Fluorescence in situ hybridization method for metaphase chromosome of mulberry
A fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosome technology, applied in the field of genetics, can solve problems such as the application of fluorescence in situ hybridization technology, chromosome swelling and deformation, chromosome production failure, etc., and achieve clear signal points, good shape, and stable number Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The fluorescence in situ hybridization method of mulberry metaphase chromosome comprises the following steps:
[0027] (1) Preparation of chromosomal slide specimens: using the young leaves of Chuanmulus mulberry as materials, the chromosomal slide specimens were prepared by the wall-removing hypotonic flame-drying method. The specific steps are as follows:
[0028] The young leaves of Chuan mulberry were pretreated in 8-hydroxyquinoline aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.002M at 25°C in the dark for 3 hours, and then fixed at 4°C for more than 2 hours with methanol: glacial acetic acid volume ratio of 3:1. Rinse 3 times with distilled water again; Then the fixed mulberry leaves are hypotonic at 25° C. for 30 minutes in 1 / 15M aqueous KCl solution, rinsed 2 times with distilled water and then soaked with 5% (W / V) cellulase and 5% (W / V) Enzymolysis at 25°C for 2 hours in a mixed solution of (W / V) pectinase, then rinsed with distilled water for 3 times and stayed i...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The fluorescence in situ hybridization method of mulberry metaphase chromosome comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) the preparation of chromosome slide specimen, the preparation method is identical with embodiment 1;
[0041] (2) 25S rDNA probe preparation: According to the conserved region sequence of 25S rDNA genes, primers for amplifying 25S rDNA were designed in the conserved region, as follows:
[0042] 25S rDNA forward primer: 5'-ccaaatgcctcgtcatctaa-3' (SEQ ID NO.3);
[0043] 25S rDNA reverse primer: 5'-gcgaatcaacggttcctct-3' (SEQ ID NO.4);
[0044] Then use the Chuanmulus genomic DNA as a template, and use SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 as primers to carry out PCR amplification to obtain the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.6, and then combine it with pMD19-T simple Vector connection to get pMD19-25S rDNA;
[0045] The obtained recombinant plasmid pMD19-25S rDNA was used as a template, and the PCR DIG Probe Synthesis Kit (Roche) was used to prepare ...
Embodiment 3
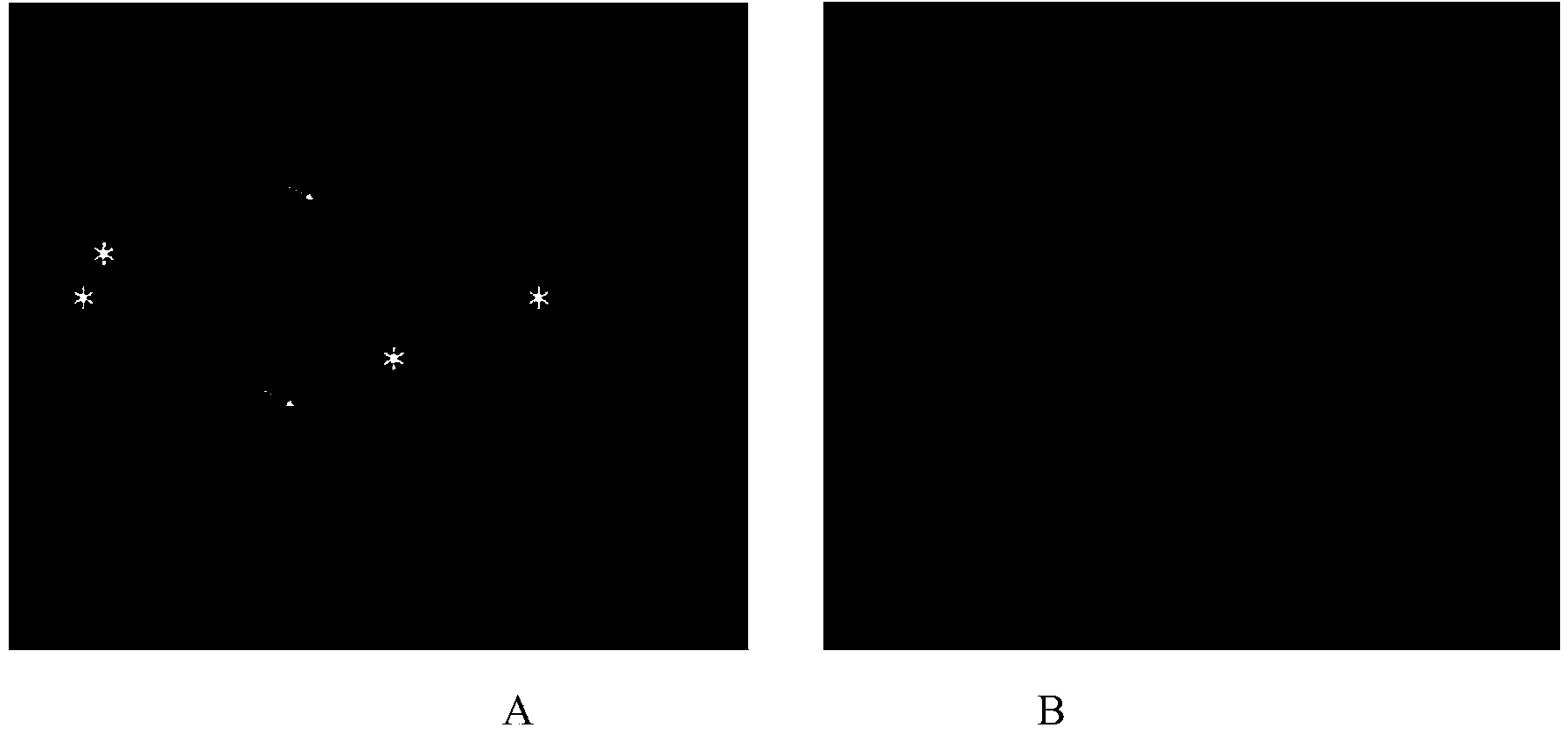
[0048] Example 3 is the same as Example 1 for the method of fluorescence in situ hybridization of mulberry metaphase chromosomes, except that the probe added in the hybridization solution is a mixture of biotin-labeled 5S rDNA probe and digoxin-labeled 25S rDNA probe Probe; The preparation method of the biotin-labeled 5S rDNA probe is the same as that of the 5S rDNA probe in Example 1, the difference is that the PCR Biotin Probe Synthesis Kit (Roche) is used to prepare the probe, which contains Biotin-dUTP . Anti-digoxigenin-fluorescein (Anti-digoxigenin-fluorescein, Fab fragments (from sheep)) with a concentration of 2 ng / μL from sheep was used to incubate for 1 h, and then with a concentration of 10 ng / μL. Cy3-labeled anti-biotin antibody (Cy TM 3-Streptavidin Conjugate (ZyMAX TM Grade)) was incubated for 1 h, and the results of microscopic examination were as follows image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com