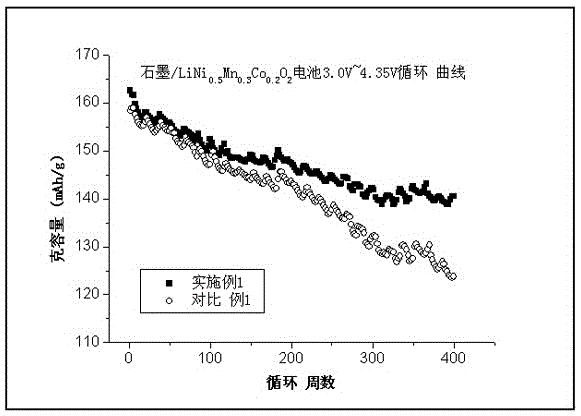
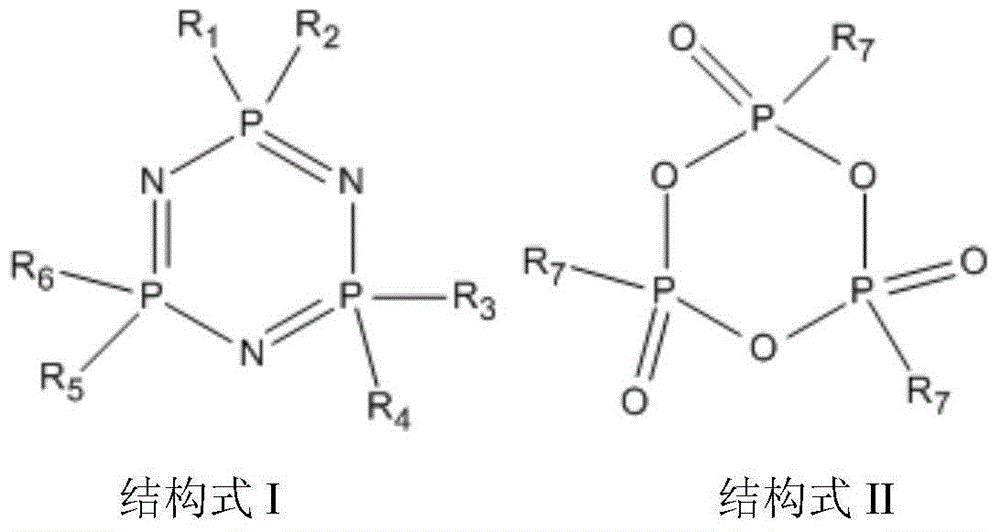
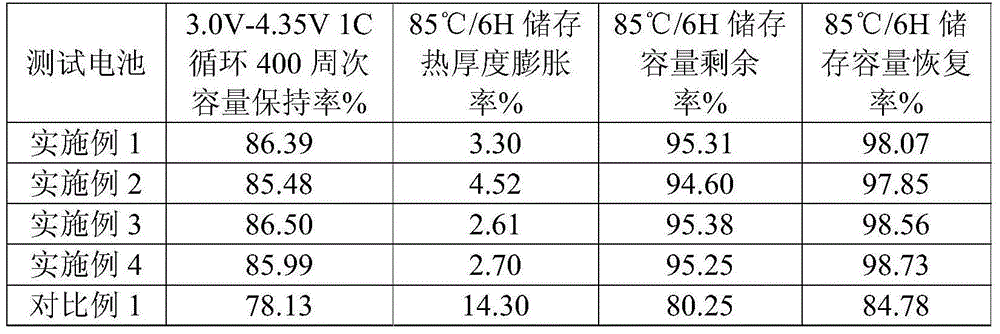
Lithium-ion battery electrolyte containing fluoroethylene carbonate and lithium-ion battery
A technology for substituting ethylene carbonate and lithium-ion batteries. It is applied in the field of lithium-ion batteries. It can solve the problems of lithium salt precipitation, reduced cycle capacity, and large internal resistance of batteries, and achieve the goals of reducing decomposition, suppressing high-temperature gas production, and improving discharge capacity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In a glove box filled with argon, ethylene carbonate, diethyl carbonate and ethyl methyl carbonate were mixed according to the mass ratio of EC:DEC:EMC=1:1:1, and 3wt% based on the total mass of the electrolyte were added successively. Fluoroethylene carbonate, 1wt% p-methoxybenzonitrile, 2wt% ethoxypentafluorocyclotriphosphazene, 0.2wt% vinylene carbonate, 3wt% 1,3-propane sultone and 1wt% % lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide; finally, slowly add lithium hexafluorophosphate accounting for 12.5wt% of the total mass of the electrolyte to the mixed solution, and stir evenly to obtain the lithium-ion battery electrolyte of Example 1.
Embodiment 2
[0029] In a glove box filled with argon, ethylene carbonate, diethyl carbonate and ethyl methyl carbonate were mixed according to the mass ratio of EC:DEC:EMC=3:6:1, and 2wt% based on the total mass of the electrolyte were added successively. Fluoroethylene carbonate, 0.5wt% benzonitrile, 2wt% ethoxypentafluorocyclotriphosphazene, 0.2wt% vinylene carbonate, 0.5wt% methylene disulfonate and 0.5wt% bis( Lithium fluorosulfonyl)imide; finally, slowly add lithium hexafluorophosphate accounting for 13wt% of the total mass of the electrolyte to the mixed solution, and stir evenly to obtain the lithium-ion battery electrolyte of Example 2.
Embodiment 3
[0031] In a glove box filled with argon, ethylene carbonate, diethyl carbonate and propylene carbonate were mixed in a mass ratio of EC:DEC:PC=3:6:1, and 5wt% based on the total mass of the electrolyte was added successively. Fluoroethylene carbonate, 1wt% phenylacetonitrile, 0.5wt% tri-n-propylphosphonic acid cyclic anhydride, 1wt% vinyl sulfate and 1wt% 1,2-bis(2-cyanoethoxy)ethane; Lithium hexafluorophosphate, accounting for 15 wt% of the total mass of the electrolyte, was slowly added into the solution, and stirred evenly to obtain the lithium ion battery electrolyte of Example 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com