Active thermophilic bacteria mutant strain and application thereof in oil displacement
A composite oil displacement agent and bacterial strain technology, applied in the direction of mutant preparation, bacteria, drilling composition, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to significantly reduce surface tension, narrow growth temperature range, poor environmental adaptability, etc., and achieve major economic benefits Value and large-scale application, improved emulsification activity, and good emulsification stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
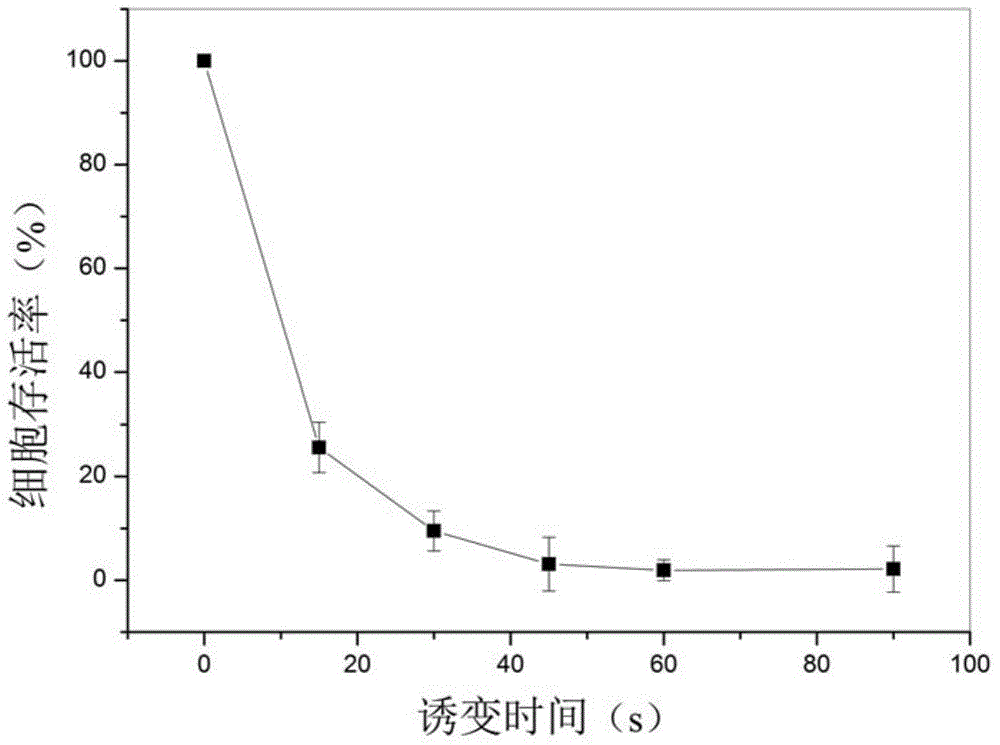
[0017] This example illustrates a method for plasma mutagenesis of an original strain.
[0018] The culture medium formulation (w / v) used wherein:
[0019] Solid plate LB (Luria-Bertani) medium: sodium chloride 10%, tryptone 10%, yeast extract 5%, agar 2%, pH 7.5.
[0020] Liquid LB medium: 10% sodium chloride, 10% tryptone, 5% yeast extract, pH 7.5. The specific method for carrying out plasma mutagenesis with the original strain Geobacillus pallidusXS2 is as follows:
[0021] 1. Prepare the original strain Geobacillus pallidusXS2 bacterial suspension
[0022] The original strain Geobacillus pallidusXS2 is a strain of thermophilic Geobacillus isolated and screened from the Yaerxia oil reservoir in Yumen Oilfield, Gansu, China by our laboratory; it is a strain of Geobacillus pallidus (Geobacillus pallidus), and the preservation number of this strain is CGMCC No.8338, was deposited on October 15, 2013 at the General Microbiology Center of the Chinese Microbiological Culture C...
Embodiment 2
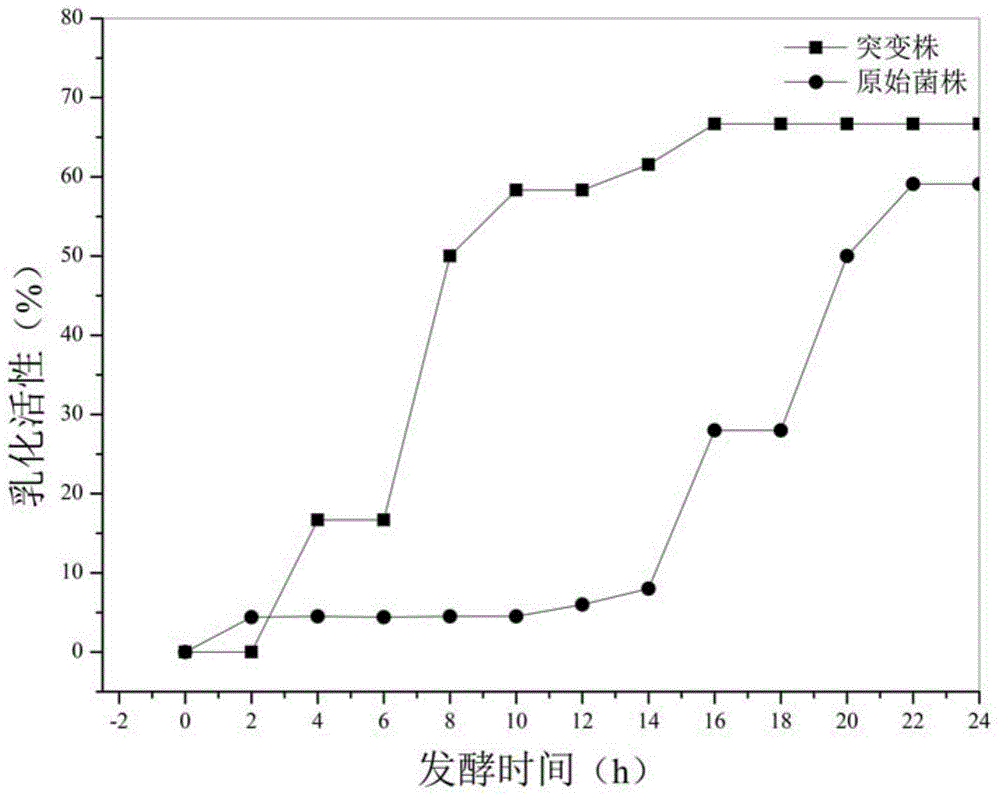
[0029] This example illustrates the screening method for producing highly active bioemulsifier strains.
[0030] The culture medium formulation (w / v) used wherein:
[0031] Solid plate LB (Luria-Bertani) medium: sodium chloride 10%, tryptone 10%, yeast extract 5%, agar 2%, pH 7.5.
[0032] Liquid LB medium: 10% sodium chloride, 10% tryptone, 5% yeast extract, pH 7.5.
[0033] Fermentation medium: glucose 2%, sodium nitrate 0.3%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.042%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.12%, ferrous sulfate 0.005%, magnesium sulfate 0.05%, calcium chloride 0.005%, vitamin 0.02%. Trace elements 0.1%, pH 7.5.
[0034] Trace elements: boric acid 0.025%, copper sulfate 0.05%, manganese sulfate 0.05%, sodium molybdate 0.006%, zinc sulfate 0.07%.
[0035] Vitamins: Calcium D-pantothenate 0.004%, inositol 0.002%, niacin 0.004%, vitamin 6.004%, p-aminobenzoic acid 0.002%, vitamin B12 0.05%.
[0036] The screening steps are as follows:
[0037] 1. Primary screening of...
Embodiment 3
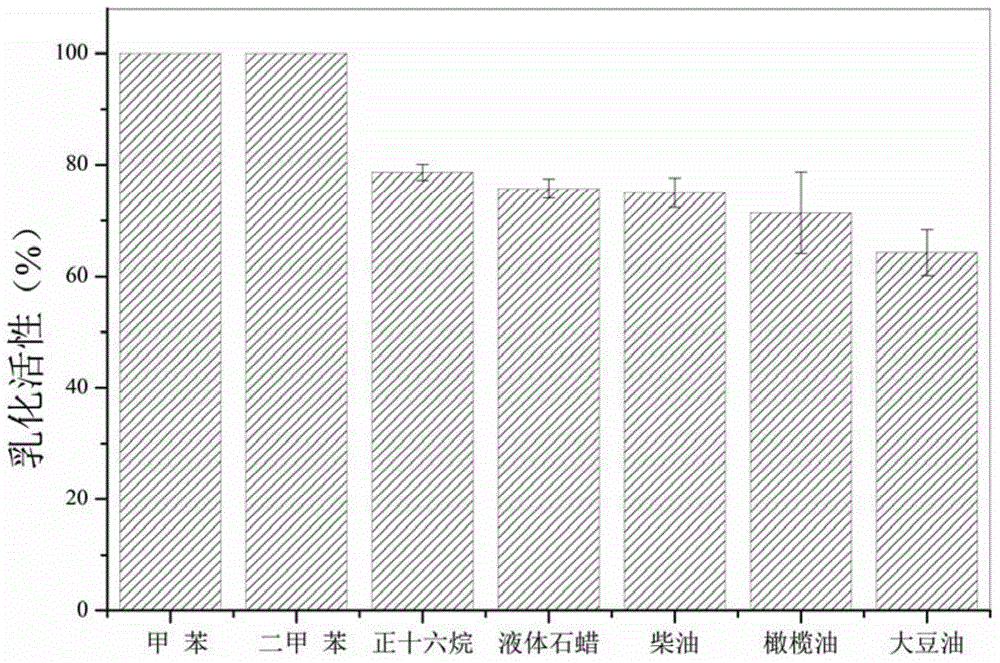
[0044] In this example, the emulsifying activity of the mutant strain XS2-450 on various hydrocarbons was determined.
[0045] The method for measuring emulsifying activity provided by the present invention is to mix the mutant strain fermentation stoste with seven different hydrocarbons (toluene, xylene, n-hexadecane, liquid paraffin, soybean oil, diesel oil, olive oil) in a certain ratio, vortex Rotate and oscillate for 2 minutes, let stand for 24 hours, emulsifying activity = height of emulsified layer / total height of liquid level * 100%. The experimental results show that the mutant strain XS2-450 has higher emulsifying activity for the above seven hydrocarbons after system optimization. Wherein the toluene can reach 100% at the highest, which is 29.6% higher than the activity of the original bacterial strain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com