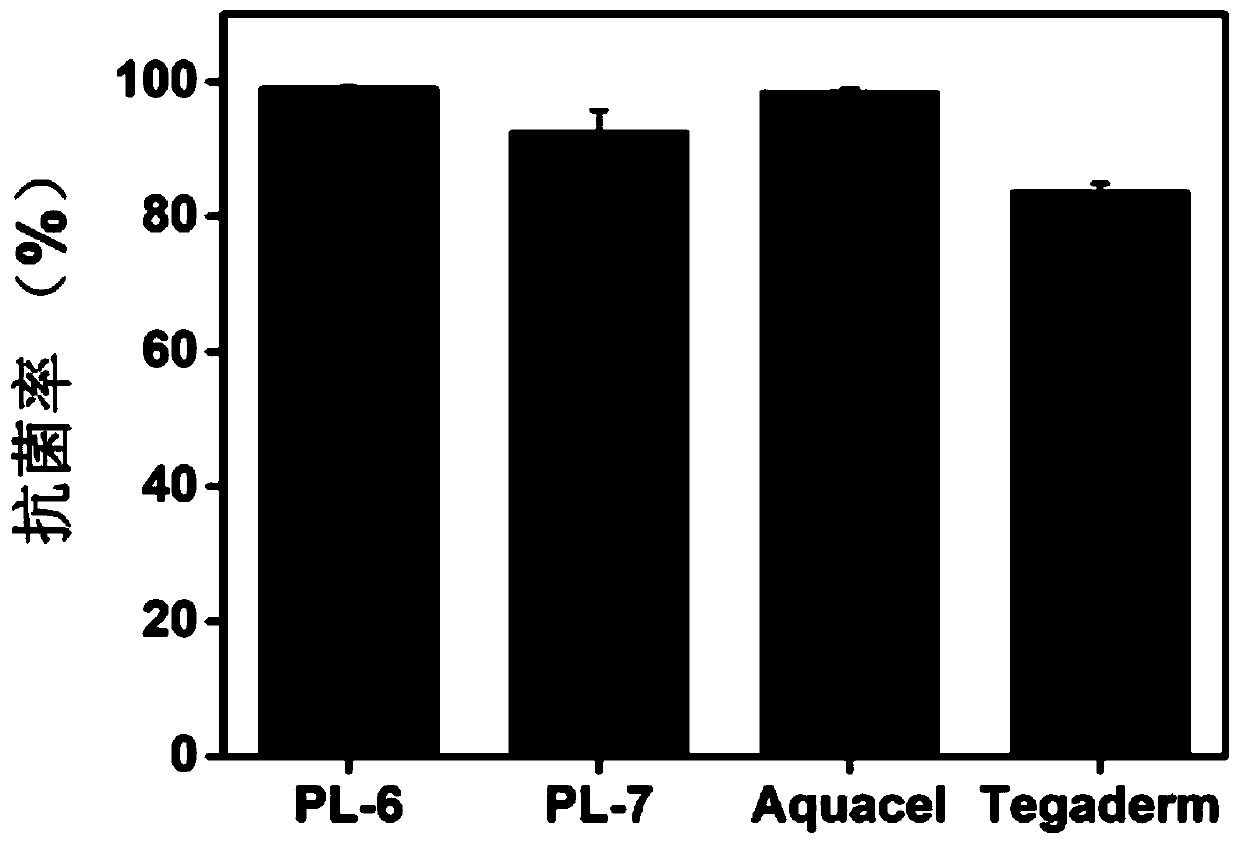
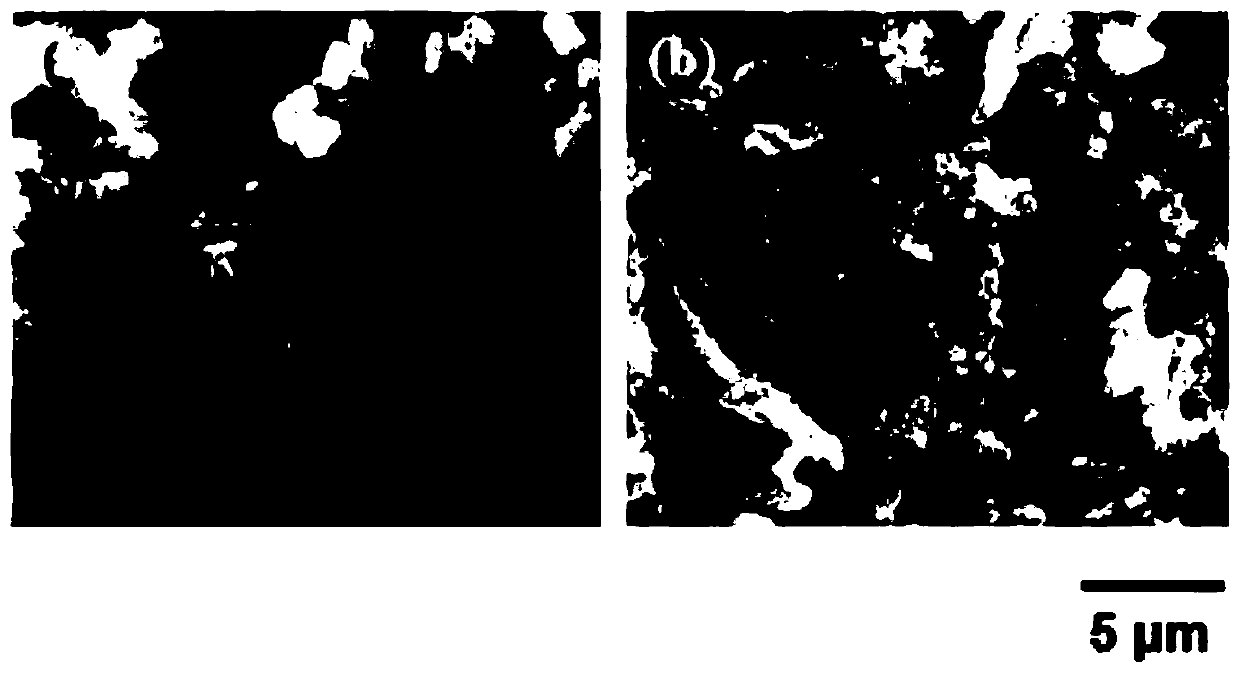
Antibacterial polysaccharide fiber material and preparation method thereof
A polysaccharide fiber and polysaccharide technology, applied in the field of antibacterial polysaccharide fiber and its preparation, can solve problems affecting the health of patients, cell toxicity, excessive silver accumulation, etc., achieve good biocompatibility, prevent microbial invasion, and inhibit bacteria broad spectrum effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
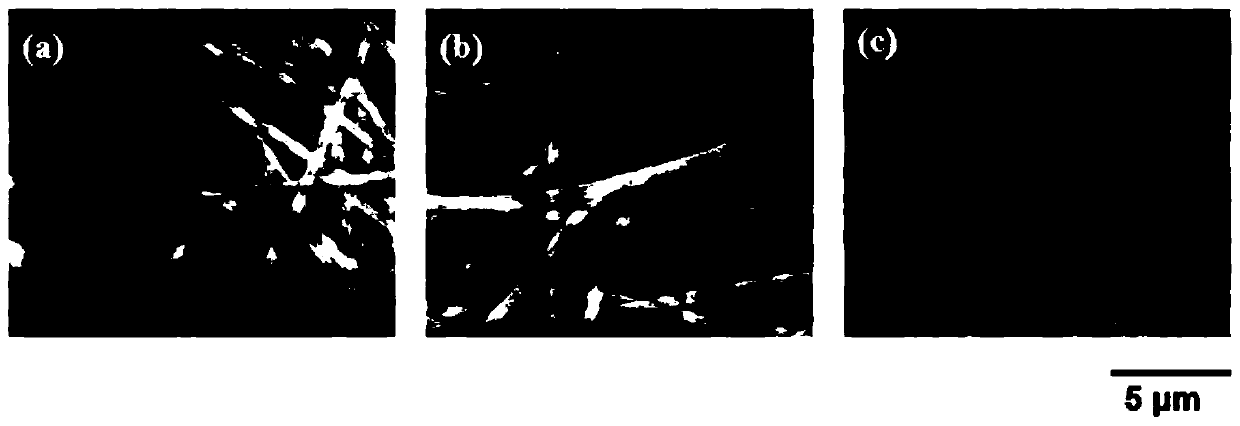
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of antibacterial polysaccharide fiber material, and the method comprises:
[0028] Step 1: Preparation of dialdehyde polysaccharides: Add sodium periodate aqueous solution to polysaccharide aqueous solution, avoid light, oxidize and stir, dialyze and freeze-dry to obtain dialdehyde polysaccharides;
[0029] Step 2: Electrospinning nanofibers: Stir the dialdehyde polysaccharide obtained in Step 1 with polyethylene oxide, a surfactant, and a co-solvent to obtain a mixed solution, and then perform electrospinning to obtain electrospun fibers;
[0030] Step 3: Cross-linking: Soak the electrospun polysaccharide fiber obtained in Step 2 into ε-polylysine solution to carry out cross-linking reaction to obtain antibacterial polysaccharide fiber material.
[0031] According to the present invention, first prepare a certain amount of polysaccharide aqueous solution and sodium periodate aqueous solution, mix the two under dark cond...
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: the starch fiber that the degree of oxidation of cross-linking under acidic (pH=6) condition is 40%
[0039] 1) Sodium periodate oxidized starch: add potato starch to an appropriate amount of water, heat and stir for 30 minutes to dissolve the potato starch, and obtain a 1.5% aqueous solution of potato starch. Then the potato starch aqueous solution was mixed with 10% sodium periodate aqueous solution, so that the molar ratio of sodium periodate to the glucose unit in the starch was 40:100, 1M hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH of the solution to be 4, and the reaction was carried out under normal temperature in the dark for 16 Hour. The mixed solution was transferred to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut off of 3500, and dialyzed with a large amount of ultrapure water for 6 times, each time for 4 hours. Then freeze-dry the oxidized starch aqueous solution with a freeze dryer to obtain dialdehyde starch with a degree of oxidation of 40%;...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: the starch fiber that the degree of oxidation of cross-linking under neutral (pH=7) condition is 30%
[0047] 1) Sodium periodate oxidized starch: add potato starch to an appropriate amount of water, heat and stir for 30 minutes to dissolve the potato starch, and obtain a 1.5% aqueous solution of potato starch. Then the potato starch aqueous solution was mixed with 10% sodium periodate aqueous solution, so that the molar ratio of sodium periodate to the glucose unit in the starch was 30:100, 1M hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH of the solution to be 4, and the reaction was carried out under normal temperature in the dark for 16 Hour. The mixed solution was transferred to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut off of 3500, and dialyzed with a large amount of ultrapure water for 6 times, each time for 4 hours. Then freeze-dry the oxidized starch aqueous solution with a freeze dryer to obtain dialdehyde starch with a degree of oxidation of 30%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com