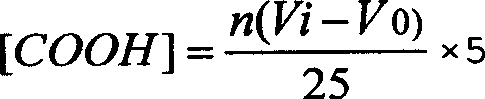Blood plasma lipide component adsorbing separation polymer porous film material, its preparing and use
A technology of adsorption, separation and polymer, which is applied in the field of biomedical materials and medical device materials, and can solve problems such as complex preparation methods and engineering, and difficulties in large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Cut the medical polypropylene non-woven fabric with an average pore size of 0.1 μm into 5cm×5cm 2 The samples were ultrasonically cleaned in acetone and water for 15 to 30 minutes, and dried in vacuum for later use. Then, soak the above-mentioned sample in an aqueous solution containing 10% (mass percentage) of acrylic acid monomer, which additionally contains 1.0% ferrous sulfate polymerization inhibitor and 0.5% sulfuric acid catalyst. After soaking for 24 hours, place the sample in 60 In the radiation field of Co γ-ray source, the total cumulative irradiation dose is controlled to 30kGy. After the above-mentioned irradiation treatment sample was taken out, it was washed, dried, weighed and calculated to obtain a copolymerization grafting rate of acrylic acid of 30 wt%, and the corresponding surface carboxyl group content of the obtained porous membrane carrier material was 25 μmol / cm 2 , ATR-FITR infrared spectrum analysis found that the sample was at 1700cm -1 A n...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Cut the 0.45μm medical polypropylene non-woven fabric into 5cm×5cm 2 The samples were ultrasonically cleaned in acetone and water for 15 to 30 minutes, and dried in vacuum for later use. The above samples were then soaked in an aqueous solution containing 15% acrylic acid monomer. The solution contains 0.5% ferrous sulfate polymerization inhibitor and 1.0% sulfuric acid catalyst at the same time. After soaking for 24 hours, the sample is placed in 60 In the radiation field of the Co γ-ray source, the total cumulative irradiation dose is controlled to be 20kGy. After the above-mentioned irradiation treatment sample was taken out, it was washed, dried, weighed and calculated to obtain a copolymerization grafting rate of acrylic acid of 84%, and the surface carboxyl content of quantitative titration was 70 μmol / cm 2 . ATR-FITR infrared spectrum analysis found that at 1700cm -1 A strong absorption peak appeared at , corresponding to the characteristic absorption signal ...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Take a 250ml volumetric three-neck bottle, after removing water and oxygen, quickly put 25 grams of p-toluenesulfonic acid into it under the protection of nitrogen, then slowly add 200ml of dry pyridine with 25 grams of cholesterol dropwise, the solution gradually turns pink. After continuing to stir and react for 24 hours, the reaction solution was poured into 5% potassium carbonate solution, stirred in an ice bath for 1 hour, the filtered solid was dissolved in dichloromethane, washed repeatedly with water, separated, and dried overnight over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After suction filtration, the dichloromethane was spin-dried and recrystallized in acetone to obtain p-toluenesulfonic acid-protected cholesterol ligand intermediates (CHOL-OTs). Then move it into a reaction flask that has been dehydrated and deoxygenated, add 20ml of 1,4-butanediol, use dioxane as a solvent, and reflux for 24 hours, remove the solvent under reduced pressure, and dissolve the residue in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com