High thermal conduction and insulating two-component epoxy pouring sealant and use method thereof
A potting glue, two-component technology, applied in the direction of heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, adhesives, etc., can solve the problems of low thermal conductivity, harshness, high cost, etc., and achieve high thermal conductivity and low dielectric loss Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
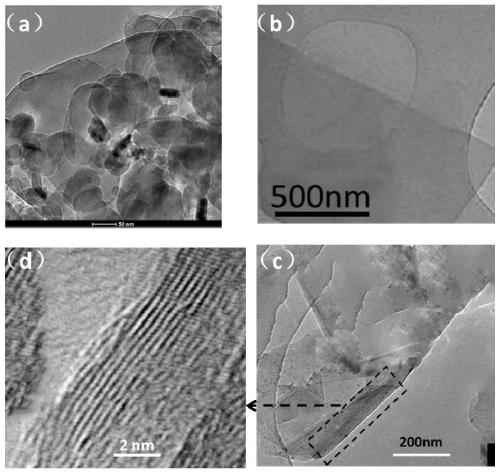
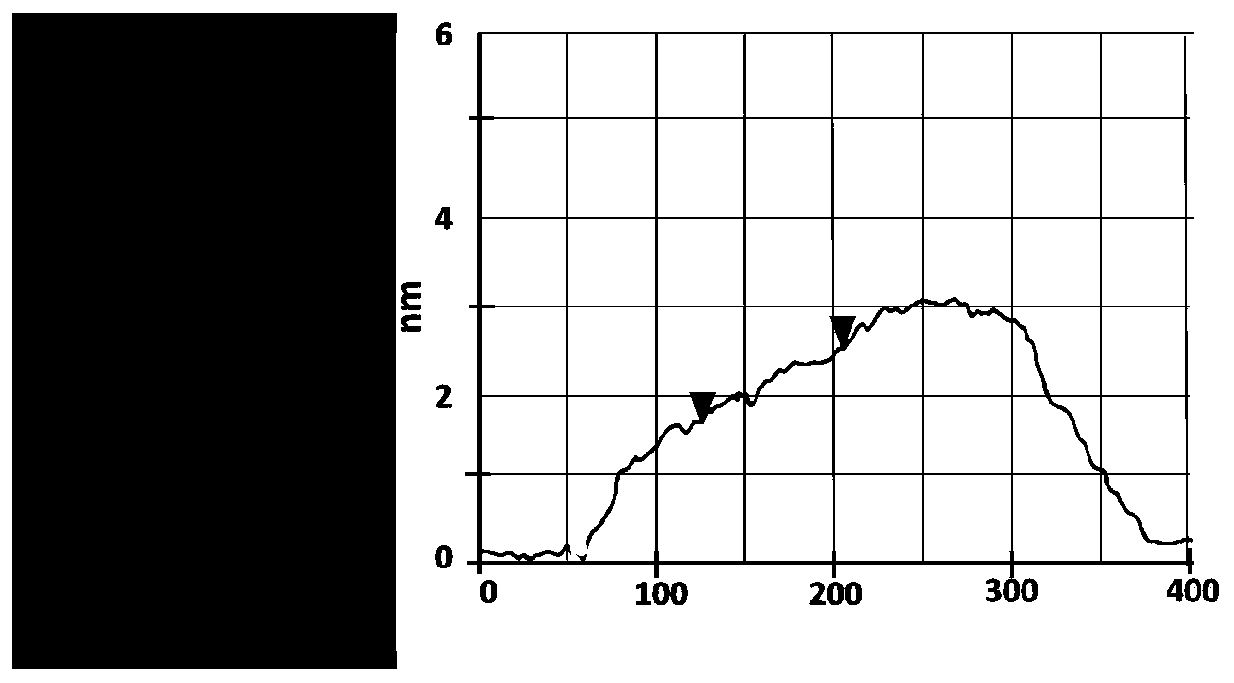
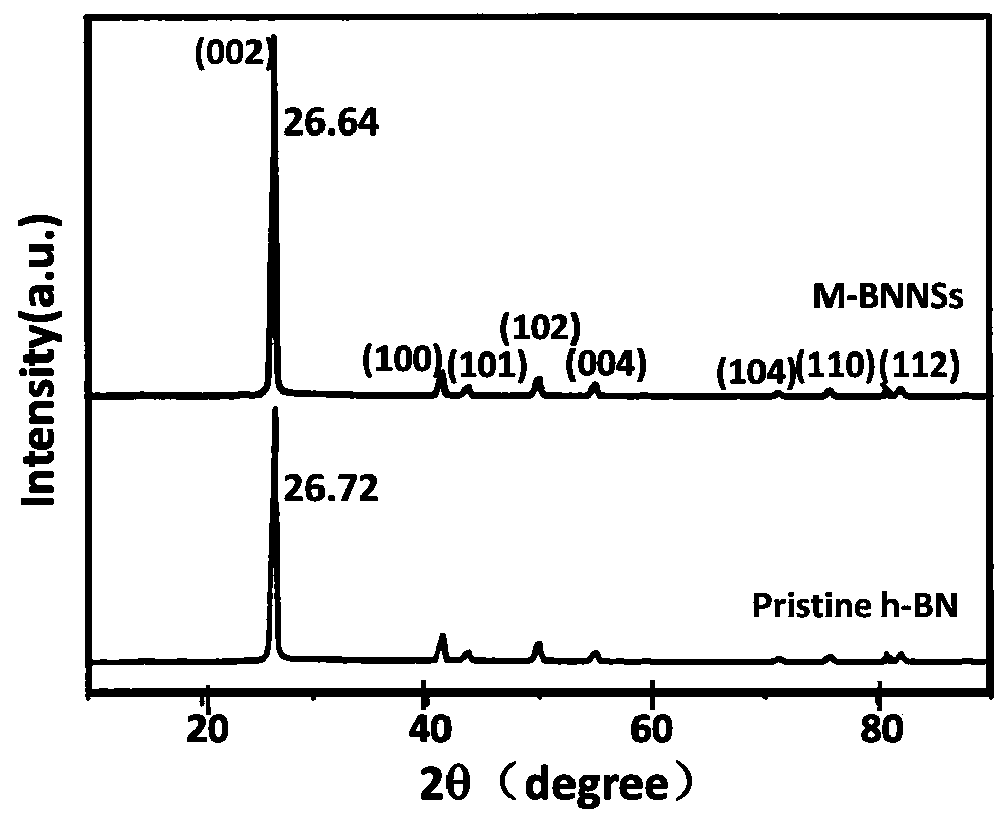
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] The preparation of compound shown in embodiment 1 formula (Ia) (that is R in formula (I) 0 for propyl)
[0063] The preparation of the compound shown in formula (Ia): take by weighing 15.8g (0.073mol) N-butylpyridinium bromide salt ([bpy]Br) and 8g (0.073mol) (sodium tetrafluoroborate) NaBF 4 In a plastic washing bottle, add 100 mL of acetone as a solvent, stir magnetically, condense and reflux at room temperature, react for 12 hours, let stand, filter under reduced pressure, discard the white solid NaBr, and obtain a light yellow clear filter night, and filter to a light yellow clear Add 100mL of dichloromethane to the solution, and a white precipitate precipitates out. Suction filtration under reduced pressure, and the filter is concentrated by rotary evaporation to remove acetone and dichloromethane. The obtained yellow oily liquid is vacuum-dried at 60°C for 8 hours to obtain the product formula (Ia ) Compound [bpy]BF 4 13.8g, yield 85.2%;
[0064]
Embodiment 2
[0065] Compound shown in embodiment 2 formula (Ib) (i.e. R in formula (I) 0 For the preparation of methyl)
[0066] The preparation of compound shown in formula (Ib): 28.2g (0.15mol) N-ethylpyridine bromide is added in the Erlenmeyer flask that fills 50mL acetone, adds 16.5g (0.15mol) NaBF 4 , magnetic stirring at room temperature for 10 h, filtration, rotary evaporation, removal of volatile acetone, and vacuum drying to obtain 25.16 g of the compound represented by formula (Ib) as a white solid, with a yield of 86.5%, m.p.53.2-53.6°C;
[0067]
Embodiment 3
[0068] The preparation of the curing accelerator adopted in embodiment 3 following examples
[0069] The structural formula of curing accelerator is as follows:
[0070]
[0071] The synthetic route is as follows:
[0072]
[0073] Its preparation method includes:
[0074] (1) Synthesis of all aromatic complex dibasic acids
[0075] Add 414g of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, 100g of sodium hydroxide, and distilled water into a 2000mL three-neck bottle in sequence, stir to dissolve, add 304.5g of terephthaloyl chloride in carbon tetrachloride solution dropwise under high-speed stirring, and dropwise add in about 4 hours. Completed, continue to react for 4 h under high-speed stirring, stop the reaction, filter with suction, wash until neutral, then acidify with 36% hydrochloric acid for 2 h, filter the product with suction, wash with distilled water until neutral, dehydrate with acetone, and place in a vacuum oven for 80 After drying at ℃ for 18 hours, 520 g of all-aromatic compl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com