Method for recovering metal at low cost from electroplating sludge and producing refined nickel sulfate
An electroplating sludge, low-cost technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
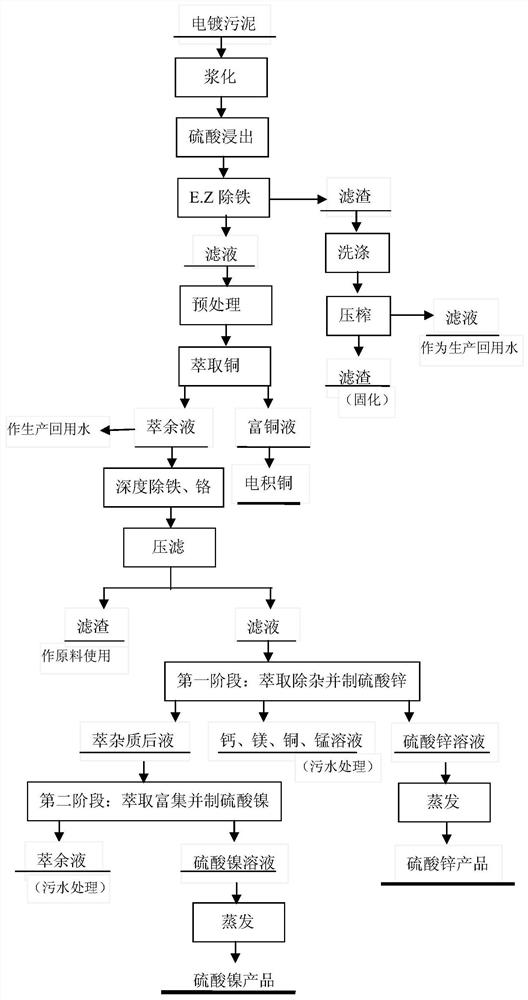
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Mass percentage (%) of main substances in electroplating sludge: CuO 1.70, NiO 1.44, ZnO 0.74, Cr 2 o 3 0.57,H 2 O 65.3.
[0058] In step (1), the electroplating sludge material is added to tap water at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 2:1; at a temperature of 30°C, turn on strong stirring, mix and make pulp for 2 hours, and sieve out sundries (bags, wood, plastic, etc.). Pulp machine slurry. After slurrying, the material is pumped into another reaction tank, and concentrated sulfuric acid is added under stirring conditions to control the final pH value of the solution to 1.5-2.5.
[0059] Step (2), adjust step (1) to the slurry with an end point pH value of 1.5 to 2.5, measure the ferrous content, add the theoretical amount of hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide mass percentage 28 to 35%), and oxidize the ferrous iron into trivalent Iron is prepared as material A; 20% sodium carbonate aqueous solution is prepared as material B in configuration mass percentage; tap water...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2 is compared with embodiment 1, except following difference, other is with embodiment 1:
[0070] In step (1), the electroplating sludge is added to the production reuse water at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 1.2:1, and the copper raffinate is extracted for slurrying.
[0071] The pre-prepared material C in the reaction tank for E.Z iron removal in step (2) is the post-material of E.Z iron removal produced in step (2) in Example 1, without the slurry before solid-liquid separation.
[0072] Step (5) Selection of extraction stages in the first stage: "1 stage for saponification, 7 stages for extraction, 4 stages for nickel washing, 4 stages for calcium, magnesium, copper and manganese washing, 4 stages for zinc washing, 3 for regeneration organic class". Acidity used: 0.6mol / L hydrochloric acid for washing nickel, 2.0mol / L hydrochloric acid for washing calcium, magnesium, copper, and manganese, 4mol / L sulfuric acid for zinc washing, and 6.0mol / L hydrochloric ac...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3 is compared with embodiment 1, except following difference, other is with embodiment 1:
[0076] In step (1), the electroplating sludge is added to the production reuse water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1.1:1, and the slag washing water in step (7) in Example 2 is used as the production reuse water.
[0077] Step (2) is the same as embodiment 2. The material C for E.Z iron removal is the slurry after E.Z iron removal in Example 2.
[0078] Step (3) The copper-specific extractant is selected from the "N902----aviation kerosene" system.
[0079] In step (5), both the first stage and the second stage of saponification are 20% by mass sodium carbonate solution. Selection of extraction stages in the first stage: "2 stages for saponification, 11 stages for extraction, 4 stages for nickel washing, 6 stages for calcium, magnesium, copper, and manganese washing, 5 stages for zinc washing, and 4 stages for organic regeneration." The selection of the second stage...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com