CRISPR-B (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-B) gene editing method for gtfB site of specific targeting streptococcus mutans and application
A Streptococcus mutans, gene editing technology, applied in the field of CRISPR-B gene editing, can solve problems such as inability to efficiently and accurately find specificity, expensive purification or synthesis, blindness in screening, etc., and achieve reduced synthesis and biofilm degradation. Effects on formation, inhibition of synthesis and biofilm formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
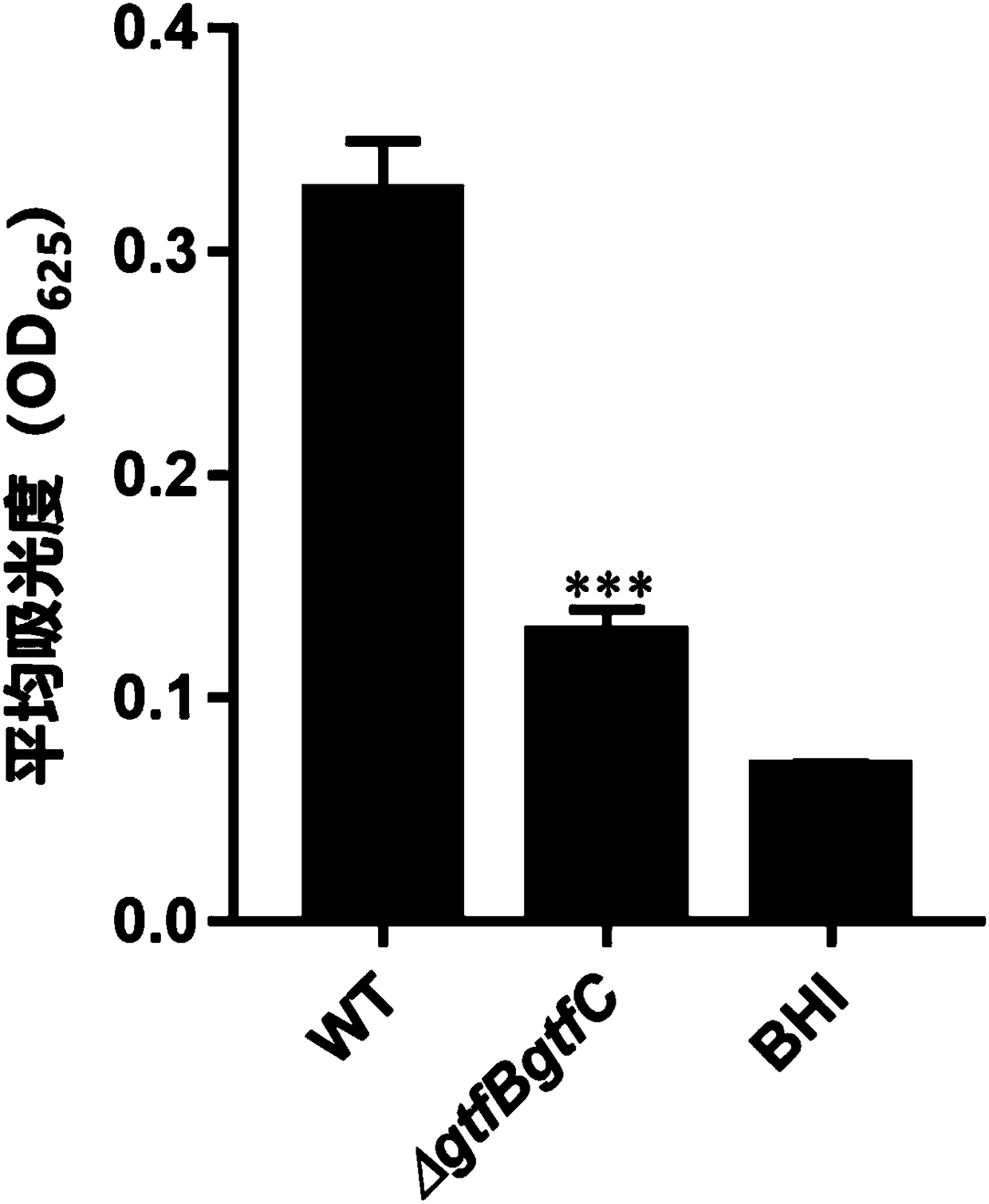
[0114] Detection of the effect of CRISPR editing vector on inhibiting the exopolysaccharide of Streptococcus mutans (anthrone method)
[0115] Experimental principle: under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid, sugar can be dehydrated to generate furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural, and the generated furfural or hydroxymethylfurfural can react with anthrone to generate blue-green furfural derivatives; within a certain range, the color The depth is proportional to the content of sugar, so it can be used for the quantification of sugar; the colored substance produced by the reaction of sugar and anthrone has an absorption peak of 625nm in the visible light region, so the colorimetry is performed at this wavelength.
[0116] (1) in 10% H 2 , 5%CO 2 and 85%N 2 Under anaerobic conditions, the gtfBgtfC double knockout strain was inoculated in BHI medium, and cultured at 37°C for 16 hours;
[0117] (2) Dilute the resuscitated bacteria in the previous step with preheated BHI medi...
Embodiment 2
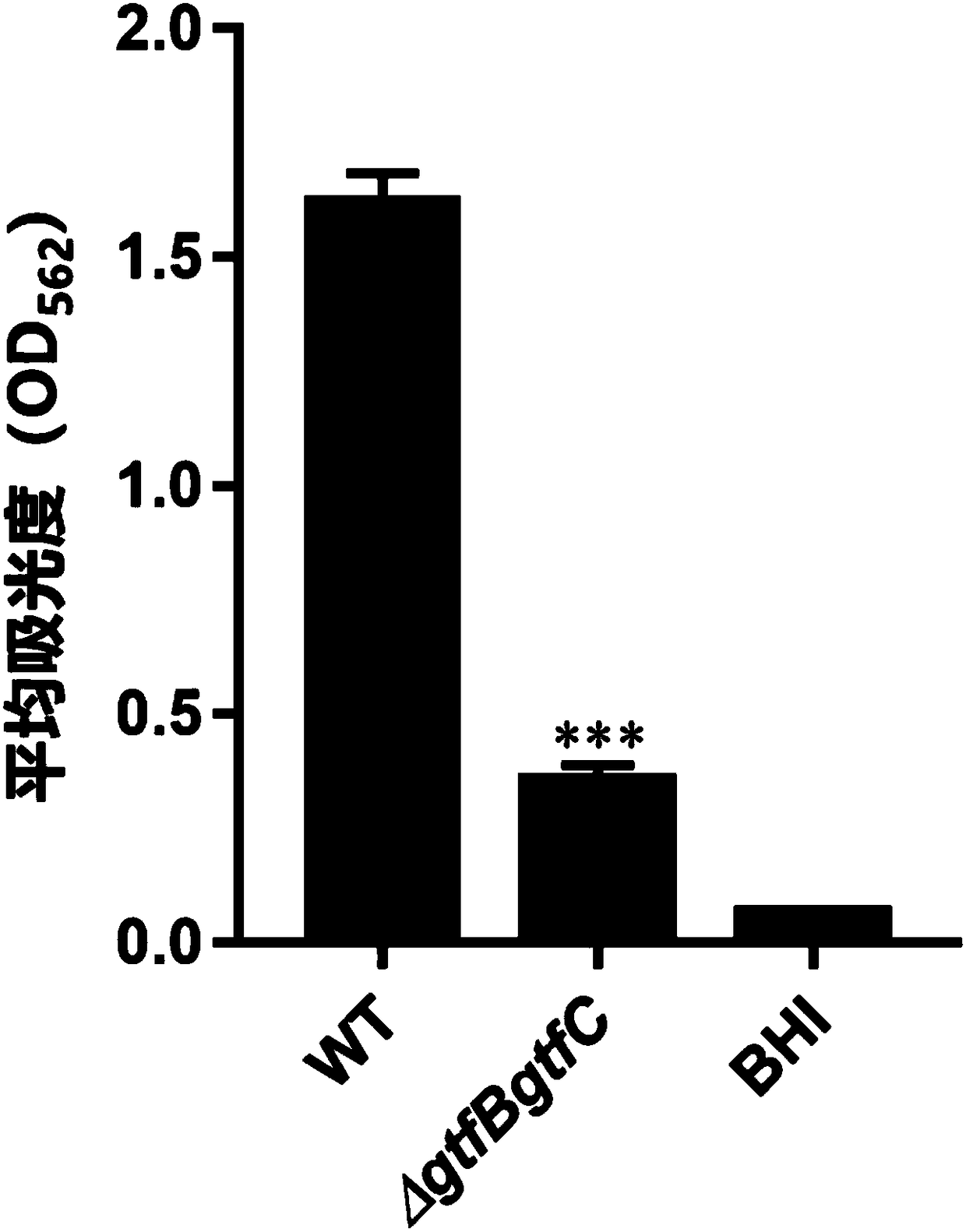
[0125] Detection of the effect of CRISPR editing vector on inhibiting Streptococcus mutans biofilm (crystal violet method)
[0126] Experimental principle: crystal violet staining solution can dye the bacterial biofilm purple, and ethanol can dehydrate the thick biofilm structure, causing the crystal violet stained on the biofilm to be competed; by detecting the solution after being reabsorbed by ethanol The light absorption value at 562nm wavelength can be used for quantitative analysis of biofilm.
[0127] (1) in 10% H 2 , 5%CO 2 and 85%N 2 Under anaerobic conditions, the gtfBgtfC double knockout strain was inoculated in BHI medium, and cultured at 37°C for 16 hours;
[0128] (2) Dilute the resuscitated bacteria in the previous step with preheated BHI medium 1:10, and continue to cultivate for 2-3 hours under the same conditions, so that OD≈0.5-0.6;
[0129] (3) The bacteria in the previous step were diluted 1:100 with BHI+1% sucrose medium, and then 200 μL of the dilute...
Embodiment 3
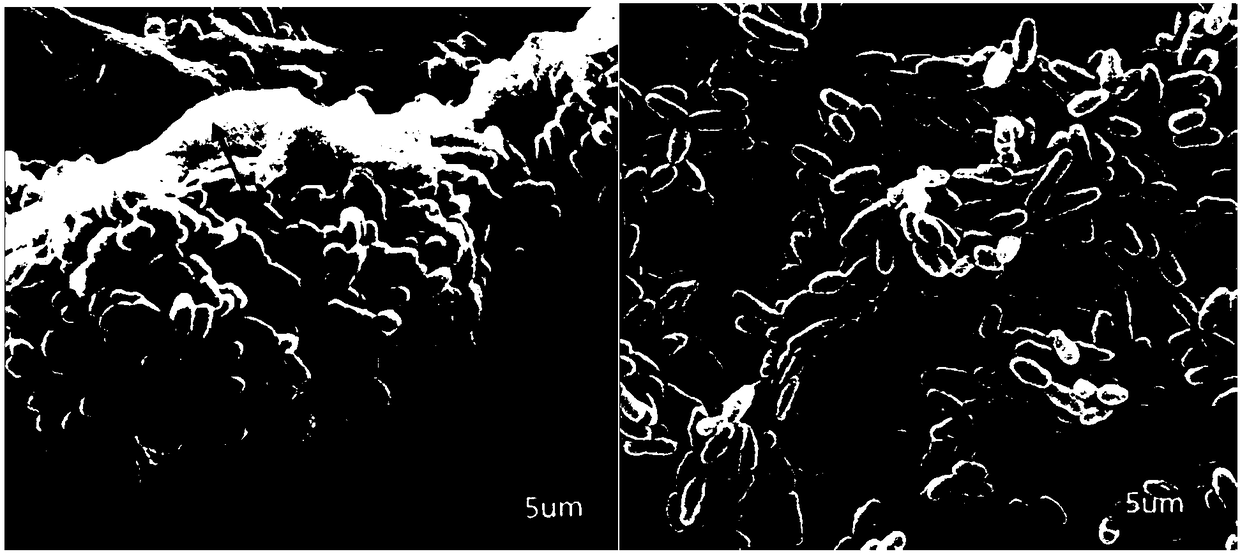
[0135] Detection of the effect of CRISPR editing vector on inhibiting Streptococcus mutans biofilm (SEM)
[0136] Experimental principle: Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) is an instrument for observing the surface morphology of samples. It has a high resolution and can clearly observe the surface morphology of bacteria. This experiment is to observe the content change of exopolysaccharide on the bacterial surface by cultivating Streptococcus mutans biofilm.
[0137] (1) in 10% H 2 , 5%CO 2 and 85%N 2 Under anaerobic conditions, the gtfBgtfC double knockout strain was inoculated in BHI medium, and cultured at 37°C for 16h.
[0138] (2) Dilute the resuscitated strain in the previous step with preheated BHI medium 1:10, and continue to cultivate for 2-3 hours under the same conditions, so that OD≈0.5-0.6.
[0139] (3) Dilute the bacteria in the previous step 1:100 with BHI + 1% sucrose medium, then take 1000 μL of the diluted bacteria and add them to a 24-well plate with st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com