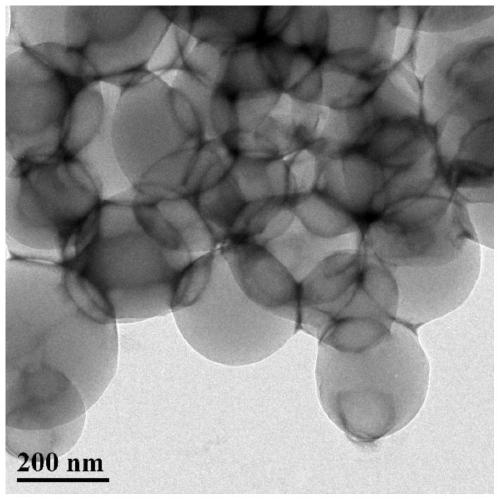
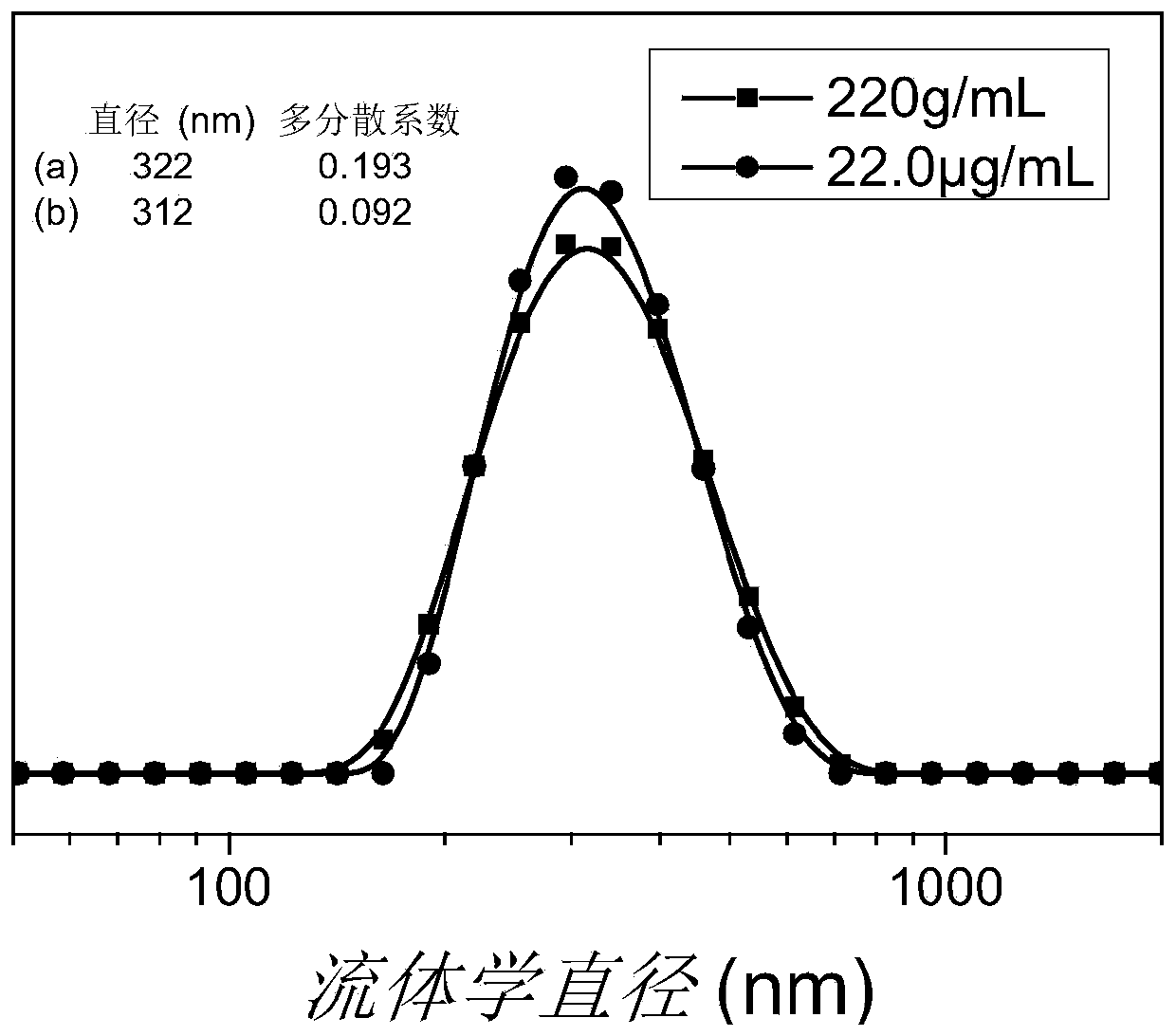
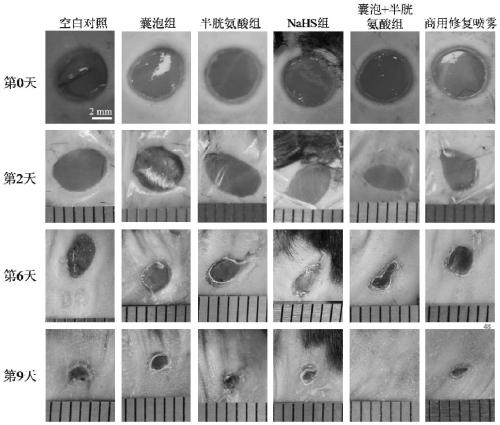
Polymer vesicle capable of promoting wound healing, and preparation method and application of polymer vesicle capable of promoting wound healing
A wound healing and polymer technology, applied in the fields of polymer materials and biomedical engineering, can solve problems such as increased antibiotic resistance and threats to human health, and achieve the effects of preventing wound infection, promoting diabetic wound healing, and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] Preparation method of polymersomes promoting wound healing:
[0045] The preparation method of the wound healing-promoting polymersome of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0046] (1) Preparation steps of antimicrobial peptide polymer and hydrogen sulfide donor
[0047] Mix polycaprolactone, lysine NCA monomer and the first type of solvent, and use a vacuum pump to evacuate and stir the reaction at room temperature for 30 to 50 hours, and then undergo dialysis, suction filtration, and vacuum drying to obtain the antibacterial peptide polymer polycaprolactone-block-polylysine;
[0048] Mix S-aroylthiohydroxylamine (SBTHA), p-aldeoxybenzoic acid, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), 3A molecular sieves and the second type of solvent, and seal the mixture at room temperature for 1 to 5 hours. After suction filtration, rotary evaporation, recrystallization, and suction filtration, a white powder, compound SATO1, was obtained. Mix SATO1, N,N-dimethylformamide a...
Embodiment 1
[0071] This embodiment provides a method for preparing polymersomes that promote wound healing, comprising the following steps:
[0072] (1) Preparation steps of antimicrobial peptide polymer PCL-b-PLys and hydrogen sulfide donor SATO2
[0073] a. Polycaprolactone PCL-NH 2 (0.426g), lysine NCA monomer (0.903g) and 20mL N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) were mixed, and the vacuum pump was used to stir the reaction for 32 hours at room temperature, followed by dialysis and suction filtration , vacuum drying to obtain the antimicrobial peptide polymer polycaprolactone-block-polylysine, referred to as PCL-b-PLys;
[0074] b. Mix S-aroylthiohydroxylamine (SBTHA) (100mg, 0.650mmol), p-aldehyde benzoic acid (107mg, 0.710mmol), 10 μL trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), 3A molecular sieves and 3 mL dichloromethane (DCM) The phases were mixed, and the mixture was left sealed at room temperature for 3 hours. After suction filtration, rotary evaporation, recrystallization, and suction filtration, a ...
Embodiment 2
[0083] This embodiment provides a method for preparing polymersomes that promote wound healing, comprising the following steps:
[0084] (1) Preparation steps of antimicrobial peptide polymer PCL-b-PLys and hydrogen sulfide donor SATO2
[0085] a. Polycaprolactone PCL-NH 2 (0.426g), lysine NCA monomer (1.43g) and 30mL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were mixed, and at room temperature using a vacuum pump vacuum stirring reaction for 50 hours, followed by dialysis, suction filtration, vacuum drying , to obtain the antimicrobial peptide polymer polycaprolactone-block-polylysine, referred to as PCL-b-PLys;
[0086]b. Mix S-aroylthiohydroxylamine (SBTHA) (100 mg, 0.650 mmol), p-formylbenzoic acid (148 mg, 0.980 mmol), 15 μL trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), 3A molecular sieves and 5 mL p-xylene, The mixture was left sealed at room temperature for 5 hours. After suction filtration, rotary evaporation, recrystallization, and suction filtration, a white powder, compound SATO1, was obtained. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com