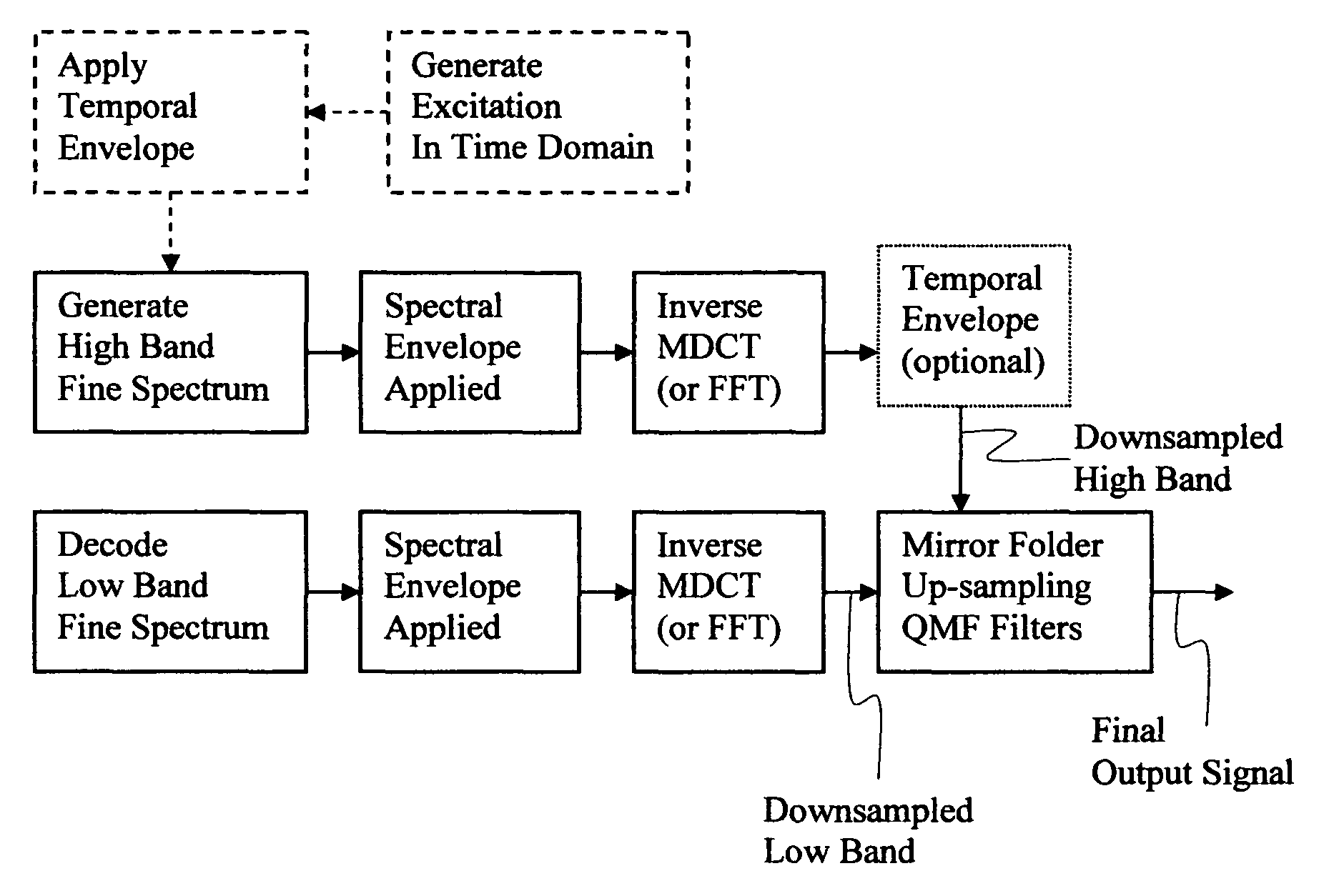
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Audio signal classification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
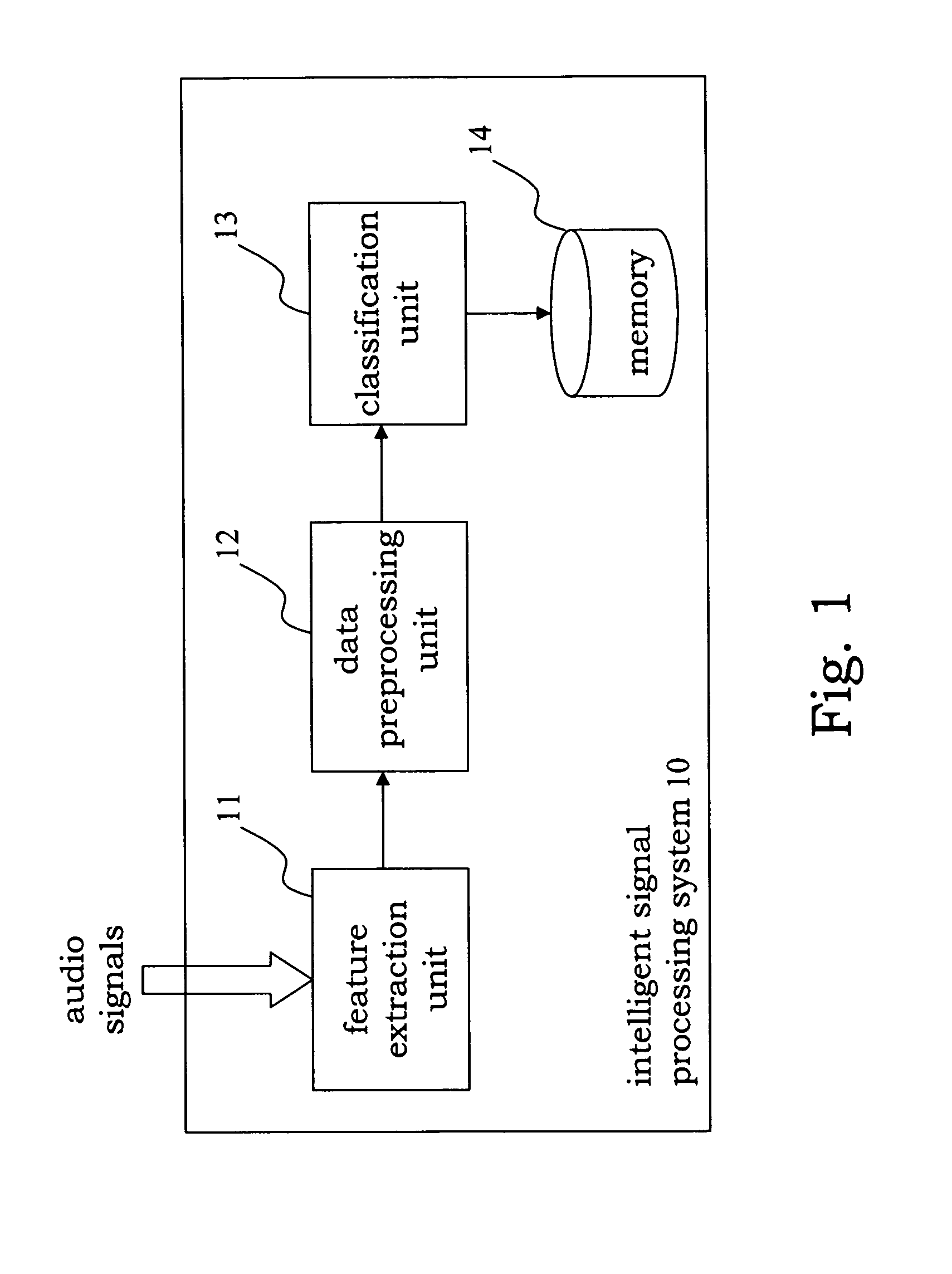
Audio signal classification consists of extracting physical and perceptual features from a sound, and of using these features to identify into which of a set of classes the sound is most likely to fit.
Systems and methods for providing acoustic classification
ActiveUS20040030550A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMore languageSpeech identification
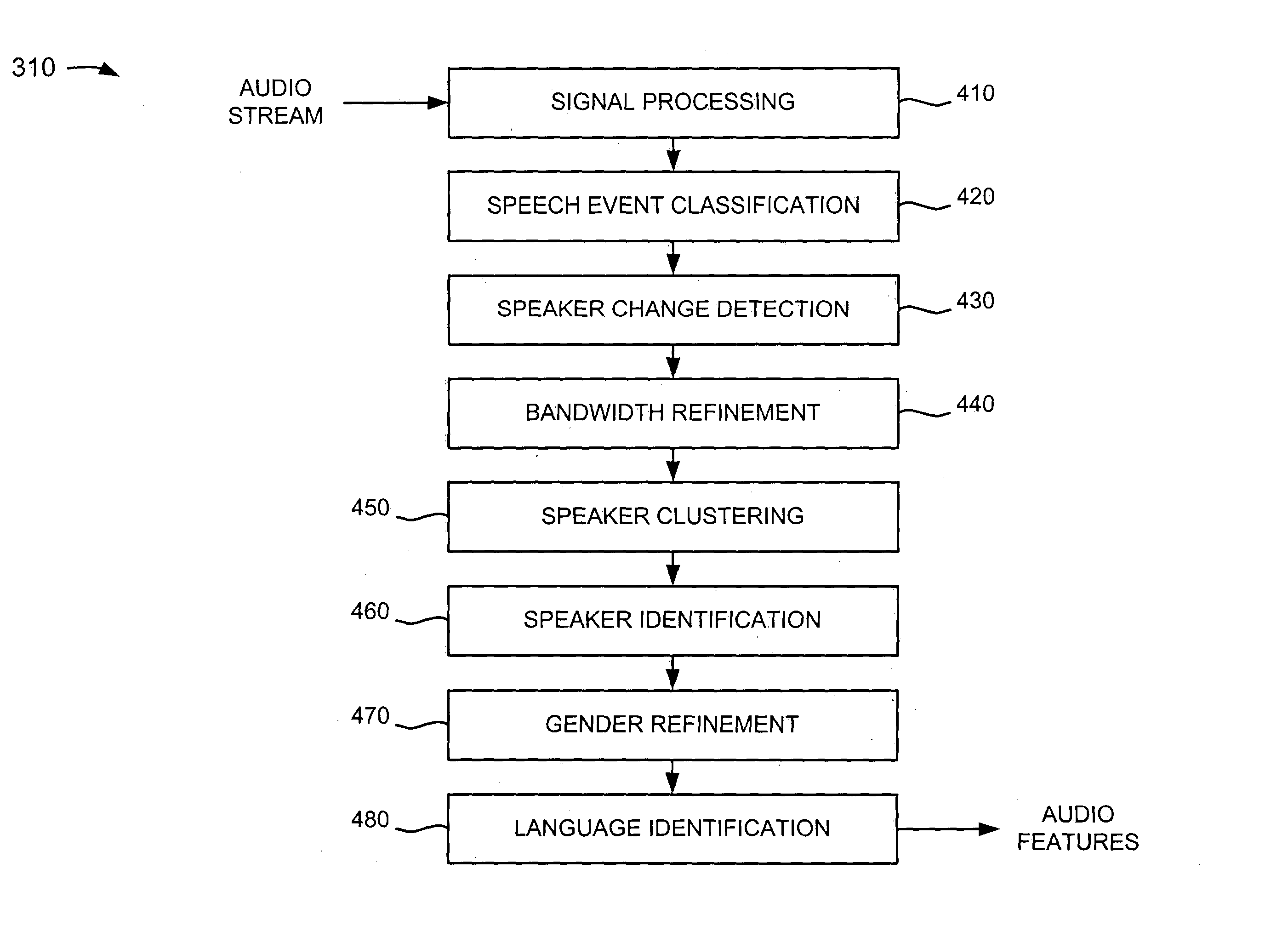
A speech recognition system receives an audio signal and detects various features of the audio signal. For example, the system classifies the audio signal into speech and non-speech portions, genders of speakers corresponding to the speech portions, and channel bandwidths used by the speakers. The system detects speaker turns based on changes in the speakers and assigns labels to the speaker turns. The system verifies the genders of the speakers and the channel bandwidths used by the speakers and identifies one or more languages associated with the audio signal. The system recognizes the speech portions of the audio signal based on the various features of the audio signal.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
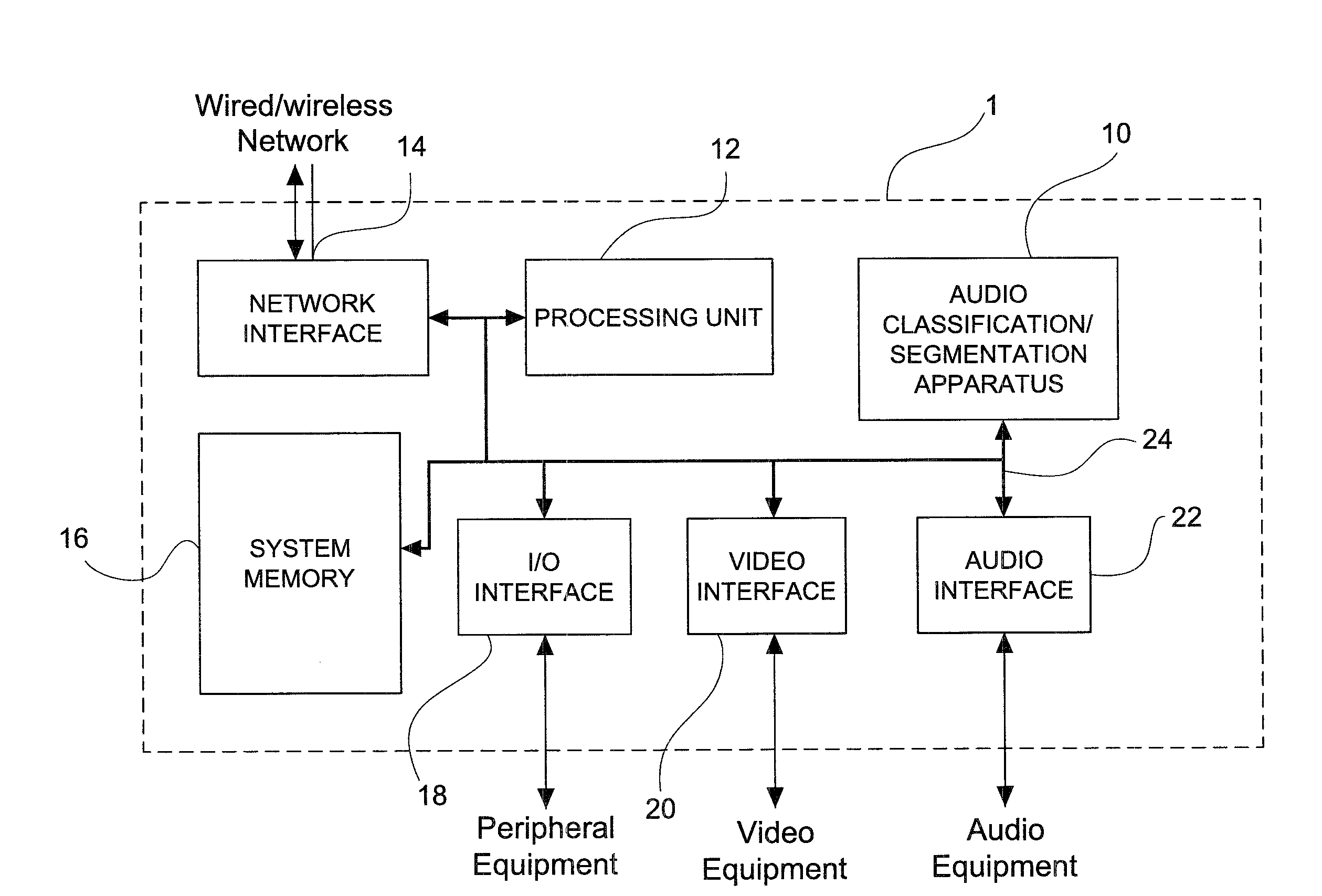
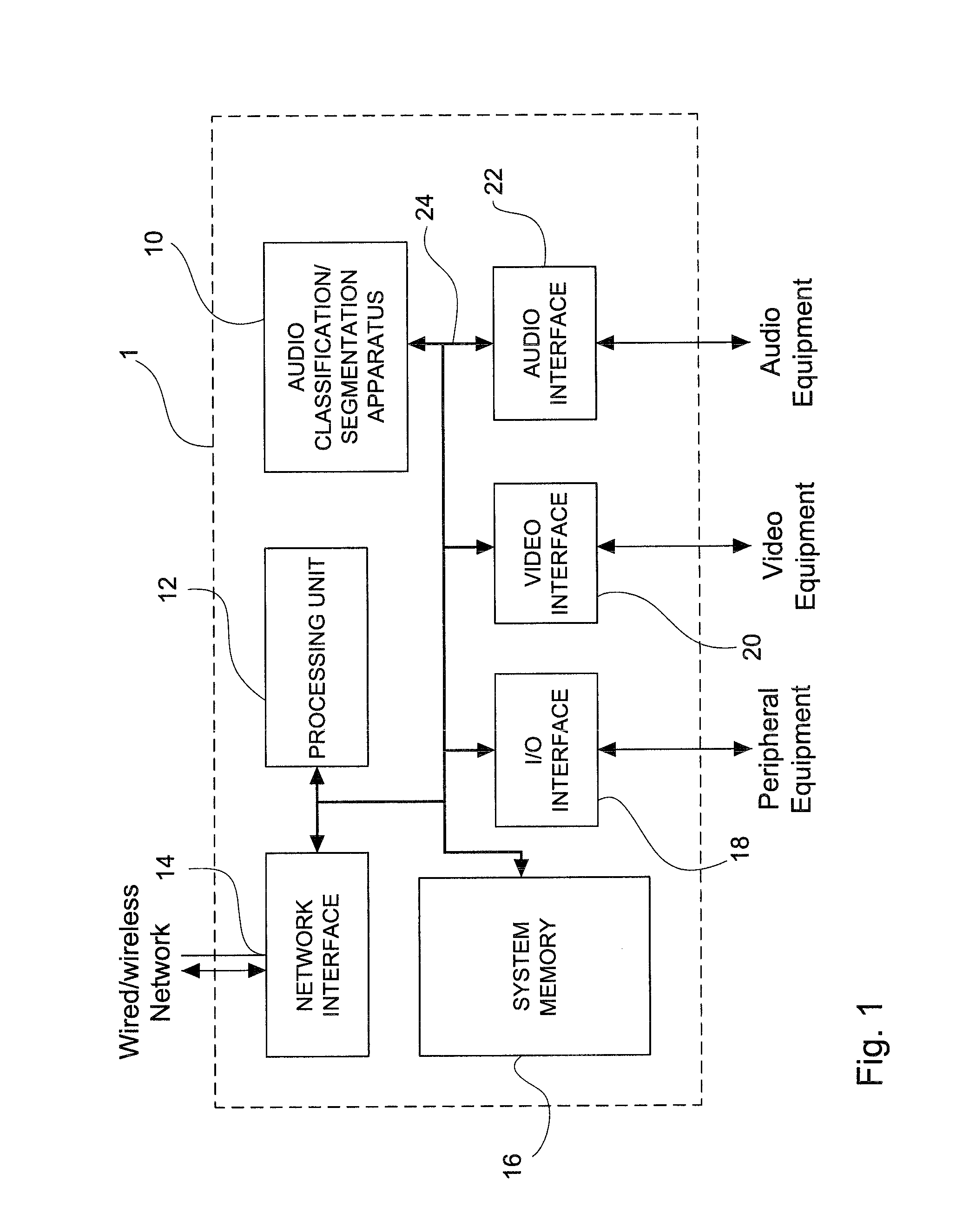
Apparatus and method for classification and segmentation of audio content, based on the audio signal
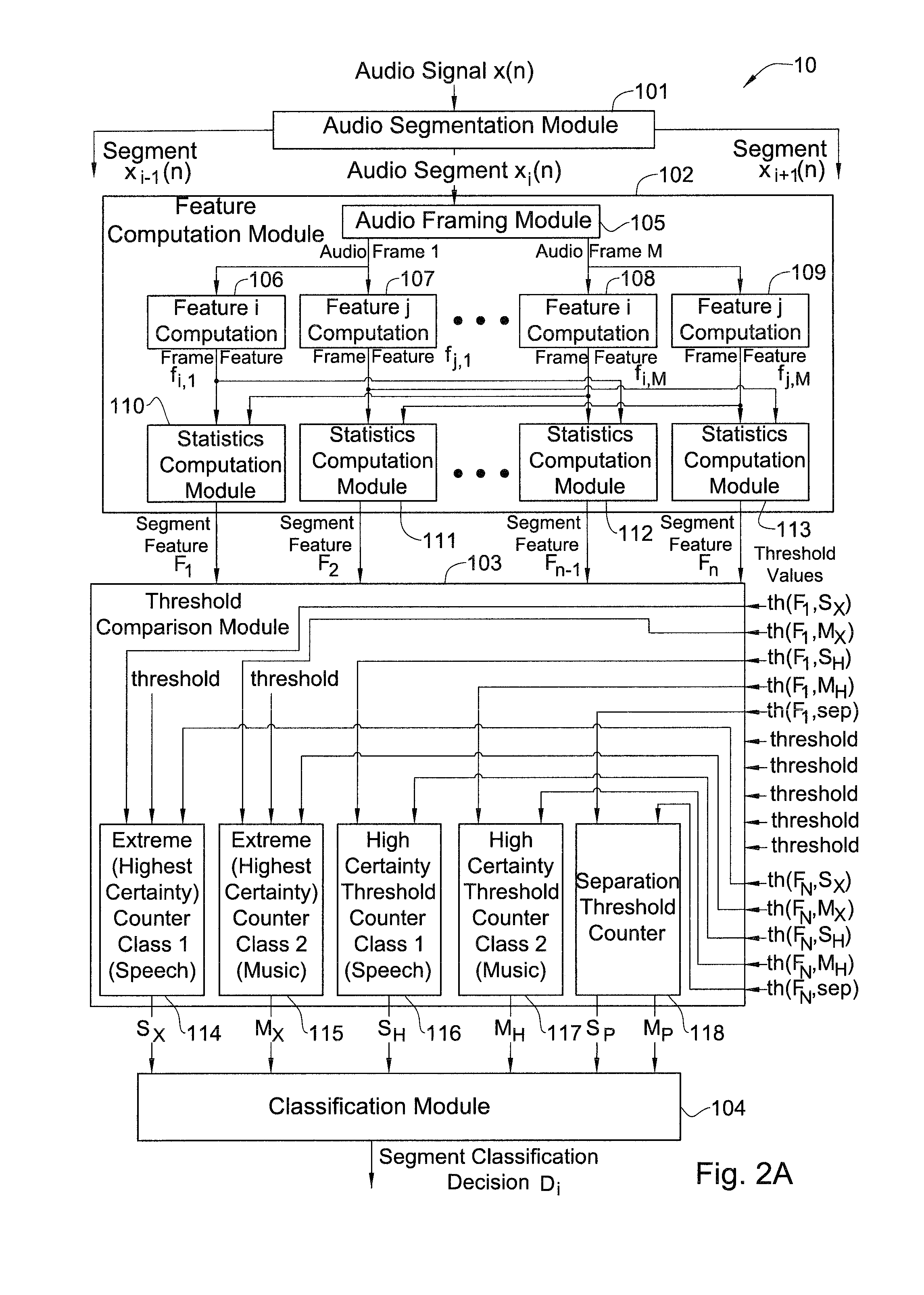
ActiveUS20100004926A1Increase the number ofEasy to adjustSpeech recognitionStereophonic arrangmentsFeature vectorAudio segmentation
An apparatus for classifying an input audio signal into audio contents of a first and second class, comprising an audio segmentation module adapted to segment said input audio signal into segments of a predetermined length; a feature computation module adapted to calculate for the segments features characterizing said audio input signal; a threshold comparison module adapted to generate a feature vector for each of said one or more segments based on a plurality of predetermined thresholds, the thresholds including for each of the audio contents of the first class and of the second class a substantially near certainty threshold, a substantially high certainty threshold, and a substantially low certainty threshold; and a classification module adapted to analyze the feature vector and classify each one of said one or more segments as audio contents of the first class, of the second class, or as non-decisive audio contents.
Owner:WAVES AUDIO
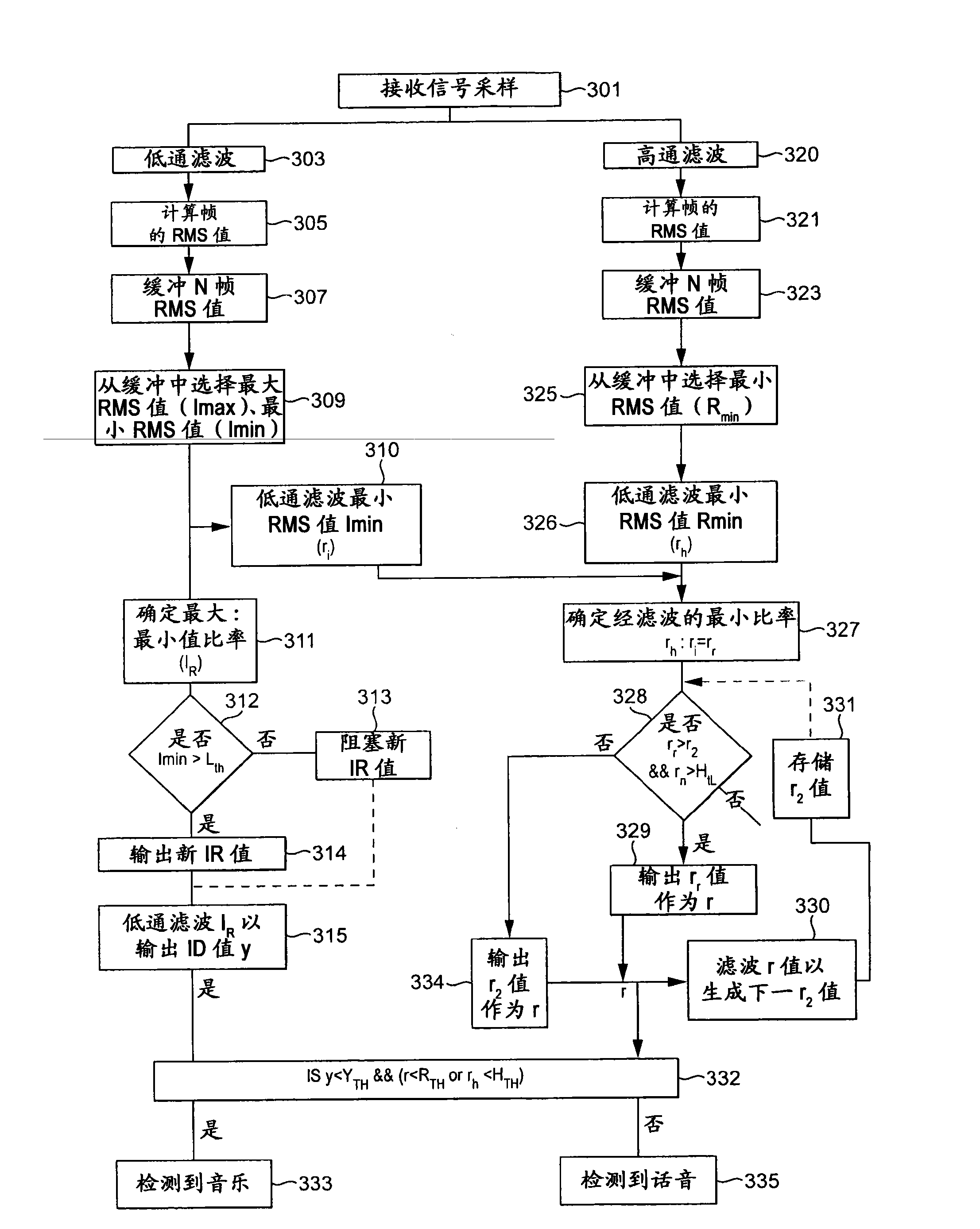
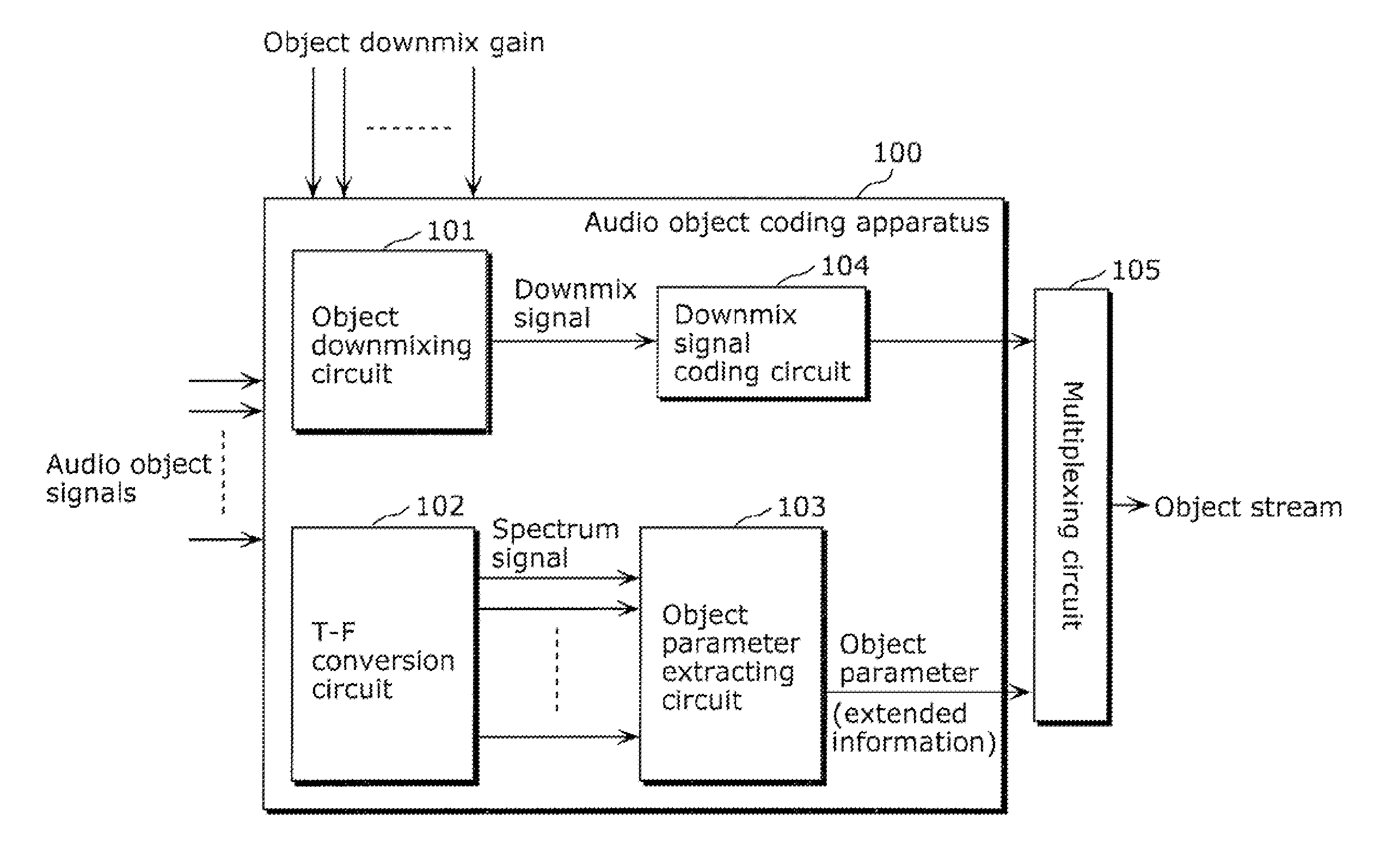
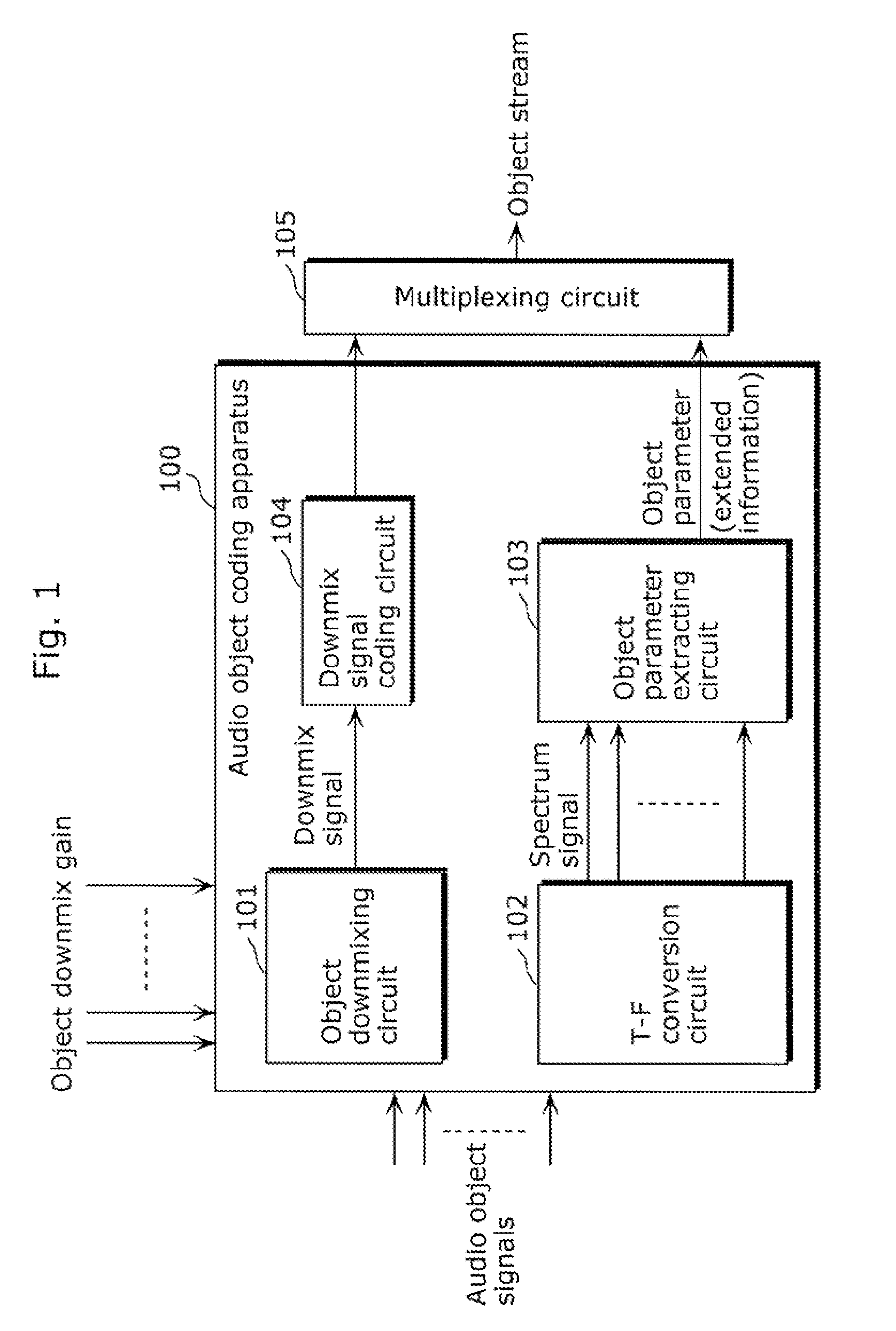
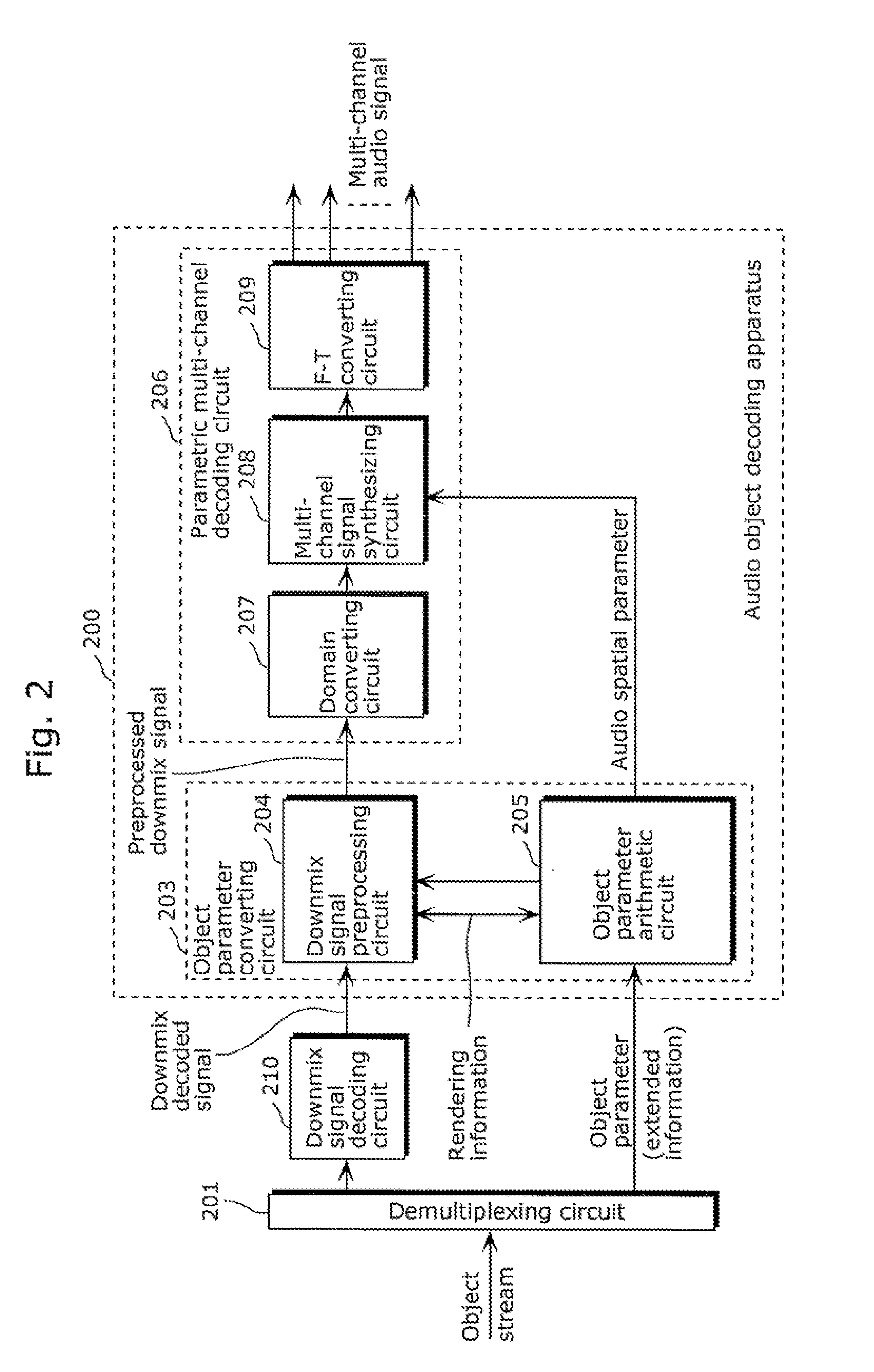
Coding apparatus and decoding apparatus
ActiveUS20110182432A1Suppress extreme increase in bit rateBit efficiency can be improvedSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsMultiplexingGranularity
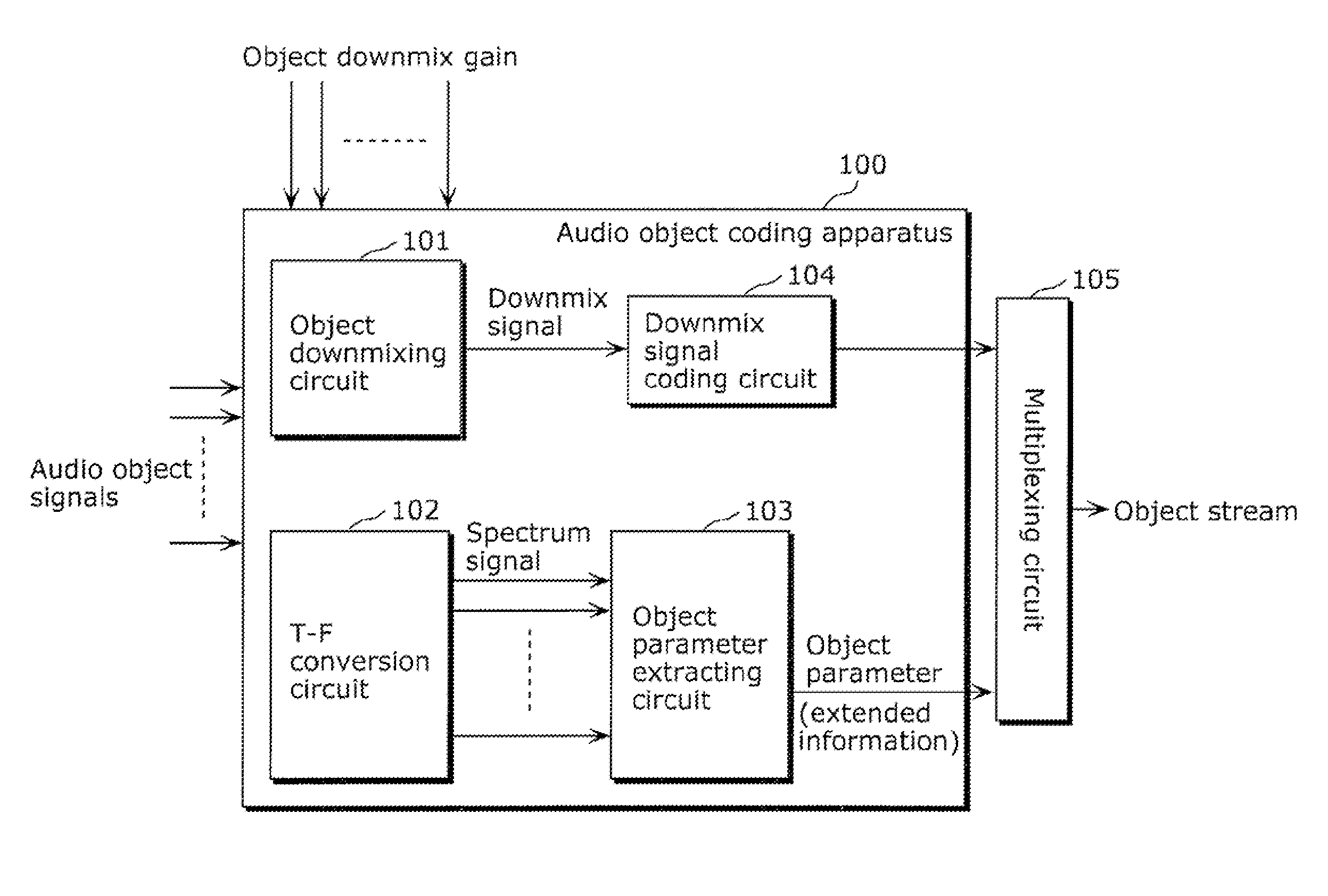
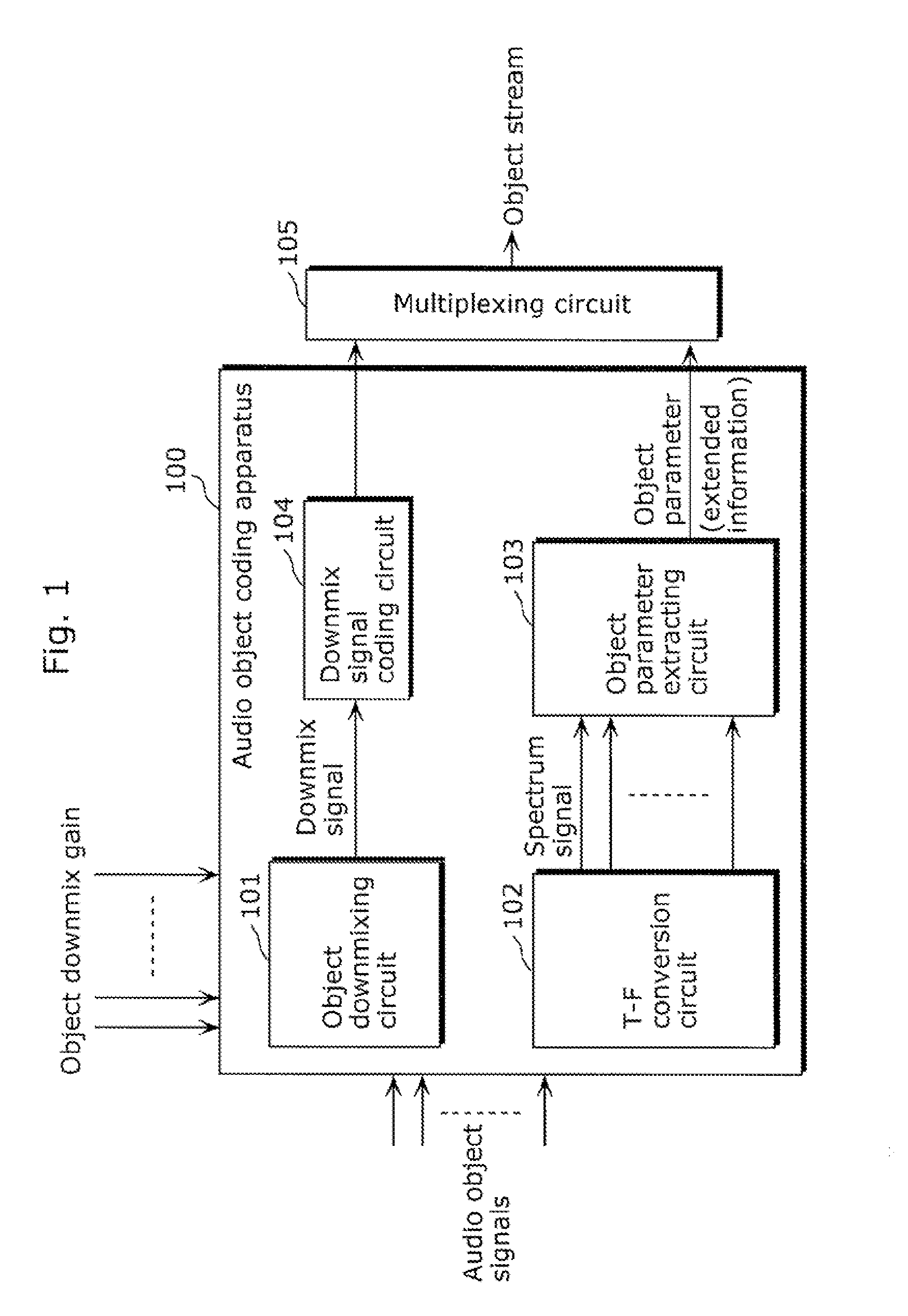
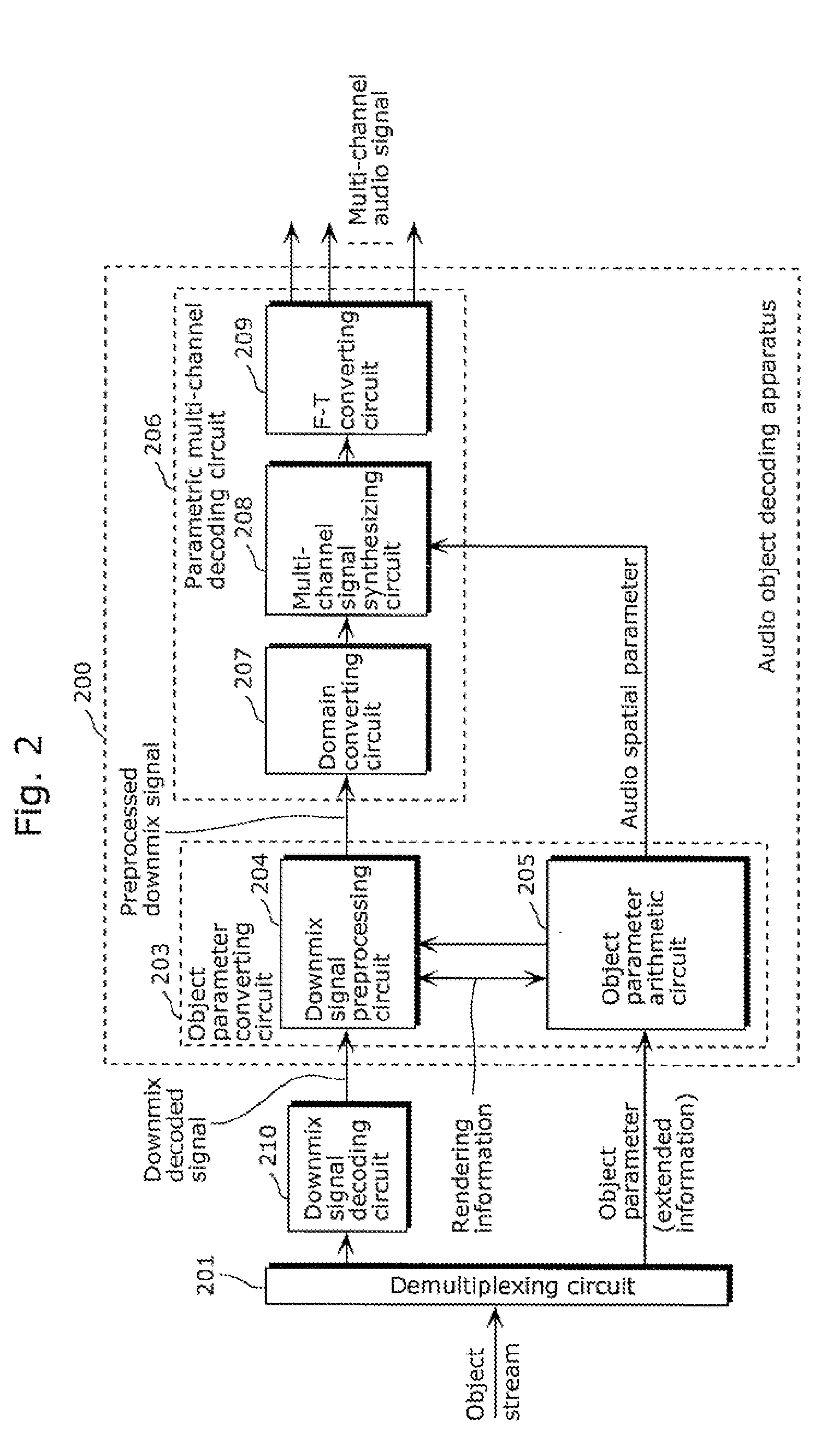
A coding apparatus which suppresses an extreme increase in a bit rate, includes: a downmixing and coding unit (301) that downmixes audio signals that have been provided, to reduce the number of channels to be fewer than the number of the provided audio signals, and to code the downmix signals; an object parameter extracting unit (304) that extracts parameters indicating correlation between the audio signals; and a multiplexing circuit (309) that multiplexes the extracted parameters with the generated downmix coded signals. The object parameter extracting unit (304) includes: an object classifying unit (305) that classifies each of the provided audio signals into a predetermined one of types based on audio characteristics; and an object parameter extracting circuit (308) that extracts parameters using a temporal granularity and a frequency granularity each of which is determined for a corresponding one of the types.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Device and method for audio classification and audio processing
InactiveCN104078050AElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisAudio frequencyAudio signal classification
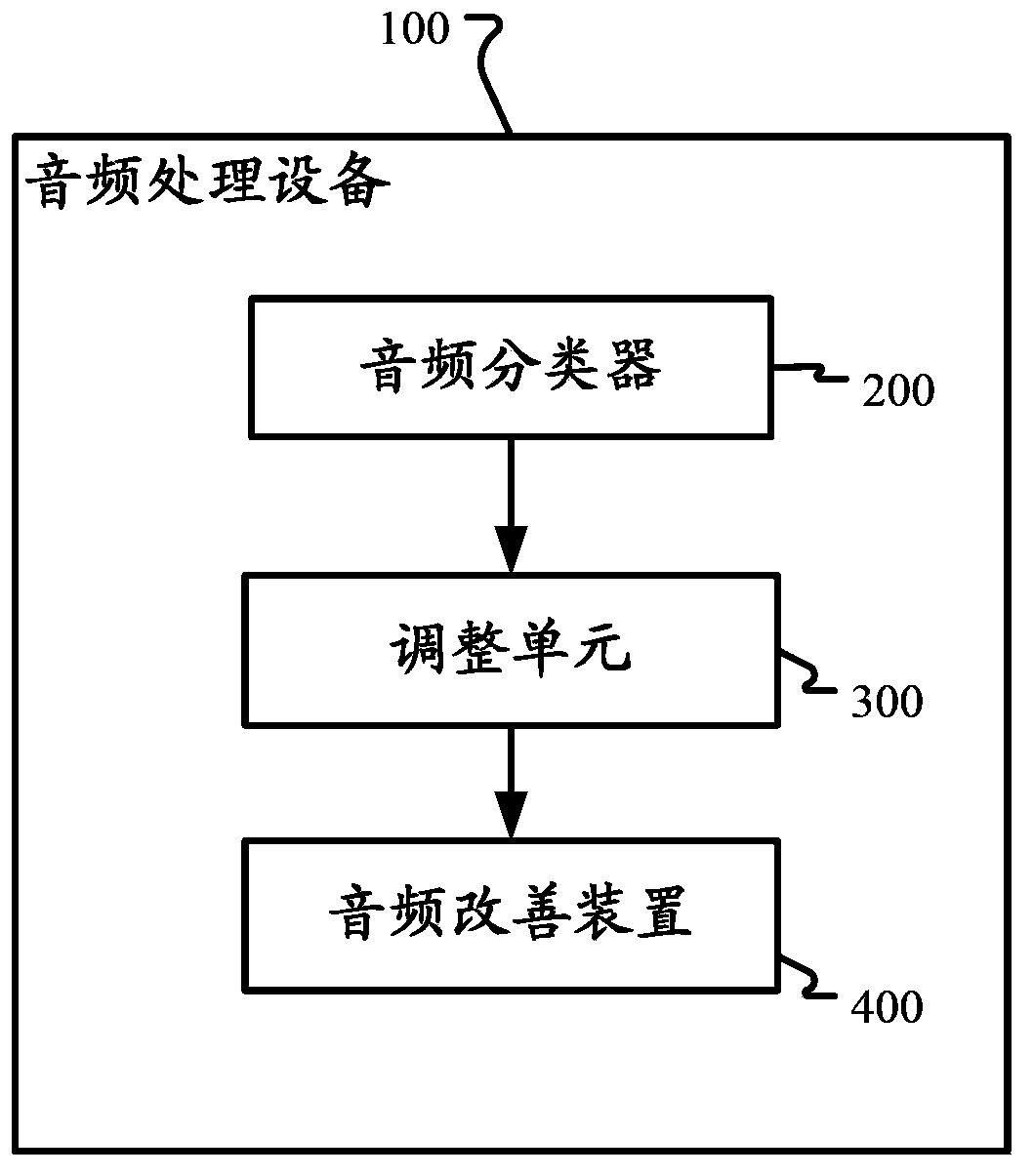
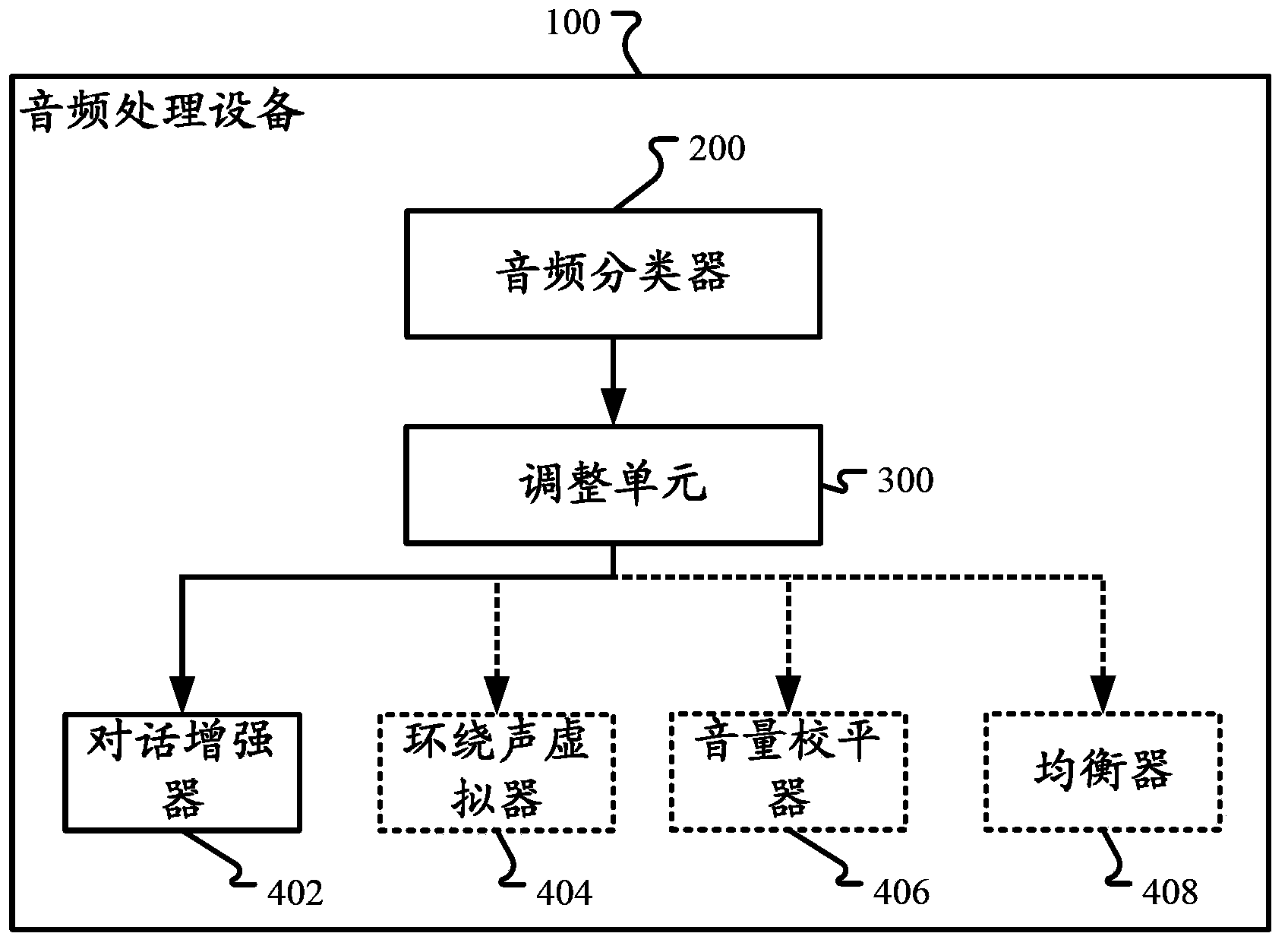
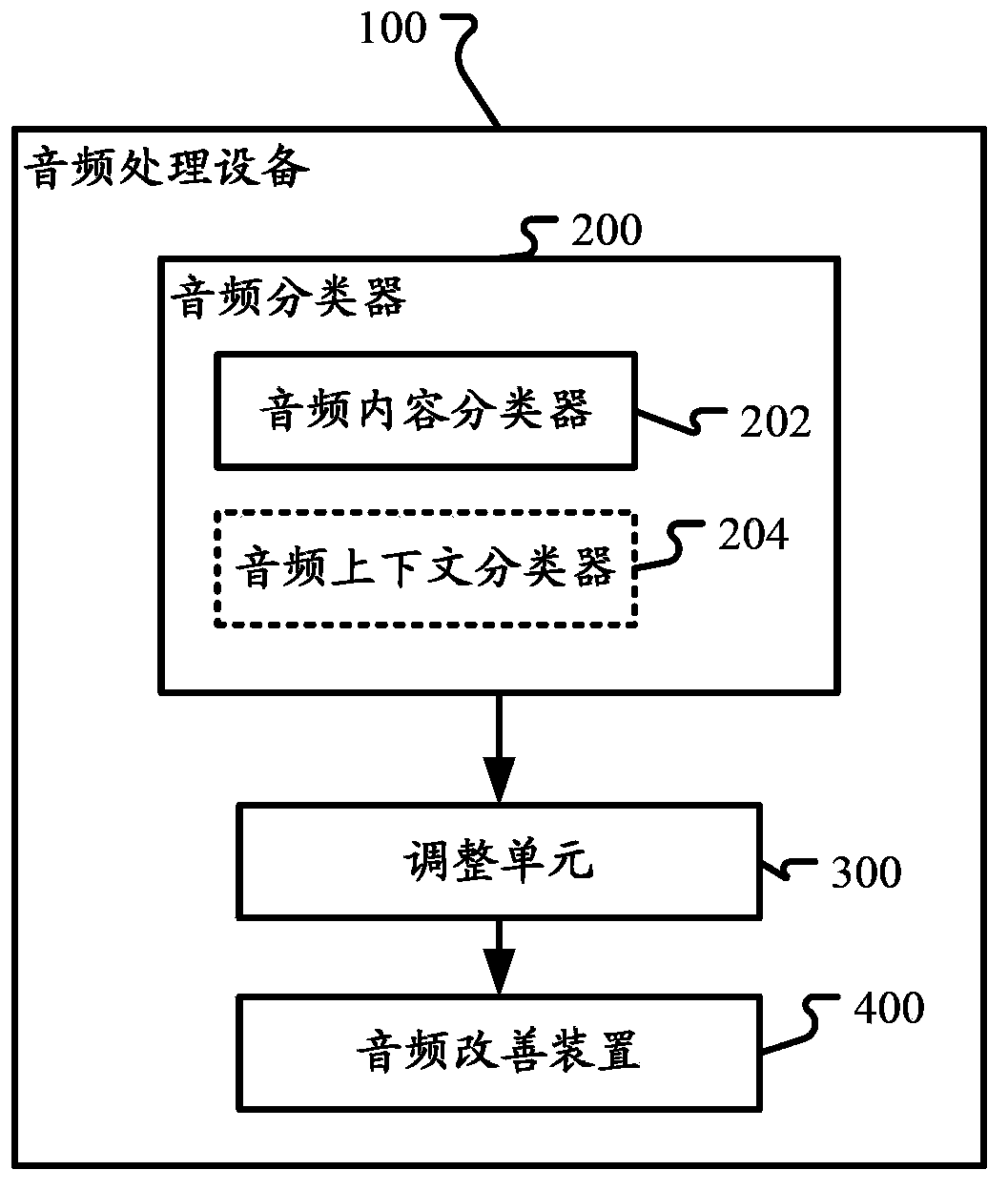
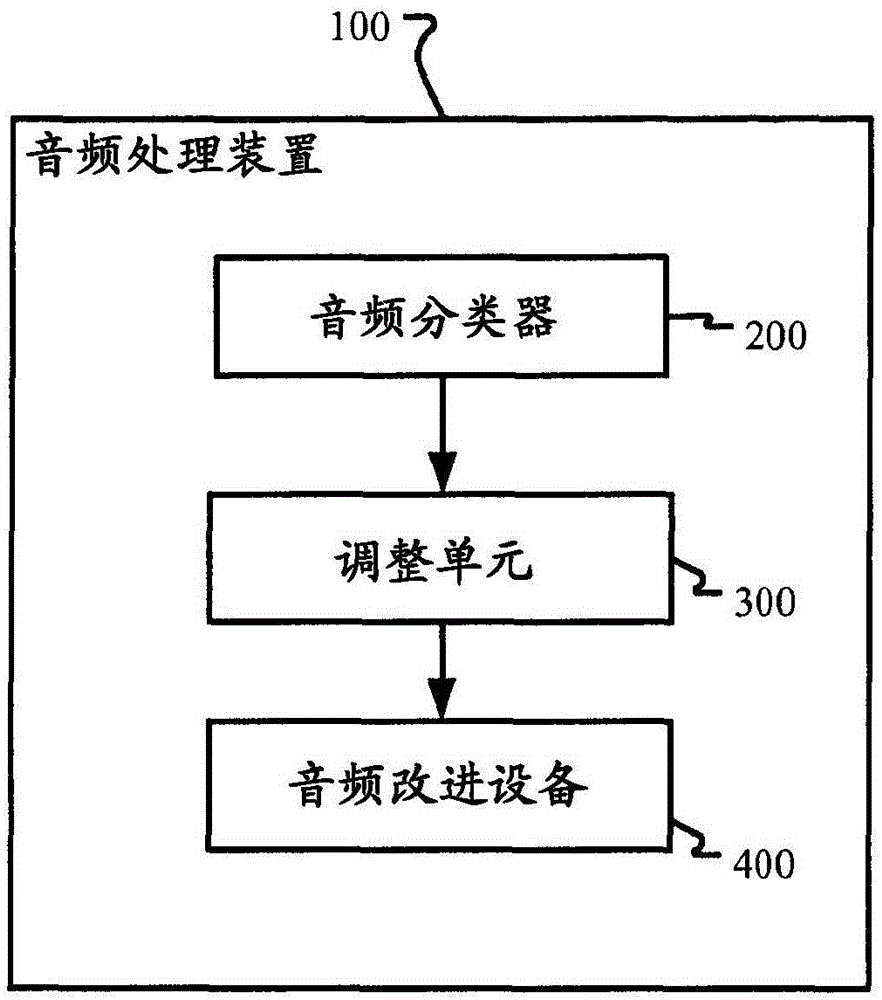
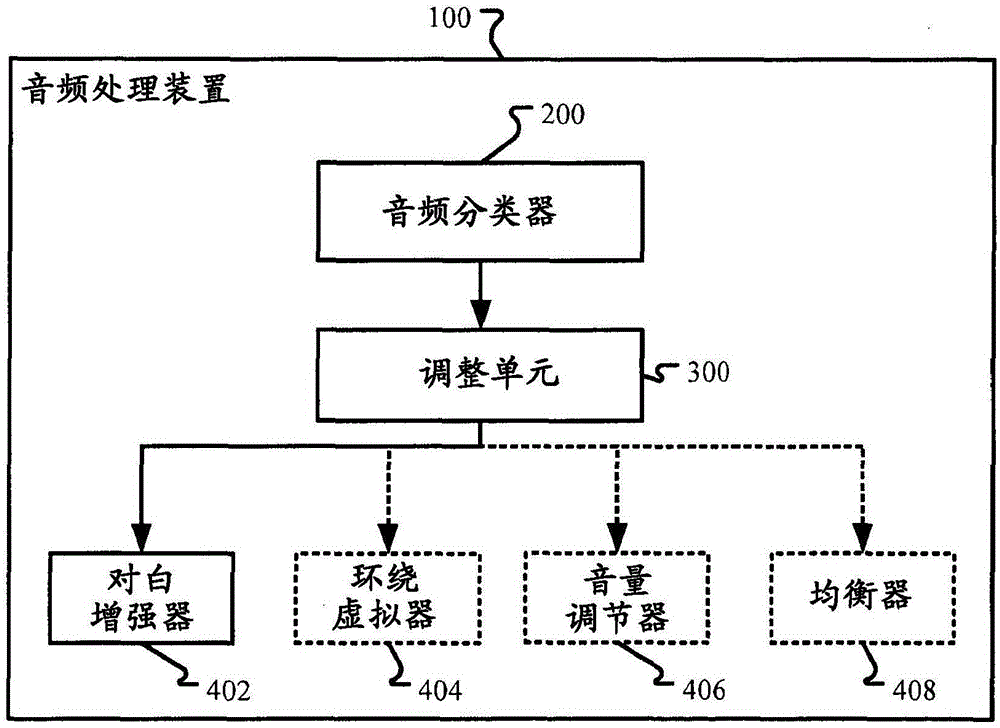
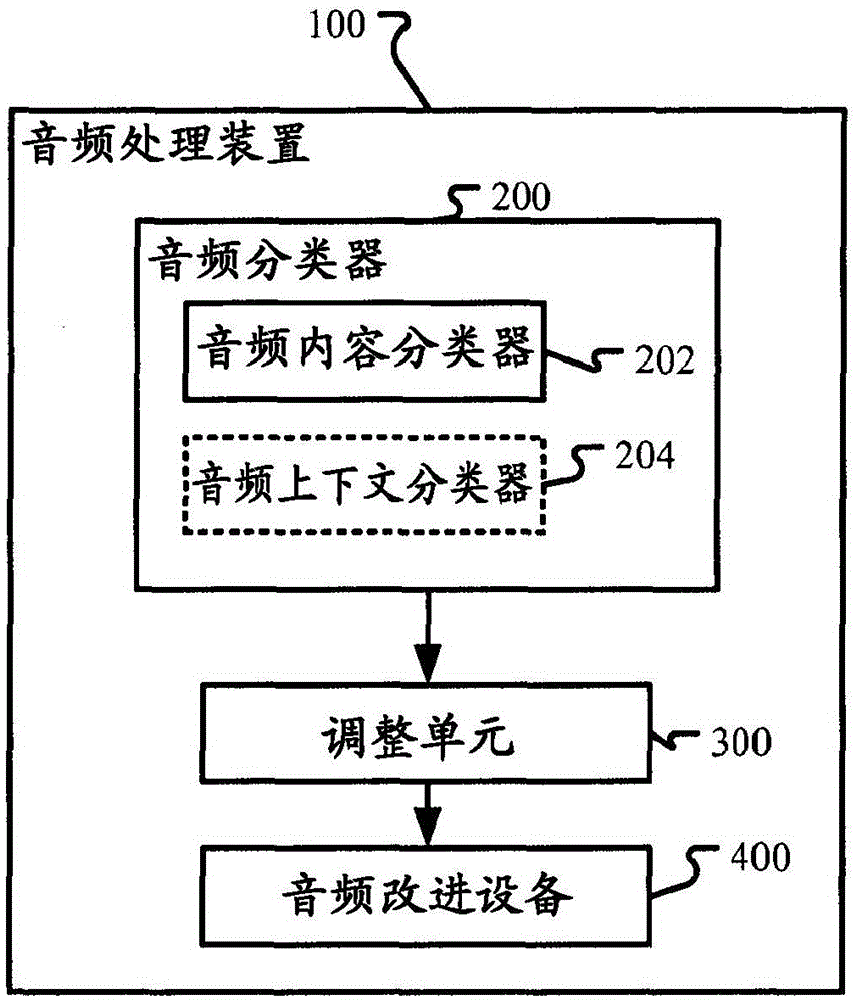
The invention discloses a device and a method for audio classification and audio processing. In one implementation mode, the audio processing device comprises an audio classifier for classifying audio signals to at least one audio type in real time, an audio improving device for improving the experience of audiences and an adjusting unit for adjusting at least one parameter of the audio improving device based on a confidence value of at least one audio type in a continuous mode.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
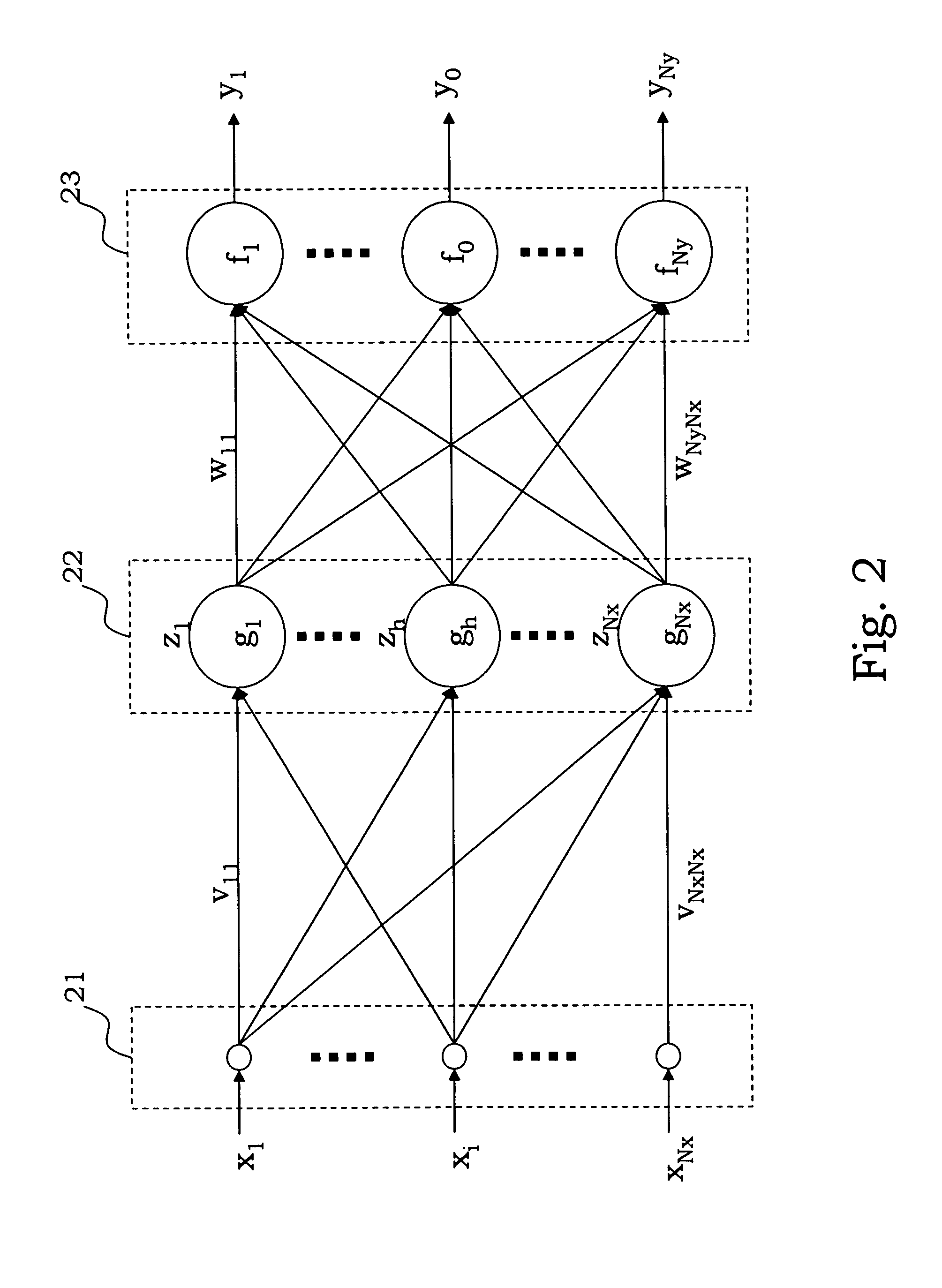
Intelligent classification system of sound signals and method thereof
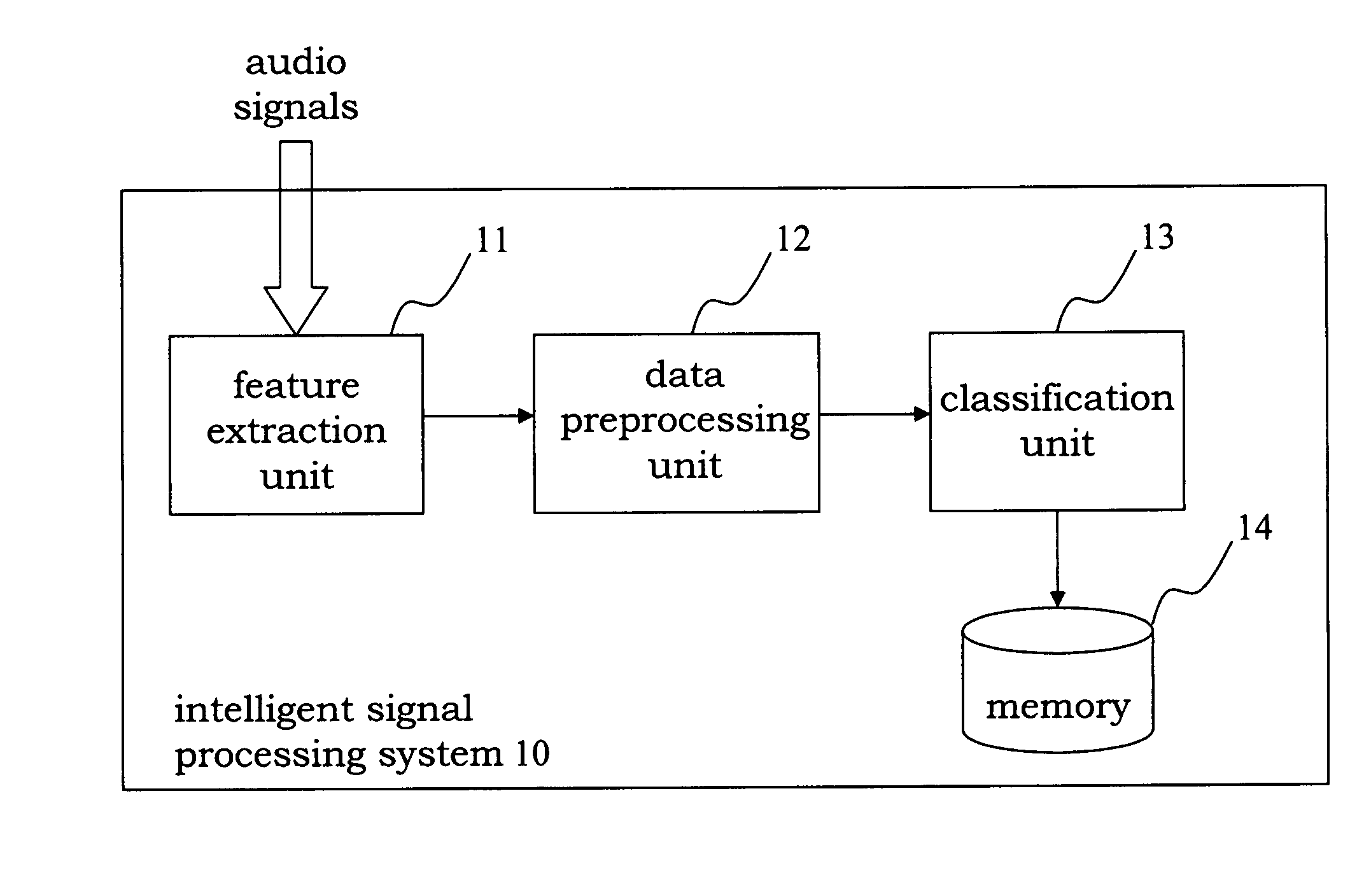
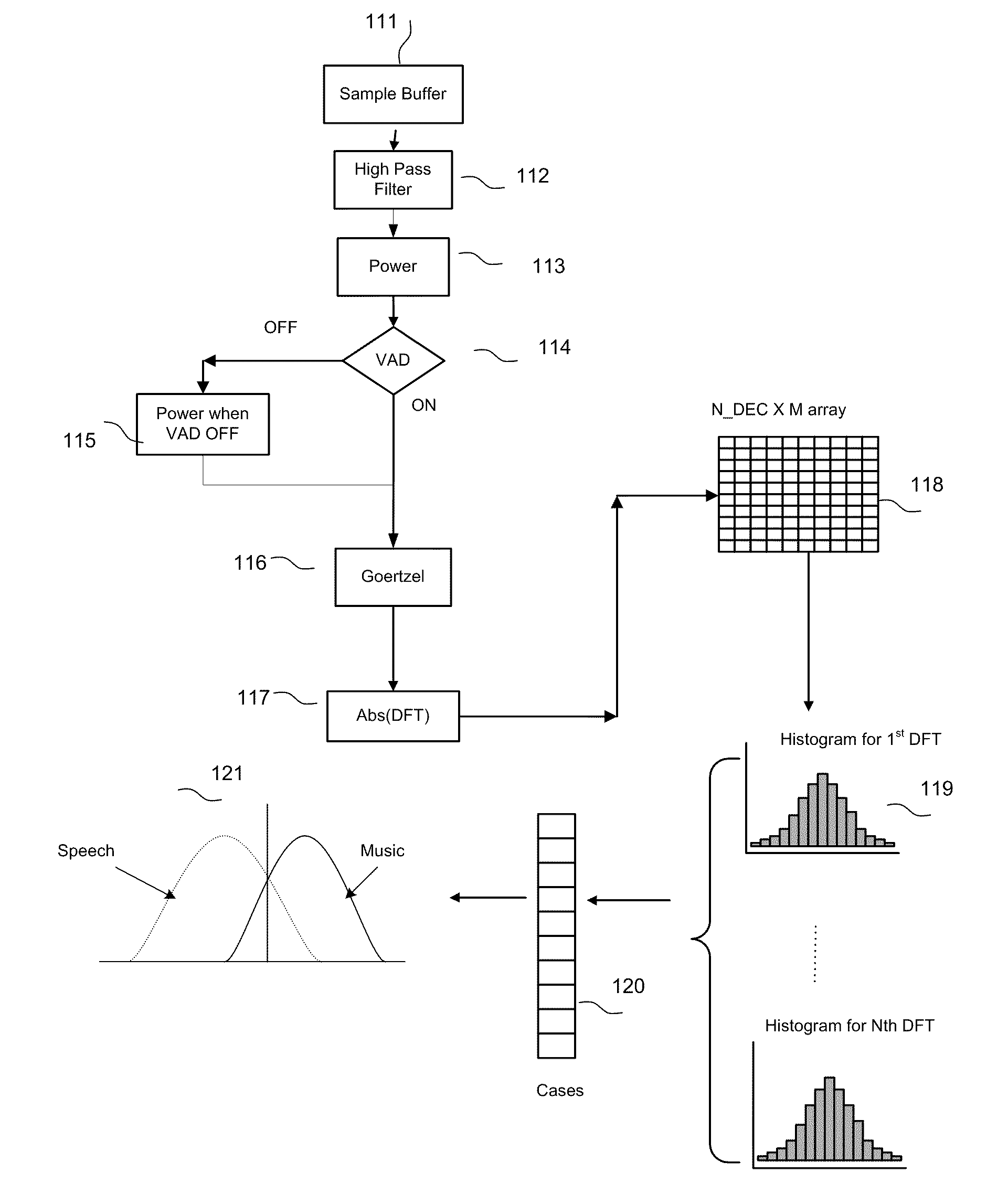
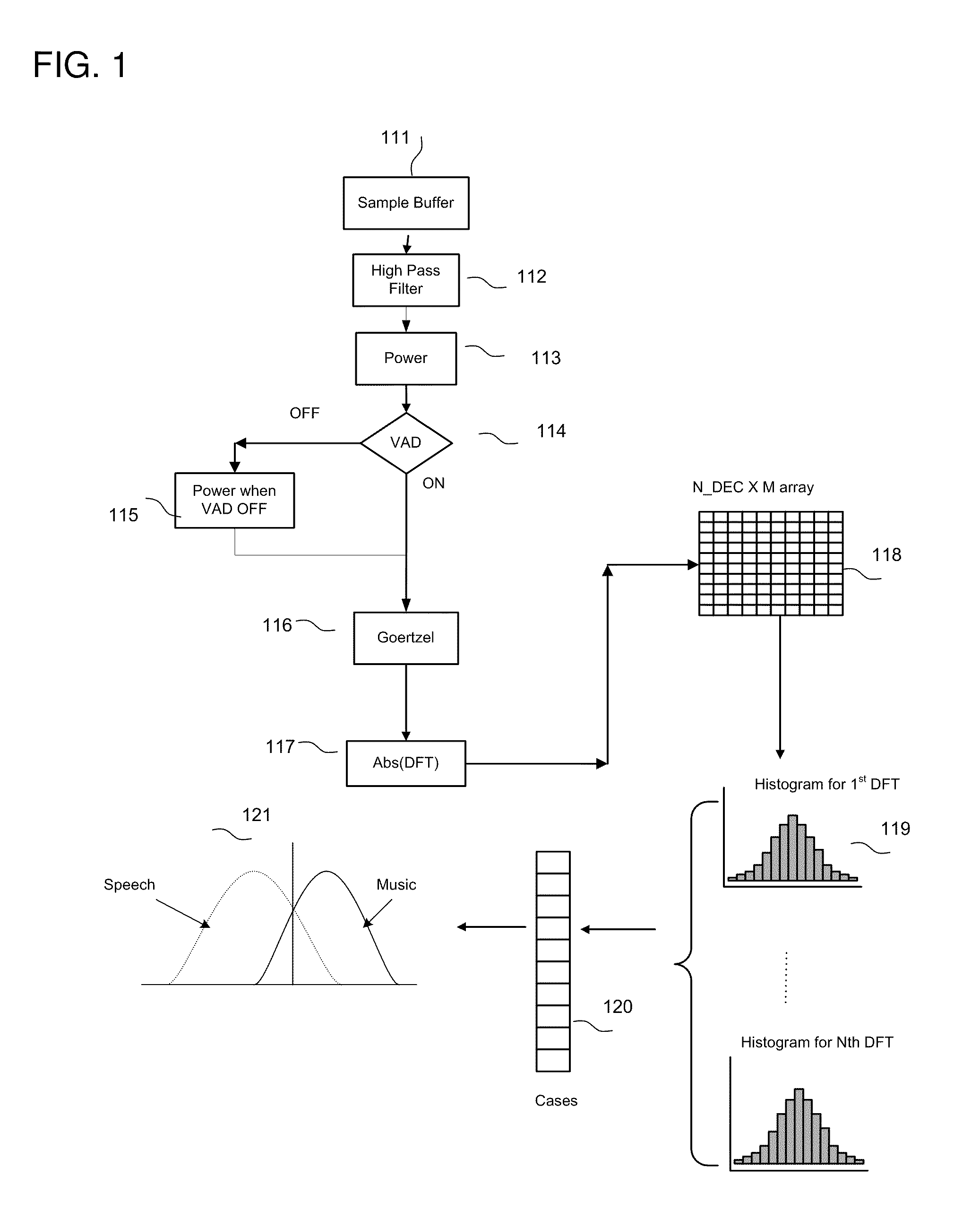
InactiveUS20080082323A1Reduce environmental noiseSpeech analysisRecognisation of pattern in signalsFeature extractionPreprocessing algorithm
A system that integrates various intelligent classification techniques and preprocessing algorithms is provided. A feature extracting unit receives audio signals and extracts audio features for identification by using various descriptors; a preprocessing unit normalized the data for data consistency; a classification unit classifying audio signals into several categories according to the audio features.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
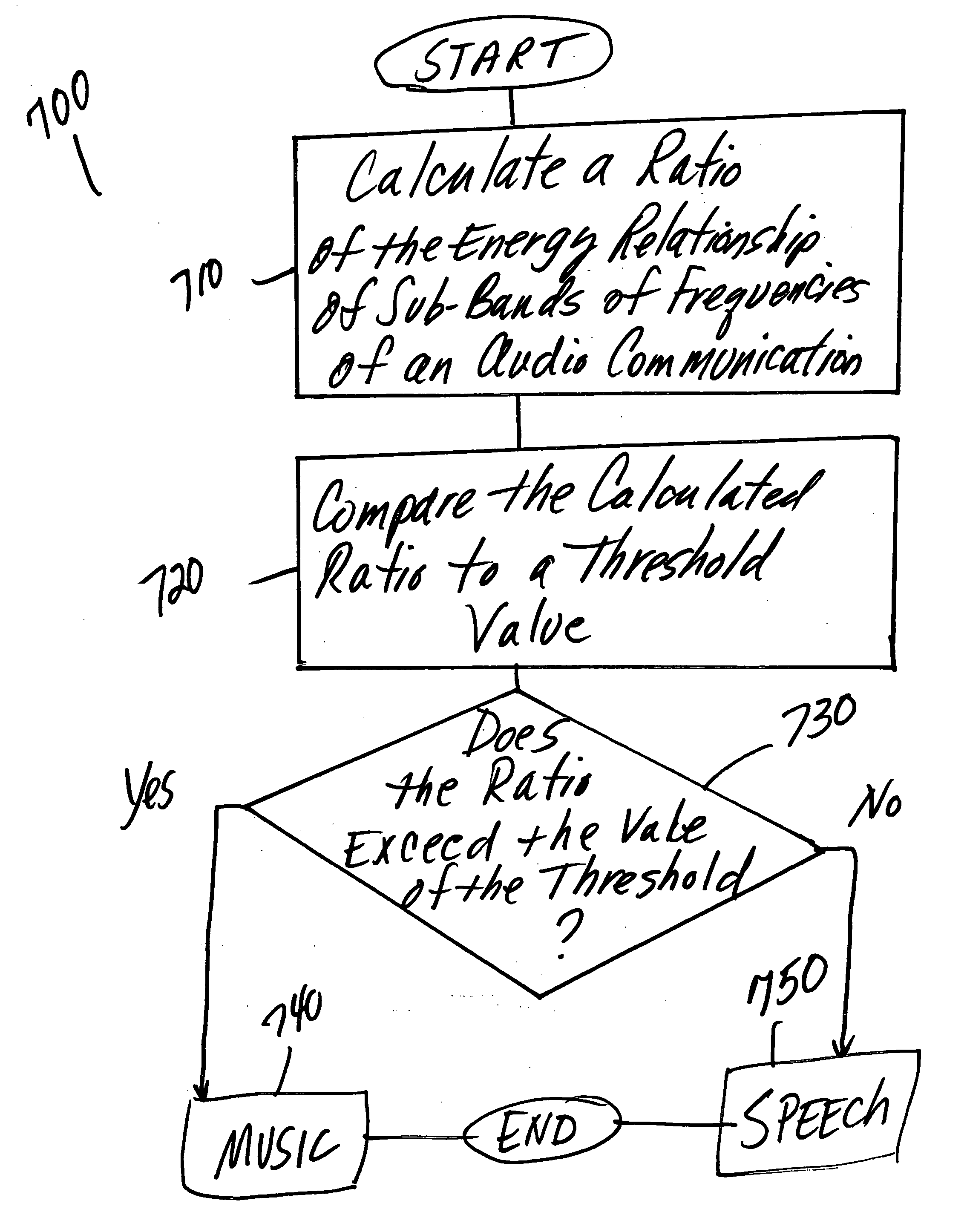
Classification of speech and music using sub-band energy
Disclosed herein is a method and system for classifying an audio signal using a sub-band energy analysis. An audio signal may be received as an input to the system for classifying an audio signal. The audio signal may be passed to a mathematical processor where the mathematical processor may perform a plurality of mathematical processes on the audio signal and calculating a ratio of energy contributable to speech and energy contributable to music. The ratio value R may be output to a comparator. The comparator may compare the calculated ratio R to a threshold value T and based upon the comparison classify the audio signal as one of speech or music.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and system for detecting abnormal use of voice input equipment
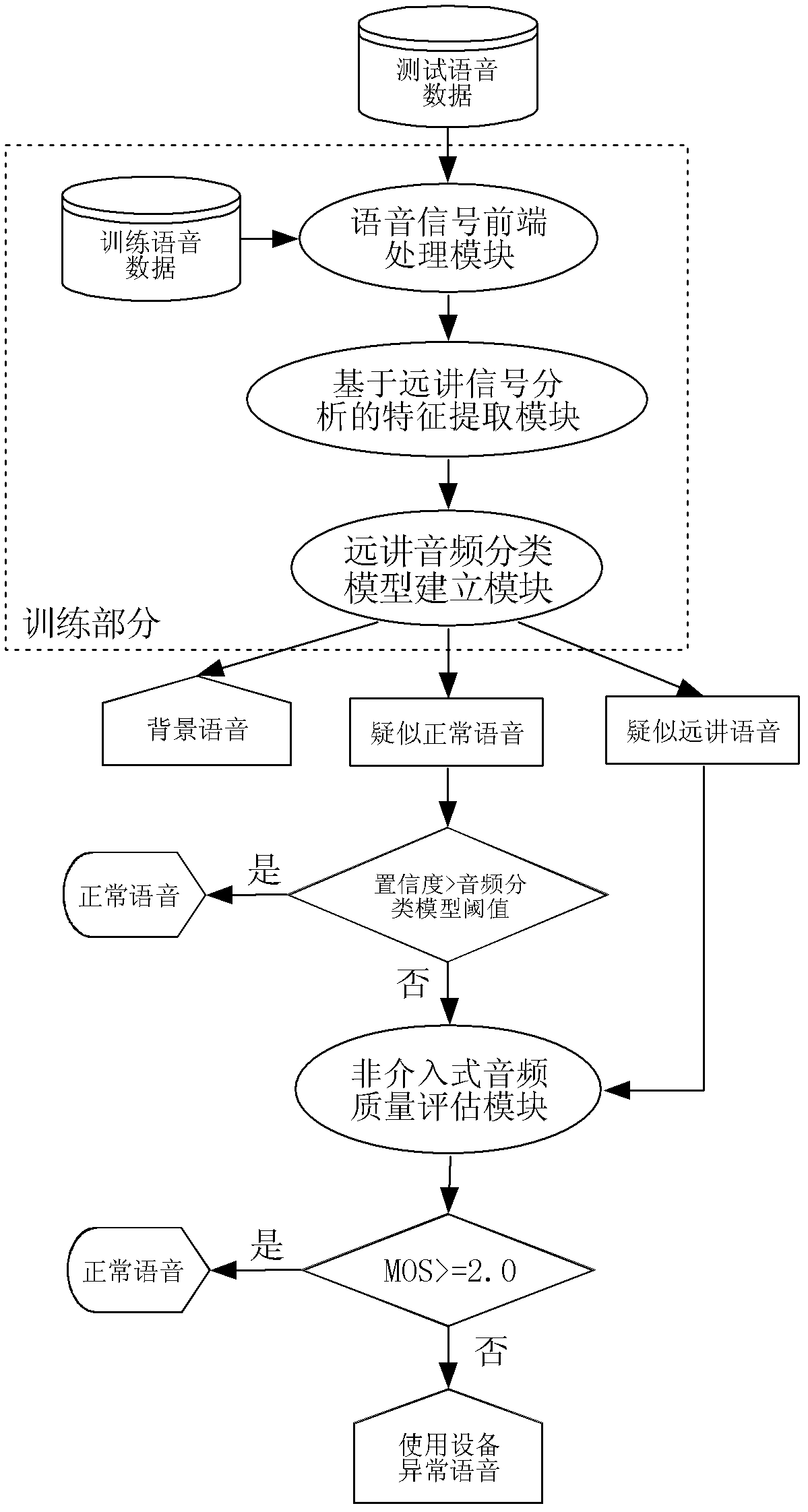
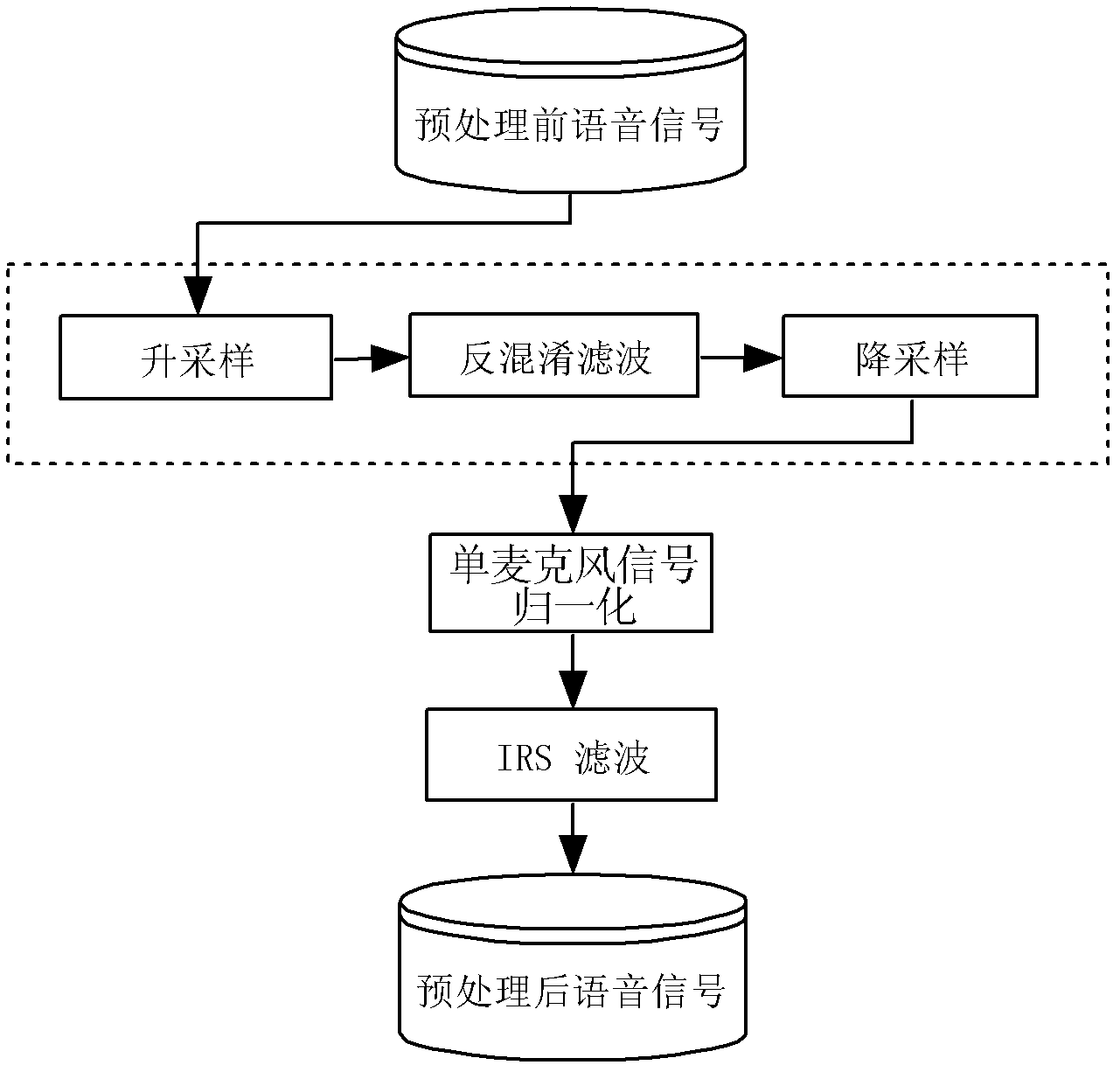
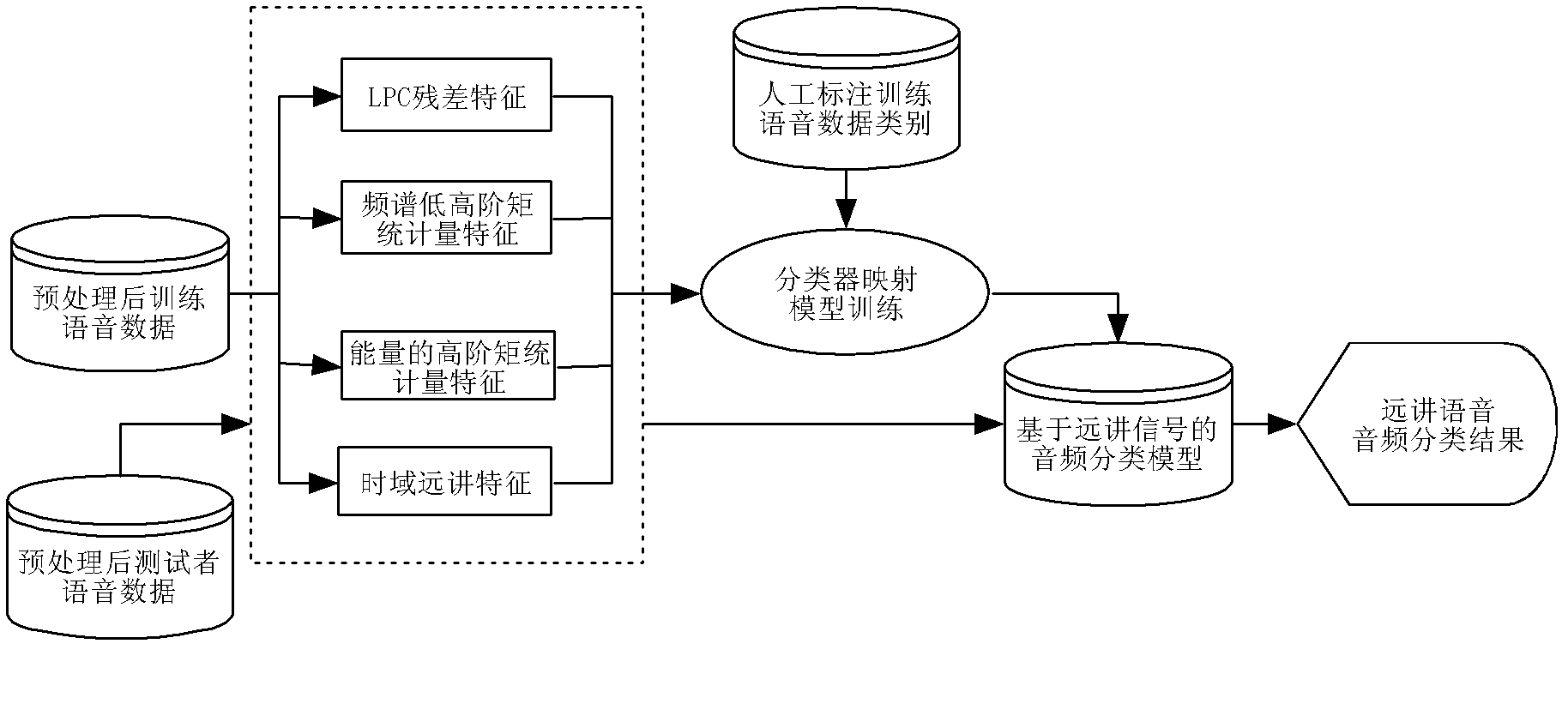
ActiveCN102324229ATroubleshoot Voice Quality DiscrepanciesEnsure fairnessSpeech analysisSpoken languageCombined method
The invention discloses a method and system for detecting abnormal use of voice input equipment. A characteristic extracting mode which is more comprehensive to remote voice signal characteristics and closer to human perception is adopted in the invention so as to roughly judge background voice, normal voice and remote voice. On the basis of classification of audio signals, by adopting the combined method of a modern signal processing technology and a statistical machine learning theory, the problem of multiple limits on front-end voice input by a traditional method is overcome so that signal-level quality scoring is closer to human scoring. According to the invention, the difference problem of front-end input voice quality due to artificial use errors of the equipment in large-scale tests of spoken language is solved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
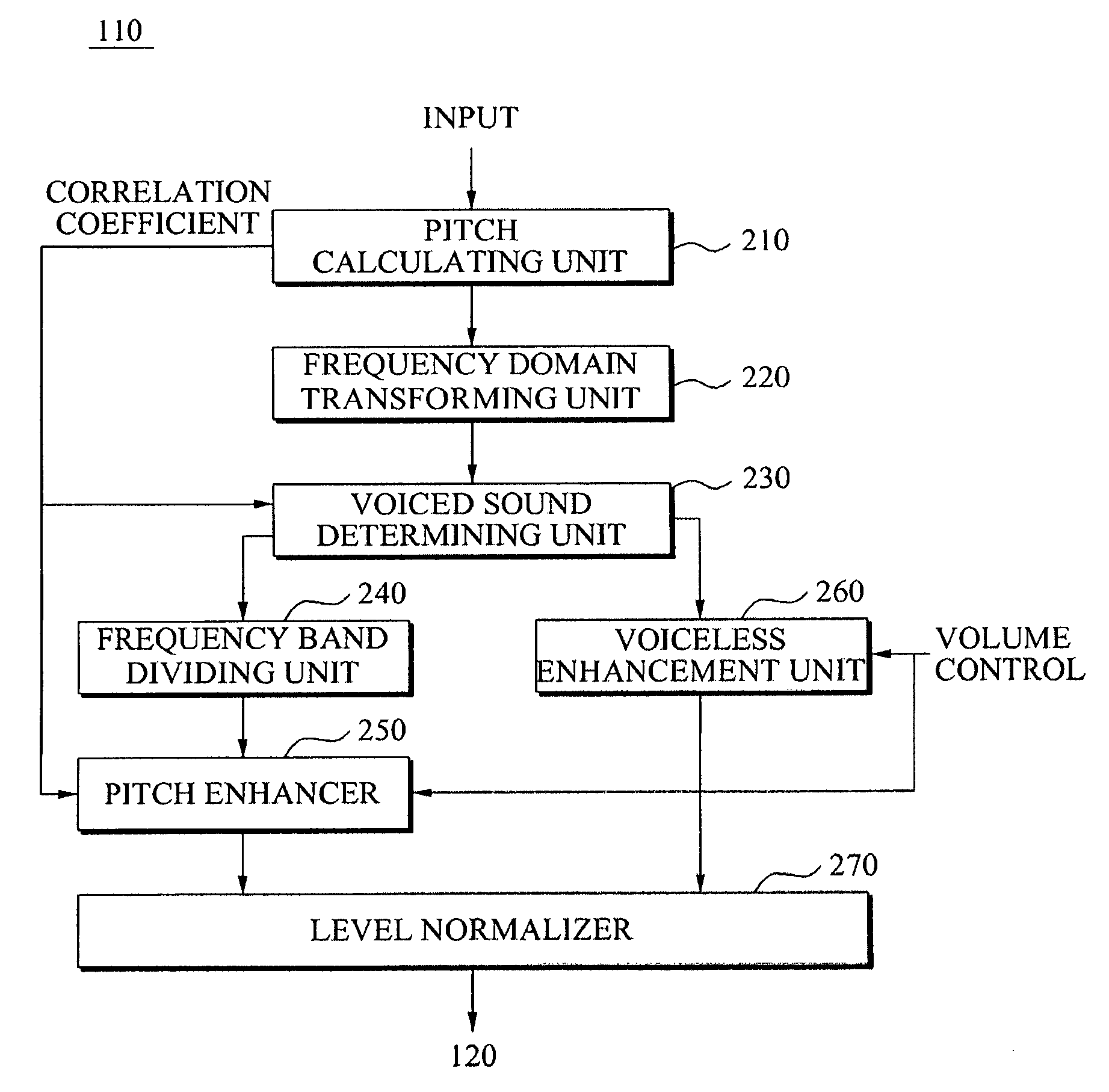
Audio signal quality enhancement apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090306971A1Improve signal qualitySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsSignal qualityAudio frequency
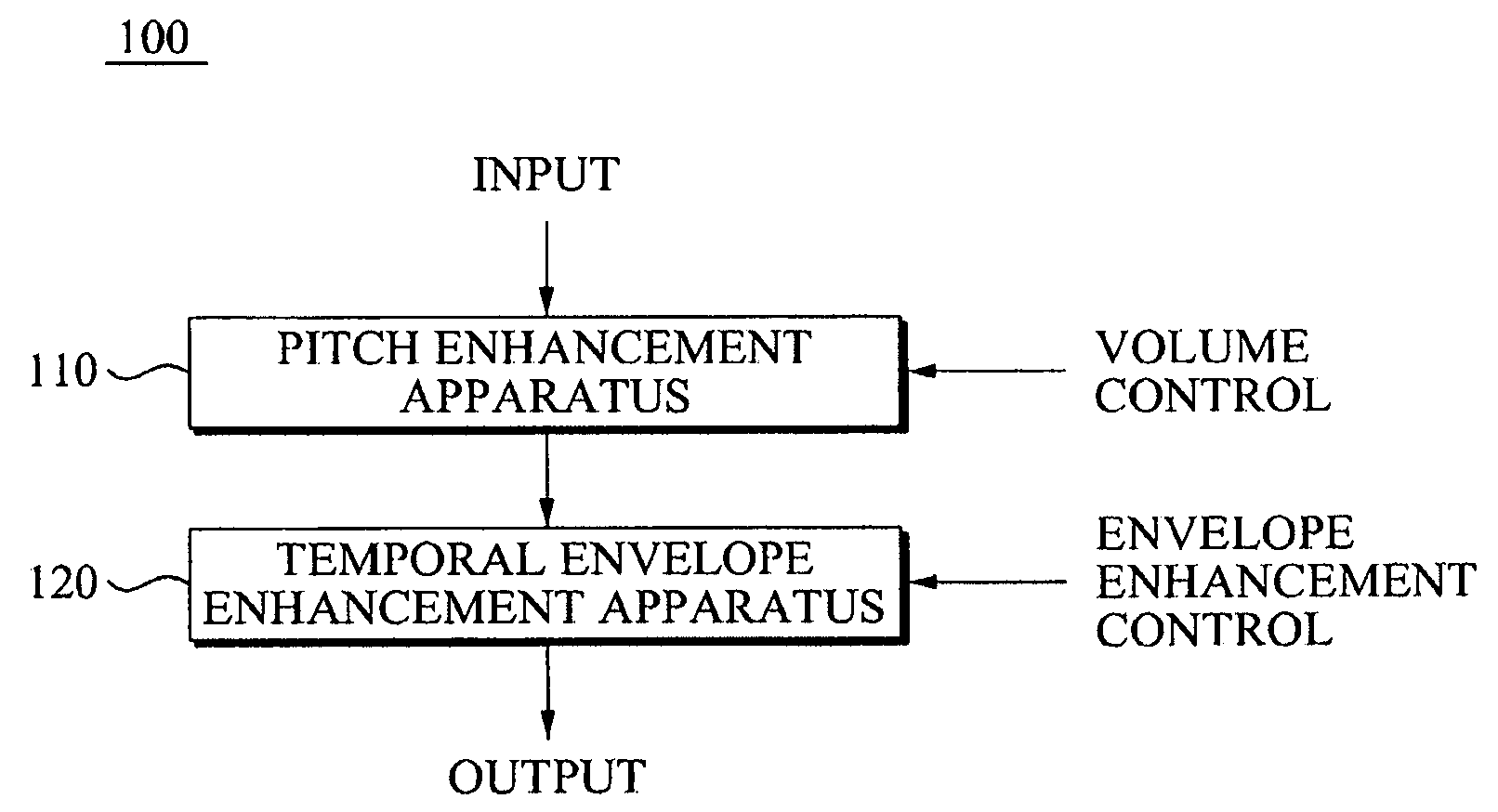
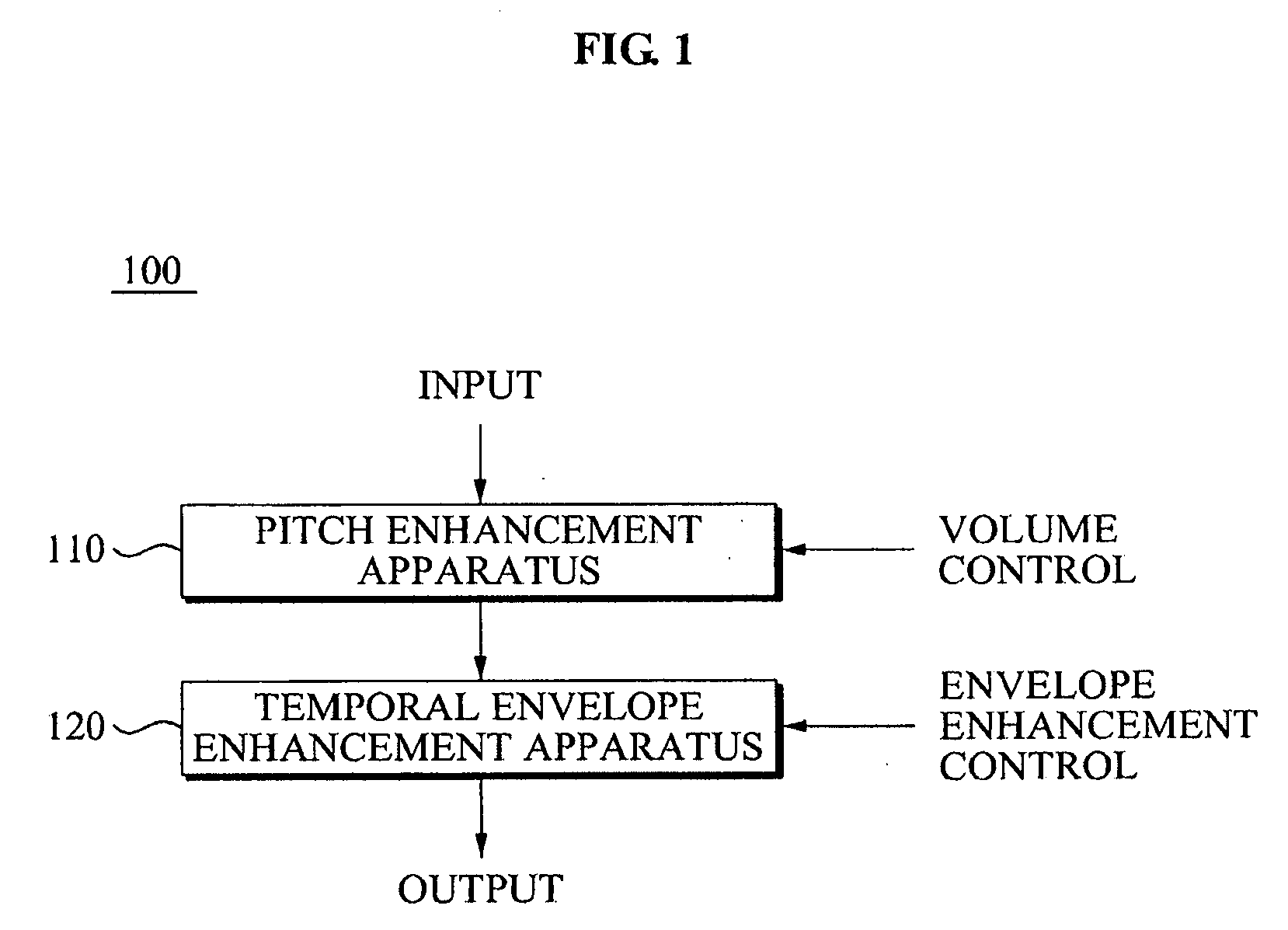
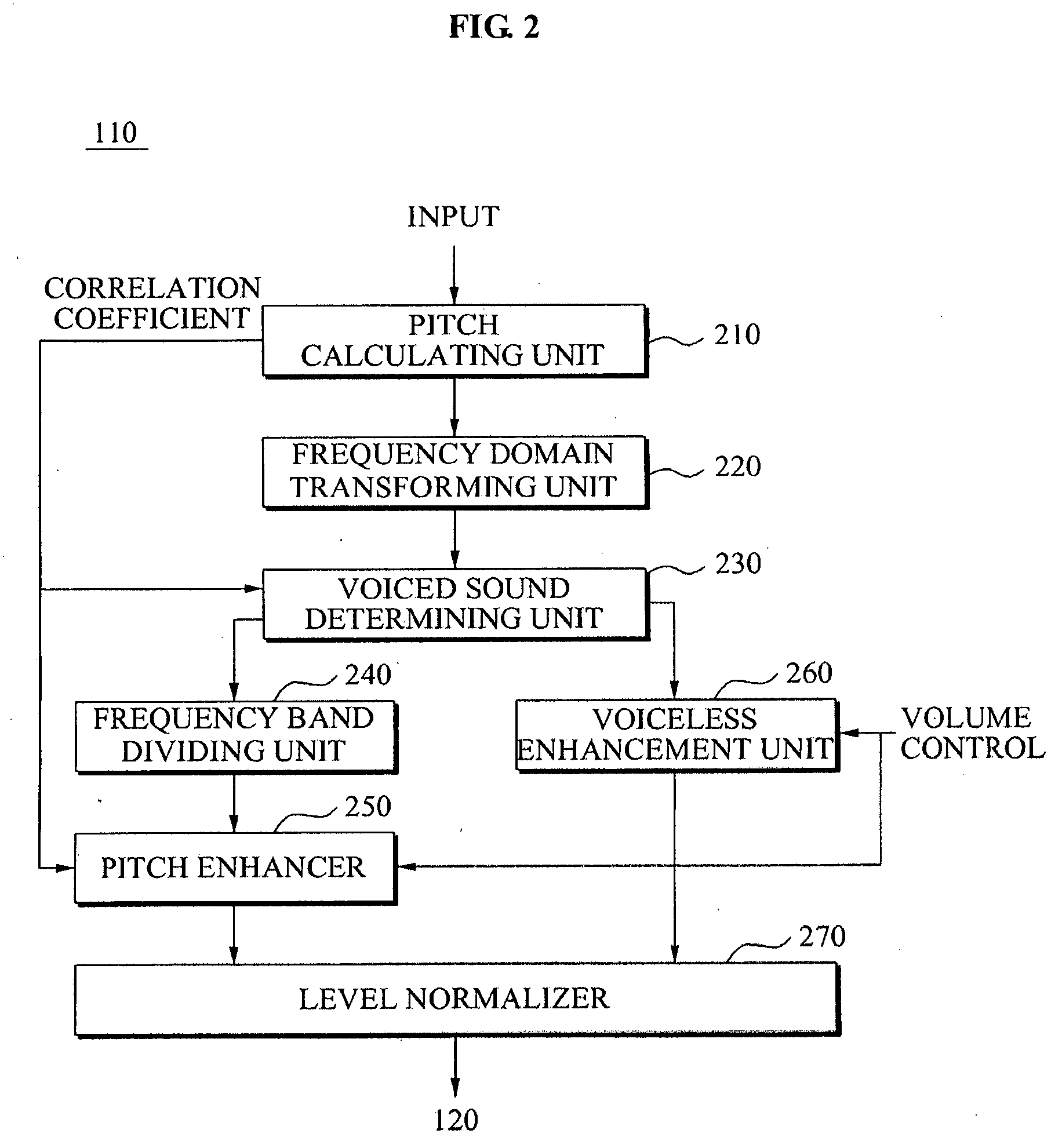
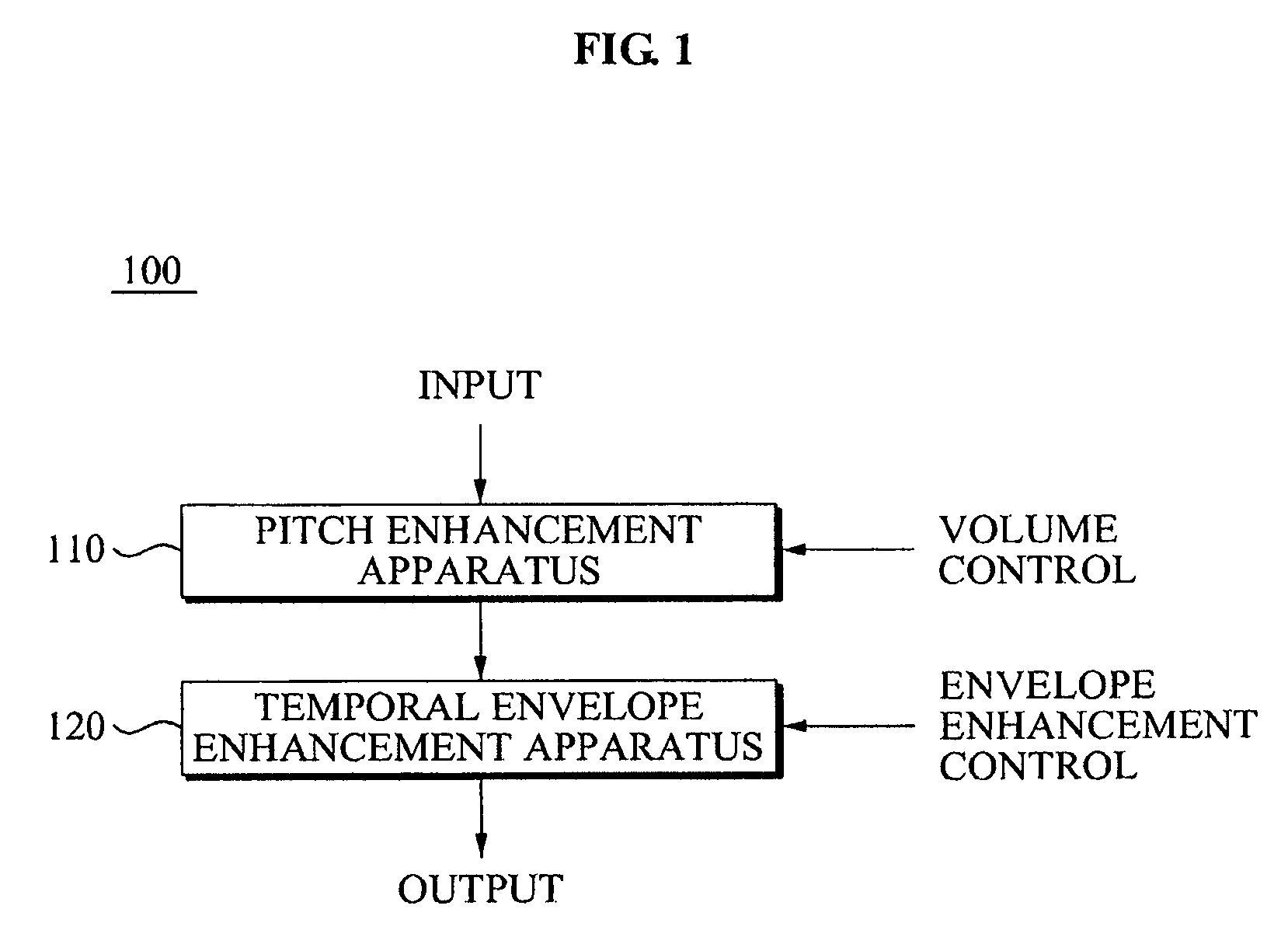
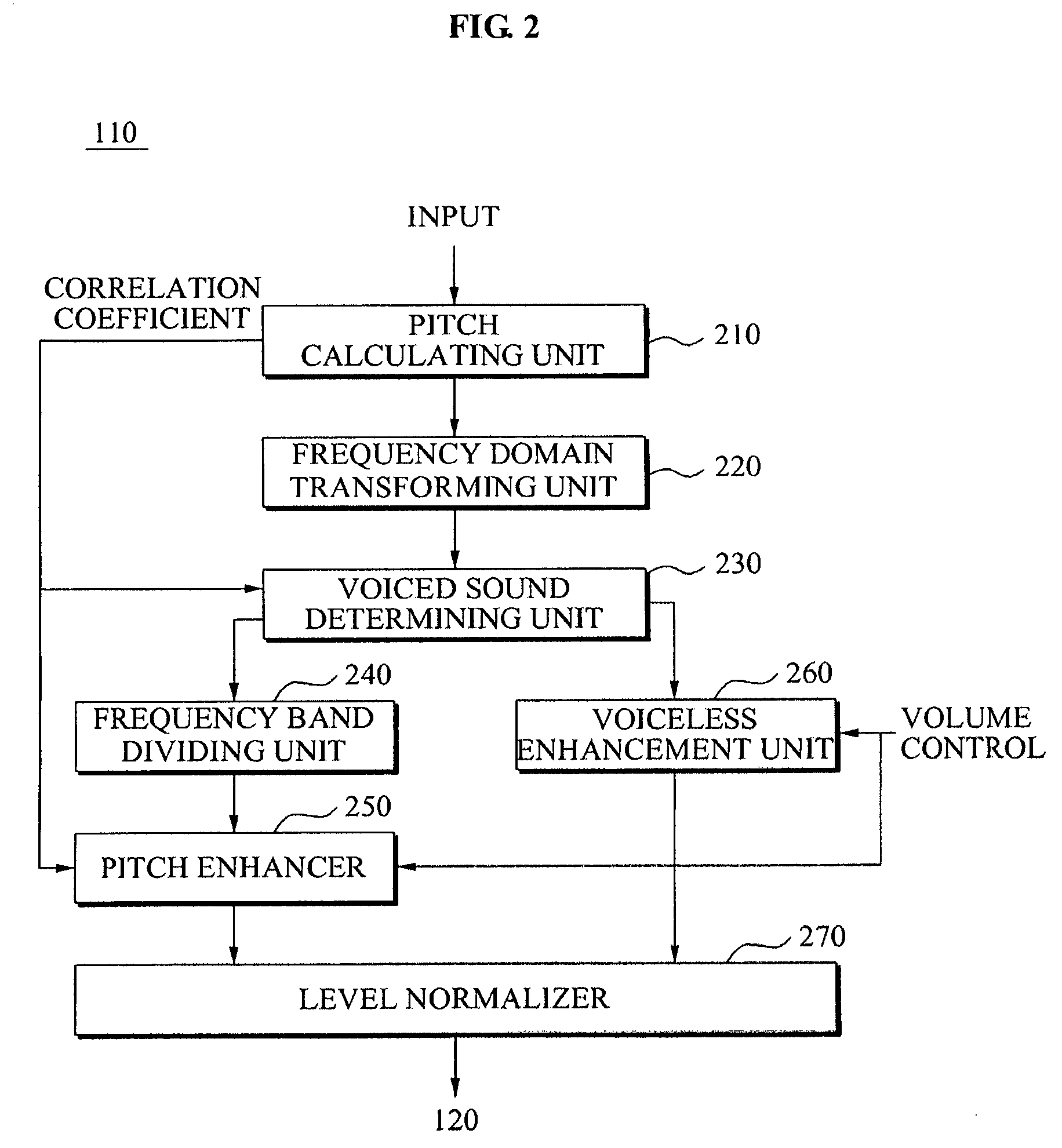
An audio signal quality enhancement apparatus and method. The apparatus includes a pitch calculating unit to extract a pitch period of an audio signal, a frequency domain transforming unit to transform the audio signal to a frequency domain, a frequency band dividing unit to classify the transformed audio signal into audio signals for each of the plurality of frequency bands based on the extracted pitch period, and a pitch enhancement unit to determine a gain based on a volume of the transformed audio signal, and to generate an output signal by multiplying each of the classified audio signals with respect to each of the plurality of frequency bands by the gain, thereby enhancing quality of the audio signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Device and method for audio classification and audio processing
Apparatus and methods for audio classifying and processing are disclosed. In one embodiment, an audio processing apparatus includes an audio classifier for classifying an audio signal into at least one audio type in real time; an audio improving device for improving experience of audience; and an adjusting unit for adjusting at least one parameter of the audio improving device in a continuous manner based on the confidence value of the at least one audio type.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and equipment for classifying audio signals in real time
InactiveCN102543079AImprove real-time classification accuracyImprove codec efficiencySpeech recognitionTime domainClassification methods
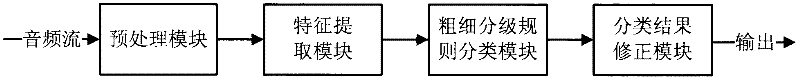
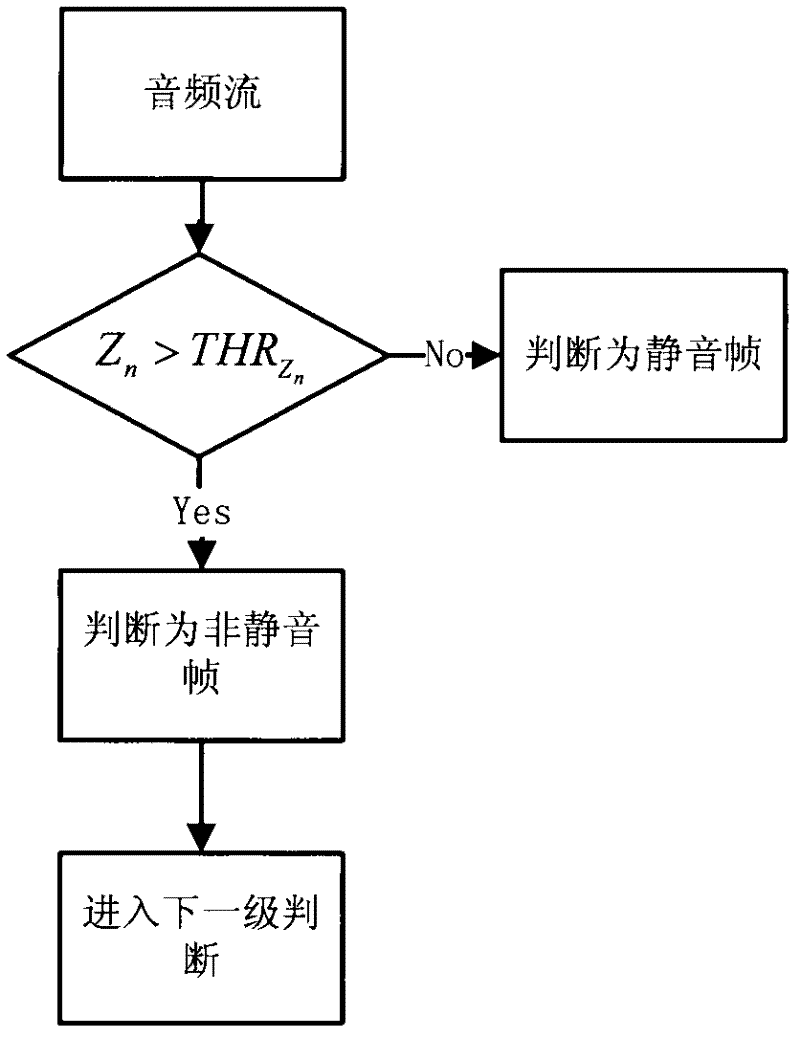
The invention discloses a method and equipment for classifying audio signals in real time, belonging to the technical field of audio encoding and decoding. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing the inputted audio signals; extracting multi-level audio features in a time domain and an MDCT domain; classifying a current frame by adopting the signal audio feature if the current frame is in a classification convergence time frame I; classifying the current frame by adopting the coarse-fine classification rule if the current frame is behind the classification convergence time frame I, and judging classification features by adopting the multi-level features; and after classifying the current frame by adopting the coarse-fine classification rule, upgrading the signal classification type of the current frame according to the historical state of the classification type of a signal frame before the current frame. Due to the adoption of the method and the equipment, the signals can be classified in real time simply and accurately.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Acoustic signal processing device and method
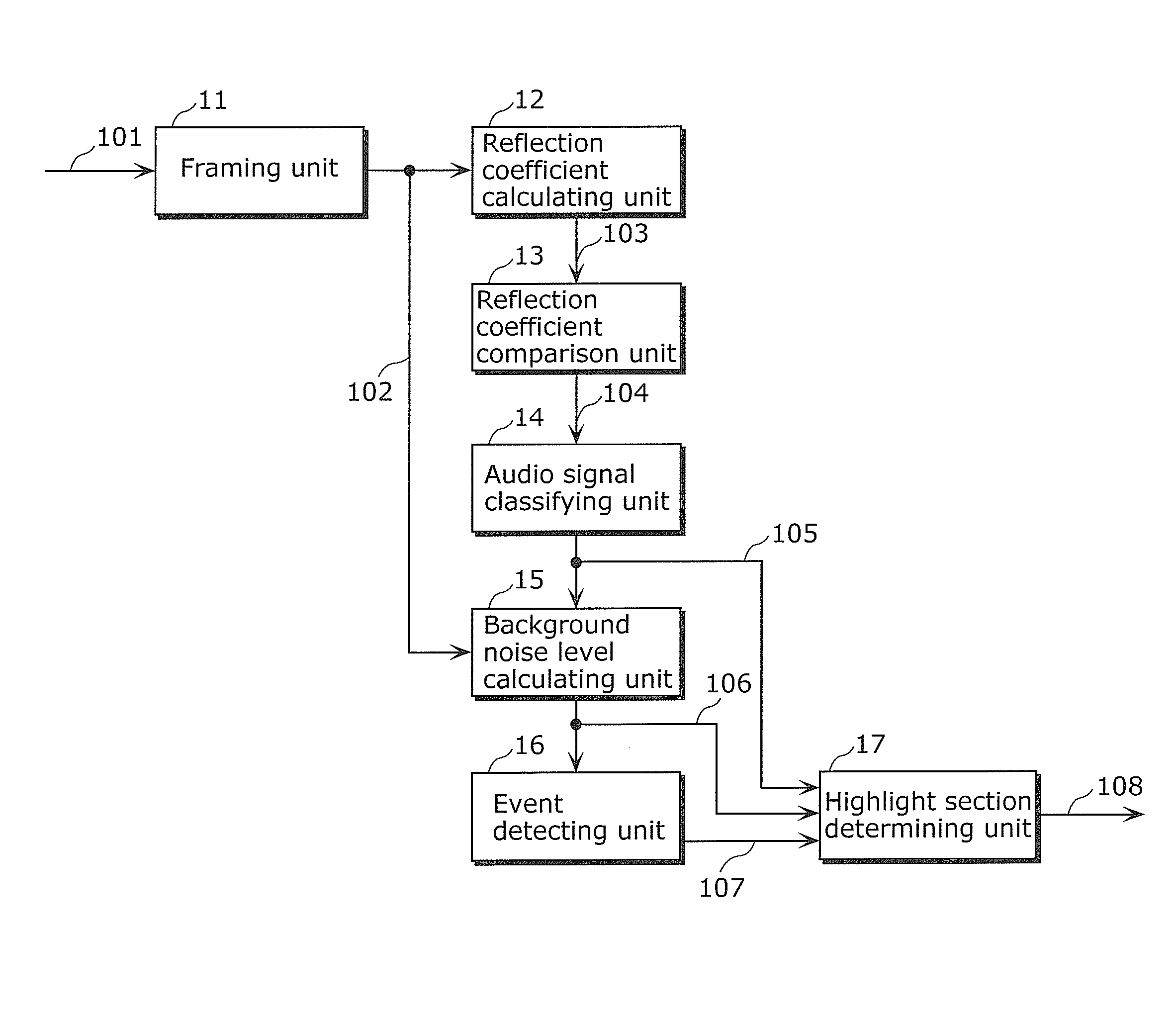
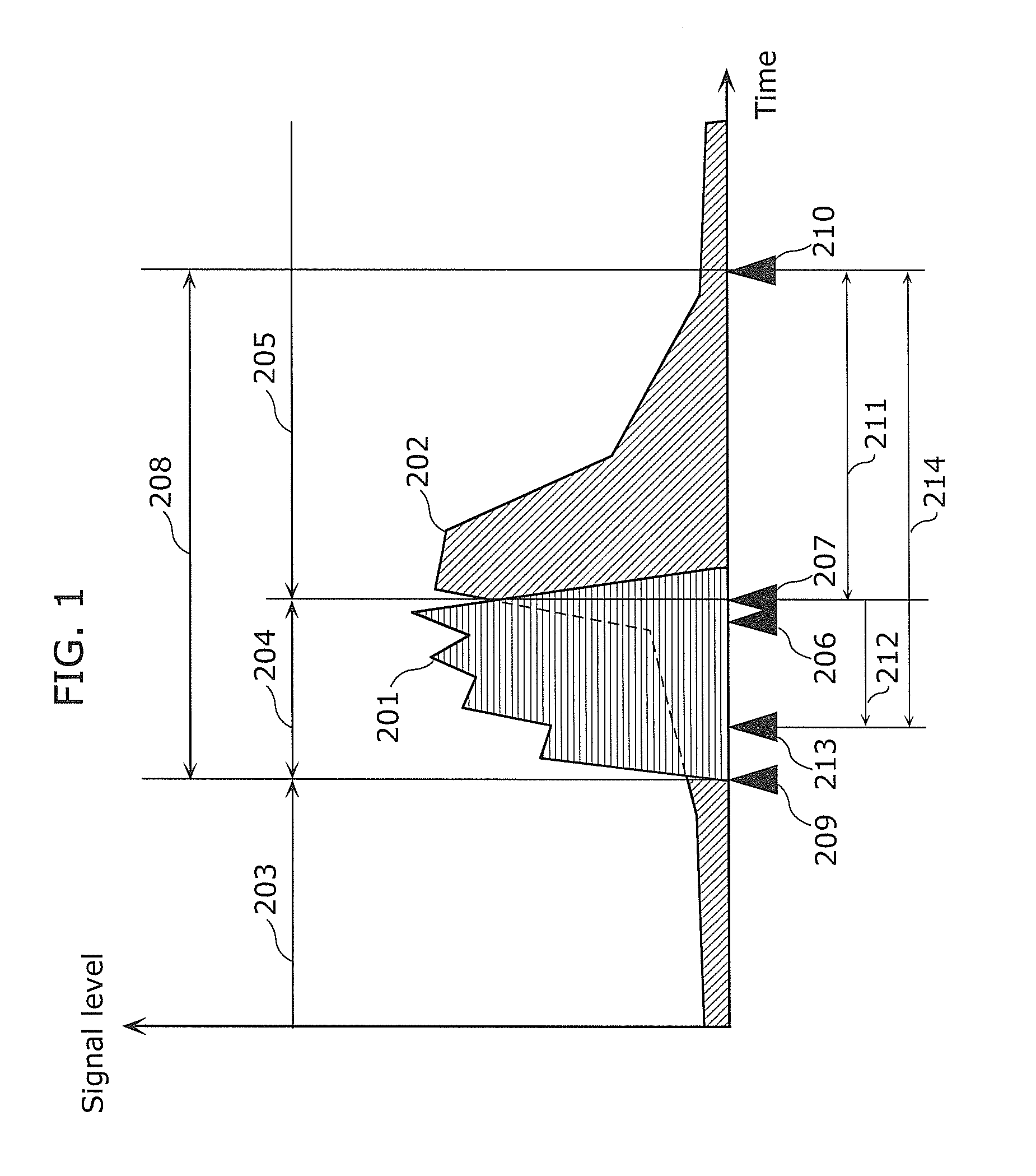
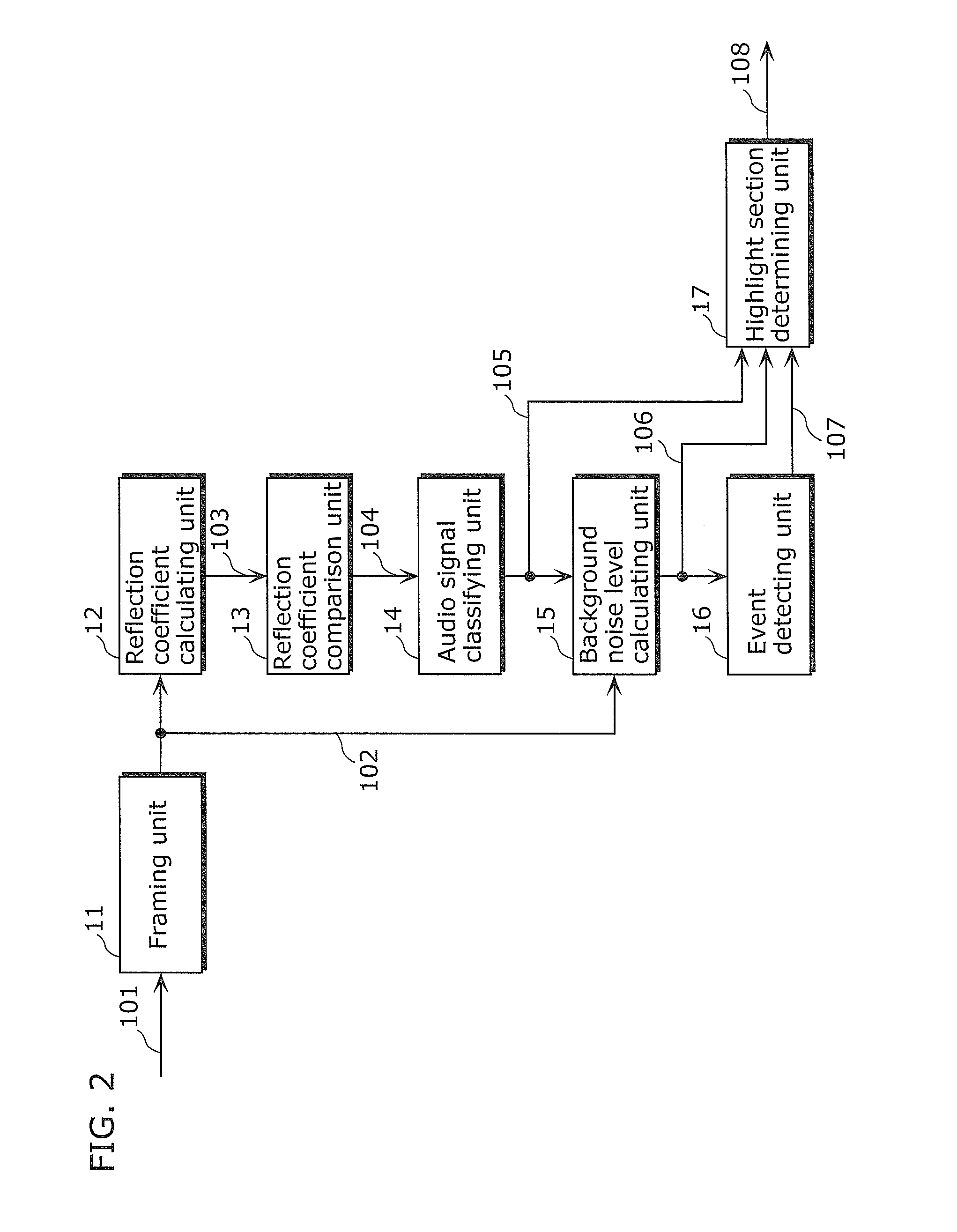
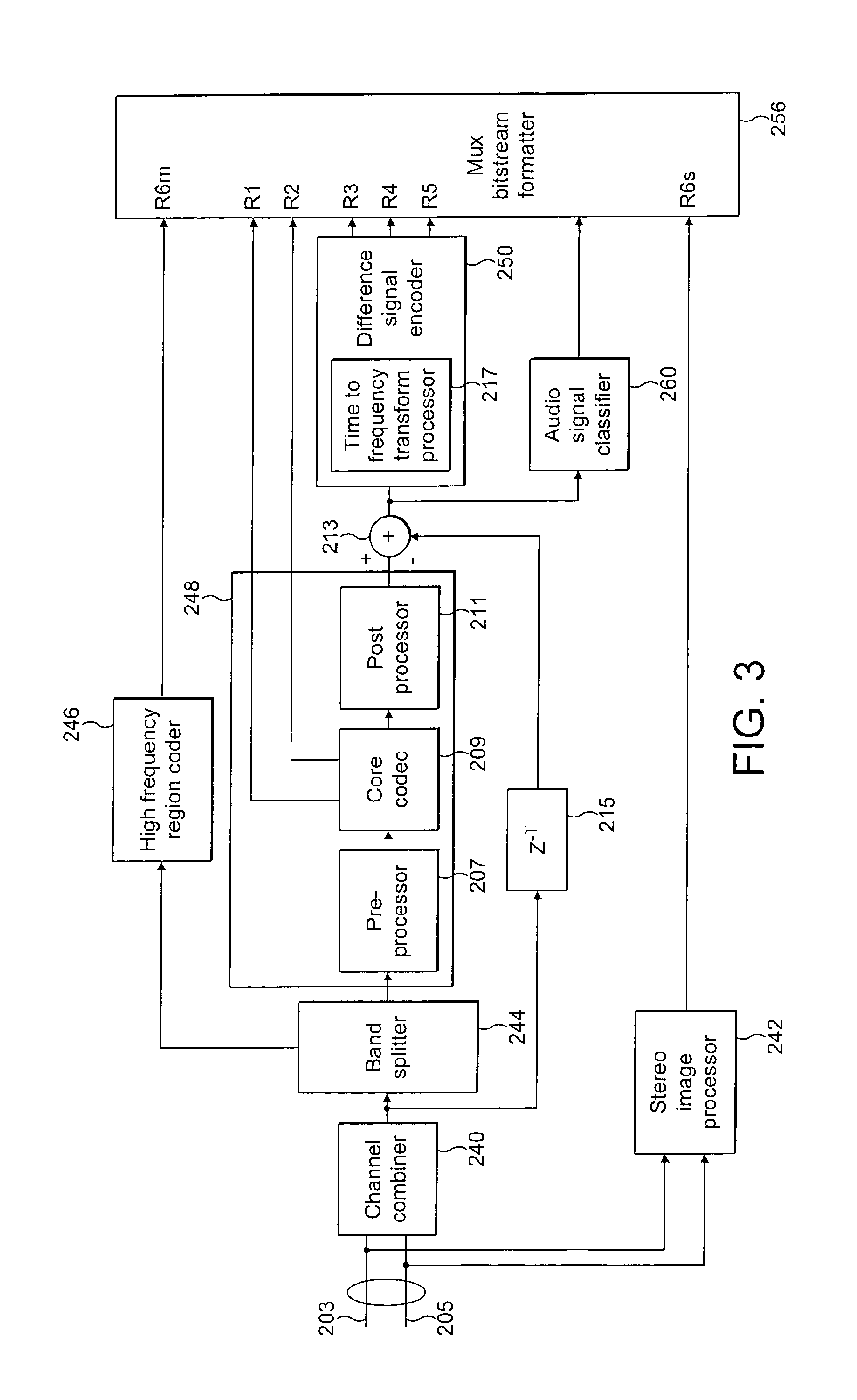
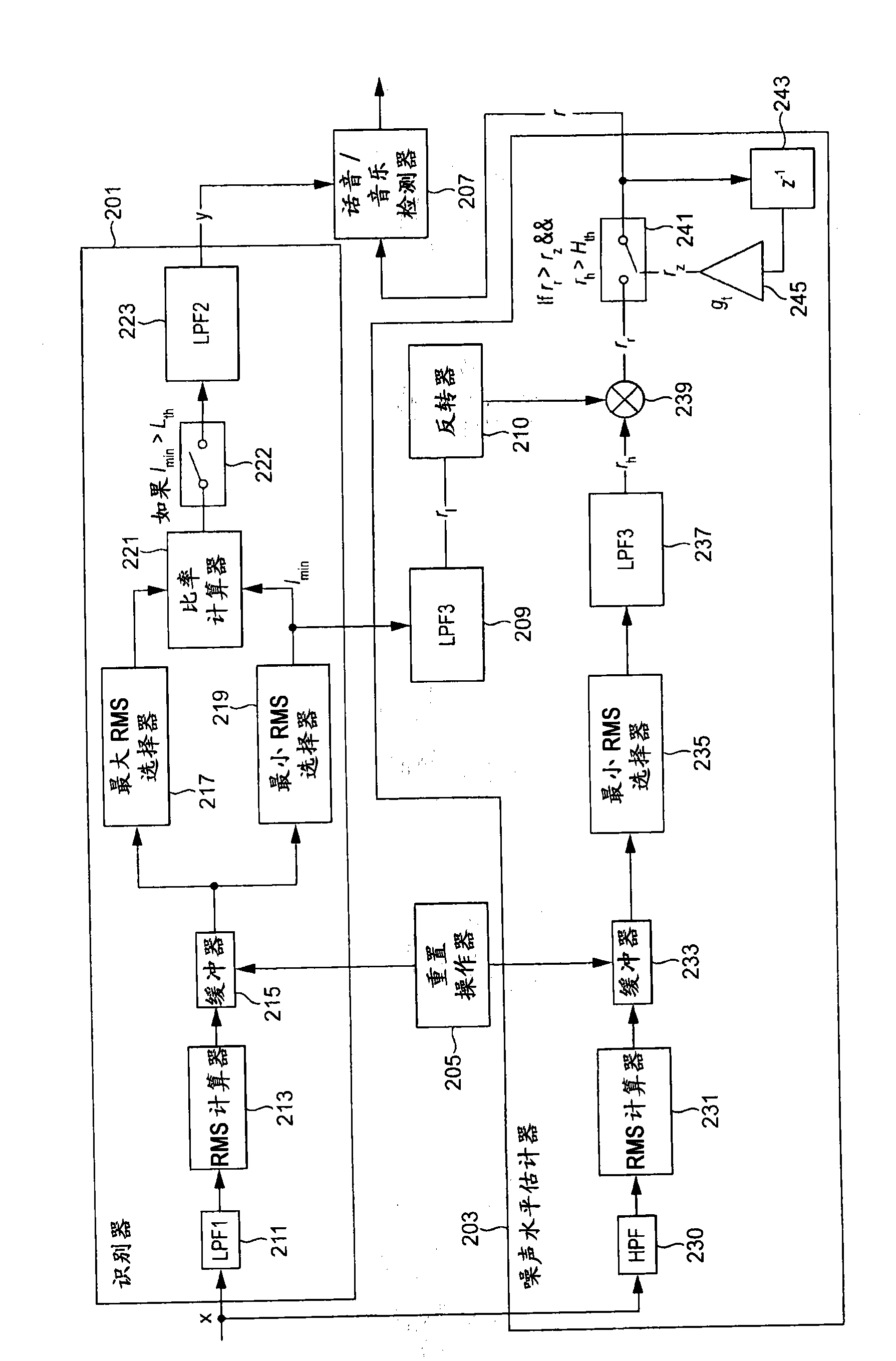
A highlight section including an exciting scene is appropriately extracted with smaller amount of processing. A reflection coefficient calculating unit (12) calculates a parameter (reflection coefficient) representing a slope of spectrum distribution of the input audio signal for each frame. A reflection coefficient comparison unit (13) calculates an amount of change in the reflection coefficients between adjacent frames, and compares the calculation result with a predetermined threshold. An audio signal classifying unit (14) classifies the input audio signal into a background noise section and a speech section based on the comparison result. A background noise level calculating unit (15) calculates a level of a background noise in the background noise section based on signal energy in the background noise section. An event detecting unit (16) detects an event occurring point from a sharp increase in the background noise level. A highlight section determining unit (17) determines a starting point and an end point of the highlight section, based on a relationship between the classification result of the background noise section and the speech section before and after the event occurring point.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Audio classification and implementation method based on reclassification
InactiveCN101751920AEasy to distinguishReduce operational complexitySpeech recognitionClassification methodsAudio frequency
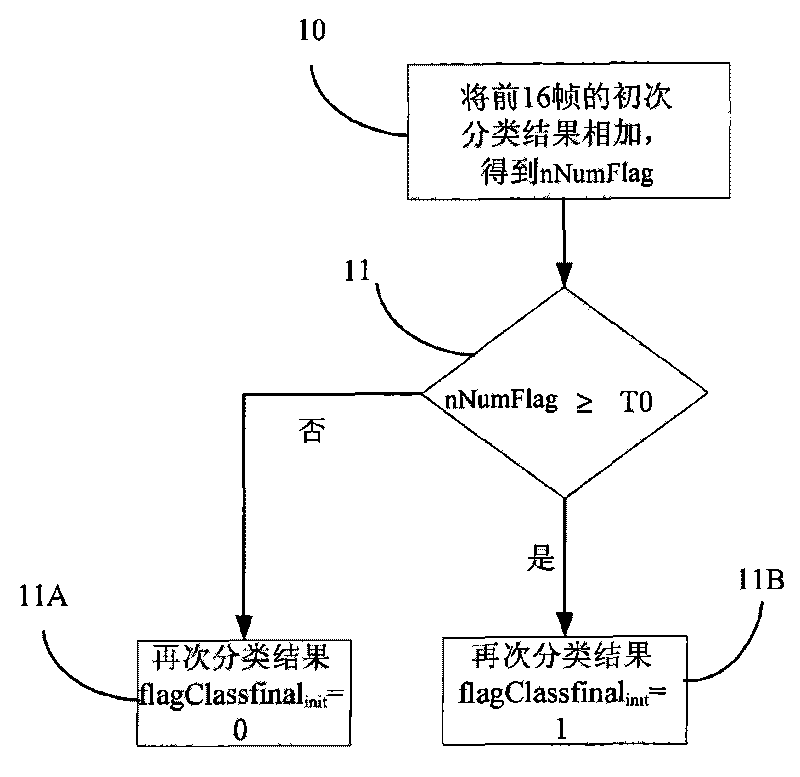
The invention relates to an audio classification method for classifying audio signals before audio coding; the audio classification method includes primary classification and reclassification, and is characterized in that the reclassification includes the primary classification result is smoothened. Besides, the invention also discloses an audio classification device arranged on the front end of an audio coder for classifying the audio signals; the audio classification device comprises a primary classifier and a reclassifier, and is characterized in that the reclassifier comprises a smoothing module for smoothing the primary classification result. The method and device of the invention are used to correctly distinguish music and voice from audio signals. As the reclassification includes the smoothening on the primary classification result, the occasional false judgment caused by overquick audio type switching is eliminated, and the operational complexity is also educed so that the correct and simple distinguishing of music and voice is realized.
Owner:数维科技(北京)有限公司
Audio signal classification method and device
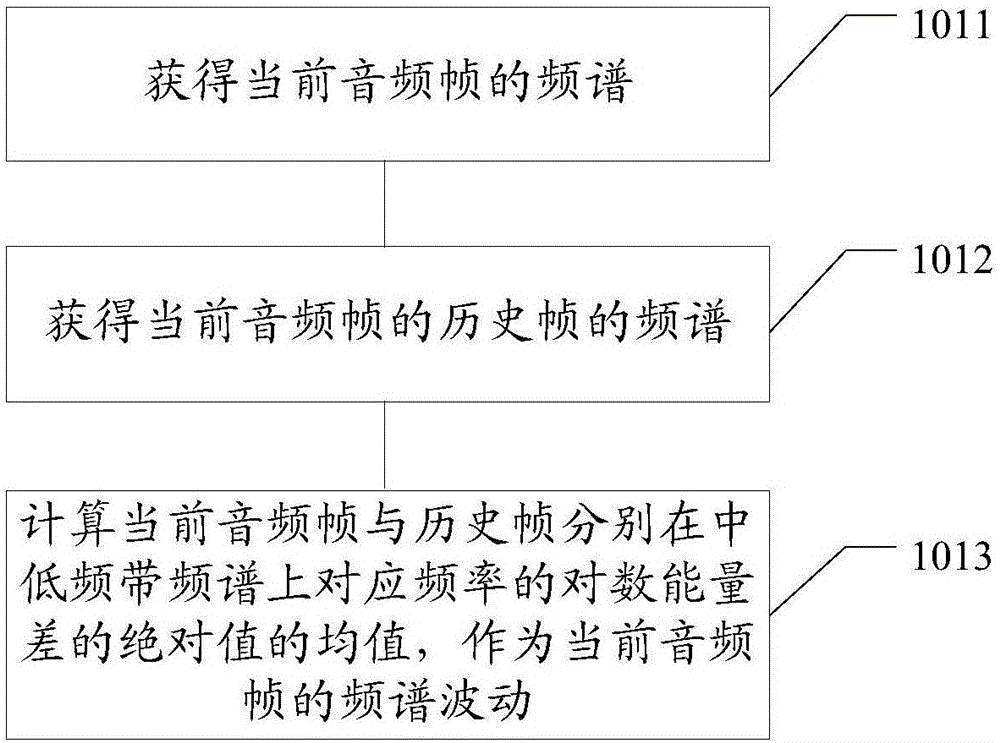
ActiveCN104347067AImprove recognition rateFew parametersSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumVoice activity
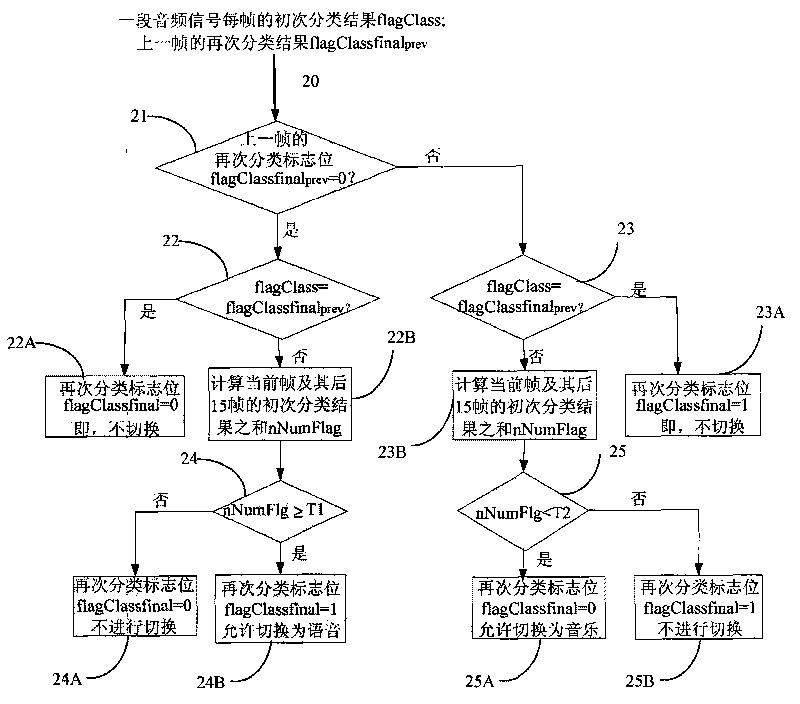
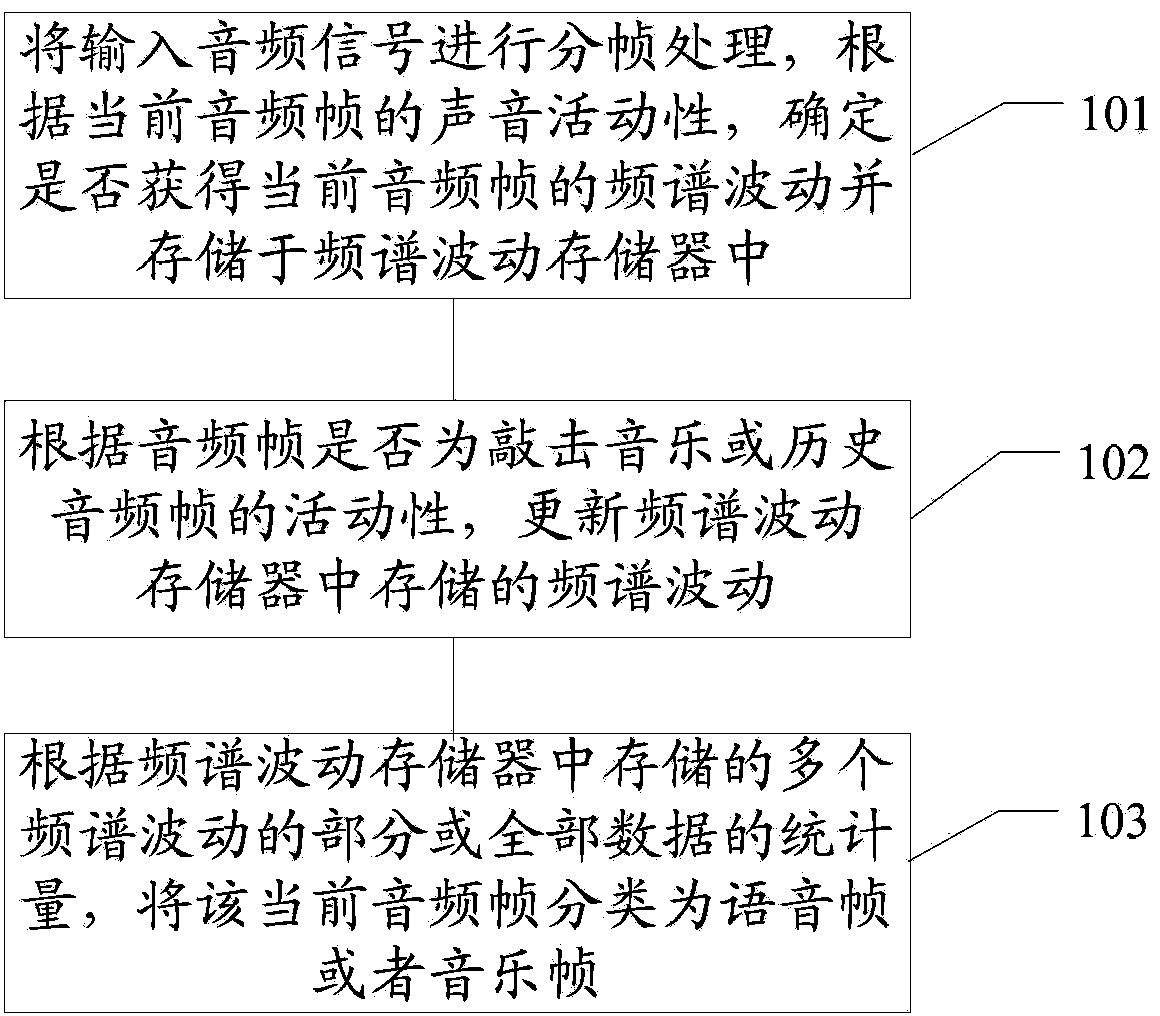
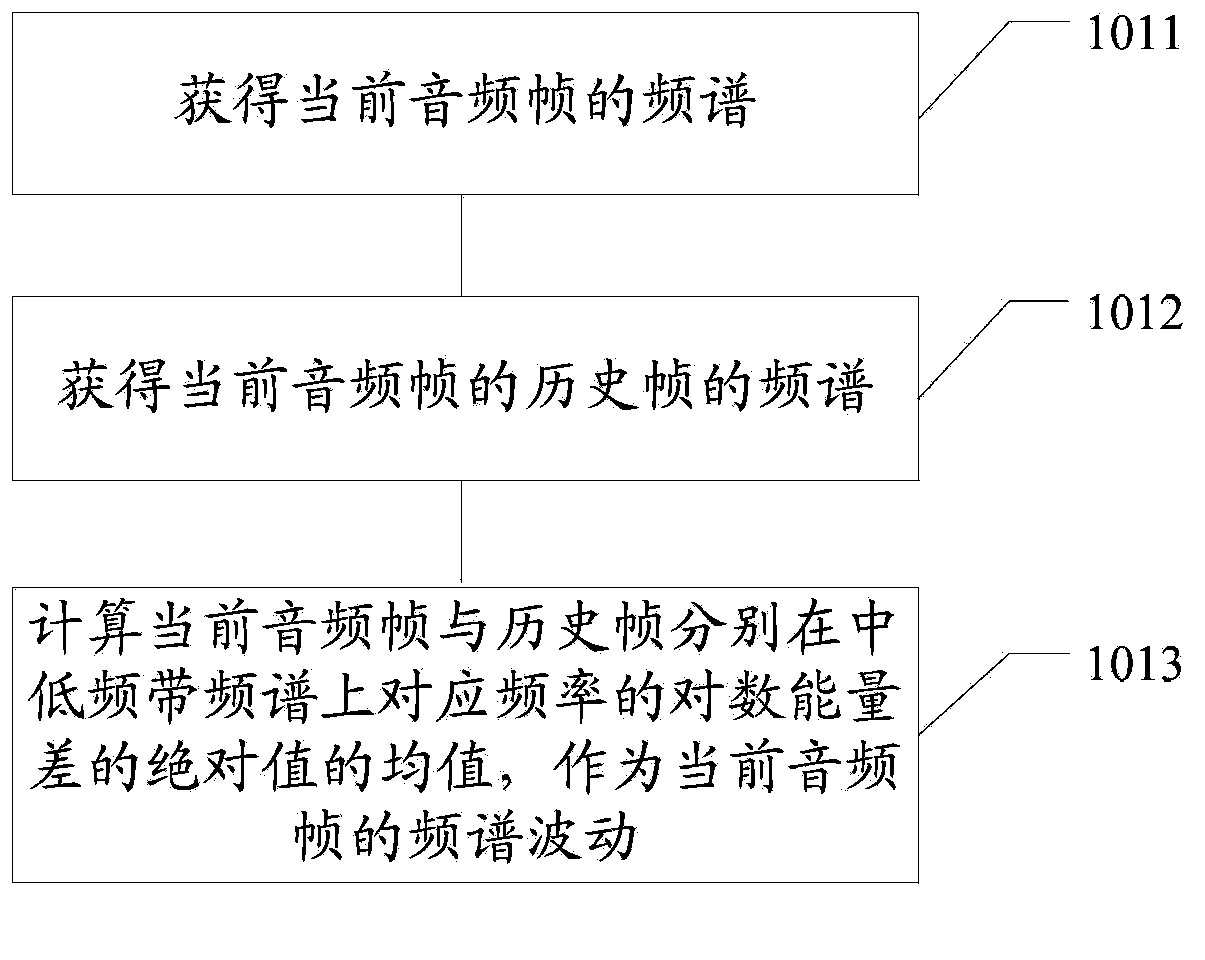
An audio signal classification method. The method comprises: according to the voice activity of a current audio frame, determining whether to obtain a frequency spectrum fluctuation of the current audio frame and store same in a frequency spectrum fluctuation memory (101); according to whether the audio frame is percussive music or the activity of a historical audio frame, updating the frequency spectrum fluctuation stored in the frequency spectrum fluctuation memory (102); and according to the statistics of some or all valid data of the frequency spectrum fluctuations stored in the frequency spectrum fluctuation memory, classifying the current audio frame as a voice frame or a music frame (103). Further provided is an audio signal classification device.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Audio signal classification apparatus and method used in wideband audio encoder and decoder
InactiveCN101393741AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumClassification methods
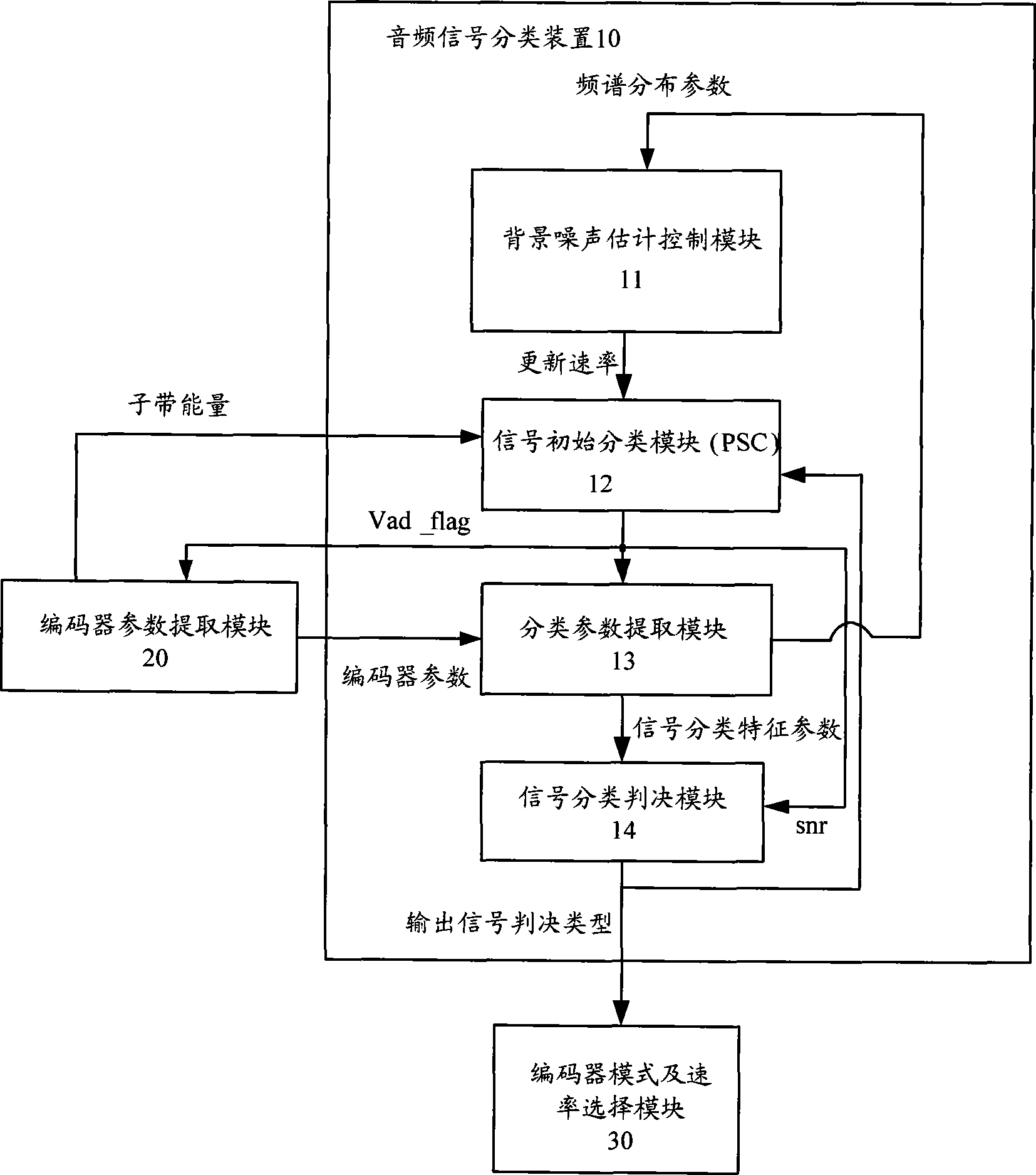
The invention discloses an audio signal sorting device in a broadband audio codec, wherein a background noise estimating and controlling module is used for receiving the spectral distribution parameter of a sorting parameter extracting module and sending the update rate to a signal initial sorting module; the signal initial sorting module is used for carrying out the initial sorting of the audio input signal according to the sub-band energy parameter and the update rate, and sending the initial sorting results to a sorted parameter extracting module and a signal sorting determining module; the sorted parameter extracting module is used for extracting and sorting the input signals, sending the sorting characteristic parameter of the acquired signal to the signal sorting determining module and feeding the acquired spectral distribution parameter back to the background noise estimating and controlling module at the same time; and the signal sorting determining module is used for setting the final sorting mark for the sorting characteristics parameter according the initial sorting results, wherein the final sorting mark is used for defining the determining sort of the output signal. The invention further discloses an audio signal sorting method in the broadband audio codec.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Support vector machine based classification method of base-band time-domain voice-frequency signal
InactiveCN102760444ARealize authenticationImplement classificationSpeech recognitionSingular value decompositionFrequency spectrum
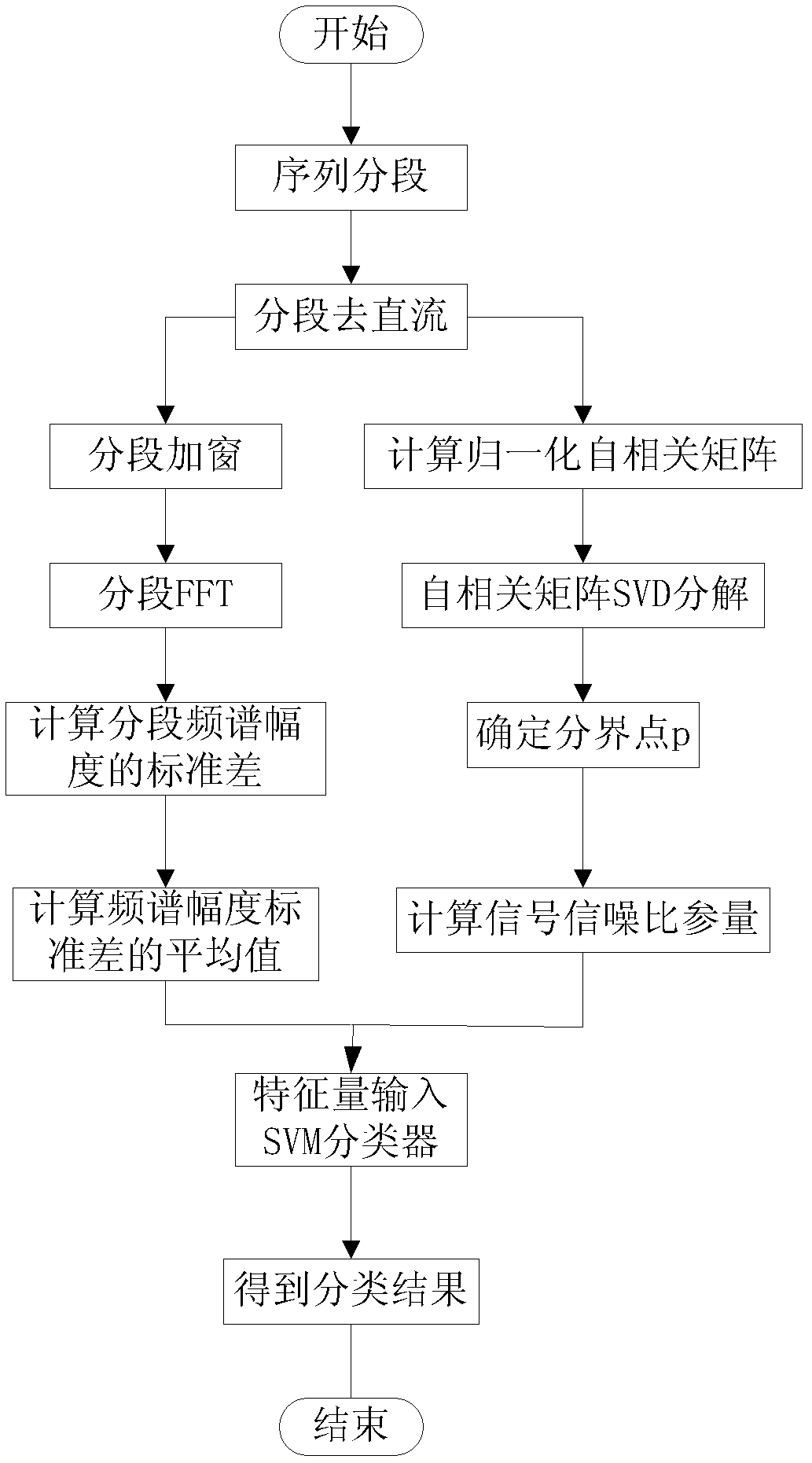
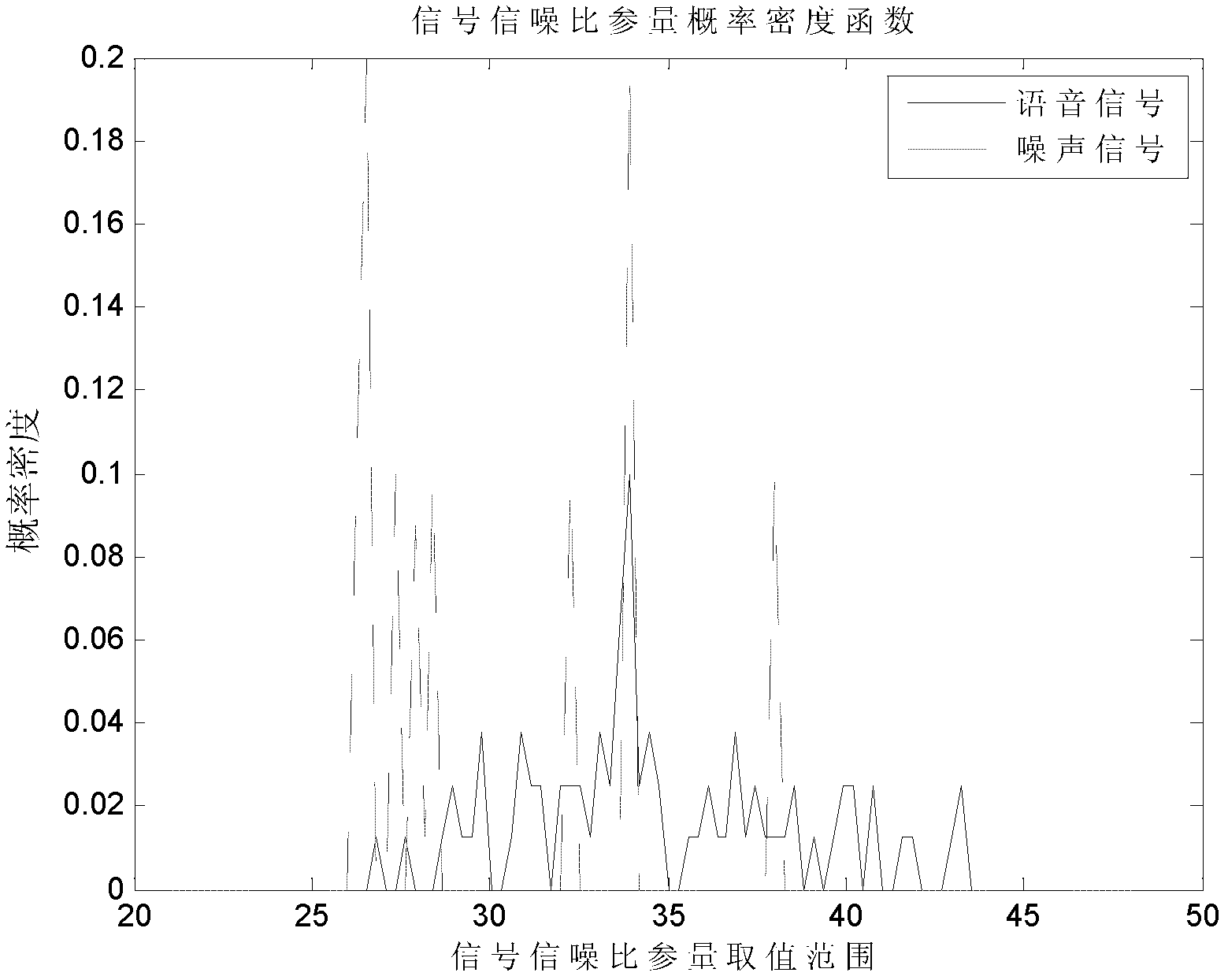
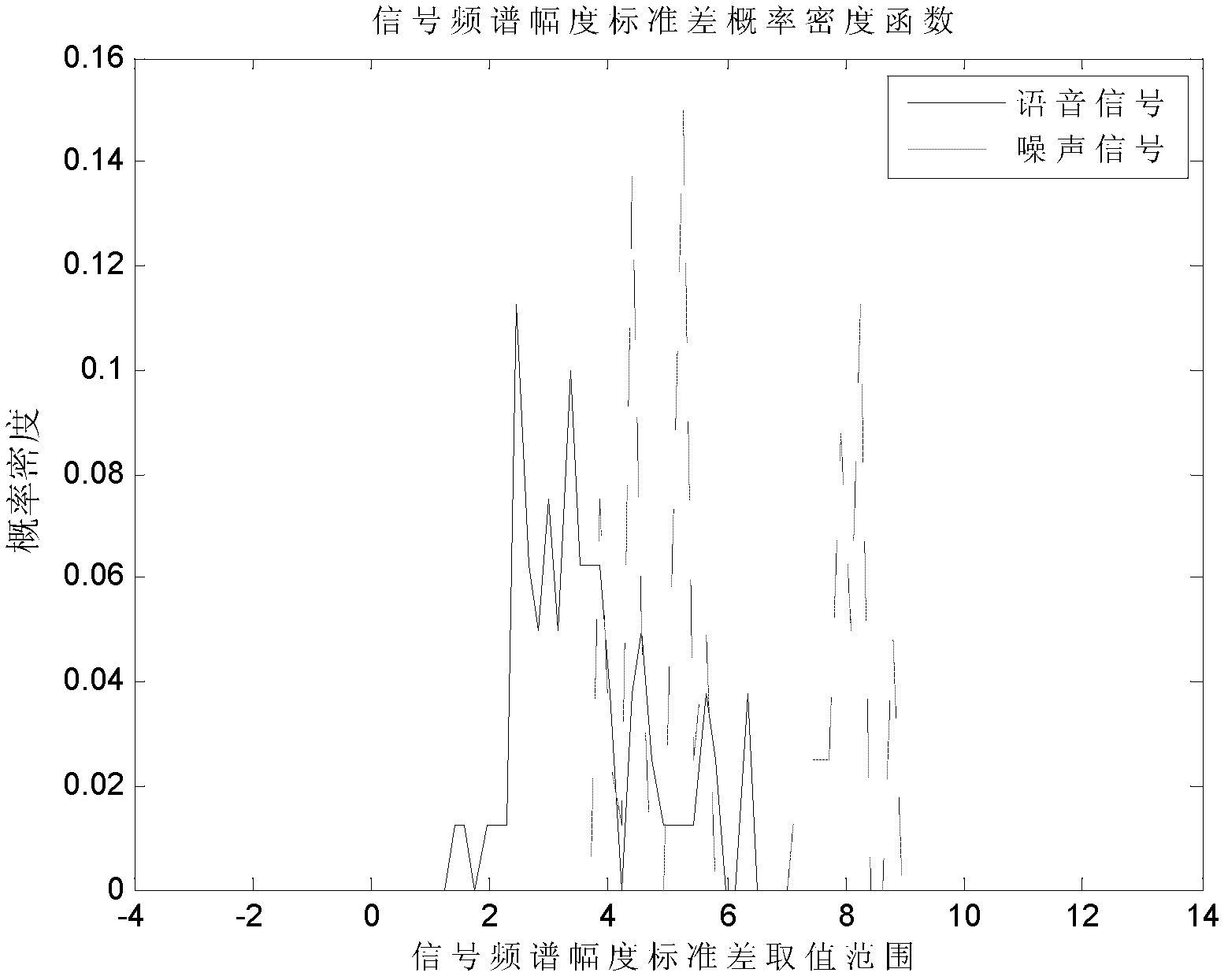
The invention relates to a support vector machine based classification method of base-band time-domain voice-frequency signals, comprising the following steps of: firstly segmenting a base-band time-domain voice-frequency signal sequence to obtain initial segmented subsequences; then respectively subtracting respective mean value from each initial segmented subsequence to obtain zero-mean-value segmented subsequences; then carrying out windowing treatment on each zero-mean-value segmented subsequence, respectively carrying out Fourier transformation treatment on results to obtain the spectrum amplitudes of the zero-mean-value segmented subsequences, and respectively solving the standard difference of each spectrum amplitude to obtain a characteristic quantity; sequentially combining the zero-mean-value segmented subsequences into a long subsequence according to an order; then calculating a normalized autocorrelation matrix of the long subsequence, and carrying out singular value decomposition on the normalized autocorrelation matrix to obtain a demarcation point of a subspace; then calculating the signal to noise ratio parameter of an other characteristic quantity; and finally sending an input vector composed of the two characteristic quantities into a trained SVM (Support Vector Machine) classifier to identify the classification of base-band time-domain voice-frequency signals and distinguish a voice signal and a noise signal.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for classifying videos based on audio signals
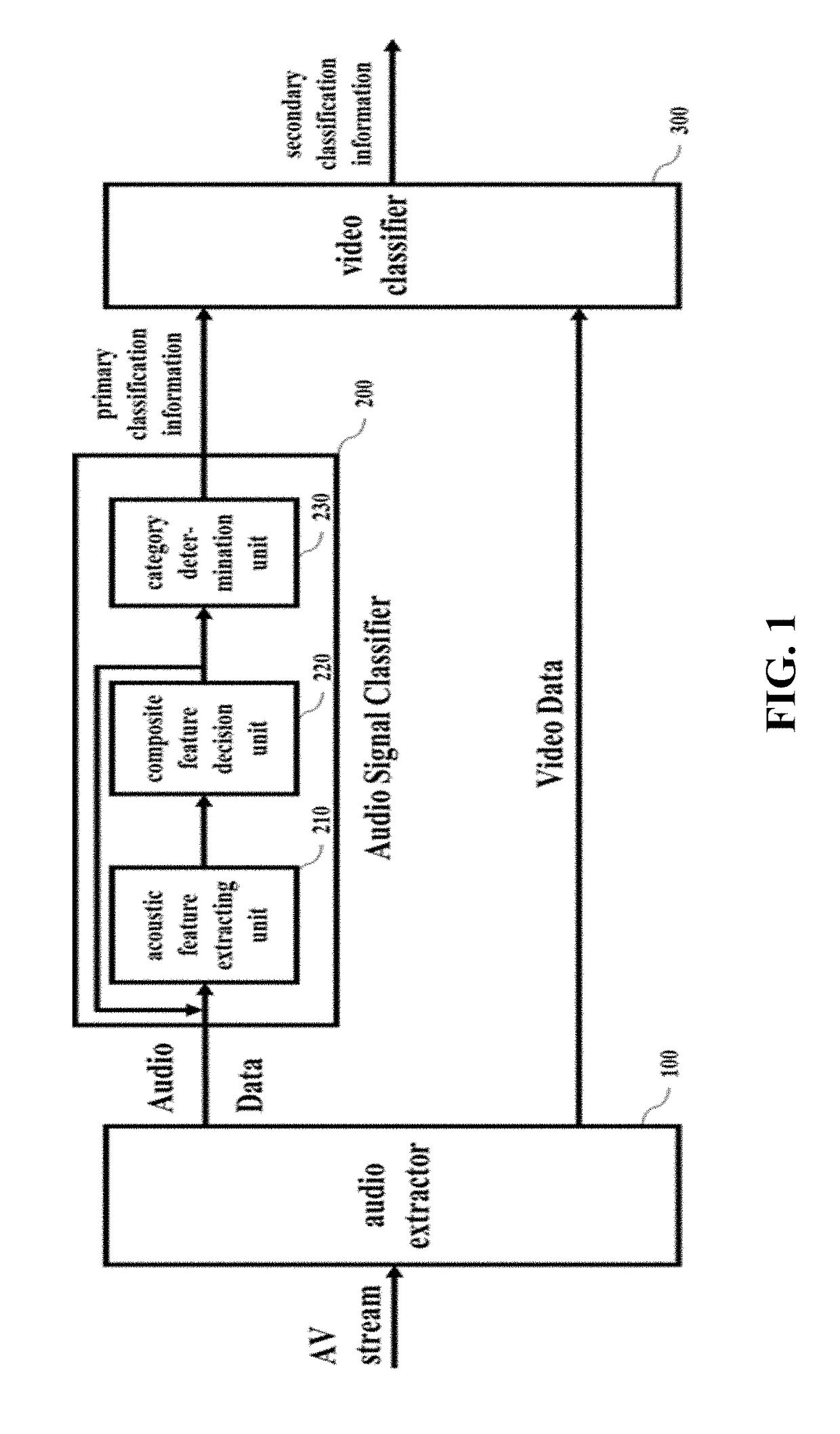
InactiveUS20180144194A1Improve accuracyImprove classificationSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAudio signal flow
An apparatus for classifying videos according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: an audio extractor for extracting an audio signal upon receiving video information; an audio signal classifier for outputting primary classification information from the audio signal; and a video classifier for performing secondary classification on video data of the video information using the primary classification information.
Owner:PARK JINSOO
Apparatus and method for detecting speech and music portions of an audio signal
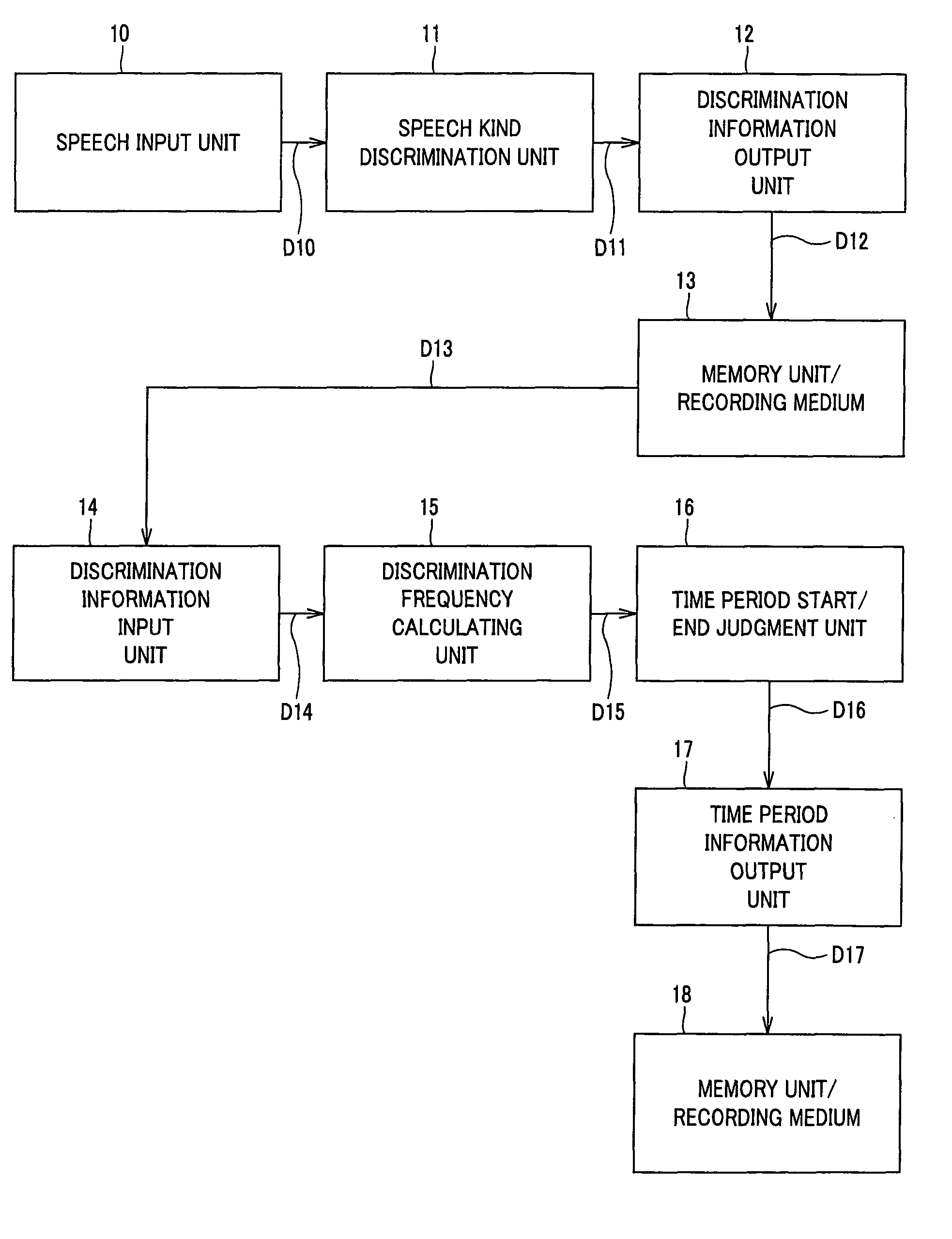
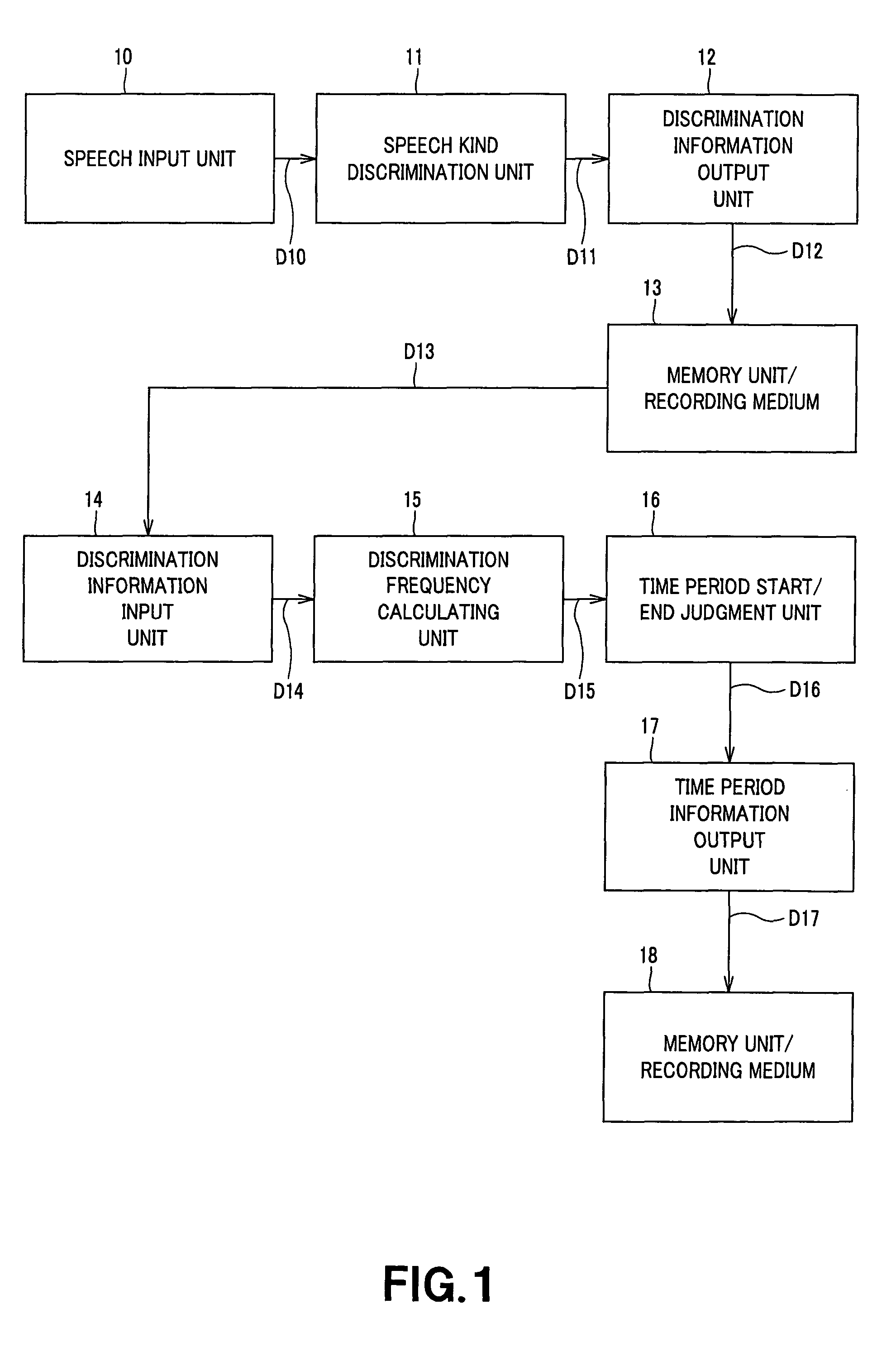
InactiveUS8195451B2Accurate detectionElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlUnit of timeComputer science
In an information detecting apparatus (1), a speech kind discrimination unit (11) discriminates and classifies an audio signal at an information source into kind (category) such as music or speech, etc. on a predetermined time basis, and a memory unit / recording medium (13) records discrimination information thereof. A discrimination frequency calculating unit (15) calculates, on a predetermined time basis, discrimination frequency every kind at a predetermined time period longer than the time unit. A time period start / end judgment unit (16) is operative so that in the case where discrimination frequency of a certain kind becomes equal to a predetermined threshold value or more for the first time, and the state where the discrimination frequency is the threshold value or more is continued by a predetermined time, start of continuous time period of the kind is detected, and in the case where the discrimination frequency becomes equal to the predetermined threshold value or less for the first time, and the state where the discrimination frequency is the threshold value or less is continued by a predetermined time, end of continuous time period of the kind is detected.
Owner:SONY CORP
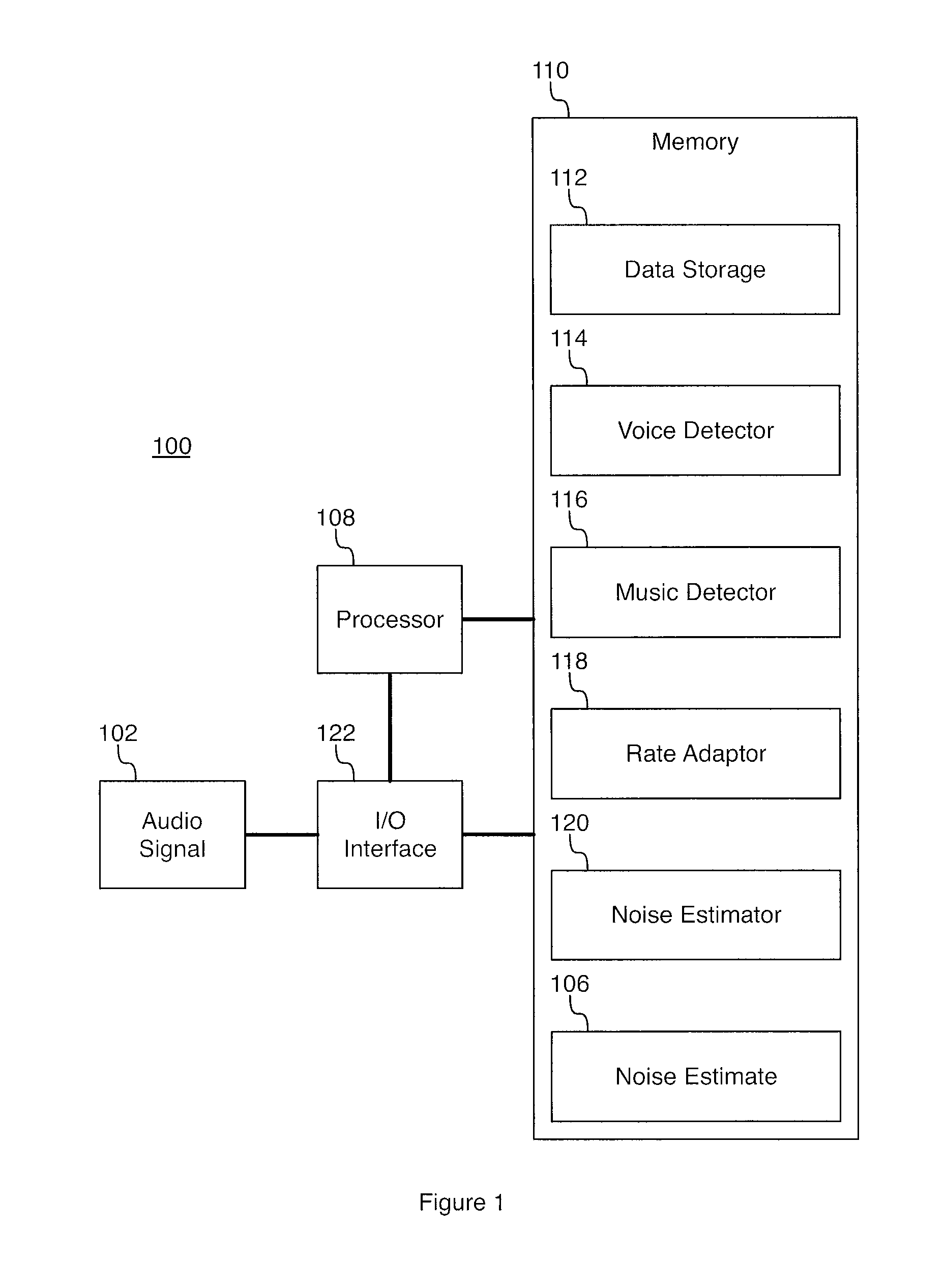
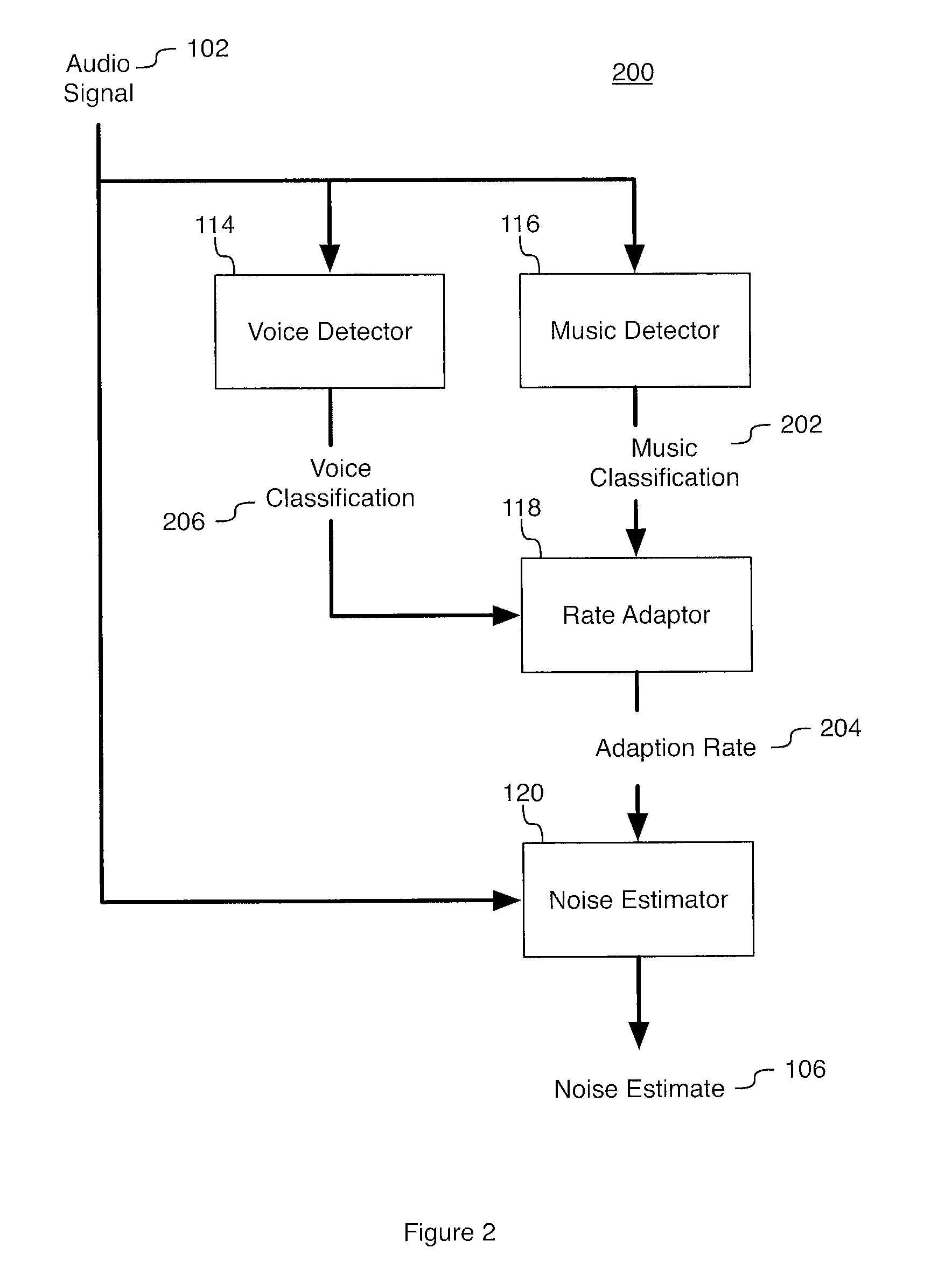
System and method for noise estimation with music detection
In a system and method for noise estimation with music detection described herein provides for generating a music classification for music content in an audio signal. The music detector may classify the audio signal as music or non-music. The non-music signal may be considered to be signal and noise. An adaption rate may be adjusted responsive to the generated music classification. A noise estimate is calculated applying the adjusted adaption rate. The system and method may mitigate the noise modeling algorithms being misled by the music components.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Method of and System For Classification of an Audio Signal
InactiveUS20080243512A1Easy to identifySimple methodElectrophonic musical instrumentsCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingFeature vectorAudio frequency
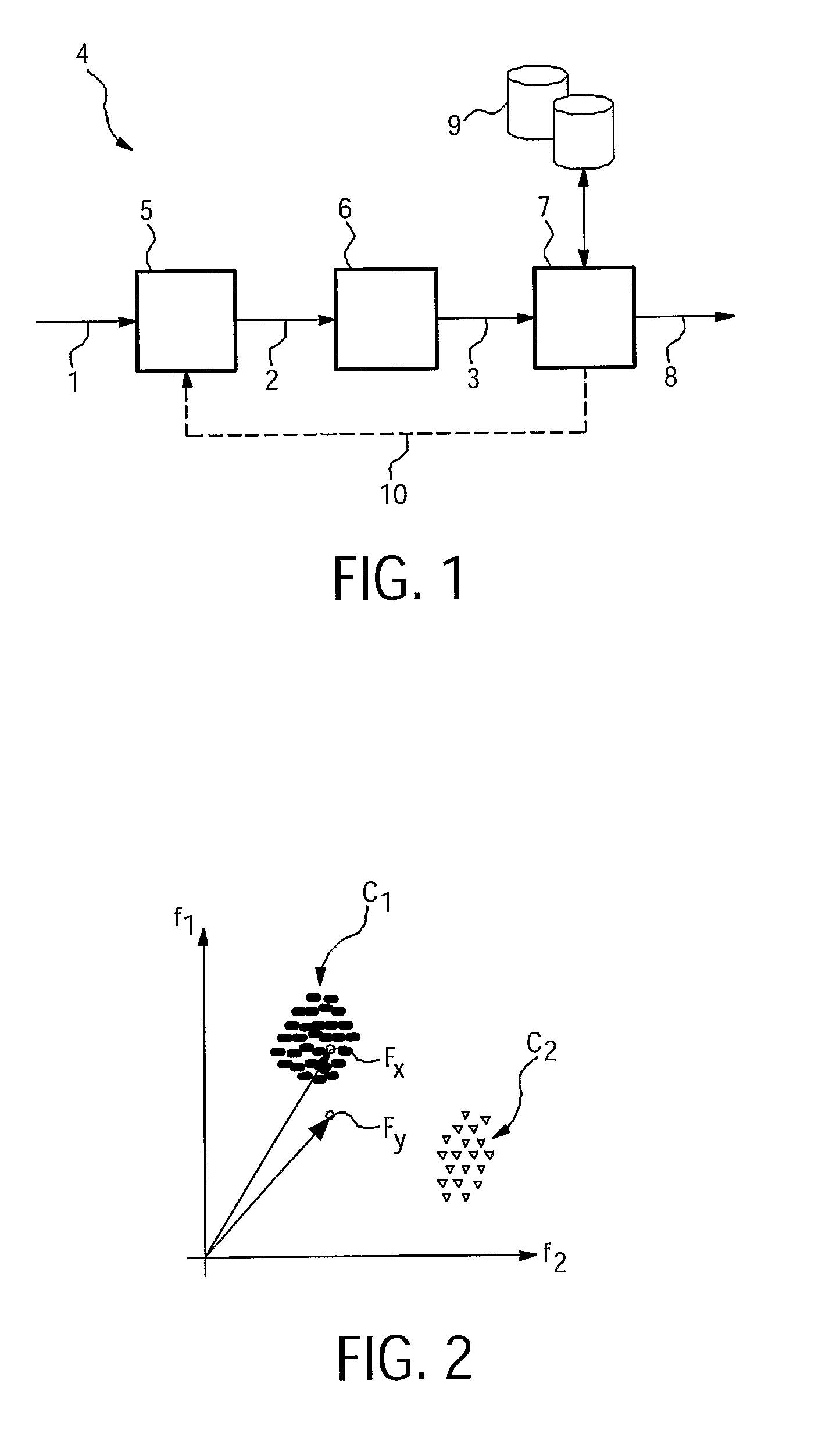
The invention describes a method of classifying an audio input signal (1), said method comprising the steps of extracting a number of features (2) of the audio input signal (1), deriving a feature vector (3) for the input audio signal (1) based on these features (2), and determining the probability that the feature vector (3) for the input audio signal (1) falls within any of a number of classes (C1, C2, . . . , Cn), each corresponding to a particular release-date information.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
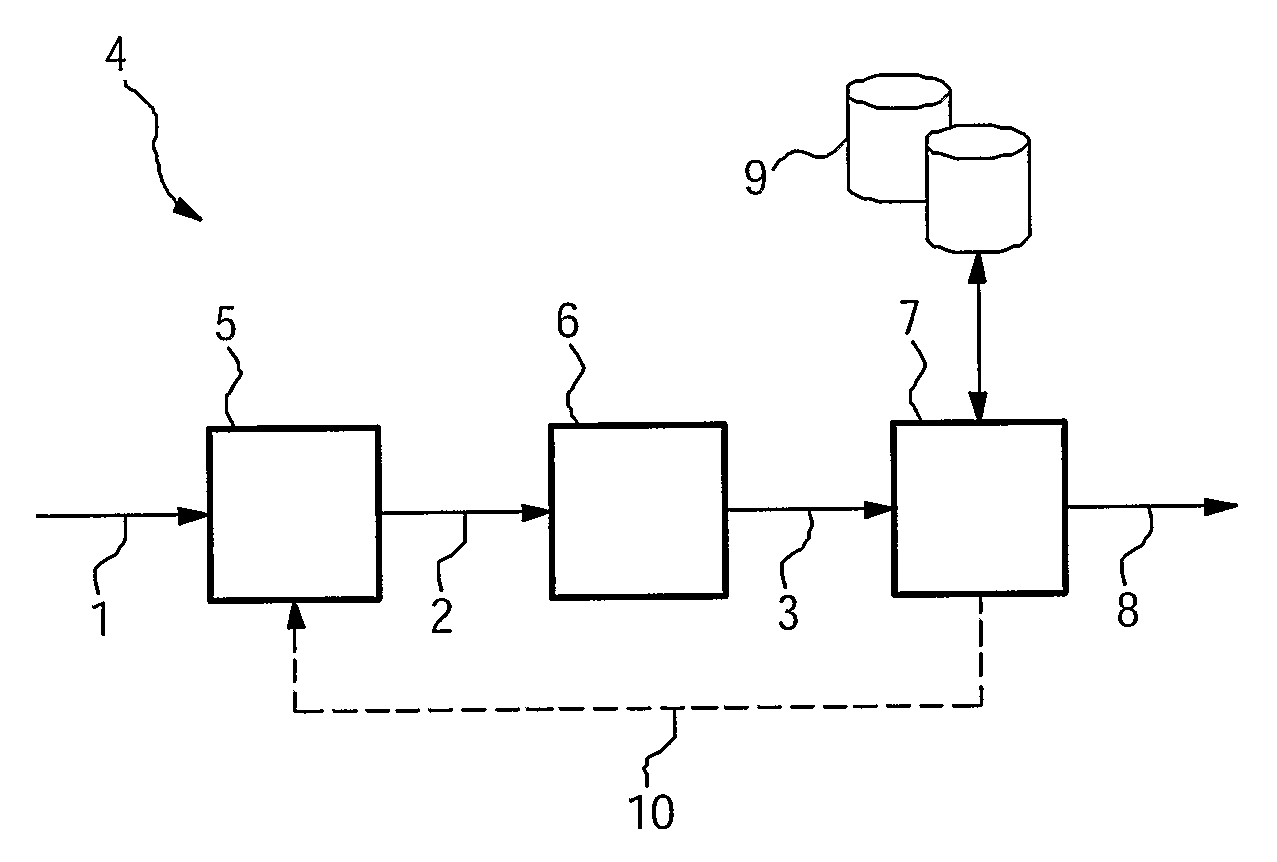
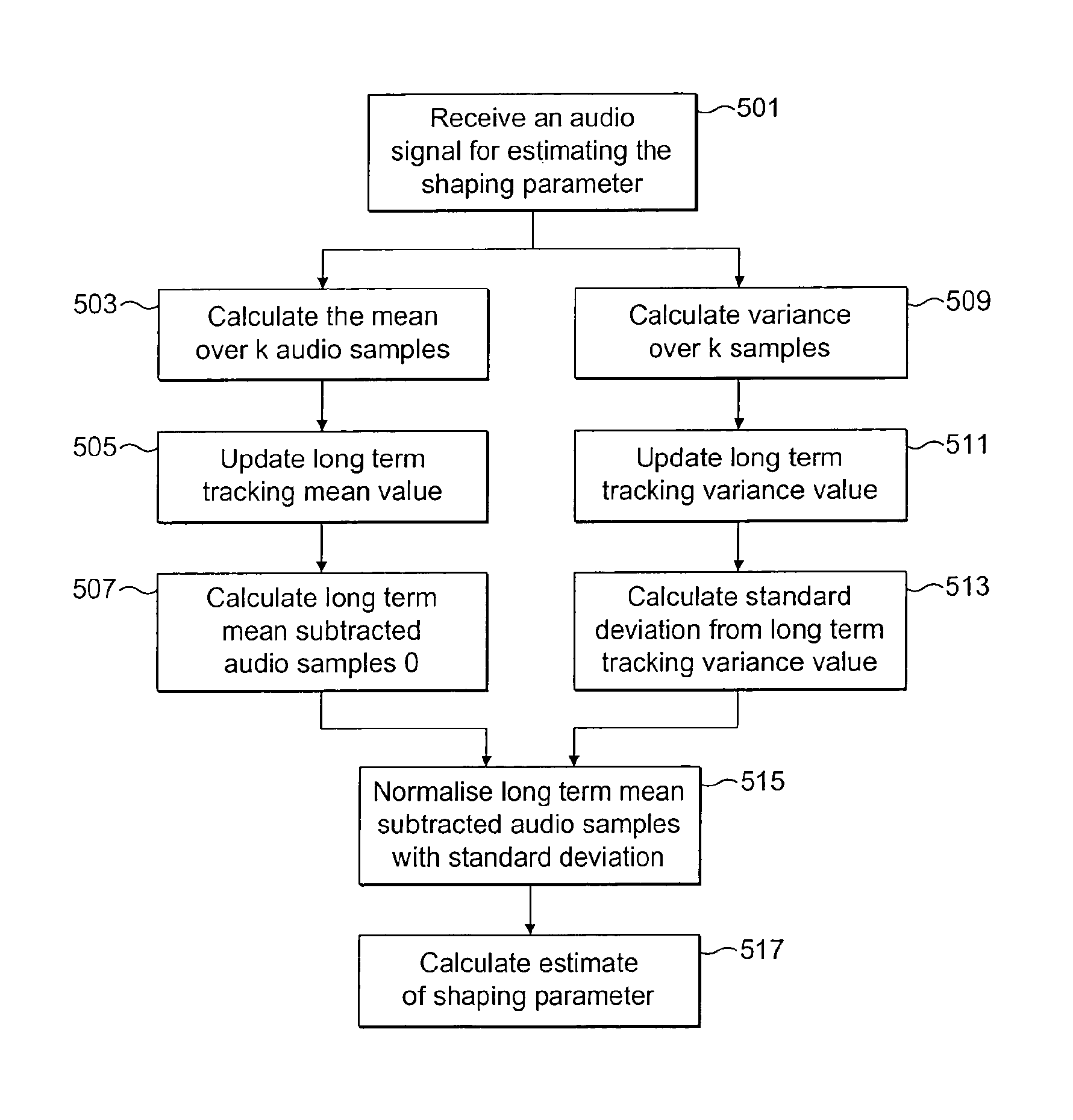
Audio signal classification by shape parameter estimation for a plurality of audio signal samples
ActiveUS8856049B2Efficiently and more accurately encode audio signalEfficiently typeDigital computer detailsDigital dataDecision takingAudio frequency
An apparatus for classifying an audio signal configured to: estimate at least one shaping parameter value for a plurality of samples of the audio signal; generate at least one audio signal classification value by mapping the at least one shaping parameter value to one of at least two interval estimates; and determine at least one audio signal classification decision based on the at least one audio signal classification value.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Speech and music discriminator for multi-media application
InactiveUS8340964B2Improve convenienceSubstation equipmentAutomatic exchangesTelecommunications linkVoice communication
The present invention relates to means and methods of classifying speech and music signals in voice communication systems, devices, telephones, and methods, and more specifically, to systems, devices, and methods that automate control when either speech or music is detected over communication links. The present invention provides a novel system and method for monitoring the audio signal, analyze selected audio signal components, compare the results of analysis with a pre-determined threshold value, and classify the audio signal either as speech or music.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
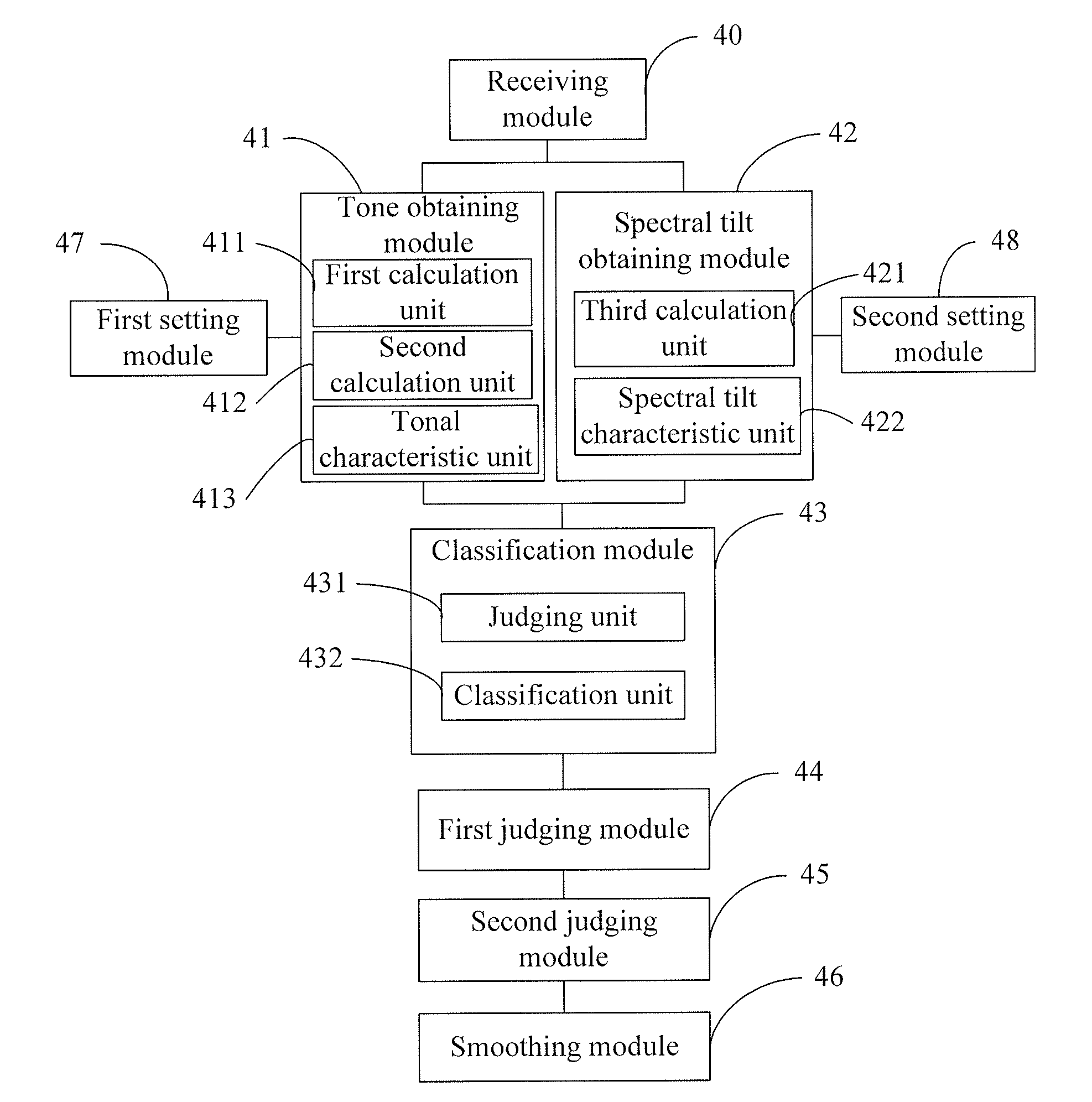
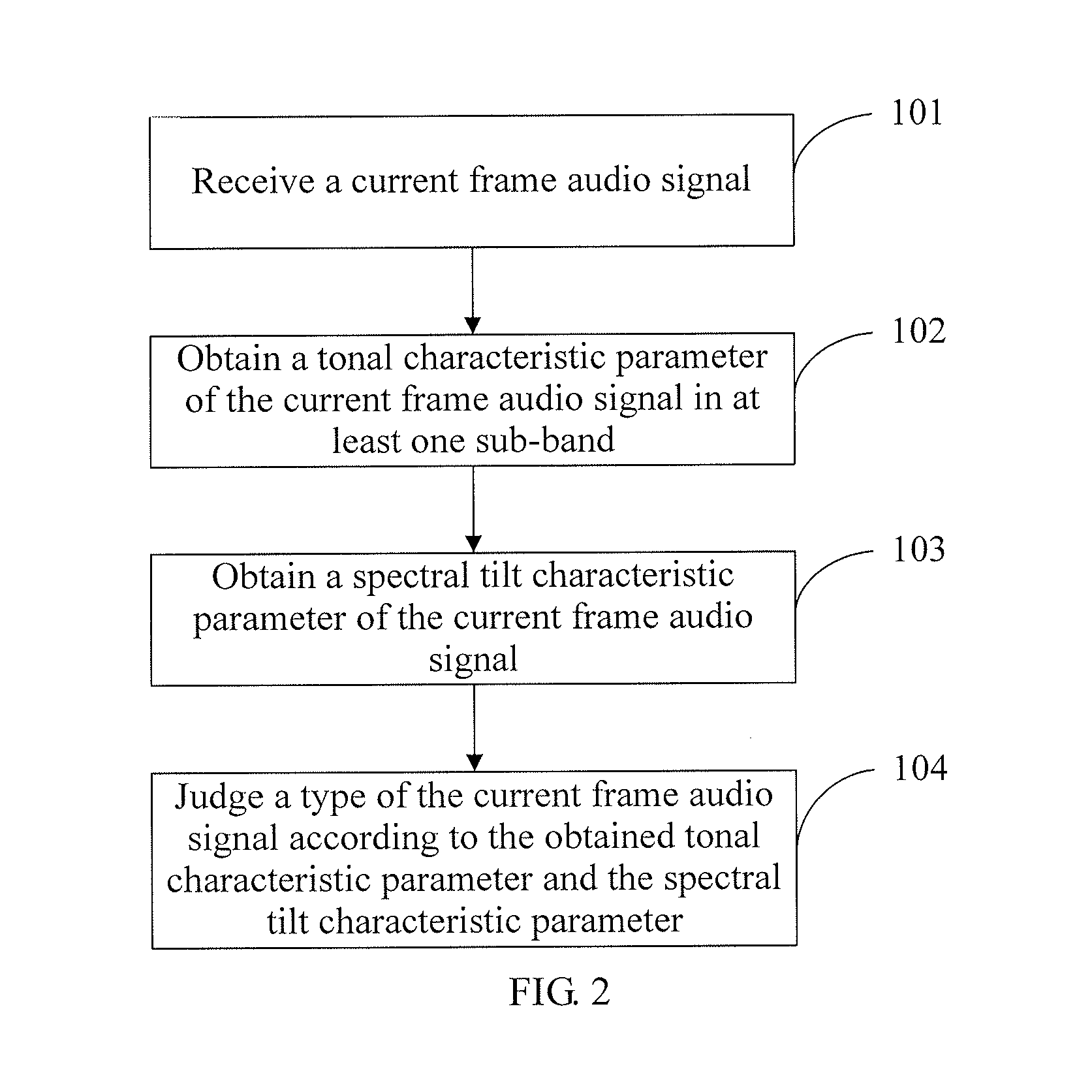
Method and device for audio signal classification
ActiveUS20120016677A1High complexityReduce complexityElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisTyping ClassificationAcquired characteristic
The present invention discloses a method and a device for audio signal classification, and relates to the field of communications technologies, which solve a problem of high complexity of type classification of audio signals in the prior art. In the present invention, after an audio signal to be classified is received, a tonal characteristic parameter of the audio signal to be classified, where the tonal characteristic parameter of the audio signal to be classified is in at least one sub-band, is obtained, and a type of the audio signal to be classified is determined according to the obtained characteristic parameter. The present invention is mainly applied to an audio signal classification scenario, and implements audio signal classification through a relatively simple method.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
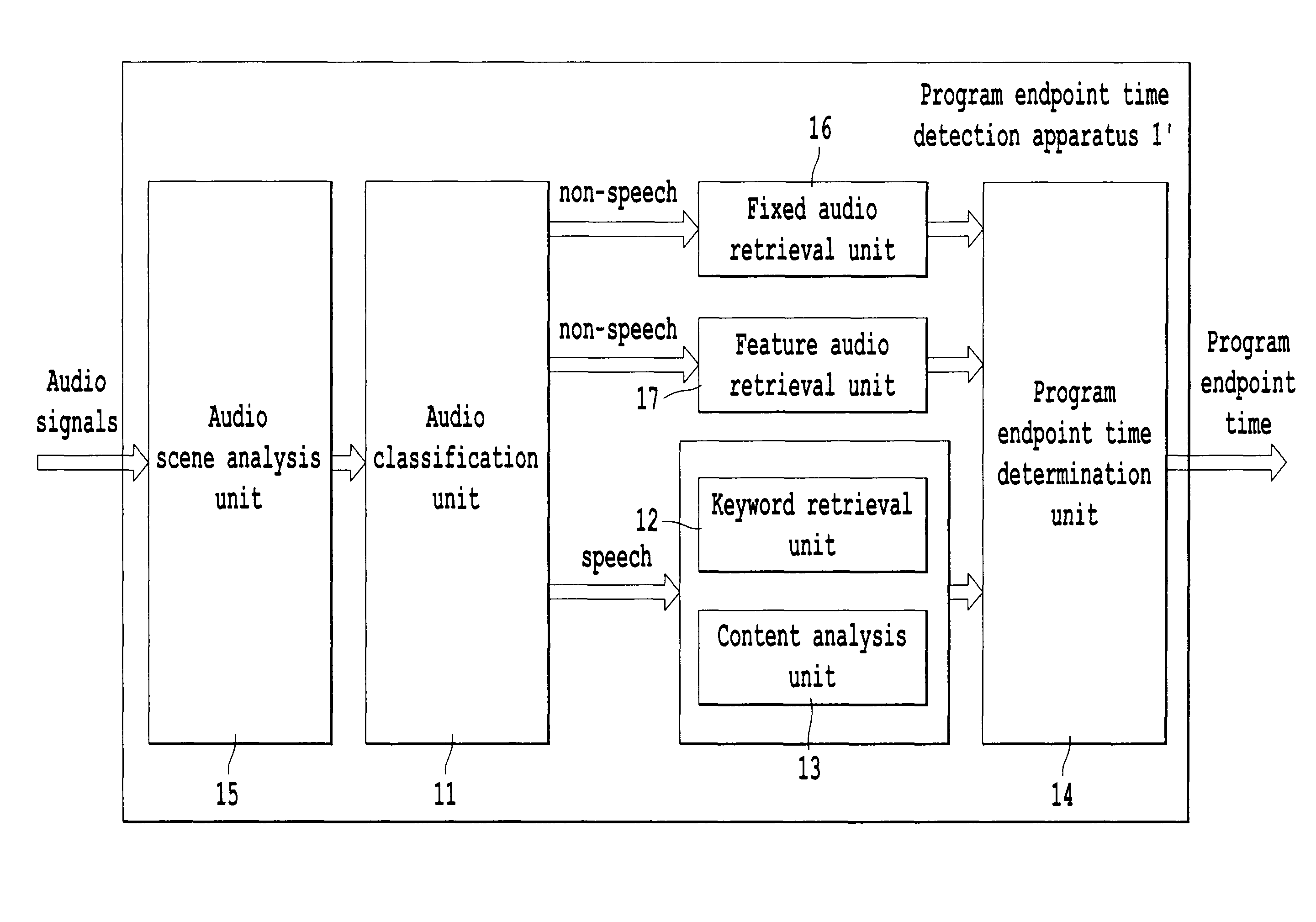
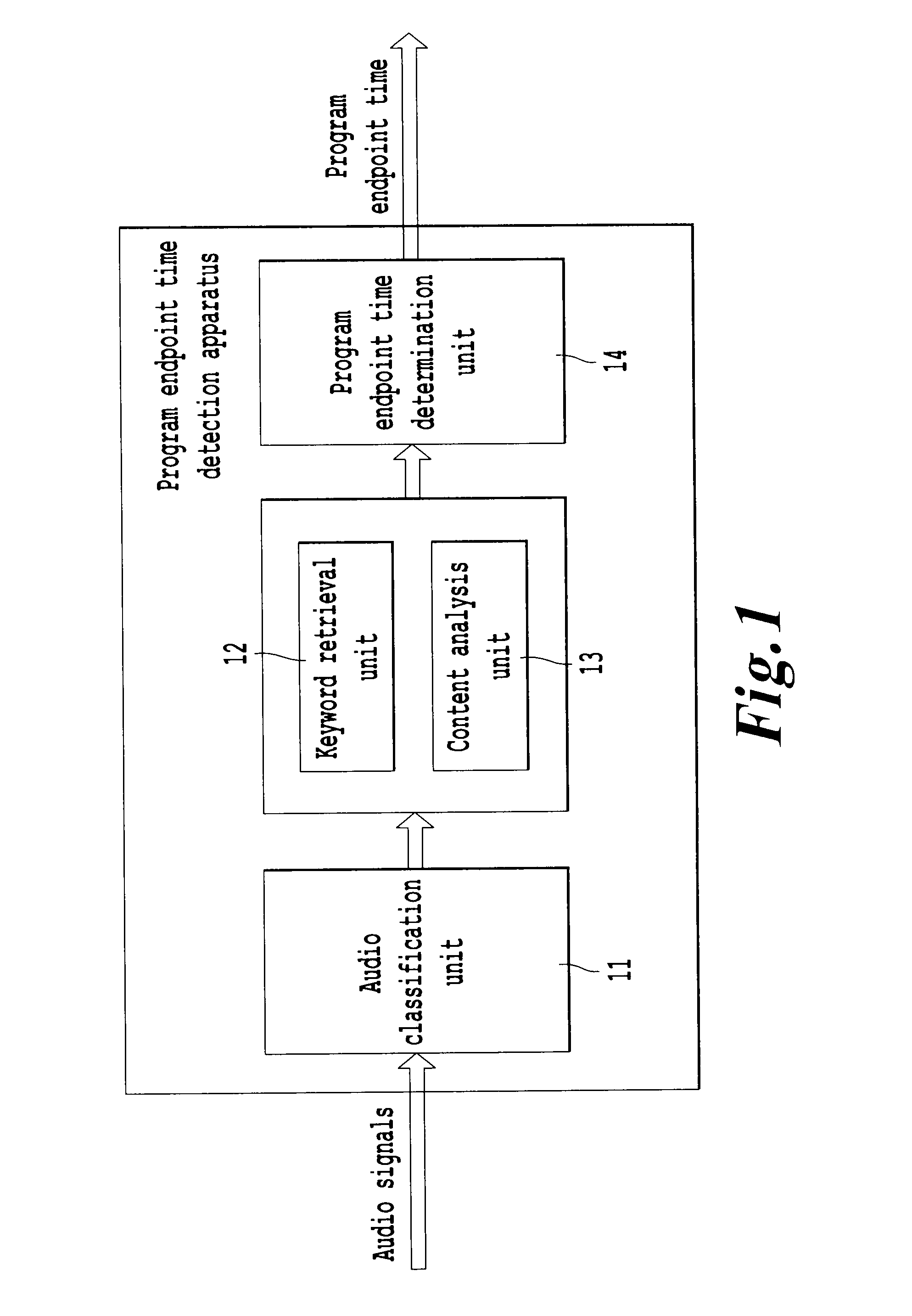
Program endpoint time detection apparatus and method, and program information retrieval system
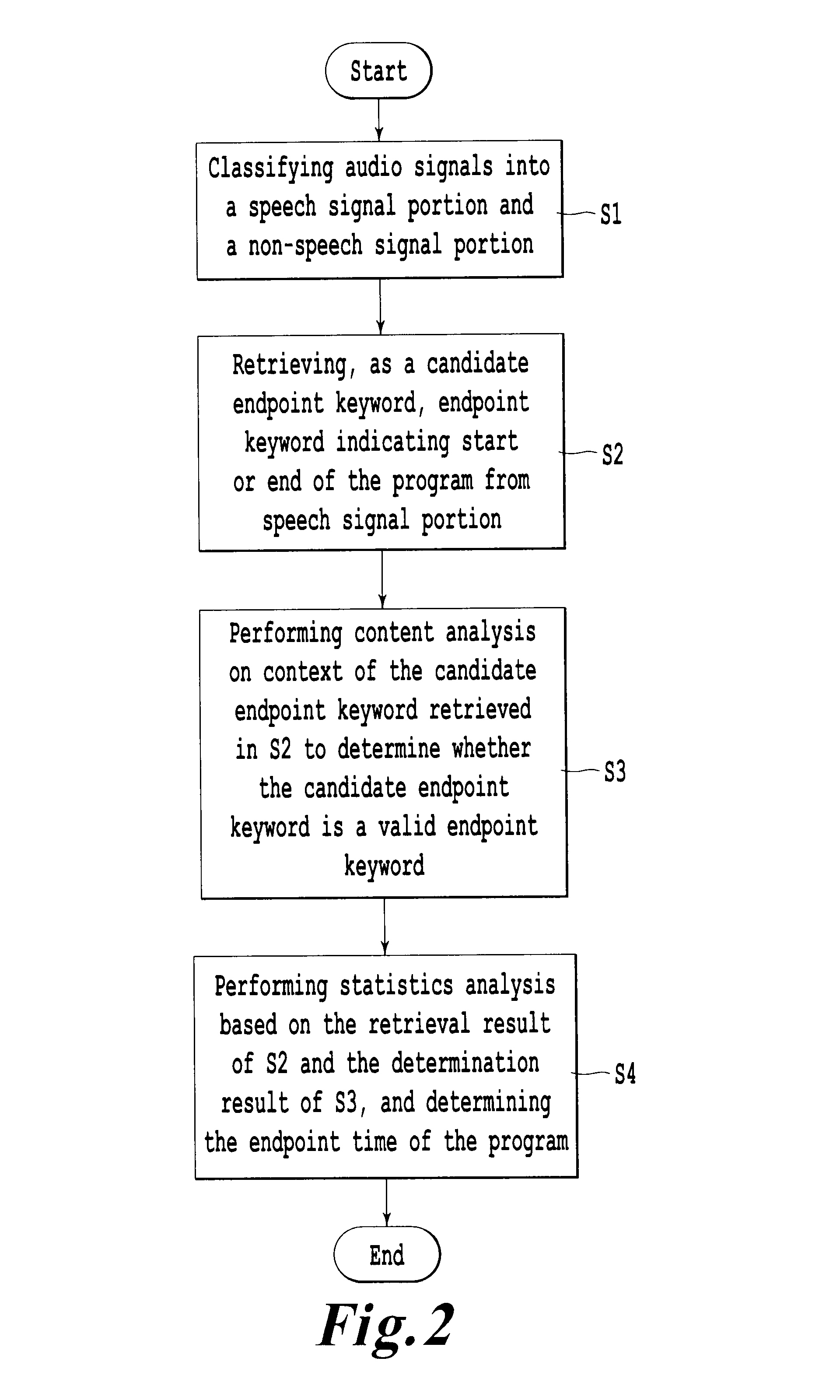
InactiveUS9009054B2Rapidly and easily findExtraction of informationMetadata audio data retrievalSpeech analysisStatistical analysisAudio frequency
This invention relates to retrieval for multimedia content, and provides a program endpoint time detection apparatus for detecting an endpoint time of a program by performing processing on audio signals of said program, comprising an audio classification unit for classifying said audio signals into a speech signal portion and a non-speech signal portion; a keyword retrieval unit for retrieving, as a candidate endpoint keyword, an endpoint keyword indicating start or end of the program from said speech signal portion; a content analysis unit for performing content analysis on context of the candidate endpoint keyword retrieved by the keyword retrieval unit to determine whether the candidate endpoint keyword is a valid endpoint keyword; and a program endpoint time determination unit for performing statistics analysis based on the retrieval result of said keyword retrieval unit and the determination result of said content analysis unit, and determining the endpoint time of the program. In addition, this invention also provides a program information retrieval system. With present invention, program information regarding a program attended by user can be rapidly obtained.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Audio signal classification method and device
ActiveCN106409310AImprove recognition rateFew parametersSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
An embodiment of the invention discloses an audio signal classification method and device, which are used for carry out classification on input audio signals. The method comprises the following steps: according to sound activity of a current audio frame, determining whether obtaining spectrum fluctuation of the current audio frame and storing the spectrum fluctuation to a spectrum fluctuation storage device, wherein the spectrum fluctuation represents energy fluctuation of frequency spectrum of the audio signals; according to the result of whether the audio frame is a percussion music or the activity of a history audio frame, updating the spectrum fluctuation stored in the spectrum fluctuation storage device; and according to statistics of a part of or all of effective data of the spectrum fluctuation stored in the spectrum fluctuation storage device, classifying the current audio frame into a speech frame or a music frame.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for classifying audio signal into fast signal or slow signal
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Audio signal quality enhancement apparatus and method
An audio signal quality enhancement apparatus and method. The apparatus includes a pitch calculating unit to extract a pitch period of an audio signal, a frequency domain transforming unit to transform the audio signal to a frequency domain, a frequency band dividing unit to classify the transformed audio signal into audio signals for each of the plurality of frequency bands based on the extracted pitch period, and a pitch enhancement unit to determine a gain based on a volume of the transformed audio signal, and to generate an output signal by multiplying each of the classified audio signals with respect to each of the plurality of frequency bands by the gain, thereby enhancing quality of the audio signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for audio signal classification
An apparatus comprising at least one processor and at least one memory including computer program code the at least one memory and the computer program code configured to, with the at least one processor, cause the apparatus at least to perform determining a signal identification value for an audio signal, determining at least one noise level value for the audio signal, comparing the signal identification value against a signal identification threshold and each of the at least one noise level value against an associated noise level threshold, and identifying the audio signal dependent on the comparison.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Coding apparatus and decoding apparatus
ActiveUS9105264B2Suppress extreme increase in bit rateImprove efficiencySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsMultiplexingGranularity
A coding apparatus which suppresses an extreme increase in a bit rate, includes: a downmixing and coding unit (301) that downmixes audio signals that have been provided, to reduce the number of channels to be fewer than the number of the provided audio signals, and to code the downmix signals; an object parameter extracting unit (304) that extracts parameters indicating correlation between the audio signals; and a multiplexing circuit (309) that multiplexes the extracted parameters with the generated downmix coded signals. The object parameter extracting unit (304) includes: an object classifying unit (305) that classifies each of the provided audio signals into a predetermined one of types based on audio characteristics; and an object parameter extracting circuit (308) that extracts parameters using a temporal granularity and a frequency granularity each of which is determined for a corresponding one of the types.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
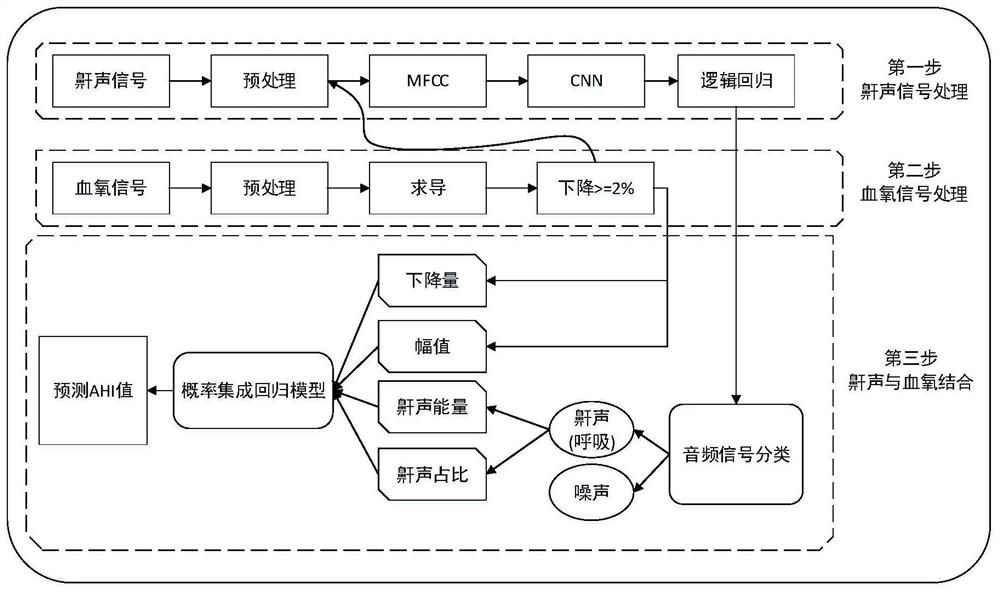
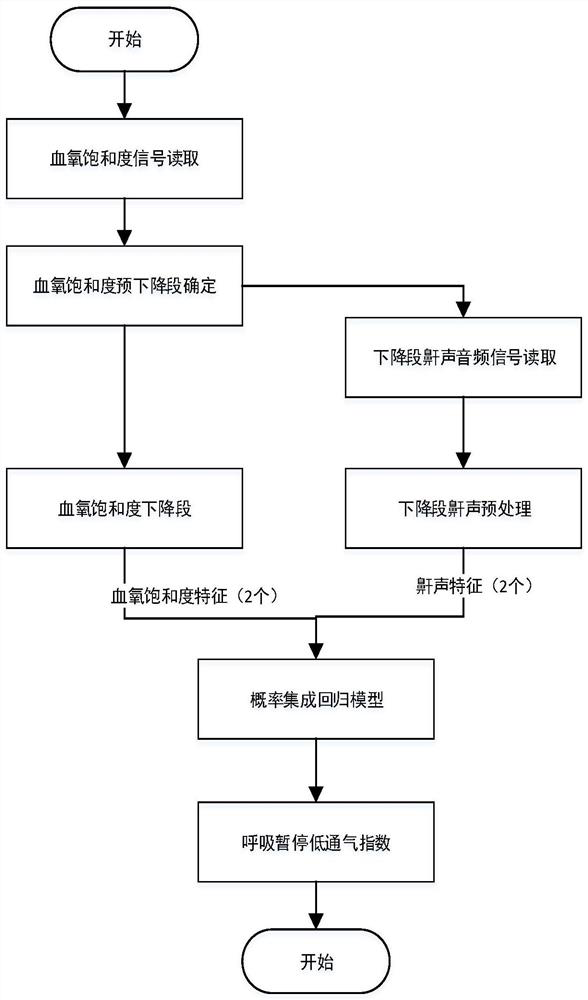
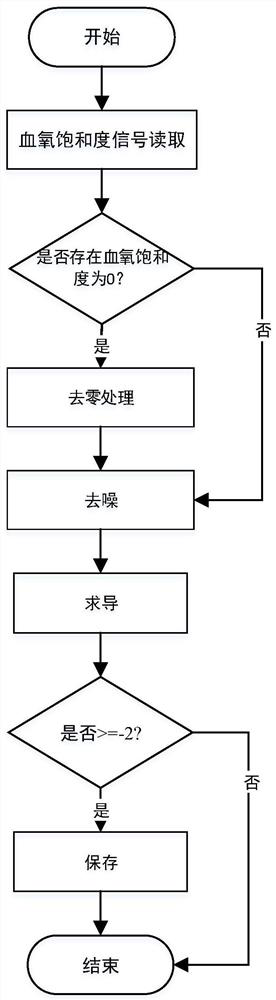
OSAHS diagnostic method based on probability integrated regression model
ActiveCN111685774ARelieve pressureAddressing PSG MonitoringRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsHypopneaNerve network
The invention discloses an OSAHS diagnostic method based on a probability integrated regression model. The method comprises the steps that blood oxygen saturation is collected and subjected to preprocessing, and a snore signal is found according to the time corresponding to a descending segment of the blood oxygen saturation; feature extraction is conducted by using the Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficient, the features are input into a convolutional neural network, the audio signals of the descending section are classified into snore, breath and noise by combining a logistic regression model, and feature extraction is conducted on the processed snore and blood oxygen saturation; and finally, the probability integrated regression model is used for automatically predicting the sleep apnea hypopnea index of a patient to diagnose the OSAHS. Thus the patient can preliminarily detect the sleep state at home, the problem that the OSAHS patient queues in a hospital for PSG monitoring is solved,and meanwhile the pressure of doctors is relieved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
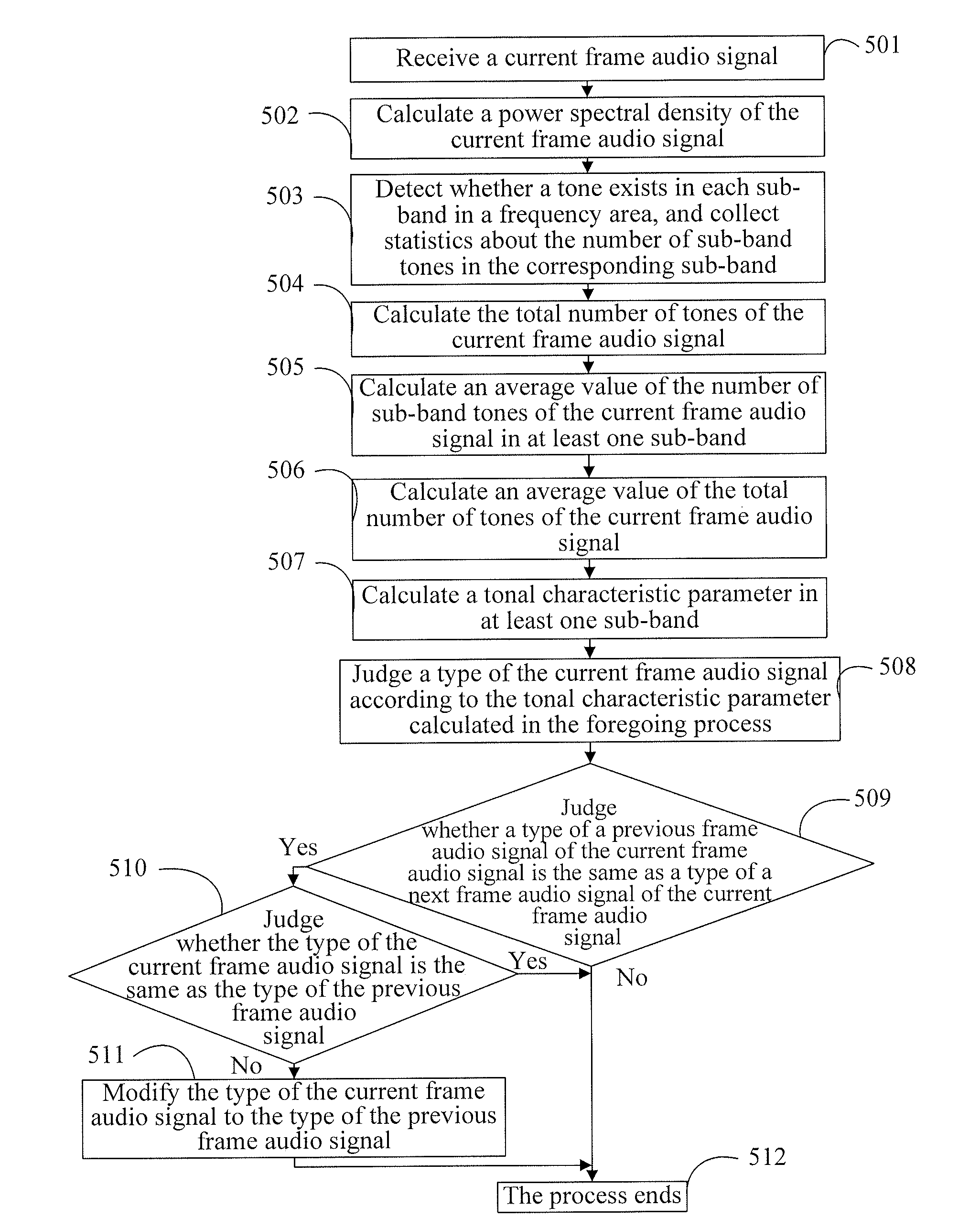
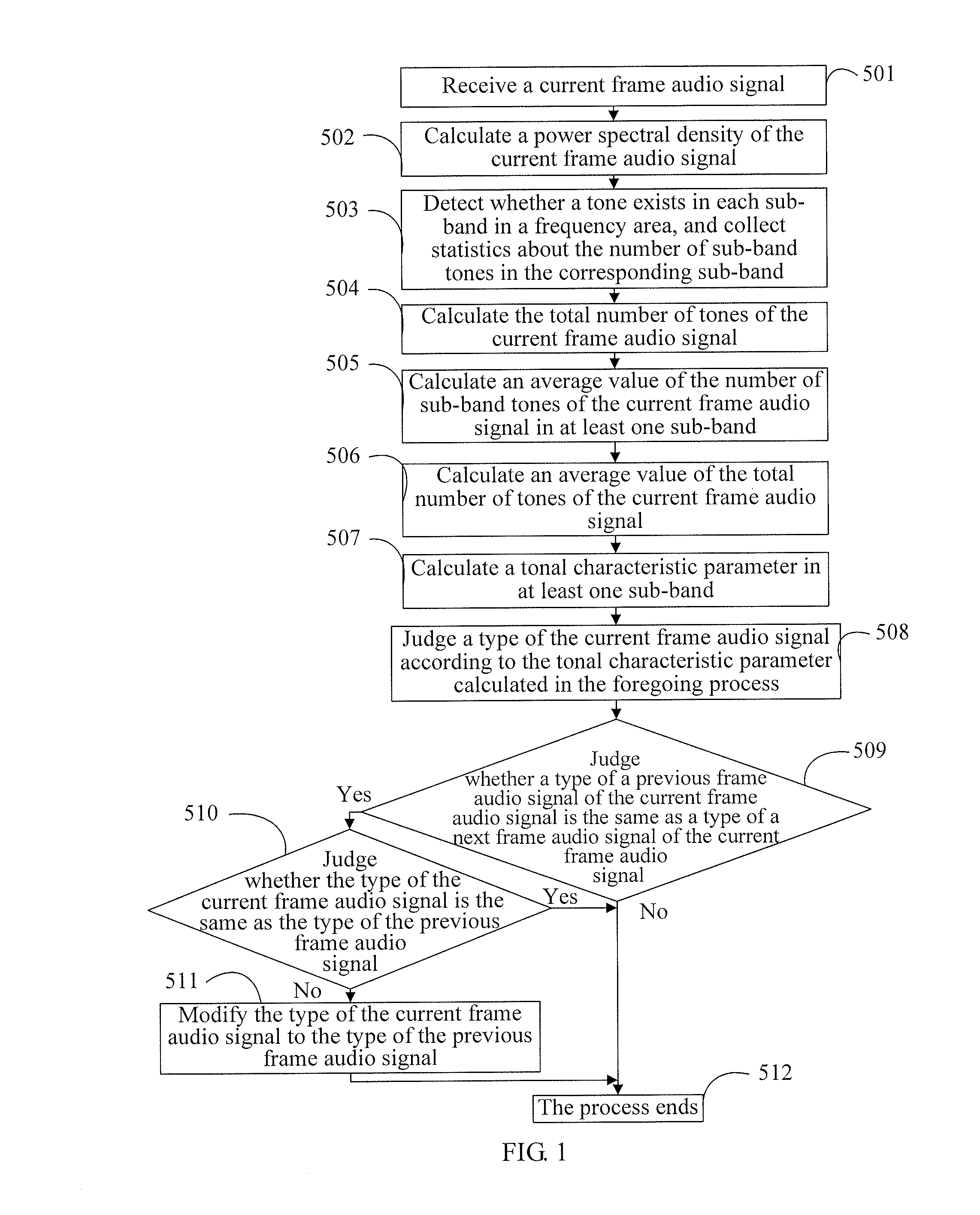
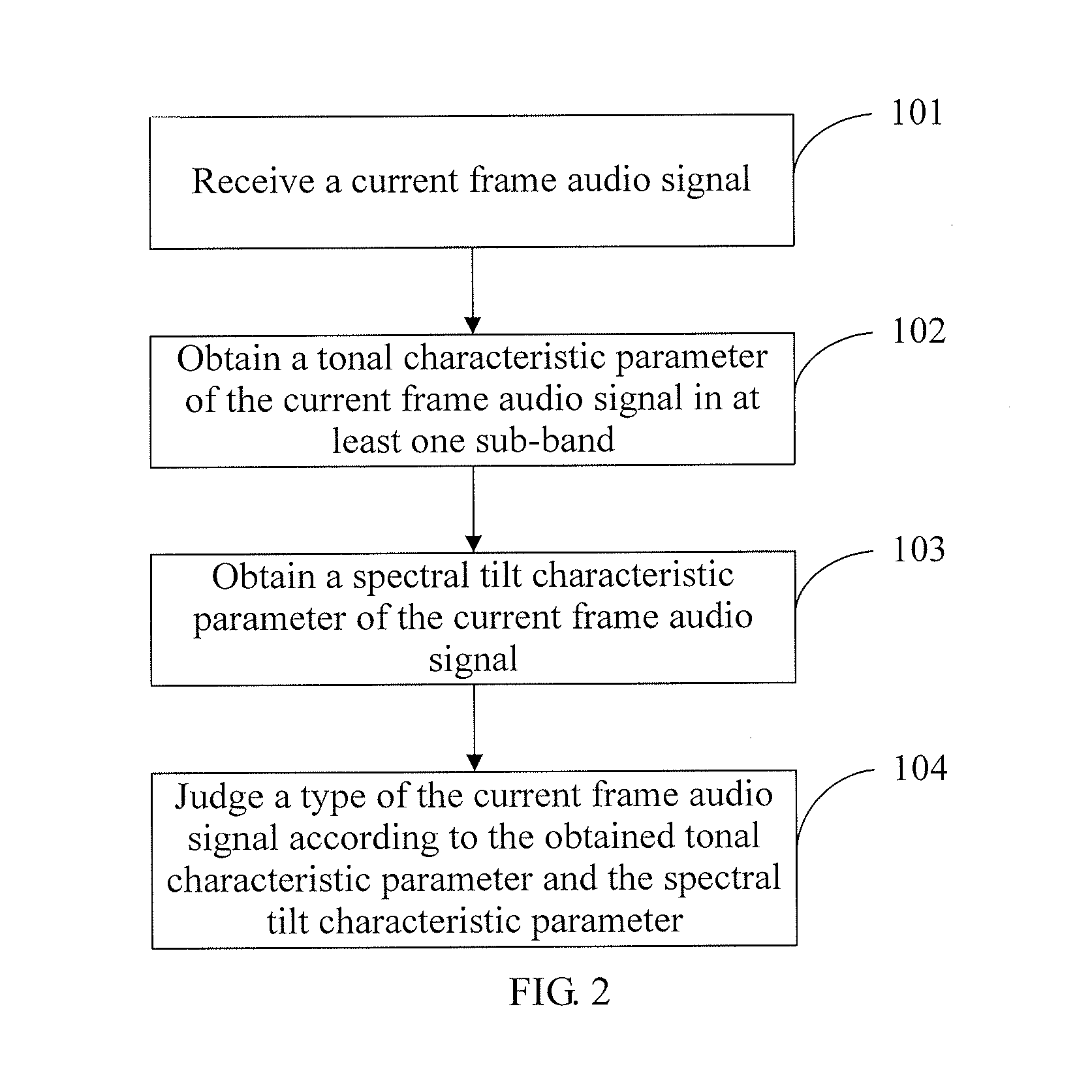
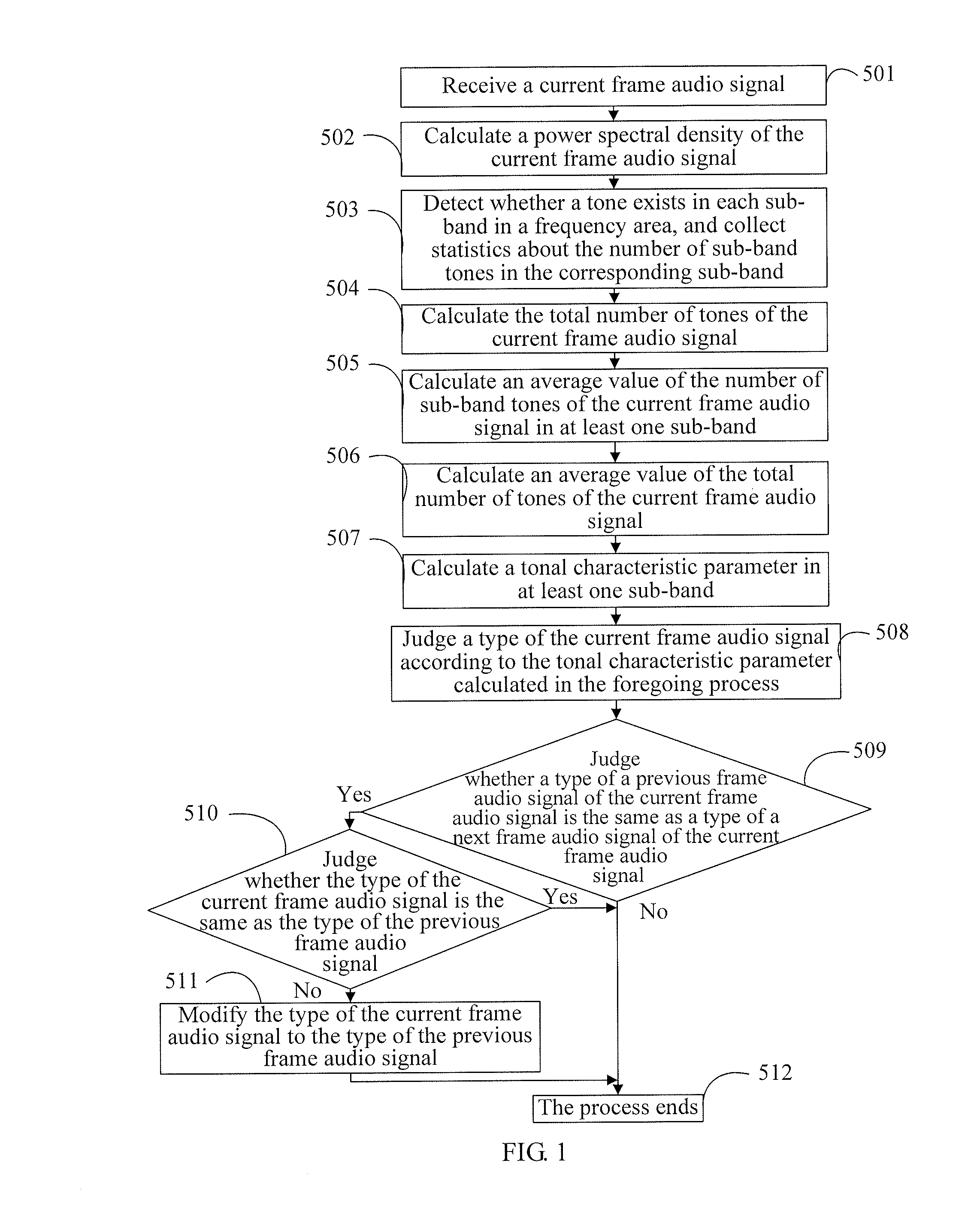
Method and device for audio signal classification using tonal characteristic parameters and spectral tilt characteristic parameters
ActiveUS8682664B2Reduce complexityReduce the amount of calculationElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech recognitionAcquired characteristicTyping Classification
The present invention discloses a method and a device for audio signal classification, and relates to the field of communications technologies, which solve a problem of high complexity of type classification of audio signals in the prior art. In the present invention, after an audio signal to be classified is received, a tonal characteristic parameter of the audio signal to be classified, where the tonal characteristic parameter of the audio signal to be classified is in at least one sub-band, is obtained, and a type of the audio signal to be classified is determined according to the obtained characteristic parameter. The present invention is mainly applied to an audio signal classification scenario, and implements audio signal classification through a relatively simple method.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com