Preparation method of nano medicine controlled release system and product and application of system
A nano drug and system technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of loss of targeting, short half-life of drug circulation, low bioavailability, etc., to reduce surface free energy, enhance anti-tumor effect, and good biocompatibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
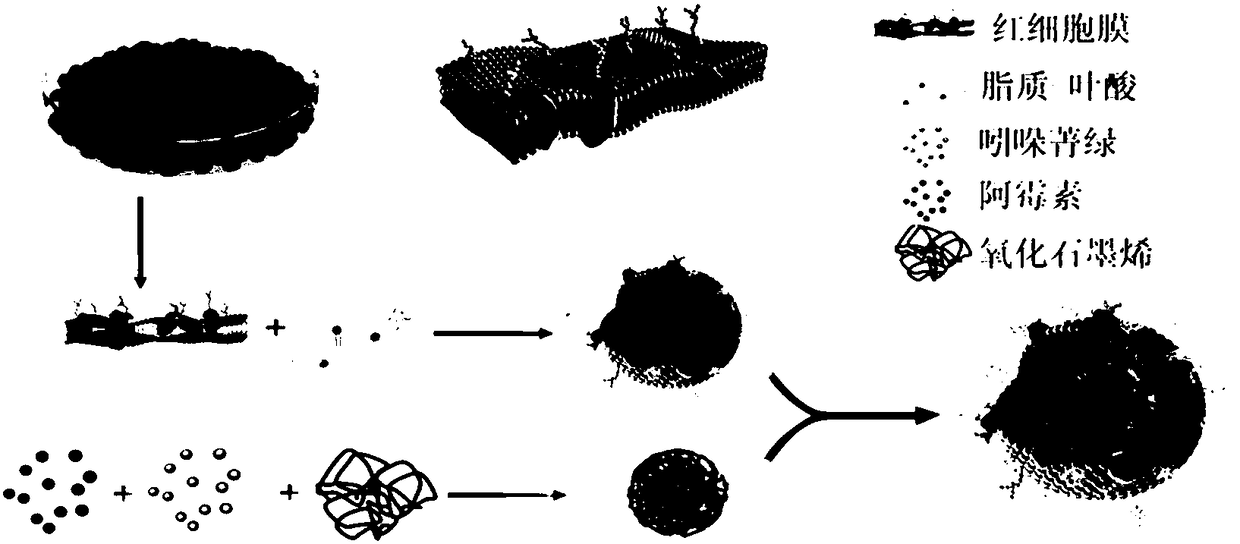
[0028] The preparation flow chart of this embodiment is as follows figure 1 Shown, its specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0029] (1) Preparation of nanoscale erythrocyte membrane vesicles (RM)
[0030] Take fresh anticoagulated whole blood from healthy people, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 5min, discard the upper layer of plasma and white blood cells and platelets; add 30 times the volume of 0.25×PBS hypotonic solution to lyse red blood cells, release hemoglobin, then centrifuge at 14000rpm for 10min, discard the upper layer of hemoglobin, collect For the red blood cell membrane at the bottom, add hypotonic solution PBS again to wash the red blood cell membrane until the supernatant is colorless, and collect the light red red blood cell membrane solution at the bottom. Take 50ul red blood cell membrane solution plus 1ml PBS, put it in an ultrasonic cleaner for 10min (350W), and then put the ultrasonic red blood cell membrane into a 400nm syringe filter to extract back a...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Particle size and microscopic test
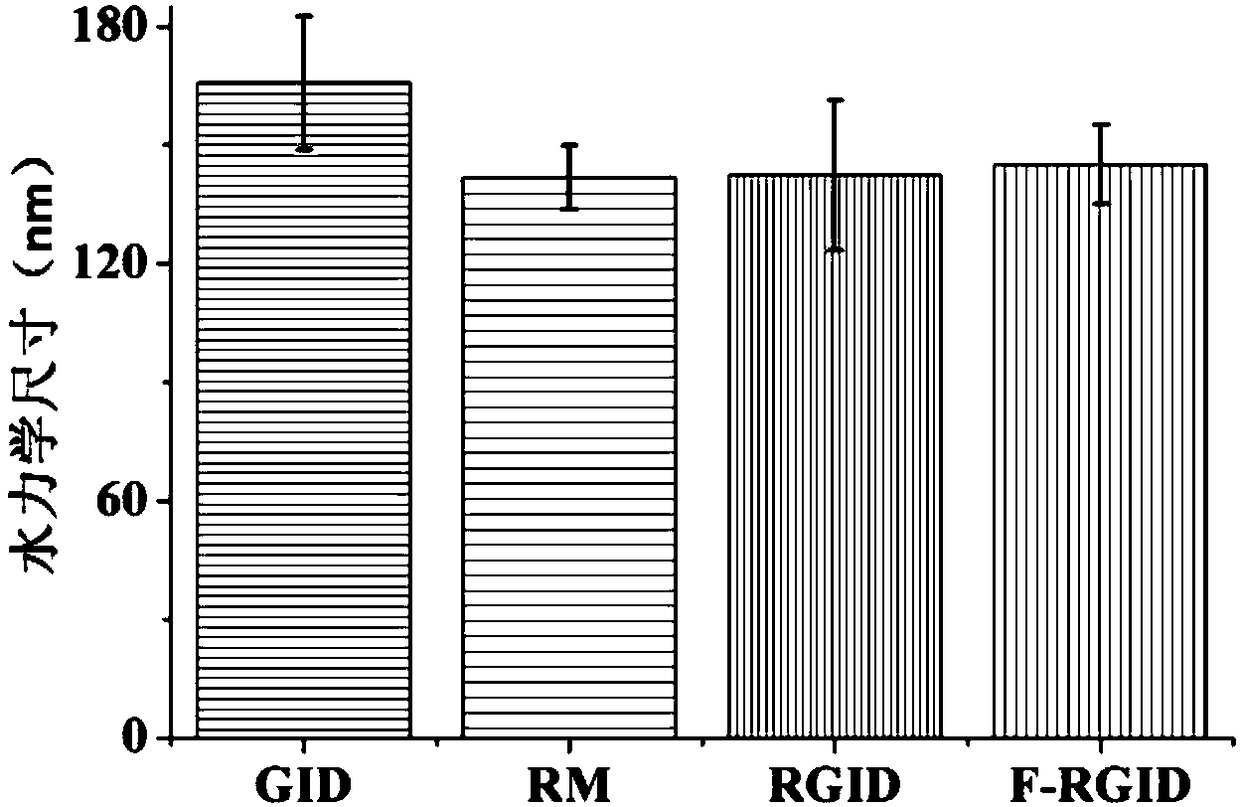
[0041] Nanoscale erythrocyte membrane vesicles (RM) prepared in Example 1, drug-loaded graphene oxide (GID), nano drug controlled release system (F-RGID) and the nano drug controlled release system (RGID) in comparative example 1 The size is tested, and the results are as follows figure 2 As shown, GID particle size: 167±11nm; RM particle size: 143±5nm; RGID particle size: 144±9nm; F-RGID particle size: 145±7nm.
[0042] The microscopic morphology of the drug-loaded graphene oxide (GID), nanoscale erythrocyte membrane vesicles (RM), and nano drug controlled release system (F-RGID) prepared in Example 1 is as follows: image 3 As shown, the GID has a sheet-like structure, the RM particle size is uniform, and the GID is successfully wrapped by the RM.
[0043] (2) Biocompatibility test
[0044]The hemolysis rate of the drug-loaded graphene oxide (GID) prepared in Example 1, the nano-drug controlled-release system (F-RGID) and t...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Application of nano drug controlled release system in the treatment of tumors
[0047] Schematic flow chart of the nano-drug controlled release system in the treatment of rat tumors. Figure 6 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048] (1) Targeted research
[0049] The drug-loaded graphene oxide (GID) prepared in Example 1, the nano-drug controlled-release system (F-RGID) and the nano-drug controlled-release system (RGID) prepared in Comparative Example 1 were studied on targeting. BALB / c female nude mice (about 20 g) were subcutaneously injected with Hela cells (1×10 6 ). Tumor volume = length × width 2 / 2; when the tumor volume reaches 100mm 3 , the nude mice were randomly divided into the above three groups. 100 μl of PBS solution of GID, RGID, and F-RGID (prepared according to the concentration of DOX in the carrier as 1 mg / L) was injected through the tail vein. Using the red fluorescence of doxorubicin, the drug distribution in vivo was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com