Methods of identifying synthetic transcriptional and translational regulatory elements, and compositions relating to same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Selection of Synthetic Transcriptional Regulatory Elements
[0118]This example describes the preparation of a vector useful for selecting transcriptional regulatory elements and the identification and characterization of synthetic transcriptional regulatory elements.
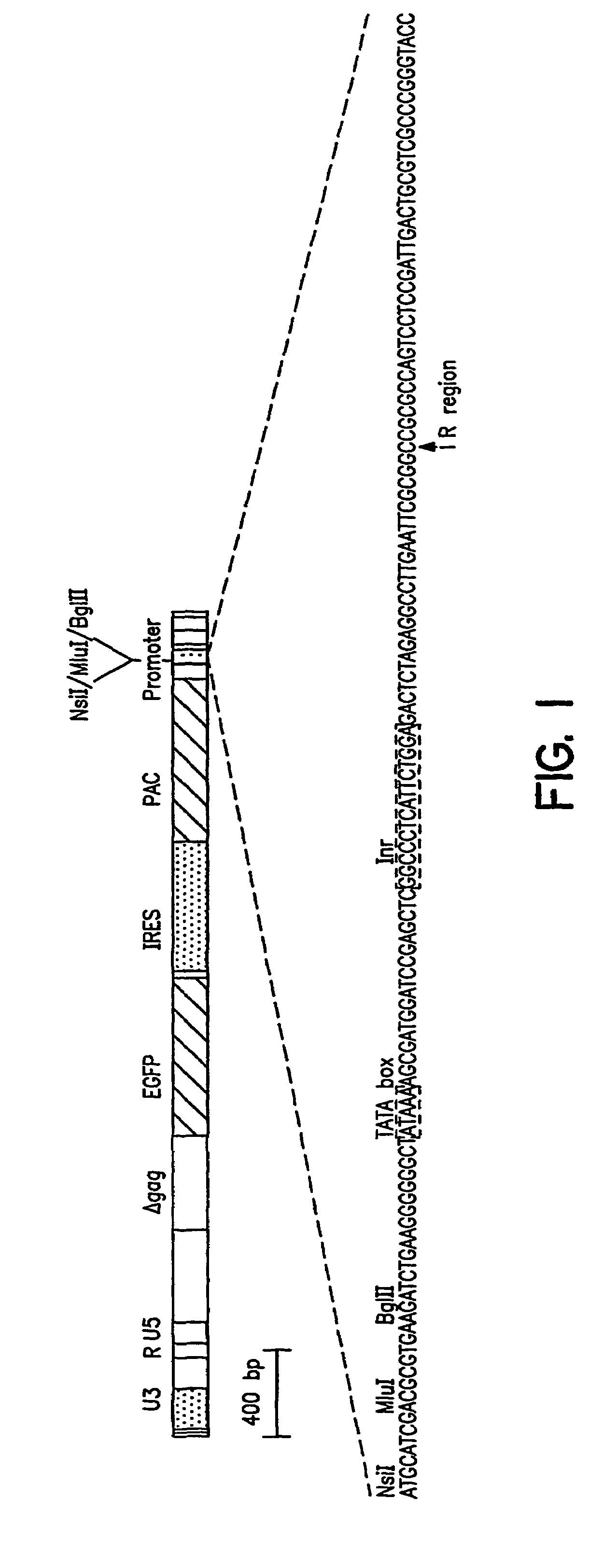
[0119]A promoter element proviral vector library was constructed using the retroviral-mediated EGFP / FACS selection strategy for synthetic promoter elements according to the disclosed methods. A library of promoter elements (random 18 mers; Ran18) was constructed in the proviral selection vector, which was packaged into retroviral particles in COS1 cells. The retroviral particles were harvested and used to infect target cells, which were then treated for 3 days with puromycin to kill uninfected or poorly expressing cells. The surviving cells were subjected to FACS analysis and the most highly fluorescent cells collected. Genomic DNA was prepared from these cells and the regulatory oligonucleotides were recovered by PCR and ...
example 2
Validation of Synthetic Regulatory Element Selection Method
[0164]This example demonstrates the disclosed synthetic regulatory element selection method can be used routinely to screen libraries of oligonucleotides and can consistently identify synthetic transcriptional regulatory elements.
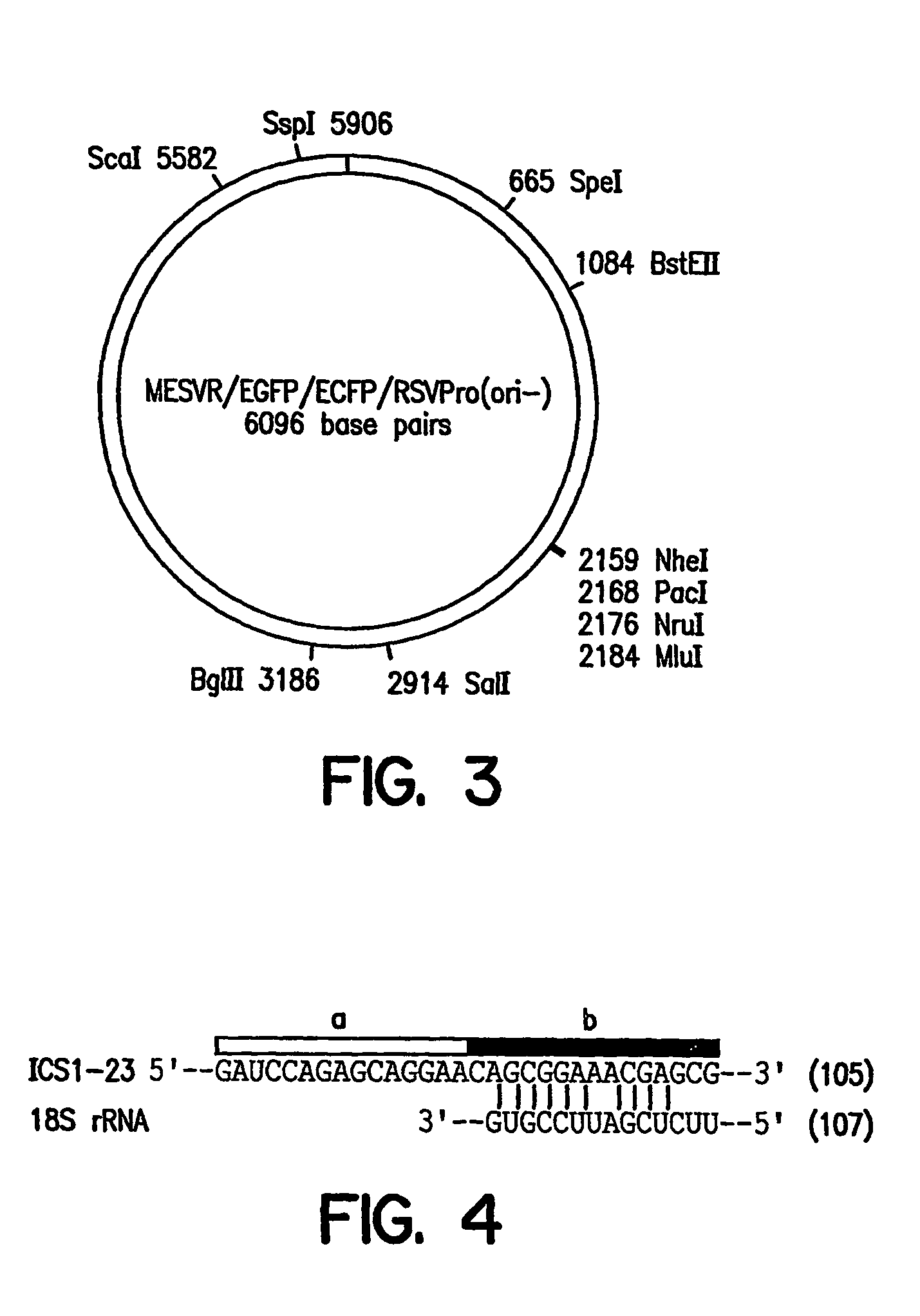
[0165]The retrovirus vector MESVR / EGFP* / IRES / pacPro(ori) (SEQ ID NO: 1; see Example 1B) was used to screen a second library of Ran 18 sequences using the synthetic promoter construction method (SPCM). More than 100 DNA sequences that showed increased promoter activity (4 to 50-fold) in the neuroblastoma cell line Neuro2A were identified. The DNA sequences of selected synthetic promoters were determined and database search using the RIGHT software package, which allowed simultaneous comparison of a database of active Ran 18 elements to existing databases such as TransFac. The search revealed a predominance of eight motifs—AP2, CEBP, GRE, Ebox, ETS, CREB, AP1, and SP1 / MAZ; about 5 to 10% of the active...
example 4
Selection of Synthetic Translational Regulatory Elements
[0199]This example describes the preparation of a vector useful for selecting oligonucleotide sequences having internal ribosome entry site (IRES) activity and the identification and characterization of such selected elements.
[0200]The disclosed synthetic IRES methodology provides a means for selecting functional IRES elements. Similar to the transcriptional regulatory element selection method disclosed above (Examples 1 to 3), the IRES selection method allows the parallel screening of 1×106 to 1×1010 or more random oligonucleotide elements or combinations of elements for activity in mammalian cells. Selection of synthetic IRES elements in mammalian cells is facilitated if 1) each cell receives a single unique cassette to avoid selection of inactive elements that are fortuitously present in the same cell as an active element; 2) the delivery system is efficient so that a complex library can be readily screened; and 3) the selec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com