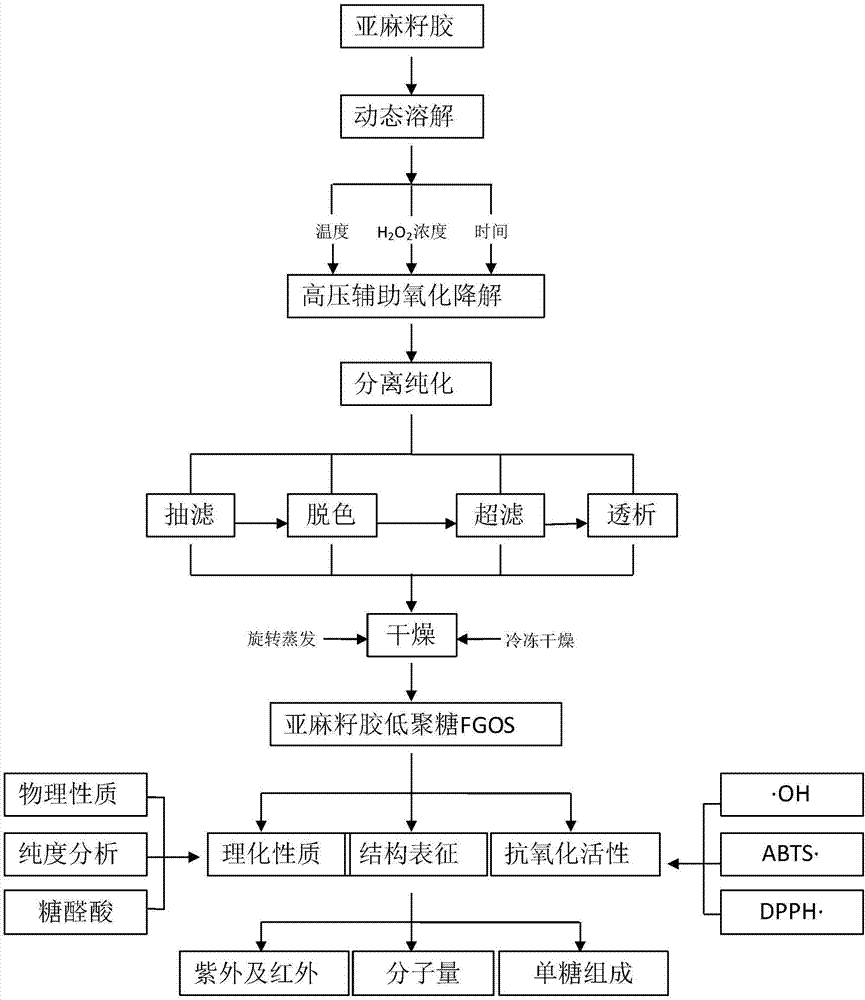
Method for preparing flaxseed gum oligosaccharides by hydrogen peroxide oxidation degradation technology
A linseed gum, oxidative degradation technology, applied in the field of biomedicine and functional food, can solve problems such as complex process, achieve the effect of economical raw material basis, simple and reliable preparation method, excellent physical and chemical properties and antioxidant capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Preparation of linseed gum oligosaccharide
[0039] Prepare flaxseed gum oligosaccharides according to the following steps:
[0040] (1) Dissolution of linseed gum: take commercially available linseed gum and dissolve it in 0.1-0.6 mol / L hydrogen peroxide solution under dynamic and continuous stirring to fully dissolve the linseed gum. The addition amount of linseed gum is 2% ( w / v, the mass of linseed gum added in 100mL of hydrogen peroxide solution is 2g);
[0041] (2) Oxidative degradation of linseed glue: take the linseed glue obtained in step (1), divide 100 mL into 150 mL screw-top glass bottles, seal them, and degrade them in a high-pressure steam sterilizer to control the reaction Time 0.5-3.0h, reaction temperature 80℃-125℃, after the reaction, take it out and cool to room temperature;
[0042] (3) Decolorization: Suction filter the mixture liquid obtained in step (2) and repeatedly wash the filter cake, combine and collect the filtrate, using 1% (w / v, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Evaluation of the degradation effect of linseed gum
[0047] The degradation effect of linseed gum was evaluated according to the following method:
[0048] (1) Changes in the degradation rate of linseed gum:
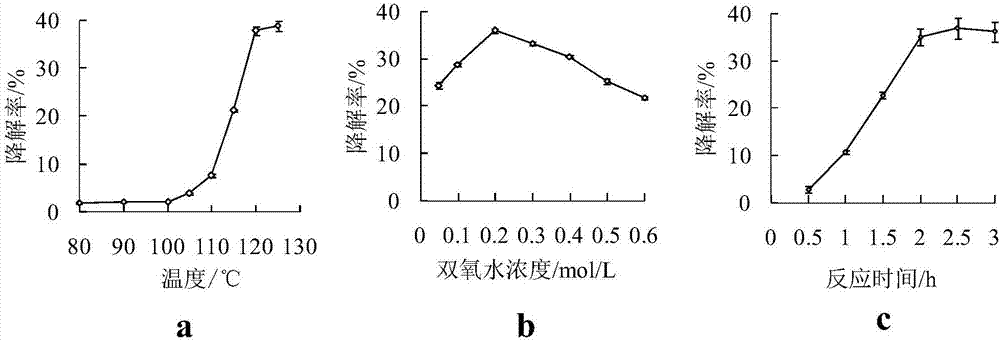
[0049] After the reaction, take it out to cool, stop the reaction in an ice water bath for 10 minutes, filter with suction, and repeatedly wash the filter cake with distilled water, combine the filtrate, concentrate to 100mL, take 0.10mL, use DNS colorimetric method to measure reducing sugar content; take another 0.01mL, use phenol -Measure the total sugar content by the sulfuric acid method, and calculate the degradation effect of flaxseed gum according to the formula (1) based on the yield of the reducing terminal sugar group. figure 2 Shown.
[0050]
[0051] by figure 2 In a, it can be seen that when the temperature is lower than 110℃, the degradation degree of linseed gum is very small. When the temperature is higher than 110℃, the degradation rate of l...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3: Evaluation of the separation and purification effect of linseed gum oligosaccharides (FGOS)
[0062] The degradation products were separated and purified according to the method described in Example 1, and the decolorization and ultrafiltration effects were evaluated according to formulas (2) and (3). The results are shown in Table 2.
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] Table 2 Decolorization and ultrafiltration results
[0066]
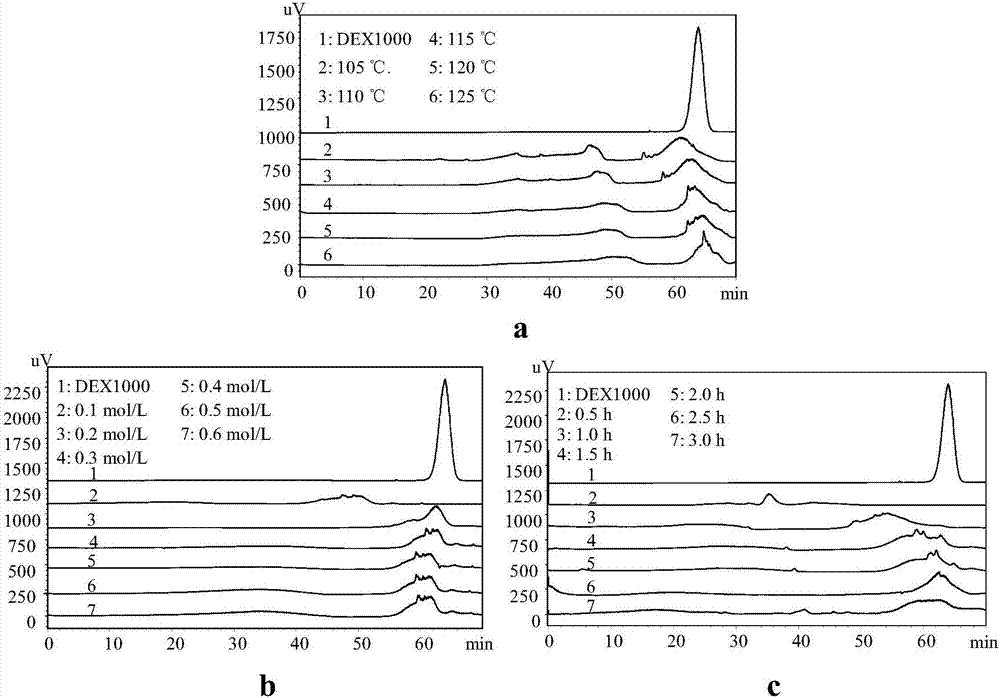
[0067] It can be seen from Table 2 that the decolorization rate can reach 86.77% by the method described in Example 1, and the obtained sugar liquid is ideally light yellow; the sugar retention rate is 97.21%, and there is almost no sugar loss. The theoretical average degree of polymerization of the product before and after ultrafiltration dropped from 5.02 to 4.65. From the SEC elution curve ( Image 6 ), after ultrafiltration, the large component broad peak (about 35-45min) disappeared, indicating that the ultrafiltration had a good role in retai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com