A carrier protein for site-directed mutation and its use in preparing vaccines
A carrier protein, site-directed mutagenesis technology, applied in the preparation methods of peptides, vaccines, multivalent vaccines, etc., can solve the problems of complex separation and purification process, reduced polysaccharide protein binding efficiency, and uneven binding process, and achieves optimization of modification conditions, Attenuate the protease activity, the effect of simple and easy modification reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Construction of carrier protein expression plasmid for site-directed mutagenesis
[0047] 1: Selection of mutation sites
[0048] The three-dimensional structures of HID and HIN47 were predicted using the online software phyre2, respectively.
[0049] 10 key amino acids were selected on the fusion proteins HIN47-HID and HID-HIN47 respectively. After these key amino acid positions are replaced, not only can the polysaccharide be bound at a fixed point, but it is expected to further reduce the residual protease activity of HIN47, which is conducive to improving the final polysaccharide binding product. stability. The information of the specific mutation site is shown in Table 1-Table 2, wherein the amino acid position refers to the position on the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2-3.
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] 2: Acquisition of expression plasmid
[0053] According to the HID and HIN47 gene sequences published by NCBI Gene Bank, the full-length DNA fragmen...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Expression and purification of embodiment 2 mutant carrier protein
[0063] Lys-azido-incorporated expression and purification of mutant protein
[0064] The expression plasmid pET9a-HIN47-HID-K522 obtained in Example 1 was cultured in LB medium at 37°C for 12-16 hours, and then amplified twice until the OD value of the bacterial solution reached 0.6-1.0, and Lys- azido to a final concentration of 1 mM, continue to amplify at 37°C for 30 minutes, add IPTG to a final concentration of 0.5mM, and arabinose to a final concentration of 0.2%, induce expression at 24°C for 12 hours and collect the cells.
[0065] The collected cells were balanced and resuspended with Ni-NTA-Bind-Buffer, ultrasonically disrupted, centrifuged to remove cell debris, subjected to Ni-NTA metal chelate affinity chromatography, fully washed with Ni-NTA-Wash-Buffer, and finally washed with Eluted with Ni-NTA-Elute-Buffer, the preliminary purified protein sample HIN47-HID--K522 was obtained with a pur...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 Coupling of Mutant Carrier Proteins and Polysaccharides by Copper-free Catalysis
[0067] The copper-free catalyzed Click reaction needs to be realized by the ring tension of cyclooctyne, and the modification is coupled with DIBO (polysaccharide with cyclooctyne structure) to perform copper-free catalyzed Click reaction with azide-containing groups.
[0068] The Click reaction system is as follows:
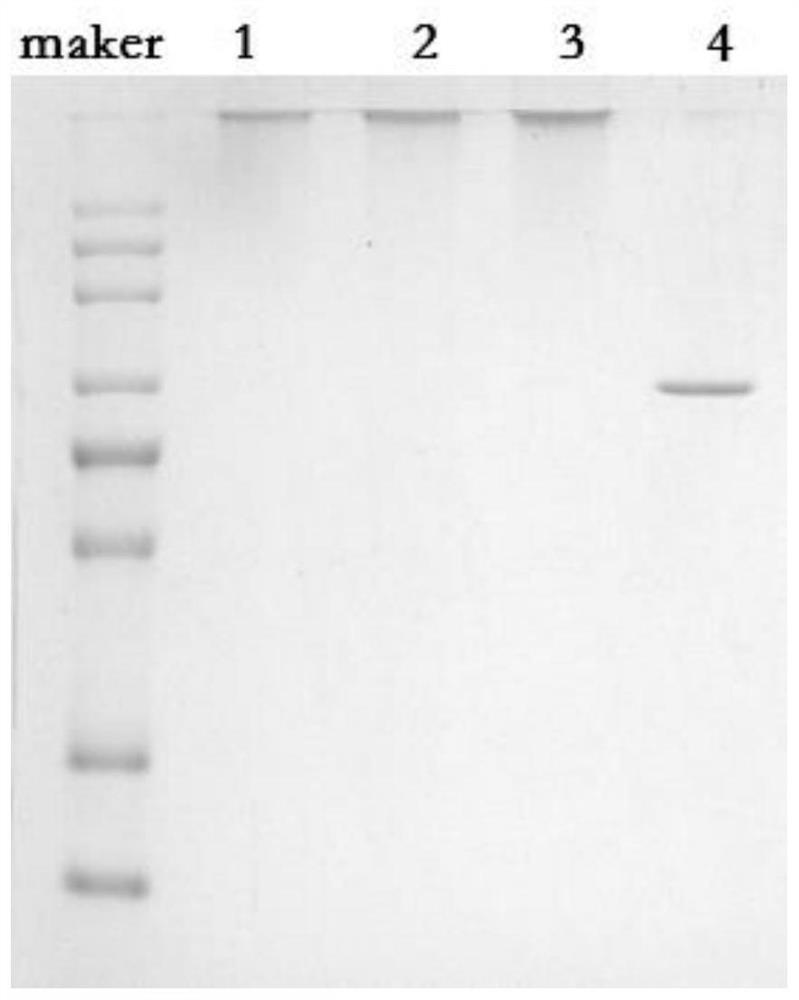
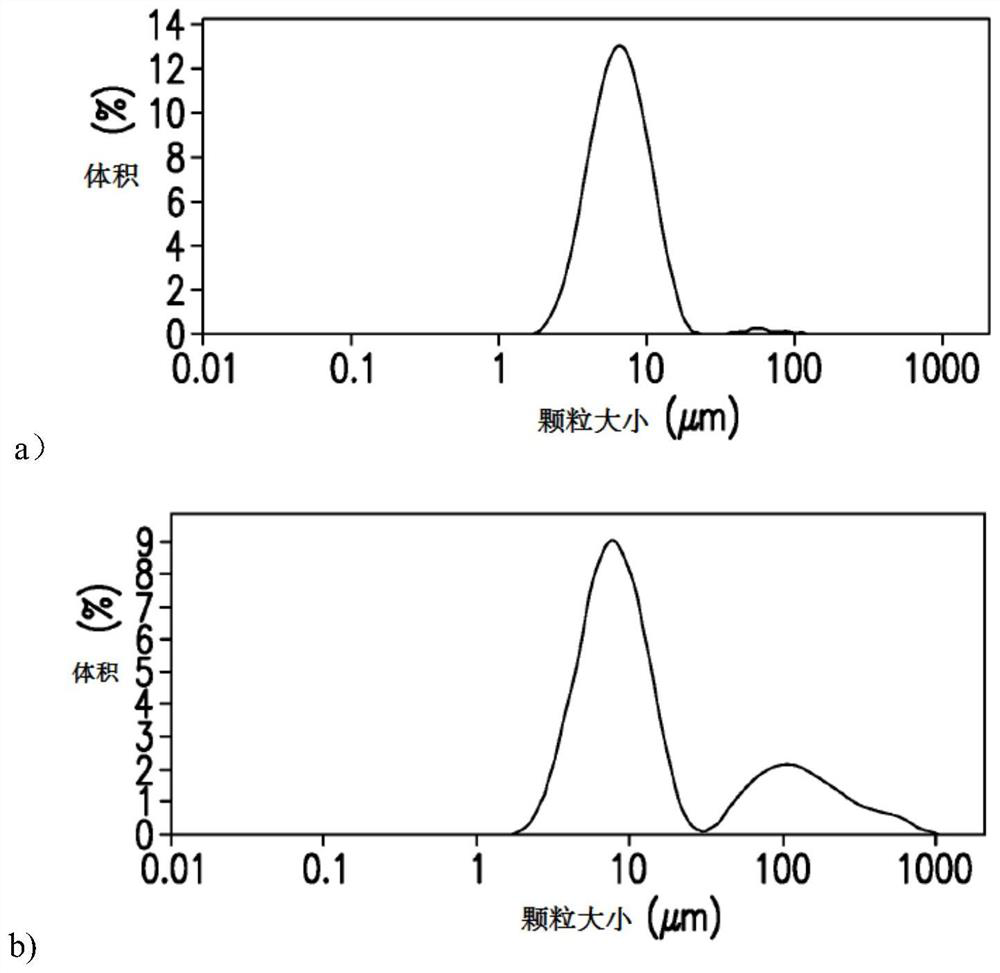
[0069] HIN47-HID--K522 protein 1 microgram per microliter, DIBO-pneumonia type 3 polysaccharide, molecular weight 200KD, 400KD, 2Mm each, vertical suspension at 4°C for 2 hours, the results showed different molecular weight (200KD, 400KD) pneumonia 3 All types of polysaccharides can be successfully modified on the protein F3-HIN47-HID--K522-200, F3-HIN47-HID--K522-400 (see figure 1 , line1, 2).
[0070] After the above reaction conditions, about 90% of the protein can be coupled to the polysaccharide within 1 hour, and the reconstituted product after the reactio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com