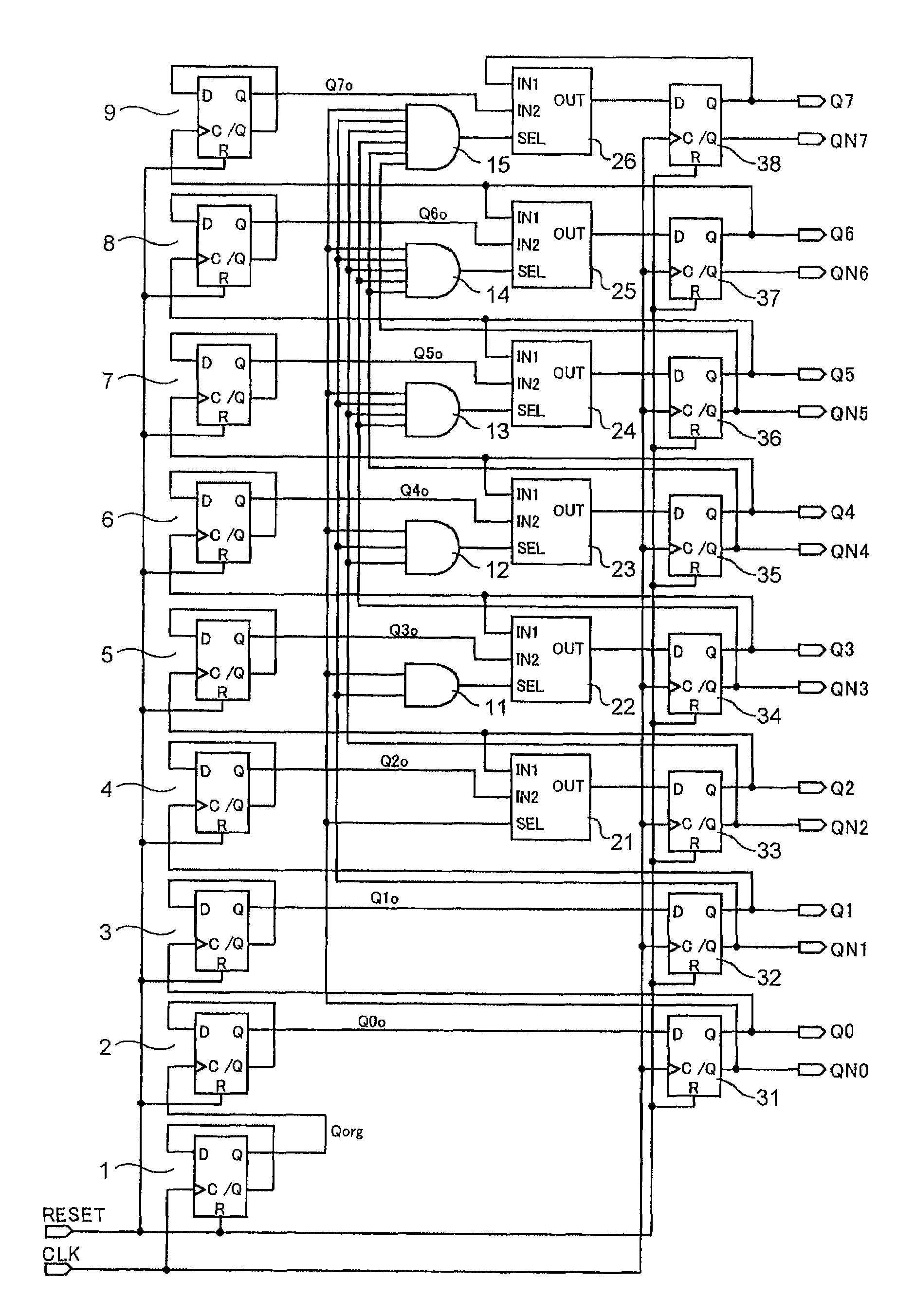
Gray code counter and display device therewith
InactiveUS20080224904A1Static indicating devicesCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderDelayed timeDisplay device
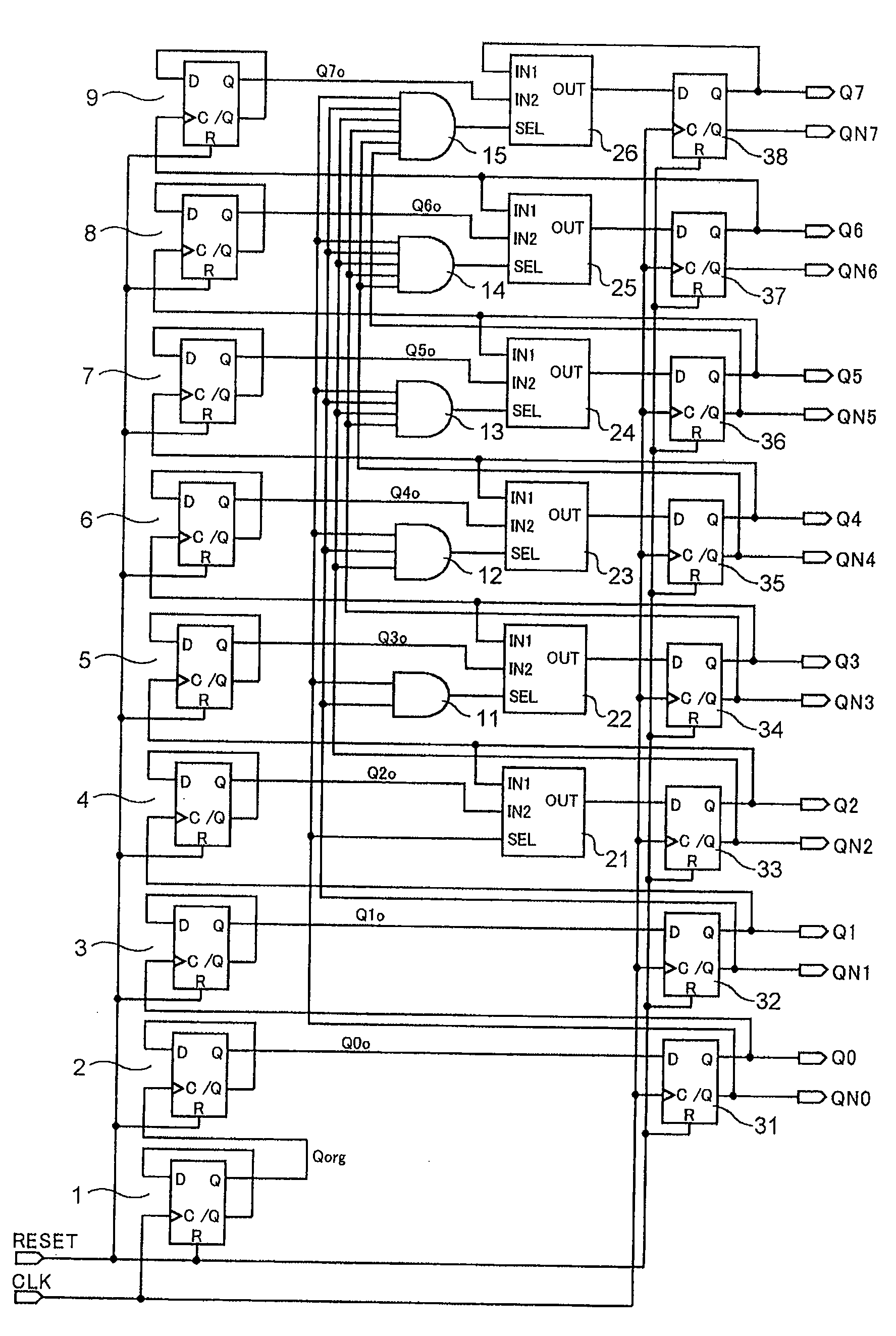
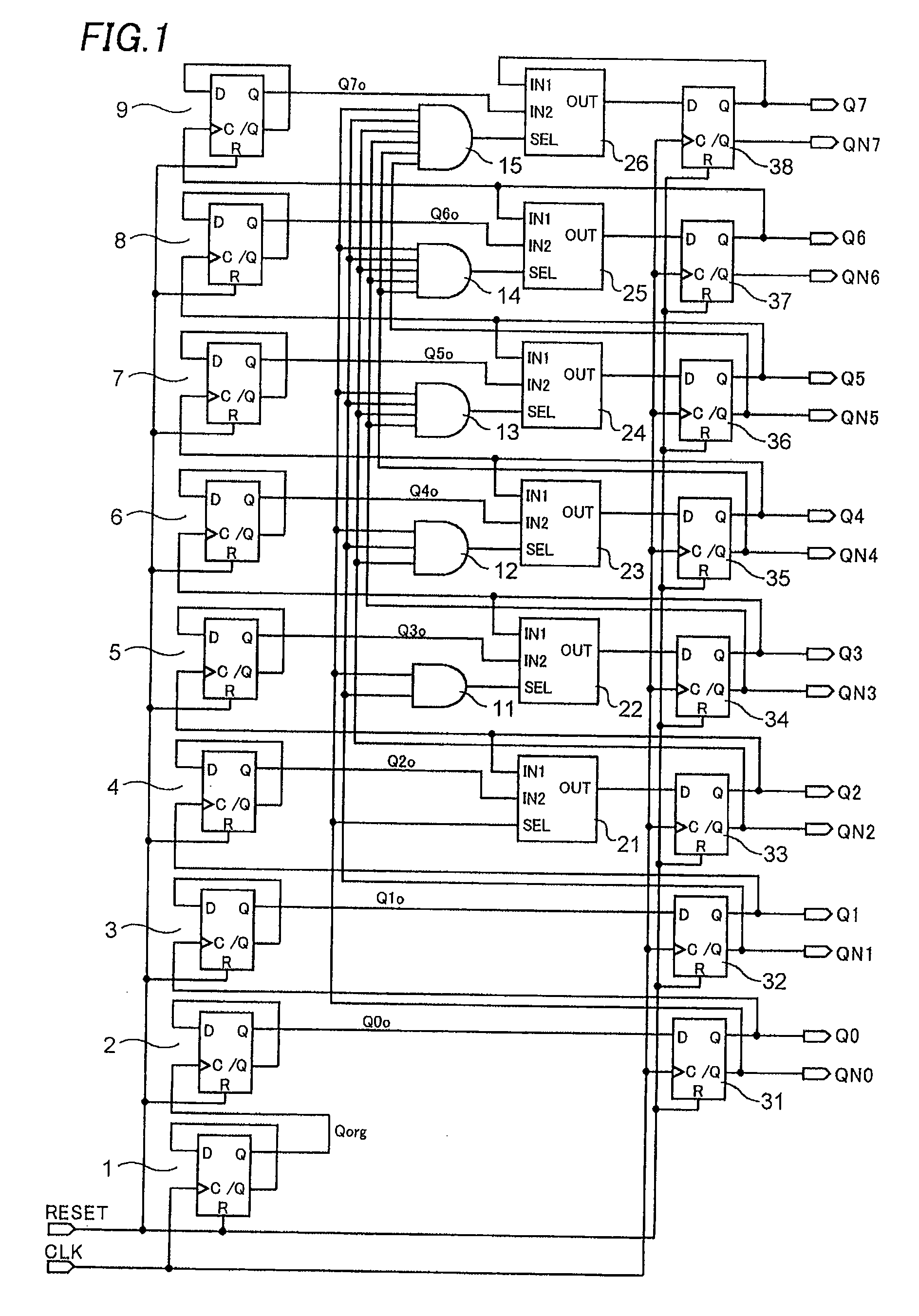
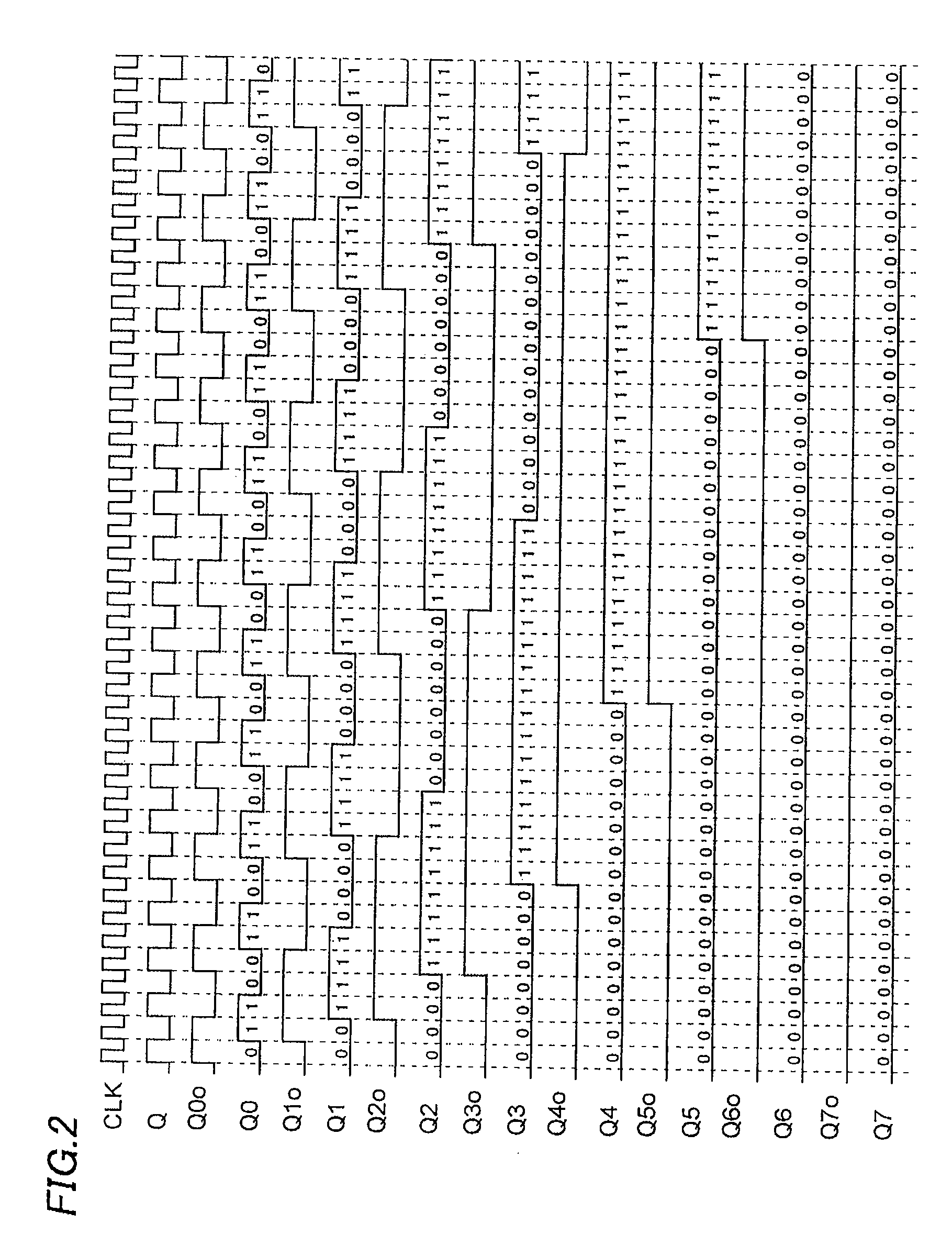
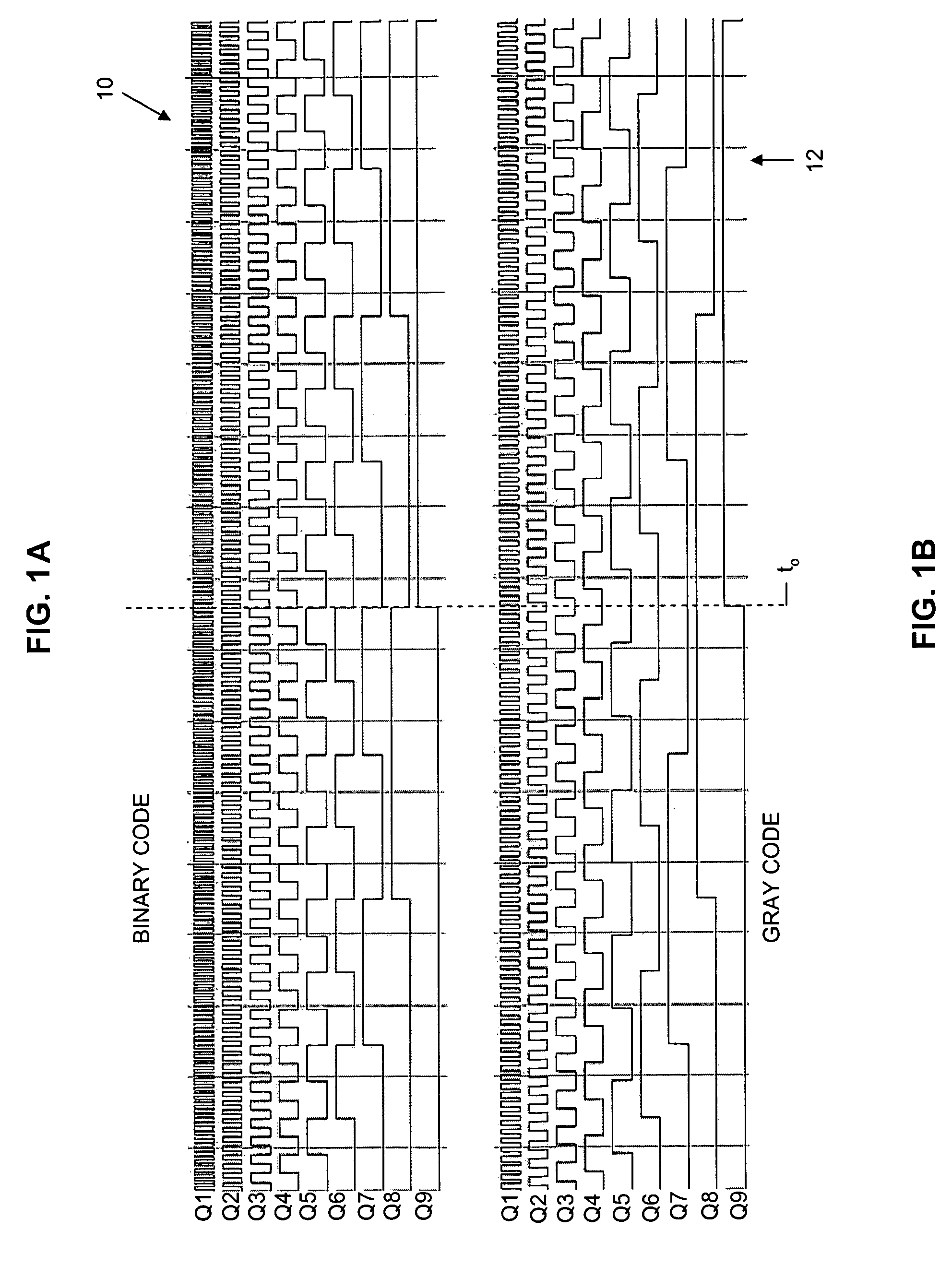
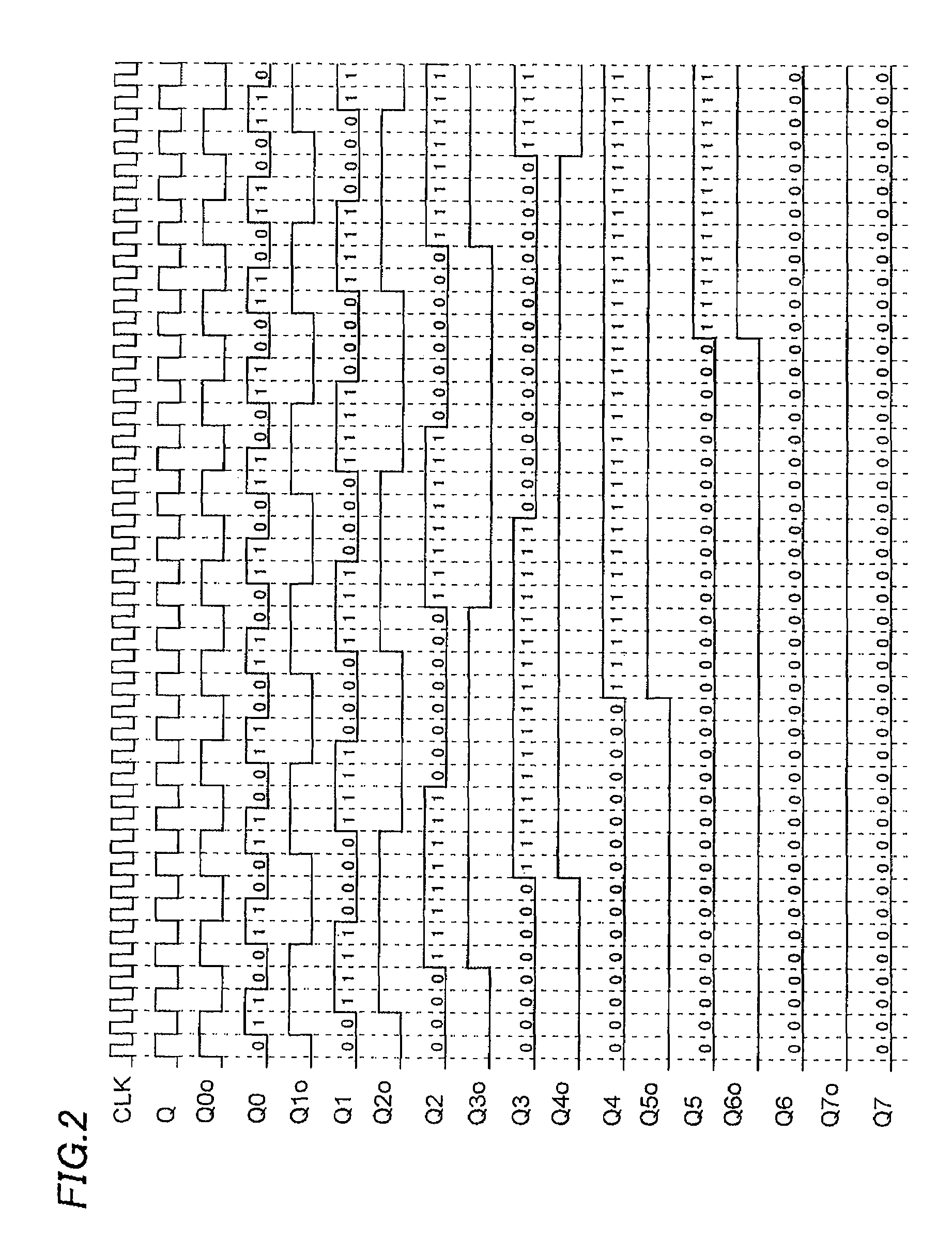
There is offered a Gray code counter with which a delay time of a critical path is reduced and a fast operation is made possible. A first Gray code bit Q0 is obtained by outputting an output signal Q0o of an RDFF 2 through an RDFF 31 to synchronize with a clock CLK. A second Gray code bit Q1 is obtained by outputting an output signal Q1o of an RDFF 2 through an RDFF 32 to synchronize with the clock CLK. A third Gray code bit Q2 is obtained by delaying an output signal Q2o of an RDFF 4 with a selection circuit 21 and outputting it through an RDFF 33 to synchronize with the clock CLK. A fourth Gray code bit Q3 is obtained by delaying an output signal Q3o of an RDFF 5 with an AND circuit 11 and a selection circuit 22 and outputting it through an RDFF 34 to synchronize with the clock CLK. Higher bits of the Gray code are similarly generated.
Owner:EPSON IMAGING DEVICES CORP +1
Apparatus and method for testing randomness
ActiveUS20160170856A1Improve securityCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer hardware
A randomness testing apparatus is disclosed. A randomness testing apparatus according to an embodiment includes a randomness testing module to conduct a randomness test on physically unclonable function (PUF)-based hardware and a processing device to determine whether the PUF-based hardware is defective on the basis of a randomness test result.
Owner:ICTK
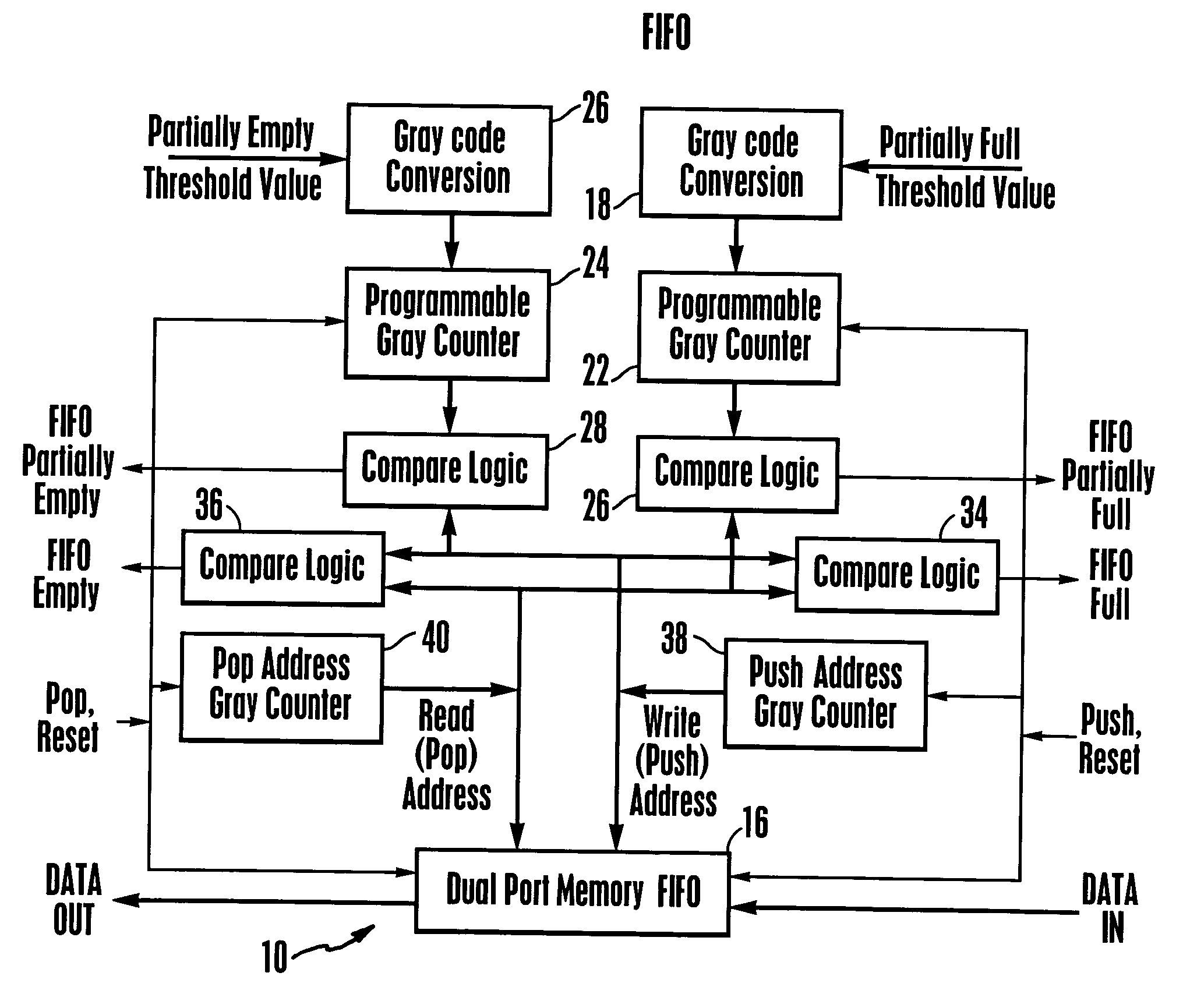
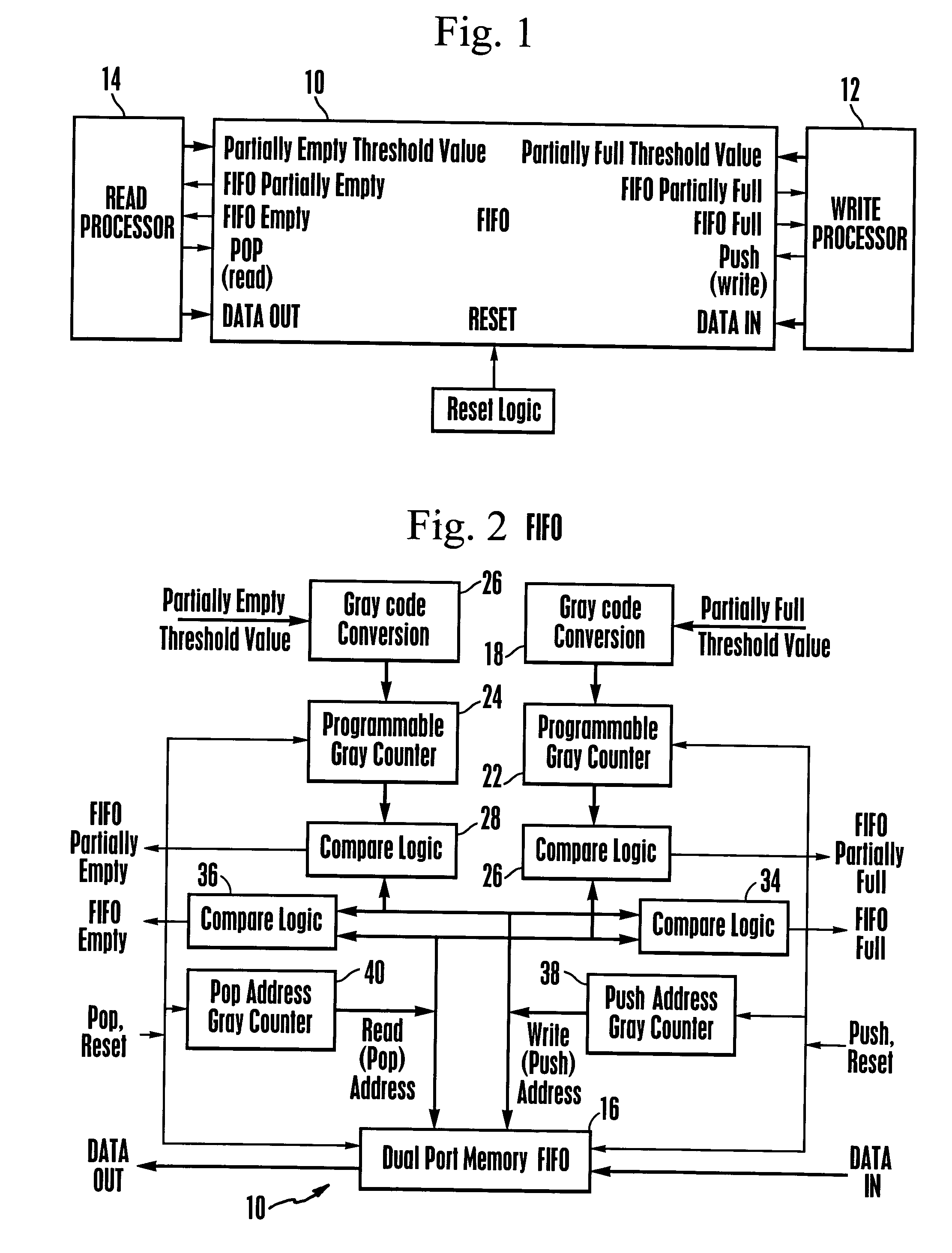
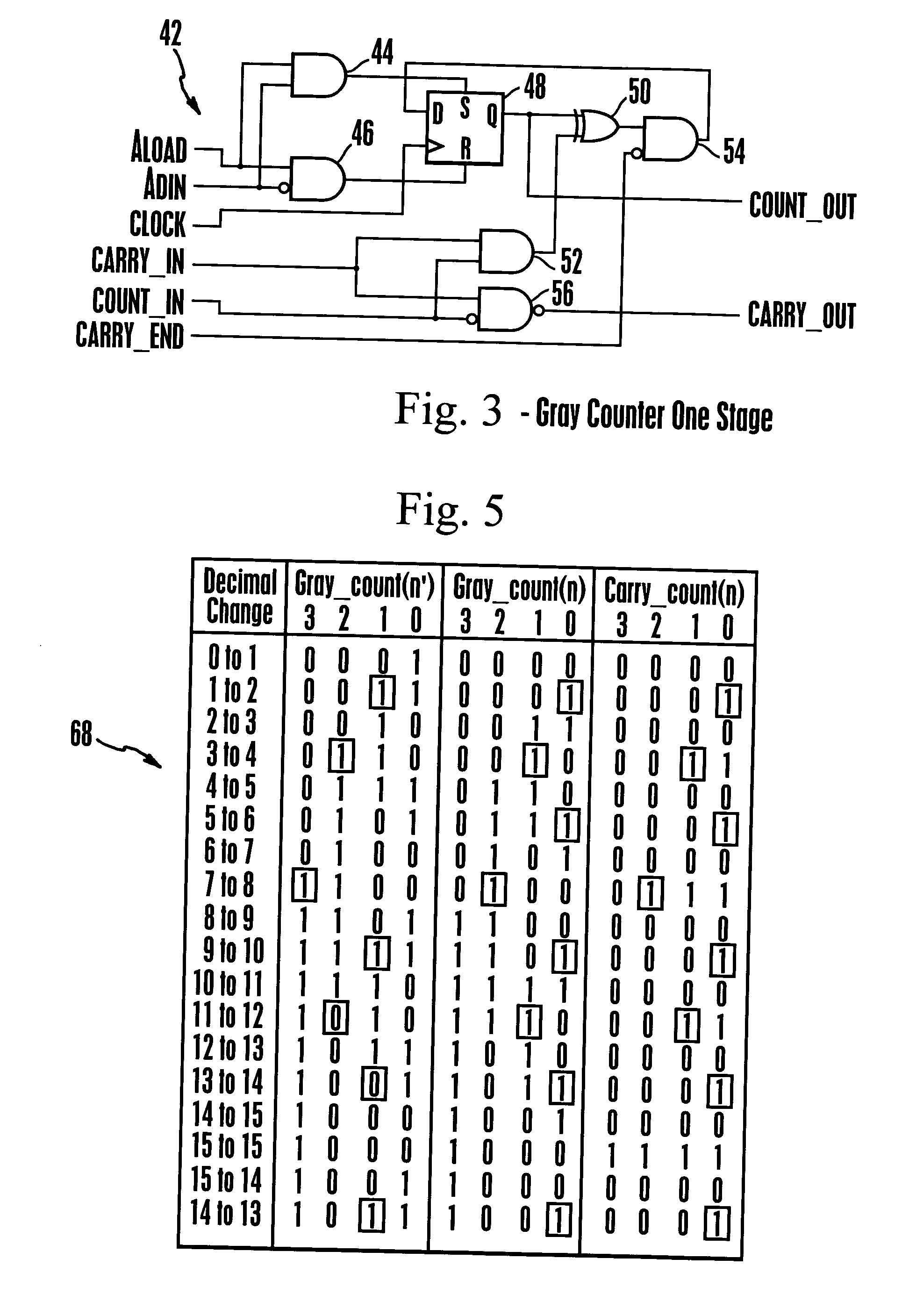
Gray code counter
ActiveUS6931091B2Exclusive-OR circuitsCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderLeast significant bitGray code
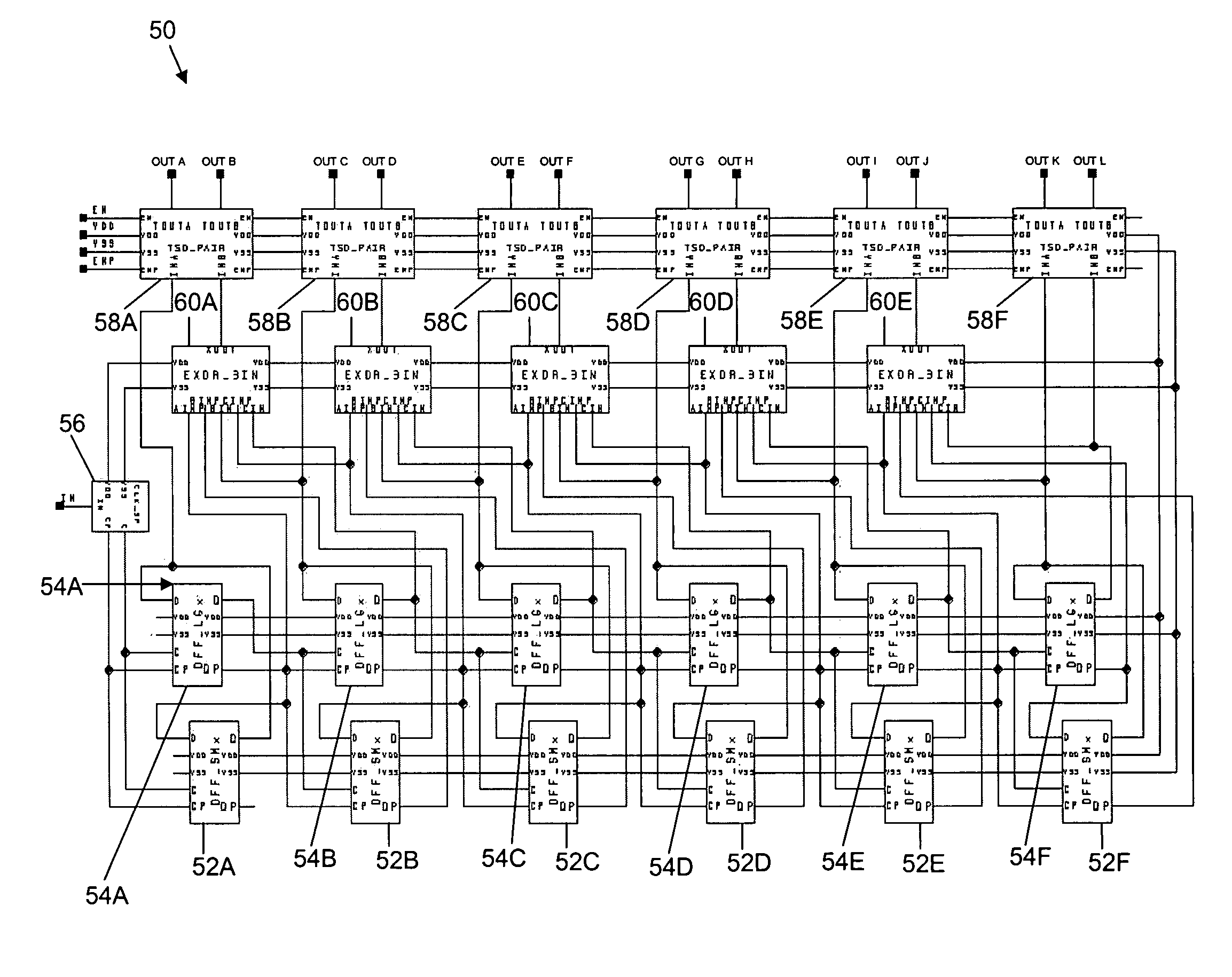
A gray code is produced from a minimum of gate logic by making available and monitoring master outputs of master-slave latch pairs, where the latch pairs are arranged to form a cascading chain of toggle flip-flop stages. The least significant bit through one less than the most significant bit in the gray code is supplied by the master latch outputs and the most significant gray code bit is supplied by the slave latch output of the last toggle stage in the chain.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
Gray code counter
InactiveUS6950138B2Reduce electrical noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer hardwareGray code
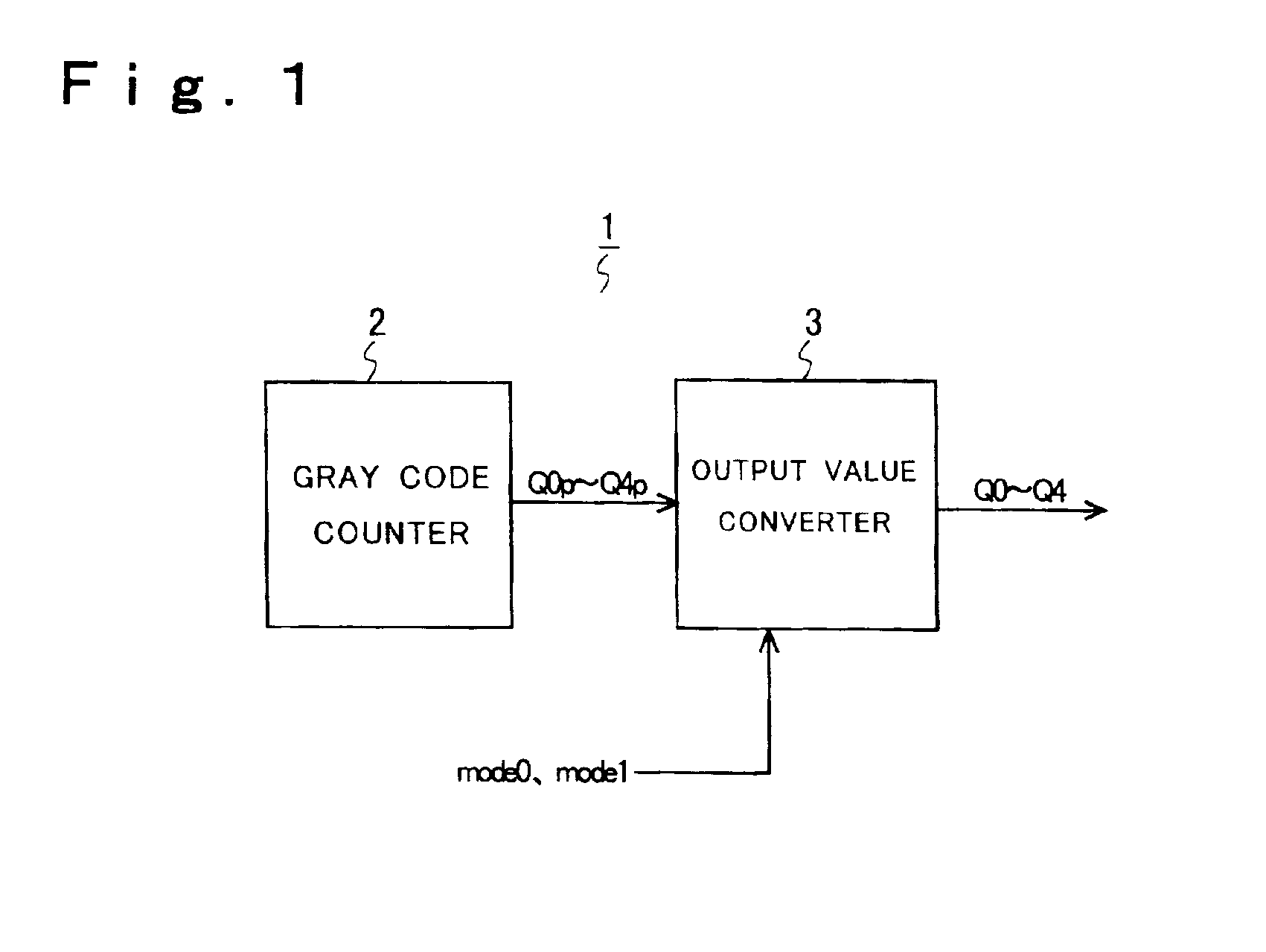
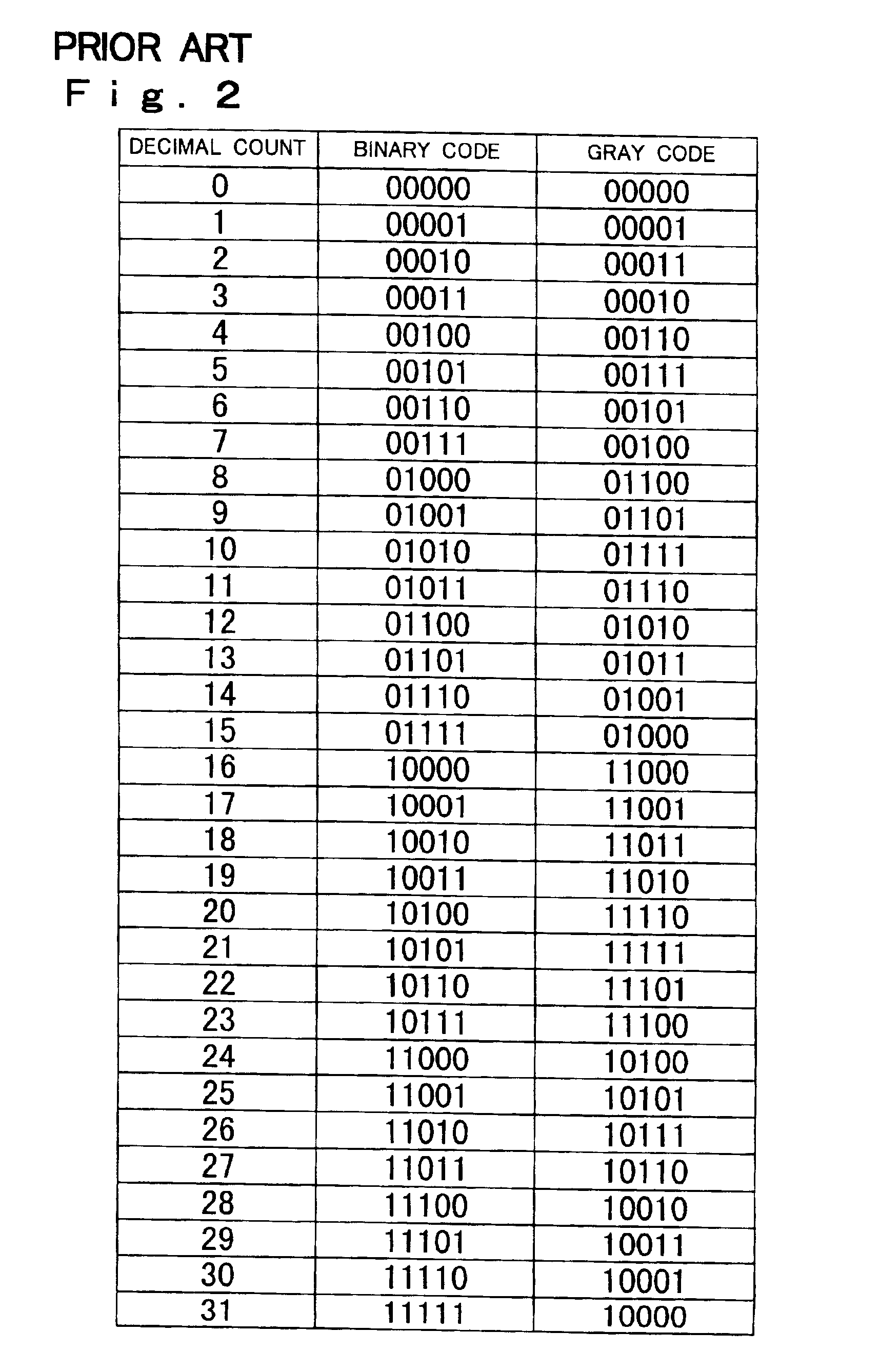
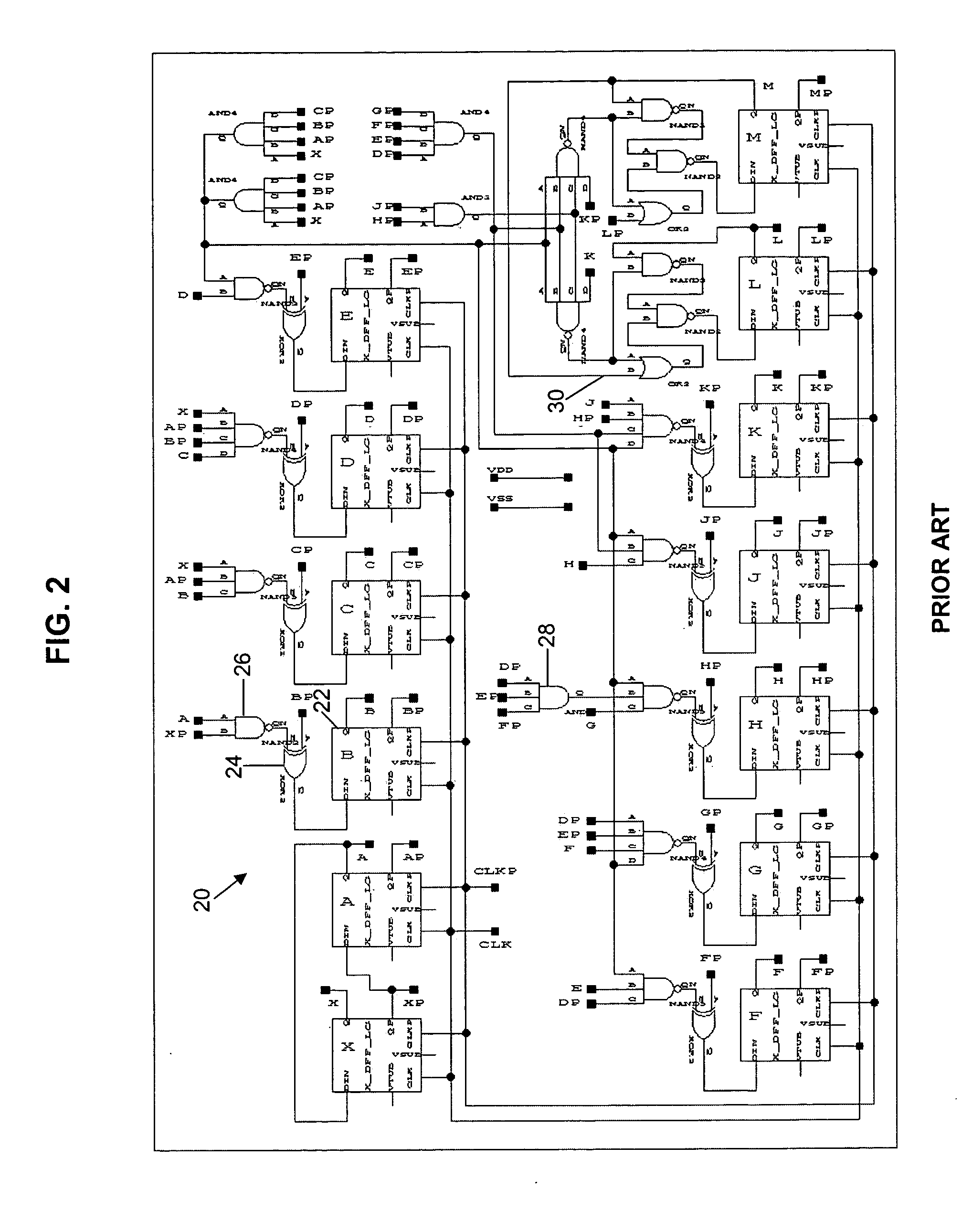
Conventionally, it is difficult to design the logic of a Gray code counter that can be used in interlaced counting. Even though interlaced counting is possible with a Gray code counter, the number of simultaneously changing bits increases greatly depending on the number of counts skipped at a time. To overcome these problems, a Gray code counter according to the present invention has a consecutively counting Gray code counter that counts in increments or decrements of one, and an output value converter circuit that converts the Gray code data output from the consecutively counting Gray code counter into a Gray code corresponding to decimal counts as obtained by counting with (2 raised to a particular power minus 1) counts skipped at a time.
Owner:SHARP KK
Gray code counter
ActiveUS20050129167A1Minimal logic circuitryExclusive-OR circuitsCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderLeast significant bitComputer science
A gray code is produced from a minimum of gate logic by making available and monitoring master outputs of master-slave latch pairs, where the latch pairs are arranged to form a cascading chain of toggle flip-flop stages. The least significant bit through one less than the most significant bit in the gray code is supplied by the master latch outputs and the most significant gray code bit is supplied by the slave latch output of the last toggle stage in the chain.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
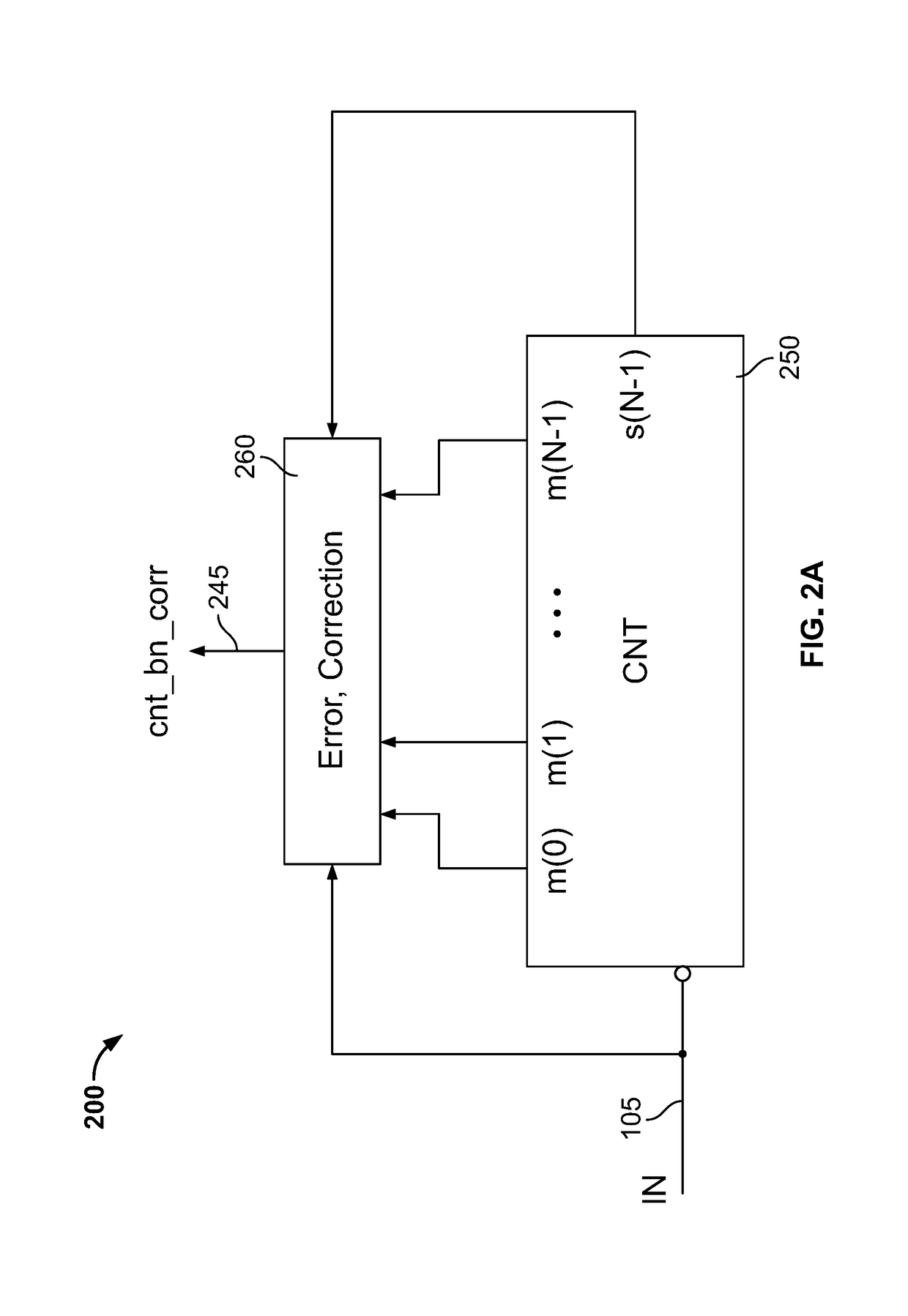
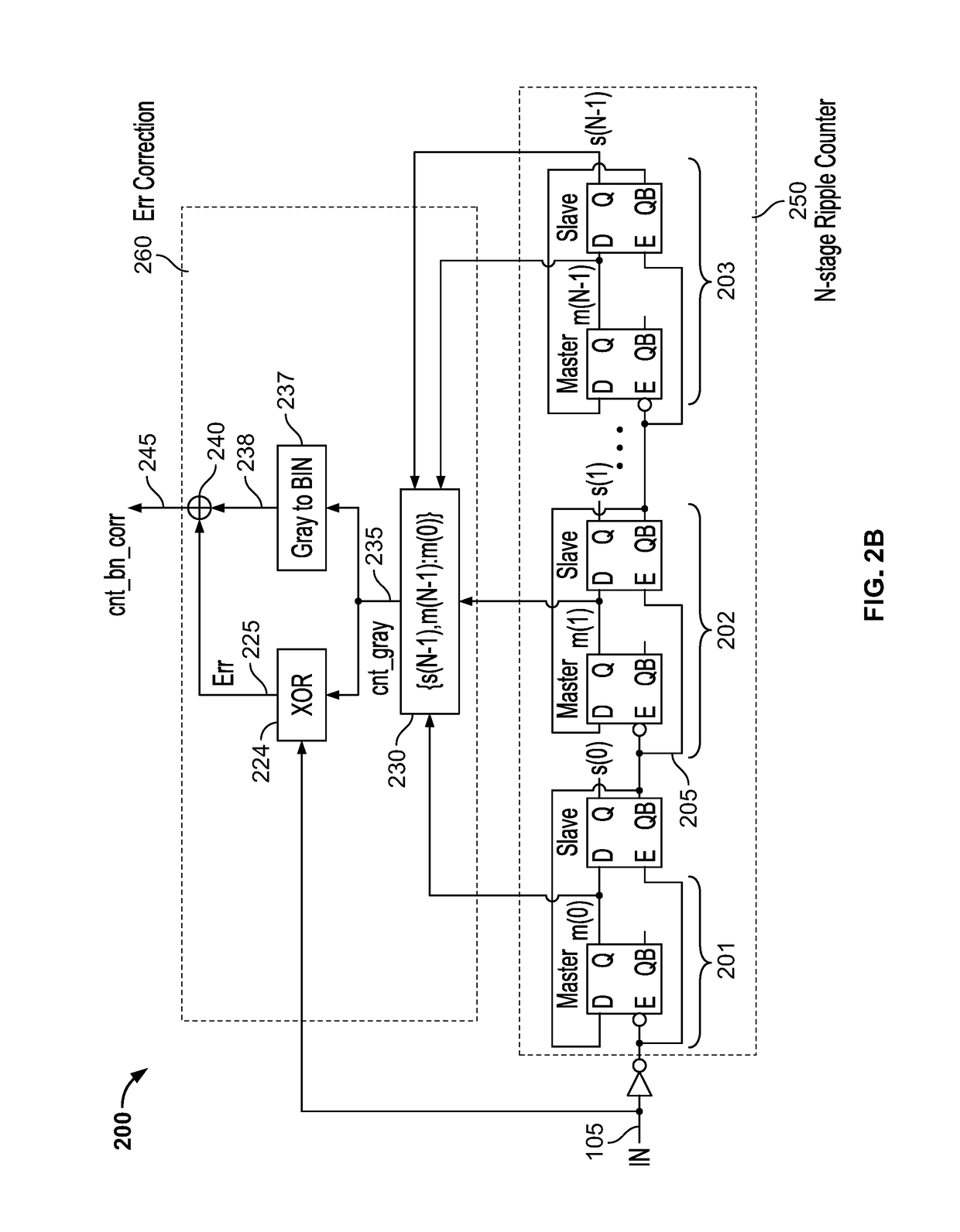
Systems and methods for gray coding based error correction in an asynchronous counter
ActiveUS10187082B1Data representation error detection/correctionCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderPropagation delayAsynchronous circuit
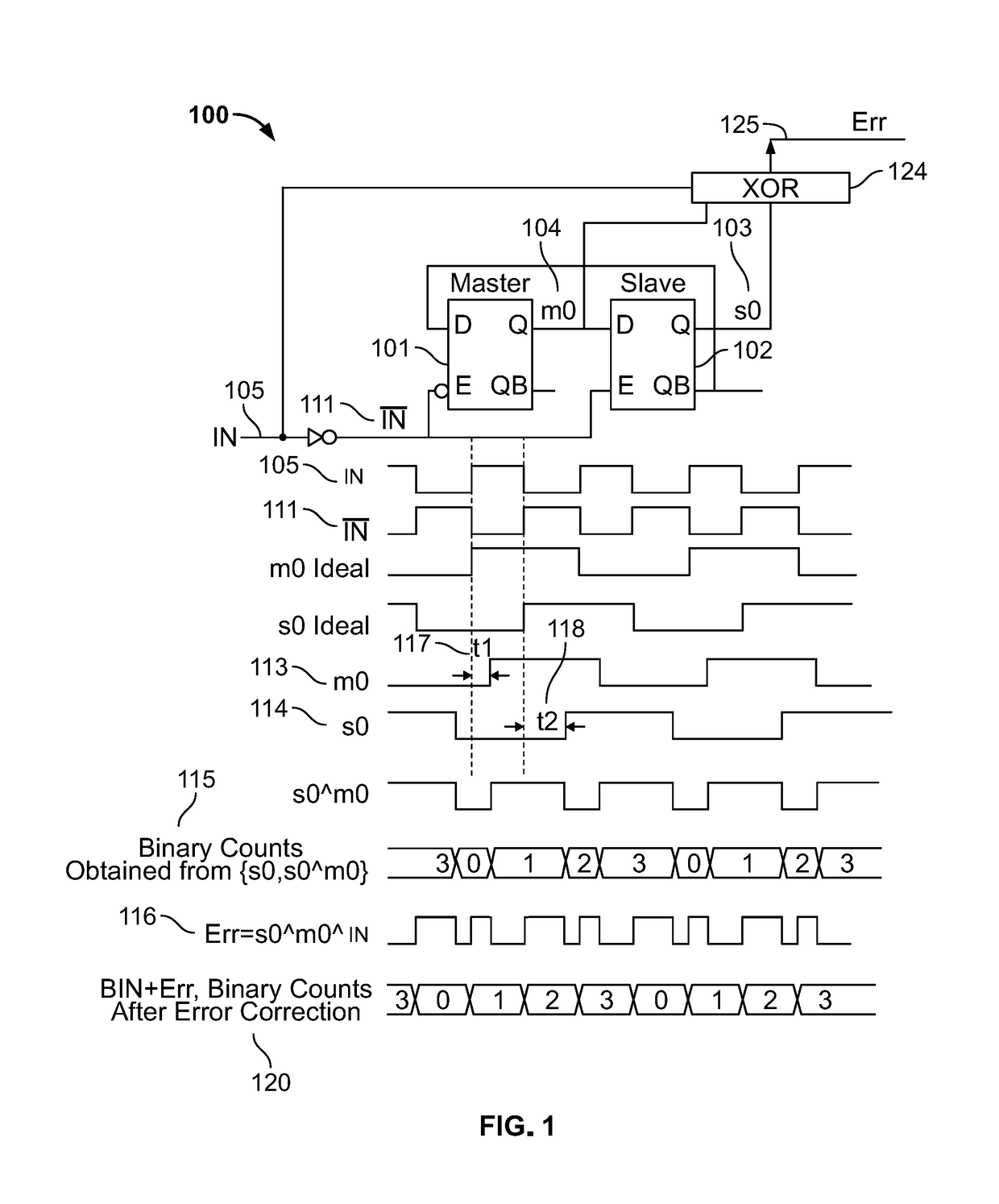
Embodiments described herein provide a method for correcting a propagation delay induced error in an output of an asynchronous counter. An input clock is applied to the asynchronous counter. A gray-code count is generated by the asynchronous counter. The gray-code count is mapped to a binary count. An error component, indicative of a counting error induced by a propagation delay between the input clock and the binary count, is generated by taking an exclusive-OR operation over the gray-code count and the input clock. The error component is added to the binary count to generate an error-corrected binary count. The error-corrected binary count is output.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Binary-to-gray converting circuits and gray code counter including the same
ActiveUS8711016B2Effectively generate a glitch-free Gray codePerform timing controlCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderCode conversionLeast significant bitComputer science
A binary-to-Gray converting circuit includes a buffer unit and a conversion unit. The buffer unit generates a data code of n bits in response to a power supply voltage and a second binary bit signal through an nth binary bit signal except for a first binary bit signal corresponding to a least significant bit of a binary code of n bits. The conversion unit generates a Gray code of n bits based on the binary code and the data code, and generates a kth Gray bit signal of the Gray code by latching a kth data bit signal of the data code in response to a kth binary bit signal of the binary code. A logic level of the kth Gray bit signal is determined corresponding to a logic level of the kth data bit signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
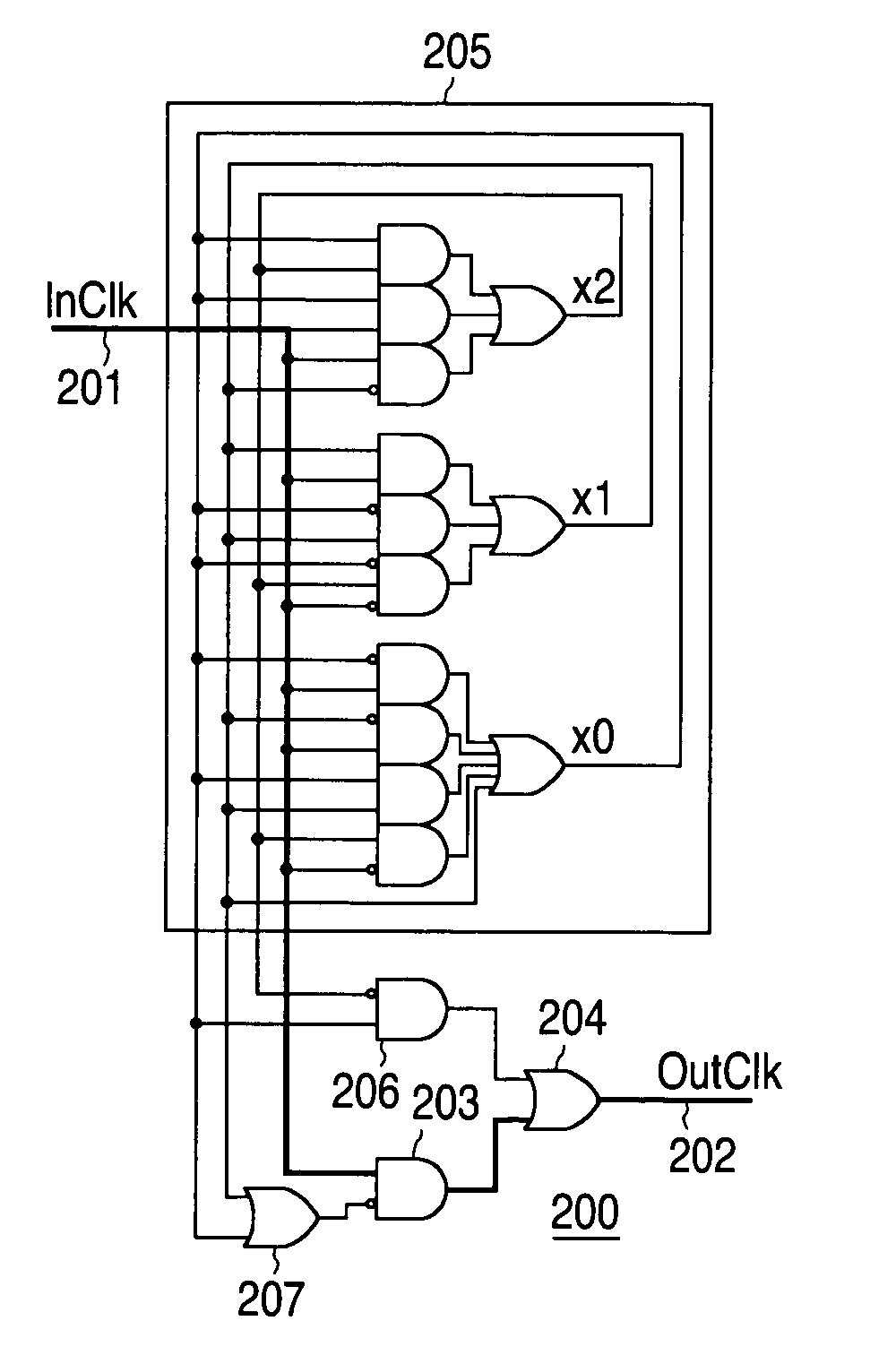
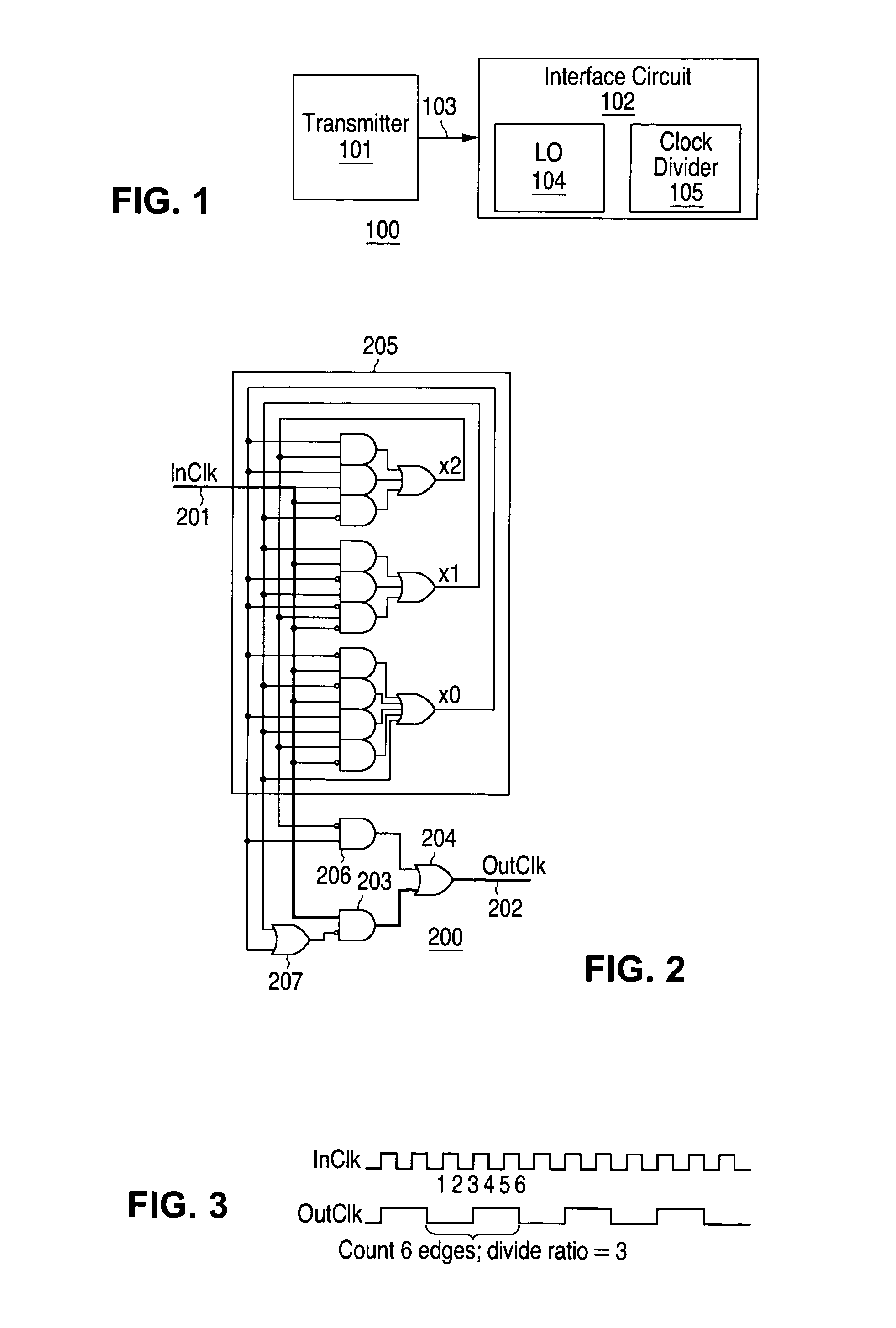
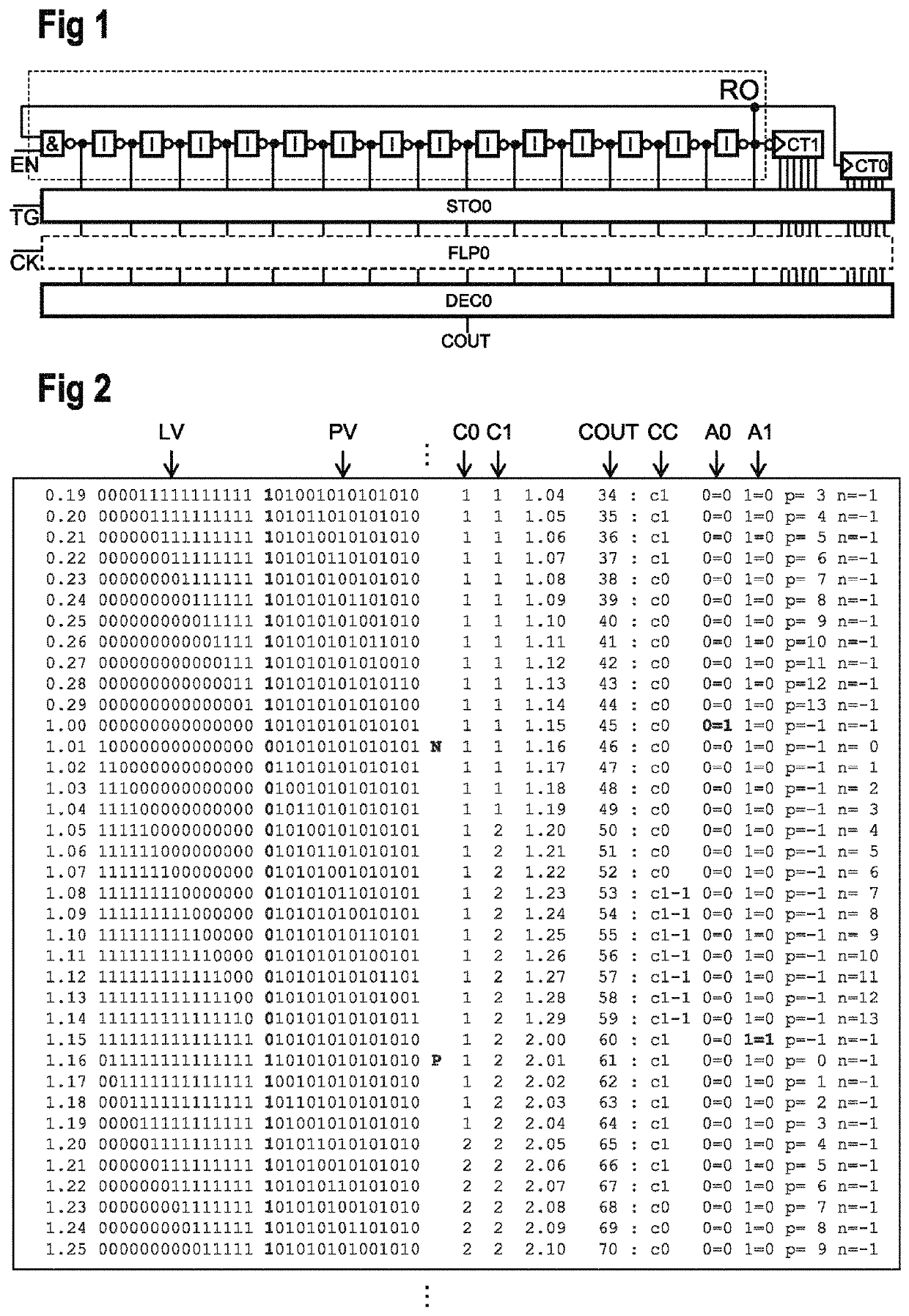
Minimum gate delay edge counter
ActiveUS7197104B1Counting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderCounting chain synchronous pulse countersSignal edgeEngineering
An edge counter counting both rising and falling edges of an input signal is implemented with combinational logic, without using flip-flops. The combinational logic is designed using intermediate signals and state transitions producing an output signal having a cycle corresponding to a predetermined odd or even number of input signal edges, with the logic optimized and protected against entry into “stuck” states. A low power, low gate count edge counter is thus implemented with an output signal duty cycle at least as balanced as the input counter duty cycle.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Gray code counter
InactiveUS6907098B2Simple circuit configurationReduce digitsCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderCounting chain synchronous pulse countersLogical operationsGray code
A Gray code counter includes a holding circuit, first and second conversin circuit and an operation circuit. The holding circuit stores gray code signals and outputs the stored gray code signals in response to a clock signal. The first conversion circuit receives the gray code signals from the holding circuit and converts the received gray code signals into first binary code signals. The operation circuit applies a logical operation to the first binary code signals so as to generate second binary code signals. The second conversion circuit receives the second binary code signals and converts the received second binary code signals into the gray code signals. The second conversion circuit outputs the gray code signals to the holding circuit.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
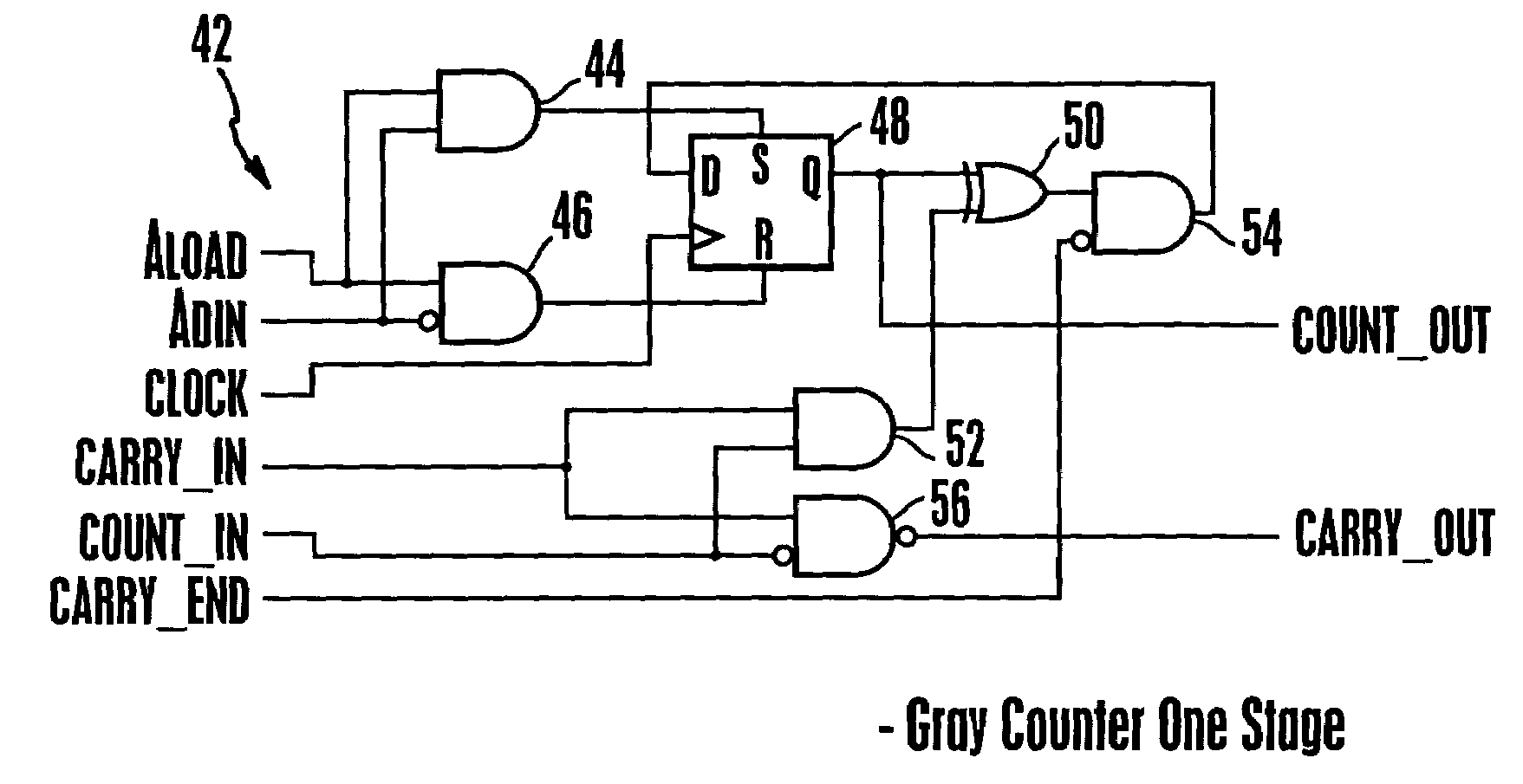
Scalable gray code counter
InactiveUS7194500B2Counting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer hardwareComputer module
The invention is a Gray code counter that uses a carry chain to determine the state of each bit of the counter. An additional bit that toggles at every clock is used to originate the carry chain, and to determine the counter direction. Then, a generic Gray count bit module is used to process the carry and count chain for each bit of the counter. Special consideration is given to the first and last bits of the counter to ensure correct termination and reset of the counter. A one bit gray code generic module is described such that a scalable counter can be generated recursively.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
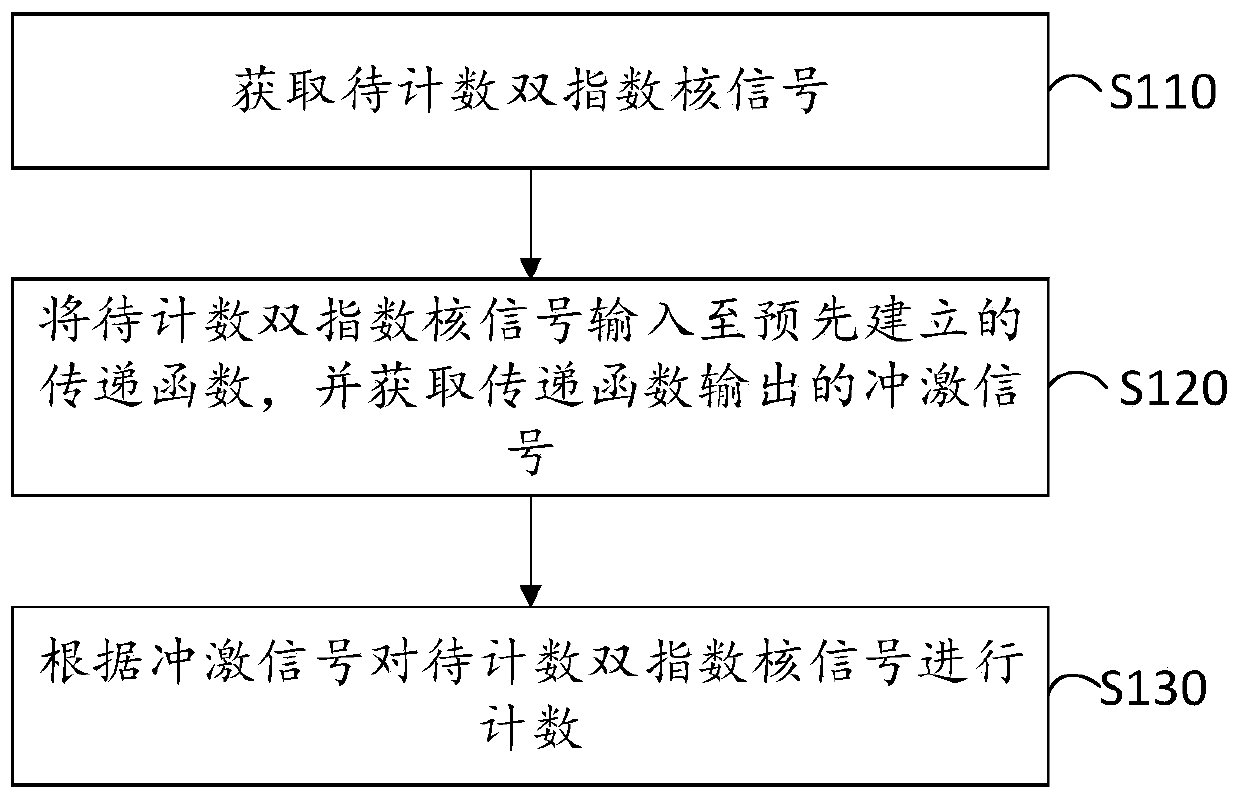
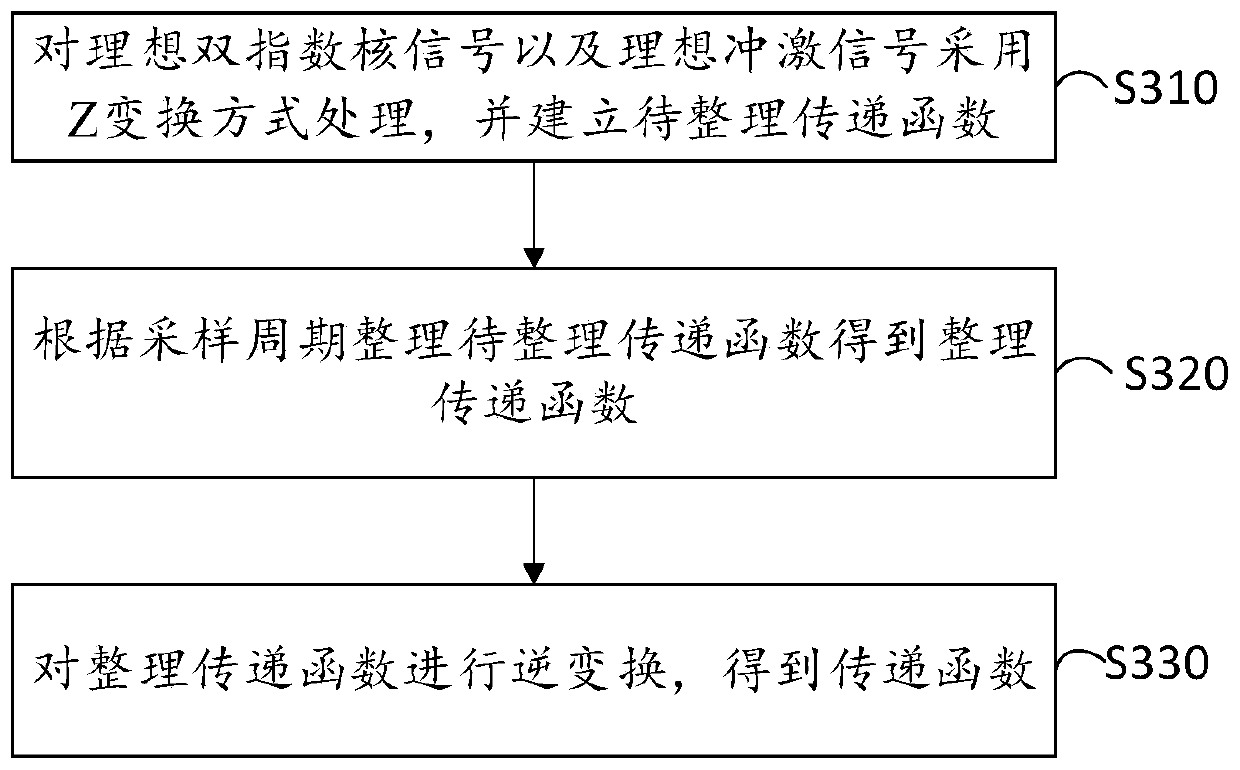
Double-exponential nuclear signal counting method and device
ActiveCN111404542ACounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderNuclear energy generationNuclear engineeringSignal processing
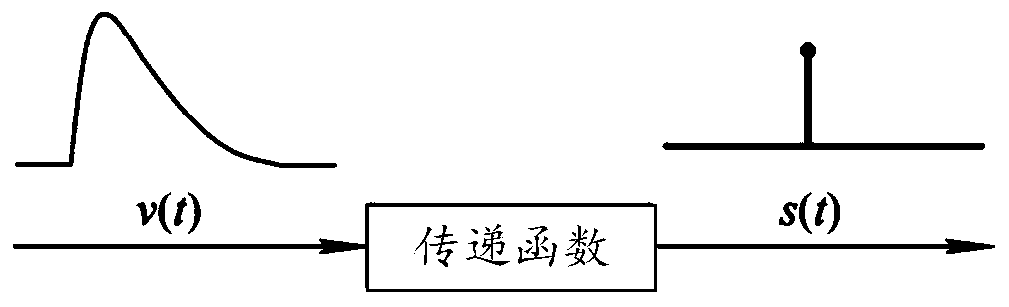
The invention provides a double-exponential nuclear signal counting method and device, and relates to the technical field of nuclear signal processing, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining ato-be-counted double-exponential nuclear signal; inputting the to-be-counted double-exponential nuclear signal into a pre-established transfer function, and obtaining an impulse signal output by the transfer function; and counting the to-be-counted double-exponential nuclear signal according to the impulse signal. In the implementation process, the to-be-counted double-exponential nuclear signalsare input into thepre-established transfer function, the output signals are impulse signals with short dead time, a sampling period is occupied, and the double-exponential nuclear signals are accurately counted by identifying the accumulated nuclear signals.
Owner:四川新先达测控技术有限公司
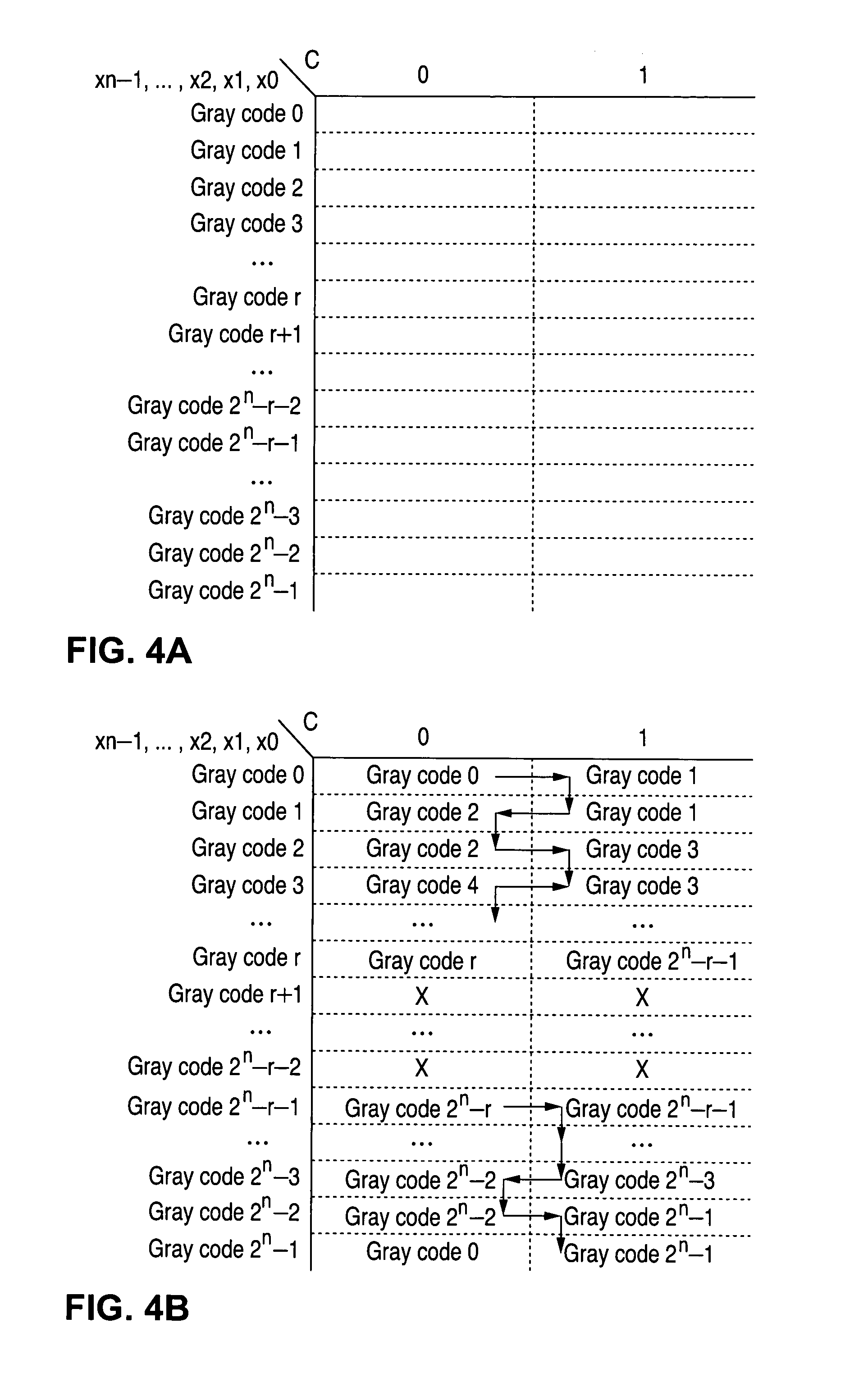
Method of scalable gray coding
InactiveUS6900745B2Counting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderCode conversionGray code
A method for generating a modulo Gray-code representation of a non-power-of-two set of binary values begins by determining a desired Gray-code sequence length. The method then continues by determining a bus width, M, in bits, based on the desired Gray-code sequence length, to represent the generated Gray-code. The method then continues by determining a set of skipped binary values based on the desired Gray-code sequence length and the bus width to obtain the non-power-of-two set of binary values. The method then continues by representing the non-power-of-two set of binary values as a set of equivalent Gray-code values.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Scalable gray code counter
InactiveUS20050017753A1Maximum countCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer hardwareGray code
The invention is a Gray code counter that uses a carry chain to determine the state of each bit of the counter. An additional bit that toggles at every clock is used to originate the carry chain, and to determine the counter direction. Then, a generic Gray count bit module is used to process the carry and count chain for each bit of the counter. Special consideration is given to the first and last bits of the counter to ensure correct termination and reset of the counter. A one bit gray code generic module is described such that a scalable counter can be generated recursively.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
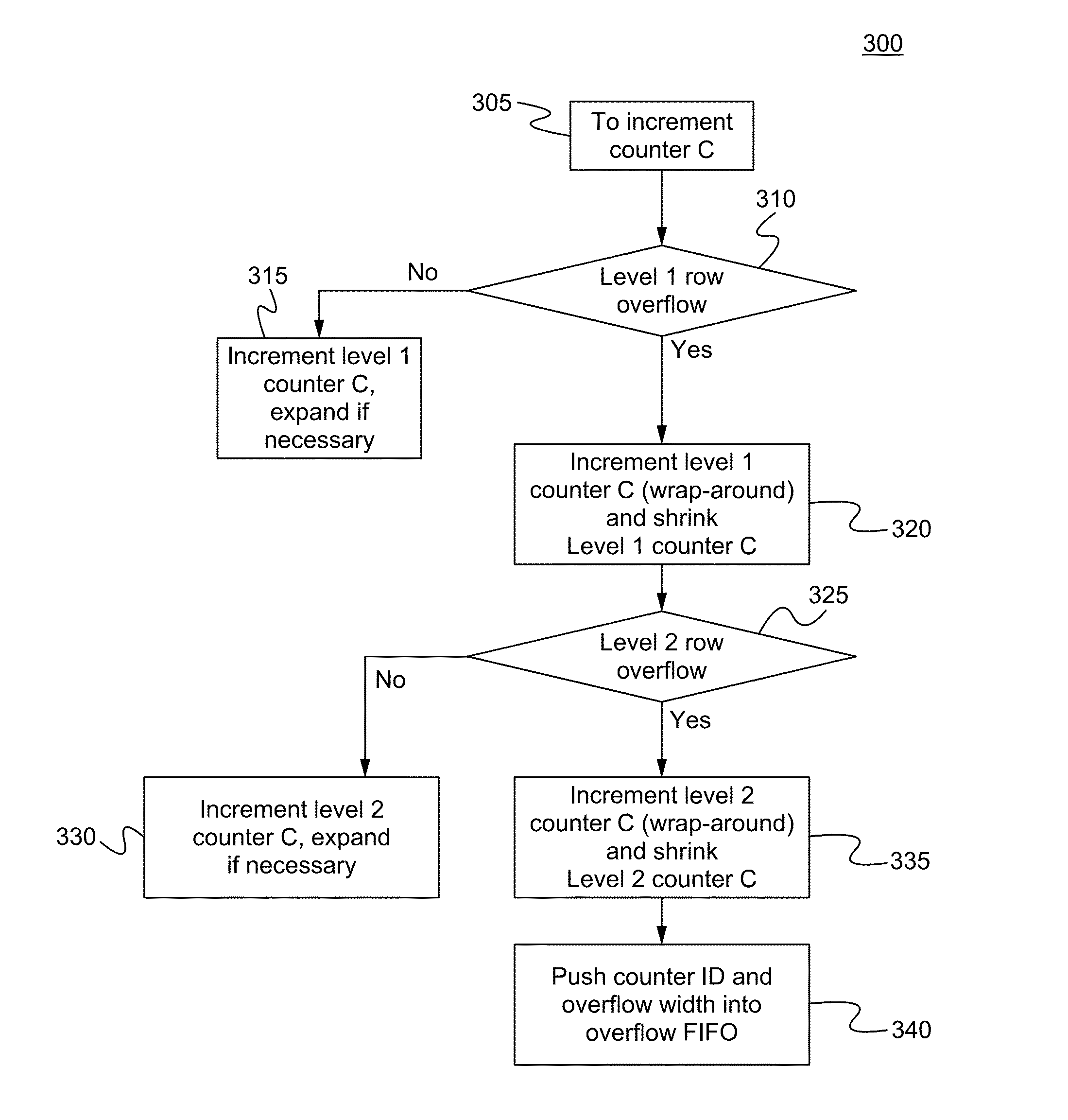
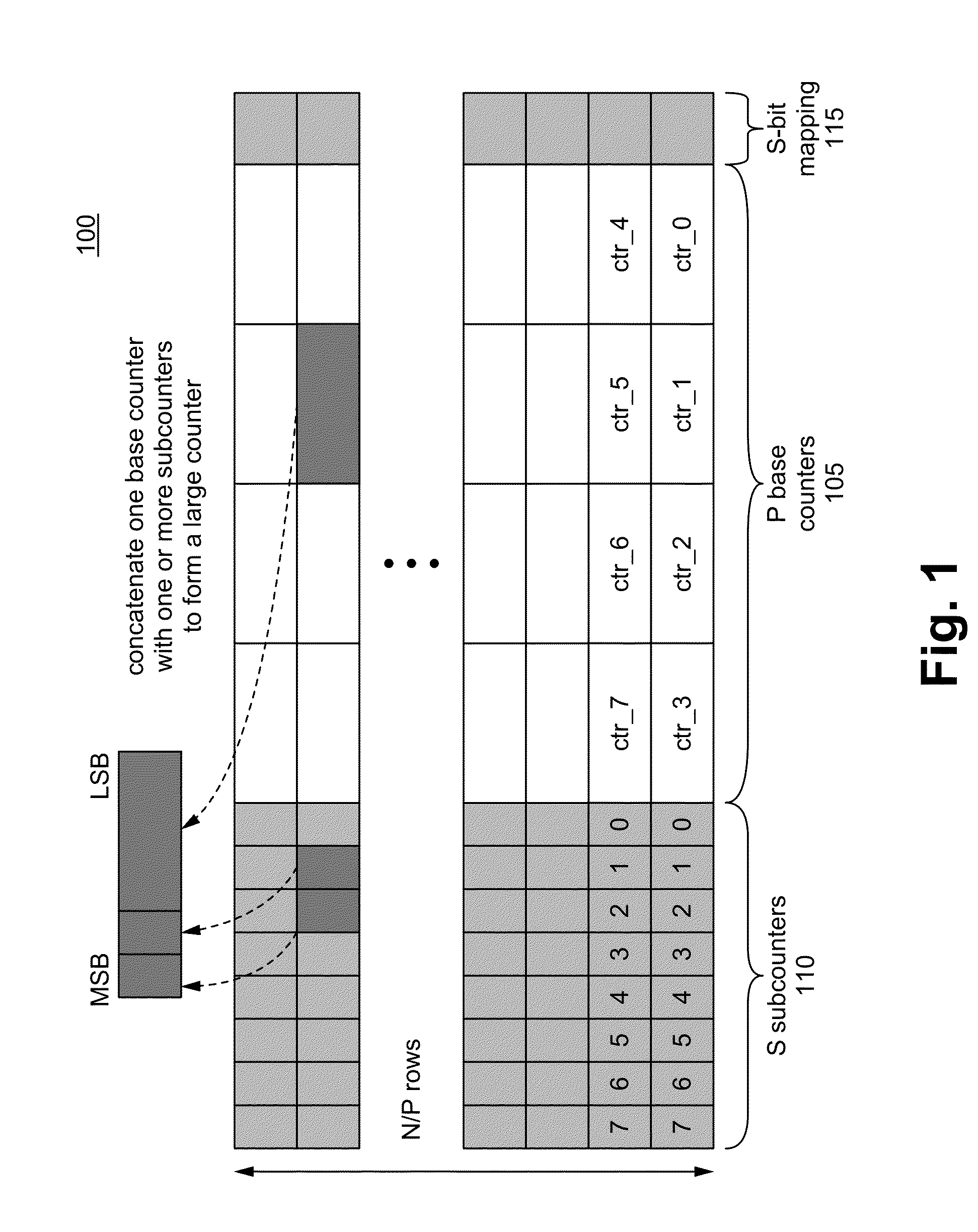
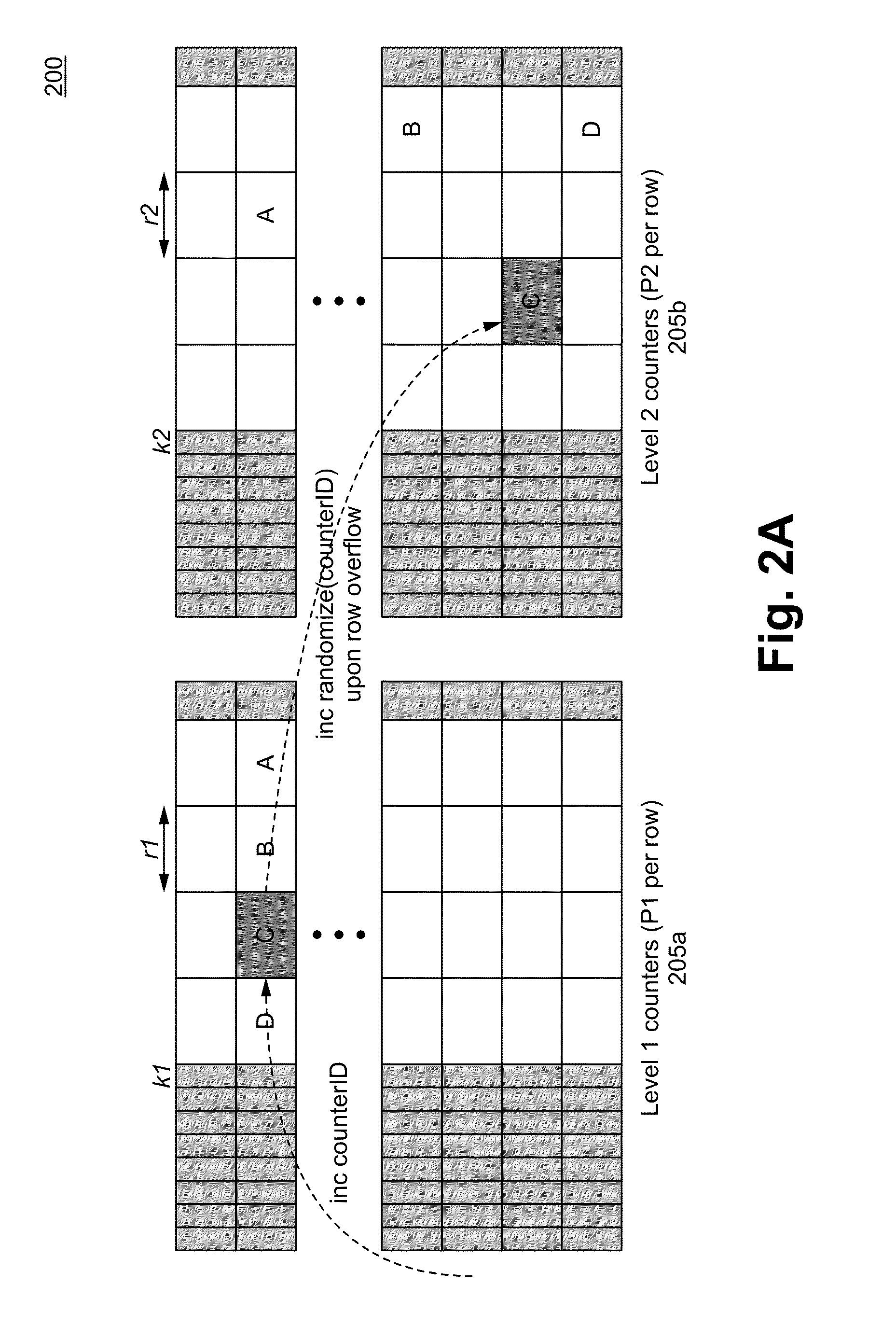
Hierarchical statistically multiplexed counters and a method therof
ActiveUS20150365355A1Extend counter lifeProlong lifeCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderData switching by path configurationOrder of magnitudeComputer architecture
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
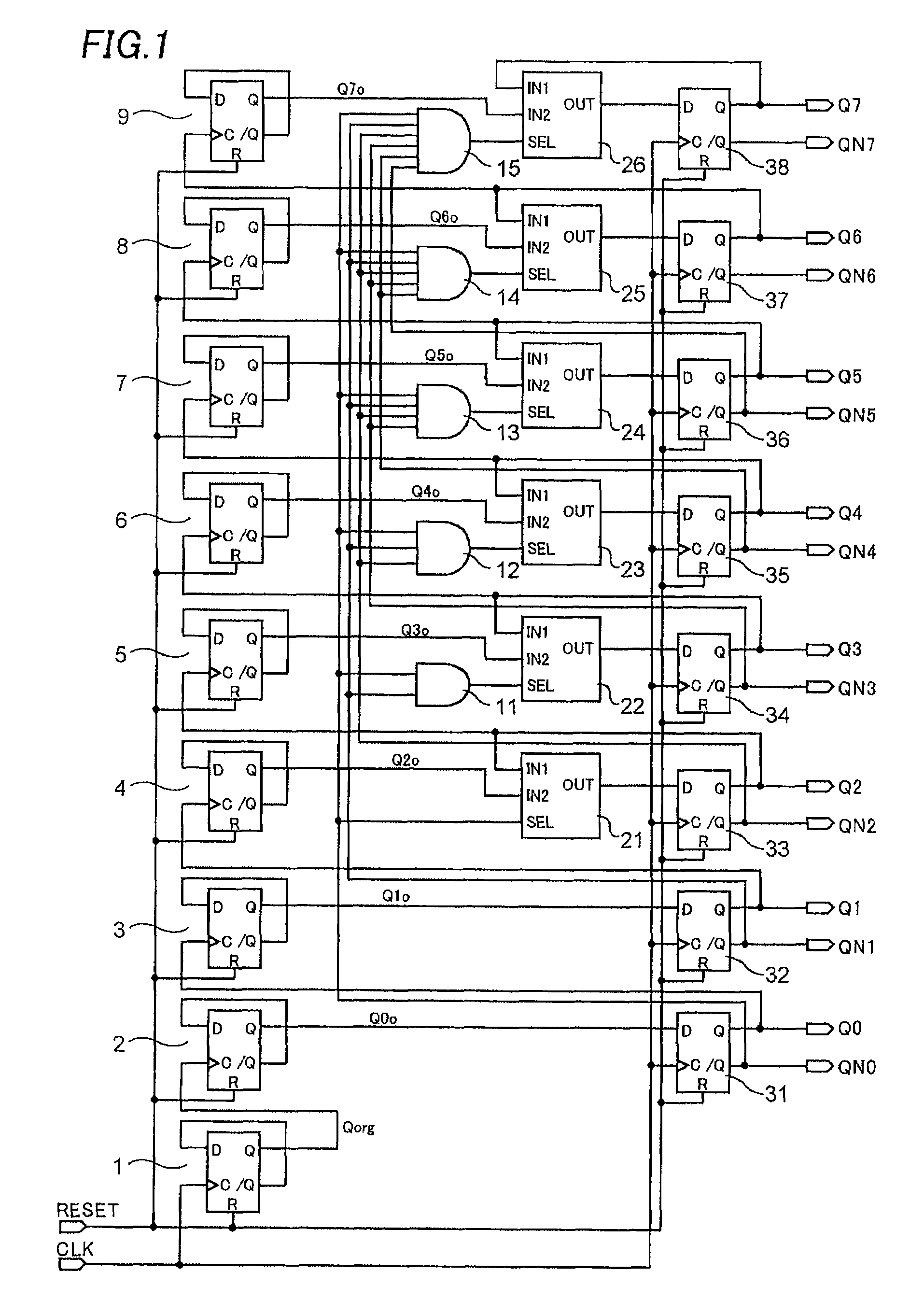
Gray code counter and display device therewith
InactiveUS7596201B2Static indicating devicesCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderDisplay deviceDelayed time
Owner:EPSON IMAGING DEVICES CORP +1
Power control method and equipment
ActiveCN108966333AImprove signal qualityImplement code division multiplexingPower managementExclusive-OR circuitsTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
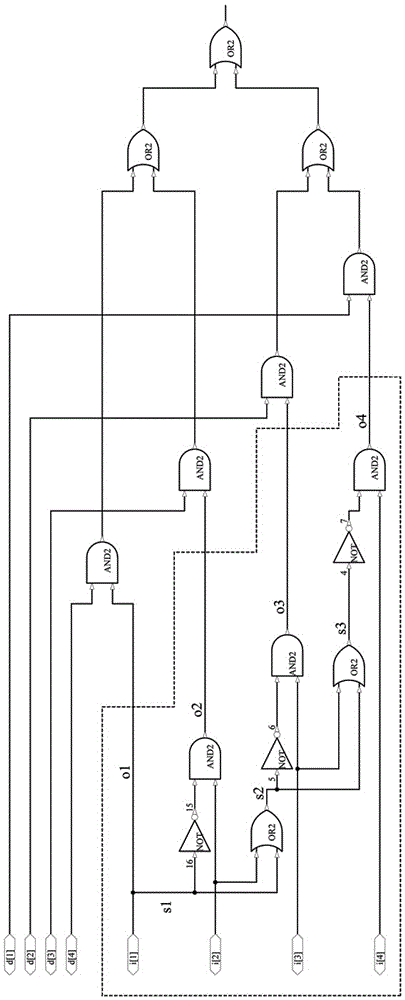
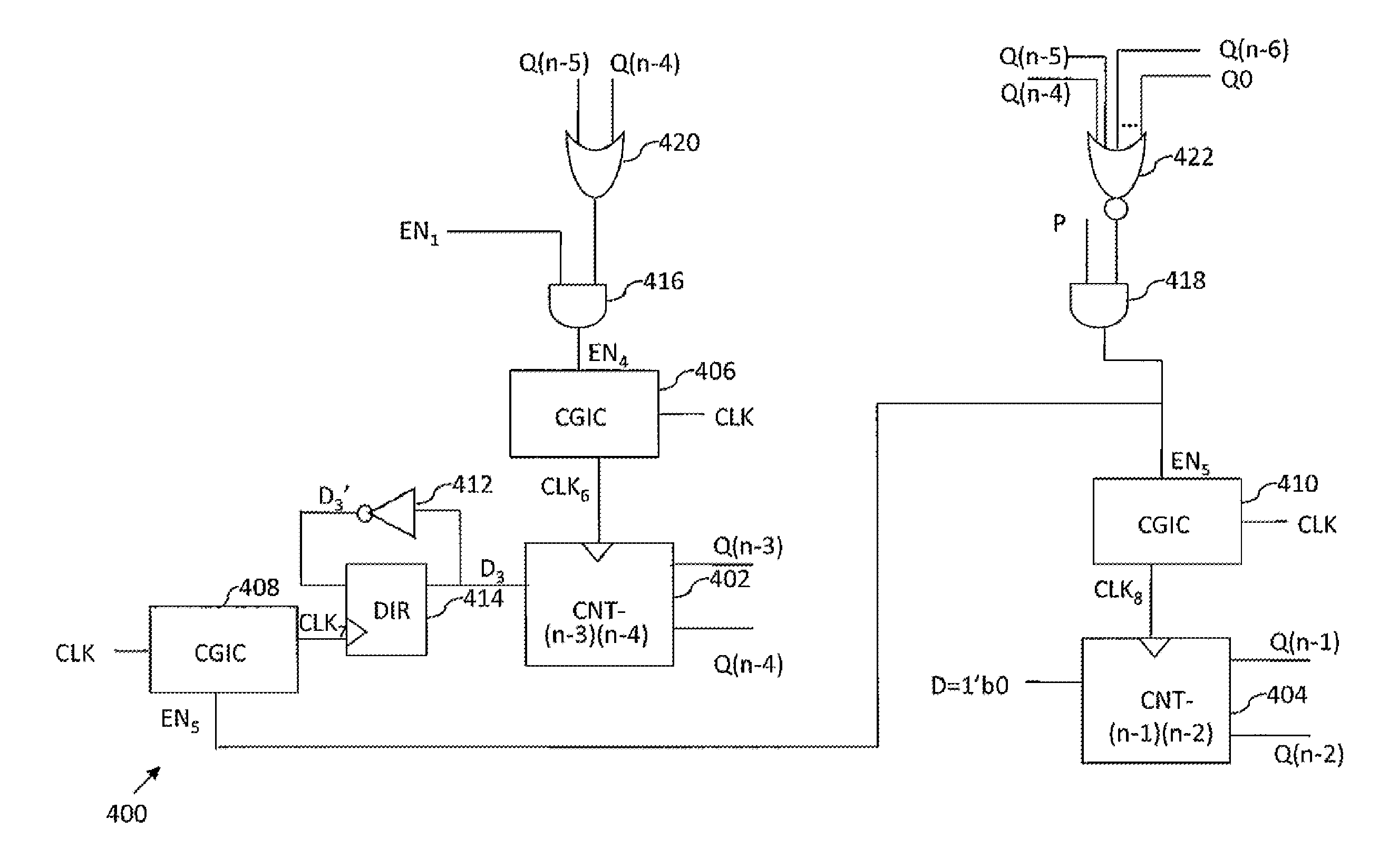
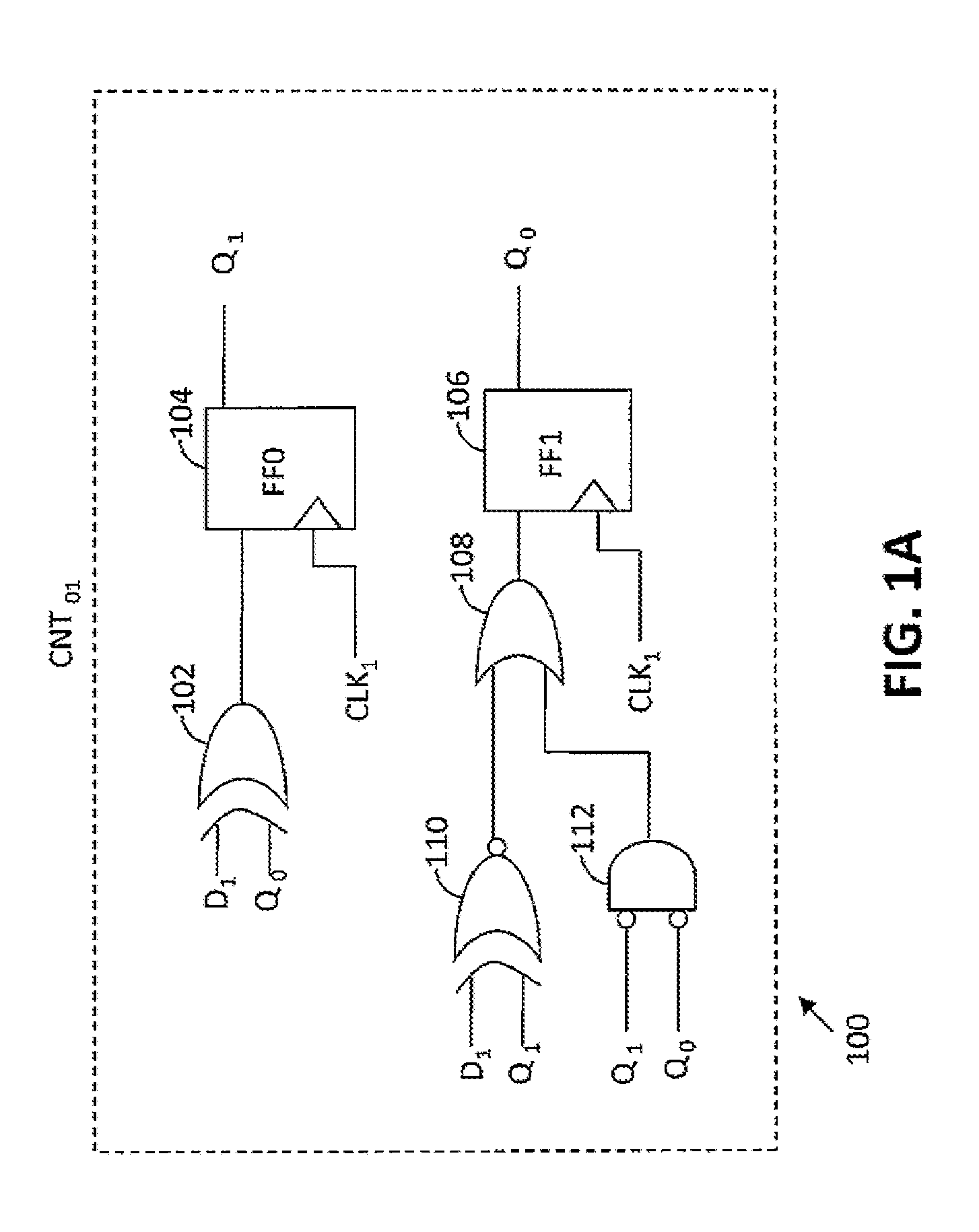
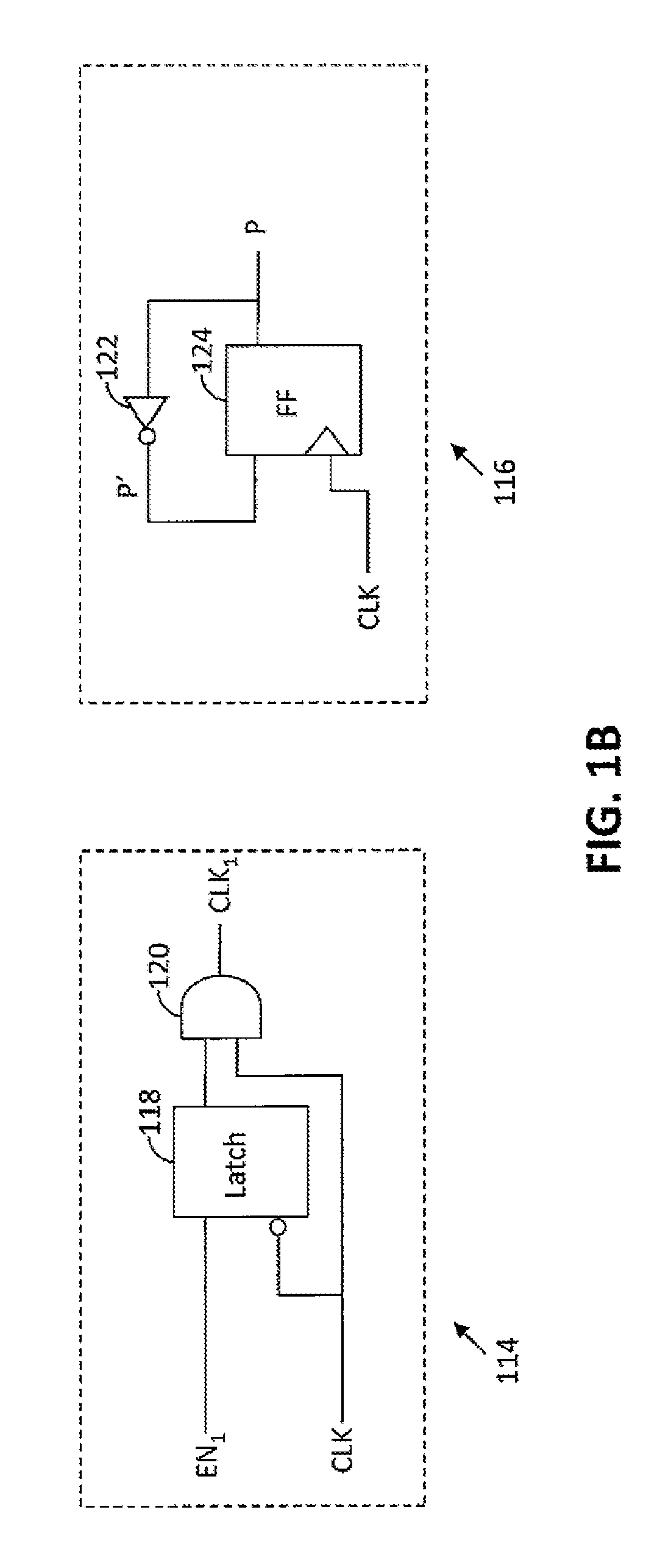
Modular gray code counter
ActiveUS8867694B1Counting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderGray codeComputer science
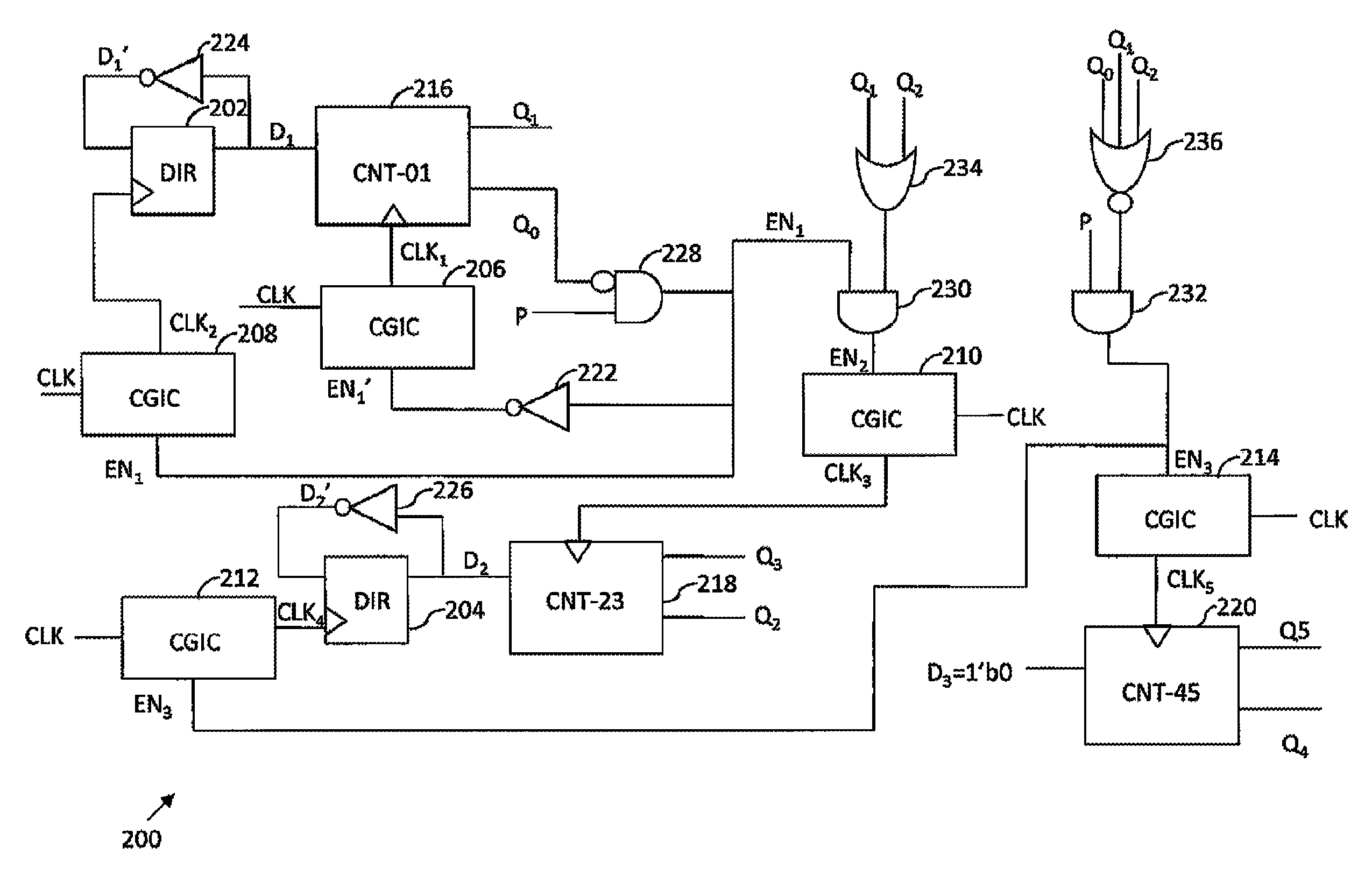
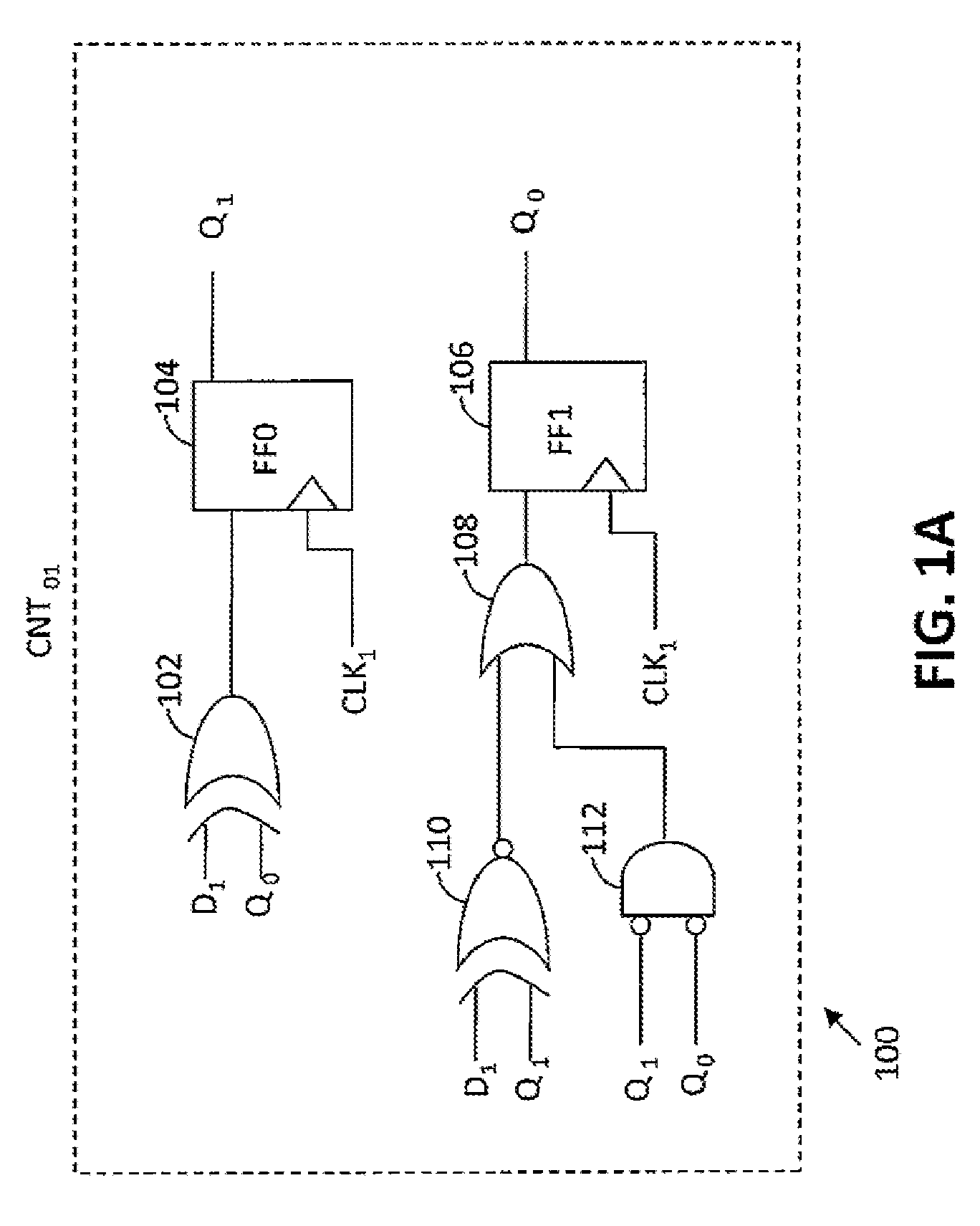
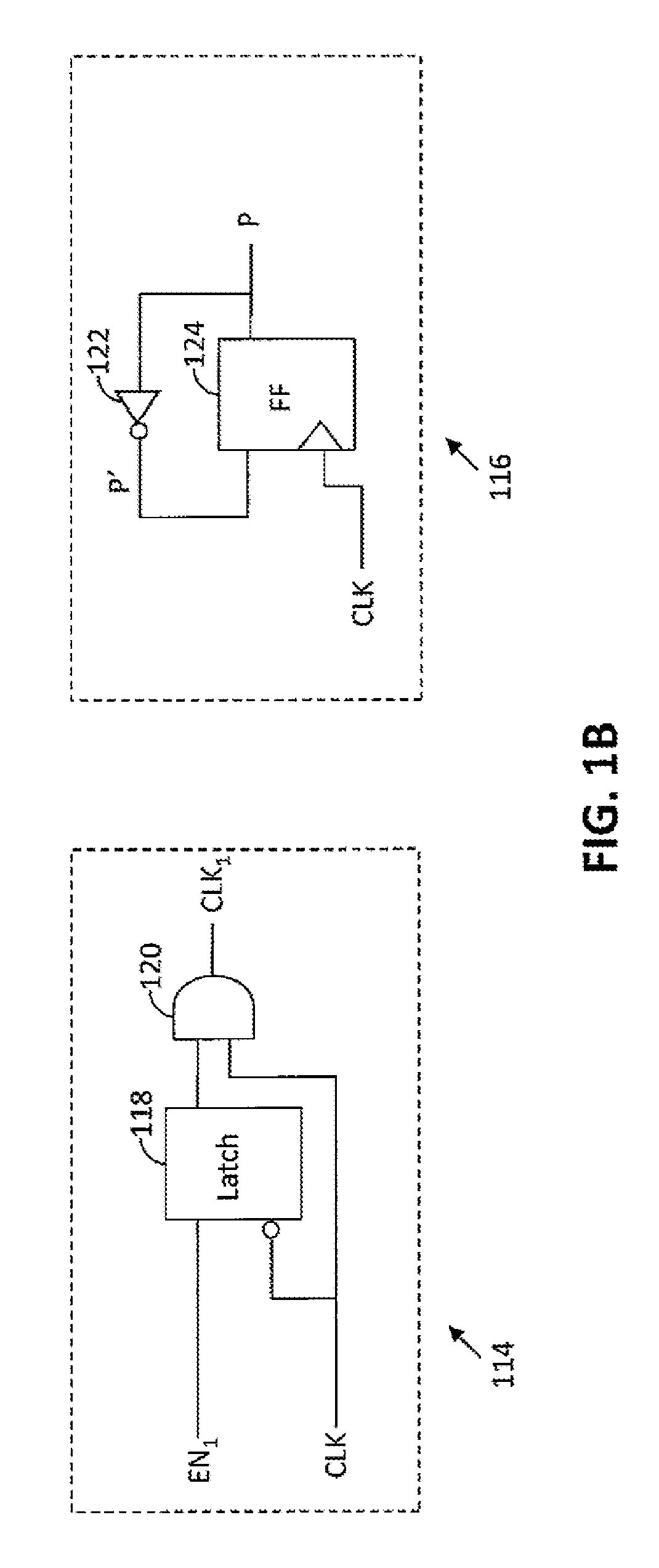
A Gray code counter has multiple two-bit Gray code counter modules, clock gated integrated cells (CGICs), and a parity bit generator. The CGICs gate clock signals provided to the two-bit counter modules, which reduces dynamic power consumption. The parity bit generator generates a parity bit that indicates a count of binary ones in a counting state.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Gray counter and analogue-digital converter using such a counter
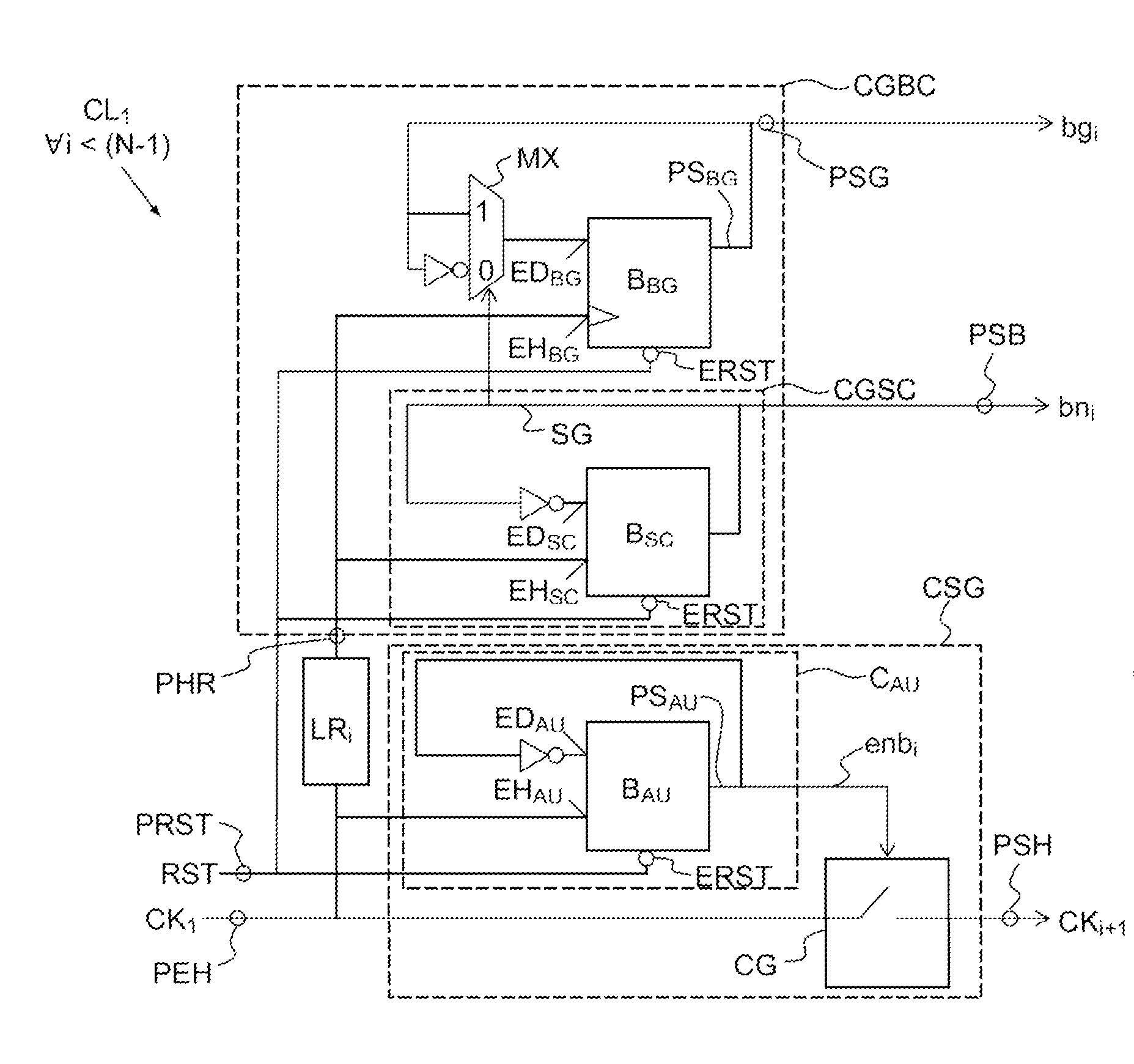
ActiveUS20160134290A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLogic cellDigital converter
An N-bit Gray counter, with N an integer greater than 1, comprises a string of N logic cells connected in cascade, wherein each logic cell comprises an input port for a succession of clock pulses, a circuit for generating a Gray count bit having an output port for the Gray count bit and a circuit for generating a clock signal having a clock output port linked to the input port of the following logic cell. An analogue-digital converter of ramp type using such a Gray counter is also provided.
Owner:PYXALIS
Data reading method, storage controller and storage device
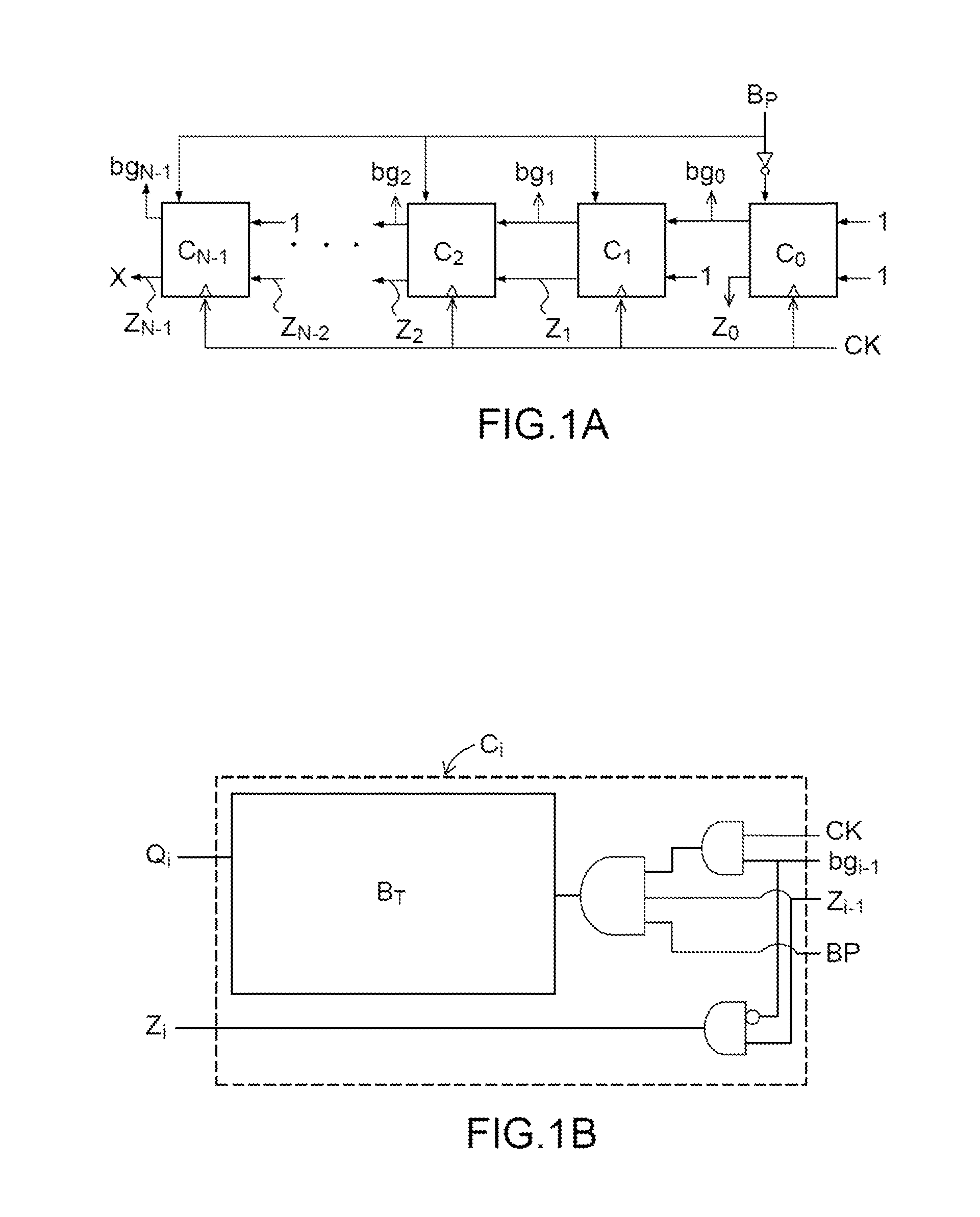
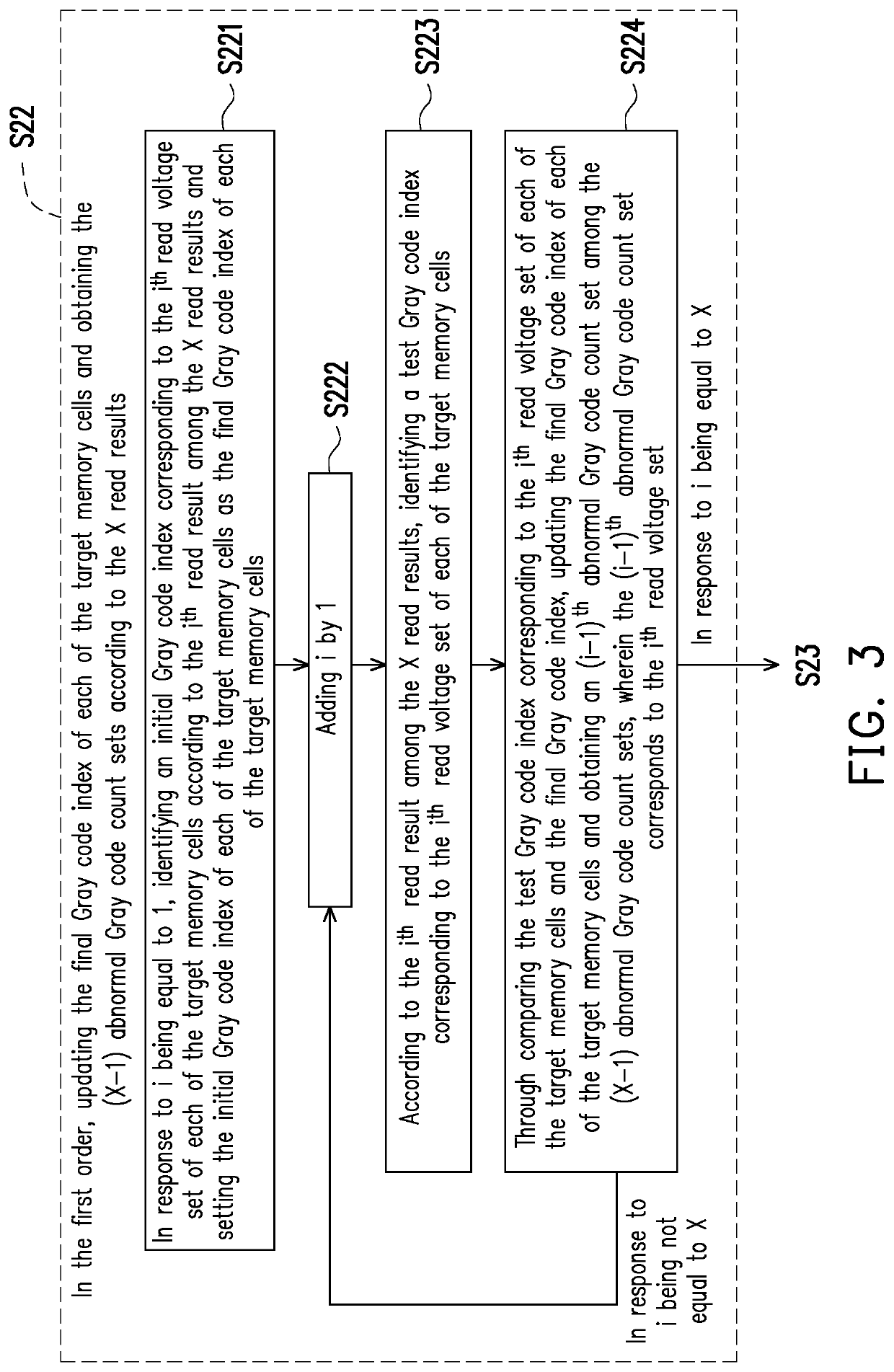
ActiveUS20200201569A1Input/output to record carriersCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderProgramming languageMemory cell
A data reading method is provided. The method includes using X read voltage sets to read a target word line, so as to obtain X read results; in a first order, updating a final Gray code index of each of a plurality of target memory cells of the target word line, and obtaining (X−1) abnormal Gray code count sets according to the X read results, wherein an ith read result among the X read results includes a Gray code corresponding to an ith read voltage set of each of the target memory cells, and the Gray code corresponds to one of N Gray code indexes; and selecting (N−1) optimized read voltages from (X−1)*(N−1) read voltages of the corresponding (X−1) read voltage sets to form an optimized read voltage set according to the obtained (X−1) abnormal Gray code count sets.
Owner:SHENZHEN EPOSTAR ELECTRONICS LTD
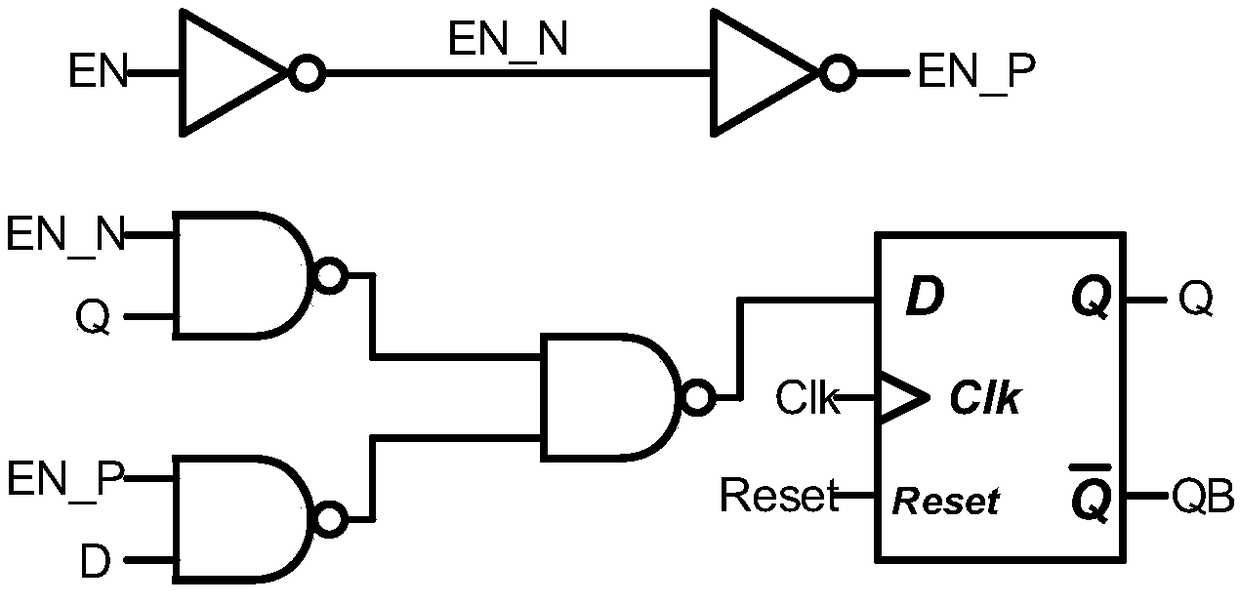
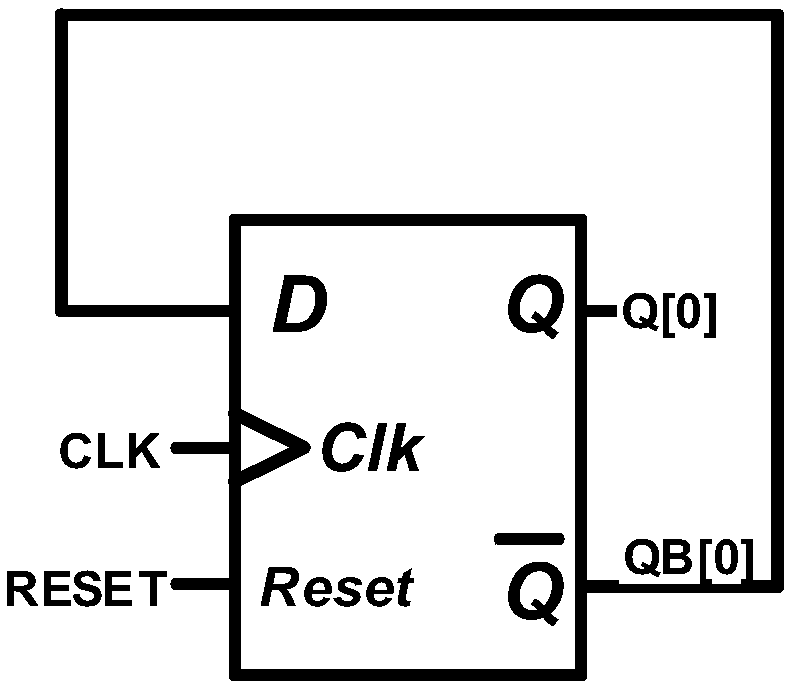
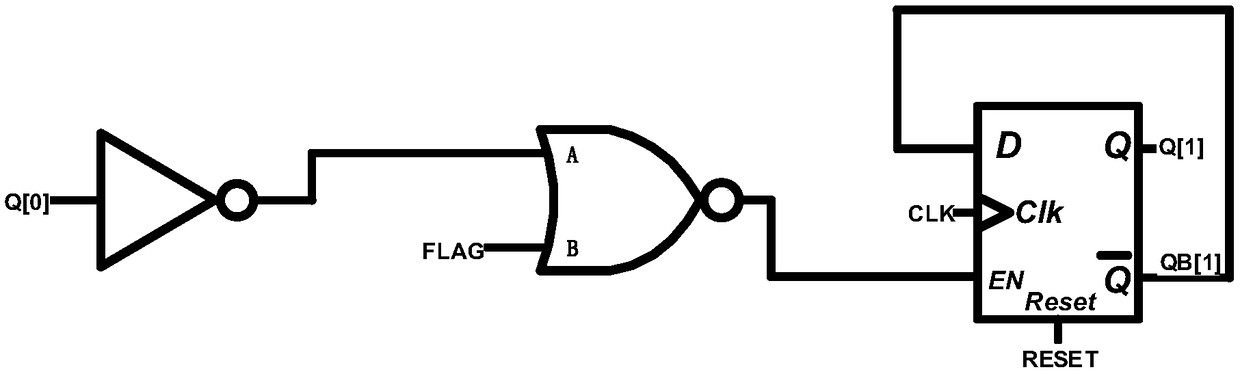
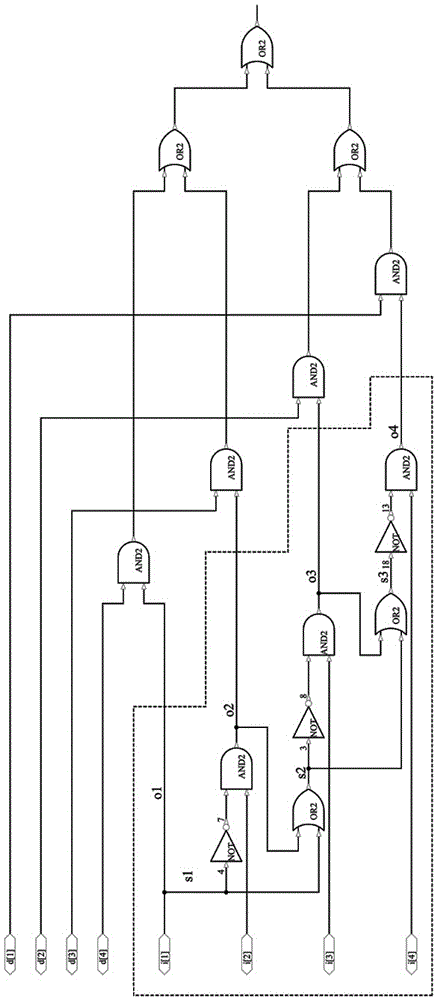
Even-number-of-times Gray code counter circuit
ActiveCN108880531AReduce error rateReduce areaCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderComputer moduleFlag signals
The invention relates to an even-number-of-times Gray code counter circuit, which belongs to the field of integrated circuits. The even-number-of-times Gray code counter circuit in the invention can count for 2N times; the output is an M-bit Gray code, wherein M and N are both positive integers, and the specific value of M is determined by the formula; the Gray code counter proposed by the invention comprises M+1 groups of triggers and a control module; it is determined that in the M+1th group to the second group of triggers, the M-bit Gray code is output by taking the Q output end or QB output end of the M+1th D trigger to the second D trigger as the output end of the M+1th group to the second group of triggers according to the Nth time of counting; the control module comprises an AND gate; the input end of the AND gate is connected with the M-bit Gray code; the output end thereof outputs a flag signal FLAG; when counting to the Nth time, the flag signal FLAG is logic 1 and logic 0 for the rest; and the M+1 groups of triggers are respectively composed of one D trigger and respective logic circuit. According to the even-number-of-times Gray code counter circuit in the invention, atransition state does not appear between the adjacent counting code values; the circuit is simple; and counting of any even number of times is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
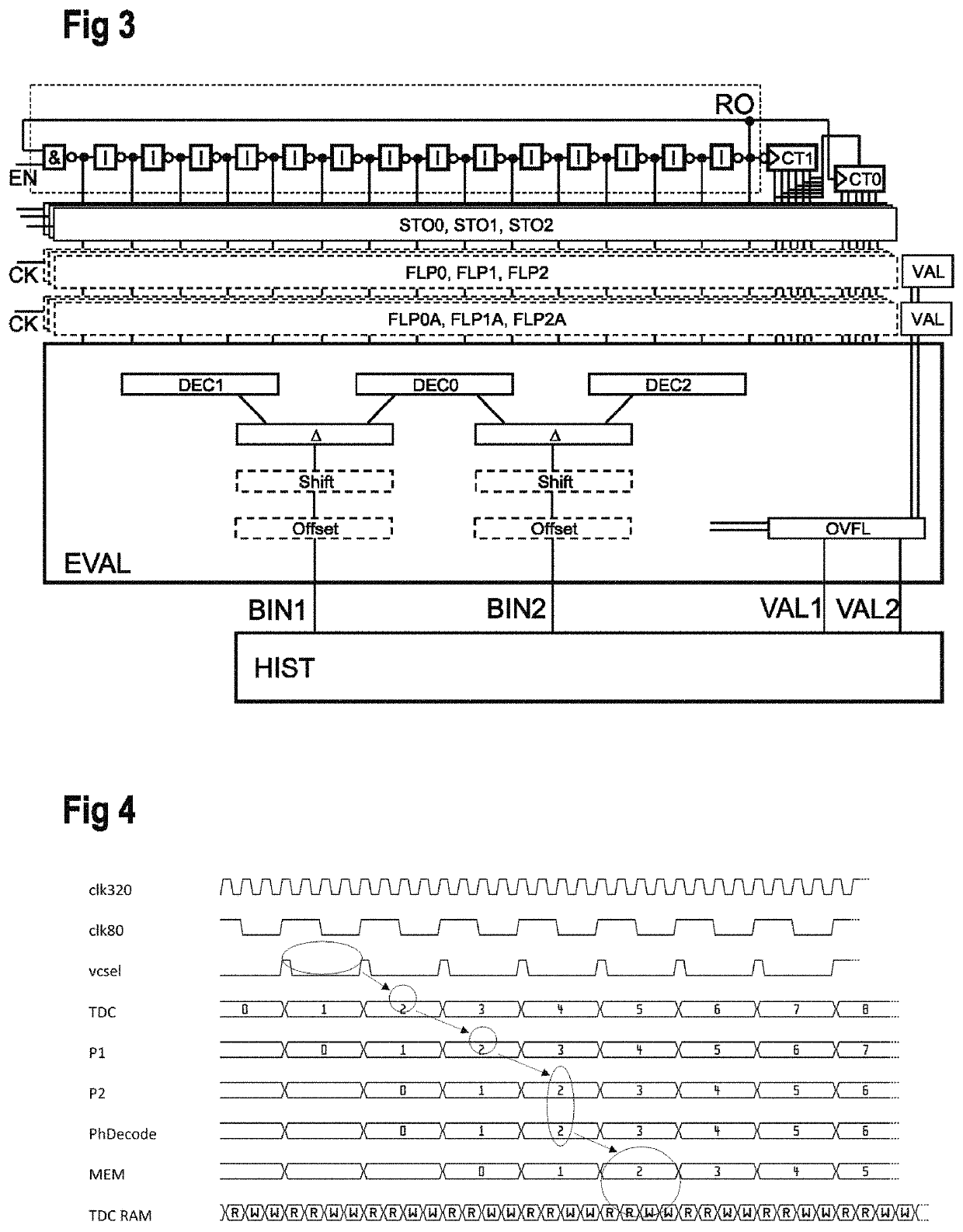
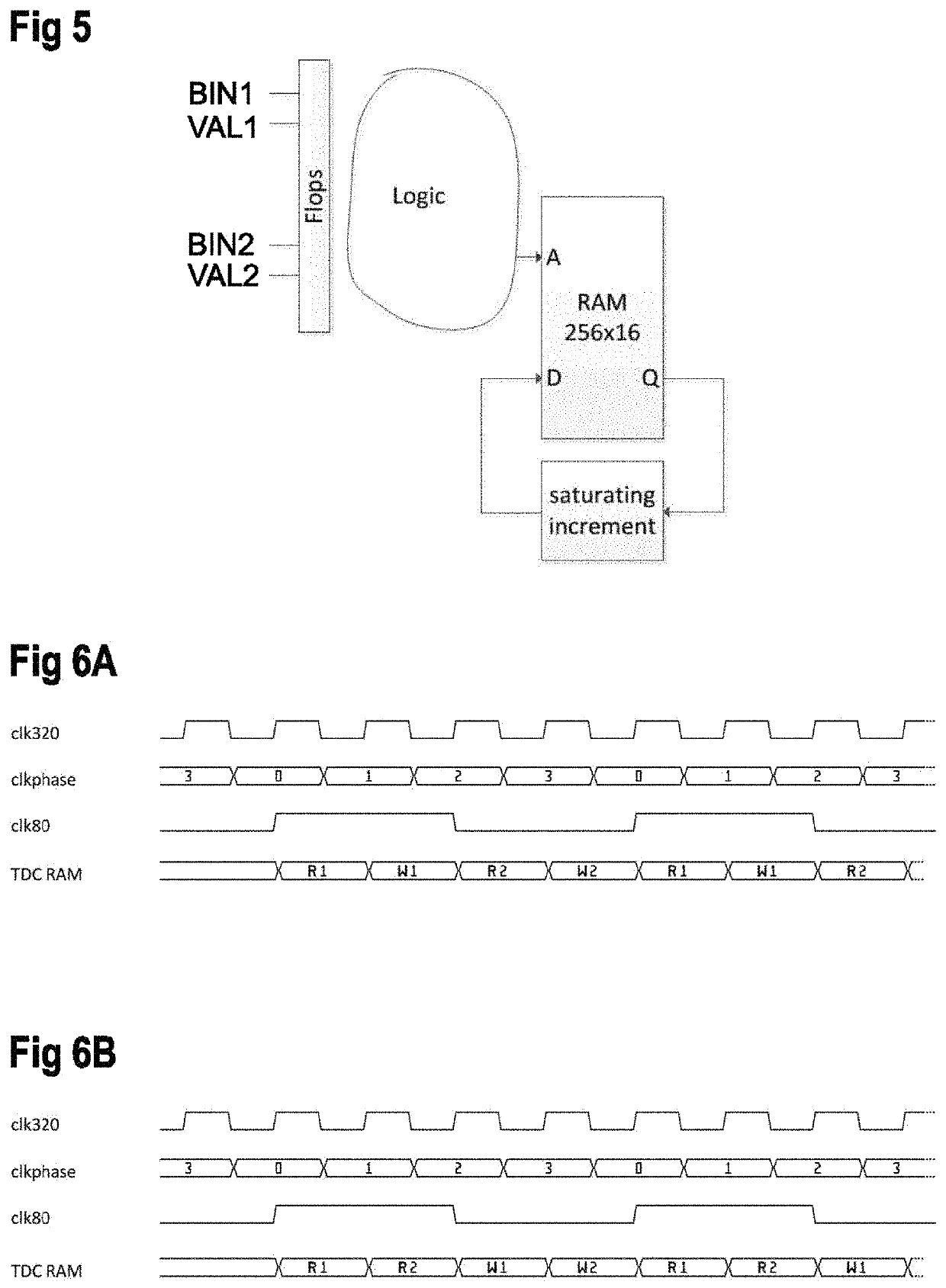
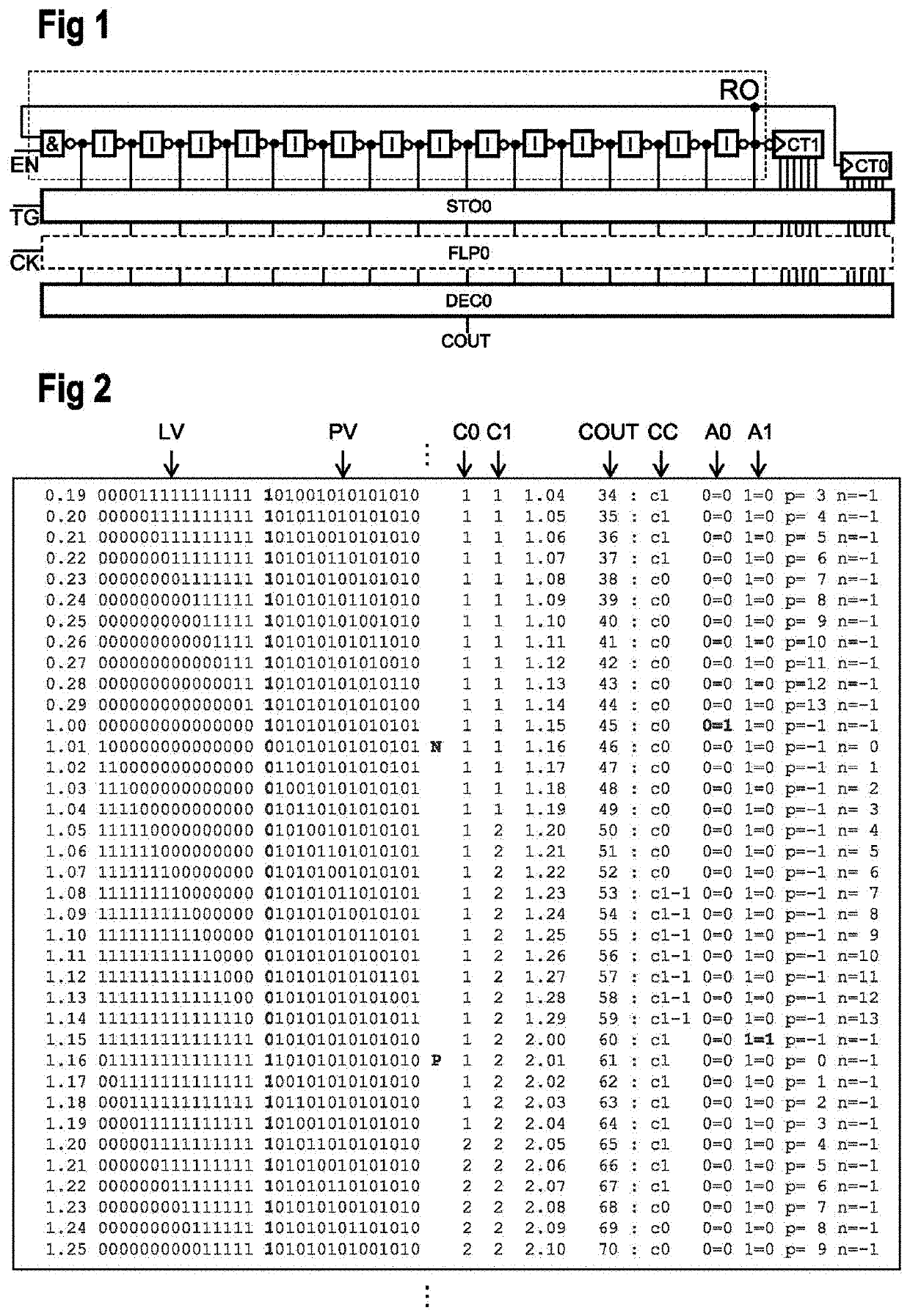
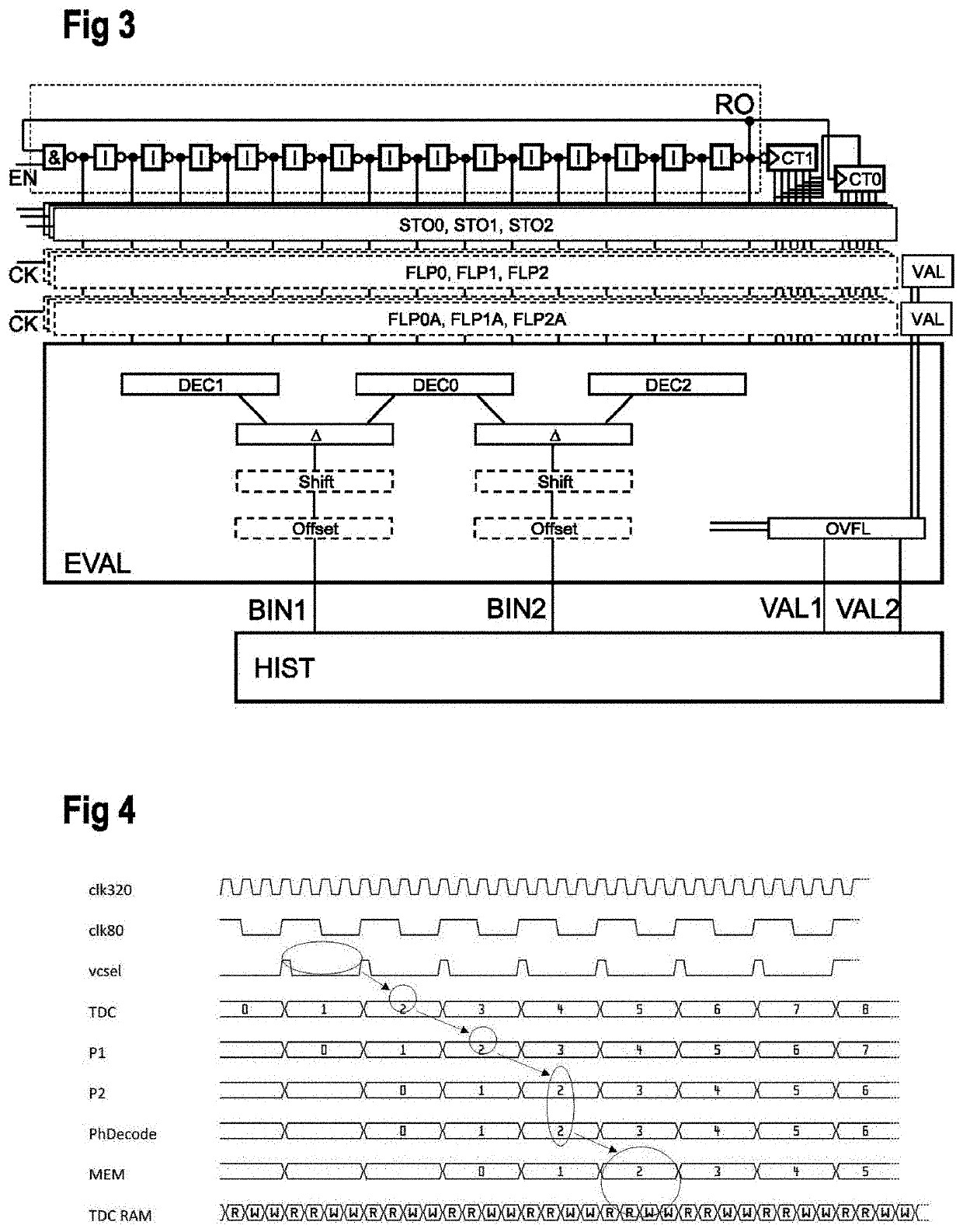
Time-to-digital converter and conversion method
ActiveUS10671025B2Improve accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlConvertersSoftware engineering
Owner:SCIOSENSE BV
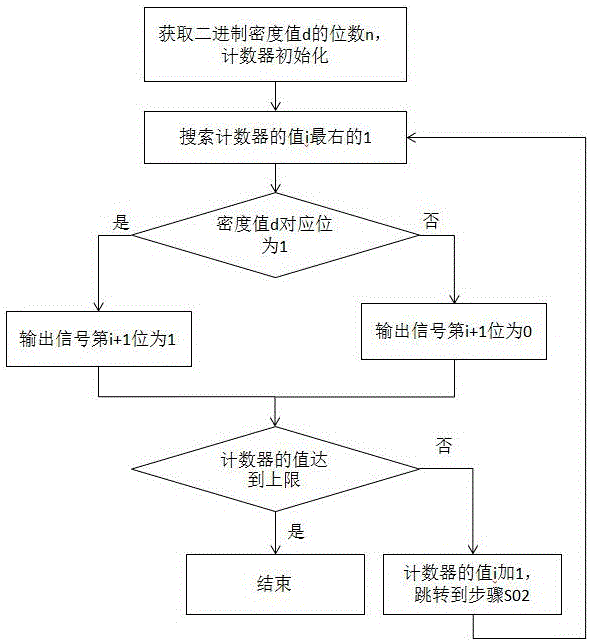
Pulse density modulation method and pulse density value signal conversion circuit
PendingCN106849955AWaveform fluctuation is smallSmall impactAnalogue/digital conversionCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderRight-to-leftComputer science
The invention discloses a pulse density modulation method and a pulse density value signal conversion circuit. The method comprises the following steps of (S01) obtaining bits n of a binary density value, setting the bits of a counter to be n and setting an initial value of the counter to be 0 or 1; (S02) searching the rightmost 1, obtaining the bits j of the count of the rightmost 1 of a current value i of the counter from right to left, wherein the number in the counter is a binary number and the minimum value of j is 1; (S03) judging whether the corresponding bit is equal or not, if the jth bit of the d from left to right is 1, the signal bit output in the period is, if the jth bit of the d from left to right is 0, the signal bit output in the period is 0; and (S04) adding 1 to the value i of the counter, entering the next period and skipping to the step (S02). Output voltage can be more even and smooth.
Owner:绍兴市上虞区幻想动力机器人科技有限公司
Modular gray code counter
InactiveUS9306576B2Counting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderGray codeComputer science
A Gray code counter has multiple two-bit Gray code counter modules, clock gated integrated cells (CGICs), and a parity bit generator. The CGICs gate clock signals provided to the two-bit counter modules, which reduces dynamic power consumption. The parity bit generator generates a parity bit that indicates a count of binary ones in a counting state.
Owner:NXP USA INC
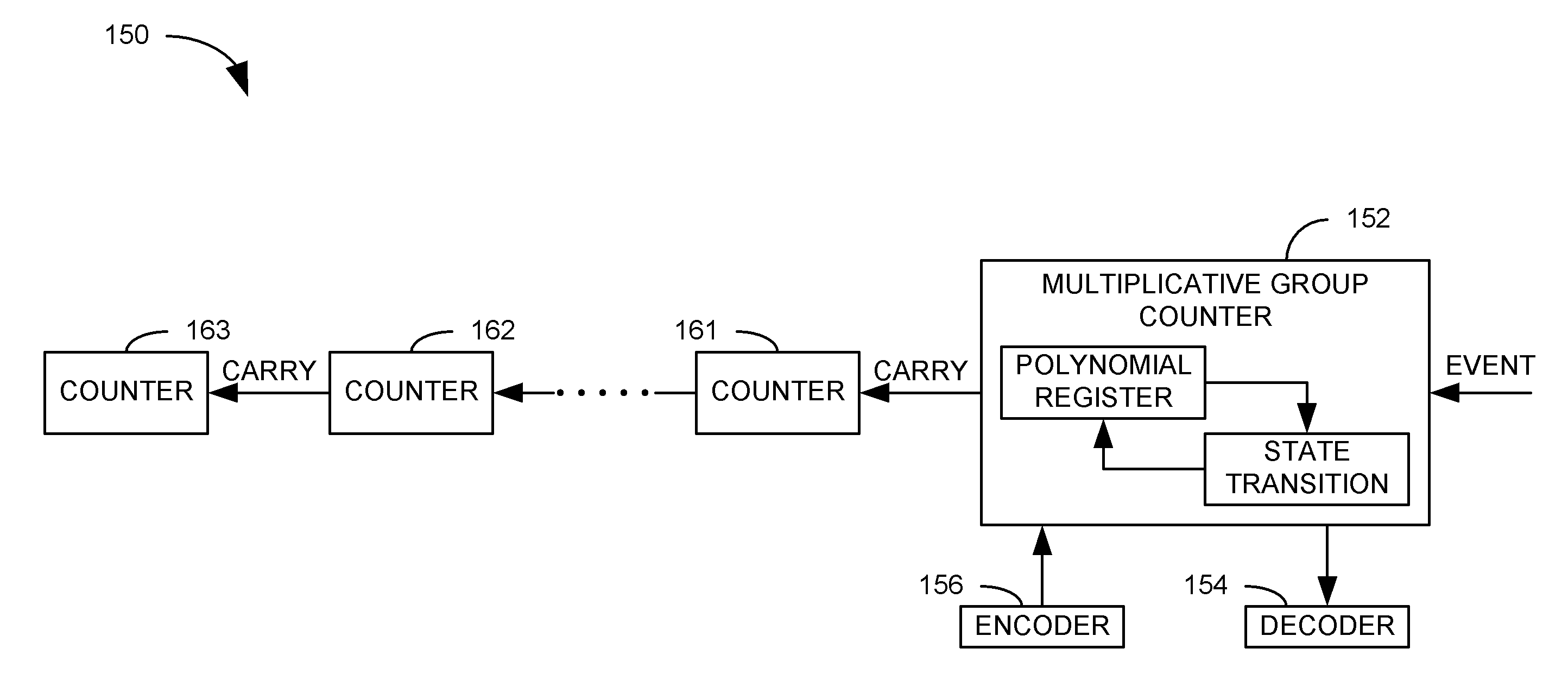
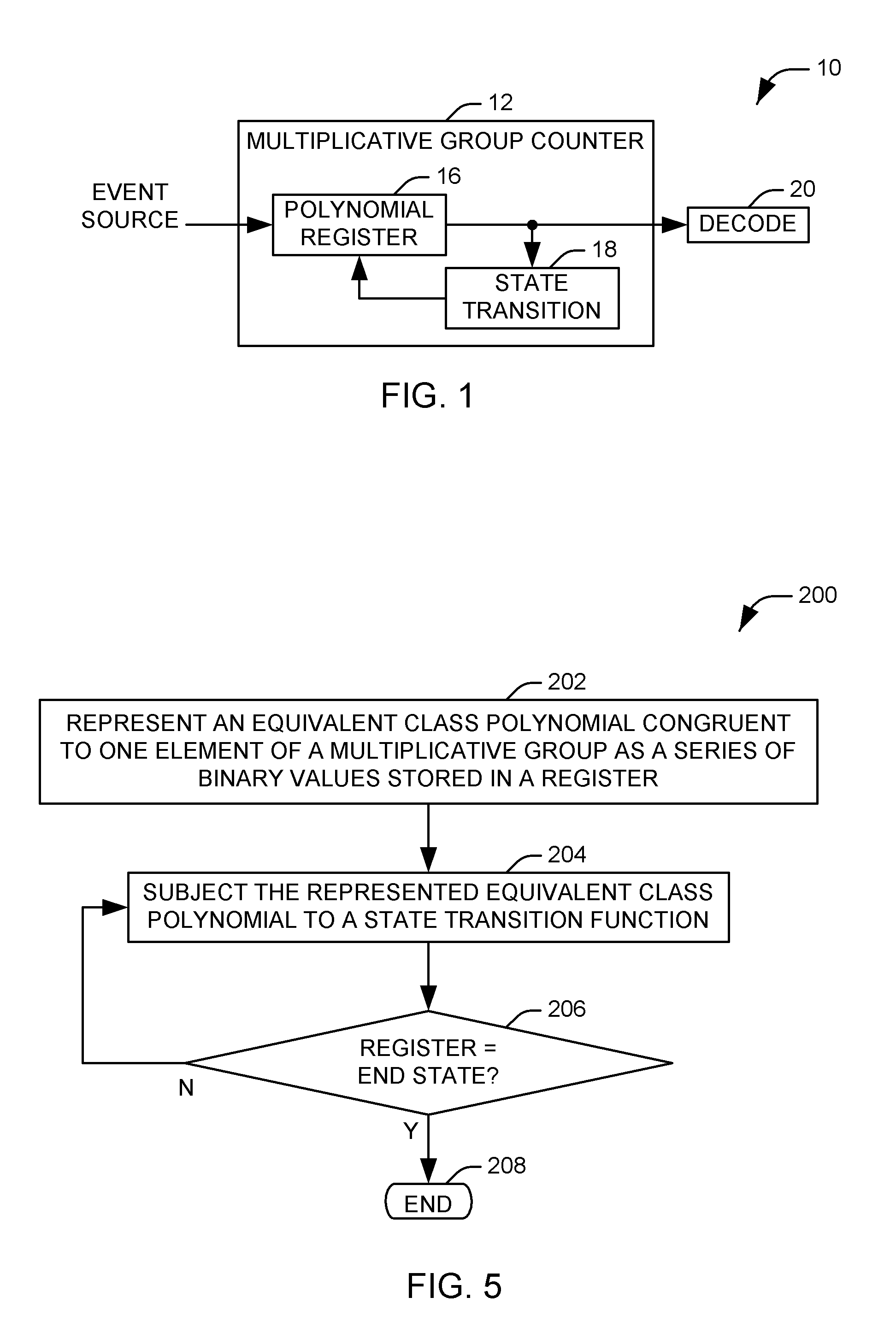
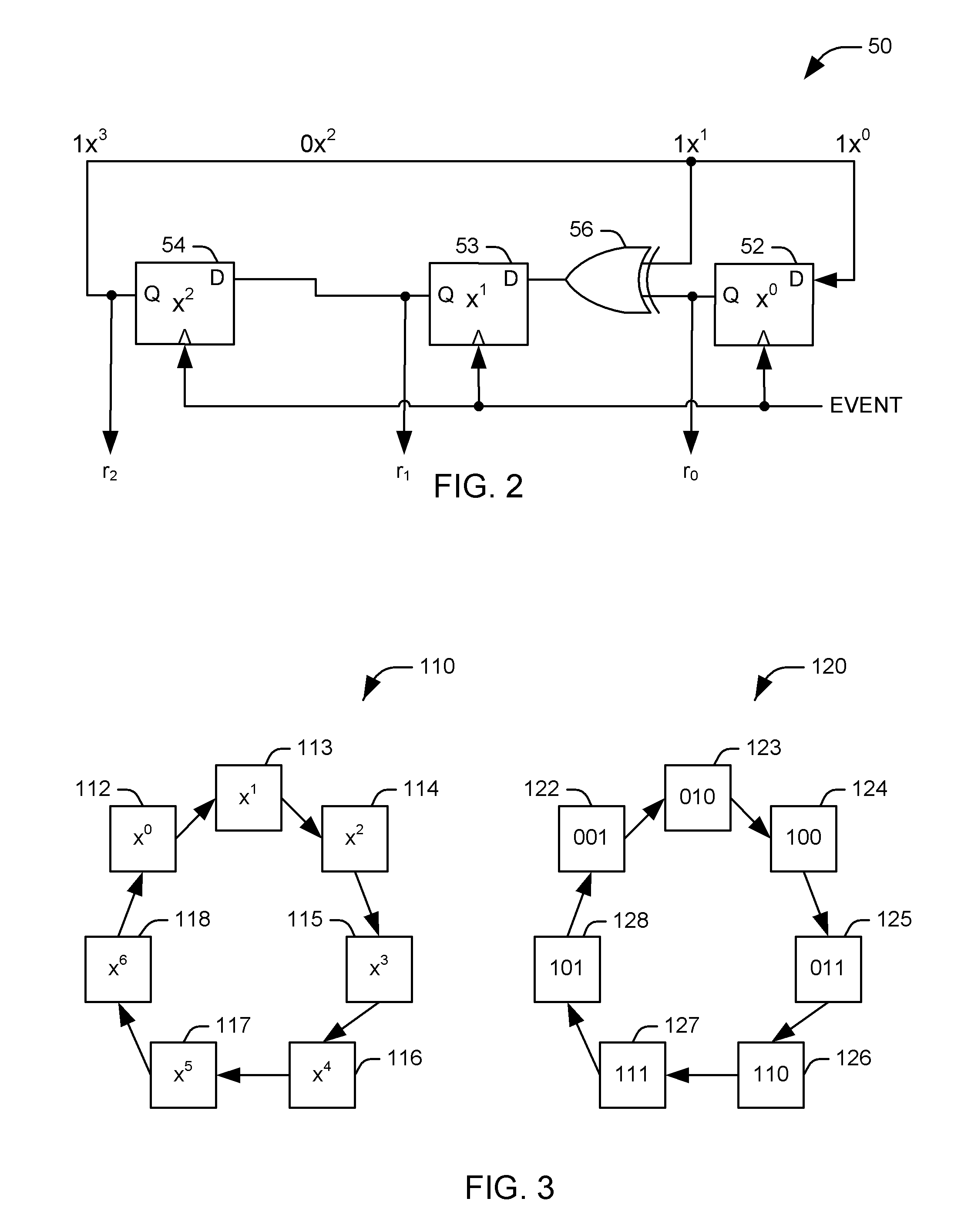
Multiplicative Group Counter
ActiveUS20090157789A1Efficient countingComputations using contact-making devicesCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderAlgorithmCounter system
Systems and methods are provided for efficiently counting detected events via a multiplicative group counter. An equivalent class polynomial congruent with a first of a plurality of elements comprising a multiplicative group is represented as a series of binary values. The represented polynomial is subjected to a state transition function as each event is detected, such that the series of binary values is altered to represent a new equivalent class polynomial congruent with a second of the plurality of elements of a multiplicative group. The series of binary values is decoded to determine a number of detected events recorded by the counter.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
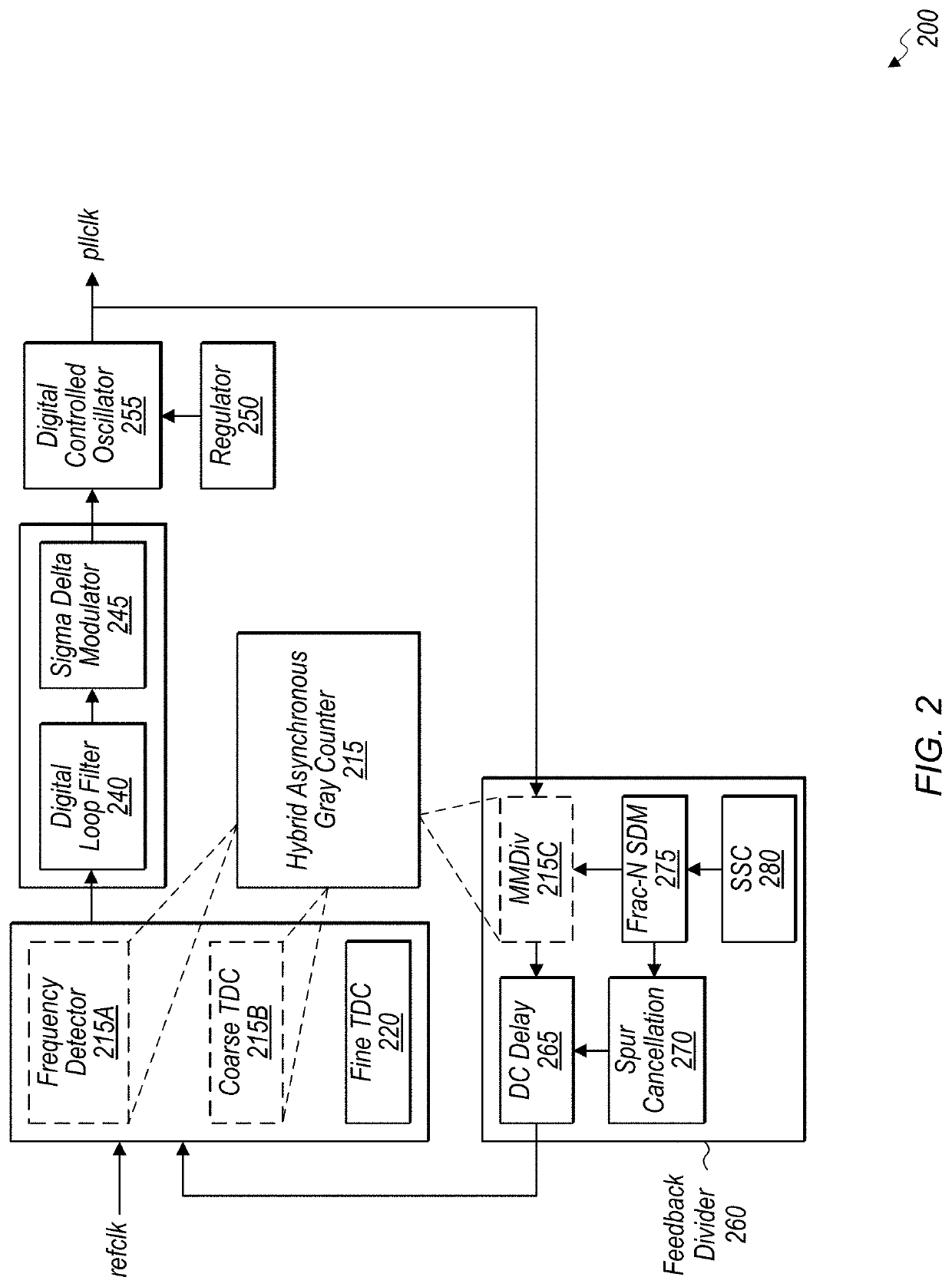
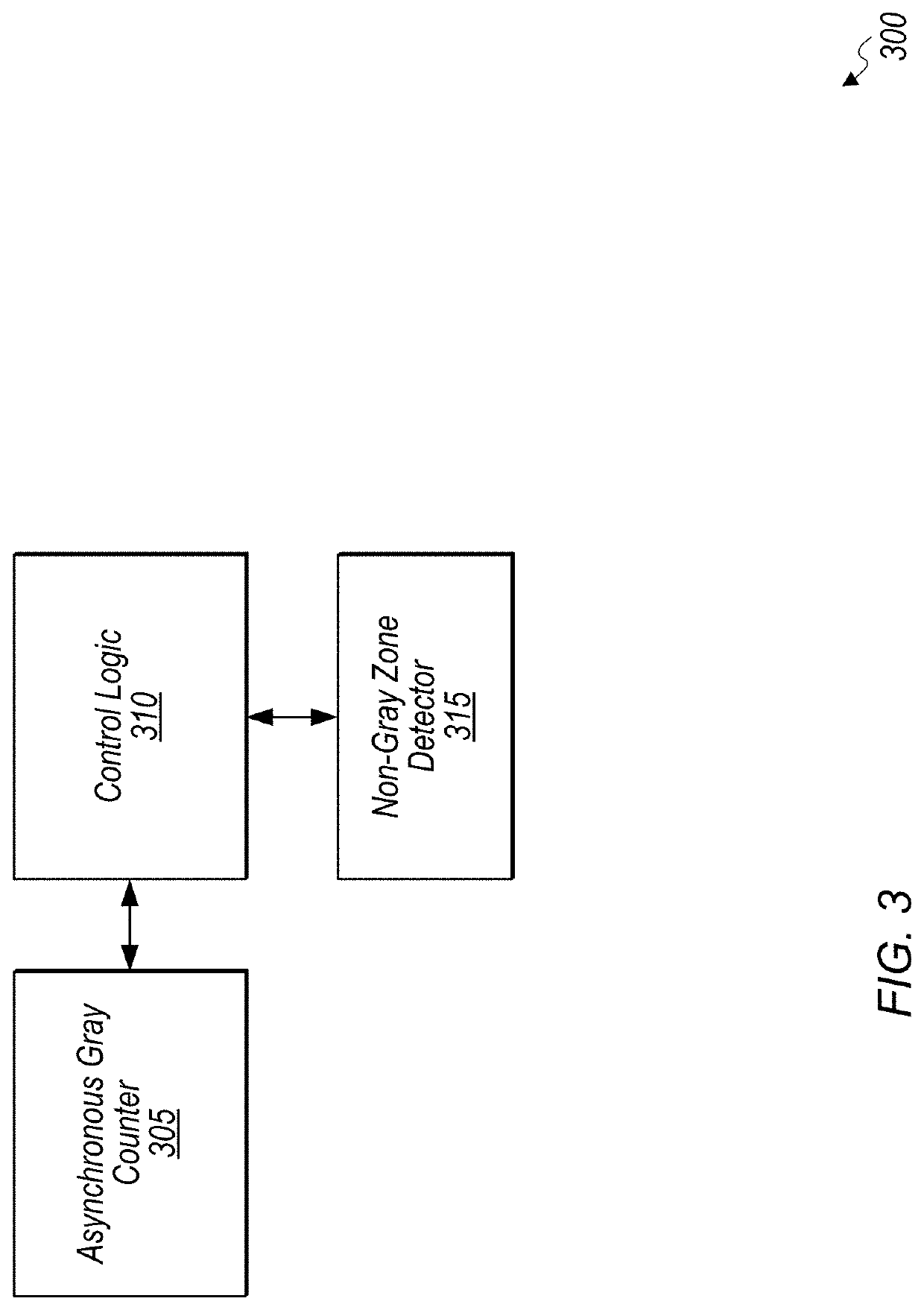
Hybrid asynchronous gray counter with non-gray zone detector for high performance phase-locked loops
ActiveUS20210208621A1Reduces area utilizationReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderPhase detectorHemt circuits
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for implementing a hybrid asynchronous gray counter with a non-gray zone detector are described. A circuit includes an asynchronous gray counter coupled to control logic. The control logic programs the asynchronous gray counter to operate in different modes to perform various functions associated with a high-performance phase-locked loop (PLL). In a first mode, the asynchronous gray counter serves as a frequency detector to count oscillator cycles within a reference clock cycle. In a second mode, the asynchronous gray counter serves as a coarse phase detector to detect a phase error between a feedback clock and a reference clock. In a third mode, the asynchronous gray counter serves as a multi-modulus divider to divide an oscillator clock down to create a feedback clock. Using a single asynchronous gray counter for three separate functions reduces power consumption and area utilization.
Owner:APPLE INC
Time-to-digital converter and conversion method
ActiveUS20200110368A1Improve accuracyPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse counters with non-natural counting orderConvertersSoftware engineering
A time-to-digital converter arrangement has a ring oscillator with a plurality of inverting elements and a first and a second counter coupled to the ring oscillator. The first counter is configured to increment a first counter value if a positive edge transition is present at one of the inverting elements. The second counter is configured to increment a second counter value if a negative edge transition is present at the one of the inverting elements. A storage element stores the first and the second counter value and logical states of the plurality of inverting elements. A decoder coupled to the storage element selects one of the first and the second counter value as a valid value based on an evaluation of the stored logical states, and outputs a total counter value based on the valid value and the stored logical states.
Owner:SCIOSENSE BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com