Pichia pastoris engineering bacterium for heterologous expression of cellulase gene EGV and application of pichia pastoris engineering bacterium
A Pichia pastoris, heterologous expression technology, applied in the field of cellulase genetic engineering, to achieve the effect of improving enzyme production efficiency and industrial production potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
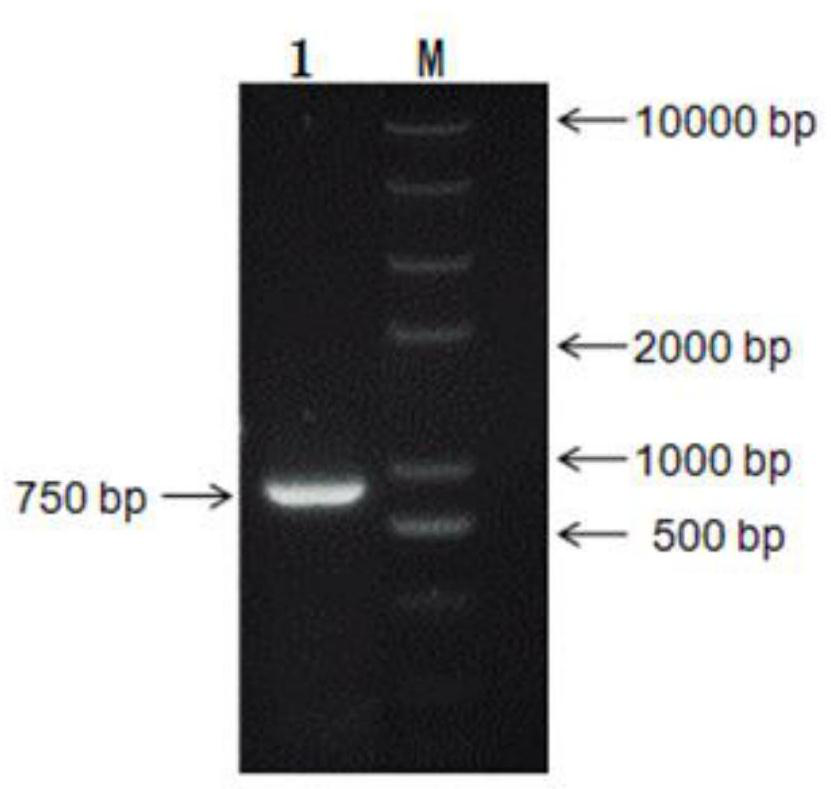
[0030] Implementation Case 1 Cloning of target gene
[0031] 1. Take the Trichoderma reesei QM9414 spore suspension stored in a glycerol tube out of the -80°C refrigerator and place it in ice (or 4°C refrigerator) to thaw until the spore suspension completely melts. Shake the spore suspension to mix evenly, dip the inoculation loop with a small amount of bacterial solution, and streak on the PDA medium plate for inoculation. After the plate was sealed with parafilm, it was placed in a 28°C incubator for cultivation. Cultivate for about 5-7 days until the surface of the medium is covered with green spores. The plates were taken out of the incubator and placed in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0032] 2. Inoculate fresh spores on cellulase solid induction culture, spread sterilized cellophane on the surface, and let the culture stand until the hyphae grow out. The hyphae were scraped off from the cellophane and treated with a liquid nitrogen freezer grinder. RNA was extra...
Embodiment example 2
[0038] Implementation Case 2 Construction of Expression Vector Ppic9k-EGⅤ
[0039] 1. Use the restriction endonuclease EcoRI / Not I to double-digest Ppic9k and the target gene eg5, and prepare a double-digestion system as shown in the table below. The metal bath was reacted at 37°C for 50 minutes, and the product was recovered by the recovery kit. The product after double enzyme digestion was reacted with Taq Mix enzyme (volume 1:1) in a PCR instrument at 72°C for 30 min, and A-terminal ligation was carried out.
[0040] Double enzyme digestion system:
[0041]
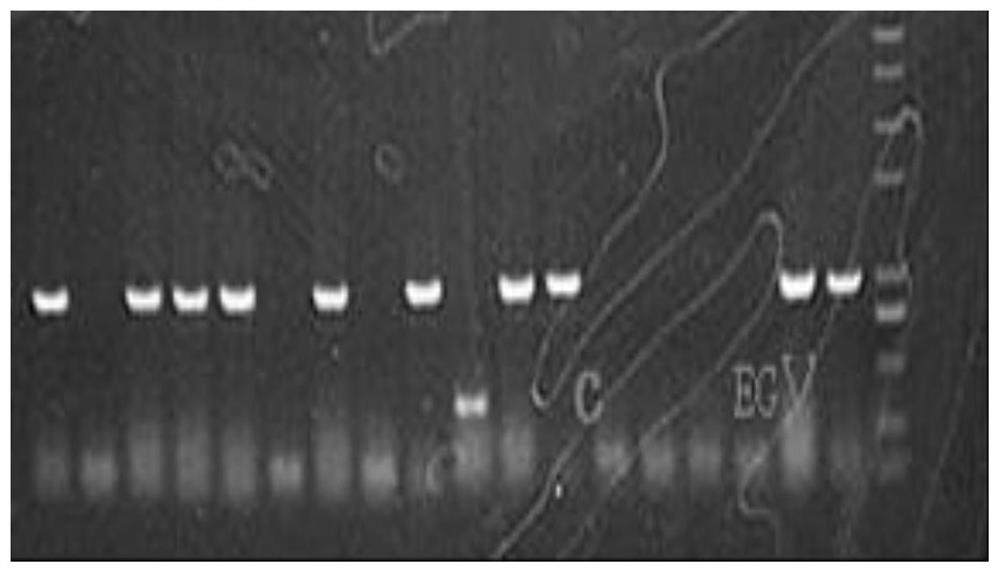
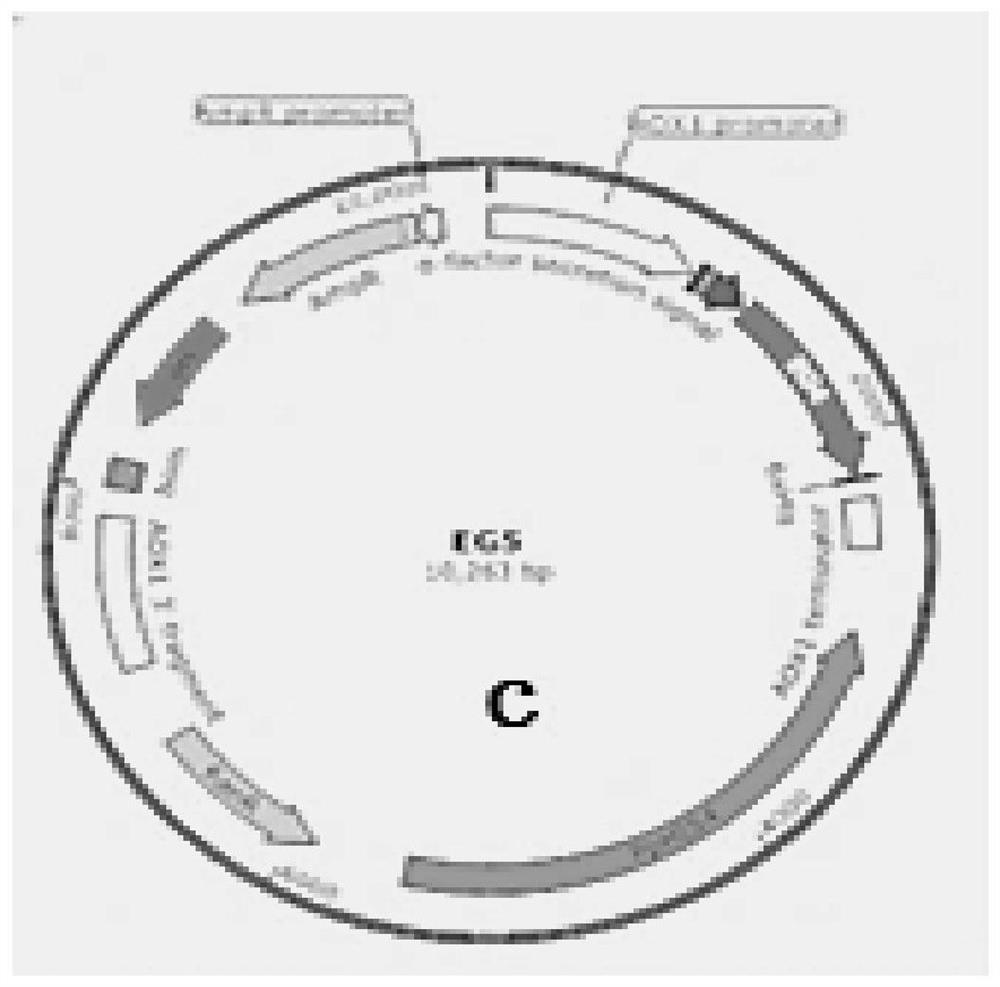
[0042]2. Using EcoRI at the 5' end and NotI at the 3' end as the restriction site, insert the Ppic9k plasmid vector promoter AOX1 downstream to construct the expression vector Ppic9k-EGⅤ. For the expression vector map, see image 3 . Colony PCR verification see figure 2 . The expression vector was verified by single enzyme digestion to confirm that the expression vector Ppic9k-EGⅤ was successfully constructed...
Embodiment example 3
[0046] Implementation case 3 Construction of recombinant Pichia pastoris
[0047] 1. Use the restriction endonuclease bglⅡ to single-enzyme digest the recombinant expression plasmid Ppic9k-EGⅤ, prepare a linearization system, mix well, and incubate in a metal bath at 37°C for 1 hour to make the expression vector change from circular to linear, which is beneficial Later conversion. Nucleic acid electrophoresis was used to verify the linearized plasmid, see Figure 4 . Transformed into Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells by electrotransformation, and plated to obtain transformants.
[0048] Linearization system:
[0049]
[0050] 2. Use the SDS pyrolysis method to roughly extract the genome of the recombinant yeast transformant obtained in 1, and verify its correctness and phenotype by PCR. The nucleic acid map of the genome PCR is shown in Figure 5 . Pick the transformants on the MM plate, spot in turn on the YPD medium plate containing different concentrations of G4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com