Patents
Literature
49 results about "Packet trace" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
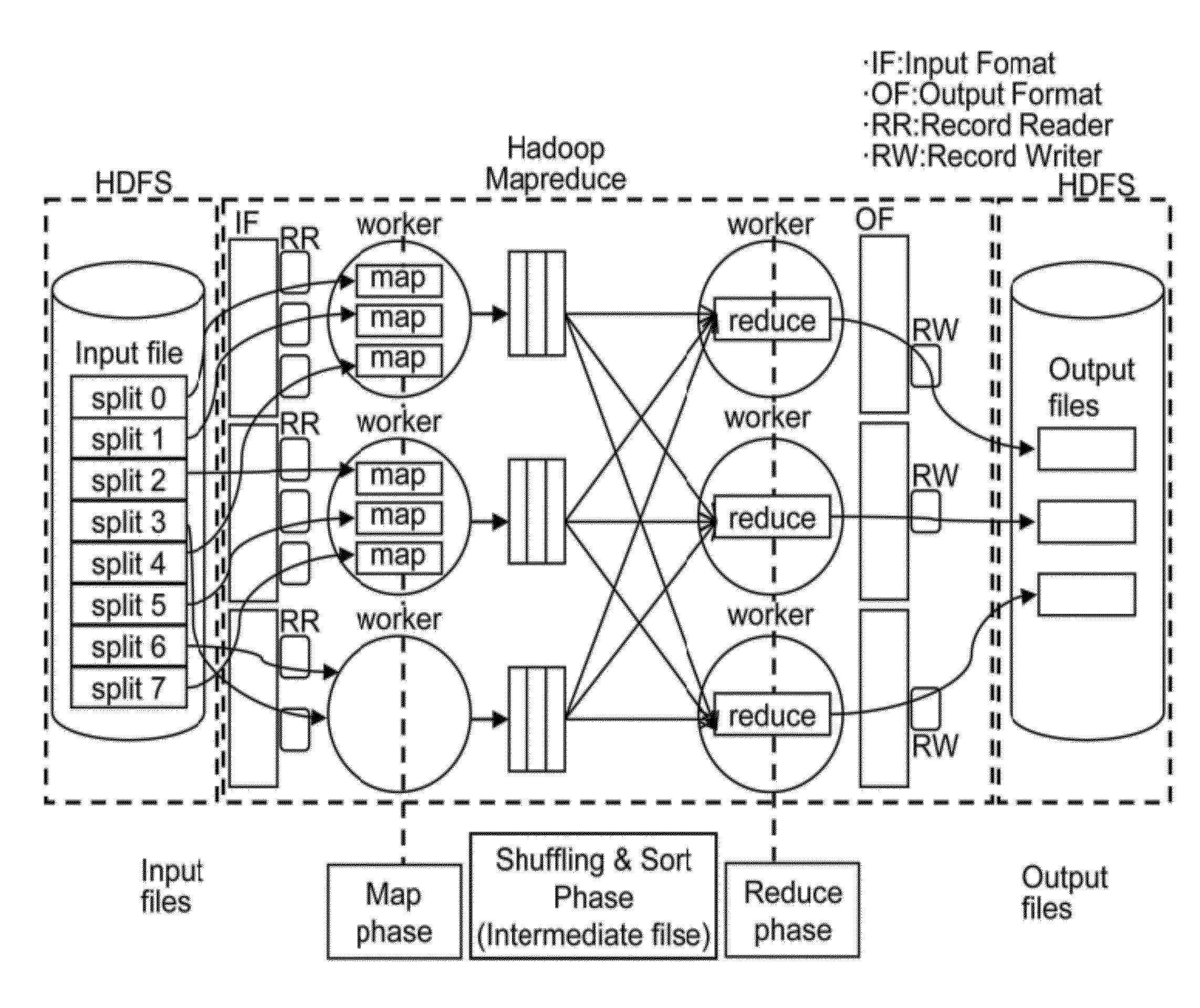
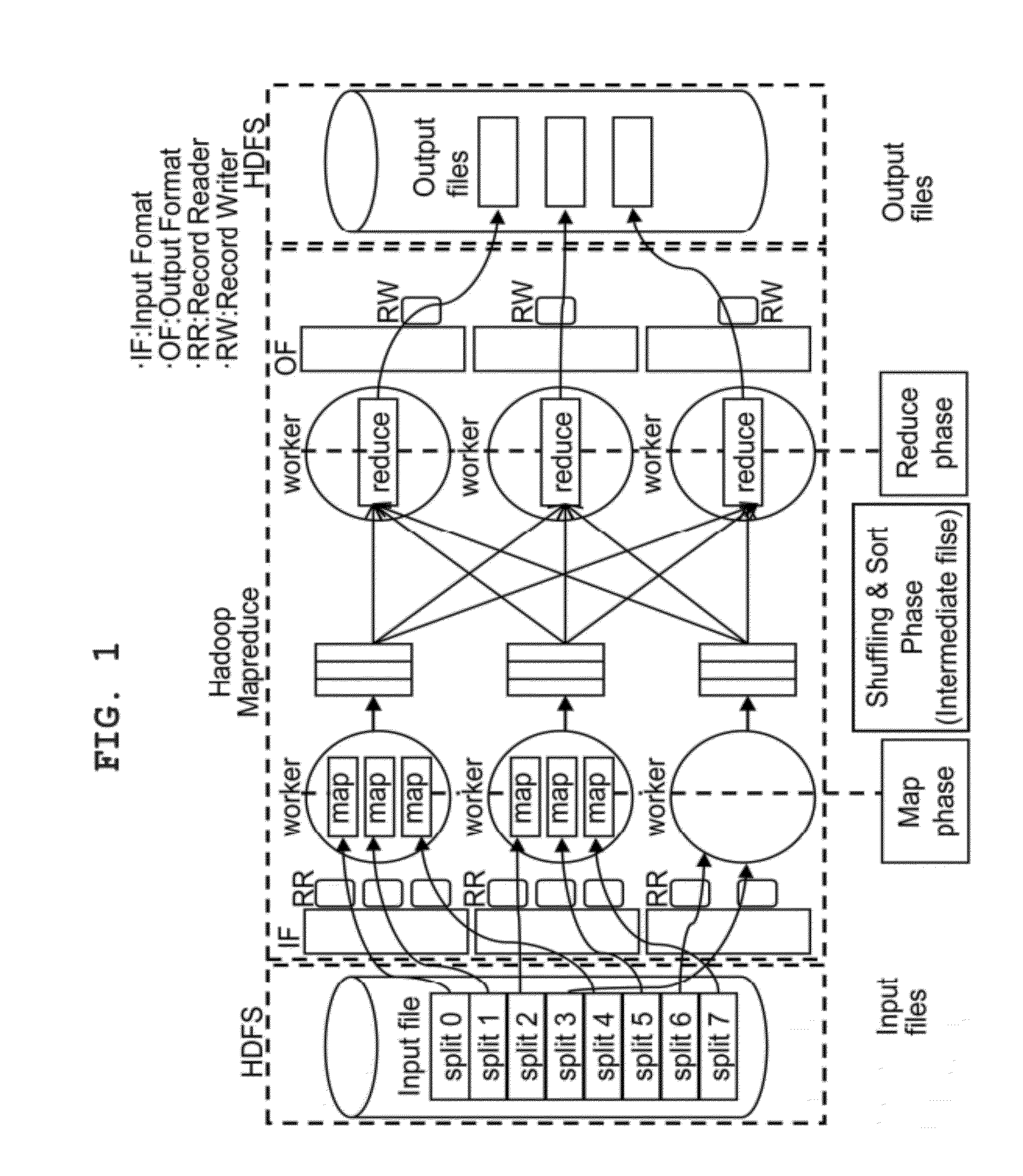
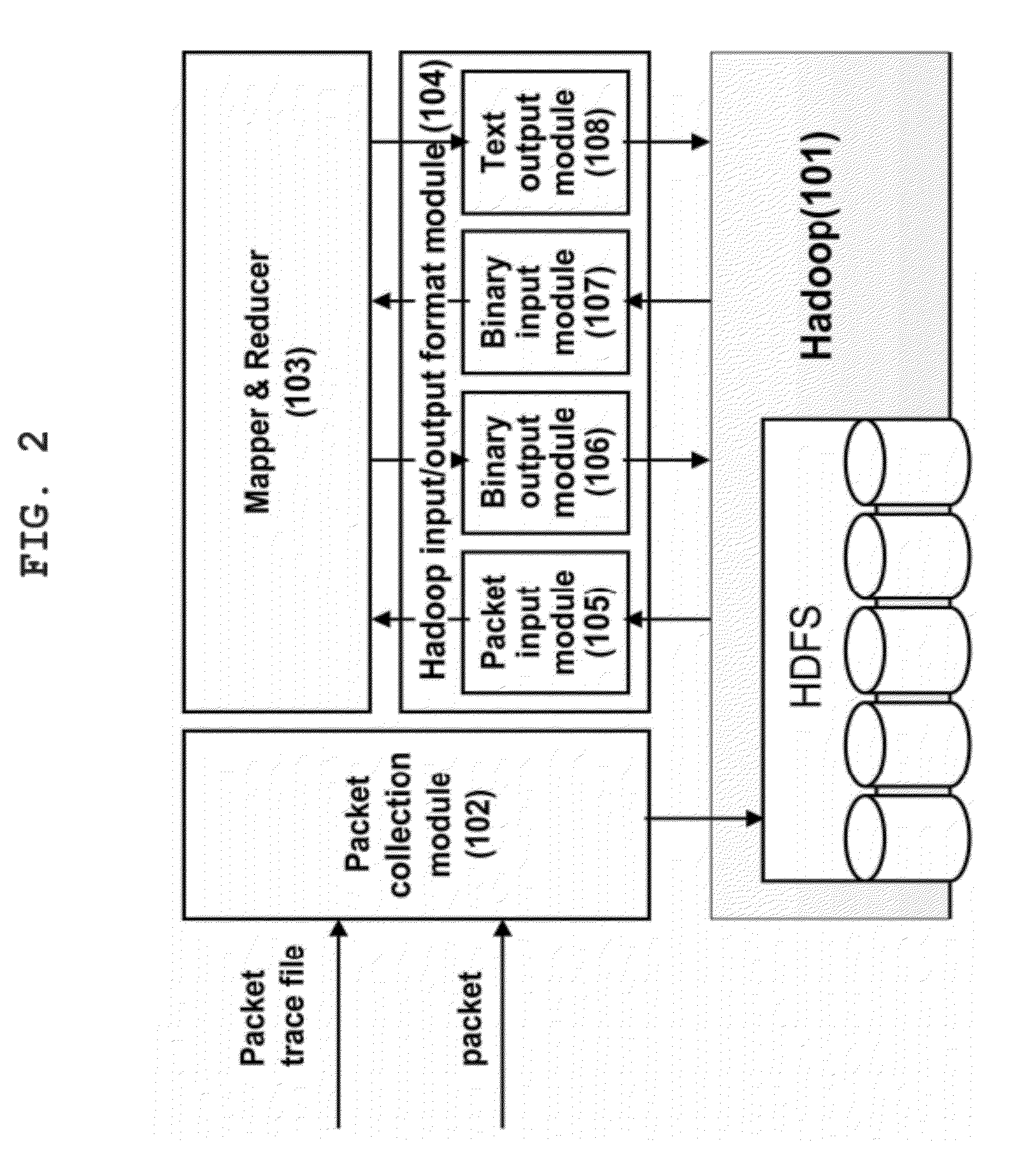
Packet analysis system and method using hadoop based parallel computation
InactiveUS20120182891A1Optimize data processingError preventionTransmission systemsDistributed File SystemOpen source
The present invention relates to a packet analysis system and method, which enables cluster nodes to process in parallel a large quantity of packets collected in a network in an open source distribution system called Hadoop. The packet analysis system based on a Hadoop framework includes a first module for distributing and storing packet traces in a distributed file system, a second module for distributing and processing the packet traces stored in the distributed file system in a cluster of nodes executing Hadoop using a MapReduce method, and a third module for transferring the packet traces, stored in the distributed file system, to the second module so that the packet traces can be processed using the MapReduce method and outputting a result of analysis, calculated by the second module using the MapReduce method, to the distributed file system.
Owner:THE IND & ACADEMIC COOP IN CHUNGNAM NAT UNIV (IAC)
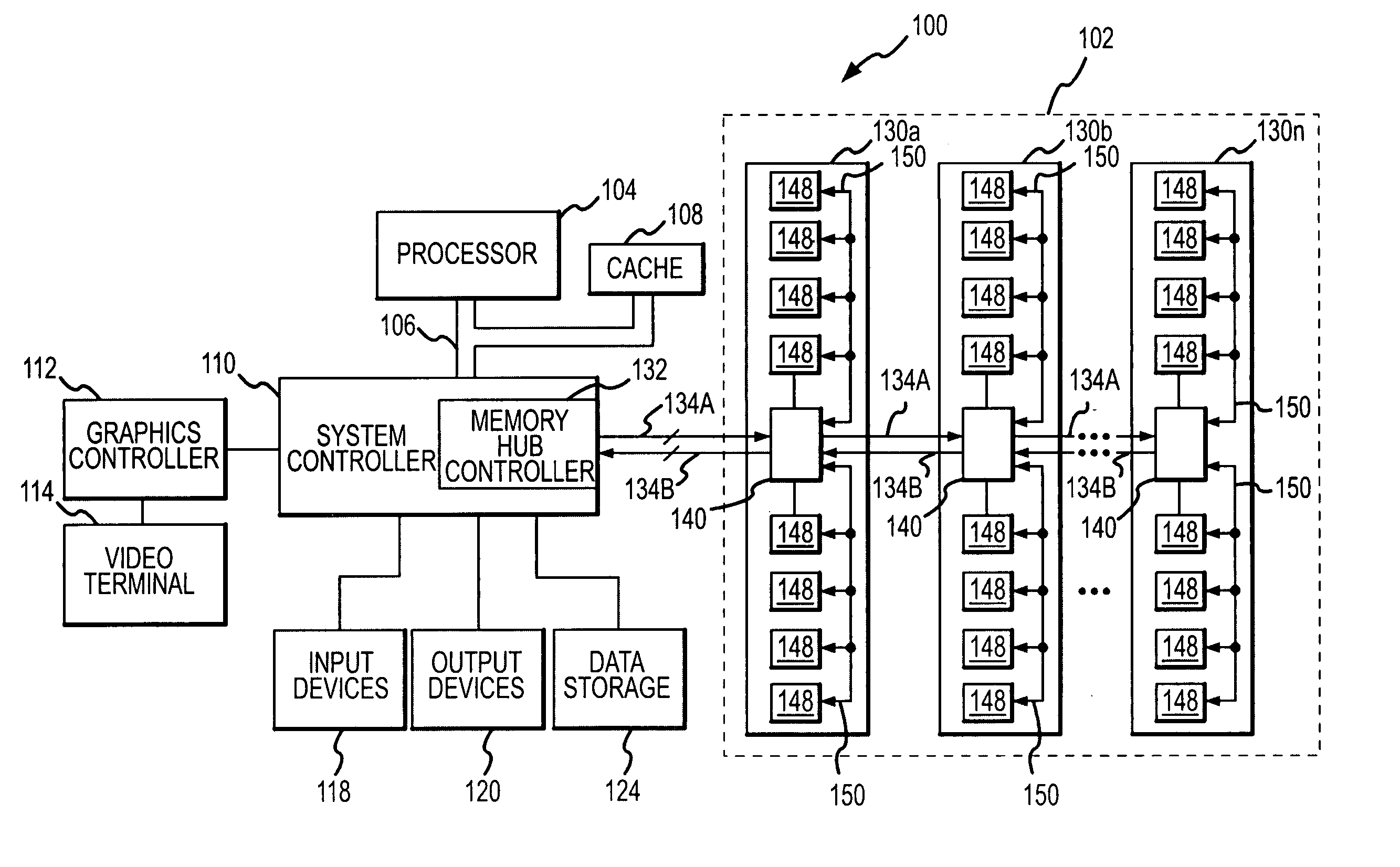
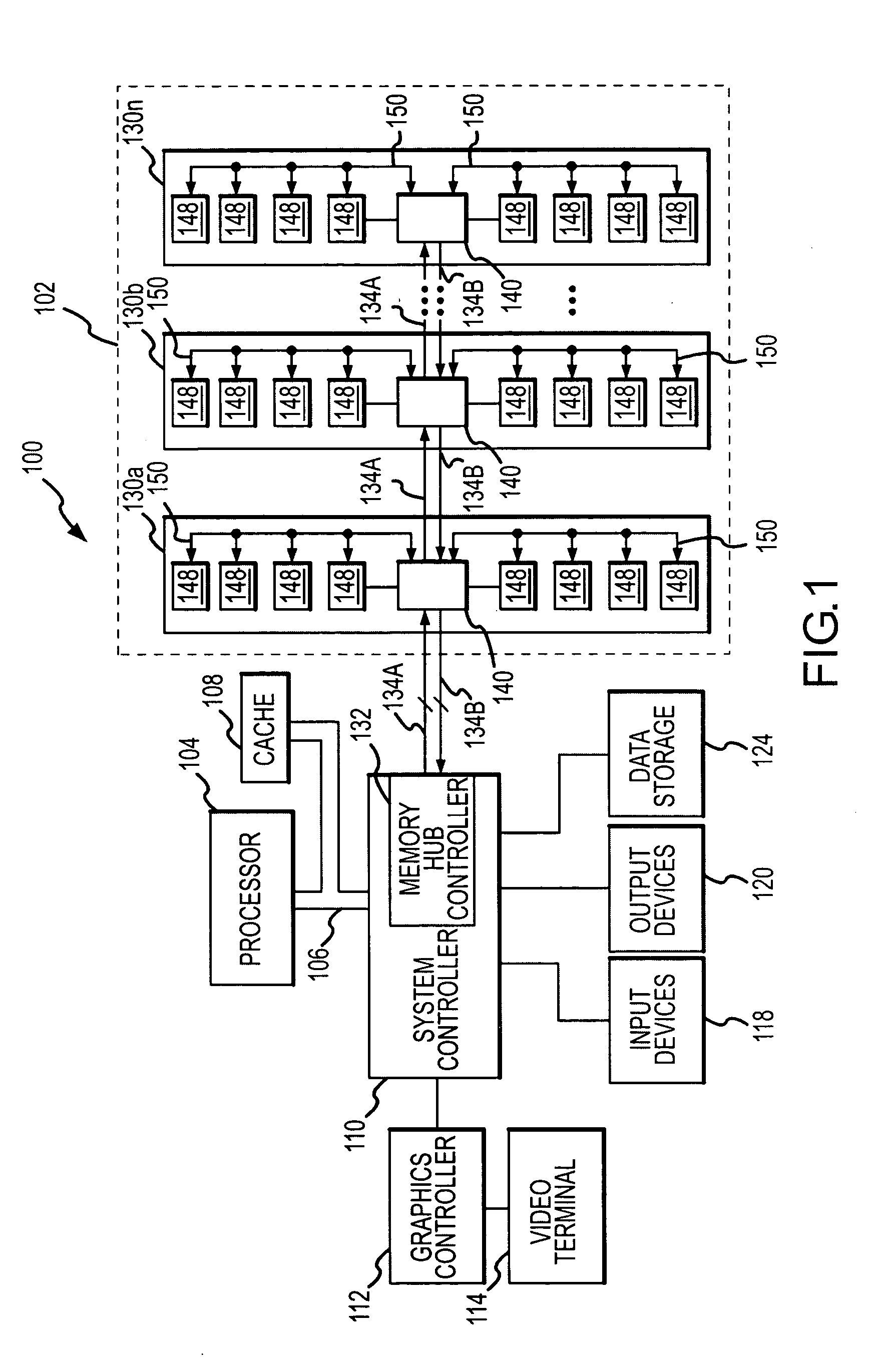
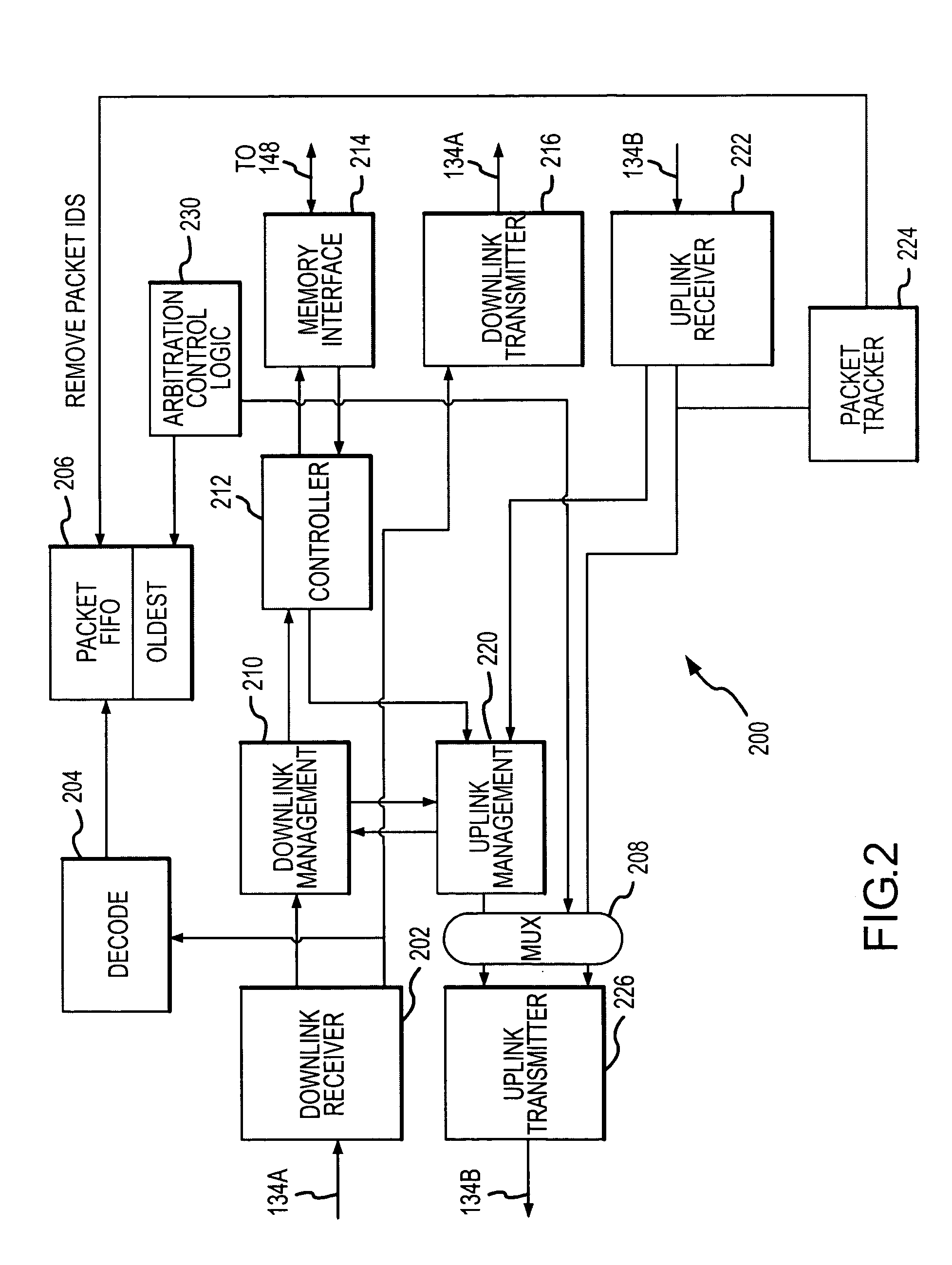
Arbitration system having a packet memory and method for memory responses in a hub-based memory system
A memory hub module includes a decoder that receives memory requests determines a memory request identifier associated with each memory request. A packet memory receives memory request identifiers and stores the memory request identifiers. A packet tracker receives remote memory responses and associates each remote memory response with a memory request identifier and removes the memory request identifier from the packet memory. A multiplexor receives remote memory responses and local memory responses. The multiplexor selects an output responsive to a control signal. Arbitration control logic is coupled to the multiplexor and the packet memory and develops the control signal to select a memory response for output.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
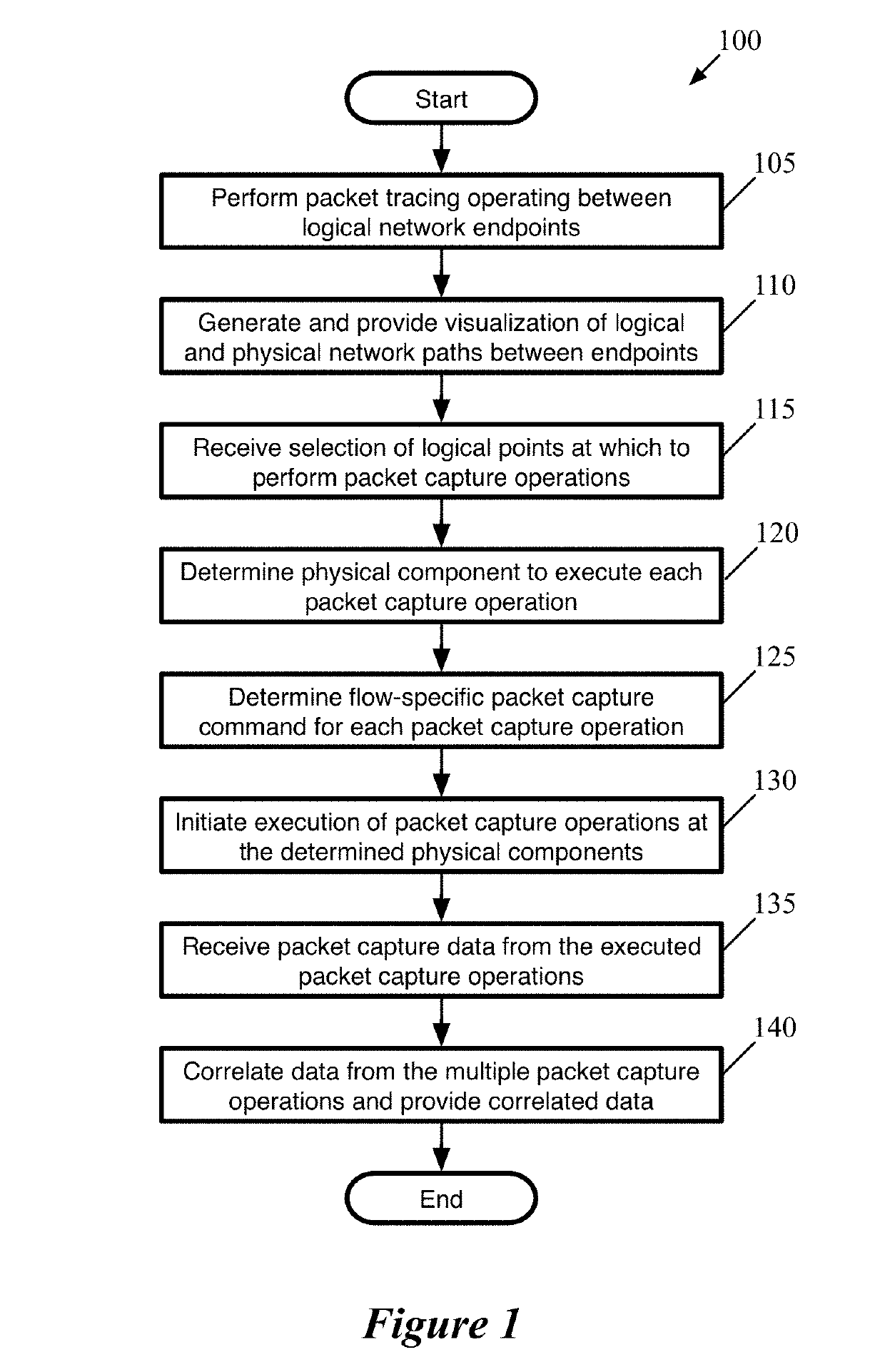
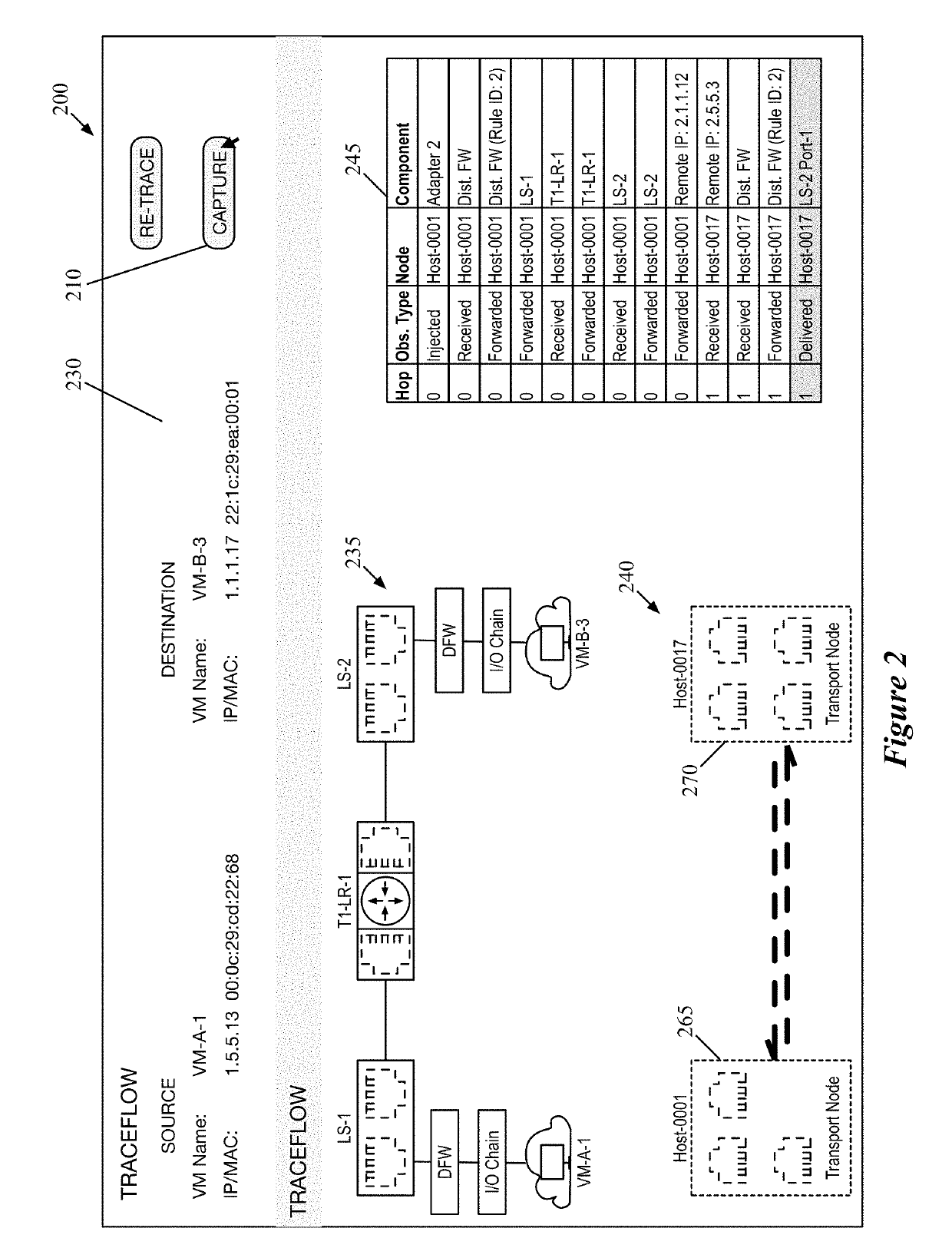
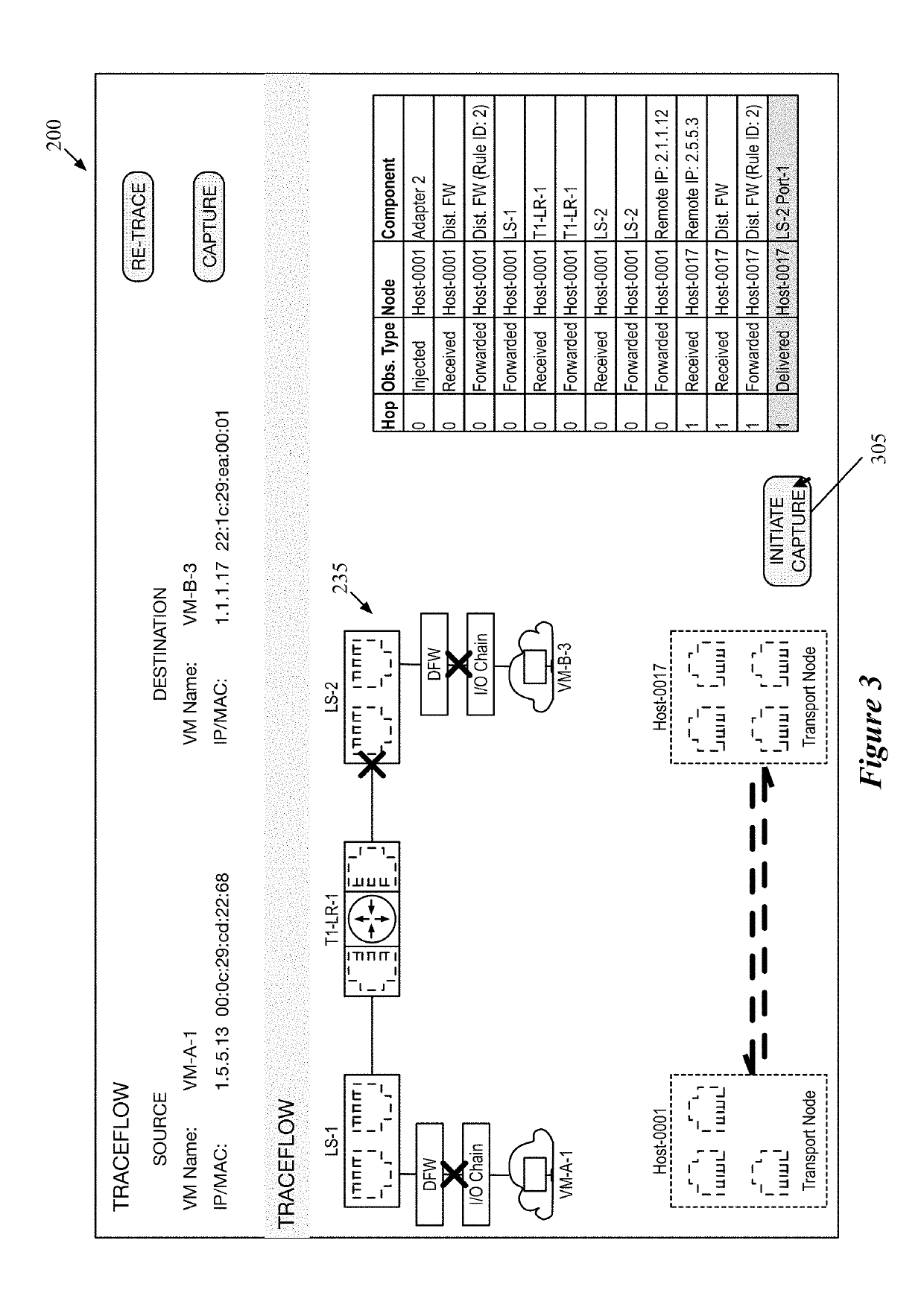
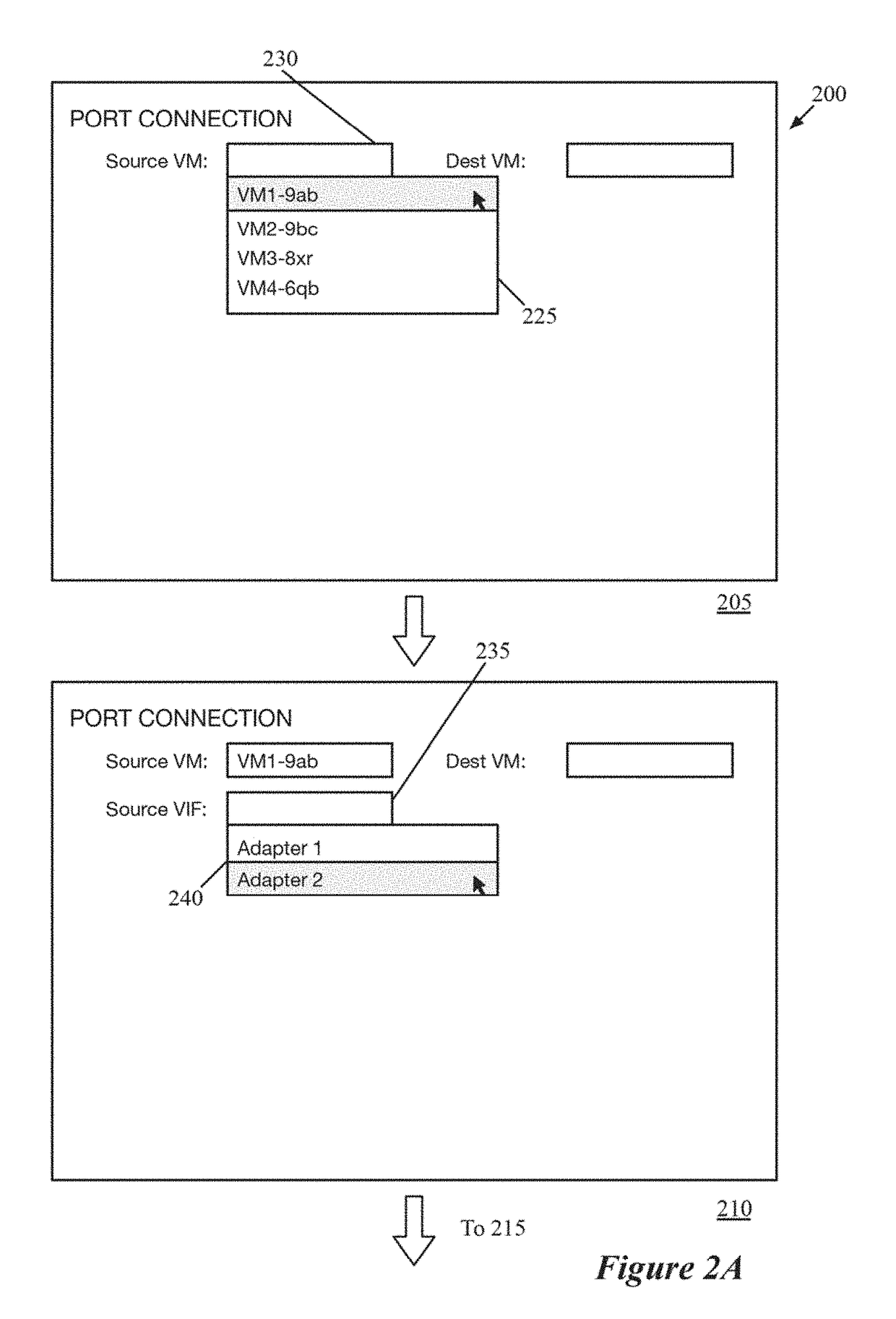
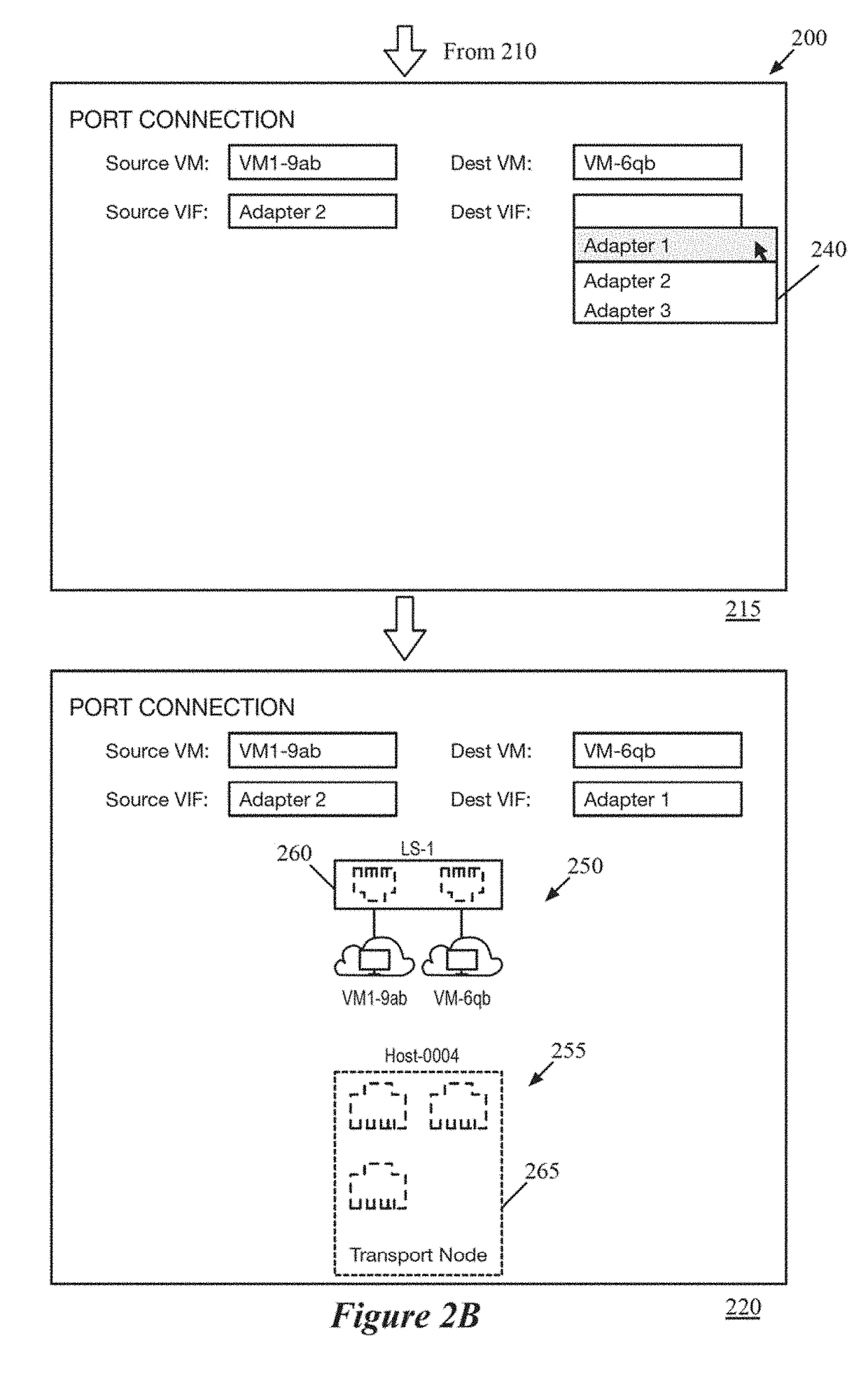
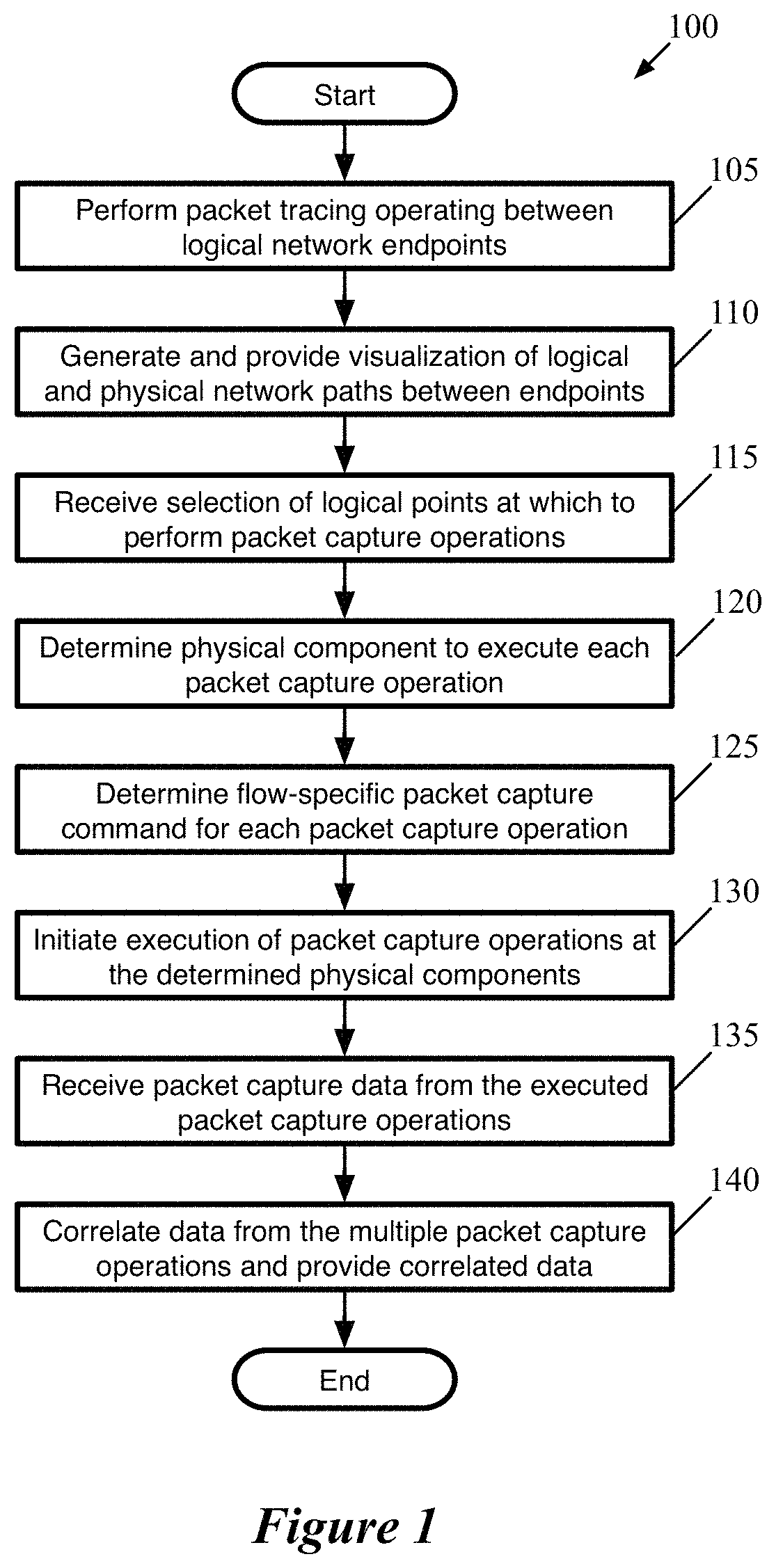
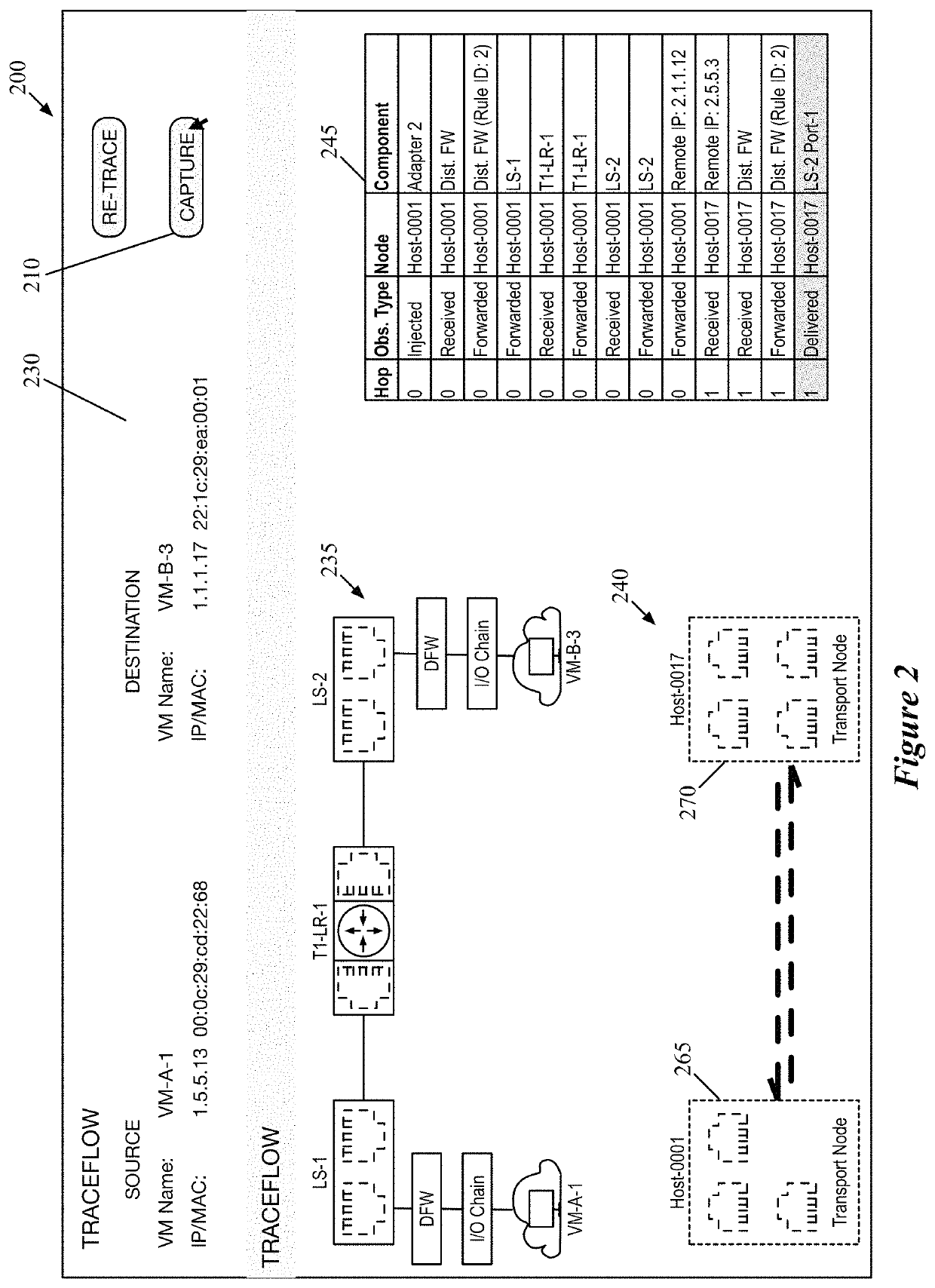
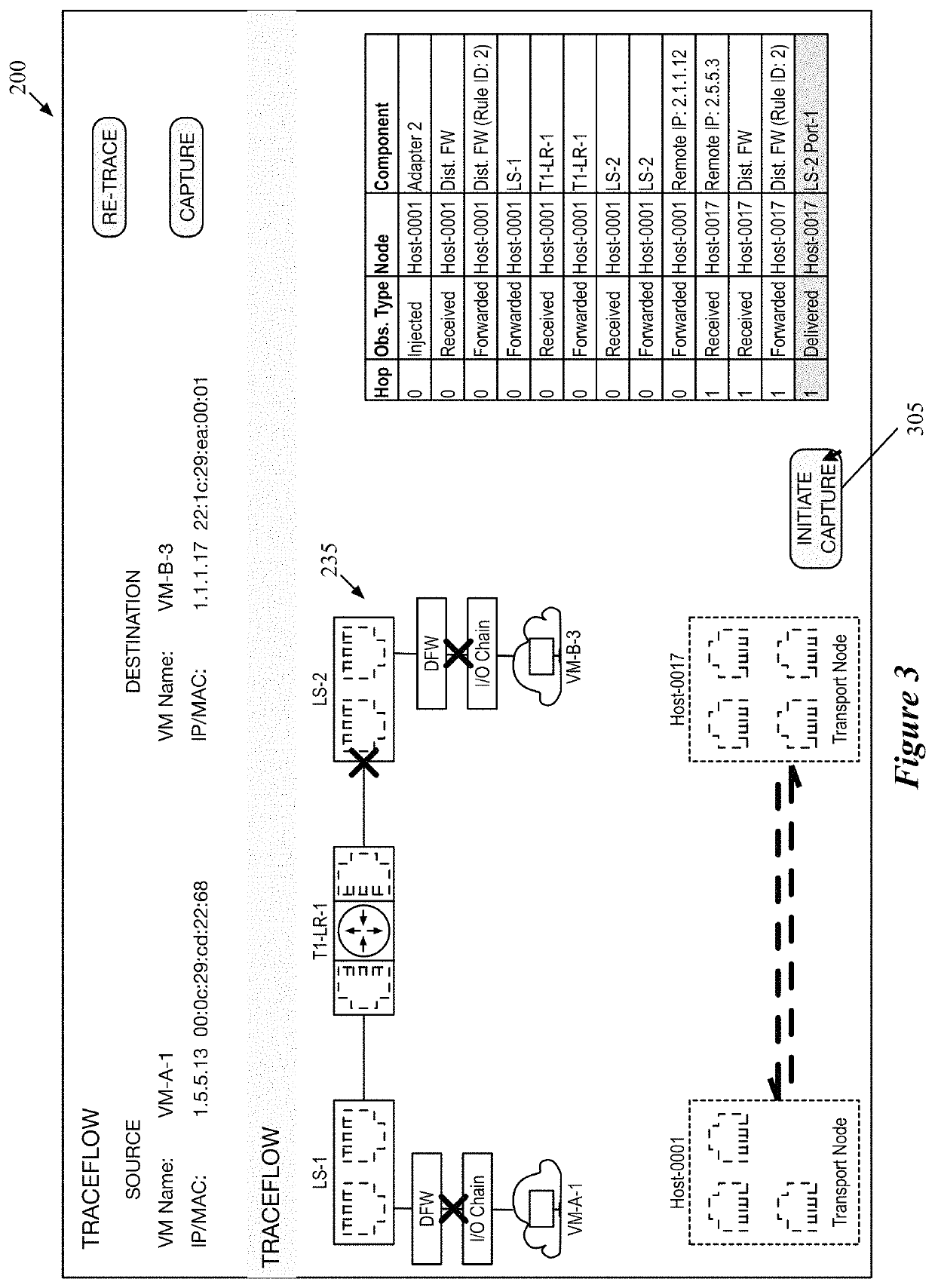
Using packet tracing tool to automatically execute packet capture operations
ActiveUS20190109769A1Limits numberEasily correlatedData switching networksComputer hardwareData stream
Some embodiments provide a method that performs a packet tracing operation for a particular data flow between endpoints of a logical network to generate a representation of logical network components along a path between the endpoints. In response to a selection of at least two of the logical network components, the method automatically generates separate packet capture operations for execution by physical components that implement each of the selected logical network components. The method uses packet header information to correlate packet data from the separate packet capture operations.
Owner:NICIRA
Systems and methods for trace filters by association of client to vserver to services
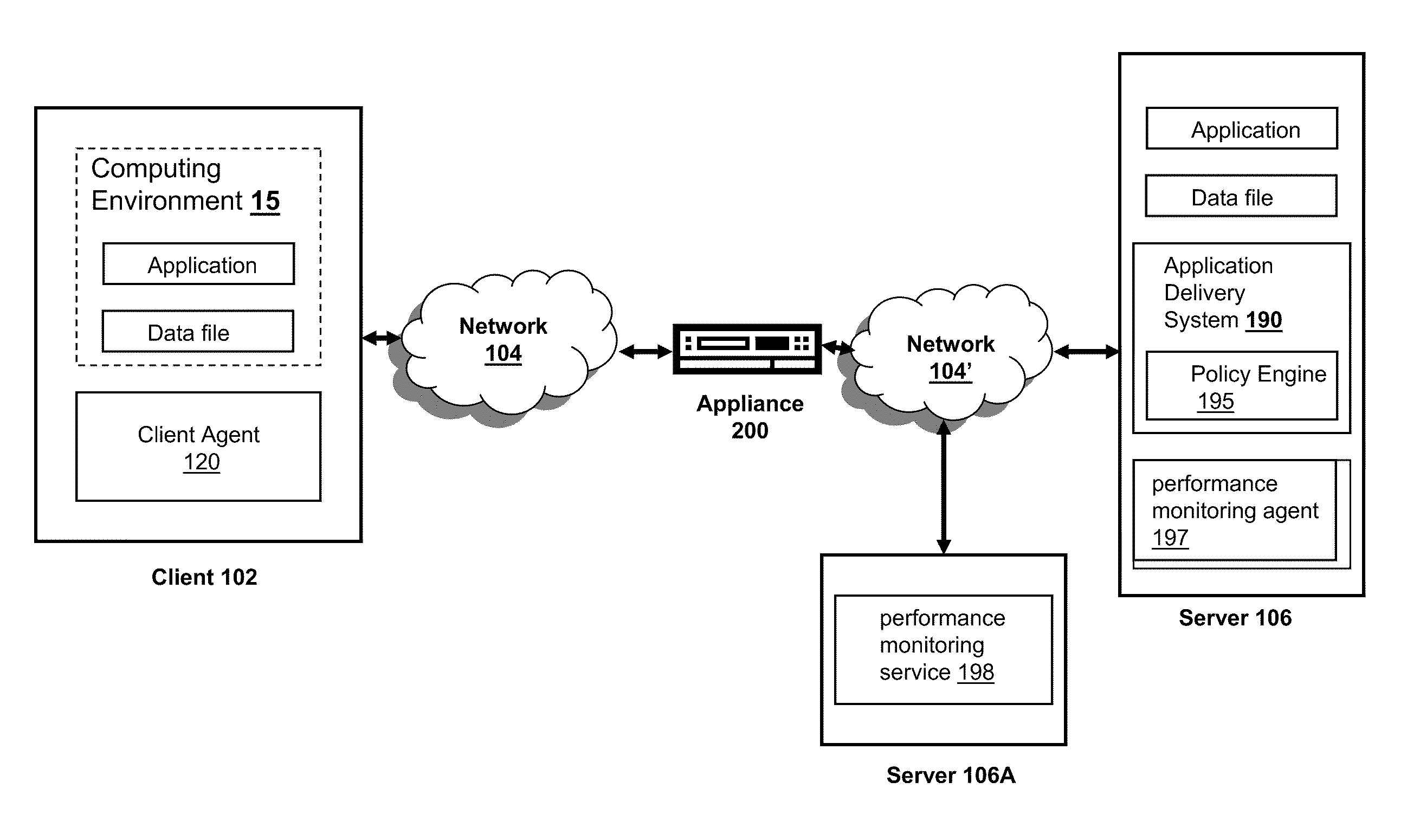
The present disclosure is directed towards systems and methods for tracing packets via an intermediary device. The systems and methods include an intermediary device that establishes connections with clients and connections with servers. The intermediary device links a connection to a server with a connection to a client to provide a client with access to the server. When the client requests a packet trace, the intermediary device applies the trace to linked connections with the client to obtain full trace information for network packets servicing the client.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
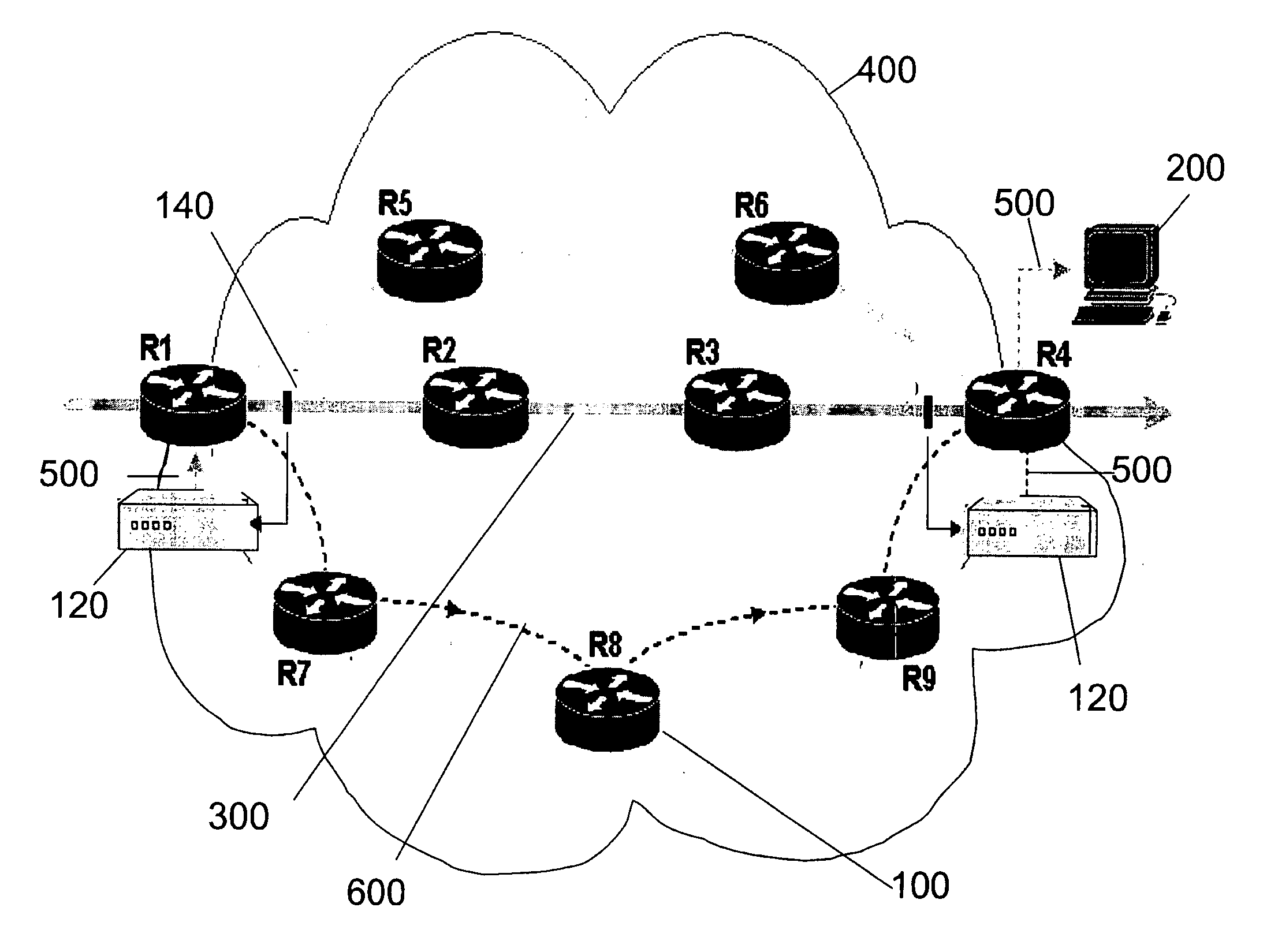
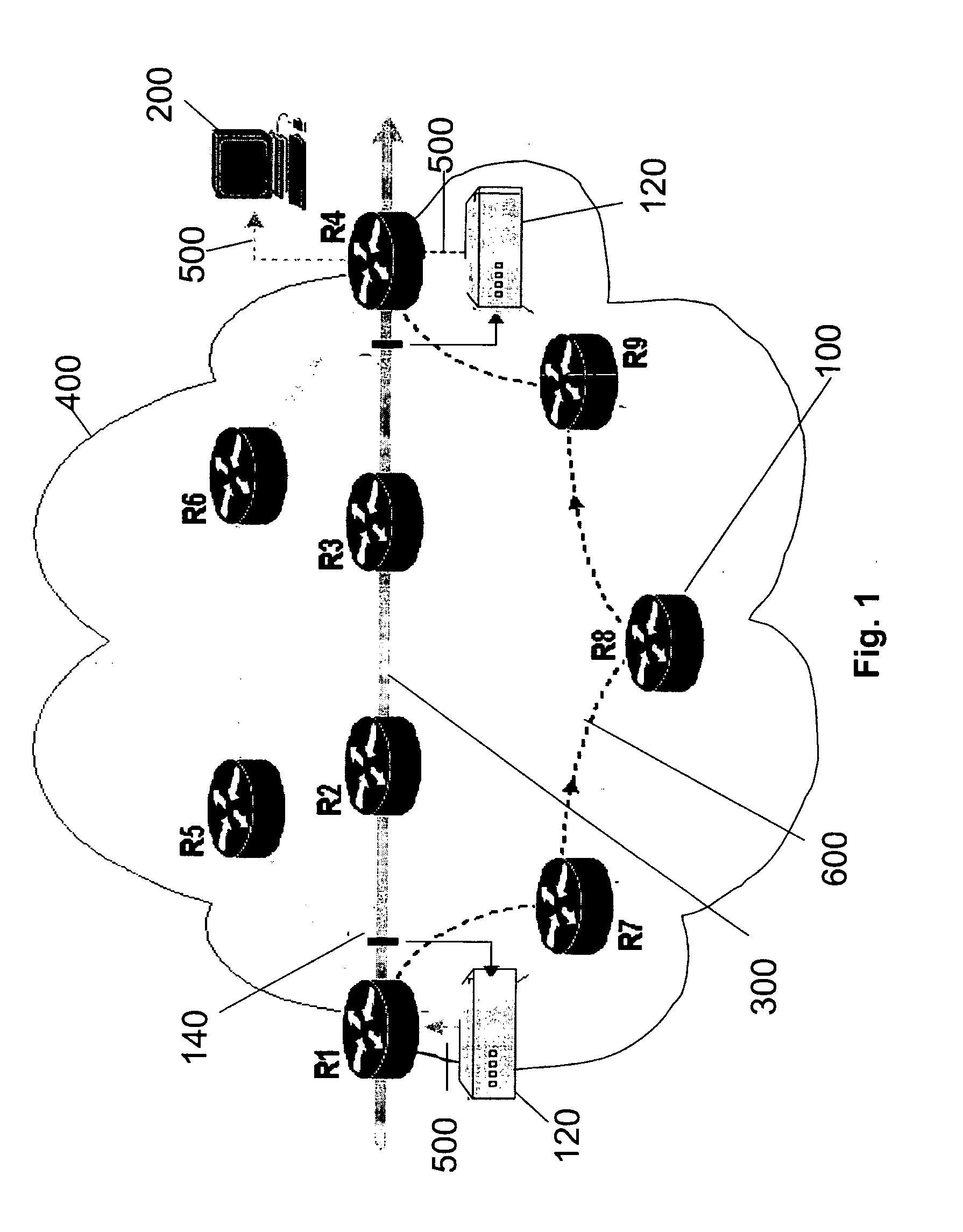
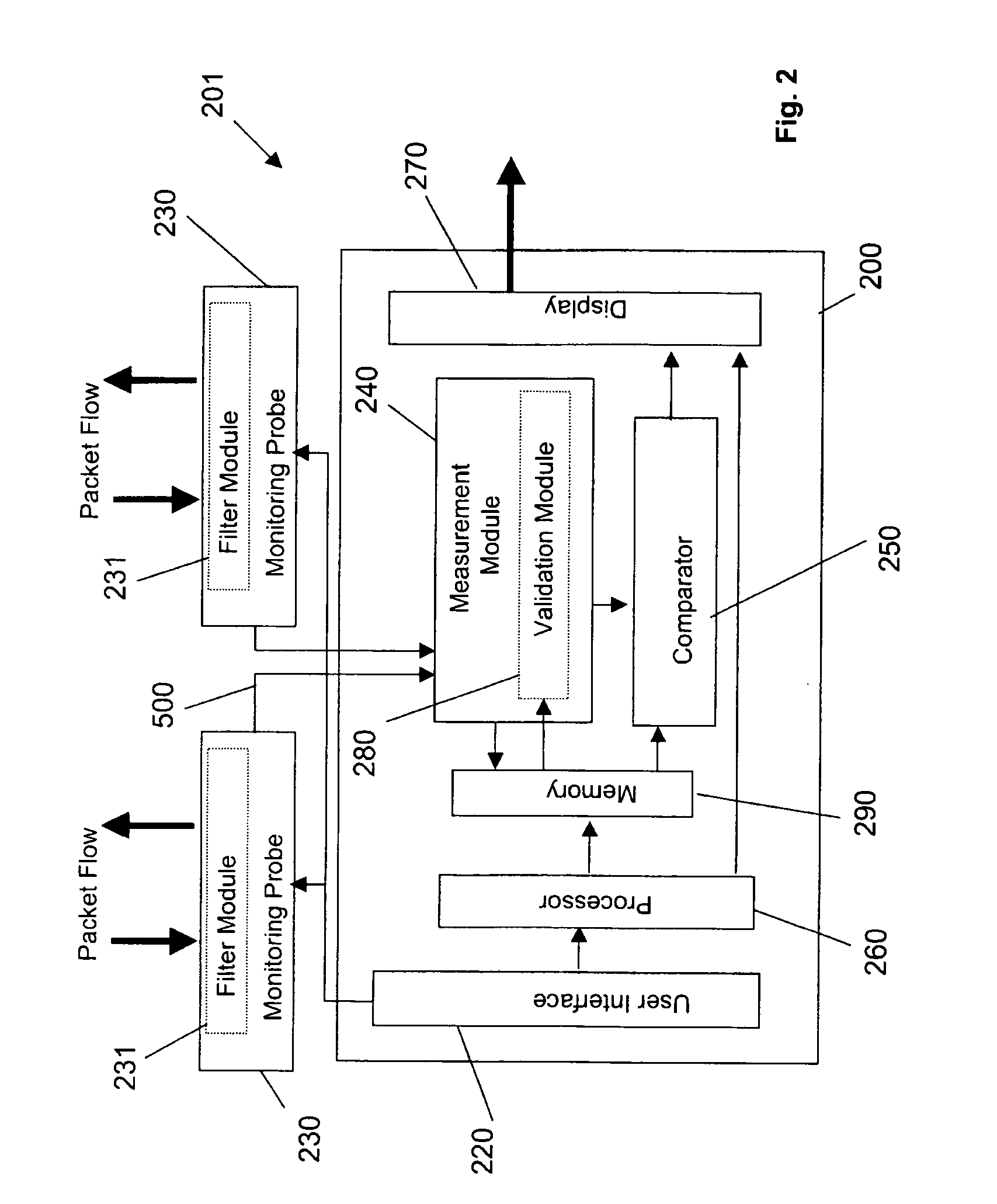
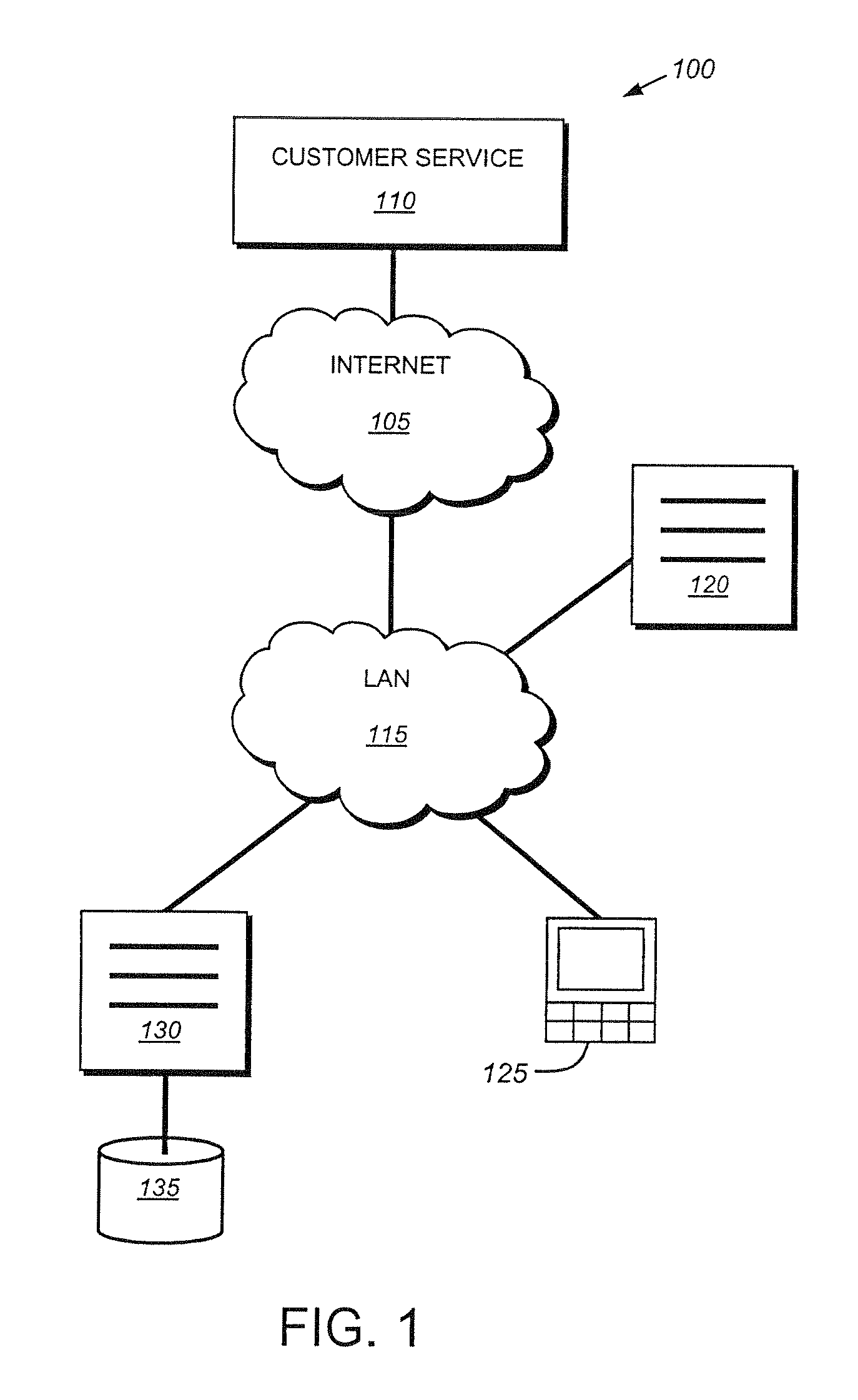
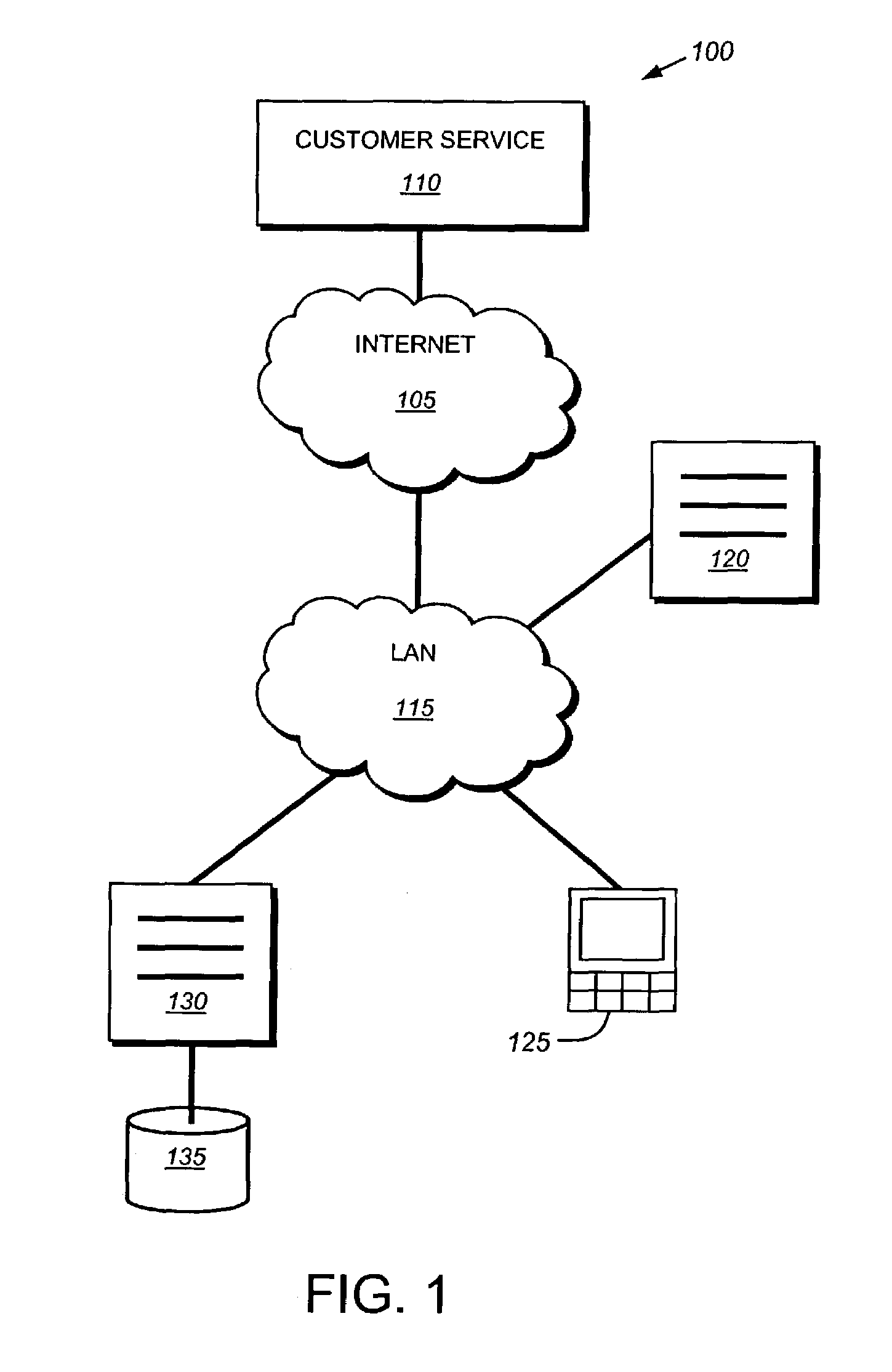
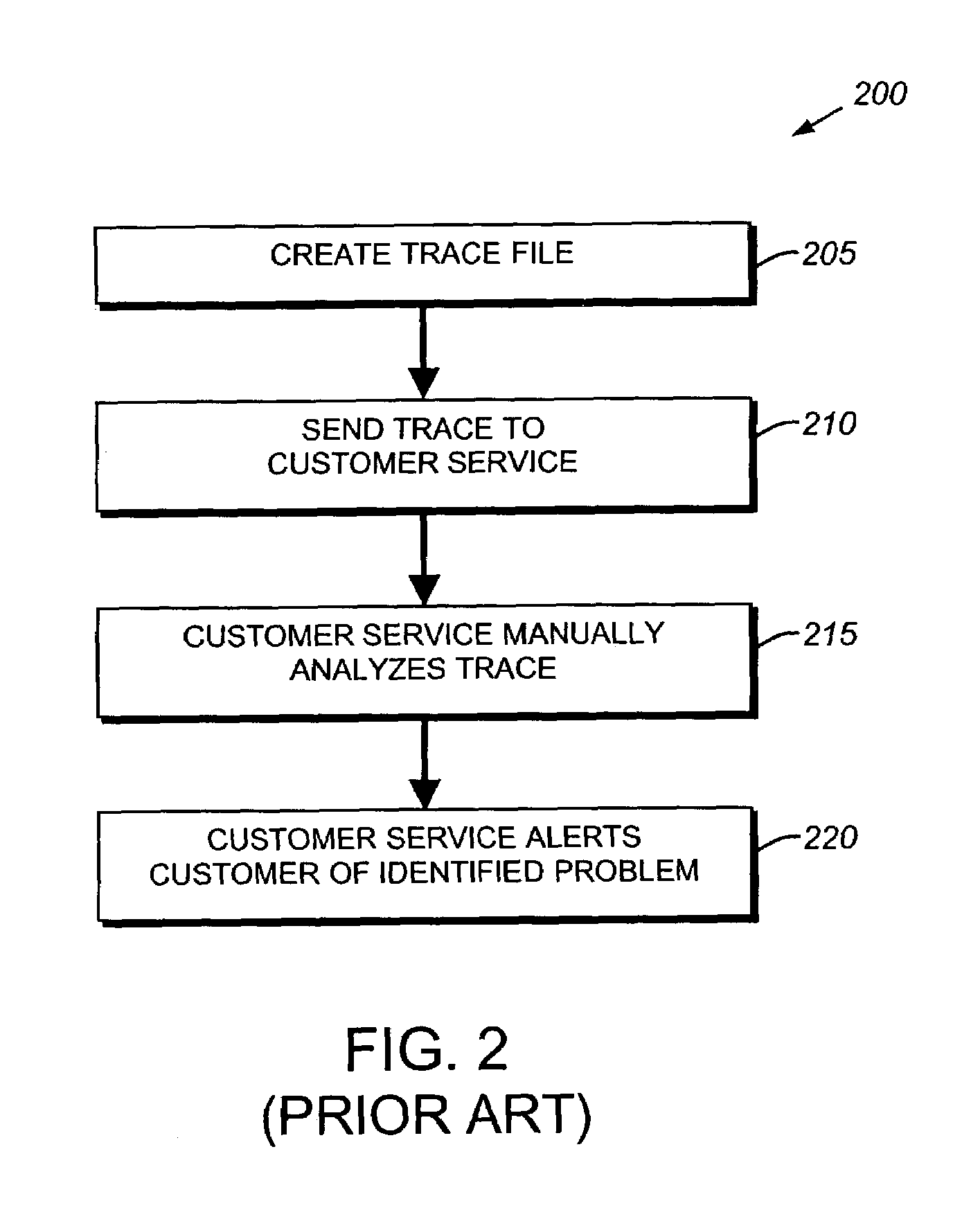
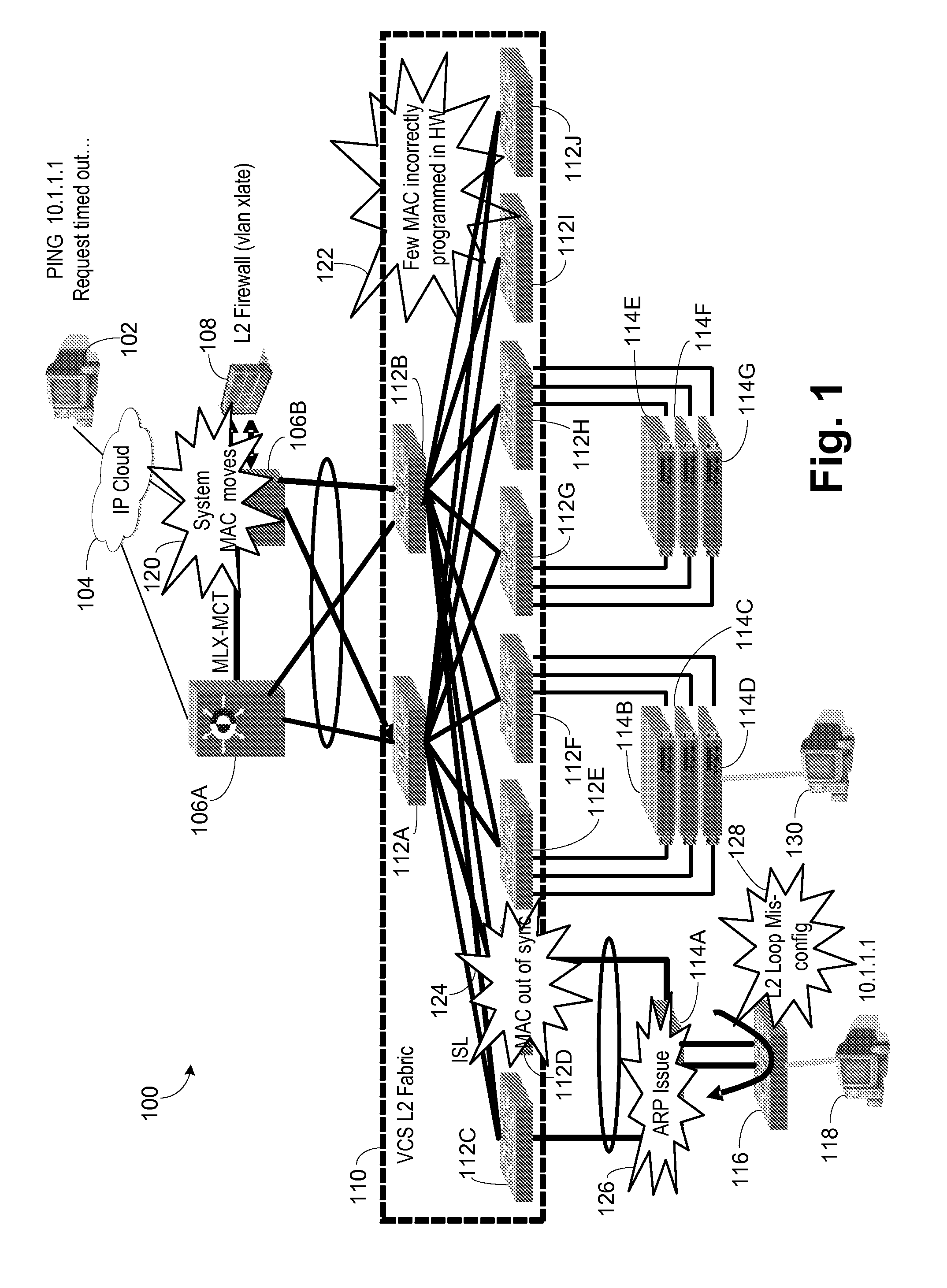
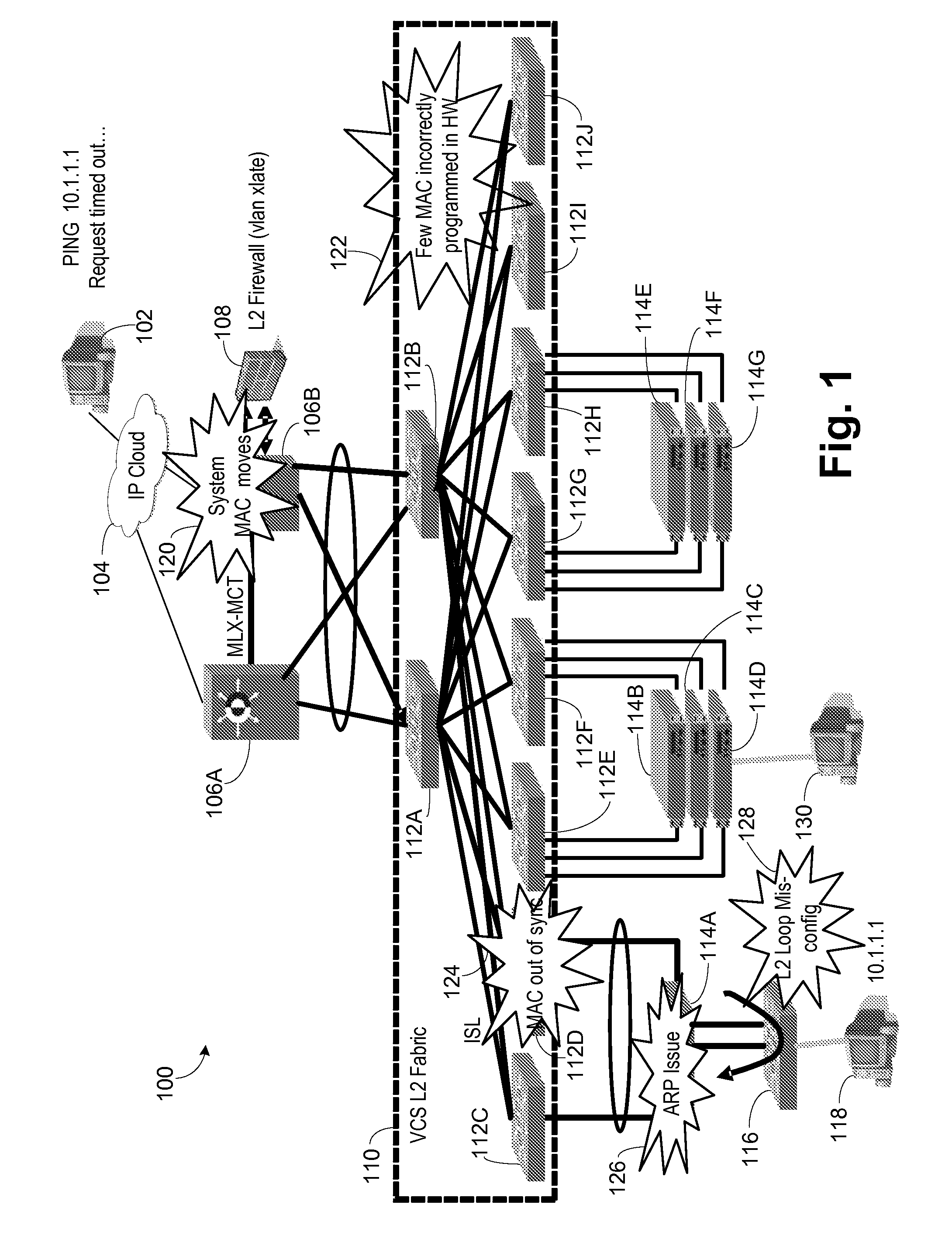
Packet trace diagnostic system
InactiveUS20060218447A1Error detection/correctionData switching networksTelecommunications networkDisplay device
A packet trace diagnostic system for monitoring and displaying packet transfers in a telecommunications network, especially so that faults or errors in the network can be detected quickly and easily, includes one or more monitoring probes for monitoring data packets being transmitted along selected communications path, a processor for predetermining acceptable data packet transfer characteristics, a measurement module for measuring data packet transfer characteristics and a comparator for comparing the measured data packet transfer characteristics to the predetermined acceptable packet transfer characteristics thereby enabling the identification of defective data packet transfers for the selected communications path. A user interface can be used to input acceptable packet transfer characteristics and a display may be used to display the results from the comparator on a message sequence chart, such as a ladder diagram. One of the packet transfer characteristics being measured may be packet transmission delay variation or “jitter”.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
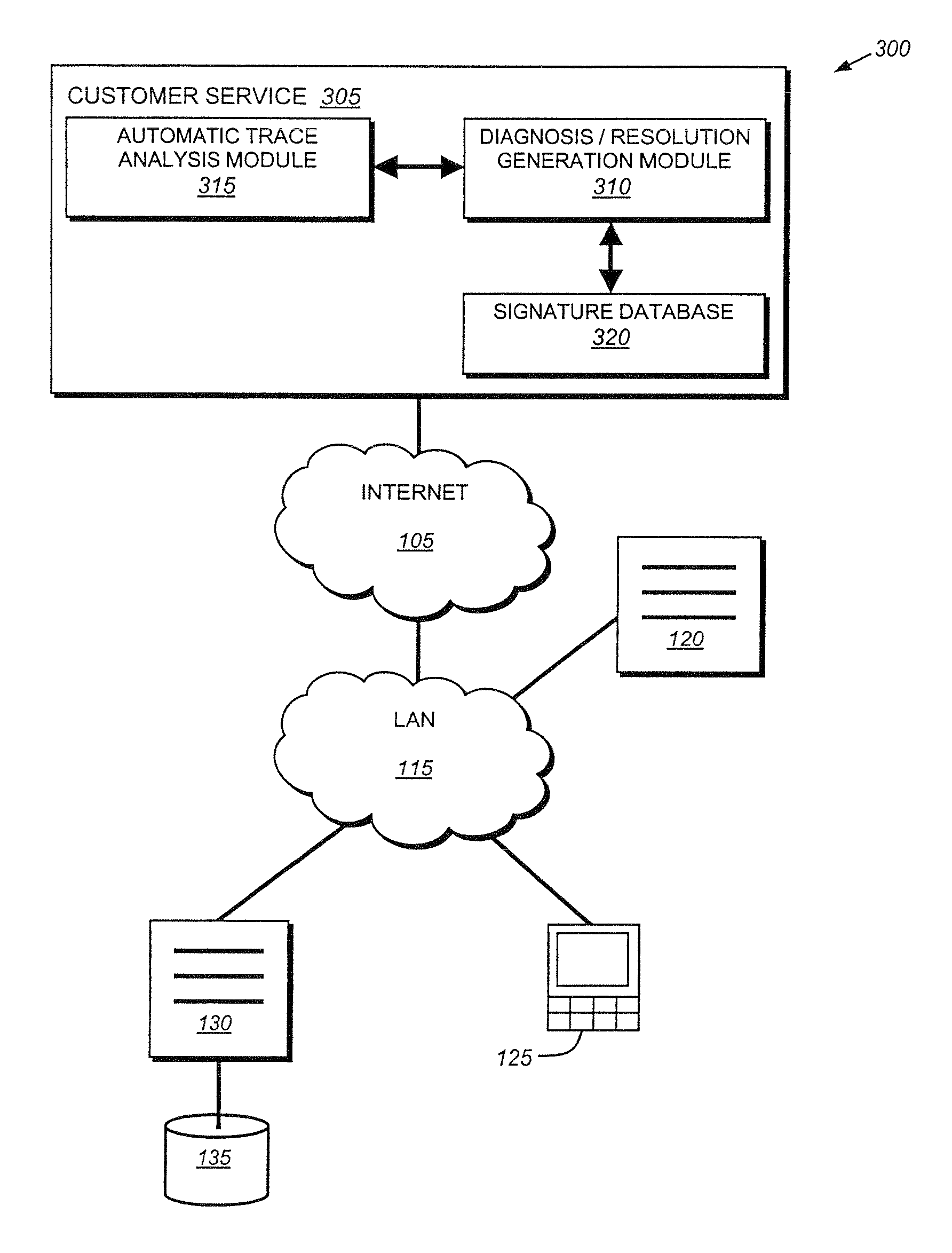
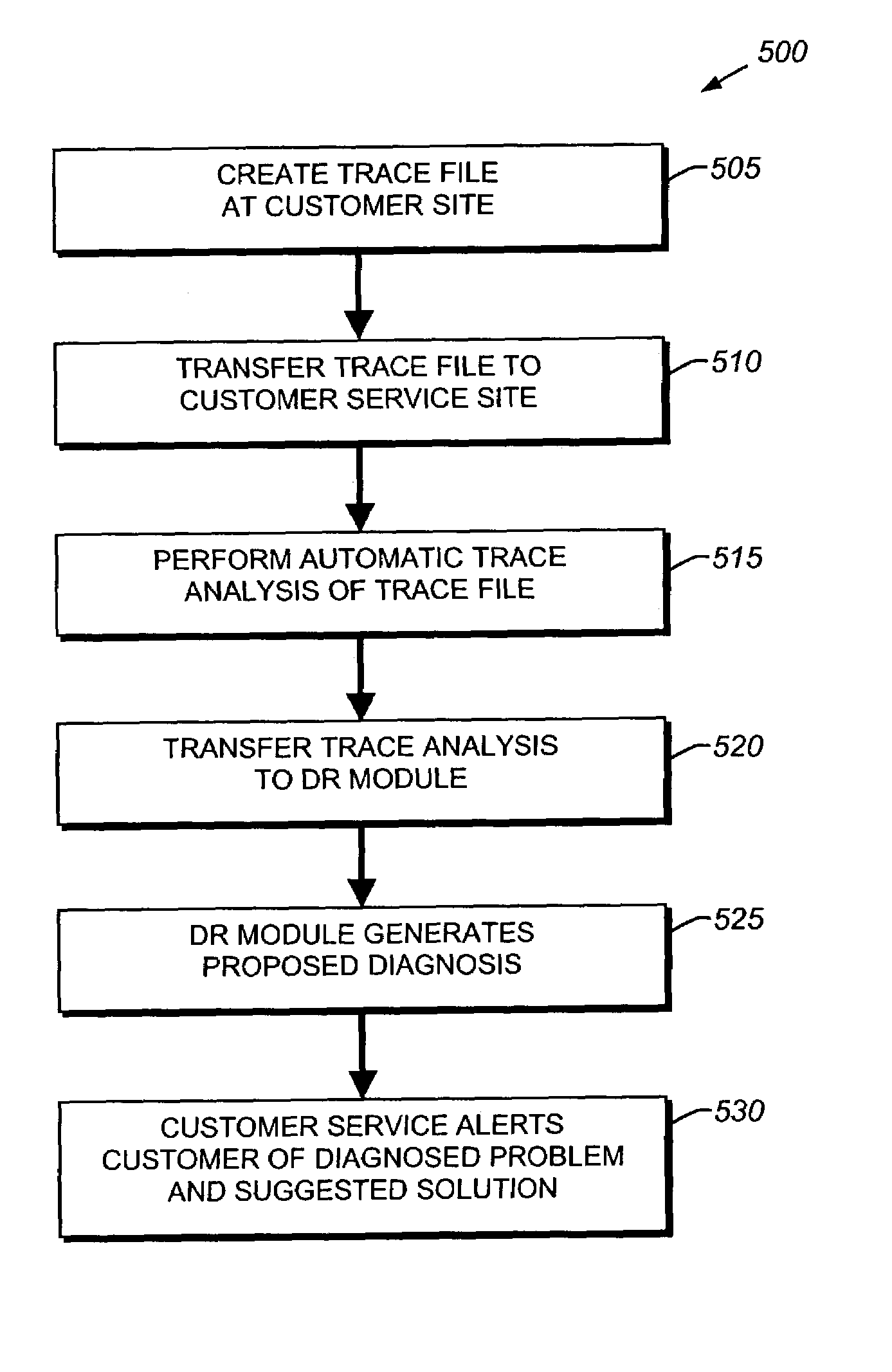
System and method for automatically diagnosing protocol errors from packet traces
A system and method for automatically diagnosing protocol errors from packet traces is provided. The system and method performs an automatic trace analysis on a packet trace to generate an analysis that is then fed into a diagnosis / resolution module. The diagnosis / resolution compares the trace analysis with the database of known problems to identify the protocol error and a suggested solution. The suggested solution then may be implemented, either by a user or by the DR module, to correct the protocol error.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
System and method for automatically diagnosing protocol errors from packet traces
InactiveUS7249286B1Automatically performError detection/correctionTransmissionPacket traceProtocol Error
A system and method for automatically diagnosing protocol errors from packet traces is provided. The system and method performs an automatic trace analysis on a packet trace to generate an analysis that is then fed into a diagnosis / resolution module. The diagnosis / resolution compares the trace analysis with the database of known problems to identify the protocol error and a suggested solution. The suggested solution then may be implemented, either by a user or by the DR module, to correct the protocol error.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Systems and methods for trace filters by association of client to vserver to services
The present disclosure is directed towards systems and methods for tracing packets via an intermediary device. The systems and methods include an intermediary device that establishes connections with clients and connections with servers. The intermediary device links a connection to a server with a connection to a client to provide a client with access to the server. When the client requests a packet trace, the intermediary device applies the trace to linked connections with the client to obtain full trace information for network packets servicing the client.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Managing network traffic for improved availability of network services
ActiveUS8095635B2Method can be usedPrecise functionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork service
Managing network traffic to improve availability of network services by classifying network traffic flows using flow-level statistical information and machine learning estimation, based on a measurement of at least one of relevance and goodness of network features. Also, determining a network traffic profile representing applications associated with the classified network traffic flows, and managing network traffic using the network traffic profile. The flow-level statistical information includes packet-trace information and is available from at least one of Cisco NetFlow, NetStream or cflowd records. The classification of network flows includes tagging packet-trace flow record data based on defined packet content information. The classifying of network flows can result in the identification of a plurality of clusters based on the measurement of the relevance of the network features. Also, the classification of network traffic can use a correlation-based measure to determine the goodness of the network features.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Lightweight Application Classification for Network Management
ActiveUS20100014420A1Method can be usedEasy to useError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityNetwork management
Managing network traffic to improve availability of network services by classifying network traffic flows using flow-level statistical information and machine learning estimation, based on a measurement of at least one of relevance and goodness of network features. Also, determining a network traffic profile representing applications associated with the classified network traffic flows, and managing network traffic using the network traffic profile. The flow-level statistical information includes packet-trace information and is available from at least one of Cisco NetFlow, NetStream or cflowd records. The classification of network flows includes tagging packet-trace flow record data based on defined packet content information. The classifying of network flows can result in the identification of a plurality of clusters based on the measurement of the relevance of the network features. Also, the classification of network traffic can use a correlation-based measure to determine the goodness of the network features.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Systems and processes of identifying p2p applications based on behavioral signatures
InactiveUS20090187653A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksApplication softwarePacket trace
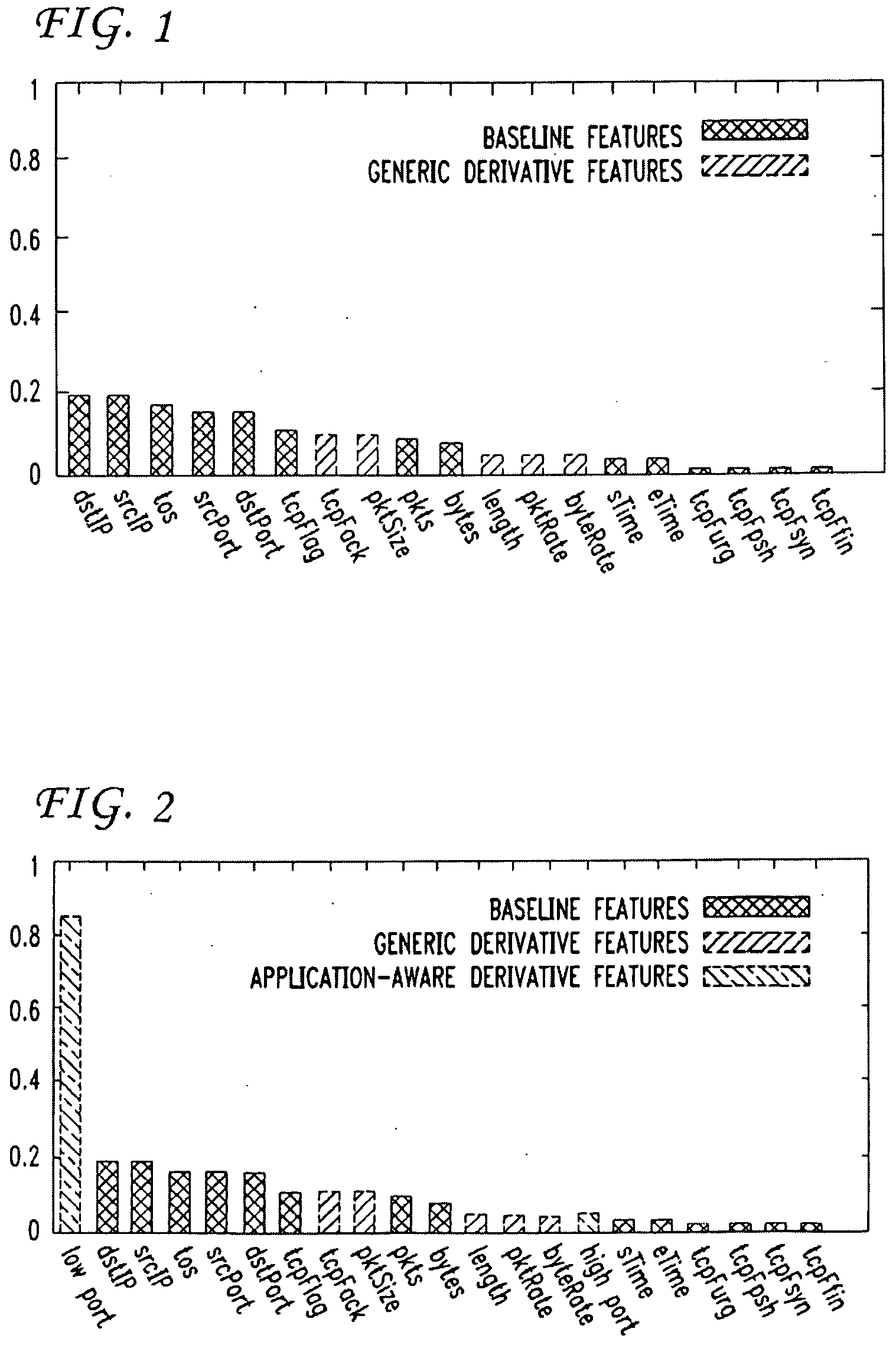
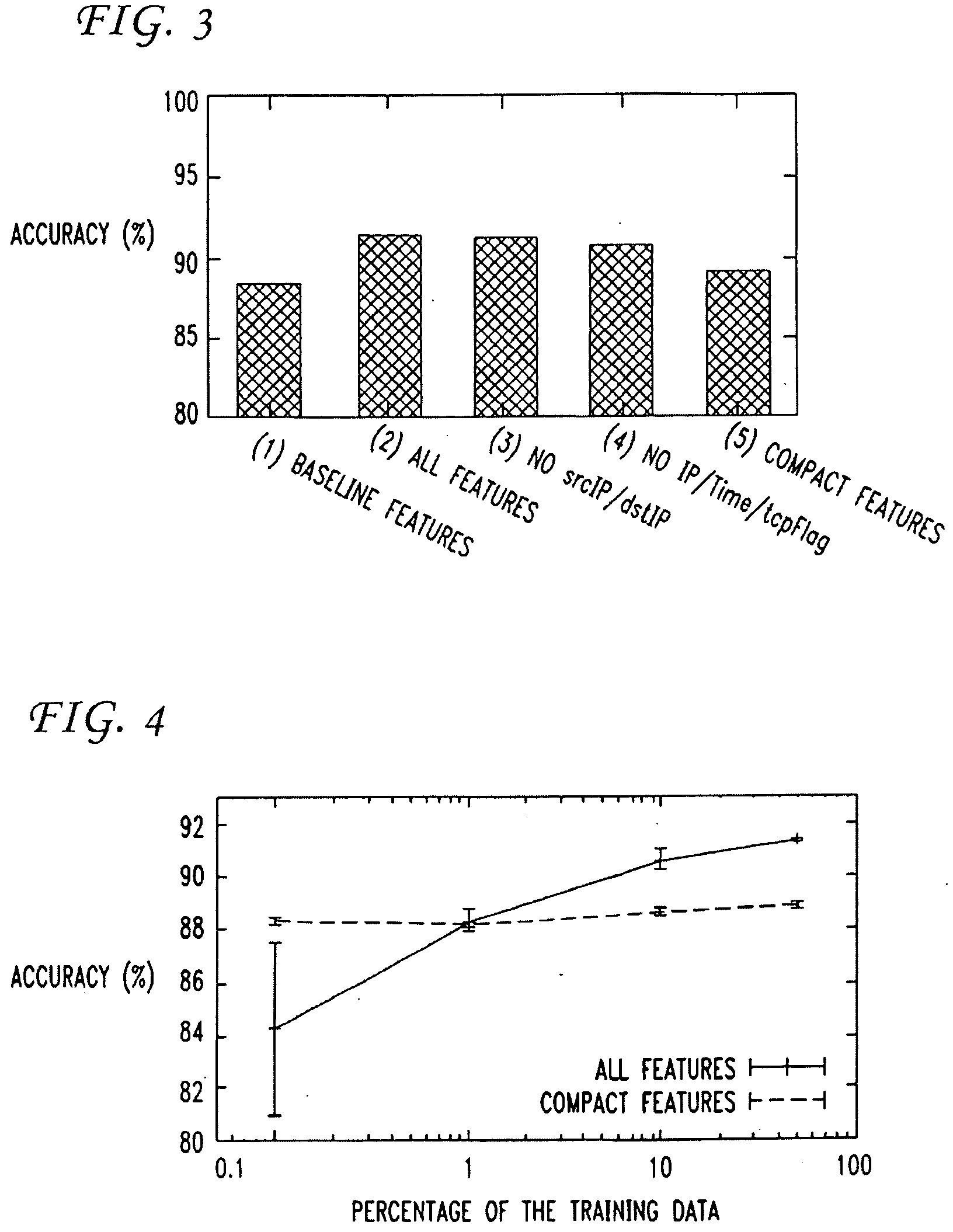
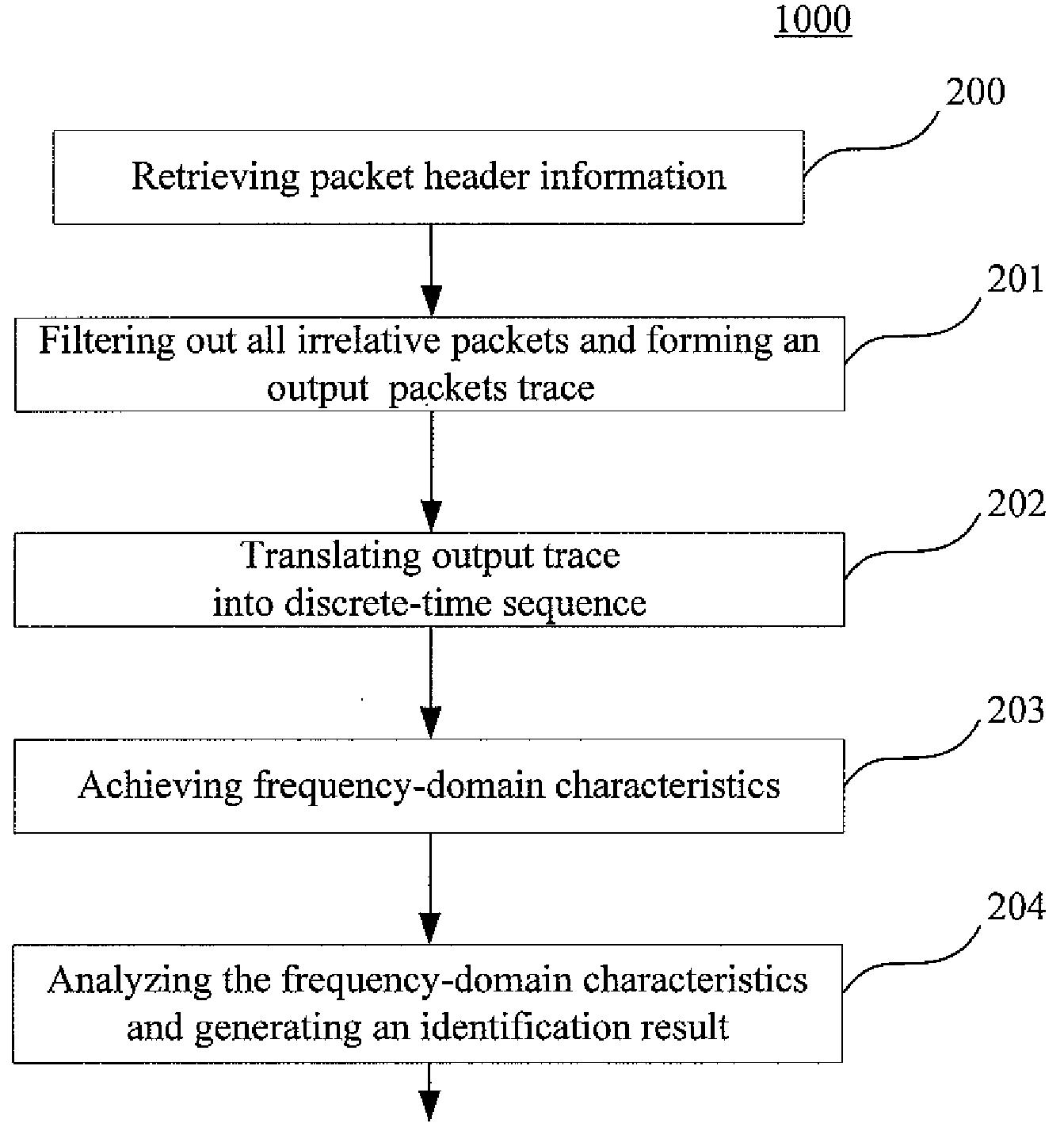
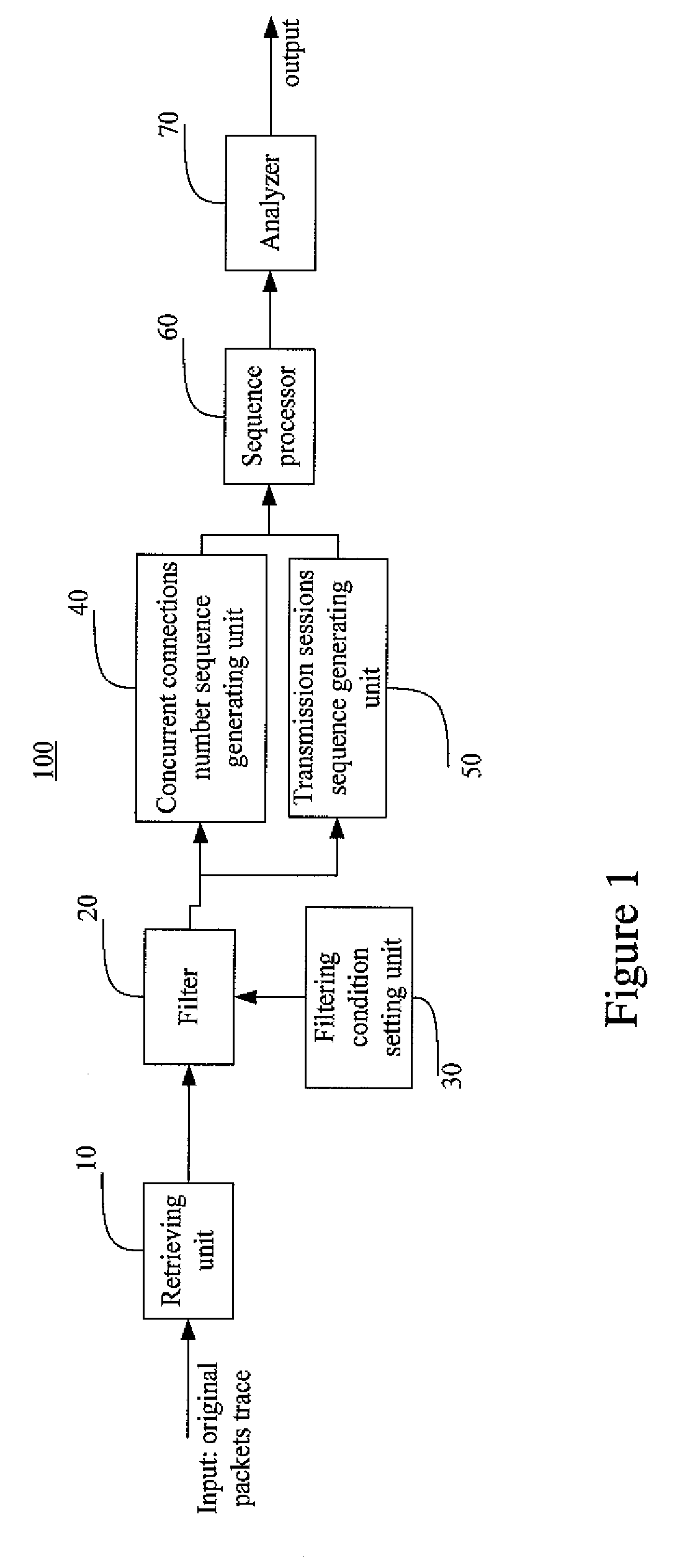
Disclosed are a system and a process for identifying P2P applications and specific P2P software as well from an original mixed packet trace based on behavioral-signatures. The behavioral-signature based system and process according to the invention is mainly to check whether the application has these specific periodic behaviors or not. The process of this invention comprises the steps of filtering out all irrelative packets; translating the filtered packet trace into discrete-time sequences; processing the sequences to obtain frequency-domain characteristics of original packet trace; and analyzing the frequency-domain characteristics and determining the identification.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
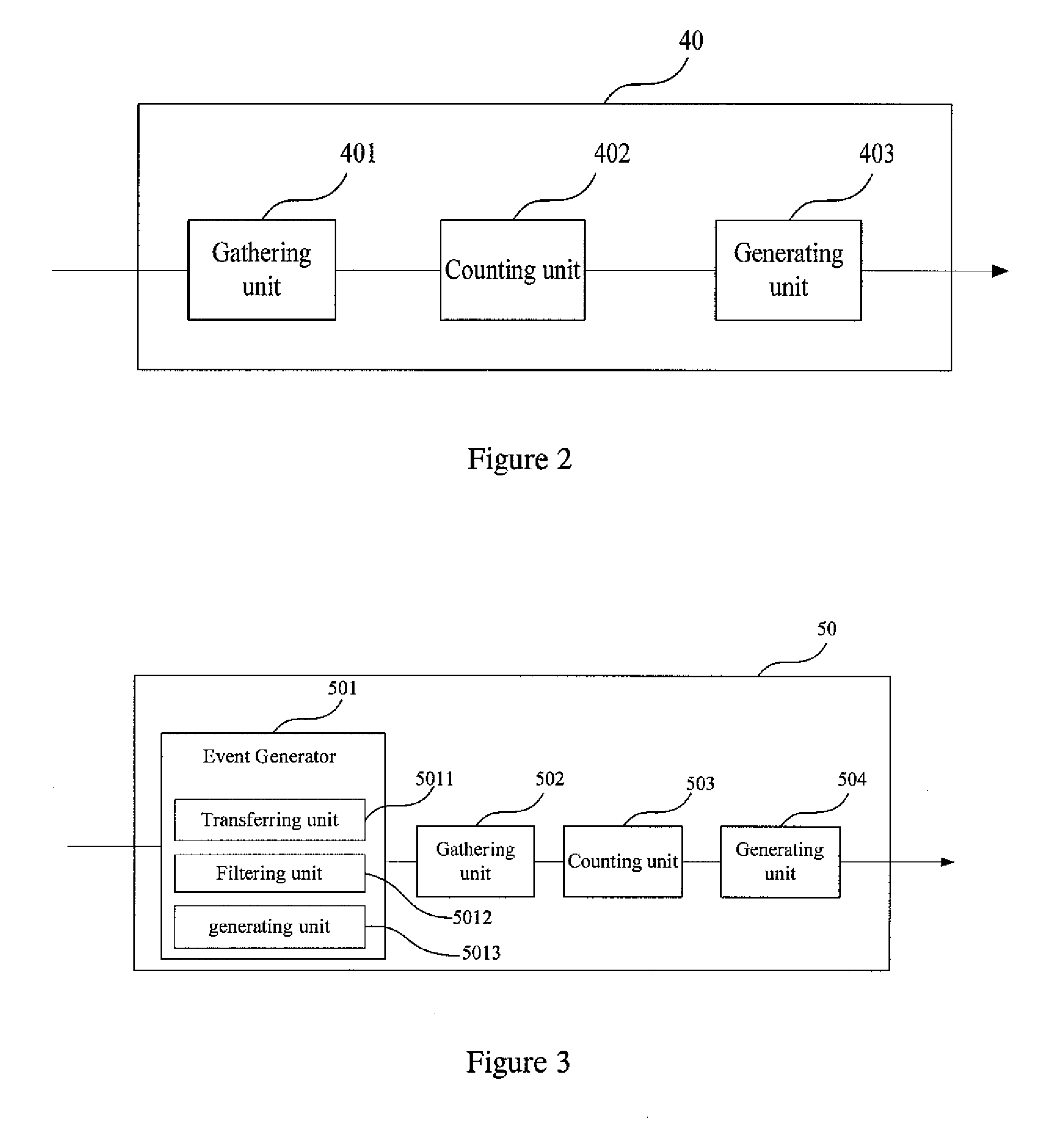
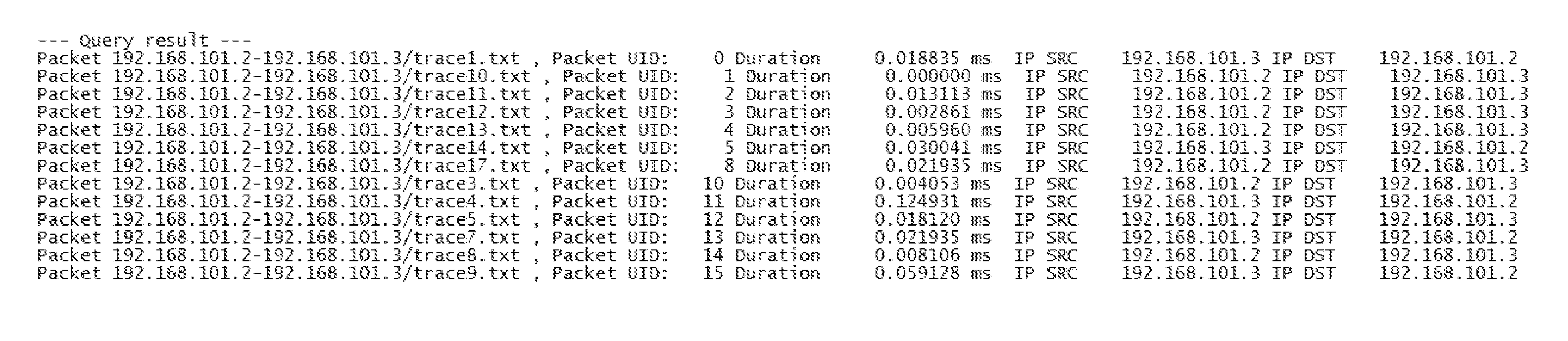
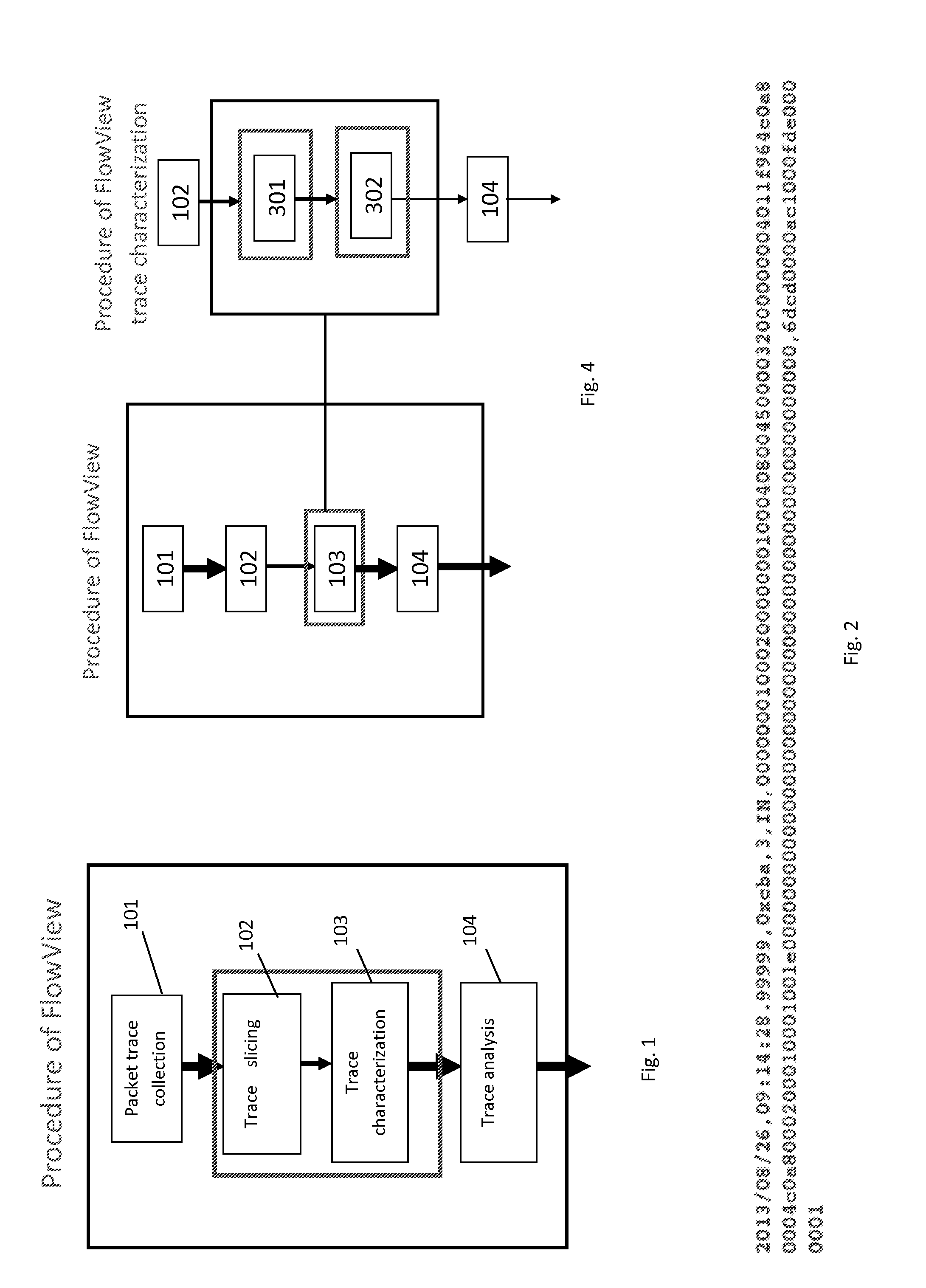
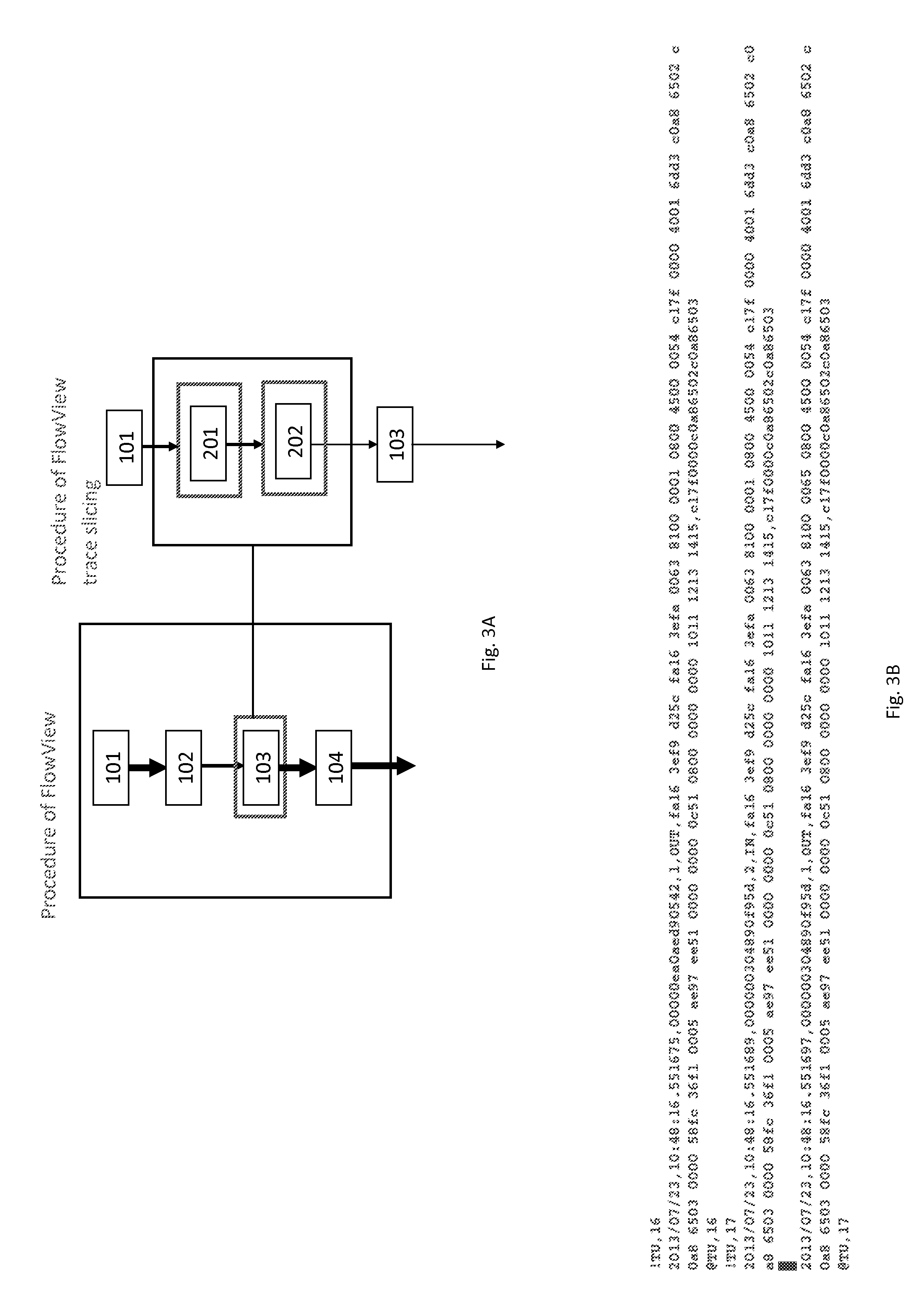
System and Method for Network Packet Event Characterization and Analysis
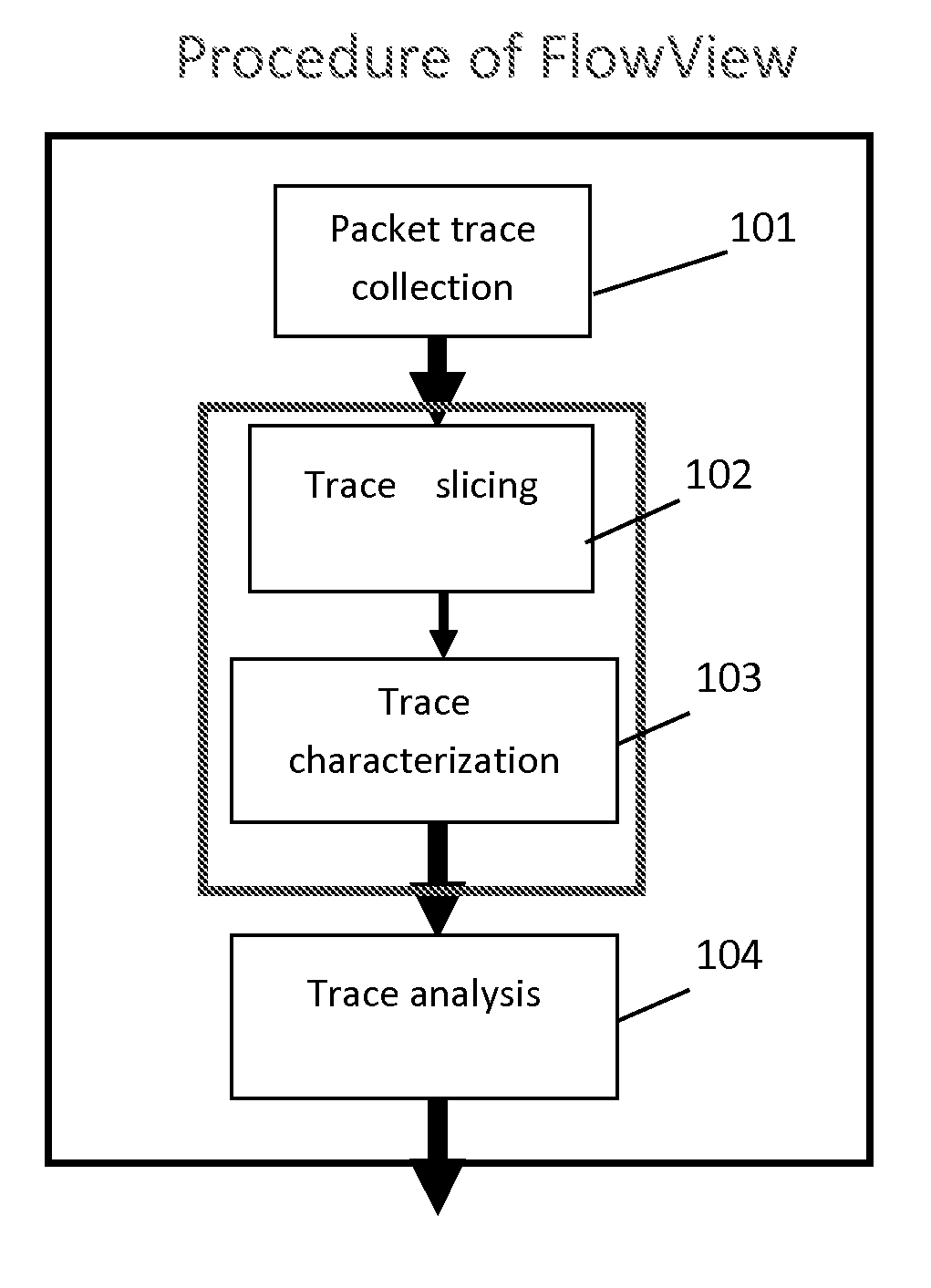
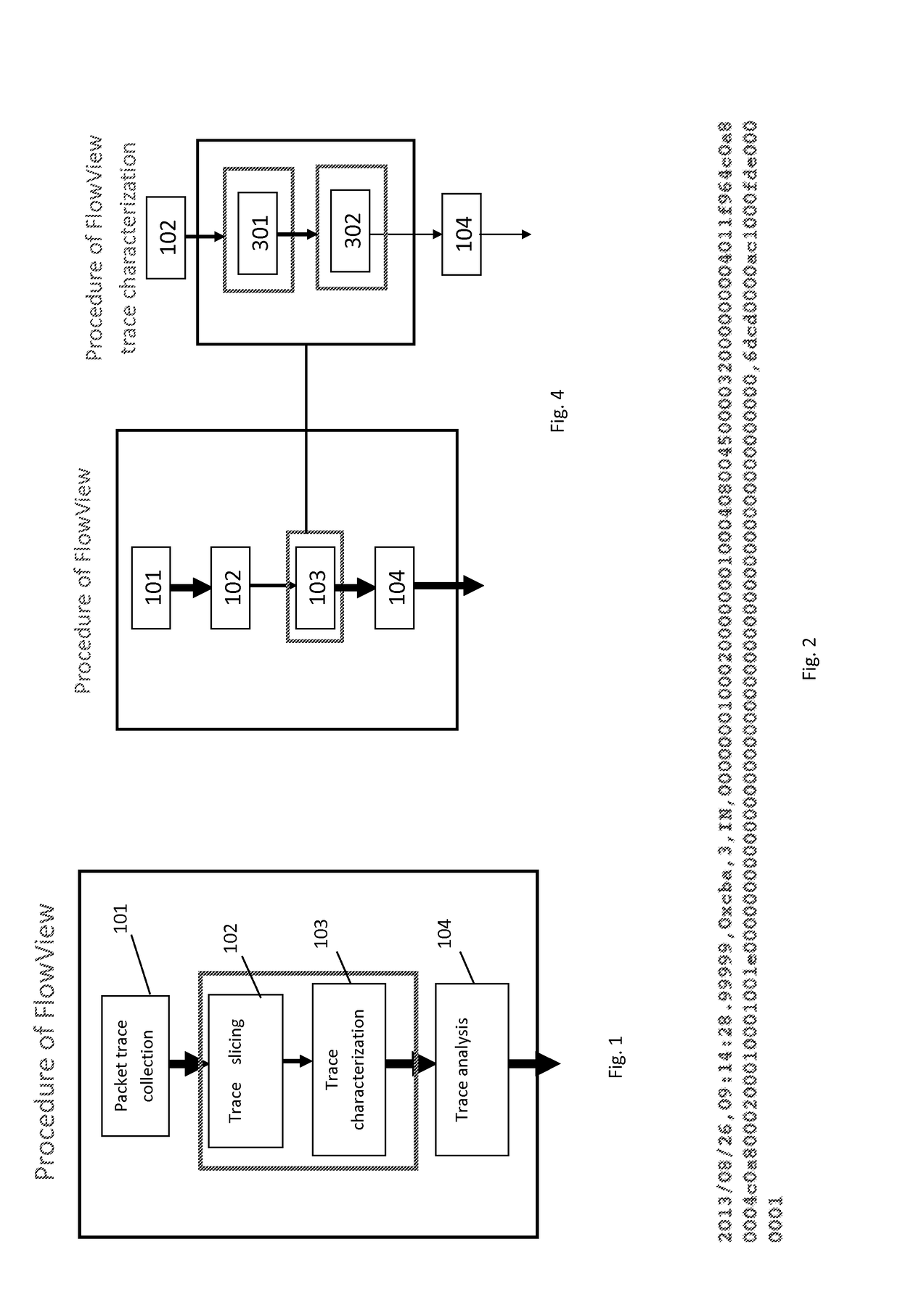
A computer implemented method for network monitoring includes providing network packet event characterization and analysis for network monitoring that includes supporting summarization and characterization of network packet traces collected across multiple processing elements of different types in a virtual network, including a trace slicing to organize individual packet events into path-based trace slices, a trace characterization to extract at least 2 types of feature matrix describing those trace slices, and a trace analysis to cluster, rank and query packet traces based on metrics of the feature matrix.
Owner:NEC CORP
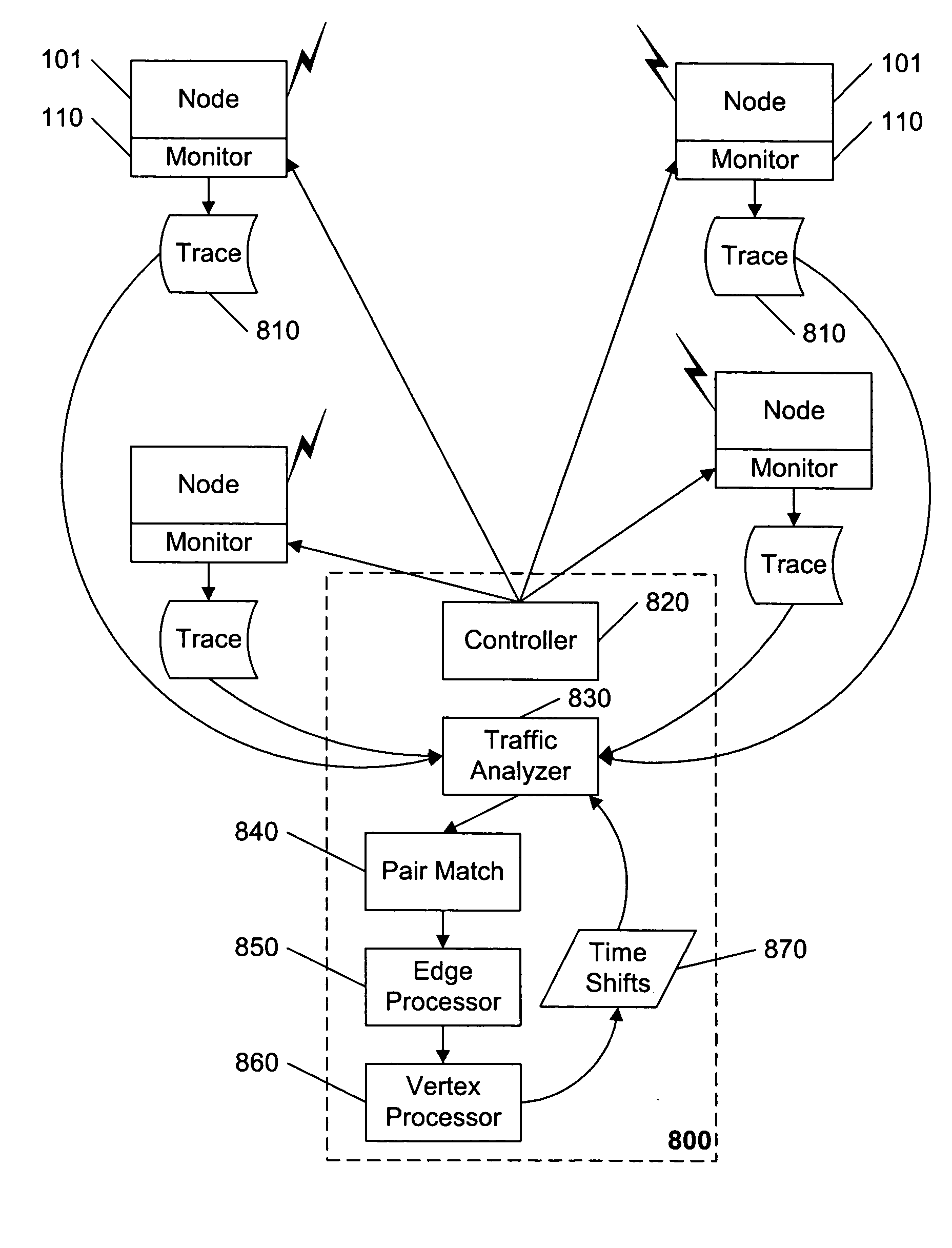
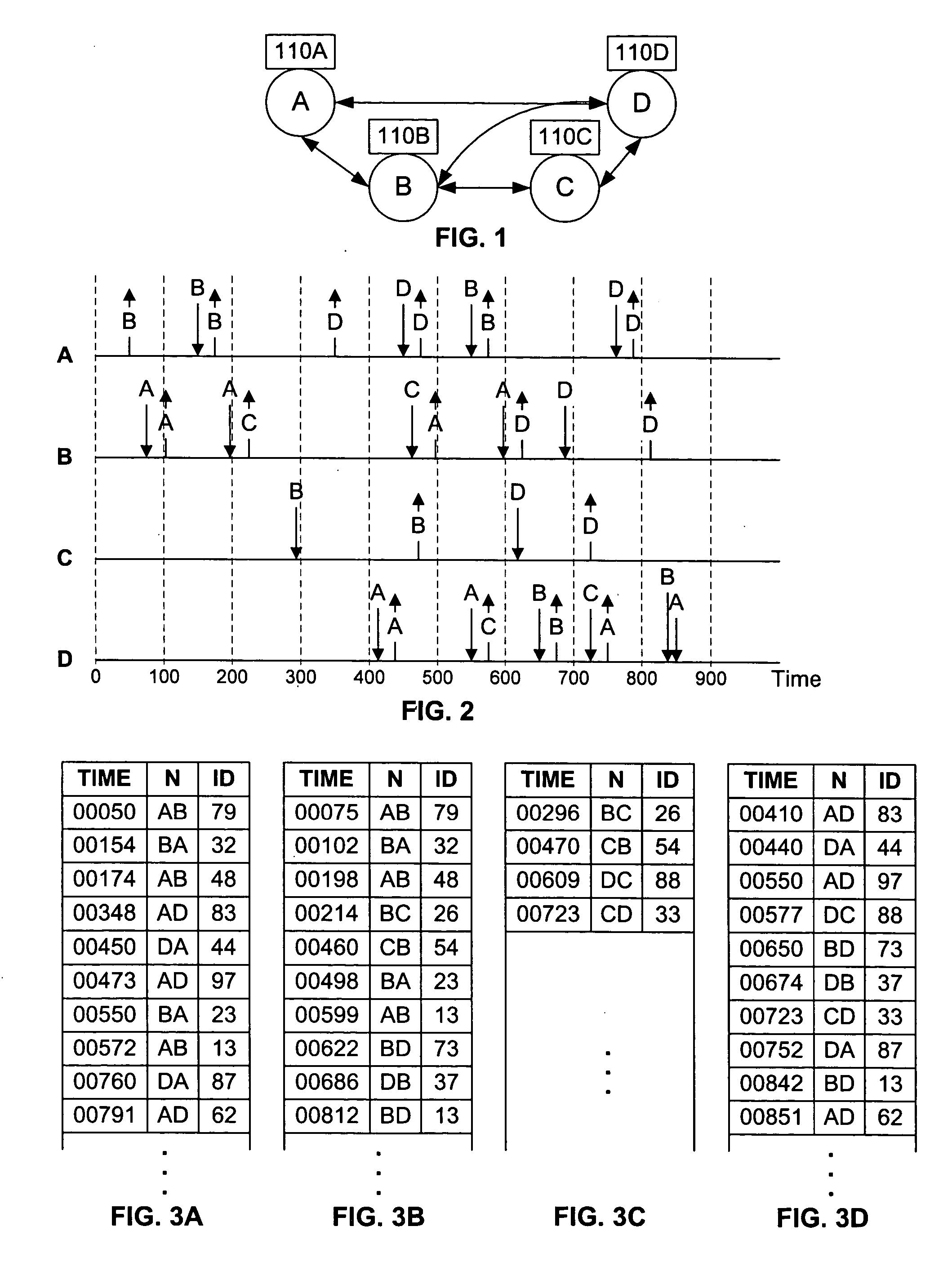
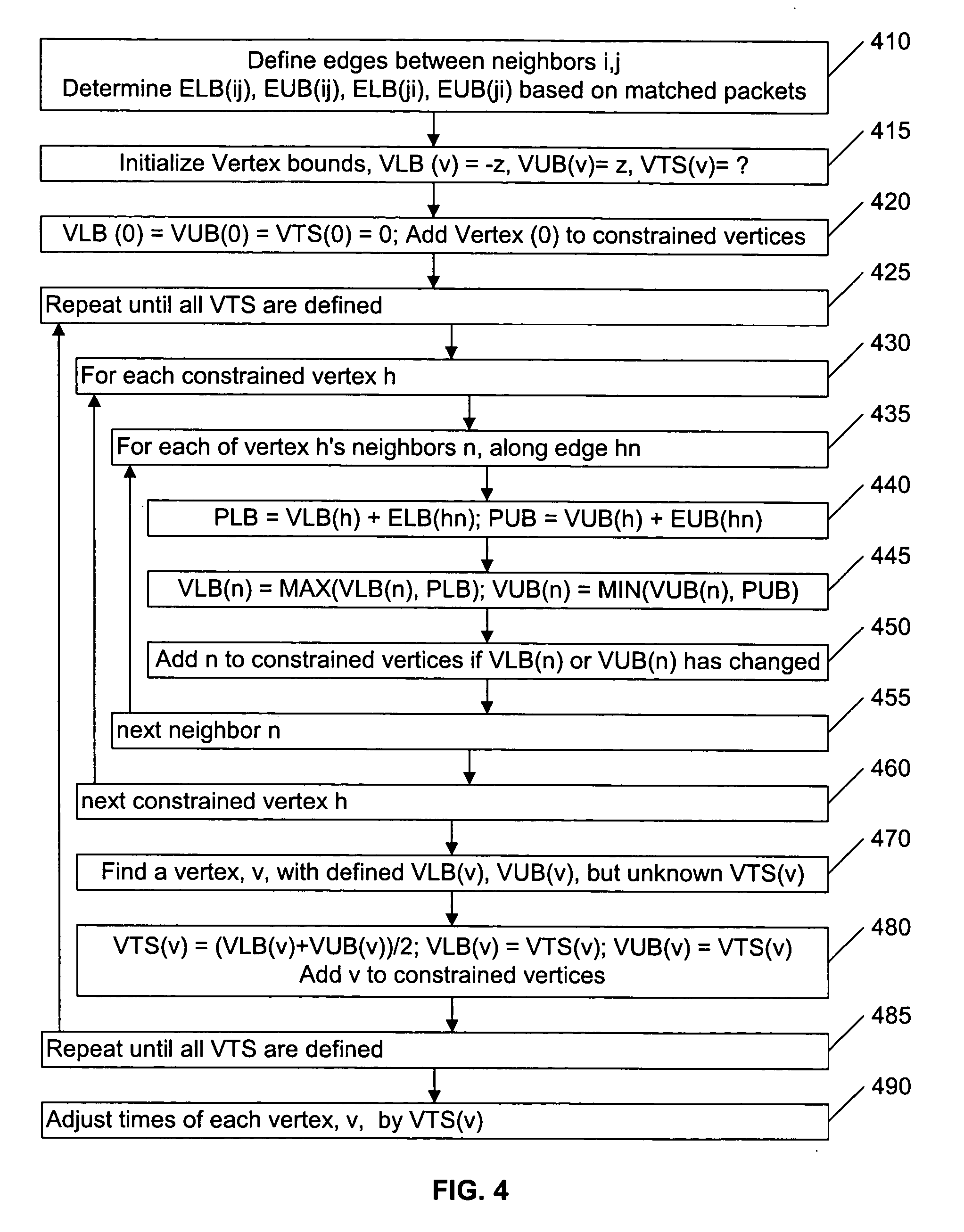
Synchronizing packet traces
A system and method for determining a common time base among nodes in a network by iteratively propagating timing constraints among the nodes, and determining a time-shift to apply to the time base of each node that conforms to these constraints. “Trace” files record the time of transmission or reception of packets at each node, based on the time base at the node. A fundamental constraint in a common time-based system is that the time of reception of a packet at a destination node cannot be prior to the time of transmission of the packet from a source node. A further constraint in a common time-based system is that the time of reacting to an event cannot be prior to the time of the event. By concurrently tracing traffic among multiple nodes in a network and subsequently processing the trace files to assure that each packet's transmission occurs prior to its reception, and that each reaction packet occurs after its corresponding causal packet, a correspondence between each node's time base and the common time base can be determined.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
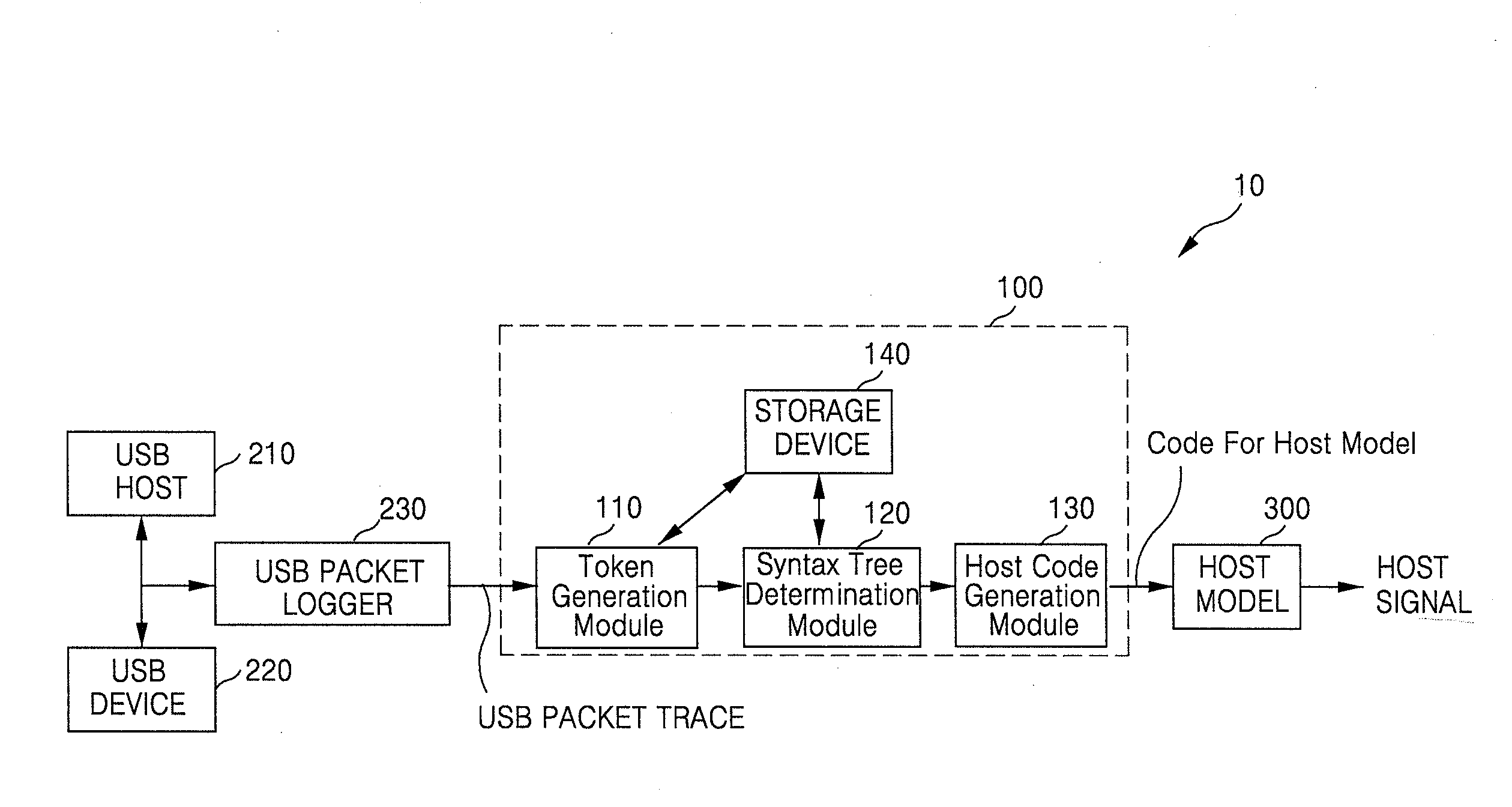
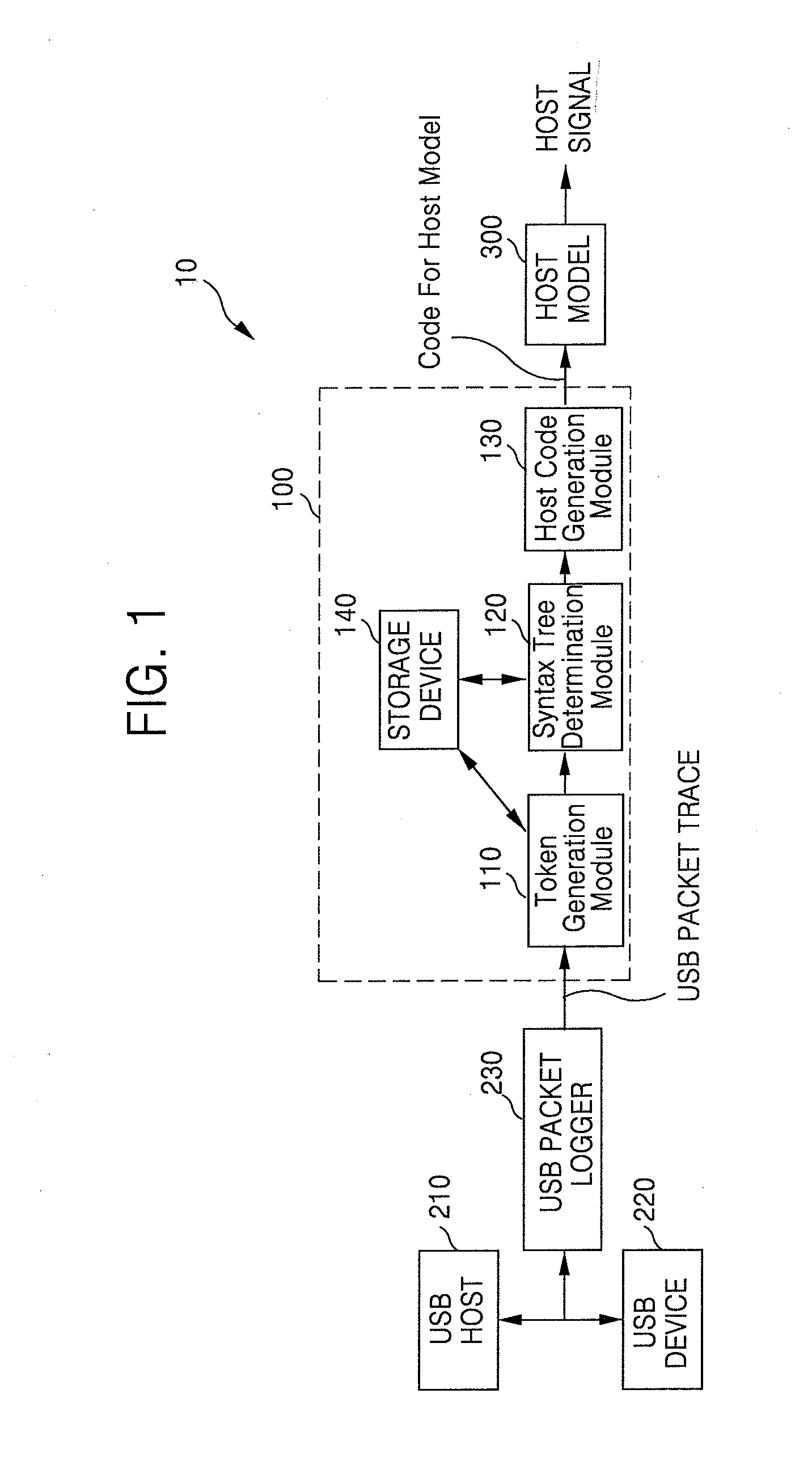
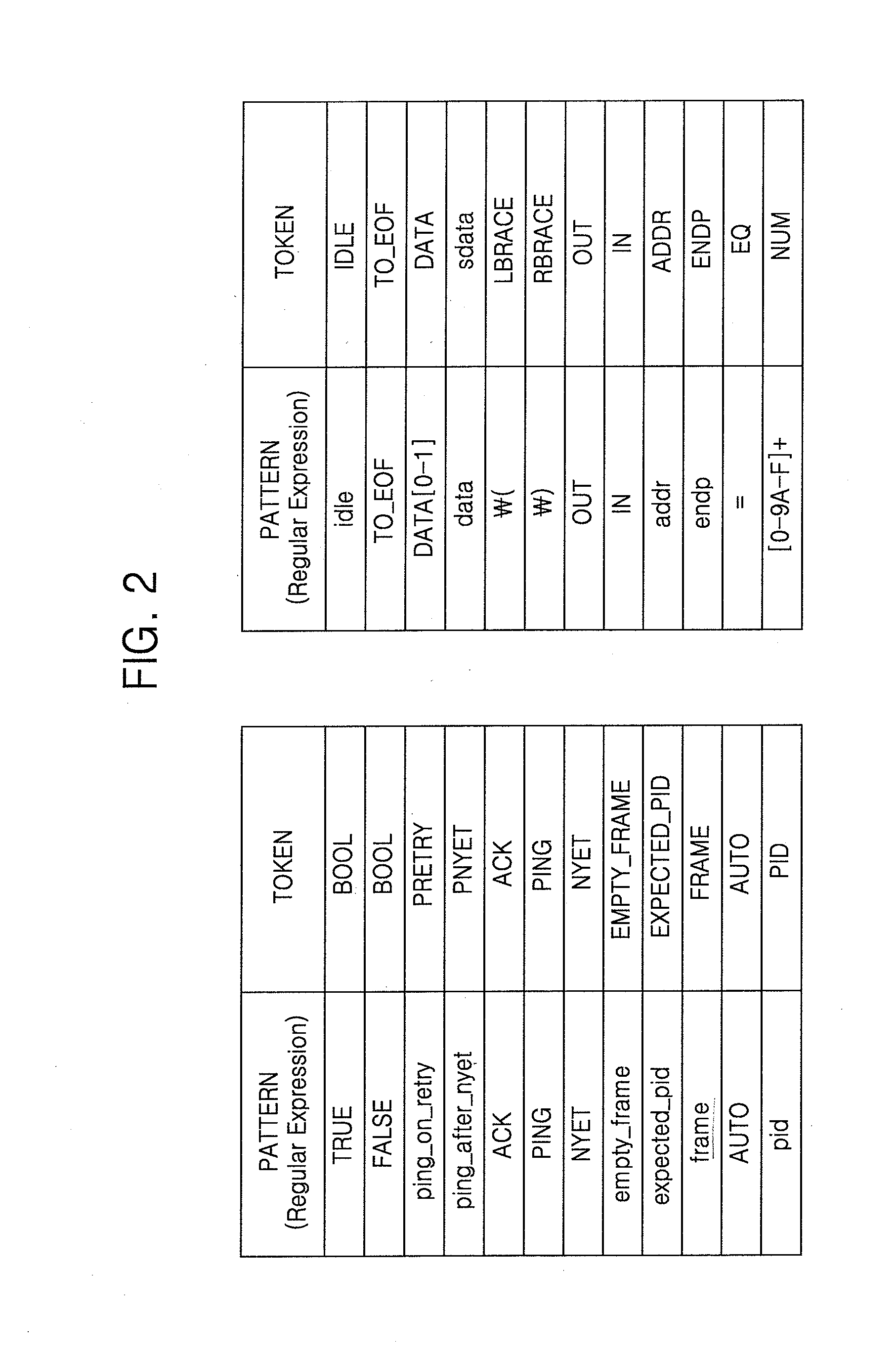
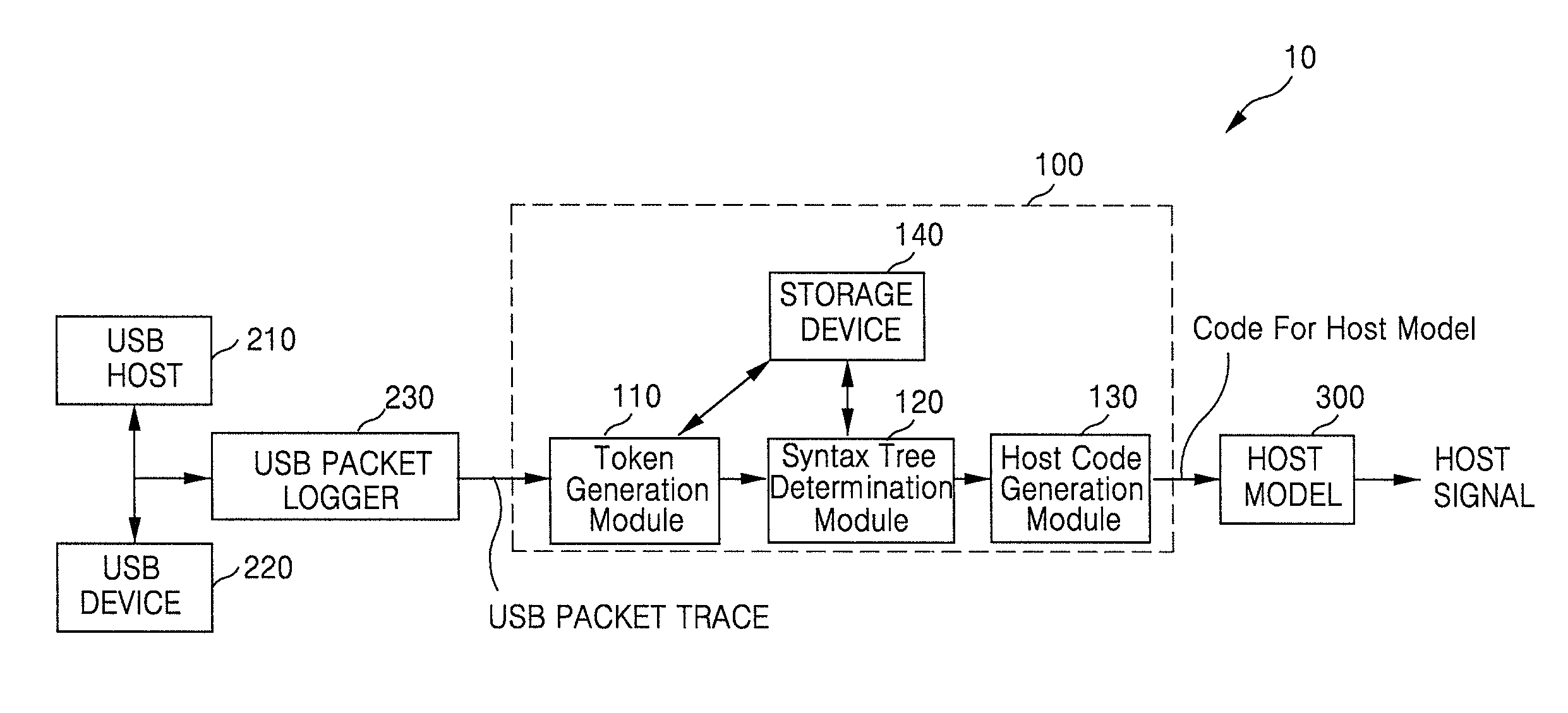
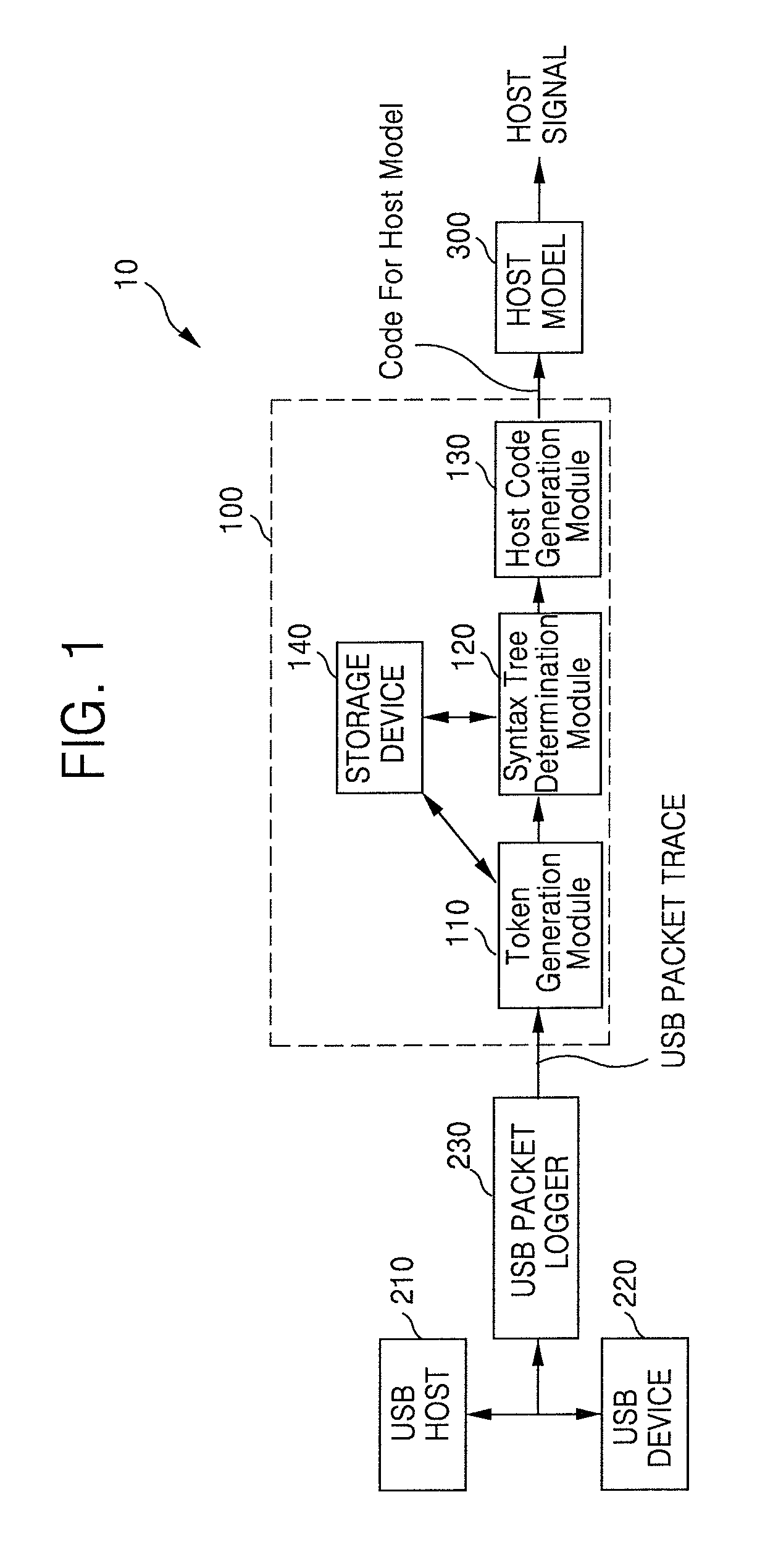
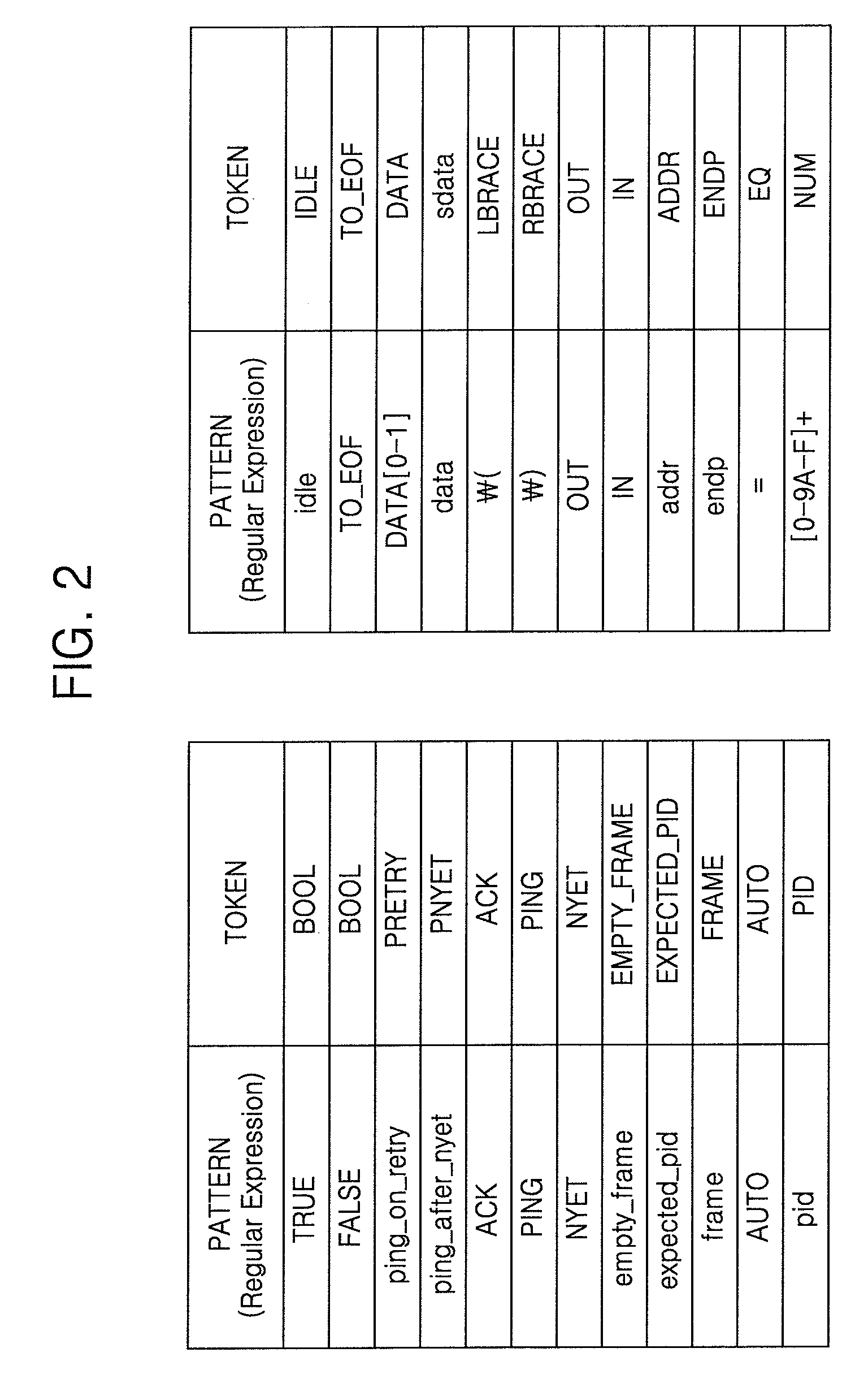
Method and System for Testing USB Device
A method for testing a USB (universal serial bus) device includes receiving a USB packet trace output from a USB host, at a USB packet trace converting apparatus, generating at least one token corresponding to the USB packet trace received from the USB host, determining a syntax tree corresponding to the at least one token, and generating a code for a USB host model corresponding to the determined syntax tree.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
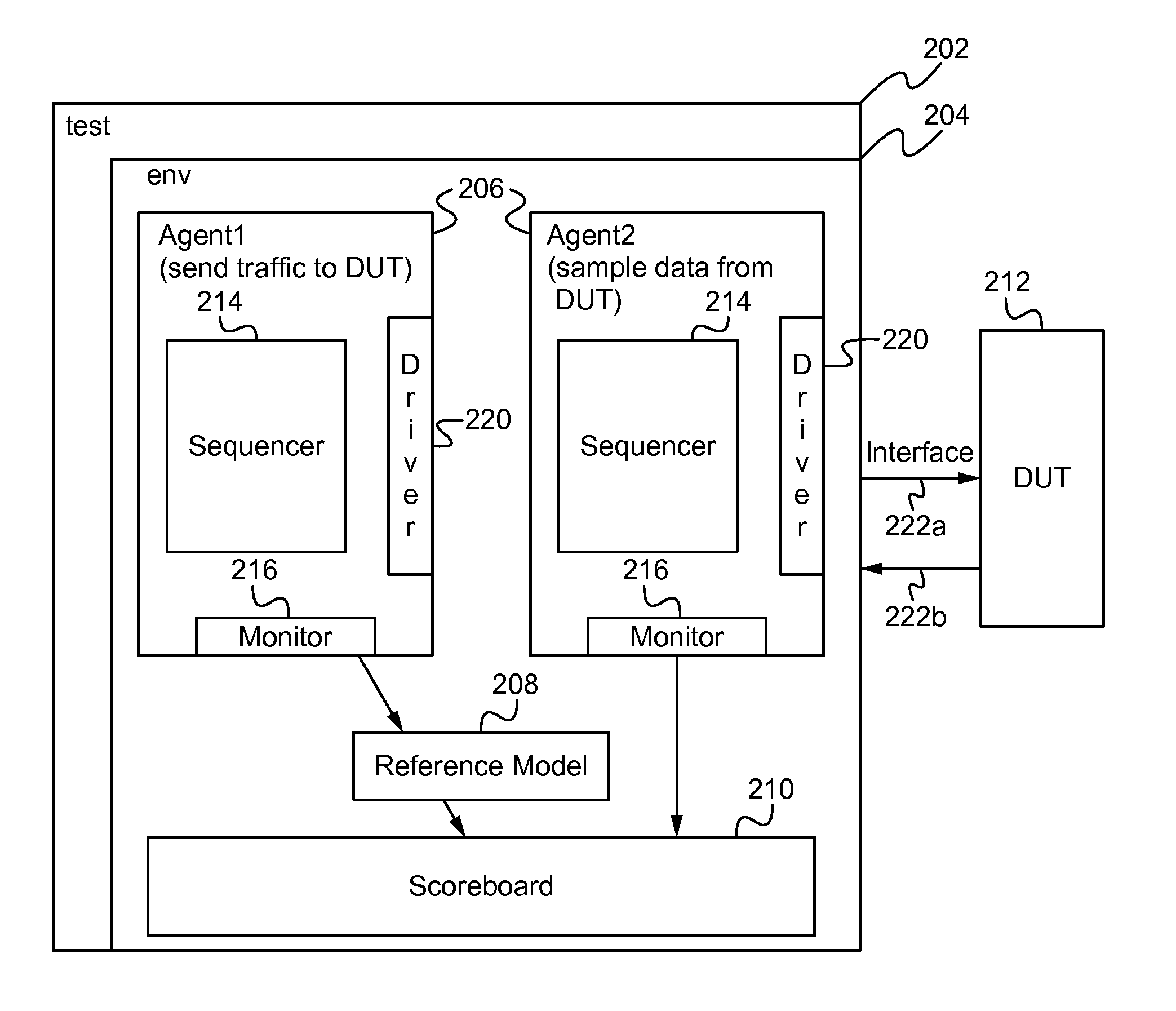
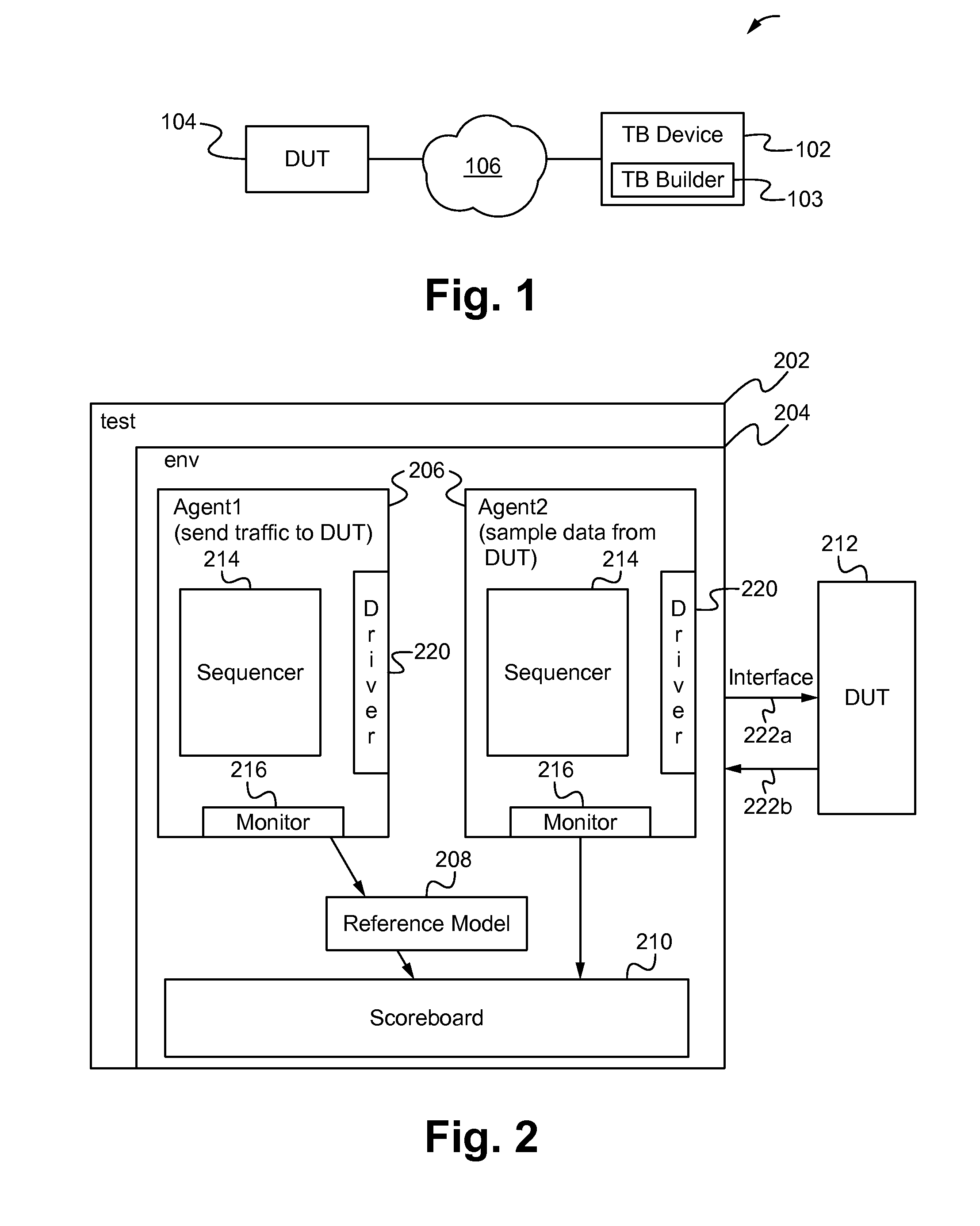
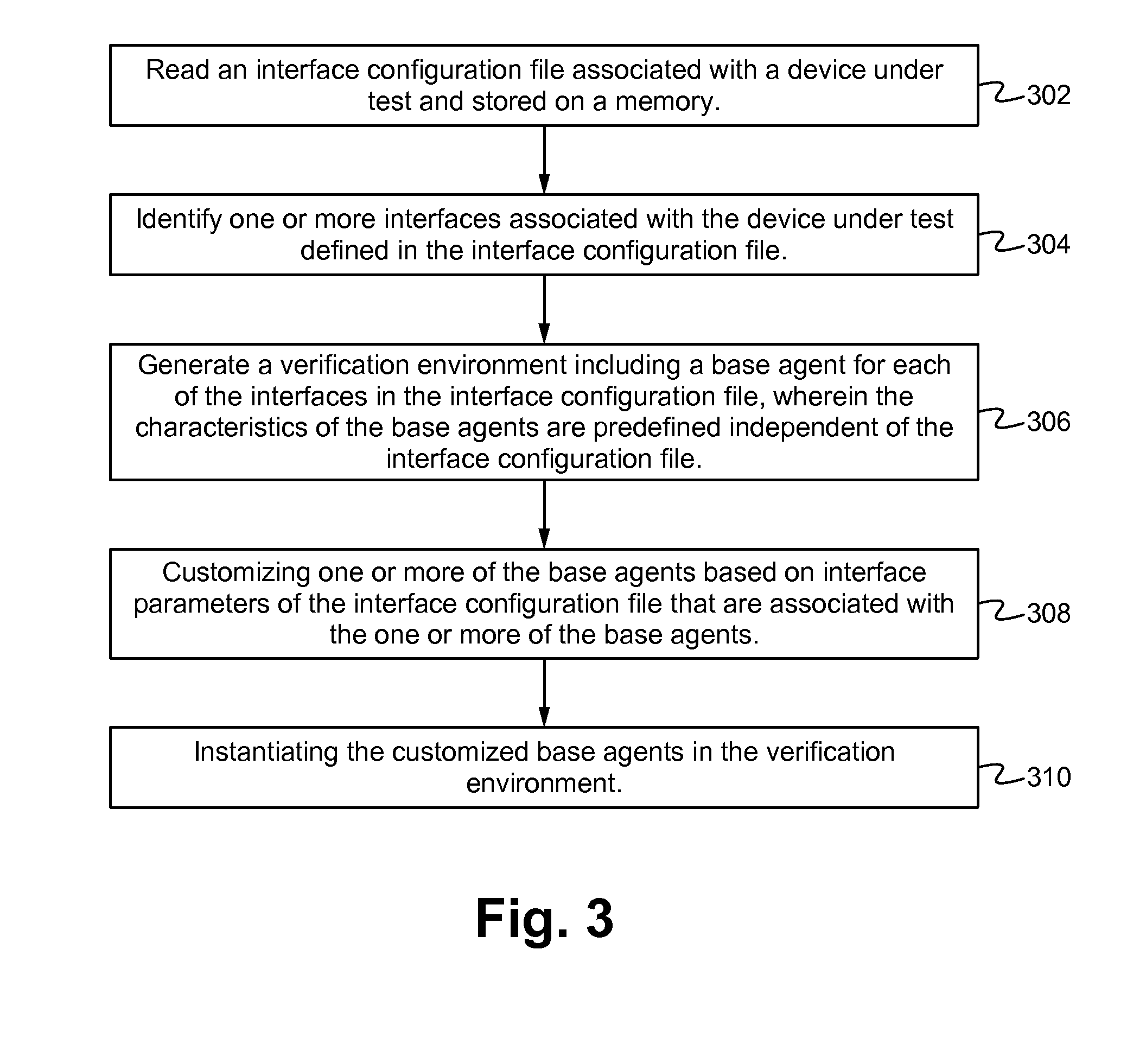
Packet tracking in a verification environment
A testbench, including a verification environment, tests a device under test (DUT). A packet tracking module, which is verification environment agnostic, is configured to track packets in the verification environment. The packet tracking module maintains an associative data structure of packet identifiers that are indexed by a unique value, a counter for identifying the packets in the verification environment, and a set of routines for tracking the packets in the verification environment during different stages of the testing.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
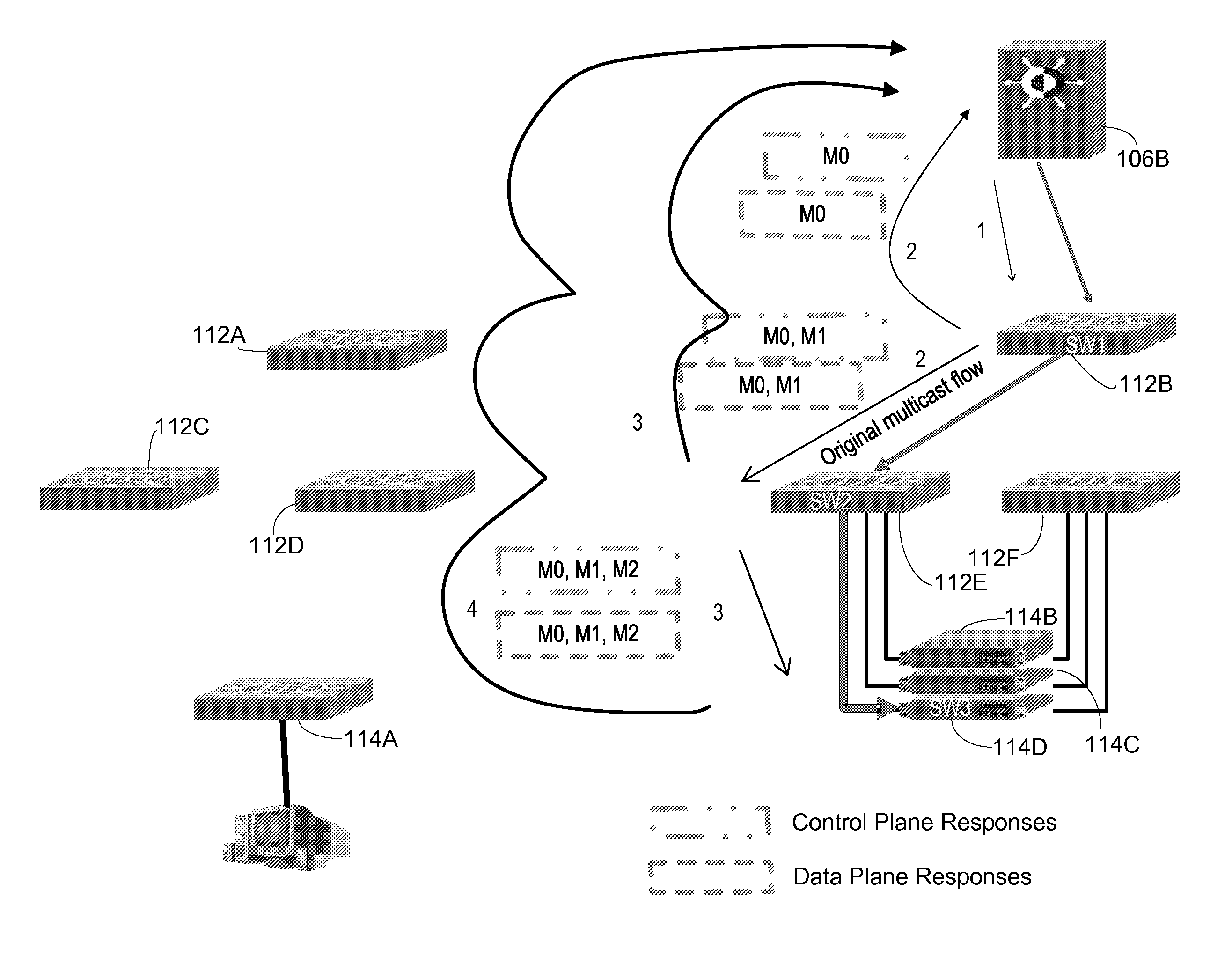
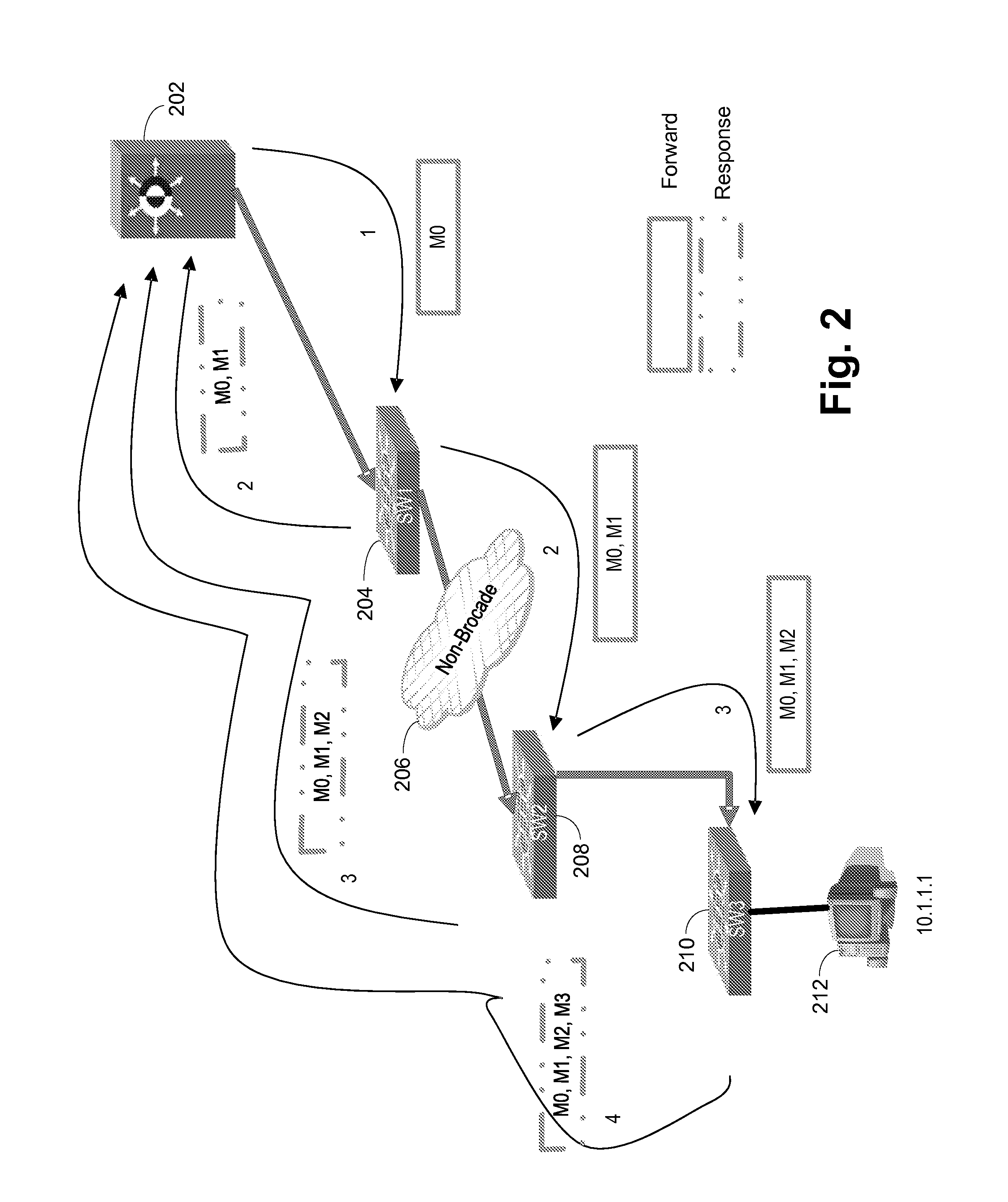
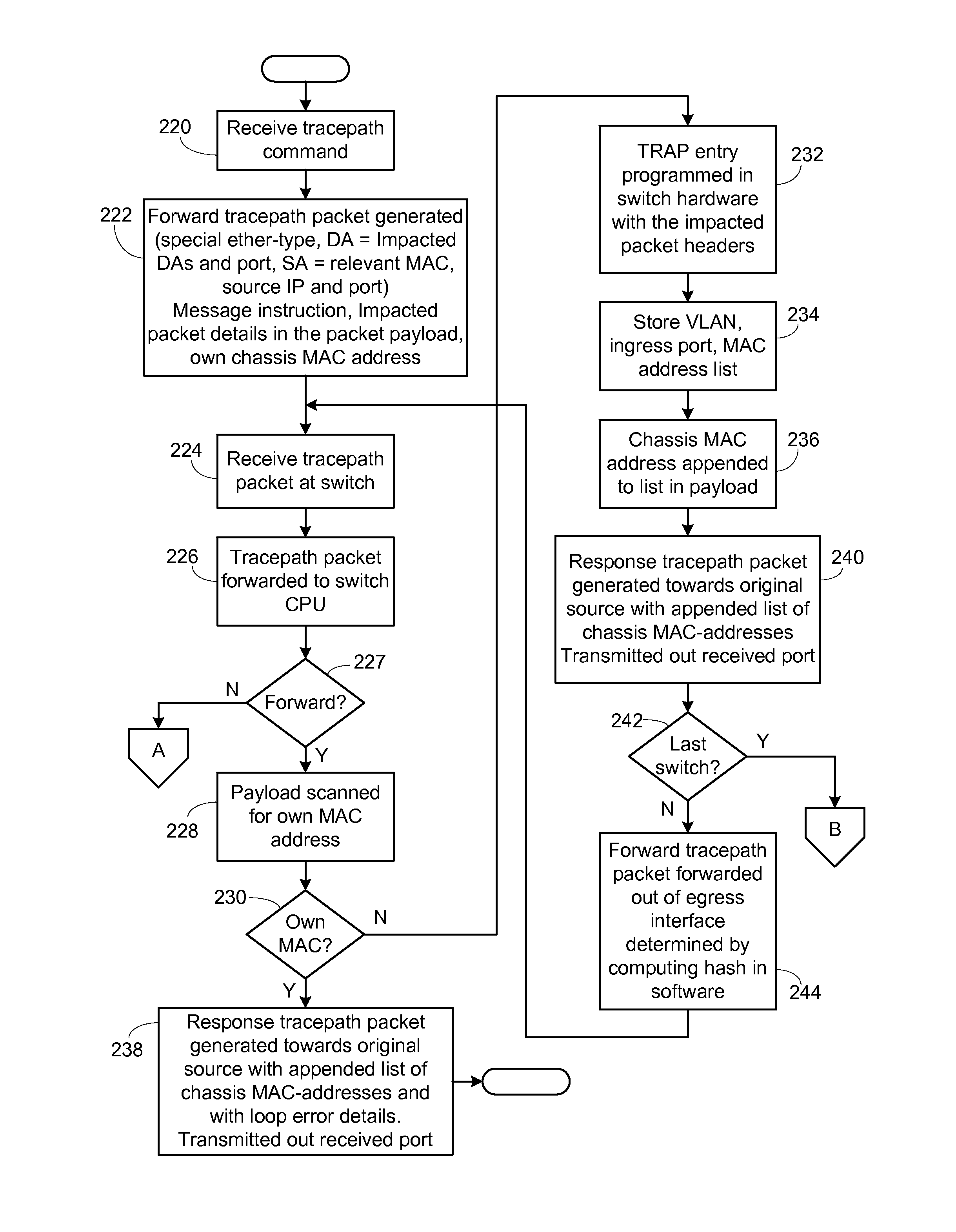
Packet tracing through control and data plane operations
InactiveUS9088496B2Avoid mistakesEasy to operateError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork dataPath tracing
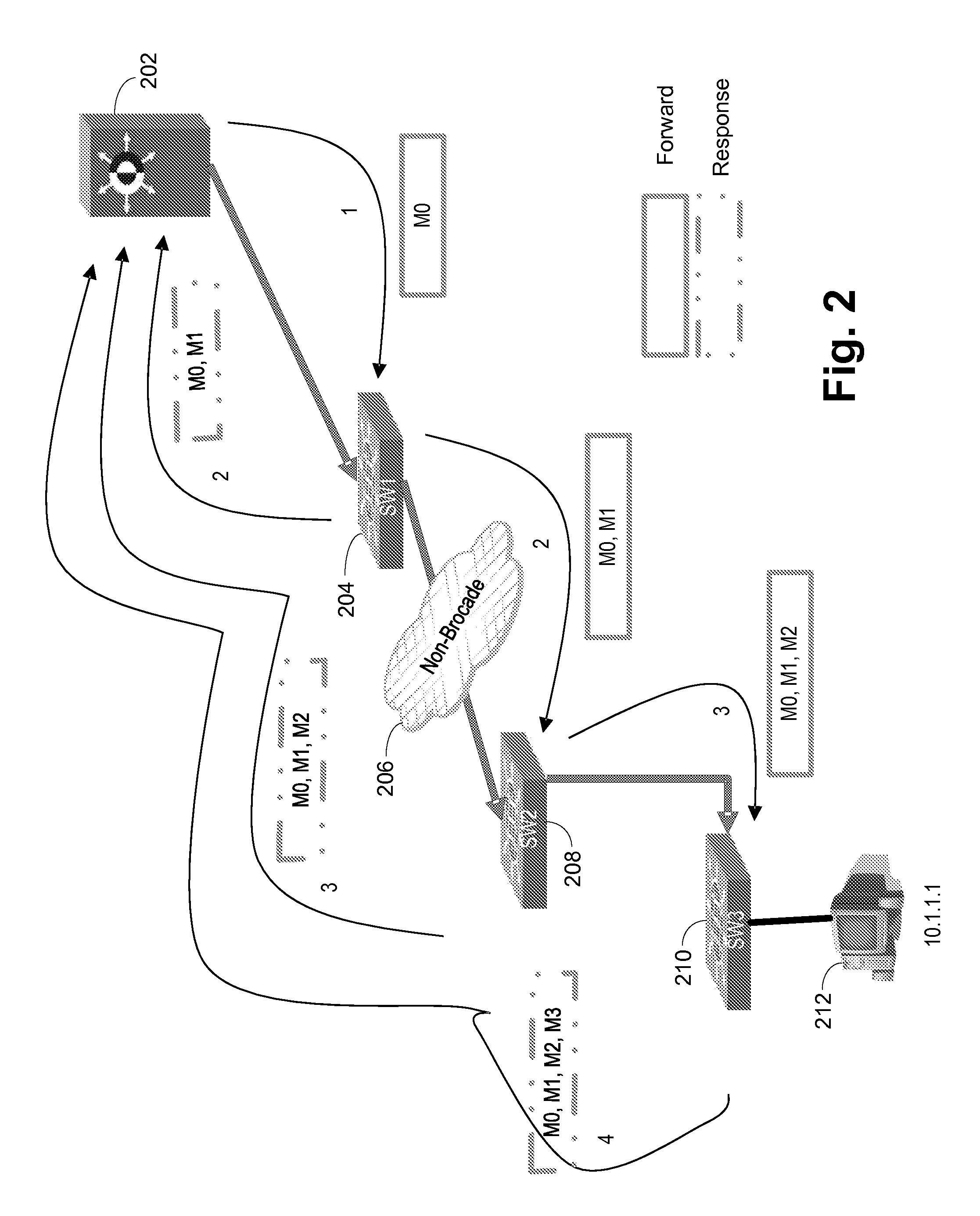
Improved debugging capabilities for network packet path tracing. Embodiments trace both the control and data planes. During control plane operations each switch appends its identity to the payload, providing a full trace of the control plan path. Responses containing the forward path payload are provided back at each hop, the responses being routing back by tracing back the forward direction control plane. The data plane is monitored by setting traps along the control plane path, with responses at each hop that indicate a given switch has been used being returned along the control plane path.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
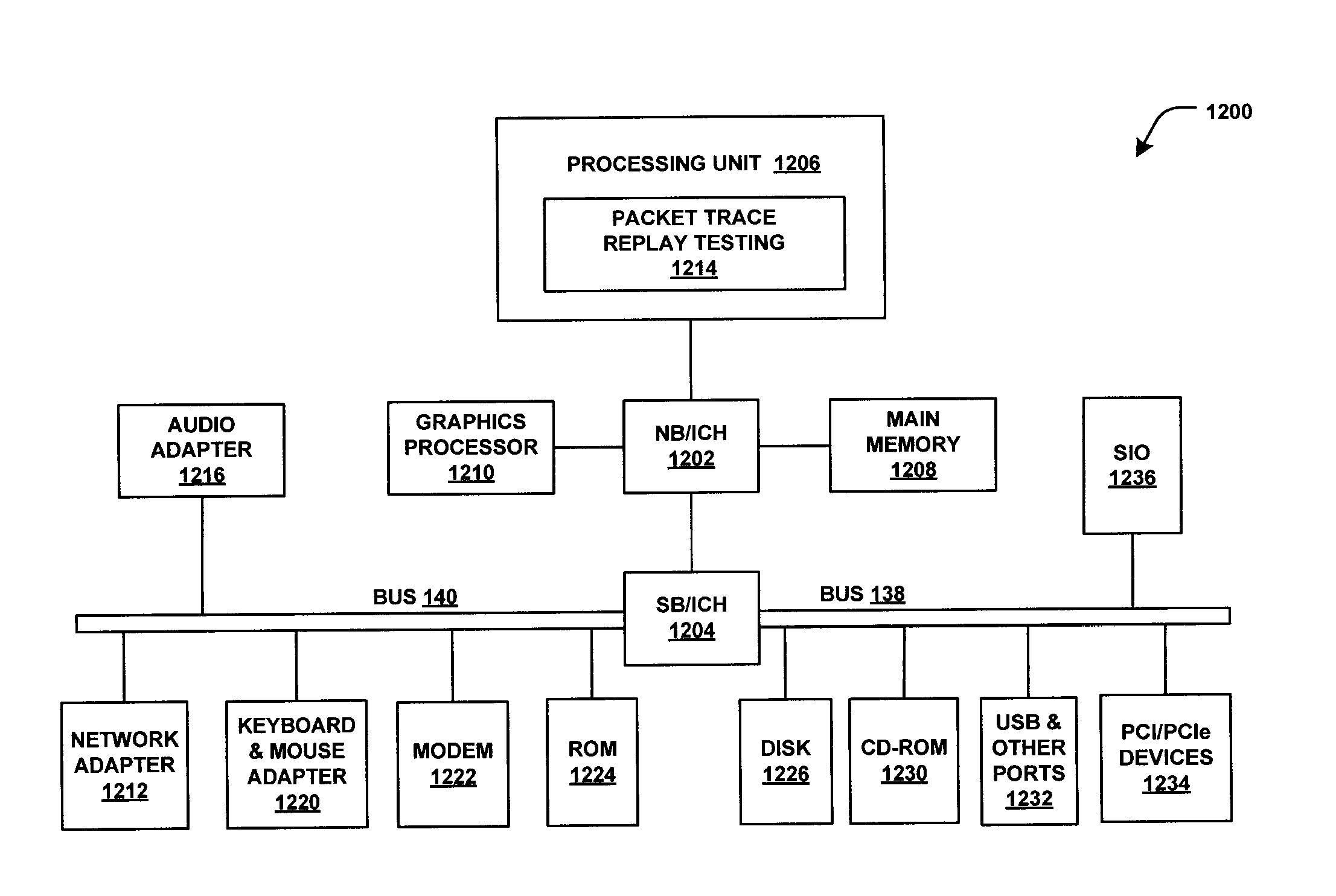
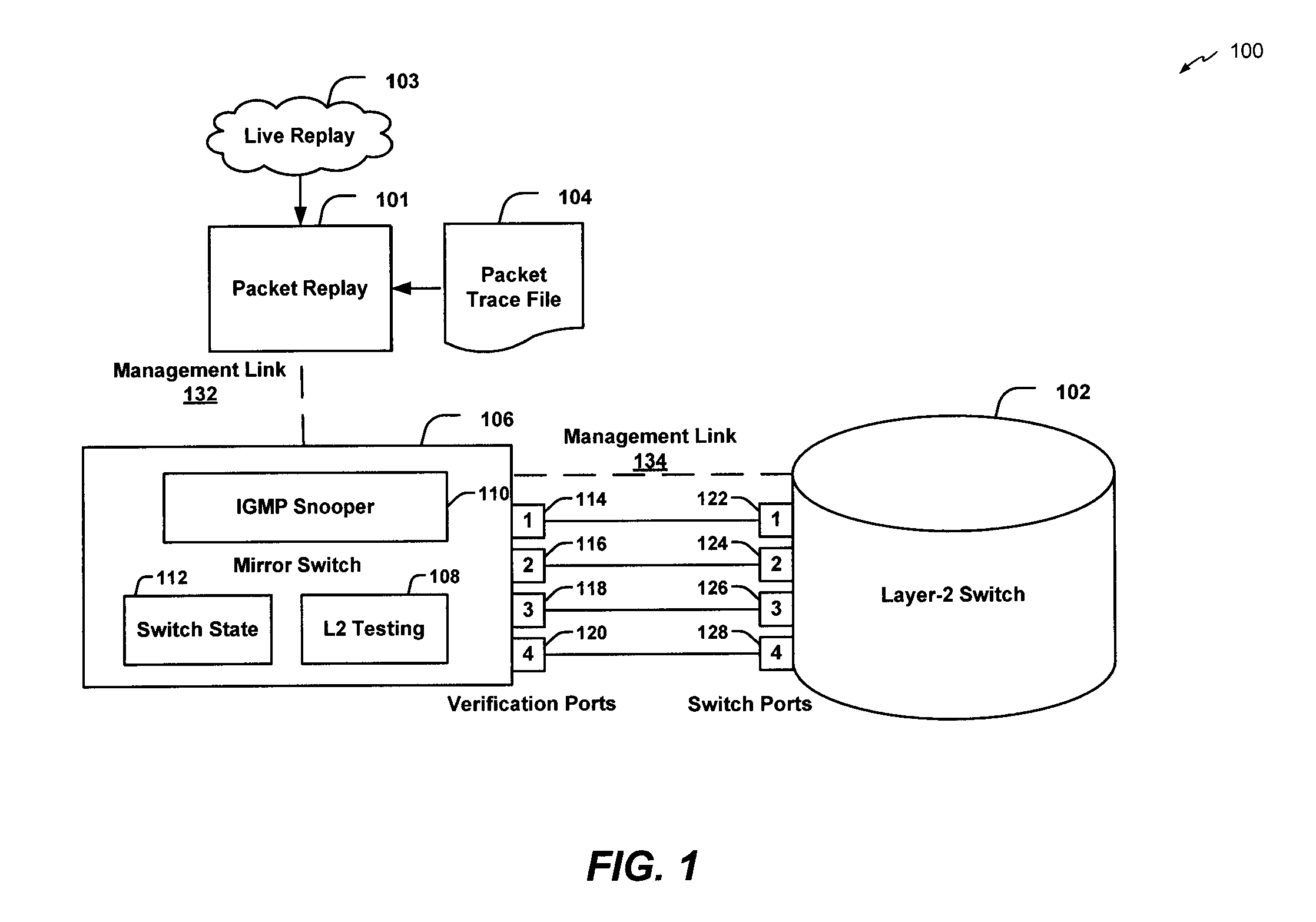
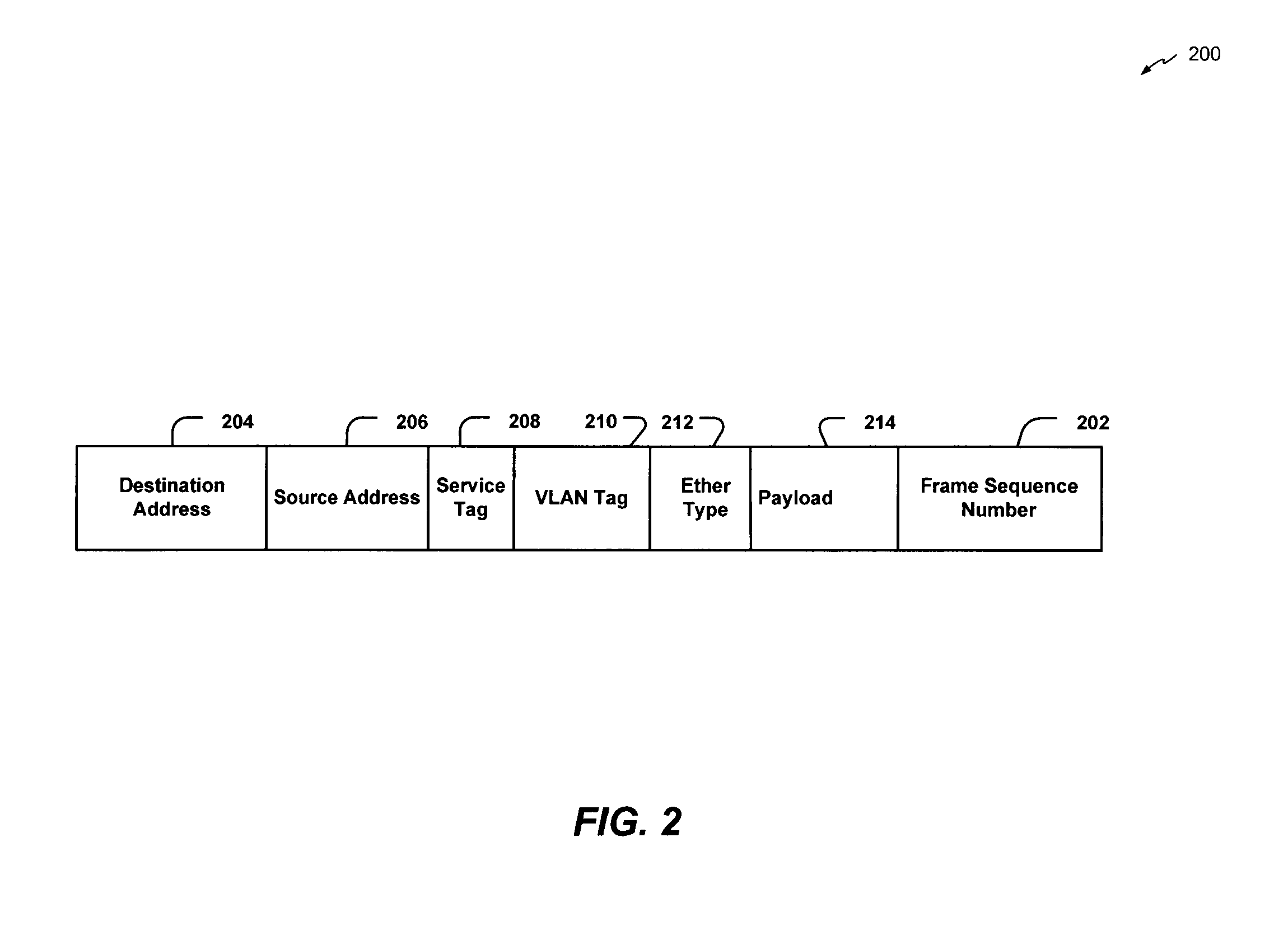
Data link layer analysis with packet trace replay
Systems and methods to analyze layer-2 data frame switch forwarding are provided. A packet replay module may be configured to replay a data frame from at least one of a packet trace file and a live network, and a first switch may include a first port and may be configured to receive the data frame from the packet replay module and to determine a runtime attribute associated with forwarding the data frame in a second switch.
Owner:LENOVO ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SINGAPORE
Packet tracing using dynamic packet filters
ActiveUS7760663B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionDynamic filteringPacket trace
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
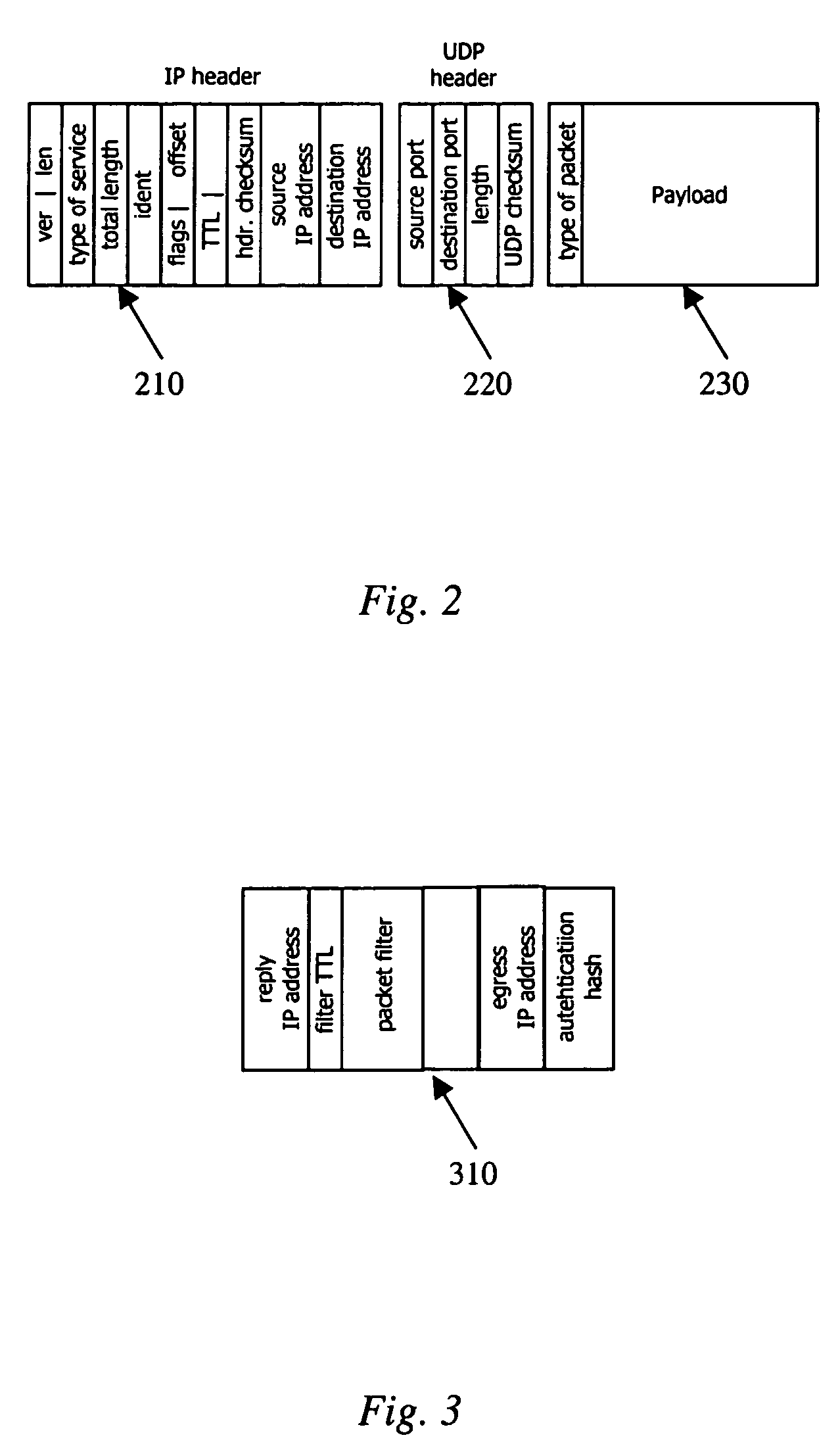
System and method for packet tracing within a packet switching asic
A packet trace device inserts a test packet or packet data into a simulation unit which mimics processing of the packet or packet data by an ASIC in a node. The packet trace device obtains data stored in memory of the ASIC. The packet trace device performs simulation of the functions of the ASIC using the data. The packet trace device then obtains packet tracing information from the simulation. The simulator unit is thus able to use data from the actual ASIC hardware, such as data from tables / registers and provides information on where a packet is dropped or other error occurs.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
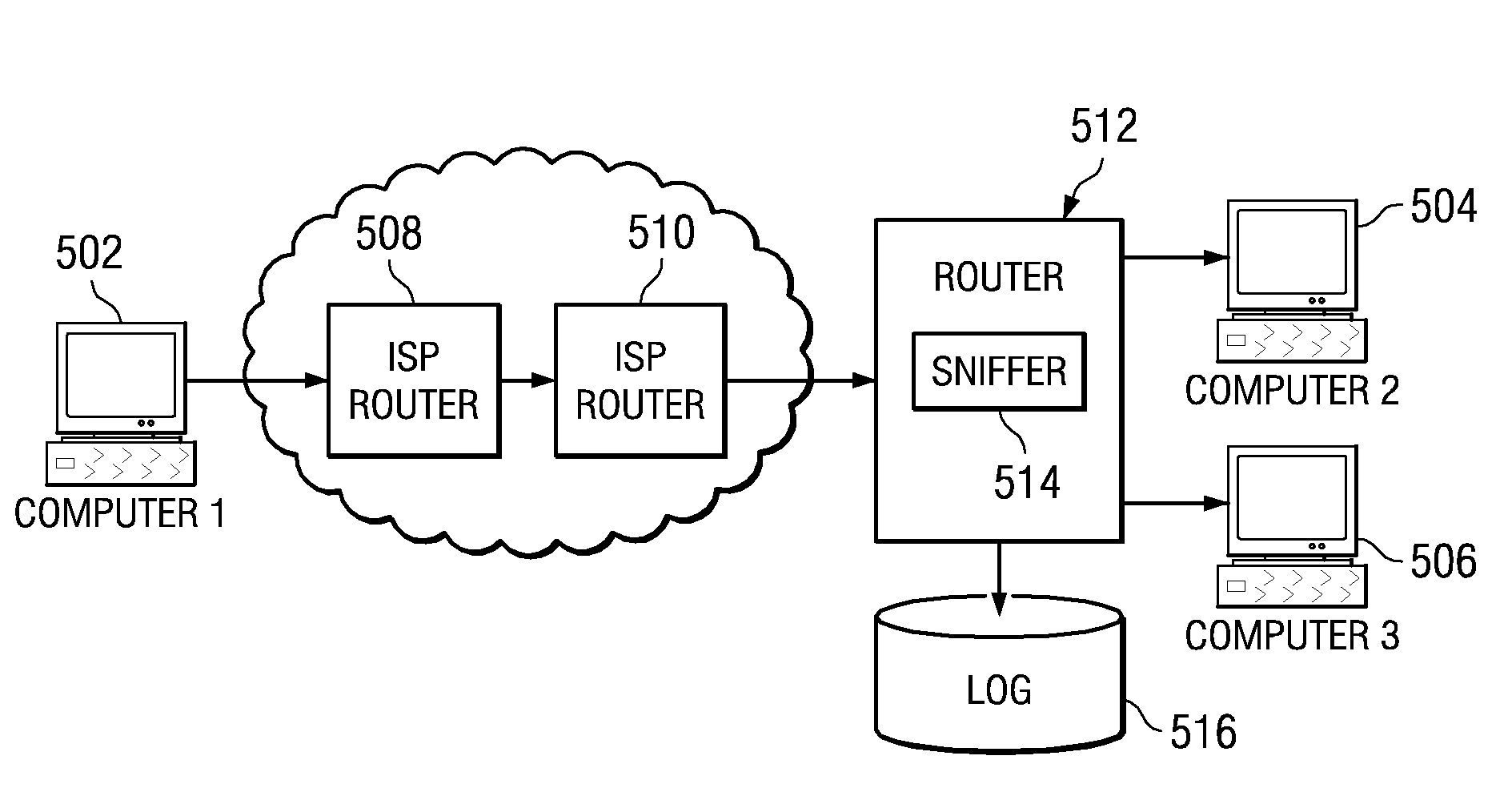
Method for notarizing packet traces
A system and method for capturing non-forgeable packet traces. Upon start-up of a sniffer, a first quote of Platform Configuration Register (PCR) values in a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) utilized by the sniffer is obtained, wherein the first quote comprises a list of starting values in the PCRs and is signed by the TPM and stored in a packet log. When a packet of interest is intercepted by the sniffer, the sniffer obtains a hash of the packet and instructs the TPM to extend a PCR with the hash value. The packet of interest is then stored in the packet log. When the sniffer is shutdown, a second quote of values in the PCRs is obtained, wherein the second quote comprises a list of current values in the PCRs, and wherein the second quote is signed by the TPM and stored in the packet log.
Owner:IBM CORP
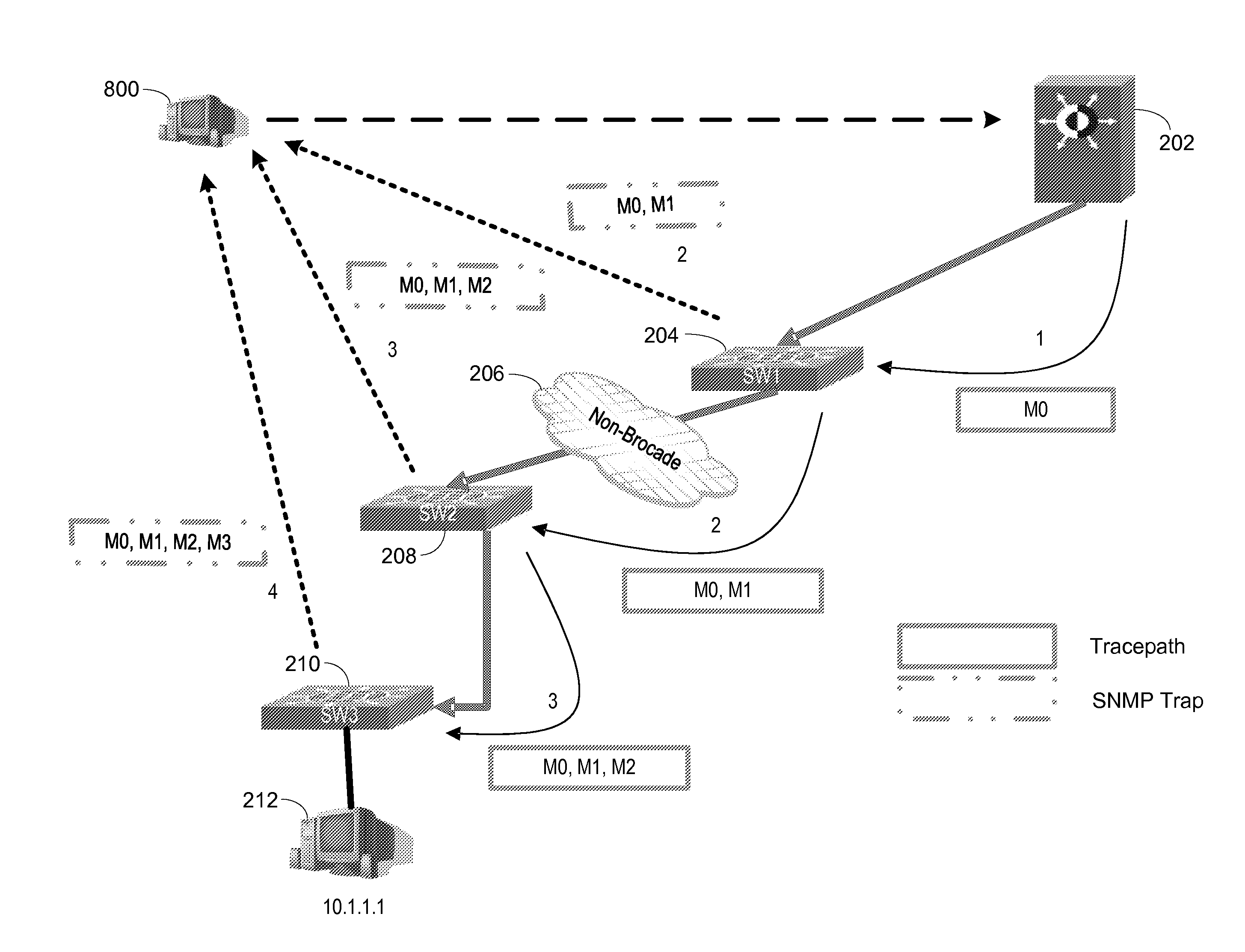
Packet Tracing through Control and Data Plane Operations using SNMP Trap Commands
InactiveUS20130242759A1Easy to detectGuaranteed uptimeError preventionTransmission systemsProgram planningNetwork data
Improved debugging capabilities for network packet path tracing. Embodiments trace both the control and data planes. During control plane operations each switch appends its identity to the payload, providing a full trace of the control plan path. SNMP Trap commands containing the forward path payload are provided back at each hop. The data plane is monitored by setting traps along the control plane path, with SNMP Trap commands at each hop being provided that indicate a given switch has been used.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
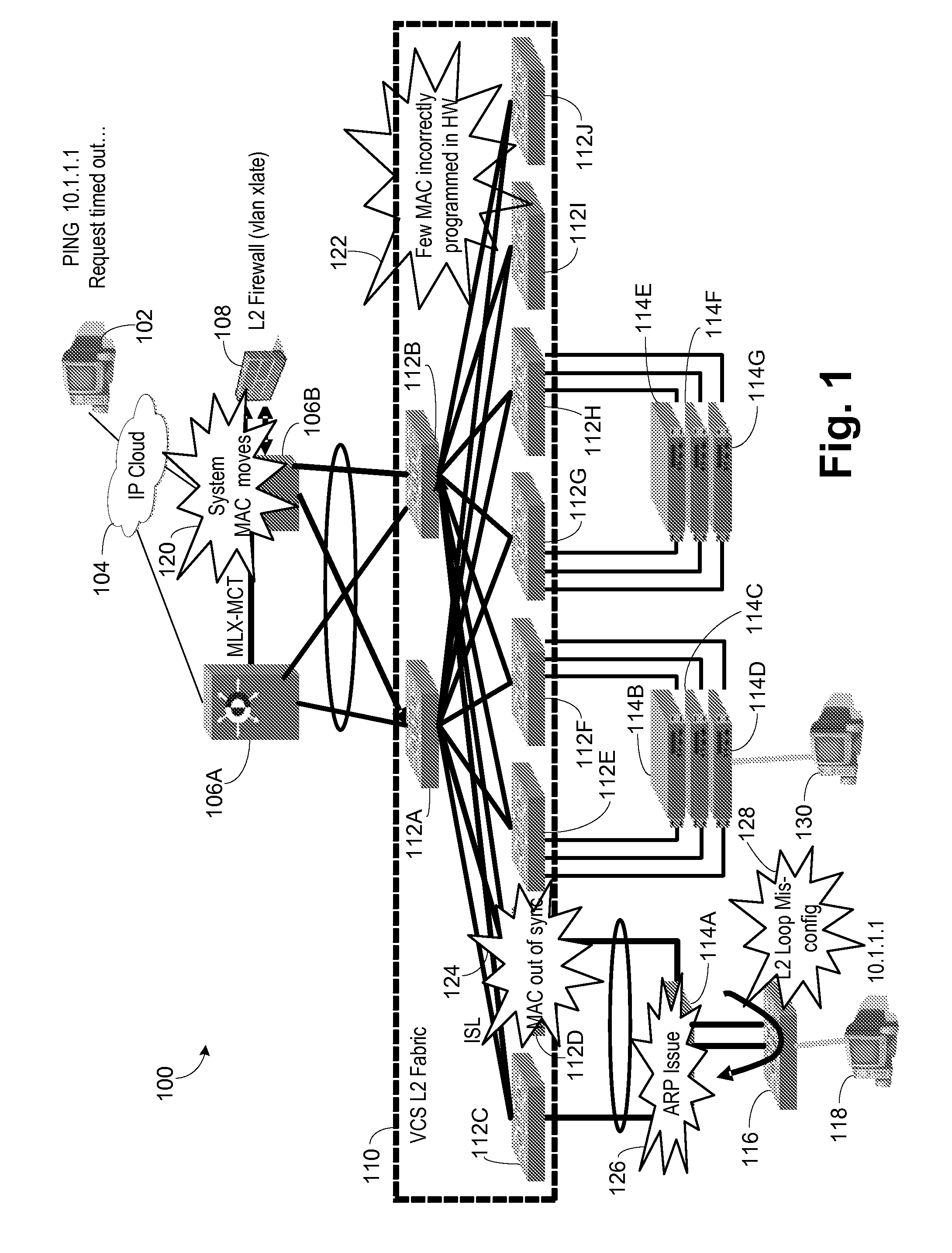
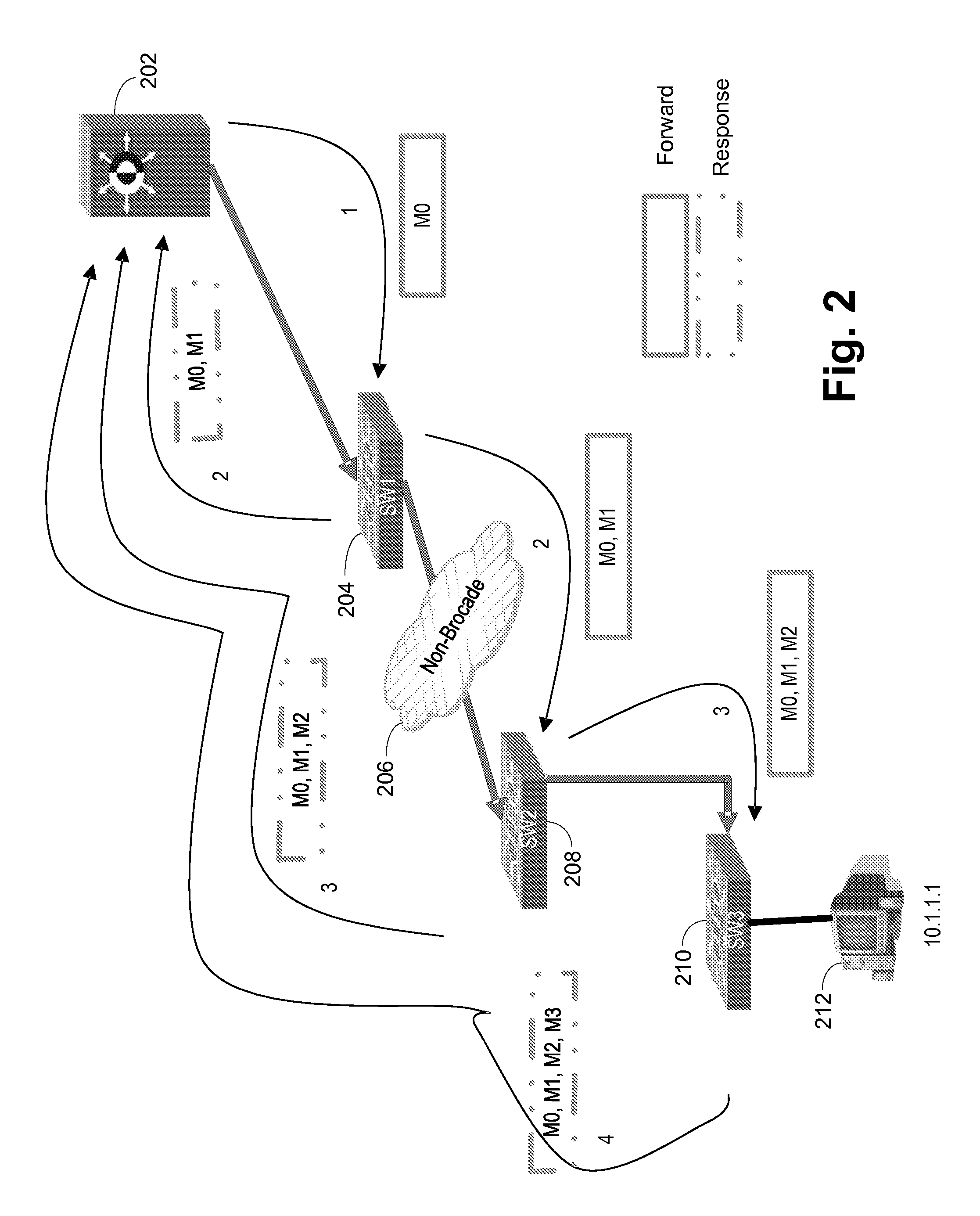
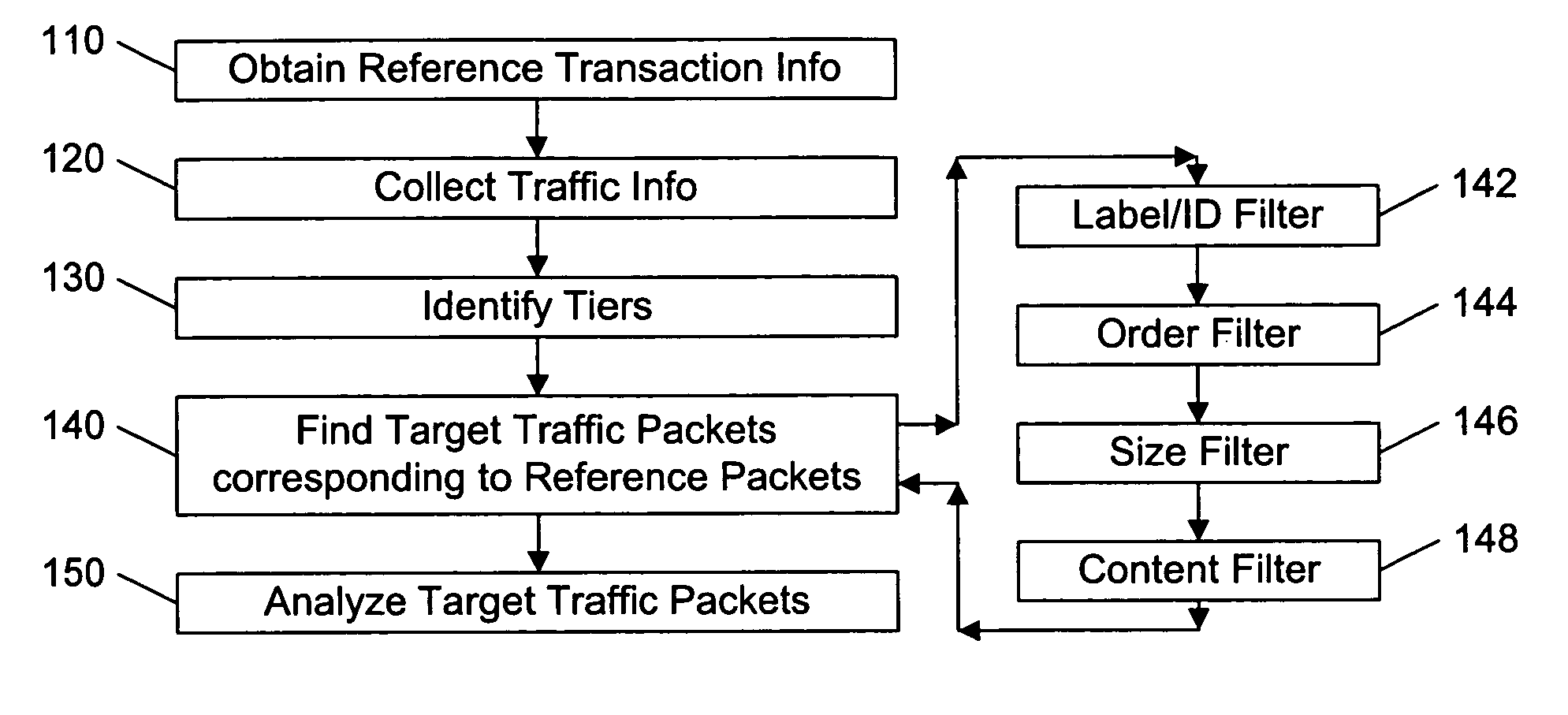
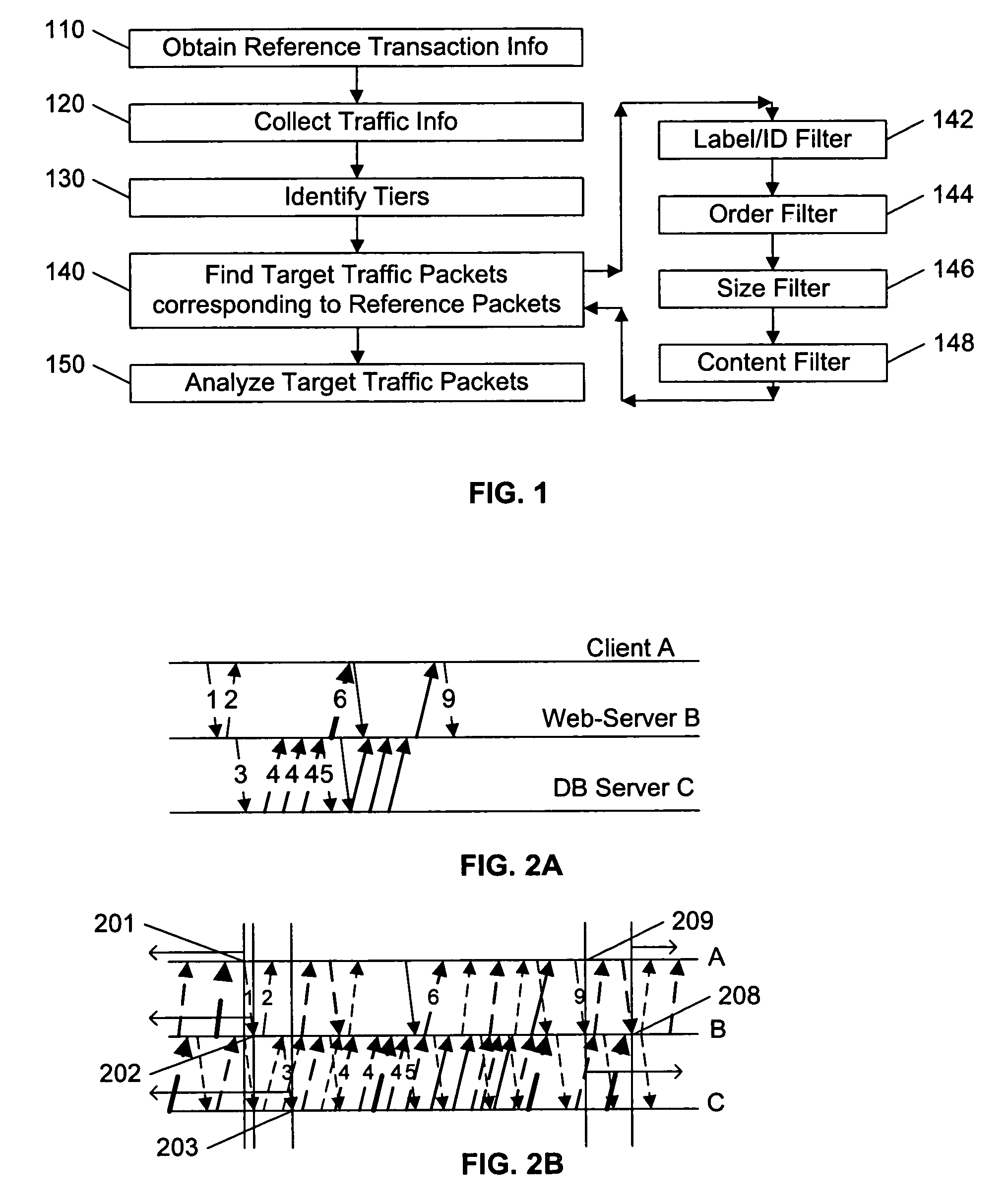
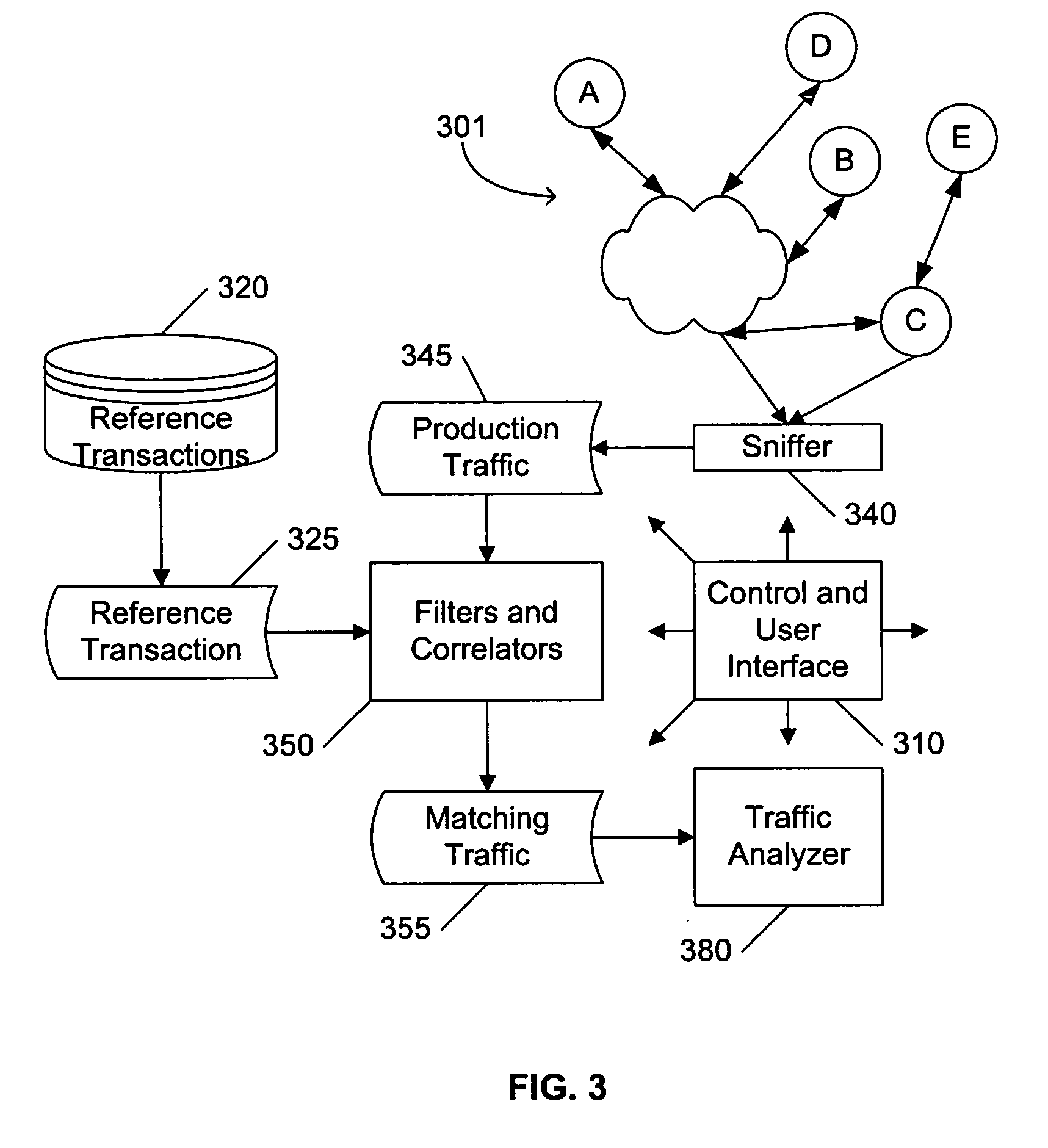
Packet tracing
To evaluate a network's performance in processing communications related to a target transaction, a set of “reference” communications corresponding to the target transaction are compared to a larger set of communications in the network in a “production” environment, to identify the occurrence of the target transaction in the production environment. Preferably, the reference communications are recorded in a laboratory environment that models the production environment, or recorded from the production environment during a period of minimal other activities. A variety of filters are used to eliminate communications in the production environment that are apparently unrelated to the target transaction, including filters based on the time-order of communications among the nodes, the size of the packets being communicated, and the content of the communications. If necessary, after eliminating the apparently unrelated communications from consideration, the remaining production communications are compared to the reference communications to identify the most likely production communications corresponding to the reference communications.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Method and system for converting USB
A method for testing a USB (universal serial bus) device includes receiving a USB packet trace output from a USB host, at a USB packet trace converting apparatus, generating at least one token corresponding to the USB packet trace received from the USB host, determining a syntax tree corresponding to the at least one token, and generating a code for a USB host model corresponding to the determined syntax tree.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
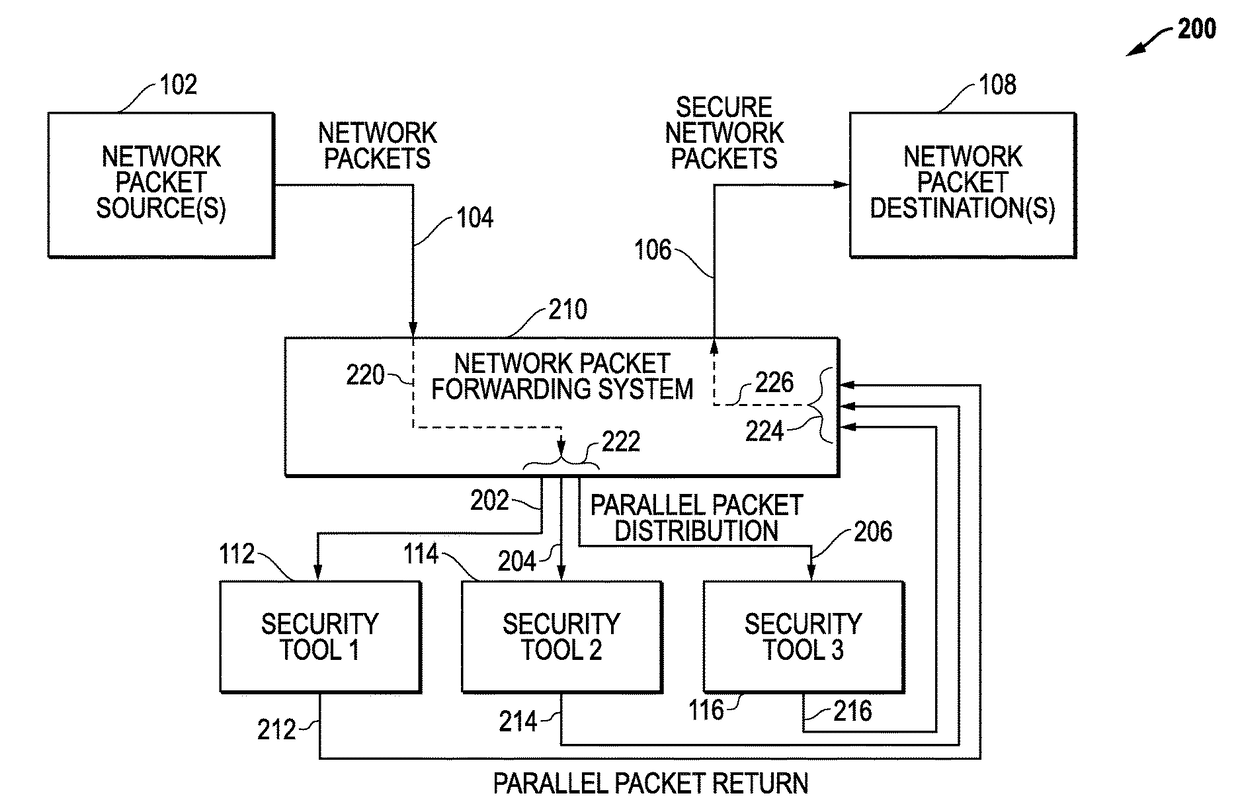
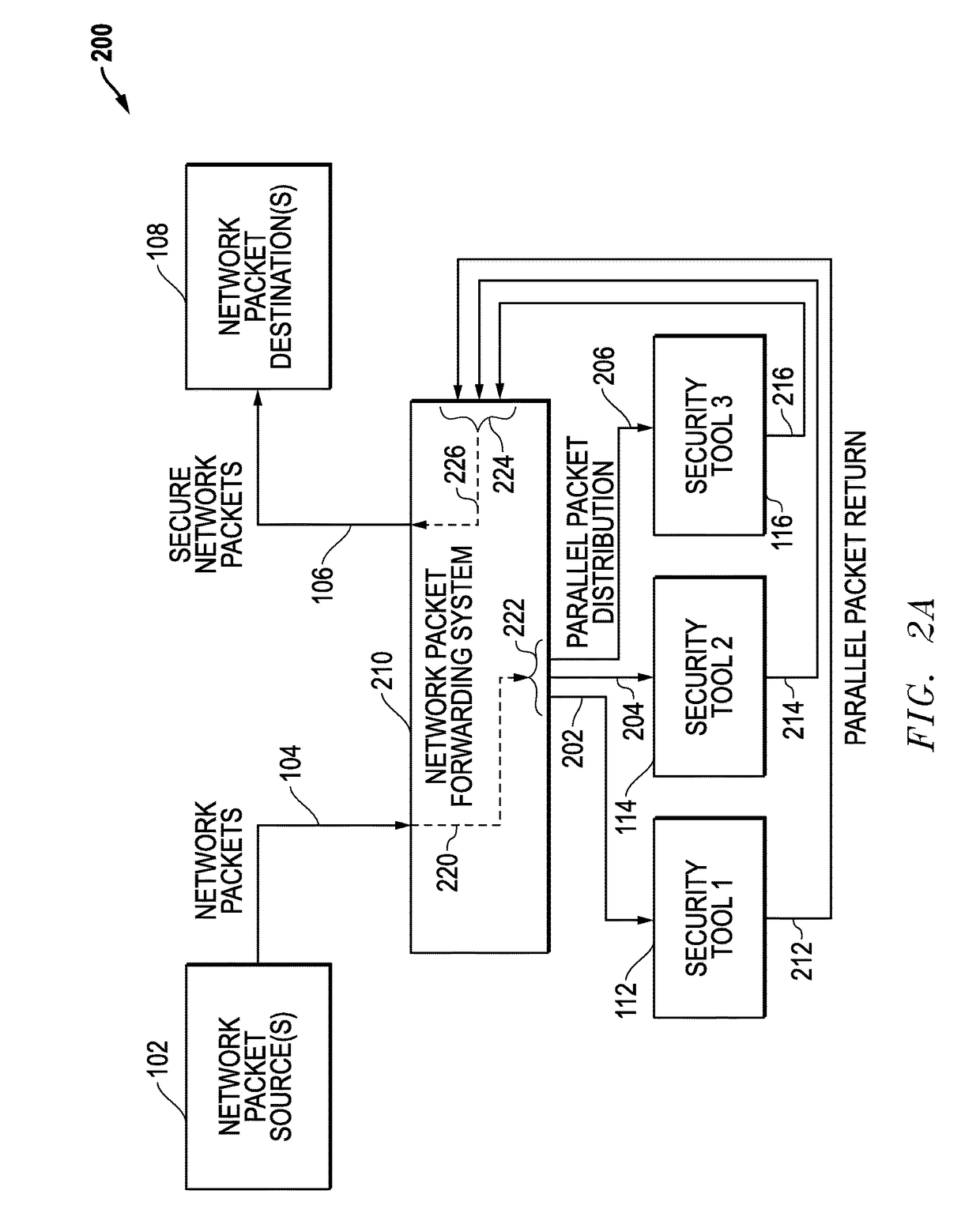
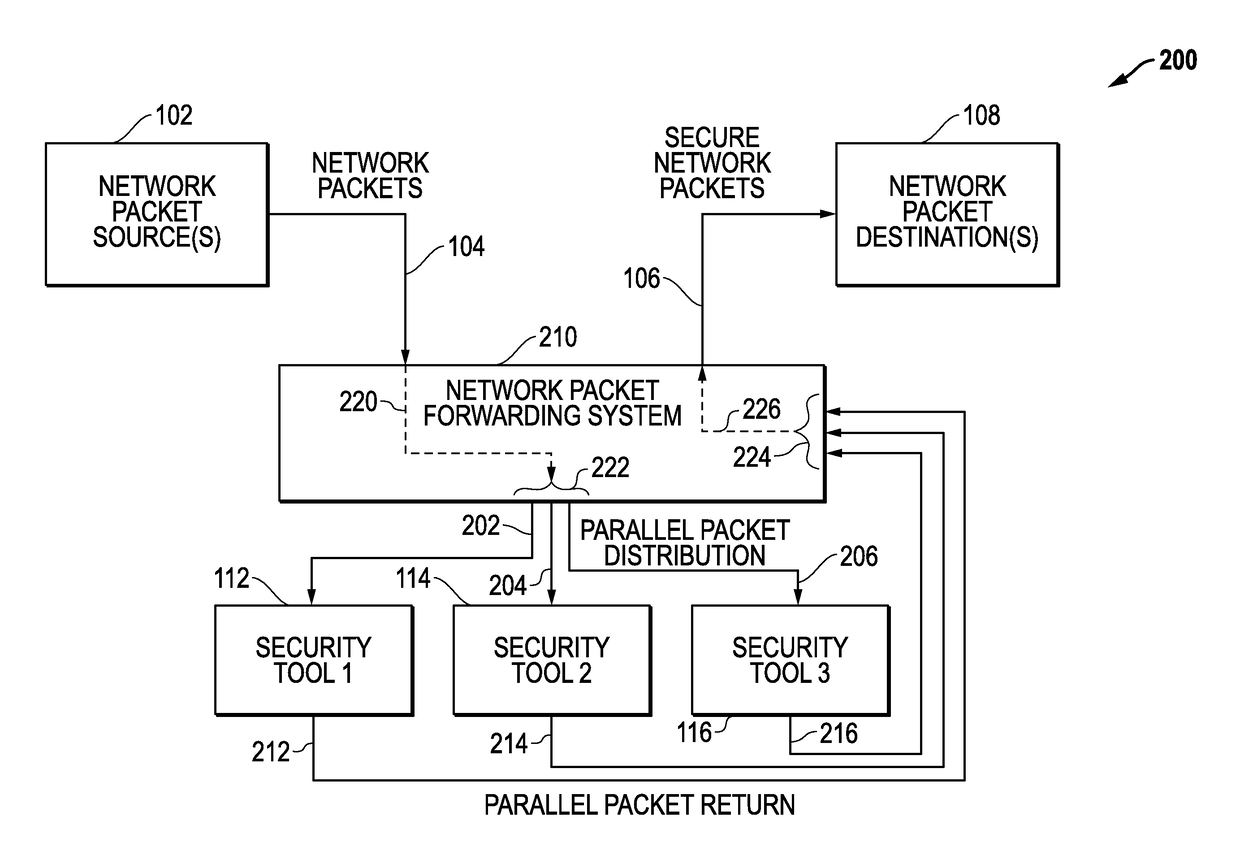
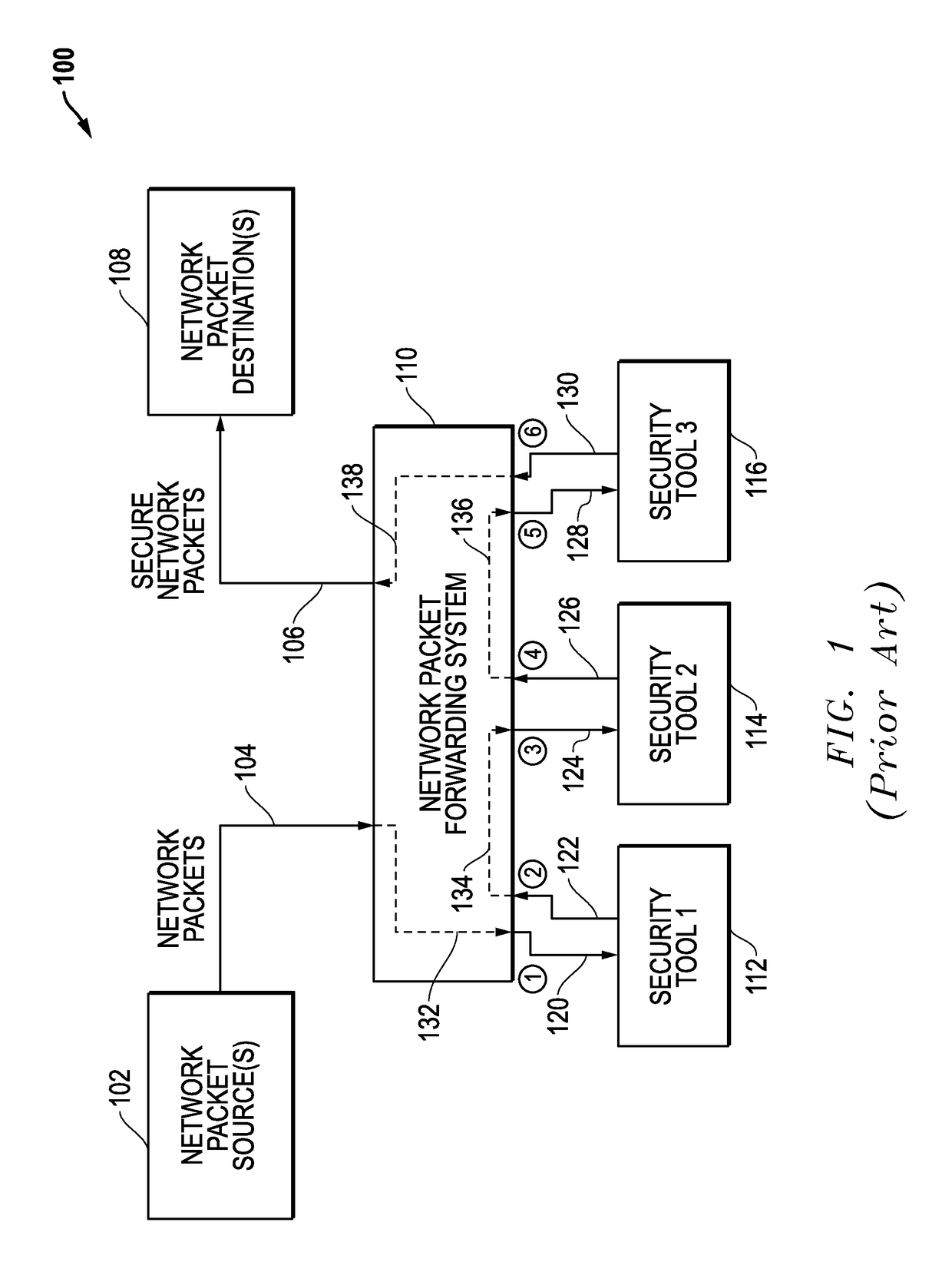
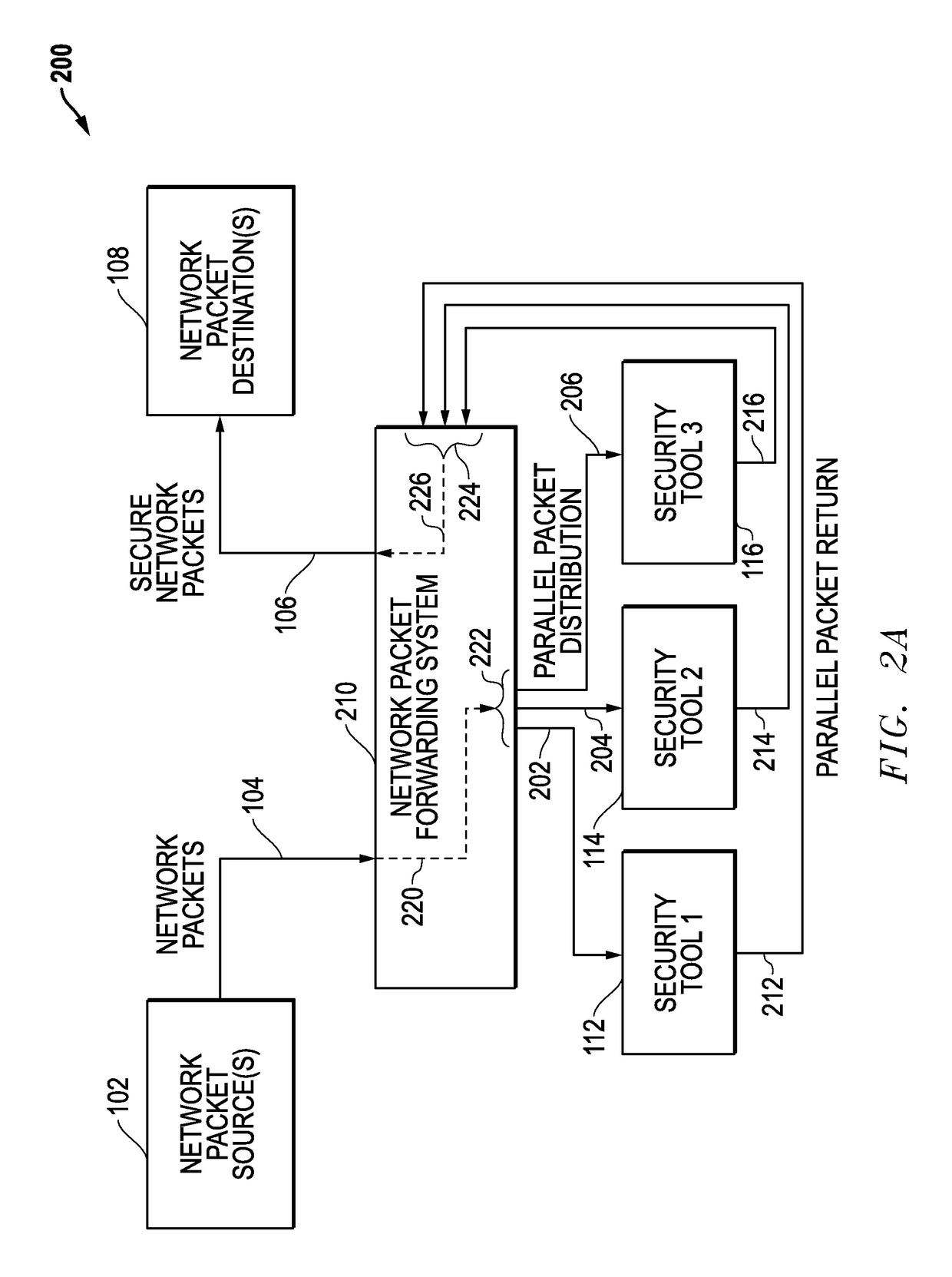
Latency-Based Timeouts For Concurrent Security Processing Of Network Packets By Multiple In-Line Network Security Tools
Latency-based timeouts are used for concurrent security processing by multiple in-line network security tools. A network system forwards secure network packets to the tools and uses latency-based timeouts with respect to the return of processed packets from the tools. Initially, the network system measures processing latencies for the tools and sets at least one timeout threshold based upon the processing latencies. The network system then receives an input packet from a network source, generates a timestamp, concurrently sends an output packet to the tools based upon the input packet, tracks return packets from the tools, and determines whether a timeout has occurred with respect to the timeout threshold based upon a difference between the timestamp and a current timestamp. If a timeout does not occur, a secure packet is forwarded to a network destination. If a timeout does occur, return packet tracking for the input packet is ended.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
Using packet tracing tool to automatically execute packet capture operations
ActiveUS10608887B2Limits numberCorrelation between the various packet captures easierData switching networksData packData stream
Some embodiments provide a method that performs a packet tracing operation for a particular data flow between endpoints of a logical network to generate a representation of logical network components along a path between the endpoints. In response to a selection of at least two of the logical network components, the method automatically generates separate packet capture operations for execution by physical components that implement each of the selected logical network components. The method uses packet header information to correlate packet data from the separate packet capture operations.
Owner:NICIRA
Packet tracing through control and data plane operations using SNMP trap commands
InactiveUS9014013B2Avoid mistakesEasy to operateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProgram planningPath tracing
Improved debugging capabilities for network packet path tracing. Embodiments trace both the control and data planes. During control plane operations each switch appends its identity to the payload, providing a full trace of the control plan path. SNMP Trap commands containing the forward path payload are provided back at each hop. The data plane is monitored by setting traps along the control plane path, with SNMP Trap commands at each hop being provided that indicate a given switch has been used.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for network packet event characterization and analysis
A computer implemented method for network monitoring includes providing network packet event characterization and analysis for network monitoring that includes supporting summarization and characterization of network packet traces collected across multiple processing elements of different types in a virtual network, including a trace slicing to organize individual packet events into path-based trace slices, a trace characterization to extract at least 2 types of feature matrix describing those trace slices, and a trace analysis to cluster, rank and query packet traces based on metrics of the feature matrix.
Owner:NEC CORP
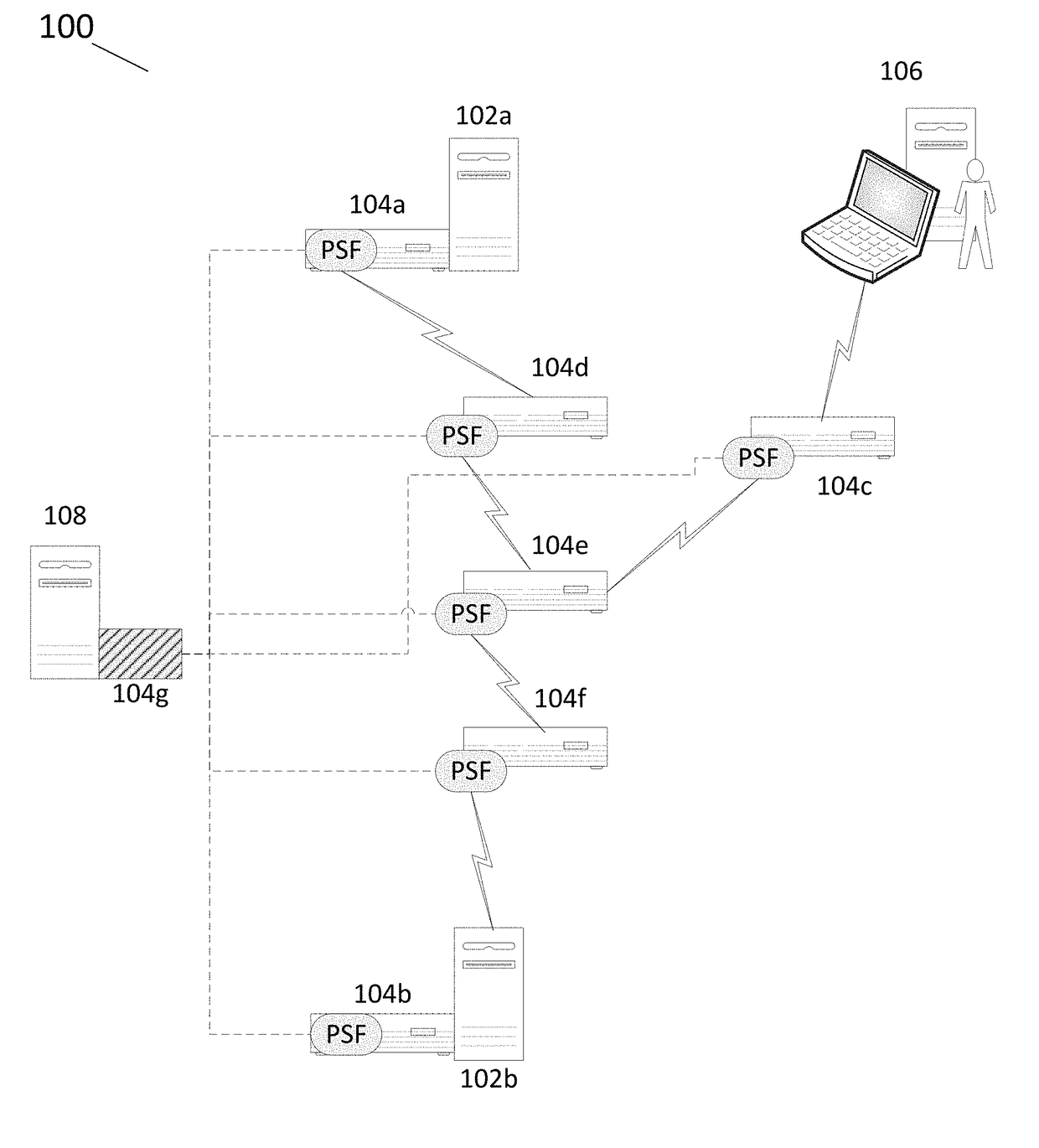
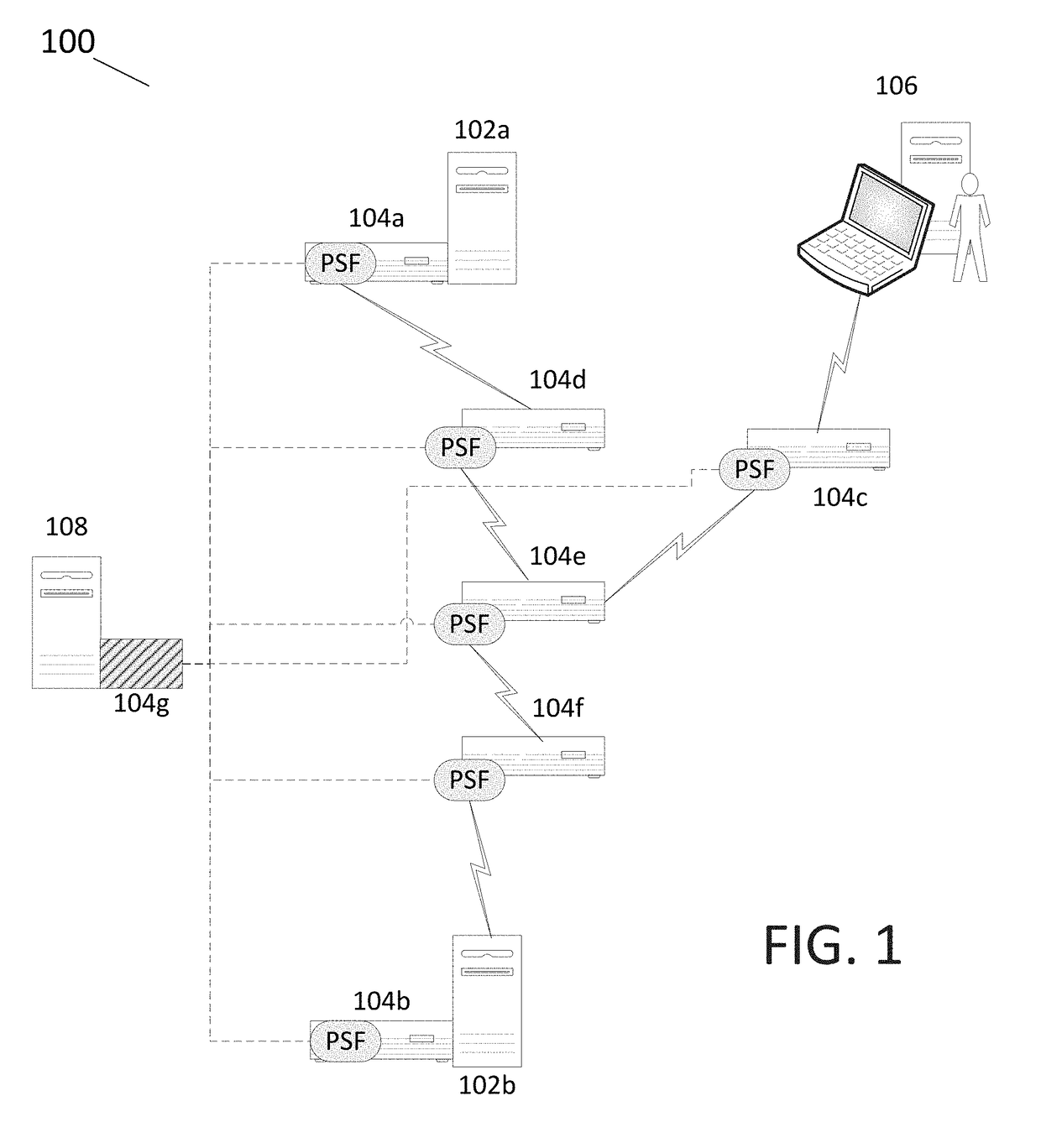
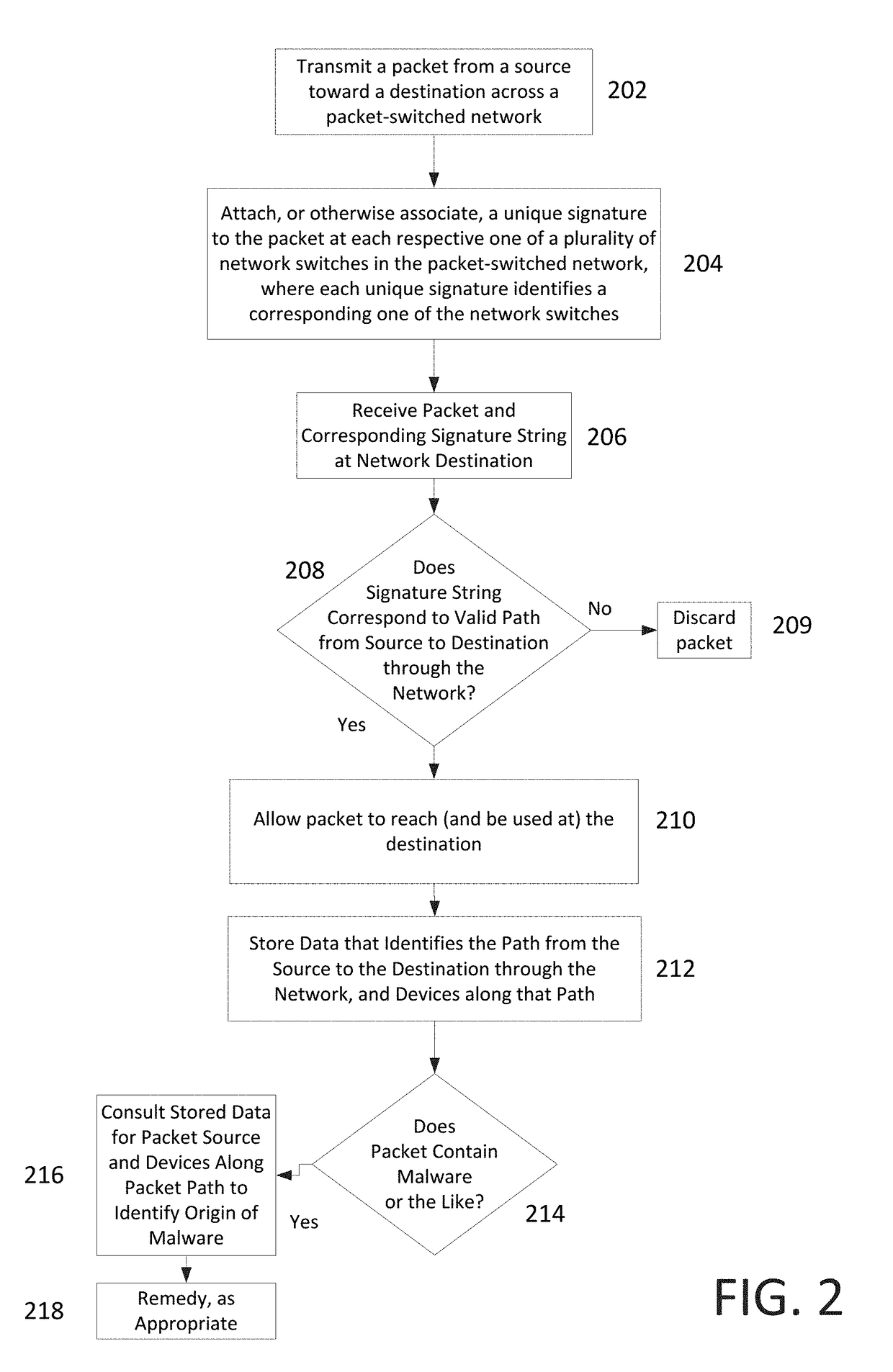
Packet tracking
A computer-based method includes transmitting a packet from a source across a packet-switched network that includes multiple network switches, and attaching, or otherwise associating, a unique signature to the packet at one or more of the network switches. Each unique signature identifies a corresponding one of the network switches, through which the packet passes as it travels from the source toward a destination. The packet and an attached, or otherwise associated, string of signatures from the plurality of network switches, is received at or near the destination in the packet-switched network. In a typical implementation, the validity of the packet is checked, by a validator (e.g., at or near the destination).
Owner:INFERSIGHT LLC
Latency-based timeouts for concurrent security processing of network packets by multiple in-line network security tools
Latency-based timeouts are used for concurrent security processing by multiple in-line network security tools. A network system forwards secure network packets to the tools and uses latency-based timeouts with respect to the return of processed packets from the tools. Initially, the network system measures processing latencies for the tools and sets at least one timeout threshold based upon the processing latencies. The network system then receives an input packet from a network source, generates a timestamp, concurrently sends an output packet to the tools based upon the input packet, tracks return packets from the tools, and determines whether a timeout has occurred with respect to the timeout threshold based upon a difference between the timestamp and a current timestamp. If a timeout does not occur, a secure packet is forwarded to a network destination. If a timeout does occur, return packet tracking for the input packet is ended.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com