Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain rich in GABA and identification method thereof
A technology for Saccharomyces cerevisiae and identification method, which is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microorganism determination/inspection, etc., and can solve the problems of poor stability of fermentation strains, low product safety factor, loss of excellent performance, etc., Achieve the effects of good strain gene stability, good bacteriostatic effect and high nutritional and health care value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
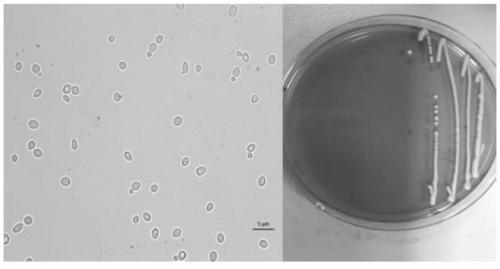
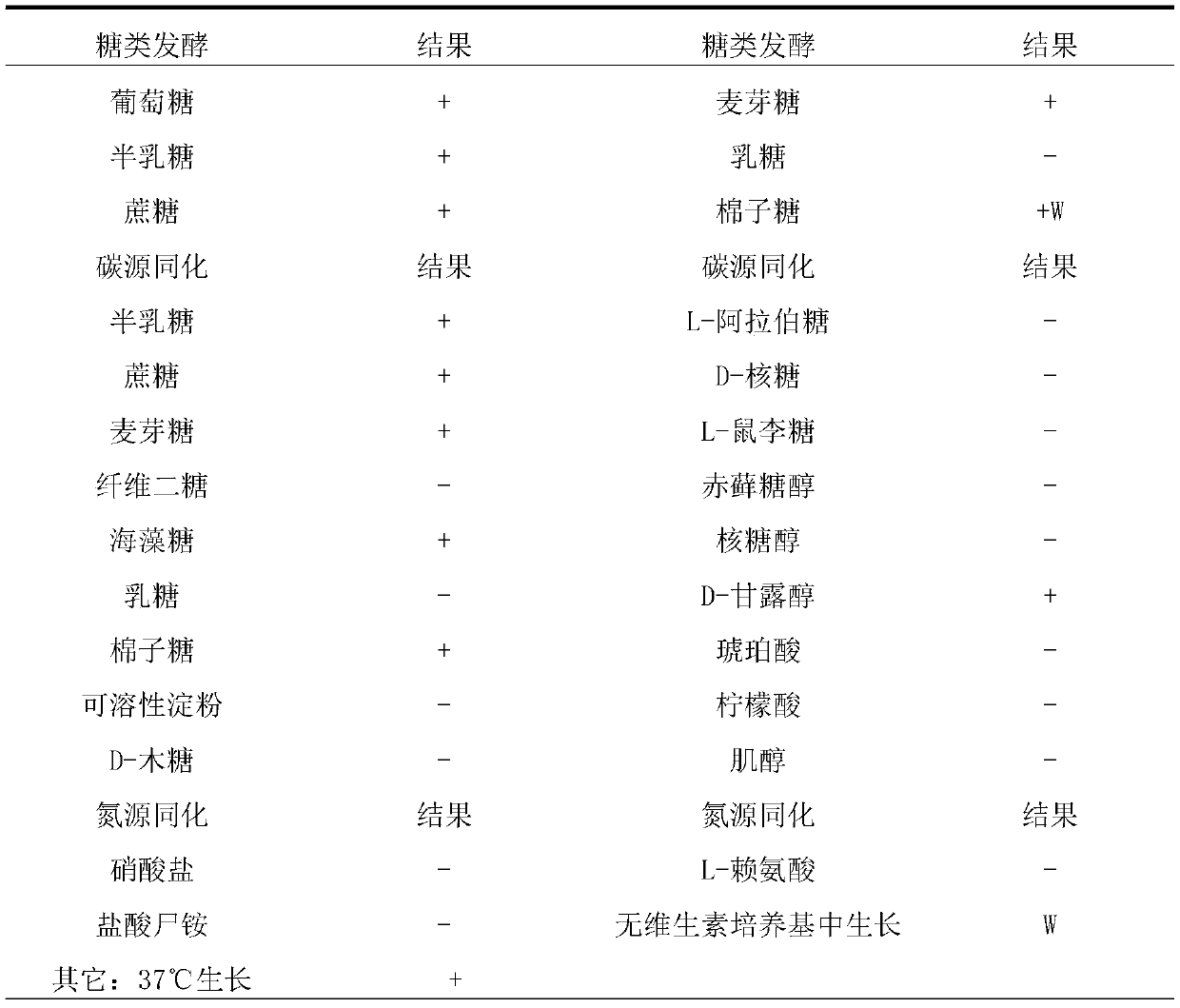
[0024] 1) Screening of bacterial strains: Take 1 mL of natural fermented liquids such as mulberry, green plum, and apple, and add them to 9 mL of sterile water, shake fully to mix them evenly, and dilute them in turn to 10 mL. -2 , 10 -3 …10 -7 , 10 -8 . Pipette 0.1 mL of each dilution to spread on the YPD medium plate and culture at 28°C. Pick a single colony that grows rapidly and robustly, and streak again on the plate until pure colonies are isolated;
[0025] 2) Obtaining DNA: using a fungal DNA extraction kit to extract fungal DNA;
[0026] 3) PCR amplification: using the fungal DNA extracted in step 2) as a template, amplification primers: ITS1-5'-CTTGGTCATTTGAGGAAGTAA-3' and ITS2 5'-GCTGCGTTTCTTCATCGATGC-3'; system: 10xbuffer2ul, 2,5MdNTP 2ul, Primer 5M each 1ul, rTaq 0.2ul, DNA 2ul, BSA 0.2ul, ddH 2 0 to 20ul; Amplification conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3min, denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 55°C for 30s, extension at 72°C for 1min and 30s, ...
Embodiment 2
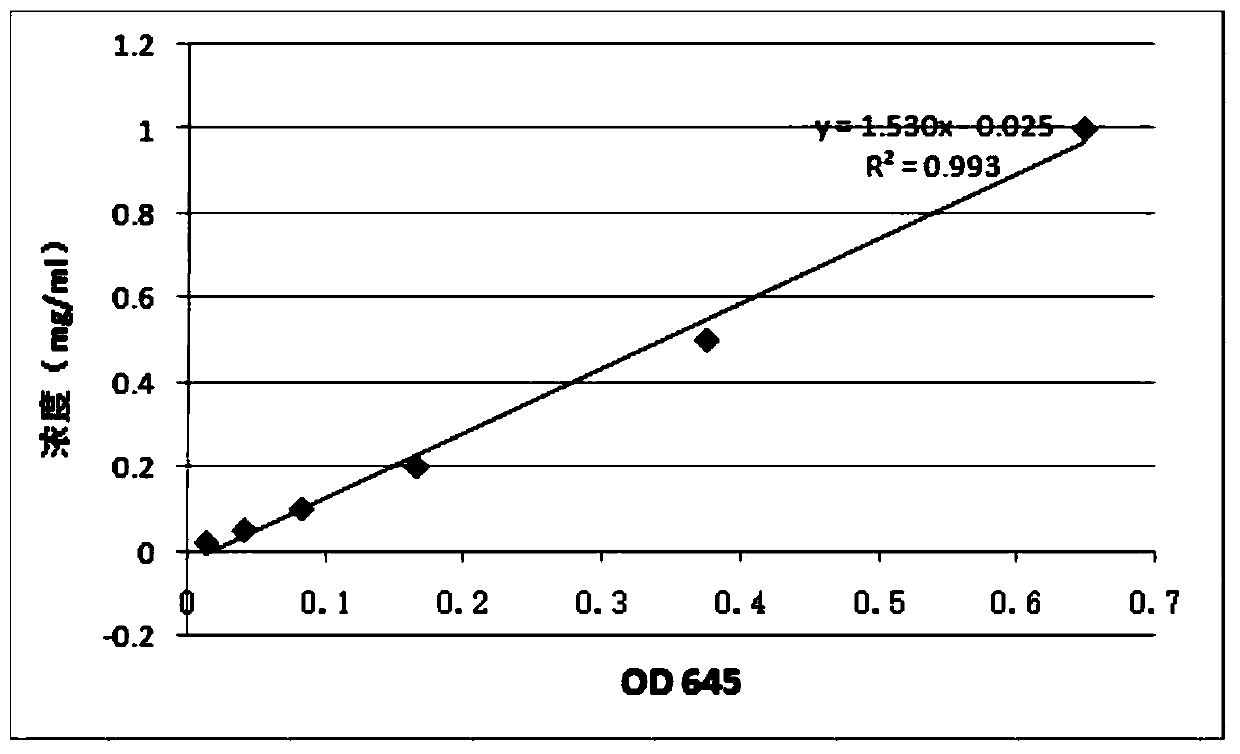
[0035] Determination of extracellular GABA content in Saccharomyces cerevisiae SS-A-1 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae SS-A-1):
[0036] 1) Solution preparation:
[0037] 0.1mol / L sodium tetraborate buffer solution: accurately weigh 9.53g of sodium tetraborate, dissolve in distilled water, and set the volume to 250ml;
[0038] 80% double-distilled phenol solution: Accurately weigh 80.00g of double-distilled phenol, dissolve it in 20ml of water, stir it in the dark to fully dissolve, and store it in the refrigerator at 4°C in the dark;
[0039] 6% double-distilled phenol solution: accurately measure 7.5ml of 80% double-distilled phenol, dissolve it in distilled water, dilute to 100ml, and prepare it immediately;
[0040] 2) Sample processing:
[0041] Take 1 g of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae sample of Example 1 and place it in a conical flask, add 50 mL of 60% ethanol solution, shake in a water bath for 3 h, centrifuge at 4000 r / min for 20 min, transfer the supernatant into an eggpl...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Antibacterial performance test:
[0058] The purified yeast was inoculated into YPD liquid medium at an inoculum size of 5%, cultured with shaking at 30° C. and 180 rpm for 24 hours, and centrifuged at 8000 rpm / min for 10 minutes. Add the supernatant to a disposable plate, place it overnight at -20°C, freeze-dry it, add 1 / 15 of the volume of the supernatant to dissolve in distilled water, and then use a 0.45um sterile filter to filter out bacteria and place in Store at 4°C for later use.
[0059] Inoculate Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Micrococcus luteus into LB liquid culture medium with 5% inoculum respectively, and culture them at 30°C and 200r / min for 24 hours, then take them out and dilute to 10 with sterile water. 6 cfu / ml (10-fold dilution for Escherichia coli, 100-fold dilution for Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella and Micrococcus luteus).
[0060] Take 100ul indicator bacteria and spread them on the LB solid medium, put them into the Oxford cup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com