Method for treating hazardous wastes through cooperation of metallurgical furnace
A hazardous waste and co-processing technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of water and soil pollution, long-term poisoning, low operating costs, etc., achieve significant economic and environmental benefits, less harmful substances, comprehensive Powerful Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
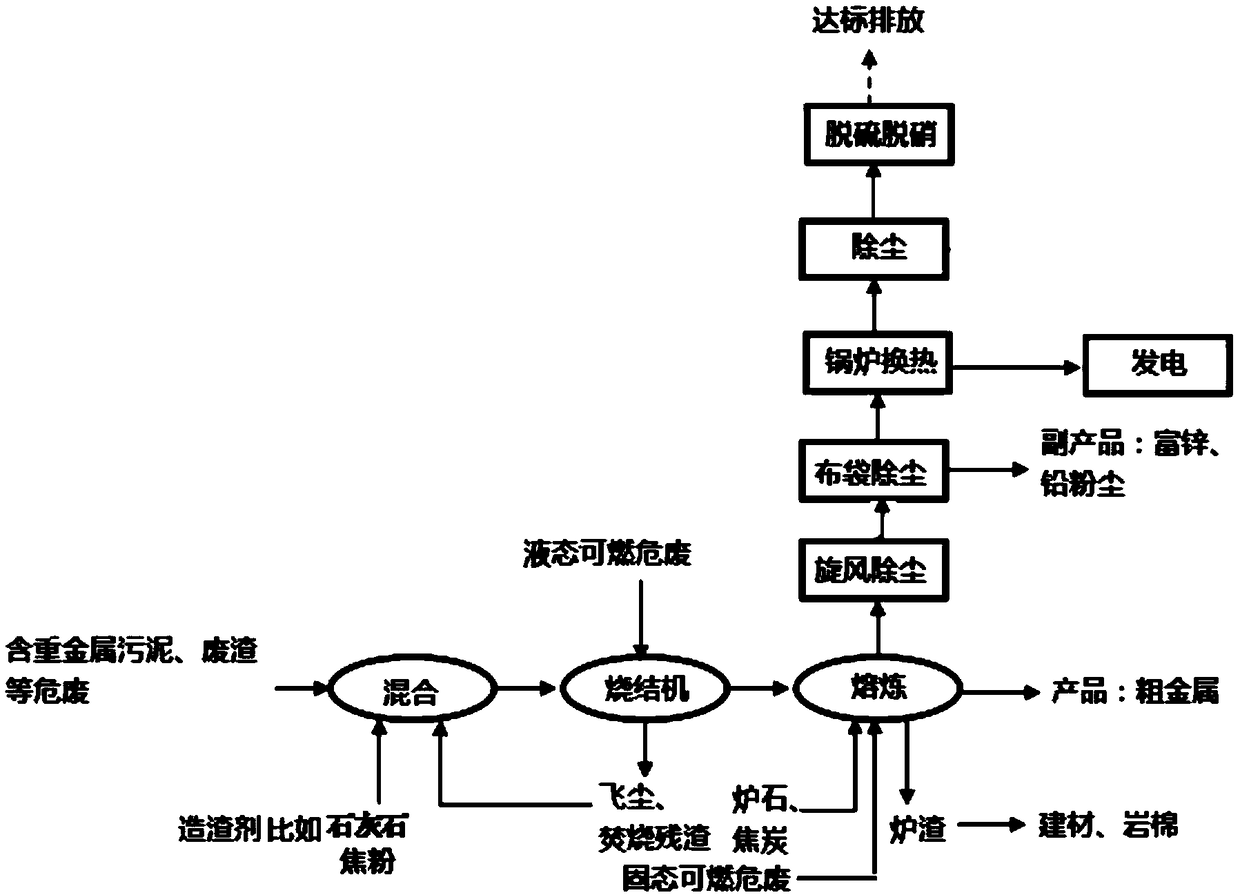
[0053] (1) The heavy metal-containing sludge / waste residue from the iron and steel industry is selected as the raw material, and the main metal components are Fe: 34.00%, Zn: 6.00%, Ni: 3.00%, Cr: 8.00%, Si: 8.5%, Ca: 9.6% . According to the mass ratio of heavy metal-containing sludge / waste residue: the first slagging agent: coke powder is about 70:25:5, after fully mixing, enter the sintering machine and sinter at 920-930°C for 10 minutes to form agglomerates. A slagging agent includes: quicklime and fly ash and incineration residue from the incineration of ordinary domestic waste, wherein the amount of fly ash and incineration residue is only 5% of the total mass of the first slagging agent, and the slag alkalinity of the sintering process is 1.2-1.4, during the sintering process, spray liquid combustible hazardous waste into the sintering machine every 10 minutes for 5 minutes, so that as much liquid combustible hazardous waste can be burned as much as possible, and it can ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) The mixed solid waste of electroplating sludge and leather sludge from the electroplating and leather industry is selected as heavy metal hazardous waste, mainly containing heavy metal compounds such as chromium, nickel, iron, copper, zinc, chromium, iron, nickel, copper and zinc The total content of iron is about 8%, including 3% chromium, 1% iron, 2% nickel, 1% copper, and 1% zinc. According to the mass ratio of heavy metal sludge and nickel-chromium alloy 200 series dust: the first slagging agent: coke powder is about 90:8:2, among which: heavy metal sludge and nickel-chromium alloy account for heavy metal sludge and nickel-chromium alloy 200 series dust (main component content (wt%): Ni: 0.65, Cr: 7.00, TFe: 37.5, Ca: 0.30, Mn: 0.40, P: 0.055, Si: 7.50, CuO: 11.0; Zn: 5.0) total 30% of the mass, after fully mixing, enter the sintering machine and sinter at 940-950°C for 20 minutes to form agglomerates. The first slag forming agent includes quicklime and fly ash ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] (1) The heavy metal-containing sludge / waste residue from the iron and steel industry is selected as the raw material, and the main metal components are Fe: 34.00%, Zn: 6.00%, Ni: 3.00%, Cr: 8.00%, Si: 8.5%, Ca: 9.6% . According to the mass ratio of heavy metal-containing sludge / waste residue: first slagging agent: coke powder: binder: water is about 60:22:5:3:10, after fully mixing, use a briquetting machine to press block, used for smelting after curing for 4 days; the first slagging agent includes: quicklime and fly ash and incineration residue from the incineration of ordinary domestic waste, wherein the amount of fly ash and incineration residue is only 5% of the total mass of the first slagging agent %, the slag basicity of the sintering process is 1.2-1.4.
[0062] (2) and (3) steps are with embodiment 1.
[0063] The crude metal is obtained in the step (2), the metal recovery rate reaches 95%, and the heavy metal content in the slag is reduced to 0.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com