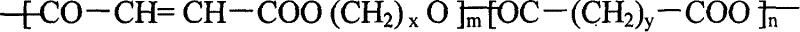Injectable pharmaceutical slow-release carrier and preparation method thereof
A slow-release carrier and drug technology, applied in the field of liquid polyanhydride-unsaturated polyester block polymer and chemical synthesis, to achieve the effect of solving the need for surgical implantation, appropriate drug release rate, and good drug slow-release performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0046] Example 1: Synthesis of polylauric acid-poly(maleic anhydride-ethylene glycol) (PDDDA-P(MA-GLY)) resin
[0047] Add 3.92 grams (0.040 mol) of maleic anhydride and 2.73 grams (0.044 mol) of ethylene glycol into a polymerization tube with a diameter of 2 cm and a length of 20 cm, place the polymerization tube in a silicone oil bath, and stir it electromagnetically. The temperature was raised to 170° C., melt polymerization was carried out for 90 minutes, and nitrogen gas was flowed for 15 seconds every 15 minutes. Cool down to 80°C, vacuum reduce to 30-50Pa, remove moisture, heat up to 170°C after 0.5 hours for melt polymerization for 1.0 hour, then add a certain mass percentage of polylauric acid for melt polymerization for 1.0 hour, and pass nitrogen every 15 minutes After 15 seconds, vacuum again; after the polymerization is completed, cool down to 80°C, add 30% diluent and crosslinking agent N-vinylpyrrolidone by mass, and cool to obtain polyanhydride-unsaturated poly...
example 2
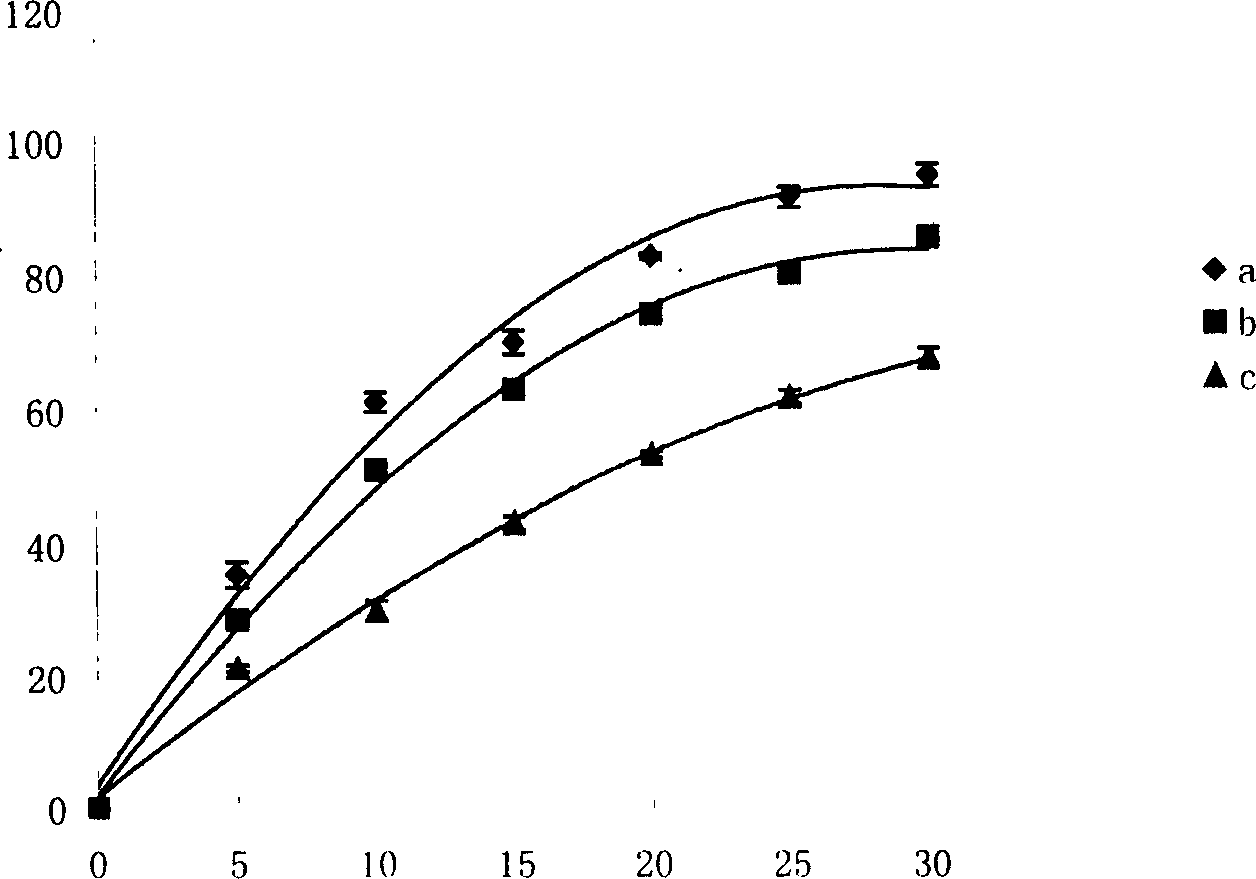
[0061] Example 2: Drug release characteristics of polylauric acid-poly(maleic anhydride-ethylene glycol) (PDDDA-P(MA-GLY)) resin stick containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride
[0062] Take ciprofloxacin hydrochloride as the model drug, blend the liquid resin with it, and then add a certain amount of curing agent (0.3%-1.0%), diluent and cross-linking agent (20%-30%) on the watch glass Stir and mix evenly, fill it into a 1ml primary syringe, inject 150mg of the drug-loaded resin into a glass catheter with a diameter of 4mm, smash the glass catheter after curing, and take out the slow-release drug stick. The drug sticks were respectively placed in 20 mL of 0.1 mol / L, pH=7.4 phosphate buffer solution, and the degradation experiment was carried out on a constant temperature shaker at 37° C. (rotating speed 60 rad / min). The buffer solution is replaced at regular intervals, and the absorbance of the release medium at a wavelength of 271nm is measured by UV spectroscopy, based on the ...
example 3
[0063] Example 3: Biocompatibility experiment of polylauric acid-poly(maleic anhydride-ethylene glycol) (PDDDA-P(MA-GLY)) resin in mice subcutaneous
[0064] According to the "National Standard of the People's Republic of China-Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices" (GB / T16886.1-1997) Part 6, the local reaction test method after implantation, polylauric acid-poly(maleic anhydride-ethylene Diol) (PDDDA-P(MA-GLY)) resin in the subcutaneous biocompatibility of mice was evaluated.
[0065] By injection, 150 mg of polylauric acid-poly(maleic anhydride-ethylene glycol) (PDDDA-P(MA-GLY)) resin plus a curing agent was aseptically injected into the right forelimb armpit of the mouse Subcutaneously, the resin cures quickly into a hard mass (5-20 minutes). After feeding for a certain period of time, the mice were killed by pulling the neck, and the tissue at the implanted site was quickly taken out and fixed with 10% formalin. The samples were made into coronal sections, the resin a...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap