Metallurgy method of metal sulfide M1S
A metal sulfide and sulfide technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of cathode deposition inclusion, low solubility, increased energy consumption, etc., and achieve the effects of short production process, less pollution, and high added value of products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
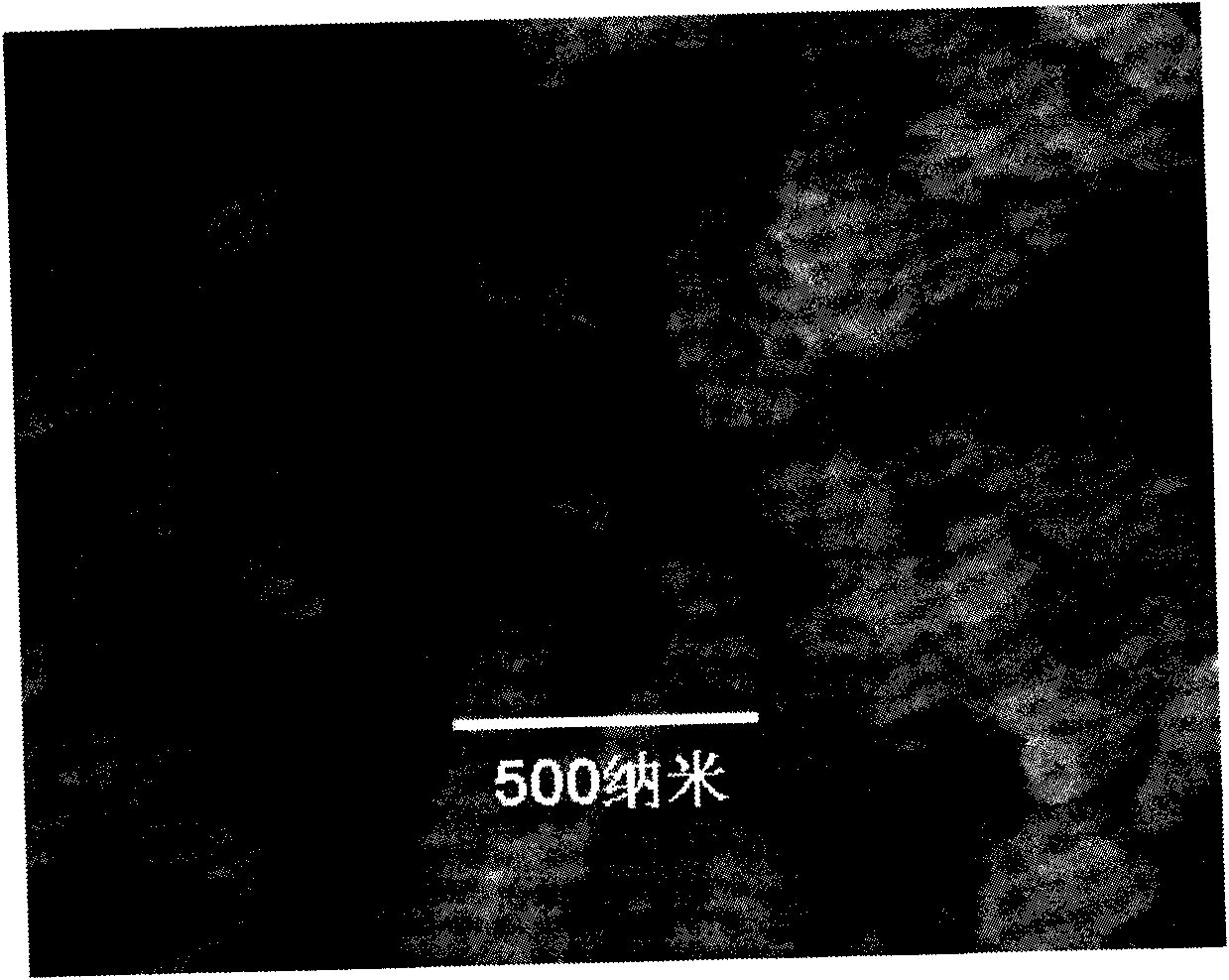
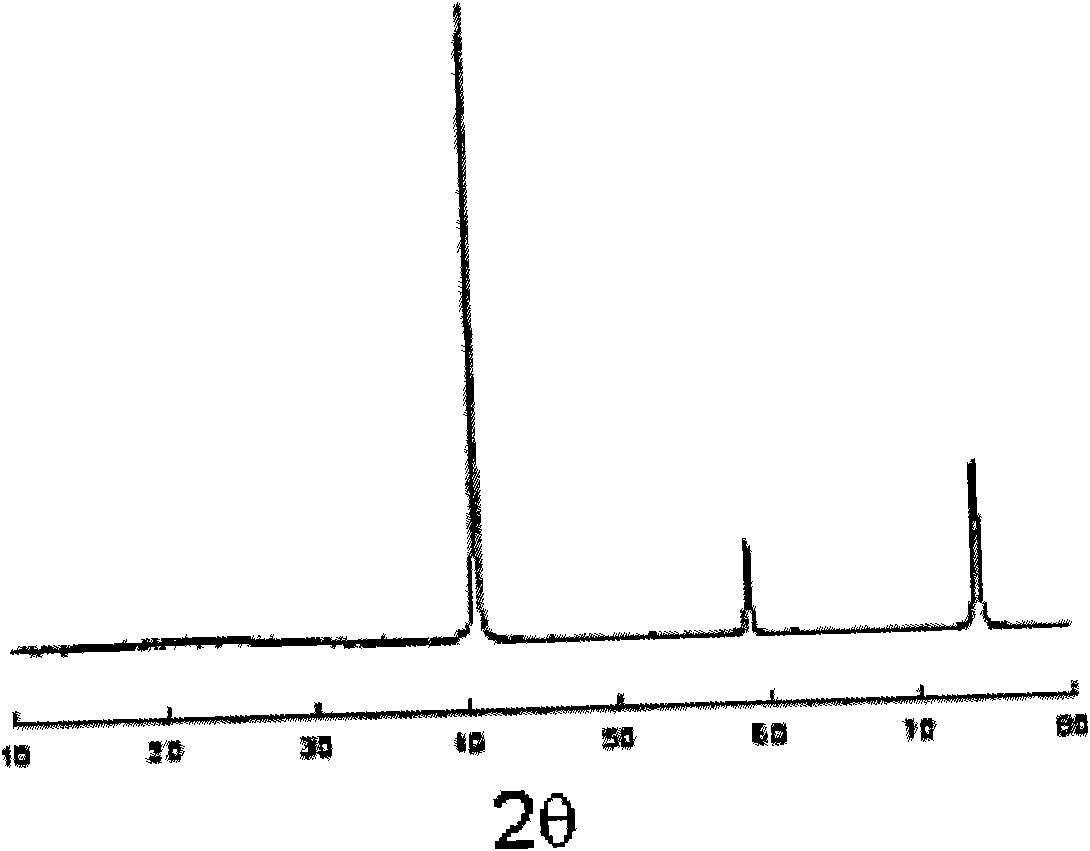
[0046] Commercially available MoS 2 The powder is about 0.5-2g, pressed by mechanical pressure at 0.5-10MPa into a sulfide test piece with a diameter of about 20mm and a thickness of 0.5-1.5mm, dried in the air at 200°C for 0.5-8 hours, and the porosity of the obtained sample is 20 ~80%. The sulfide test piece and the conductive cathode current collector are combined as the working electrode, the graphite rod is used as the counter electrode, and the graphite electrode is separated from the gas phase of the electrolytic cell by a quartz tube to export the anode product. Molten KCl+NaCl is used as the electrolyte, in an argon environment, the temperature is 680 and 750°C, and the electrolysis voltage is controlled at 1.2-2.4V. After 30, 60, 120, 180, and 300 minutes of electrolysis respectively, the metal product was taken out and washed and dried with water. The SEM of the obtained metal product molybdenum was as follows: figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that the o...
Embodiment 2
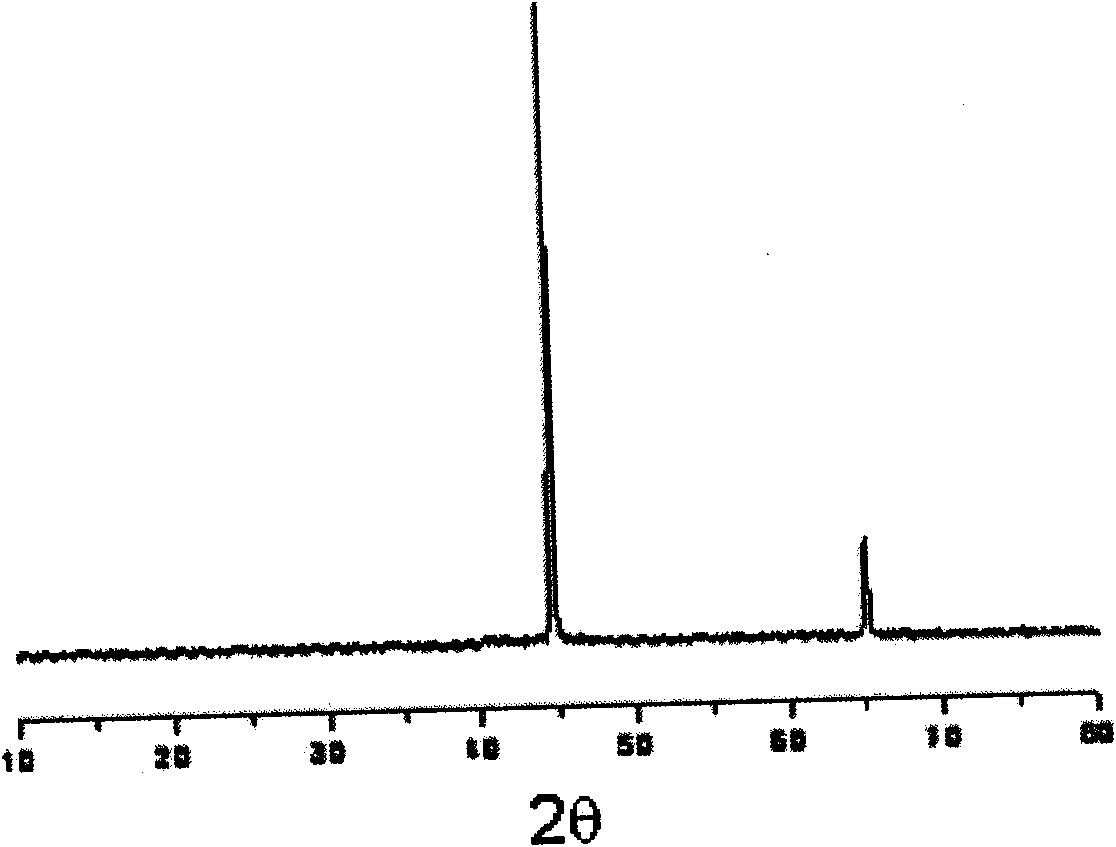
[0048] About 2g of commercially available FeS blocks, with a porosity of basically 0, are combined with a conductive cathode current collector as a working electrode, and a graphite rod is used as a counter electrode, and a quartz tube is used to separate the graphite electrode from the gas phase of the electrolytic cell to export the anode product . Using molten KCl+NaCl as the electrolyte, in an argon atmosphere, the temperature is 680°C, and the electrolysis voltage is controlled at 1.2-2.4V. After electrolysis for 30, 60, 120, 180, and 300 minutes respectively, the metal product is taken out and washed and dried to obtain porous iron with a basic particle size of 5-50 microns. The XRD of the obtained product iron is as follows figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that the obtained iron is pure metal; the anode product is gaseous elemental sulfur.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Ti will be weighed proportionally 2 S 3 The powder and FeS powder are about 0.5-2g, mixed uniformly by mechanical ball milling, and then pressed at 0.5-10MPa to form a sulfide test piece with a diameter of about 20mm, and dried in the air at 200°C for 0.5-8 hours. The porosity of the obtained sample is 20- 80%. The sulfide test piece and the conductive cathode current collector are combined as the working electrode, the graphite rod is used as the counter electrode, and the graphite electrode is separated from the gas phase of the electrolytic cell by a quartz tube to export the anode product. Using molten KCl+KF as the electrolyte, in an argon atmosphere, the temperature is 650°C, and the electrolysis voltage is controlled at 2.4-3.2V. After 240-900 minutes of electrolysis, the metal product is taken out and washed and dried to obtain a TiFe alloy. The anode product is gaseous elemental sulfur.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com