Extraction method of bile salt hydrolase in Lactococcus lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus
A technology of bile salt hydrolysis enzyme and Lactococcus lactis, which is applied in the field of extraction of bile salt hydrolysis enzymes from Lactococcus lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus, to achieve the effects of simple extraction process, short fermentation cycle and convenient source of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
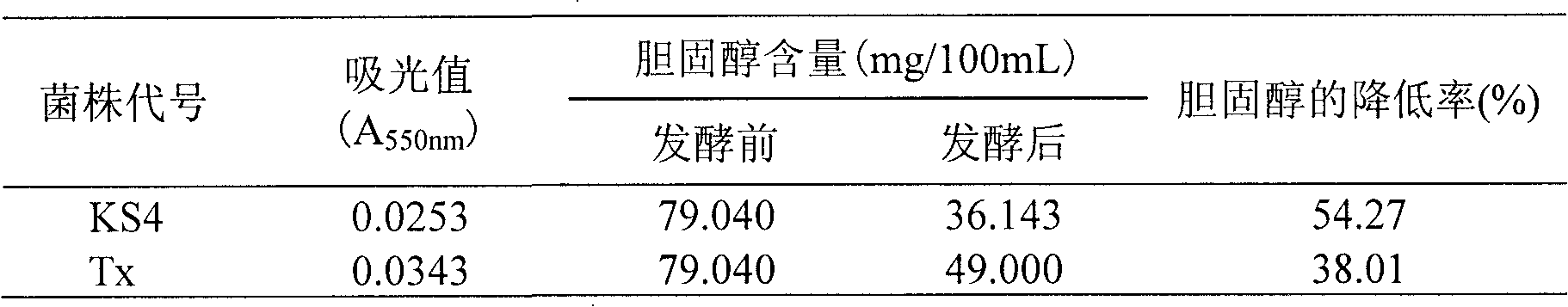
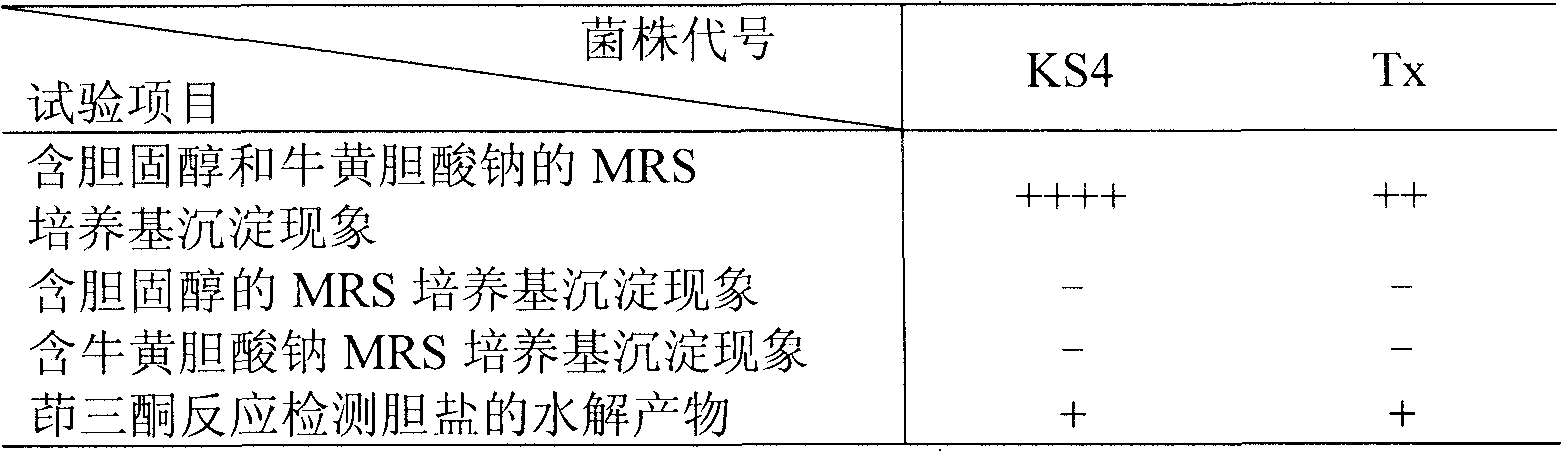
[0034] Example 1. Screening and Identification of Lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis KS4 and Streptococcus thermophilus Tx with High Efficiency in Lowering Cholesterol and High Production of Bile Salt Hydrolase and Exopolysaccharide
[0035] 1. Screening of high-efficiency cholesterol-lowering and high-production bile salt hydrolase strains
[0036] Take 5mL of the filtrate of Zangling mushroom and pour it into 45mL sterile saline with glass beads, shake it fully for 30min to make a bacterial suspension, and then dilute it 10 times to 10 -4 ~10 -6 diluted bacterial solution. Inoculate the plate with the dilution pouring method, pour into the MRS selective medium containing calcium carbonate and natamycin, incubate at 37°C for 24 hours, pick a single colony with a dissolution circle and inoculate it in the MRS slant medium, and incubate at 37°C Cultivate for 24h. Gram staining, depending on the individual shape and purity. Inoculate in MRS liquid medium, enrich the bacteria fo...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2, using Lactococcus lactis subspecies lactic acid KS4 and Streptococcus thermophilus Tx to extract bile salt hydrolyzing enzyme
[0063] 1. Fermentation process conditions for high production of bile salt hydrolase
[0064] Medium composition (w / v) for culturing Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis KS4, Streptococcus thermophilus Tx high-yielding bile salt hydrolase: glucose 2%, soybean peptone 2%, MnSO 4 0.025%, beef extract 1%, yeast extract 0.5%, Tween 80 0.1%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2%, sodium acetate 0.5%, diammonium citrate 0.2%, magnesium sulfate 0.058%, distilled water 1000mL, 0.07MPa sterilization 20min.
[0065] Fermentation process conditions for high production of bile salt hydrolase: fermentation temperature 37° C., fermentation time 12 hours, initial pH value of medium 6.0, inoculum size 2%.
[0066] Under these fermentation conditions, the enzyme activity of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis KS4 was 11.84 times that before optimization.
...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3, Utilizing Streptococcus thermophilus Tx and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactic acid KS4 to extract exopolysaccharide
[0073] 1. Fermentation conditions for high-yield exopolysaccharide
[0074] Medium components (w / v) for cultivating Streptococcus thermophilus Tx and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis KS4 high-yielding exopolysaccharide: 6% sucrose, 3% tryptone, 0.025% manganese sulfate, 1.0% beef extract, yeast Powder 0.50%, Tween 80 0.10%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.20%, sodium acetate 0.50%, diammonium citrate 0.20%, magnesium sulfate 0.058%, distilled water 1000mL, 0.07MPa sterilization for 20min.
[0075] Fermentation conditions for high exopolysaccharide production: fermentation temperature 32° C., fermentation time 16 hours, initial pH value of medium 6.5, inoculum size 3%.
[0076] Under these fermentation conditions, the yield of Streptococcus thermophilus Tx exopolysaccharide was 2.6 times that before optimization.
[0077] 2. Extraction method...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com