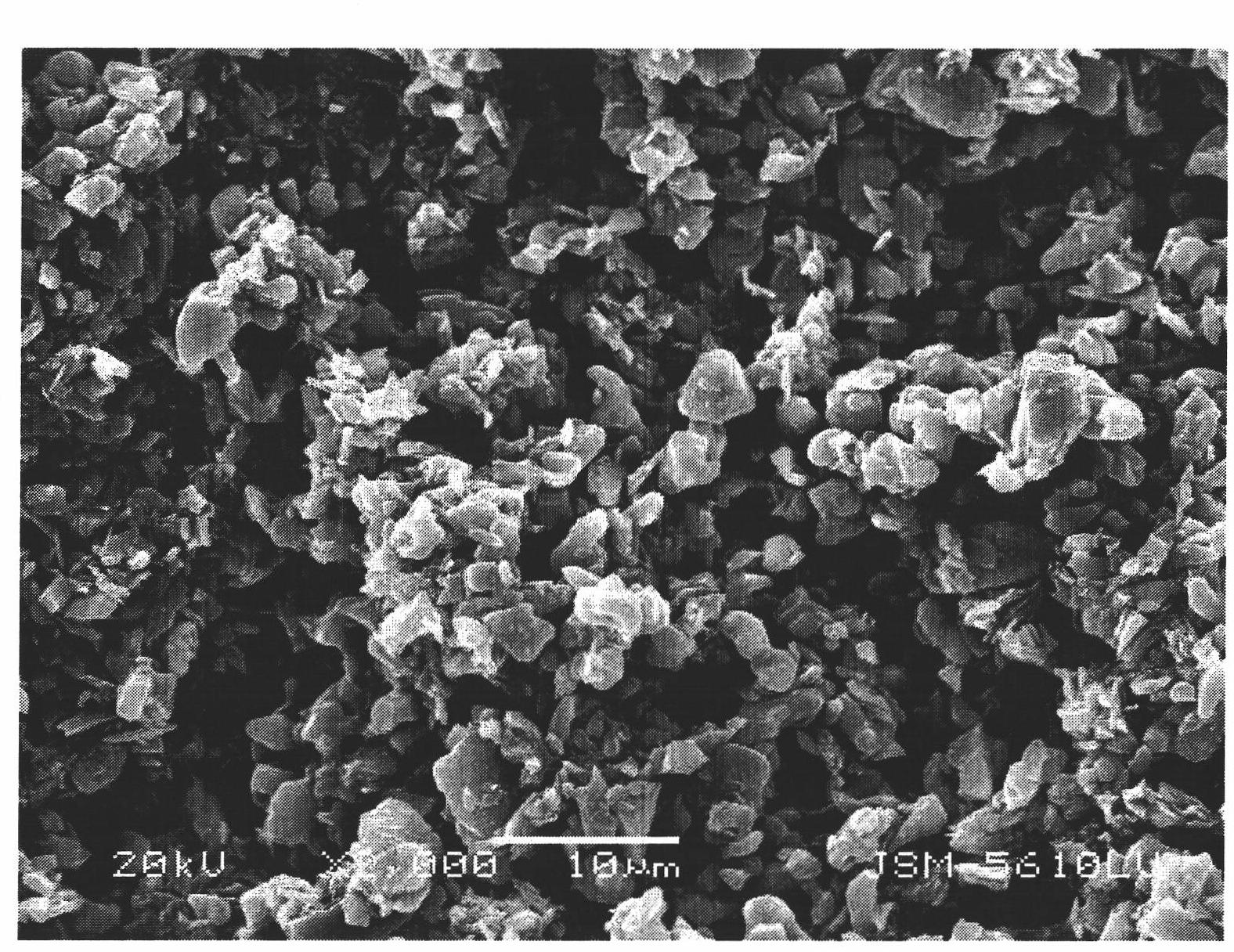
Magnesium-based bone filling adhesive and preparation method and application thereof
An adhesive and cohesive technology, which is applied in application, surgical adhesives, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of slow strength development, poor biocompatibility, poor collapse resistance, etc., and achieve low raw material cost and high cohesiveness. Strong, good anti-collapse effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
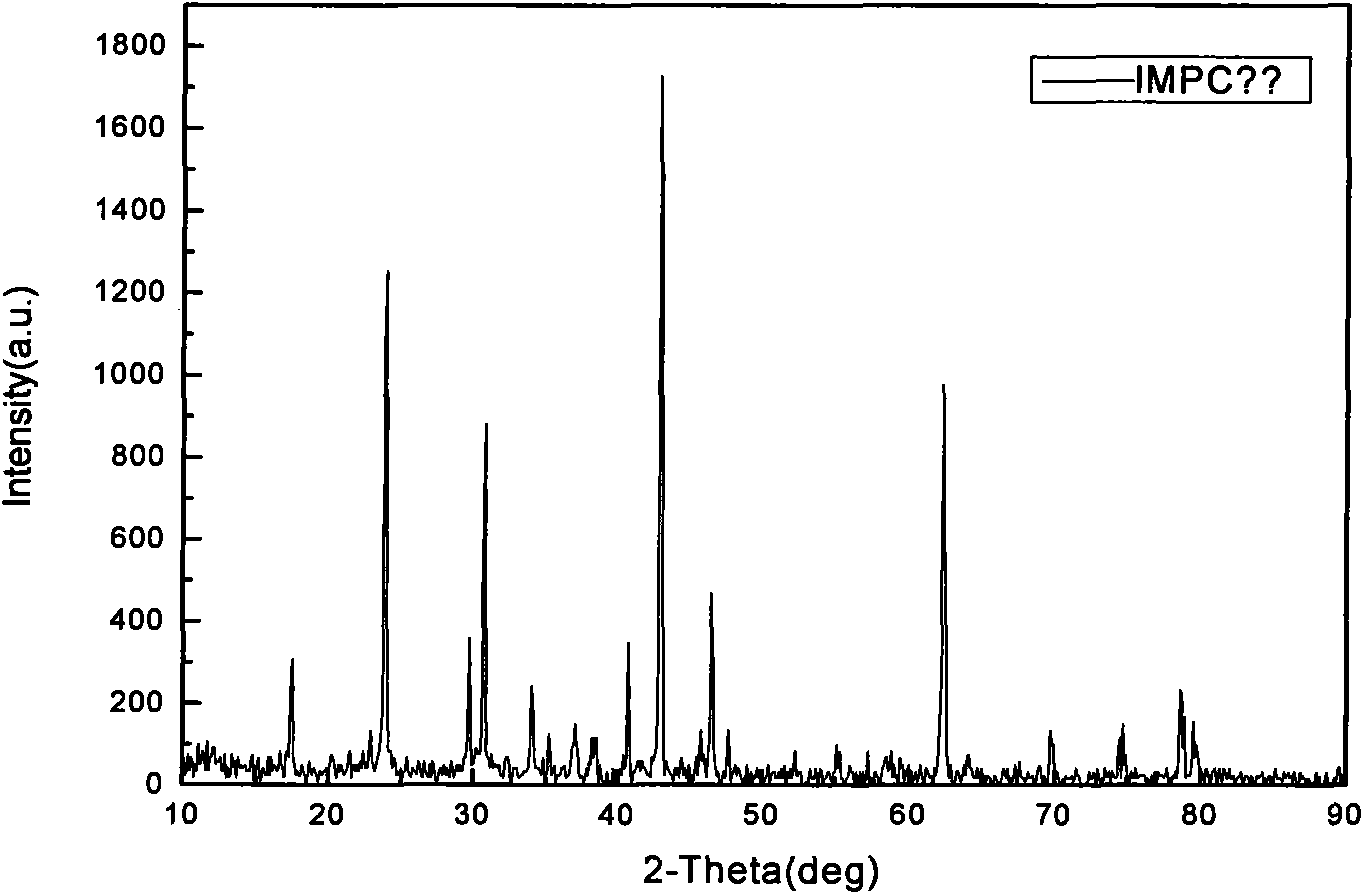
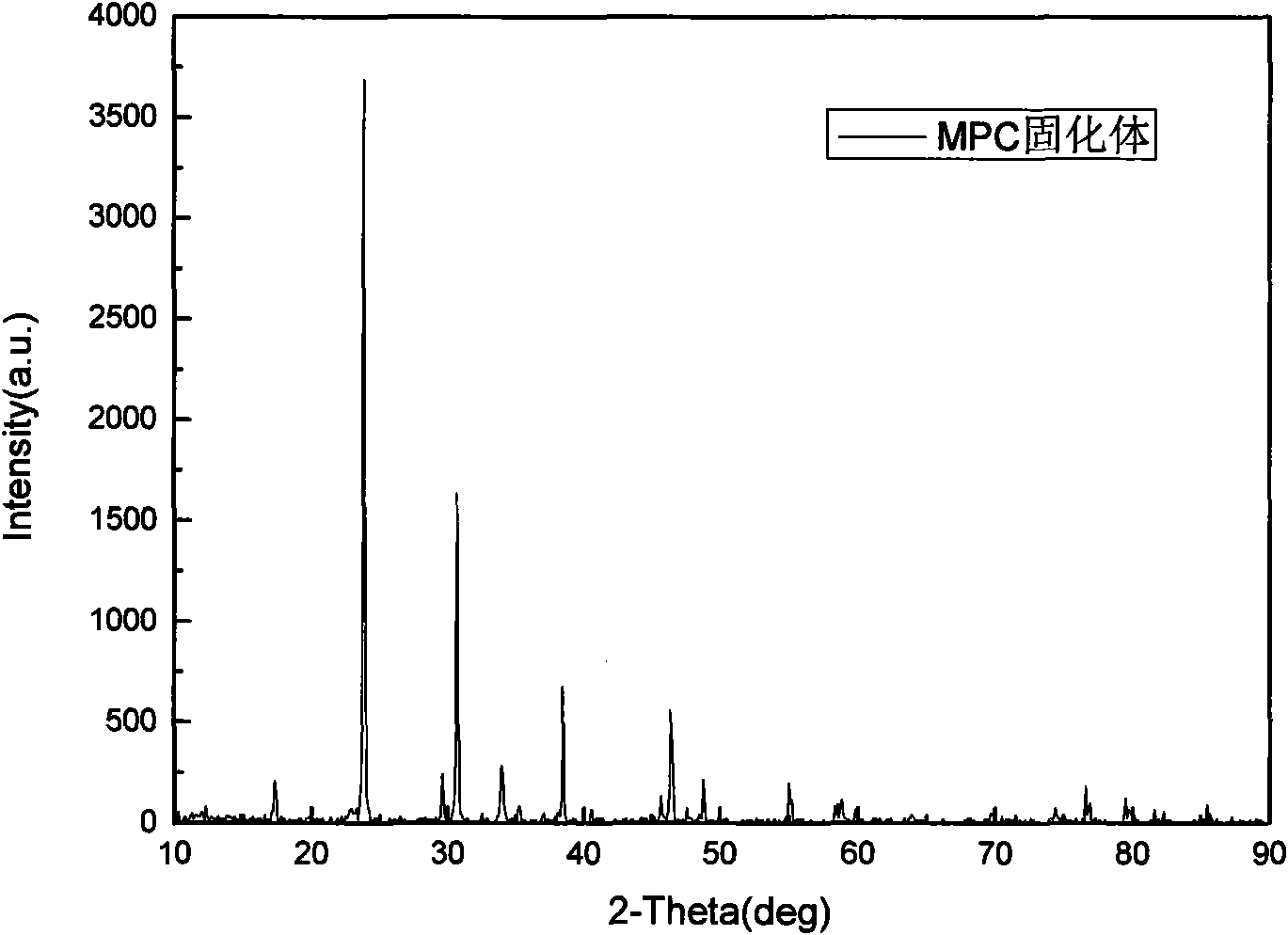
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Alkaline oxides are taken in parts by weight, and 20% to 30% of one of magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, zinc oxide, strontium oxide, and aluminum oxide is selected. The hydrogen phosphate is sodium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, dibasic phosphate Potassium hydrogen phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate or a mixture of two or more 15-40%, magnesium phosphate 20%-40%, calcium phosphate salt (α, β)-tricalcium phosphate, tetracalcium phosphate, octacalcium phosphate One or both of calcium, calcium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous, calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, calcium dihydrogen phosphate, calcium pyrophosphate, hydroxyapatite, fluoroapatite, strontium apatite, and carbonate-containing apatite and mixtures of the above. 5-10% starch, 5-10% starch, uniformly mixed to obtain a powdery solid phase component with a particle size of less than 20 μm. In addition, sugars include polysaccharides, sugar derivatives, glucose, sucrose, dextrin, cellulose, c...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate and calcium carbonate were weighed at a molar ratio of 2:1, mixed thoroughly, heated to 950°C in a muffle furnace, kept for 3 hours, taken out and ball milled for 10 hours to obtain β-tricalcium phosphate. Magnesium oxide was calcined at a high temperature of 1500°C and kept for 1 hour. Weigh 1.0g β-tricalcium phosphate, 2.2g magnesium oxide, 3.6g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 2.7g magnesium phosphate, 0.5g starch, the particle size is less than 20μm, and mix uniformly to form a solid phase powder. Weigh 2.0 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.5 g of sucrose, and 0.5 g of glucose and dissolve them fully in 10 ml of 0.1 mol / L phosphoric acid solution to obtain a solidified solution. The solidified liquid is poured into the solid phase powder at a liquid-solid ratio of 0.3 (ml / mg), and mixed uniformly in a vessel to obtain a magnesium-based bone filling adhesive.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate and calcium carbonate were weighed at a molar ratio of 2:1, mixed thoroughly, heated to 1250°C in a muffle furnace, kept for 3 hours, taken out and ball milled for 10 hours to obtain α-tricalcium phosphate. Magnesium oxide was calcined at a high temperature of 1600°C and kept for 1 hour. Weigh 1.0g α-tricalcium phosphate, 2.2g magnesium oxide, 3.6g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 2.7g magnesium phosphate, 0.5g starch, the particle size is less than 20μm, and mix uniformly to form a solid phase powder. Weigh 1.0 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.0 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and 0.8 g of glucose and fully dissolve them in 10 ml of 0.1 mol / L phosphoric acid solution to obtain a solidified solution. The solidified liquid is poured into the solid phase powder at a liquid-solid ratio of 0.4 (ml / mg), and mixed uniformly in a vessel to obtain a magnesium-based bone filling adhesive.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com