A kind of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate and its preparation method and application
A technology for cross-linking hyaluronic acid and sodium hyaluronate, which is used in pharmaceutical formulations, cosmetic preparations, cosmetic preparations, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in effectively removing cross-linking agents, residual organic reagents, and complicated processes, and achieves Widen use and application effects, mild reaction conditions, and improved reaction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Cross-linking test in the environment provided by the present invention in embodiment 1
[0054] 1) Add 1.0 g of sodium hyaluronate with a molecular weight of 2 million Daltons and 0.5 g of NaCl into 100 mL of 0.02% (w / w) NaOH solution, and stir at room temperature for 4 hours until completely dissolved.
[0055] 2) Take 0.2mL of 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether, dilute it with 50mL of distilled water and keep it for later use.
[0056] 3) Heat the NaOH solution of sodium hyaluronate to 45°C and keep it at a constant temperature, and add the BDDE solution to the system dropwise for 30 minutes, then continue the reaction at constant temperature for 1.5 hours.
[0057] 4) Add 0.005 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution to adjust to pH = 7.2, and stir for 2 hours to balance, then add 500 mL of absolute ethanol, precipitate for 2 hours, and take out the massive solid.
[0058] 5) After the obtained solid was lyophilized, 1 g of the product was dialyzed in 200 mL of PBS buffer so...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Cross-linking test in the environment provided by the present invention in embodiment 2
[0060] Only the amount of NaCl added was changed, and the amount of NaCl was replaced by 0.9g, 1.5g, and 3.0g, respectively, and added to the reaction system. Other conditions remained unchanged, and the test was carried out according to the method in Example 1.
experiment example
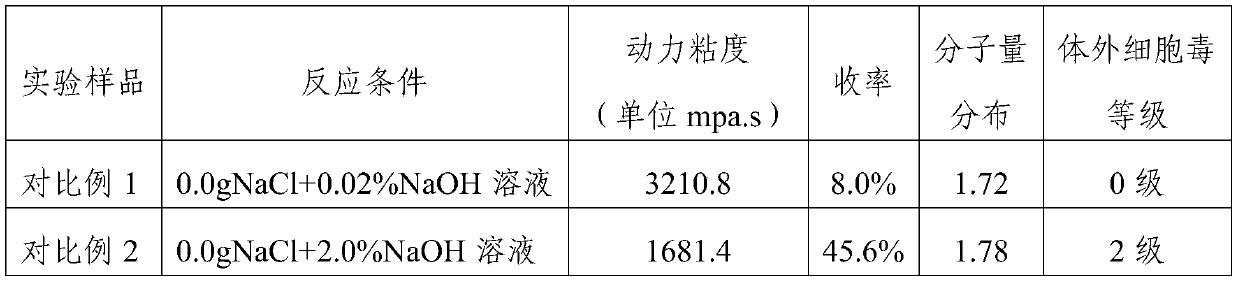
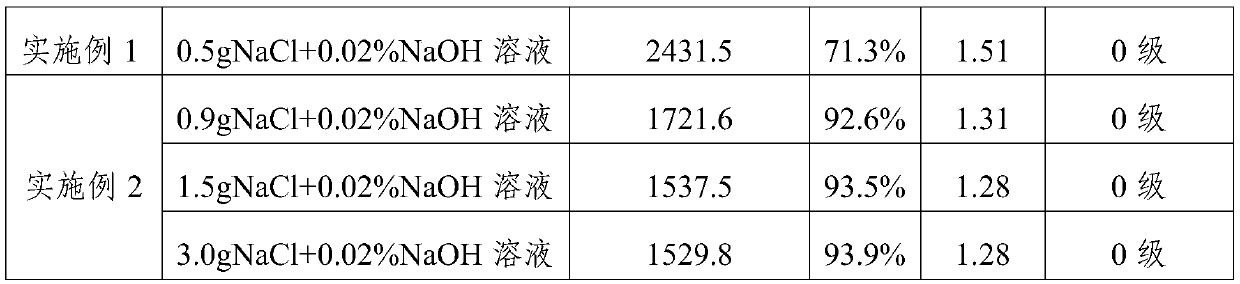
[0074] The dynamic viscosity, molecular weight distribution and in vitro cytotoxicity of the cross-linked sodium hyaluronate prepared in Example 1-2 and Comparative Example 1-2 were respectively tested, and the results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0075] Table 1
[0076]
[0077]
[0078] The results in Table 1 show that, 1) the reaction yield is low under the weak base environment, and the molecular weight distribution is wider; 2) the yield is improved under the concentrated alkali environment, but the molecular weight distribution is still wide, and the cytotoxicity is larger; 3) in the inorganic Under the reaction environment of salt NaCl, the yield is obviously increased, the molecular weight distribution is also obviously narrowed, and the cytotoxicity is not significantly affected. It can be seen that inorganic salts such as NaCl play an important role in this reaction.
[0079] Although the above only gave the example of using BDDE as the cross-linking agent, i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com