Method for producing butyric acid through fermentation
A technology of butyric acid and Clostridium tyrobutyricum is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve the problems of reducing the yield of butyric acid, high cost, and low concentration of fermentation products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
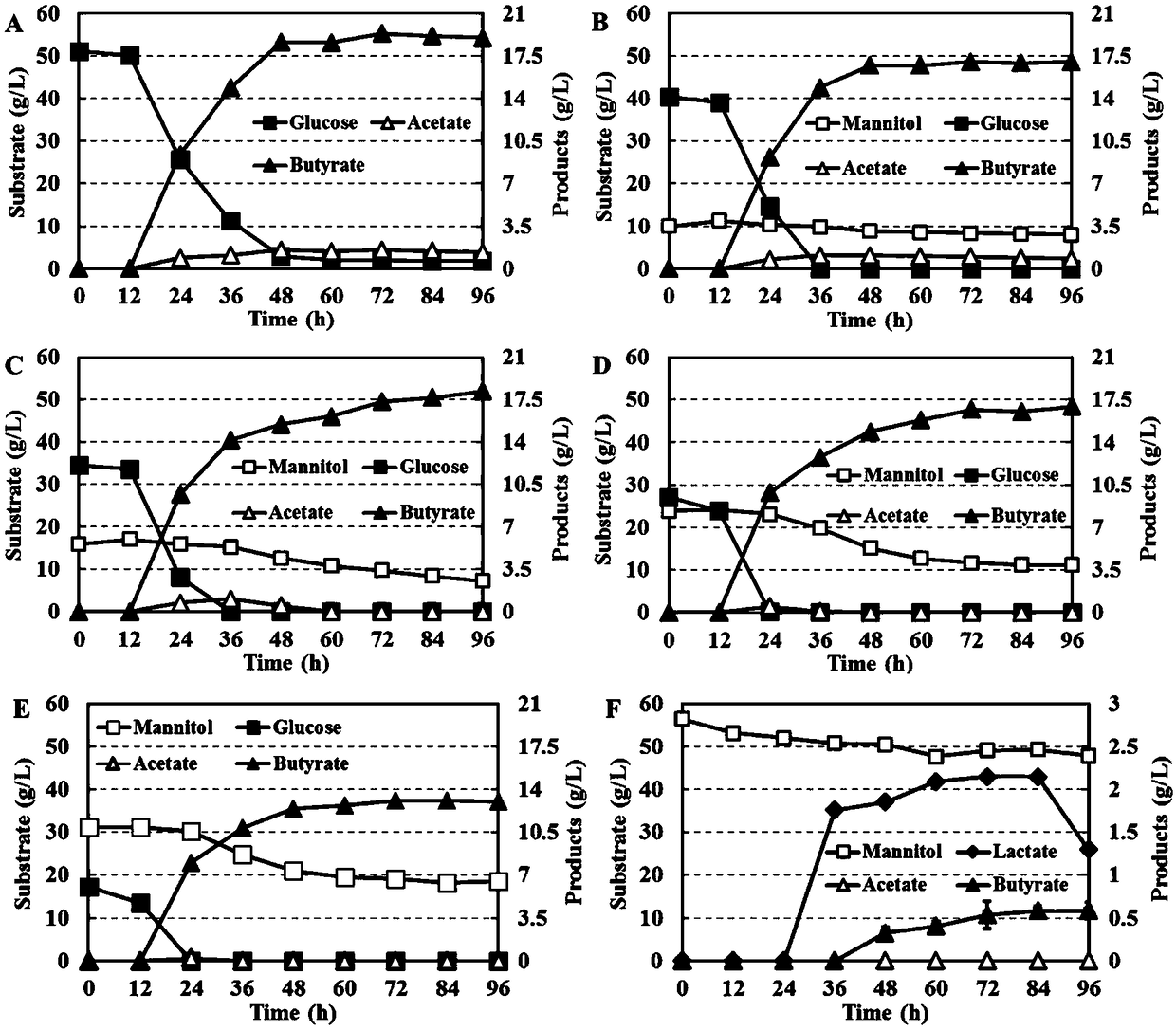
[0034] Example 1: Effects of Different Proportions of Glucose and Mannitol Mixed Substrate Fermentation on Butyric Acid Fermentation
[0035] (1) Preparation of culture medium
[0036] CGM (Clostridium Growth Medium) medium (1L system): 2g yeast extract, 4g tryptone, 2g (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 1g K 2 HPO 4 , 0.5g KH 2 PO 4 , 0.1g MgSO4 ·7H 2 O, the carbon source is glucose and / or mannitol, and the carbon and nitrogen are sterilized separately from the medium (121°C, 20min).
[0037] (2) Shake flask fermentation experiment
[0038] In a 100mL anaerobic bottle (filled with 50mL sterile CGM medium without carbon source and 2g / L CaCO 3 ) in different proportions, sterilized glucose and / or mannitol were added as carbon sources. Clostridium tyrobutyricum ATCC 25755 (American Type Culture Collection, American Type Culture Collection) was activated and cultured in CGM medium overnight, and then the seed solution was inserted into the anaerobic bottle, then cultured at 37 °С, 150 r...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: the preparation of kelp hydrolyzate
[0042] (1) Determination of kelp components
[0043] Kelp was purchased from the Vegetable Market in Suishi Village, University City, Guangzhou. The determination of moisture, total ash, protein, fat and total sugar content in kelp was determined according to GB5009.3-2016, GB5009.4-2016, GB5009.52010, GB5009.6-2016 respectively and phenol-sulfuric acid method. The specific ingredients are shown in the table below:
[0044]
total ash
Fat
total sugar
content(%)
9.56
28.67
7.21
1.30
58.95
[0045] (2) Preparation of kelp acid hydrolyzate
[0046] The dry kelp was crushed into powder by mechanical pulverization, passed through a 100-mesh sieve and stored in an oven at 65°C for drying, and then the above-mentioned kelp powder was mixed with 0.1M H 2 SO 4 well mixed. Pretreatment at 121°C for 45 minutes, after cooling, the hydrolyzed solution was...
Embodiment 3
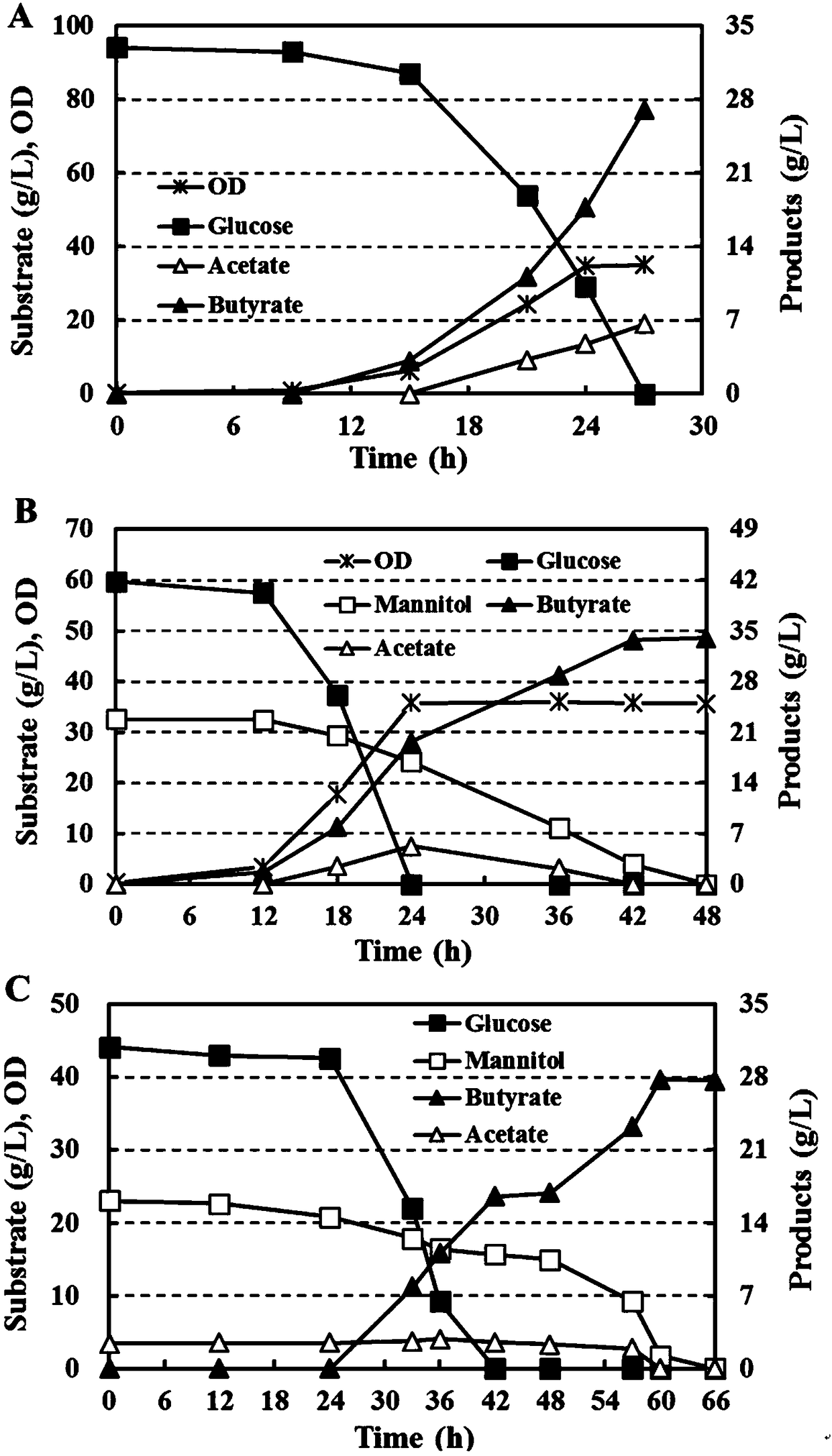
[0049] Example 3: Clostridium tyrobutyricum uses glucose, glucose / mannitol mixture, and kelp enzymatic hydrolyzate as substrates to ferment and produce butyric acid respectively
[0050] Glucose (~90g / L), glucose / mannitol mixed substrate (~60g / L glucose and ~30g / L mannitol), kelp enzymatic hydrolysis solution (ammonium acetate in the medium instead of ammonium sulfate, and glucose , make glucose:mannitol=44:23) as the carbon source of the fermentation experiment. The fermentation experiment was carried out in a 5L fully automatic mechanical stirring fermenter. Before fermentation, first sterilize the fermenter device at 121°C for 20 minutes, then add CGM medium (1L), and sterilize it at 121°C for 20 minutes, and after cooling, replace the air in the tank with sterile nitrogen to achieve anaerobic environment. Clostridium tyrobutyricum ATCC25755 was activated and cultured overnight in CGM medium, then the seed liquid was introduced into the fermenter according to the inoculum...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com