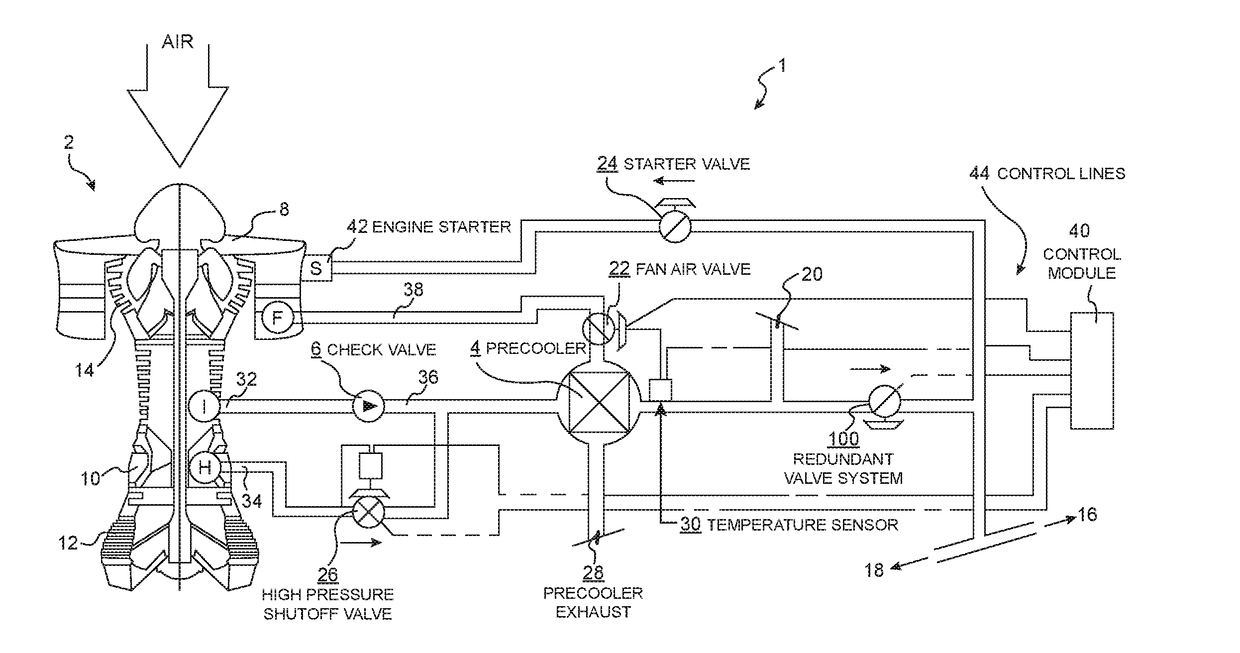
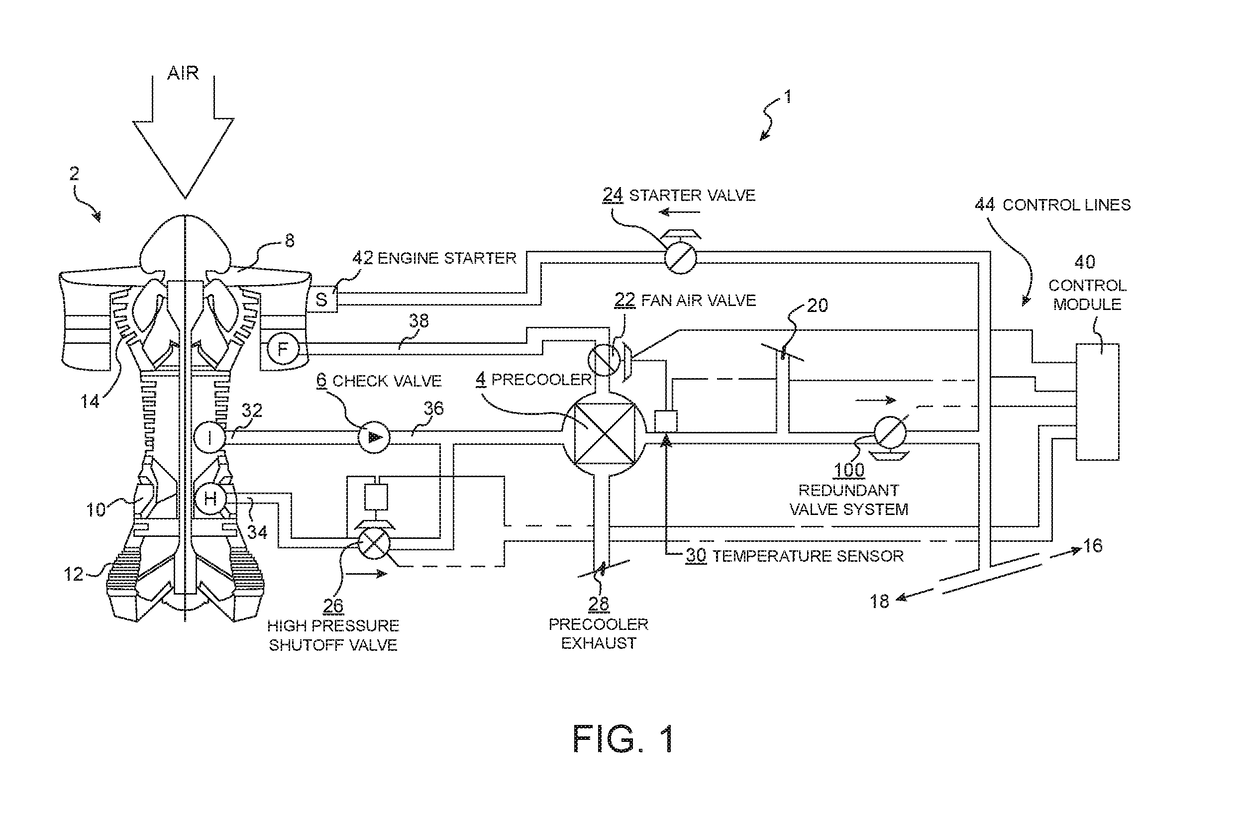
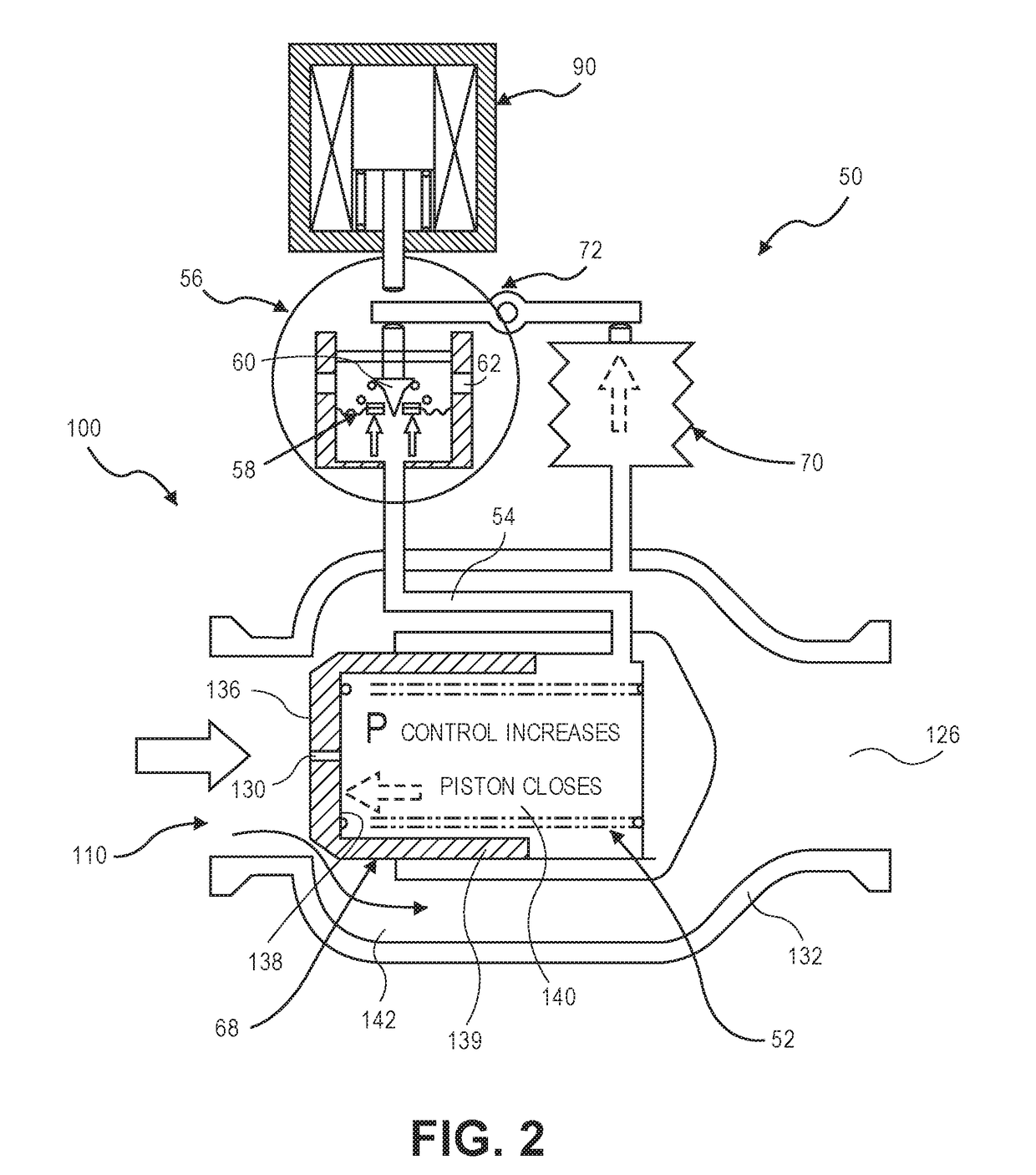
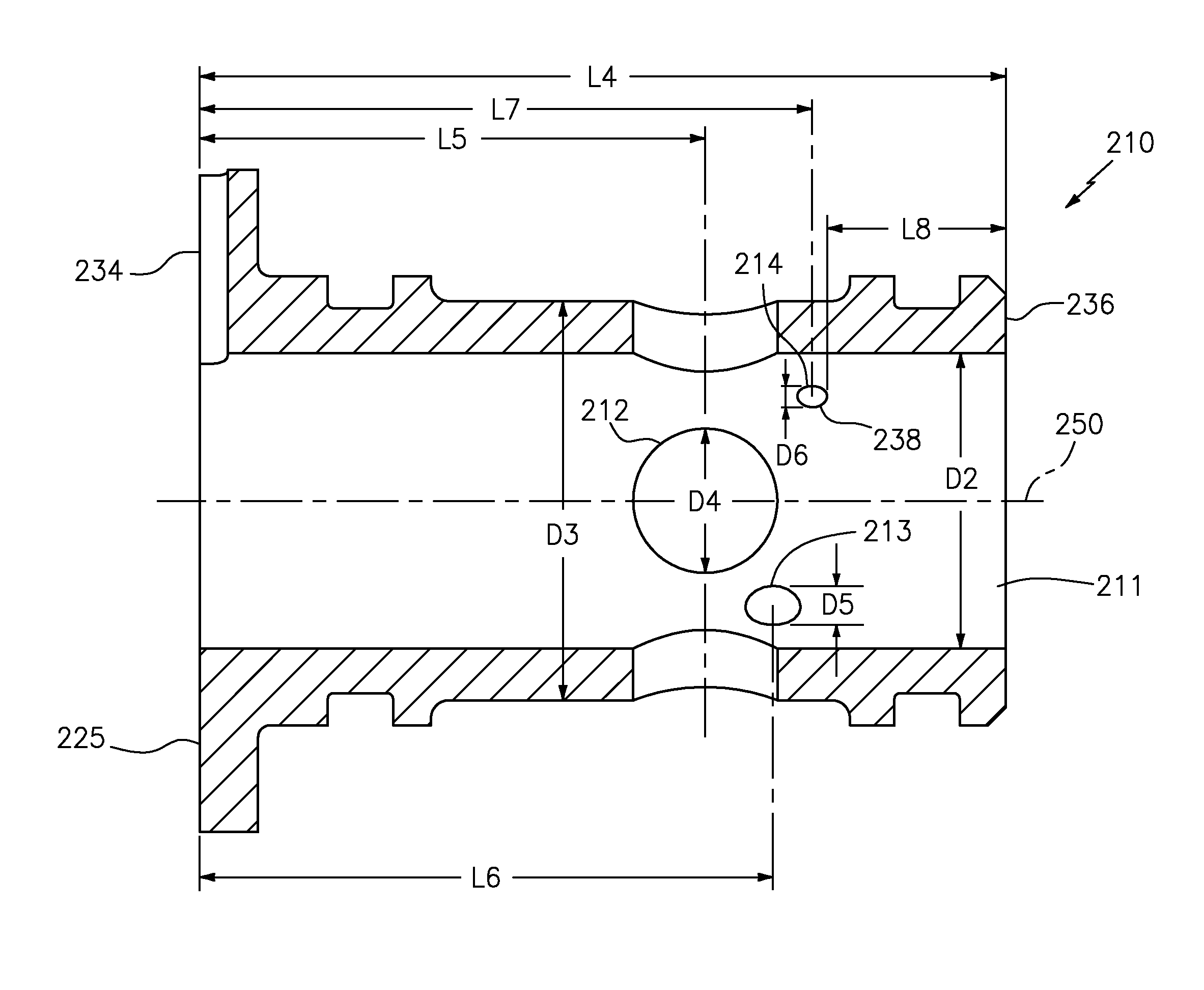
Patents
Literature
73results about "Inlet pressure control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
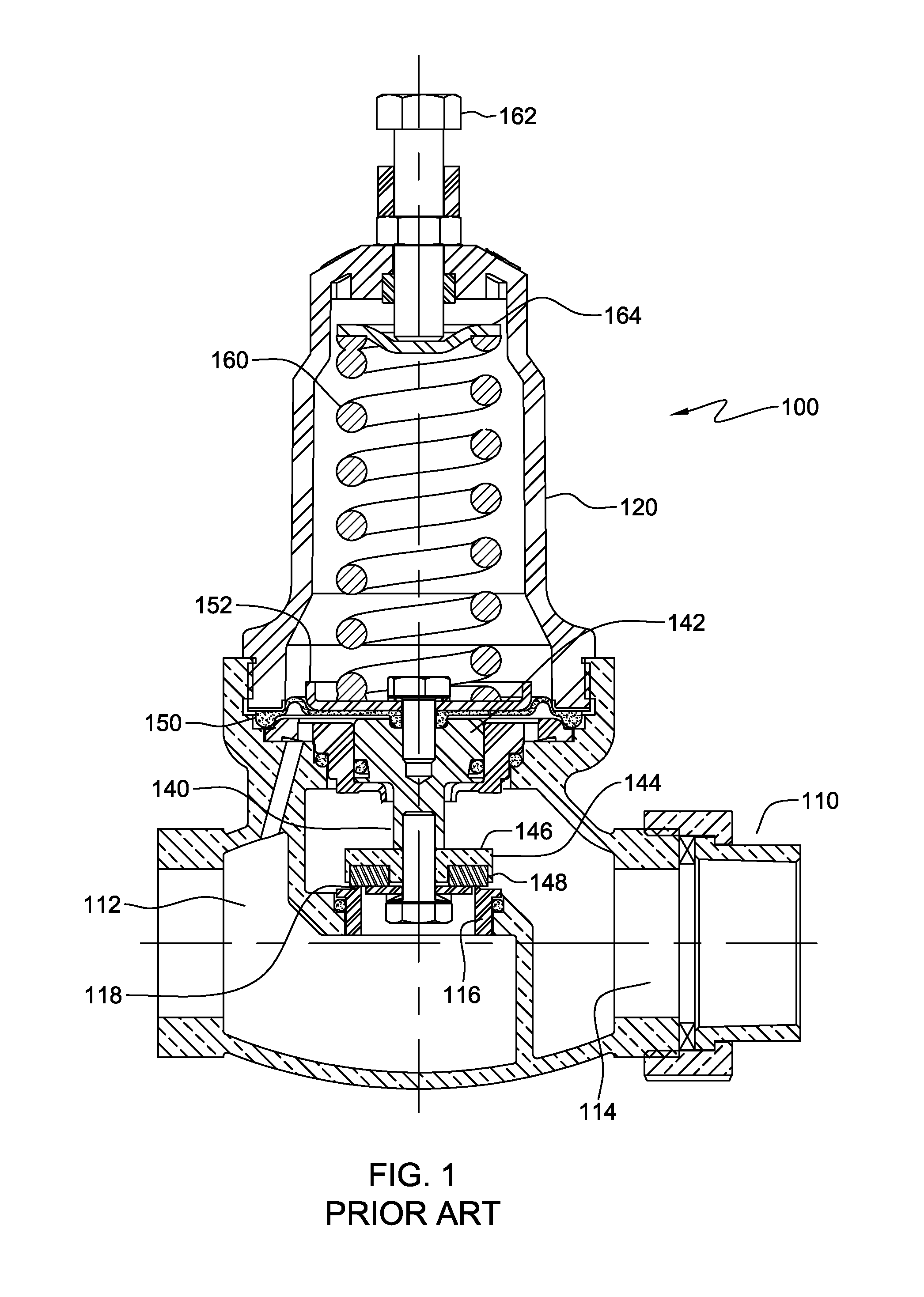
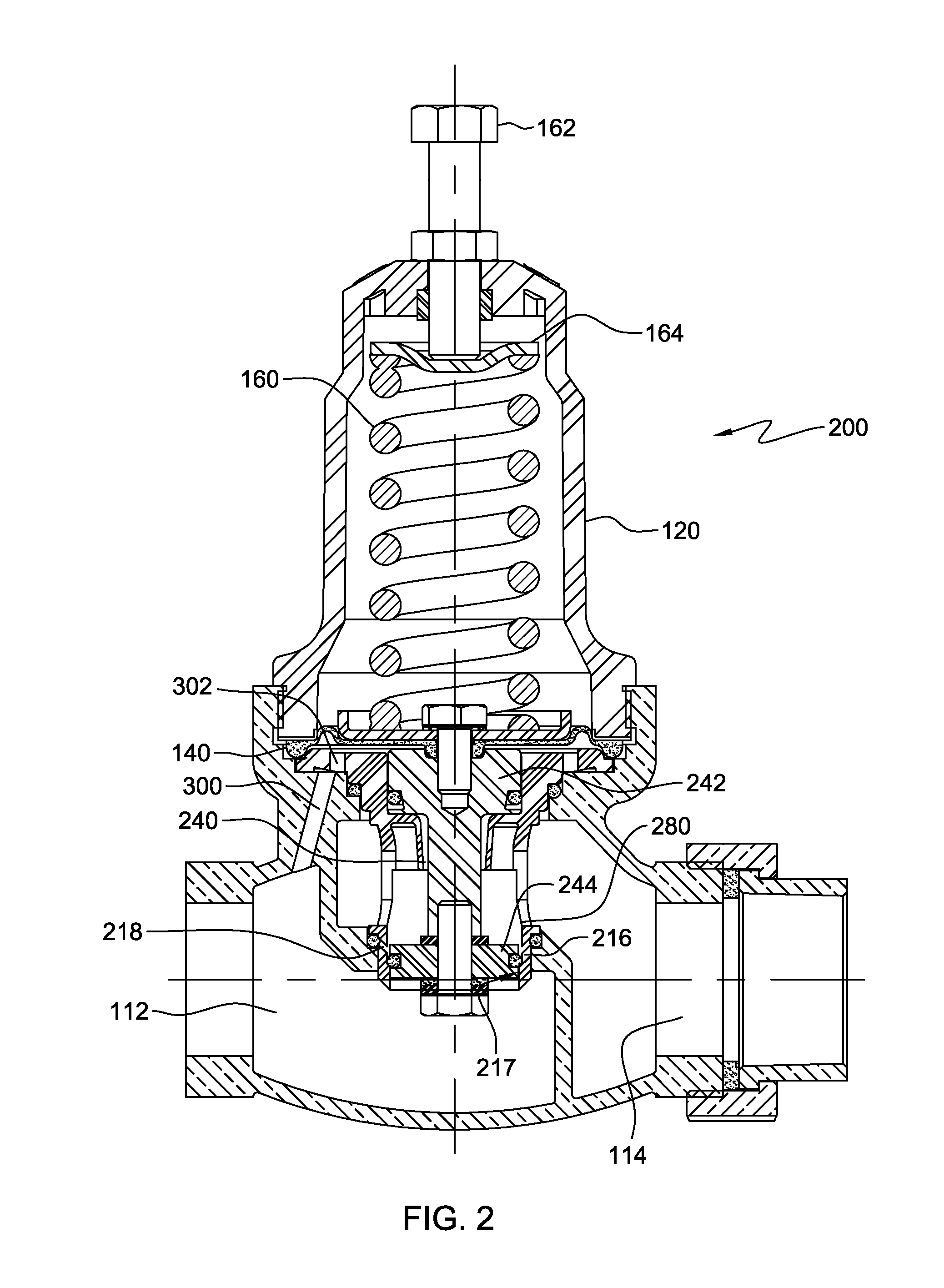
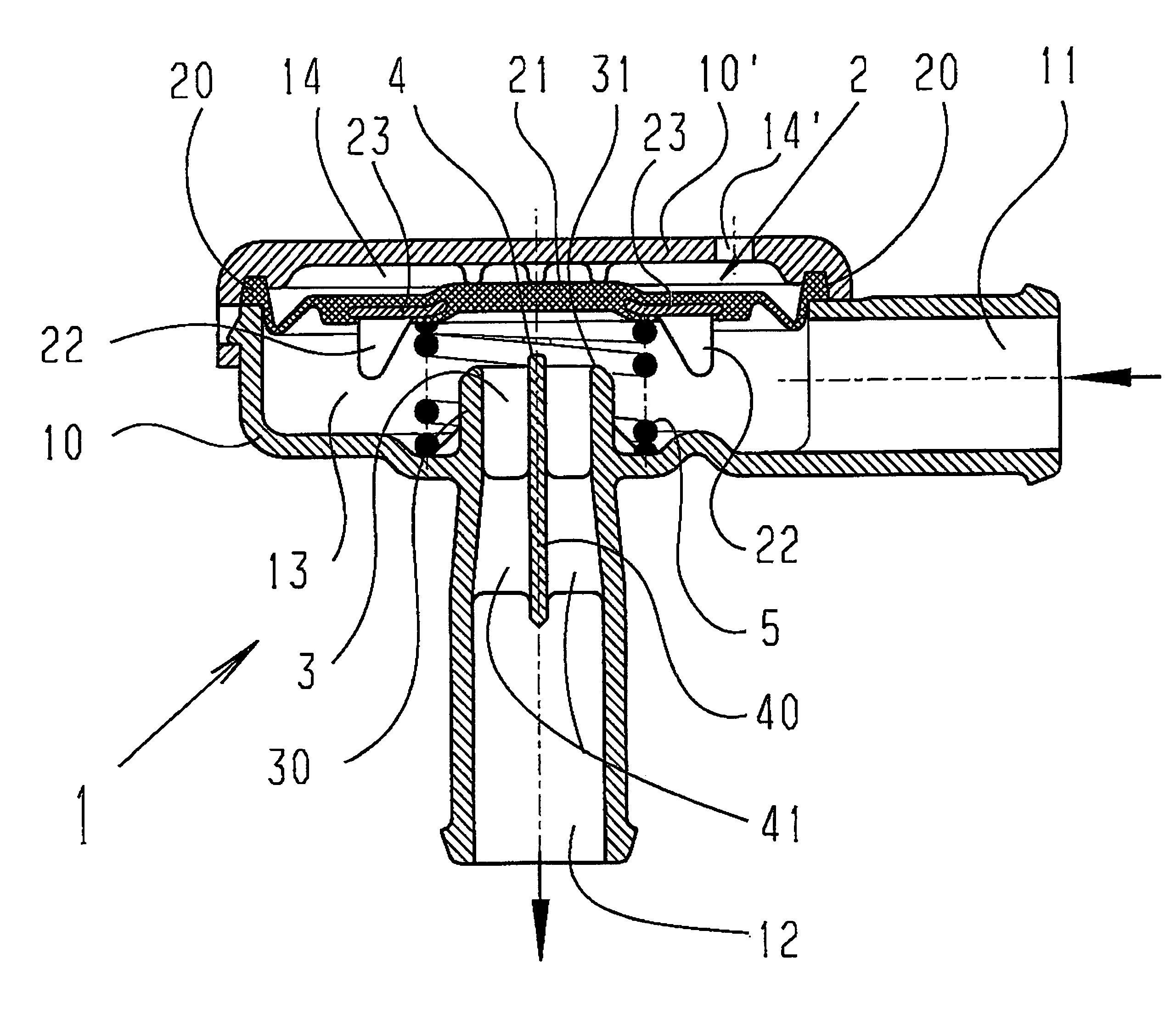
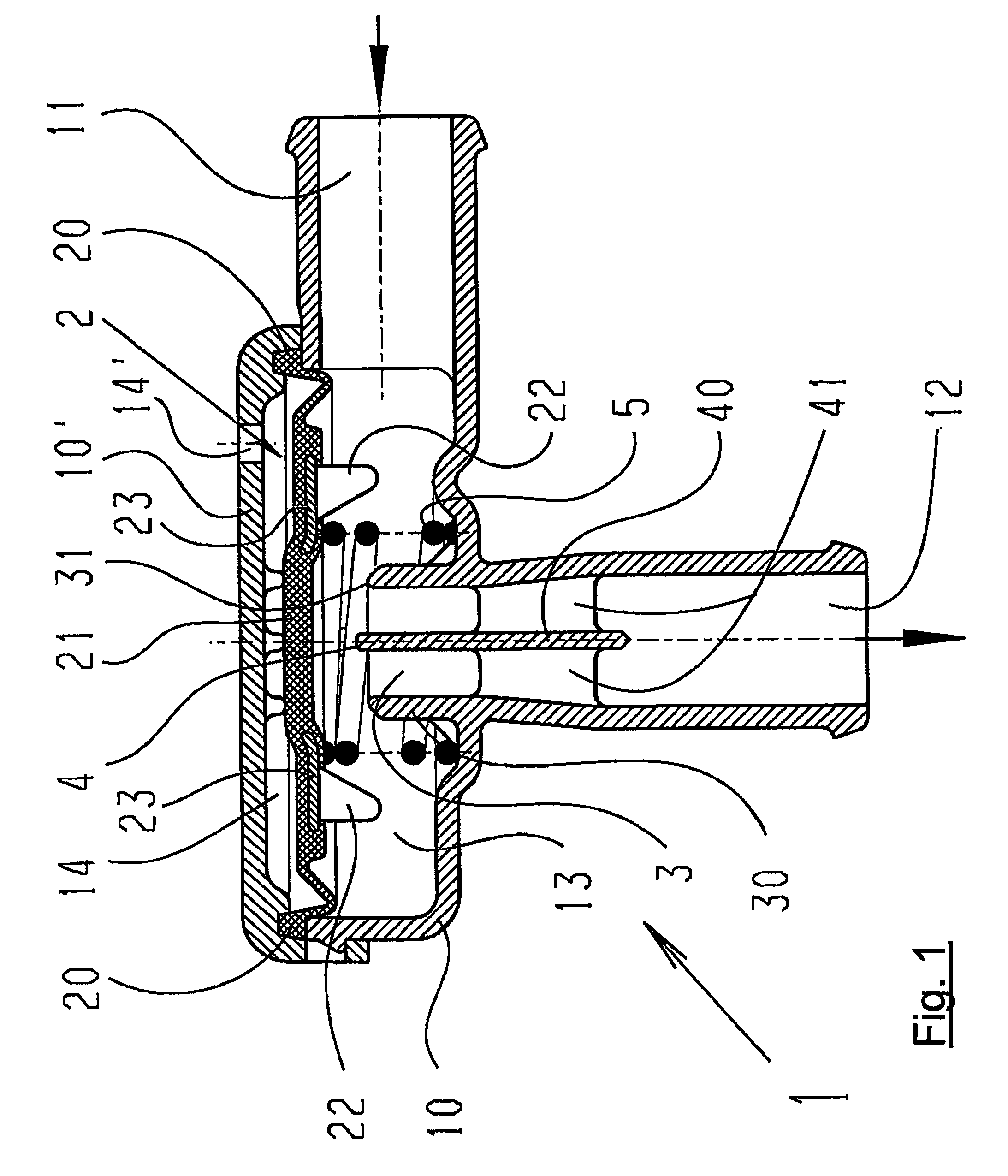
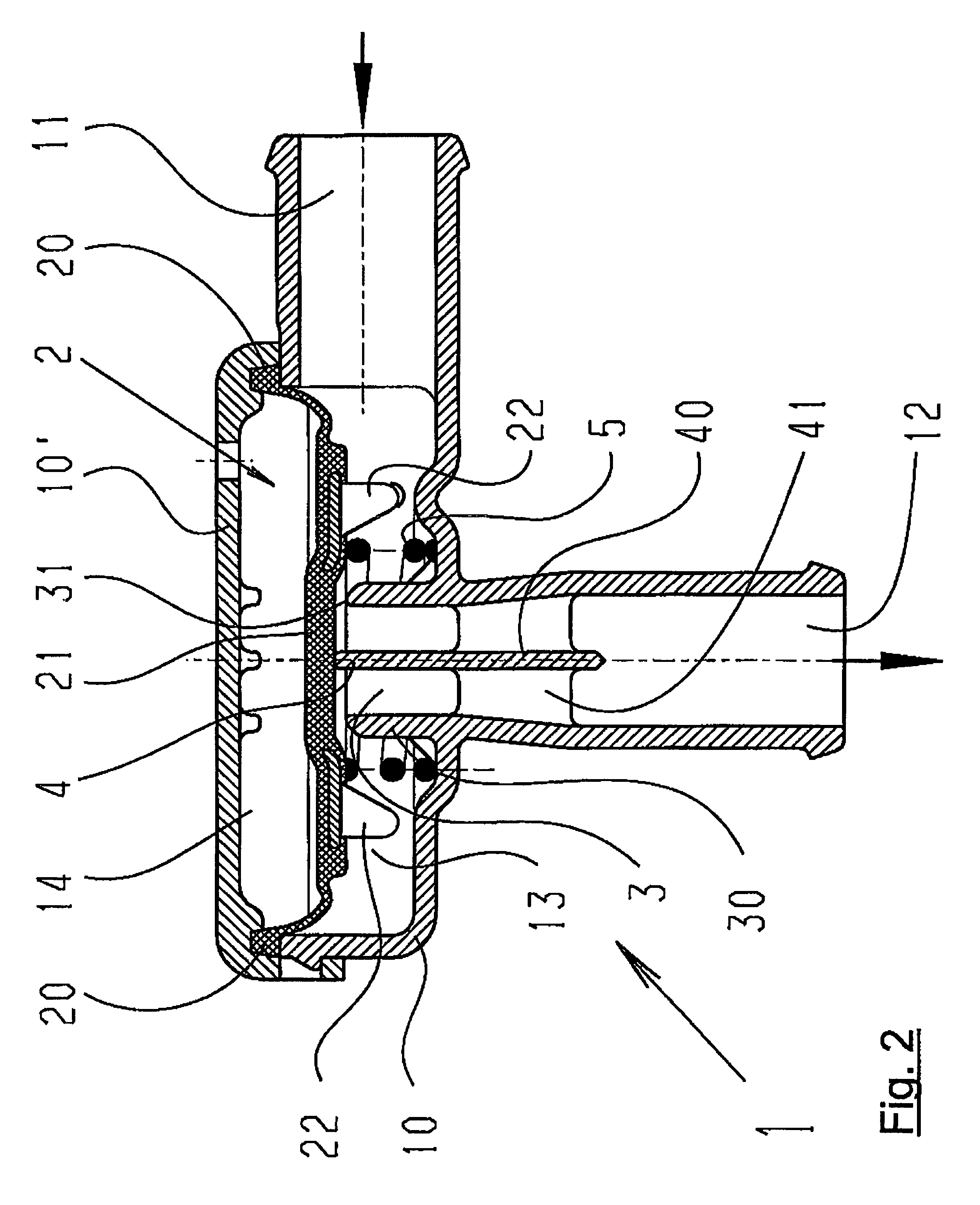
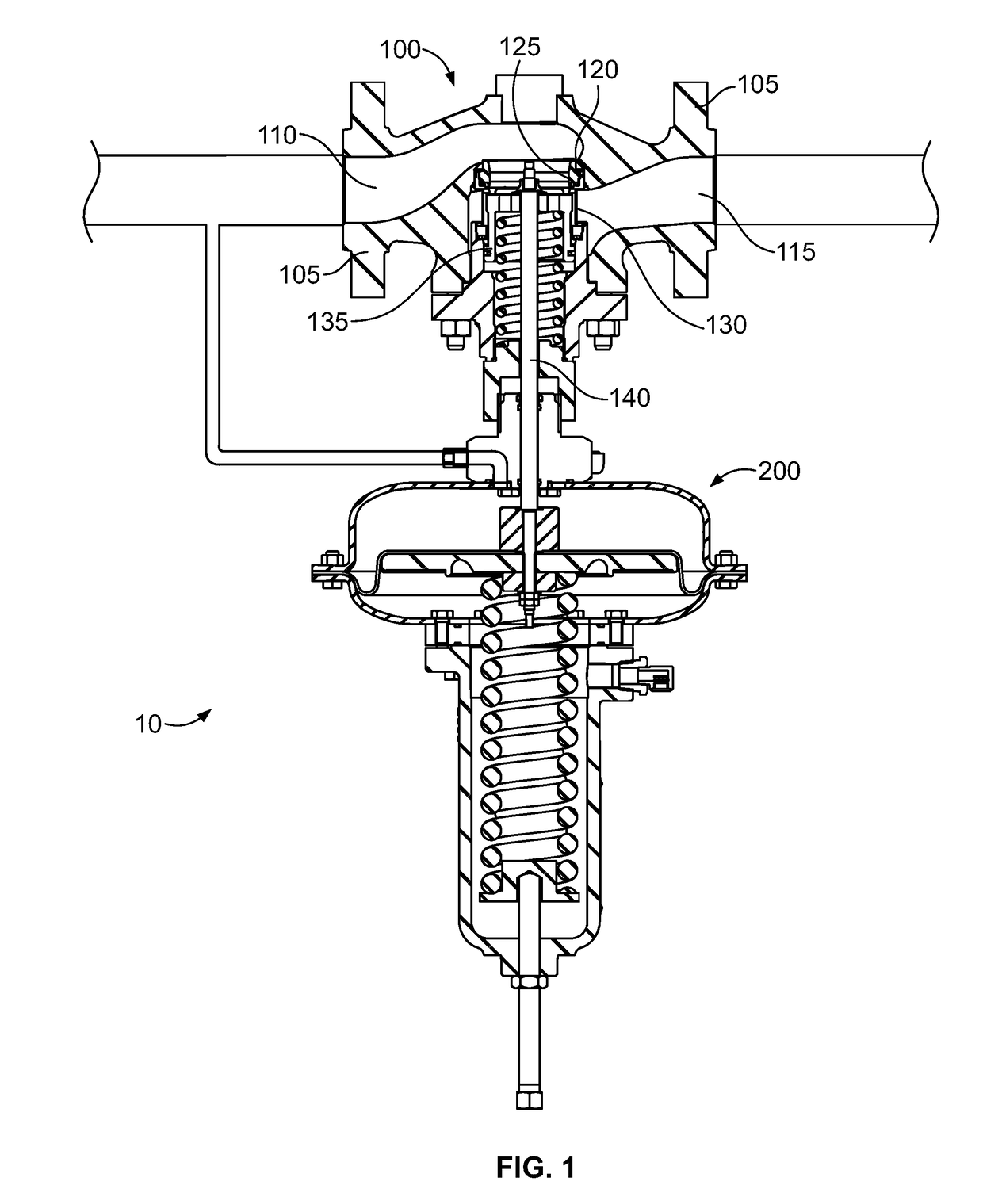
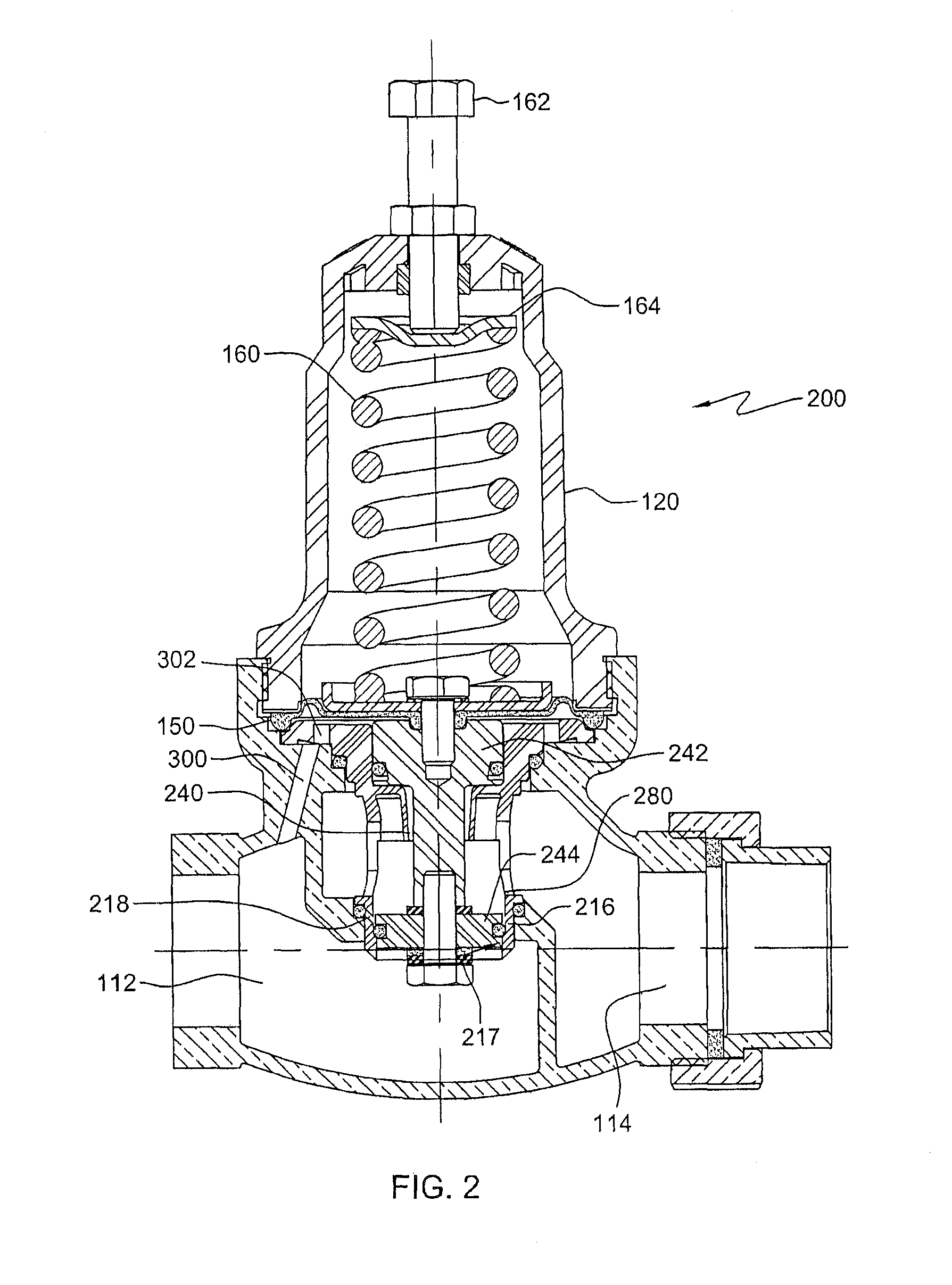
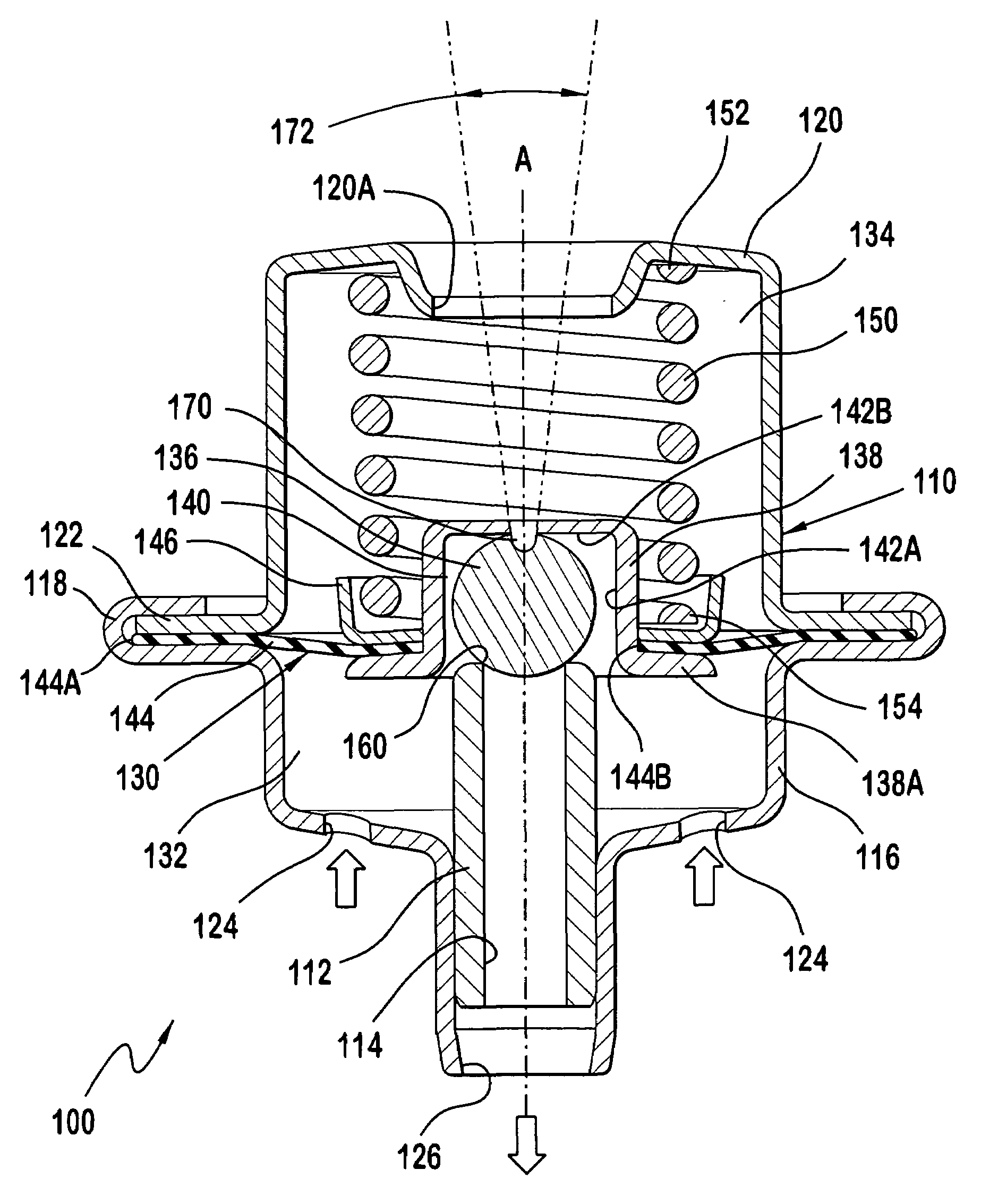
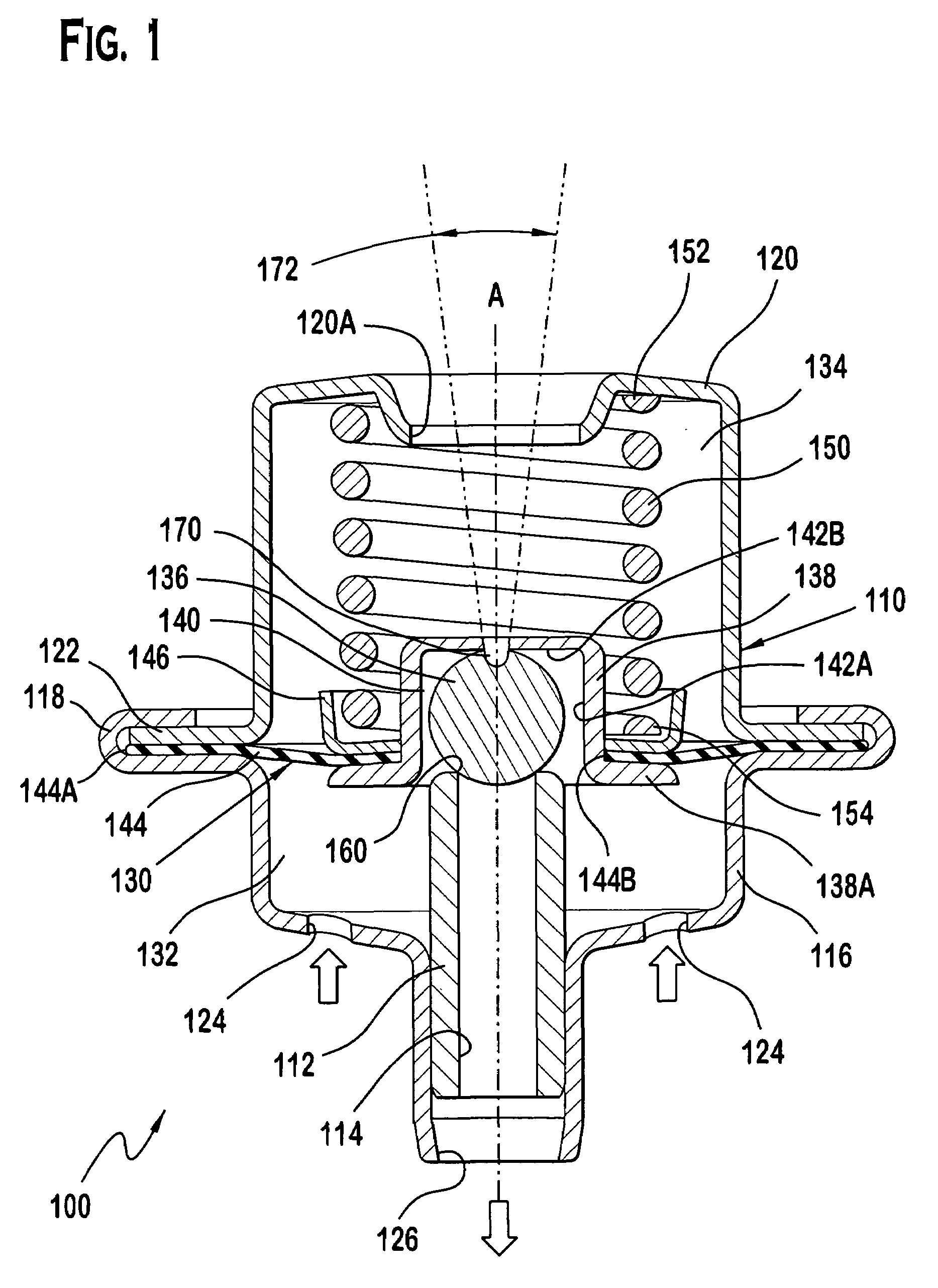
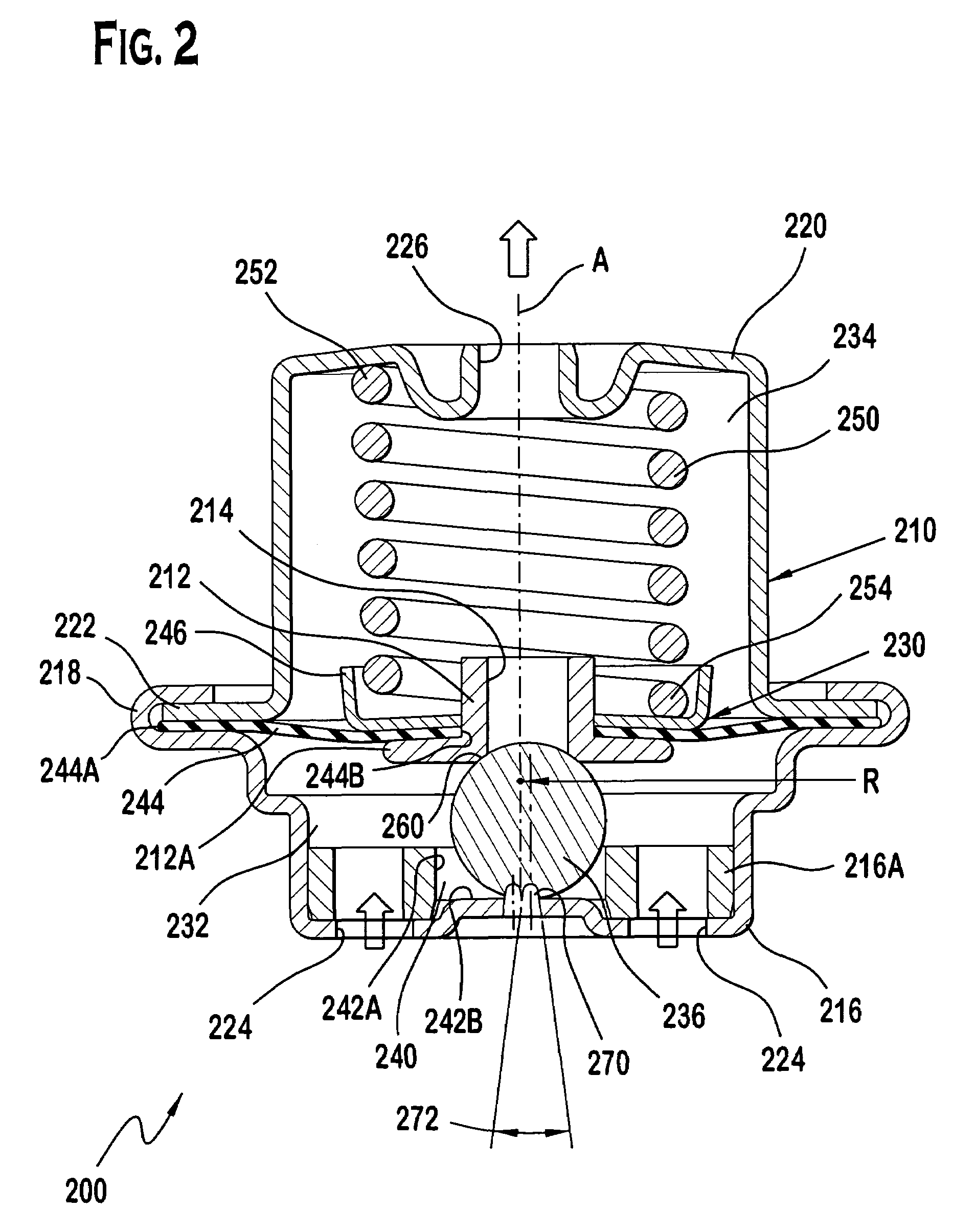
Pneumatic Pressure Regulation Valve
ActiveUS20080142091A1Guaranteed uptimePrevent freezingDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDifferential pressureEngineering
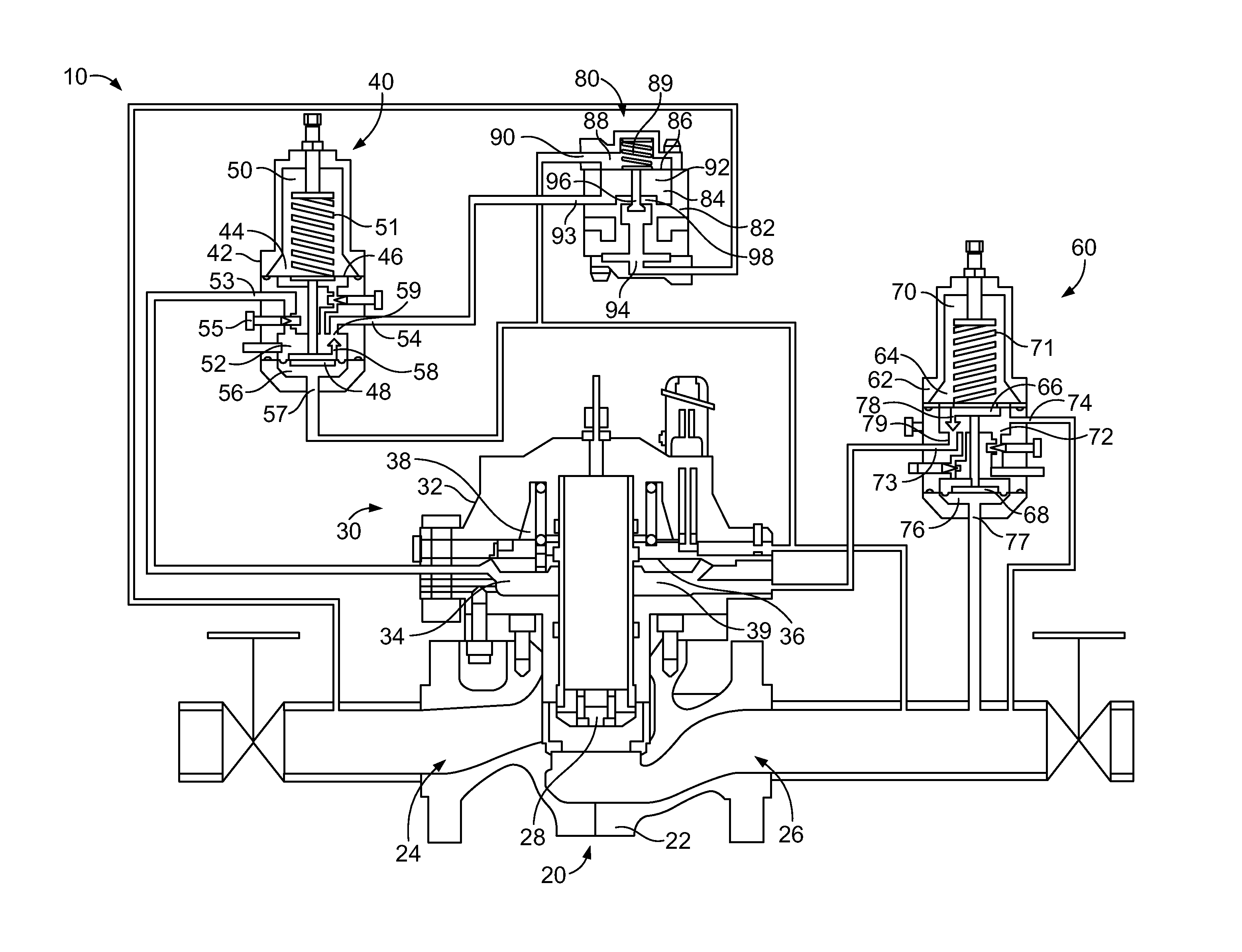
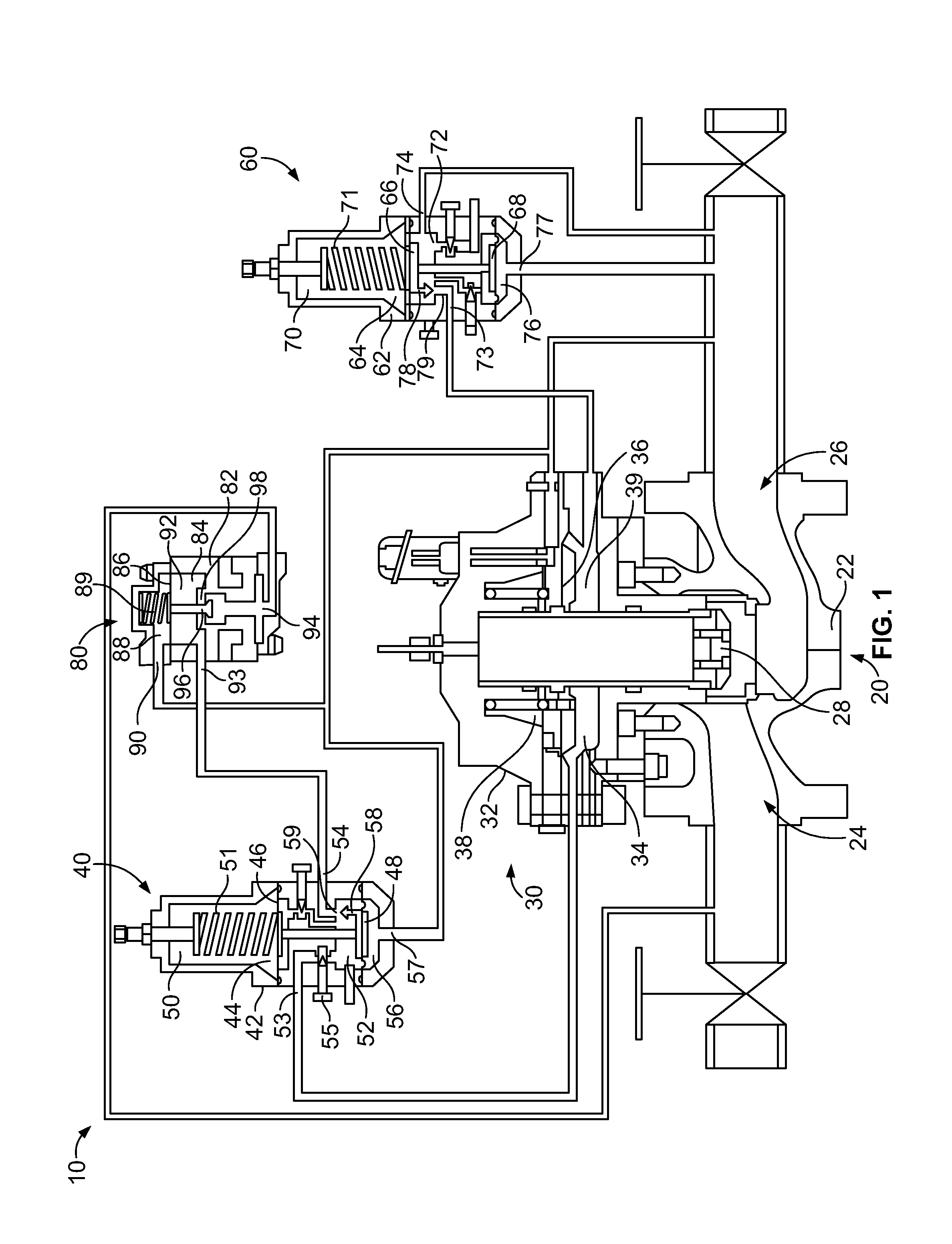
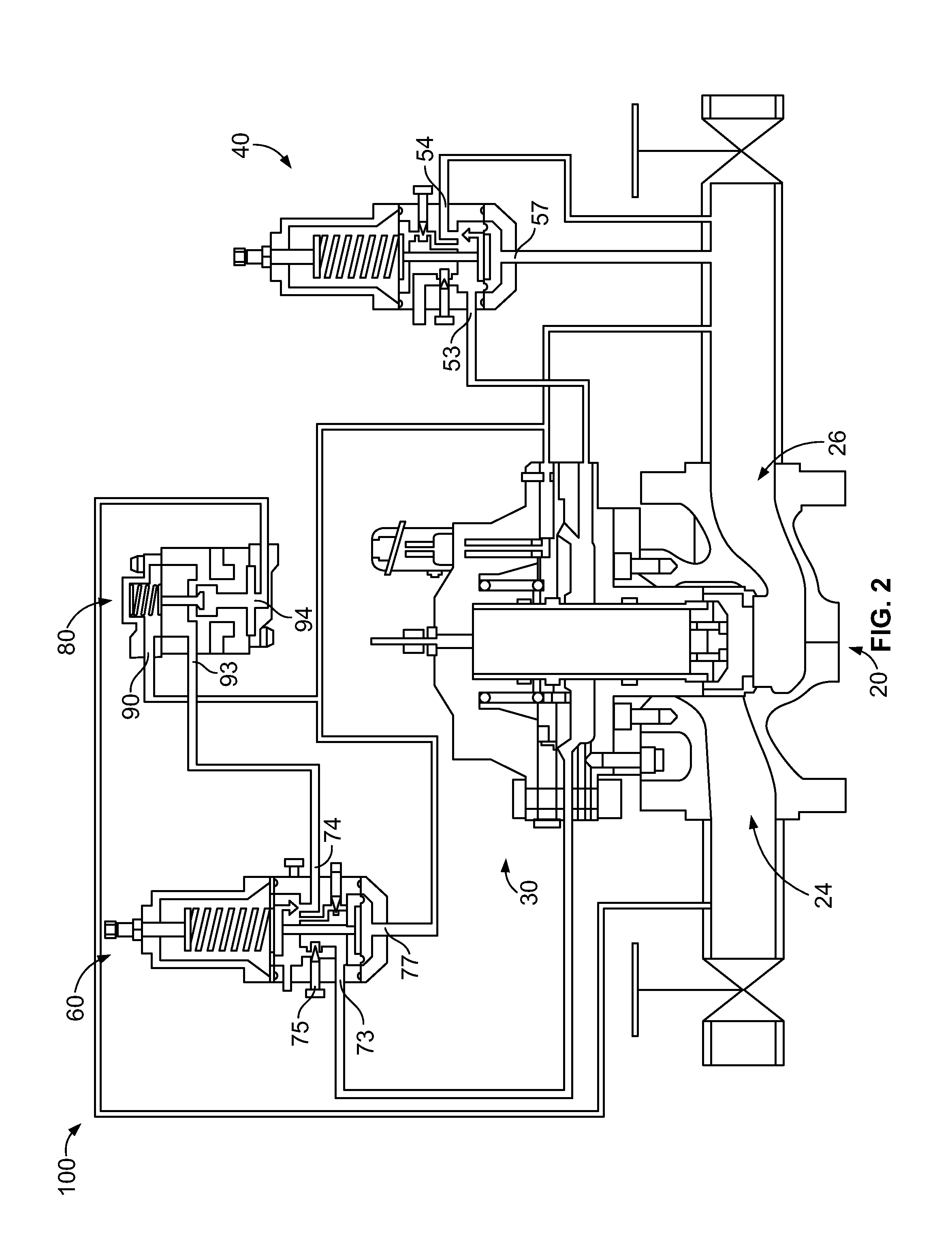
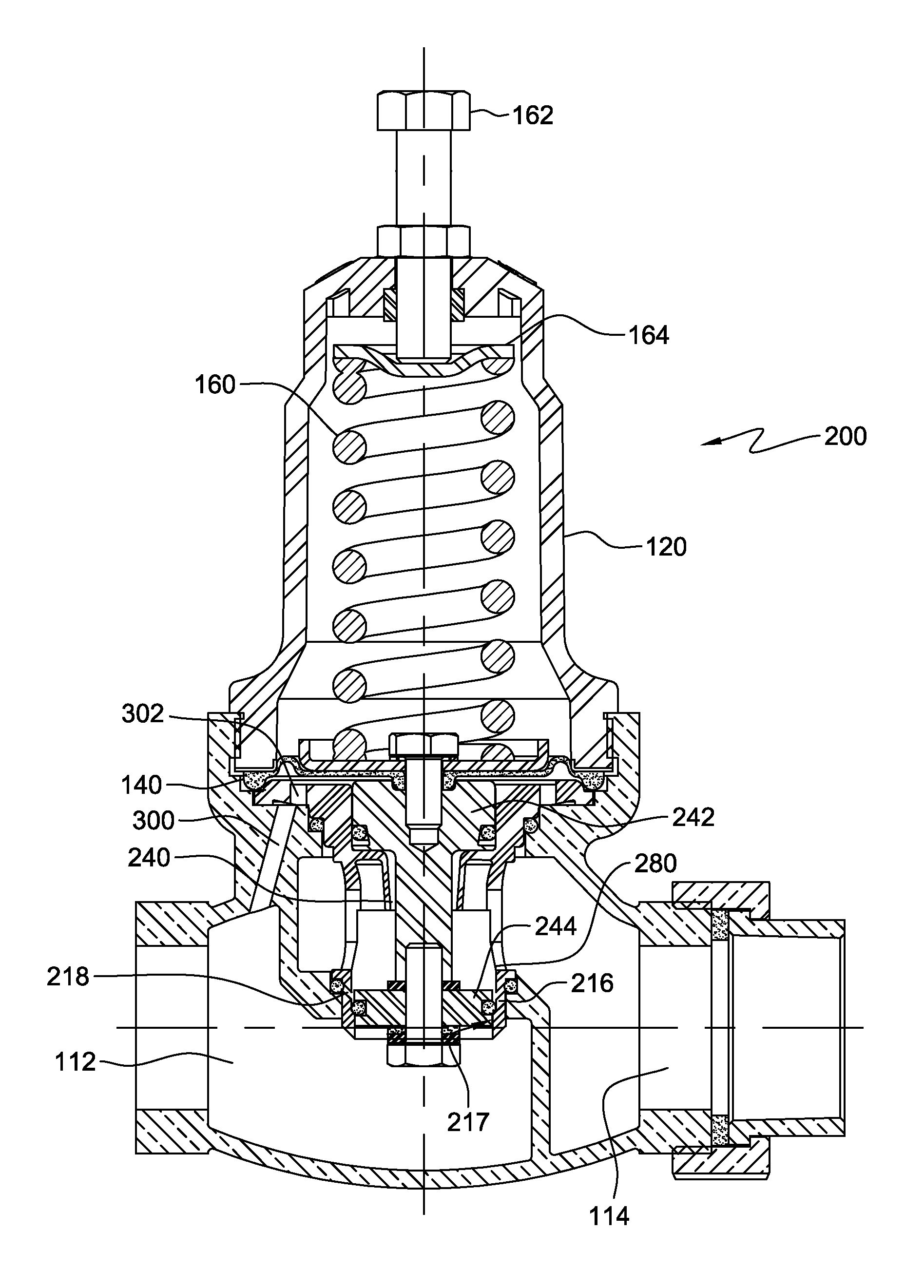
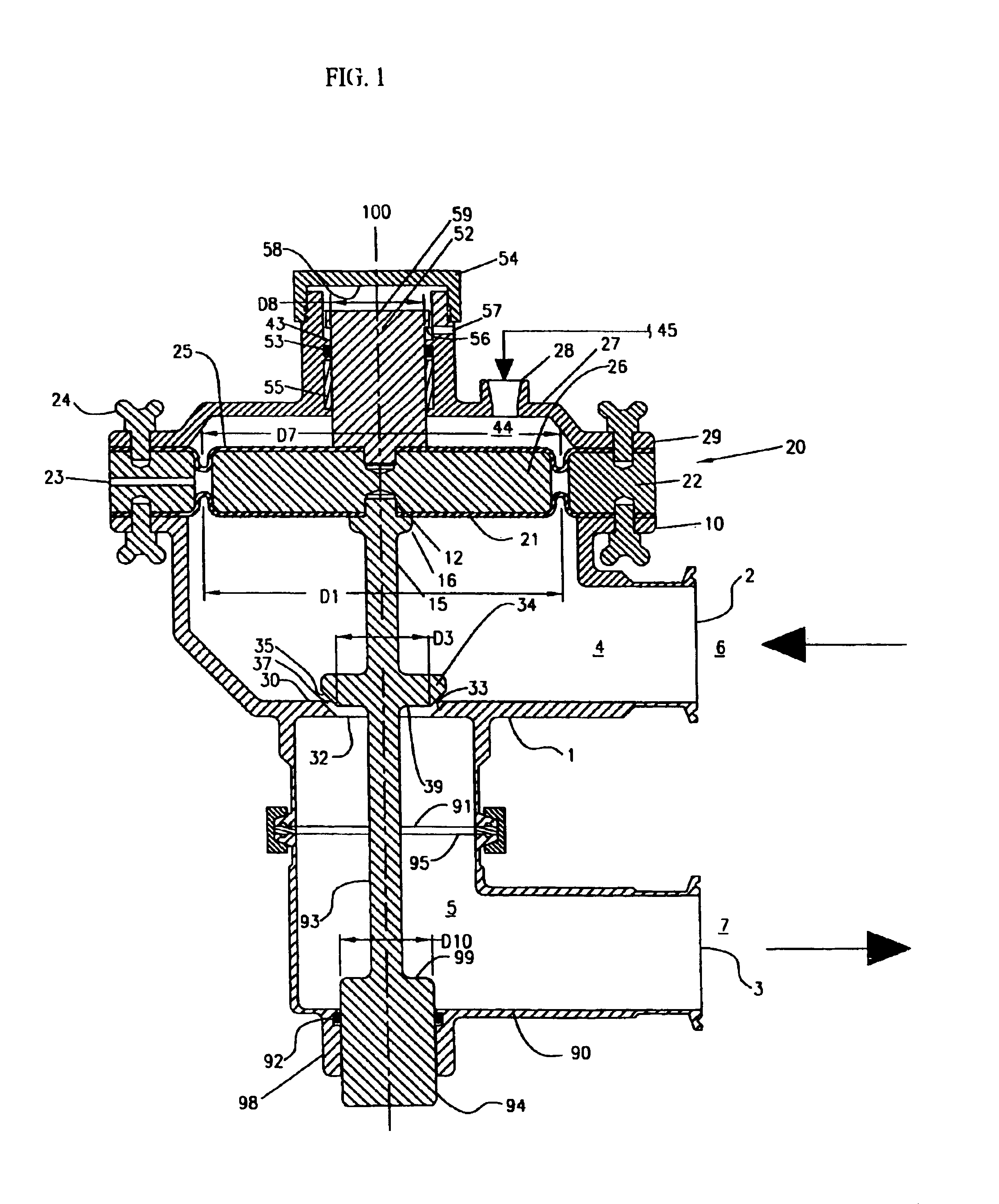
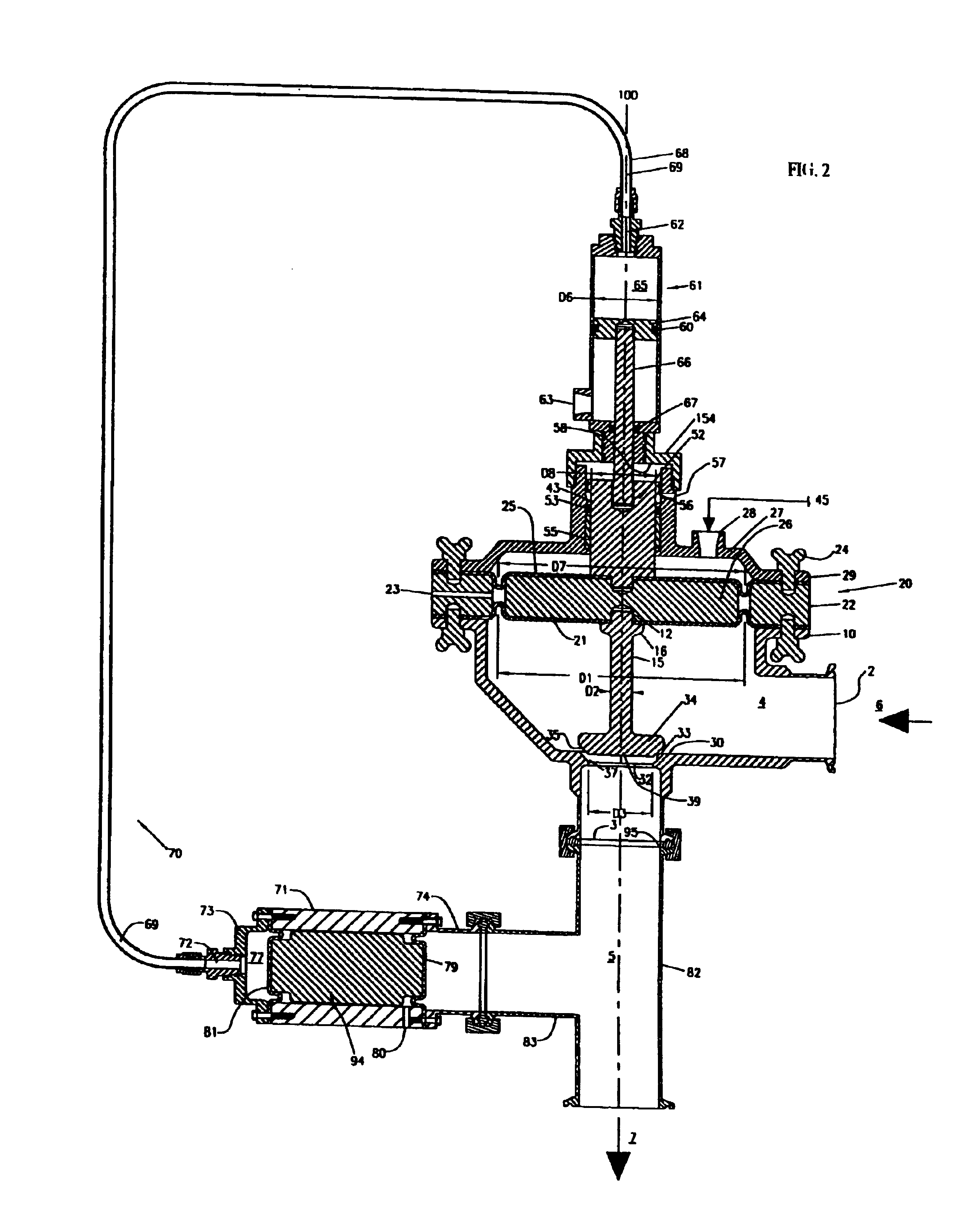
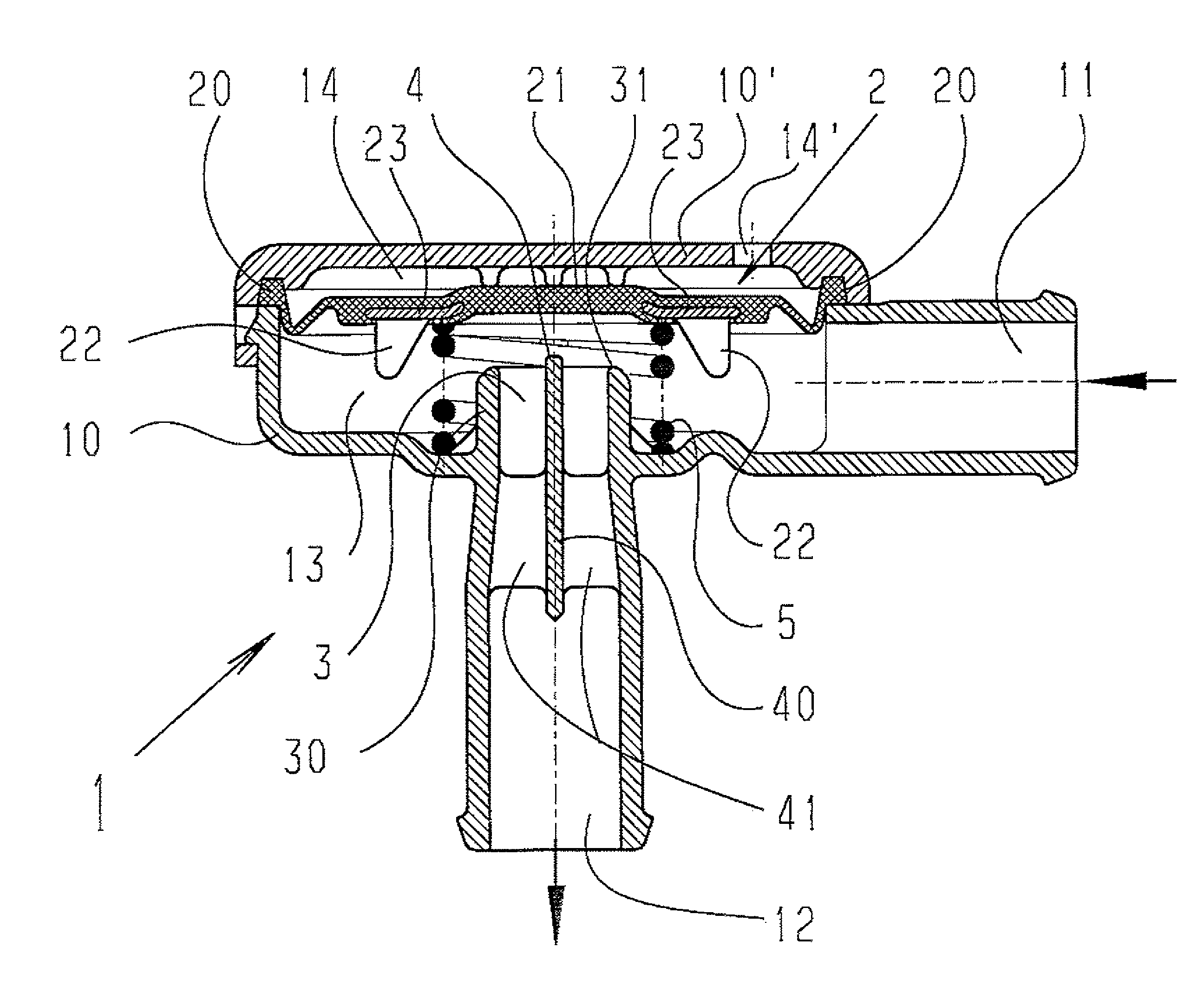
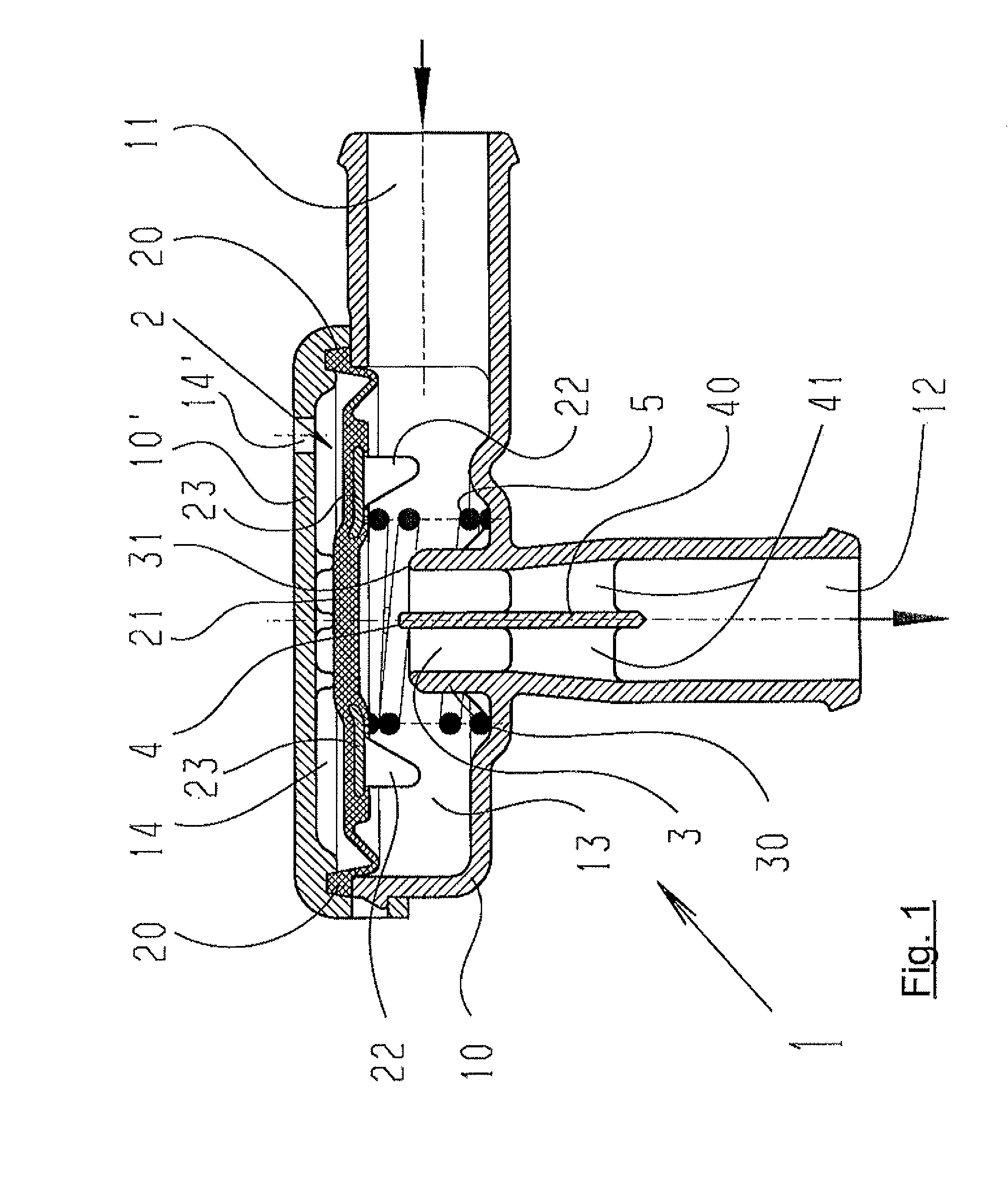
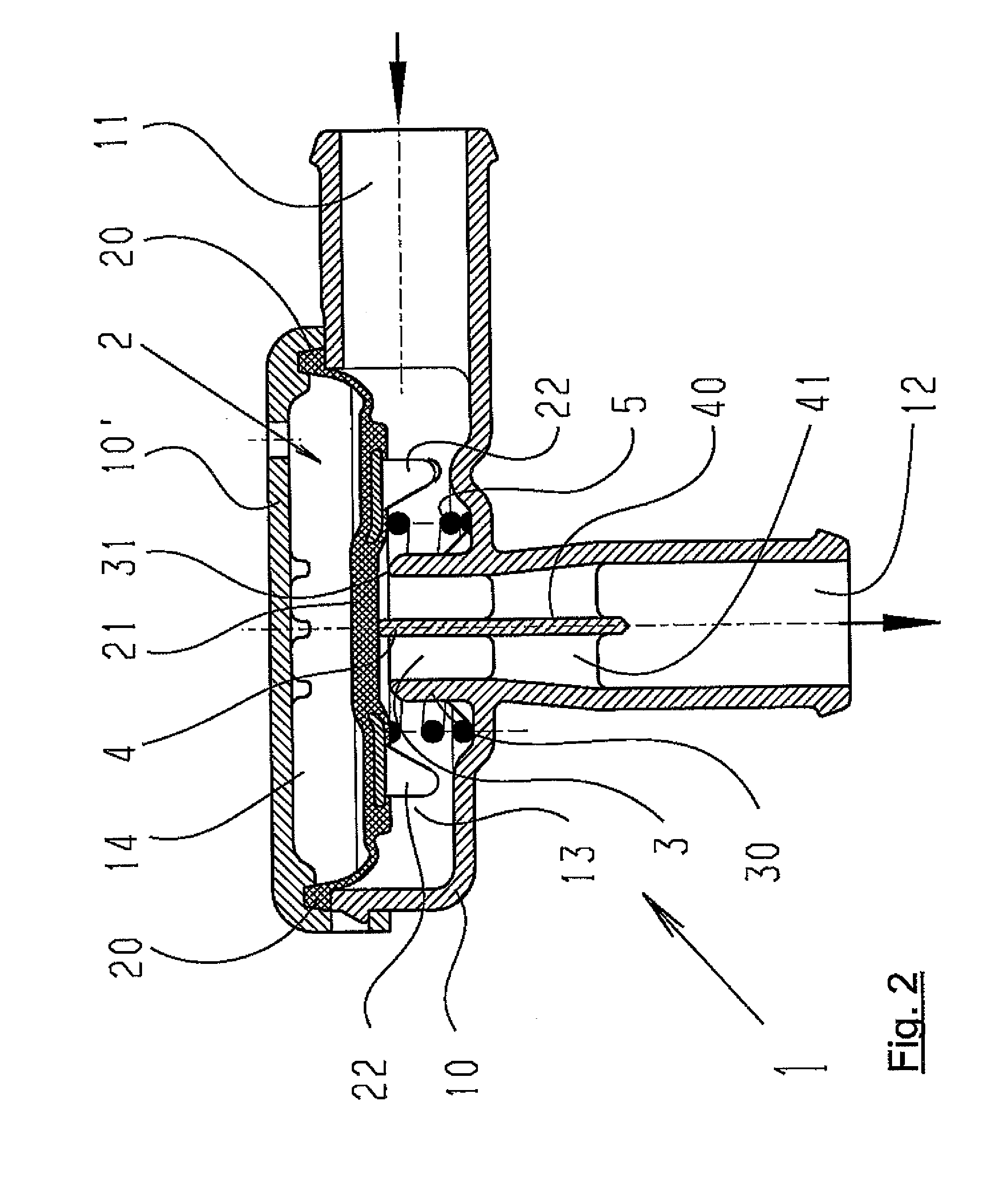
A pneumatic pressure regulating valve, the opening of which can be automatically changed in a pressure-related manner, including a control diaphragm that is subjected to a reference pressure, to the gas pressure as well as to a governor spring, wherein a change in the differential pressure causes an adjustment of the control diaphragm and the latter itself or a closing element actuated by it changes the opening through an outflow cross-section, and wherein a structure that is arranged adjacent to the outflow cross-section on the diaphragm side forms a stop for the control diaphragm or for the closing element in the closed position of said control diaphragm. At least one preliminary stop is arranged in the pressure regulating valve such that, when the control diaphragm is moving in its closing direction, the control diaphragm or the closing element first comes into contact with the preliminary stop and that, when the control diaphragm is moving further in its closing direction, the control diaphragm or the closing element will then, while being subjected to elastic and flexible deformation or being further subjected to elastic and flexible deformation respectively, further reduces the opening and, in a final position, also comes into contact with the stop.
Owner:HENGST WALTER
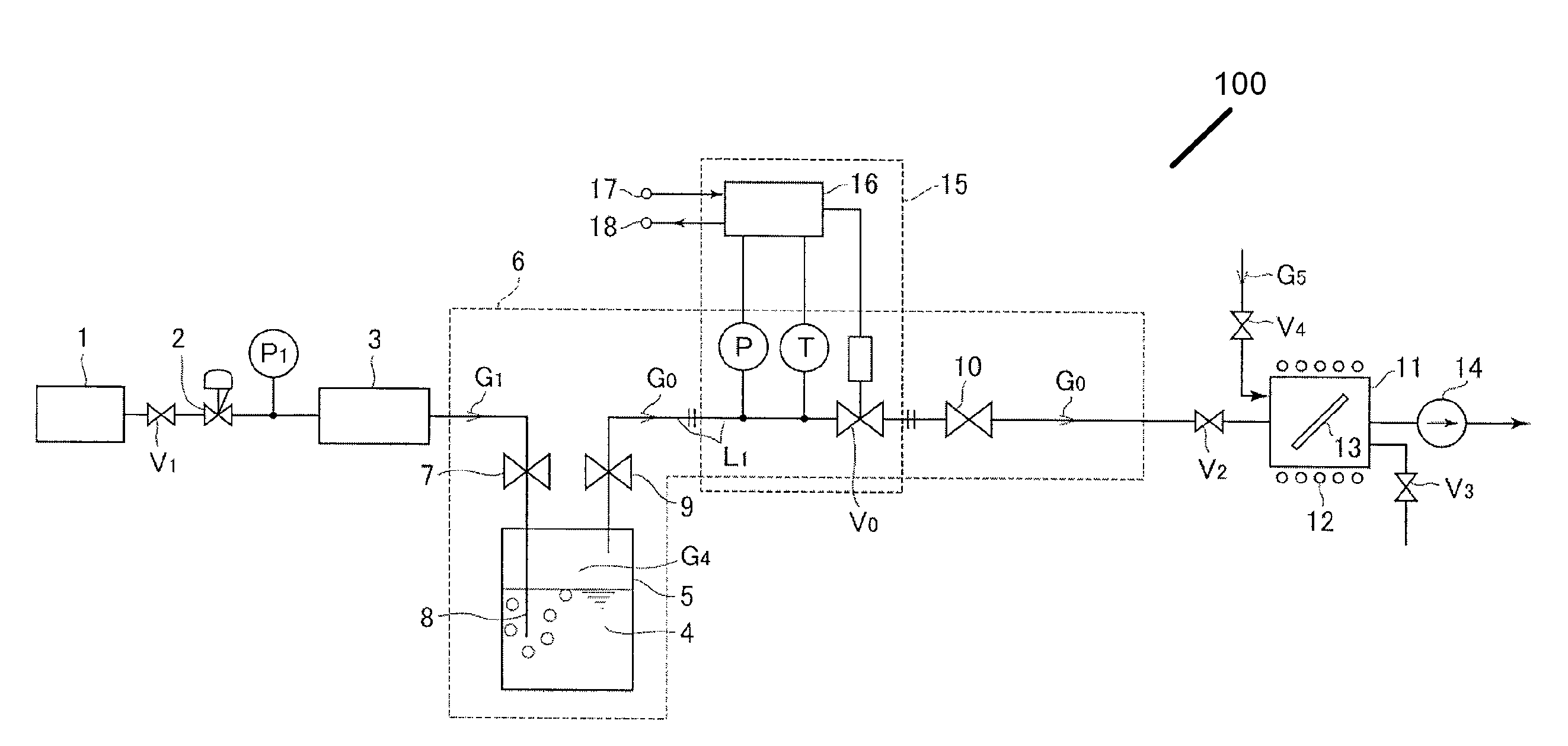
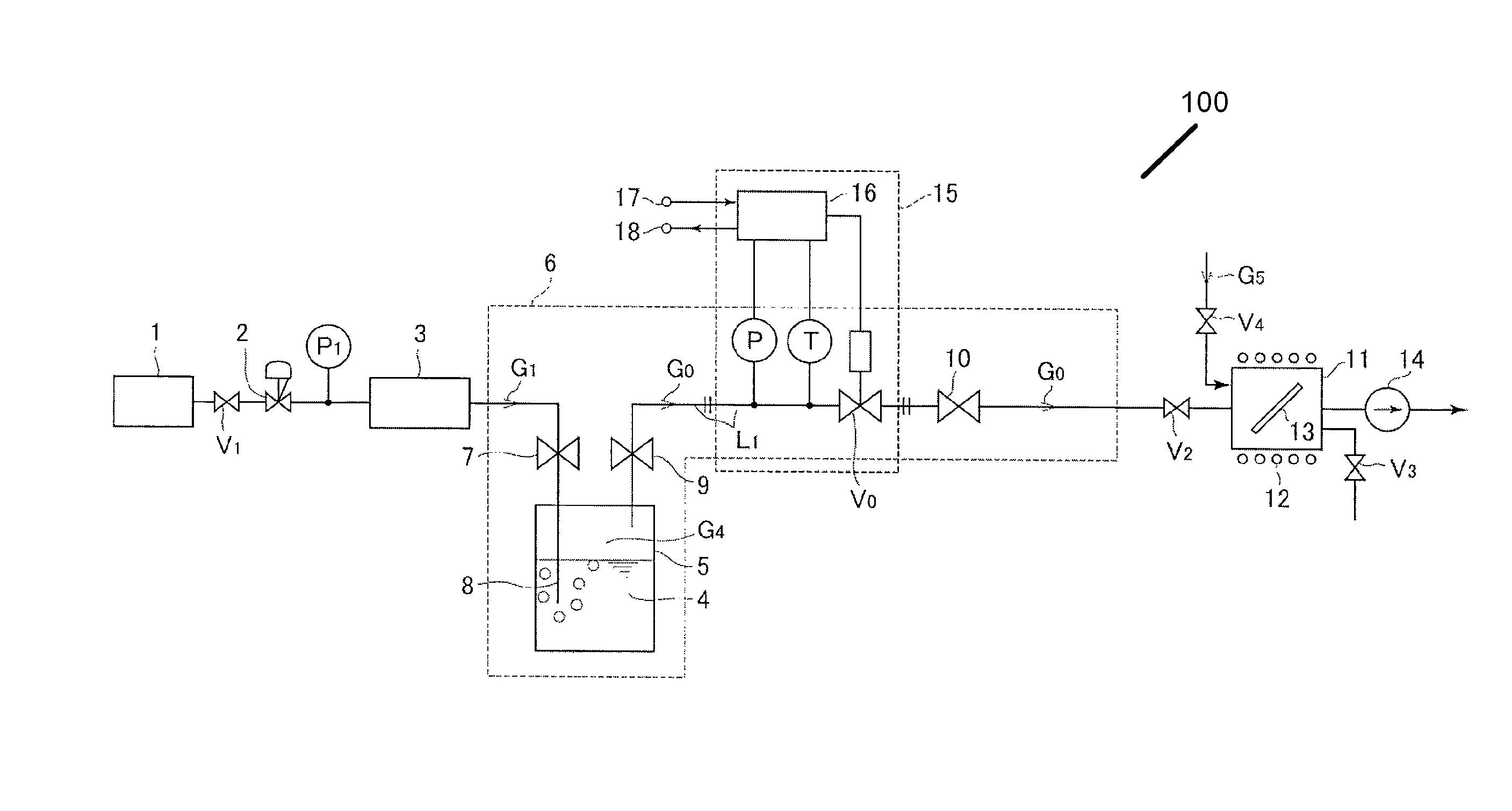
Evaporation supply apparatus for raw material and automatic pressure regulating device used therewith
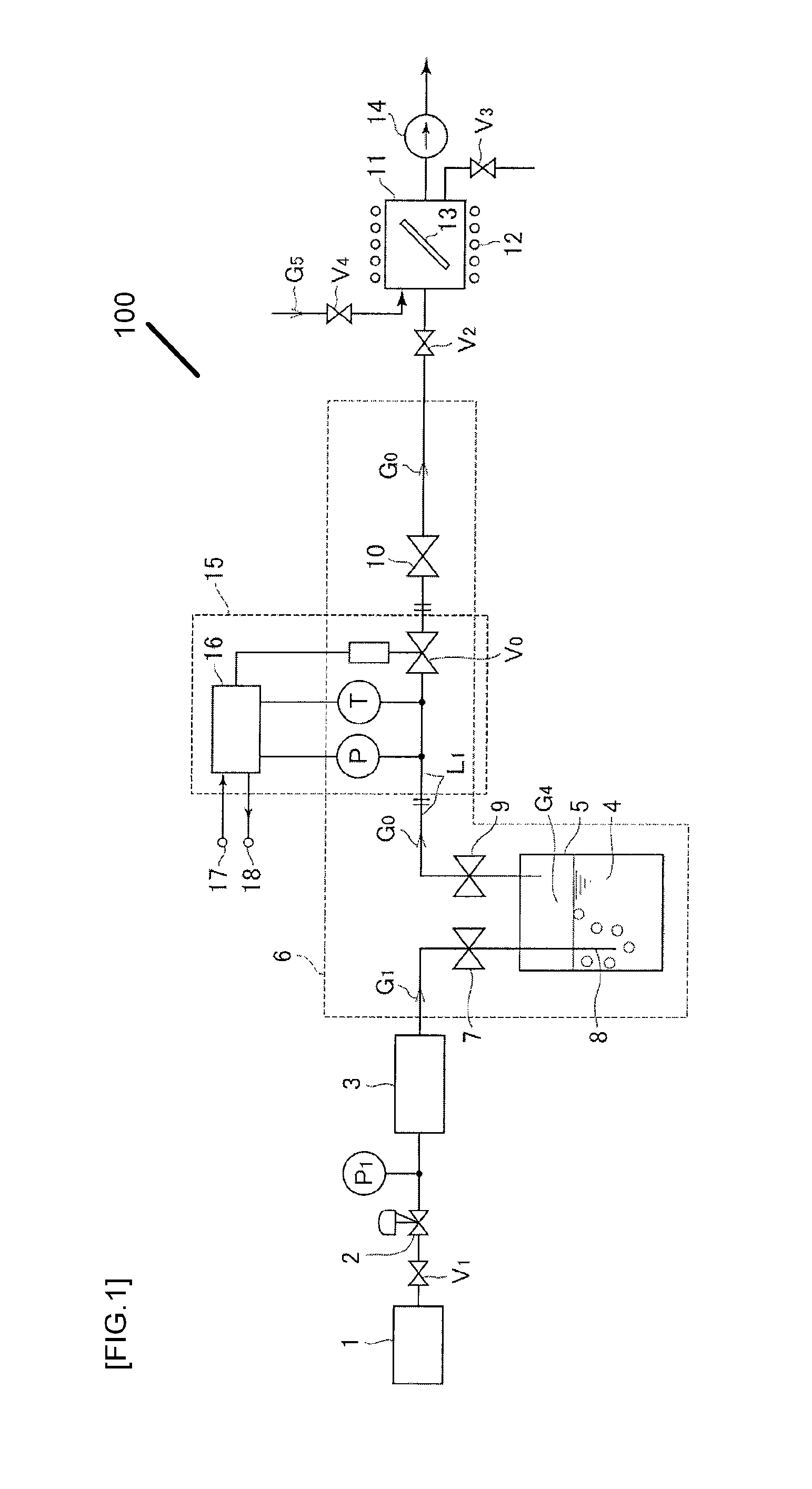
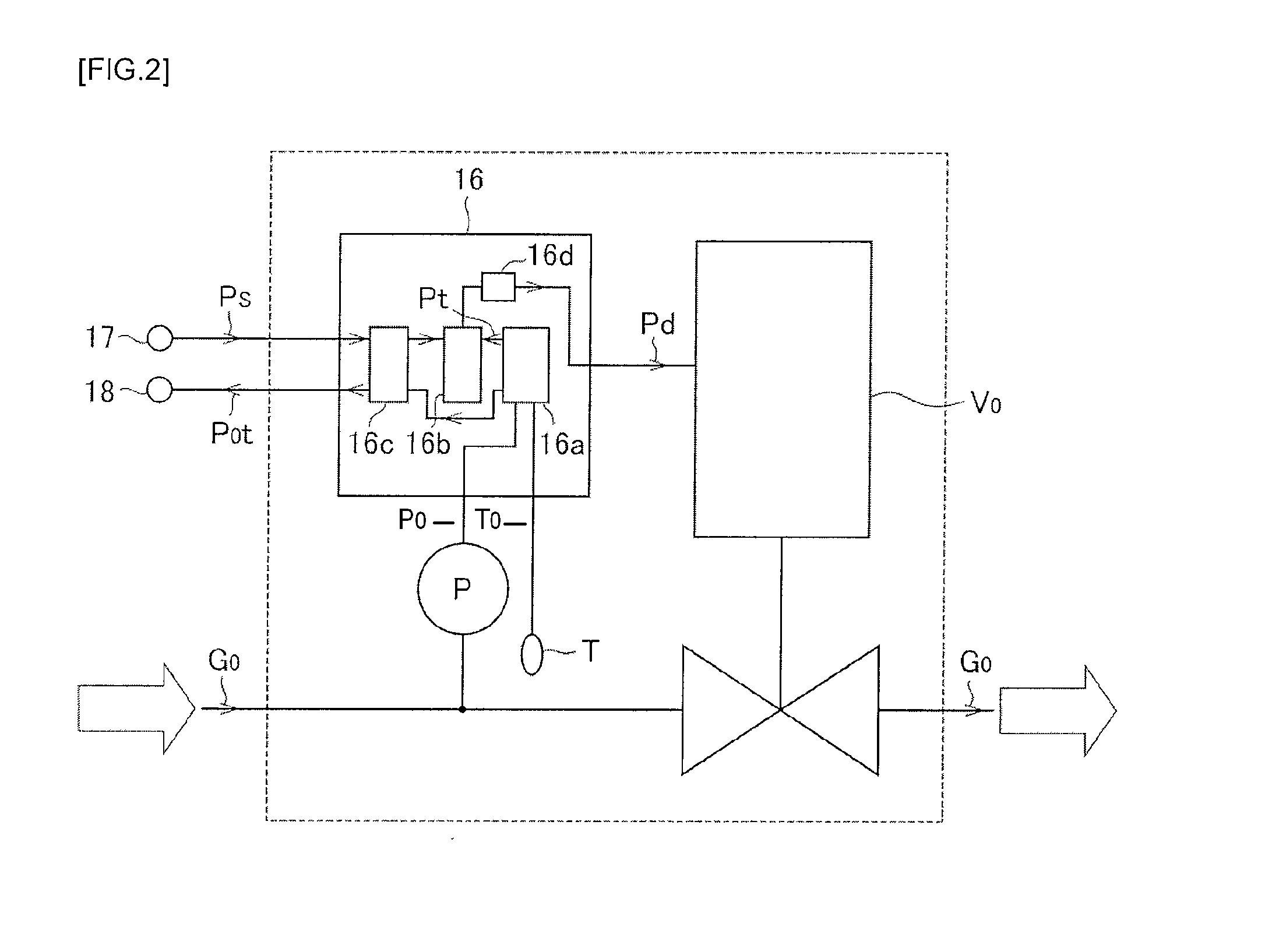
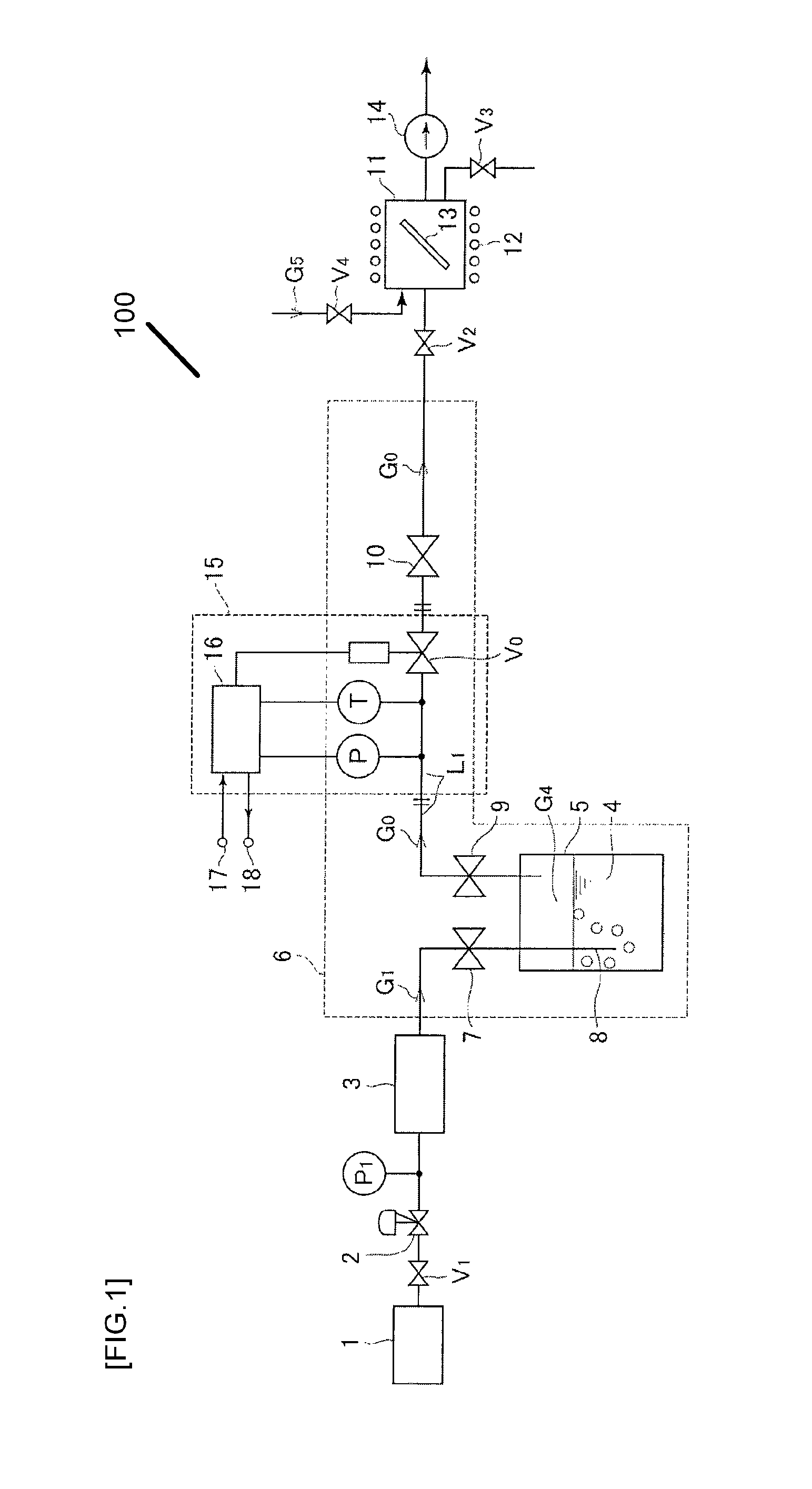
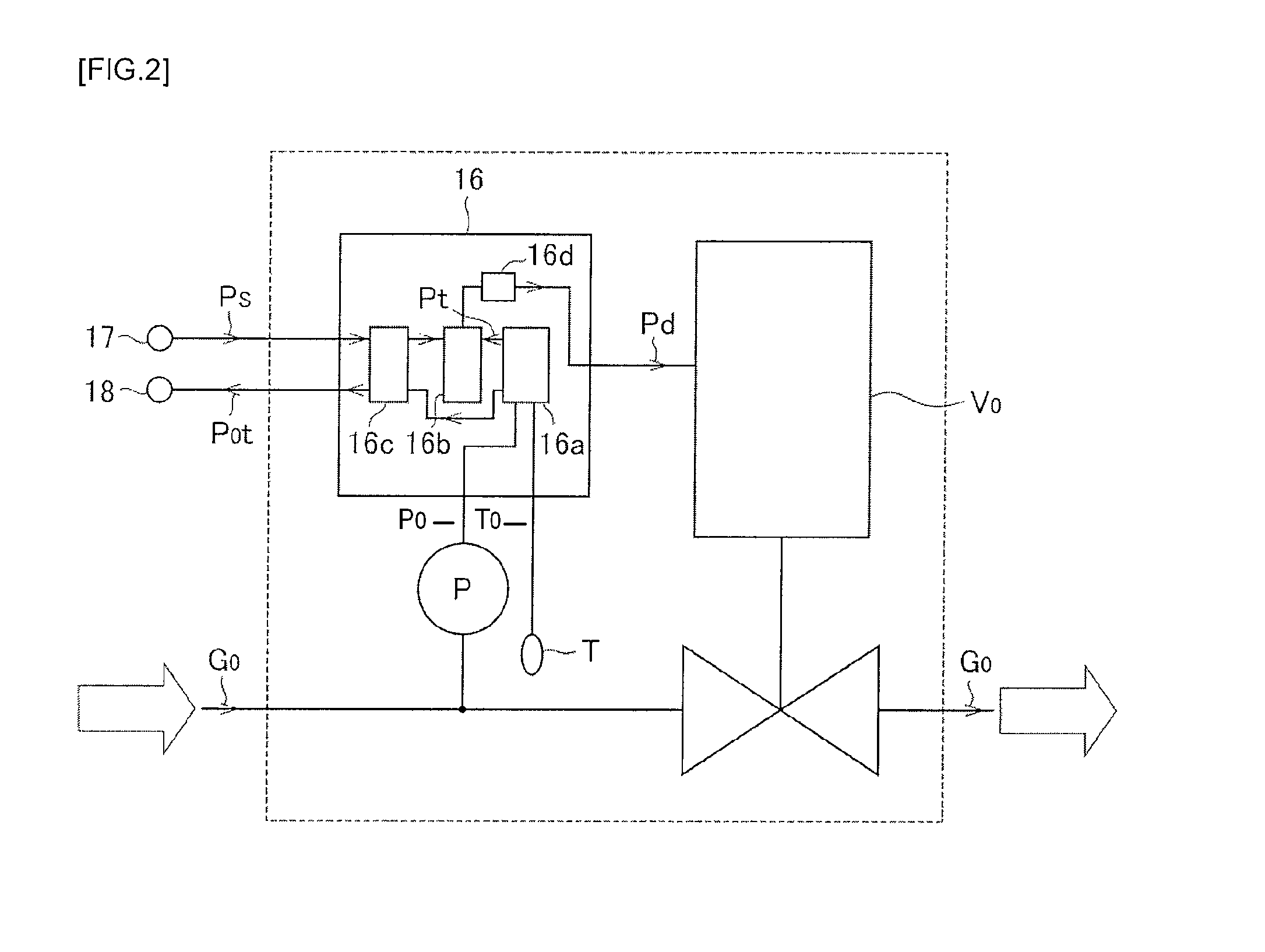
ActiveUS20100012026A1Accelerate evaporationQuality improvementCarburetting airFunctional valve typesEvaporationProduct gas
An evaporation supply apparatus for raw material used in semiconductor manufacturing includes a source tank in which a raw material is pooled; a flow rate control device that supplies carrier gas at a regulated flow rate into the source tank; a primary piping path for feeding mixed gas G0, made up of raw material vapor G4 and carrier gas G1, an automatic pressure regulating device that regulates a control valve based on the detected values of the pressure and temperature of mixed gas G0 to regulate the cross-sectional area of the passage through which the mixed gas G0 is distributed so as to hold the pressure of the mixed gas G0 inside the source tank constant; and a constant-temperature heating unit for heating the source tank to a set temperature, in which mixed gas G0 is supplied to a process chamber while controlling the pressure inside the source tank.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC
Force feedback poppet valve having an integrated pressure compensator
ActiveUS7621211B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsControl roomPilot valve
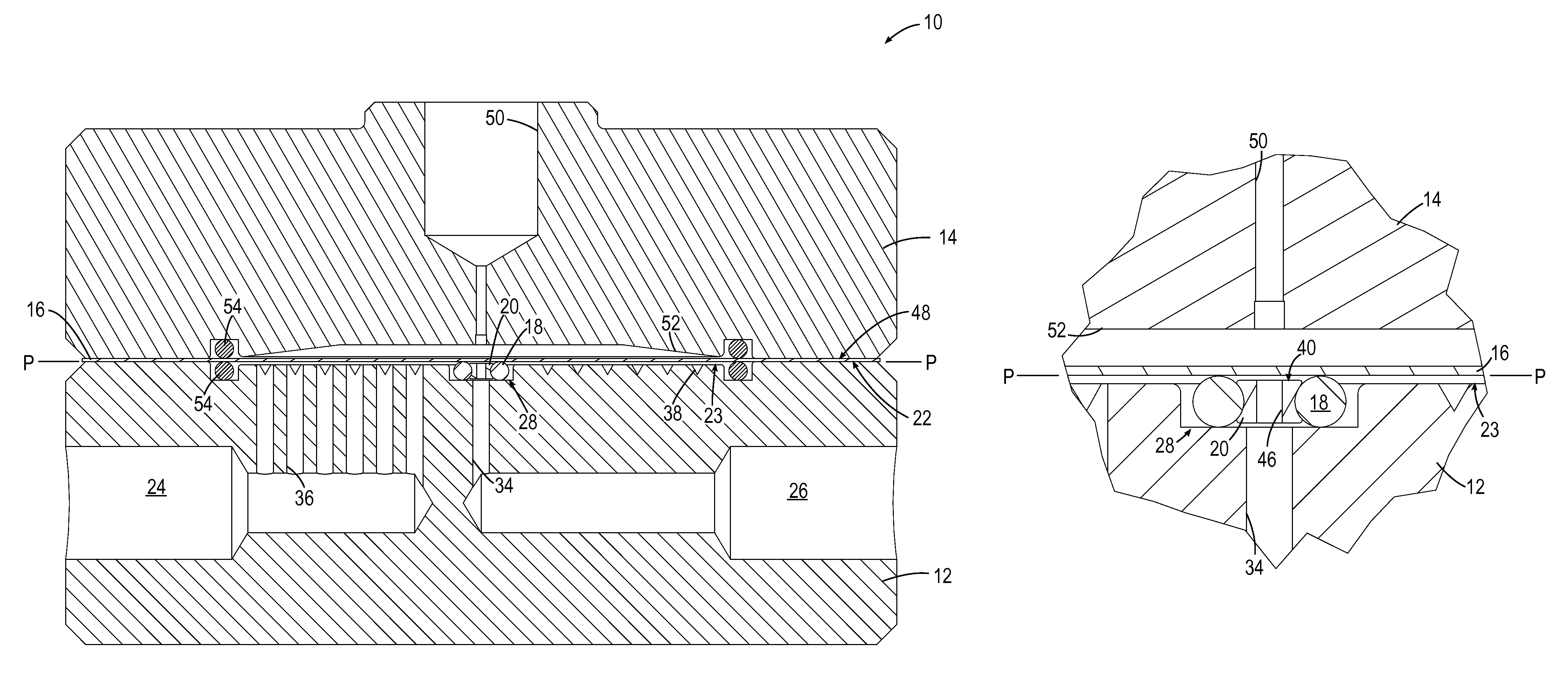
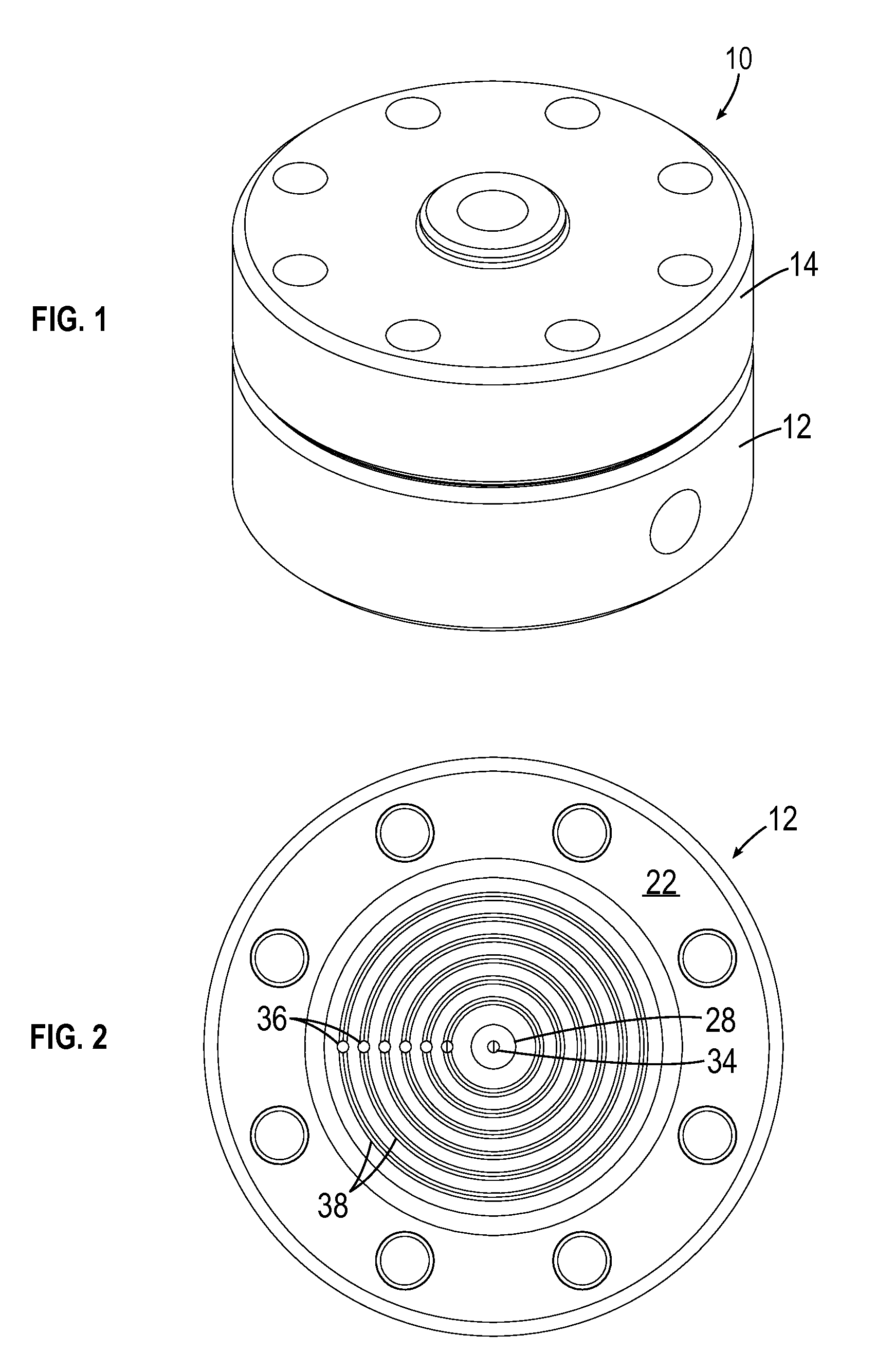
The force feedback poppet valve includes a valve body having a main chamber, a first port, and a second port. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a main poppet disposed within the main chamber and movable between an open position and a closed position to control fluid flow between the first port and the second port. The main poppet forms a control chamber within the main chamber. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a first passage communicating the control chamber with the second port, a second passage communicating the control chamber with the first port, and a pilot valve having a pilot poppet for controlling fluid flow between the control chamber and the first port through the second passage. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a pressure compensator disposed within the main poppet, and fluidly connected to the second port via the first passage. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a first spring coupled between the main poppet and the pilot poppet to provide a force proportional to a distance between the main poppet and the pilot poppet, and a second spring coupled between the pressure compensator and the pilot poppet to provide a force proportional to a distance between the pressure compensator and the pilot poppet.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC +1
Oil pressure regulating valve for generator applications
A generator includes a rotor to be driven to rotate and generate electricity and a housing receiving the rotor. An oil supply includes an oil inlet port and an oil outlet port. A pressure regulating valve regulates the flow of oil from the inlet port to the outlet port. The pressure regulating valve includes a valve sleeve mounted within the housing. The valve sleeve extends into a bore within the housing. A valve spool is mounted within the valve sleeve. The valve sleeve has a flange abutting an outer face of the housing. Bolts tighten the flange against the housing. An inner end of the valve sleeve extends radially inwardly to form a ledge. The ledge is spaced away from an inner face of the housing. A valve sleeve, a sense piston and a valve spool are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
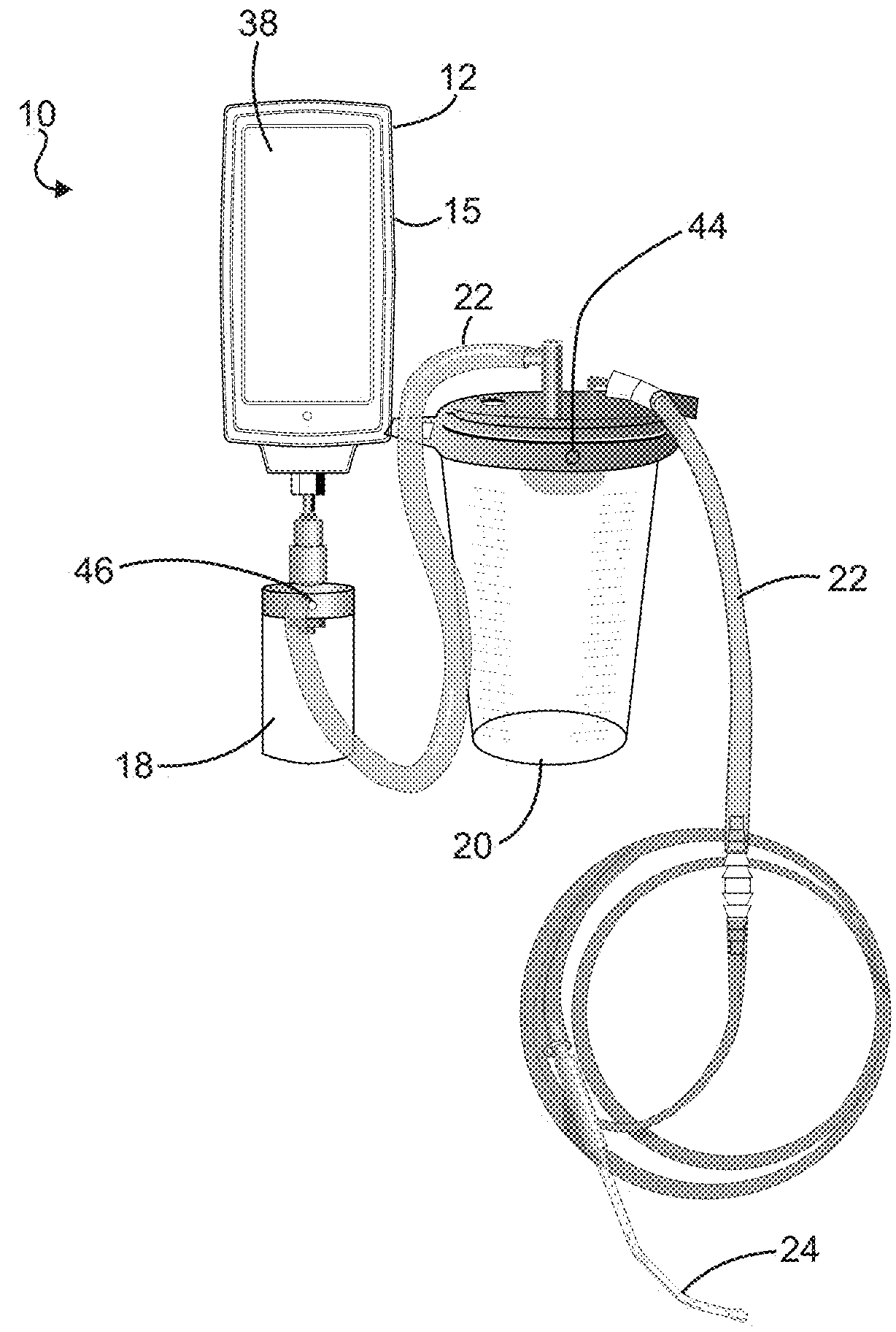
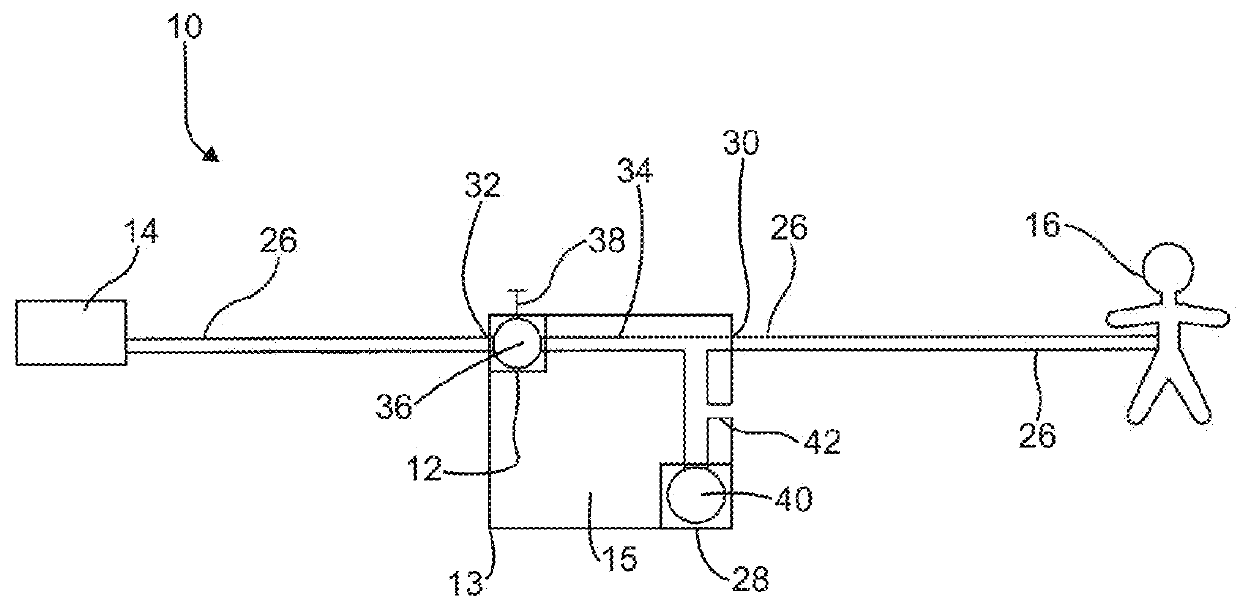
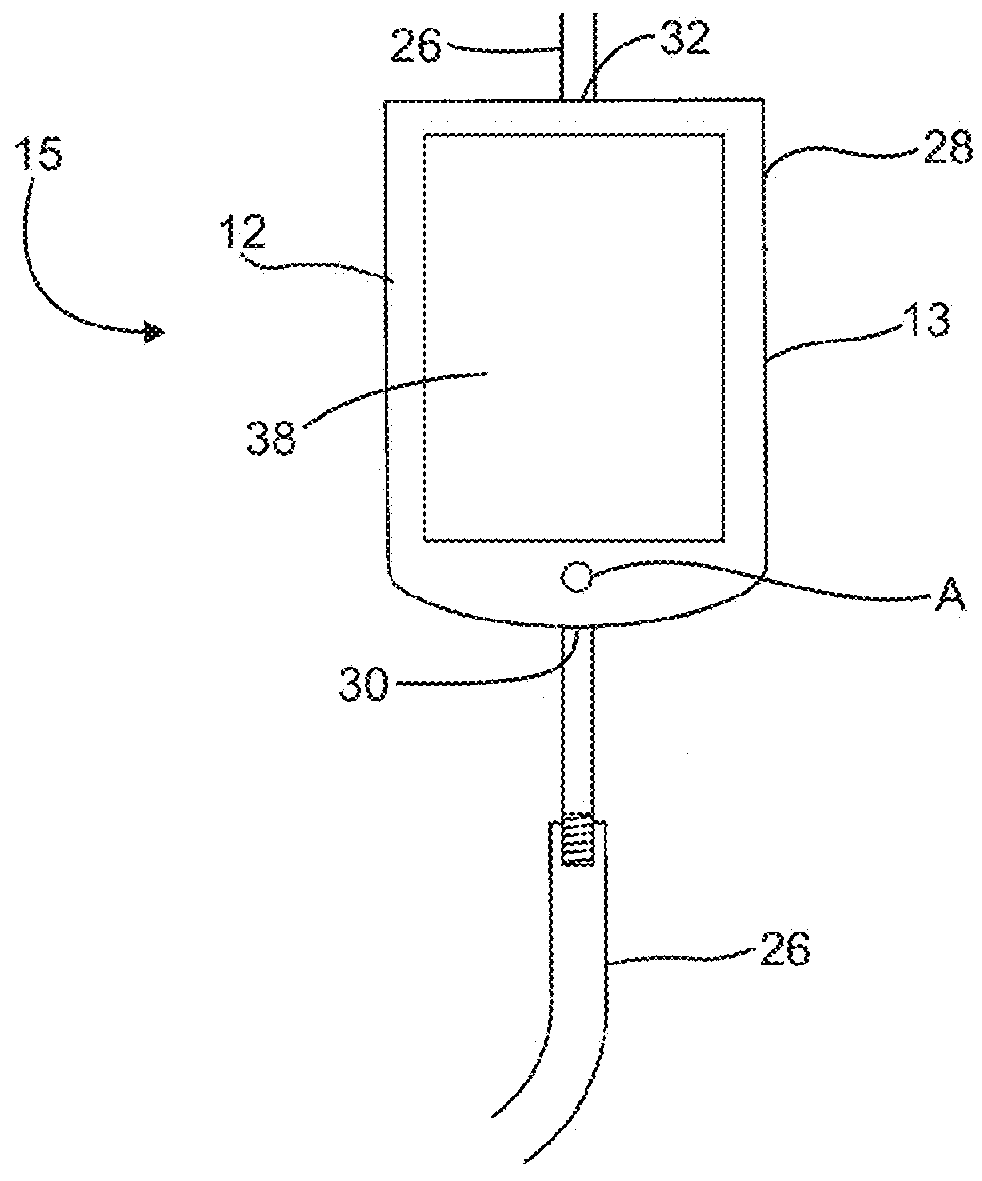
Electronic vacuum regulator device
ActiveUS20180104390A1Medical devicesIntravenous devicesElectronElectrical and Electronics engineering
A vacuum regulator device having a vacuum regulator and a vacuum gauge on a housing line that is configured to be in fluid communication with a patient include an electronic valve that selectively opens and closes the housing line. The vacuum gauge is located between the vacuum regulator and the patient and includes an electronic flow sensor upstream. The electronic flow sensor provides feedback to the vacuum regulator.
Owner:MEDTEC MEDICAL INC
Evaporation supply apparatus for raw material and automatic pressure regulating device used therewith
InactiveUS8047510B2Accelerate evaporationQuality improvementCarburetting airFunctional valve typesEvaporationProcess engineering
An evaporation supply apparatus for raw material used in semiconductor manufacturing includes a source tank in which a raw material is pooled; a flow rate control device that supplies carrier gas at a regulated flow rate into the source tank; a primary piping path for feeding mixed gas G0, made up of raw material vapor G4 and carrier gas G1, an automatic pressure regulating device that regulates a control valve based on the detected values of the pressure and temperature of mixed gas G0 to regulate the cross-sectional area of the passage through which the mixed gas G0 is distributed so as to hold the pressure of the mixed gas G0 inside the source tank constant; and a constant-temperature heating unit for heating the source tank to a set temperature, in which mixed gas G0 is supplied to a process chamber while controlling the pressure inside the source tank.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC
Force feedback poppet valve having an integrated pressure compensator
ActiveUS20080295508A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid couplingsControl roomEngineering
The force feedback poppet valve includes a valve body having a main chamber, a first port, and a second port. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a main poppet disposed within the main chamber and movable between an open position and a closed position to control fluid flow between the first port and the second port. The main poppet forms a control chamber within the main chamber. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a first passage communicating the control chamber with the second port, a second passage communicating the control chamber with the first port, and a pilot valve having a pilot poppet for controlling fluid flow between the control chamber and the first port through the second passage. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a pressure compensator disposed within the main poppet, and fluidly connected to the second port via the first passage. The force feedback poppet valve further includes a first spring coupled between the main poppet and the pilot poppet to provide a force proportional to a distance between the main poppet and the pilot poppet, and a second spring coupled between the pressure compensator and the pilot poppet to provide a force proportional to a distance between the pressure compensator and the pilot poppet.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC +1
Back pressure regulator with floating seal support
ActiveUS20140203198A1Diaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringPressure regulator
A sealing apparatus for a back pressure regulator includes: a body defining a process surface, and including: at least one process void communicating with the process surface; a recess disposed in the process surface; a floating support hub disposed in the recess, carrying an O-ring; a vent void communicating with the recess; an inlet port disposed in fluid communication with the at least one process void and adapted to be coupled in fluid communication with a fluid at a process pressure; and an outlet port disposed in fluid communication with the vent void; and a diaphragm having opposed reference and process sides, the diaphragm disposed against the body such that the process side is substantially coplanar with the process surface.
Owner:EQUILIBAR
Adjustable deadband control system
ActiveUS20160356389A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesEqualizing valvesEngineeringDeadband
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT REGULATOR TECH INC
Back pressure valve
InactiveUS20140261785A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesEqualizing valvesEngineeringPressure regulator
A back pressure valve comprises a pressure regulator housing affixed to a pressure controller housing and a diaphragm disposed between the pressure regulator housing and the pressure controller housing. In one aspect, the back pressure valve includes a valve member moveable between a fully open position and a fully closed position. The pressure regulator housing includes an inlet chamber communicating with an outlet chamber through at least one fluid passage in a sleeve. The valve member includes a stem connected to a valve head. The valve head includes an outer surface that is received and guided during movement by an inner surface of the sleeve. The outer surface of the valve head includes an upper outer surface and a lower outer surface separated by a cavity adapted to receive a sealing element. Upper and lower outer surface of the valve head provide stability to the valve member during opening and closing of the back pressure valve.
Owner:FLOMATIC CORP
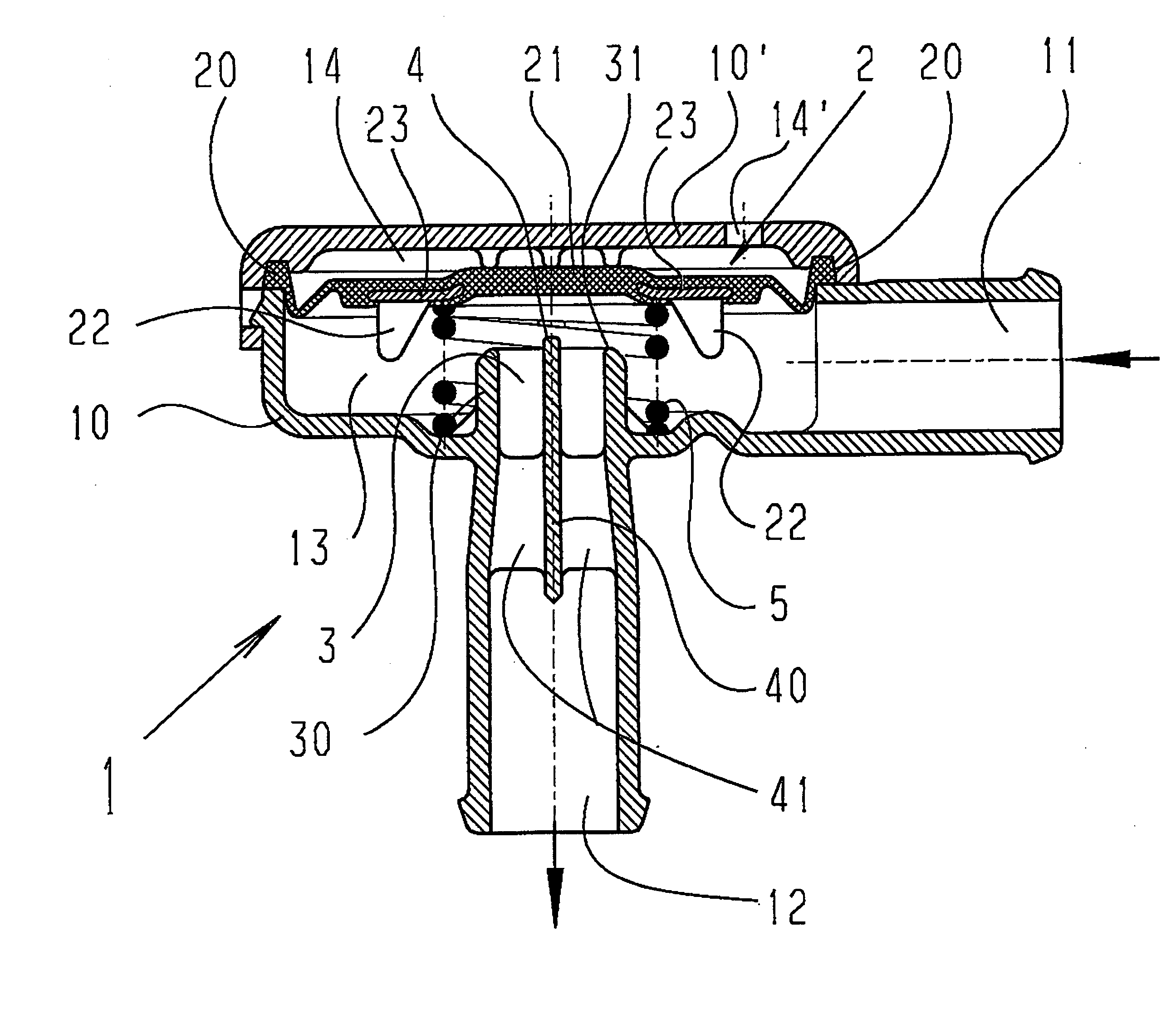
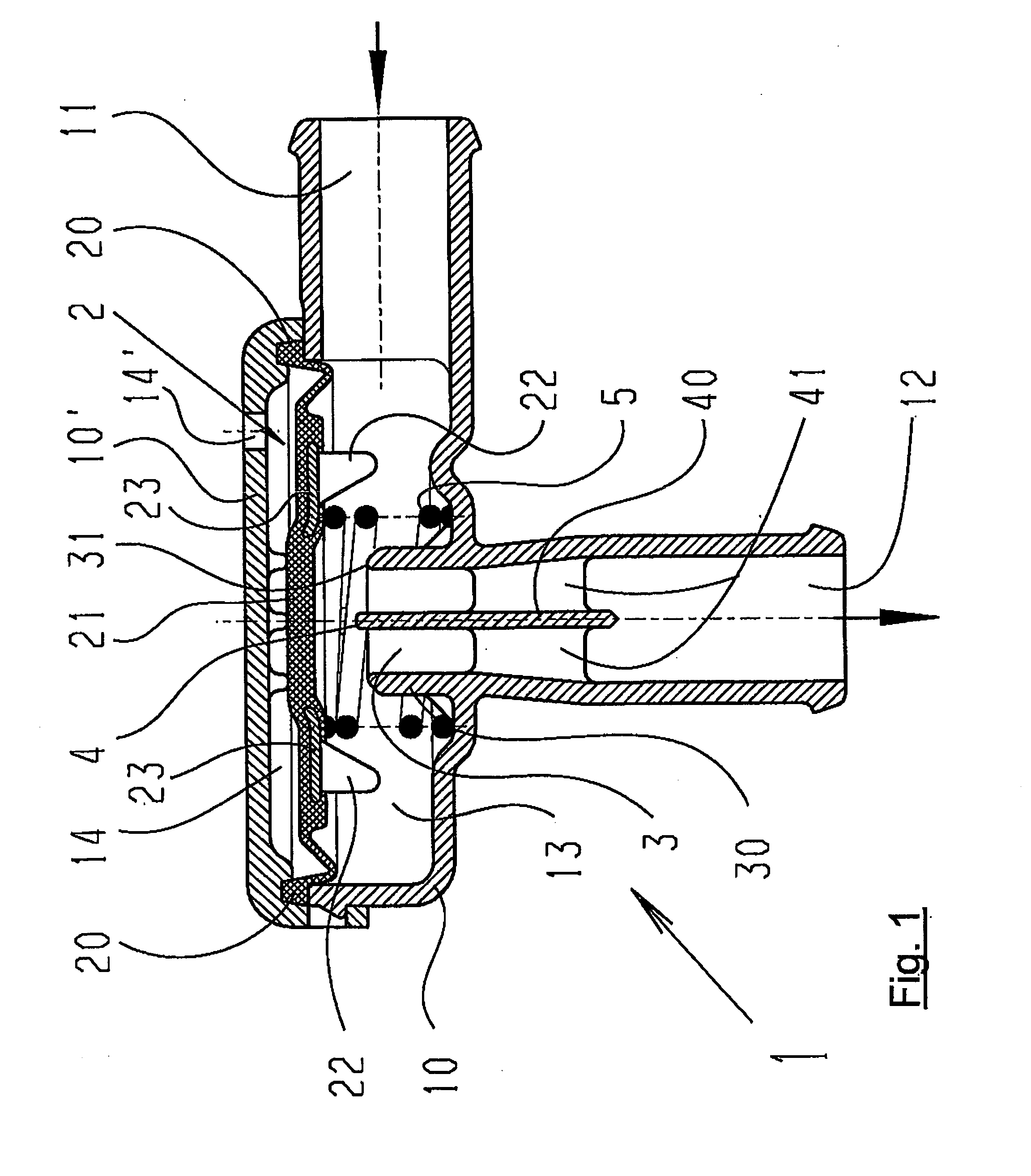
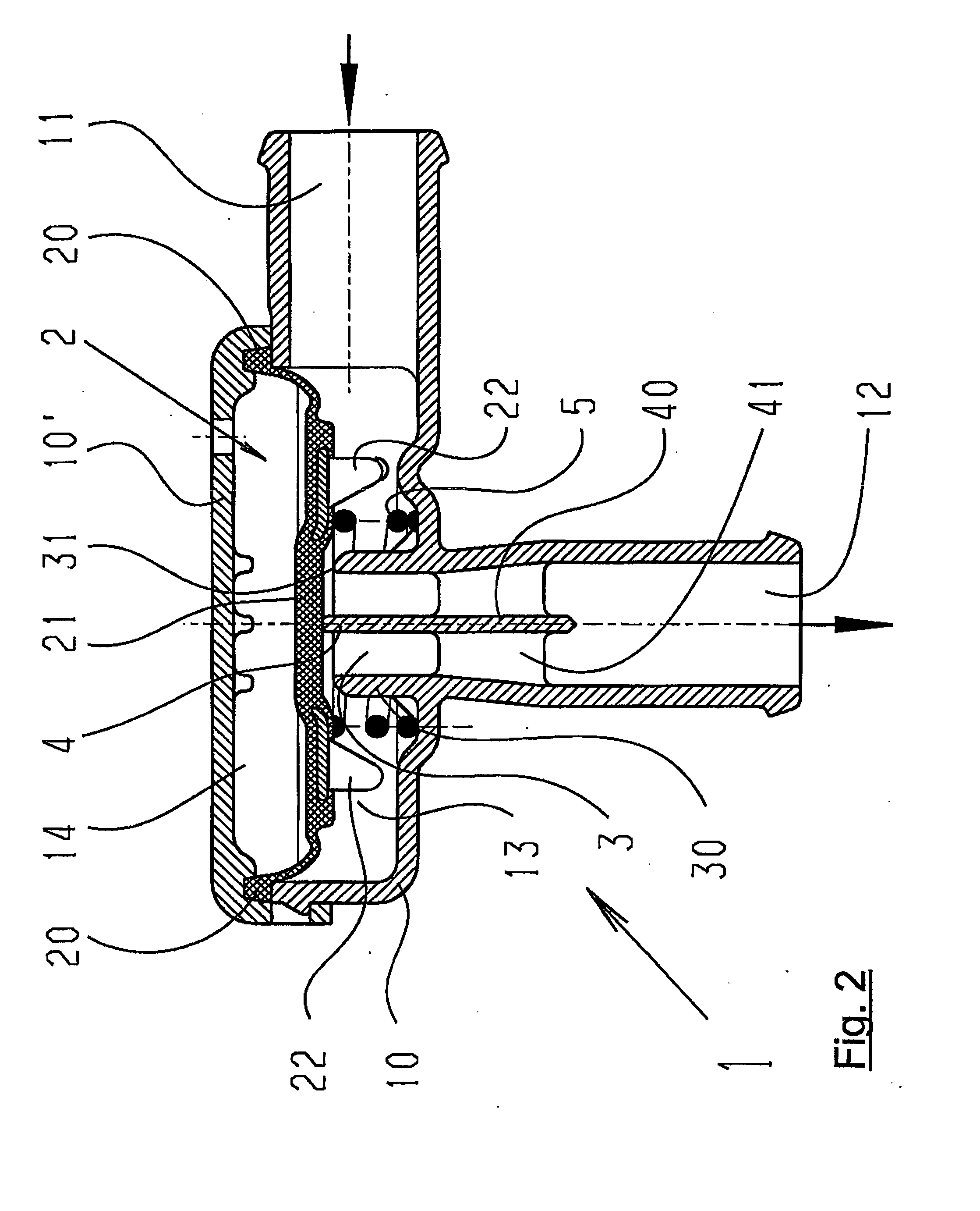
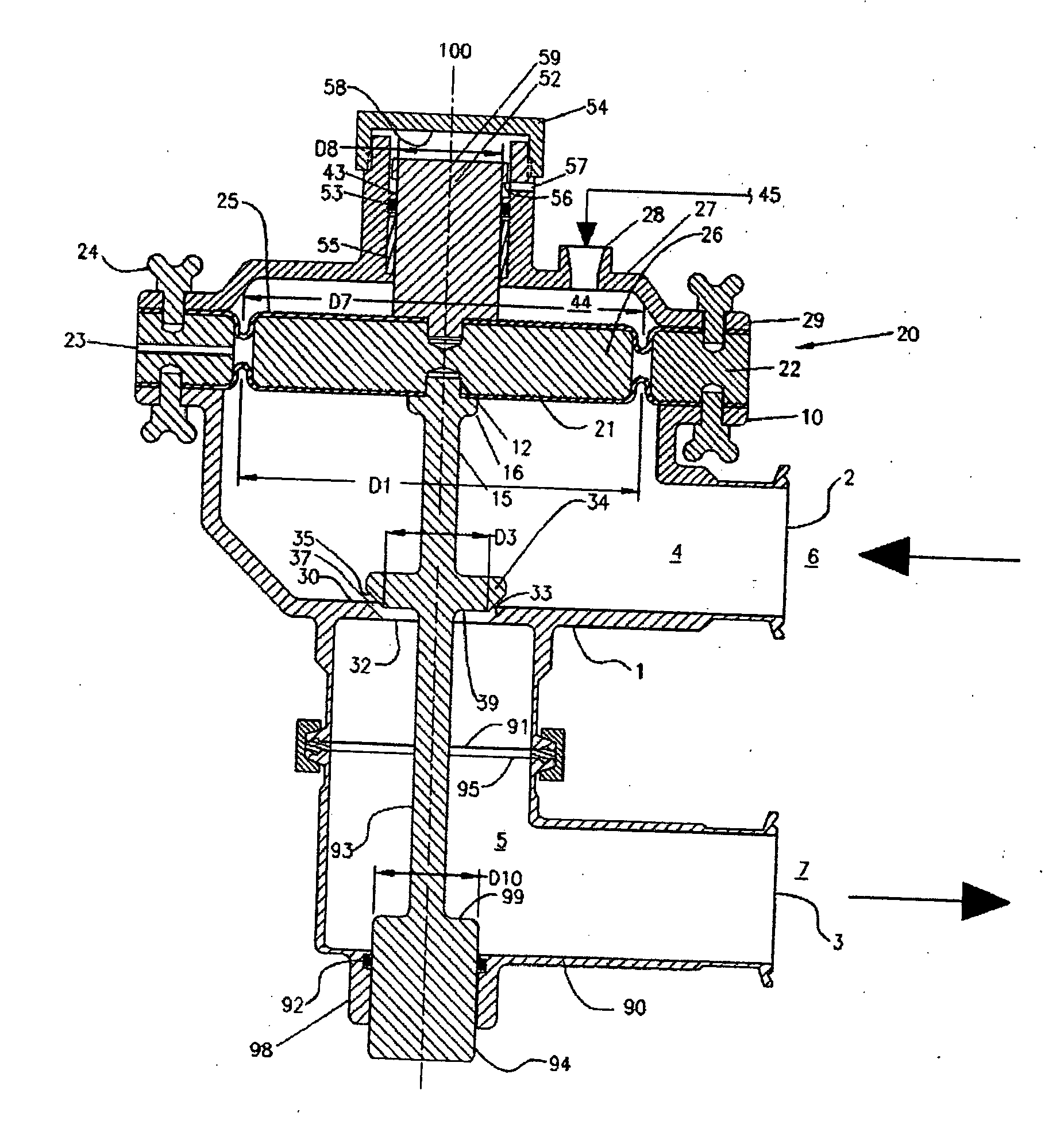
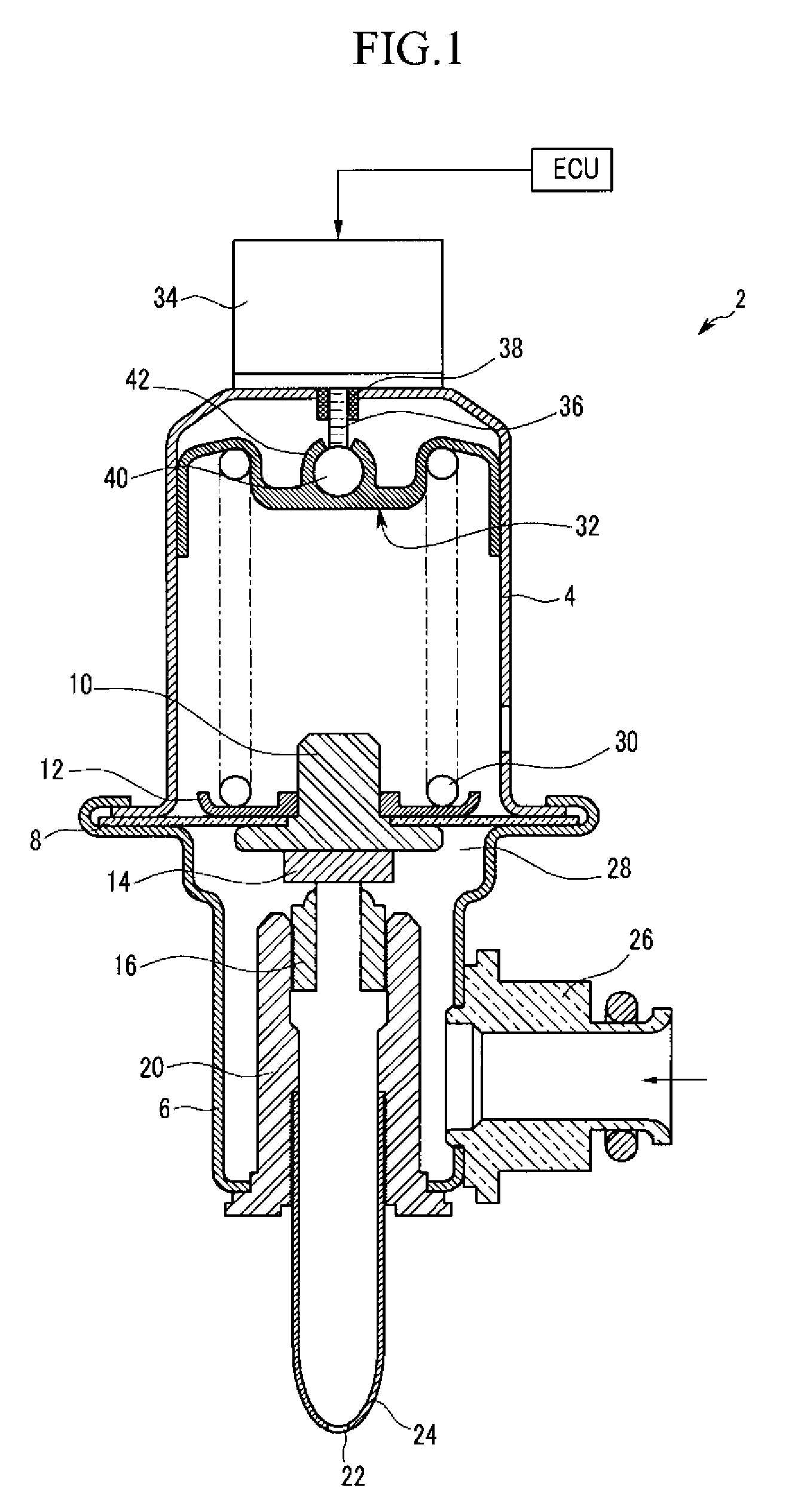
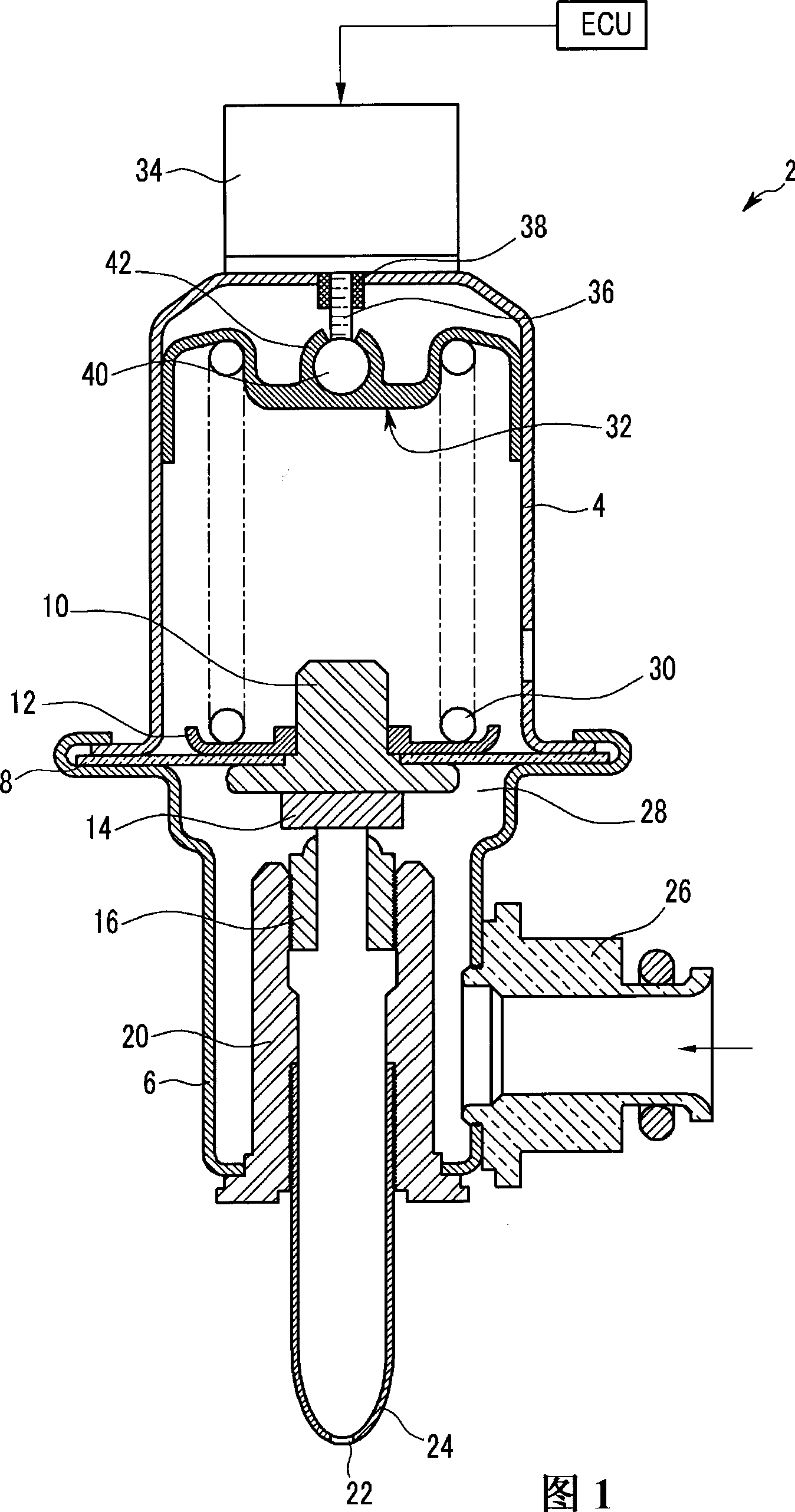
Pneumatic pressure regulation valve
ActiveUS7950621B2Reliable functionImprove control characteristicsDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDifferential pressureVALVE PORT
A pneumatic pressure regulating valve, the opening of which can be automatically changed in a pressure-related manner, including a control diaphragm that is subjected to a reference pressure, to the gas pressure as well as to a governor spring, wherein a change in the differential pressure causes an adjustment of the control diaphragm and the latter itself or a closing element actuated by it changes the opening through an outflow cross-section, and wherein a structure that is arranged adjacent to the outflow cross-section on the diaphragm side forms a stop for the control diaphragm or for the closing element in the closed position of said control diaphragm. At least one preliminary stop is arranged in the pressure regulating valve such that, when the control diaphragm is moving in its closing direction, the control diaphragm or the closing element first comes into contact with the preliminary stop and that, when the control diaphragm is moving further in its closing direction, the control diaphragm or the closing element will then, while being subjected to elastic and flexible deformation or being further subjected to elastic and flexible deformation respectively, further reduces the opening and, in a final position, also comes into contact with the stop.
Owner:HENGST WALTER
Sanitary liquid pressure regulator
InactiveUS20050056318A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control without auxillary powerLiquid productEngineering
A liquid pressure reducing regulator having a pressure receiving means in liquid communication with the liquid inlet passage, upon which a liquid in the liquid inlet passage can exert a balancing force, and a means for communicating the balancing force to the diaphragm opposing an overpressure force exerted by the inlet liquid on the pressure control diaphragm. The liquid pressure regulator typically employs a balancing piston that can transfer pressure fluctuations in the flow outlet into an equal and opposite force on the valve plug, and results in a net force of zero in the diaphragm plate. As a result, changes in the liquid pressure downstream of the valve plug only nominally, and typically negligibly, affect the upstream control of the liquid product. The invention also relates to a liquid pressure control valve having a liquid housing defining a liquid flow passage having a first flow passage, a second flow passage, and an orifice means intermediate between and providing communication between the first flow passage and the second flow passage, the orifice means having an opening, and a diaphragm assembly comprising a diaphragm having a liquid side forming a portion of the first flow passage, and an opposed control side, the diaphragm being moveable along a central axis. A control housing has a control means for applying a control force to the control side of the diaphragm. A valve plug is positioned proximate the opening of a valve orifice having a variable effective area as a function of the position of the valve plug. The valve plug has an opposed second side having a second surface in liquid communication with the second flow passage, where against a liquid in the second flow passage can exert a differential force against the diaphragm. The control valve has a pressure receiving means in liquid communication with the second flow passage, upon which a liquid in the second flow passage can exert a balancing force, and a means for communicating the balancing force to the diaphragm opposing the differential force.
Owner:ARLINGHAUS JR JOSEPH WILFRED
Adjustable deadband control system
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT REGULATOR TECH INC
Sanitary liquid pressure regulator
InactiveUS6929026B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control without auxillary powerLiquid productNet force
A pressure building regulator having a pressure receiving means in liquid communication with the liquid outlet passage, upon which a liquid in the liquid outlet passage can exert a balancing force, and a means for communicating the balancing force to the diaphragm opposing the backpressure force. The liquid pressure regulator typically employs a balancing piston which can transfer pressure fluctuations in the flow outlet into an equal and opposite force on the valve plug, and results in a net force of zero in the diaphragm plate. As a result, changes in the liquid pressure downstream of the valve plug only nominally, and typically negligibly, affect the upstream control of the liquid product.The invention also includes a pressure reducing regulator, configured with a balancing piston which can transfer pressure fluctuations in the flow outlet into an equal and opposite force on the valve plug, and results in a net force of zero in the diaphragm plate.The invention further provides a liquid pressure regulator having a differential diaphragm plate having a rigid structure, having a first side of a first surface area, and an opposed second side of a second surface area, where the first surface area and the second surface area are unequal. The differential diaphragm plate permits the use of conventional compressed air control regulators with the liquid pressure regulator to control a high pressure liquid system more accurately.
Owner:ARLINGHAUS JR JOSEPH WILFRED
Back pressure regulator with floating seal support
ActiveUS9447890B2Diaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure regulatorBack pressure
A sealing apparatus for a back pressure regulator includes: a body defining a process surface, and including: at least one process void communicating with the process surface; a recess disposed in the process surface; a floating support hub disposed in the recess, carrying an O-ring; a vent void communicating with the recess; an inlet port disposed in fluid communication with the at least one process void and adapted to be coupled in fluid communication with a fluid at a process pressure; and an outlet port disposed in fluid communication with the vent void; and a diaphragm having opposed reference and process sides, the diaphragm disposed against the body such that the process side is substantially coplanar with the process surface.
Owner:EQUILIBAR
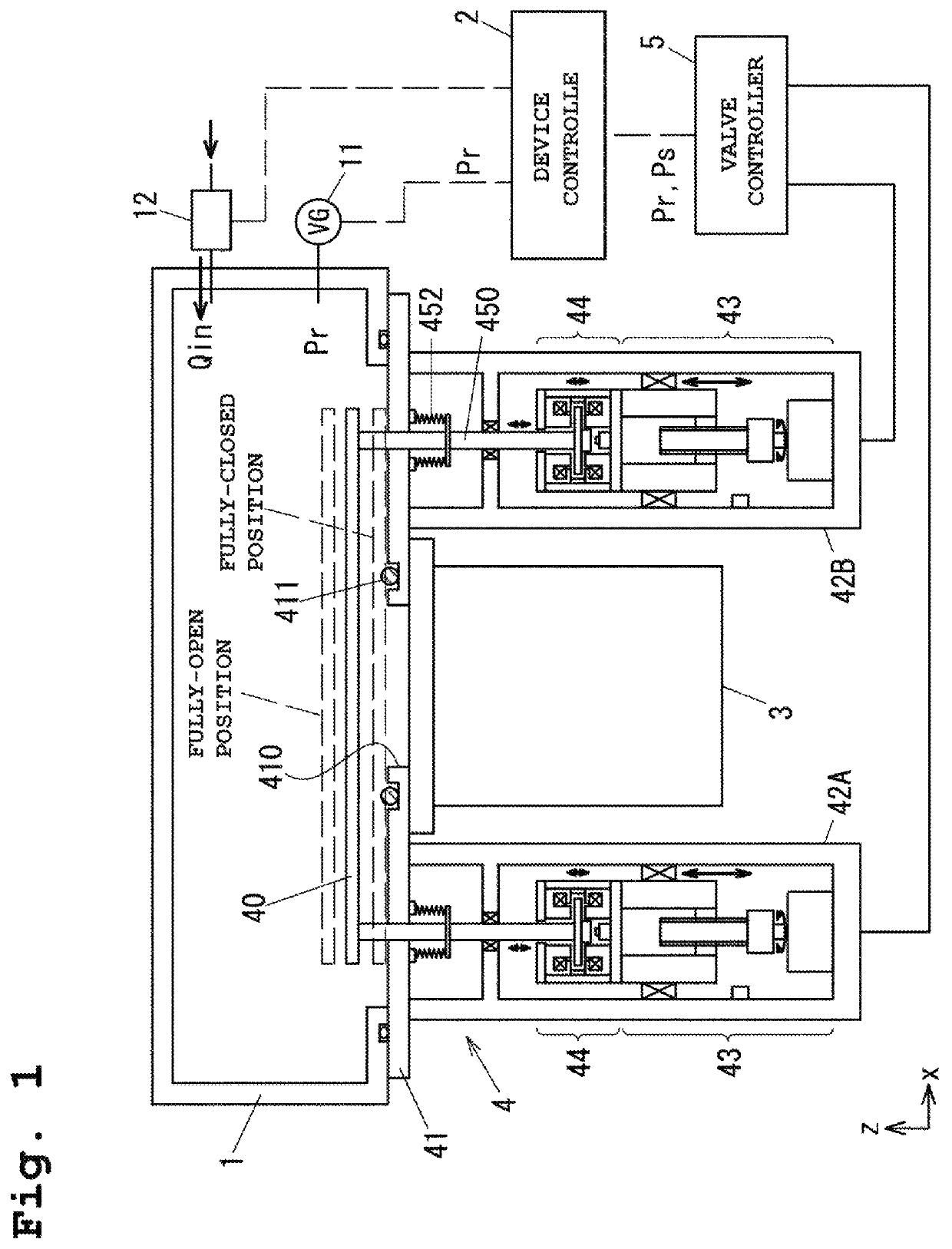
Vacuum pressure regulation system
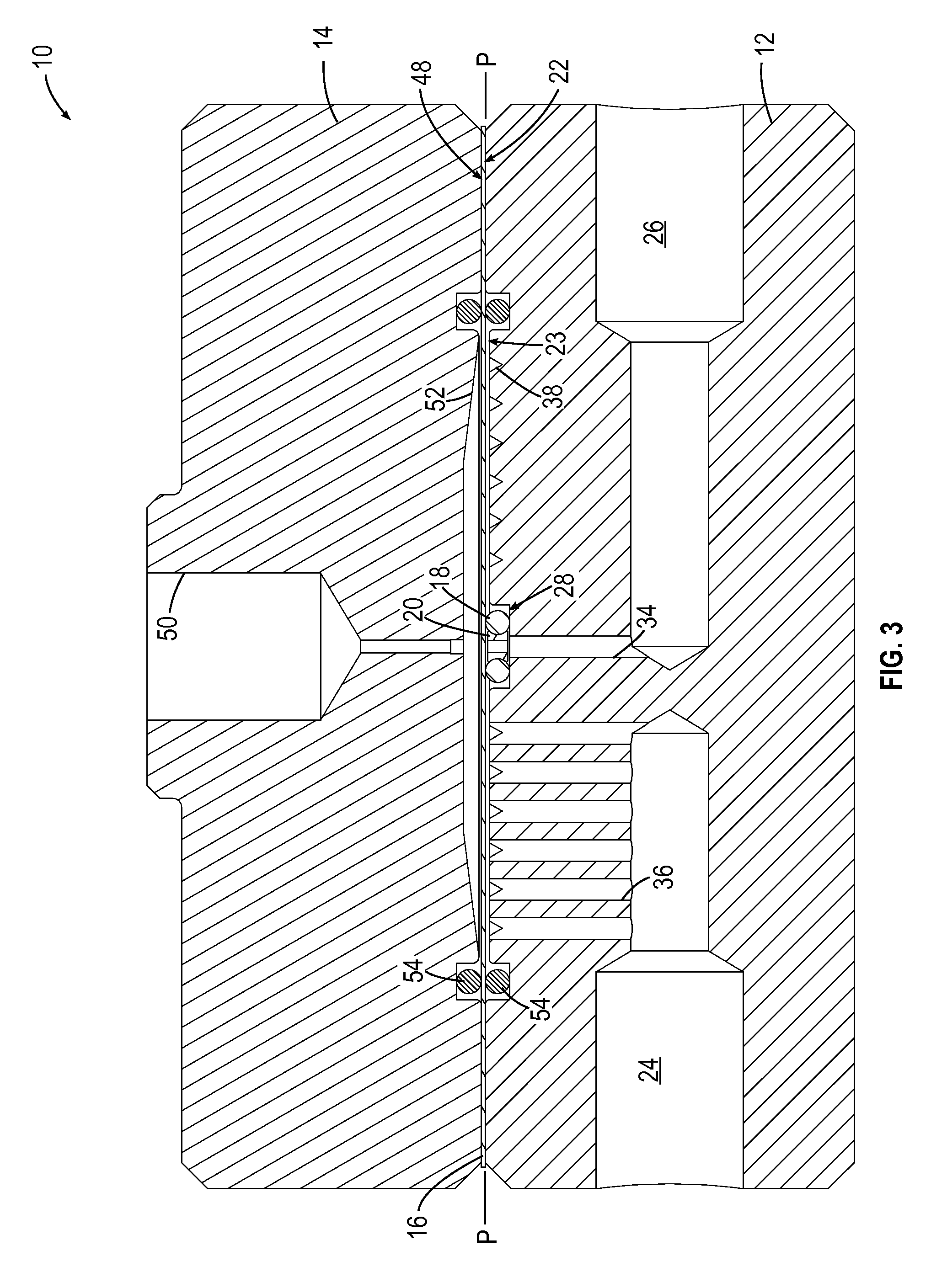
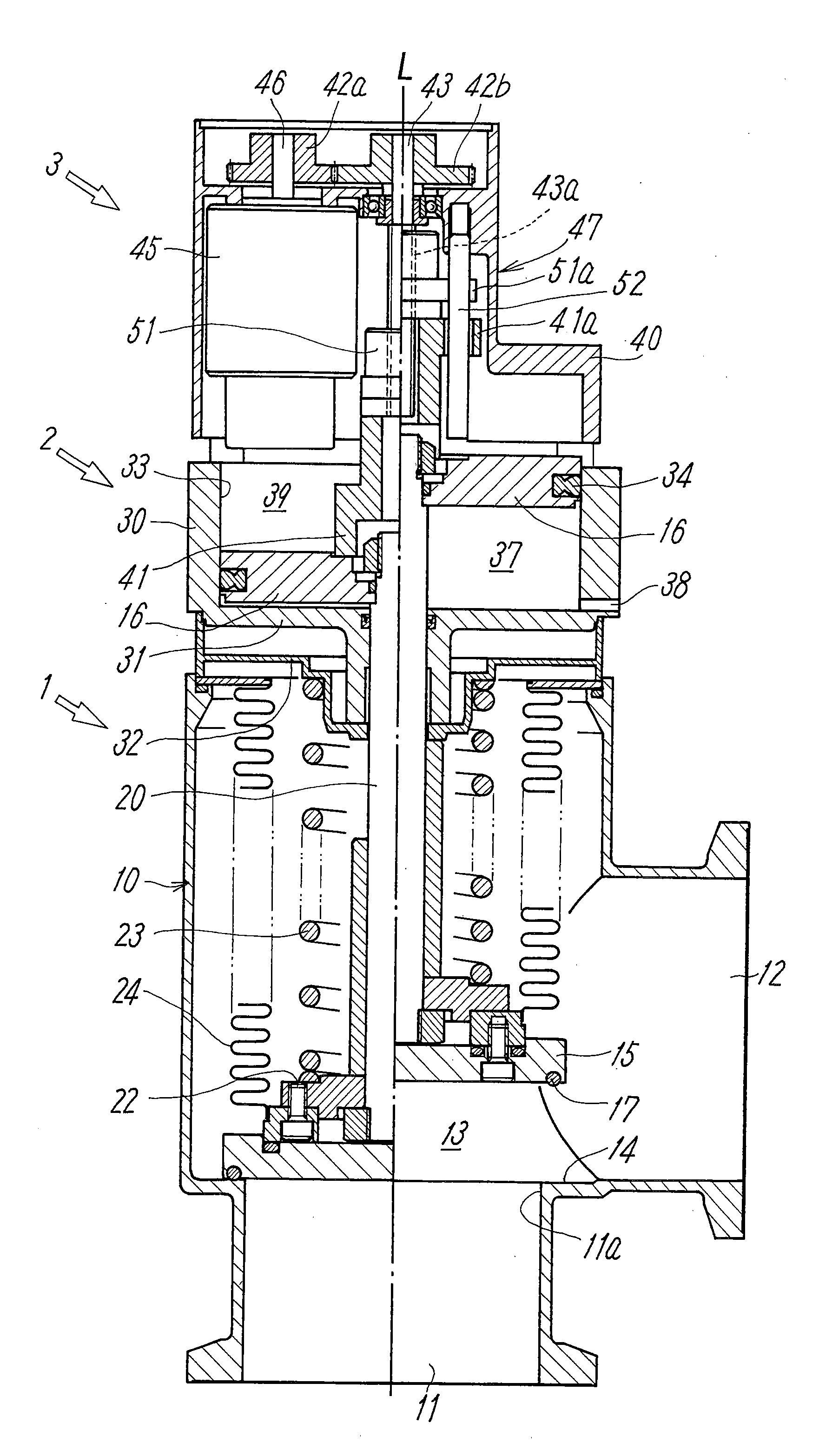
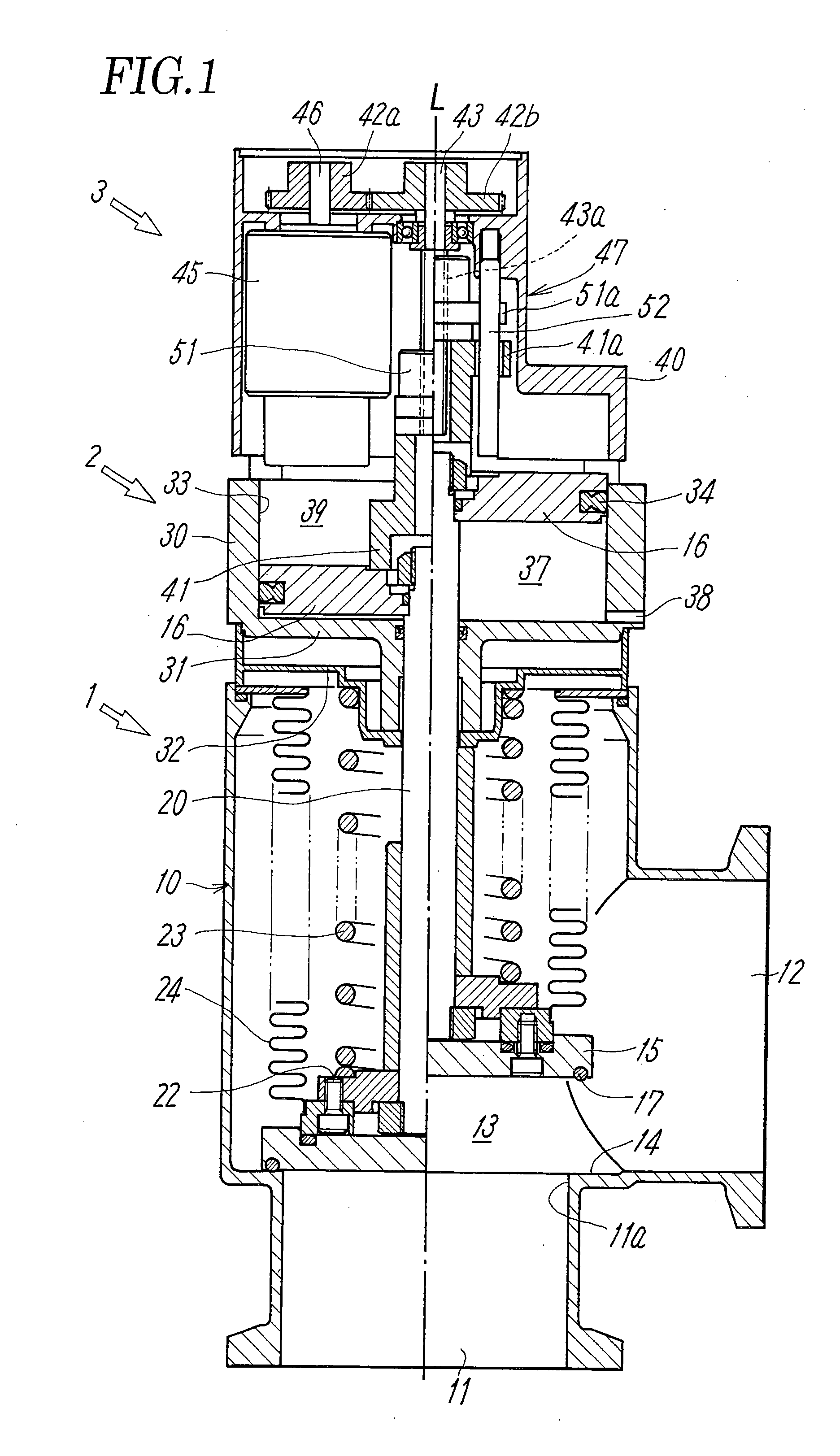
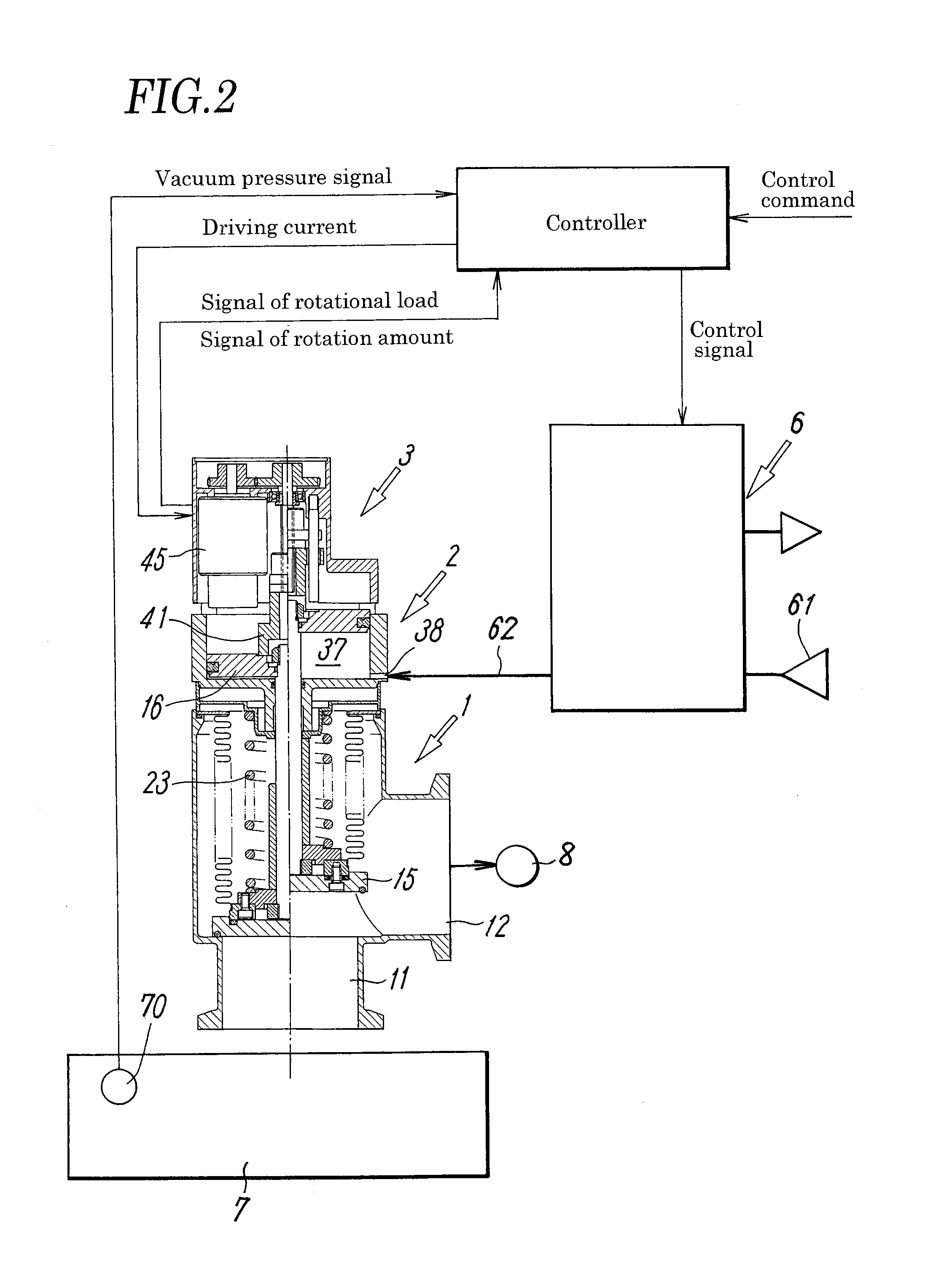
ActiveUS20140130907A1Easily and securely deciding and announcingAvoid failureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control using electric meansVacuum pressureEngineering
A valve main body including a valve member that opens and closes a valve seat is associated with a fluid pressure driving unit including a pressure-receiving member (piston) that drives the valve member, a valve aperture adjusting unit that sets the aperture of the valve member, an electromagnetic valve unit that supplies and discharges a pilot fluid to and from the fluid pressure driving unit, and a controller that controls the aperture of the valve member. The controller controls the aperture of the valve member by controlling the position of the pressure-receiving member, such that the vacuum chamber attains a predetermined target pressure, and monitors a difference between an actual pressure in the vacuum chamber obtained from the pressure sensor and the target pressure, and announces abnormality in the case where the difference deviates from a tolerance range.
Owner:SMC CORP
Oil pressure regulating valve for generator applications
A generator includes a rotor to be driven to rotate and generate electricity and a housing receiving the rotor. An oil supply includes an oil inlet port and an oil outlet port. A pressure regulating valve regulates the flow of oil from the inlet port to the outlet port. The pressure regulating valve includes a valve sleeve mounted within the housing. The valve sleeve extends into a bore within the housing. A valve spool is mounted within the valve sleeve. The valve sleeve has a flange abutting an outer face of the housing. Bolts tighten the flange against the housing. An inner end of the valve sleeve extends radially inwardly to form a ledge. The ledge is spaced away from an inner face of the housing. A valve sleeve, a sense piston and a valve spool are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Vacuum valve and valve control device
ActiveUS11035488B2Improve vacuuming effectImprove adjustabilitySpindle sealingsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringVALVE PORT
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
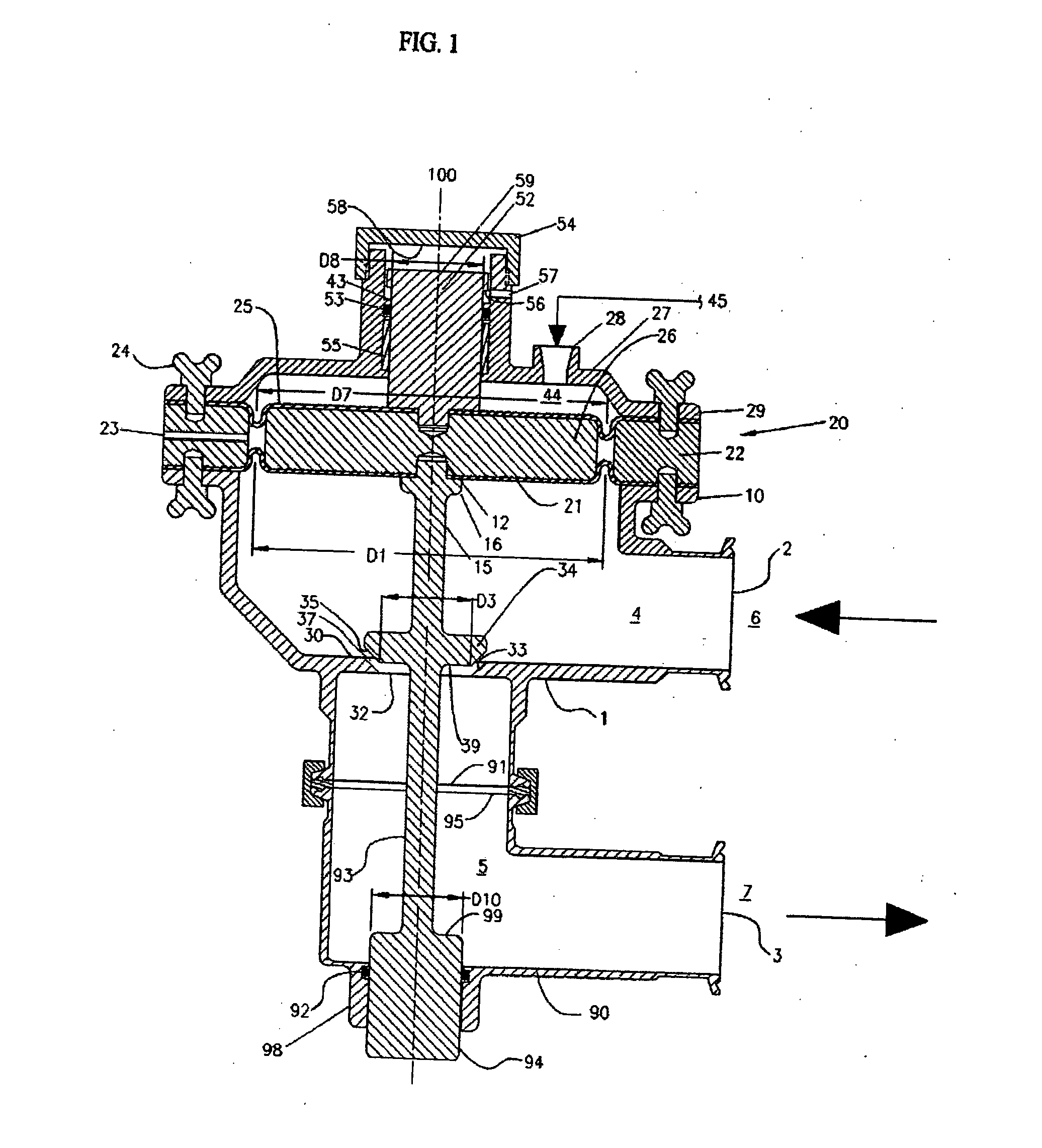
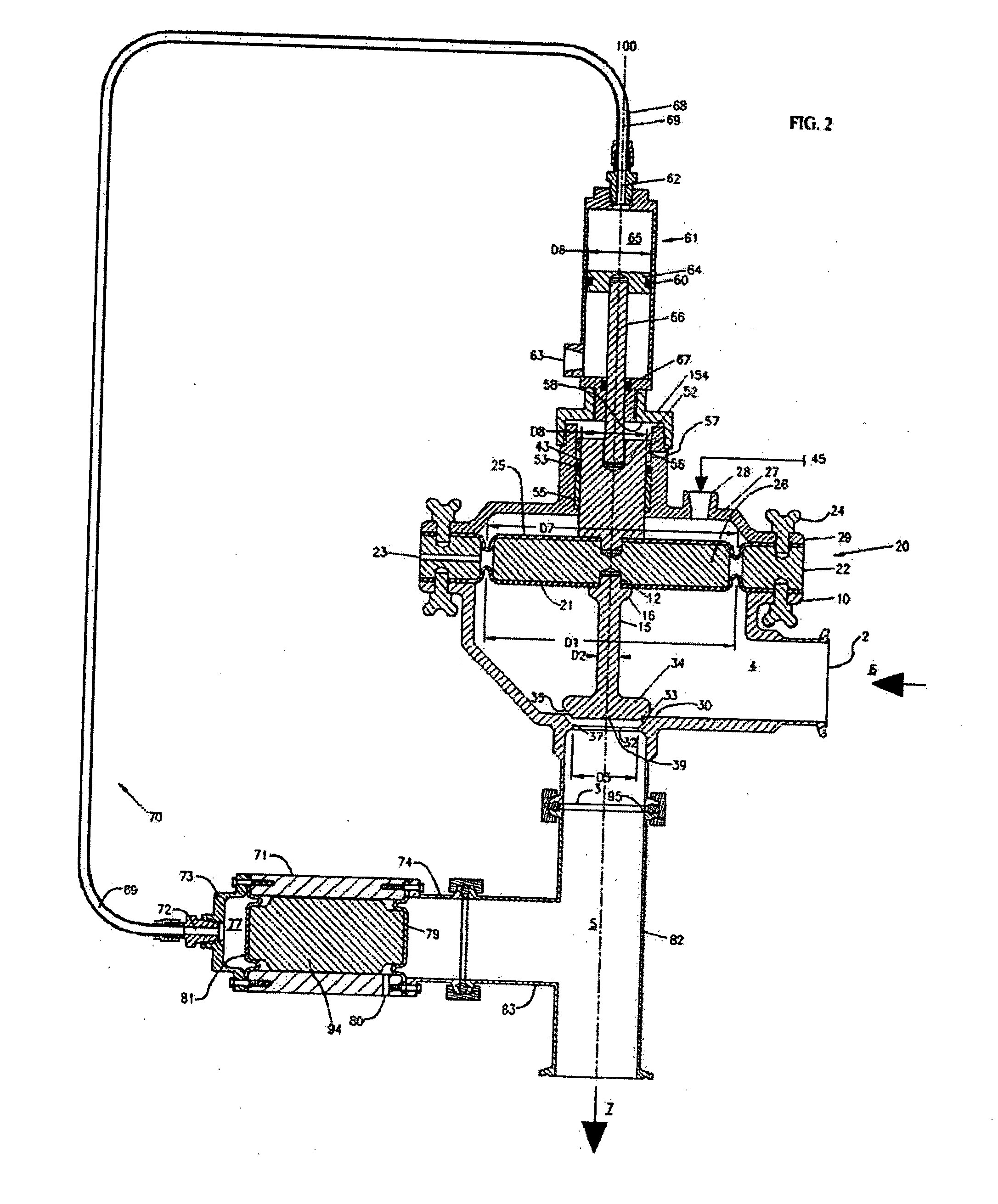
Pneumatic pressure regulating valve
ActiveUS20110192473A1Reliable functionImprove control characteristicsDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDifferential pressureGas pressure
A pneumatic pressure regulating valve, the opening of which can be automatically changed in a pressure-related manner, including a control diaphragm that is subjected to a reference pressure, to the gas pressure as well as to a governor spring, wherein a change in the differential pressure causes an adjustment of the control diaphragm and the latter itself or a closing element actuated by it changes the opening through an outflow cross-section, and wherein a structure that is arranged adjacent to the outflow cross-section on the diaphragm side forms a stop for the control diaphragm or for the closing element in the closed position of said control diaphragm. At least one preliminary stop is arranged in the pressure regulating valve such that, when the control diaphragm is moving in its closing direction, the control diaphragm or the closing element first comes into contact with the preliminary stop and that, when the control diaphragm is moving further in its closing direction, the control diaphragm or the closing element will then, while being subjected to elastic and flexible deformation or being further subjected to elastic and flexible deformation respectively, further reduces the opening and, in a final position, also comes into contact with the stop.
Owner:HENGST WALTER
In-line back pressure fluid regulator
In-line back pressure fluid regulators are described. An example in-line fluid regulator includes a regulator body defining a sensing chamber and an outlet of a fluid flow path of the fluid regulator. The outlet is in fluid communication with the sensing chamber via a first flow passageway in the regulator body. A bonnet is coupled to the regulator body and defines an inlet of the fluid flow path and a loading chamber disposed between the sensing chamber and the inlet. The loading chamber is substantially sealed relative to the fluid flow path of the fluid regulator. A pressure sensor is disposed between the inlet and the sensing chamber, where the pressure sensor defines a second flow passageway to fluidly couple the inlet and the sensing chamber.
Owner:TESCOM CORP
Mobile hydrogen dispenser for fuel cell vehicles
ActiveUS20190271439A1Vessel mounting detailsGas handling applicationsDifferential pressureEngineering
A mobile dispenser may be used to at least partially fill hydrogen tanks of fuel cell-powered vehicles. The dispenser uses a purely mechanical control of the fill using an orifice plate across which a pressure differential is maintained through use of a backpressure regulator whose reference pressure is controlled by a differential pressure regulator. Because it does need or use electrical power, it may be used in situations where no electrical power is available or convenient.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE ADVANCED TECH U S
Pressure adjusting valve for vehicle fuel line
InactiveUS20090152486A1Diaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringFuel line
A pressure adjusting valve for a vehicle fuel line includes a diaphragm disposed in a housing and dividing the interior of the housing into first and second compartments. A valve plate is provided in the second compartment and attached to the diaphragm. A return unit is provided in the second compartment. An elastic member provides an elastic force to the diaphragm toward the second compartment. An elastic force adjusting unit controls the elastic force of the elastic member.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
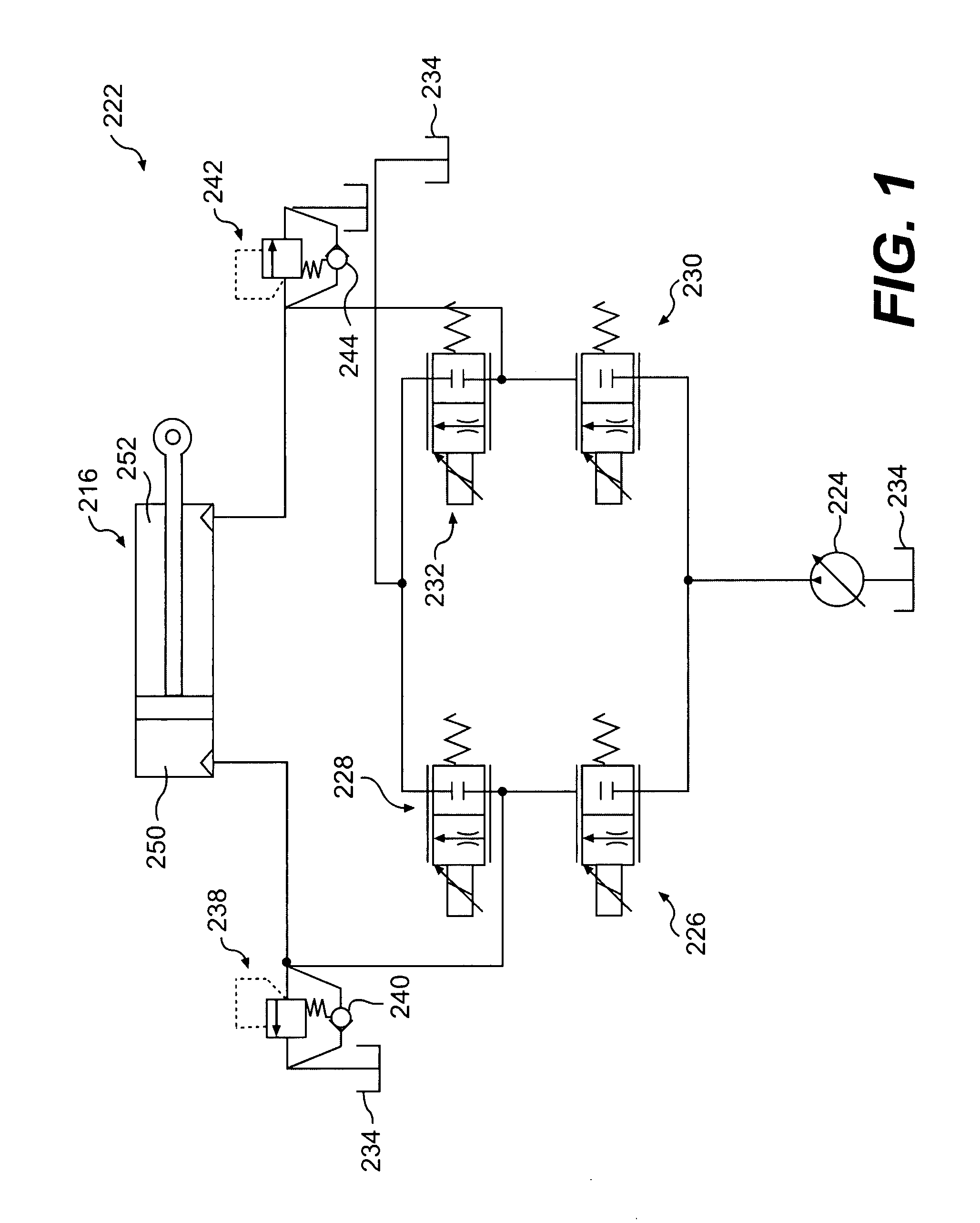
Pressure regulating method and apparatus
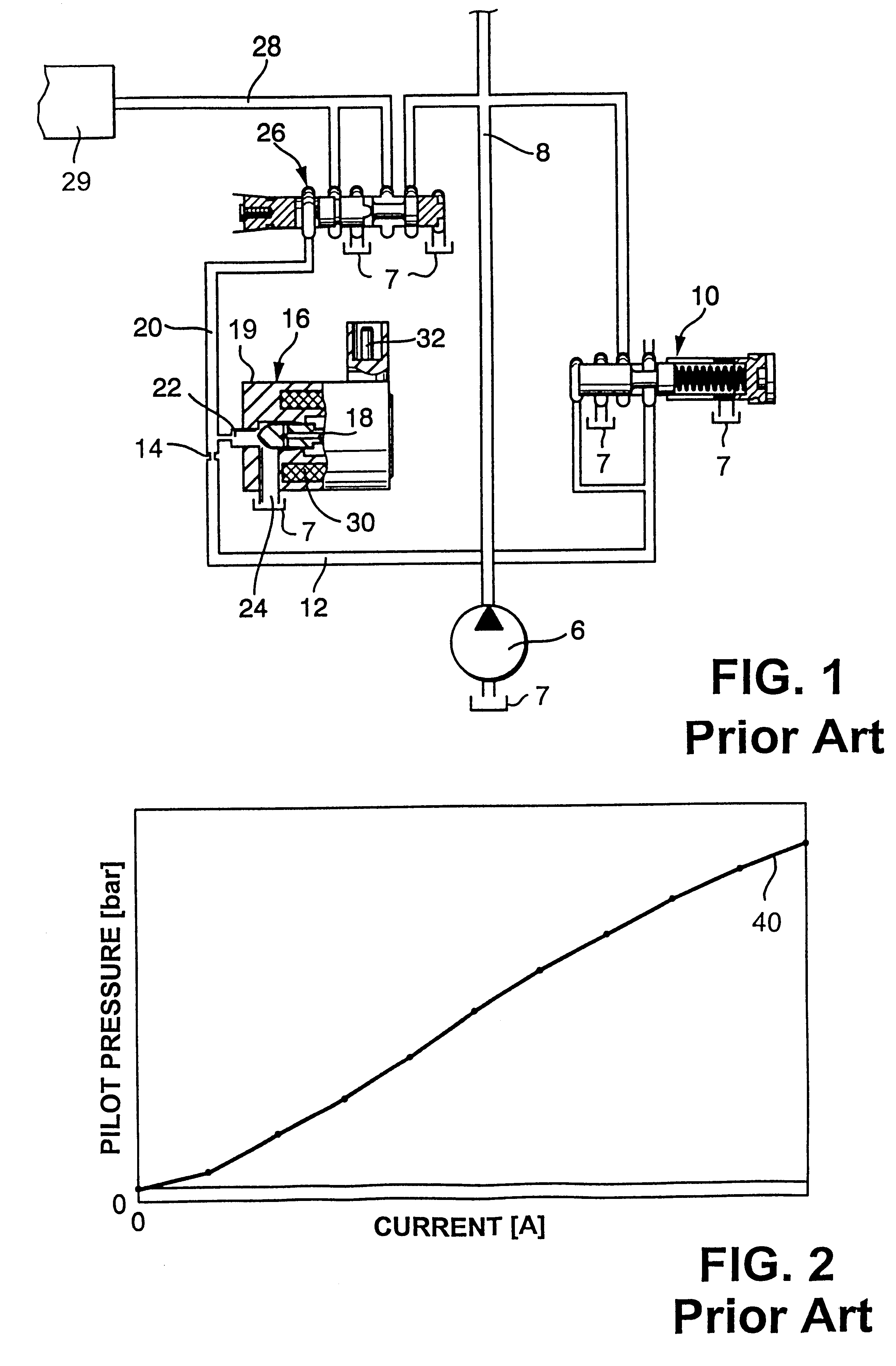
InactiveUS6196249B1Simple and compactDecrease in pilot pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsStream flowEngineering
The pressure of hydraulic fluid which is supplied to the continuously variable transmission in the power train of a motor vehicle is regulated by an apparatus wherein an adjustable pilot valve can receive fluid from a pilot conduit leading to a pressure reducing valve. The pilot conduit normally receives fluid from a further conduit, wherein the pressure of fluid is at least substantially constant, by way of a flow restrictor. A branch conduit serves to evacuate fluid from the pilot conduit into the pilot valve when the latter is at least partially open. The fluid-discharging end of the flow restrictor confronts the inlet of the branch conduit, and such inlet is narrowed to reduce the likelihood of turbulence developing in the fluid stream flowing from the pilot conduit, across the further conduit and into the inlet of the pilot valve.
Owner:LUK GETRIEBE SYST
Vacuum pressure regulation system
ActiveUS9329603B2Easily and securely deciding and announcingAvoid failureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control using electric meansVacuum pressureEngineering
A valve main body including a valve member that opens and closes a valve seat is associated with a fluid pressure driving unit including a pressure-receiving member (piston) that drives the valve member, a valve aperture adjusting unit that sets the aperture of the valve member, an electromagnetic valve unit that supplies and discharges a pilot fluid to and from the fluid pressure driving unit, and a controller that controls the aperture of the valve member. The controller controls the aperture of the valve member by controlling the position of the pressure-receiving member, such that the vacuum chamber attains a predetermined target pressure, and monitors a difference between an actual pressure in the vacuum chamber obtained from the pressure sensor and the target pressure, and announces abnormality in the case where the difference deviates from a tolerance range.
Owner:SMC CORP
Pressure adjusting valve for vehicle fuel line
A pressure adjusting valve for a vehicle fuel line includes a diaphragm disposed in a housing and dividing the interior of the housing into first and second compartments. A valve plate is provided in the second compartment and attached to the diaphragm. A return unit is provided in the second compartment. An elastic member provides an elastic force to the diaphragm toward the second compartment. An elastic force adjusting unit controls the elastic force of the elastic member.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
High capacity linear valve cage
InactiveUS20170102076A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringControl valves
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT REGULATOR TECH INC
Back pressure valve
InactiveUS9081390B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure control without auxillary powerEngineeringStress regulation
A back pressure valve comprises a pressure regulator housing affixed to a pressure controller housing and a diaphragm disposed between the pressure regulator housing and the pressure controller housing. In one aspect, the back pressure valve includes a valve member moveable between a fully open position and a fully closed position. The pressure regulator housing includes an inlet chamber communicating with an outlet chamber through at least one fluid passage in a sleeve. The valve member includes a stem connected to a valve head. The valve head includes an outer surface that is received and guided during movement by an inner surface of the sleeve. Upper and lower outer surface of the valve head provide stability to the valve member during opening and closing of the back pressure valve.
Owner:FLOMATIC CORP
Pressure regulator including a fixed valve ball and method of assembling the same
InactiveUS7040344B2Avoid communicationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLow pressure fuel injectionEngineeringPressure regulator
A pressure regulator includes a housing, a divider, and a valve. The housing includes an inlet and an outlet. The divider separates the housing into a first chamber and a second chamber. And the valve includes a spherical valve ball and a seat. The spherical valve ball is fixed with respect to a first one of the housing and the divider, and the seat is fixed with respect to a second one of the housing and the divider. A first configuration of the spherical valve ball with respect to the seat substantially prevents fluid communication between the inlet and the outlet, and a second configuration of the spherical valve ball with respect to the seat permits fluid communication between the inlet and the outlet.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
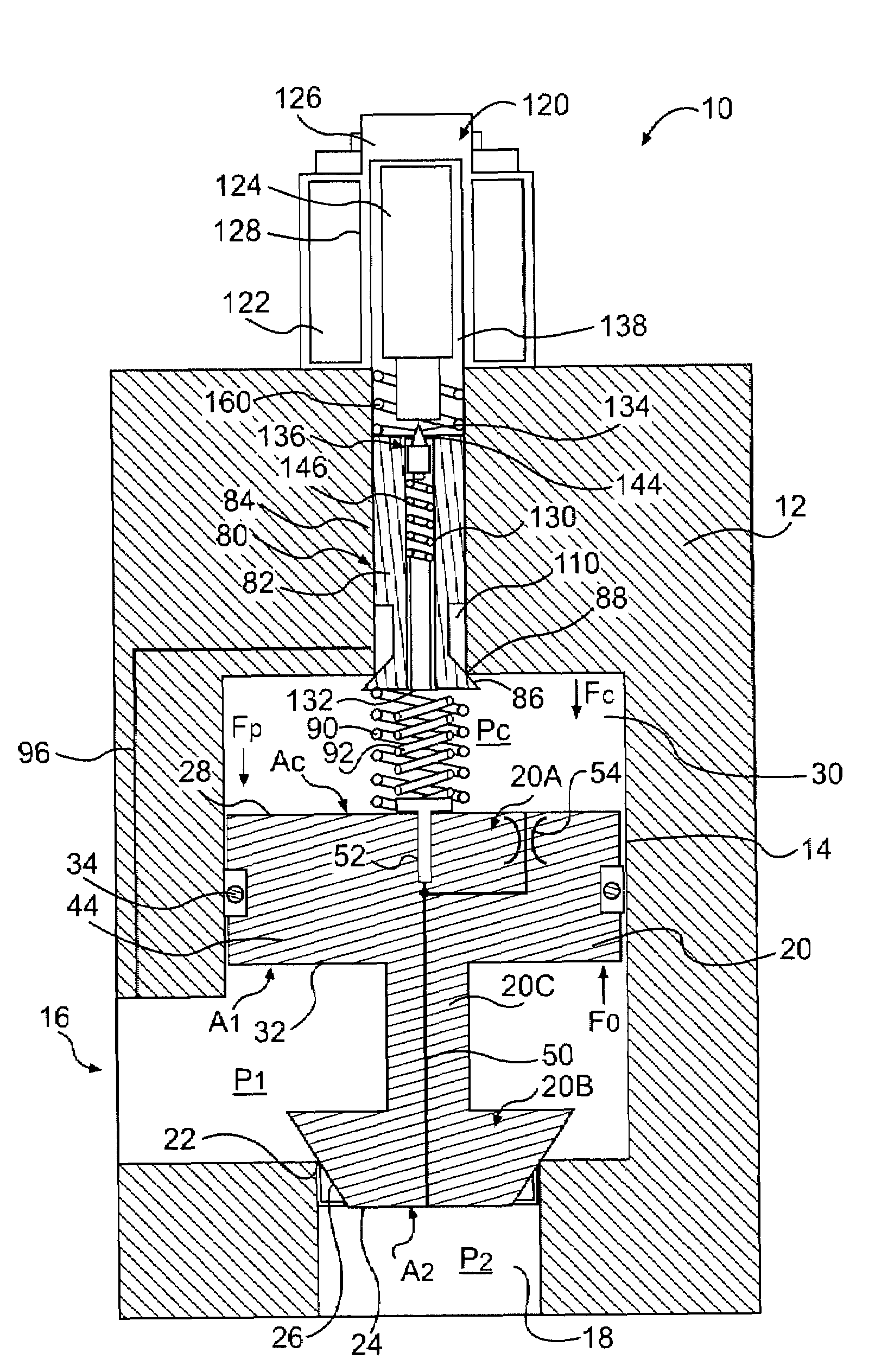
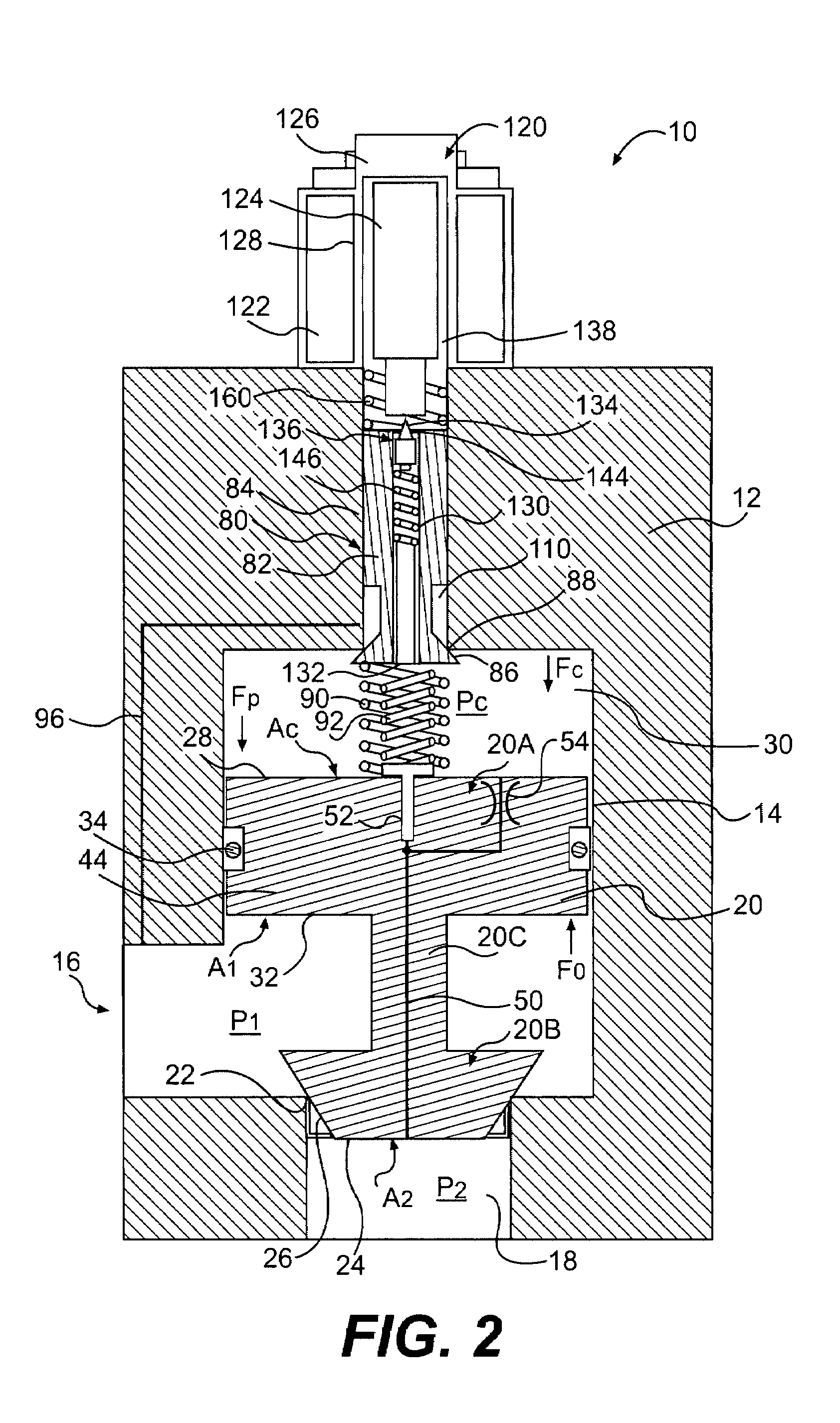
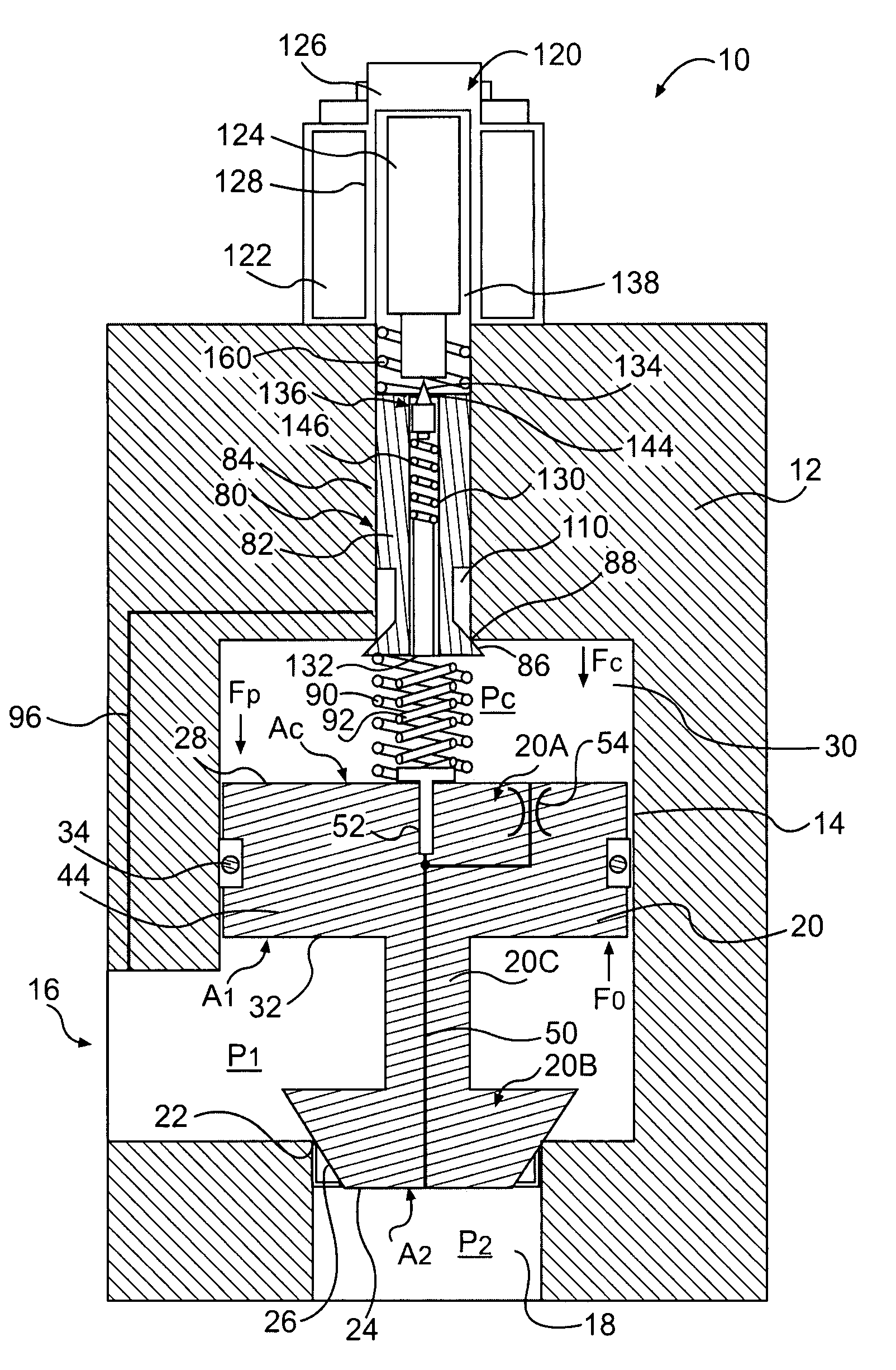
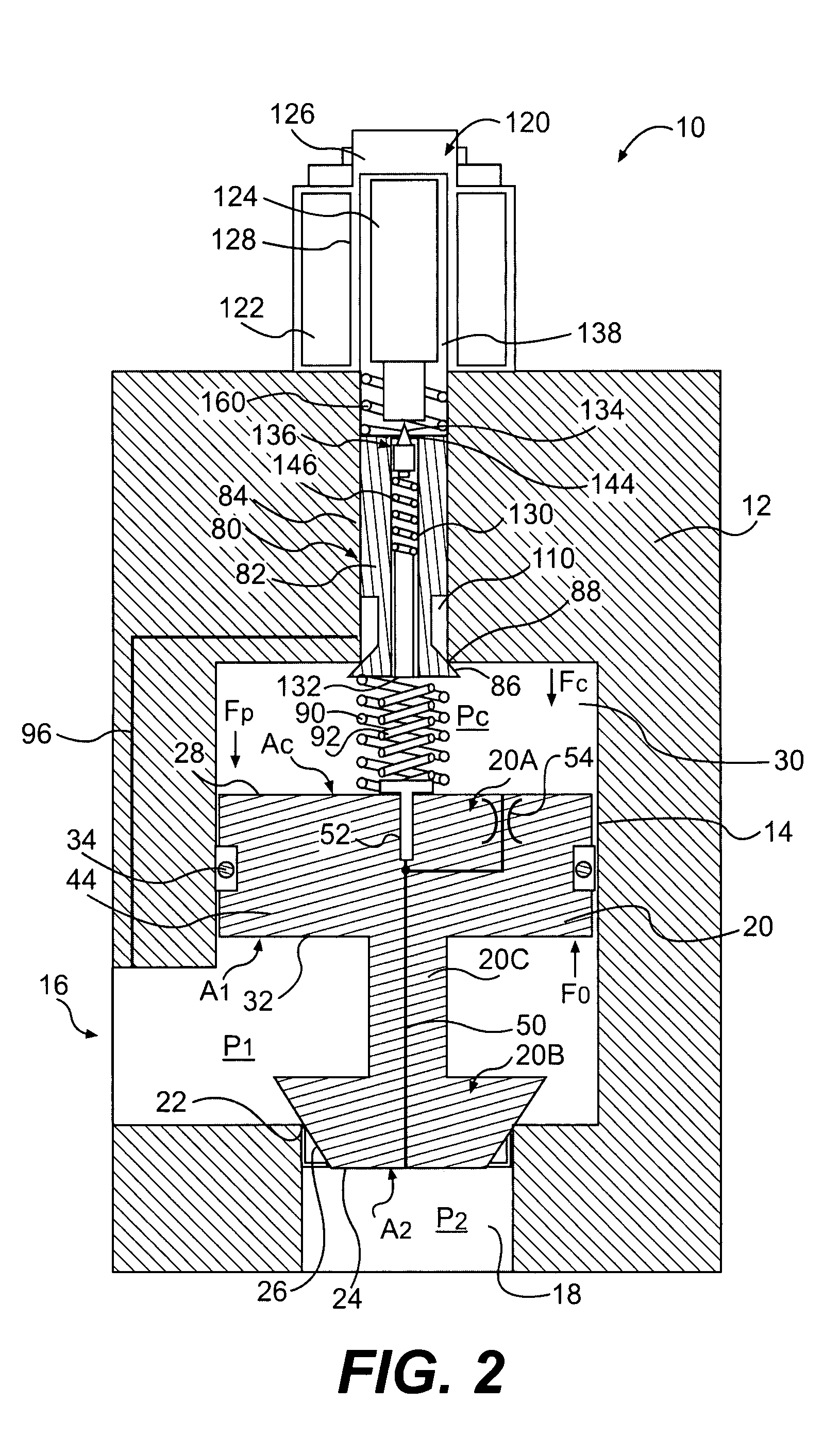
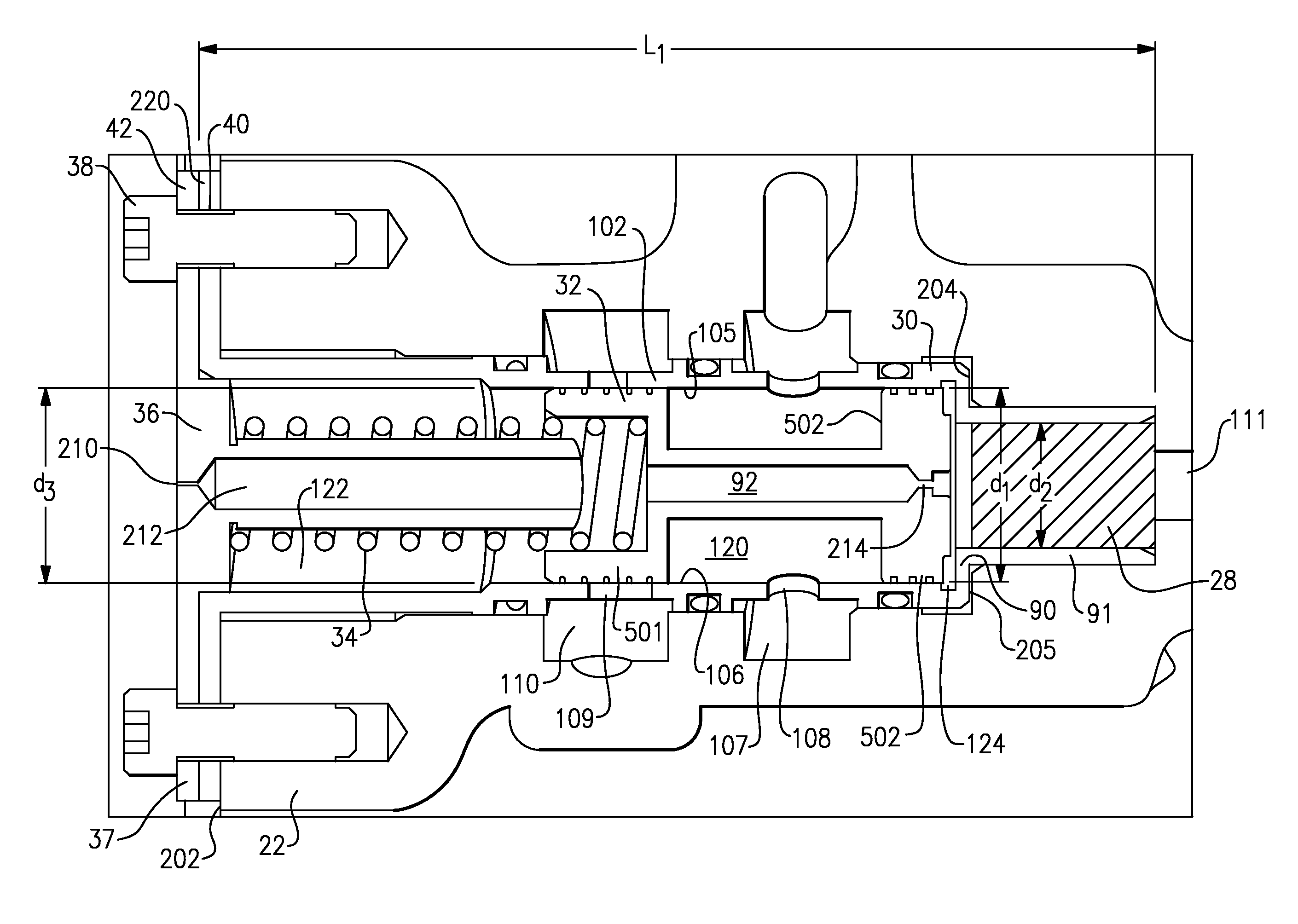
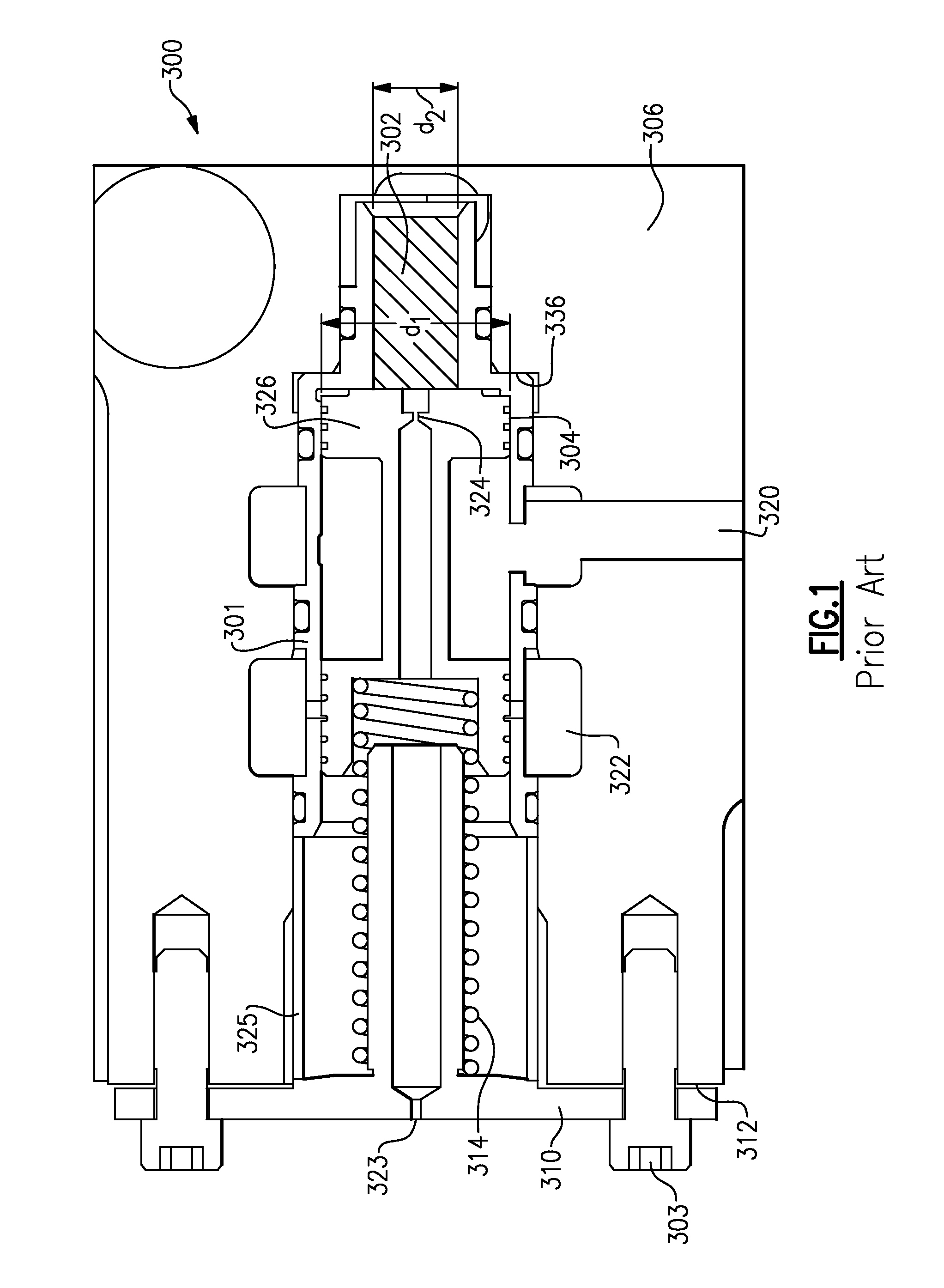
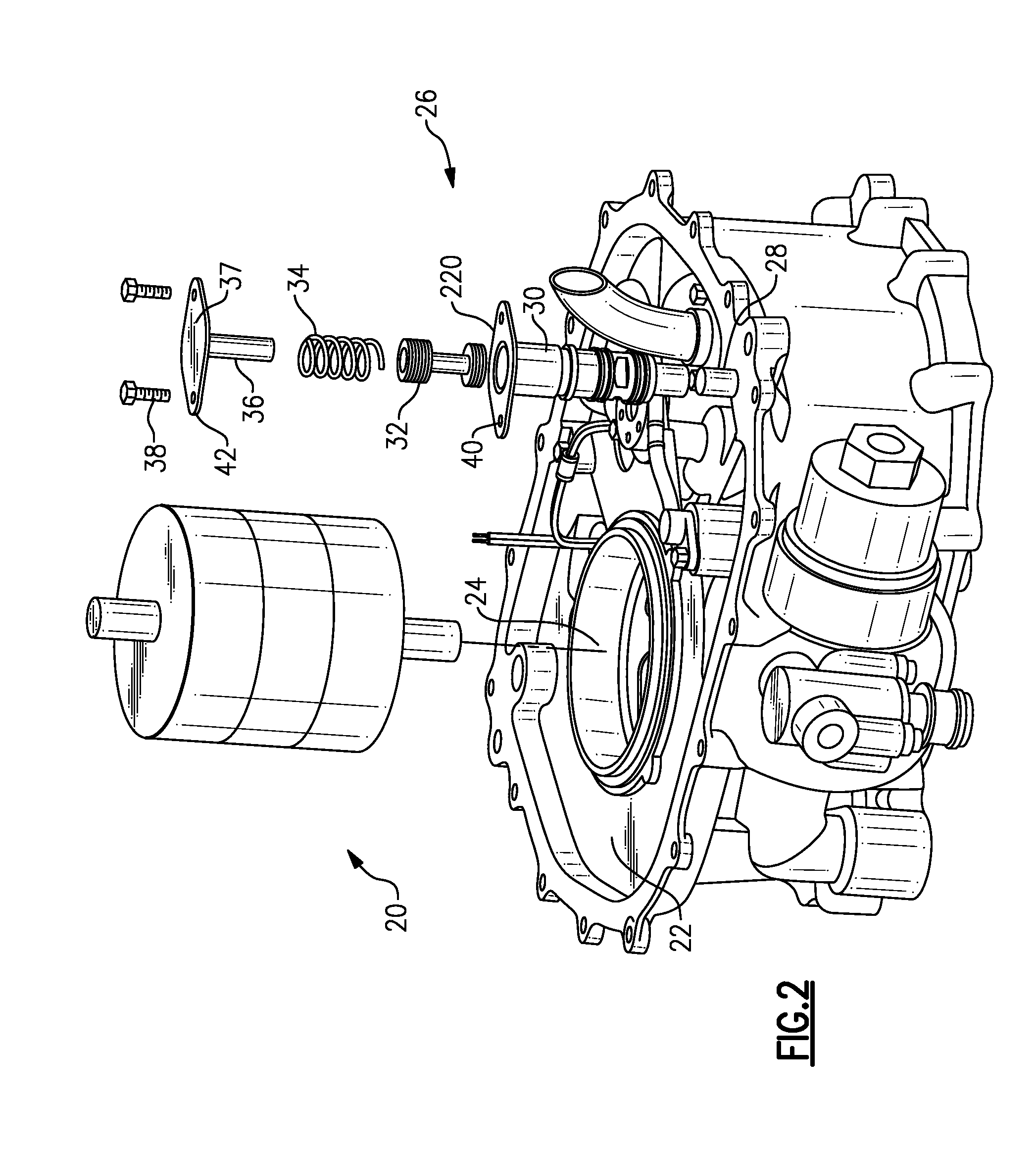
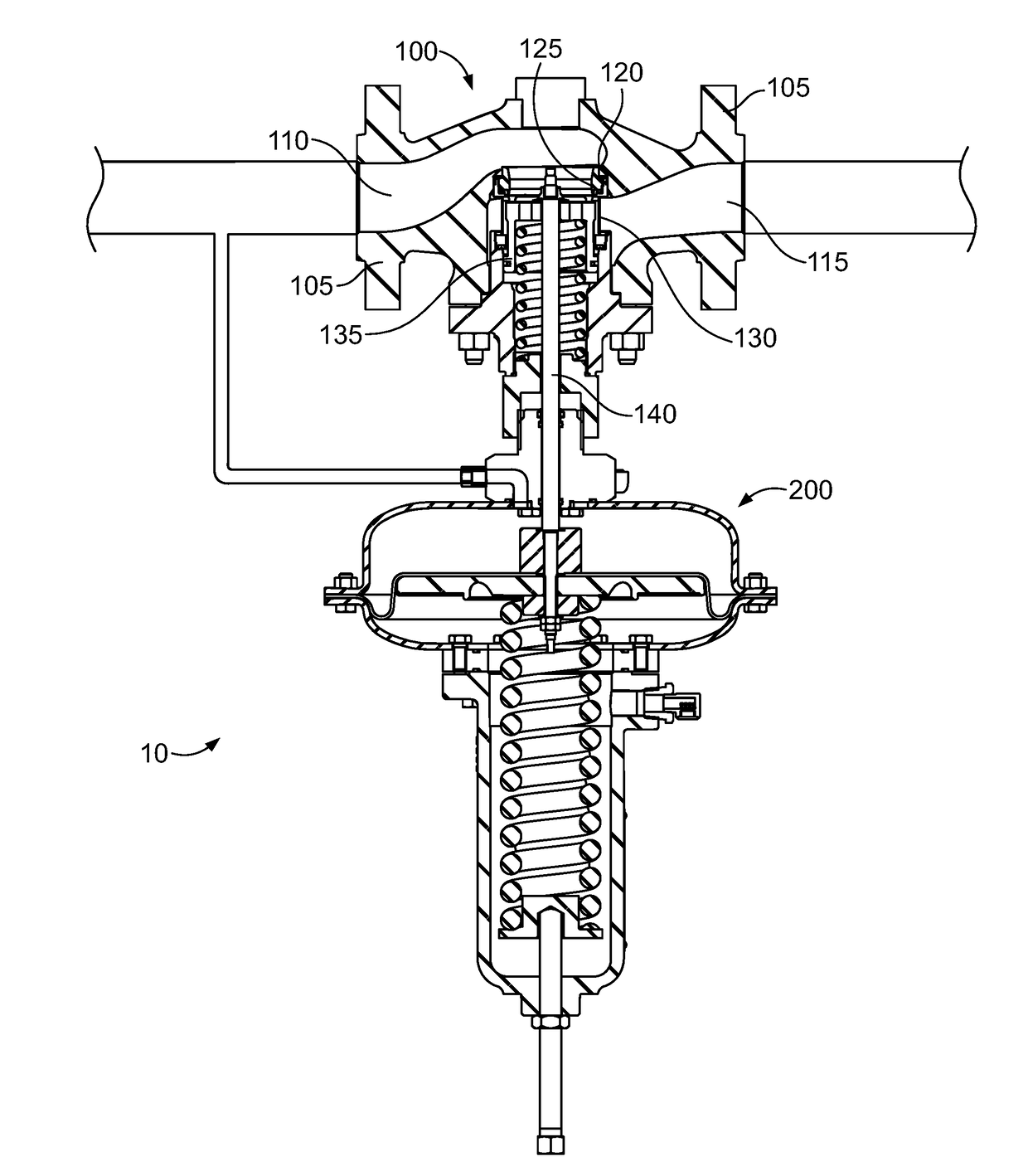
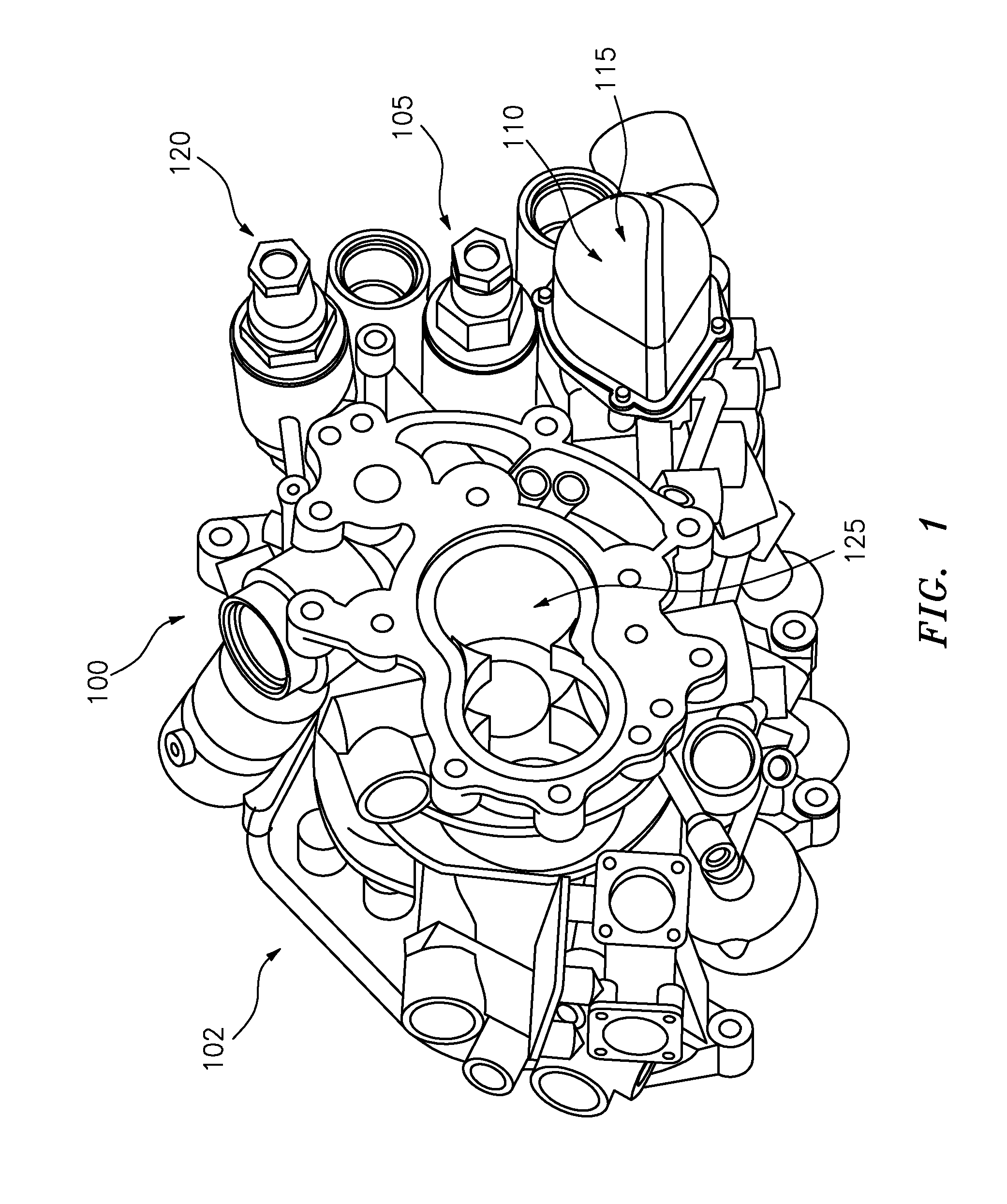
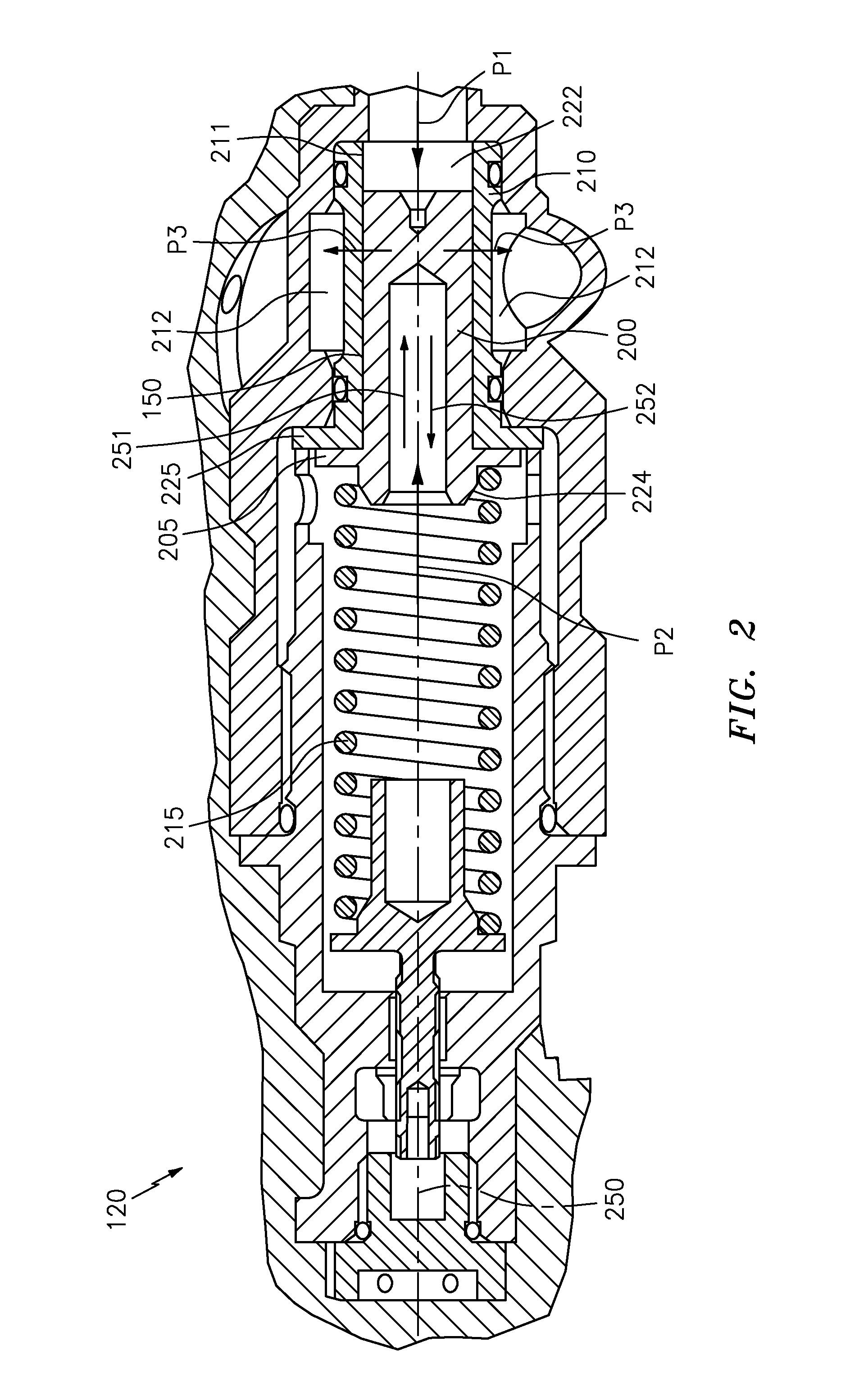
Inlet Pressure Compensation for a Valve System
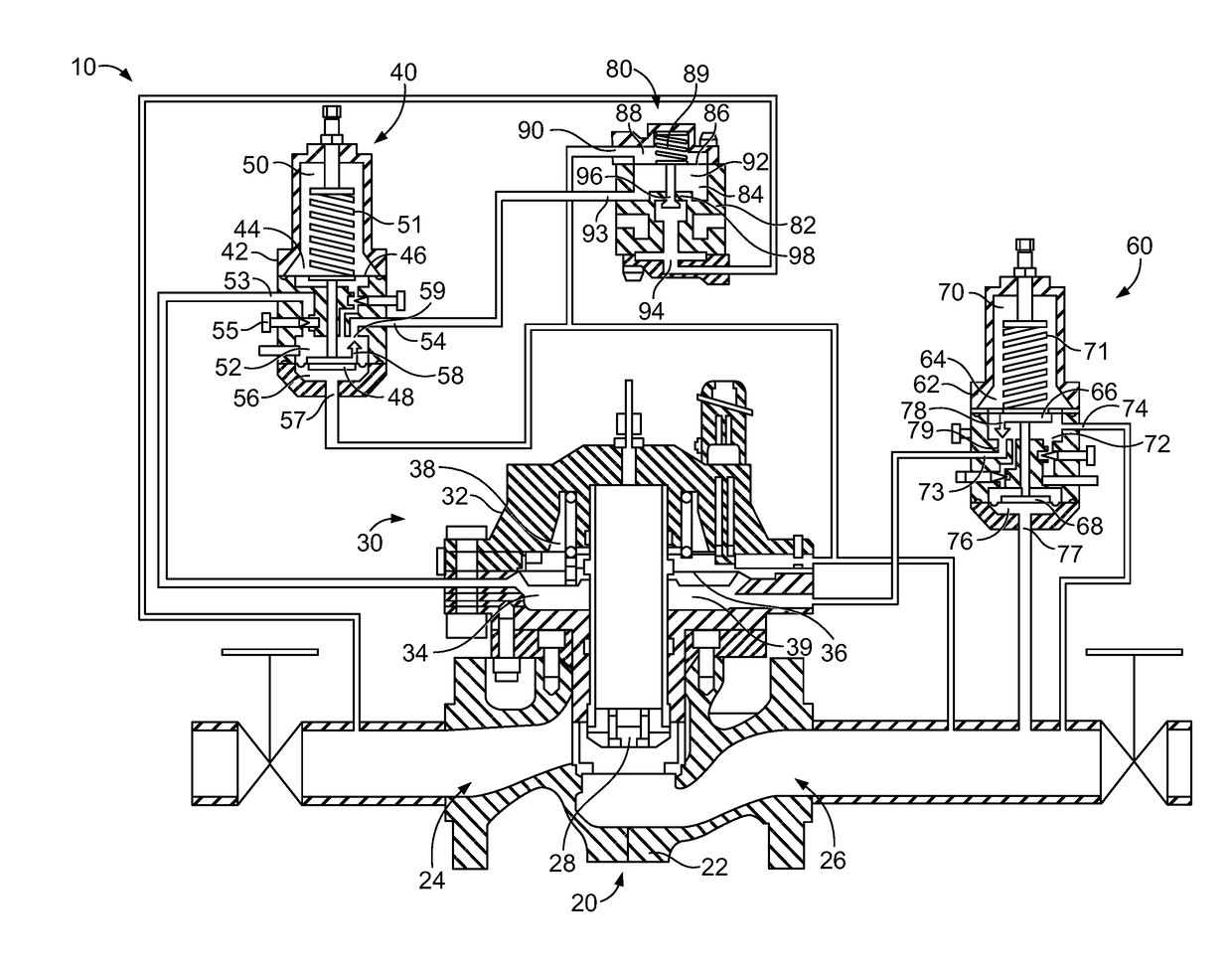
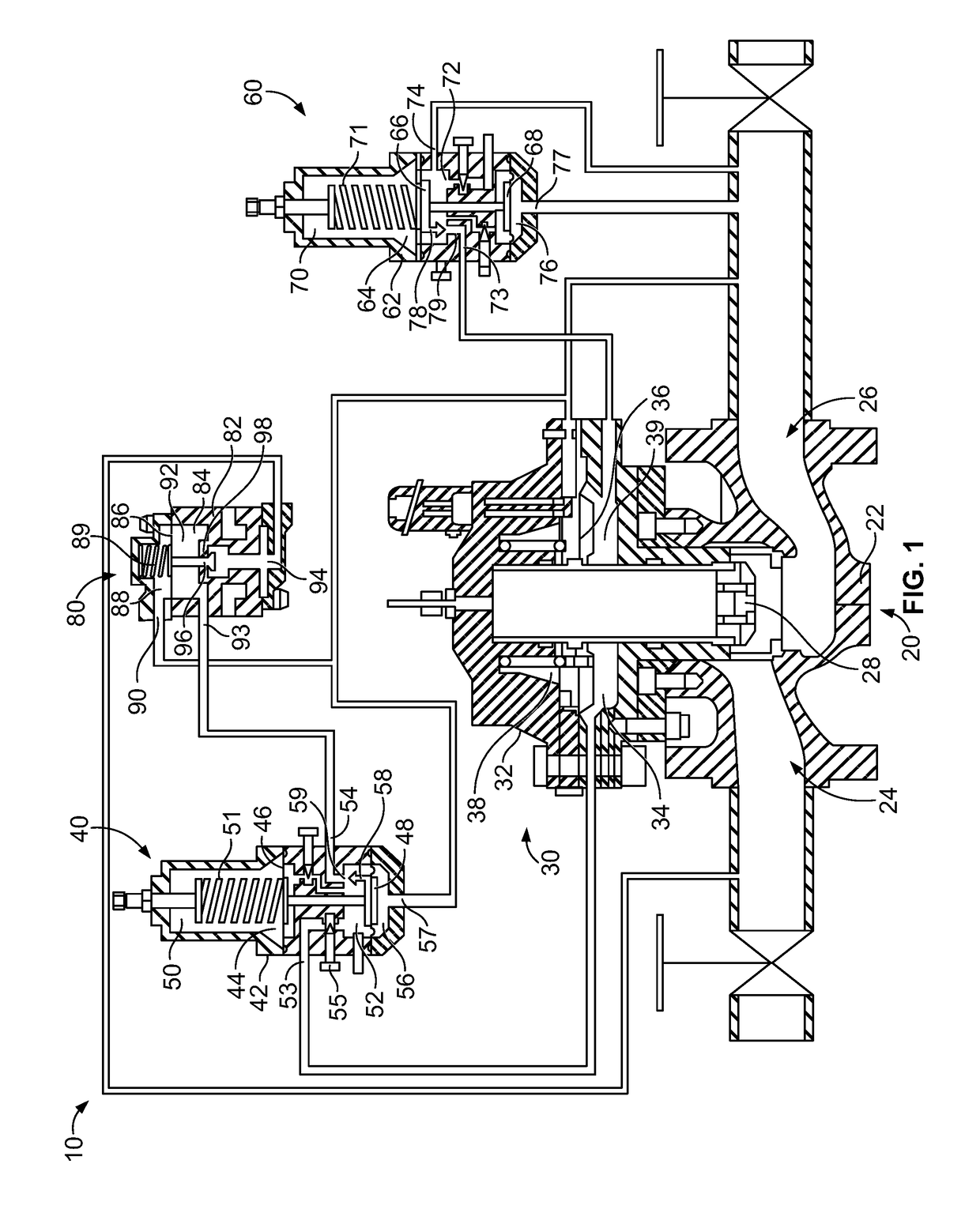
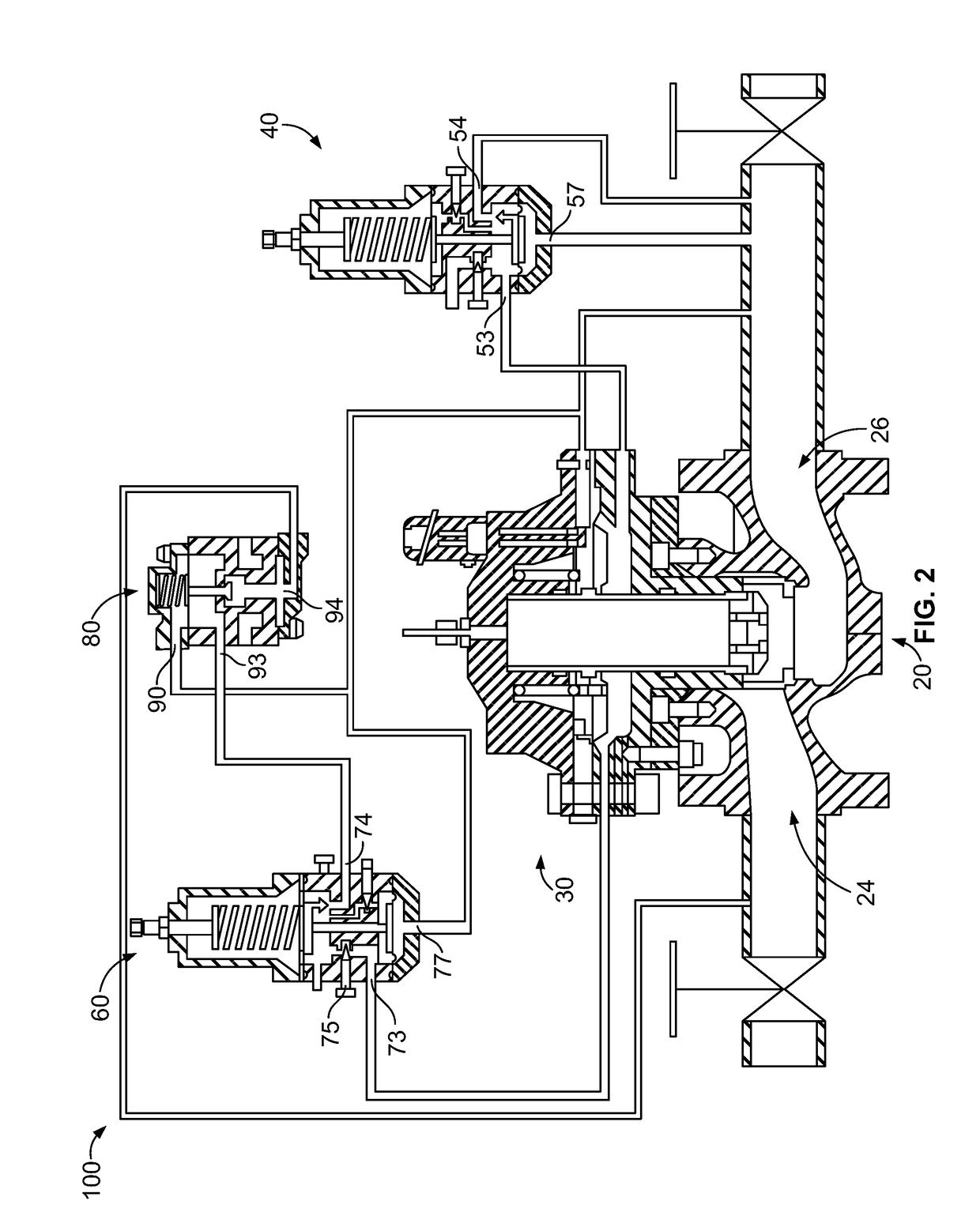
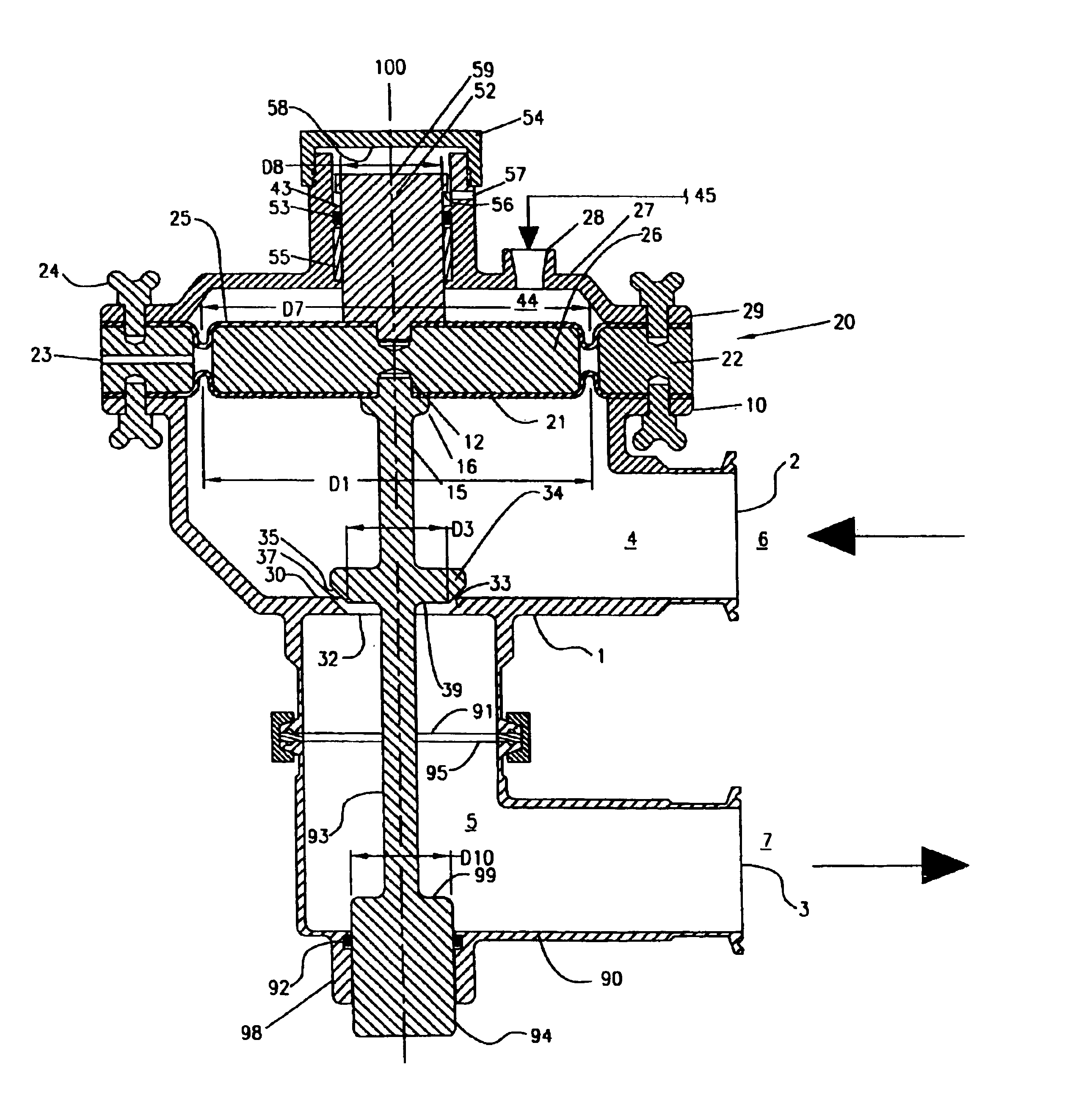
ActiveUS20180231128A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesEngine fuctionsInlet pressurePiston
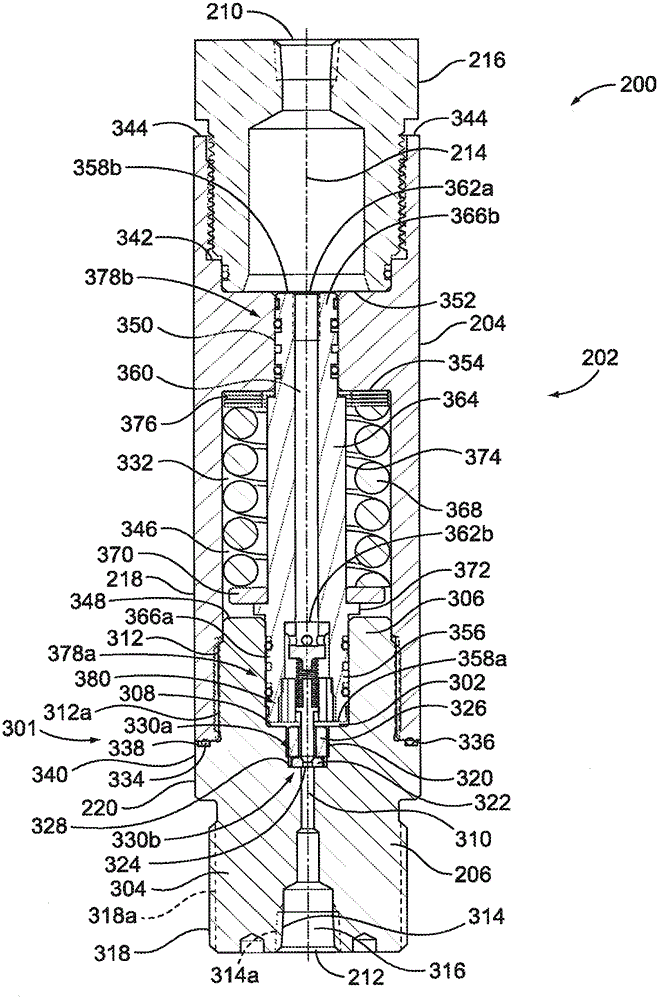
An inlet pressure valve regulation system to provide a regulated fluid flow includes a housing, first piston assembly, regulating valve, and inlet pressure conduit. The housing has an inlet at an inlet end which receives a pressurized fluid and an outlet at an outlet end which provides the regulated fluid flow. The piston assembly is arranged in the housing and has a first cavity and a control orifice to fluidly connect the inlet to the first cavity. The first piston assembly is configured to regulate the fluid flow. The regulating valve has a first valve chamber, a second valve chamber fluidly connected to a vent, a floating valve seat disposed between the first valve chamber and the second valve chamber, and a valve component. The floating valve seat includes a diaphragm and a seat having a passageway to fluidly connect the first valve chamber and the second valve chamber.
Owner:DUKES AEROSPACE
Servo minimum pressure valve
ActiveUS8511330B1Turbine/propulsion fuel valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyControl theoryVALVE PORT
A servo minimum pressure valve assembly includes a servo minimum pressure sleeve and a servo minimum pressure valve spool. The servo minimum pressure sleeve includes an inlet aperture, a first window set, a second window set, and a third window set. A ratio of an outlet window diameter of the first window set to an outlet window diameter of the second window set is between 2.34 and 2.65. The outlet window diameter of the second window set is greater than an outlet window diameter of the third window set. The servo minimum pressure valve spool is configured to move bi-directionally along a longitudinal axis of the servo minimum pressure valve sleeve. The servo minimum pressure valve spool includes a cylindrical portion to control a fluid flow between the inlet aperture of the servo minimum pressure sleeve and the first, second, and third window sets of the servo minimum pressure sleeve.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com