Preparation method of hydrophobically modified poly-cation chelating agent
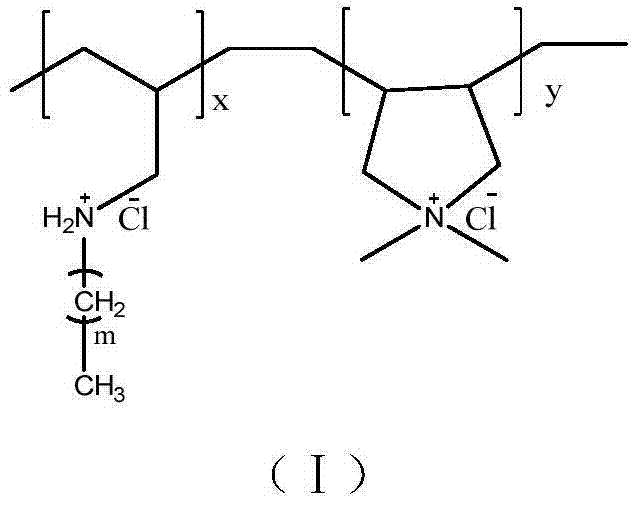
A polycationic and hydrophobic modification technology is used in the preparation of hydrophobically modified polycationic polymer chelating agents, the free radical polymerization of hydrophobically modified allylamine copolymers, and the preparation of bile acid chelating agents. Causes nausea, low degree of polymerization, abdominal discomfort and other problems, and achieves the effects of high polymer molecular weight, mild reaction, and convenient monomer storage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A preparation method of hydrophobically modified polycation chelating agent, comprising the steps of:
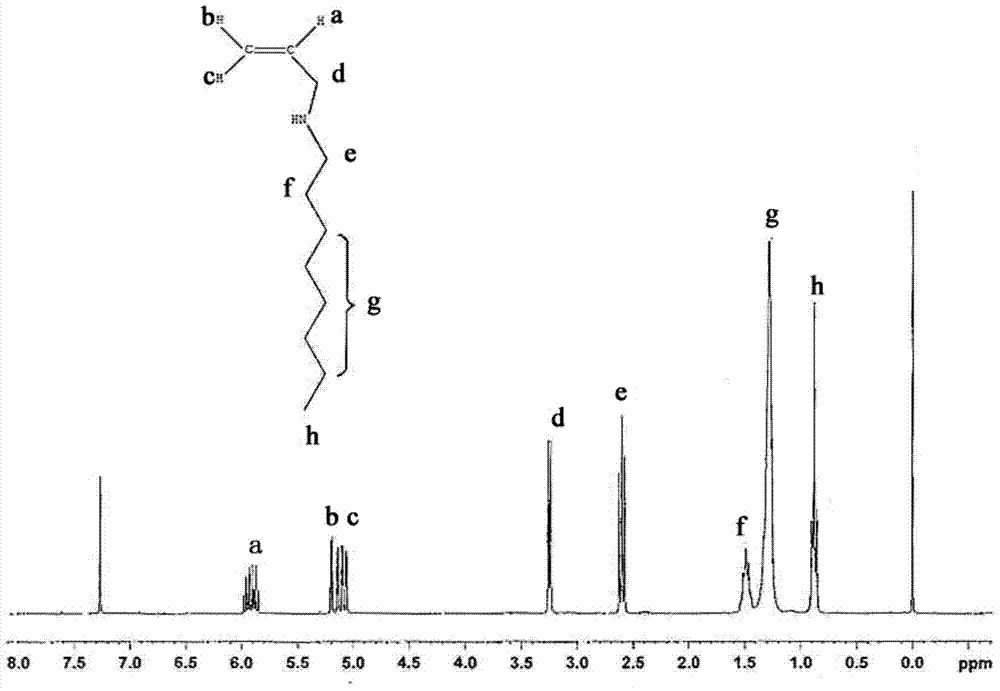
[0037] (1) Weigh 95g (1mol) of allylamine solution with a mass concentration of 60%, 85g (1mol) of dichloromethane, and 10.6g (0.1mol) of sodium carbonate, and pour them into funnel and a 250mL three-necked flask with an electromagnetic stirrer, and then placed in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C, and mixed evenly under the condition of a stirring speed of 50r / min.
[0038] Weigh 19.3g (0.1mol) of n-bromooctane and pour it into a constant pressure dropping funnel, add dropwise under stirring, complete the dropwise addition within 20min, react for 8h, remove sodium carbonate by suction filtration, and keep the filtrate. The unreacted allylamine was recovered by distillation under normal pressure at 90°C to obtain a two-phase system containing a colorless supernatant and a brown-red lower layer. Add 50 mL of dichloromethane and wash with 20 mL of deionized wat...
Embodiment 2
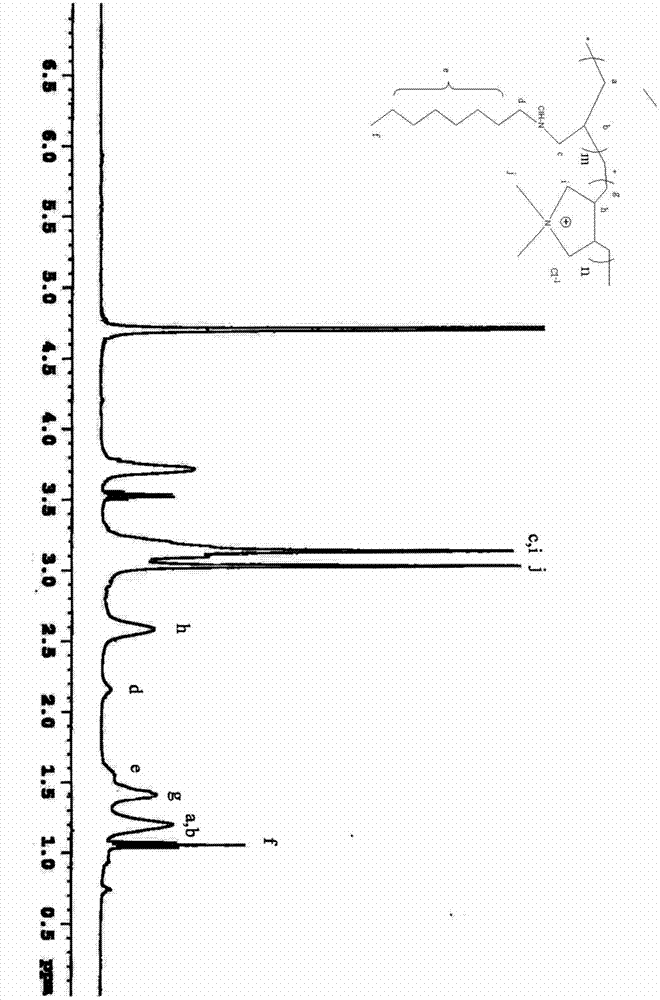
[0042] Take by weighing 2.06g of N-octylallylamine hydrochloride and 10.78g of dimethyldiallyl ammonium chloride prepared in Example 1 and add them to water to form an aqueous solution with a monomer mass concentration of 70%. into a 50mL three-neck flask. Stir at 35°C until the light yellow solid gradually dissolves, then add 0.65g of potassium persulfate (KPS), stir until dissolved, pass N 2 Deoxygenation for 30min, at 60℃, N 2 Polymerize in the air for 24 hours, then add it dropwise into absolute ethanol, take the light yellow precipitate, dissolve the light yellow precipitate in water, and precipitate with alcohol, repeat three times, dry in vacuum at room temperature for 48 hours, and obtain a light yellow powdery solid that is hydrophobic Modified polycation chelating agent, the productive rate is 88%, and the weight-average molecular weight measured by light scattering method is 148,000.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Weigh 3.10 g of N-octylallylamine hydrochloride and 9.43 g of dimethyldiallyl ammonium chloride prepared in Example 1 and add them to water to form an aqueous solution with a monomer mass concentration of 70%. into a 50mL three-neck flask. Stir at 35°C until the light yellow solid gradually dissolves, then add 0.65g of potassium persulfate (KPS), stir until dissolved, pass N2 Deoxygenation for 30min, at 60℃, N 2 Polymerize in the air for 24 hours, then add it dropwise into absolute ethanol, take the light yellow precipitate, dissolve the light yellow precipitate in water, and precipitate with alcohol, repeat three times, dry in vacuum at room temperature for 48 hours, and obtain a light yellow powdery solid that is hydrophobic Modified polycation chelating agent, the productive rate is 87%, and the weight-average molecular weight measured by light scattering method is 97,000.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com