Method for preparing fertilizer product by resourceful treatment of fermentation waste residues of tetracyclic antibiotics
A technology for fermenting waste residues and preparing fertilizers, which is applied to fertilizers made of biological wastes, calcium fertilizers, inorganic fertilizers, etc. The effect of recycling and energy recycling, promoting dissolution and dispersion, and saving the dosage of pharmaceuticals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
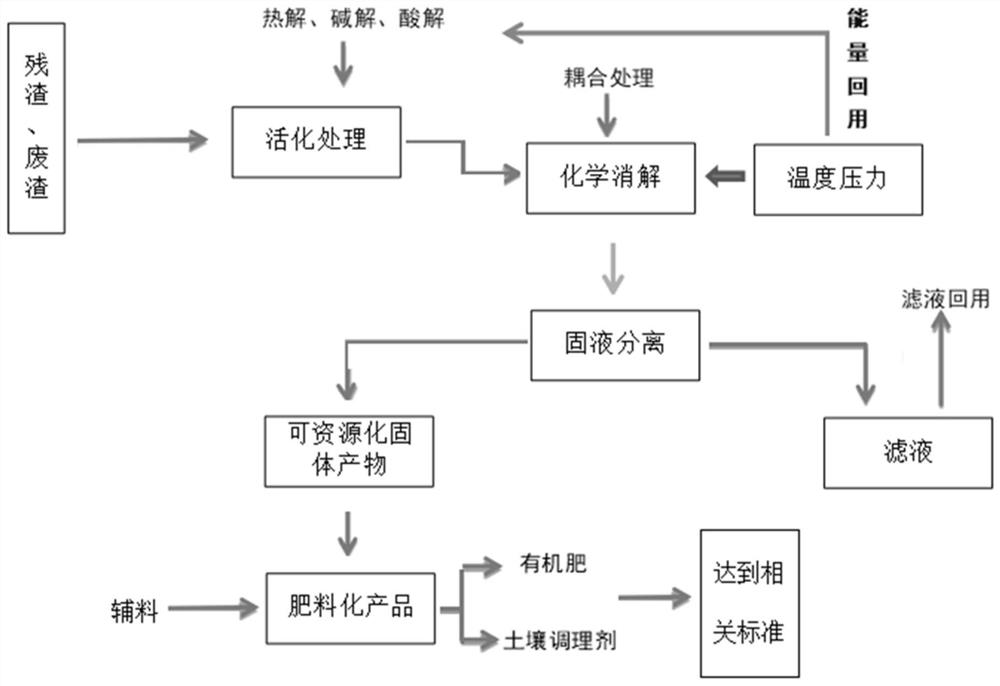
[0037] 200g tetracycline content is 2000mg / kg waste residue, add reuse filtrate 50g, activator concentrated sulfuric acid 4g, control pH is 3.5, fast stirring forms the slurry that solid content is 50%, by carrying out heat exchange with reaction material, slurry is heated to 70°C, heated to 70°C with constant power, the required time is 5min; then add the digestion agent FeSO into the slurry 4 ·7H 2 O2g, coupling agent sodium lauryl sulfate 0.1g, continue to heat up to 90 ℃, react under normal pressure for 3 hours; After separation and filtration, obtain 130.14g of solid product that can be recycled and utilized, filtrate 102g, then temperature The filtrate at about 85°C is returned to the next batch of initial slurry to realize the reuse of materials and energy, and the solid raw materials after the reaction are separated. After testing, the residual amount of tetracycline is less than 1mg / kg, and the degradation rate reaches more than 99.9%. Finally, 10 g of dolomite powde...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 150g of chlortetracycline content is 3812mg / kg waste residue, add reuse filtrate 60g, activator nitric acid 0.5g, control pH 5.0, form the slurry that solid content is 45%, by carrying out heat exchange with reaction material, slurry is heated to 55 ℃; then add 10g of hypochlorous acid as a digestion agent and 1.5g of sodium lauryl sulfate as a coupling agent to the slurry, and react for 2.5 hours at 75°C under normal pressure; after separation, filtration and drying, a solid product that can be used as a resource is obtained 132.35g, filtrate 80g; then return the filtrate with a temperature of about 82°C to the next batch of initial slurry to realize the reuse of materials and energy, and separate the reacted solid raw materials. After testing, the residual amount of aureomycin is 0.1 mg / kg. Then add 15g of humic acid and 10g of plant ash to the treated filtered filter residue, add a small amount of filtrate, and prepare, stir and extrude to obtain a fertilizer product...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 500g oxytetracycline content is 1290mg / kg waste residue, add reuse filtrate 250g, and activator acetic acid 45g, control pH 4.5, form the slurry that solid content is 20%, by carrying out heat exchange with reaction mass, slurry temperature is raised to 60°C; then add 50g of disintegrating agent potassium permanganate and 0.05g of coupling agent sodium dodecyl sulfate to the slurry, continue to rise to 90°C, and react for 2 hours under normal pressure; after filtration, separation and drying, the available resource 183.8g of solid product and 640g of filtrate were used for chemical utilization; then the filtrate with a temperature of about 82°C was returned to the next batch of initial slurry to realize the reuse of materials and energy, and the solid raw materials after the reaction were separated. The residual amount of the element is less than 10mg / kg, and the removal rate reaches more than 99%; then add 20g of potassium sulfate and 20g of plant ash to the filtered fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com