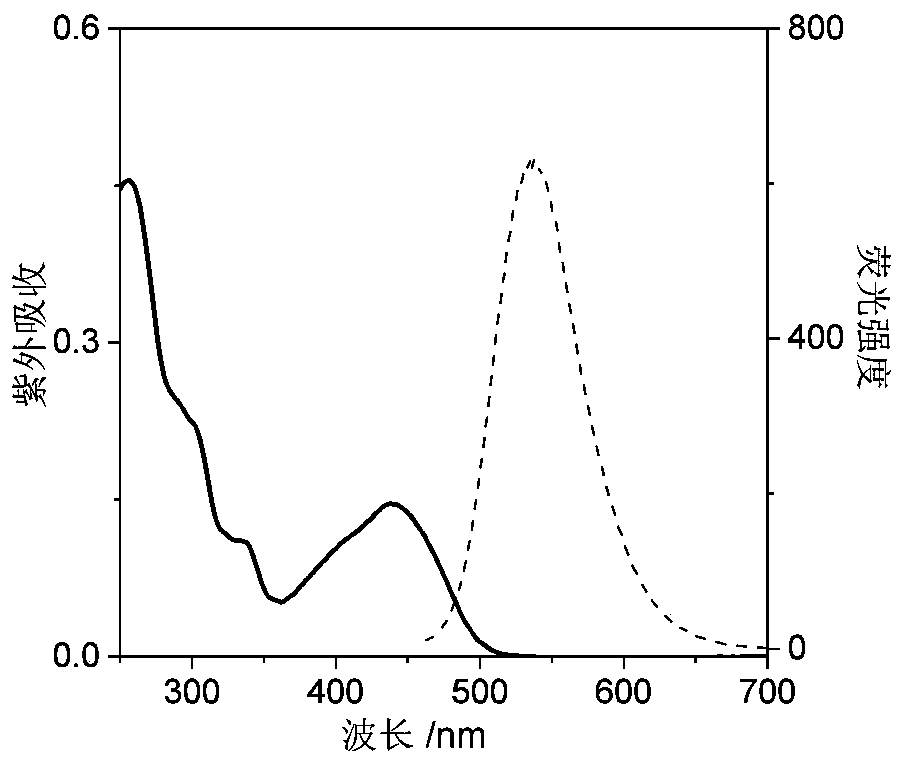
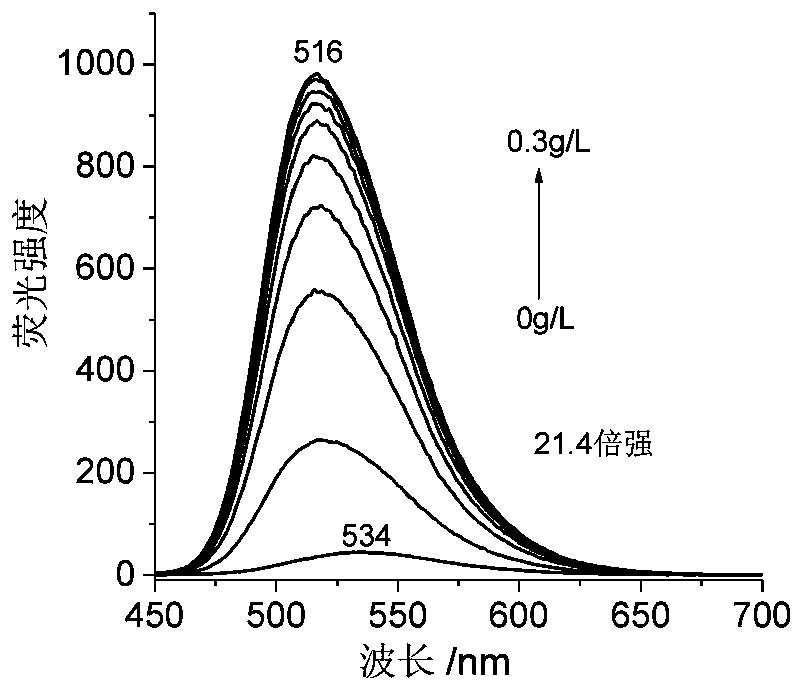
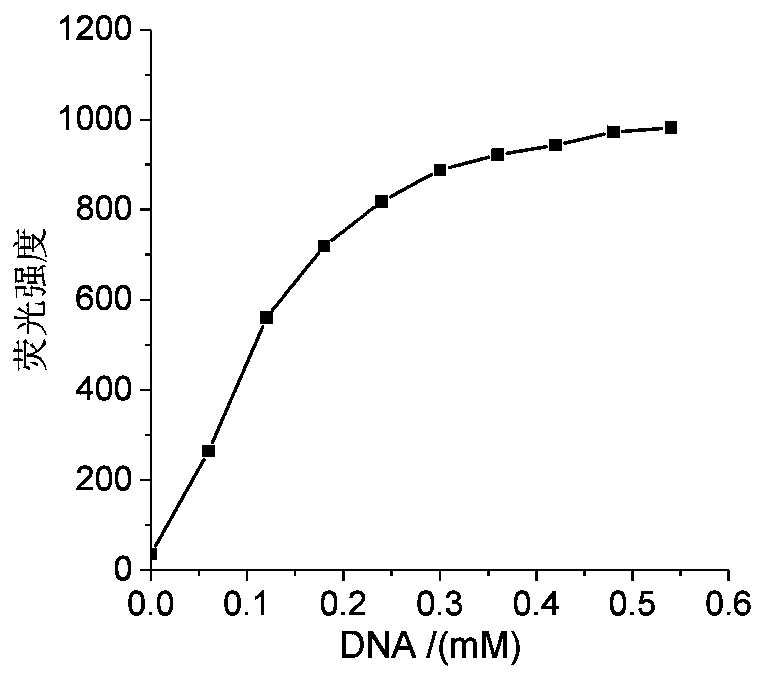
A nucleic acid fluorescent probe for nuclear staining and its preparation method
A fluorescent probe and cell nucleus technology, applied in the field of cell nucleus fluorescent probes, can solve the problems of high biological toxicity and low anti-biological metabolism ability, and achieve the effects of strong resistance to enzymolysis, good fluorescent properties, and low cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A, the preparation of intermediate 1
[0030] At room temperature, dissolve 1.26mmol 6-amino-2-methylquinoline in acetonitrile and add it to a 250ml flask, then slowly add 1.33mmol N-bromosuccinimide and a catalytic amount of silica gel, and continue stirring for 15min Afterwards, the liquid in the bottle turned dark brown, and thin-layer chromatography determined that new spots were generated in the reaction, and the raw materials were not completely reacted, and the reaction was continued for 12 hours. After the reaction was finished, extracted with ethyl acetate, spin-dried the solvent, and the residue was separated and purified through a chromatographic column (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether volume ratio=1:6) to obtain 207 mg of a yellow solid product, namely intermediate 1, with a yield of 69%.
[0031] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ = 8.23 (d, J = 8.6Hz, quinoline-H, 1H), 7.81 (d, J = 9.0Hz, quinoline-H, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 8.6Hz, quinoline-H, 1H), 7.20 (d, J=9...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A, the preparation of intermediate 1
[0046] At room temperature, dissolve 1.26mmol 6-amino-2-methylquinoline in acetonitrile and add it to a 250ml flask, then slowly add 1.33mmol N-bromosuccinimide and a catalytic amount of silica gel, and continue stirring for 15min Afterwards, the liquid in the bottle turned dark brown, and thin-layer chromatography determined that new spots were generated in the reaction, and the raw materials were not completely reacted, and the reaction was continued for 16 hours. After the reaction was finished, extracted with ethyl acetate, spin-dried the solvent, and the residue was separated and purified by chromatographic column (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether volume ratio=1:6) to obtain 222 mg of a yellow solid product, namely intermediate 1, the yield was 74%.
[0047] B, the preparation of intermediate 2
[0048] Add 90mg of intermediate 1 to a round bottom flask, dissolve it in 16ml of a mixed solution of water:ethanol:toluene at a volu...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A, the preparation of intermediate 1
[0053] At room temperature, dissolve 1.26mmol 6-amino-2-methylquinoline in acetonitrile and add it to a 250ml flask, then slowly add 1.33mmol N-bromosuccinimide and a catalytic amount of silica gel, and continue stirring for 15min Afterwards, the liquid in the bottle turned dark brown, and thin-layer chromatography determined that new spots were generated in the reaction, and the raw materials were not completely reacted, and the reaction was continued for 18 hours. After the reaction, extract with ethyl acetate, spin to dry the solvent, and the residue is separated and purified by chromatographic column (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether volume ratio=1:6) to obtain 216 mg of a yellow solid product, namely intermediate 1, the yield was 72%.
[0054] B, the preparation of intermediate 2
[0055] Add 90mg of intermediate 1 to a round bottom flask, dissolve it in 16ml of a mixed solution of water:ethanol:toluene at a volume ratio of 3:3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com