Antiviral emulsion composition, coating and preparation method thereof
An emulsion composition and emulsion technology, applied in antifouling/underwater coatings, polyurea/polyurethane coatings, coatings, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the density of anti-virus units, poor dispersion of nanoparticles, and single effective components, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of inhibiting virus and inactivating virus activity, stabilizing redox, and not easily affected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
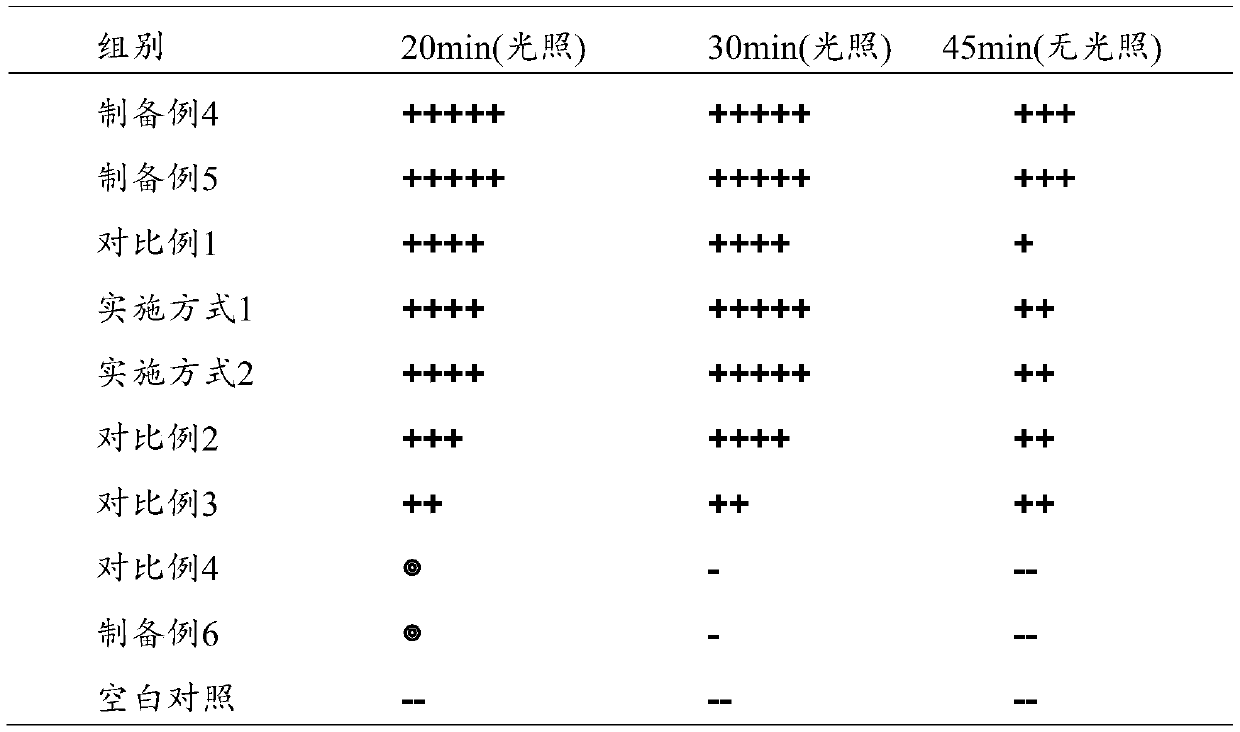
Examples
preparation example 1
[0090] S1: Disperse 12 g of anatase-type nano titanium dioxide (particle size 30-40 nm) in 100 mL of distilled water under stirring conditions to obtain a titanium dioxide suspension; add 0.35 g of cuprous oxide (median particle size 20 nm) to the suspension, Stir and disperse, then add 1.2 g of polyoxyethylene lauryl ether phosphate zinc salt (AEO-Zn) under rapid stirring, and disperse quickly until uniform, to obtain a cuprous oxide-doped titanium dioxide dispersion.
[0091] S2: Add 1.2g of 40-50nm zinc-loaded zirconium phosphate powder dispersed in 10ml methyl ethyl ketone solvent to the above titanium dioxide dispersion under stirring condition; add the above lauryl polyoxyethylene ether phosphate salt surface activity after stirring evenly to 2 wt%, heated to 45° C. and stirred for 15 minutes, and cooled to room temperature to obtain an inorganic metal nanocomposite dispersion.
preparation example 2
[0093] In a four-necked flask equipped with magnetic stirring and a reflux condenser, replace the air atmosphere with nitrogen gas, first add 100ml of chloroform solvent and 0.11mol of triphenylphosphine, and slowly use a dropping funnel at 50°C under stirring conditions. Add 0.1 mol of p-bromostyrene dropwise, after the dropwise addition, heat up to reflux and continue to stir for 6 hours; after the reaction is completed, cool to room temperature, add 30ml of distilled water, extract 3 times with dichloromethane, combine the organic phases and evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure , the obtained solid was recrystallized with ether and then dried in a vacuum oven to obtain a solid monomer of styryl triphenylphosphine quaternary phosphonium salt whose coordination anion is bromide ion, with a yield of 88%.
[0094] 1 H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): 5.1 (2H, =CH2), 6.0 (1H, =CH), 7.2-8.0 (ArH).
preparation example 3
[0096] Add 0.5 g of emulsifier octylphenol polyoxyethylene ether into a water-bath reaction kettle containing 110 ml of distilled water, start stirring, mix well, and add dropwise an aqueous suspension containing 0.2 mol of styryl triphenylphosphine and 0.12 mol of Hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 0.1mol butyl acrylate; after 1h, the dropwise addition is completed, and when the temperature rises to 55°C, 0.4g of the initiator ammonium persulfate is added dropwise, and after the initiator is dropped, the temperature is raised to 70°C for continuous stirring reaction for 2h After the reaction is completed, cool down to 40°C, add 0.5 g of polyoxyethylene lauryl ether phosphate under stirring, then cool to room temperature, add concentrated ammonia water dropwise to adjust the pH to 7.8-8.0, and filter through a 120-mesh filter to obtain an aqueous quaternary phosphine salt For the high molecular polymer emulsion, adjust the solid content of the emulsion to about 40% with distilled water...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com