Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Reduce the cogging torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
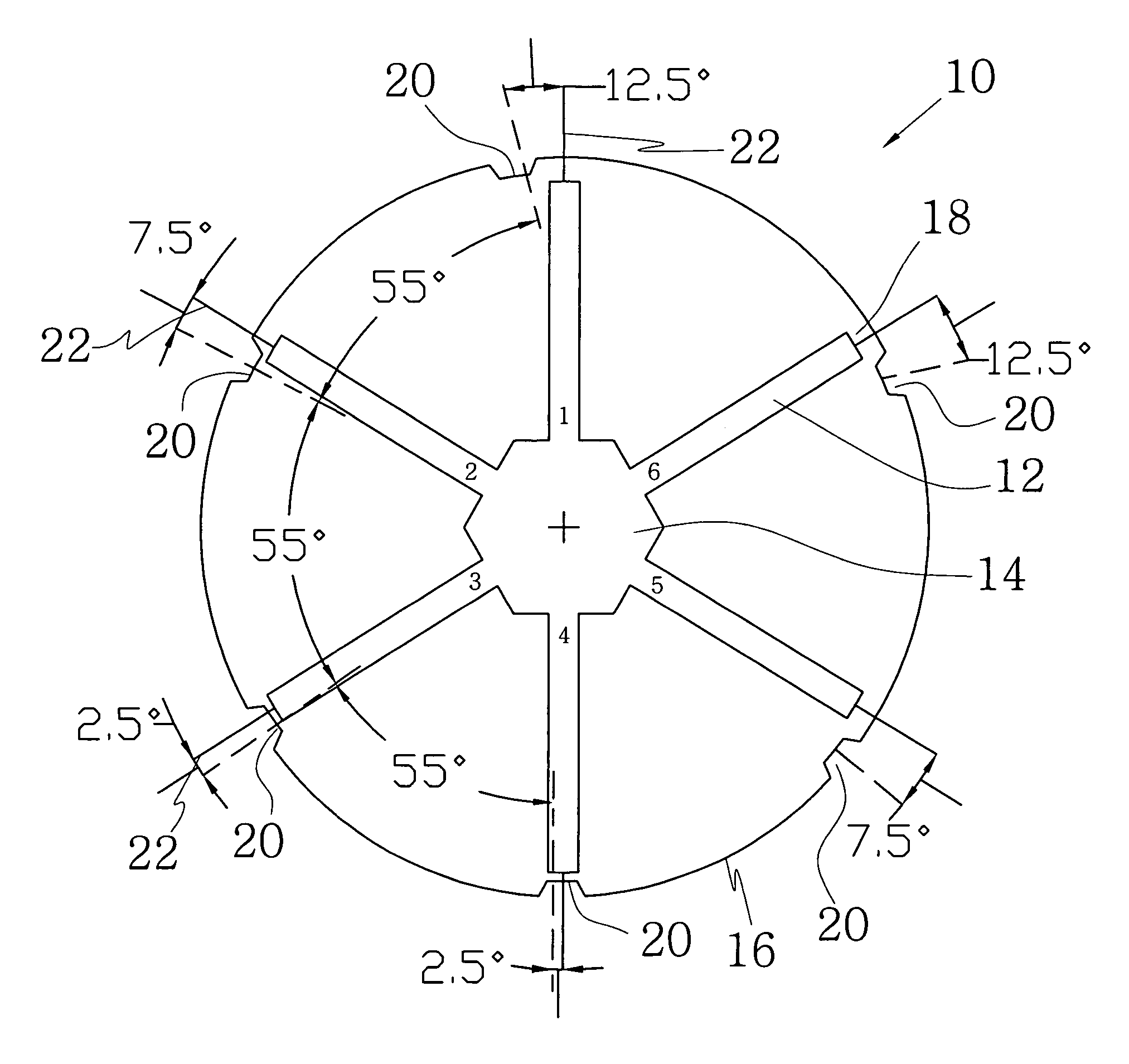
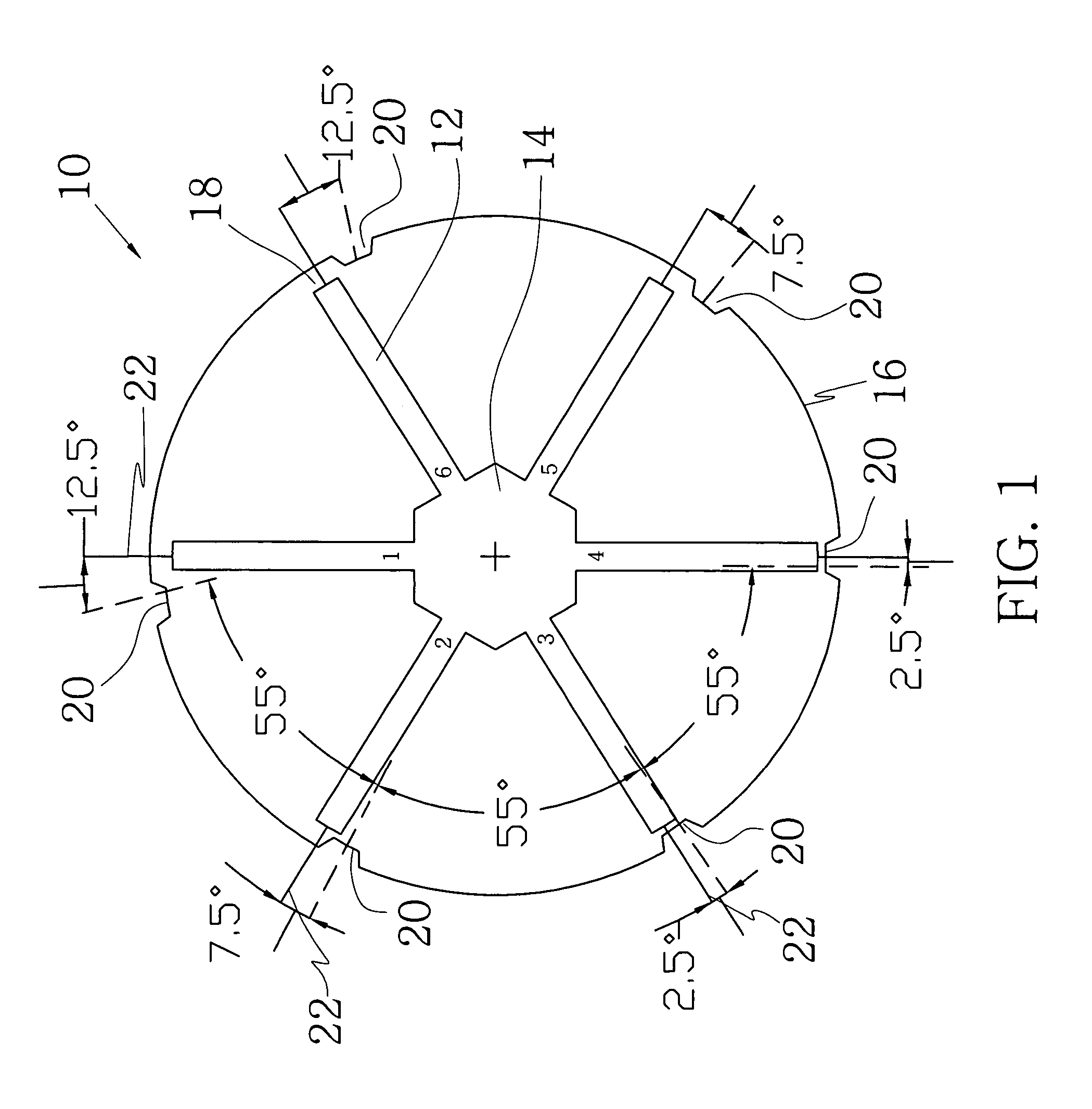
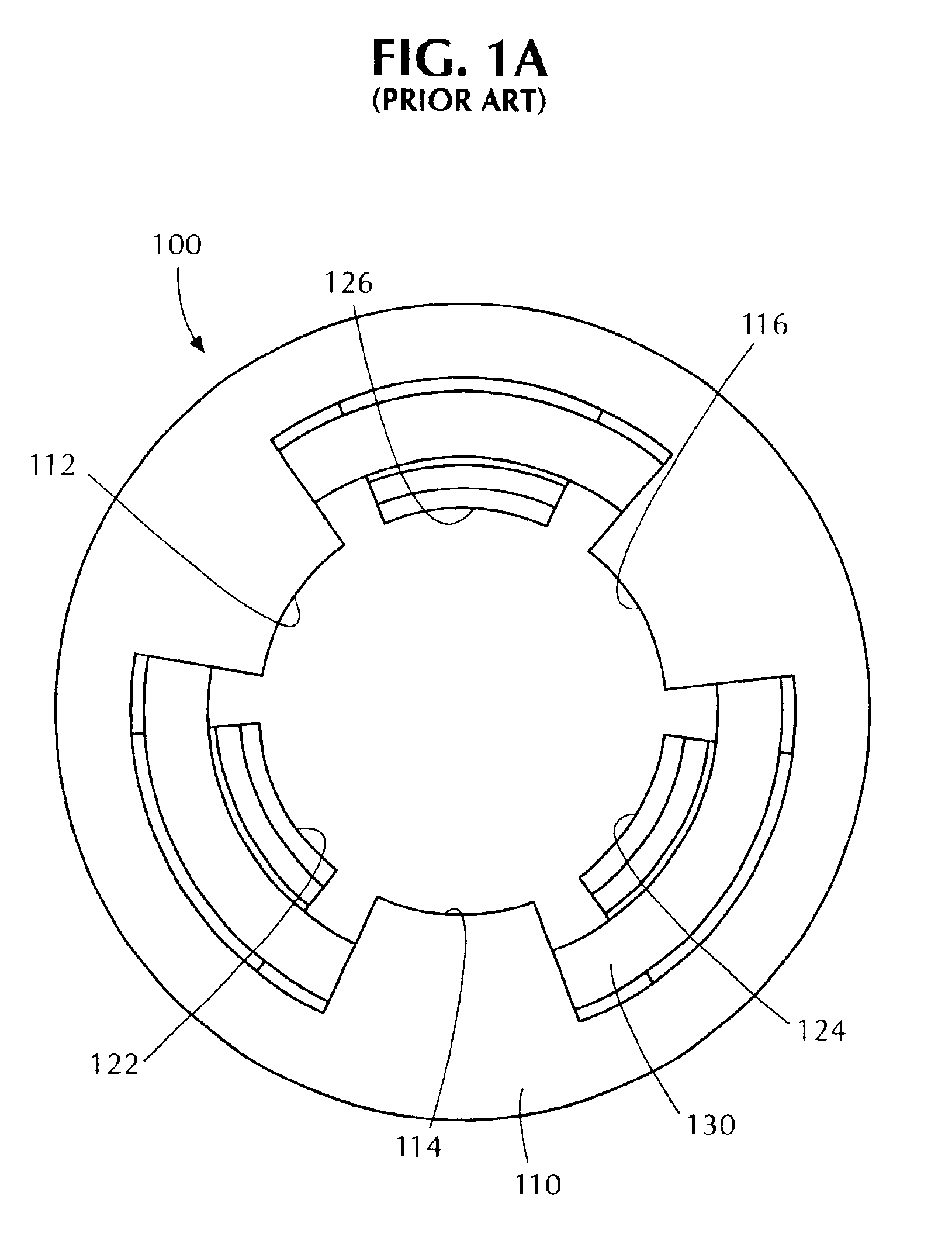
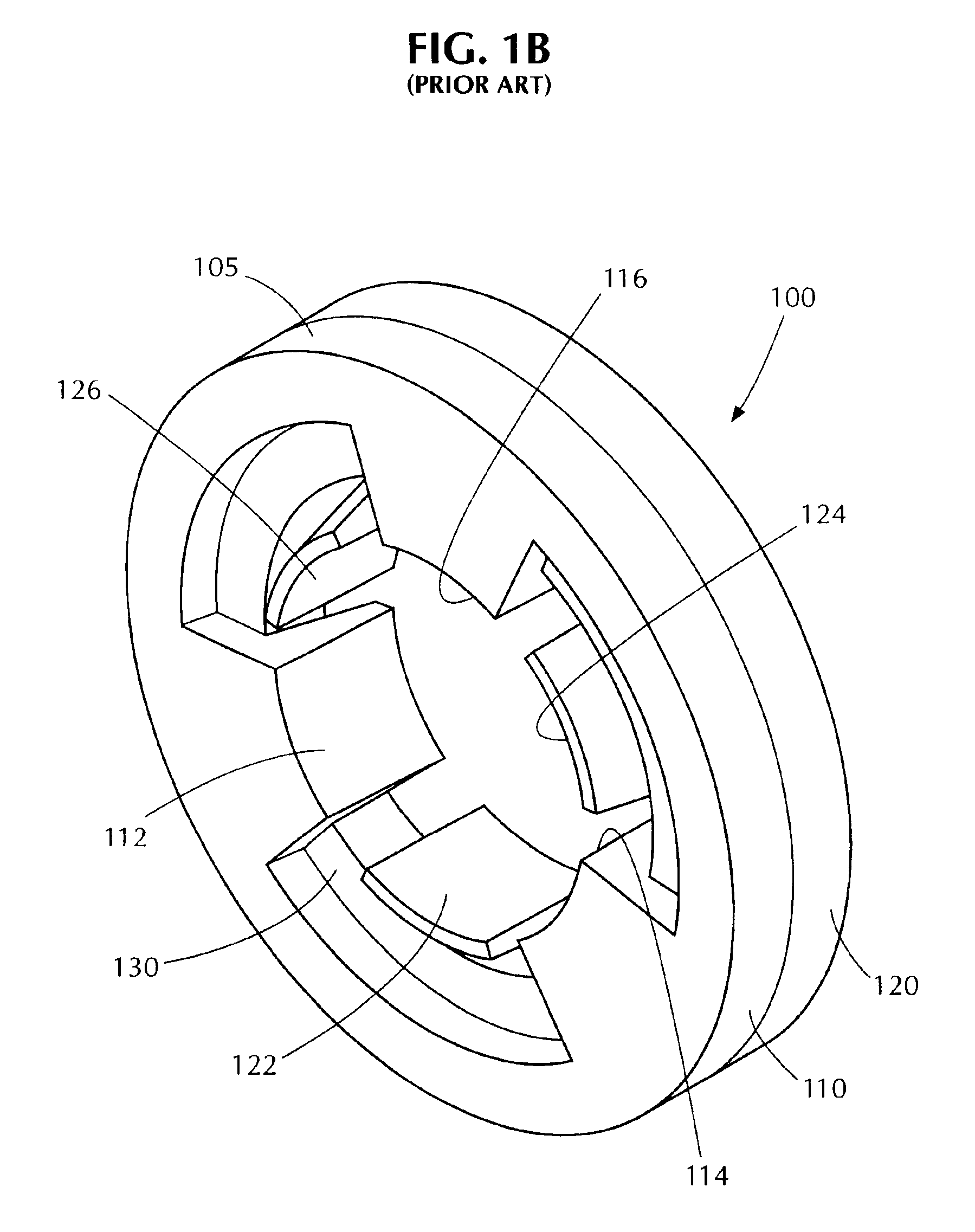
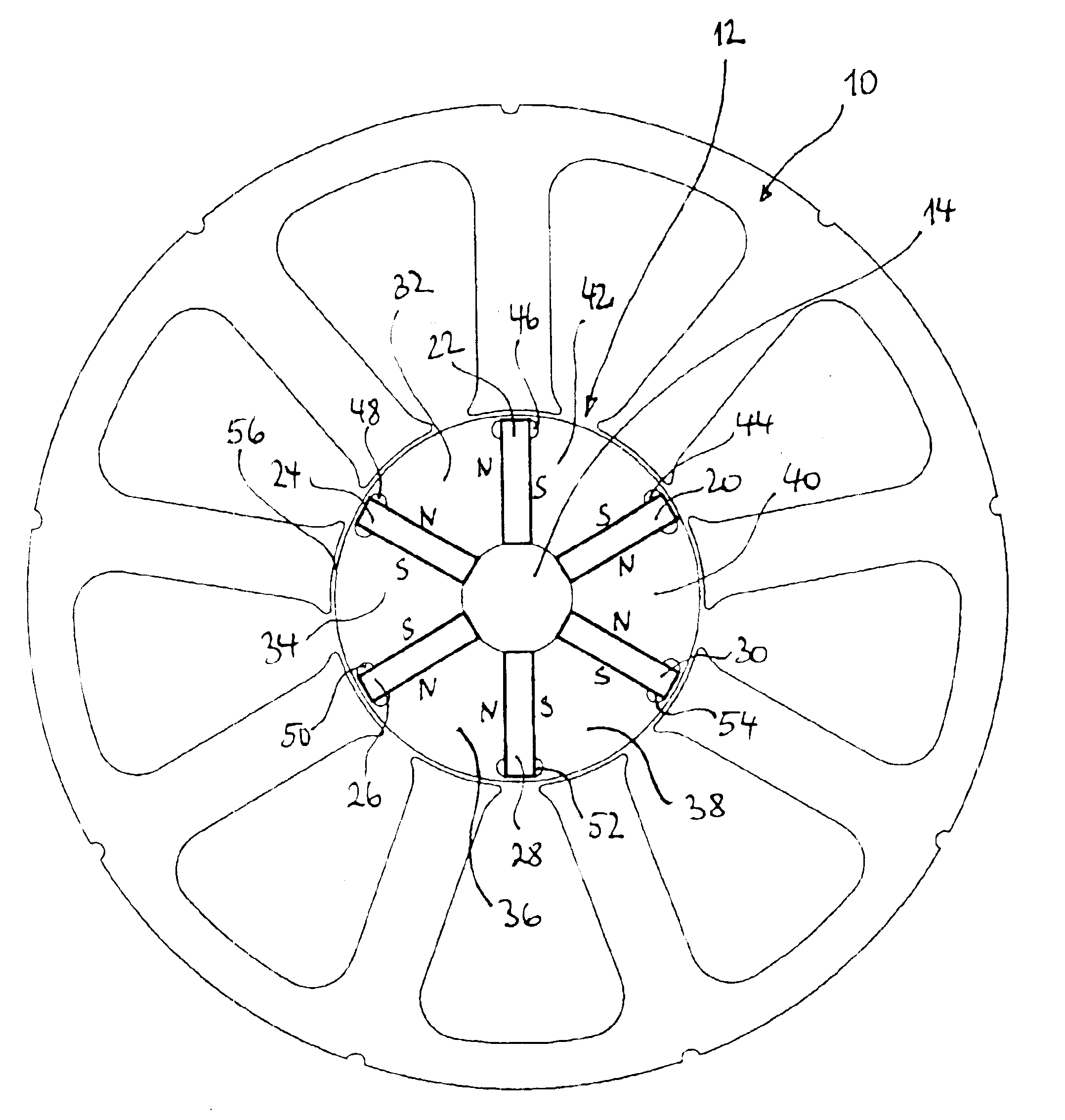
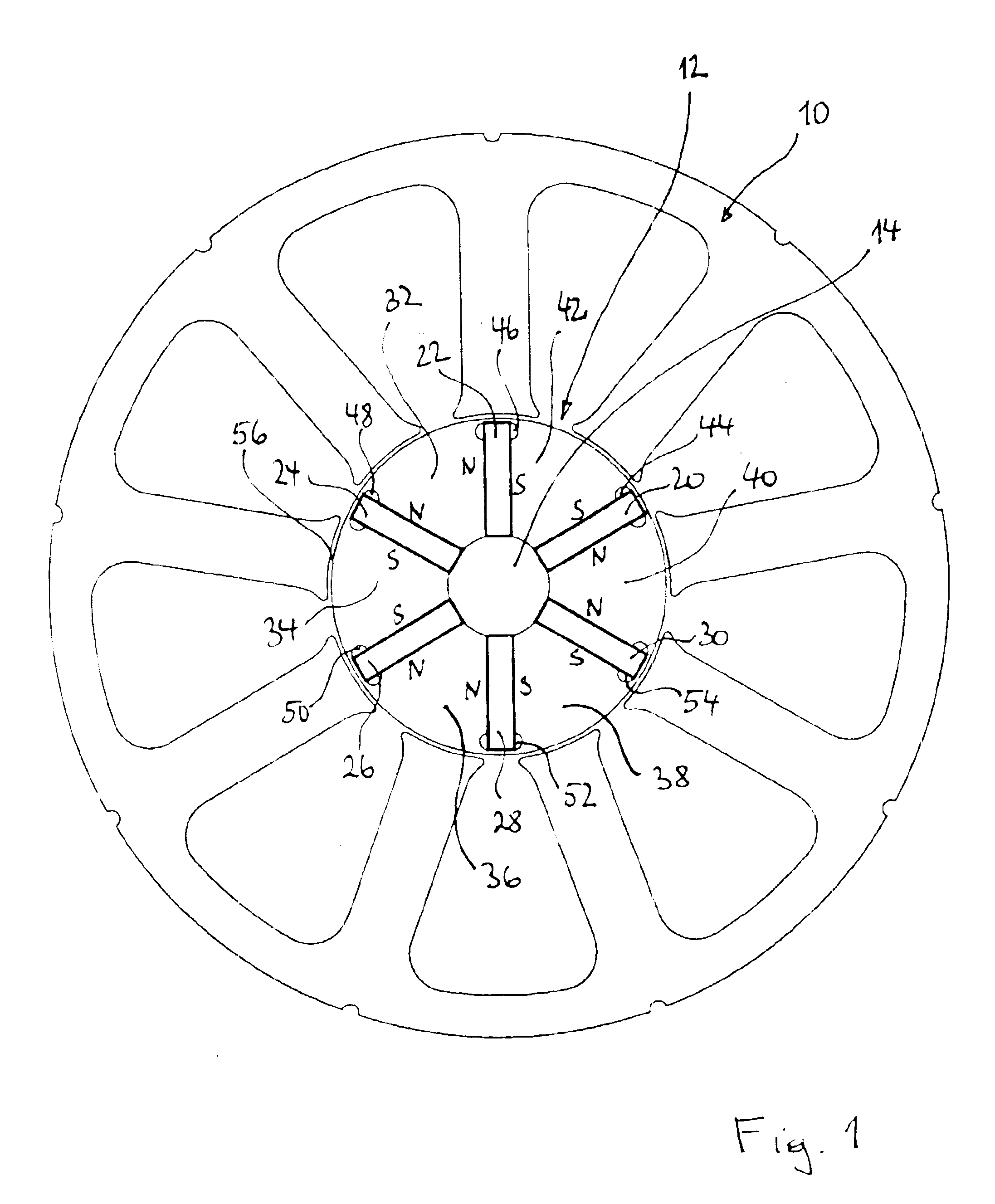
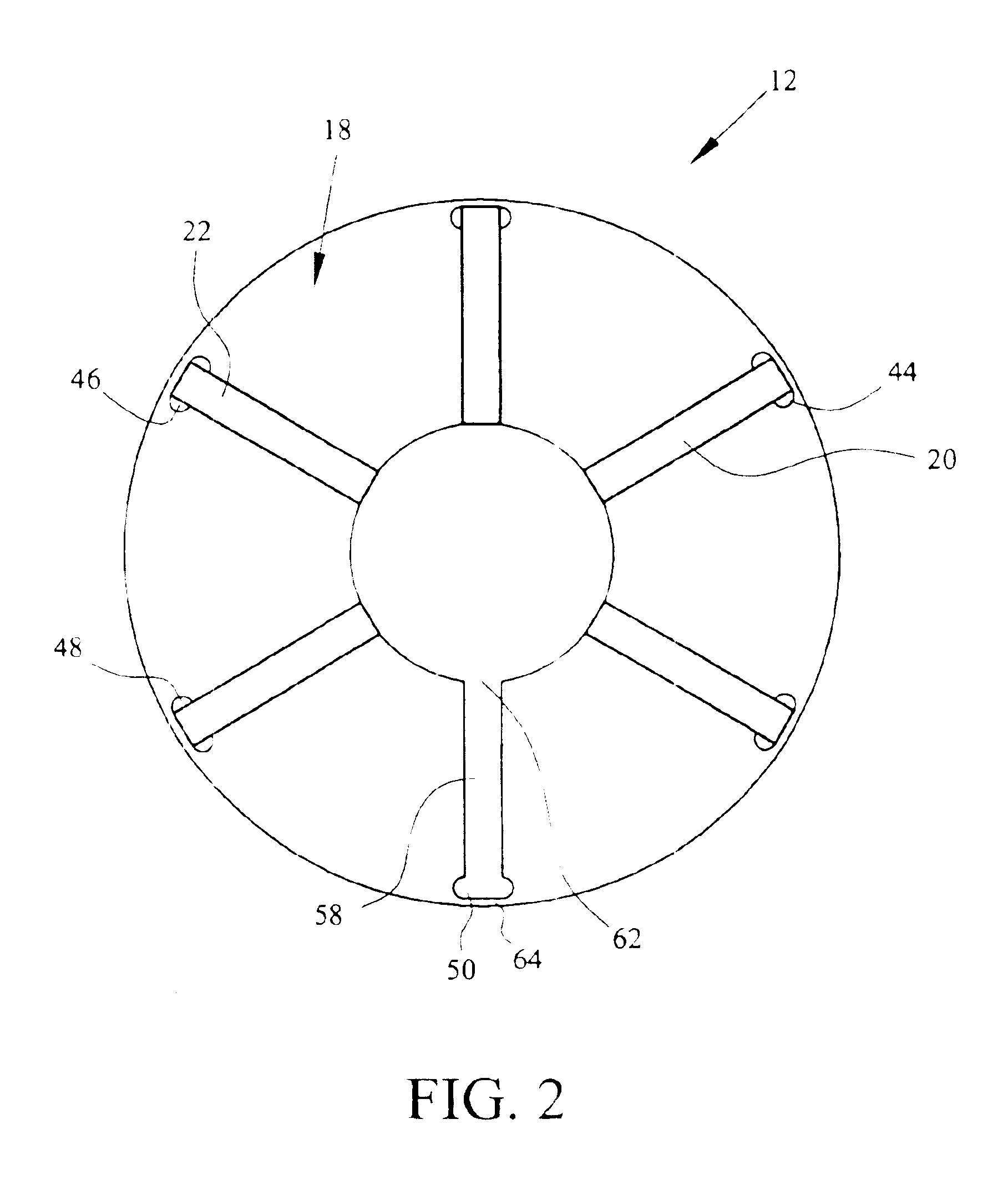
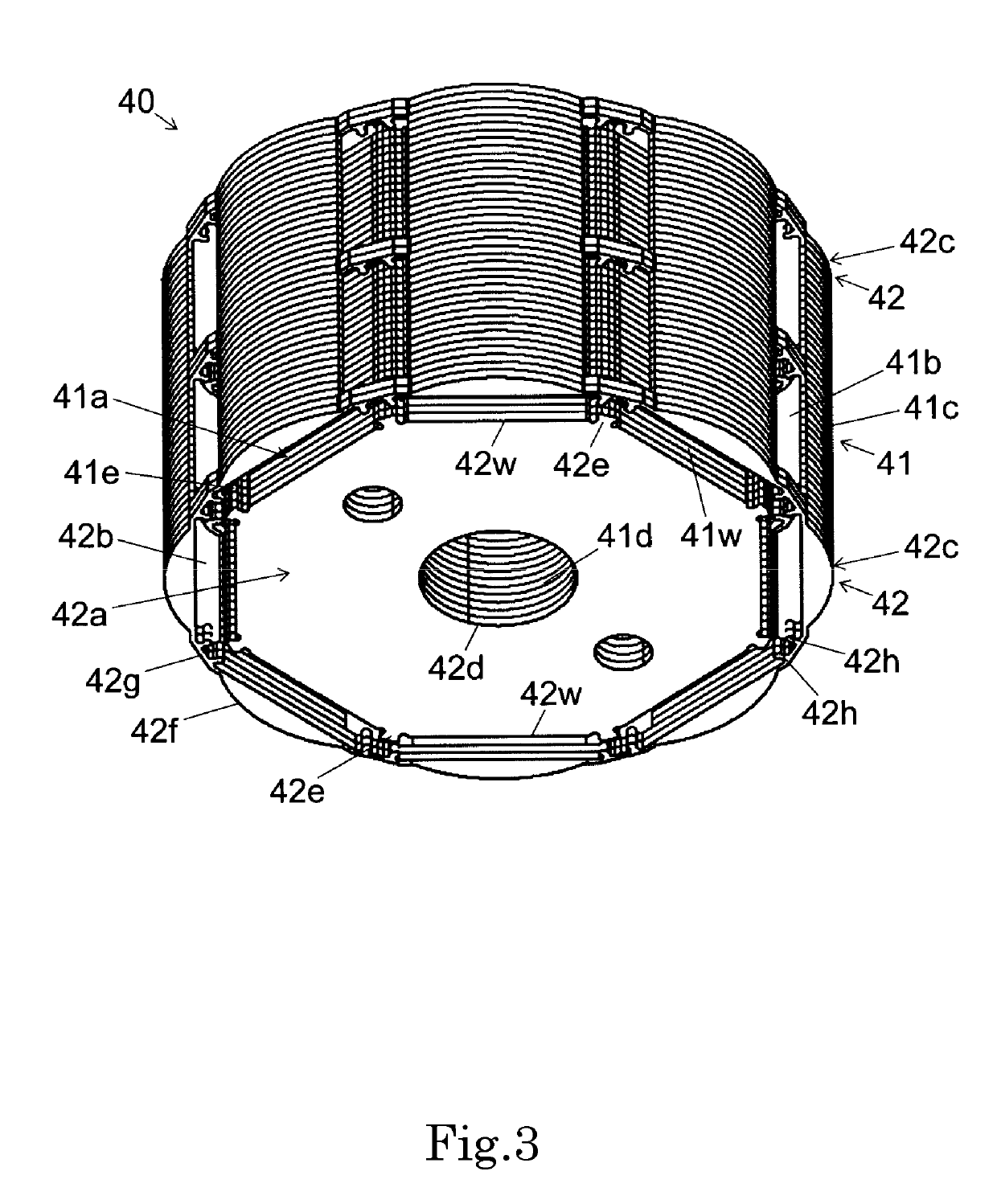
Rotor assembly and stator assembly for an electrical machine
InactiveUS6967424B2Easily influencedReduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineMagnetic flux
The present invention relates to a rotor assembly for an electrical machine, comprising: a rotor body of generally cylindrical shape having a substantially cylindrical surface configured for facing an air-gap between the rotor assembly and a stator of the electrical machine, and permanent magnets embedded in said rotor body, wherein grooves are formed in said air-gap facing surface for manipulating the distribution of magnetic flux created by said permanent magnets.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Polyphase claw pole structures for an electrical machine
InactiveUS6946771B2Reduce the cogging torqueLimit amplitudeMagnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineEngineering
A magnetic circuit component having a plurality of claws arranged in a plurality of rows, with the base of each claw connected to a common yoke. A plurality of non-interlaced coils constituting a multi-phase winding are included, with the coils being wound around the bases of corresponding claws, and being distributed uniformly in the direction of motion.
Owner:QUEBEC METAL POWDERS
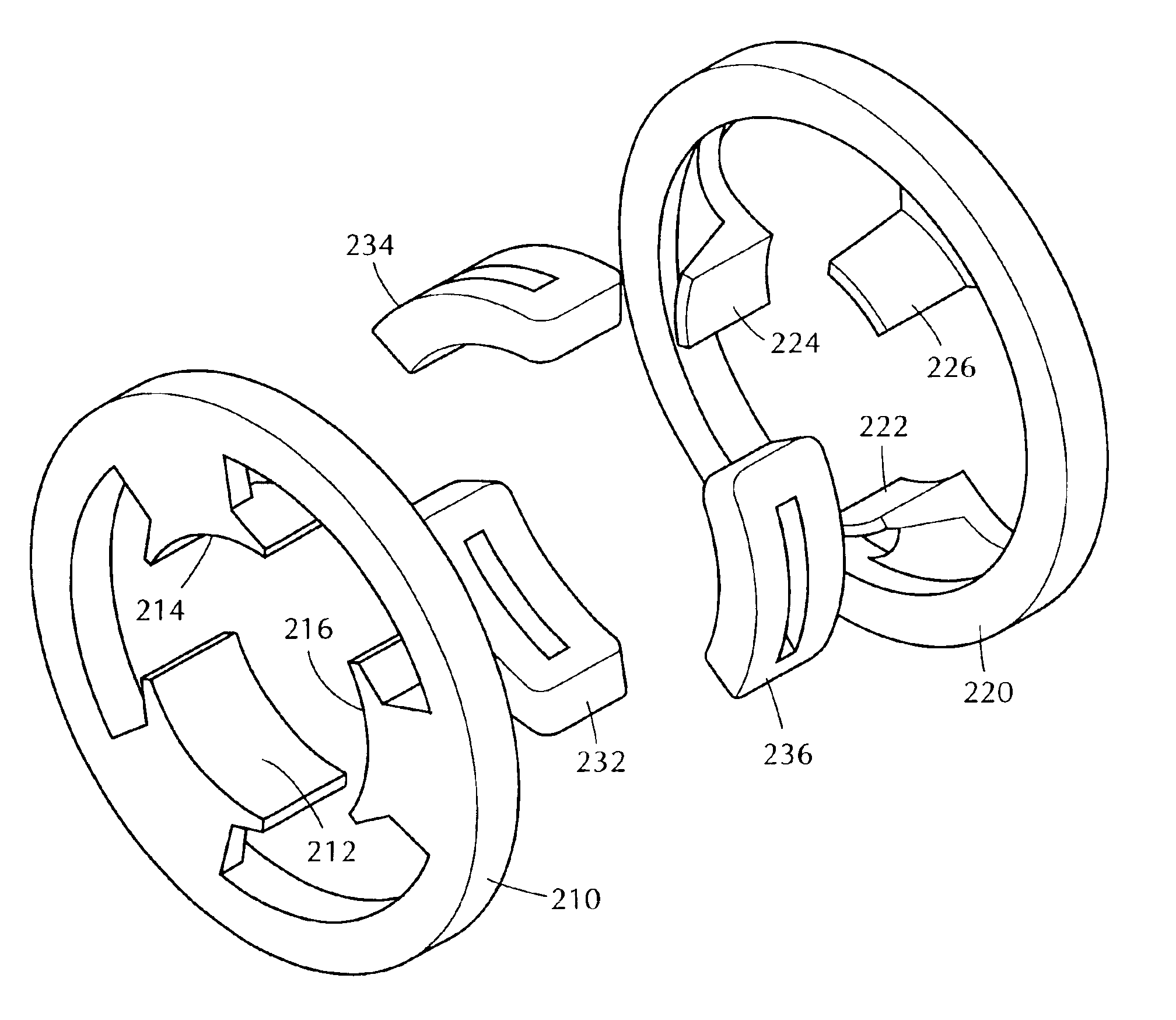
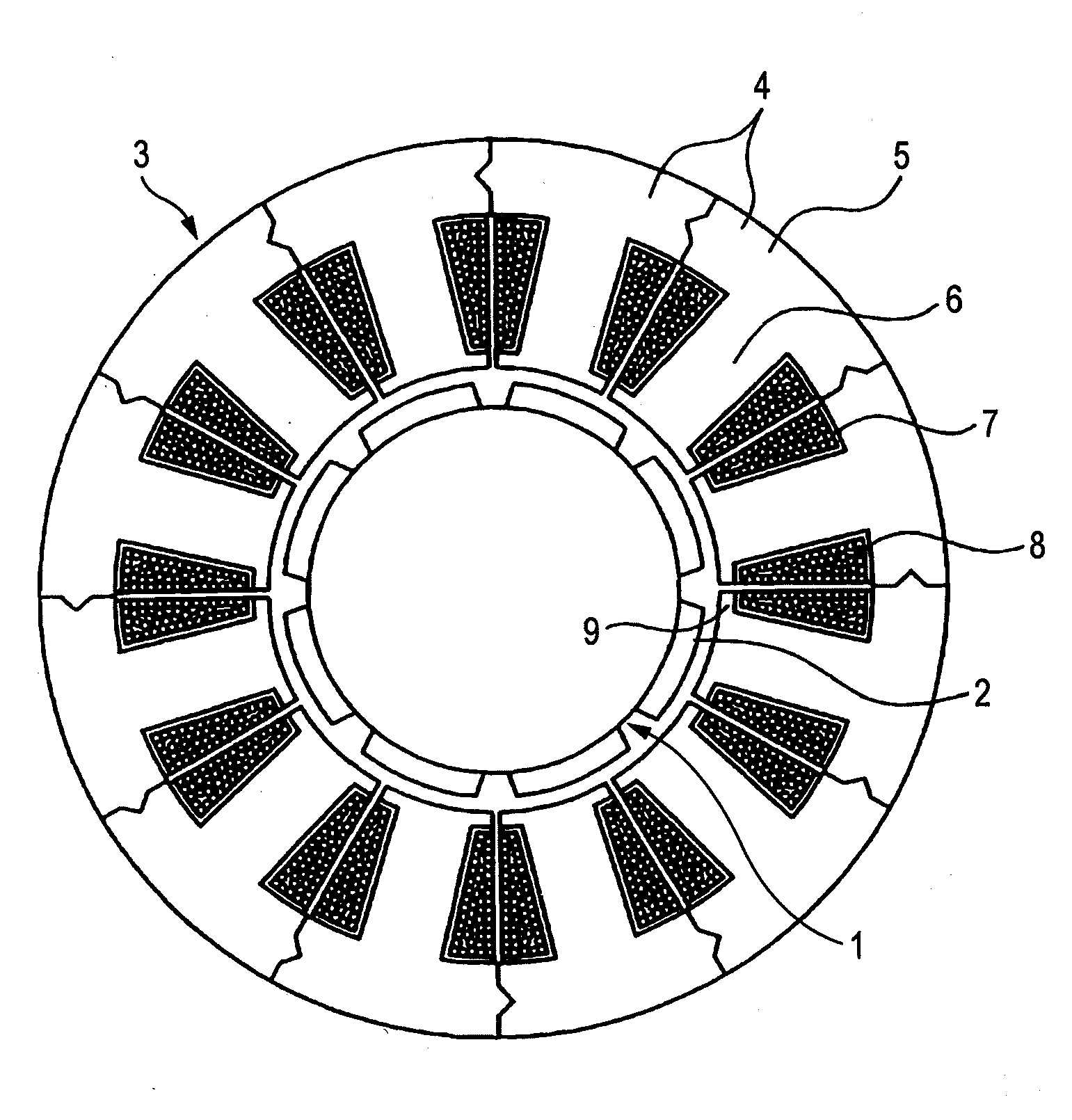
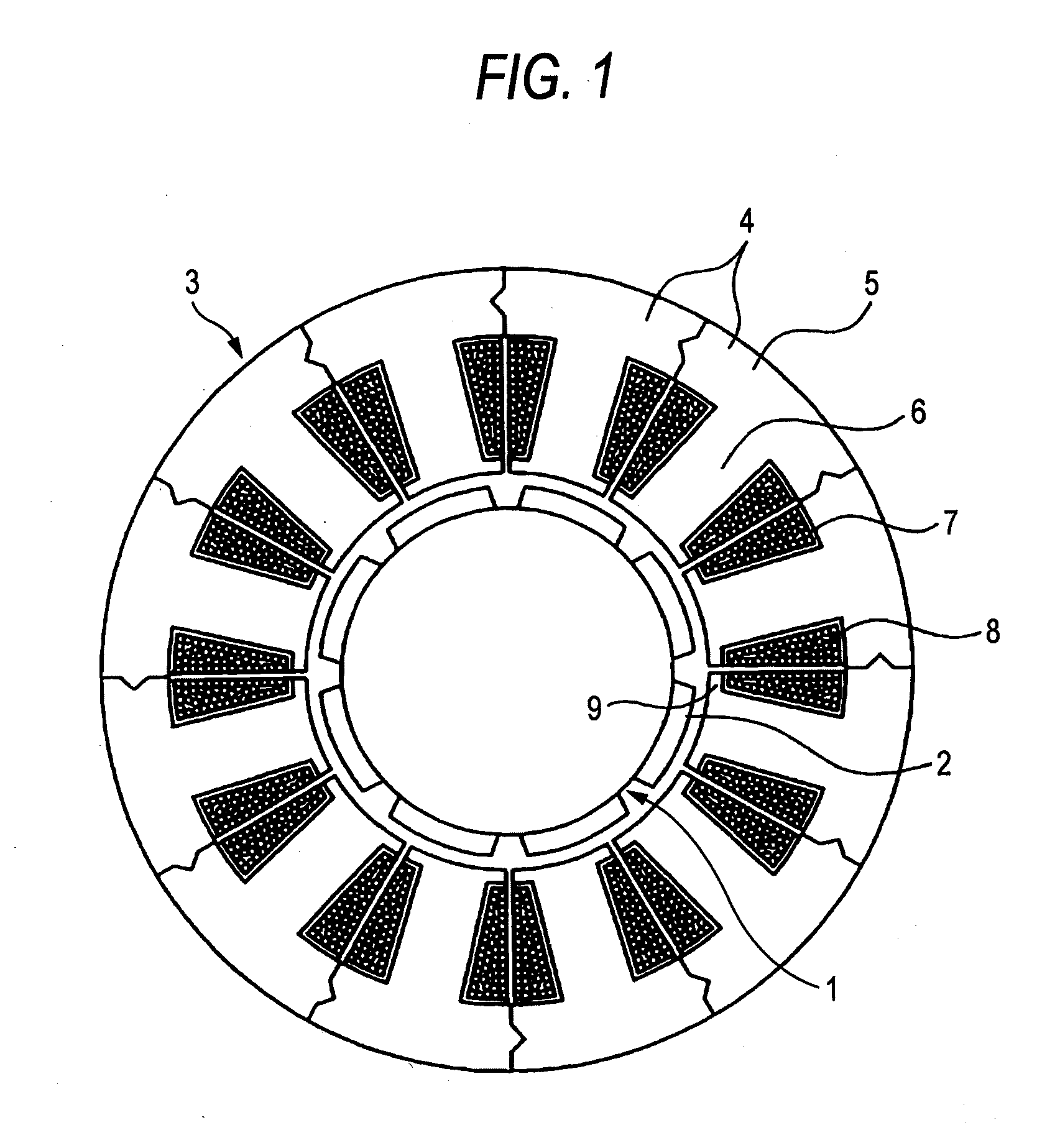
Split cores for motor stator, motor stator, permanent magnet type synchronous motor and punching method by split core punching die
ActiveUS20090026872A1Improve rigidityImprove assembly accuracyMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous motorPunching
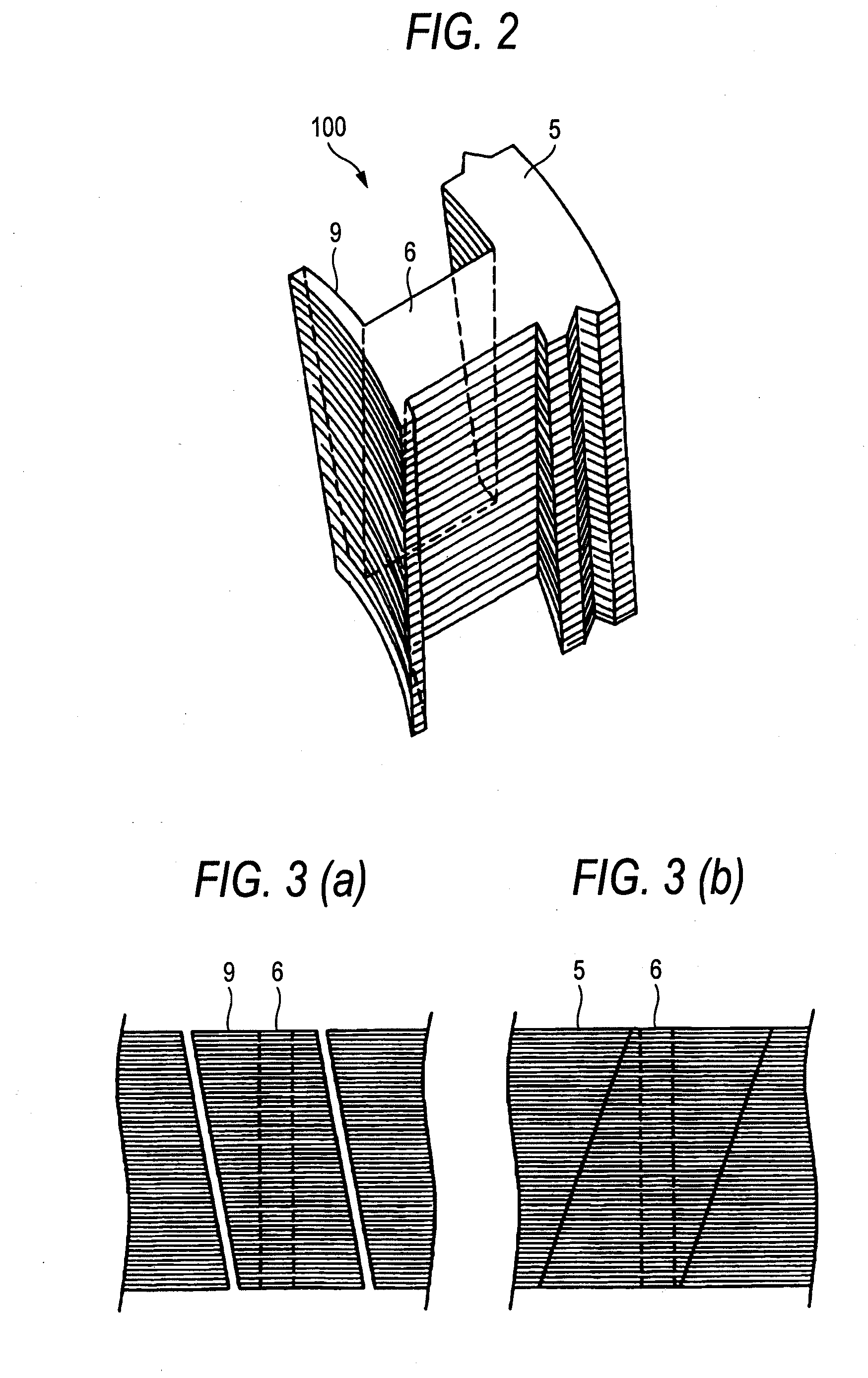
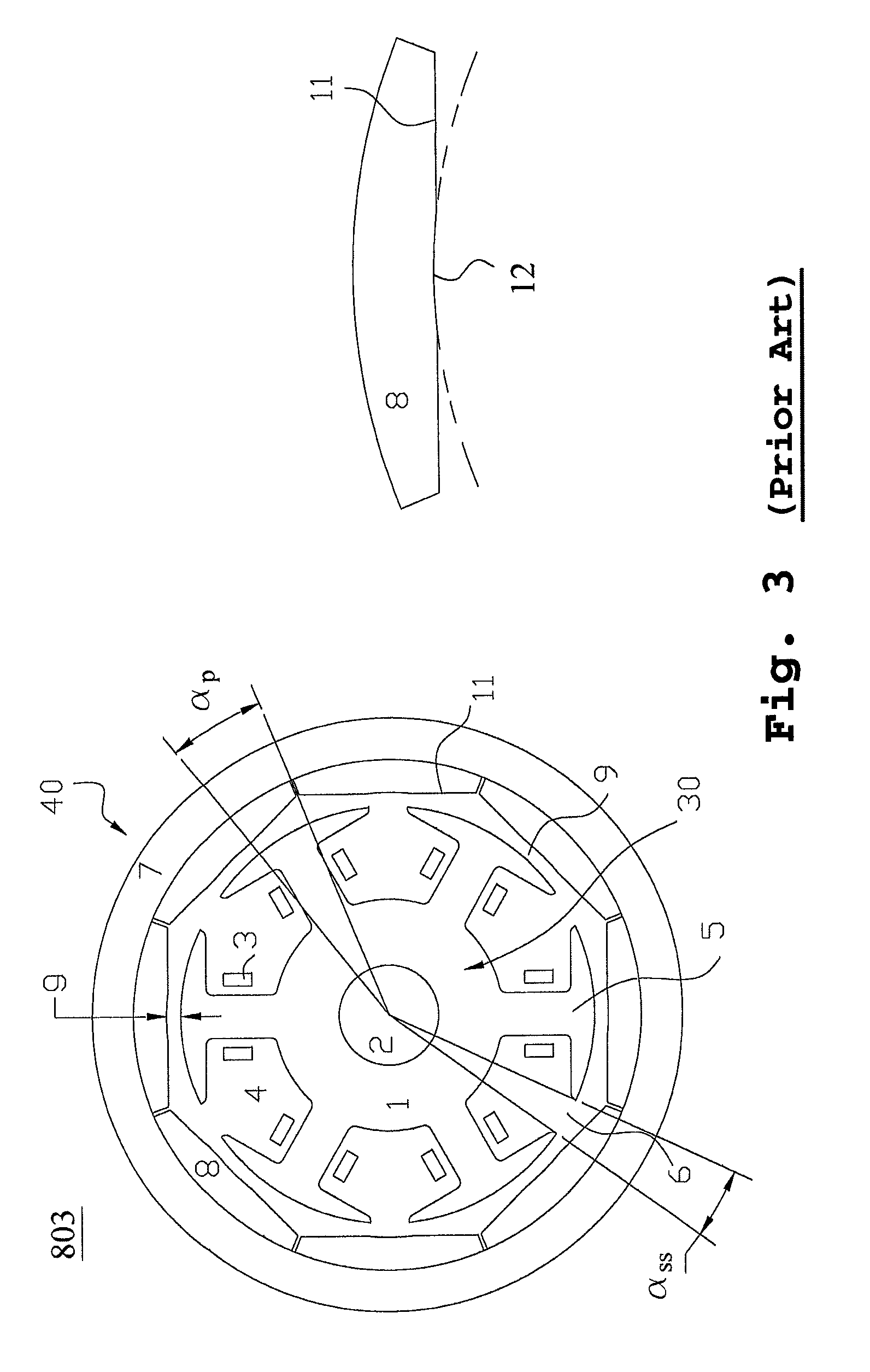
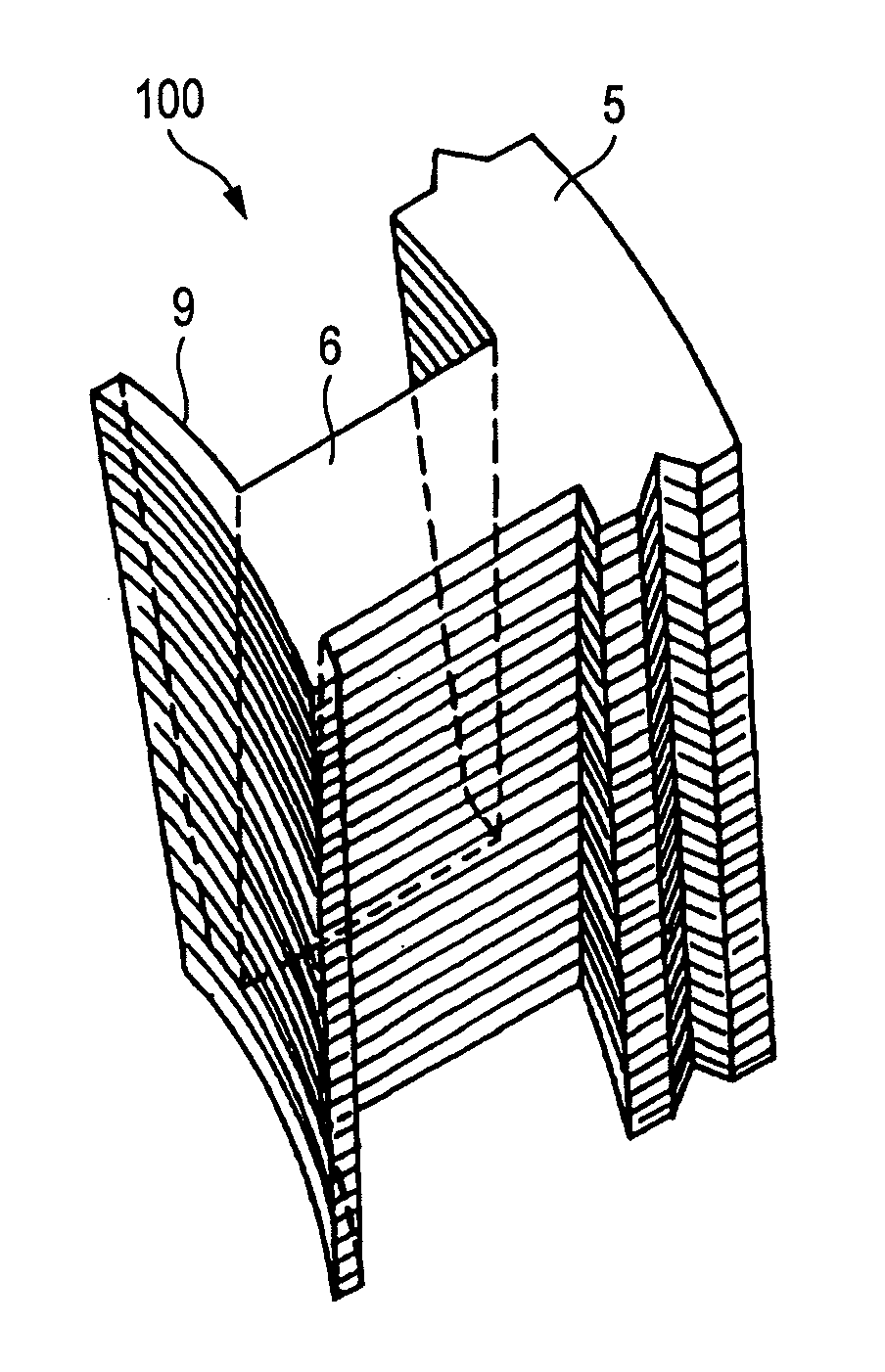
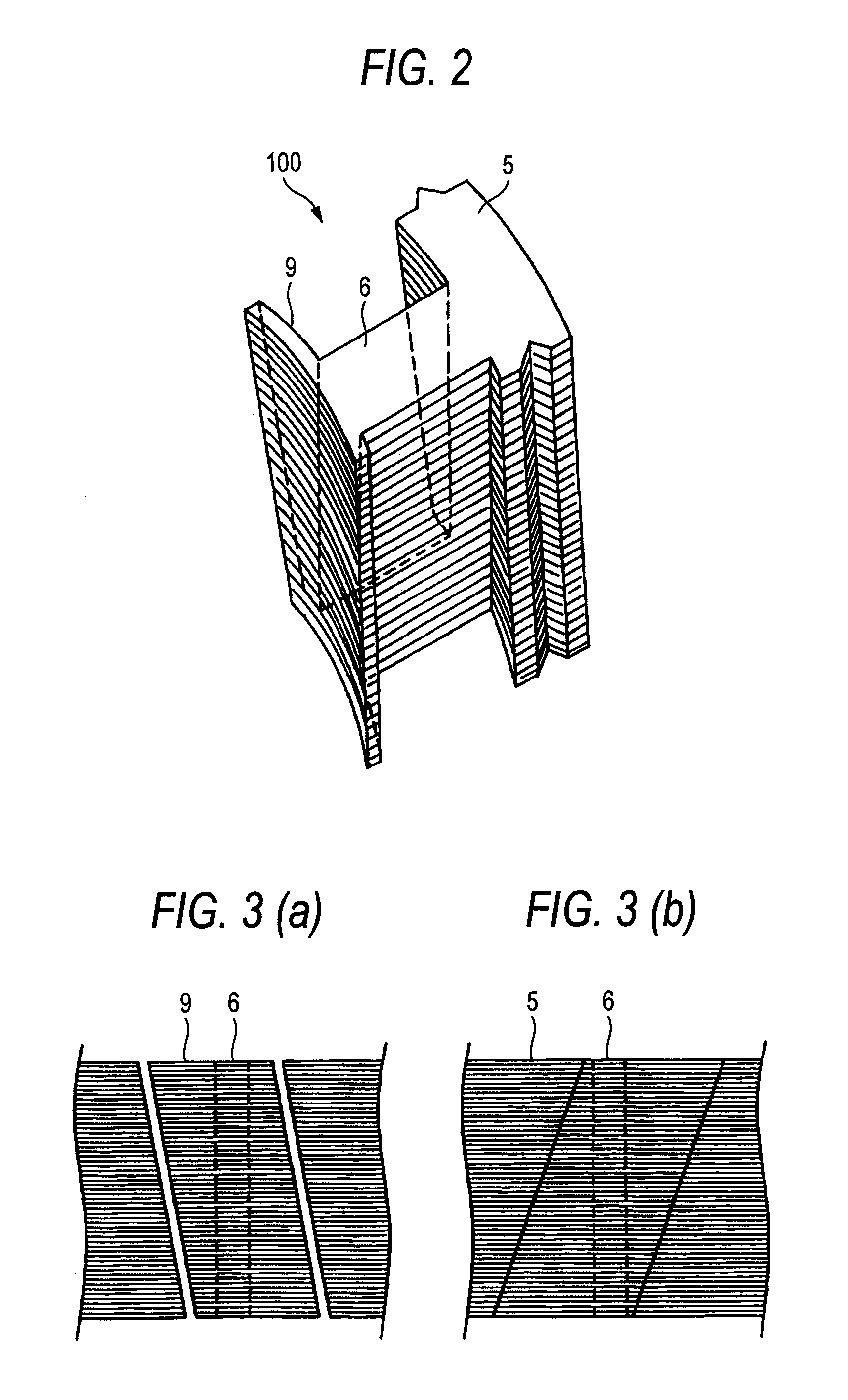
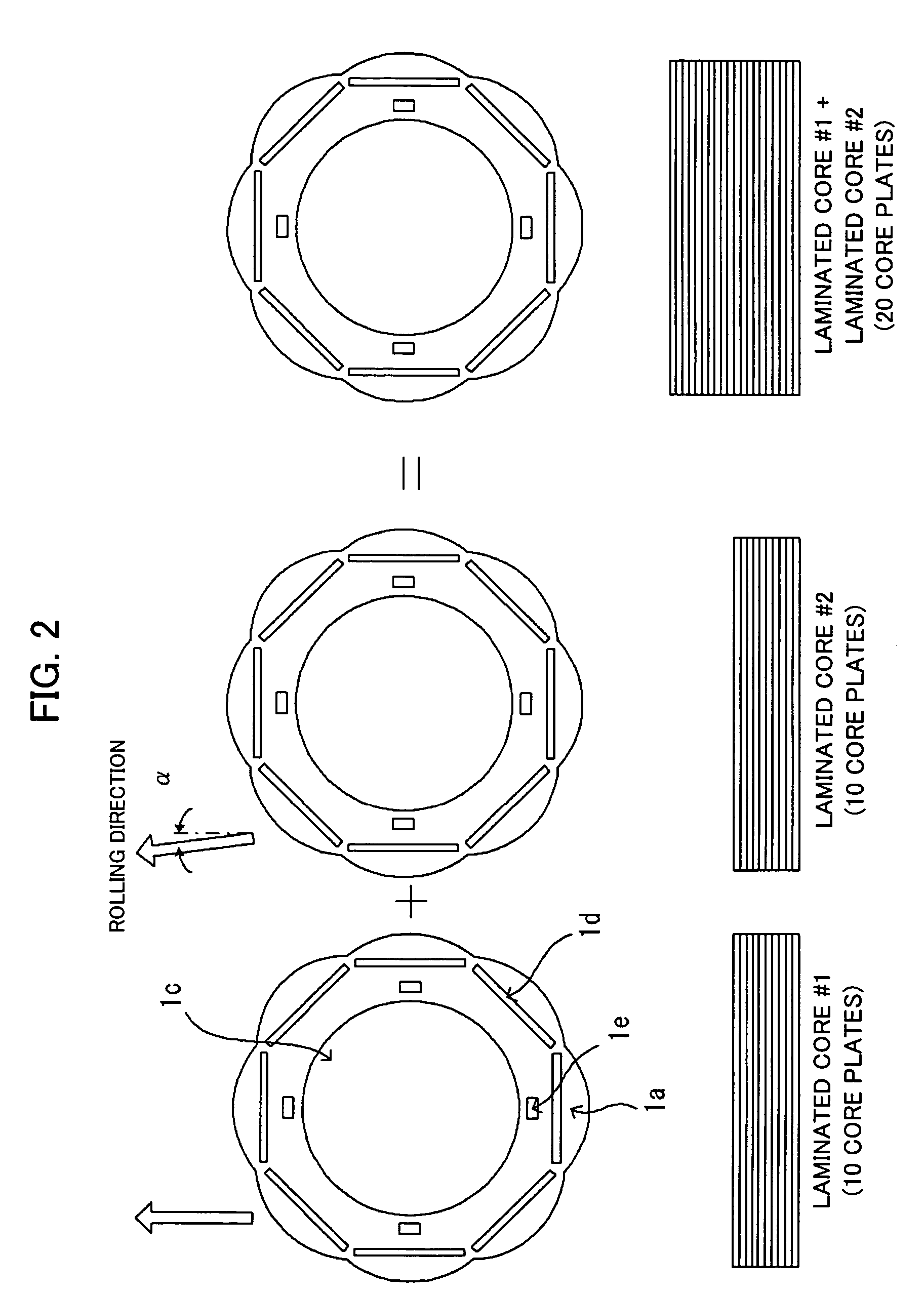
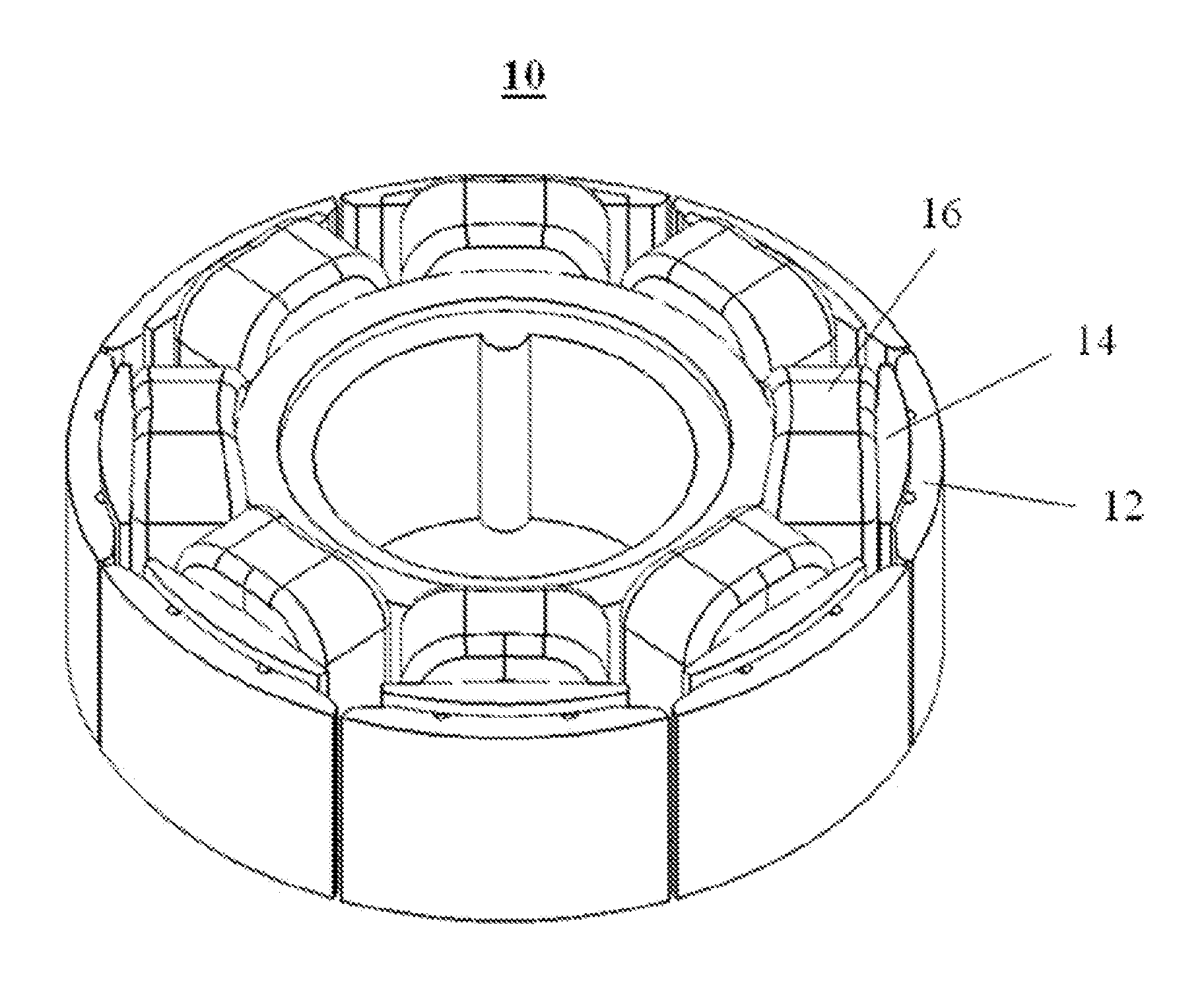
Although in a conventional permanent magnet type synchronous motor, cogging torque is reduced by displacing permanent magnets of a rotor in a circumferential direction or displacing a stator core in a circumferential direction, since the skew so produced reduces the output of the motor and moreover the winding work of windings cannot be automated to make the resulting motor highly expensive, split cores are provided which solves those problems and enables the winding work of windings to be automated so as to obtain an inexpensive and high-output motor.There are provided a plurality of split cores (100) made up of laminated iron cores each having formed thereon a tooth (6), and a yoke (5) and a pole piece (9) which are made to connect to the tooth (6) at both ends thereof, and arranged and connected together into an annular shape to make up a stator, characterized in that both ends of the yokes (5) and both ends of the pole pieces (9) are displaced in one circumferential direction by laminated iron core from a top laminated layer to a bottom laminated layer of the iron cores of the split cores.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Permanent magnet motor
InactiveUS20060038457A1Reduce the cogging torque of servomotorsImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringElectric machine
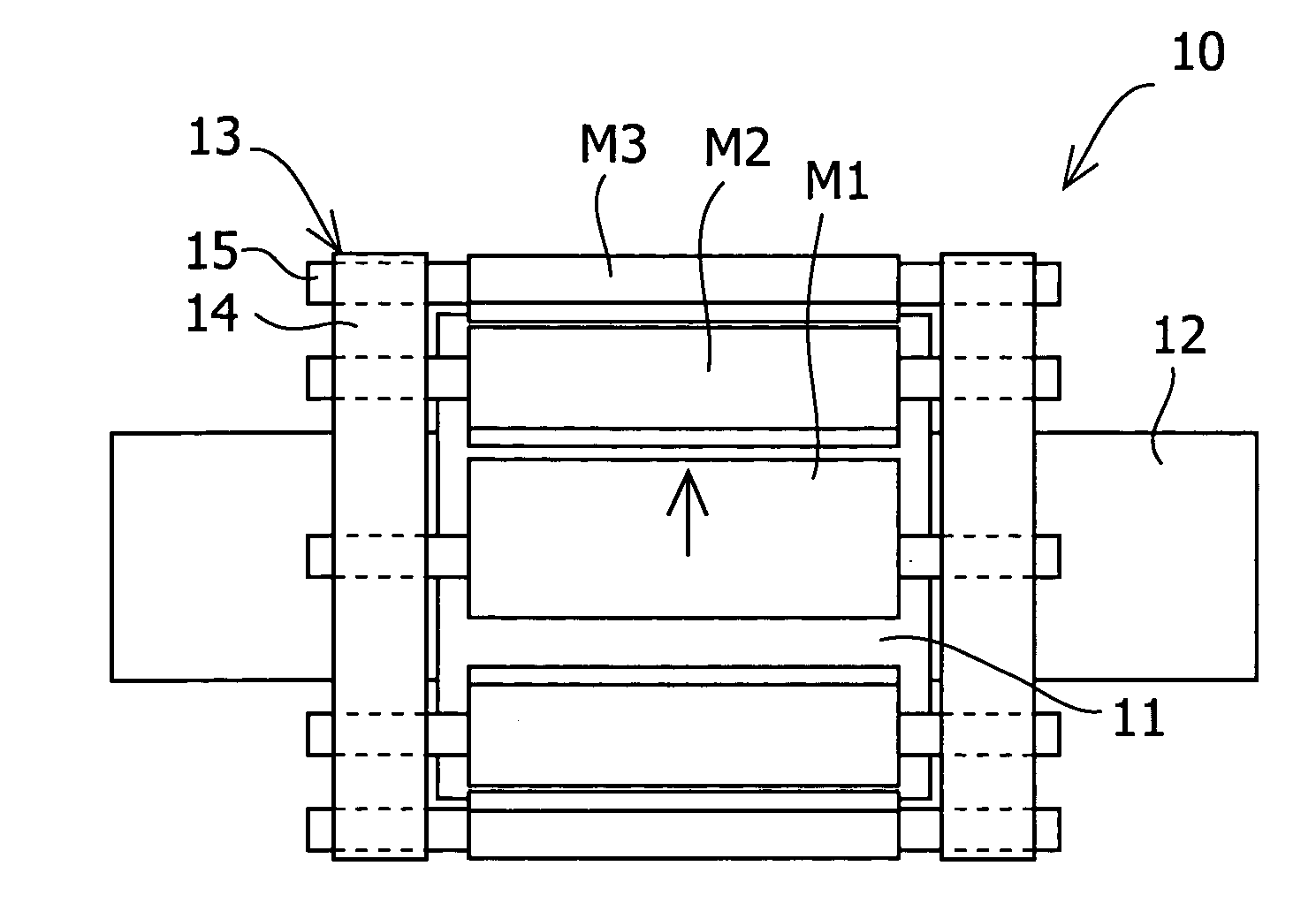
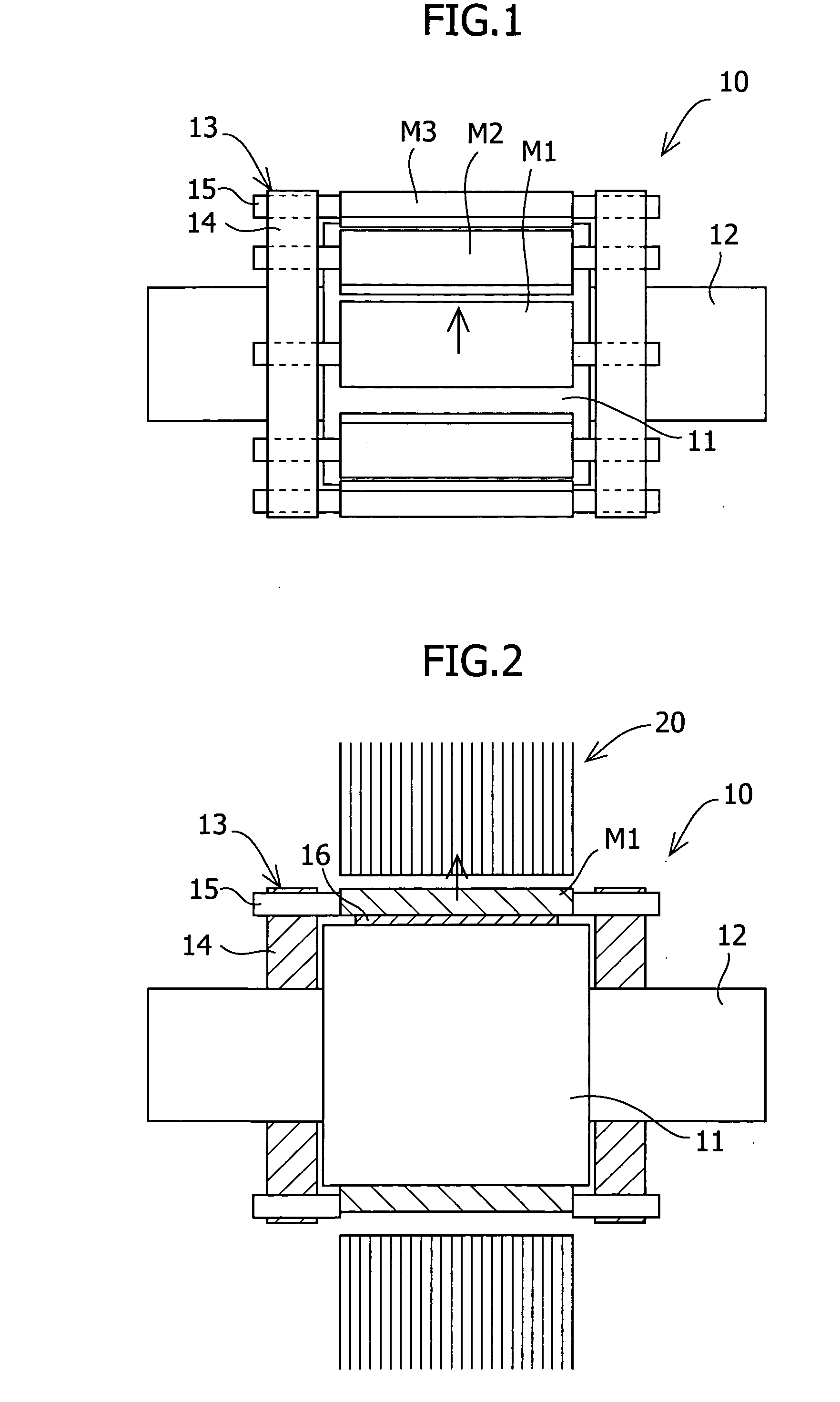
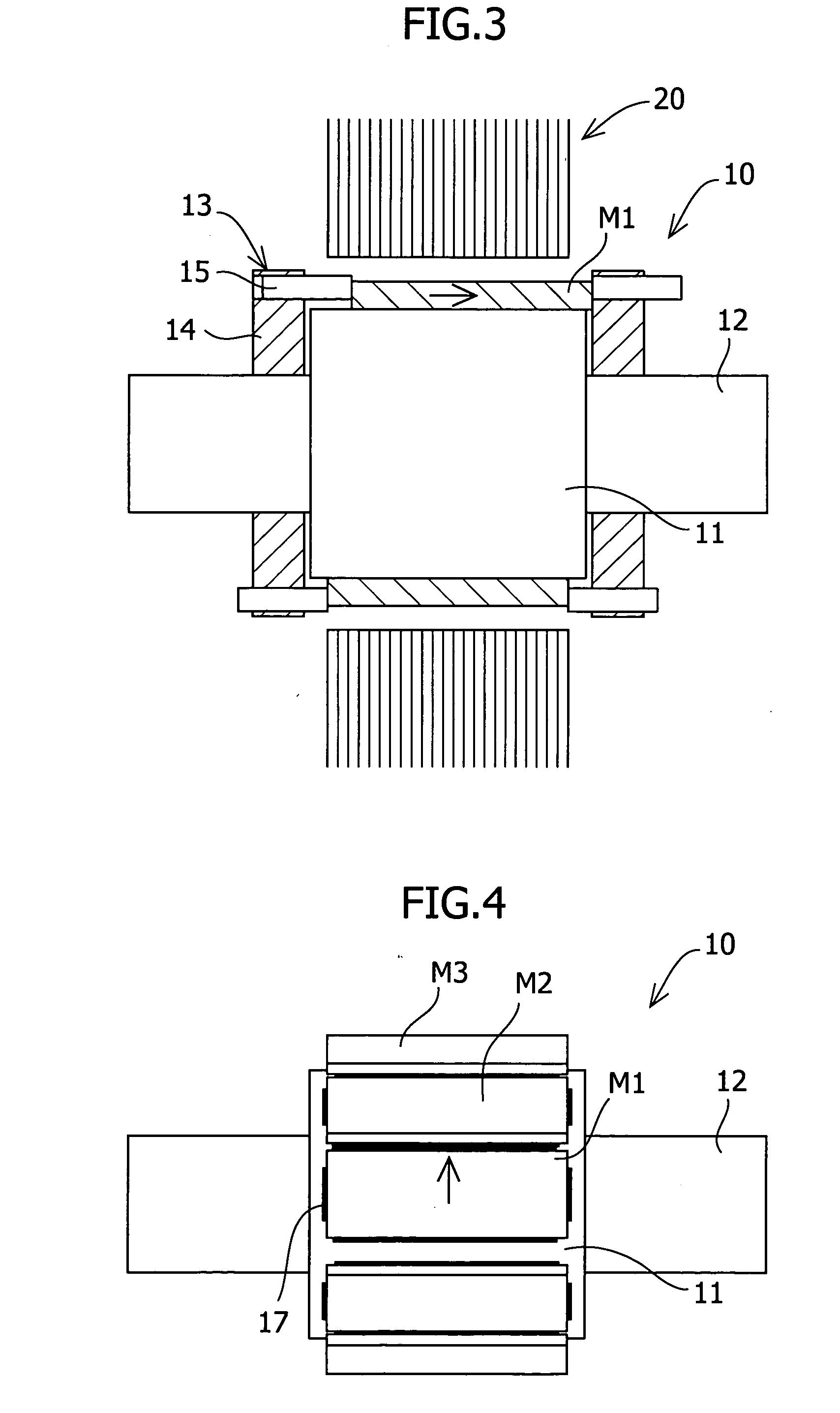
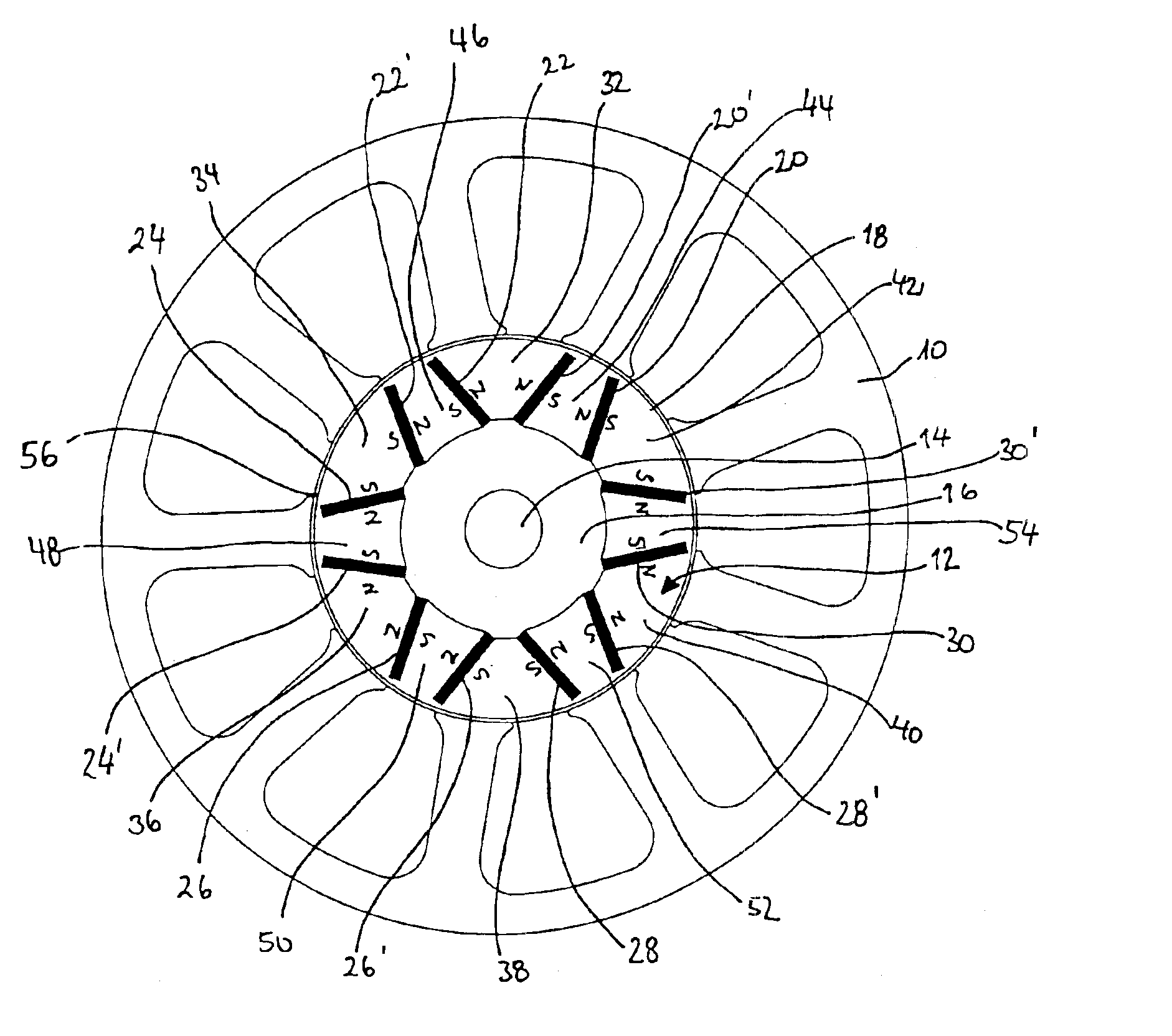
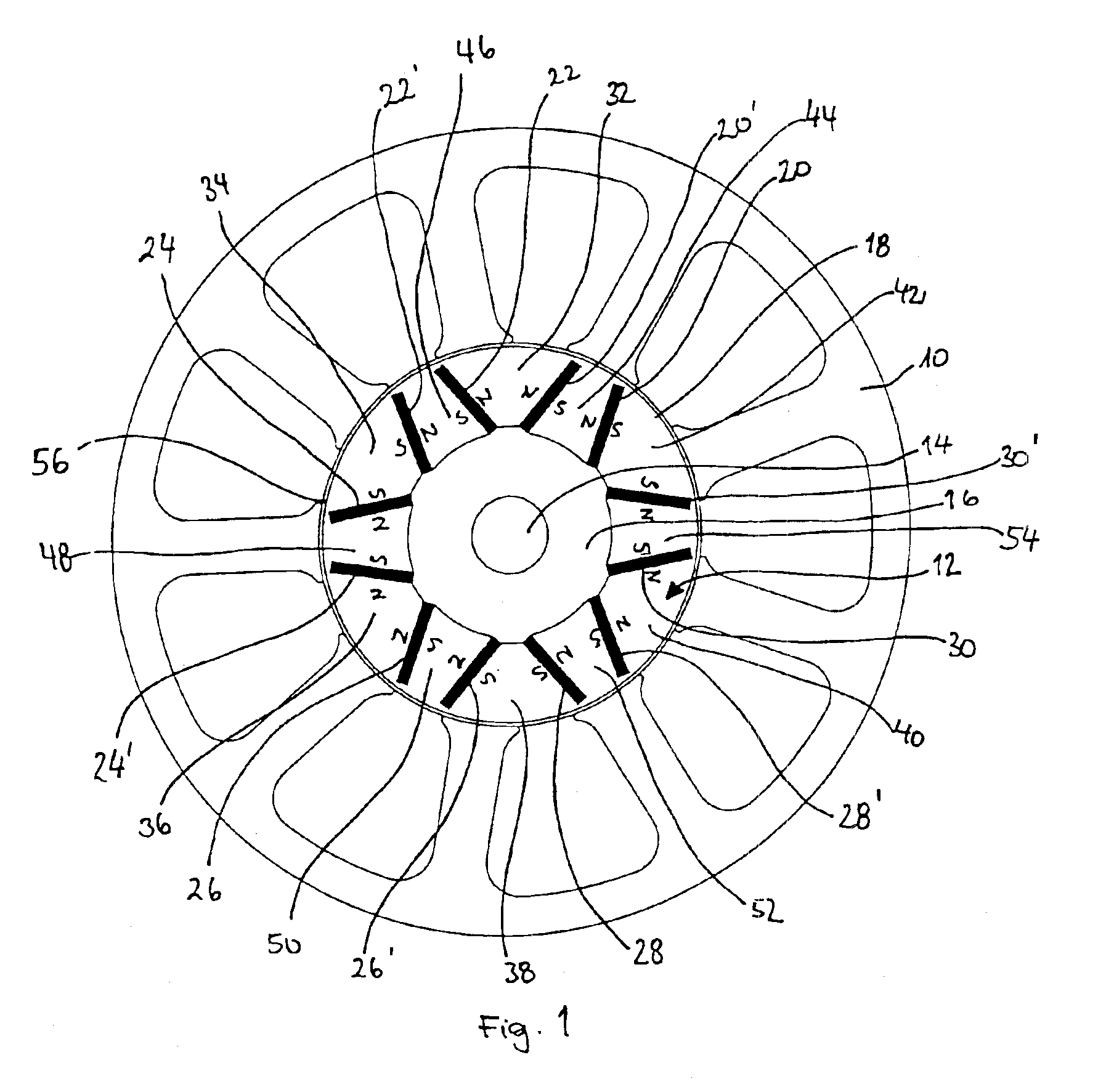
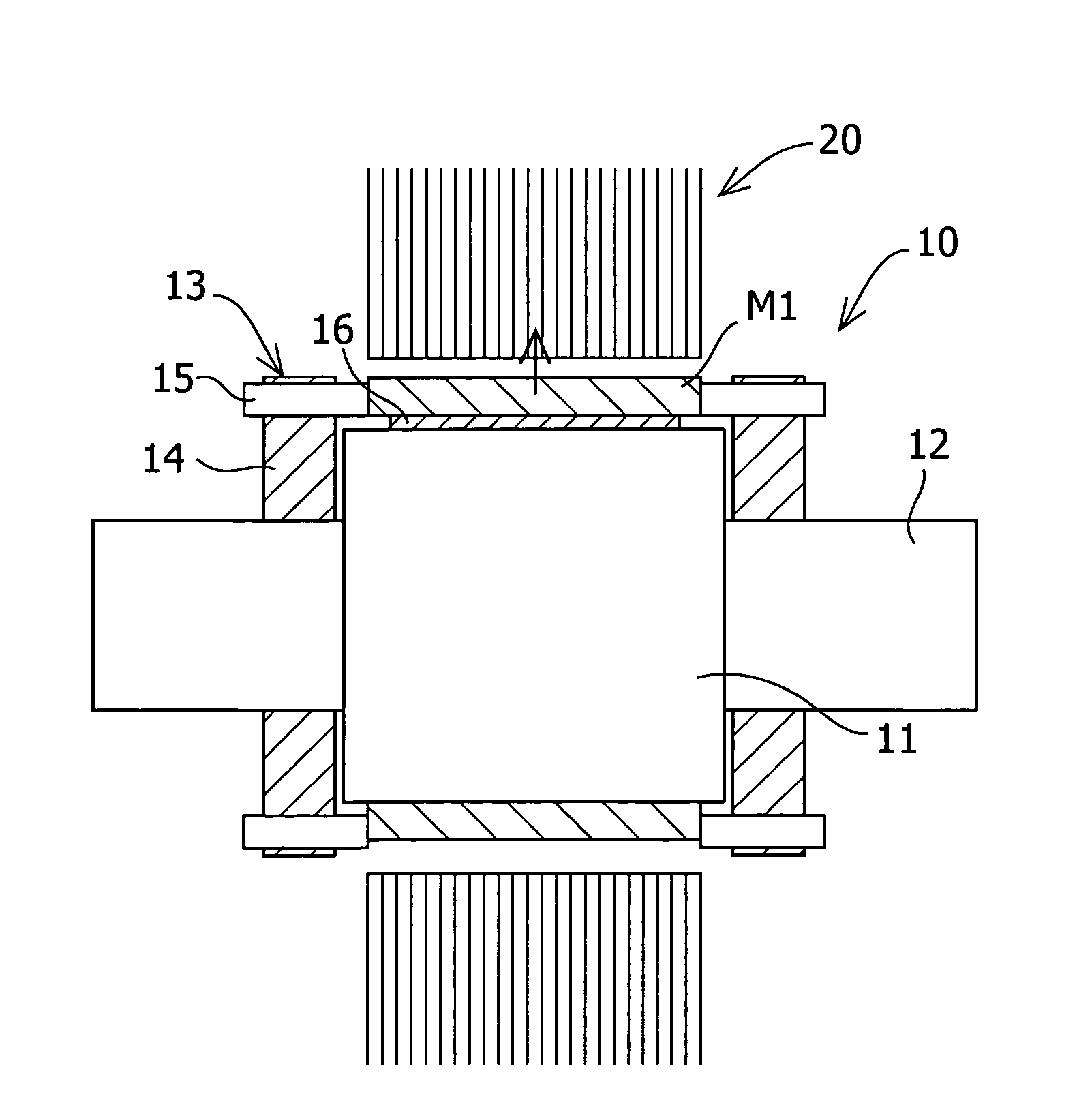
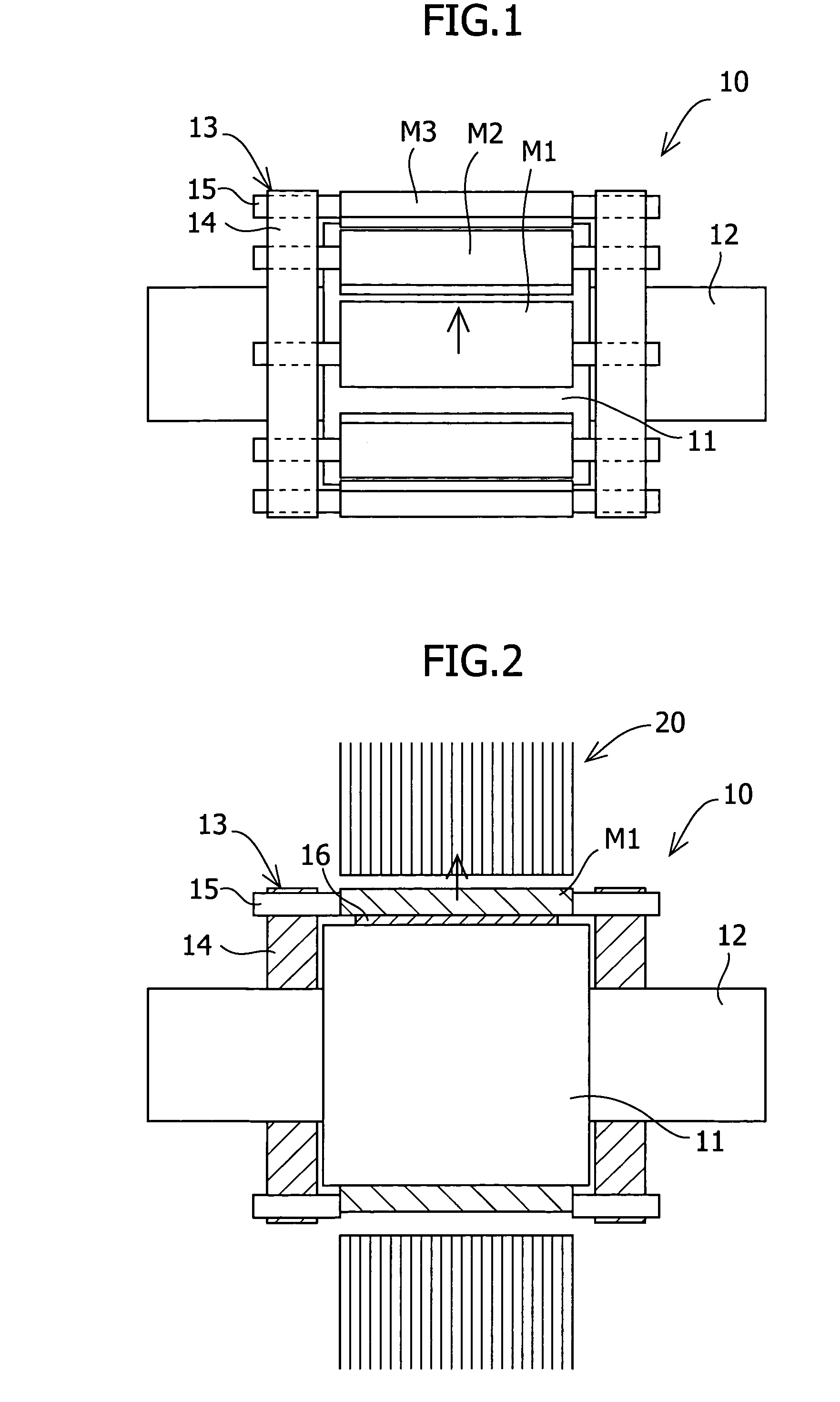
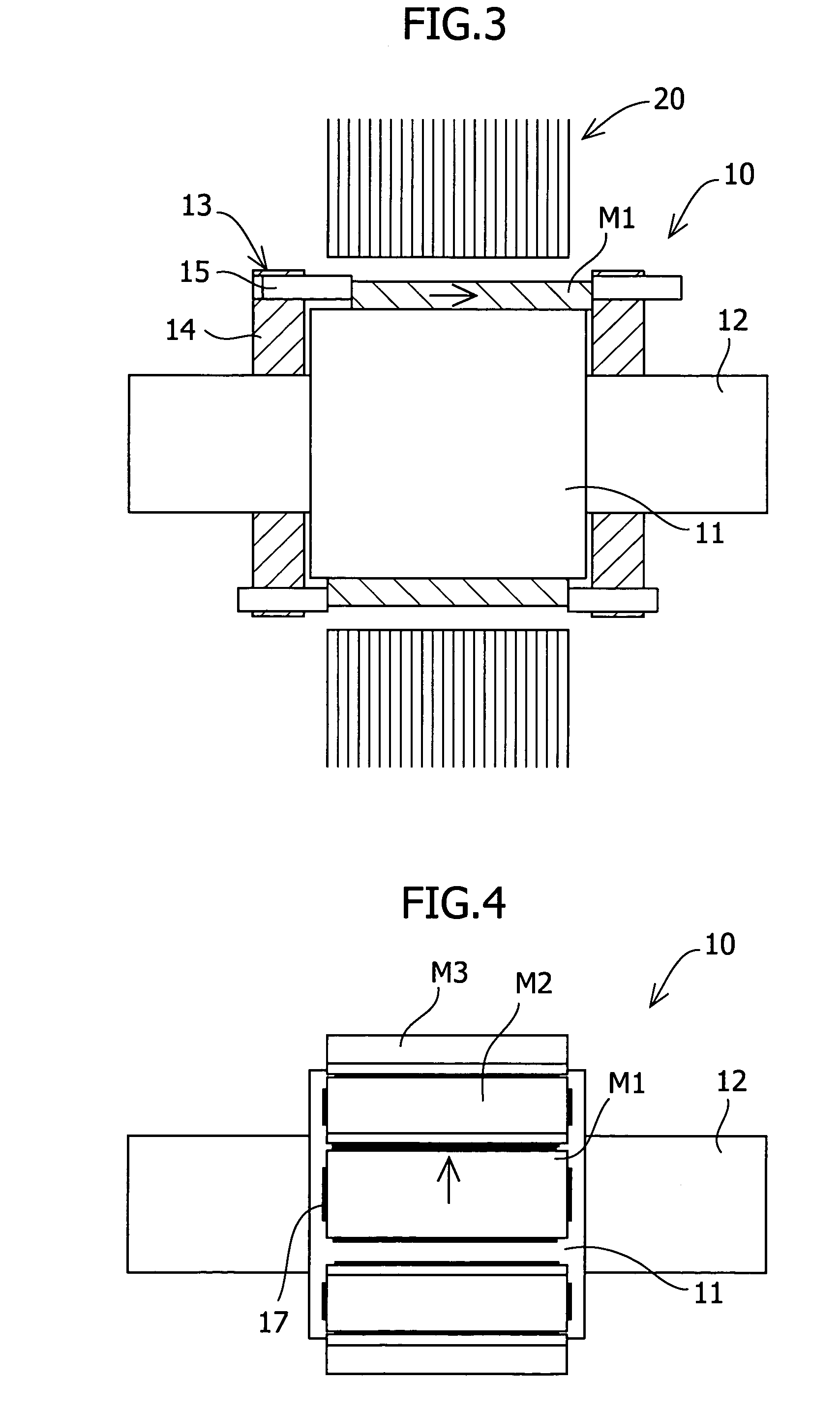
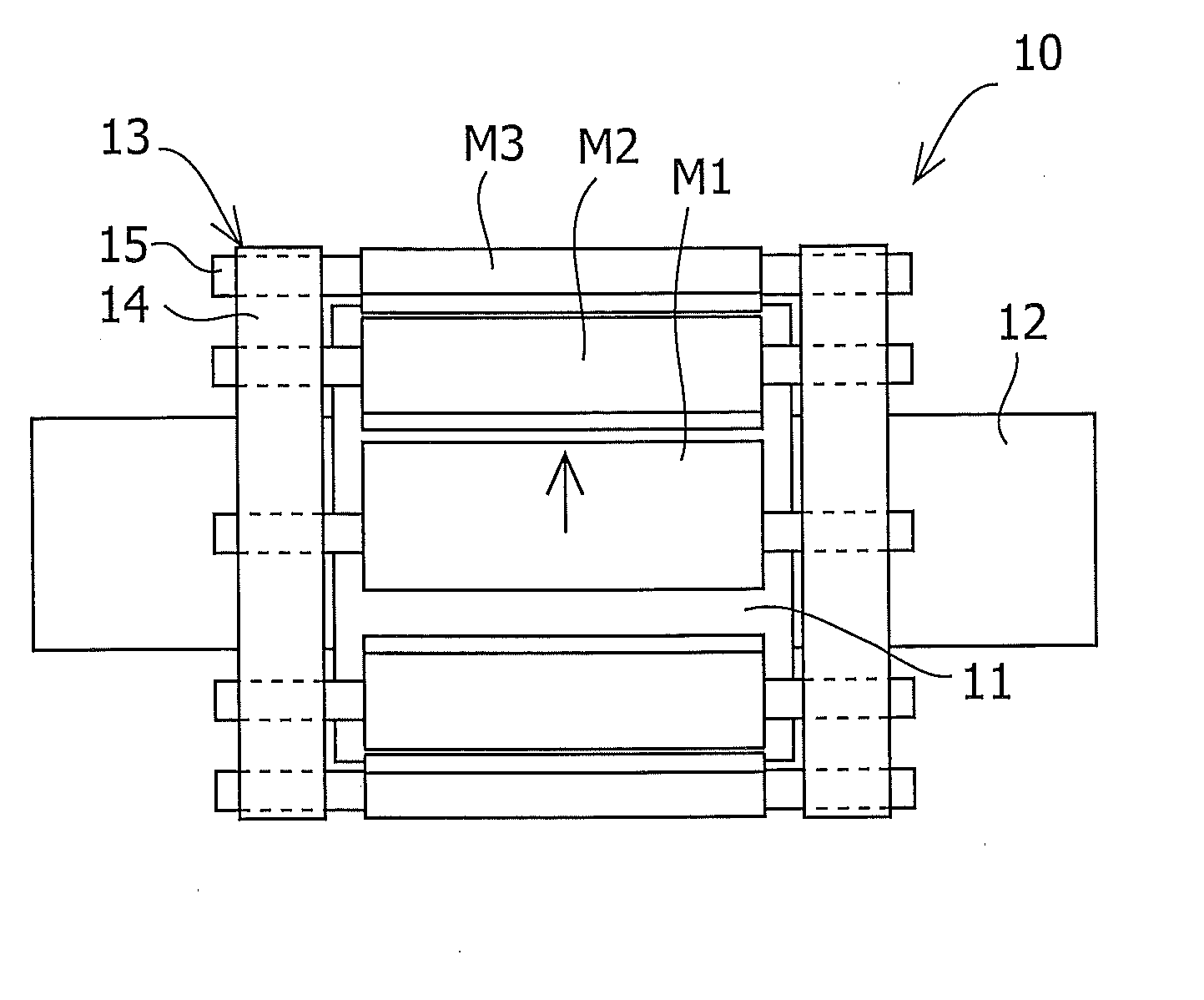
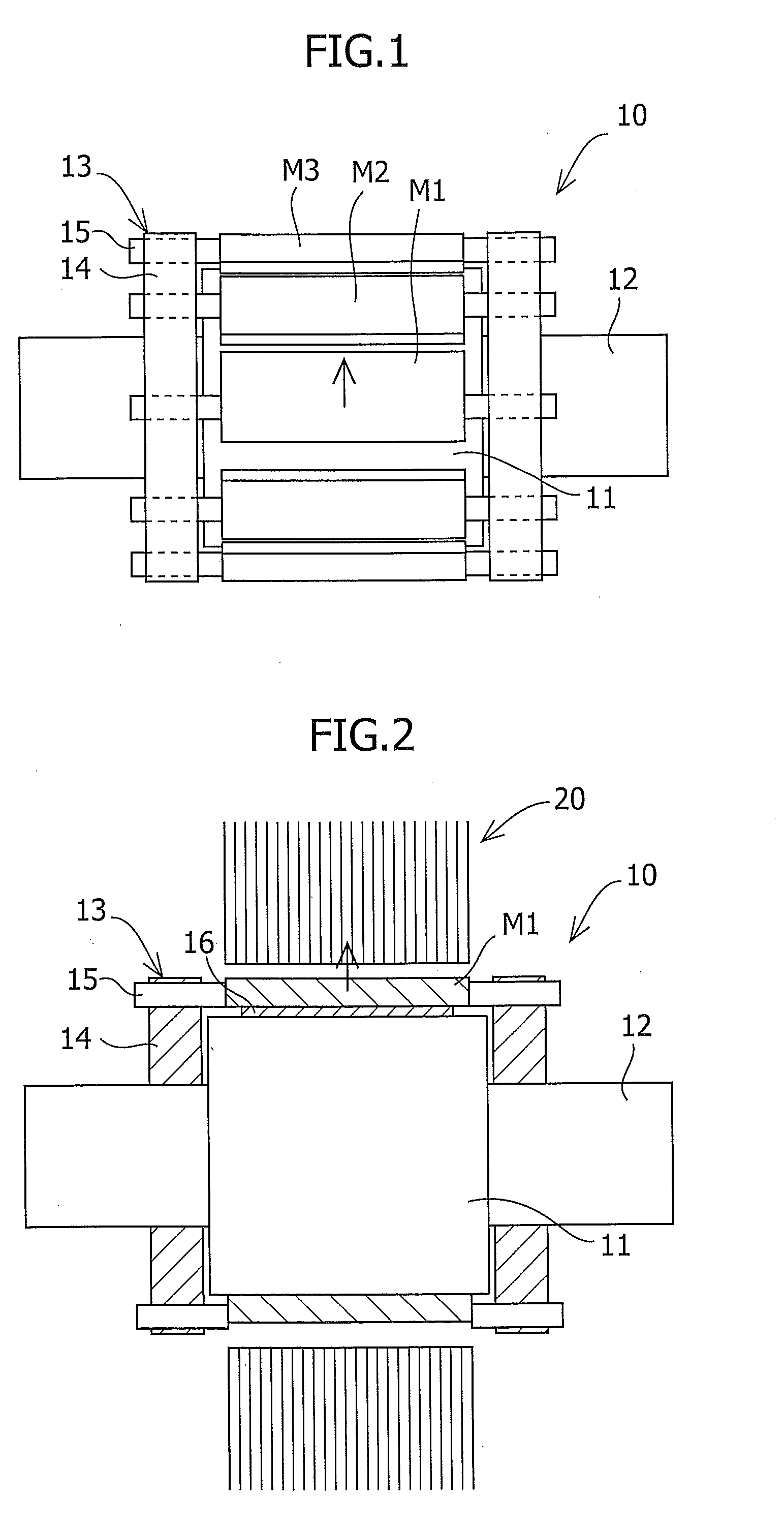
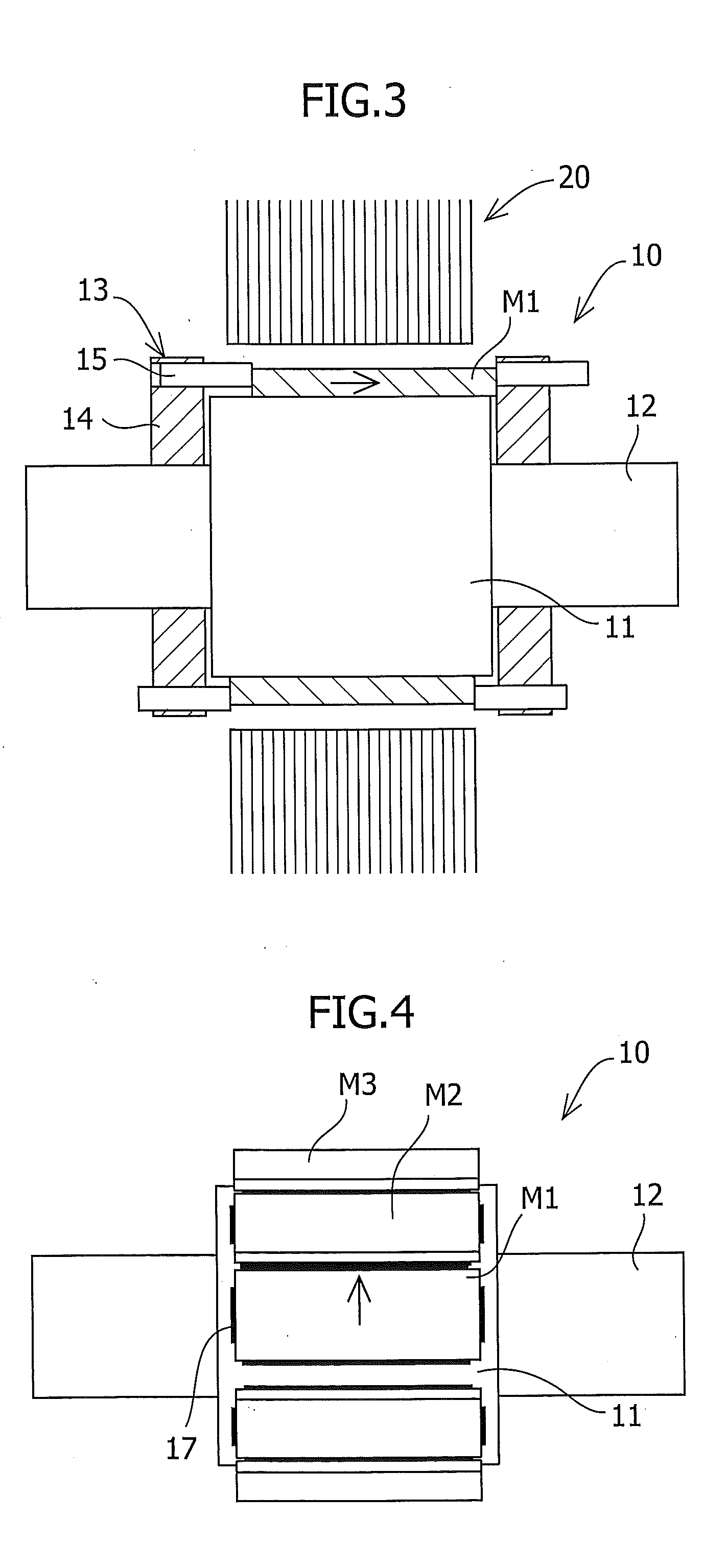
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Permanent magnet rotary structure of electric machine
InactiveUS20080157619A1Reduce the cogging torqueMagnetic circuitSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor is provided. The permanent magnet motor includes a stator having a stator shaft having an outer surface, K salient teeth formed upon the outer surface, and K winding slots formed among the K salient teeth, and a rotor having a first inner surface facing the outer surface, and P pairs of permanent magnets formed on the first inner surface, each of which has a second inner surface facing the outer surface and at least a groove formed on the second inner surface to reduce a cogging torque.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
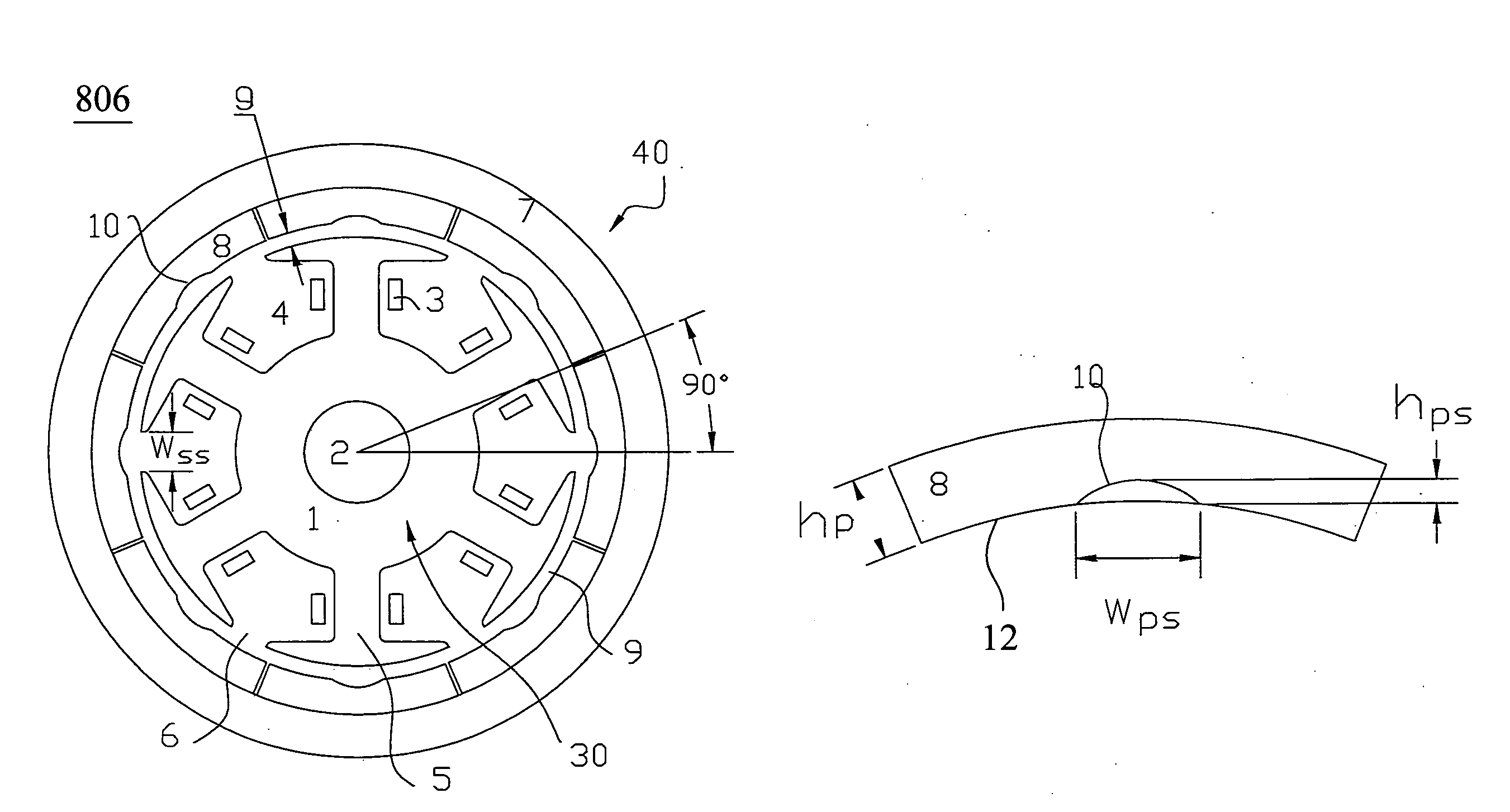
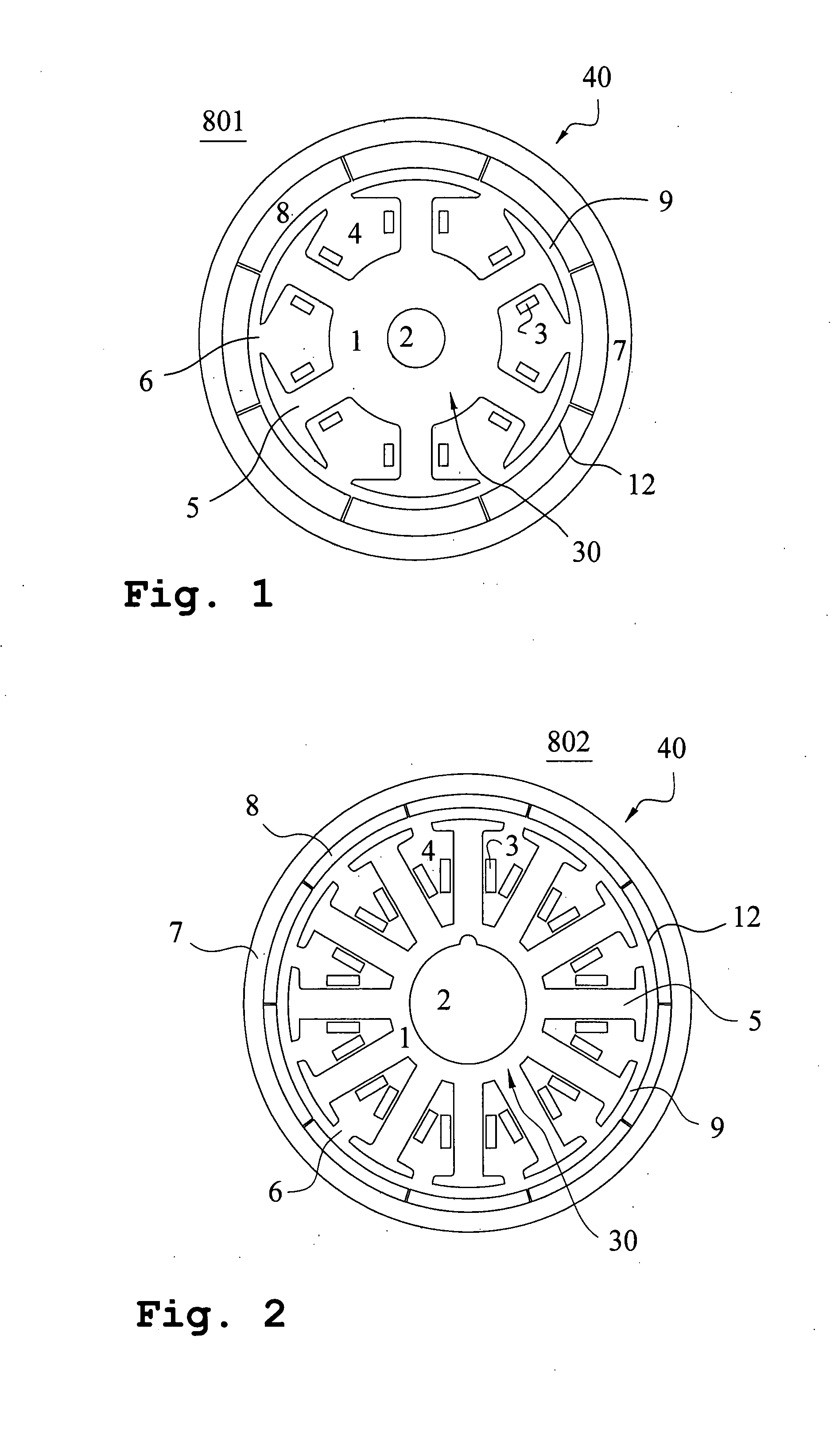
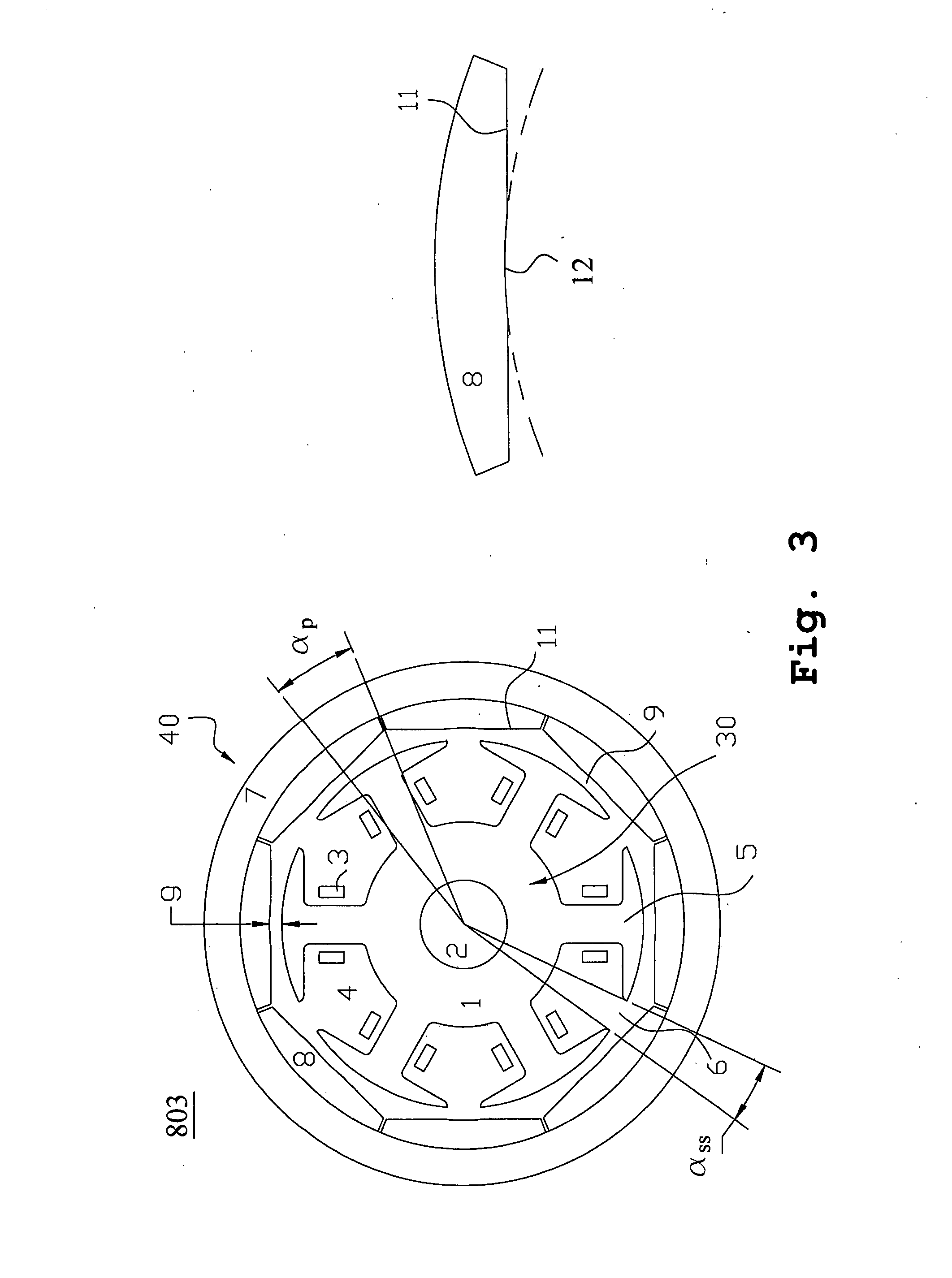
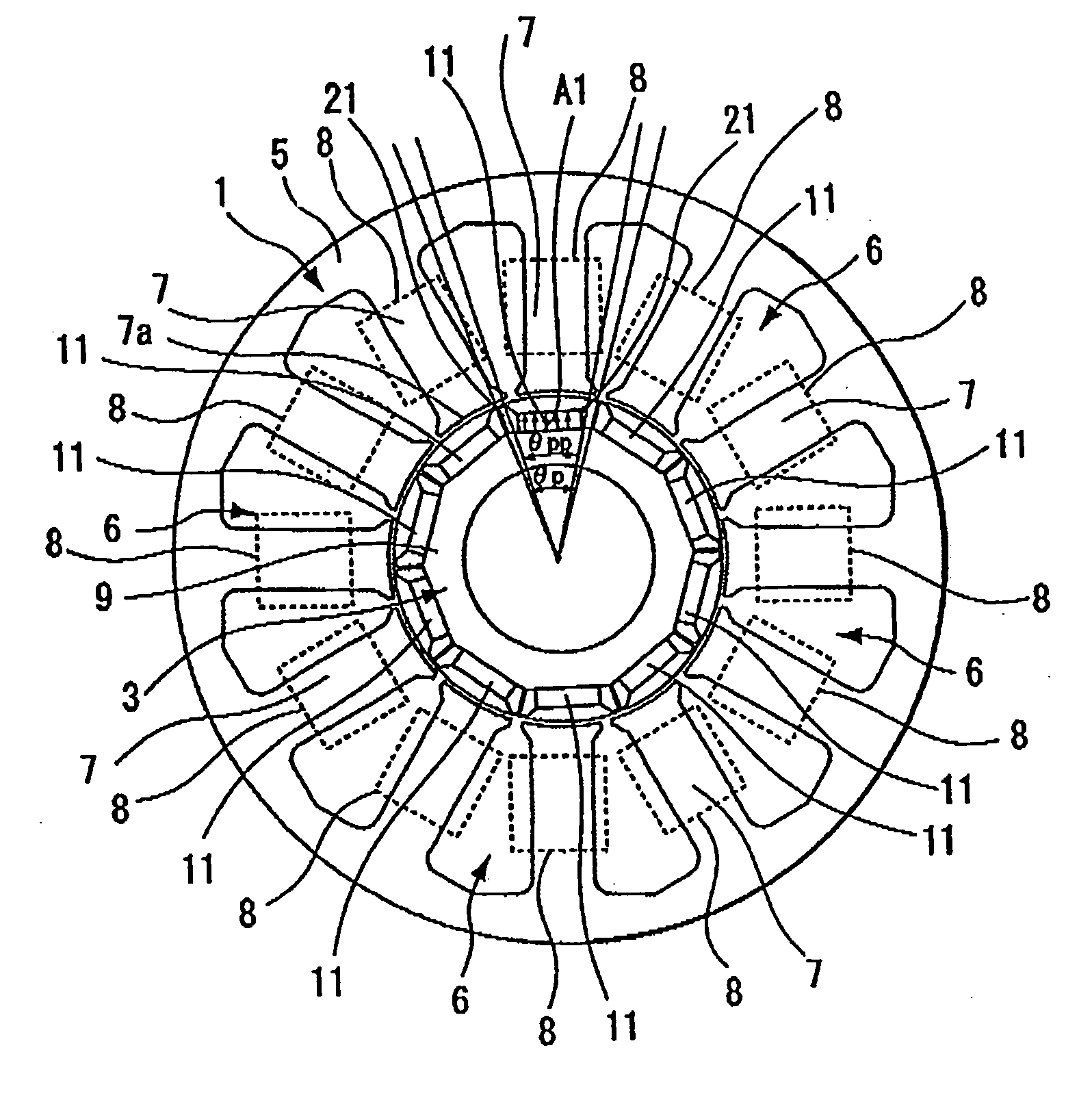
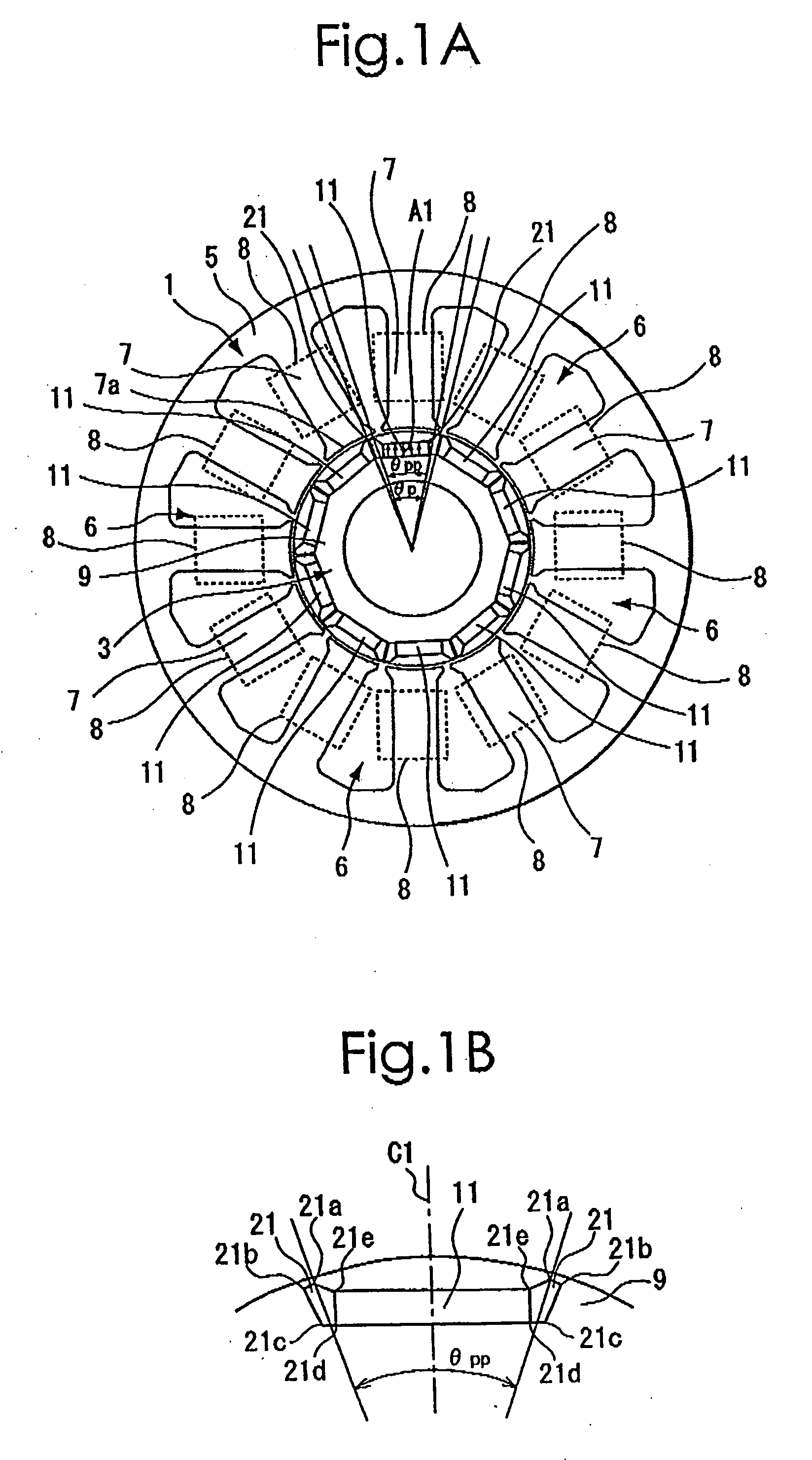
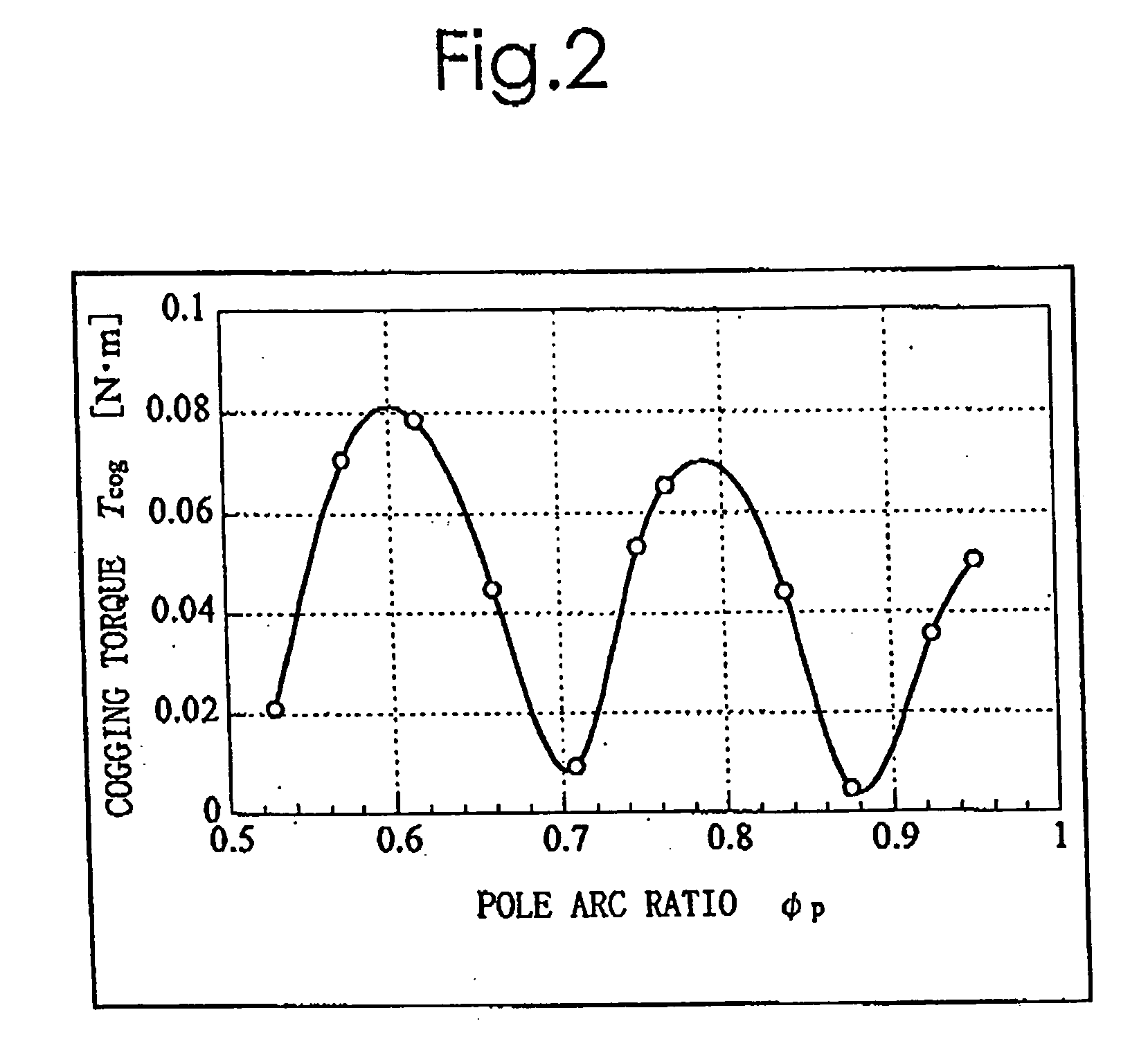
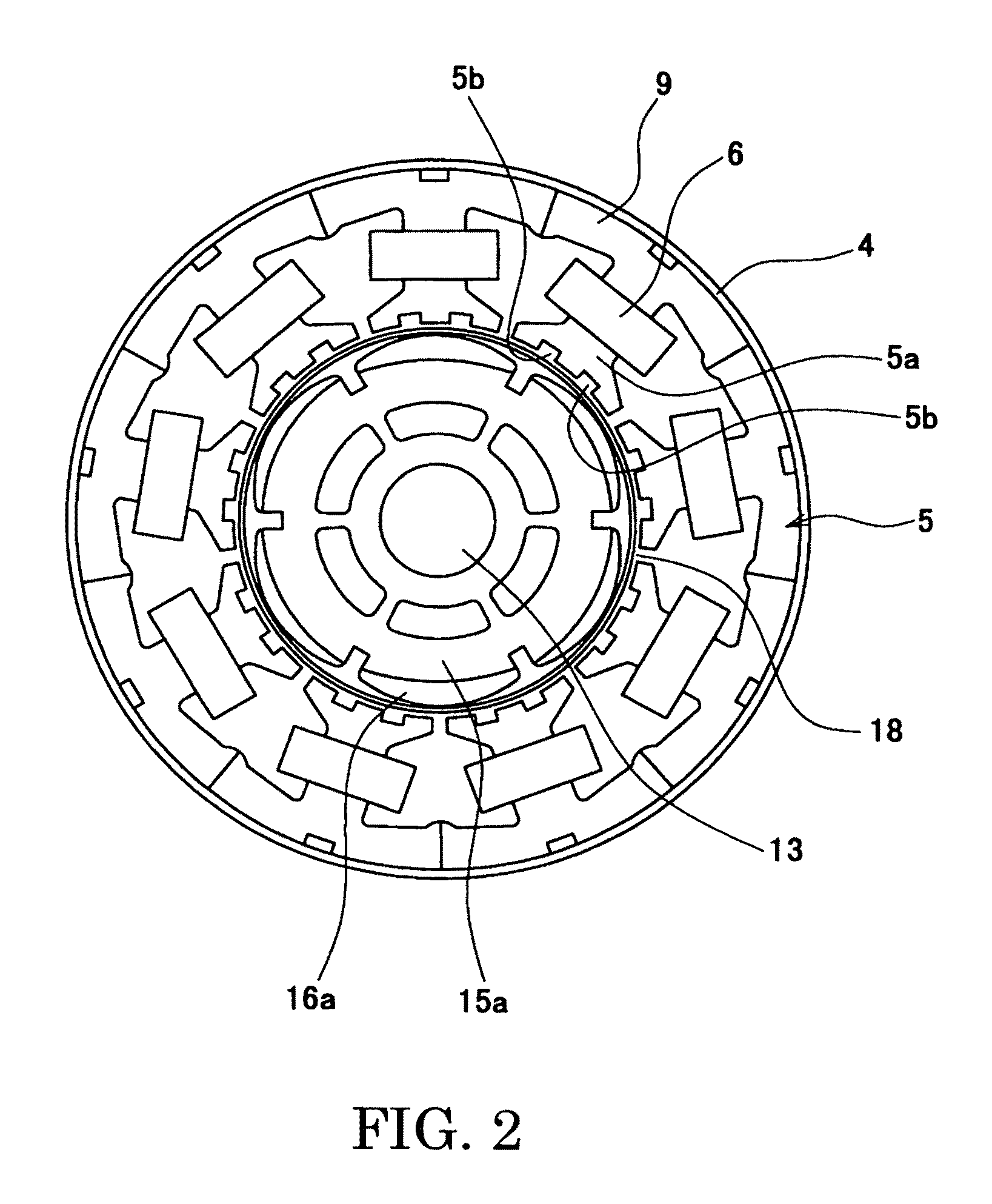
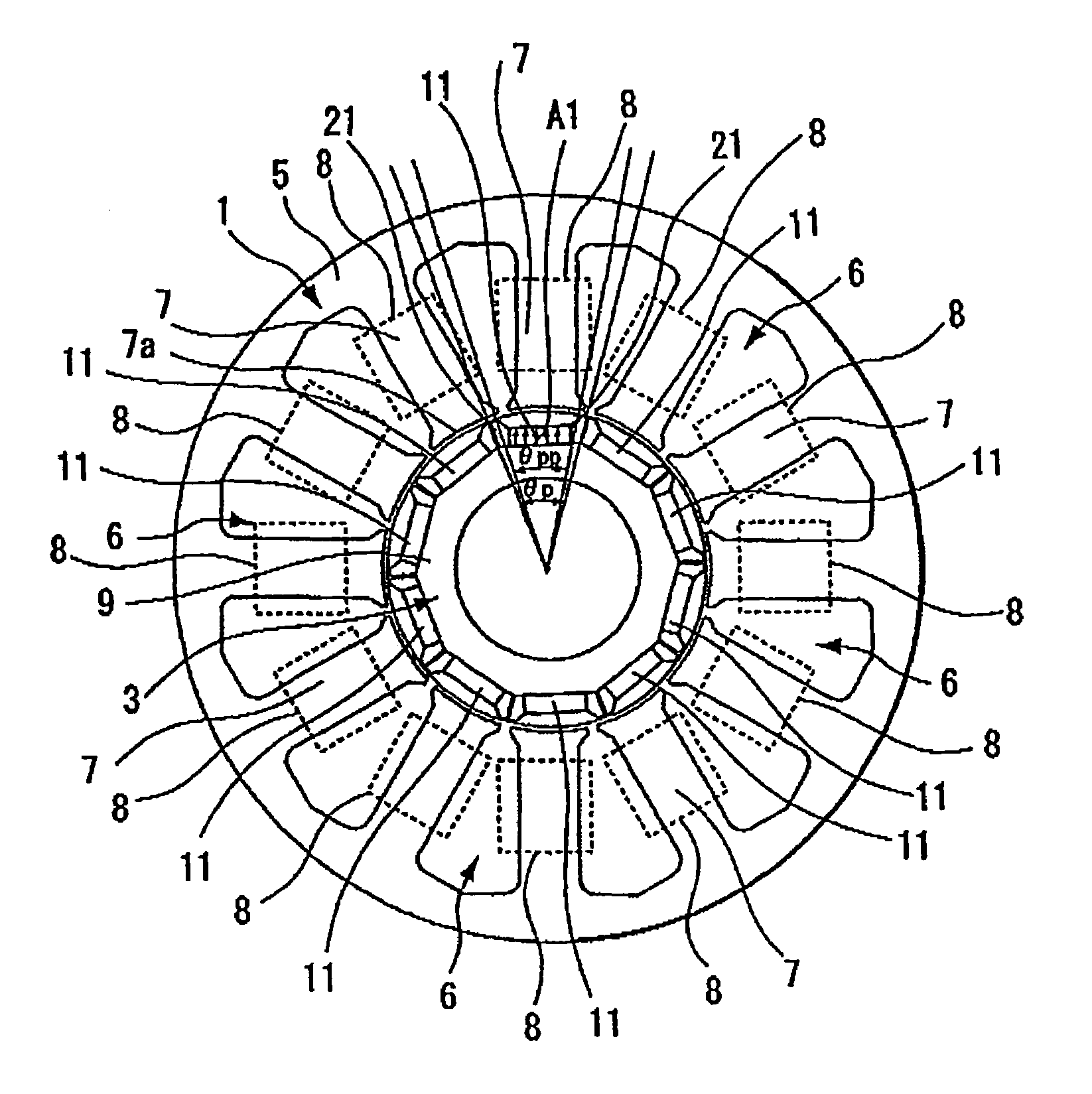
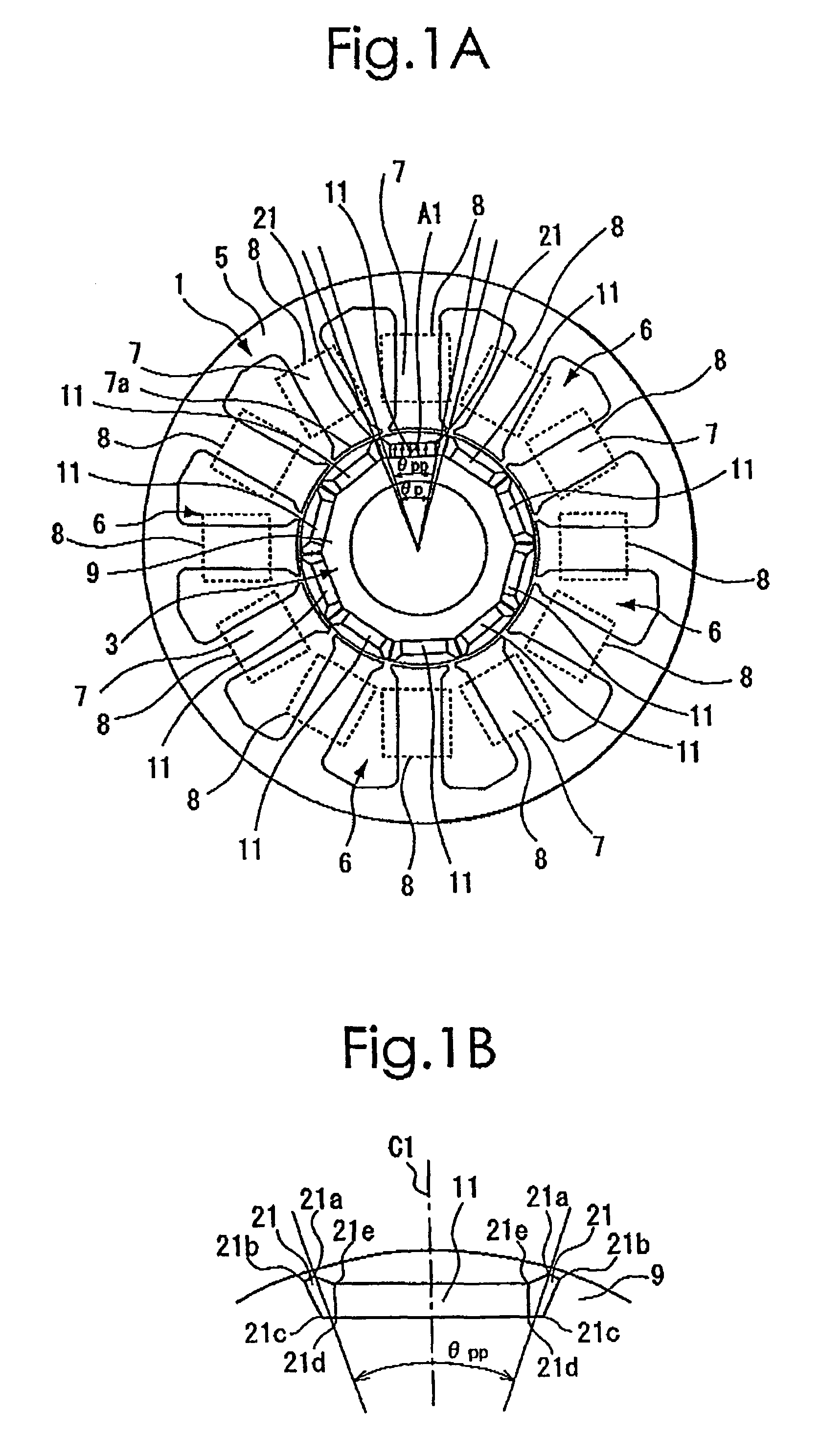
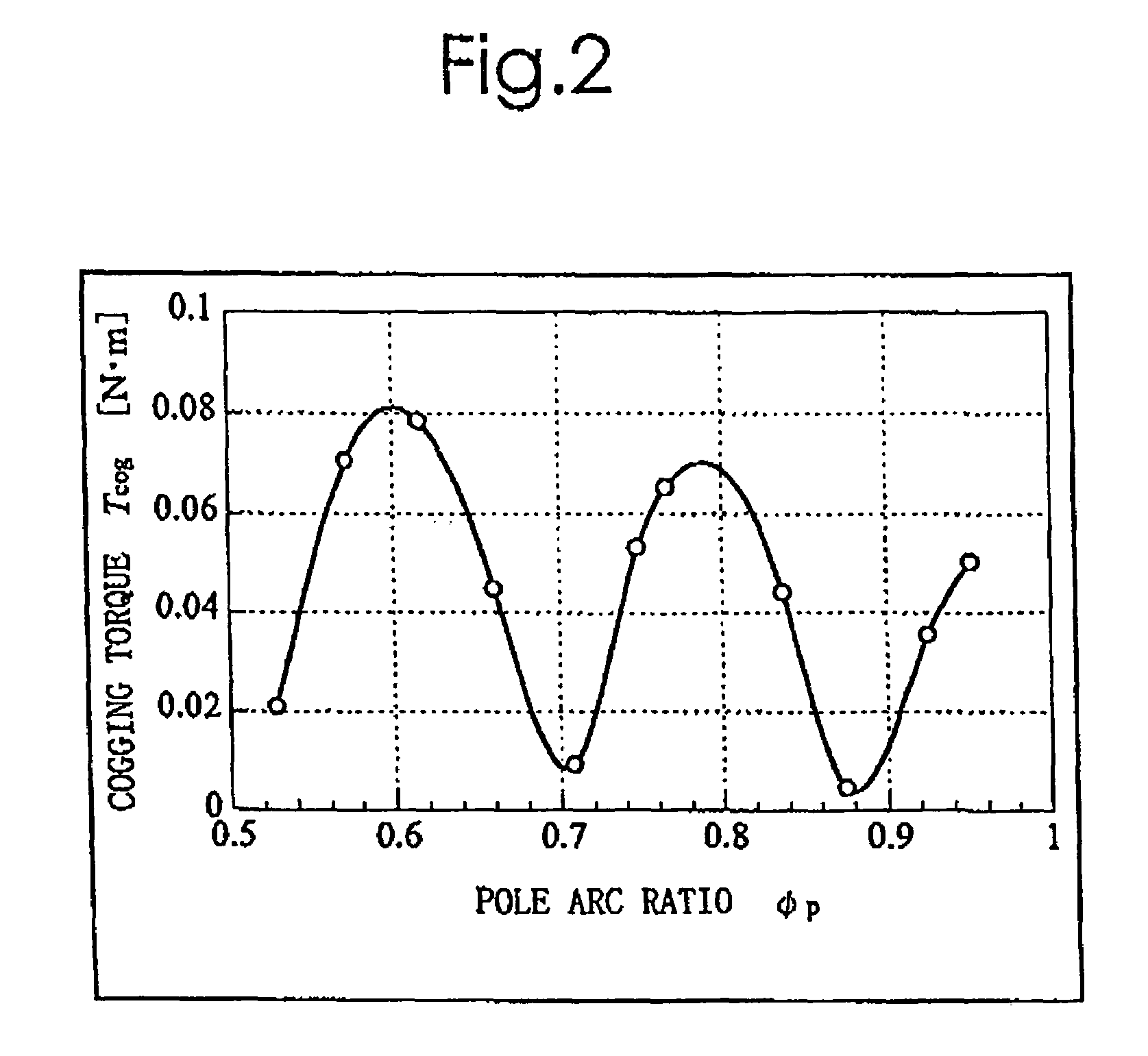
Method of determining pole arc ratio of interior permanent magnet rotary motor and interior permanent magnet rotary motor
InactiveUS20050168089A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic polesControl theory
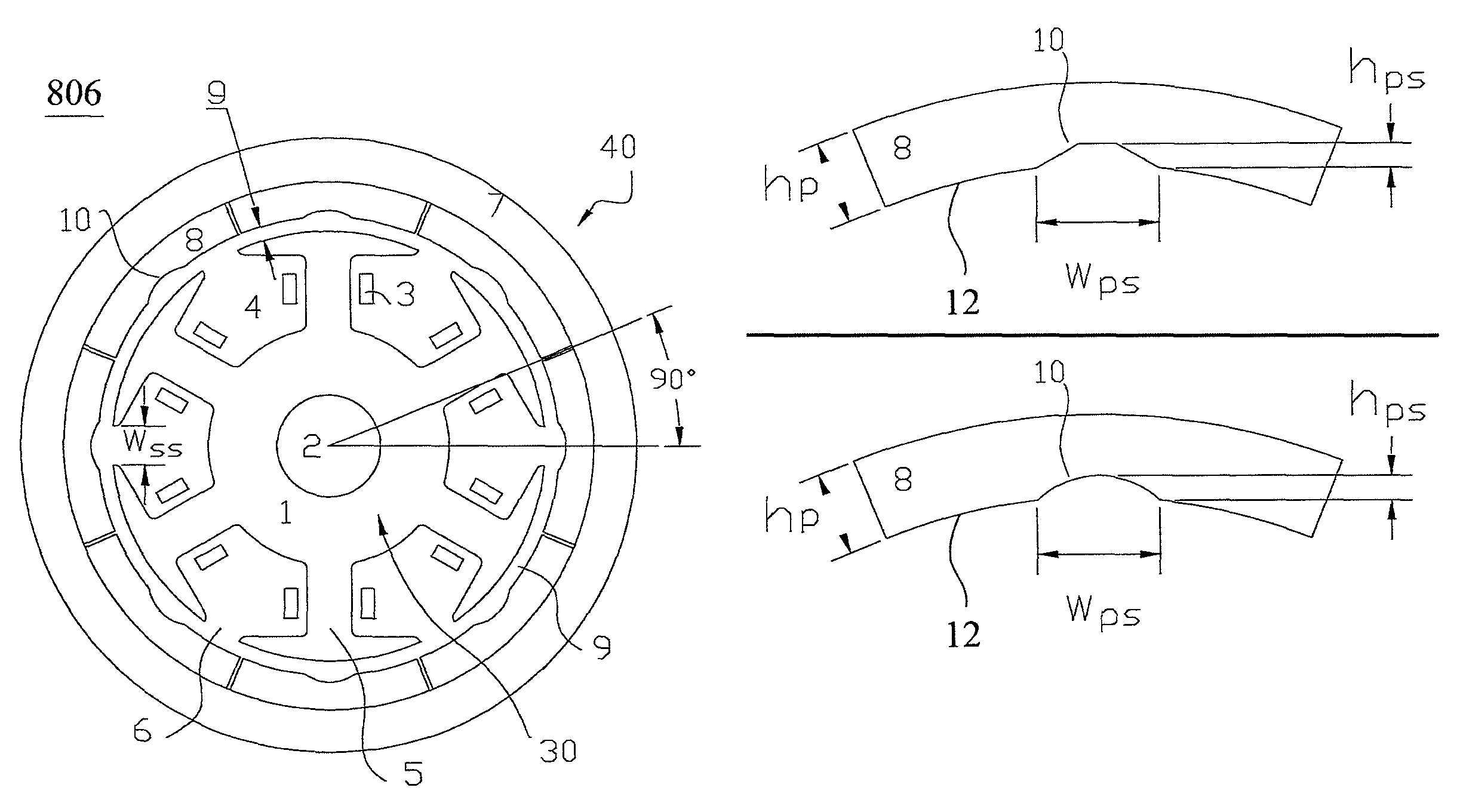
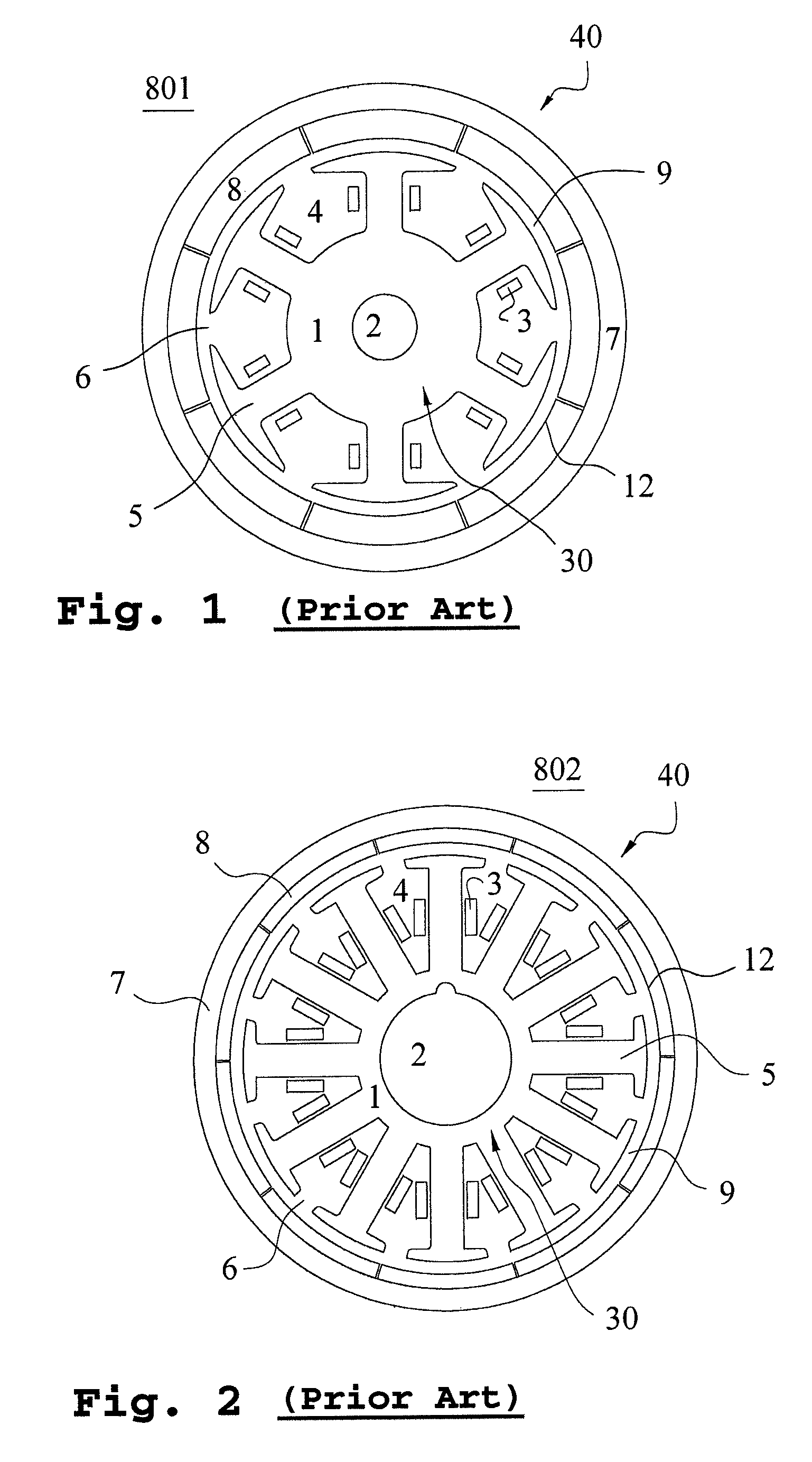
There is provided an interior permanent magnet rotary motor that can reduce cogging torque and can also reduce the amount of permanent magnet used, without reducing torque. In an interior permanent magnet rotary motor of the present invention having N slots 6 and P permanent magnet magnetic pole sections 11, in which P / N is set in the range of ⅔ to 43 / 45 and Po in a irreducible fraction Po / No of the P / N is set to be an odd number, an pole arc ratio ψp is defined to be the ratio of θpp / θp where an angle between two line segments assumed for a pair of flux barriers 21, each of which connects the center of a rotor core and one of a plurality of corners of the section of each flux barrier that is closest to the surface of the rotor core 9 is indicated by the θpp and an angle obtained by dividing the full circumference angle (360°) of the rotor core by the number of the permanent magnet pole sections is indicated by the θp. Then, the pole arc ratio indicated by Ψp is determined is so as to satisfy the relation of Ψp=2mP / N+P / 4LCM (P, N)−2n, in which LCM (P, N) is the least common multiple between P and N, m and n are arbitrary natural numbers, and the Ψp is larger than zero but smaller than one.
Owner:SANYO DENKI CO LTD
Motor and motor manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050229384A1Reduce the cogging torqueEliminate dependenciesManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionMagnetic anisotropyManufactured apparatus
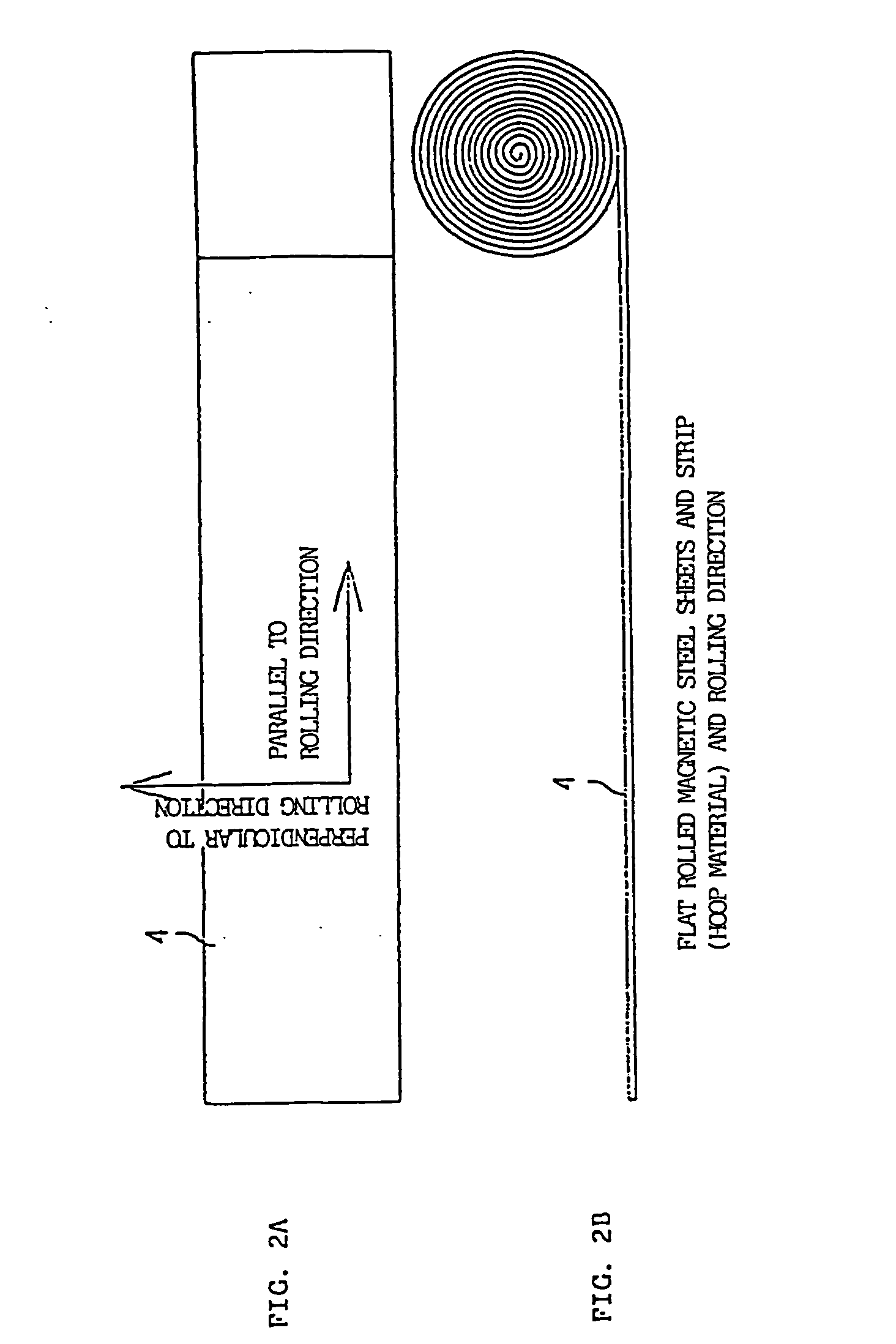
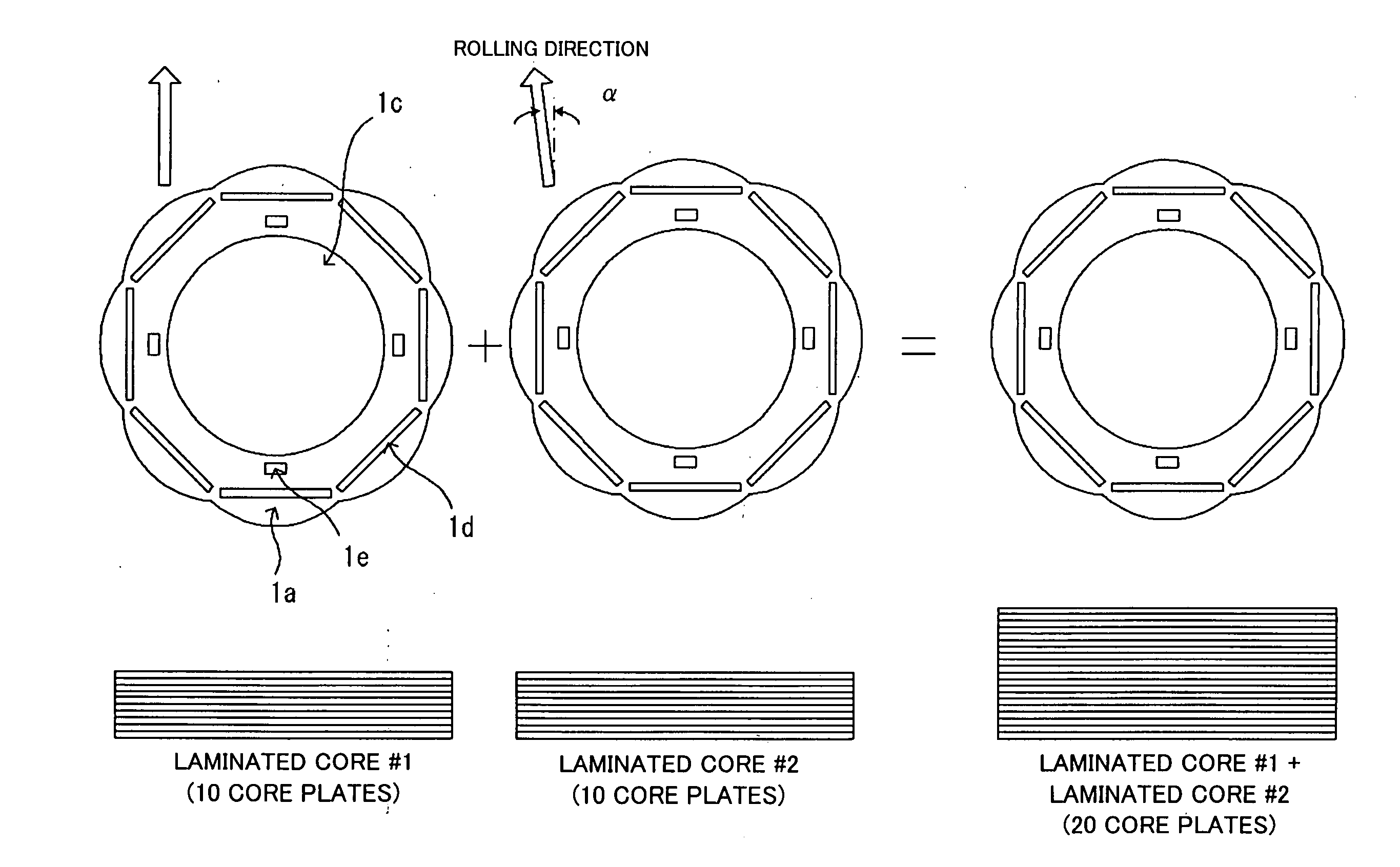
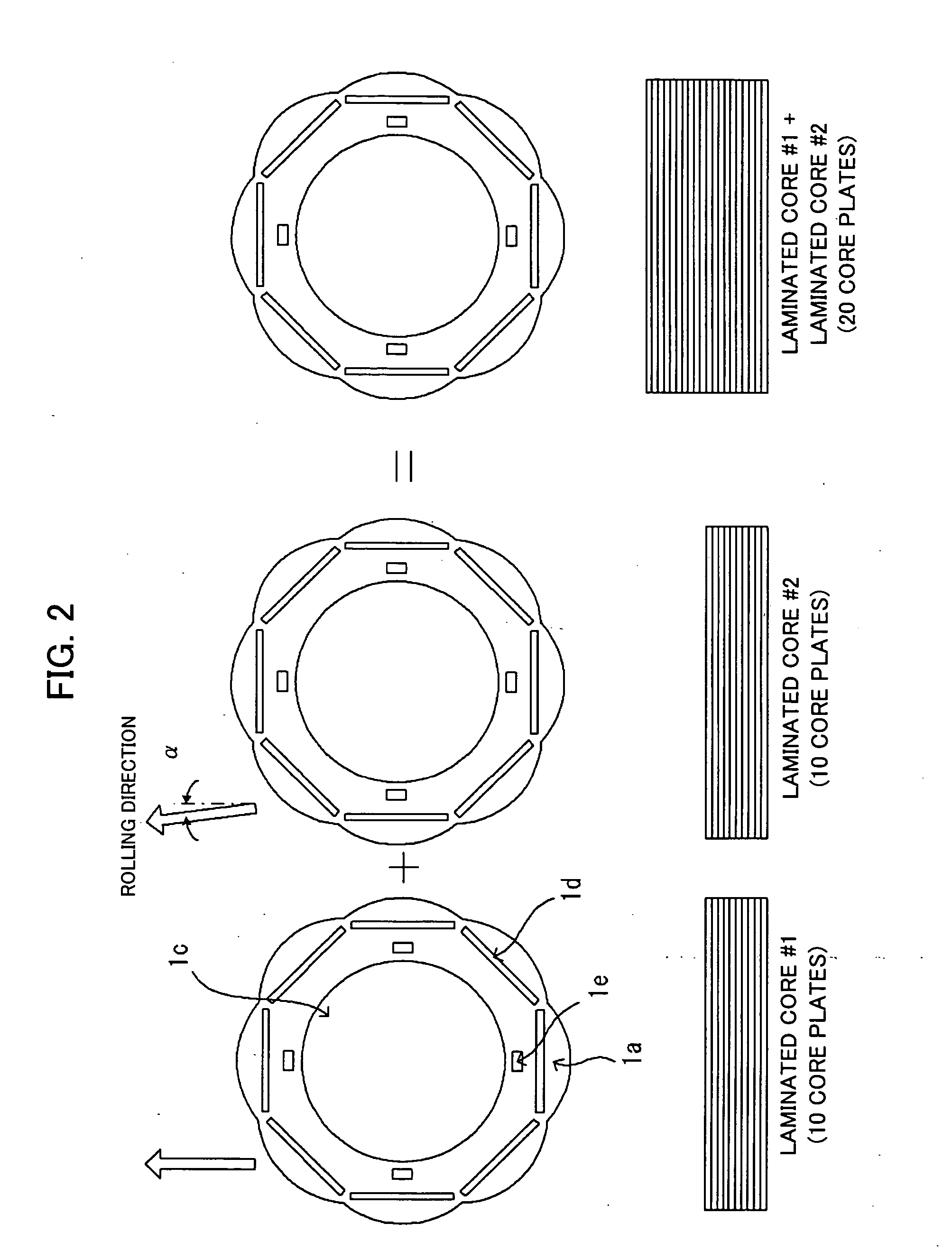
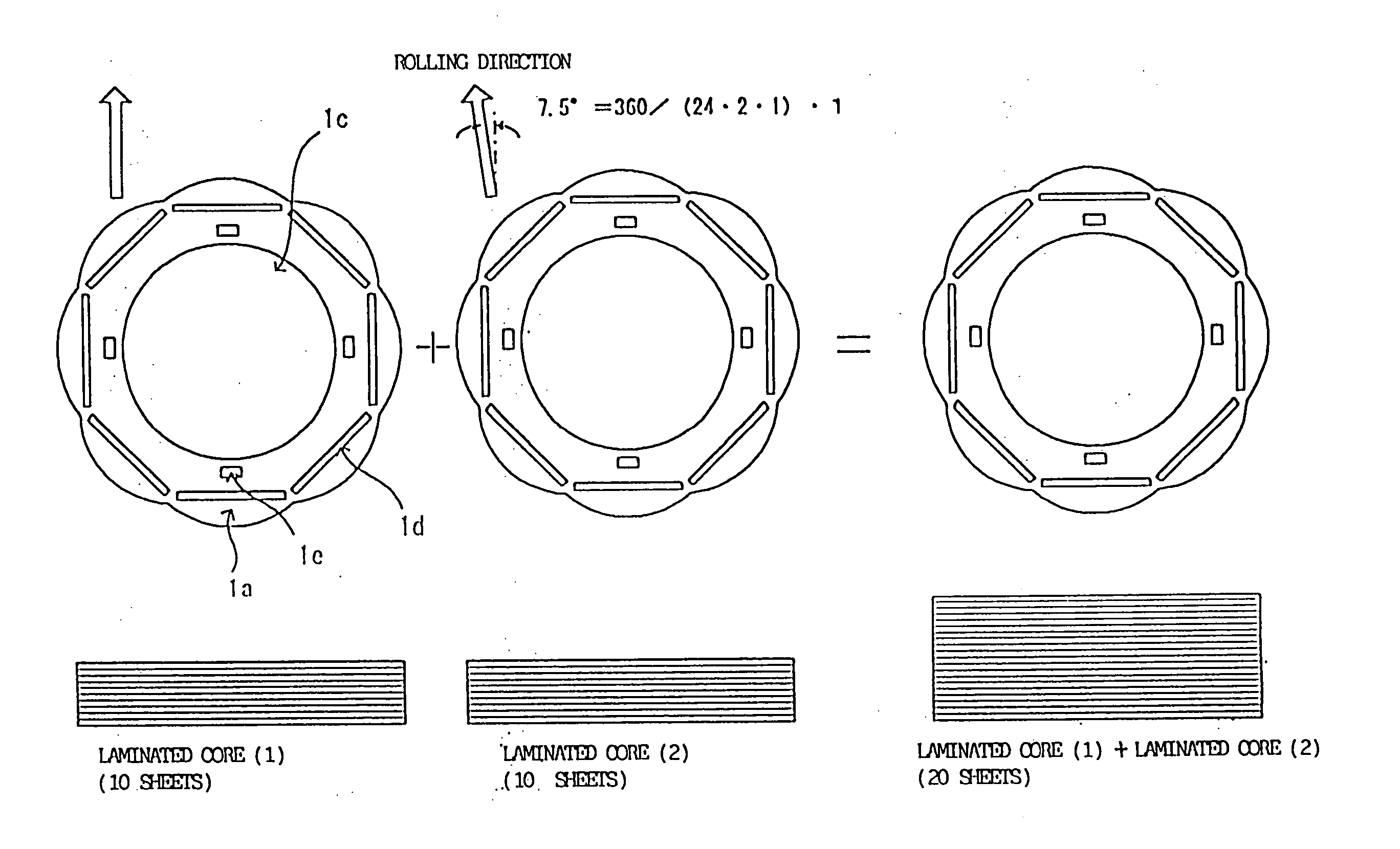
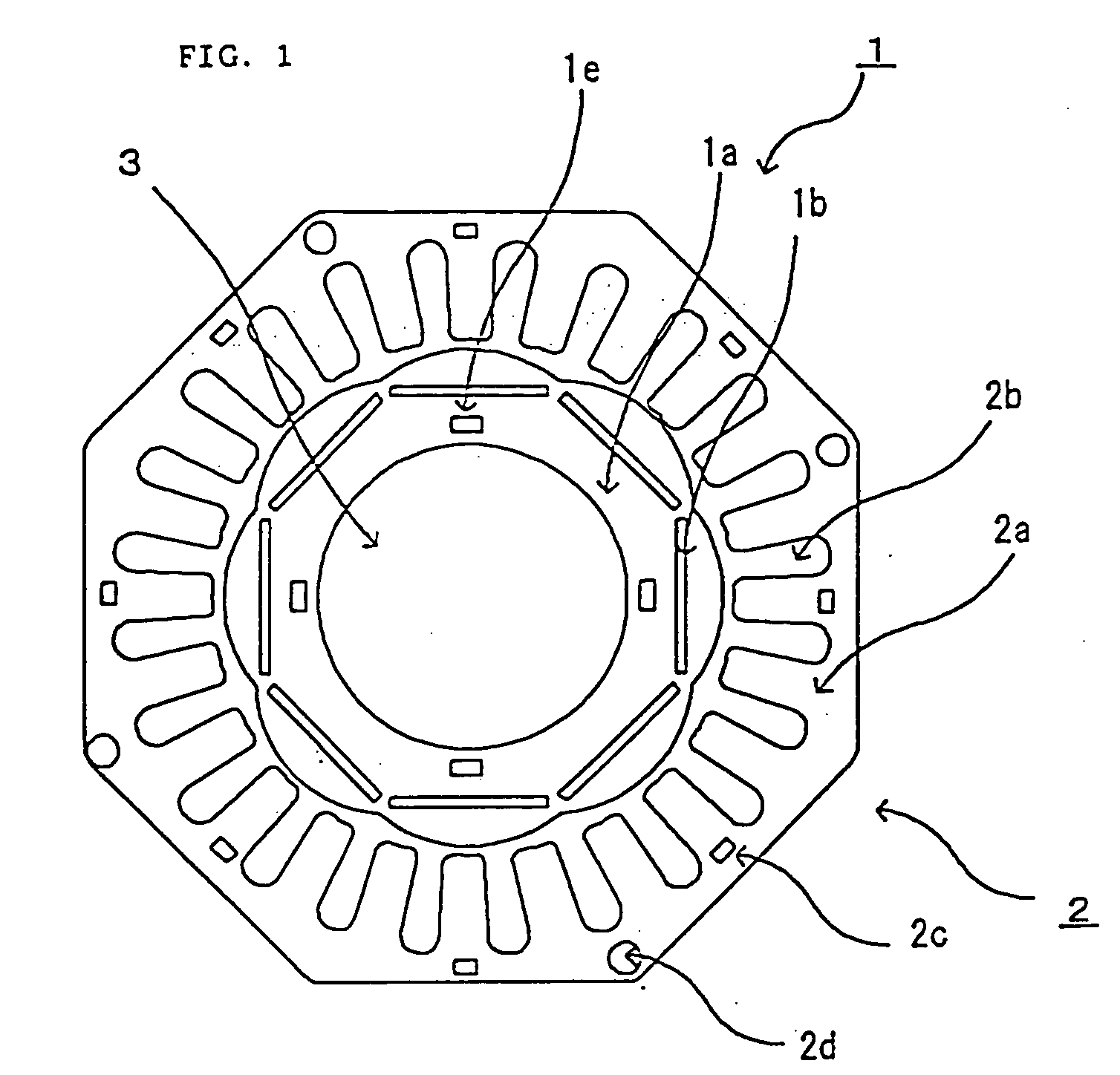
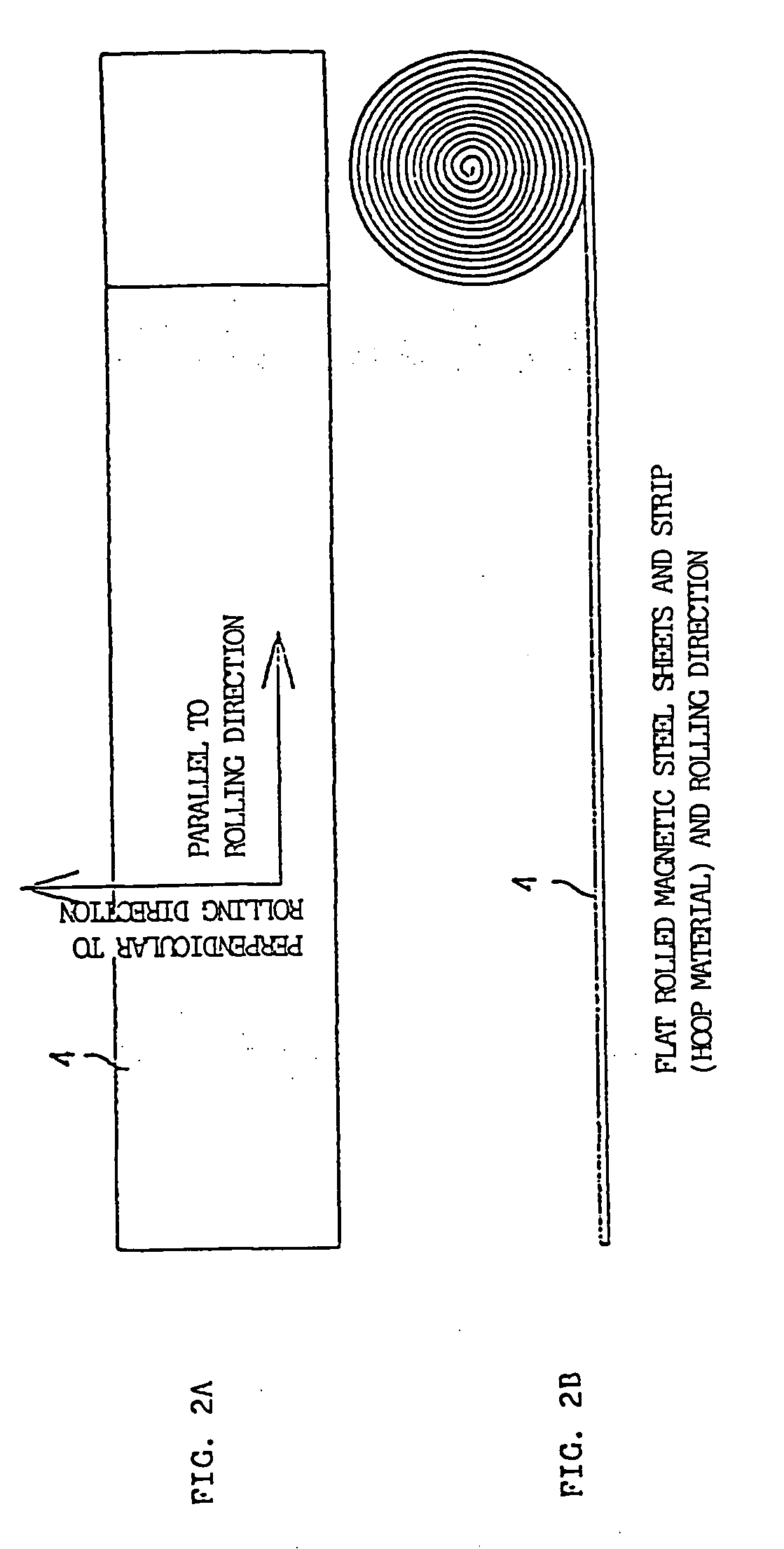
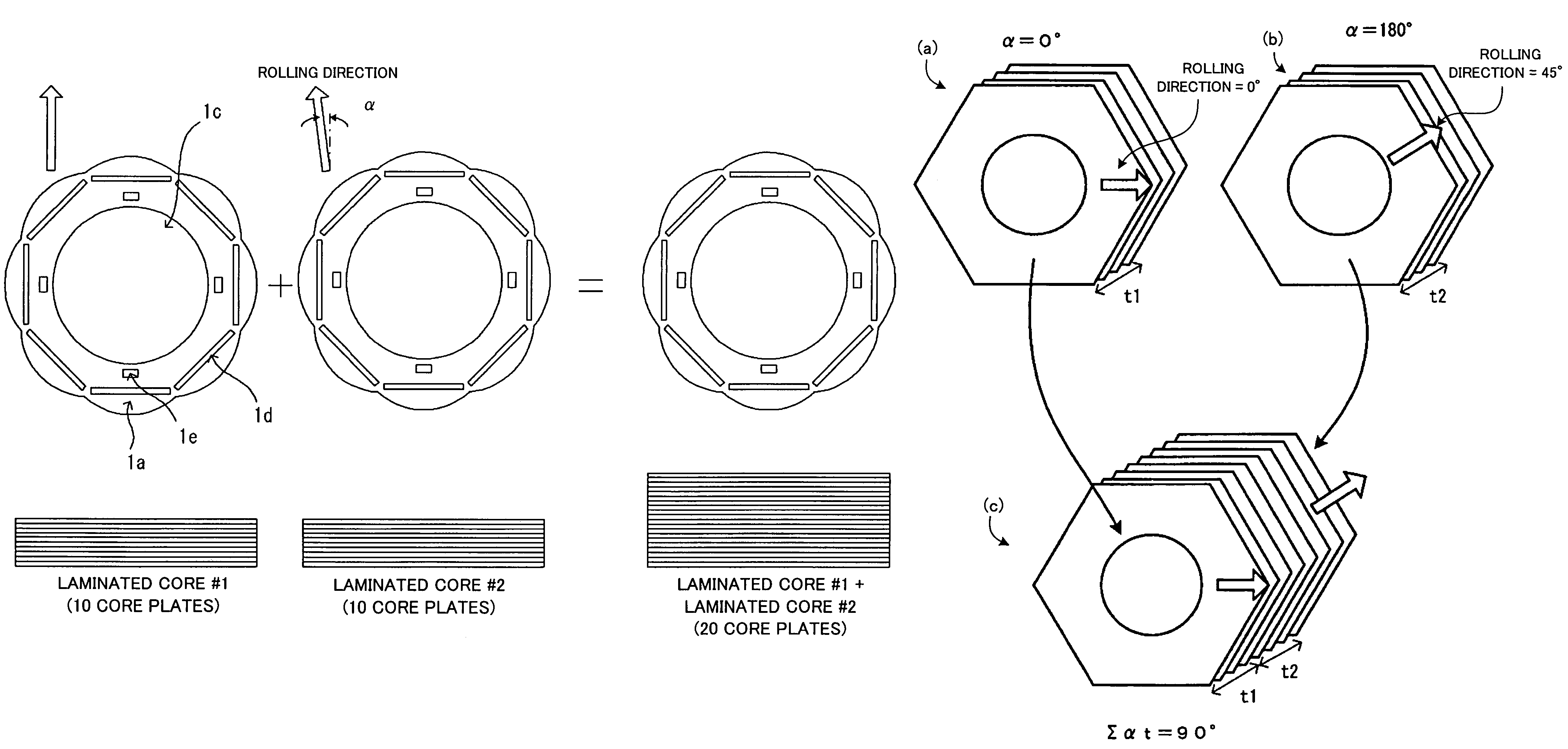
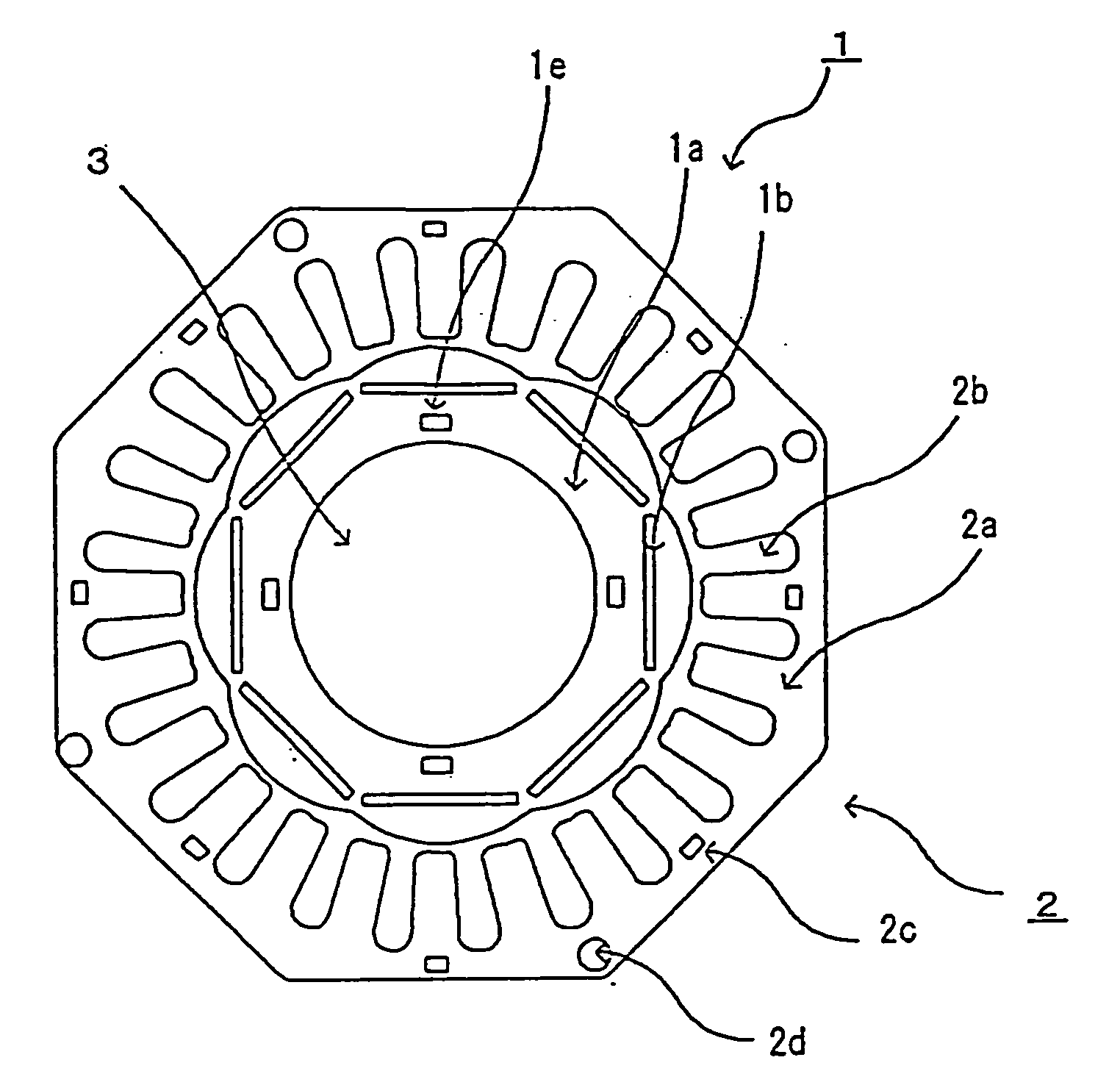
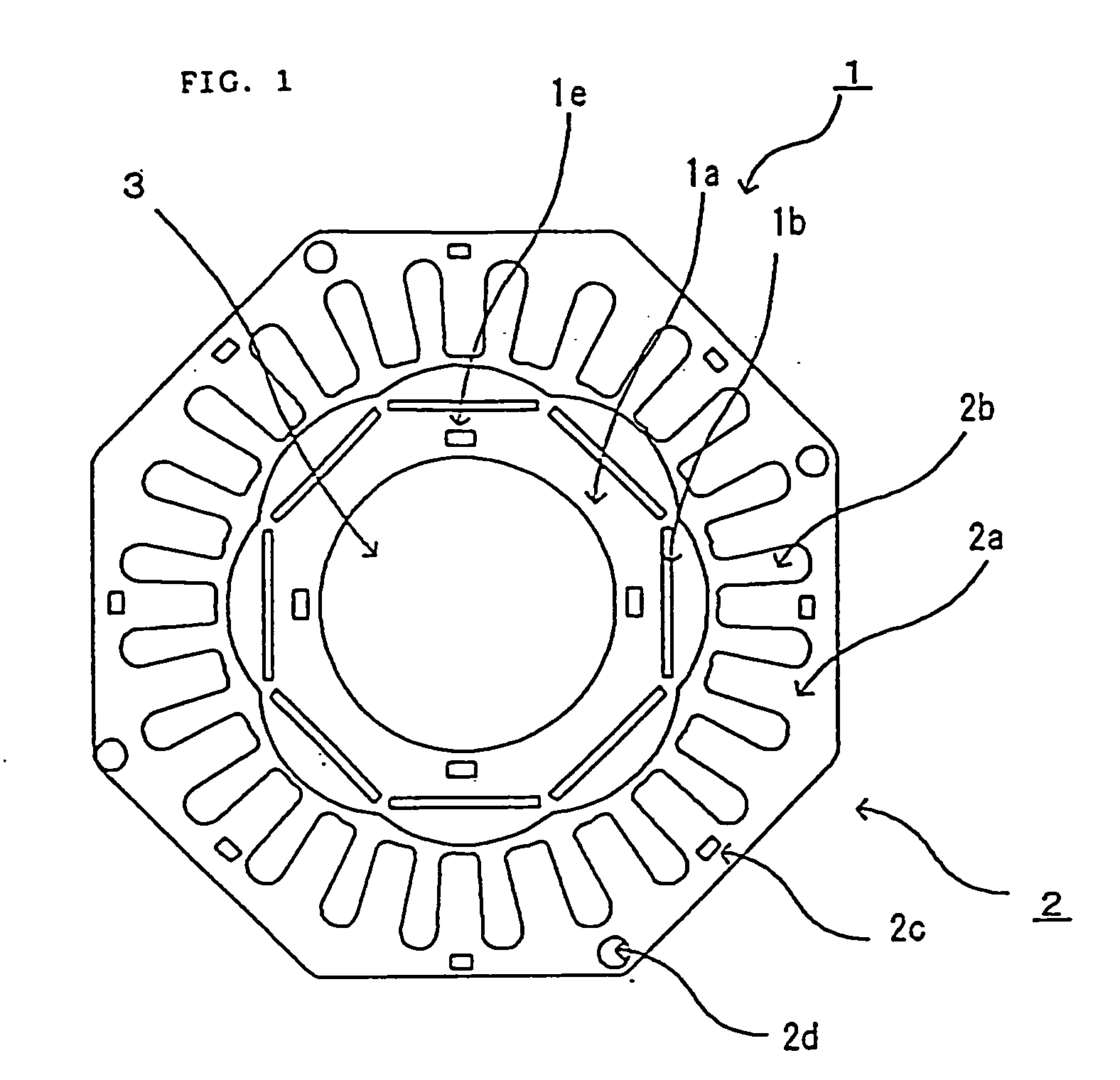
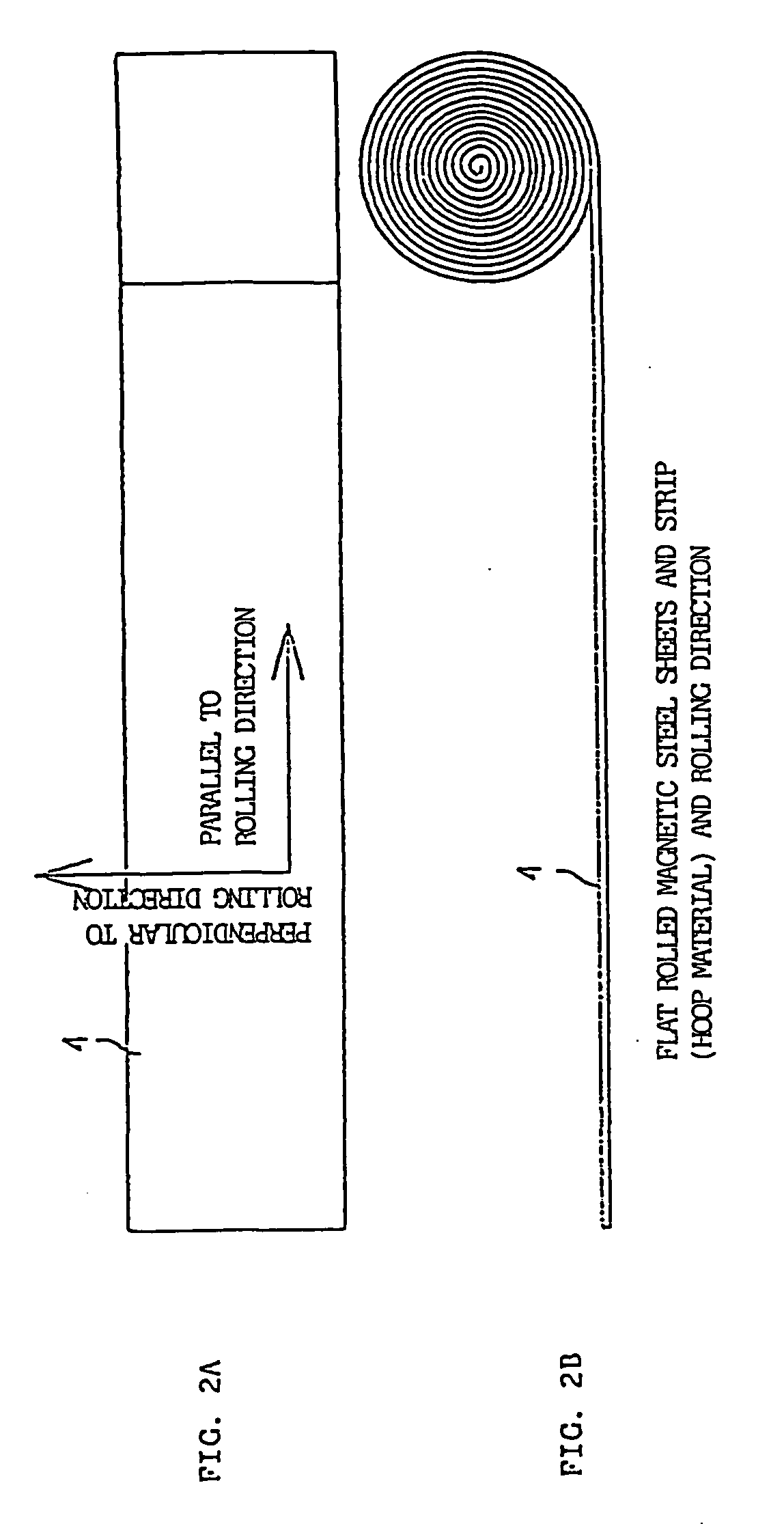
Flat rolled magnetic steel sheets and strip or a die is turned in the press forming process. Rotor cores are stacked with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple of about (360° / (number of slots in the motor×natural number n×2)) and stator cores are stacked with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple of (360° / (number of poles in the motor×natural number n×2)). Stacking with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple converts the phases of cogging torques into mutually opposite phases and cancels and reduces the cogging torque caused by magnetic anisotropy.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Rotor assembly for an electrical machine and permanent magnet motor comprising such a rotor assembly
InactiveUS6927519B2Low cogging torqueEasy to changeMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet motorEngineering
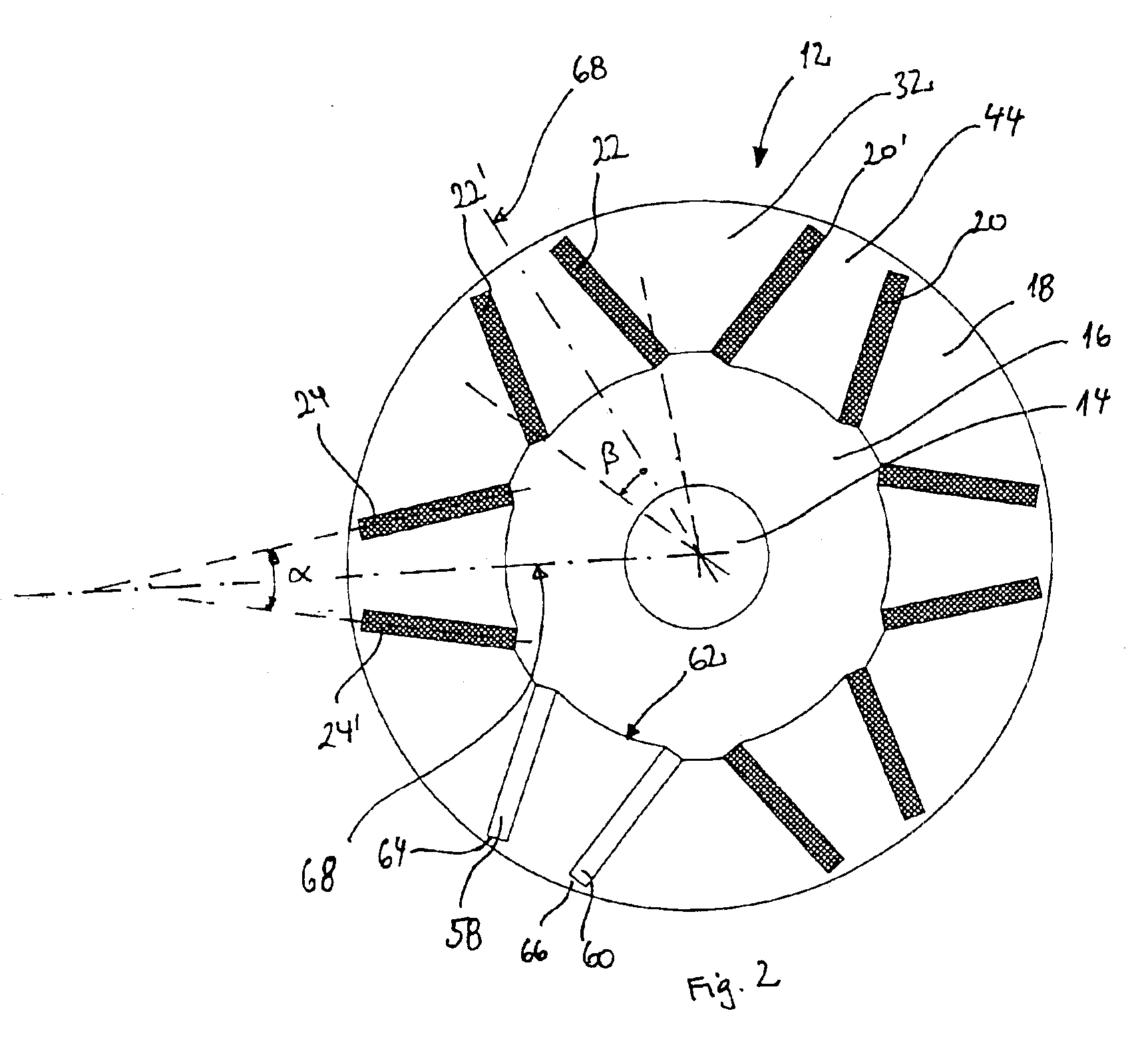
Rotor assembly for an electrical machine, wherein a body of generally cylindrical shape having an inner opening for coaxially mounting the body on a shaft, permanent magnets embedded in said body, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is split in at least two magnet sections which extend from about the inner opening towards the outer periphery of the body and are inclined towards a plane, which extends in a radial direction of the body.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Electric motor and apparatus for manufacturing electric motor
ActiveUS20060163967A1Long processEfficient punchingMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsMagnetic anisotropySheet steel
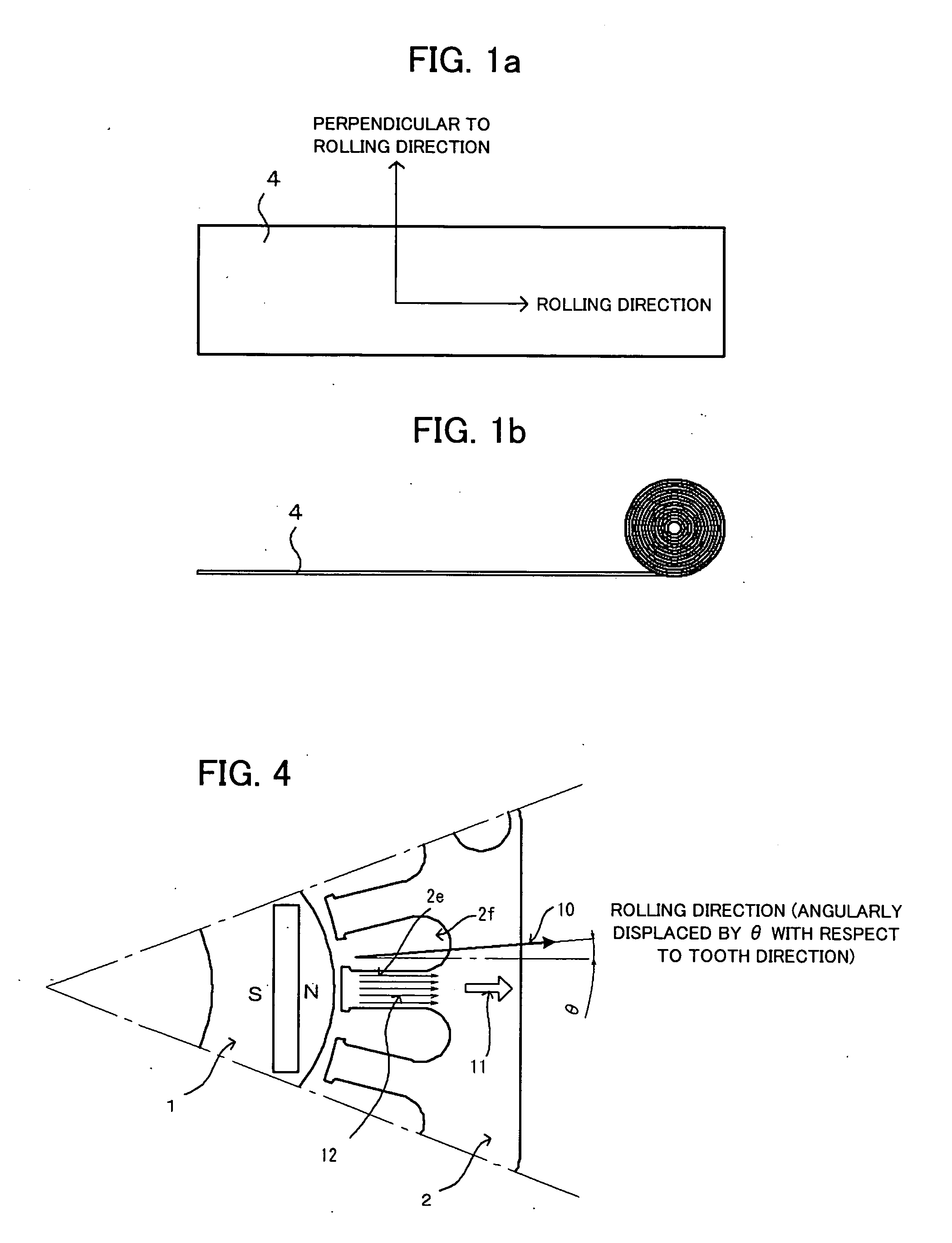
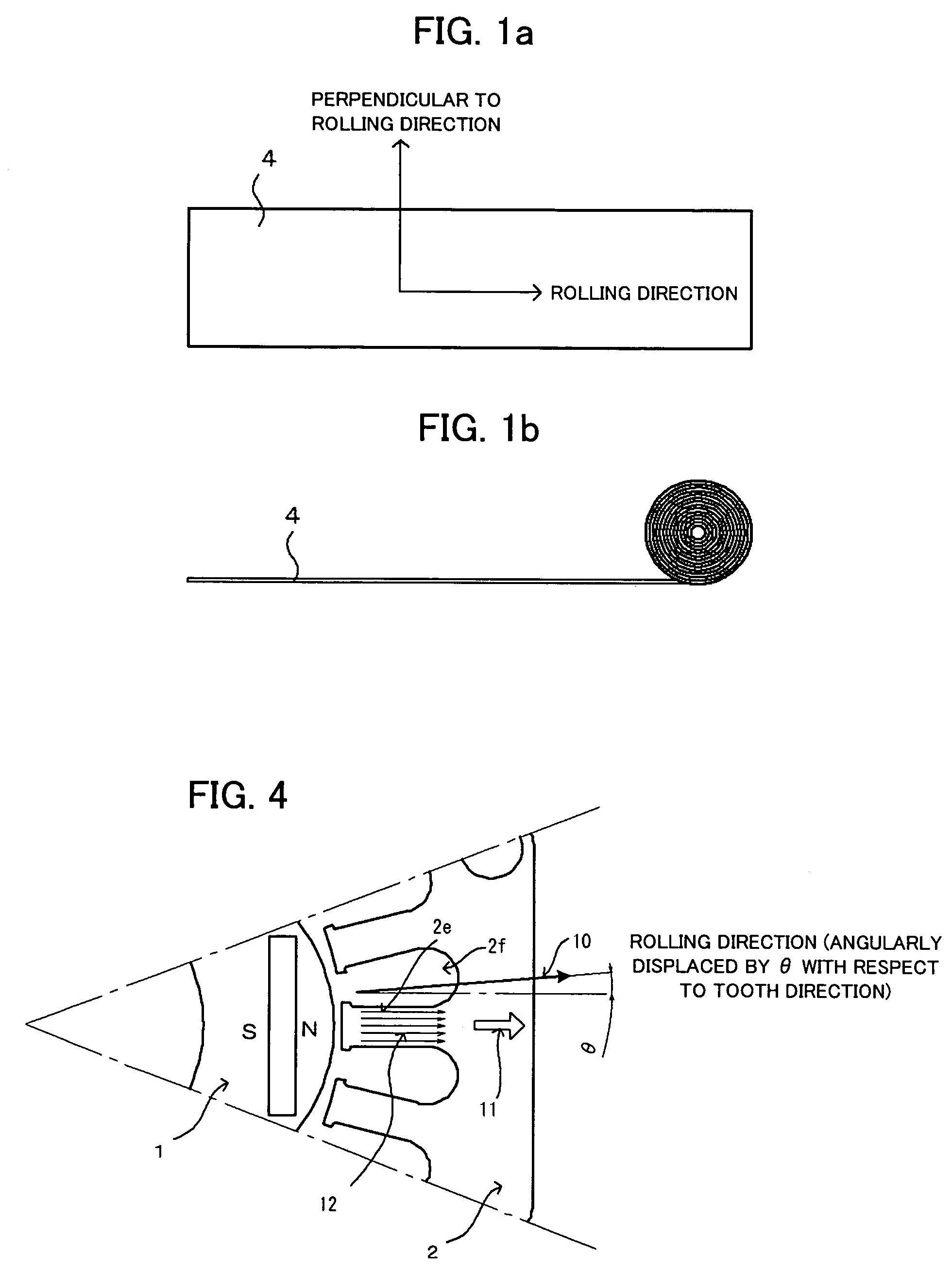
A motor capable of reducing cogging torque depending on teeth of a stator, and a motor manufacturing apparatus for manufacturing this motor. The angles of rolling directions of cores stacked are set so that the phase difference between the phases of cogging torques produced on the cores is 180° so that the cogging torques produced on the cores cancel each other to reduce the total cogging torque in the motor. The motor comprises a laminated core formed by stacking a plurality of cores made from a rolled electromagnetic sheet steel. The cores forming the laminated core have rolling directions different from each other by a specified machine angle determined depending on the number of slots and / or the number of poles, where the specified machine angle is an angle which produces a phase difference of 180° between the phases of cogging torques produced due to magnetic anisotropy of the cores and the arrangement of teeth depending on the number of slots and / or poles of the motor.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Motor and motor manufacturing apparatus
ActiveUS20050023925A1Reduce cogging torqueReduce the cogging torqueDC motor speed/torque controlMagnetic circuitMagnetic anisotropyManufactured apparatus
Flat rolled magnetic steel sheets and strip or a die is turned in the press forming process. Rotor cores are stacked with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple of about (360° / (number of slots in the motor×natural number n×2)) and stator cores are stacked with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple of (360° / (number of poles in the motor×natural number n×2)). Stacking with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple converts the phases of cogging torques into mutually opposite phases and cancels and reduces the cogging torque caused by magnetic anisotropy.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Permanent magnet rotary structure of electric machine
InactiveUS7839045B2Reduce the cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSupports/enclosures/casingsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor is provided. The permanent magnet motor includes a stator having a stator shaft having an outer surface, K salient teeth formed upon the outer surface, and K winding slots formed among the K salient teeth, and a rotor having a first inner surface facing the outer surface, and P pairs of permanent magnets formed on the first inner surface, each of which has a second inner surface facing the outer surface and at least a groove formed on the second inner surface to reduce a cogging torque.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Split cores for motor stator, motor stator, permanent magnet type synchronous motor and punching method by split core punching die
ActiveUS8102092B2Improve rigidityImprove assembly accuracyManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionSynchronous motorPunching
Split cores comprising laminated iron cores each having formed thereon a tooth, and a yoke and a pole piece which are connected to the tooth at both ends thereof, and arranged and connected together into an annular shape to make a stator. Both ends of the yokes and both ends of the pole pieces are displaced in one circumferential direction by laminated iron core from a top laminated layer of the iron cores of the split cores to a bottom laminated layer of the iron cores or split cores.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
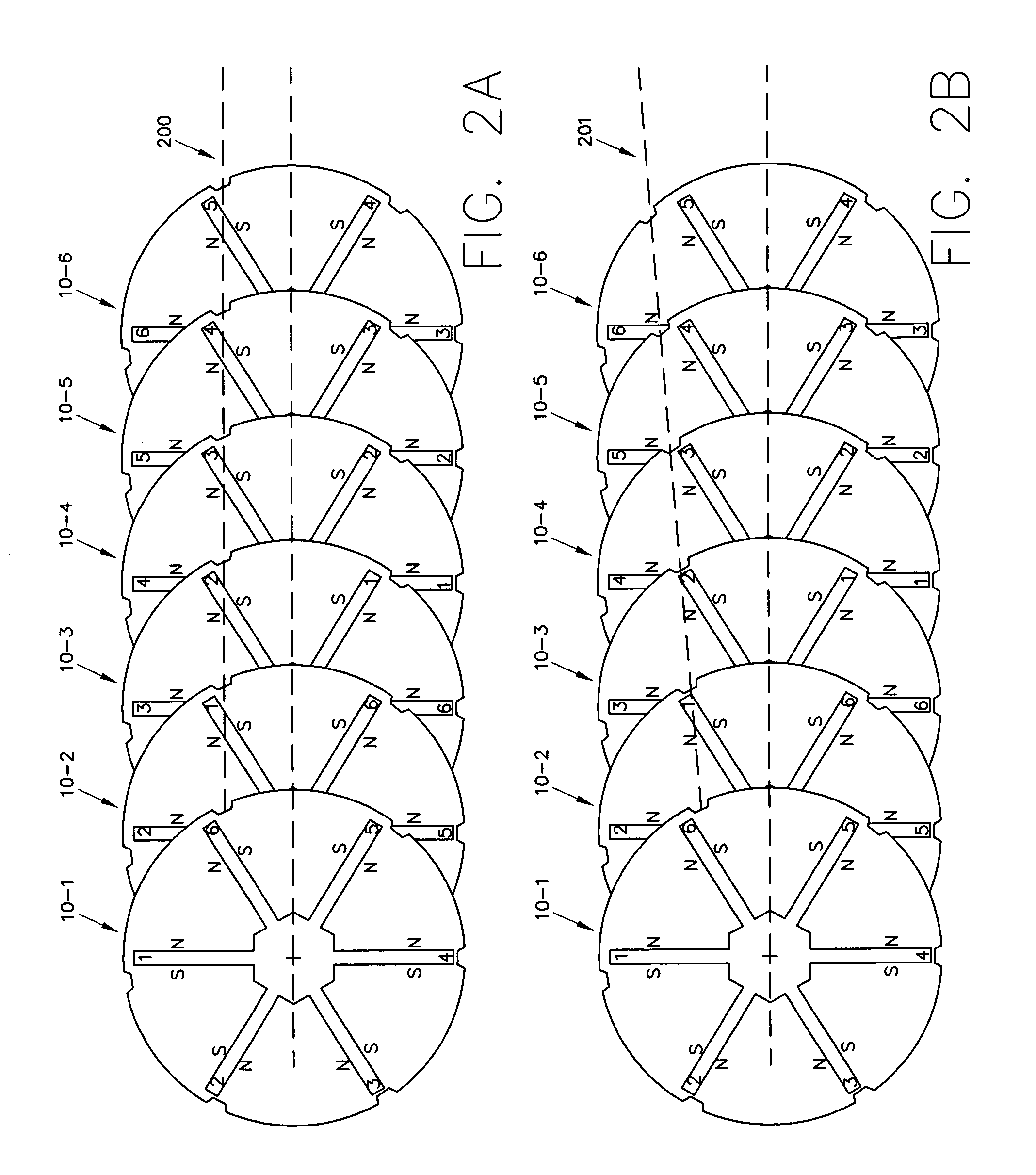
Brushless motor
InactiveUS20090224619A1Reduce cogging torqueIncrease output torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsBrushless motorsSkew angle
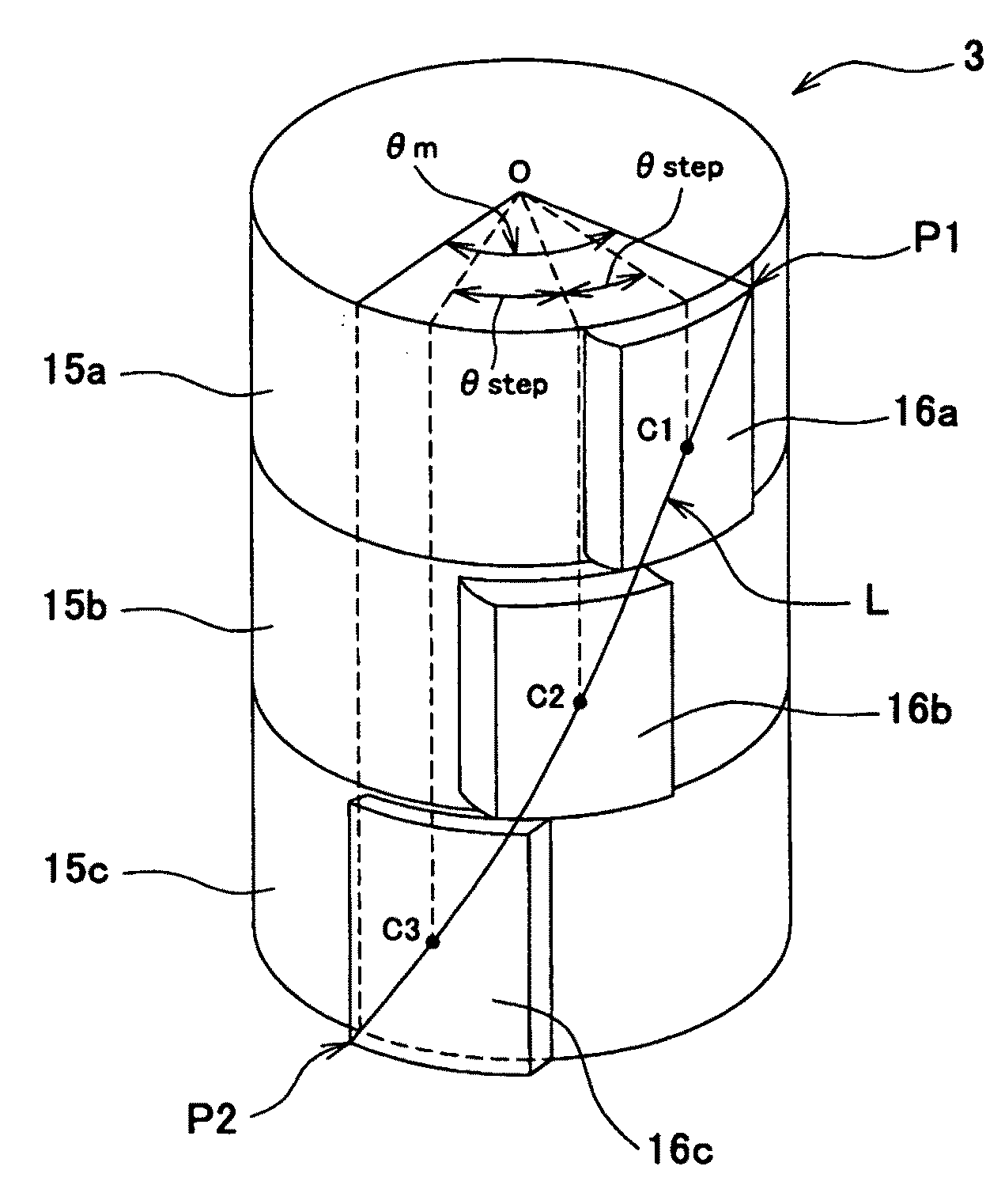
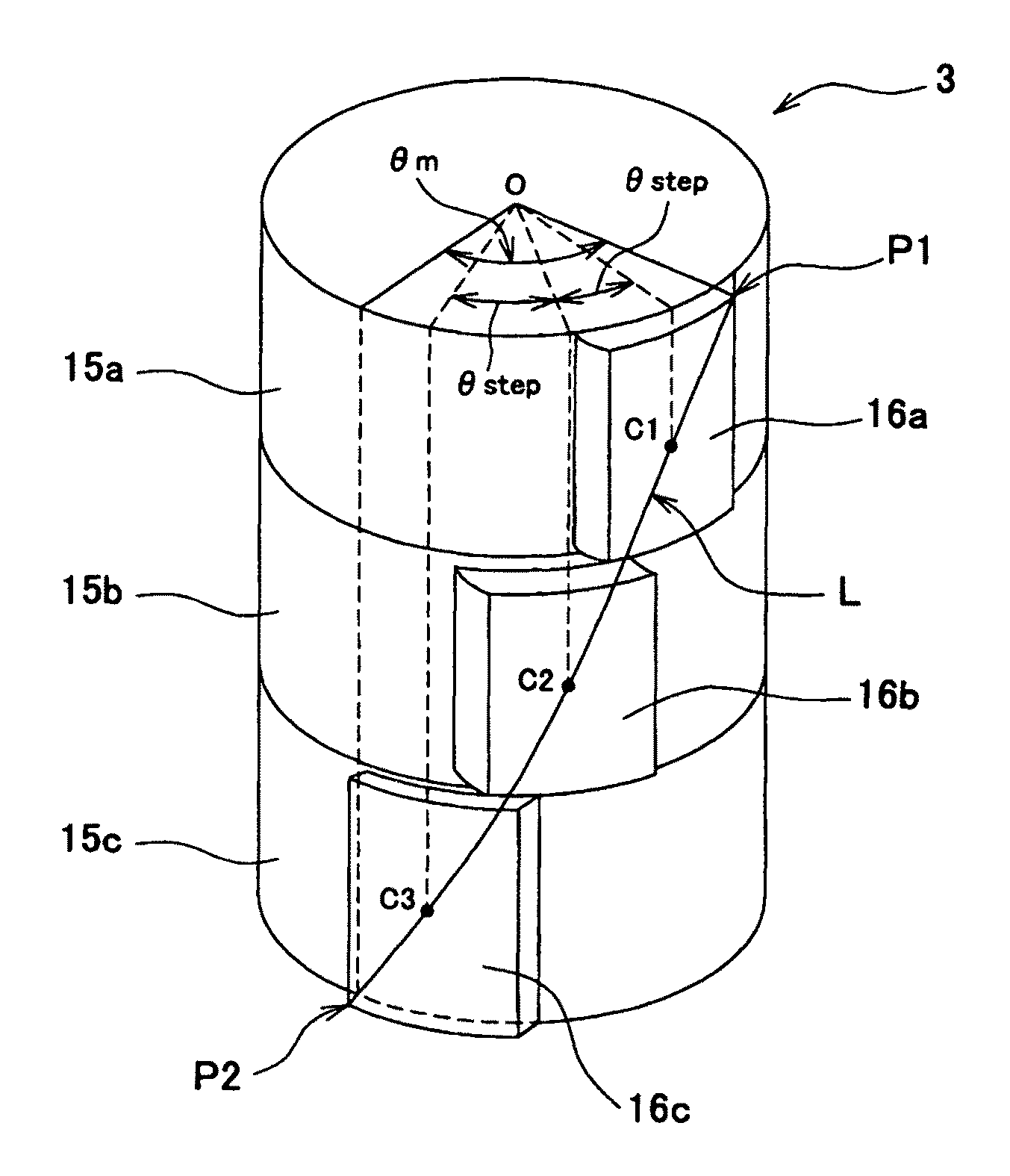
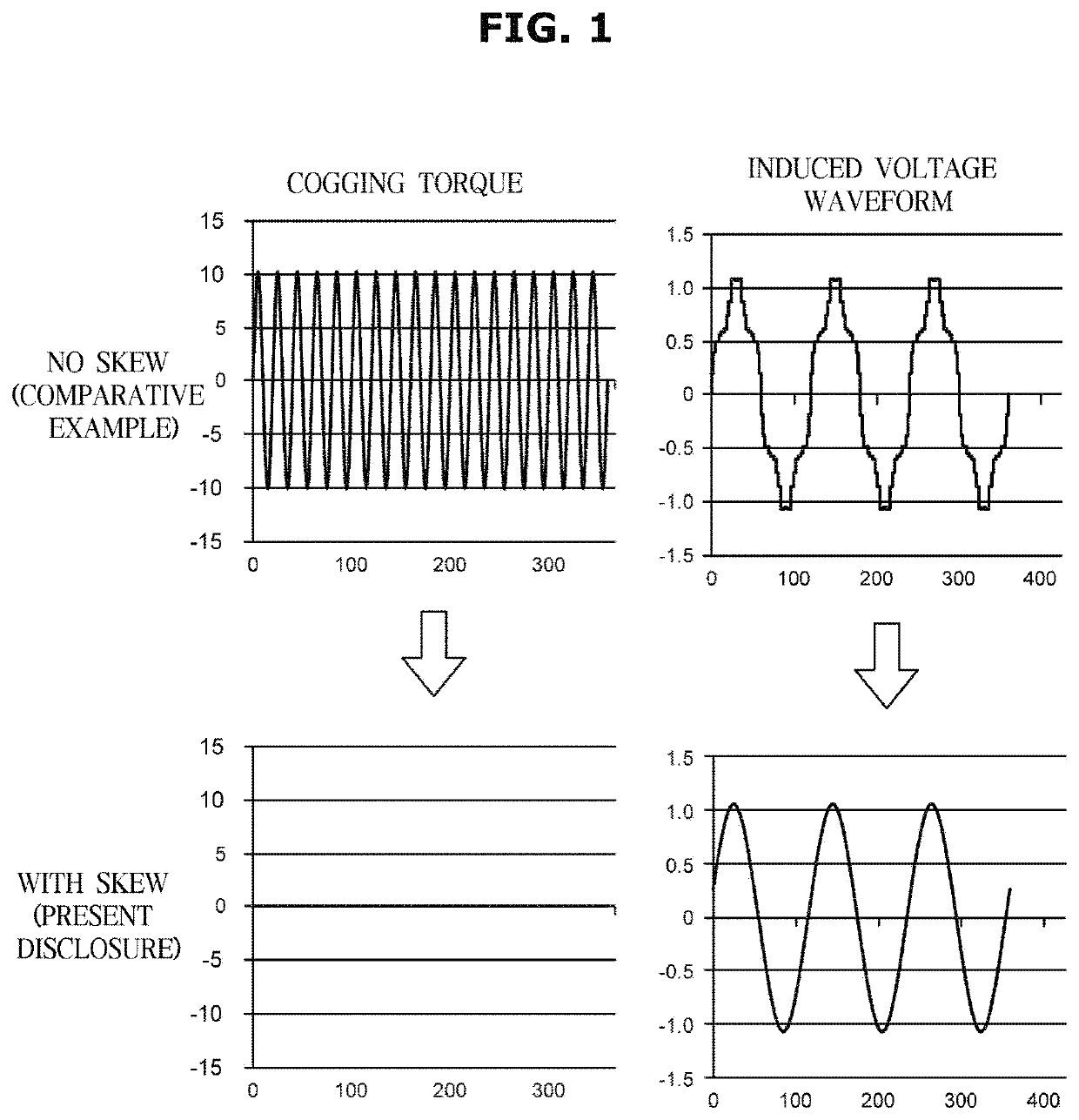
In a brushless motor includes a rotor having 2n magnetic poles and a stator having 3n slots, the magnetic poles of the rotor are composed of segment magnets arranged in three columns extending in an axial direction. The magnets of each column are displaced from the magnet of either adjacent column in a circumferential direction, forming a 3-stage step-skew structure. The segment magnets have a skew angle θskew ranging from 36° to 57° in terms of electrical angle.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Electric motor and apparatus for manufacturing electric motor
ActiveUS7298064B2Punching can be carried out without problems, very efficientlyLong processMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic anisotropySheet steel
A motor capable of reducing cogging torque depending on teeth of a stator, and a motor manufacturing apparatus for manufacturing this motor. The angles of rolling directions of cores stacked are set so that the phase difference between the phases of cogging torques produced on the cores is 180° so that the cogging torques produced on the cores cancel each other to reduce the total cogging torque in the motor. The motor comprises a laminated core formed by stacking a plurality of cores made from a rolled electromagnetic sheet steel. The cores forming the laminated core have rolling directions different from each other by a specified machine angle determined depending on the number of slots and / or the number of poles, where the specified machine angle is an angle which produces a phase difference of 180° between the phases of cogging torques produced due to magnetic anisotropy of the cores and the arrangement of teeth depending on the number of slots and / or poles of the motor.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Brushless motor with skewed rotor segments
InactiveUS7928622B2Easy to assembleLarge outputMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsBrushless motorsSkew angle
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Method of determining pole arc ratio of interior permanent magnet rotary motor and interior permanent magnet rotary motor
InactiveUS7358638B2Reduced dimensionReduce the amount requiredMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMagnetic polesLine segment
An interior permanent magnet rotary motor of the present invention has N slots and P permanent magnet magnetic pole sections, (2 / 3<=P / N<= 43 / 45). Po is an irreducible fraction Po / No of the P / N is an odd number, and a pole arc ratio psip equals thetapp / thetap. thetapp is an angle between two line segments assumed for a pair of flux barriers, each of which connects the center of a rotor core and one of corners of the section of each flux barrier that is closest to the surface of the rotor core. thetap is an angle obtained by dividing 360° by the number of the permanent magnet pole sections. The pole arc ratio indicated by Psip (0<4n<1) is determined by the expression of Psip=2mP / N+P / 4LCM (P, N)-2n, where LCM (P, N) is the least common multiple between P and N, m and n are arbitrary natural numbers.
Owner:SANYO DENKI CO LTD
Rotor assembly for a permanent magnet electrical machine comprising such a rotor assembly
InactiveUS6897590B2Improves flux concentrationIncrease widthMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsEngineeringMagnet
Rotor assembly for an electrical machine, including a body of generally cylindrical shape having an inner opening, wherein slots are provided in the body, the slots extending from the inner opening towards the outer periphery of the body; permanent magnets disposed in said slots; wherein at least one of the slots comprises an end section near the outer periphery of the body having an area of enlarged width.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Drive Apparatus
ActiveUS20150375824A1Safer and reliable operationLow costToothed gearingsElectric machinesMotor driveMotor unit
A drive apparatus for an electric bike includes a hollow housing body, an internal ring gear fixed to the housing body, and a main shaft. At least two motor units are mounted in the housing body. Each motor unit includes a support bracket and a number of motors mounted on the support bracket. Each motor drives the internal gear through a transmission mechanism to rotate the housing body about the main shaft. The motors share one controller. Peaks of the motor cogging torque can be staggered.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC INTERNATIONAL AG
Permanent magnet motor with magnets in an adjusted position to reduce cogging torque
InactiveUS7948136B2Reduce the cogging torque of servomotorsImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringMagnetic poles
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Method of making a motor with reduced cogging torque
ActiveUS20110192018A1Reduce vibrationReduce the cogging torque of servomotorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectronic circuit testingElectric power steeringElectric machine
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Motor and motor manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050229382A1Reduce the cogging torqueEliminate dependenciesManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionMagnetic anisotropyManufactured apparatus
Flat rolled magnetic steel sheets and strip or a die is turned in the press forming process. Rotor cores are stacked with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple of about (360° / (number of slots in the motor×natural number n×2) and stator cores are stacked with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple of (360° / (number of poles in the motor×natural number n×2)). Stacking with turning through an angle which is an odd number multiple converts the phases of cogging torques into mutually opposite phases and cancels and reduces the cogging torque caused by magnetic anisotropy.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Single-Phase Outer-Rotor Motor and Stator Thereof
InactiveUS20160329791A1Easy windingReduce cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringElectric motor
A single-phase outer-rotor motor and a stator thereof are provided. The stator includes a stator core having a yoke and a number of teeth. Each tooth includes a tooth body and a toot tip. A winding slot is formed between each two adjacent tooth bodies. A slot opening is formed between each two adjacent tooth tips. The tooth tip protrudes beyond the tooth body. Inner surfaces of at least part of the tooth tips facing the stator are formed with cutting grooves such that a portion of the tooth tip outside the cutting groove is capable of being tilted outwardly to enlarge the slot opening and deformed inwardly to narrow the slot opening.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
Magnet-embedded motor and compressor using same
ActiveUS20200313478A1Reduce cogging torqueLow torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machineSkew angle
The present disclosure may reduce cogging torque by stacking steel plates which can form a stage skew by stacking the steel plates without reversing the front and back sides or by forming the stage skew by stacking the steel plates capable of easily distinguishing the front and back sides, and reduce both the sixth-order and twelfth-order dq coordinates of harmonic components, thereby achieving low toque ripple, high efficiency, and improved controllability. To this end, the present disclosure is an internal permanent magnet motor having a rotor in which a predetermined skew angle θs is formed between adjacent stages along the axial direction, wherein the rotor is formed by stacking a plurality of the steel plates having the same shape, each of the steel plates has a group of fastening holes made of the same number of the fastening holes as the number of the stages, and each of the fastening holes constituting the fastening group is formed at a position where the skew angle θs changes along a circumferential direction one by one.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Single-phase outer-rotor motor and stator thereof
InactiveUS10243439B2Effectively reduce the cogging torqueEasy windingMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringConductor Coil
A single-phase outer-rotor motor and a stator thereof are provided. The stator includes a stator core having a yoke and a number of teeth. Each tooth includes a tooth body and a tooth tip. A winding slot is formed between each two adjacent tooth bodies. A slot opening is formed between each two adjacent tooth tips. The tooth tip protrudes beyond the tooth body. Inner surfaces of at least part of the tooth tips facing the stator are formed with cutting grooves such that a portion of the tooth tip outside the cutting groove is capable of being tilted outwardly to enlarge the slot opening and deformed inwardly to narrow the slot opening.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
Rotor for Electric Power Steering Motor, Electric Power Steering Motor with This, and Manufacturing Therefor
InactiveUS20160141930A1Reduce cogging torqueReduce the cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringShrink-fitting
A rotor for an electric power steering motor is configured to include a rotor core having a step skew structure constituted of two independent cores as well as to use shrink fitting to fasten the two cores to a shaft. It may also be configured such that a magnetic center of the rotor core is adjusted by controlling a dimension thereof from a tip of the shaft and by shrink fitting the two cores.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Drive apparatus
ActiveUS9762104B2Light weightImprove power densityElectric machinesMechanical energy handlingEngineeringMotor unit
A drive apparatus for an electric bike includes a hollow housing body, an internal ring gear fixed to the housing body, and a main shaft. At least two motor units are mounted in the housing body. Each motor unit includes a support bracket and a number of motors mounted on the support bracket. Each motor drives the internal gear through a transmission mechanism to rotate the housing body about the main shaft. The motors share one controller. Peaks of the motor cogging torque can be staggered.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
Rotor and motor
ActiveUS20190214866A1Suppress generationImprove featuresMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesEngineeringMagnet
A rotor includes a rotor core in which laminate steel plates extending in a radial direction with respect to a central axis are laminated in an axial direction, and magnets are inserted into the rotor core. Each of the laminate steel plates includes a base portion positioned on a radially outer side of the central axis, and pieces separately disposed on a radially outer side of the base portion with penetrating portions therebetween, and arranged side by side at predetermined intervals in a circumferential direction. The magnets are inserted into the penetrating portions and arranged side by side at predetermined intervals in the circumferential direction. Space portions are provided between the magnets adjacent to each other in the circumferential direction. A circumferential length of the pieces is shorter than a circumferential length of the magnets.
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Magnet-embedded motor with a shew angle forward therein and compressor using same
ActiveUS10998783B2Reduce the cogging torqueLow torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machineClassical mechanics
The present disclosure may reduce cogging torque by stacking steel plates which can form a stage skew by stacking the steel plates without reversing the front and back sides or by forming the stage skew by stacking the steel plates capable of easily distinguishing the front and back sides, and reduce both the sixth-order and twelfth-order dq coordinates of harmonic components, thereby achieving low toque ripple, high efficiency, and improved controllability. To this end, the present disclosure is an internal permanent magnet motor having a rotor in which a predetermined skew angle θs is formed between adjacent stages along the axial direction, wherein the rotor is formed by stacking a plurality of the steel plates having the same shape, each of the steel plates has a group of fastening holes made of the same number of the fastening holes as the number of the stages, and each of the fastening holes constituting the fastening group is formed at a position where the skew angle θs changes along a circumferential direction one by one.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rotor and motor
ActiveUS11056938B2Suppress generationImprove featuresMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric machineMagnet
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Motor provided with noncircular stator core, apparatus for production of motor, and method for production of motor
InactiveUS10256706B2Easy to useReduce the amount of wasteMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
A motor which reduces the manufacturing cost while able to reduce the cogging torque. The stator core is provided with a first core sheet and a second core sheet which is stacked with the first core sheet so that its rolling direction becomes a direction rotated from the rolling direction of the first core sheet by exactly an angle of an odd multiple of 360° / (number of poles of motor×2). The outside edge of the first core sheet has a first side and a second side at two sides in a direction perpendicular to the rolling direction. The outside edge of the second core sheet has a third side and a fourth side in a direction perpendicular to the rolling direction. The dimension between the first side and the second side and the dimension between the third side and the fourth side are the same.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com