High-yield nattokinase gene engineering strain constructing method
A technology of genetically engineered strains and nattokinase, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low enzyme activity, long fermentation time, complicated separation and purification process, etc., and achieves the effects of good safety, less impurities in fermentation products and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Construct nattokinase genetically engineered bacterial strain, comprises the following steps:
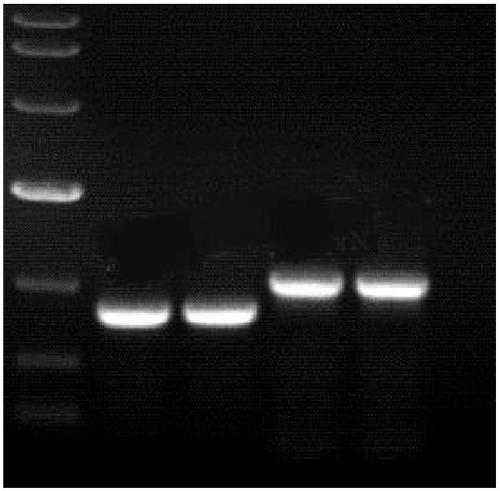
[0025] 1) Obtain the sequence of nattokinase gene fragment from GenBank, use Clone Manager software to design primers, and synthesize them by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Company. Using PCR technology to amplify the nattokinase gene fragment;
[0026] 2) Perform BamH I and Sma I double-enzyme digestion treatment on the PCR amplification product and the carrier plasmid, and use T4DNALigase to connect to construct a recombinant plasmid;
[0027] 3) Transform the recombinant plasmids into Bacillus subtilis using an electric transformation apparatus, culture overnight at 37°C on a plate containing antibiotics, and select positive transformants for sequencing verification.
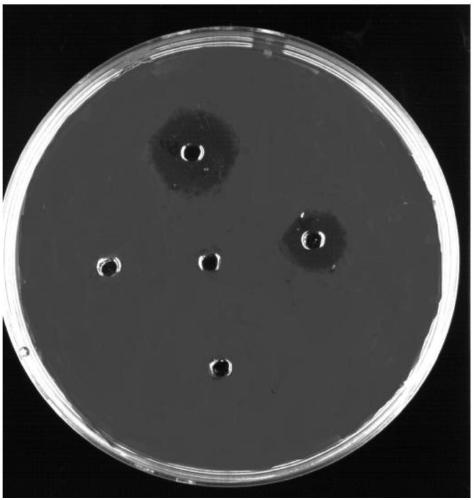
[0028] 4) Enzyme activity detection: Inoculate the seed bacteria liquid into 25mL fresh liquid medium with 2% inoculum amount, and culture on a shaking table at 30°C until OD 600nm Between 0.6 and 0.8, 0.1...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Optimizing the expression conditions of the recombinant strains, including the following steps:
[0032] 1) Determination of optimal IPTG concentration
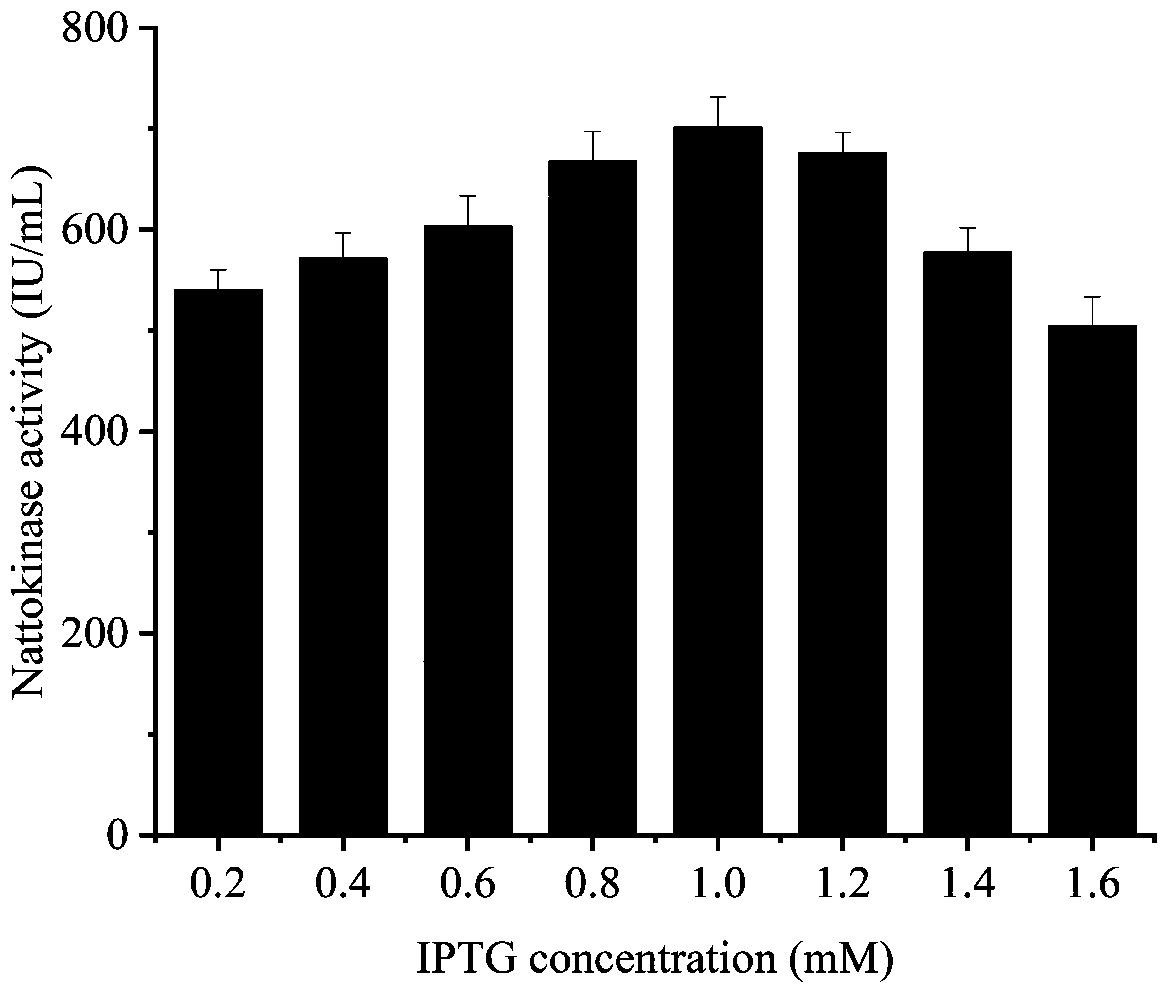
[0033] Inoculate the seed bacterium solution of the recombinant strain in 25mL of fresh liquid medium with 2% inoculum amount, and culture it on a shaking table at 30°C to OD 600nm Between 0.6-0.8, different concentrations (0.2mM, 0.4mM, 0.6mM, 0.8mM, 1.0mM, 1.2mM, 1.4mM and 1.6mM) were added to induce expression of IPTG for 24 hours, and then the enzyme activity of nattokinase was detected . image 3 The optimal IPTG concentration was shown to be 1.0 mM.
[0034] 2) Determination of the optimal expression temperature
[0035] Inoculate the seed bacterium solution of the recombinant strain in 25mL fresh liquid medium with 2% inoculum amount, and culture it on a shaking table until OD 600nm At 0.6-0.8, 1.0 mM IPTG was added to induce expression at 18°C, 25°C, 30°C, 37°C and 40°C, respectively. Figure 4 The optimum...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Optimization of recombinant strain fermentation medium, comprising the following steps:
[0040] 1) Determination of the best carbon and nitrogen sources
[0041] In order to determine the impact of optimum carbon source and nitrogen source type and mass concentration on nattokinase, select carbon source to have: glucose, sucrose, maltose, xylose, glycerol, lactose, cellulose, soluble starch, mass concentration is 20g / L; nitrogen source: soybean peptone, peptone, tryptone, yeast powder, NH 4 NO 3 , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , NH 4 Cl, NaNO 3 , the mass concentration is 20g / L. The mass concentration gradients of nitrogen source and carbon source were 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 g / L. The results showed that the optimum nitrogen source was peptone 20g / L, and the optimum carbon source was glucose 20g / L.
[0042] 2) Effects of sodium glutamate and sodium citrate on the activity of nattokinase
[0043] The concentration gradients of sodium glutamate and sodium citrate were ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration gradient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com