Patents
Literature
41 results about "Voxel intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Voxel A voxel is a volume element (volumetric and pixel) representing a value in the three dimensional space, corresponding to a pixel for a given slice thickness. Indicates cross talk of signal intensity from one voxel to an adjacent voxel in spectroscopic imaging. A voxel that is uniform in all directions.
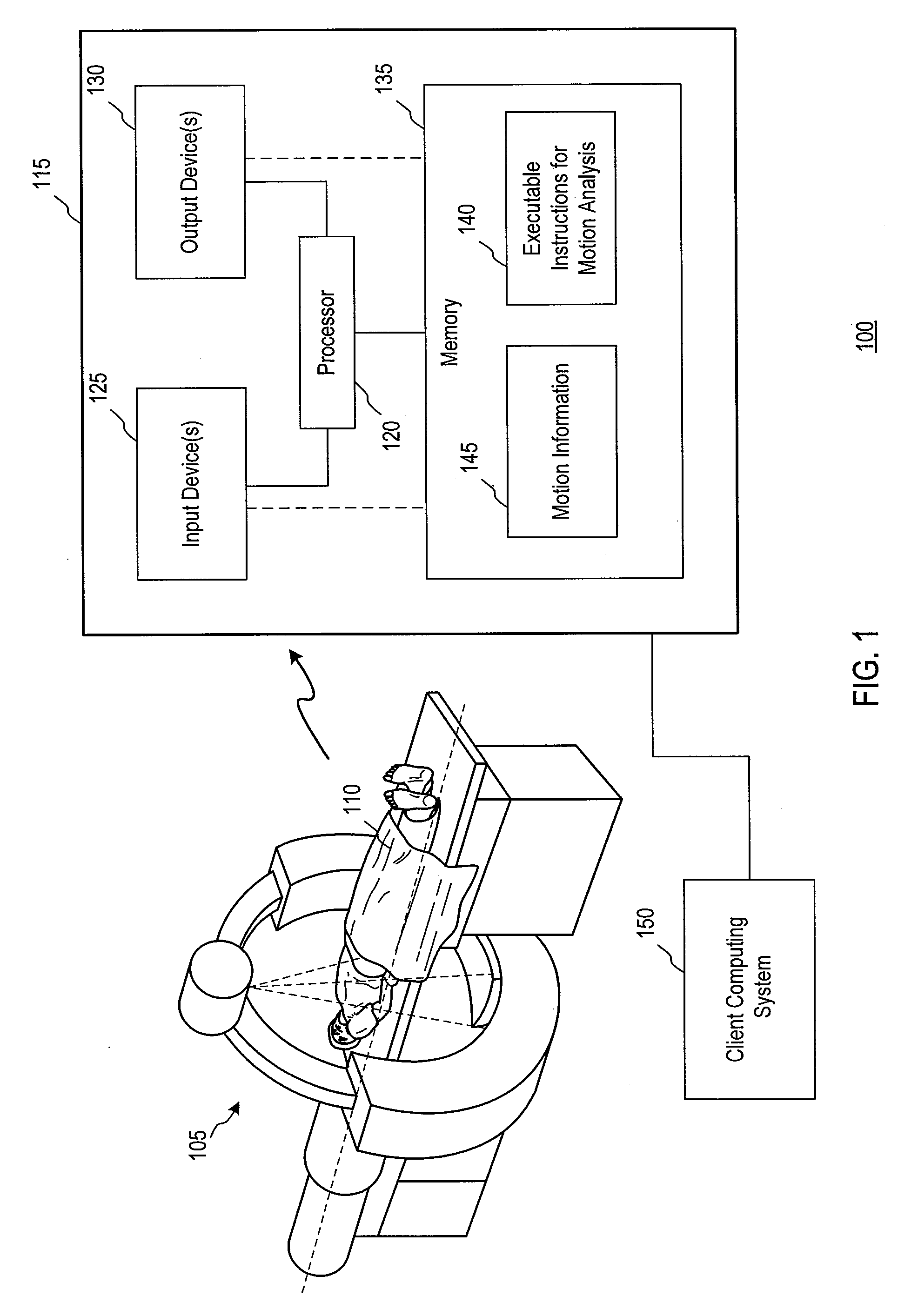
Method and apparatus for visualization of biological structures with use of 3D position information from segmentation results
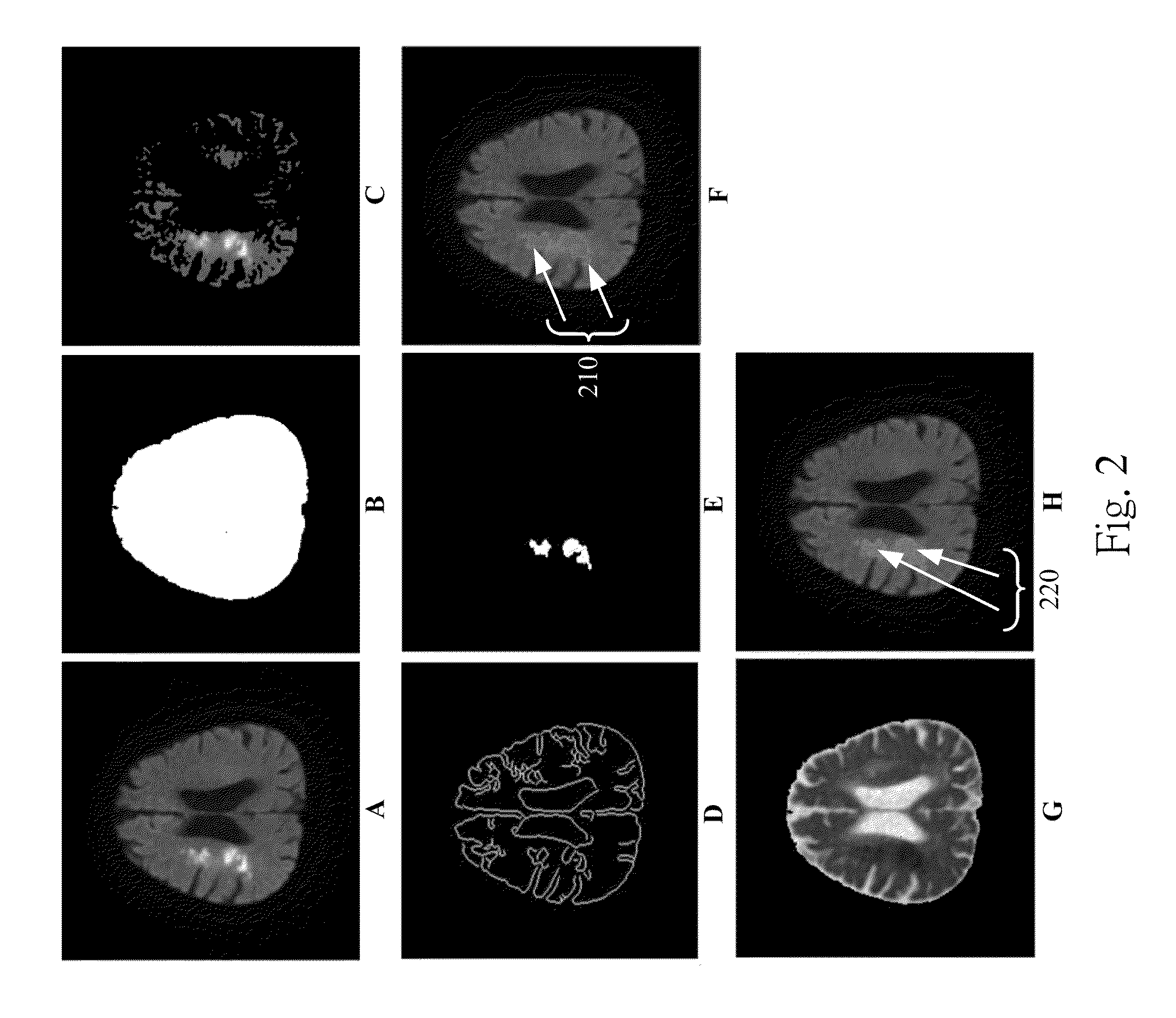
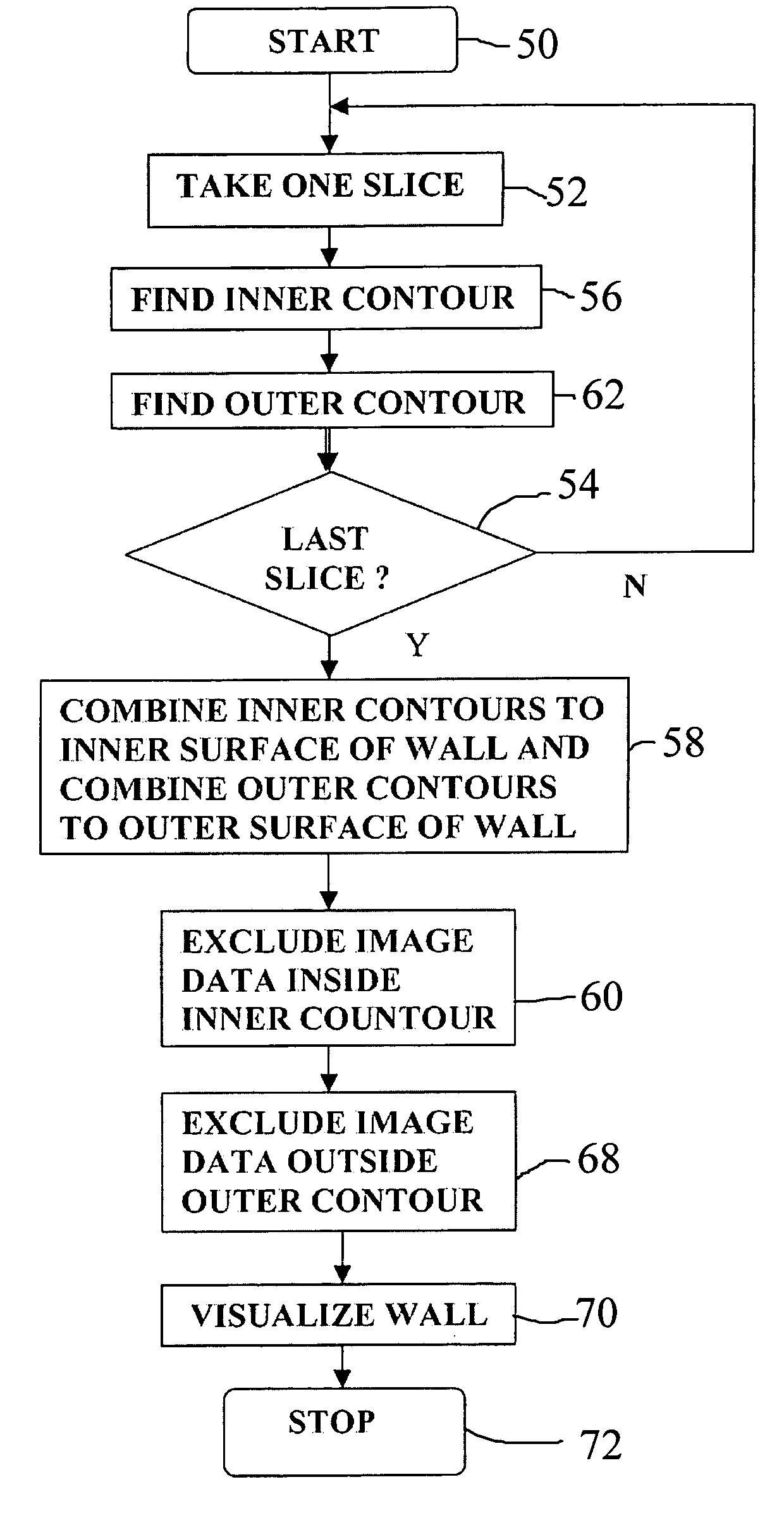
A data processing methodology and corresponding apparatus for visualizing the characteristics of a particular object volume in an overall medical / biological environment receives a source image data set pertaining to the overall environment. First and second contour surfaces within the environment are established which collectively define a target object volume. By way of segmenting, all information pertaining to structures outside the target object volume are excluded from the image data. A visual representation of the target object based on nonexcluded information is displayed. In particular, the method establishes i) the second contour surface through combining both voxel intensities and relative positions among voxel subsets, and ii) a target volume by excluding all data outside the outer surface and inside the inner surface (which allows non-uniform spacing between the first and second contour surfaces). The second contour surface is used as a discriminative for the segmenting.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Image enhancement using anisotropic noise filtering
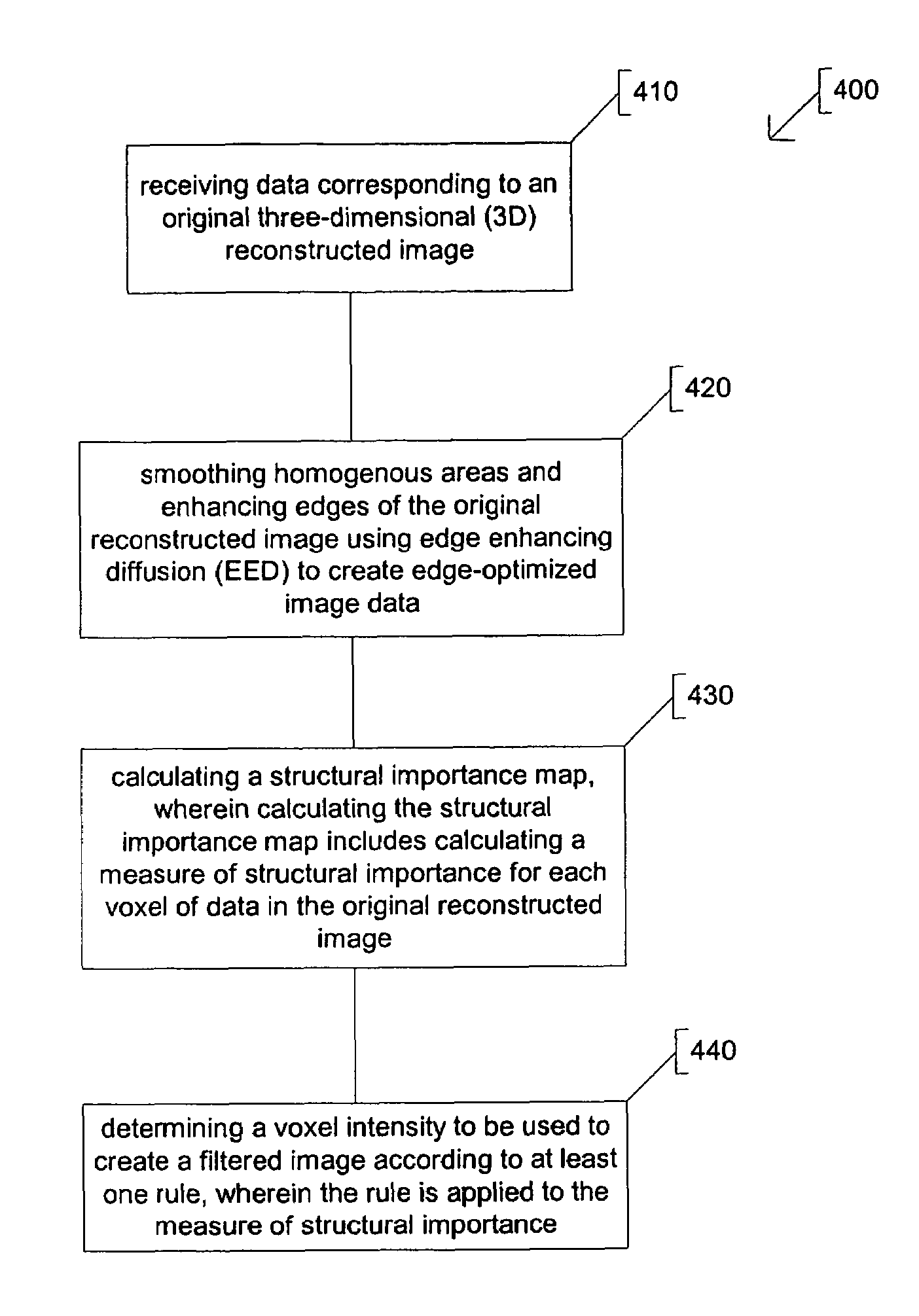
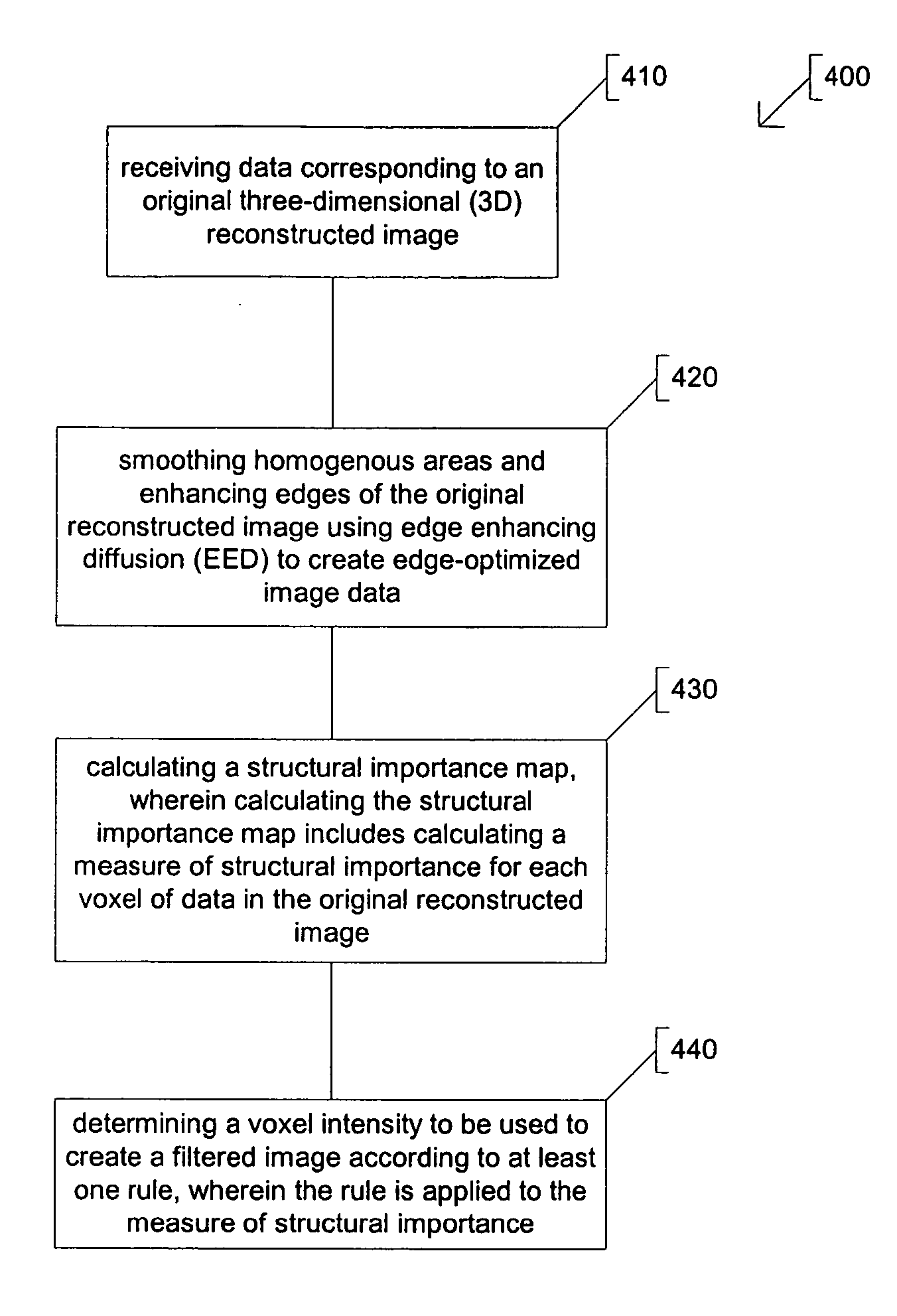
A method including receiving data corresponding to an original three-dimensional (3D) reconstructed image, smoothing homogenous areas and enhancing edges of the original reconstructed image using edge enhancing diffusion (EED) to create edge-enhanced image data, and calculating a structural importance map. The structural importance map includes a measure of structural importance for each voxel of data in the original reconstructed image. Voxel intensities to be used to create a filtered image are determined according to at least one rule applied to the measure of structural importance.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
Cardiac visualization systems for displaying 3-D images of cardiac voxel intensity distributions with optional physician interactive boundary tracing tools
Physician interactive workstations with global cardiac voxel distribution visualization may also include one or more of a 3-D color scale image of a population of voxel in the heart and / or an electronic boundary-tracing tool configured to accept user input to electronically define at least one boundary of a target region of a heart in a medical image of a patient on a display. The workstation may be configured to evaluate intensity of voxels associated with tissue within the defined boundary of the target region of the heart whereby cardiotoxicity is evaluated.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Method and apparatus for visualization of biological structures with use of 3D position information from segmentation results
A data processing methodology (and corresponding data processing apparatus) for visualizing the characteristics of a particular object volume in an overall medical / biological environment comprises the following computer operated steps: receiving a source image data set as pertaining to the overall environment; establishing a first contour surface within the environment, and through using the first contour surface as seed data, establishing a second contour surface within the environment, which contour surfaces collectively defining a target object volume; by way of segmenting, excluding from the image data set all information pertaining to structures outside the target object volume; and visualizing the target object as being based on nonexcluded information. In particular, the method establishes the second contour surface through combining both voxel intensities and relative positions among voxel subsets, a target volume by excluding all data outside the outer surface and inside the inner surface, thereby allowing non-uniform spacing between the first and second contour surfaces, and uses the second contour surface as being discriminative for the segmenting.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Image enhancement using anisotropic noise filtering
ActiveUS20070110294A1Improve diagnostic capabilitiesReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionImportance map
A method including receiving data corresponding to an original three-dimensional (3D) reconstructed image, smoothing homogenous areas and enhancing edges of the original reconstructed image using edge enhancing diffusion (EED) to create edge-enhanced image data, and calculating a structural importance map. The structural importance map includes a measure of structural importance for each voxel of data in the original reconstructed image. Voxel intensities to be used to create a filtered image are determined according to at least one rule applied to the measure of structural importance.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
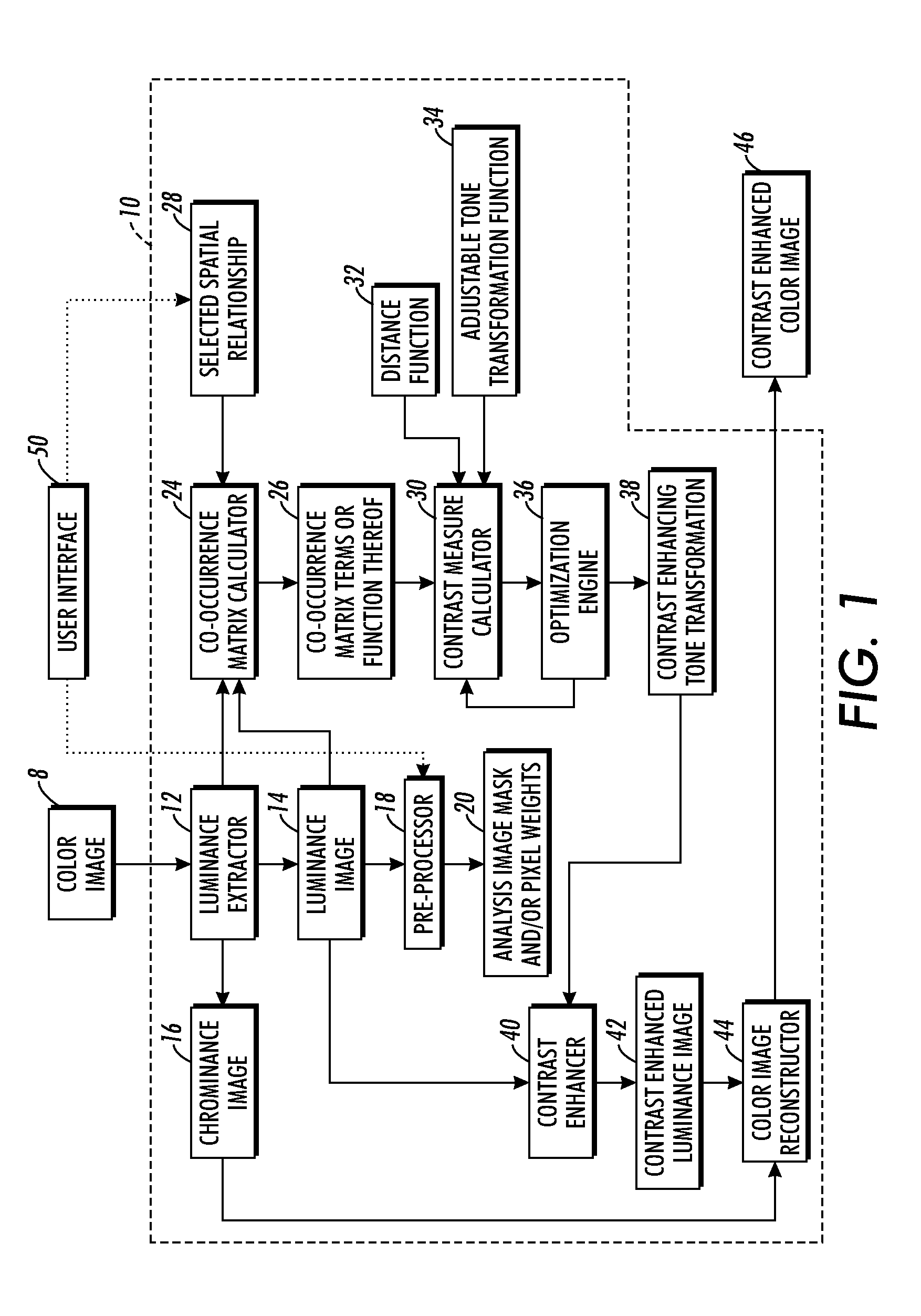
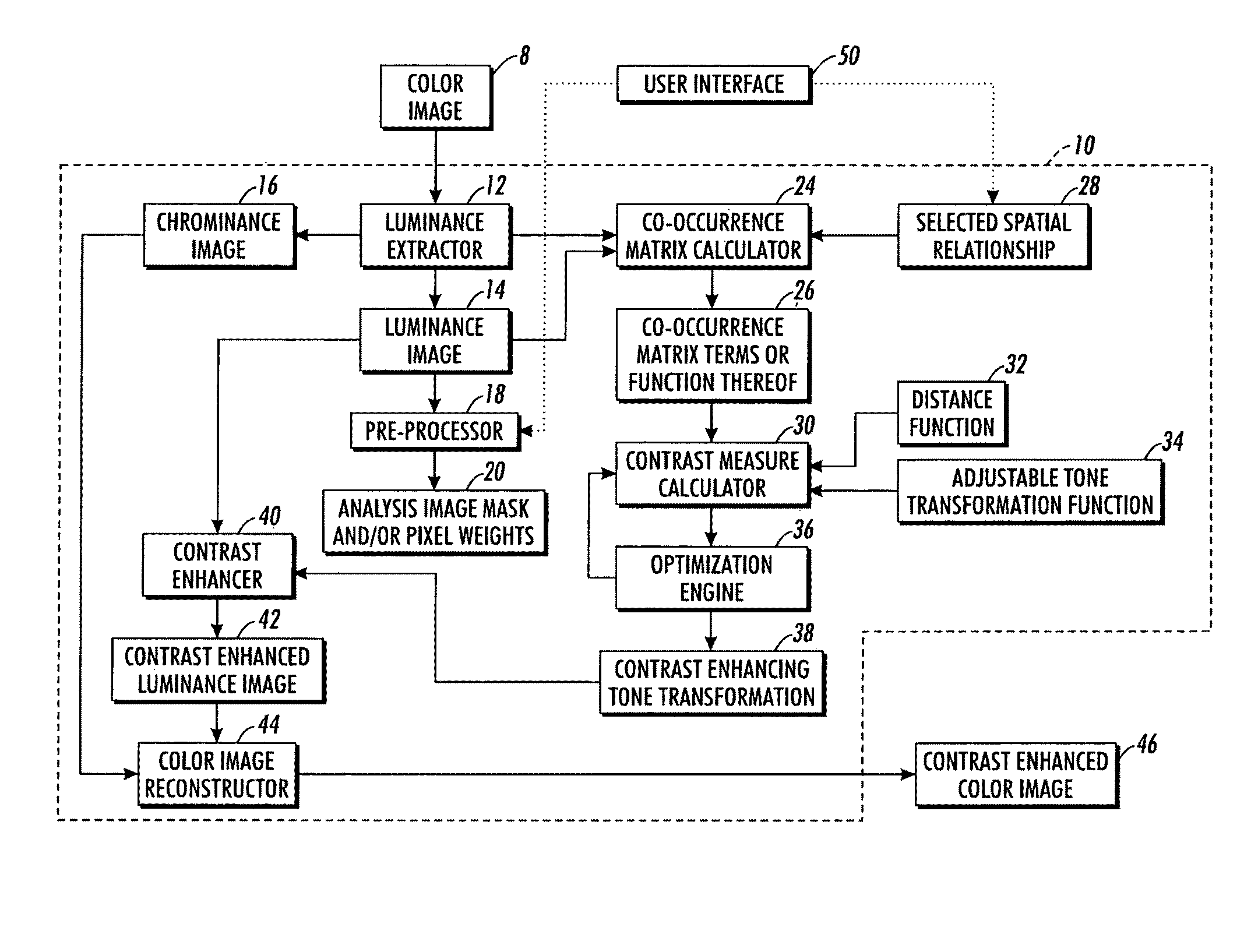
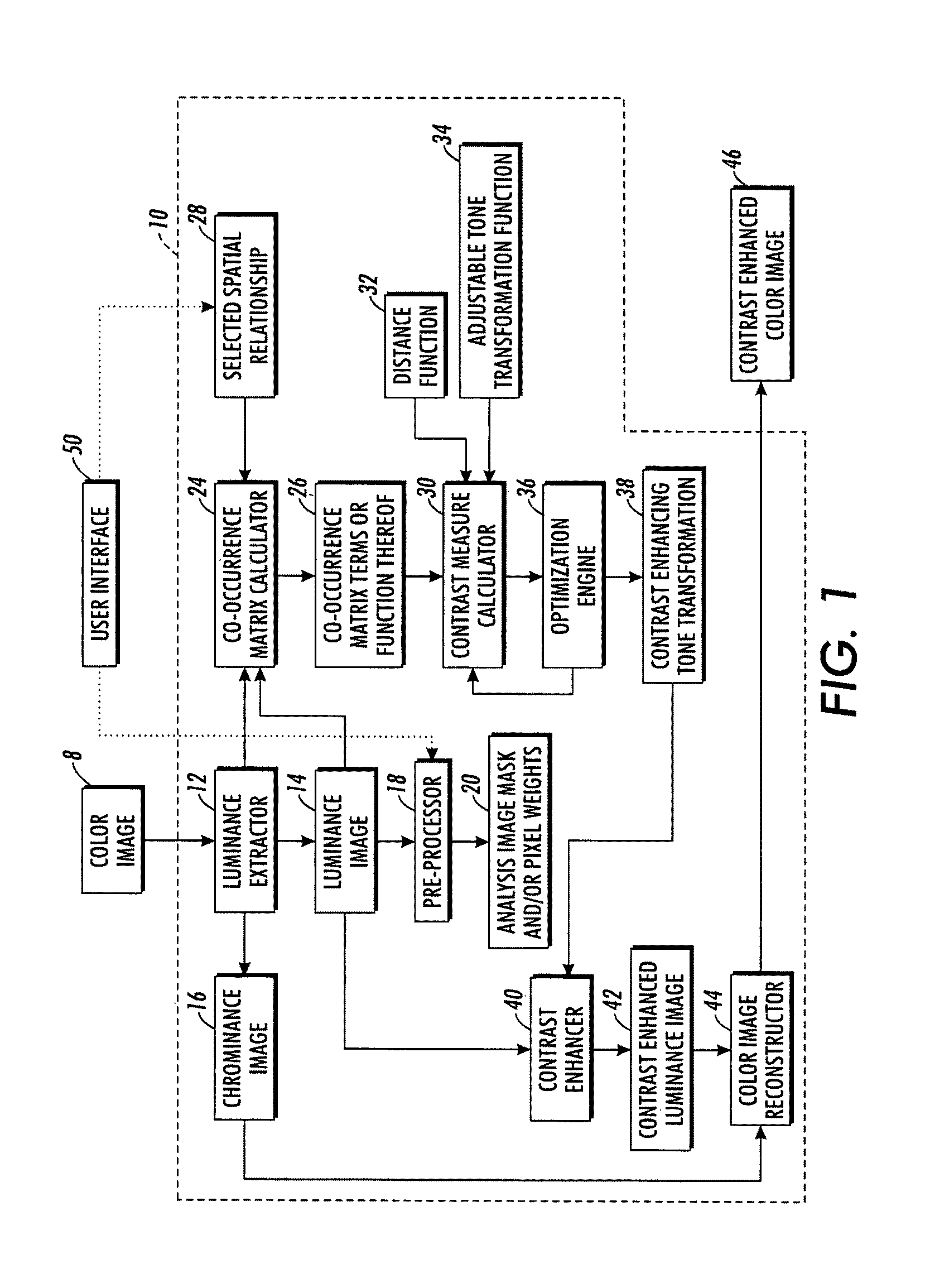
Contrast enhancement methods and apparatuses
ActiveUS20080285853A1Optimizes contrast measureTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage contrastContrast enhancement
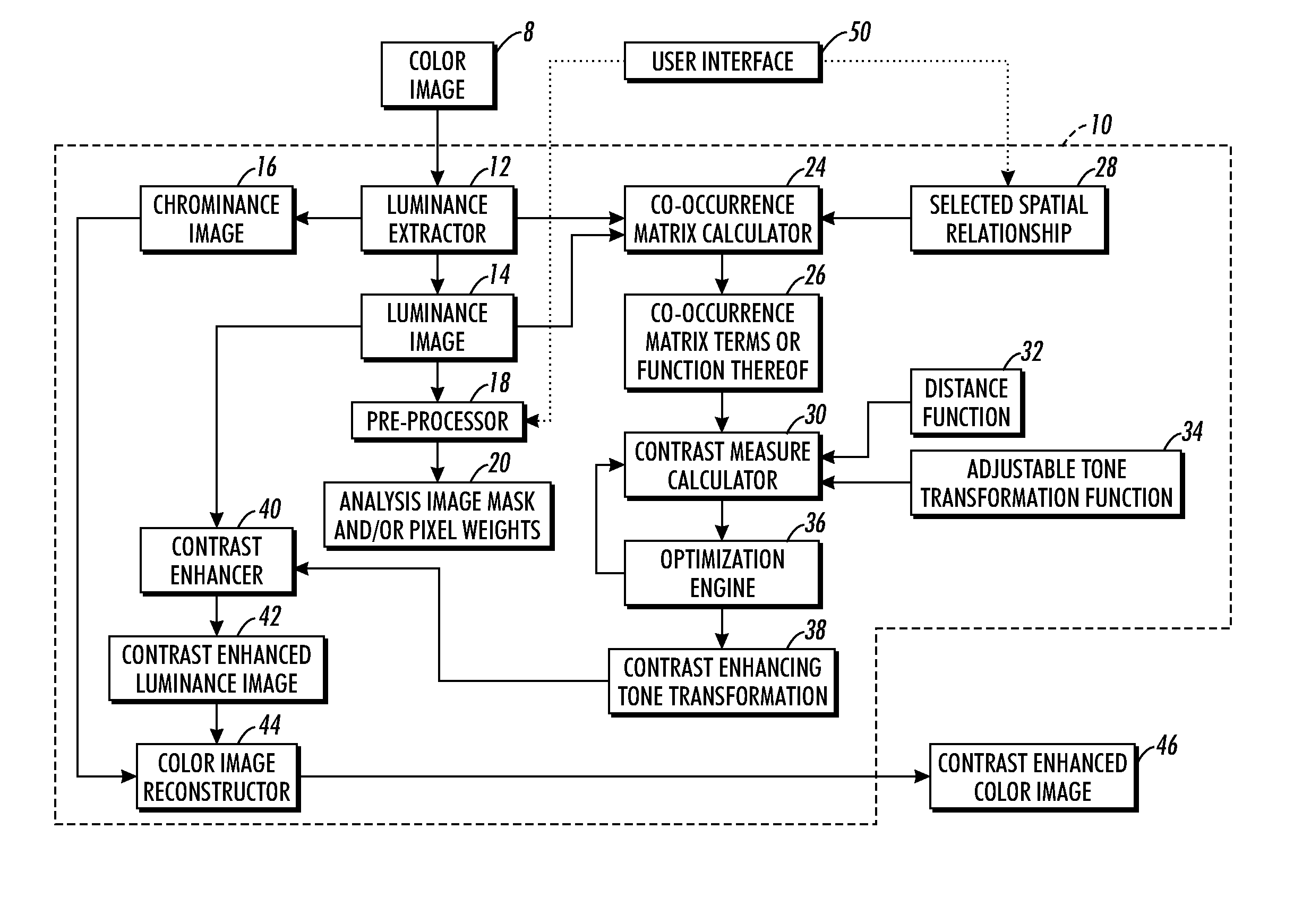
Image contrast enhancement includes (i) computing a contrast measure incorporating an adjustable tone transformation function and one or more statistical measures of selected spatial arrangements of pixel or voxel intensities in an analysis image or image portion, (ii) adjusting the adjustable tone transformation function to increase contrast as indicated by the contrast measure, and (iii) enhancing contrast of a target image or image portion using the adjusted tone transformation function.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Cardiac visualization systems for displaying 3-d images of cardiac voxel intensity distributions with optional physician interactive boundary tracing tools
Physician interactive workstations with global cardiac voxel distribution visualization may also include one or more of a 3-D color scale image of a population of voxel in the heart and / or an electronic boundary-tracing tool configured to accept user input to electronically define at least one boundary of a target region of a heart in a medical image of a patient on a display. The workstation may be configured to evaluate intensity of voxels associated with tissue within the defined boundary of the target region of the heart whereby cardiotoxicity is evaluated.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
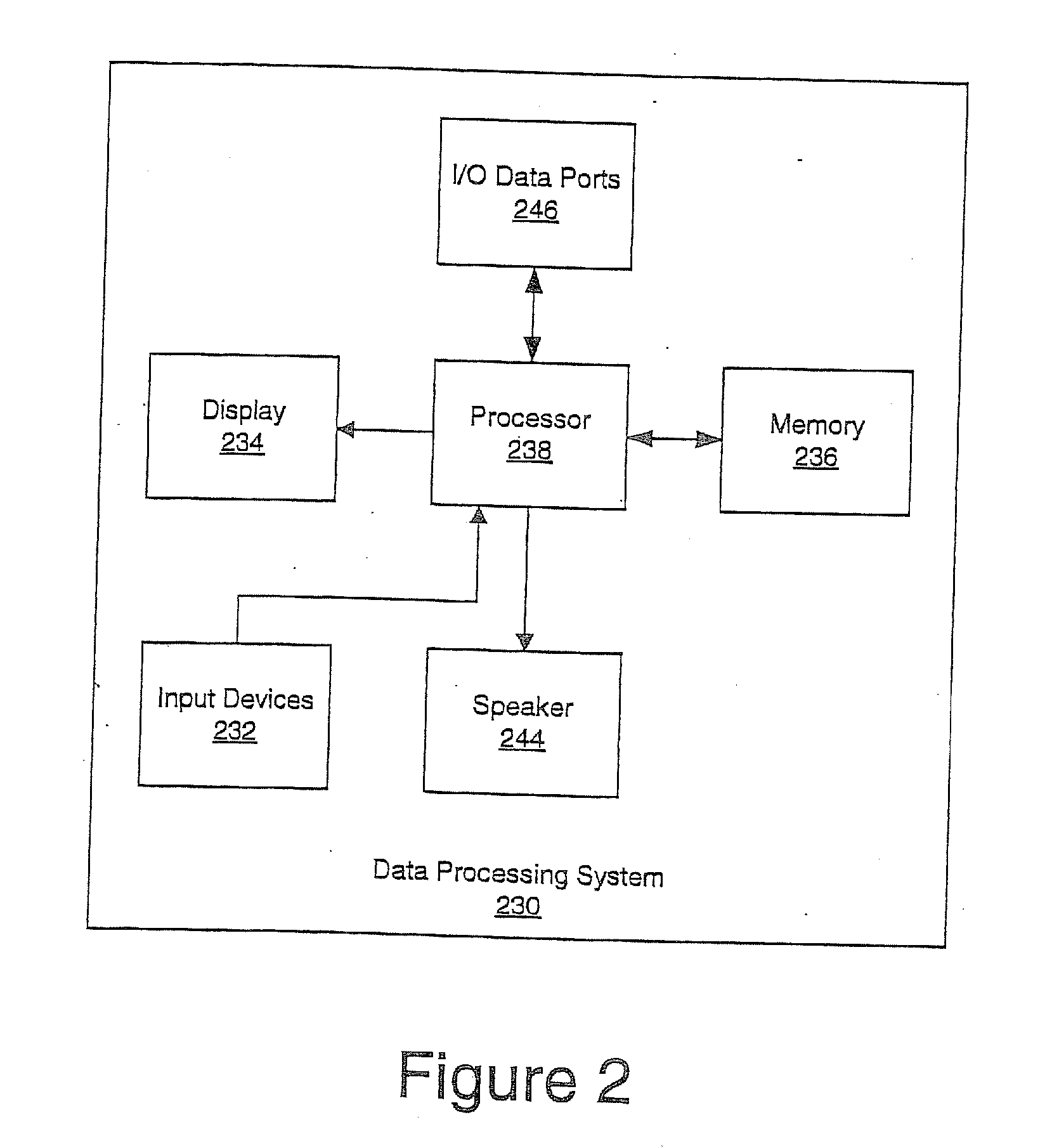
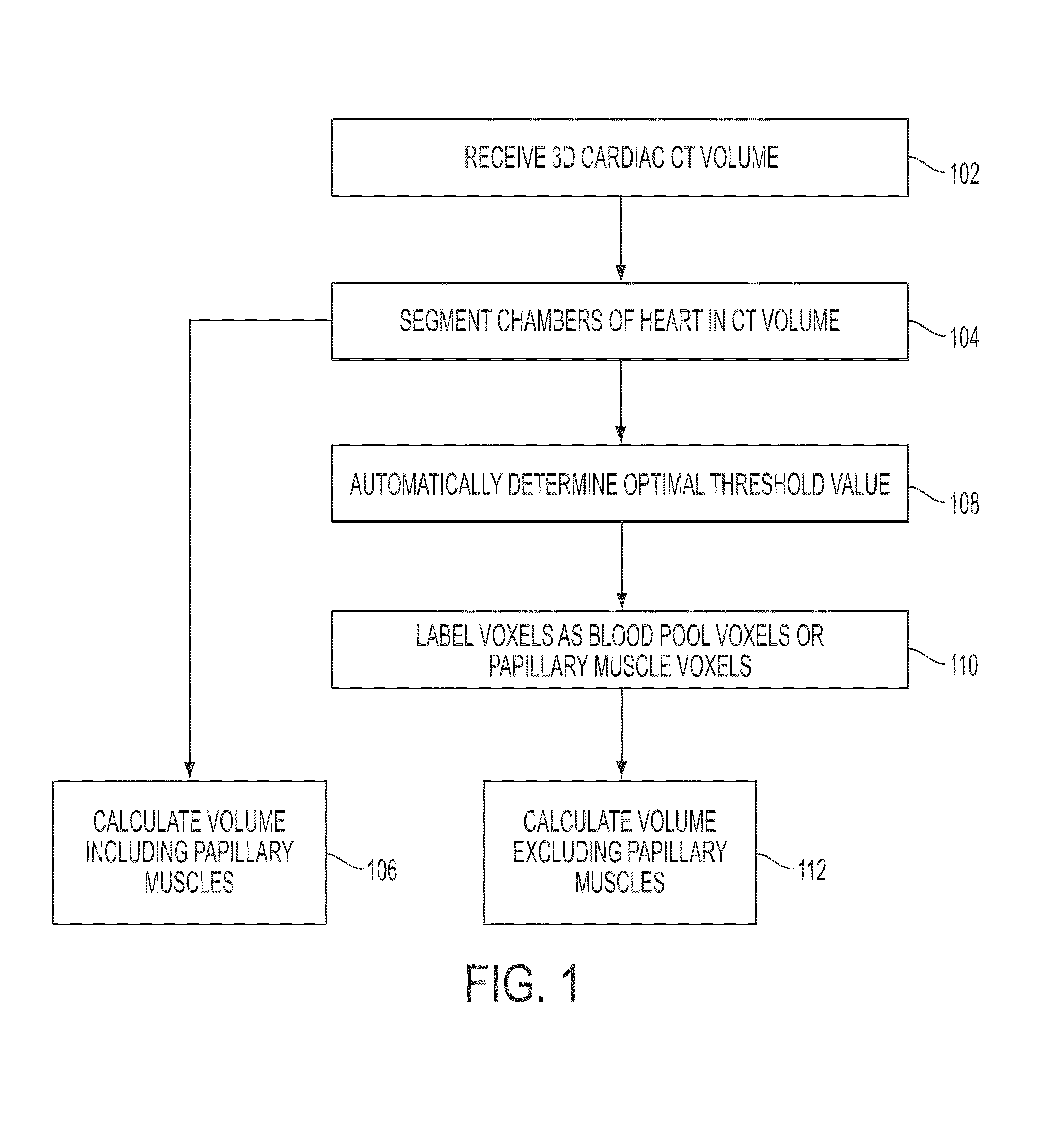
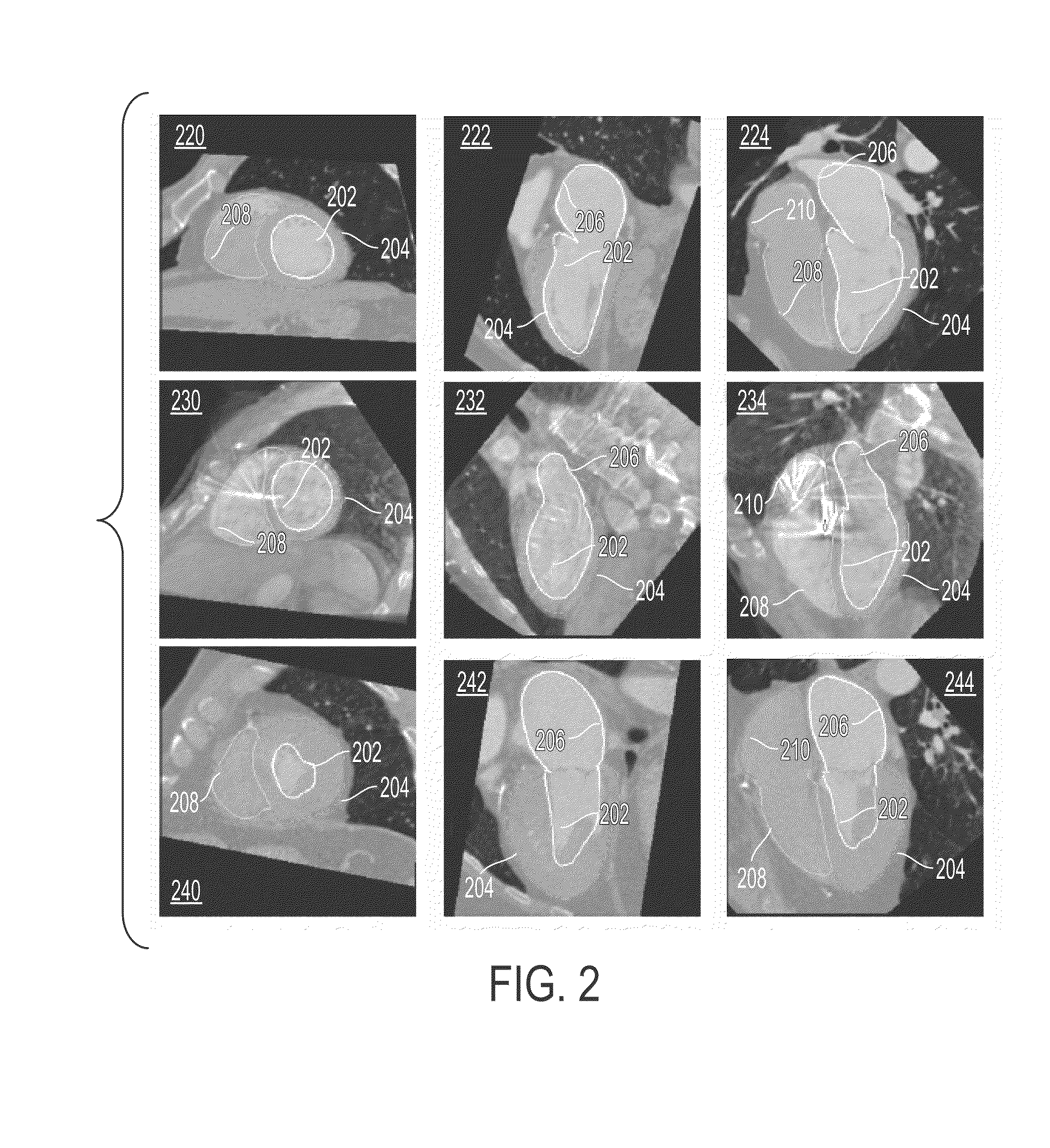
Method and system for measuring left ventricle volume
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
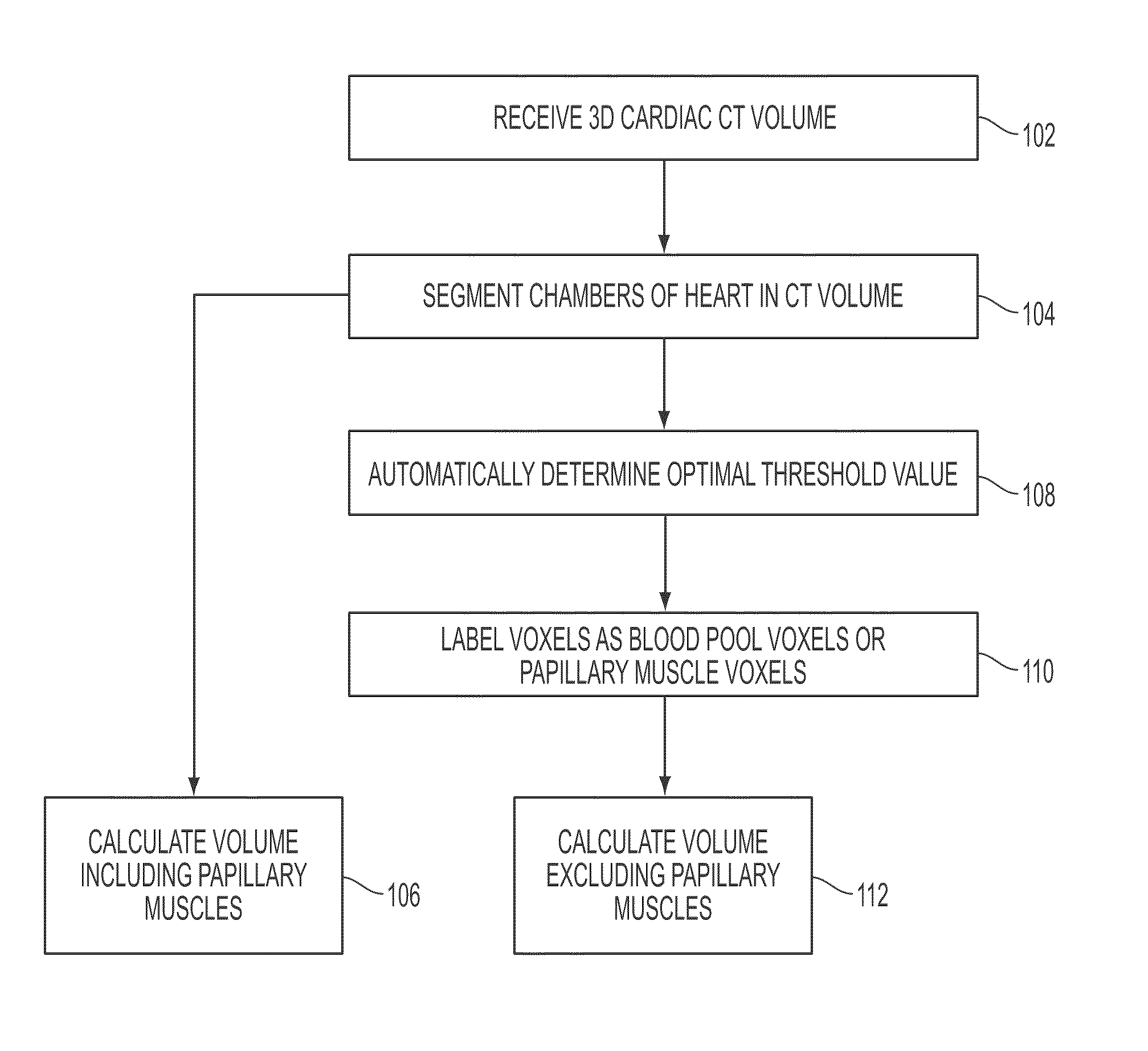
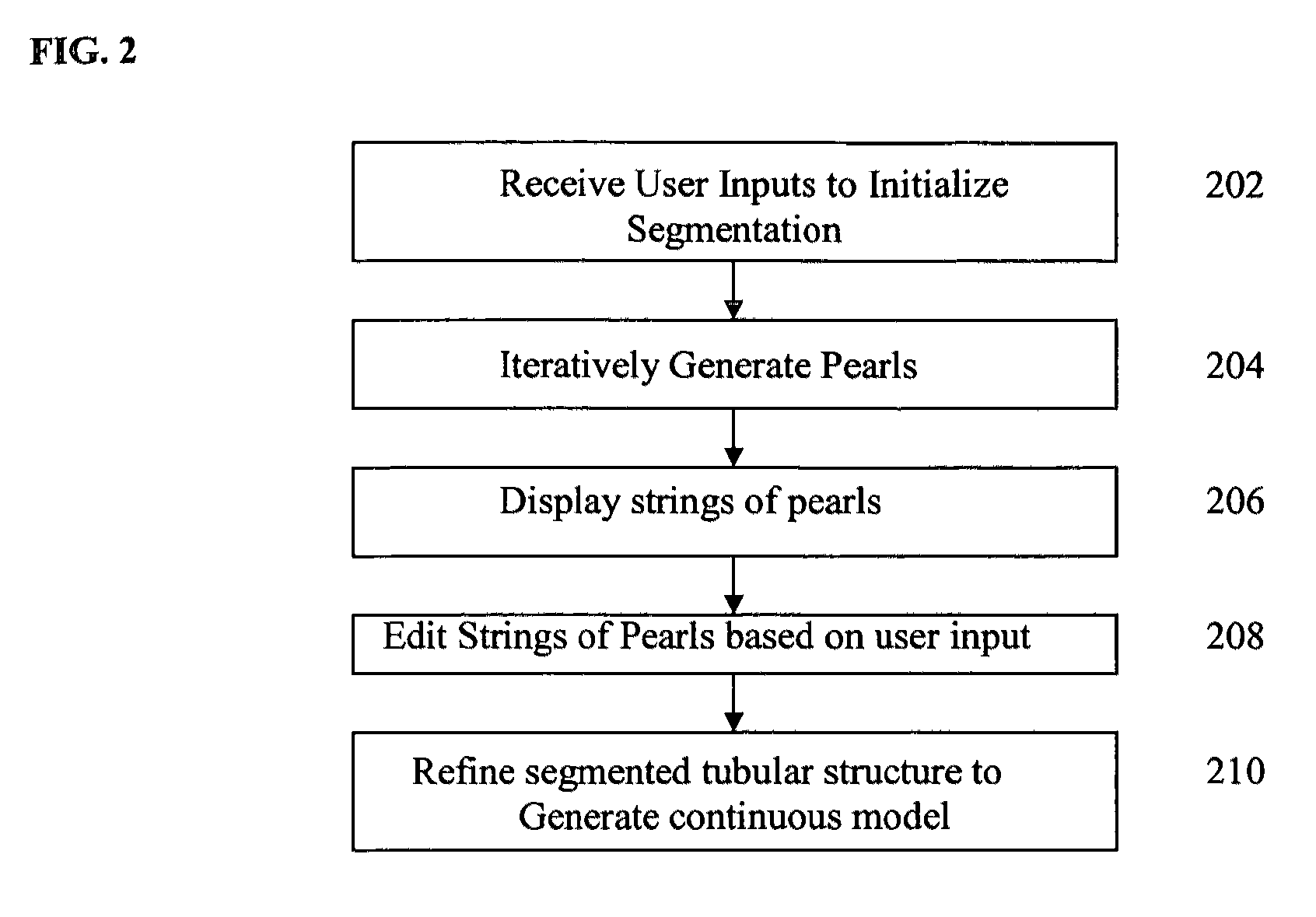
Method and system for segmentation of tubular structures in 3D images
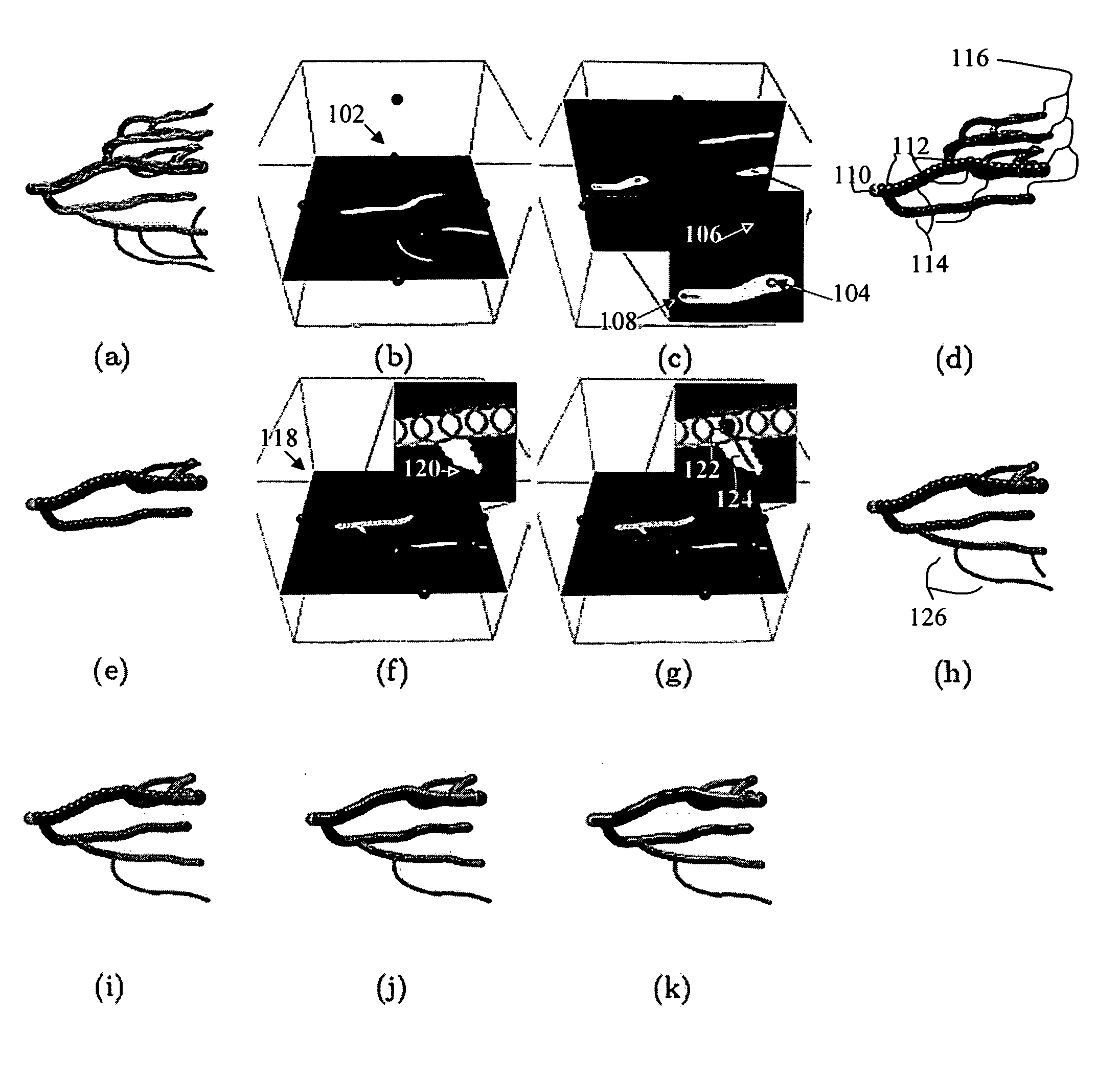
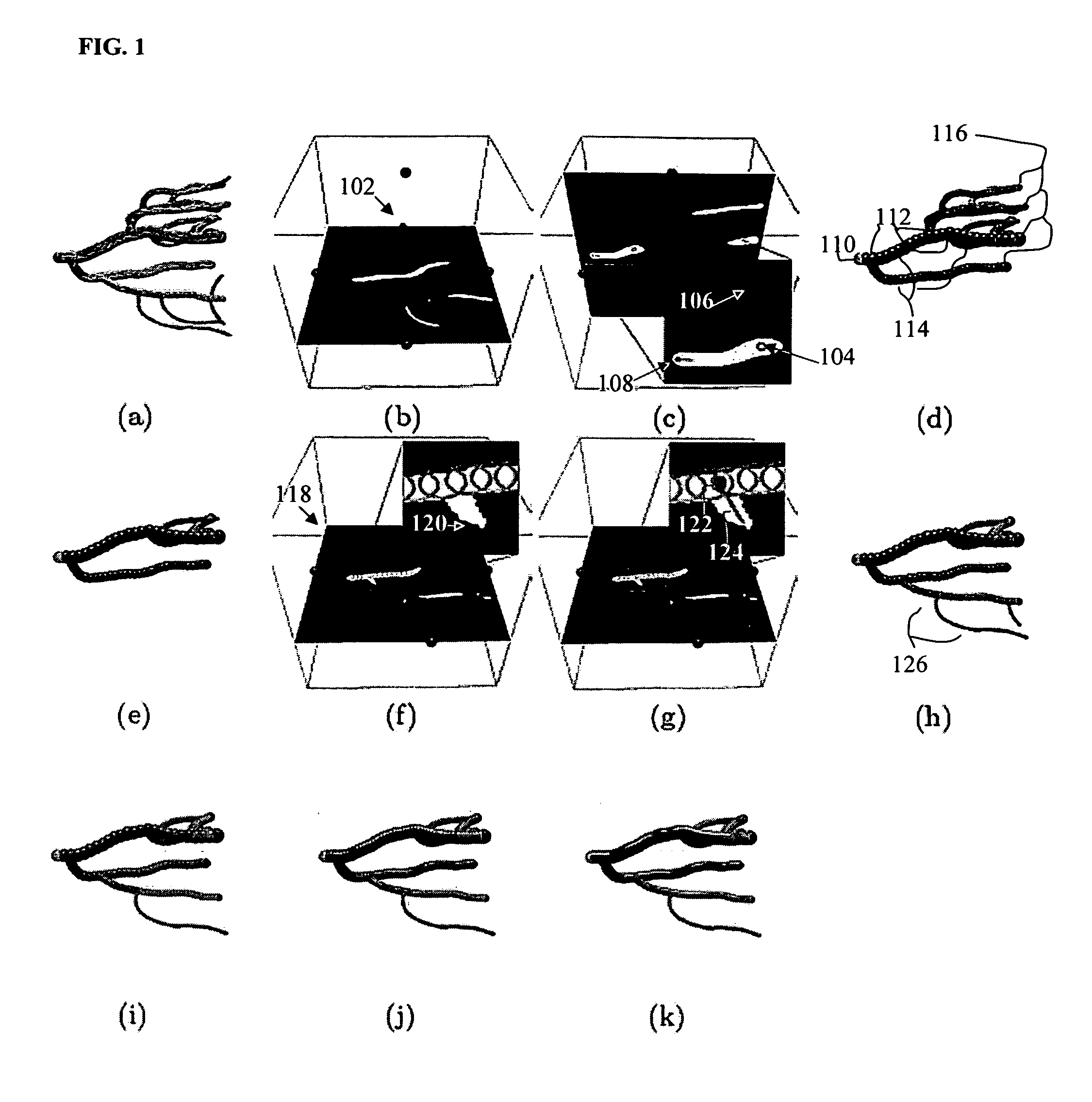
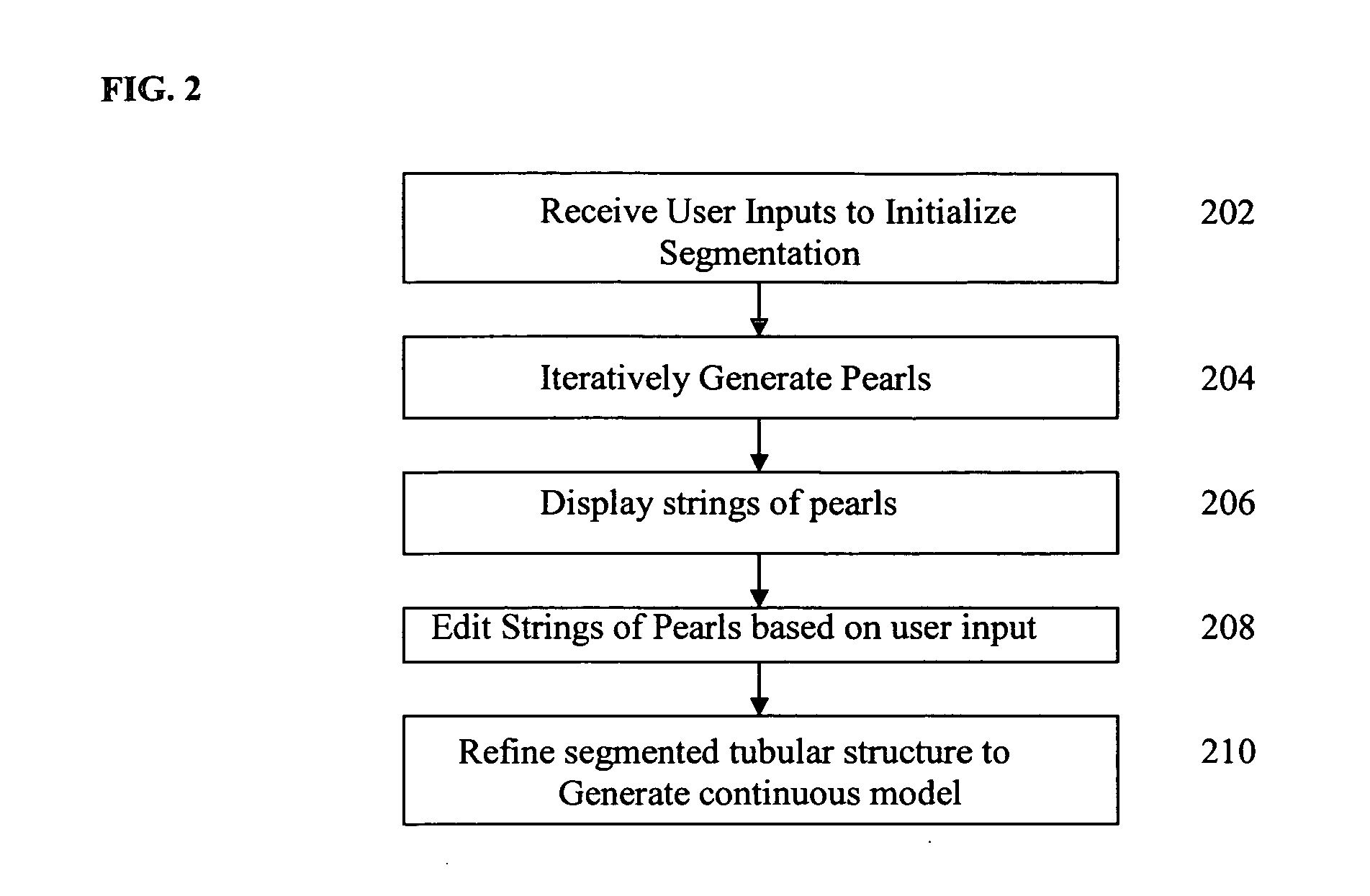
A method and system for segmenting tubular structures in 3D images is disclosed. User inputs identifying a first region on the image inside of a tubular structure and a second region of the image outside of the tubular structure are received. Based on this information, an ordered series of pearls are generated along the tubular structure. Pearls are spheres, each having a center location and a radius determined based on the center locations and radii of previous pearls and on local voxel intensities in the image. A continuous model of the tubular structure can be generated by interpolating the center locations and radii of the ordered series of pearls. The ordered series of pearls can be displayed and easily edited in response to user input, thus providing an efficient and flexible method for interactive segmentation of a potion of interest in a tubular structure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
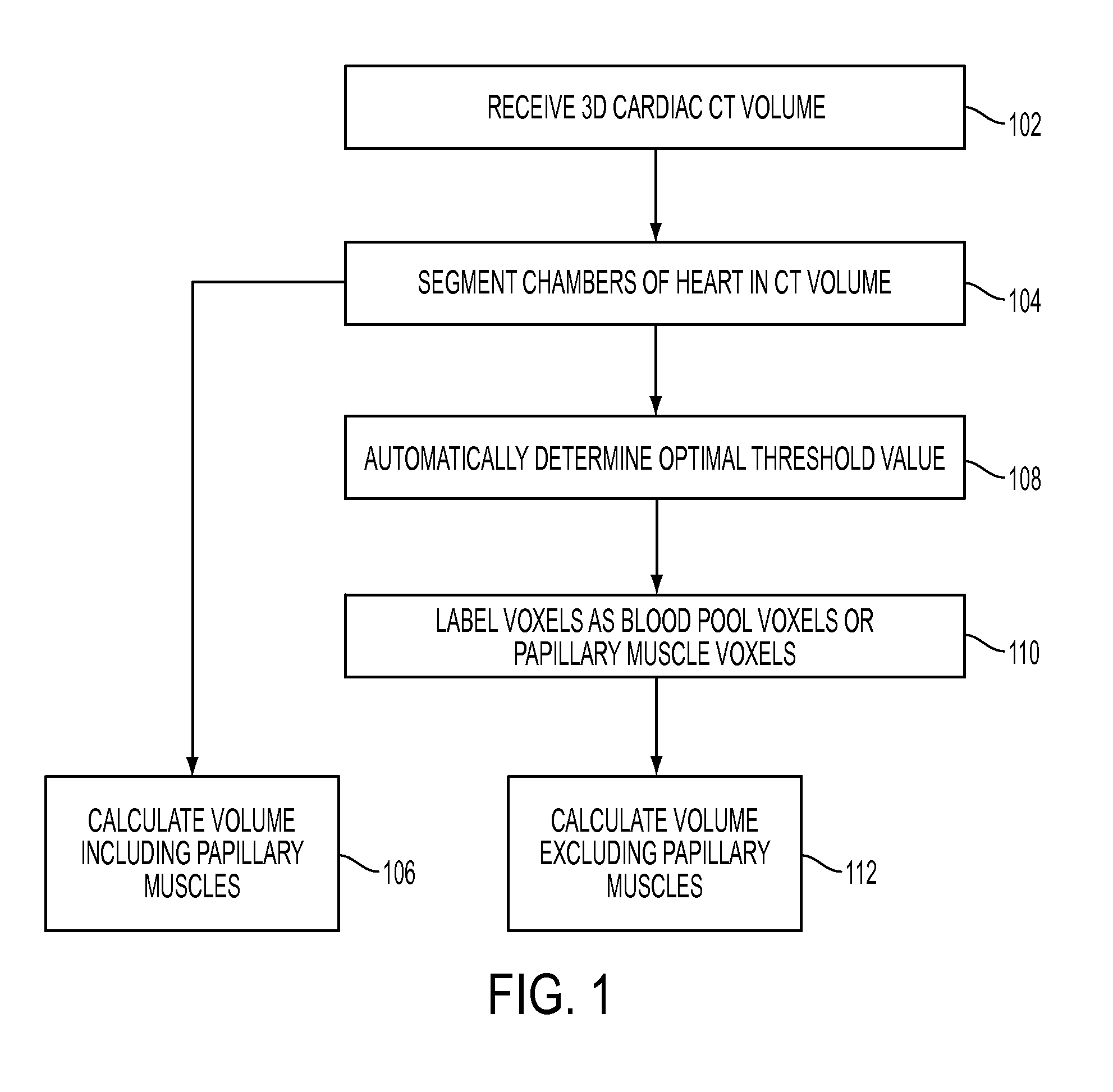
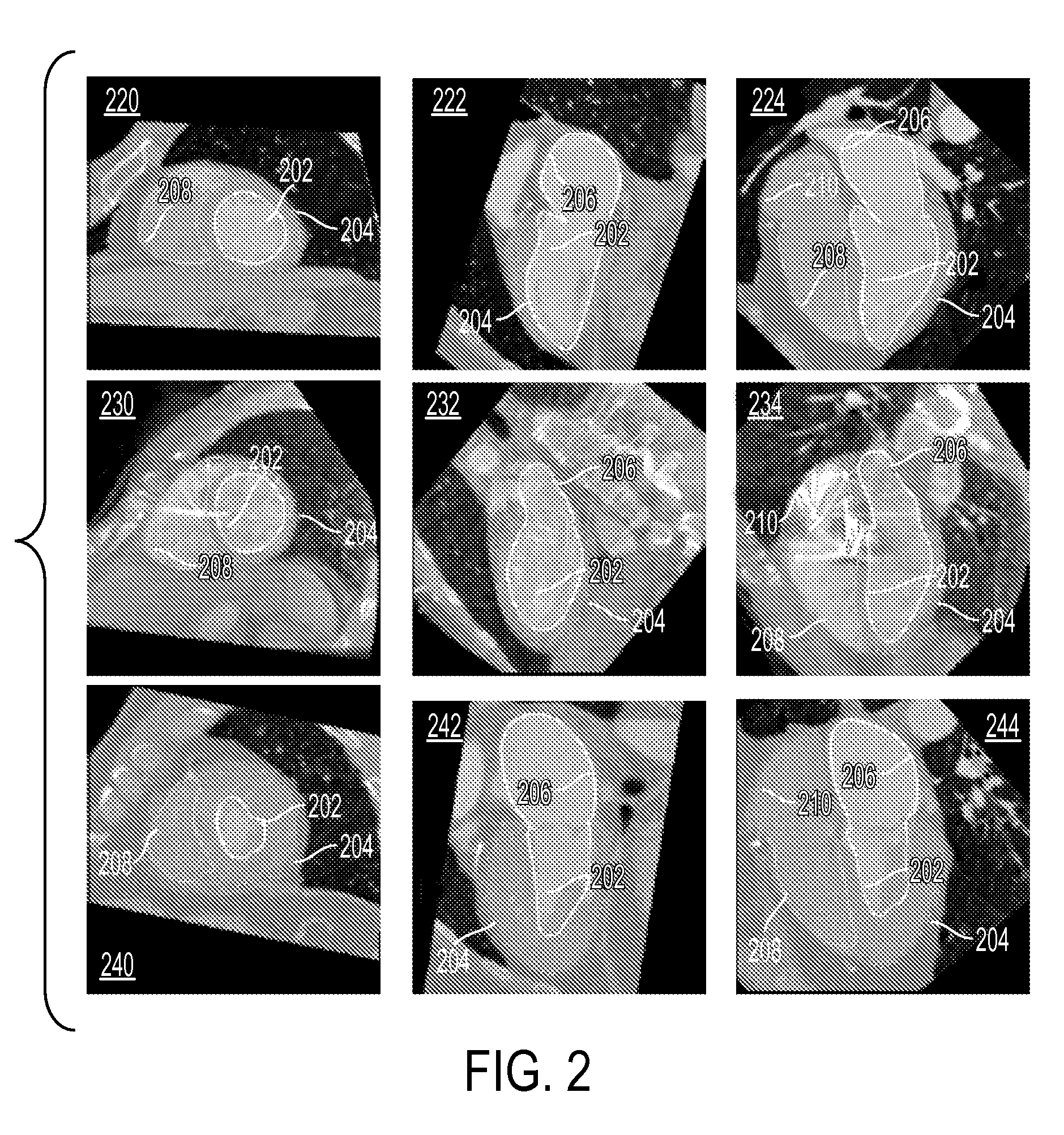
Method and system for measuring left ventricle volume
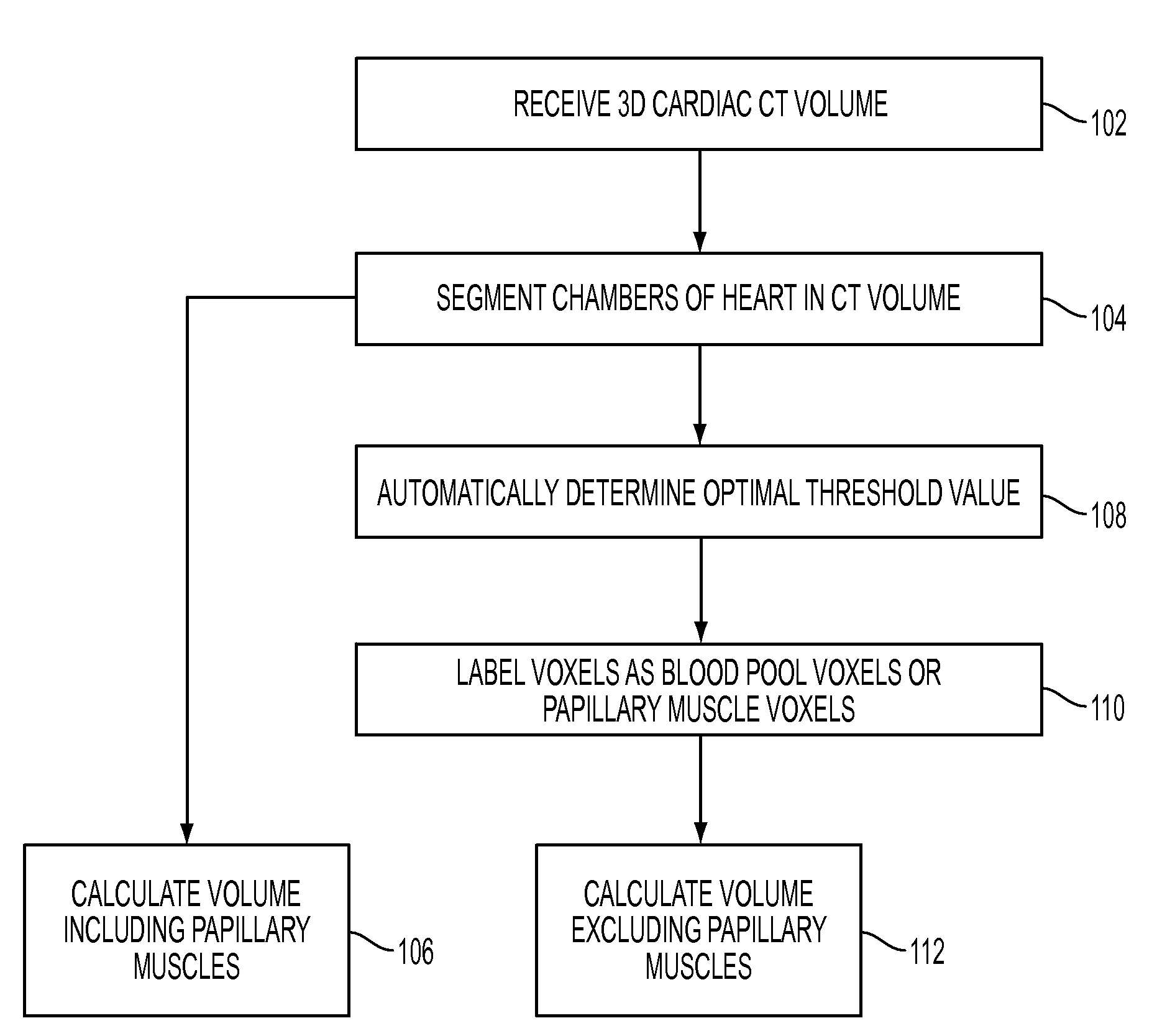
A method and system for measuring the volume of the left ventricle (LV) in a 3D medical image, such as a CT, volume is disclosed. Heart chambers are segmented in the CT volume, including at least the LV endocardium and the LV epicardium. An optimal threshold value is automatically determined based on voxel intensities within the LV endocardium and voxel intensities between the LV endocardium and the LV epicardium. Voxels within the LV endocardium are labeled as blood pool voxels or papillary muscle voxels based on the optimal threshold value. The LV volume can be measured excluding the papillary muscles based on the number of blood pool voxels, and the LV volume can be measured including the papillary muscles based on the total number of voxels within the LV endocardium.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
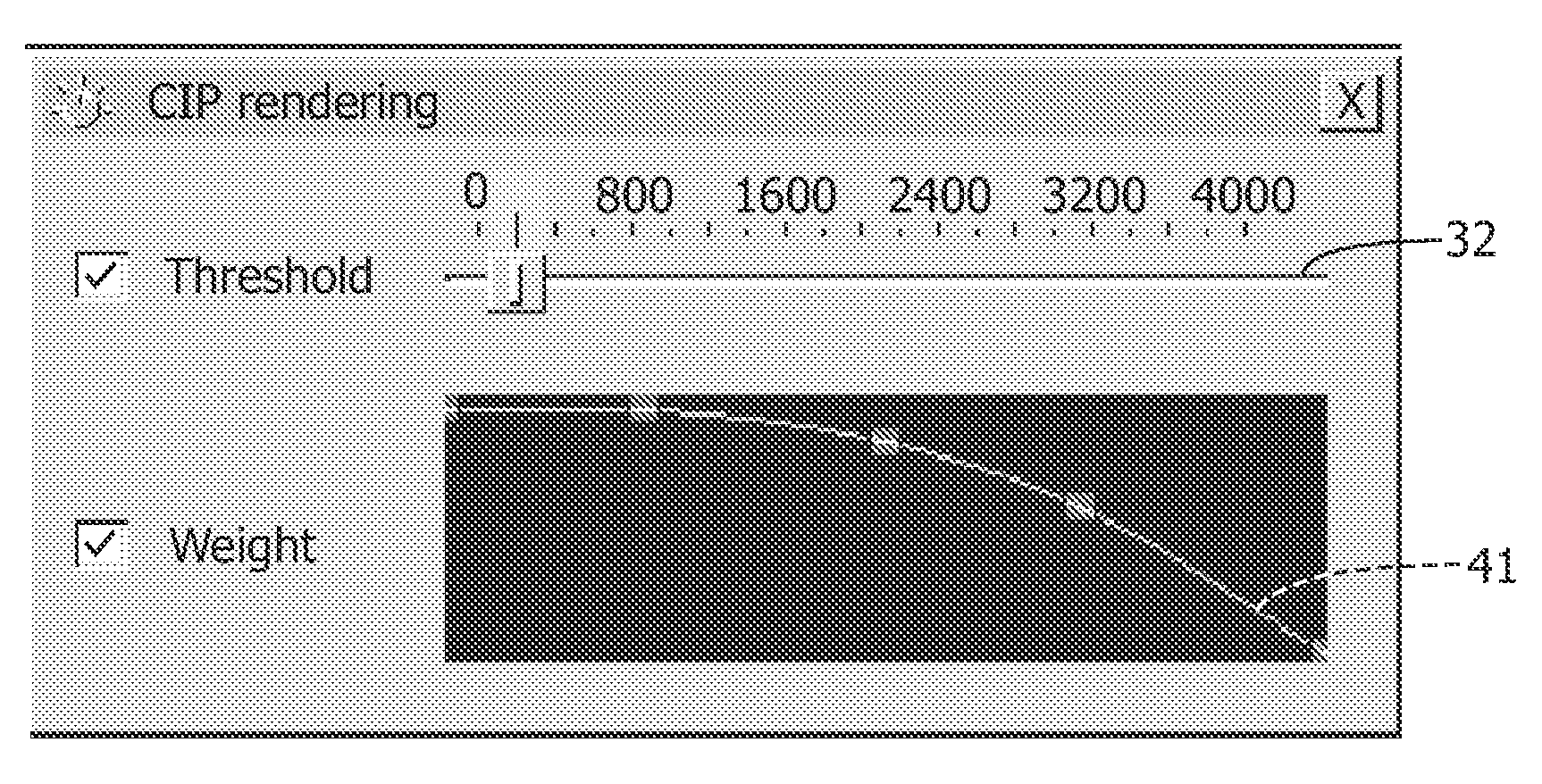
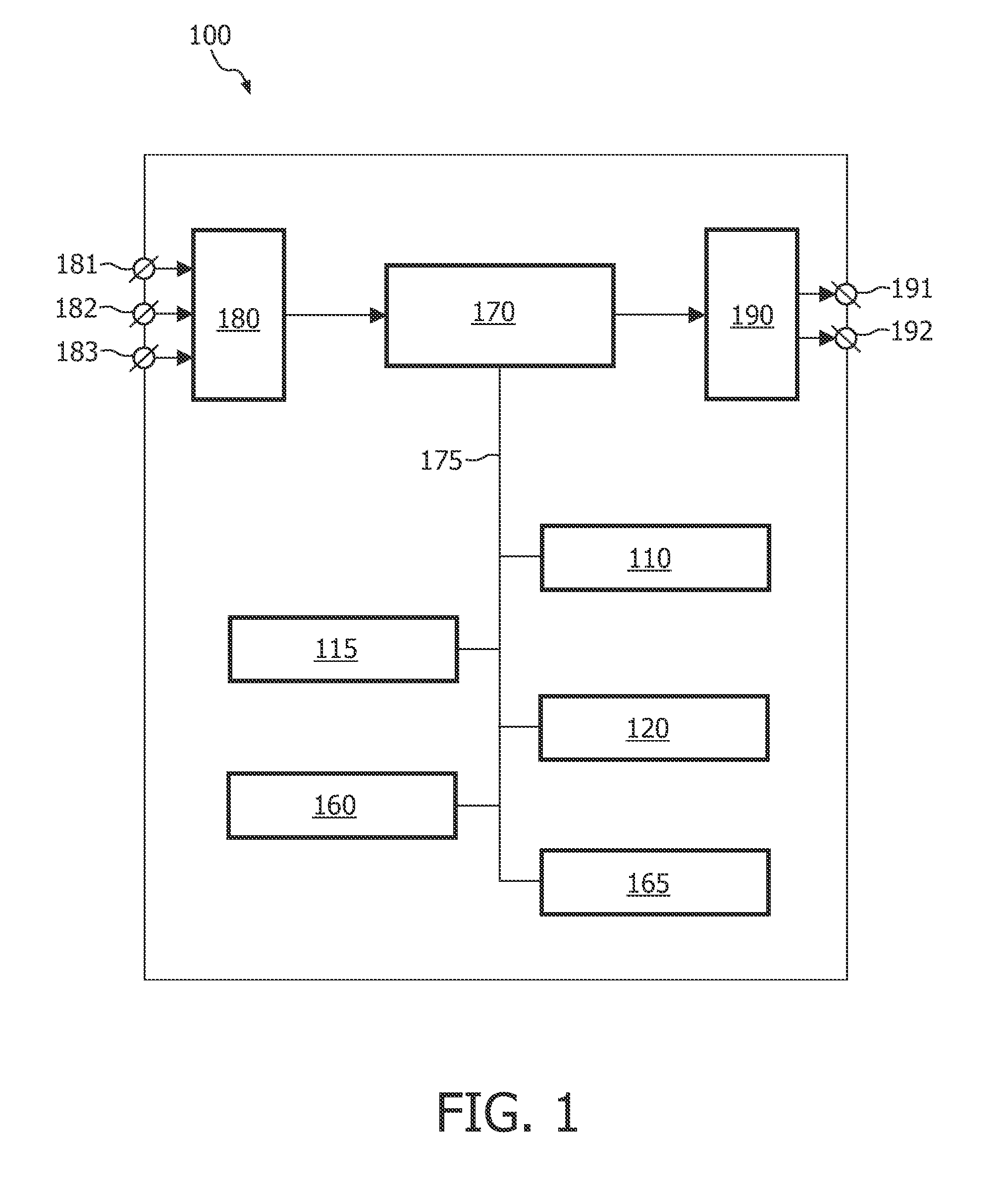
Combined intensity projection
ActiveUS20100053159A1Computational complexity is reducedIncrease awarenessDrawing from basic elementsGeometric image transformationComputation complexityData set
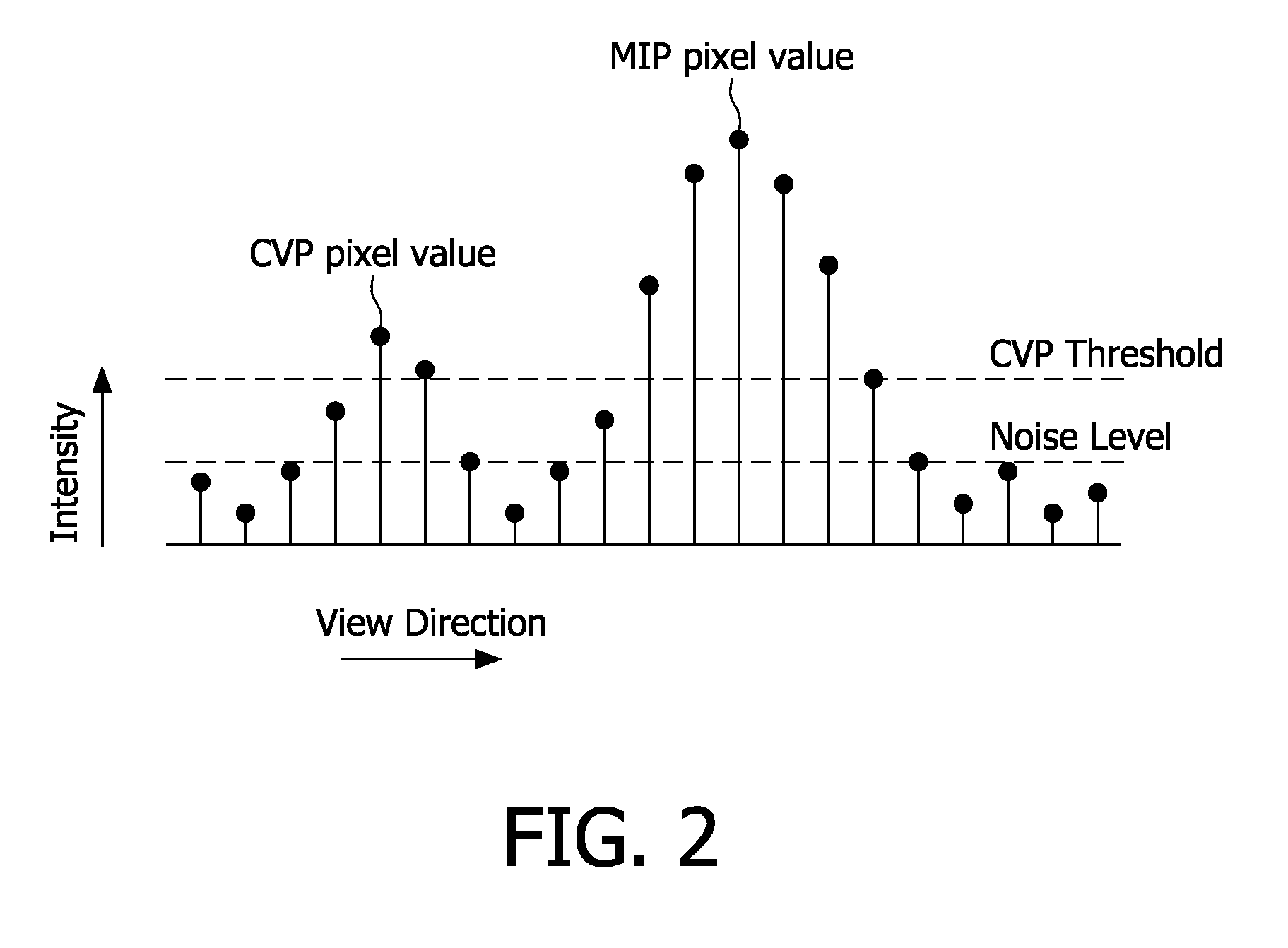
The invention relates to a system (100) for rendering an image based on a volumetric image data set, the system comprising: a computation unit (110) for computing an initial pixel intensity of a pixel of the image, defined by a corresponding voxel intensity of a corresponding voxel comprised in the volumetric image data set; and an adjustment unit (120) for computing a final pixel intensity of the pixel, based on the initial pixel intensity and on a location of the corresponding voxel. Thus, the system of the invention enables new visualizations of volumetric image data sets. Advantageously, unlike a system using the VIP technique, which requires adjusting intensities of voxels comprised in the image data set, the system of the current invention is arranged to adjust intensities of pixels. This reduces the computational complexity of the rendering technique employed by the system relative to the computational complexity of the VIP technique.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
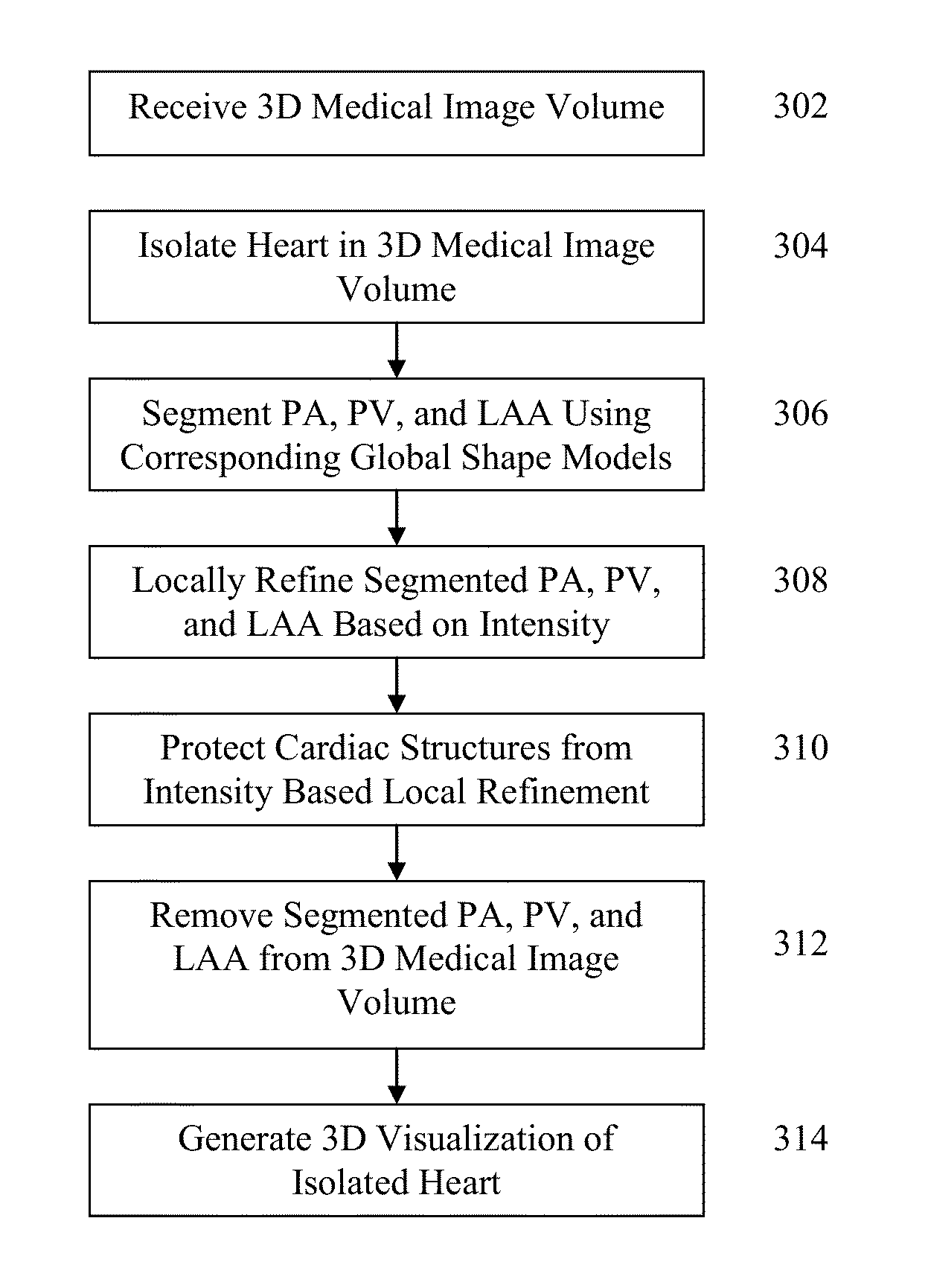
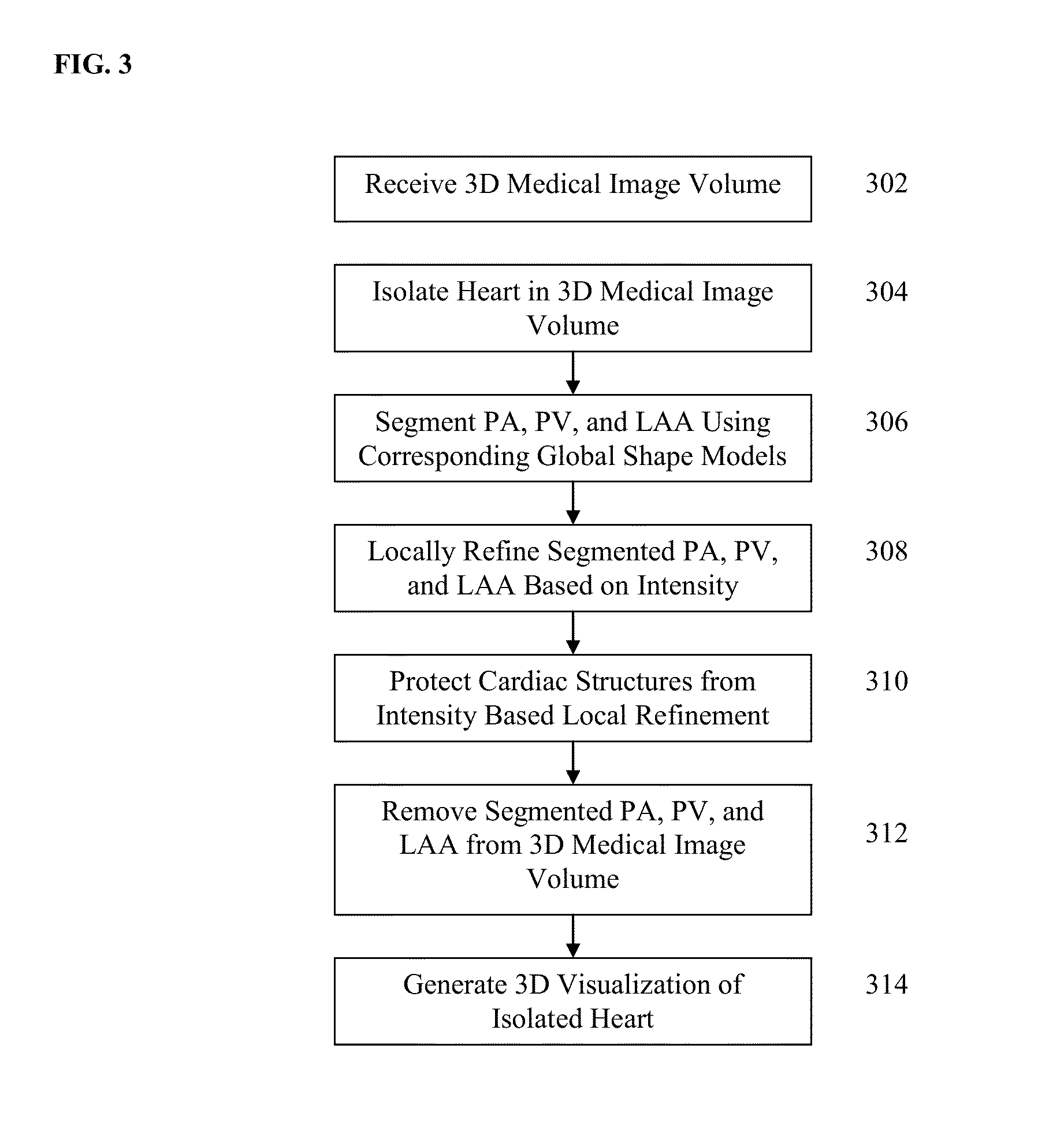
Method and System for Segmentation and Removal of Pulmonary Arteries, Veins, Left Atrial Appendage
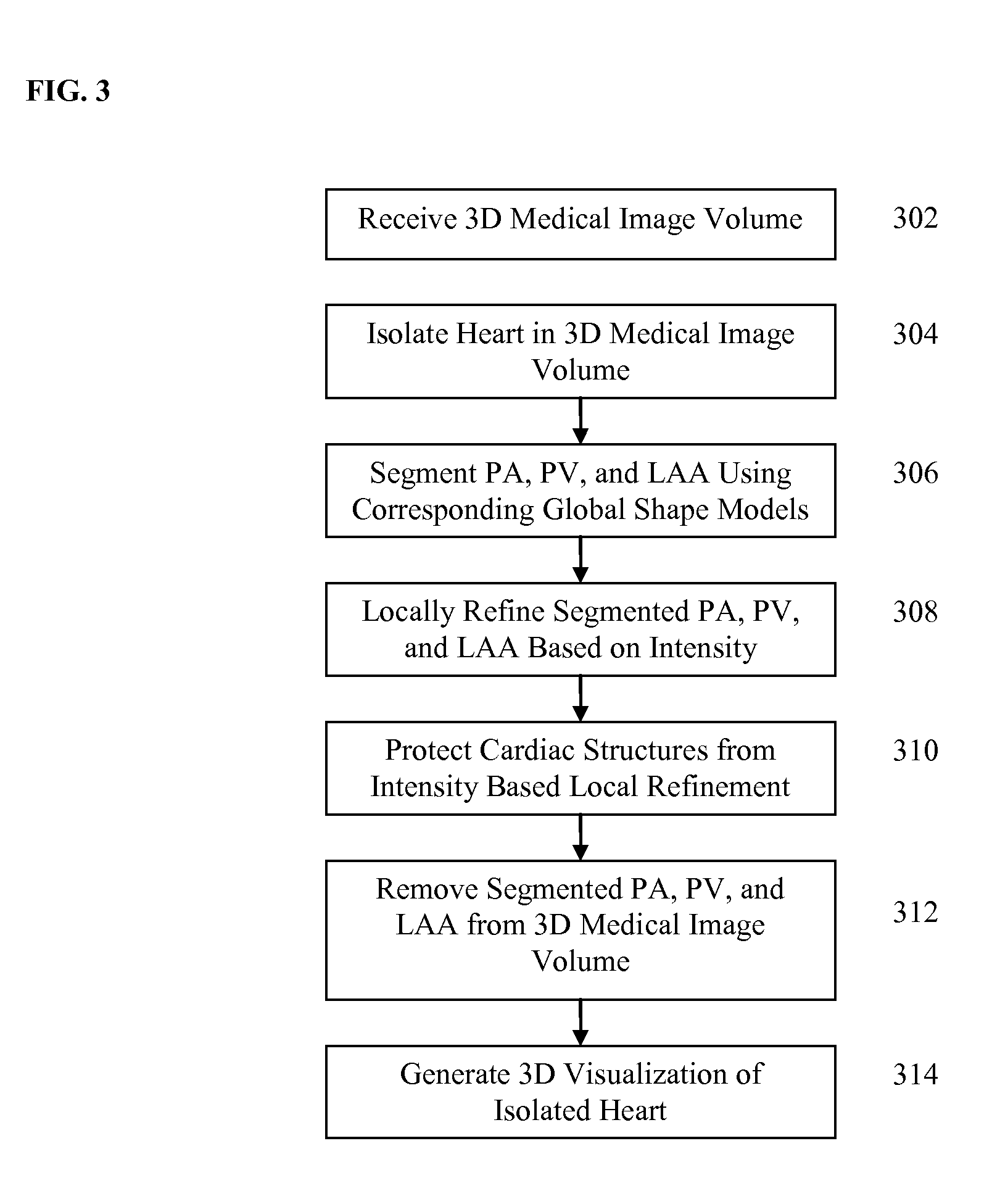
A method and system for segmentation and removal of pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and a left atrial appendage from 3D medical image data, such as 3D computed tomography (CT) volumes, is disclosed. A global shape model is segmented for each of pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and a left atrial appendage in a 3D volume. The segmented global shape model for each of the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and left atrial appendage is locally refined based in local voxel intensities in the 3D volume, resulting in a respective mask for each structure. The mask is used to remove voxels belonging to the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and left atrial appendage from the 3D volume in order to better visualize coronary arteries and bypass arteries.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
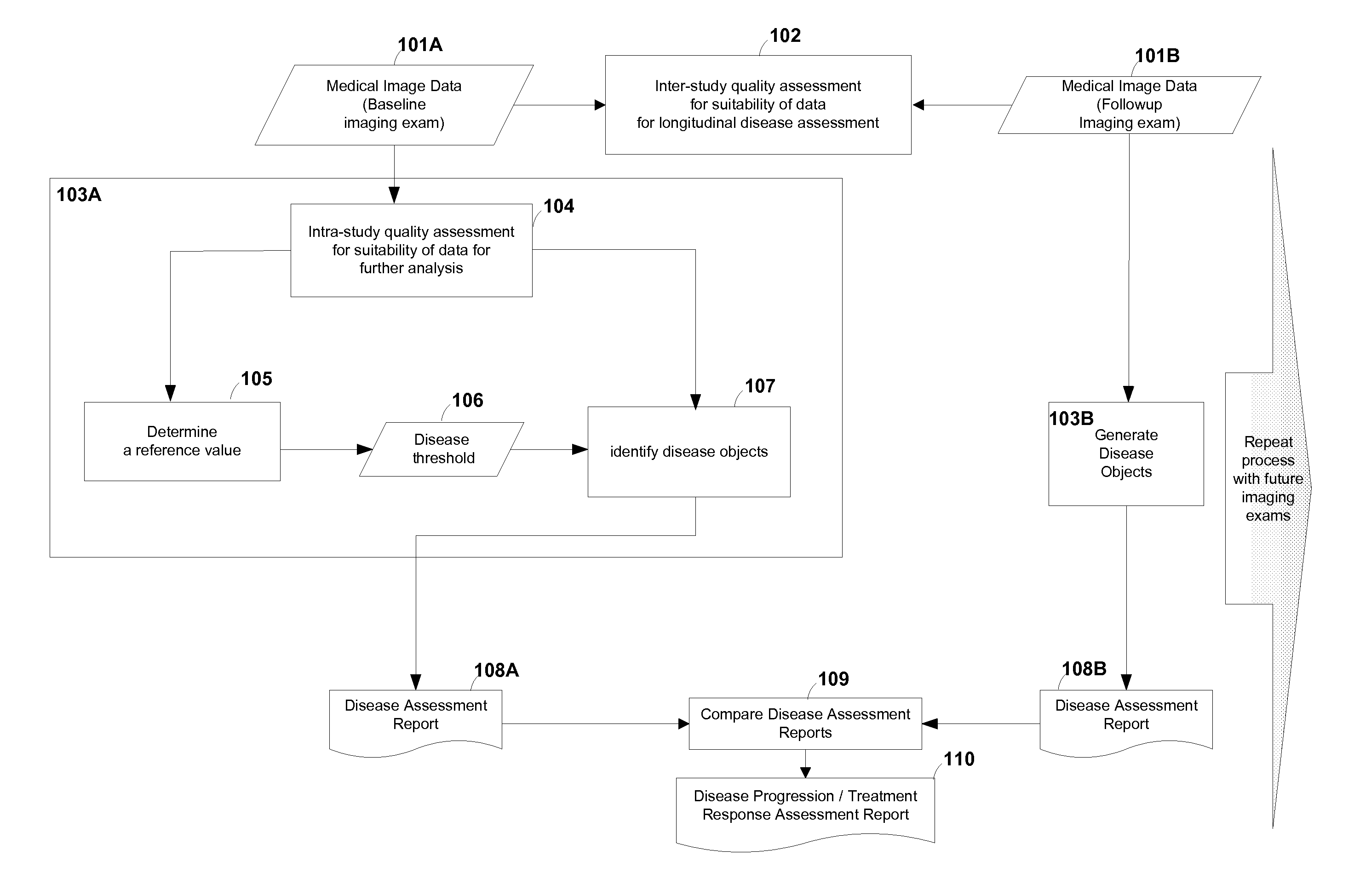
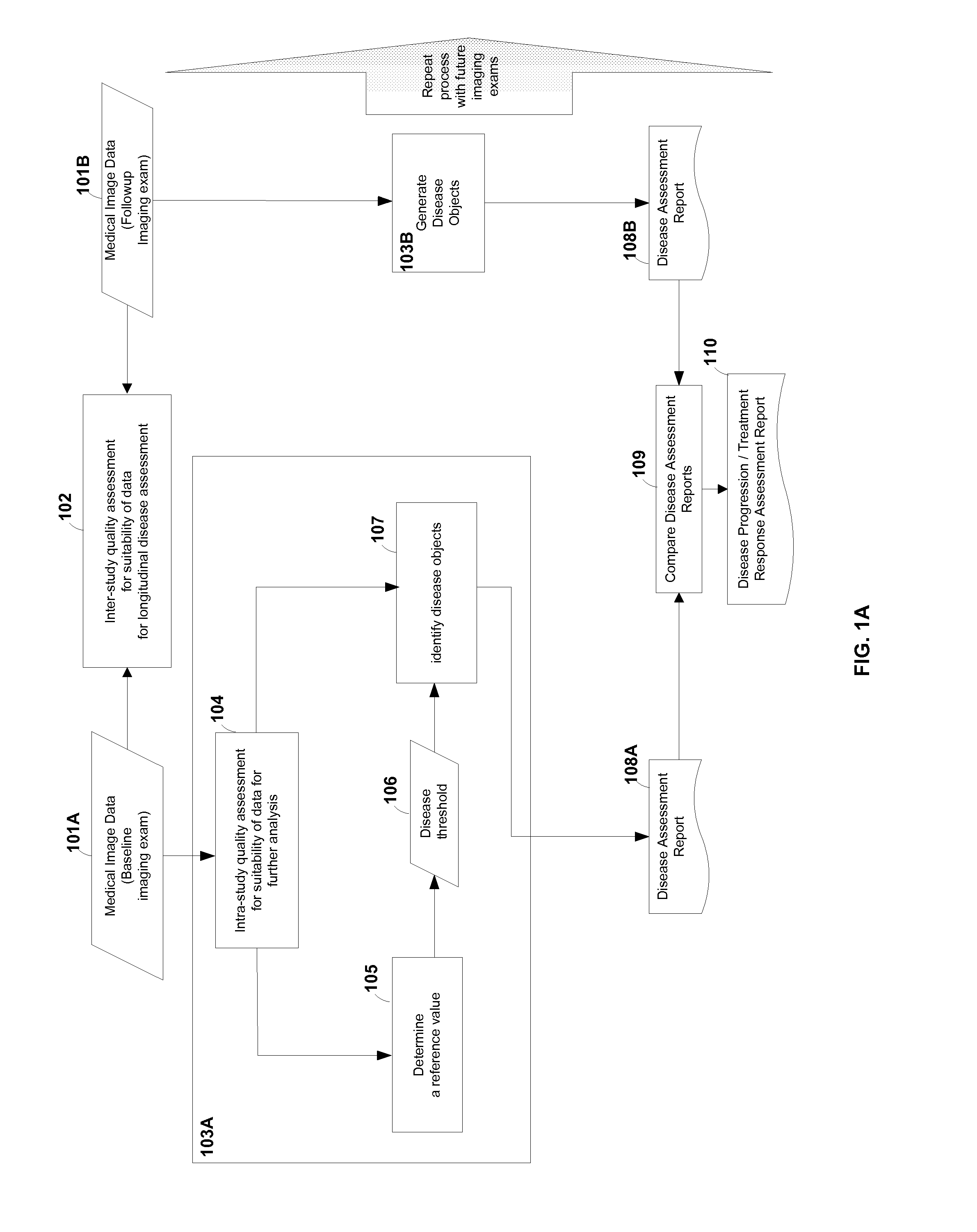
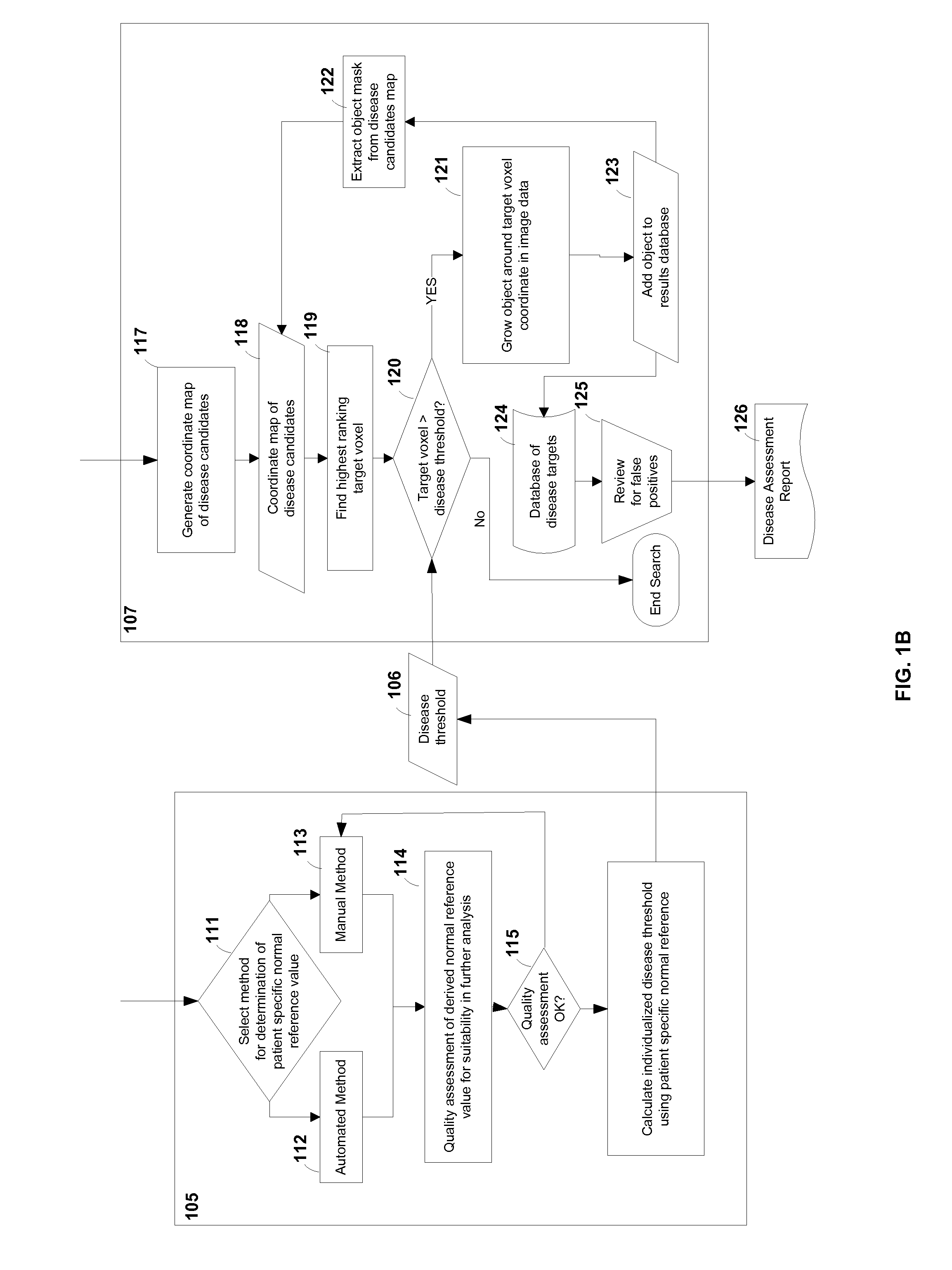
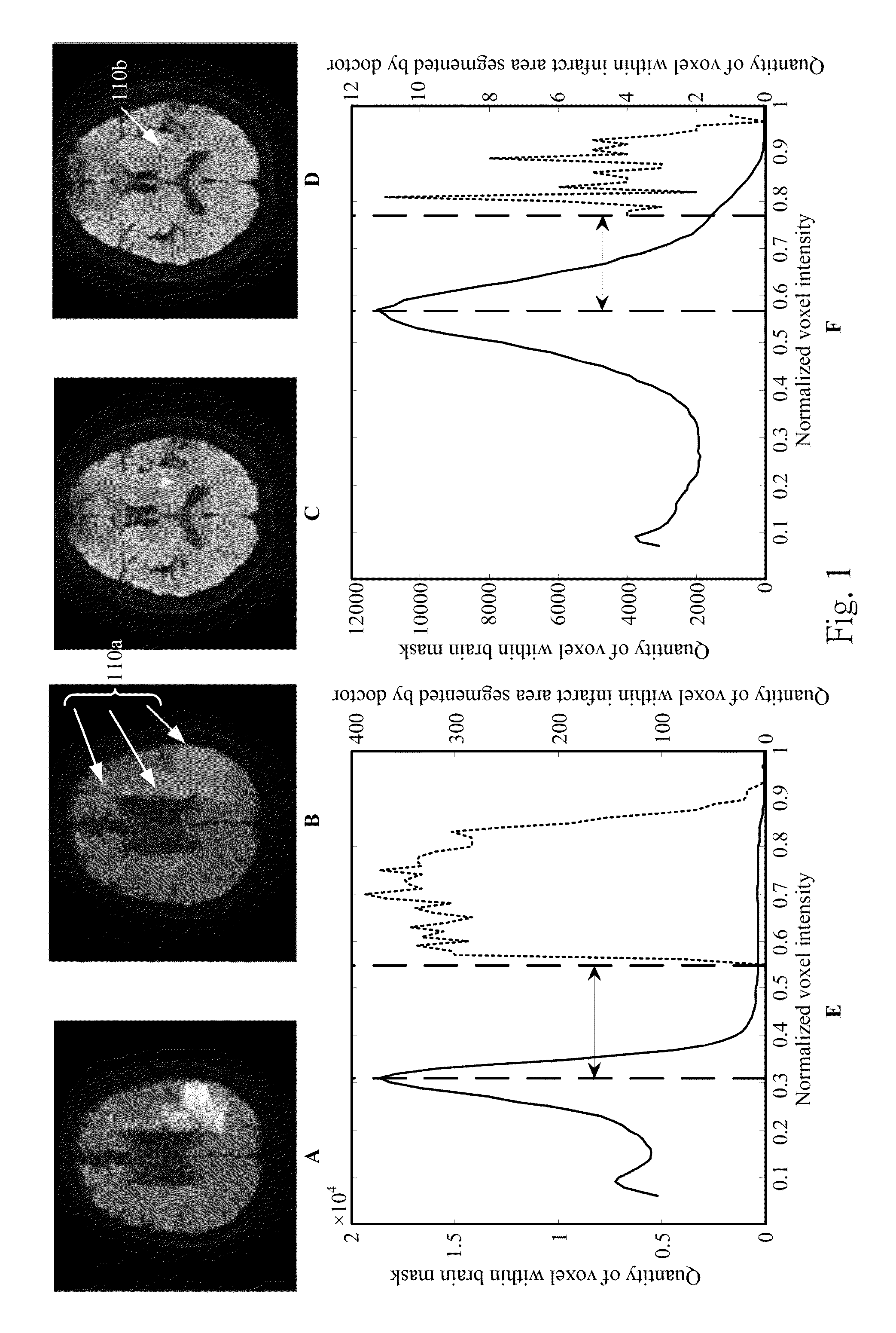
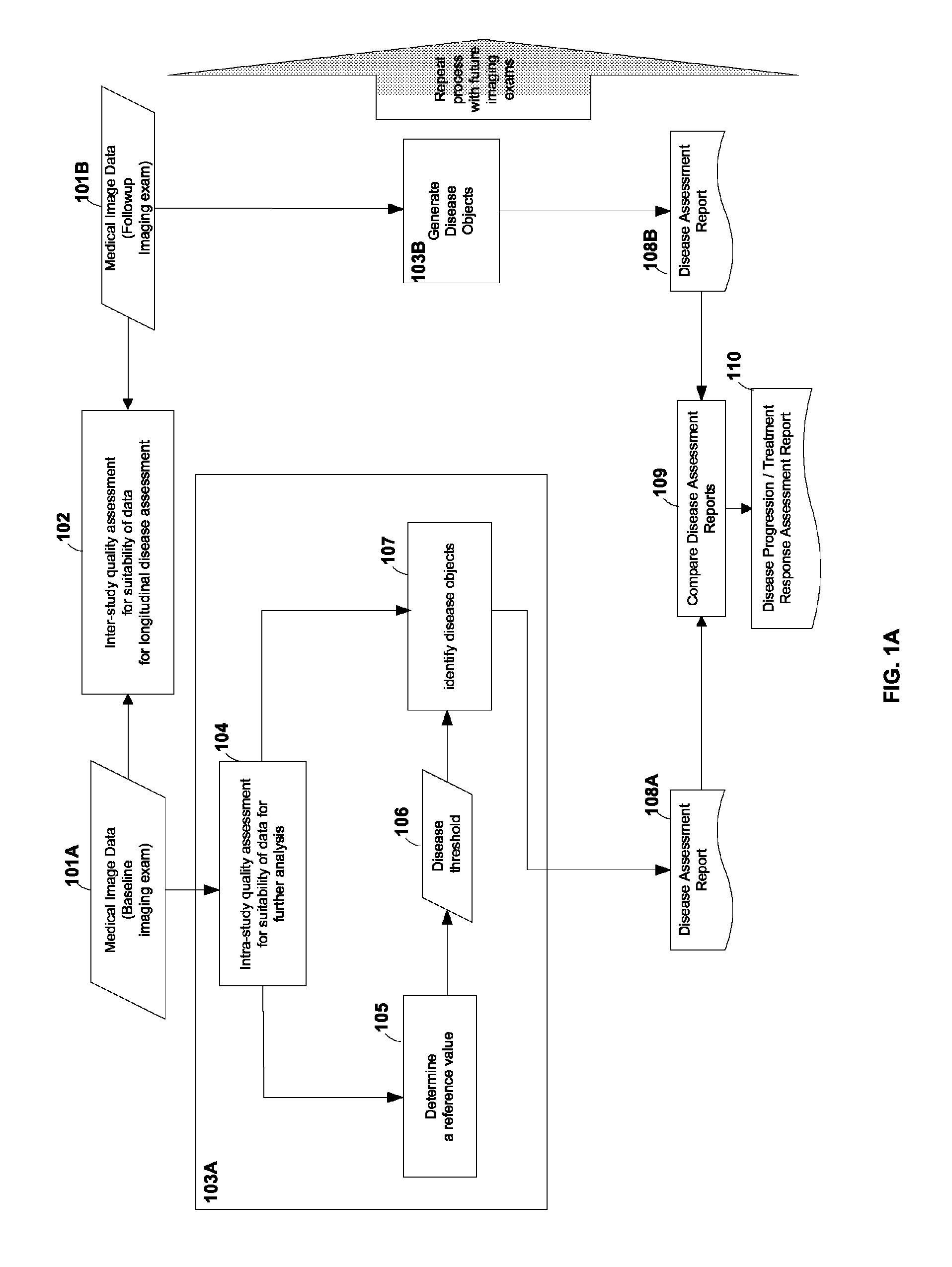
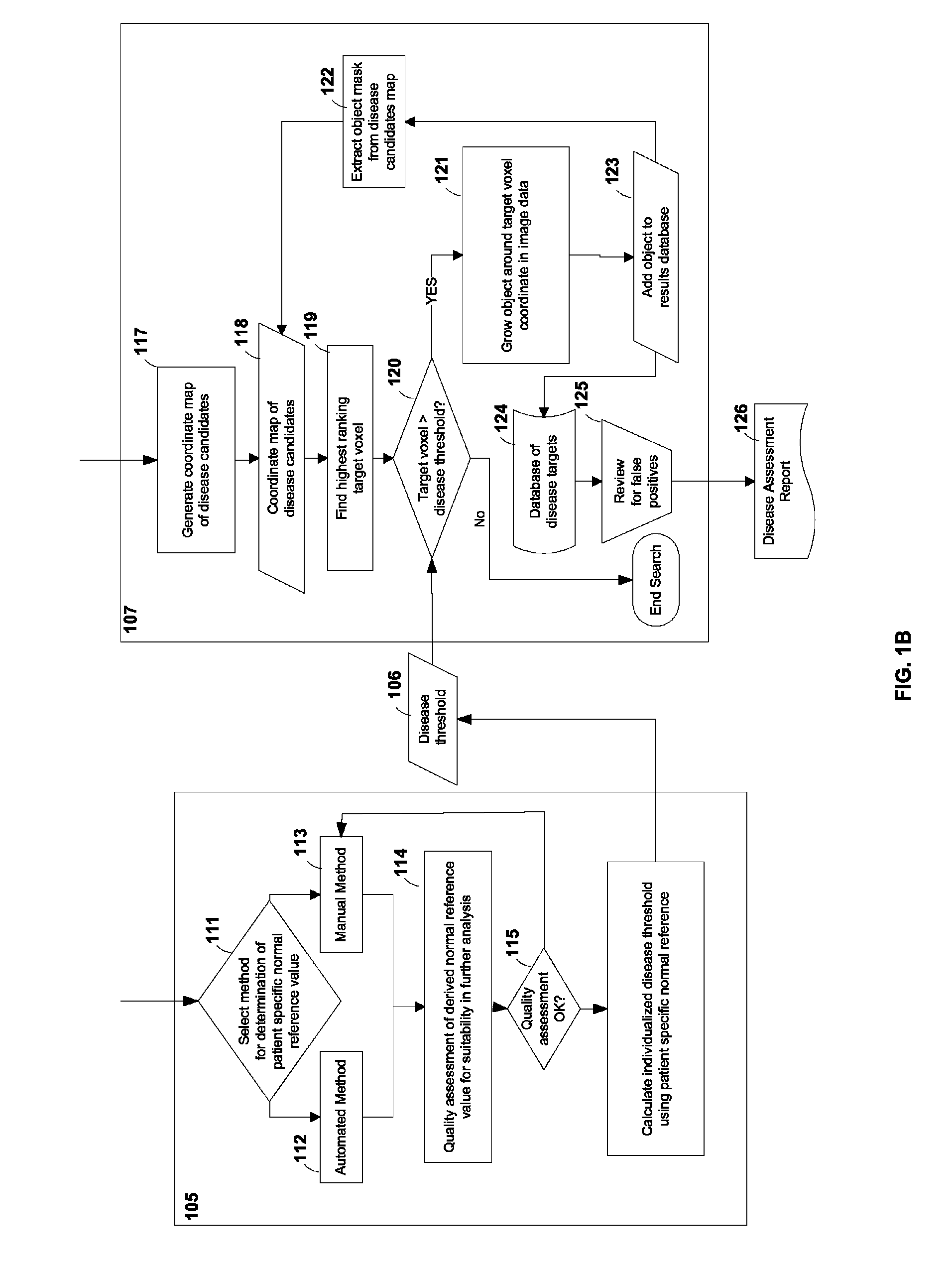
Computer-aided detection (CAD) system for personalized disease detection, assessment, and tracking, in medical imaging based on user selectable criteria
An embodiment of the current invention includes computer-implemented method for image processing. The method includes receiving a first medical image from a data storage device, the first medical image comprising a plurality of image voxels and representing a plurality of tissue regions of a subject; automatically determining a reference value based on the first medical image, the reference value capable of providing a range of background level of voxel intensity values within at least one non-disease tissue region of the subject; generating a disease threshold based on the reference value; identifying portions of the medical image corresponding to disease-tissue regions according to the disease threshold, each of the portions comprising a plurality of connected image voxels in the medical image; and entering data encoding the disease-tissue regions into a database for subsequent comparisons.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and method for calibration of CT scanners and display of images in density units without the use of water phantoms
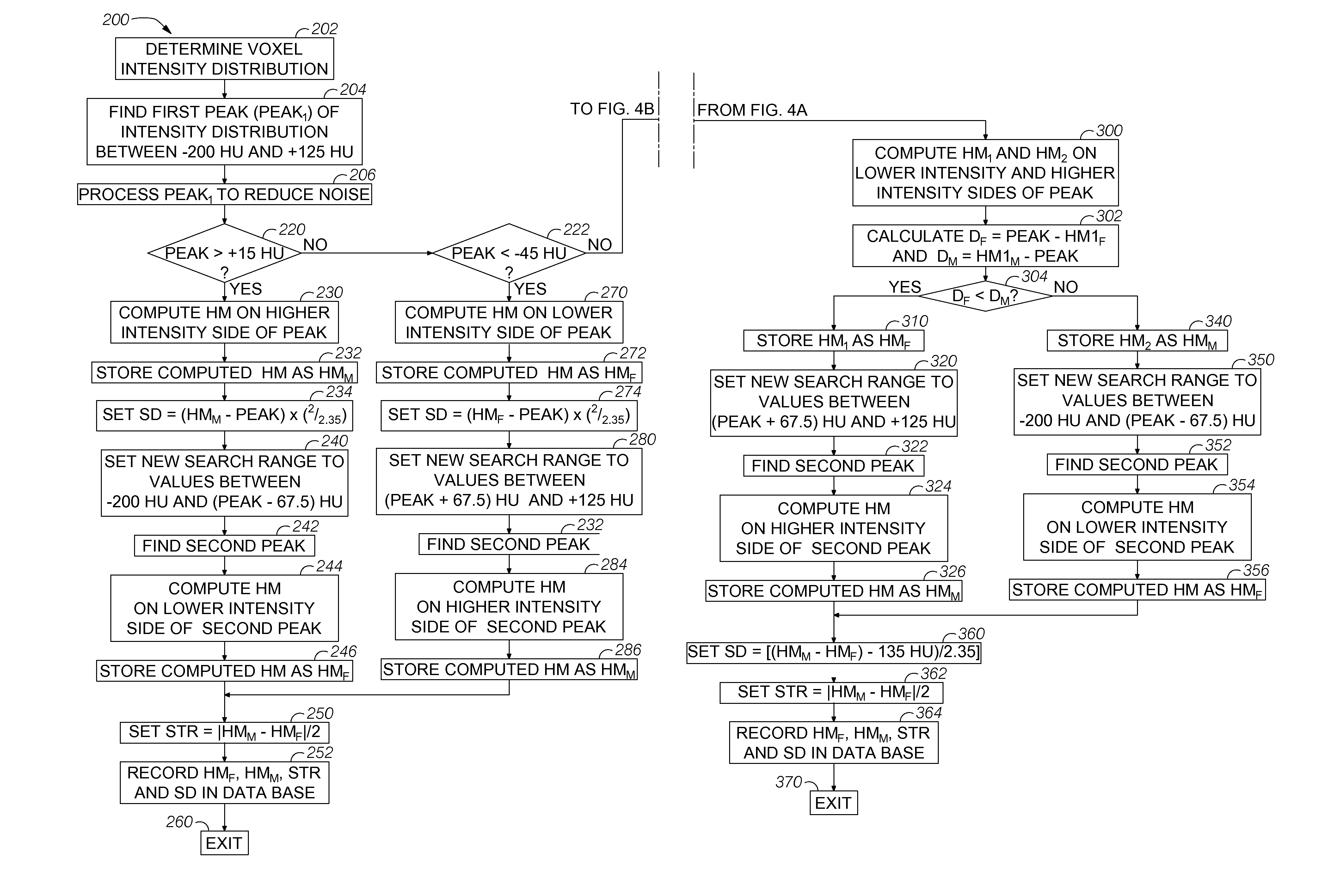
A system and method enable calibration of CT scanners without using water phantoms. Tissue densities are expressed in either the Hounsfield Scale units (HU) referenced back to water or the proposed Gram Scale units (GU) with voxel intensities expressed in true density units. The fully automatic software-only method requires no interactions with the images. Routine calibration of CT scanners with water phantoms can be eliminated. The method further provides accurate calibrations that are patient, scanner, and scan specific and are repeatable over long time durations. The calibrations are based on the uniquely defined intensity of voxels with equal contributions of two tissues types. This calibration point is immune to the many variables found in ROI histogram measurements of mean, mode, SD or other measures of voxel intensities. The disclosed CT scanner system provides consistent CT image voxel intensities of the various tissues across a great variety of patients.
Owner:ARNOLD BEN A
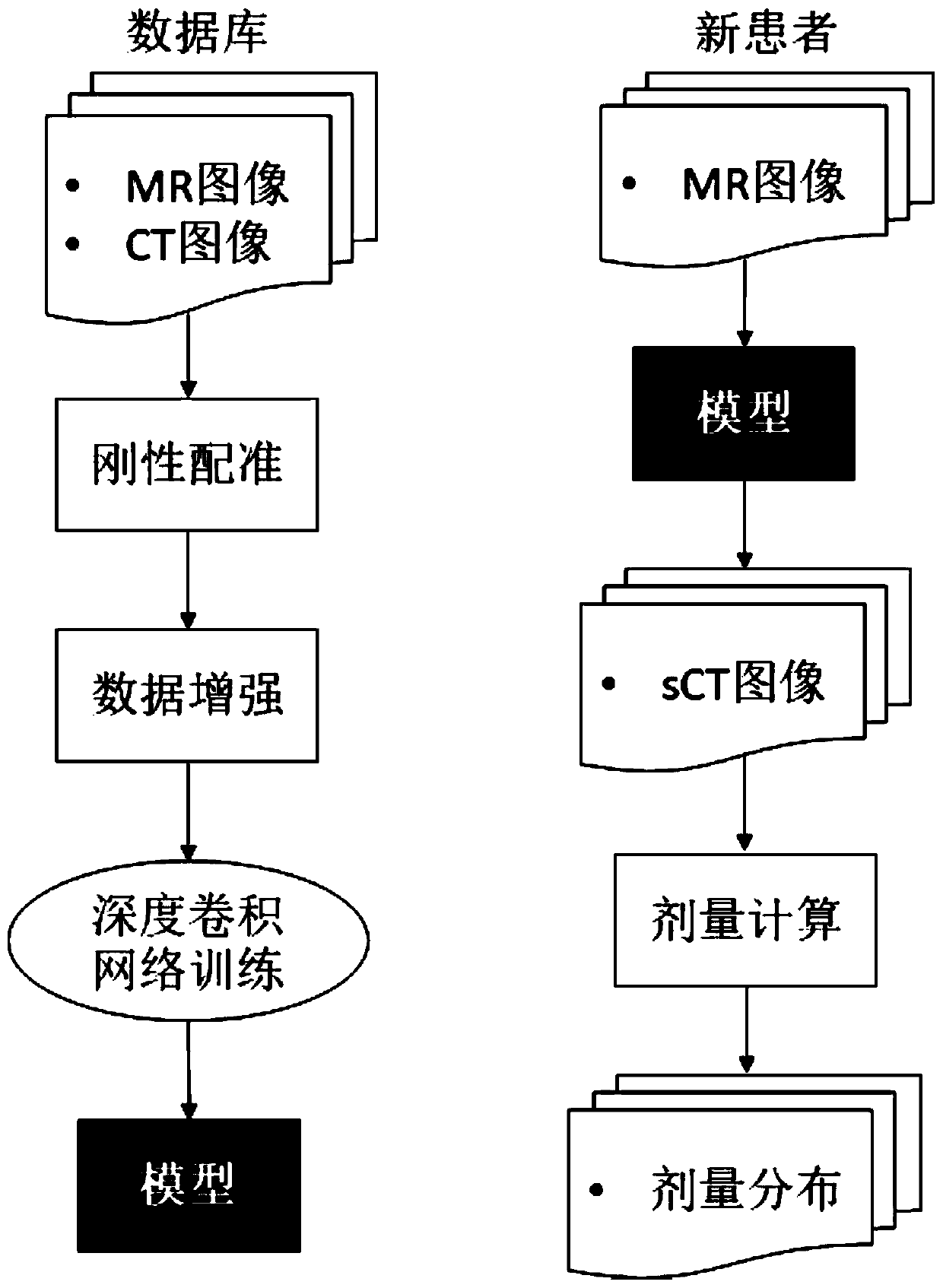
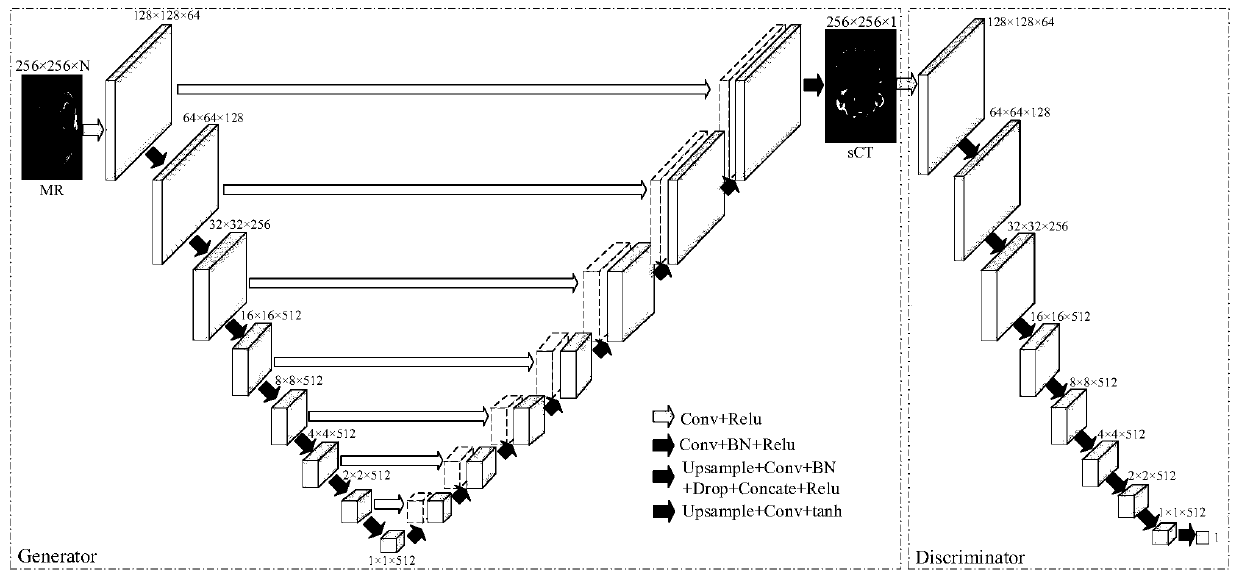
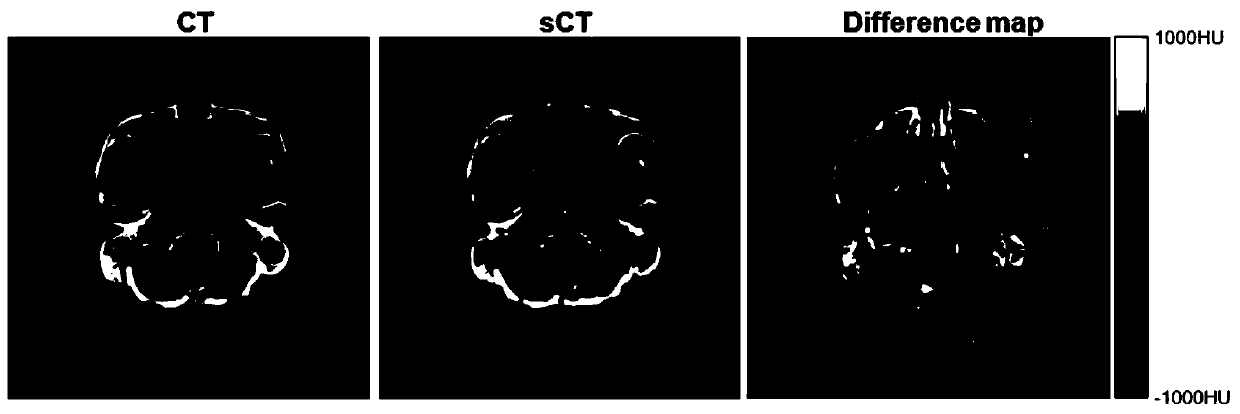
Pseudo CT synthesis method and application based on deep convolutional neural network
InactiveCN110464353AAchieve synthesisQuick buildComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringSynthesis methodsMri image
The invention relates to a pseudo CT synthesis method and application based on deep convolutional neural network. At present, a used model needs to extract features artificially, wherein the extractedfeatures directly affect the accuracy of pseudo CT prediction. The invention provides the pseudo CT synthesis method based on the deep convolutional neural network, wherein the pseudo CT synthesis method includes the steps: 1, collecting an MRI image, a CT image and radiotherapy plan information of a patient; 2, adjusting the voxel size of the MRI image to be consistent with the voxel size of theCT image, and then carrying out image registration on the MRI image and the CT image; 3, building a correlation model between the registered MRI image and the CT image by the deep convolutional neural network, and learning the mapping relationship between the MRI voxel intensity value and the CT gray value by the deep convolutional neural network; and 4, predicting a pseudo CT image of the patient by the correlation model. The synthetic pseudo CT is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Contrast enhancement methods and apparatuses
Image contrast enhancement includes (i) computing a contrast measure incorporating an adjustable tone transformation function and one or more statistical measures of selected spatial arrangements of pixel or voxel intensities in an analysis image or image portion, (ii) adjusting the adjustable tone transformation function to increase contrast as indicated by the contrast measure, and (iii) enhancing contrast of a target image or image portion using the adjusted tone transformation function.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for identification of a contrasted blood vessel in digital image data
InactiveCN1943515AReduced risk of missegmentationEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageCurrent threshold
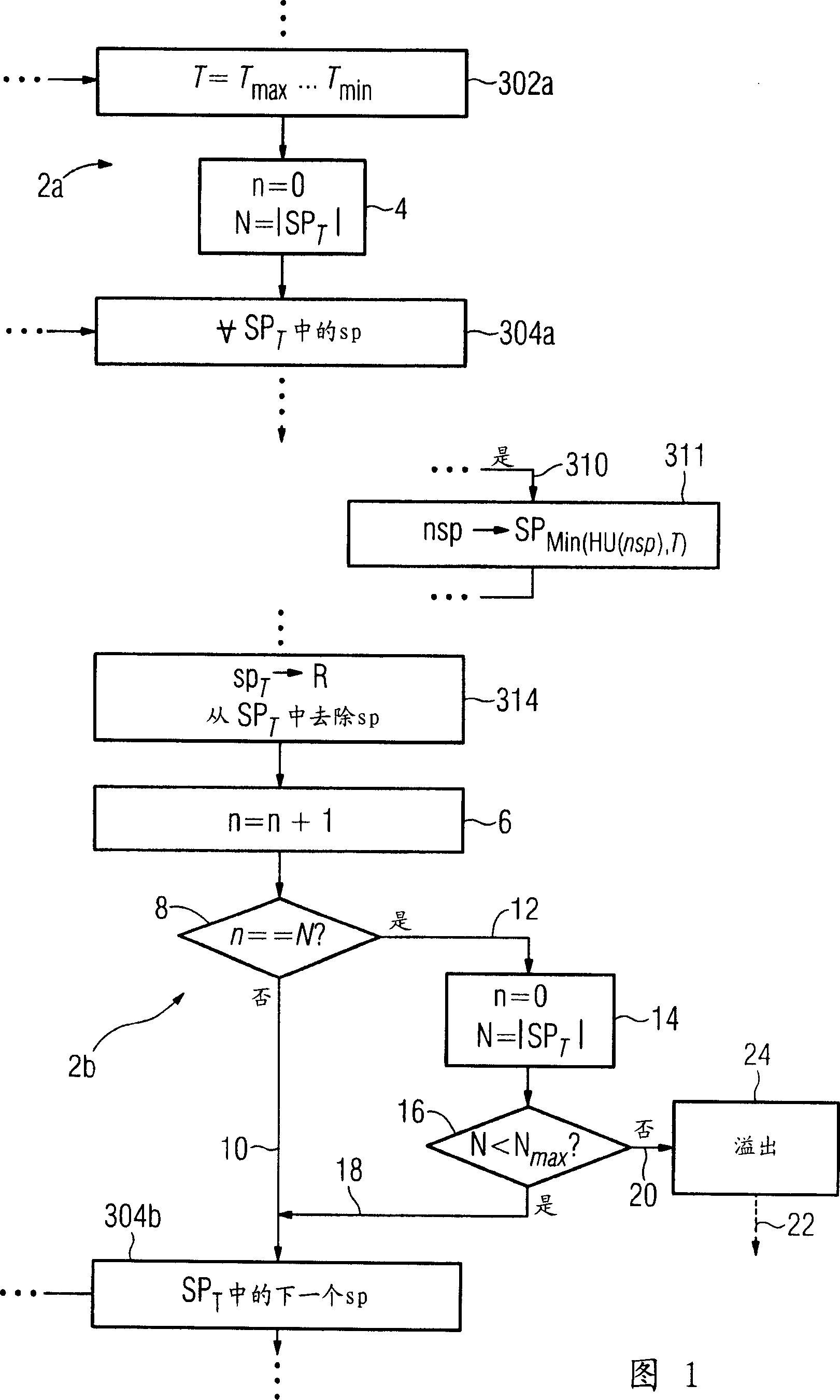
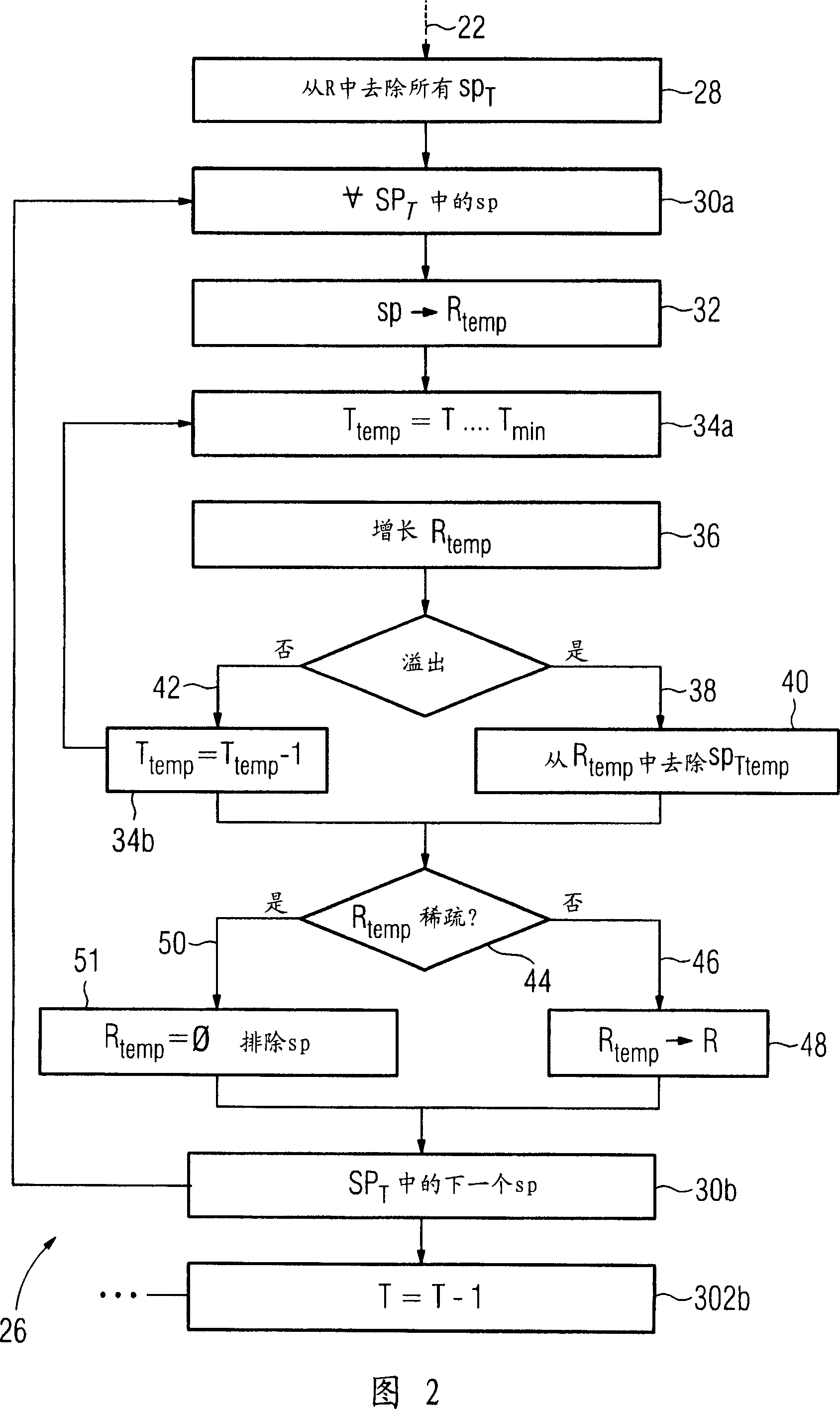
A method is disclosed for identification of a contrasted blood vessel in digital 3D image data. The method includes: a) one image voxel, which is associated with the blood vessel, in the 3D image data is selected as a seed point, b) a current threshold value for the intensity of image voxels is selected as the intensity of the seed point, and the seed point is associated with the threshold value, c) a test criterion for finding new seed points is used to search for new seed points in the image voxels which are adjacent to the seed point, and are associated with specific threshold values as a function of their intensities and the current threshold value, d) step c) is repeated until no further seed points can be found with the current threshold value, e) the seed points which have been found are stored as vessel voxels associated with that blood vessel, and are associated with the current threshold value, f) the current threshold value is reduced, g) steps c) to f) are repeated until a termination criterion is satisfied, h) the blood vessel is identified as the set of all vessel voxels in the image data, in which prior knowledge exists, on the basis of which a corresponding method step specifically linked to the blood vessel to be identified can lead to incorrect identification, and at least one of the method steps a) to h) is modified or extended, taking into account the prior knowledge.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
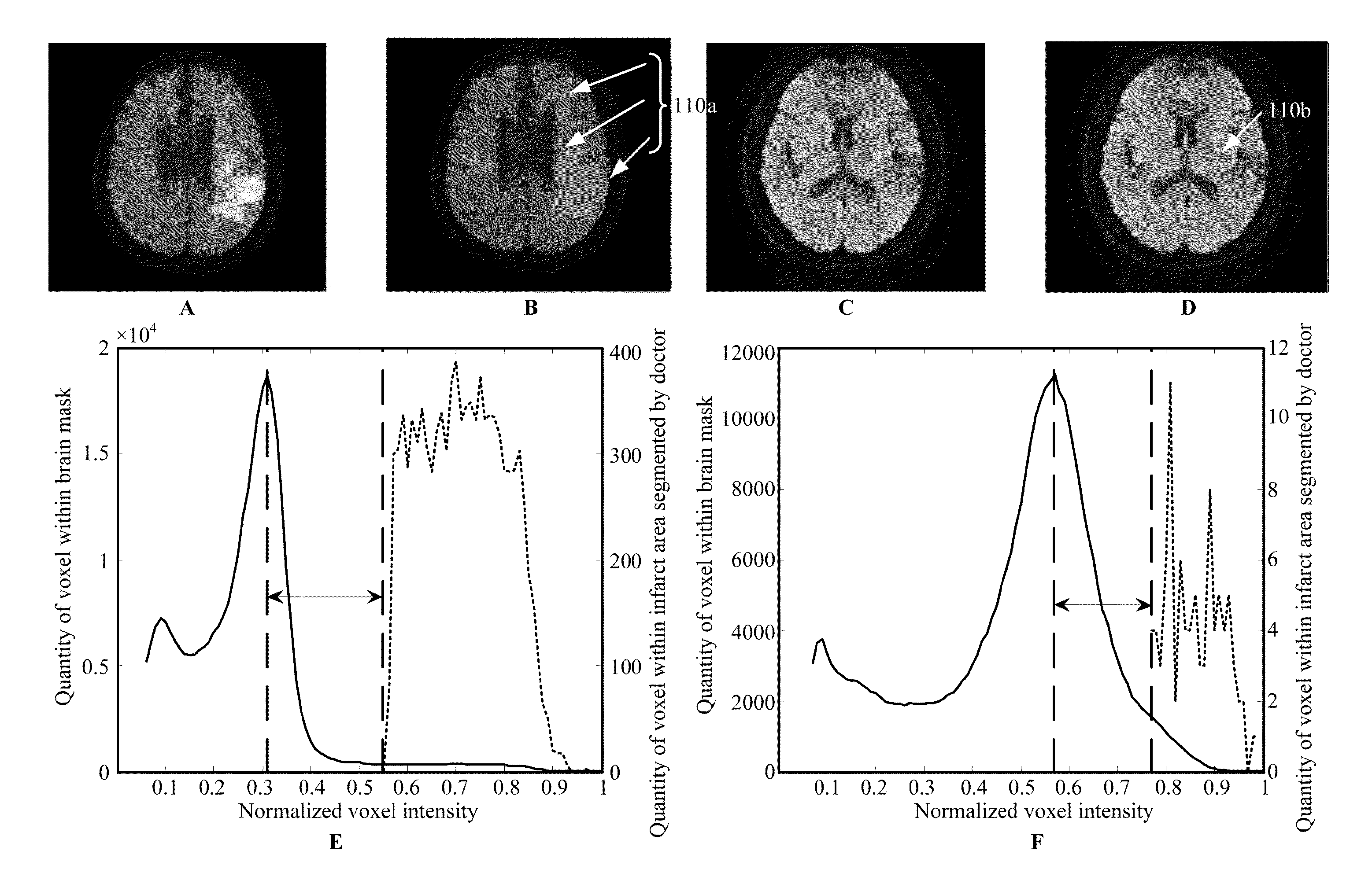
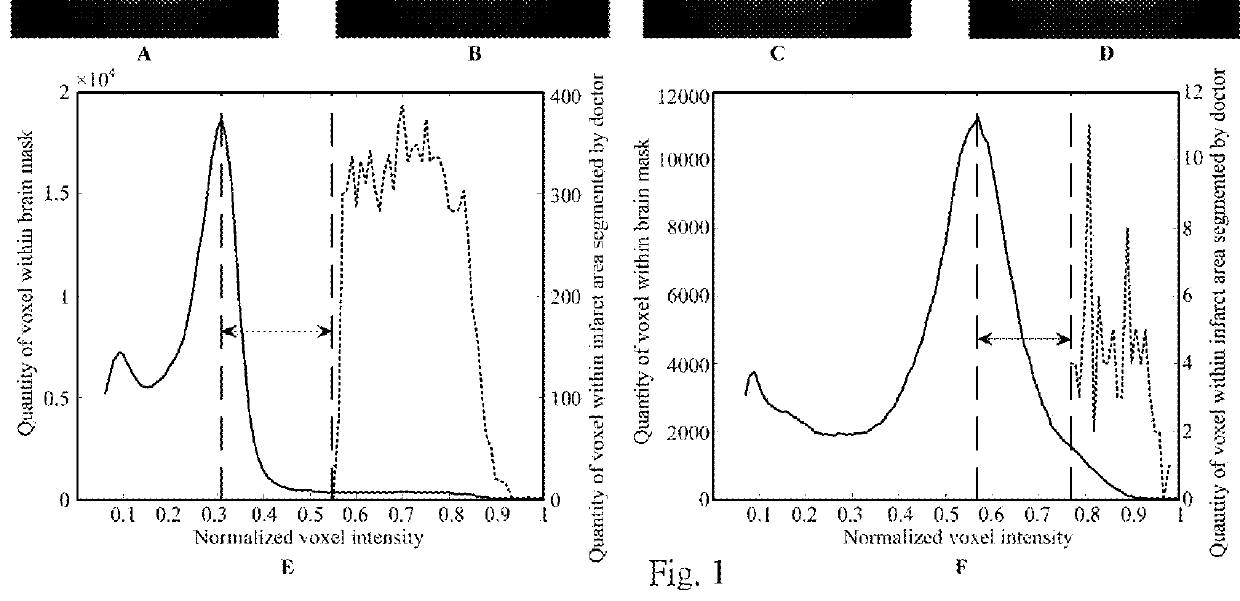
Method for detecting and quantifying cerebral infarct
A method for detecting a cerebral infarct includes receiving an image of a brain of a subject from a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, wherein the image has a plurality of voxels, and each of the voxels has a voxel intensity. Then, the voxel intensities are normalized, wherein the normalized voxel intensities have a distribution peak, and the normalized voxel intensity of the distribution peak is Ipeak. A threshold is determined, which is the Ipeak+ a value. Voxel having the normalized voxel intensity larger than the threshold is selected, wherein the selected voxel is the cerebral infarct. A method for quantifying the cerebral infarct is also provided.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV +1
Computer-aided detection (CAD) system for personalized disease detection, assessment, and tracking, in medical imaging based on user selectable criteria
An embodiment of the current invention includes computer-implemented method for image processing. The method includes receiving a first medical image from a data storage device, the first medical image comprising a plurality of image voxels and representing a plurality of tissue regions of a subject; automatically determining a reference value based on the first medical image, the reference value capable of providing a range of background level of voxel intensity values within at least one non-disease tissue region of the subject; generating a disease threshold based on the reference value; identifying portions of the medical image corresponding to disease-tissue regions according to the disease threshold, each of the portions comprising a plurality of connected image voxels in the medical image; and entering data encoding the disease-tissue regions into a database for subsequent comparisons.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Computer aided diagnostic method and device
ActiveUS20130012805A1Better contrast resolutionSuppress artifactsMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer aided diagnosticsMr diffusion
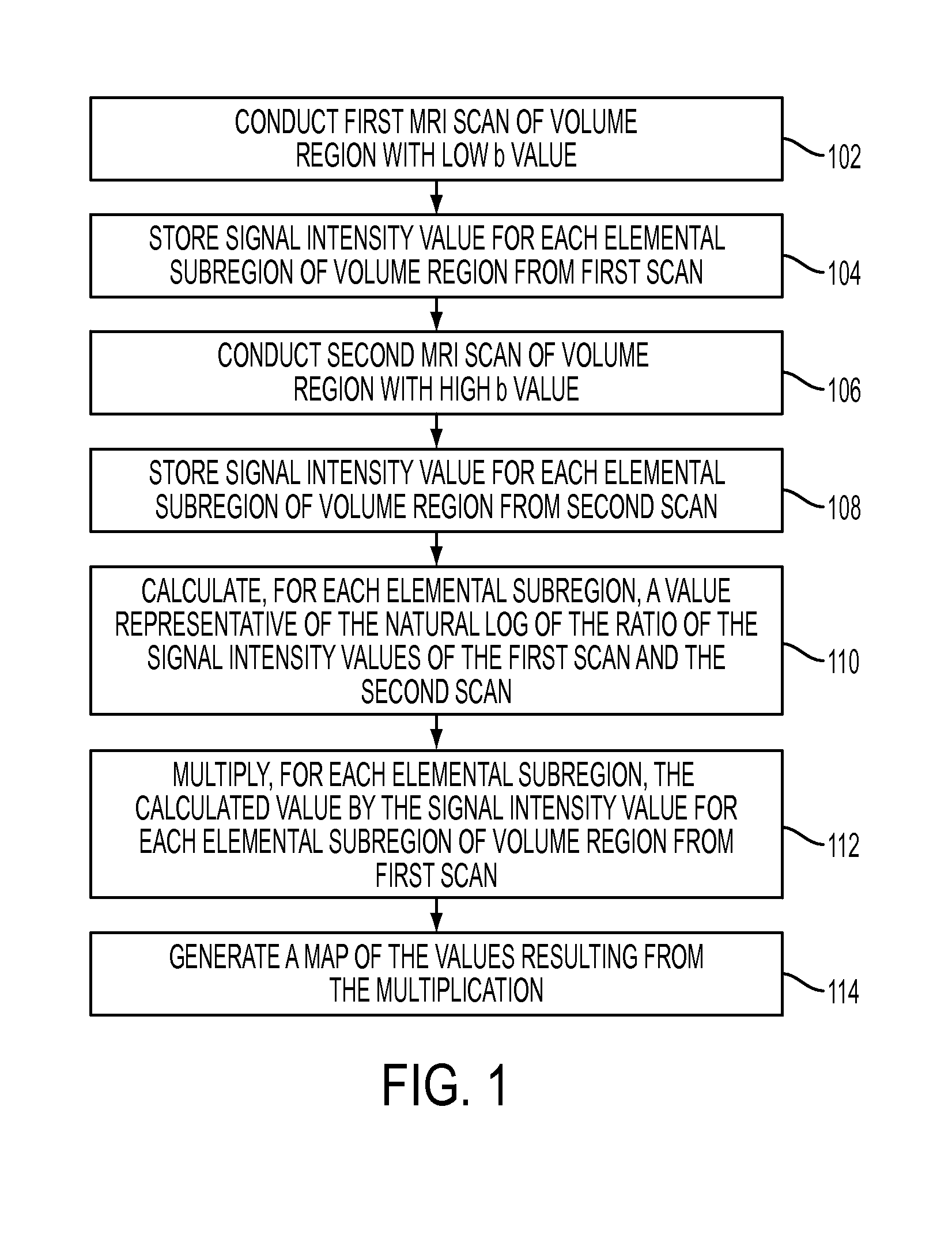
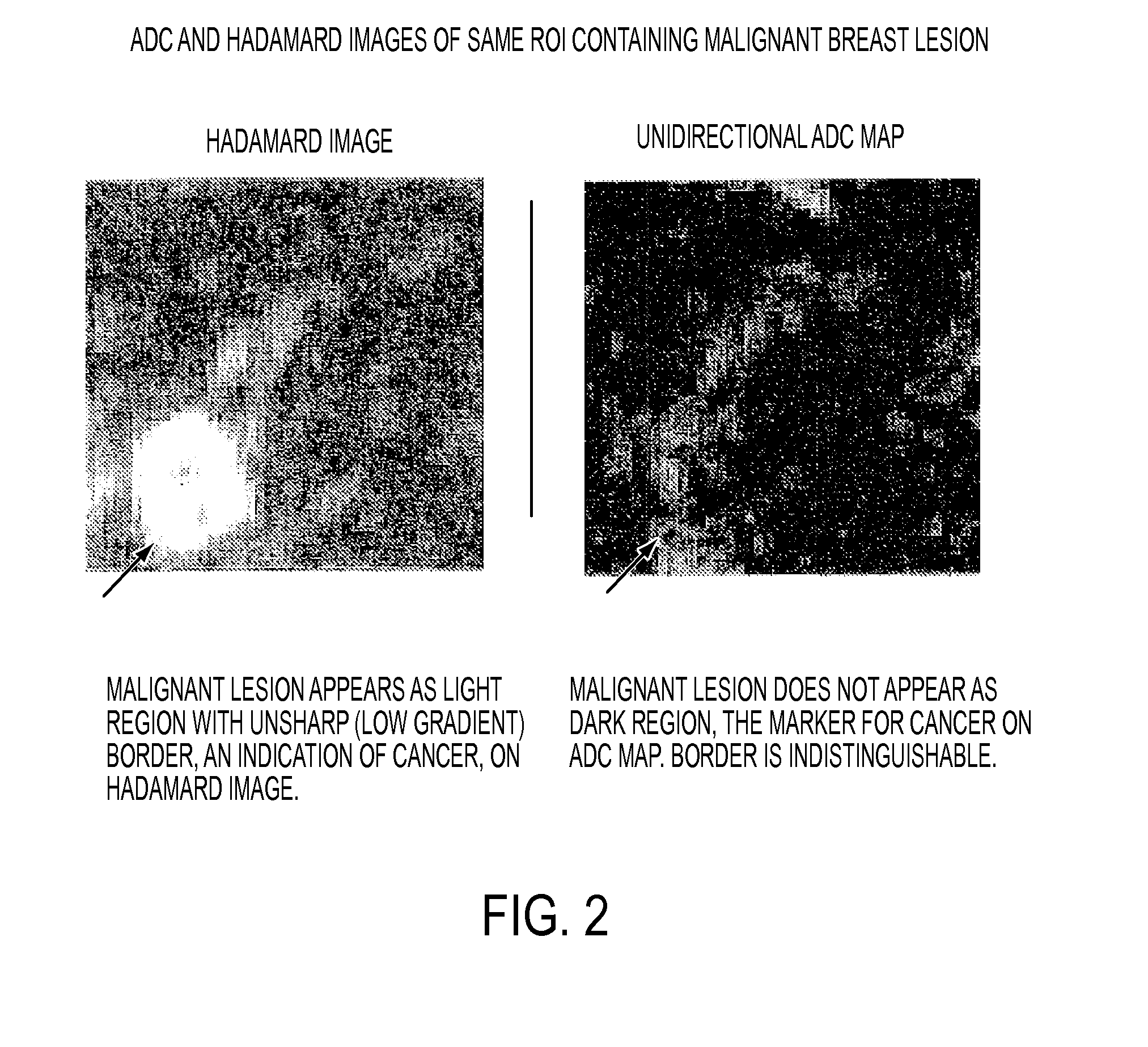
A method for generating a map of a region of a patient's body containing one or more lesions that provides information about MR diffusion properties and / or level of suspicion of malignancy. Performing at least one first scan of the region with an MRI apparatus set to a first b value to obtain a first matrix of pixel or voxel values, int(B1); performing at least one second scan of the region with the apparatus set to a second b value to obtain a second matrix of pixel or voxel intensity values, int(B2); deriving a first computed value that is a monotonic function of ln(int(B1) / int(B2); multiplying each computed value by a value proportional to int (B1) to obtain a second computed value; and producing a representation of all the second computed values that is indicative of the likelihood that one or more of the lesions are malignant.
Owner:PENN ALAN
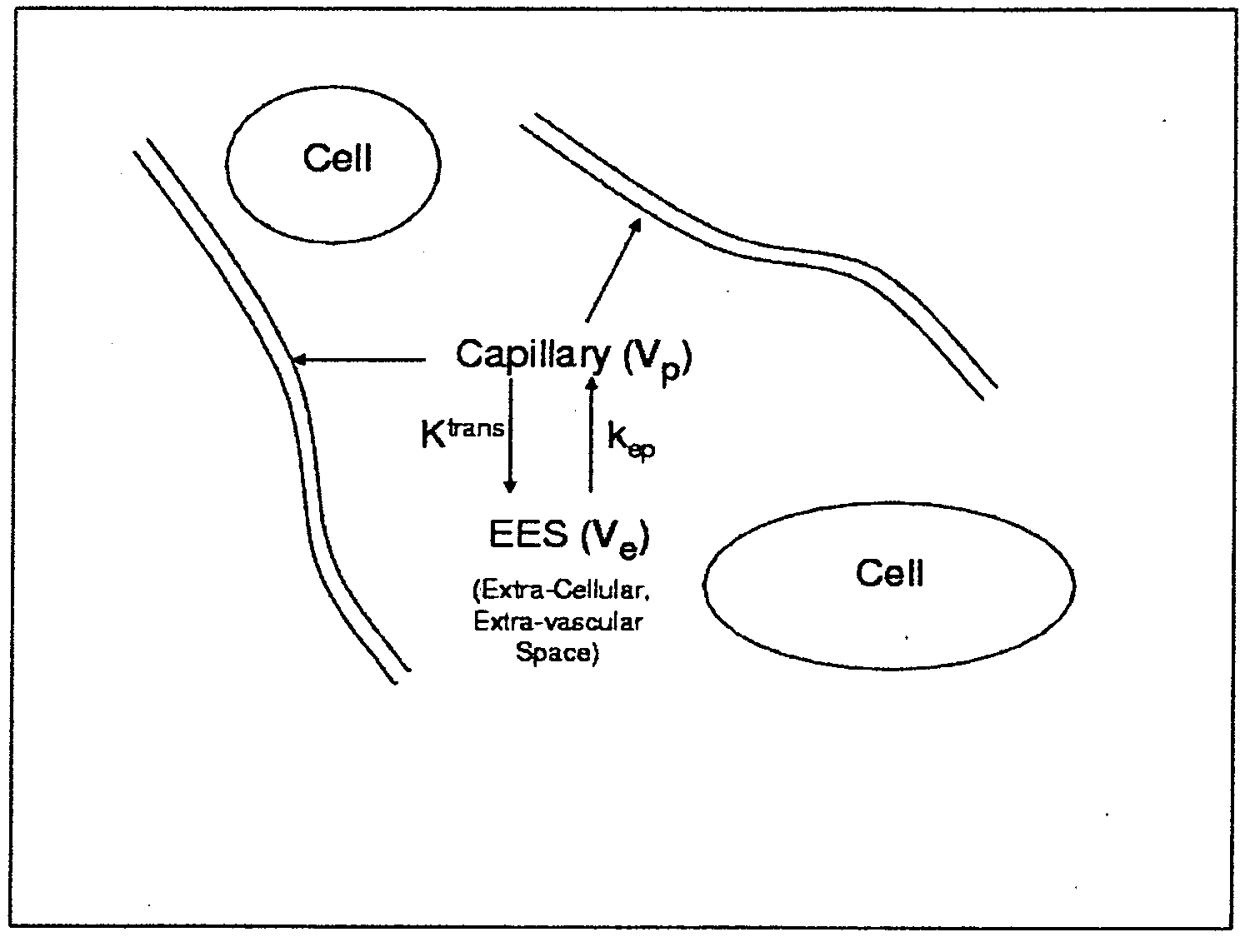
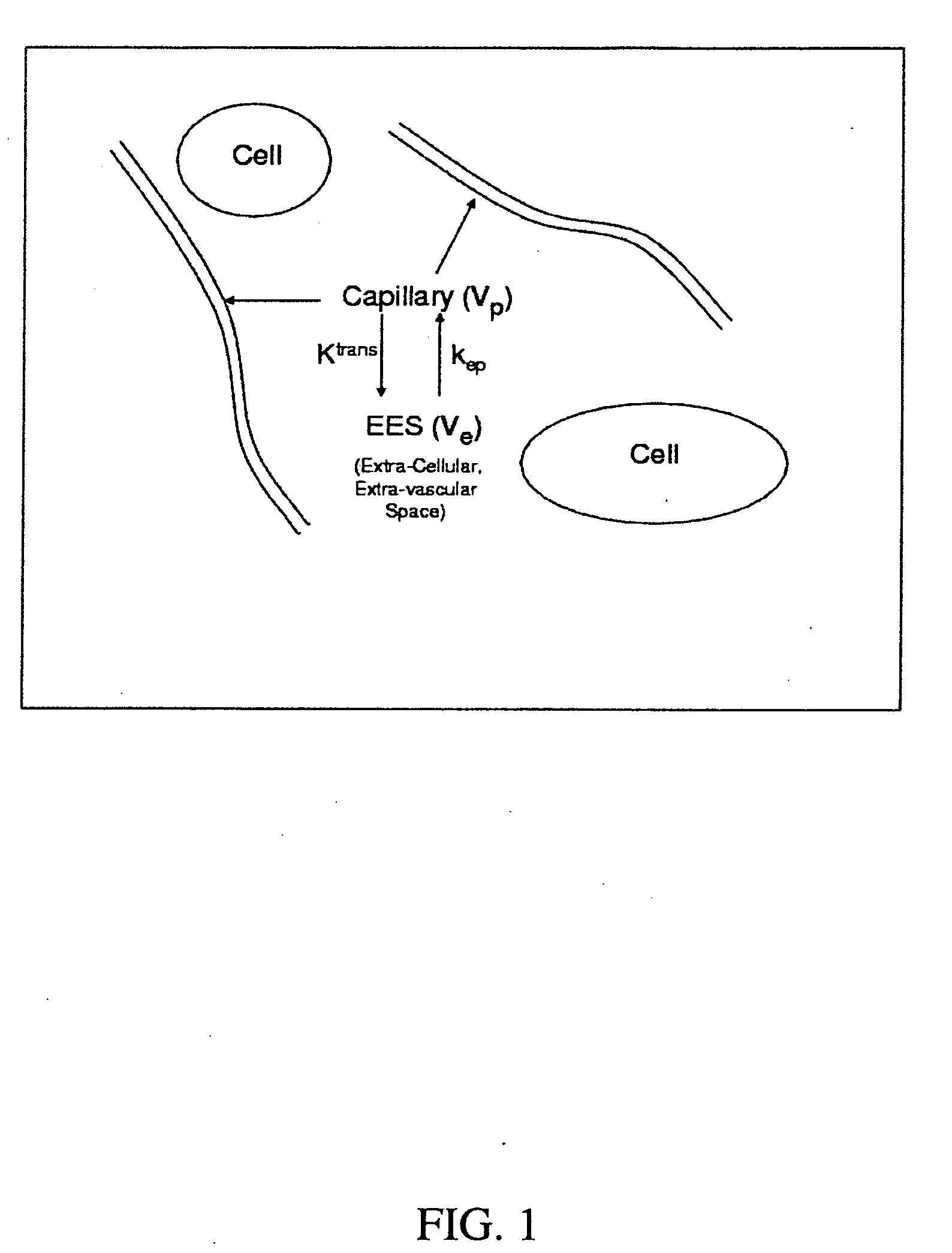
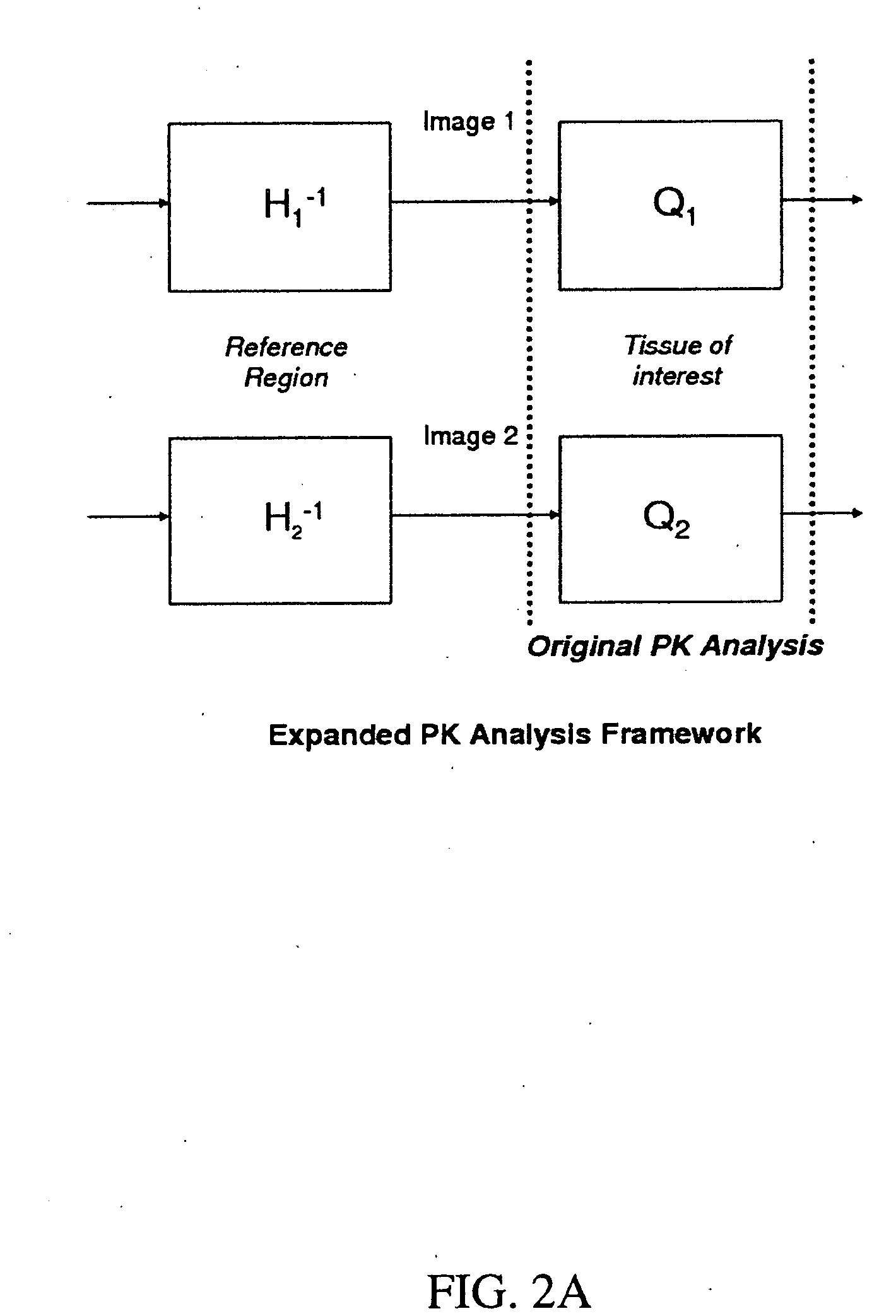
Expanded Pharmacokinetic Model for Population Studies in Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A method for pharmacokinetic analysis, including: receiving time-series medical image data of a patient introduced with a contrast agent; identifying a reference region in the medical image data; identifying a plurality of points of interest in the medical image data; measuring an intensity of voxels in the reference region; and for each point of interest, measure an intensity of voxels therein, use the measured reference region and point of interest intensities to obtain an expression relating the point of interest's voxel concentration to that of the reference region, wherein the expression is a five-parameter nonlinear model with no reference to an arterial input function; and obtain values for each of the five-parameters by solving the expression and use the obtained values to determine whether the point of interest is malignant.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
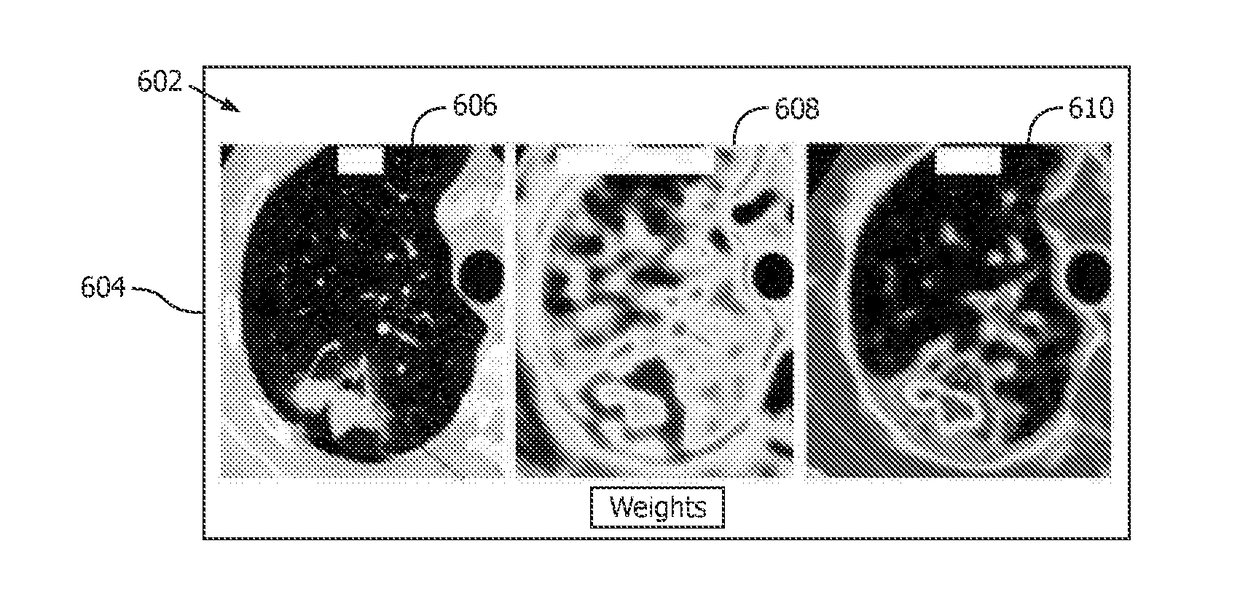
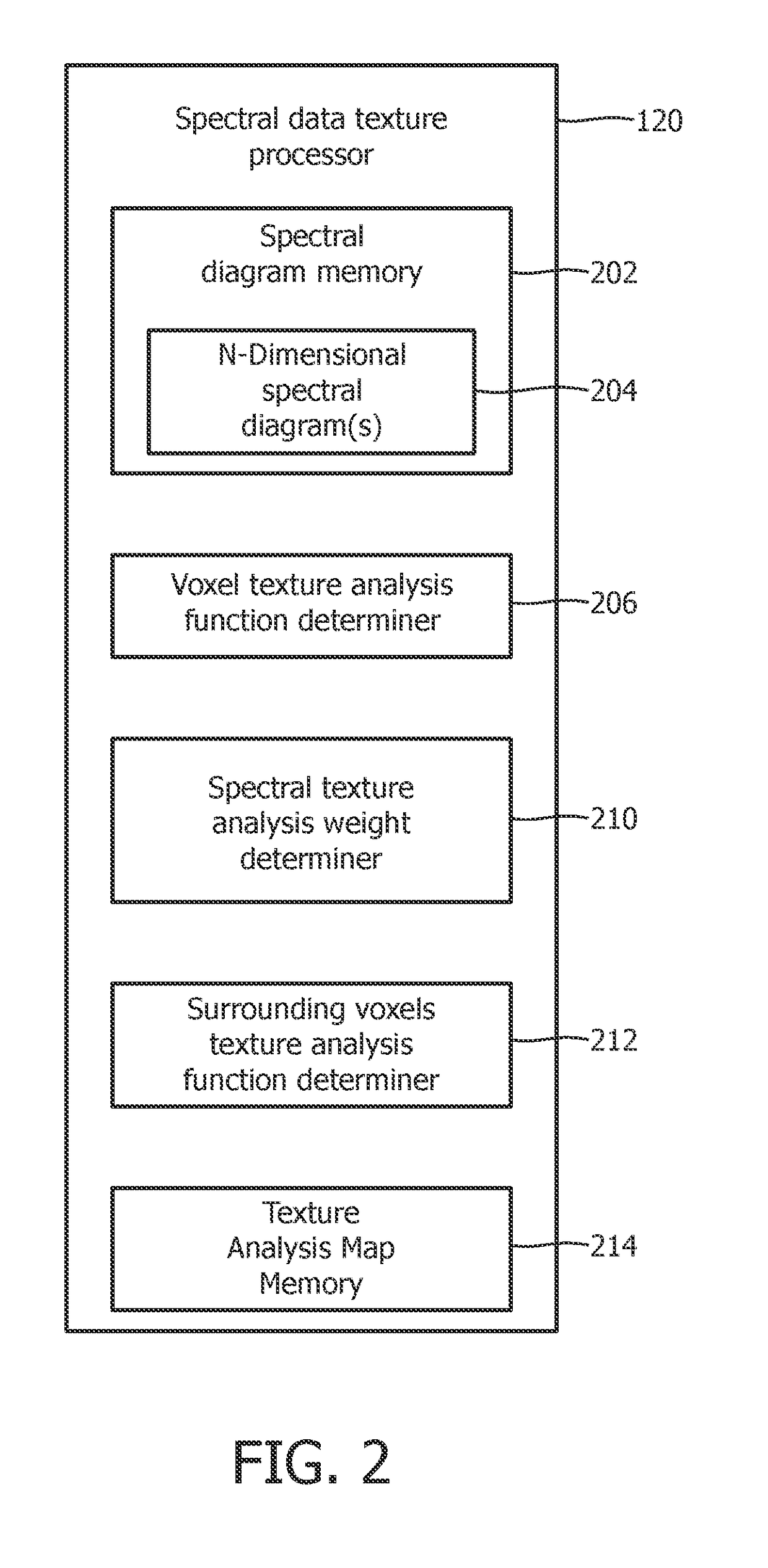
Texture analysis map for image data
ActiveUS20170243364A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionMulti dimensionalEnergy dependent
A method includes obtaining at least a first energy dependent spectral image volume and a second different energy dependent spectral image volume from reconstructed spectral image data. The method further includes generating a multi-dimensional spectral diagram that maps, for each voxel, a value of the first energy dependent spectral image volume to a corresponding value of the second energy dependent spectral image volume. The method further includes generating a set of spectral texture analysis weights from the multi-dimensional spectral diagram. The method further includes retrieving a set of texture analysis functions, which are generated as a function of voxel intensity and voxel gradient value from a co-occurrence matrix histogram. The method further includes generating a texture analysis map through a texture analysis of the reconstructed spectral image data with the set of texture analysis functions and the set of spectral texture analysis weights and visually presenting the texture analysis map.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
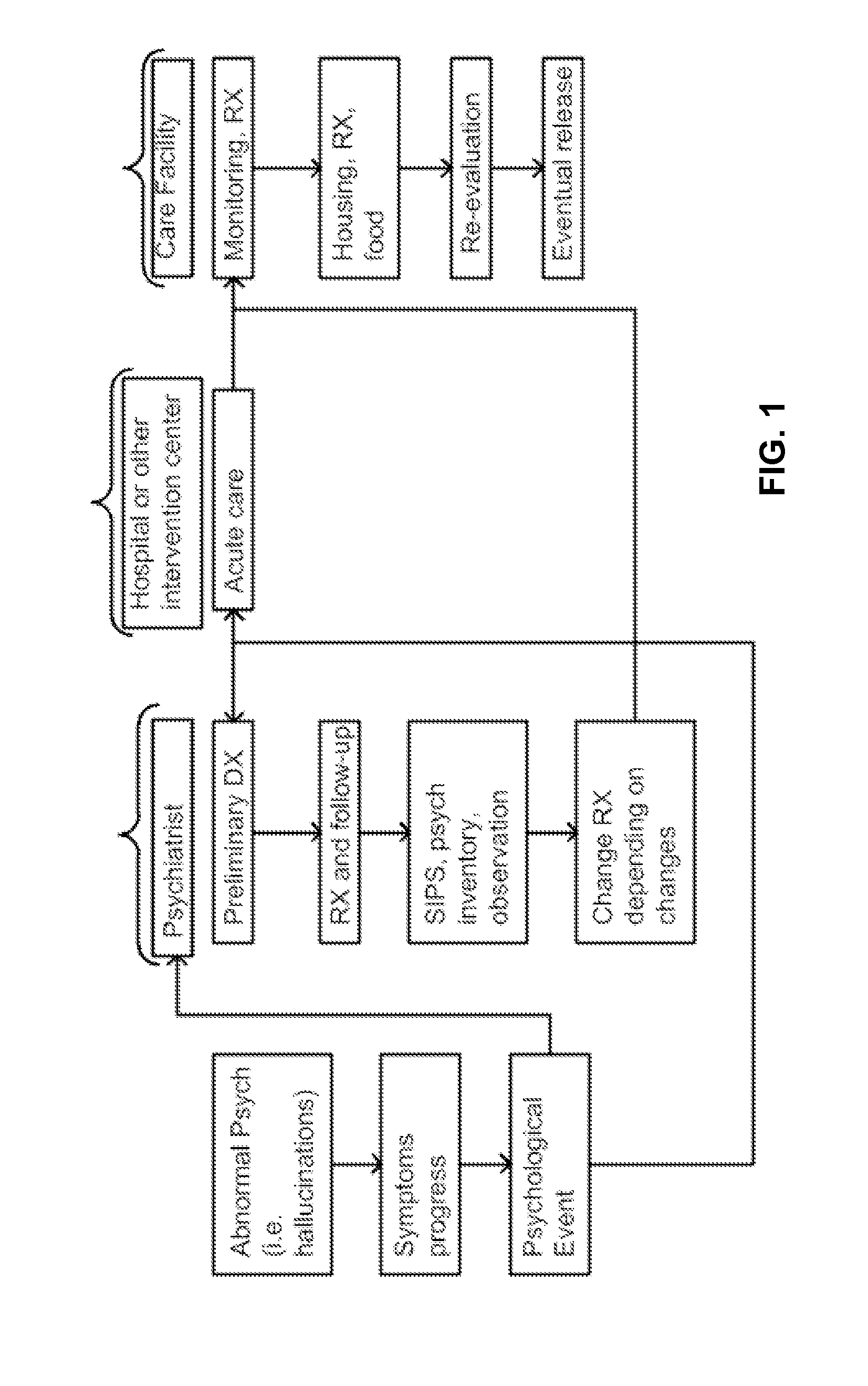
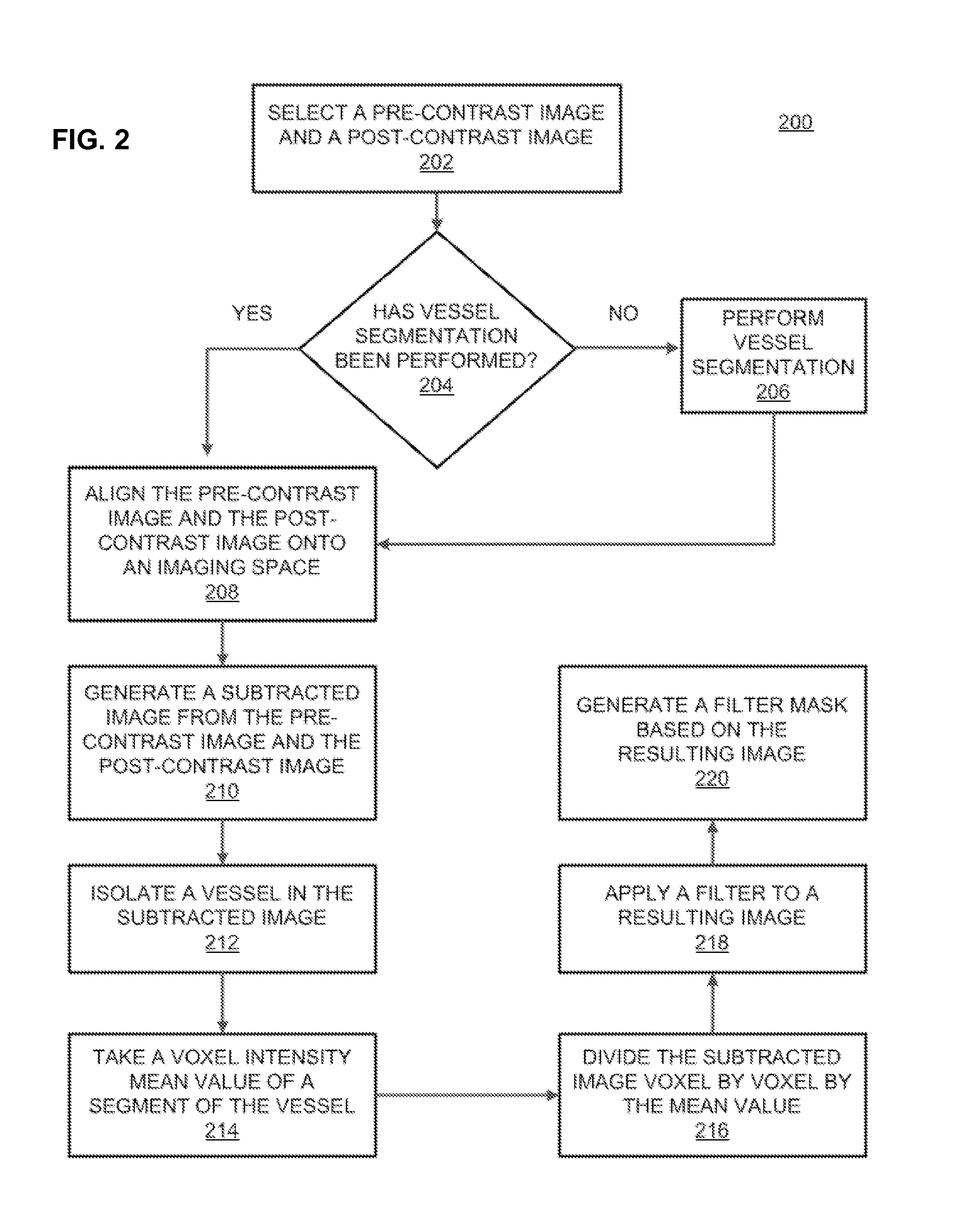
Technologies for diagnosing neurological or psychiatric illnesses
A technology which enables identifying, via a computer, a vessel in a third image. The third image is obtained from a subtraction of a second image from a first image. The second image and the first image are aligned on an imaging space. The first image is post-contrast. The second image is pre-contrast. The technology enables determining, via the computer, a voxel intensity mean value of a segment of the vessel in the third image. The technology enables obtaining, via the computer, a fourth image from a division of the third image by the voxel intensity mean value. The technology enables applying, via the computer, a filter onto the fourth image. The technology enables generating, via the computer, a filter mask based on the fourth image.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
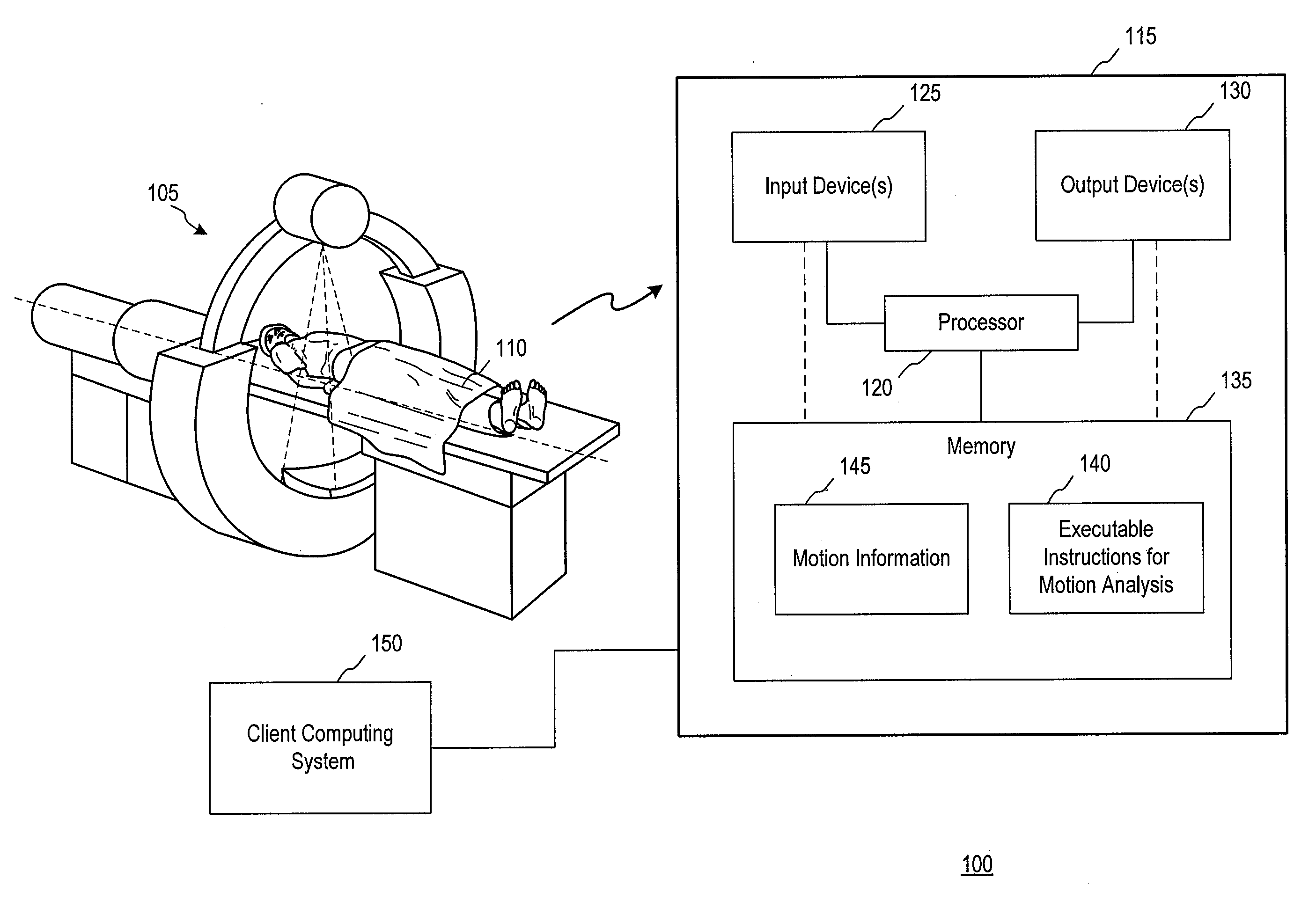
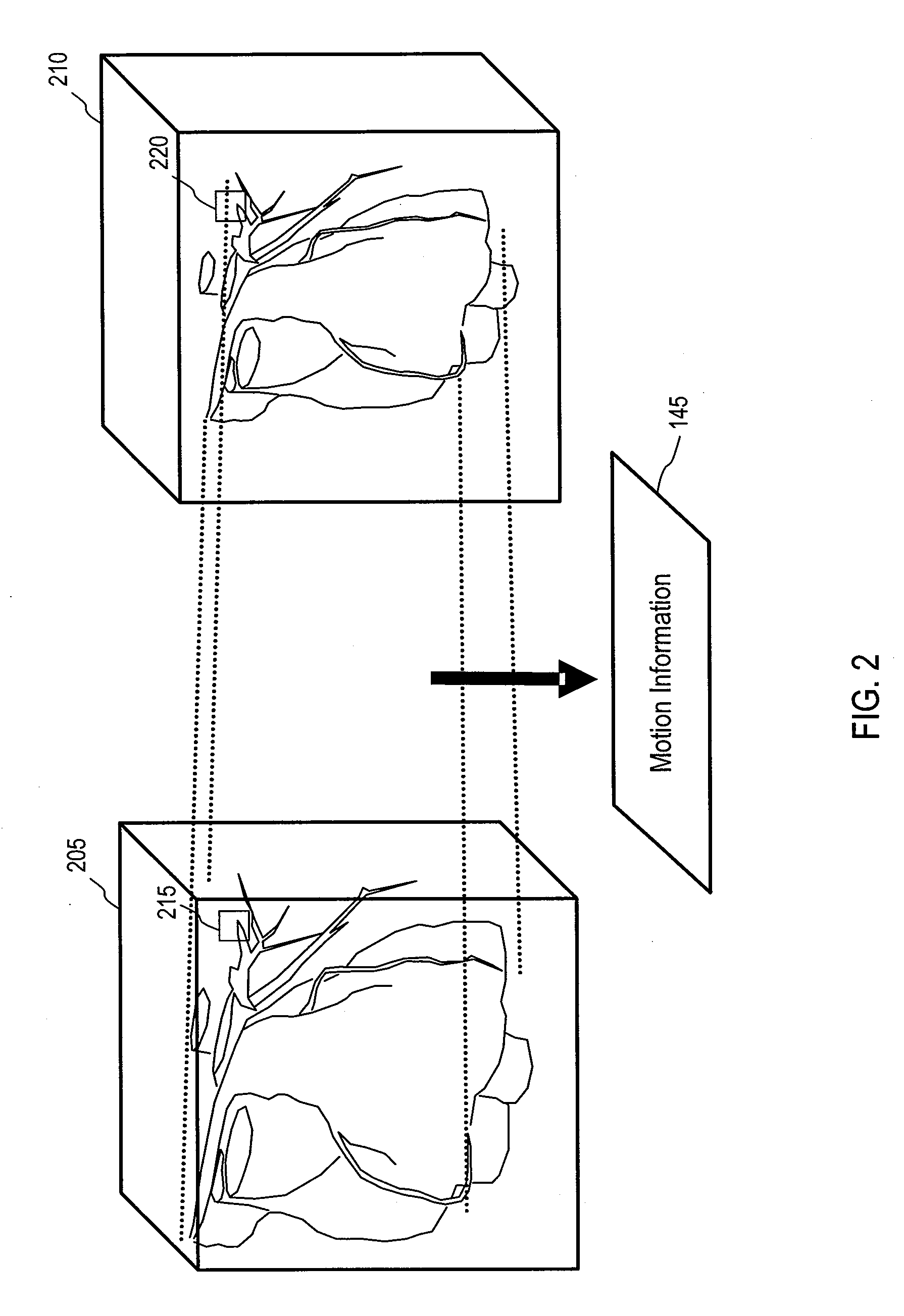
Computer readable medium, systems and methods for improving medical image quality using motion information
InactiveUS20110075888A1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityImage quality
Motion information generated by comparing one or more instances of clinical volume data may be used in a variety of applications. Examples of applications described herein include filtering volume data and adjusting voxel intensity based on the motion information. Motion information may also be used to compress volume data. Combinations of these effects may also be achieved.
Owner:QI IMAGING
Method and system for segmentation of tubular structures in 3D images
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Method and system for segmentation and removal of pulmonary arteries, veins, left atrial appendage
A method and system for segmentation and removal of pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and a left atrial appendage from 3D medical image data, such as 3D computed tomography (CT) volumes, is disclosed. A global shape model is segmented for each of pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and a left atrial appendage in a 3D volume. The segmented global shape model for each of the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and left atrial appendage is locally refined based in local voxel intensities in the 3D volume, resulting in a respective mask for each structure. The mask is used to remove voxels belonging to the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and left atrial appendage from the 3D volume in order to better visualize coronary arteries and bypass arteries.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
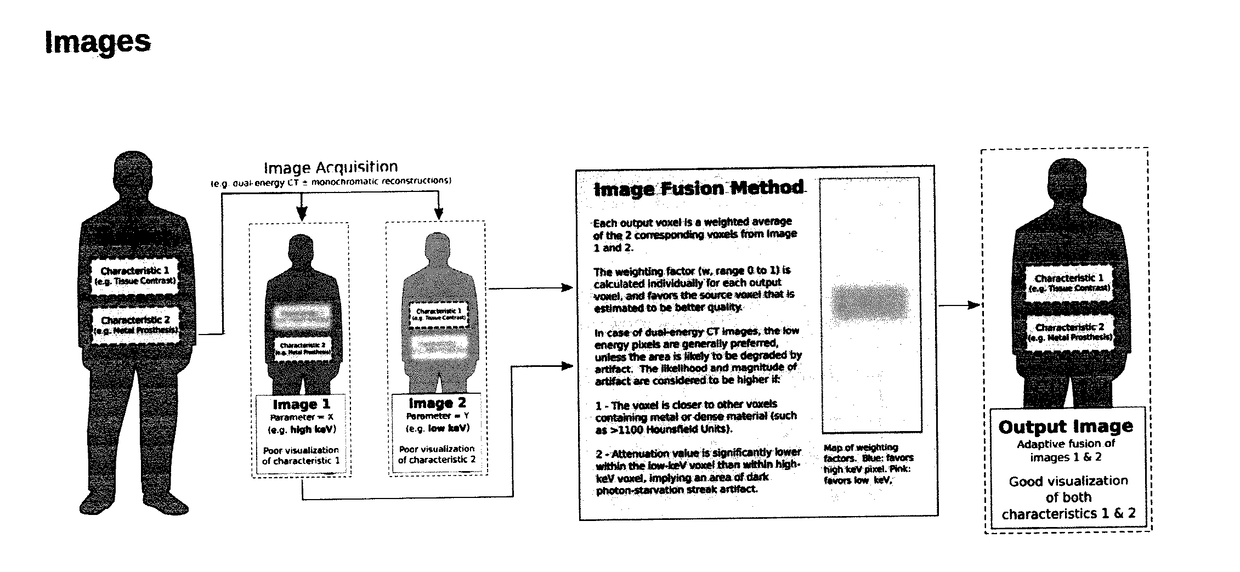
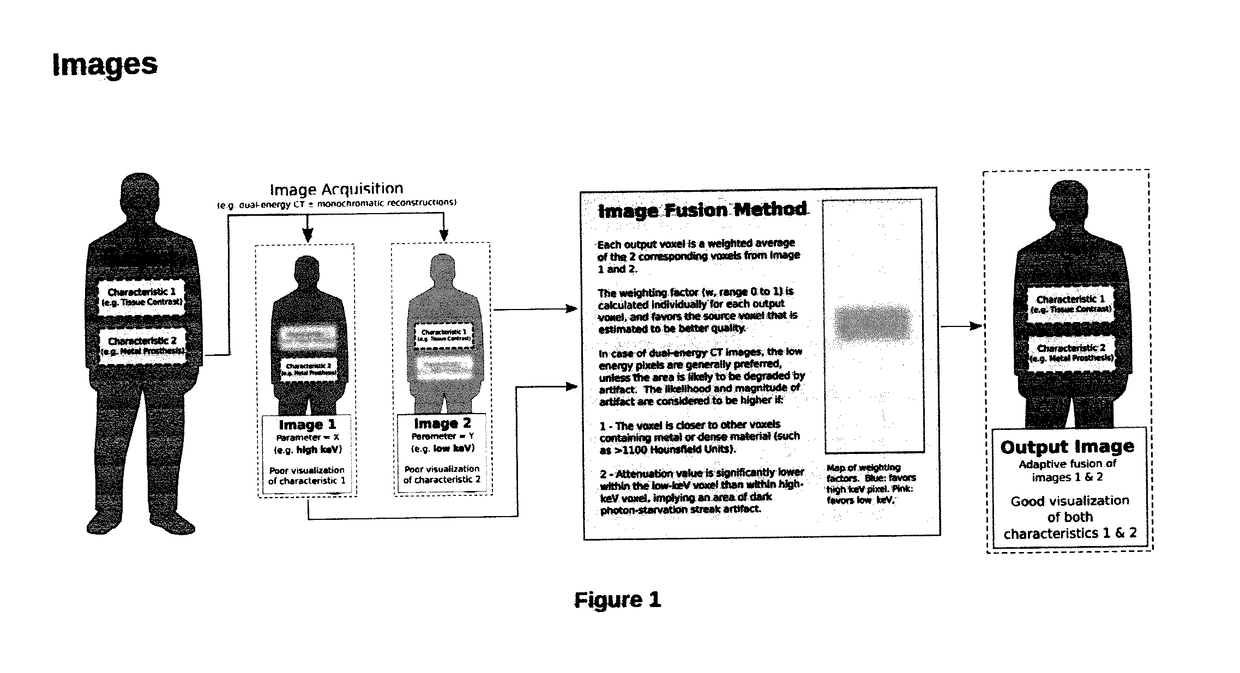
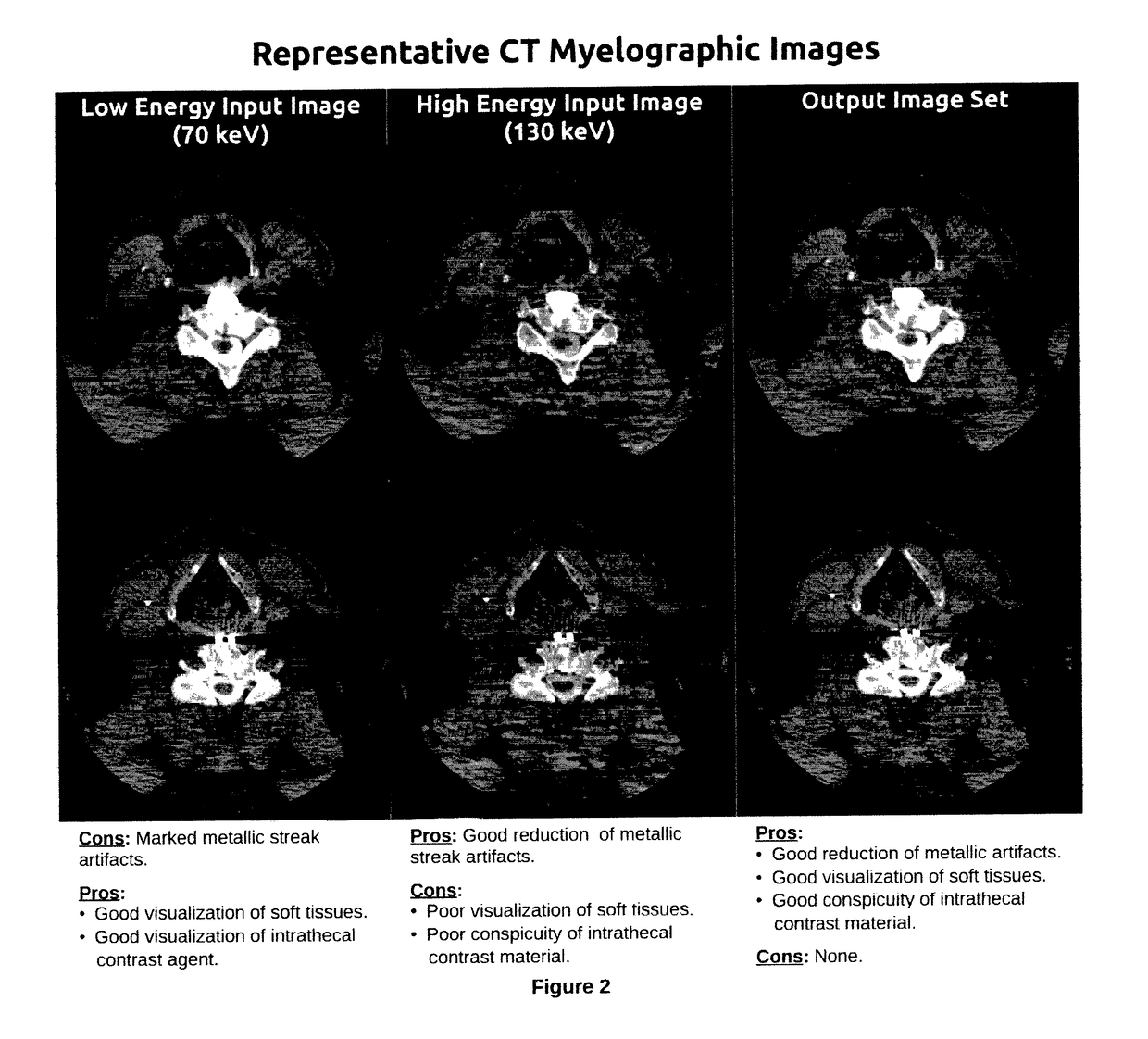
Method for Reduction of Artifacts and Preservation of Soft Tissue Contrast and Conspicuity of Iodinated Materials on Computed Tomography Images by means of Adaptive Fusion of Input Images Obtained from Dual-Energy CT Scans, and Use of differences in Voxel intensities between high and low-energy images in estimation of artifact magnitude
InactiveUS20170109903A1Fast approachReduce in quantityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionImaging processing
Image processing method is presented along with reference source code and sample outputs. This method processes 2 (or more) input images which were obtained at different photon energies (or differing in another parameter), and produces an output image that emphasizes the best characteristics of each of the input images, while suppressing the undesired characteristics of each input image. This is different from prior dual-energy CT methods which produce an intermediate compromise image, with an intermediate soft tissue contrast and intermediate artifact suppression, and also different from prior methods that sacrifice soft tissue contrast to maximize artifact reduction.
Owner:RADIOLOGY UNIVERSE INST
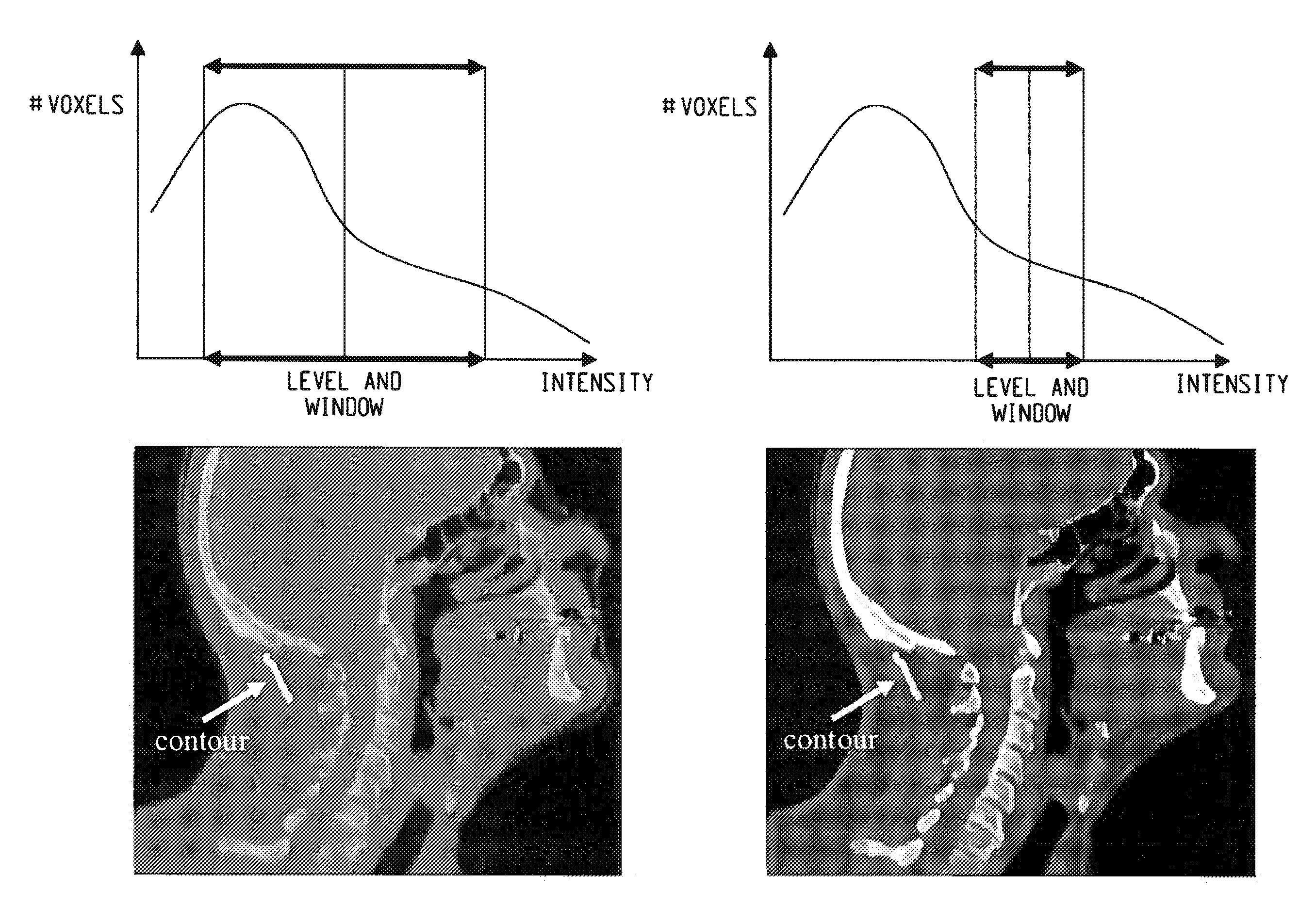
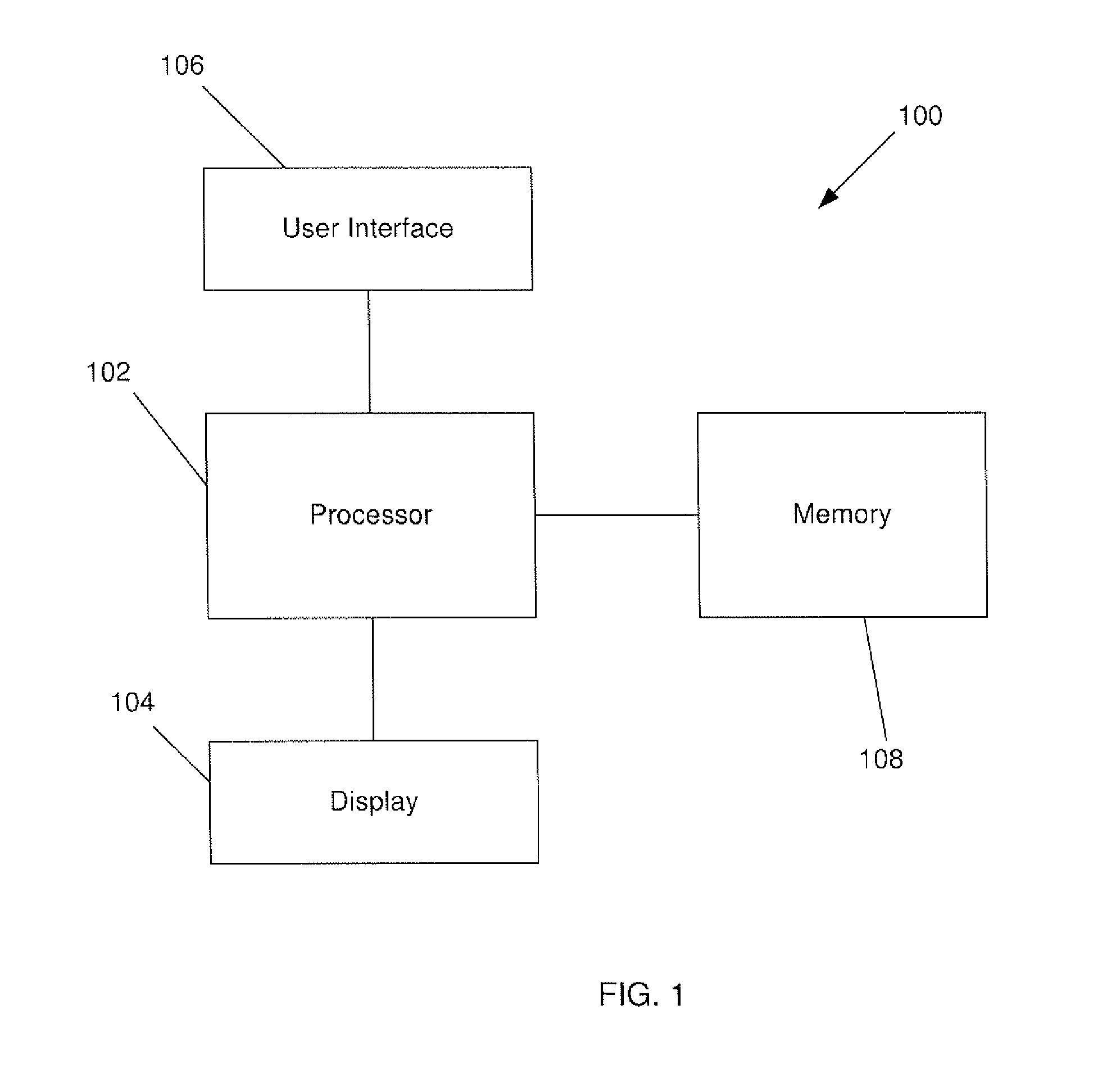
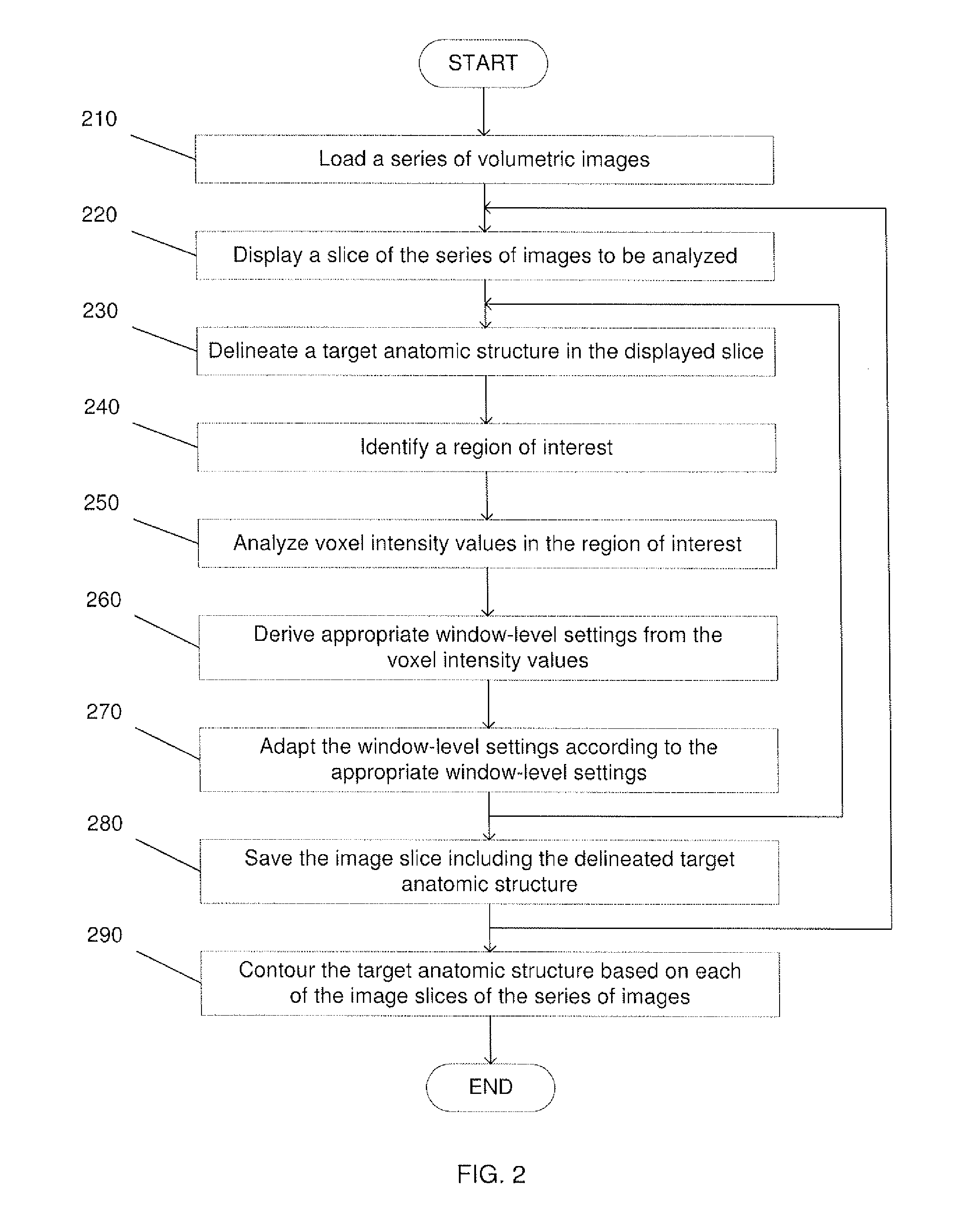
Automated contrast enhancement for contouring
A system and method for automatic contrast enhancement for contouring. The system and method including displaying a volumetric image slice to be analyzed, receiving a delineation of a target anatomic structure in the volumetric image slice, identifying a region of interest based upon an area being delineated in the volumetric image slice, analyzing voxel intensity values in the region of interest and determining an appropriate window-level setting based on the voxel intensity values.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
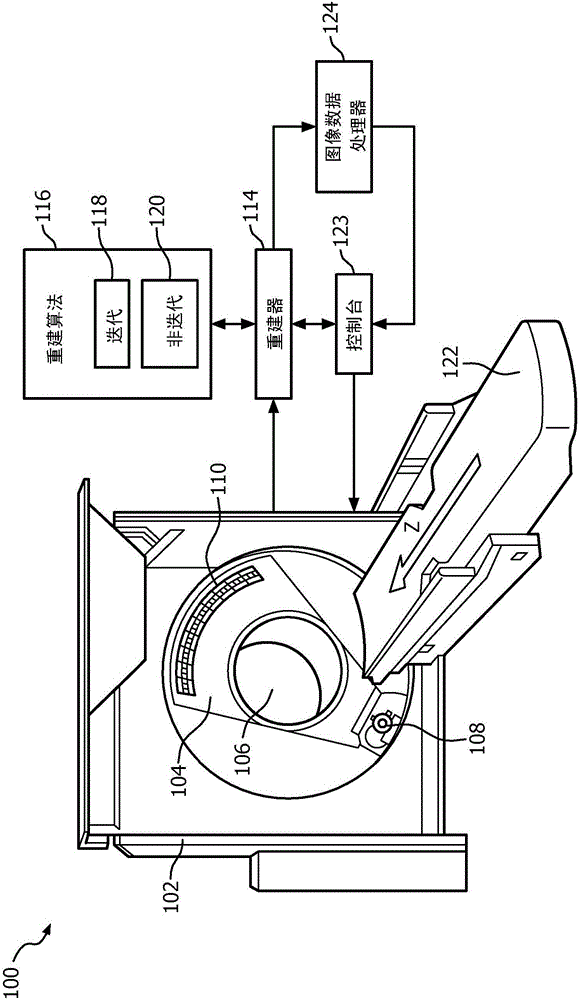
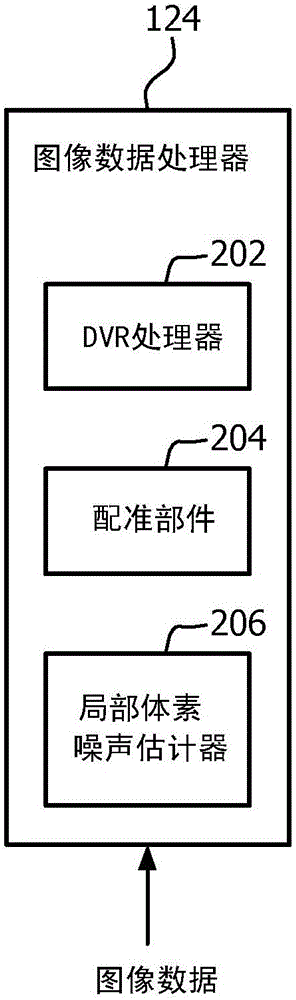
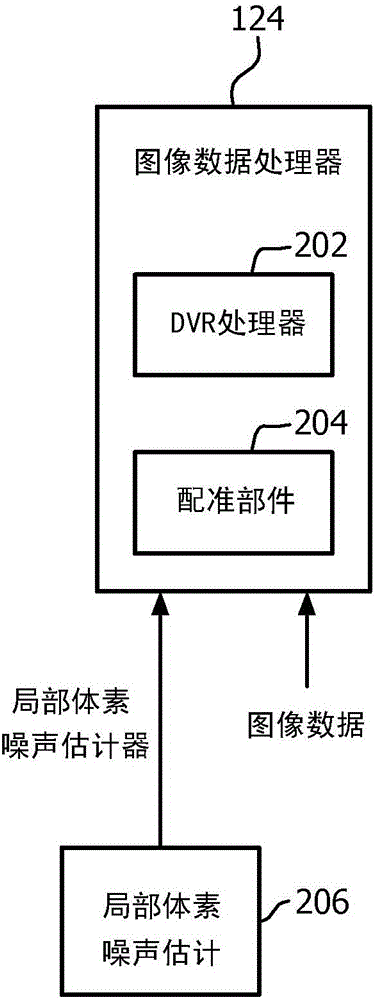
Image data processing
A method for processing image data includes obtaining a first set of 3D volumetric image data. The 3D volumetric image data includes a volume of voxels. Each voxel has an intensity. The method further includes obtaining a local voxel noise estimate for each of the voxels of the volume. The method further includes processing the volume of voxels based at least on the intensity of the voxels and the local voxel noise estimates of the voxels. An image data processor (124) includes a computer processor for at least one of: generating a 2D direct volume rendering from first 3D volumetric image data based on voxel intensity and individual local voxel noise estimates of the first 3D volumetric image data, or registering second 3D volumetric image data and first 3D volumetric image data based at least one individual local voxel noise estimates of second and first 3D volumetric image data sets.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for detecting and quantifying cerebral infarct
A method for detecting a cerebral infarct includes receiving an image of a brain of a subject from a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, wherein the image has a plurality of voxels, and each of the voxels has a voxel intensity. Then, the voxel intensities are normalized, wherein the normalized voxel intensities have a distribution peak, and the normalized voxel intensity of the distribution peak is Ipeak. A threshold is determined, which is the Ipeak+ a value. Voxel having the normalized voxel intensity larger than the threshold is selected, wherein the selected voxel is the cerebral infarct. A method for quantifying the cerebral infarct is also provided.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com