Agricultural microbial preparation and application thereof to control of melon root-knot nematode disease and watermelon wilt disease
A microbial preparation and preparation technology, applied in the field of microbial preparations, can solve problems such as human health hazards, increased energy consumption, soil environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing the occurrence of diseases and insect pests, enhancing stress resistance, and restraining growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
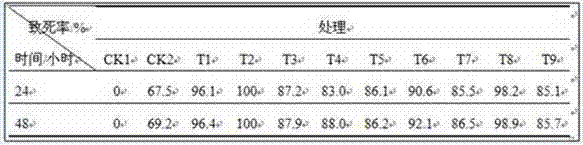
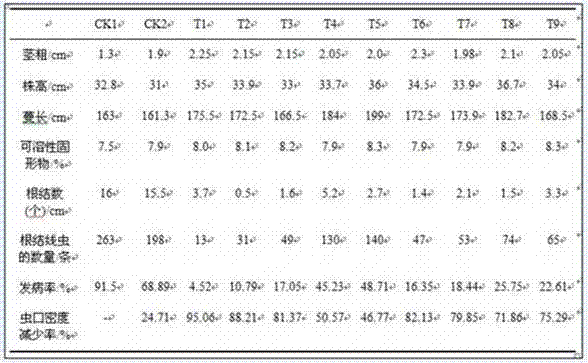
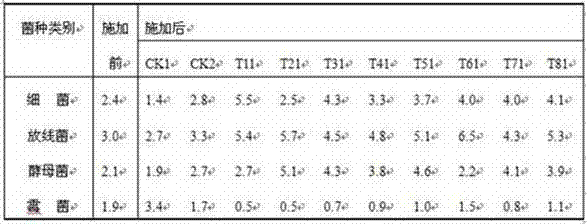
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Weigh 200 g of peeled and cut potatoes into 1400 mL of deionized water, boil at 100 ° C for 10 minutes, filter through three layers of gauze and set the volume to 1000 mL as a solvent; weigh 20 g of glucose, add it to the solvent and stir evenly, and pack in In the triangular flask, seal the package and sterilize it in a sterilizing pot at 121°C for 20 minutes. After cooling, it will be the prepared mold liquid culture medium;
[0034] The mold liquid culture is based on the inoculation ring of mold spores—Paecilomyces lilacinus—inoculated on the aseptic operation table, and the sealed package is placed in a shaker at 28°C for 4 days to obtain the mold—Paecilomyces lilacinus fermentation broth. Leave it for 5 days to make the liquid surface form a layer of spores for later use;
[0035] Weigh 100 g of soybean meal, 400 g of cornmeal, 200 g of bran, and 300 g of sawdust in a fermenter and stir evenly, then add 600 mL of deionized water and mix evenly, seal the package and ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Weigh 5 g of beef extract, 10 g of peptone, and 5 g of sodium chloride into a measuring cup, add deionized water to 1000 mL, stir evenly and adjust the pH to 7.0~7.2, then pack them into Erlenmeyer flasks, seal and store Sterilize in a sterilizing pot at 121°C for 20 minutes, and wait to cool to obtain a bacterial liquid culture medium;
[0039] Inoculate the sterilized and cooled liquid culture medium on the aseptic operating table with bacteria—Bacillus subtilis, seal the package and put it in a shaker at 36°C for 24 hours to obtain the bacteria—Bacillus subtilis fermentation broth;
[0040] Weigh 180 g of soybean meal, 300 g of cornmeal, 320 g of bran, and 200 g of sawdust in a fermenter and stir evenly, then add 600 mL of deionized water and mix evenly, seal the package and sterilize it in a sterilizing pot at 121°C for 40 minutes. Acquired bacterial agent preparation medium;
[0041] Inoculate 400 mL of bacteria—Bacillus subtilis fermentation broth on the aseptic ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The method in Example 2 was adopted to prepare bacterial liquid culture medium. Bacterial liquid culture is based on the inoculation of bacteria-Pseudomonas fluorescens on the aseptic operation table, and the sealed package is placed in a shaker at 36°C for 24 hours to obtain the bacteria-Pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation broth;
[0044] Adopt the method in the embodiment 2 to prepare bacterial inoculum preparation culture medium. After cooling to room temperature, the preparation and cultivation of the bacterial agent is based on inoculating 400 mL of bacteria—Pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation broth on the aseptic operation table, stirring evenly, sealing the package and placing it in an incubator at 36°C for 24 hours. After successful fermentation Air-dried in a cool place and crushed into powder to obtain bacteria—Pseudomonas fluorescens biological agent T3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com