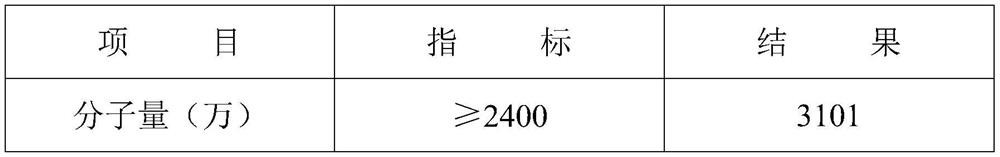
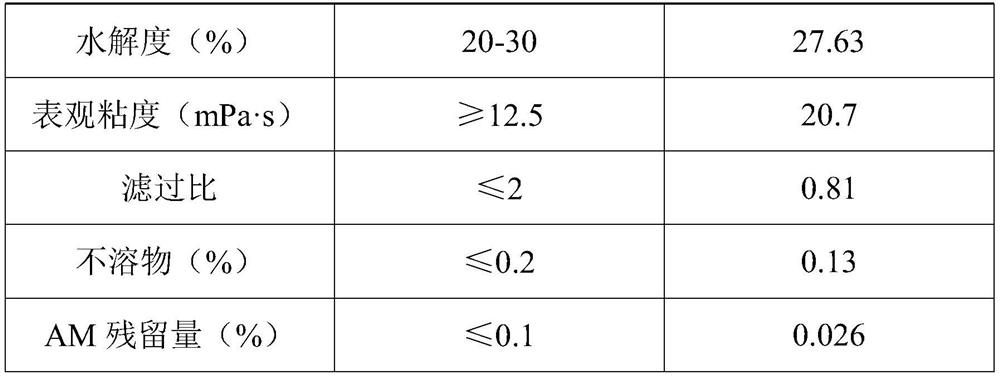
A kind of preparation method of post-hydrolyzed ultrahigh molecular weight comb polyacrylamide
An ultra-high molecular weight, polyacrylamide technology, applied in the field of functional polymers, can solve problems such as viscosity and viscoelasticity decrease, molecular chain structure instability, and needs to be further improved, so as to reduce the degree of fracture, improve rigidity, and high molecular weight Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
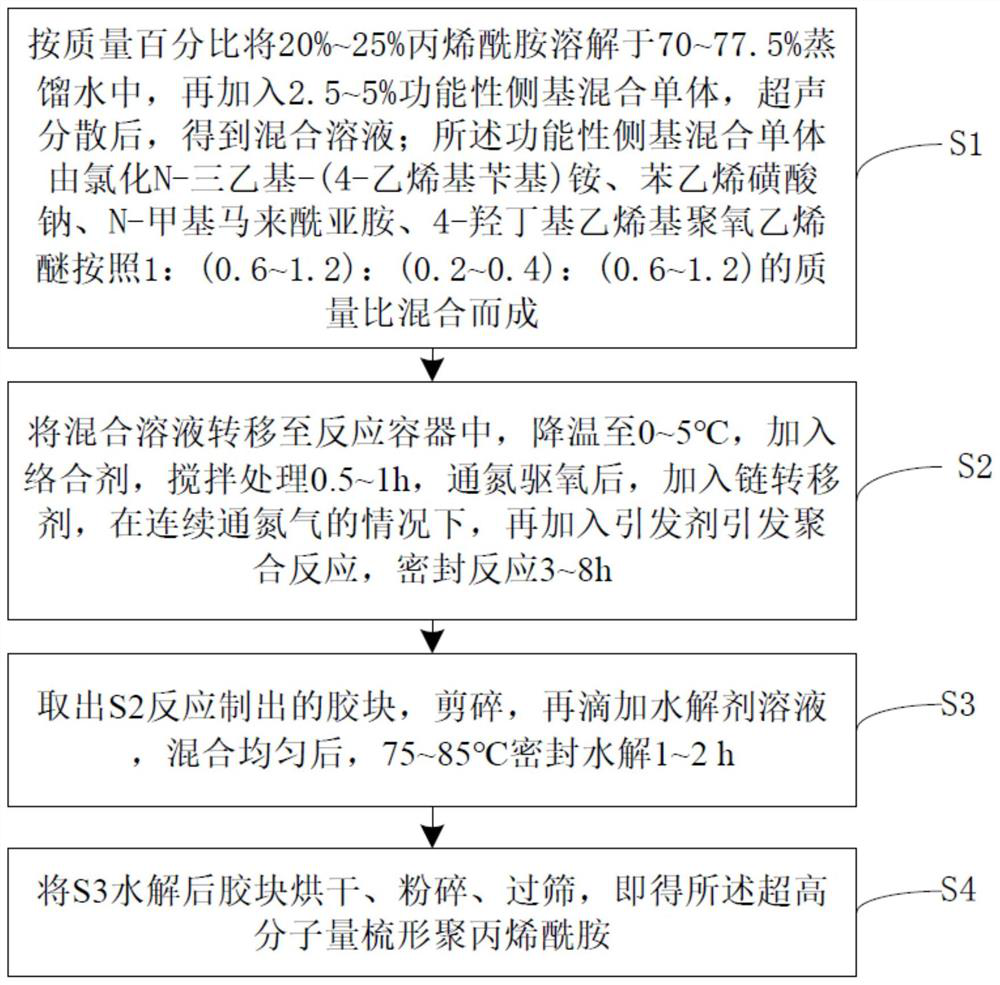
[0025] A preparation method of post-hydrolyzed ultra-high molecular weight comb polyacrylamide, comprising the following steps:
[0026] S1: Preparation of functional side group mixed monomers: N-triethyl-(4-vinylbenzyl)ammonium chloride, sodium styrene sulfonate, N-methyl Maleimide and 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether are evenly mixed to obtain functional side group mixed monomer;
[0027] S2: preparation of redox system initiator: according to the mass ratio of 1:2.5, the oxidant ammonium persulfate and the reducing agent sodium bisulfite are respectively prepared for use.
[0028] S3: Dissolve 125 g of acrylamide in 362.5 g of distilled water, add 12.5 g of functional side group mixed monomer, and ultrasonically disperse to obtain a mixed solution;
[0029] S4: Transfer the mixed solution to a reaction vessel, cool down to 1°C, add 0.003g of a complexing agent EDTA disodium salt, stir for 0.5h, and introduce high-purity nitrogen (nitrogen purity ≥ 99.99%) to Dri...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A preparation method of post-hydrolyzed ultra-high molecular weight comb polyacrylamide, comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1: Preparation of functional side group mixed monomers: N-triethyl-(4-vinylbenzyl)ammonium chloride, sodium styrene sulfonate, N-methyl Maleimide and 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether are evenly mixed to obtain functional side group mixed monomer;
[0038] S2: preparation of redox system initiator: according to the mass ratio of 1:2.5, the oxidant sodium persulfate and the reducing agent sodium bisulfite are mixed uniformly to obtain the initiator;
[0039] S3: Dissolve 115g of acrylamide in 370g of distilled water, add 15g of functional side group mixed monomers, and ultrasonically disperse to obtain a mixed solution;
[0040] S4: Transfer the mixed solution to a reaction vessel, cool down to 1°C, add 0.005g of a complexing agent ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium salt, stir for 0.5h, introduce high-purity nitrogen (nitro...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A preparation method of post-hydrolyzed ultra-high molecular weight comb polyacrylamide, comprising the following steps:
[0047]S1: Preparation of functional side group mixed monomer: N-triethyl-(4-vinylbenzyl)ammonium chloride, sodium styrene sulfonate, N-methyl Maleimide and 4-hydroxybutyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether are evenly mixed to obtain functional side group mixed monomer;
[0048] S2: preparation of redox system initiator: according to the mass ratio of 1:3, the oxidant ammonium persulfate and the reducing agent bisulfite sodium sulfite are uniformly mixed to obtain the initiator;
[0049] S3: Dissolve 105g of acrylamide in 382.5g of distilled water, then add 12.5g of functional side group mixed monomer, and ultrasonically disperse to obtain a mixed solution;
[0050] S4: Transfer the mixed solution to a reaction vessel, cool down to 1°C, add 0.005g of a complexing agent EDTA disodium salt, and after stirring for 1 hour, introduce high-purity nitrogen (nitro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shear viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com