Method for synthesizing cyanoacetylene derivatives
A synthetic method and derivative technology, applied in the field of chemistry, can solve the problems of toxic, expensive raw materials, troublesome separation, etc., and achieve the effects of simple process operation, simple post-processing, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
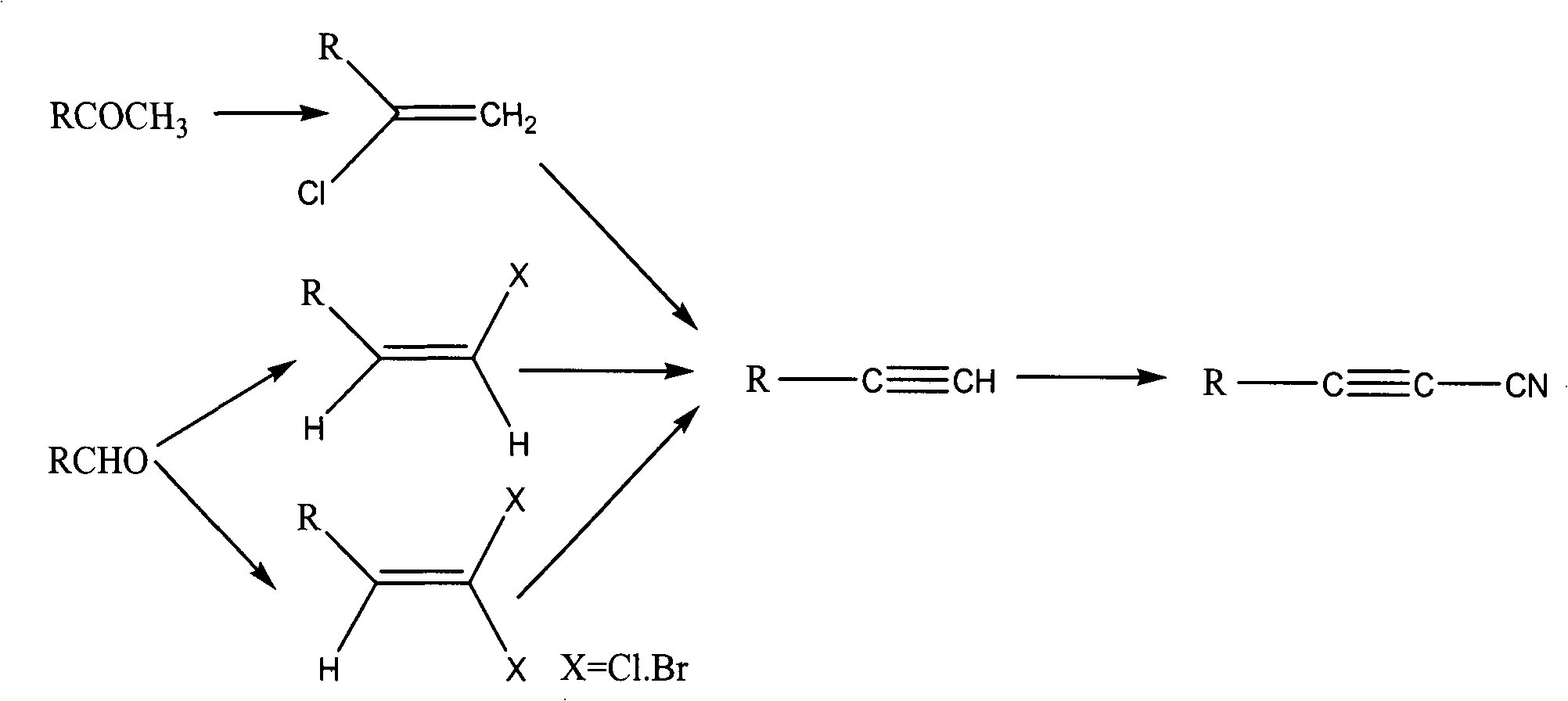
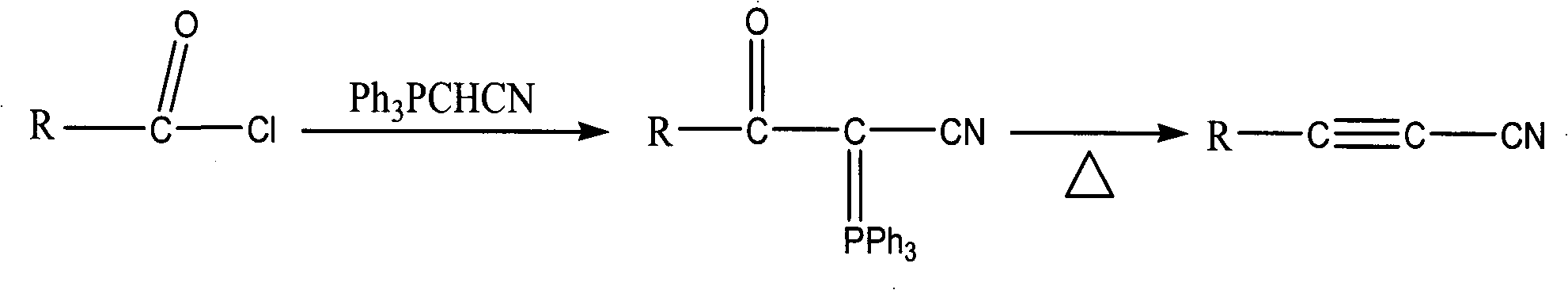
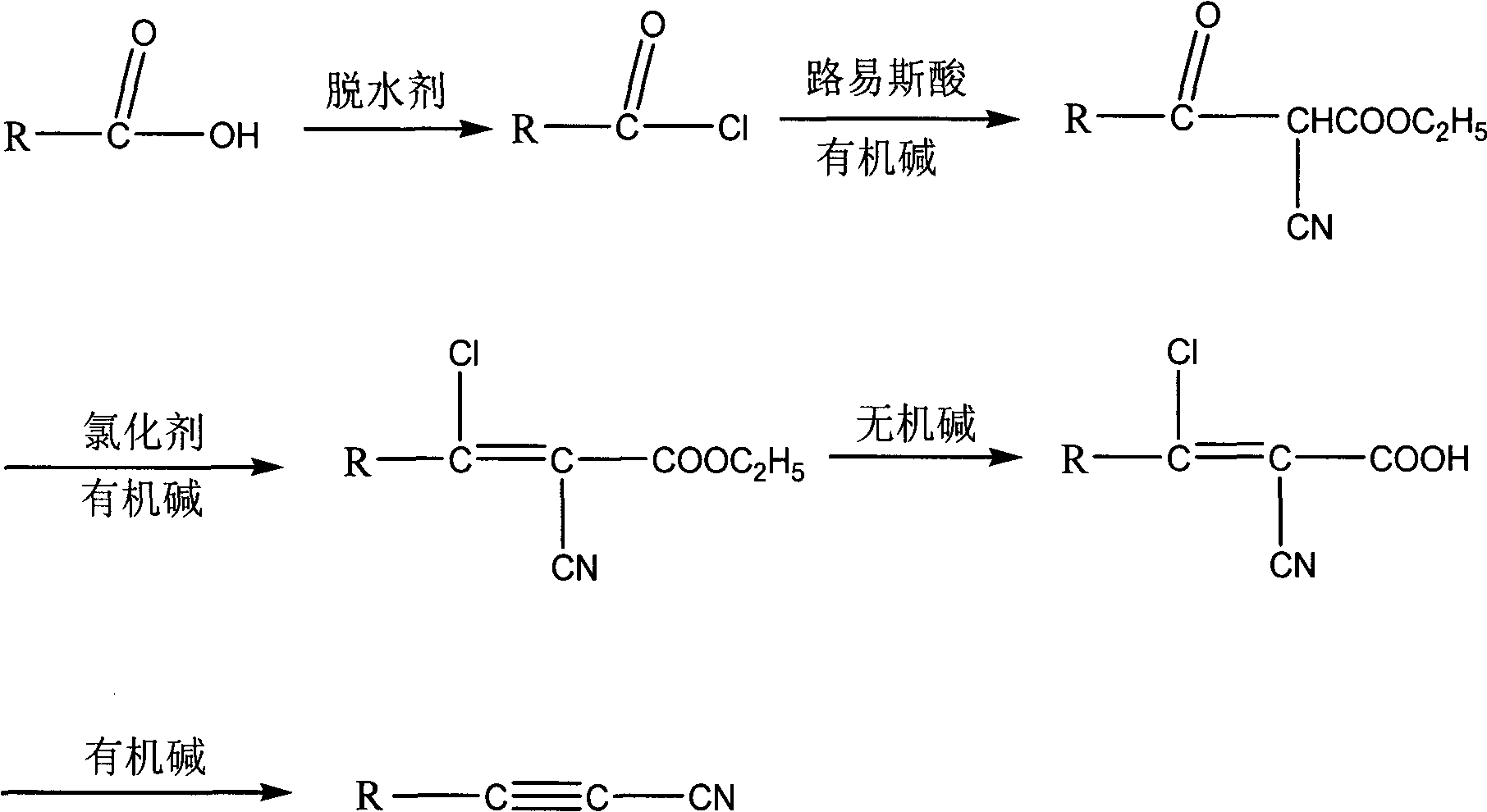
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The synthetic method of embodiment 1 cyclopentyl propylonitrile (R is cyclopentyl)
[0031] 1) Preparation of cyclopentylformyl chloride: Add 115g (1mol) cyclopentylformic acid into a 250ml there-necked flask, and add 165g (1.4mol) thionyl chloride dropwise at room temperature, and the time for dropping is about 1 hour. After the dropwise addition, react at room temperature, monitor the reaction by GC and show that there is no remaining formic acid after this period of time, then heat up, evaporate excess thionyl chloride under normal pressure, and carry out vacuum distillation on the residue to obtain about 118g~125g of product. The rate is 90% to 95%.
[0032] 2) Preparation of ethyl α-cyano-β-carbonylcyclopentylpropionate: under nitrogen protection, dissolve 100g (1.0mol) of ethyl cyanoacetate in 1000ml tetrahydrofuran and add 95g (1mol) of anhydrous magnesium chloride to cool to 0°C. Add 200g (2mol) of triethylamine dropwise to this system, and control the dropwis...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The preparation of embodiment 2 3-phenyl propylonitrile (R is 3-phenyl)
[0037]At room temperature, 50 g (0.5 mol) of triethylamine was dripped into 87 g of the crude product of α-cyano-β-chlorophenylacrylic acid (using 1 mol of benzoic acid as the starting material according to the steps 1-4 in Example 1) obtained by imitation) and 300ml of dichloroethane and heated to reflux for 24 hours. Cool to room temperature and add 100ml of water, stir to dissolve and then let stand to separate layers. The lower organic layer was separated, and the organic layer was washed once with 50 ml of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution and then allowed to stand for separation. The organic phase was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and filtered with suction. After dichloroethane was evaporated under normal pressure, the residue was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 43 g of the product. The crude product was crystallized with 30 ml of n-hexane and dri...
Embodiment 3
[0038] The preparation of embodiment 3 3-isopropyl propylonitrile (R is 3-isopropyl)
[0039] At room temperature, 75g (0.75mol) of triethylamine was dripped into 109g of the crude product of α-cyano-β-chloroisopropylacrylic acid (using 1mol of isobutyric acid as the starting material according to 1- 4 steps were imitated) and 300ml of dichloroethane and heated to reflux for 24 hours. Cool to room temperature and add 100ml of water, stir to dissolve and then let stand to separate layers. The lower organic layer was separated, and the organic layer was washed once with 50 ml of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution and then allowed to stand for separation. The organic phase was separated, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and filtered with suction. After dichloroethane was distilled off under normal pressure, the residue was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 48.6 g of oily substance, with a total yield of 52%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com