Preparation method of optically active AIE fluorescent material and water-based polymer thereof
A water-based polymer, fluorescent polymer technology, applied in the chemical field, can solve the problems of no light, weak fluorescence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
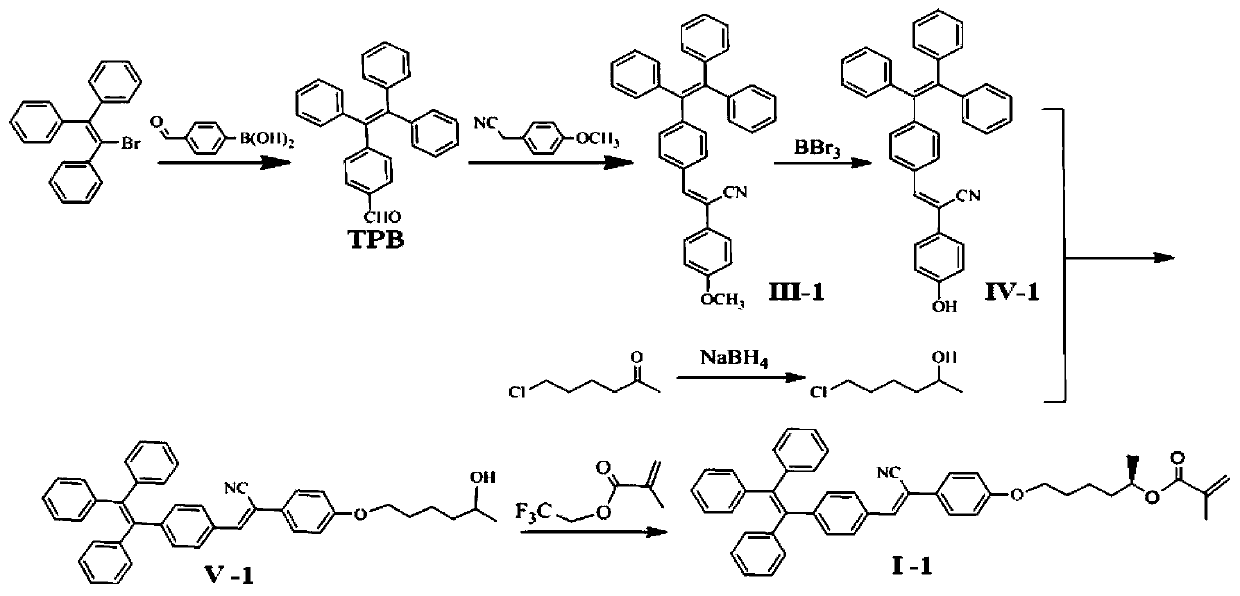
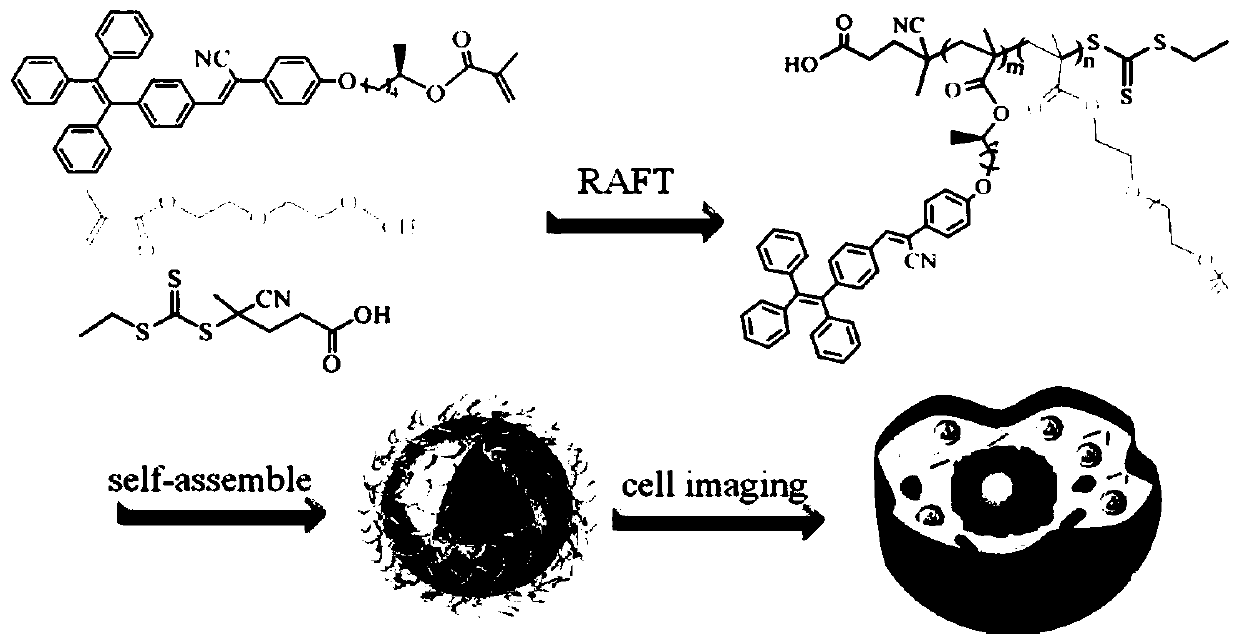
[0045] Embodiment 1: Preparation of aqueous optically active fluorescent polymer (II-1), its synthetic route diagram is as follows figure 1 and figure 2 shown, including:
[0046] Step 1: Add triphenylbromoethylene (7.04mmol, 2.3581g), 4-formylphenylboronic acid (8.48mmol, 1.2647g), tetrabutylammonium bromide (0.704mmol, 0.2268g), 2mol / L carbonic acid Potassium aqueous solution (12.6mL) and toluene (12.6mL) were successively added to the reaction tube, and stirred at room temperature for 0.5h; tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) (8.22×10 -3 mmol, 9.5 mg), the reaction tube was placed in an oil bath at 90°C under the protection of nitrogen for 48 hours; after the reaction, deionized water was added, extracted with ethyl acetate, the organic layer was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, After distillation under reduced pressure, the obtained crude product was separated and purified by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: n-hexane / dichloromethane 2:1 vo...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: AIE characteristic of aqueous optically active fluorescent polymer:
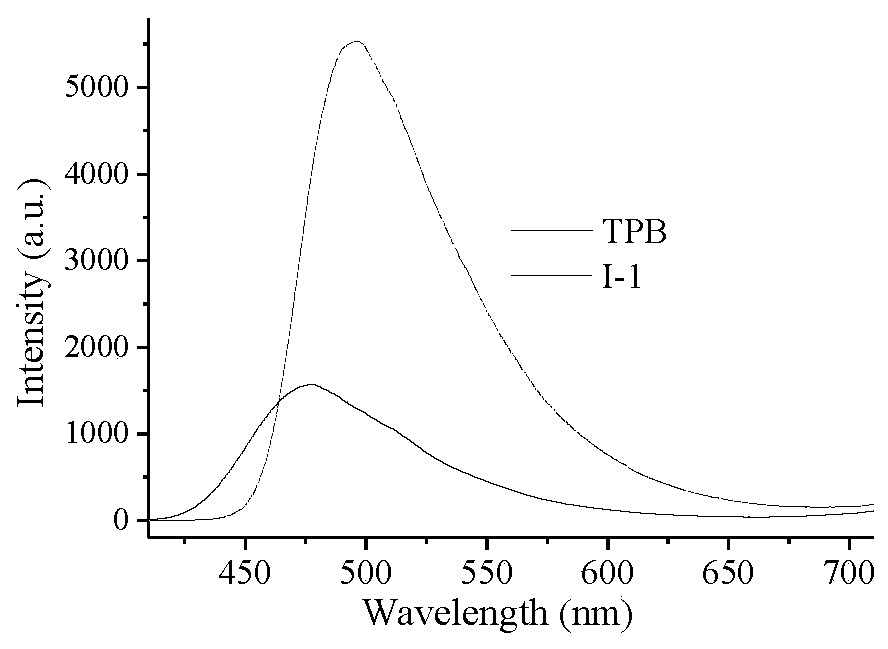
[0061] The solid-state fluorescence of the optically active AIE fluorescent monomer Ⅰ-1 was measured. Compared with the reported TPB fluorescent dye, its fluorescence intensity was significantly enhanced, and the fluorescence emission wavelength increased from 475nm to 496nm, and a significant red shift occurred (see image 3 ). to CDCl 3 As a solvent, the obtained compound IV-1, V-1, I-1, II-1 and II-2 1 The spectrum of H NMR is as Figure 4 As shown, each compound has its own characteristic peaks, indicating that each compound has been successfully prepared. Weigh 10 mg of water-based optically active fluorescent polymer II-1 and dissolve them in 4 mL of mixed solutions of deionized water and tetrahydrofuran with different volume ratios, and measure the fluorescence emission intensity (see Figure 5 ). In aqueous solution, there is an obvious fluorescence emission peak at 495nm, b...
Embodiment 3
[0062]Example 3: Optical activity characteristics of optically active AIE fluorescent monomer Ⅰ-1 and its amphiphilic polymer:
[0063] Weigh a certain amount of optically active AIE fluorescent monomer Ⅰ-1 and its water-based polymer, dissolve it in 20mL of acetone (concentration: 10.0mg / mL), make a uniform and transparent solution, add it to a 20cm long optical tube, and measure the fluorescent monomer and the specific optical rotation of the polymer. The calculated specific rotations of AIE fluorescent monomer Ⅰ-1 and its water-based polymer Ⅱ-2 are [α] 20 D = -9.67° and [α] 20 D =-3.74°.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific rotation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com