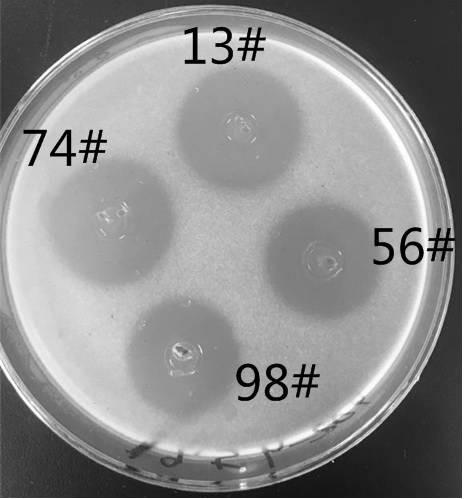
Method for screening high-producing strains of Polyoxin B
A technology of polyoxin and high-yield strains, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, which can solve the problems of low content of polyoxin B components and achieve low cost , a wide range of sources, the effect of important industrial and agricultural application potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: original bacterial strain spore preparation
[0038] Take Streptomyces aureus Chromogenes 98#, the starting strain of polyoxin, dilute and spread the slant medium, and culture at a constant temperature of 28°C for 7 days, select the fast-growing and plump single colony spores on the plate, cut off half of the single colony spores and add them to the physiological saline to make a spore suspension. The composition of 100mL slant medium is 0.5g of corn flour, 0.5g of maltose, 0.4g of yeast extract, 2.0g of agar, the rest is distilled water, and the pH before digestion is 7.0-7.2.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: Mutagenesis of polyoxin starting strain
[0040] Add half of the single bacterial colony excised in Example 1 into physiological saline containing 20% glycerol, vibrate and disperse to make a spore suspension. Pipette 15 μL of the spore suspension and drop it on the slide of the ARTP mutagenesis breeding instrument, and spread it evenly. Using the ARTP mutagenesis breeding instrument, first ultraviolet mutagenesis (15W ultraviolet lamp 30cm away from the suspension, irradiation for 30 seconds), then fluorescent lamp irradiation for 3 minutes, and then ARTP mutagenesis (irradiation power 120W, helium flow rate 8-12SLM, irradiation for 70 seconds) , to obtain the mutagen solution. Wash the mutagenesis solution with sterile saline under red light, and dilute the mutagenesis solution with normal saline gradient to 10 -4 、10 -5 、10-6 , smeared on the medium plate, and cultured in the dark at 26°C for 8 days. Select and cultivate the mutant single colony, ...
Embodiment 3
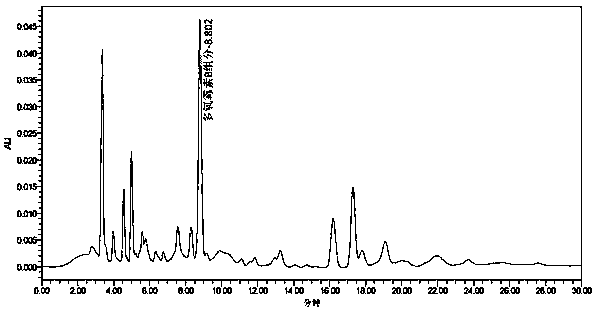
[0043] Embodiment 3: fermented liquid analysis
[0044] Use HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) to detect the change of polyoxin components in the fermentation product, and screen the strains with differences in secondary metabolite components from the starting strain 98# through the increase or decrease of peak shape and the change of relative peak area.
[0045] Sample processing: take 1 mL of fermentation broth and centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes, take 200 μL of supernatant and add 200 μL of ultrapure water to dilute. Add 80 μL methanol aqueous solution containing 0.5% trifluoroacetic acid, mix thoroughly, and centrifuge at 14000 rpm for 10 minutes. Take 400 μL of the supernatant for HPLC analysis.
[0046] HPLC conditions: the chromatographic column adopts Thermo 250mm, 4.6μm C18 chromatographic column. The mobile phase of HPLC was 10% methanol aqueous solution (containing 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid), the detection wavelength was 260nm, the injection volu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com