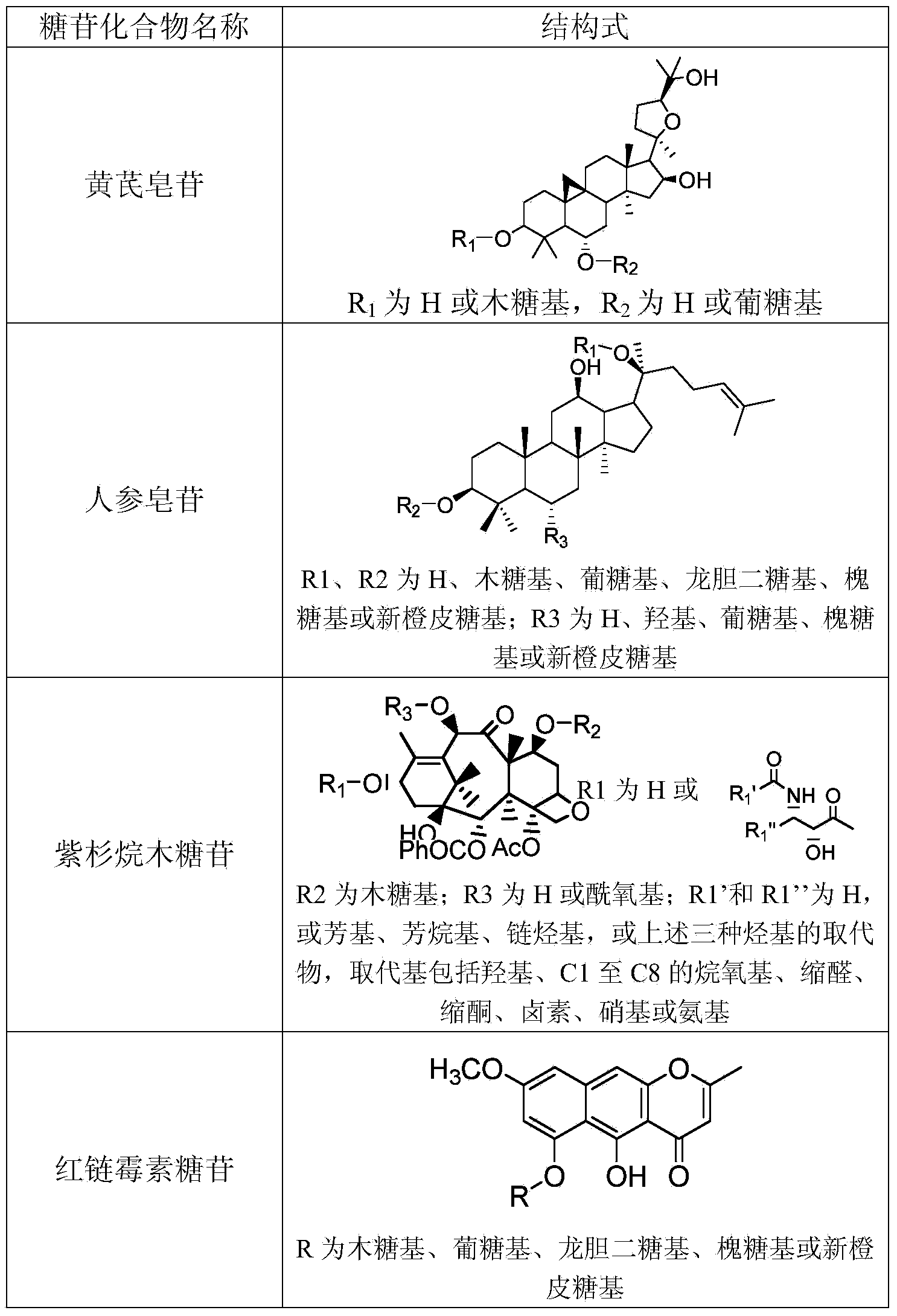
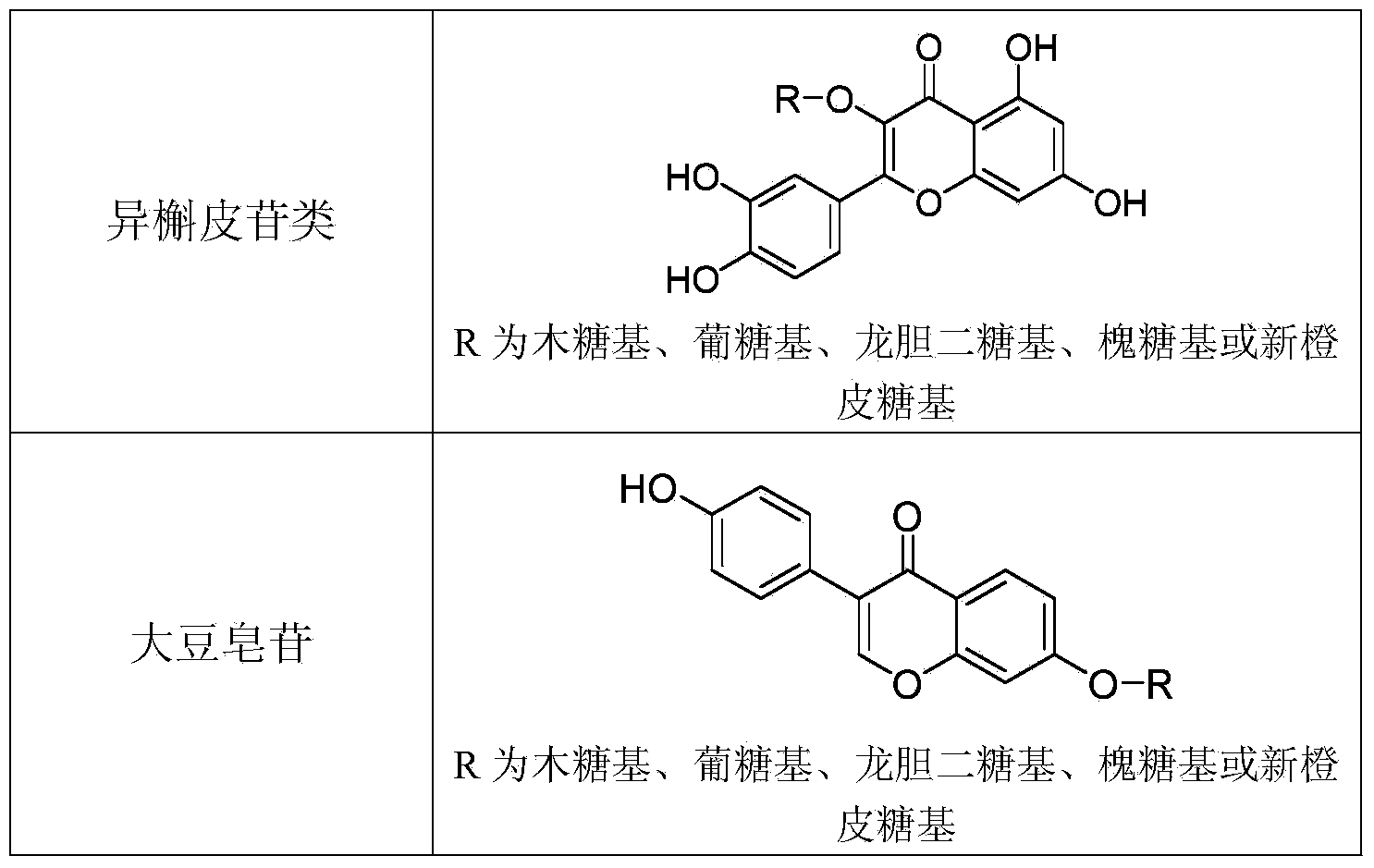
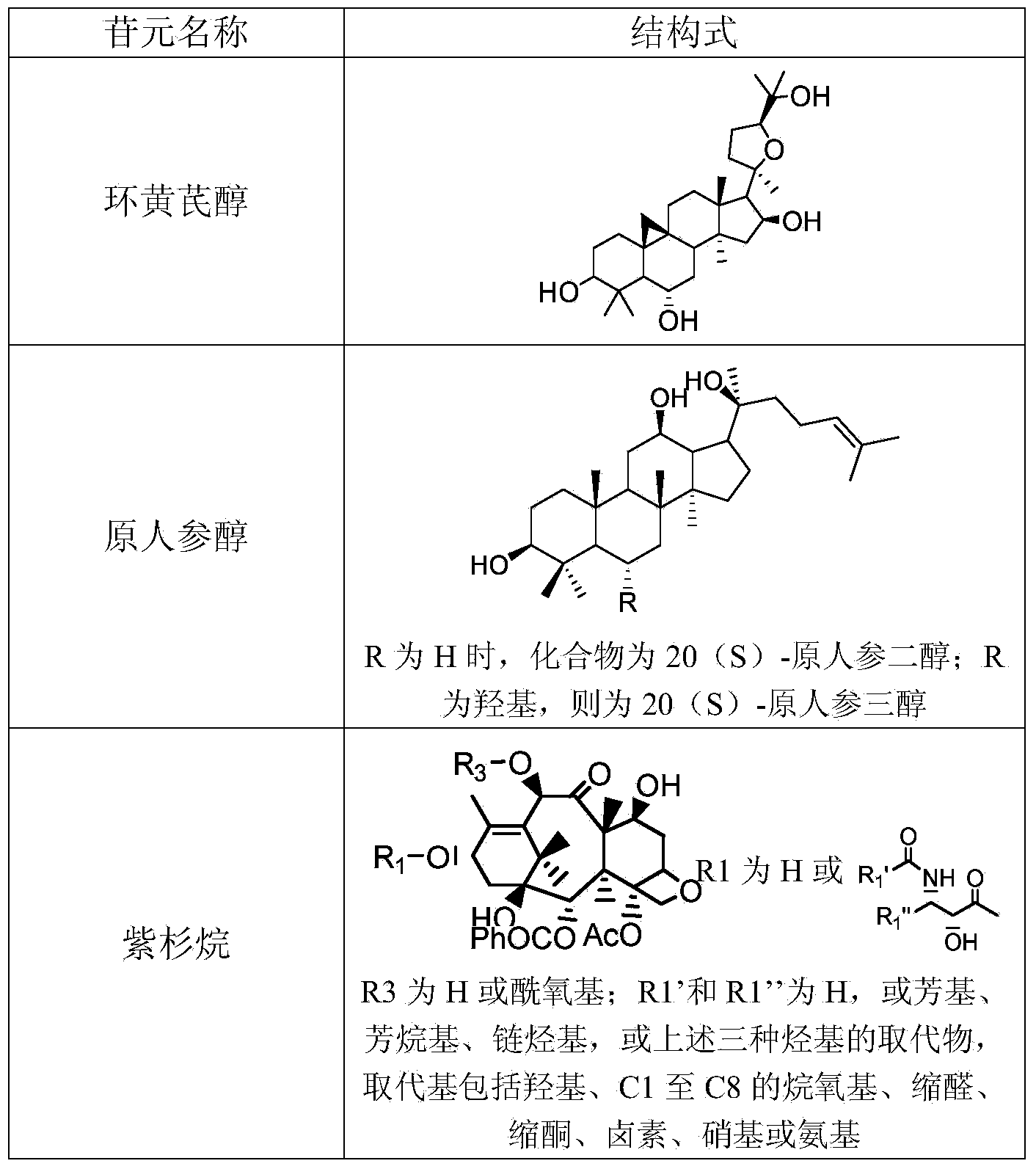
Cellulosimicrobium cellulans strain and application thereof
A kind of bacterial strain and chemical fiber technology, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low enzyme production and conversion efficiency, difficult hydrolysis of common glycosidases, etc., and achieve good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: the preparation of crude enzyme liquid
[0036] A medium containing 1% starch, 0.2% peptone, 0.2% yeast extract, and 0.2% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (pH 7.0 before sterilization) was used as the seed medium.
[0037] Distribute 20 ml of the above-mentioned seed medium into 100 ml conical flasks, sterilize at 120 degrees for 15 minutes, inoculate the agar slant culture of Cellulomonas cellulosus F16 strain into it, and shake and cultivate it at 30 degrees for 2 days as seed liquid.
[0038] Put 100ml of 1% birch xylan, 0.2% yeast extract, 0.2% ammonium chloride, 0.1% NaH into a 500ml Erlenmeyer culture bottle 2 PO 4 and 0.1%Na 2 HPO 4 Medium, pH7, autoclaved at 121°C for 30min. Inoculate 1ml of seed liquid into this medium, shake the flask at 150rpm, and culture at 30°C for 5 days. Centrifuge to collect the supernatant, which is the crude enzyme solution.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: the preparation of the hydrolysis crude enzyme liquid of astragaloside IV
[0040] Add 1ml of 50mM Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH7.5) to 0.9ml of the crude enzyme solution in Example 1, and then add 0.1ml of astragaloside IV methanol solution (concentration: 10mg / ml). After incubation at 100 rpm and 35°C for 8 hours, using cycloastragenol standard as a control, TLC analysis showed that almost all of astragaloside IV was converted into cycloastragenol.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Preparation of compound CK by hydrolysis of ginsenoside Rb1
[0042] Add 1ml of 50mM Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH7.5) to 0.9ml of the crude enzyme solution in Example 1, and then add 0.1ml of methanol solution of ginsenoside Rb1 (concentration: 10mg / ml). 100 rpm, incubate at 35°C for 4 hours. Add 2ml of methanol to terminate the reaction, centrifuge at 15,000 rpm for 20 minutes, and take the supernatant for UPLC analysis. The ginsenoside Rb1 in the reaction solution was almost completely converted to produce compound K (ie, CK, with a yield of 75%), an incompletely hydrolyzed intermediate product and a small amount of final product PPD.
[0043] UPLC method:
[0044] Chromatographic column: Kromasil ODS (2.1×150mm, 3μm)
[0045] Mobile phase: acetonitrile: water (0→30min: 20:80→95:5 gradient elution)
[0046] Flow rate: 0.4ml / min
[0047] Column temperature: room temperature
[0048] Detection wavelength: 203nm
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com