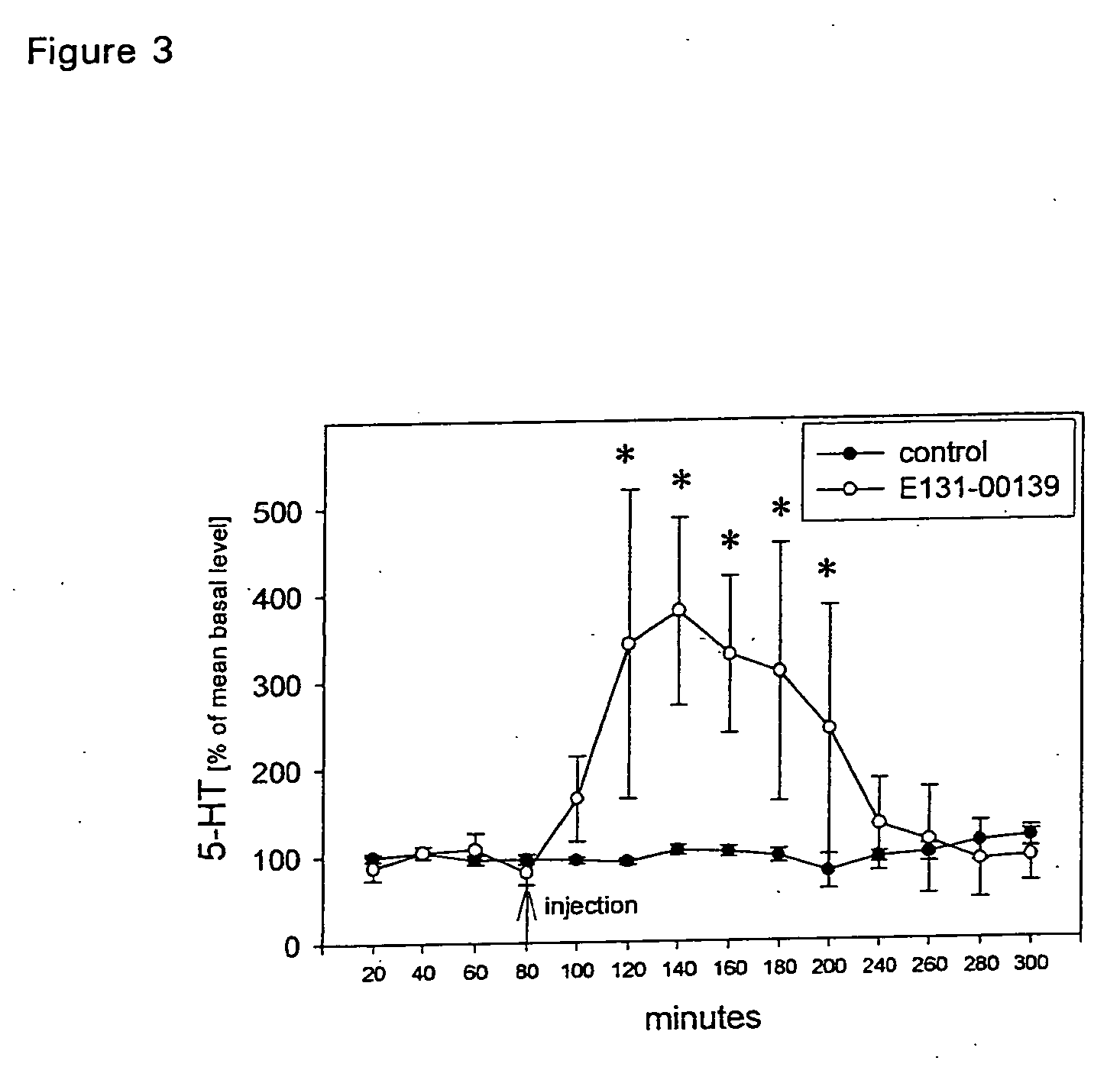
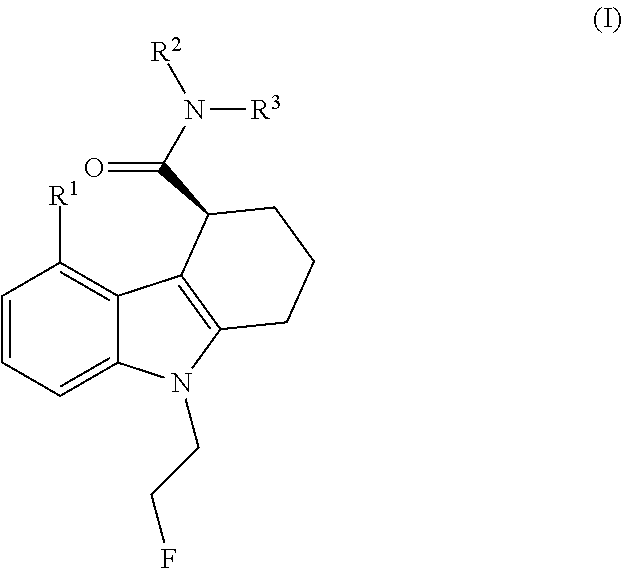
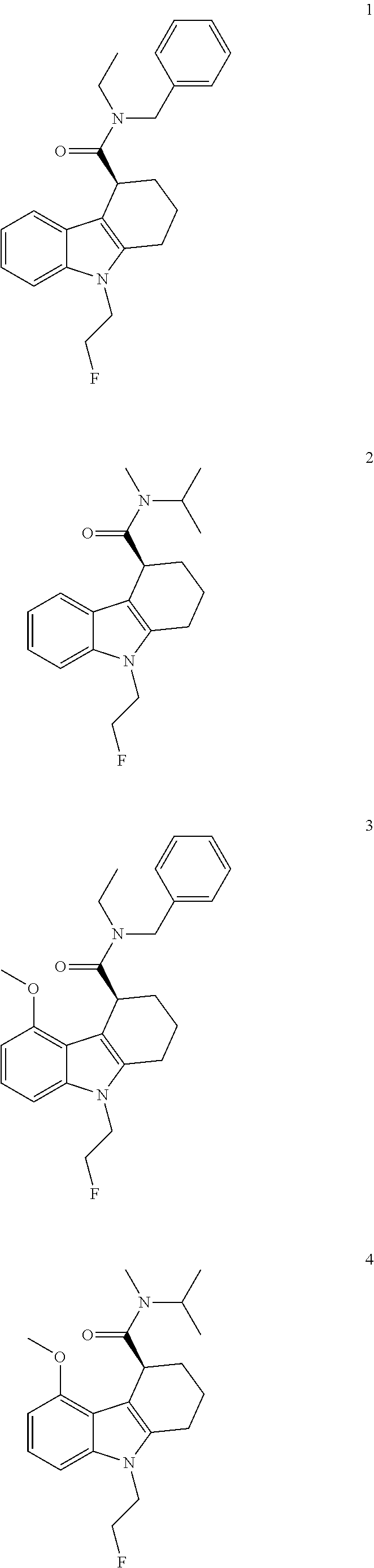
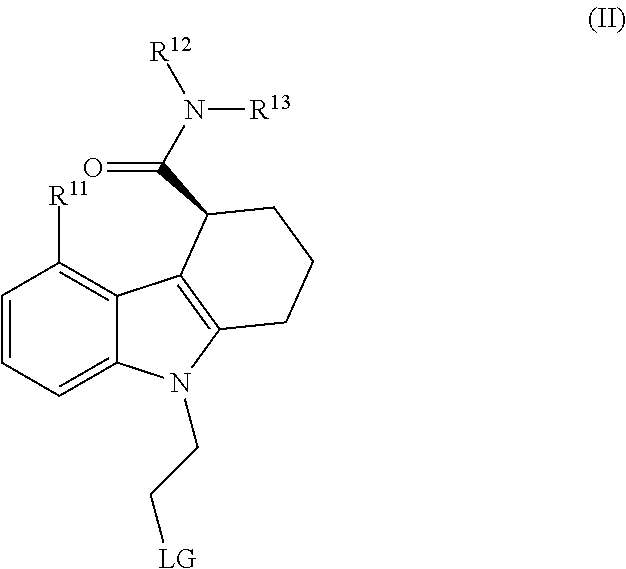
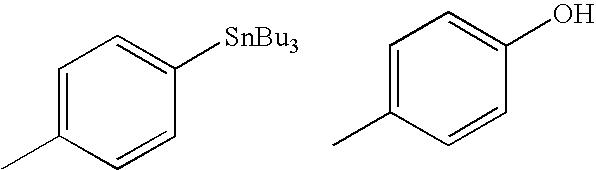Patents
Literature
44 results about "Benzodiazepine receptor ligand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
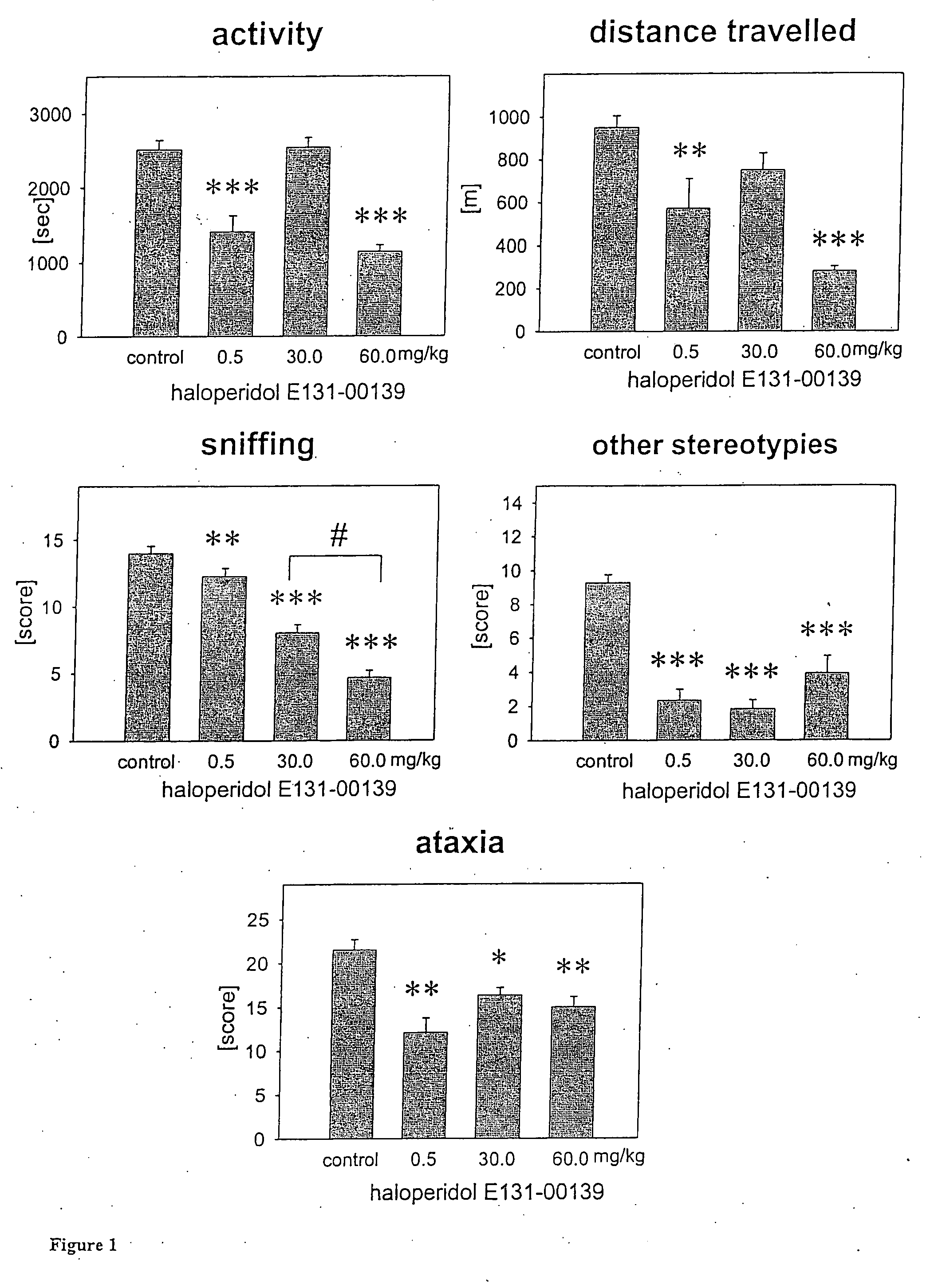
For instance, benzodiazepine receptor ligands with high activity at the α1 and/or α5 tend to be more associated with sedation, ataxia and amnesia, whereas those with higher activity at GABAA receptors containing α2 and/or α3 subunits generally have greater anxiolytic activity.
Targeted, NIR imaging agents for therapy efficacy monitoring, deep tissue disease demarcation and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20060147379A1Maximize signal-to-background ratioUseful in therapyCompounds screening/testingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseCellular respiration
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Methods and compositions for treating disorders, using optically pure (+) zopiclone
InactiveUS6436936B1Improve performanceReduce adverse effectsBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseSleeping disorders
Methods and compositions are disclosed utilizing the optically pure (+) isomer of zopiclone. This compound is a potent drug for the treatment of sleep disorders, such as insomnia, and convulsive disorders, such as epilepsy. Similarly, these novel compositions and methods are useful for the treatment of sleep disorders and convulsive disorders while avoiding the concomitant liability of adverse effects associated with the racemic mixture of zopiclone. The optically pure (+) isomer of zopiclone is also useful for treating disorders that are affected by the binding of agonists to central nervous system or peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Also described are methods and compositions for treating disorders that are affected by binding of agonists to central nervous system or peripheral benzodiazepine receptors while avoiding the adverse effects associated with the administration of the racemic mixture of zopiclone.
Owner:SUNOVION PHARMA INC
Agents for therapy efficacy monitoring and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20080031823A1Limited applicationImprove clinical efficacyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideCellular respirationFunctional imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Targeted, NIR imaging agents for therapy efficacy monitoring, deep tissue disease demarcation and deep tissue imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
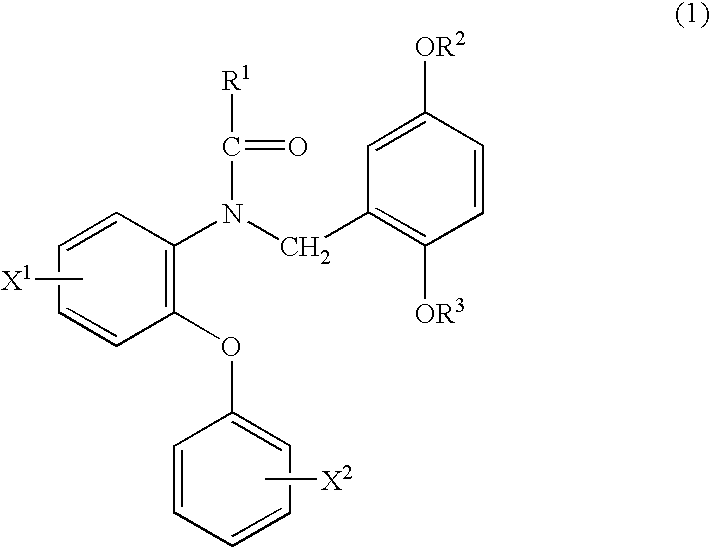
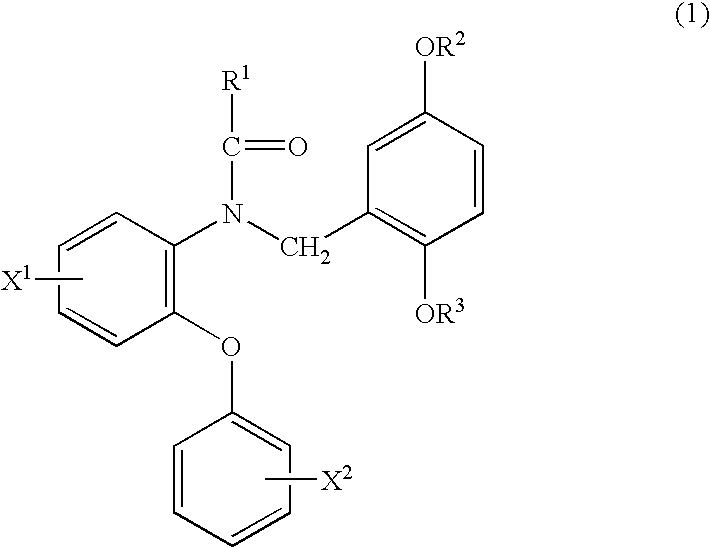
Phenyloxyaniline derivatives
ActiveUS6870069B2High affinityHigh selectivityBiocideFatty acid chemical modificationHydrogen atomHalogen
A phenyloxyaniline derivative useful as a ligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptor having a strong affinity and a high selectivity, which is represented by formula (1): wherein X1 and X2 are same or different and each is hydrogen atom or halogen atom; R1 and R2 are same or different and each is hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon(s) or a halogen-substituted alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon(s); and R3 is a halogen-substituted alkyl group having 1 to 5 carbon(s), or a radioisotope thereof.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI +2
Composition and method for treating hyperproliferative diseases
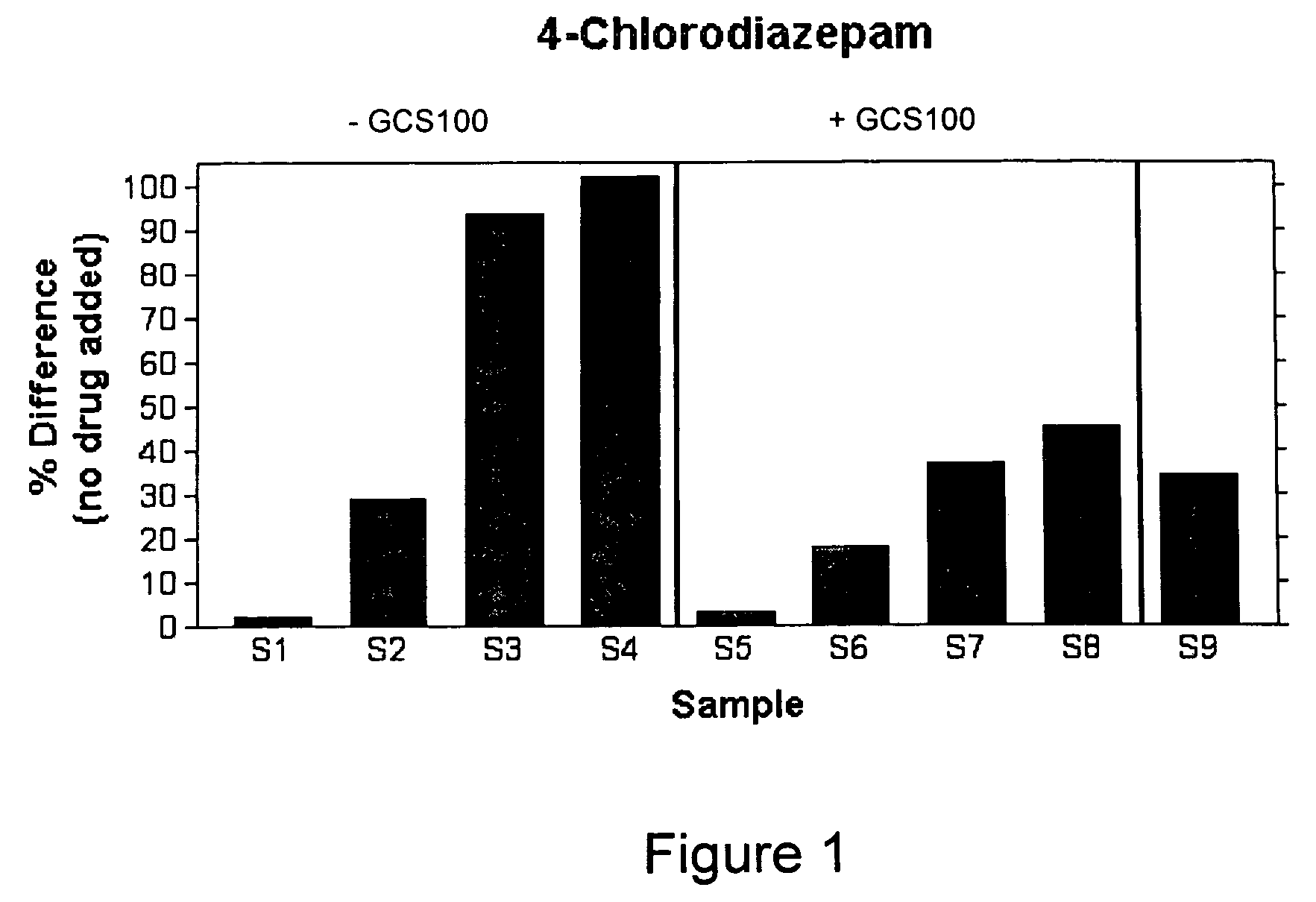
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for treatment of hyperproliferative diseases. The composition of the invention comprises a carbohydrate having a backbone comprising polygalacturonan and a ligand of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. The present compositions and methods are used to treat various cancers and other diseases where cells undergo pathological and unwanted proliferation.
Owner:PROSPECT THERAPEUTICS
Active enantiomer
ActiveUS20110070161A1High affinityTo promote metabolismIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersEnantiomerCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention provides a PET tracer that has improved properties for imaging the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) as compared with known such PET tracers. The present invention also provides a precursor compound useful in the preparation of the PET tracer of the invention and methods for the preparation of said precursor compound and said PET tracer. Also provided by the present invention is a radiopharmaceutical composition comprising the PET tracer of the invention. Methods for using the PET tracer and the radiopharmaceutical composition are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Agents for therapy efficacy monitoring and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS8188116B2Improve clinical efficacyHighly expressed in leukemiaUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideCellular respirationMolecular imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Peripheral benzodiazepine receptor independent superoxide generation
InactiveUS20060111288A1Antagonizing activitiesHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsBiocideSuperoxideCompound (substance)
A method of treating cancer through the application of a compound that causes the intra-mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species in tumor cells by a mechanism that is independent of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor.
Owner:QUEEN MARY UNIV OF LONDON
Tricyclic indole derivatives as PBR ligands
ActiveCN102834379AOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersRadioactive drugPharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides a PET tracer that has improved properties for imaging the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) as compared with known such PET tracers. The present invention also provides a precursor compound useful in the preparation of the PET tracer of the invention and methods for the preparation of said precursor compound and said PET tracer. Also provided by the present invention is a radiopharmaceutical composition comprising the PET tracer of the invention. Methods for using the PET tracer and the radiopharmaceutical composition are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Treatment of down syndrom with benzodiazepine receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20090270373A1Safety managementObject recognitionBiocideNervous disorderBenzodiazepine receptor ligandReceptor antagonist
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating Down Syndrome, mental retardation or both are provided. The pharmaceutical compositions comprise one or more benzodiazepine receptor antagonists, such as flumazenil.
Owner:CYPRESS BIOSCI
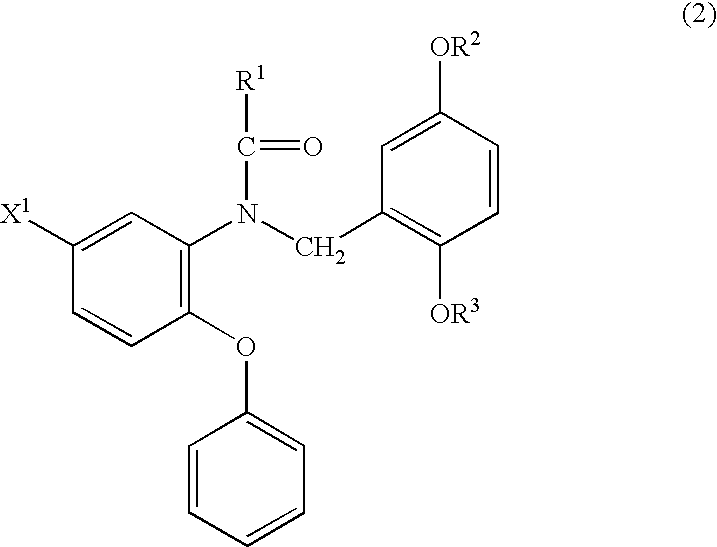
Aryloxyanilide derivatives
InactiveUS20120003154A1Maintain good propertiesGood selective bindingIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersImaging agentIn vivo kinetics
The present invention provides a novel radiolabeled aryloxyalinine derivative suitable for in vivo imaging. In comparison to known aryloxyalinine derivative in vivo imaging agents, the in vivo imaging agent of the present invention has better properties for in vivo imaging. The in vivo imaging agent of the present invention demonstrates good selective binding to the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR), in combination with good brain uptake and in vivo kinetics following administration to a subject.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
18F-Labeled Daa Analogues and Method of Labeling These Analogues as Positron Emission Tomography (Pet) Tracers For Imaging Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptors
InactiveUS20080293969A1Isotope introduction to acyclic/carbocyclic compoundsSynthesis methodsCombinatorial chemistry
Methods for selecting novel DAA analogues for a peripheral type benzodiazepine receptor were labeled with 18F using one-step syntheses are provided. Analogues labeled with the 18F using the one-step synthesis method are also provided. Additionally, the purification of the Br, I, Cl, TsO, MsO, or RfSO3 precursors in the compound of formula (II) by solid phase extraction is provided as is the precursor compounds of formula (II). A kit claim for comprising an effective amount of an 18F labeled compound, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and solvates thereof are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
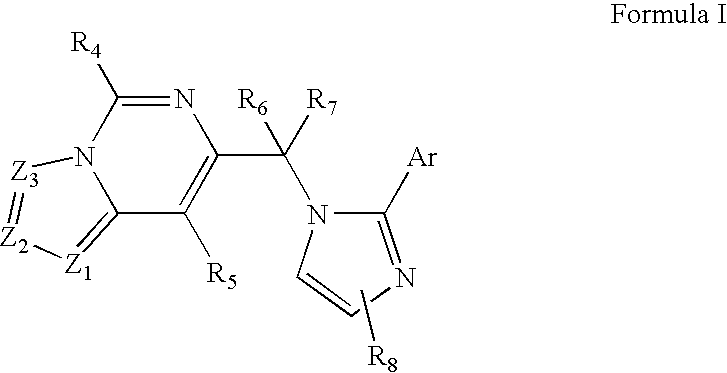
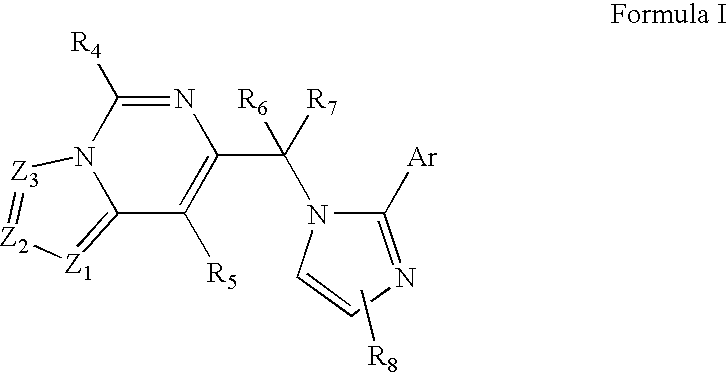
Imidazo-pyrimidines and triazolo-pyrimidines: benzodiazepine receptor ligands
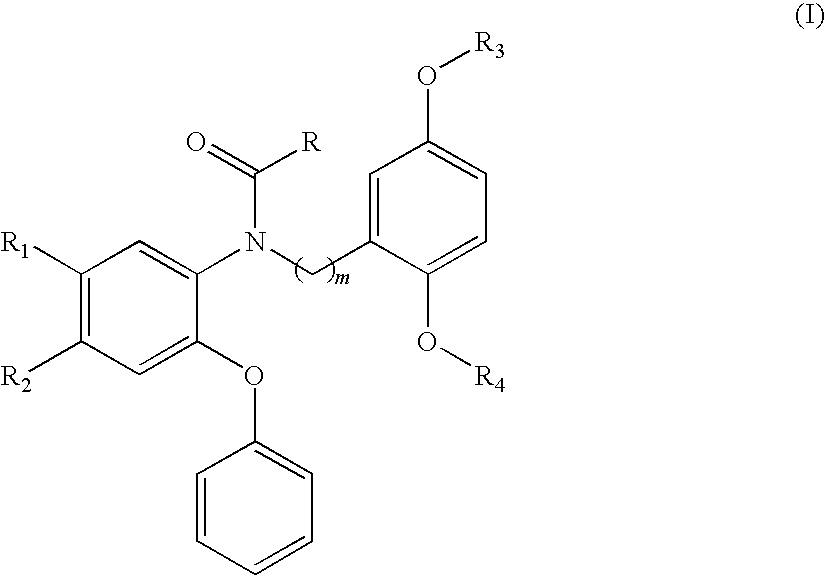
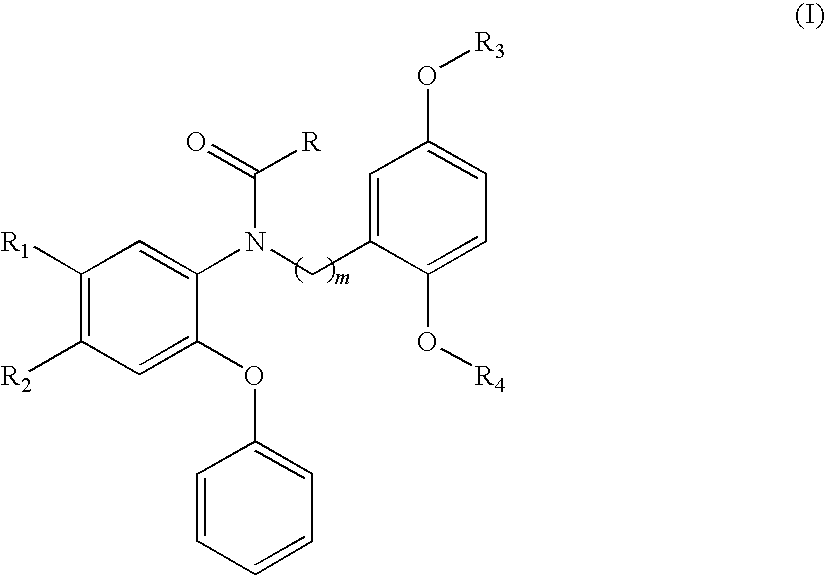
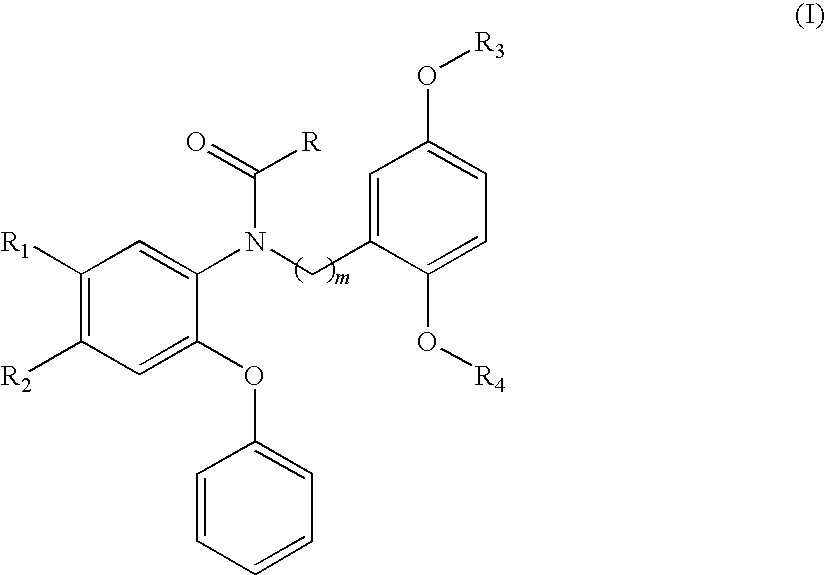
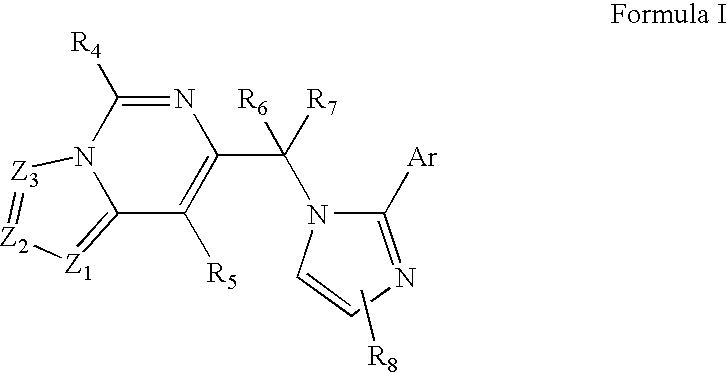
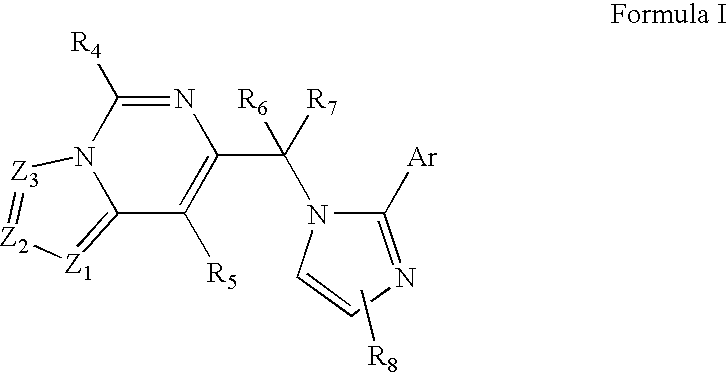
Compounds of Formula I are provided, as are methods for their preparation. The variables Z1, Z2, Z3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8 and Ar in the above formula are defined herein. Such compounds may be used to modulate ligand binding to GABAA receptors in vivo or in vitro, and are particularly useful in the treatment of a variety of central nervous system (CNS) disorders in humans, domesticated companion animals and livestock animals. Compounds provided herein may be administered alone or in combination with one or more other CNS agents to potentiate the effects of the other CNS agent(s). Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating such disorders are provided, as are methods for using such ligands for detecting GABAA receptors (e.g., receptor localization studies).
Owner:NEUROGEN
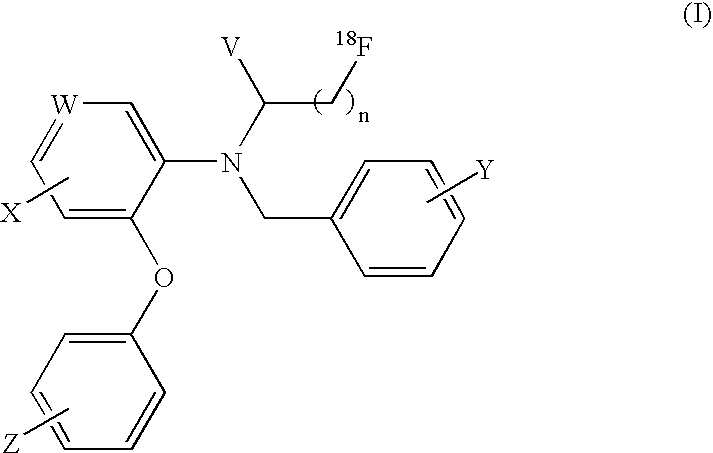
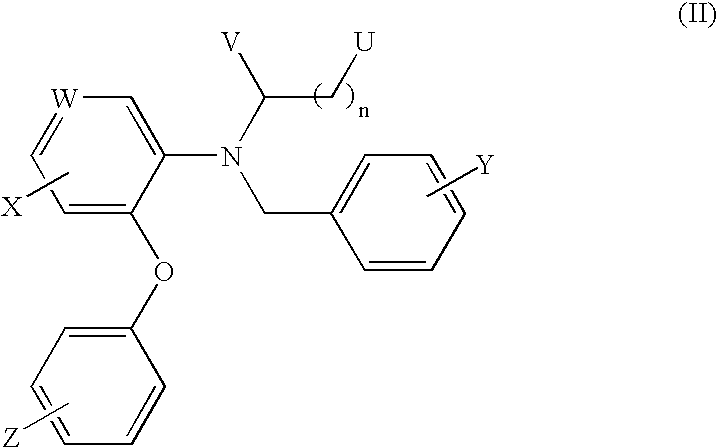
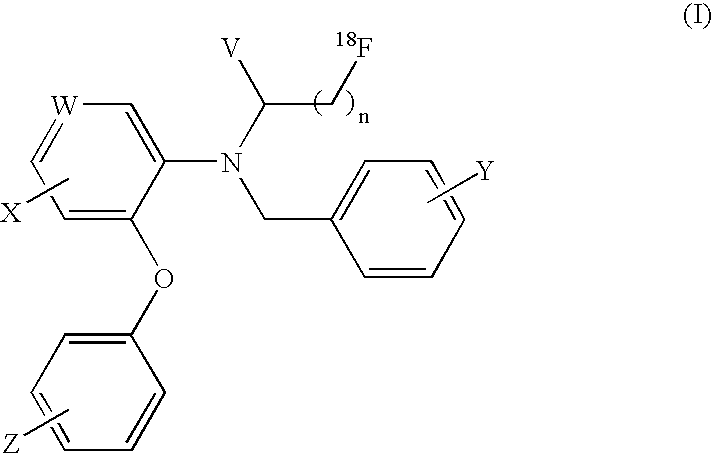
[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same
InactiveCN105530961AIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsAntipyreticDiseaseRadioactive tracer
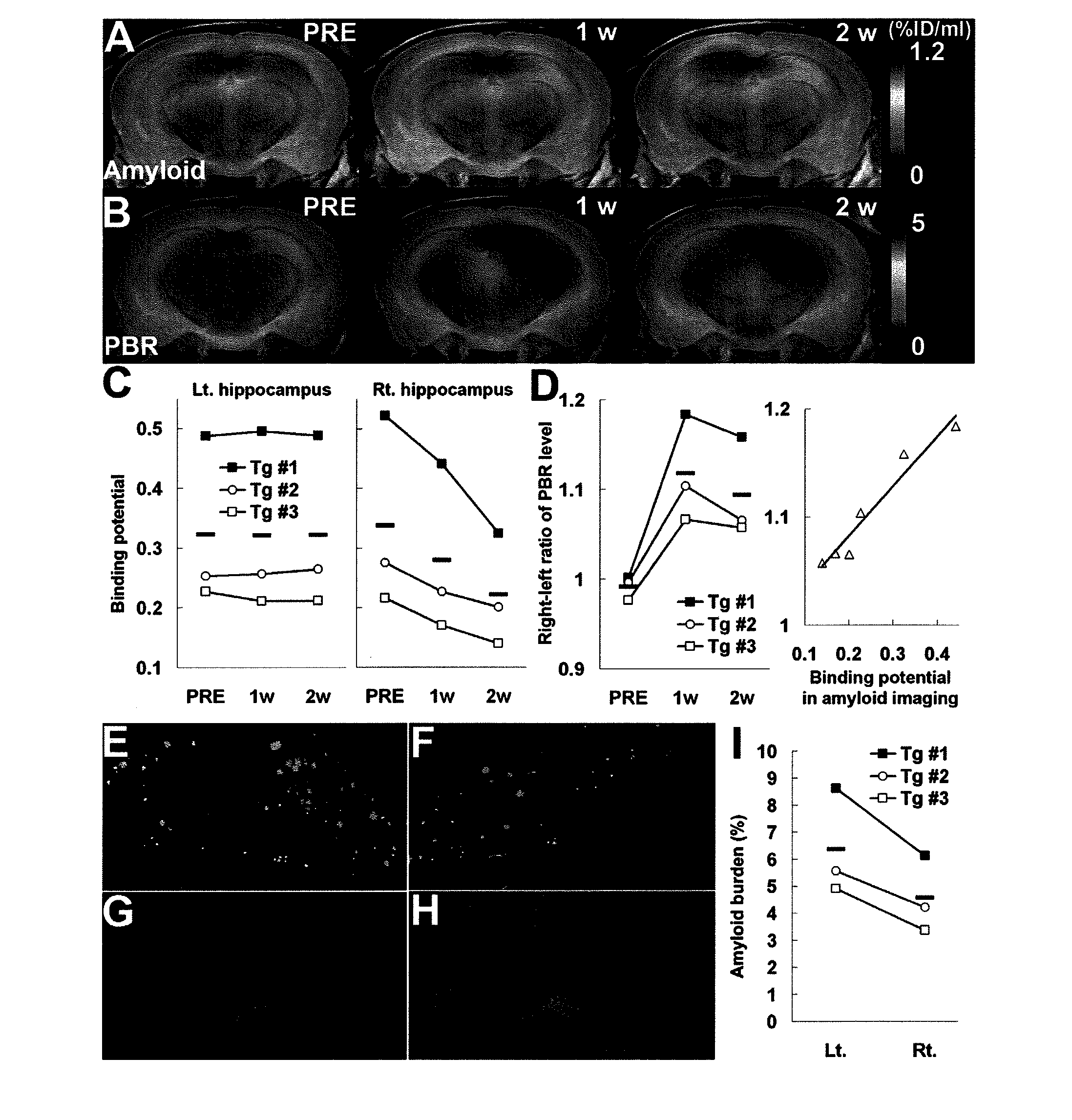
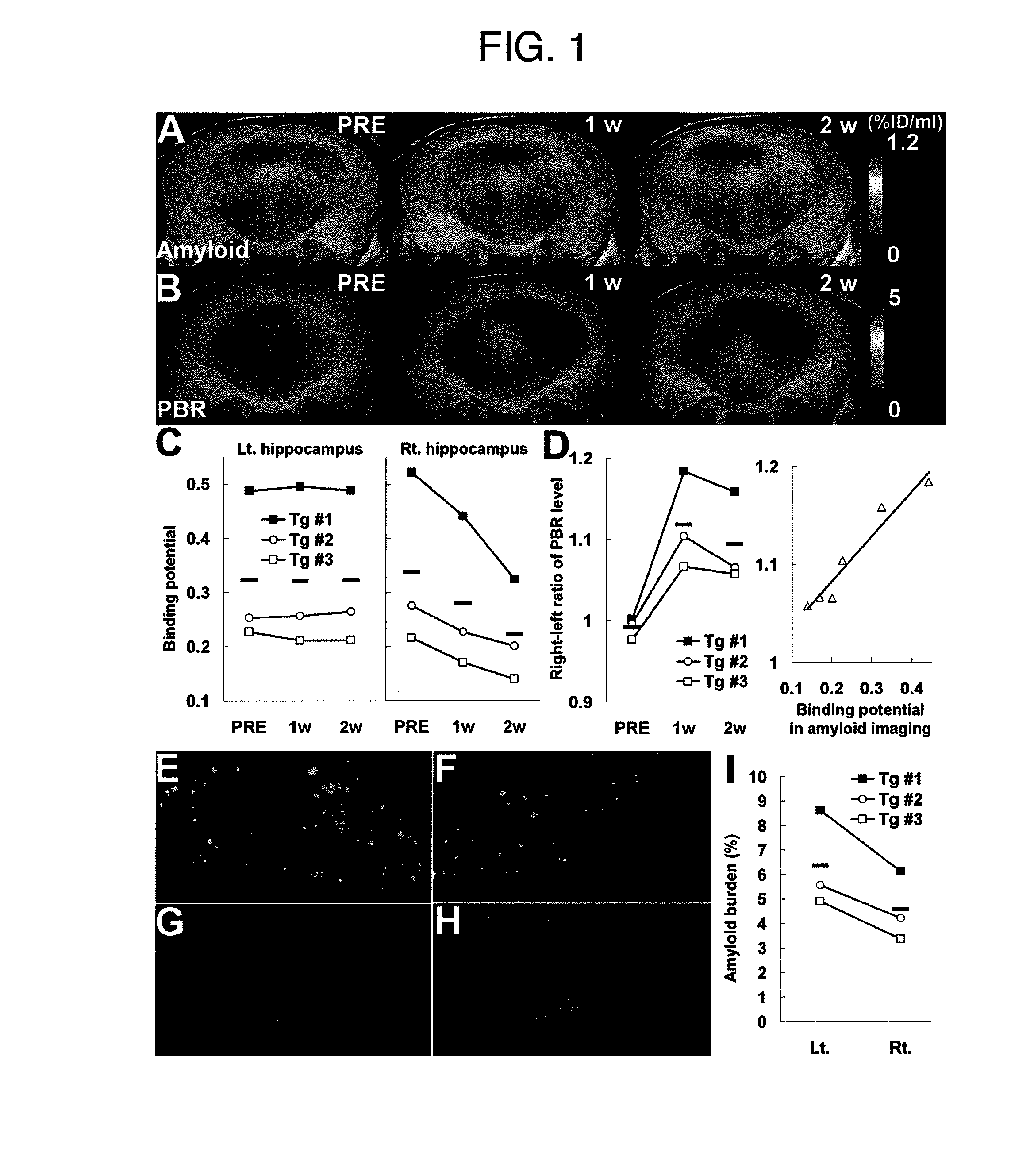
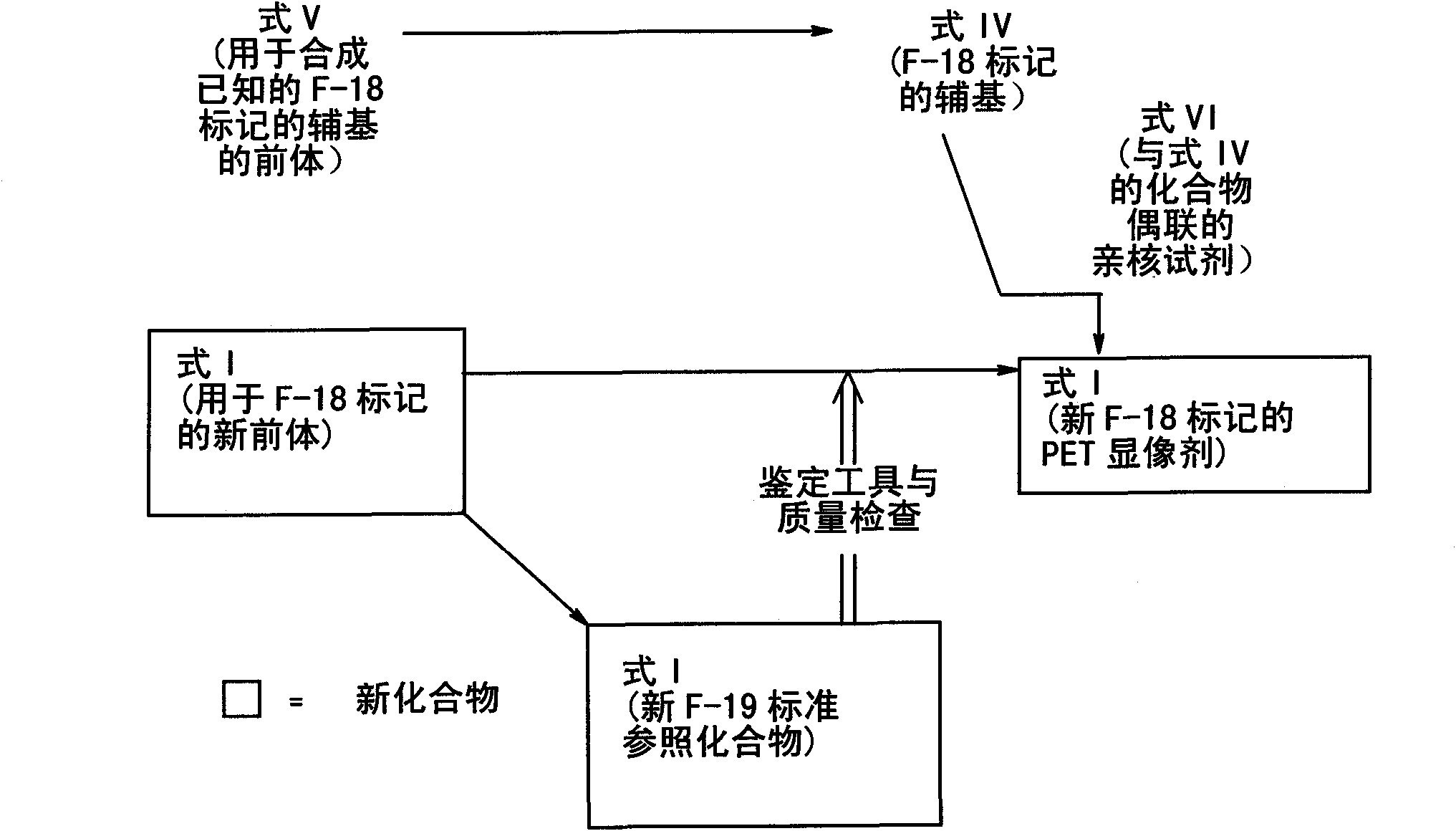
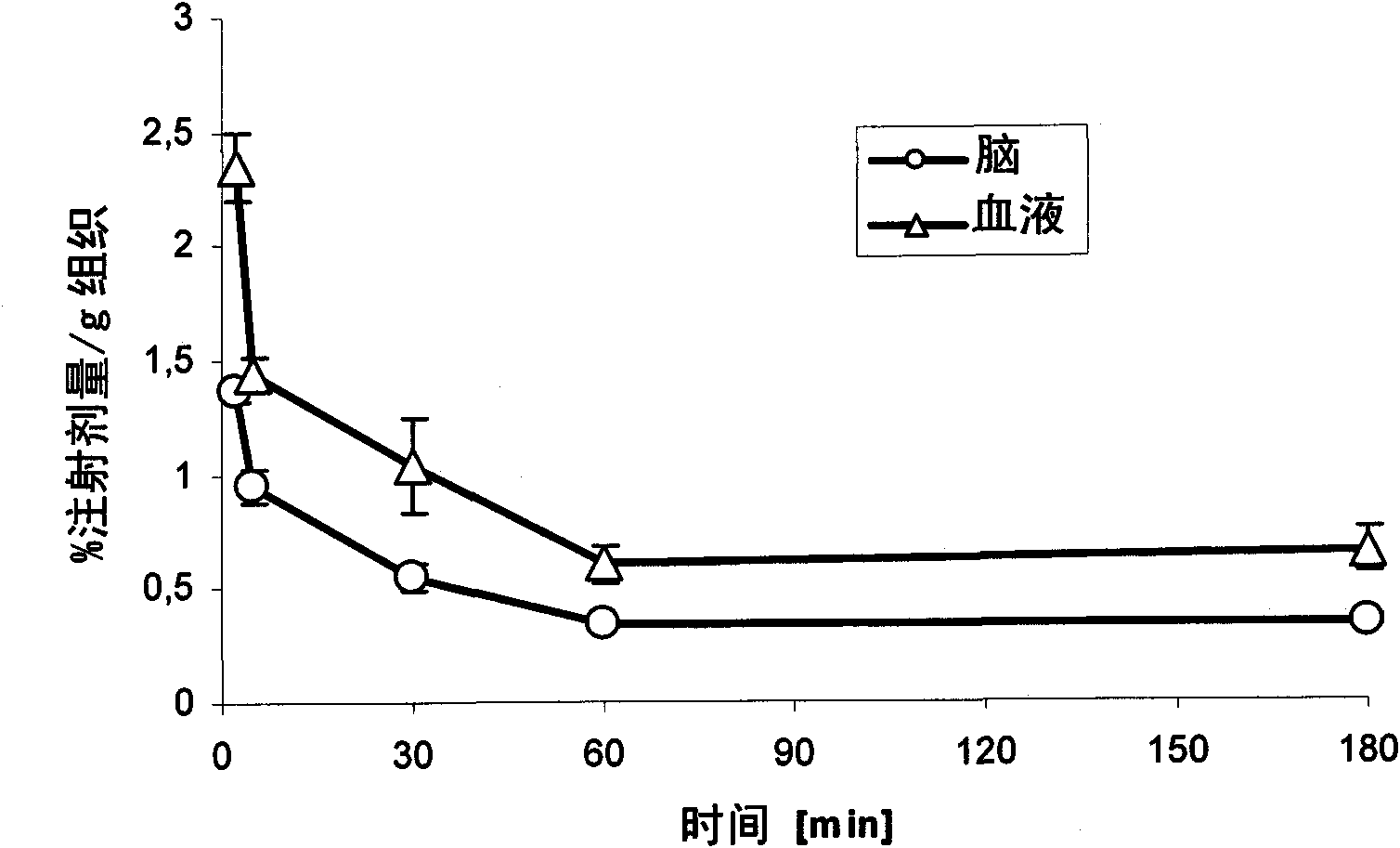
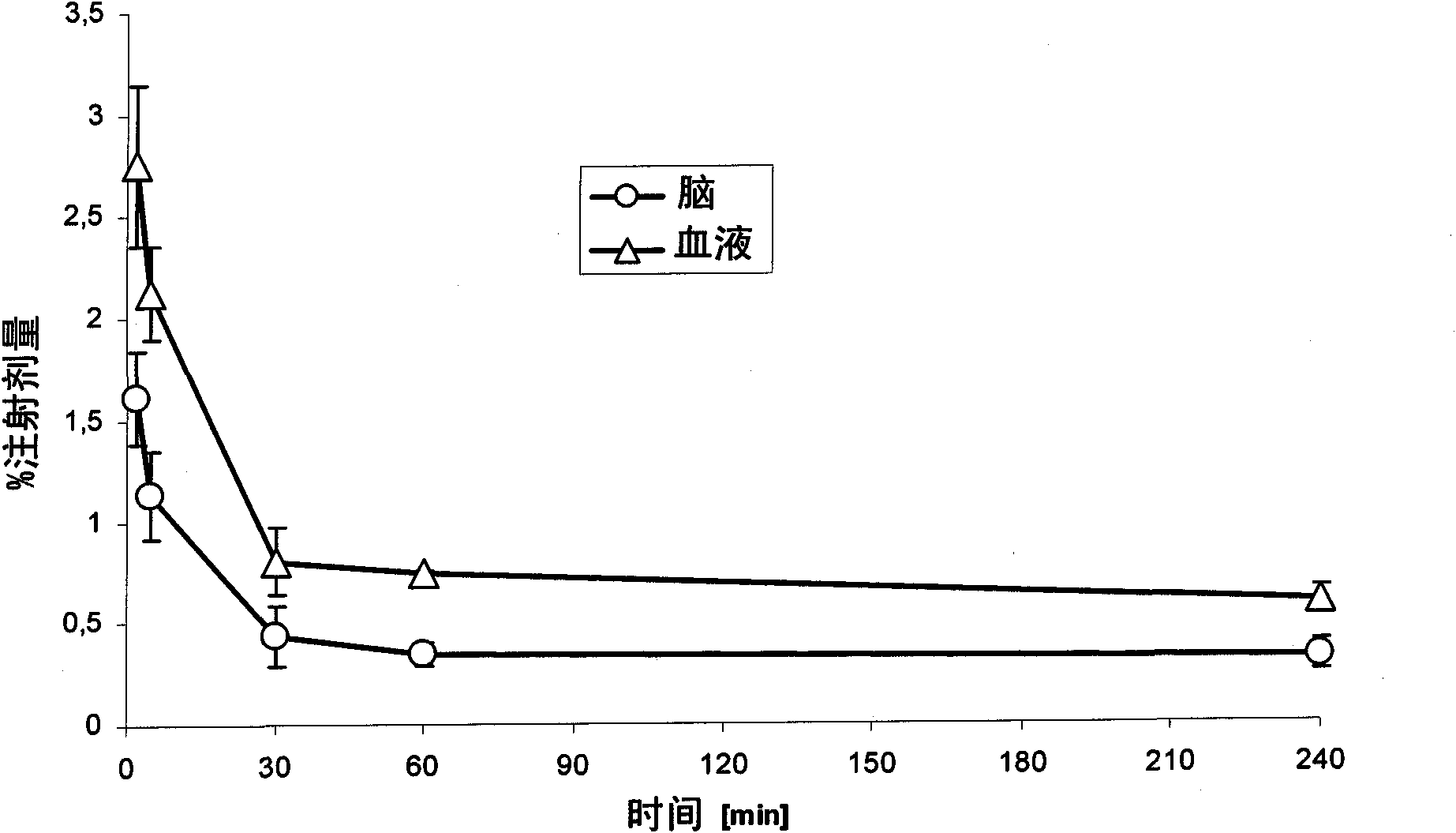
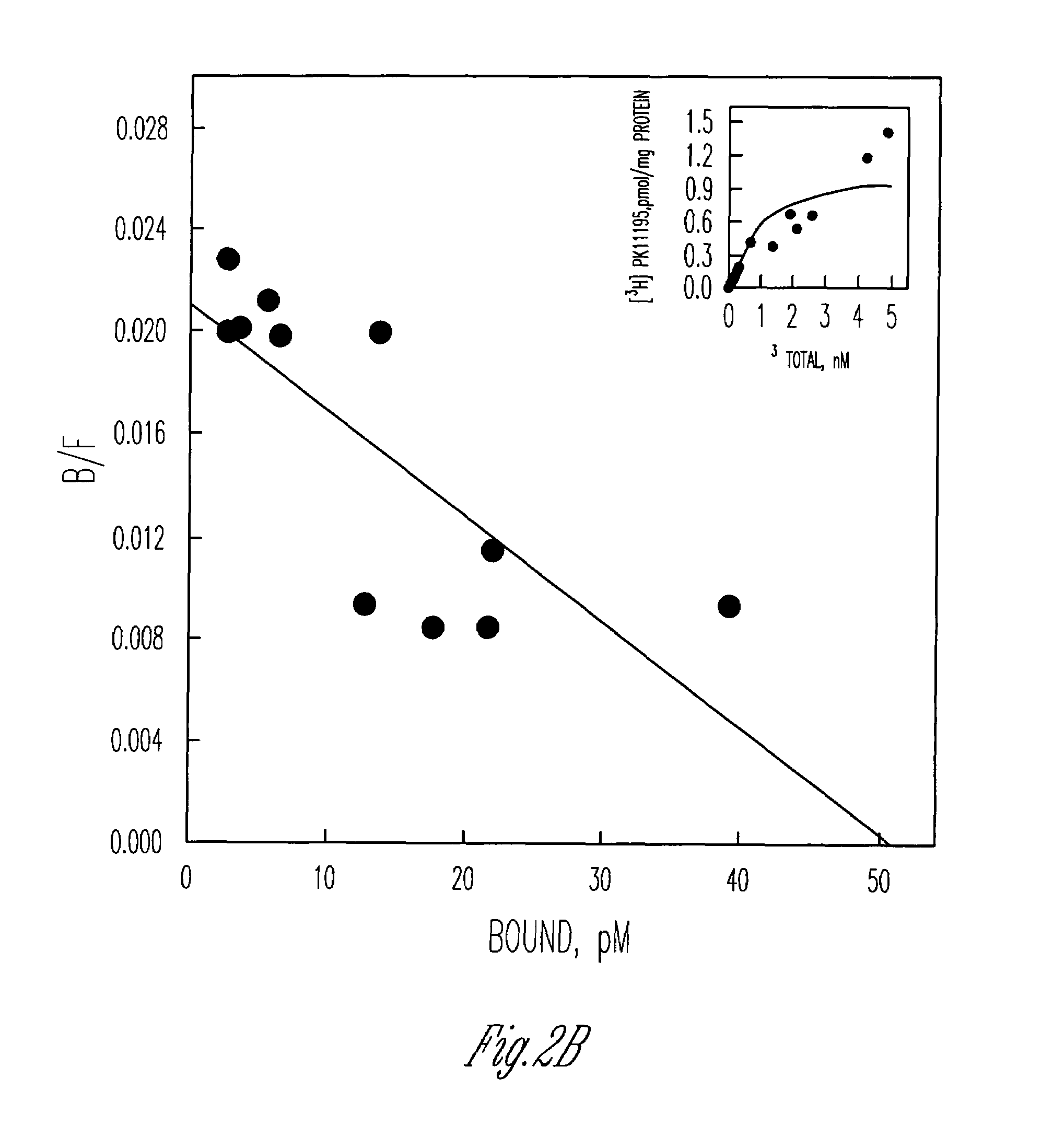
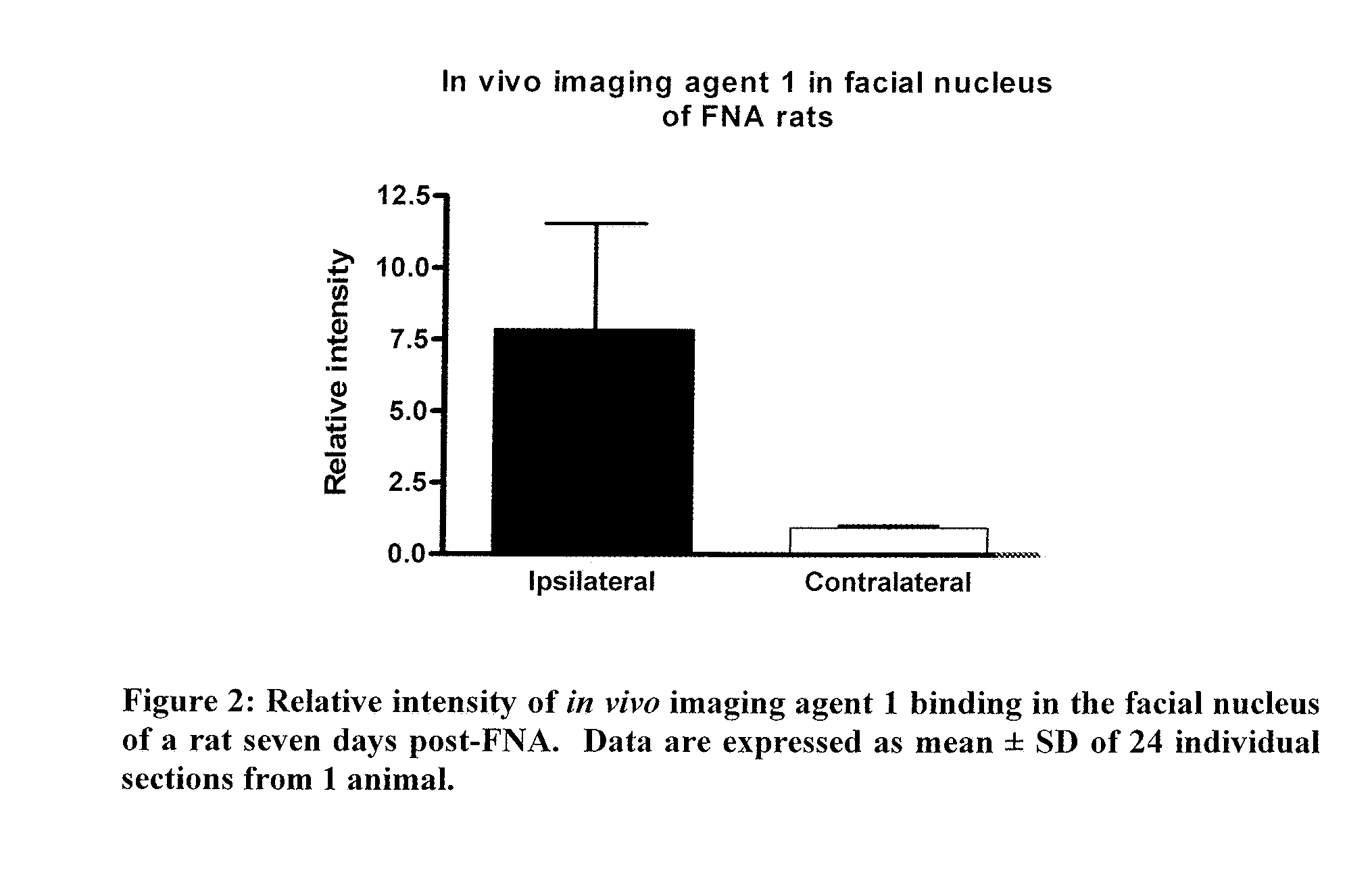
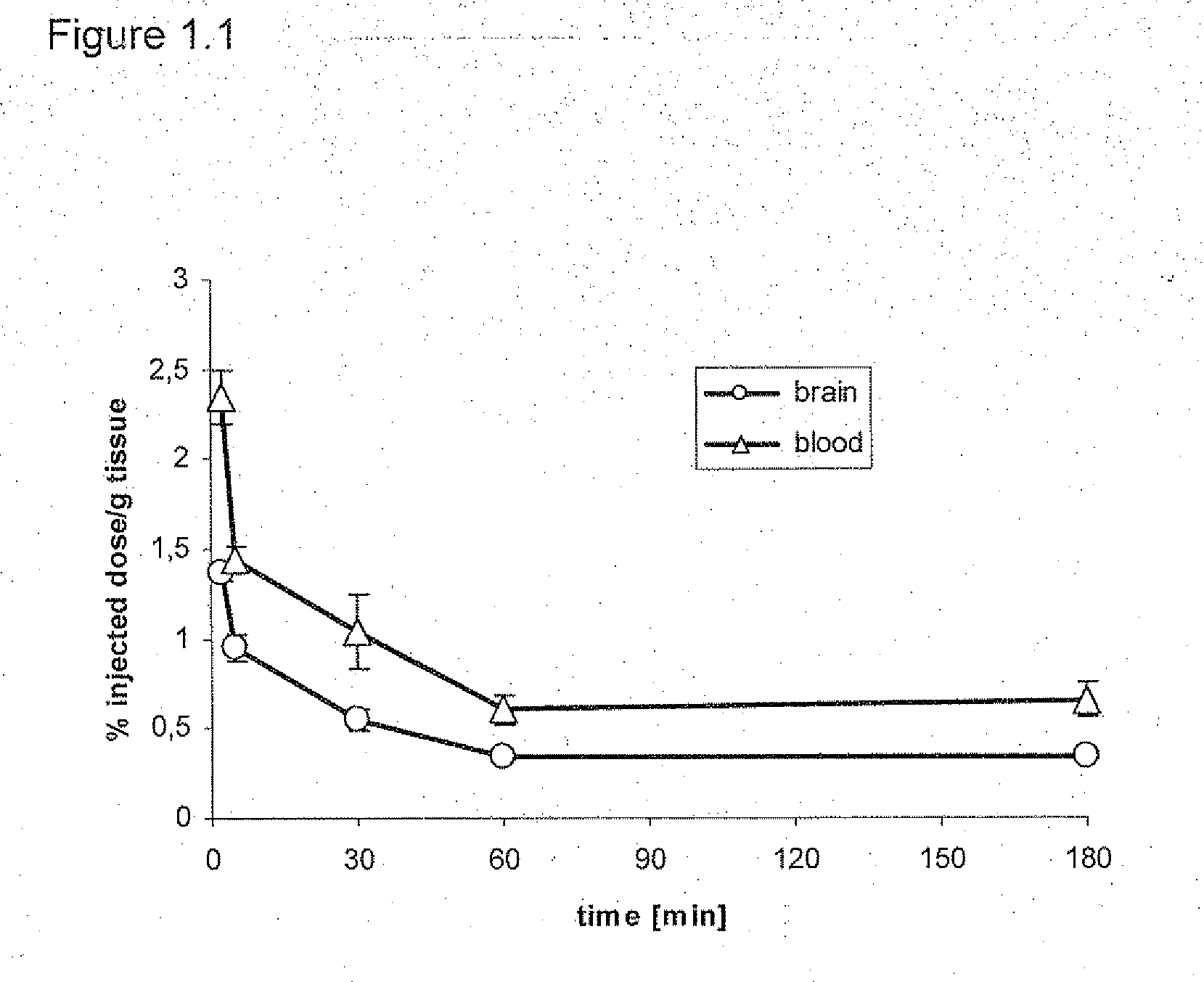
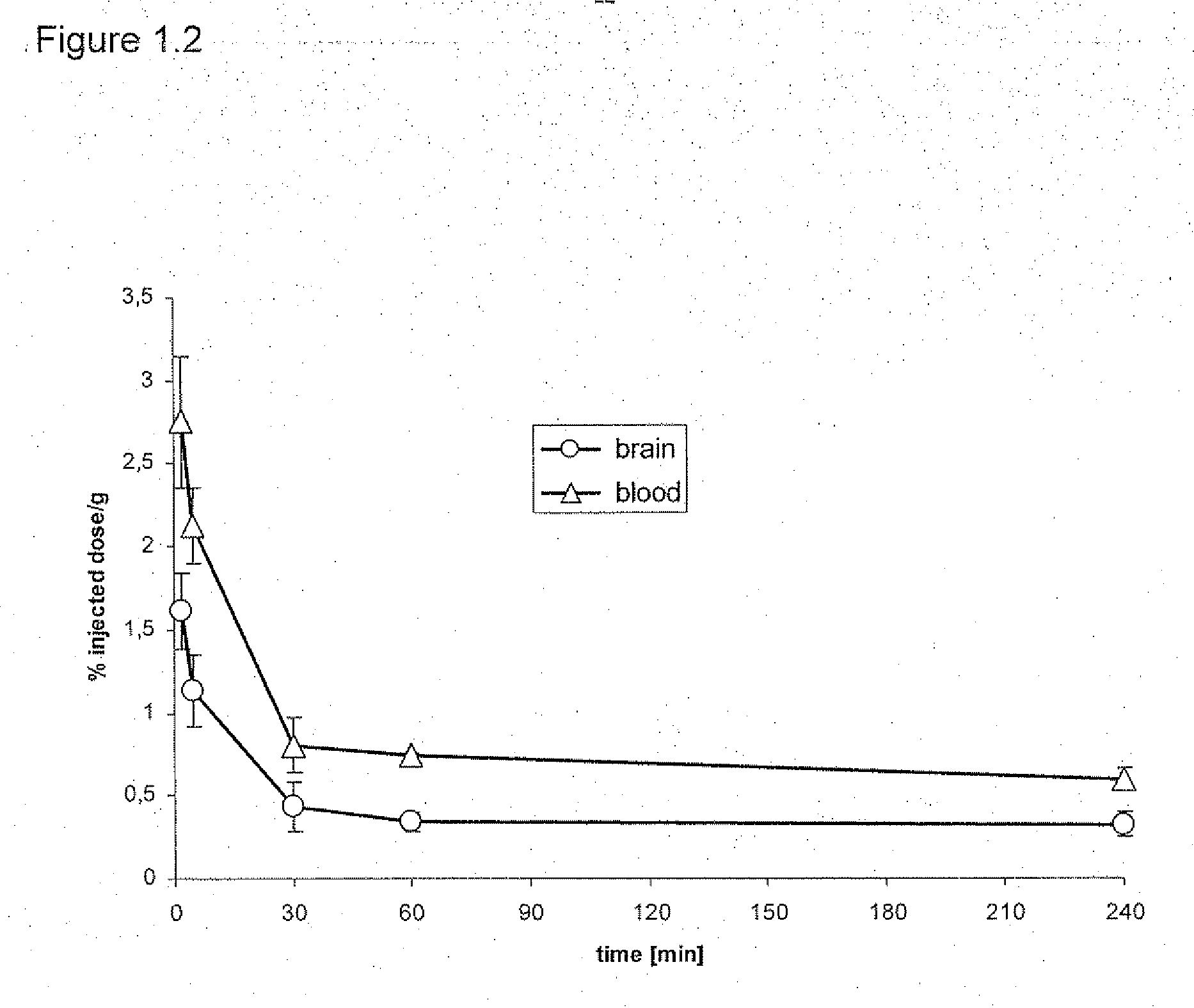
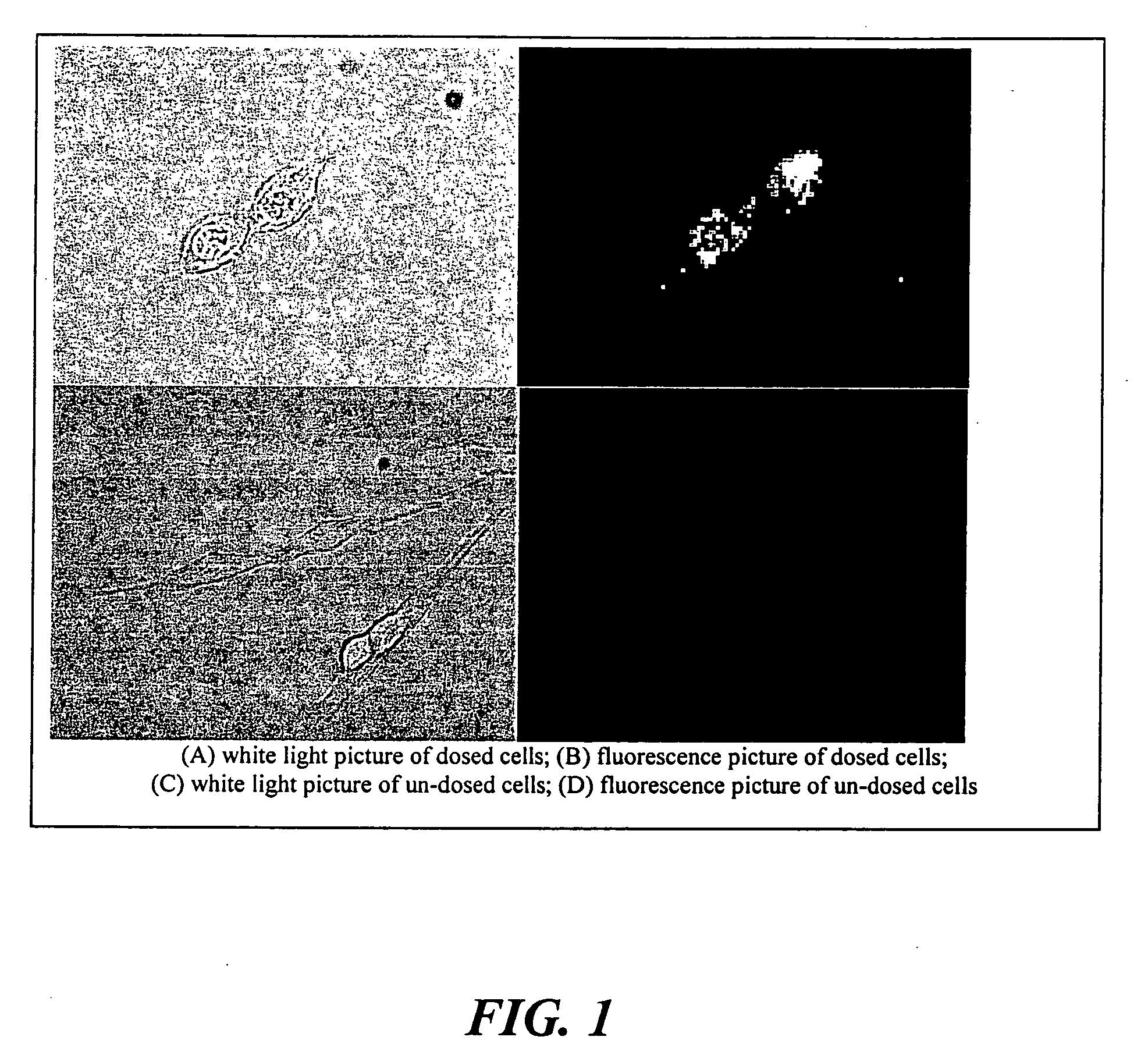
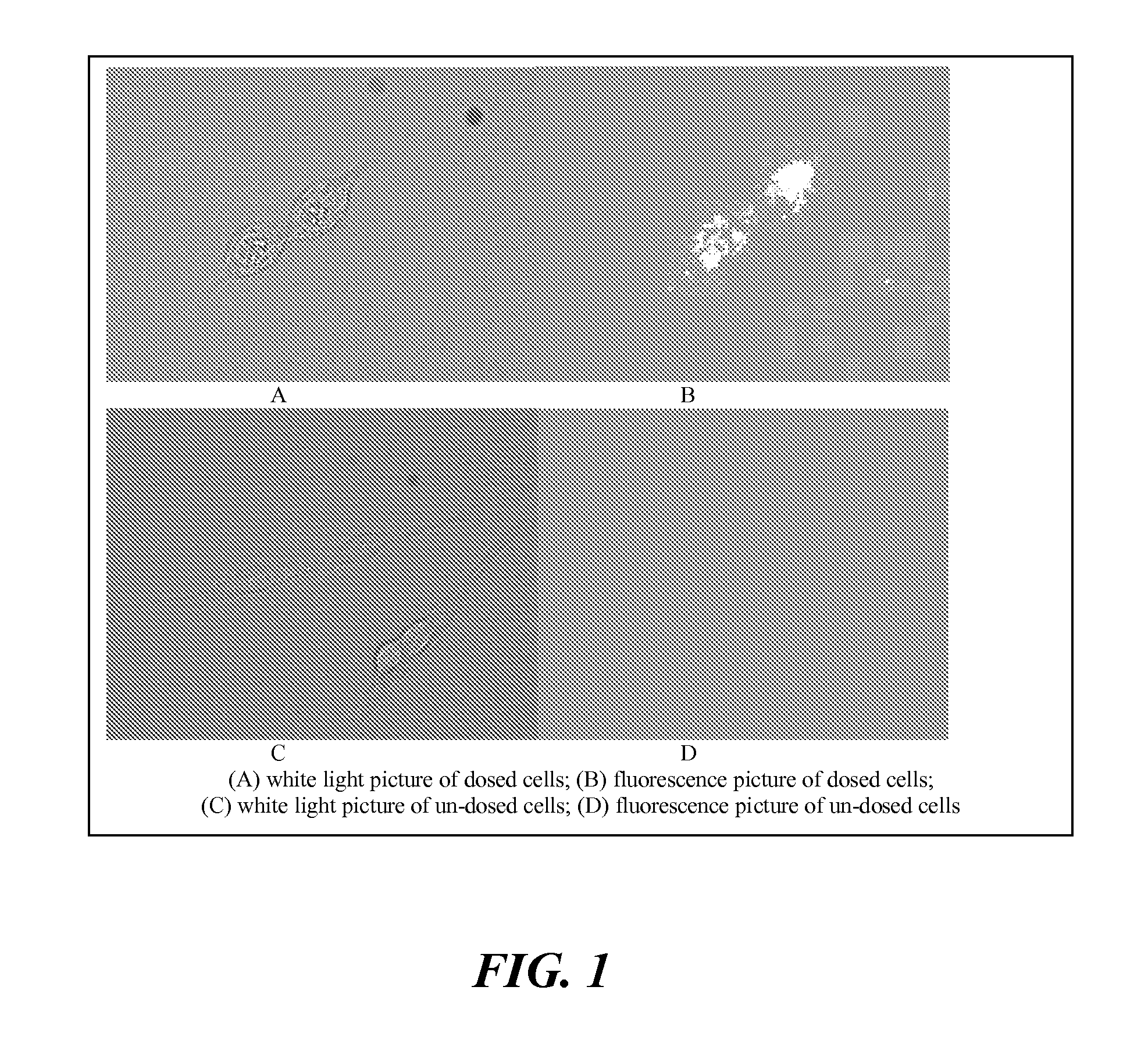
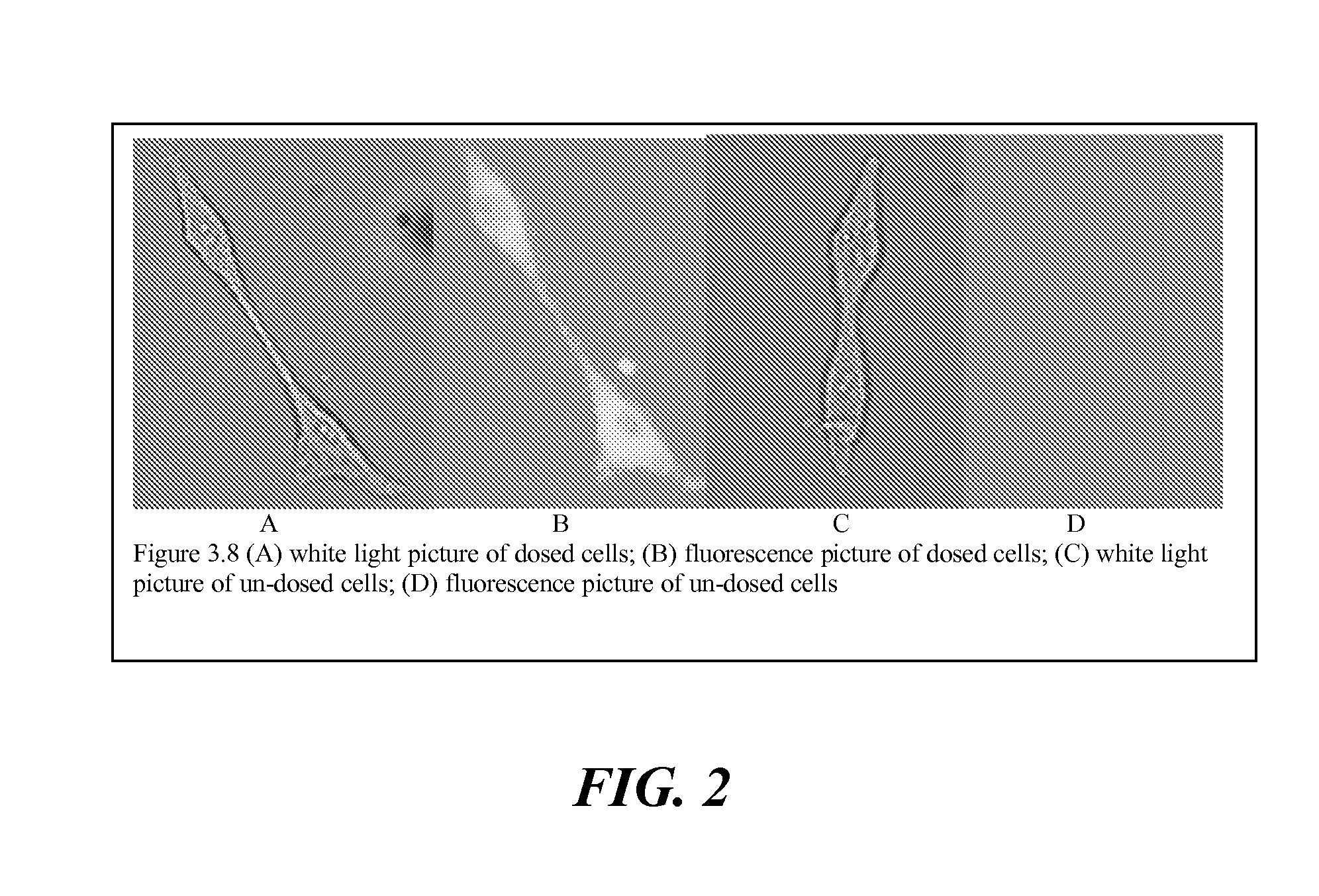
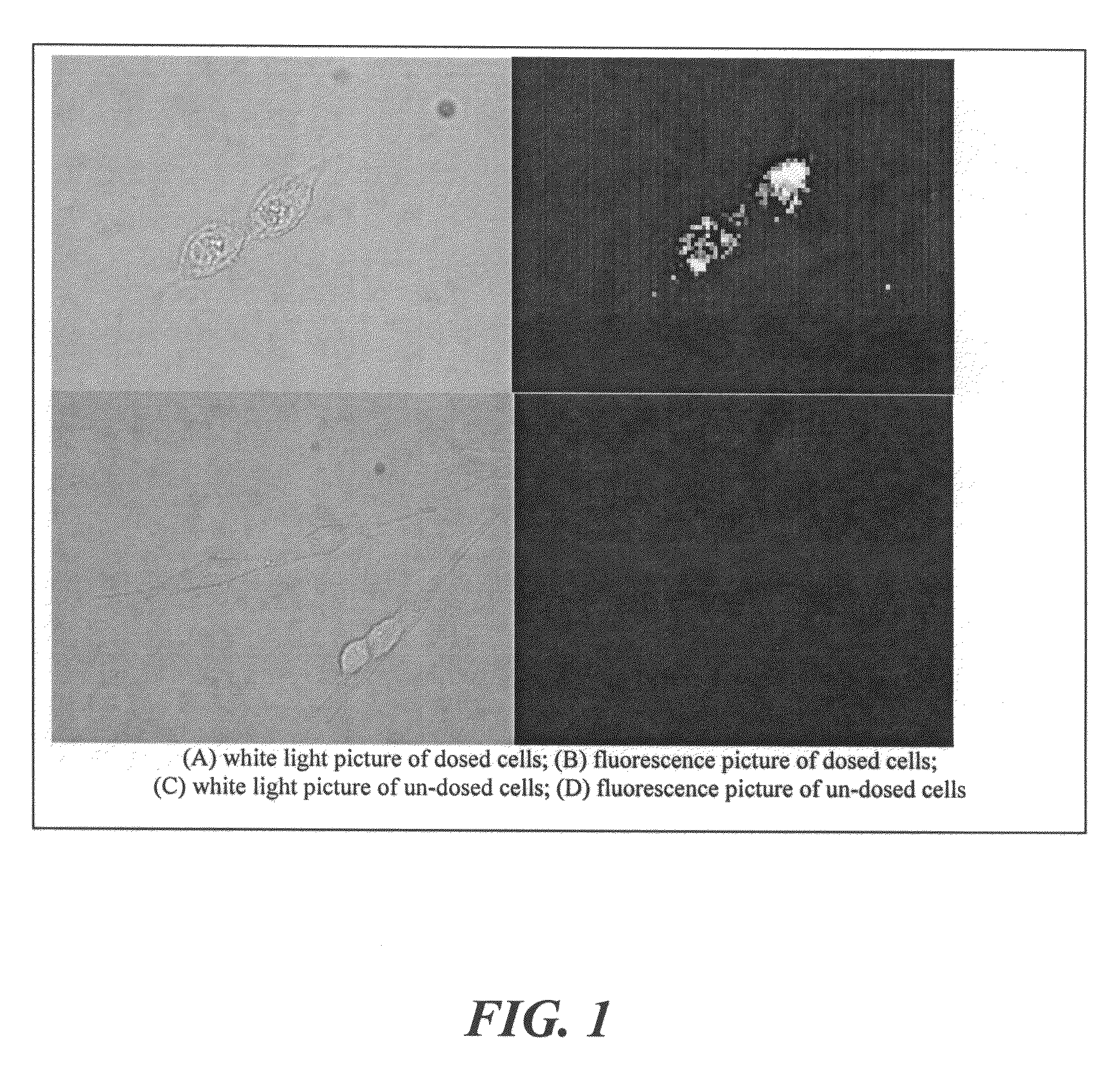
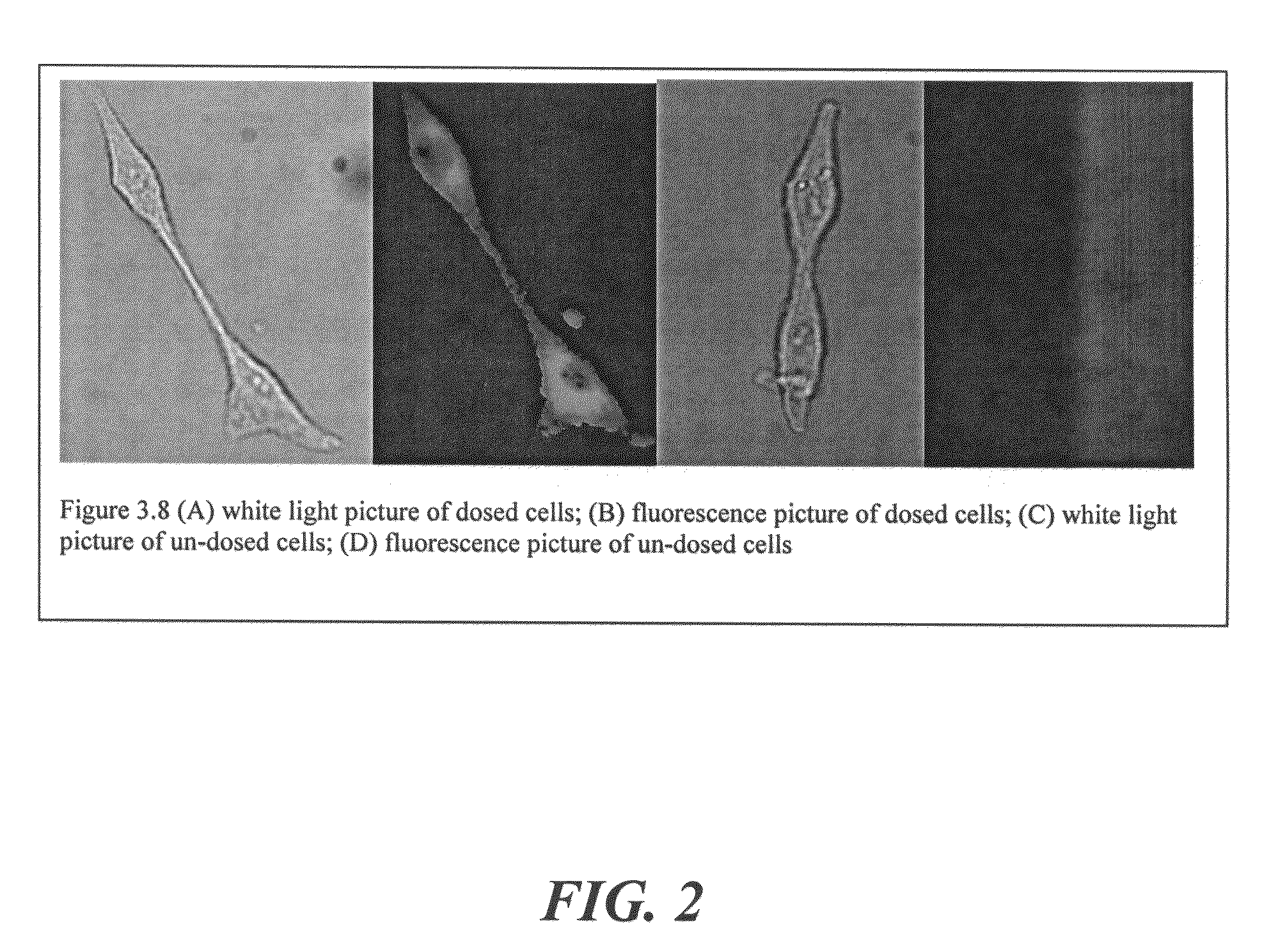
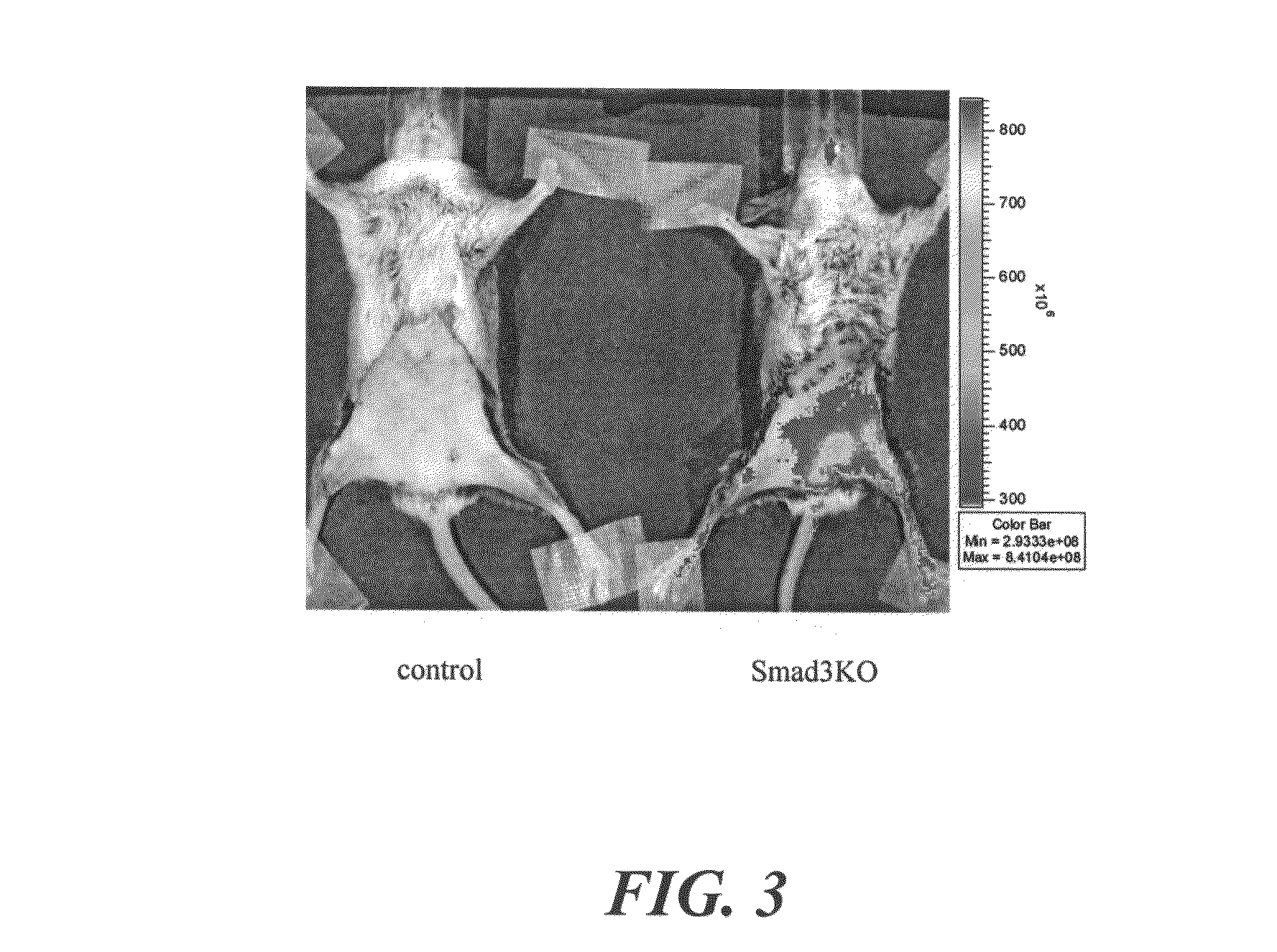
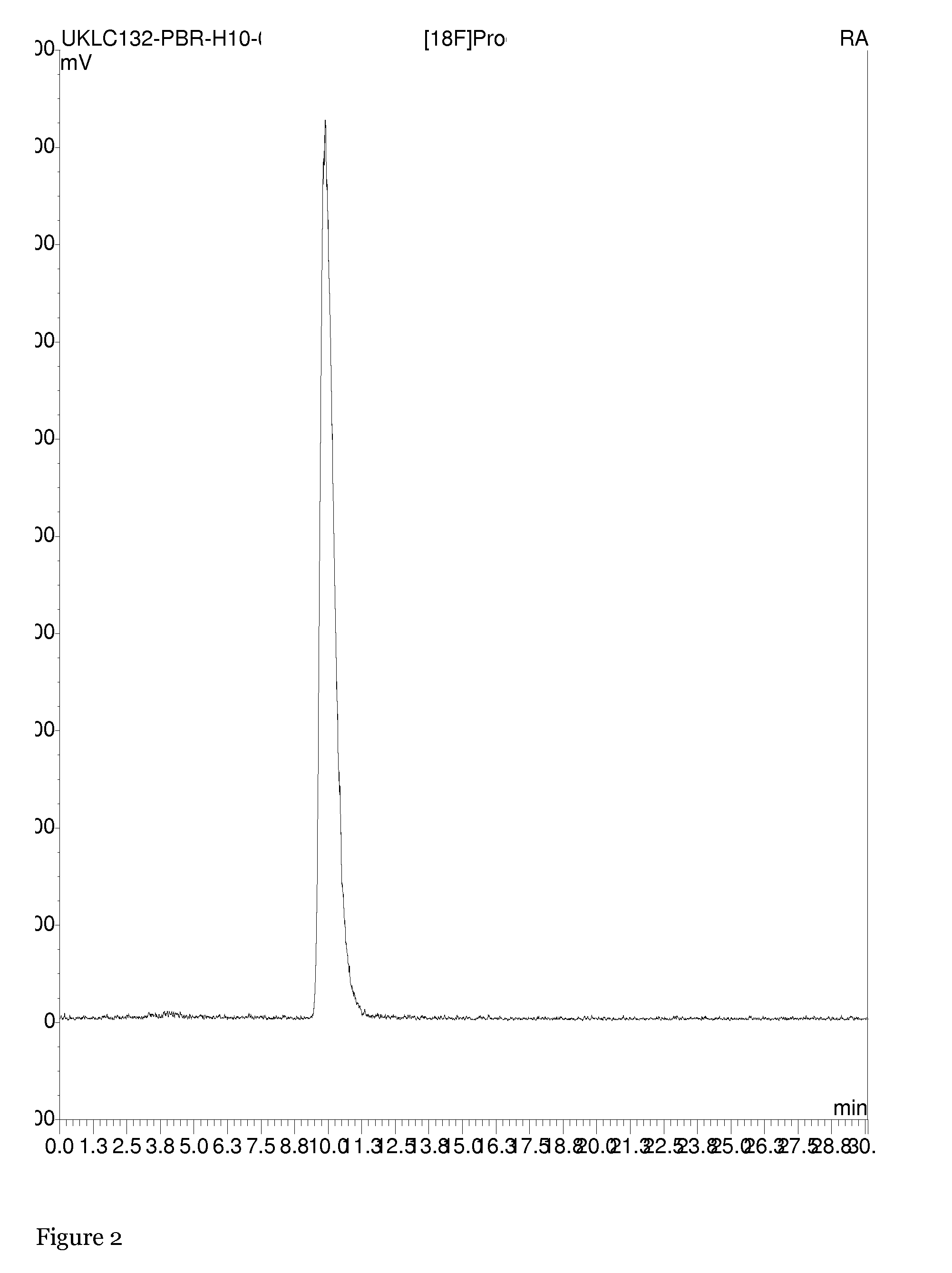
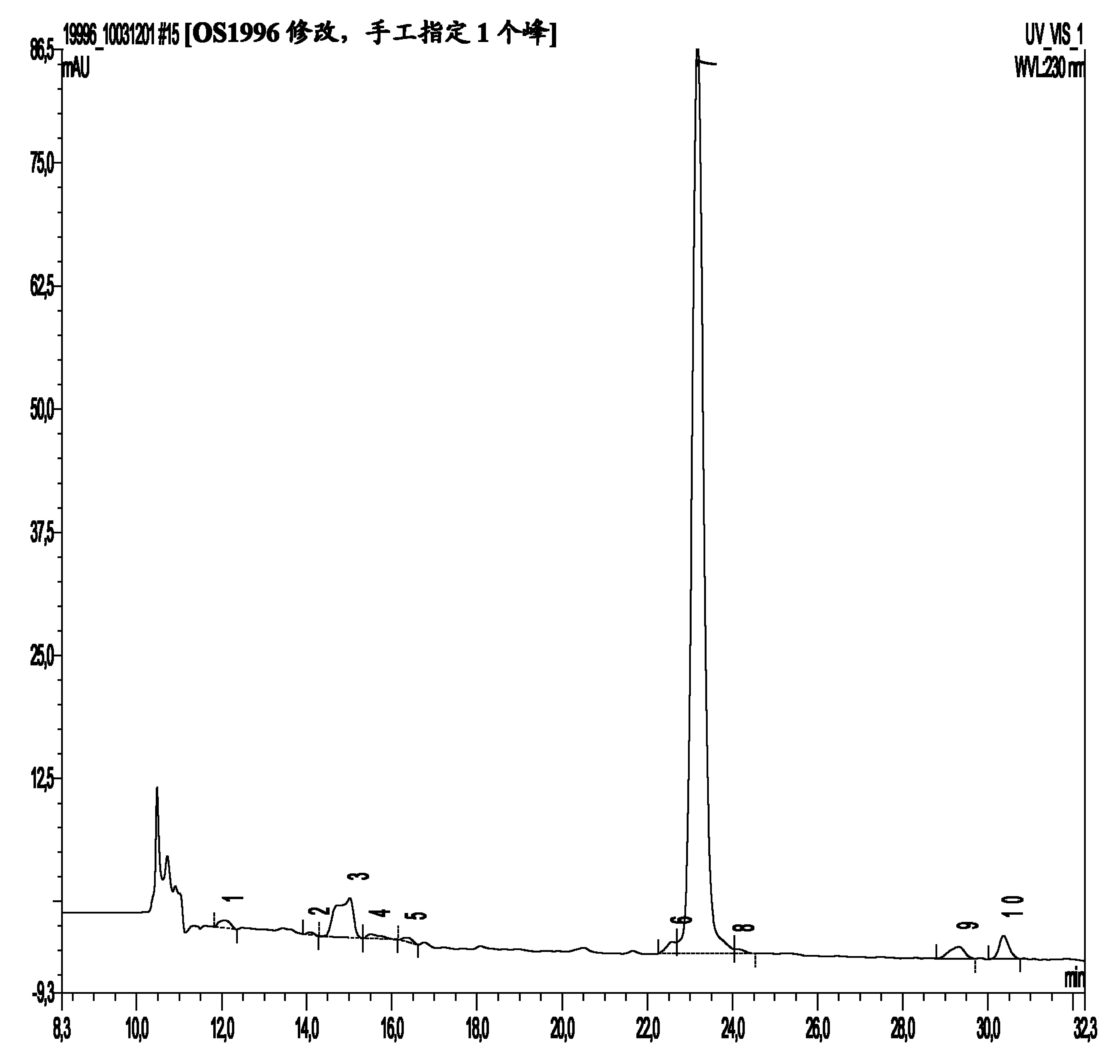
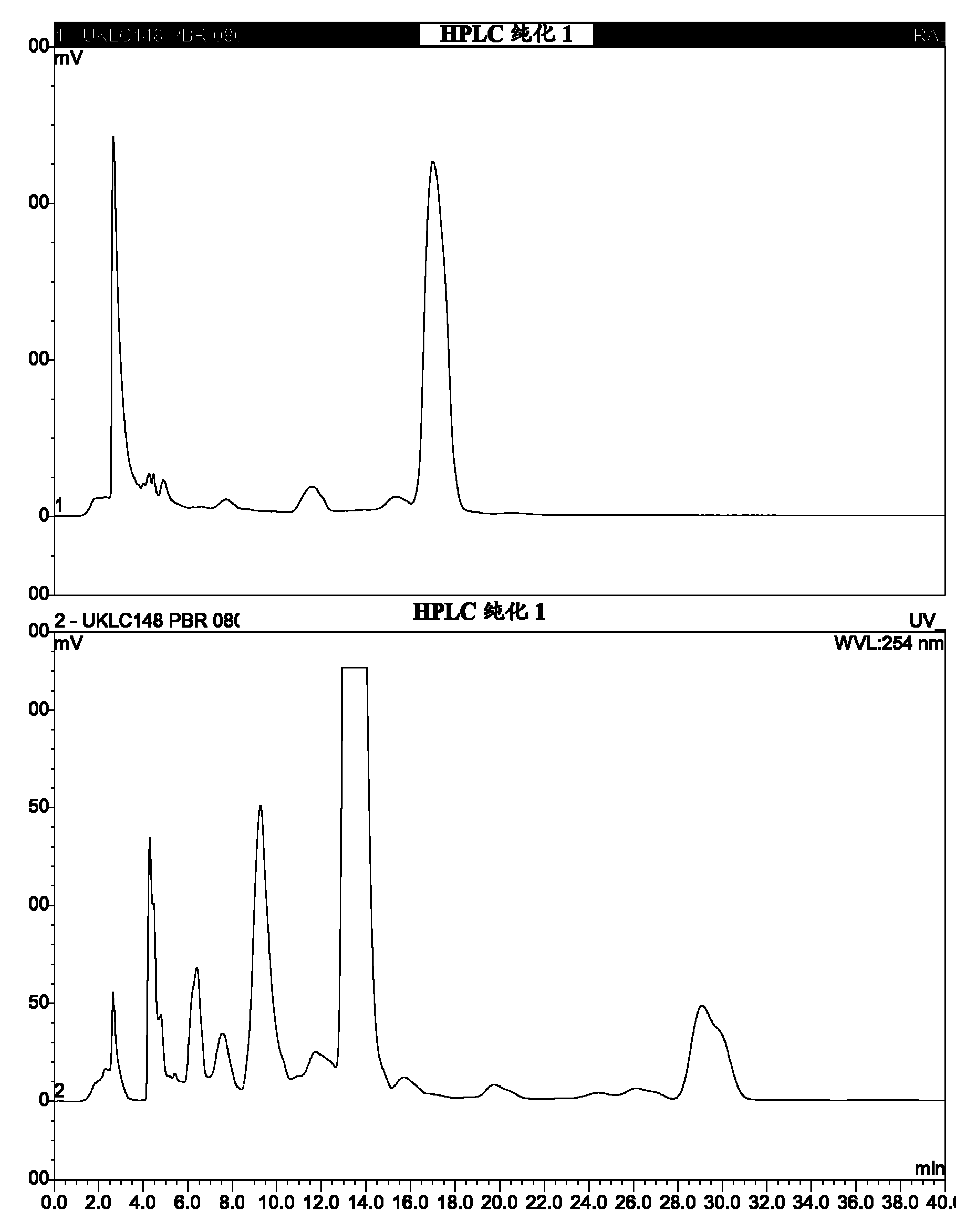
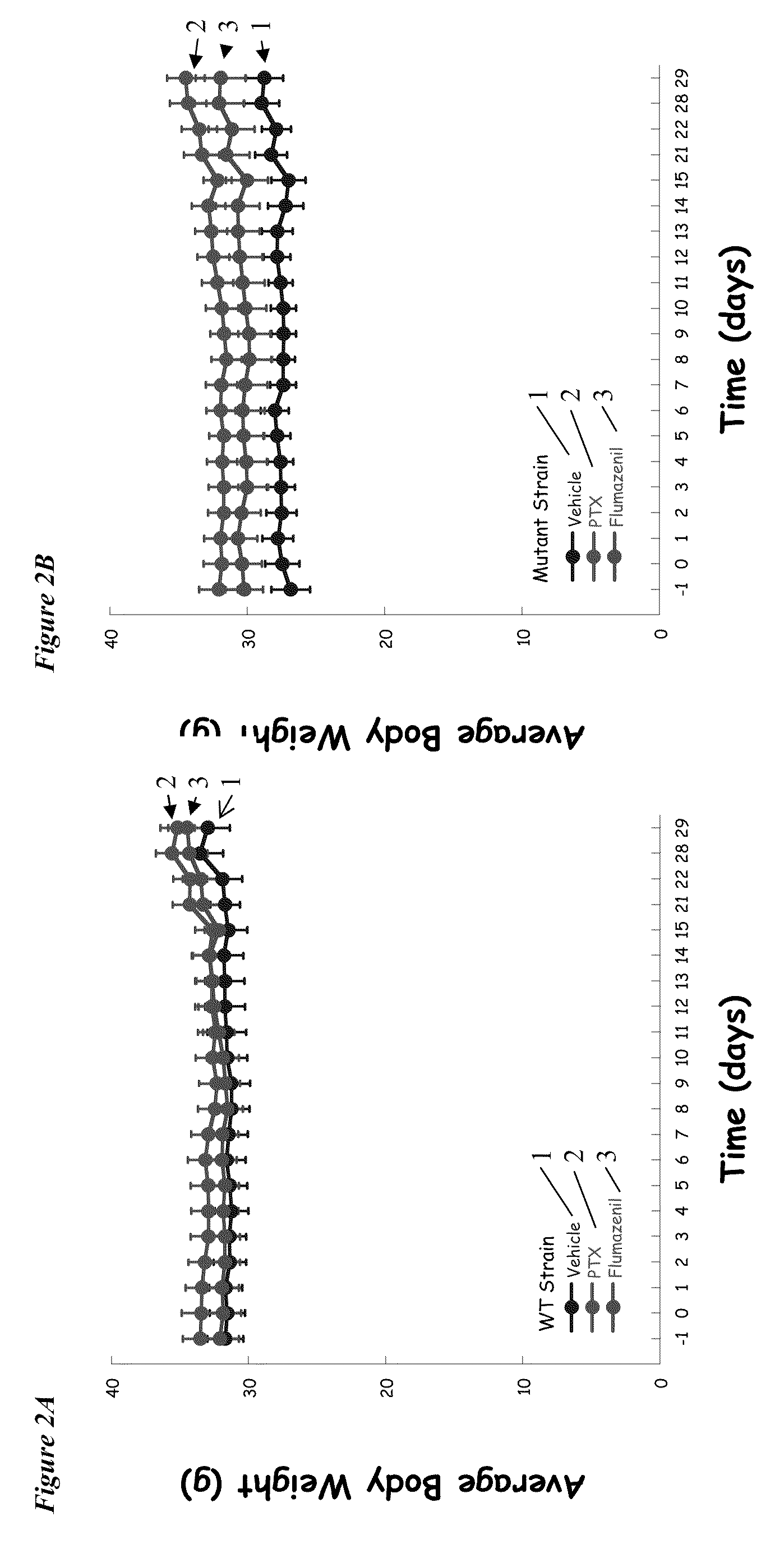
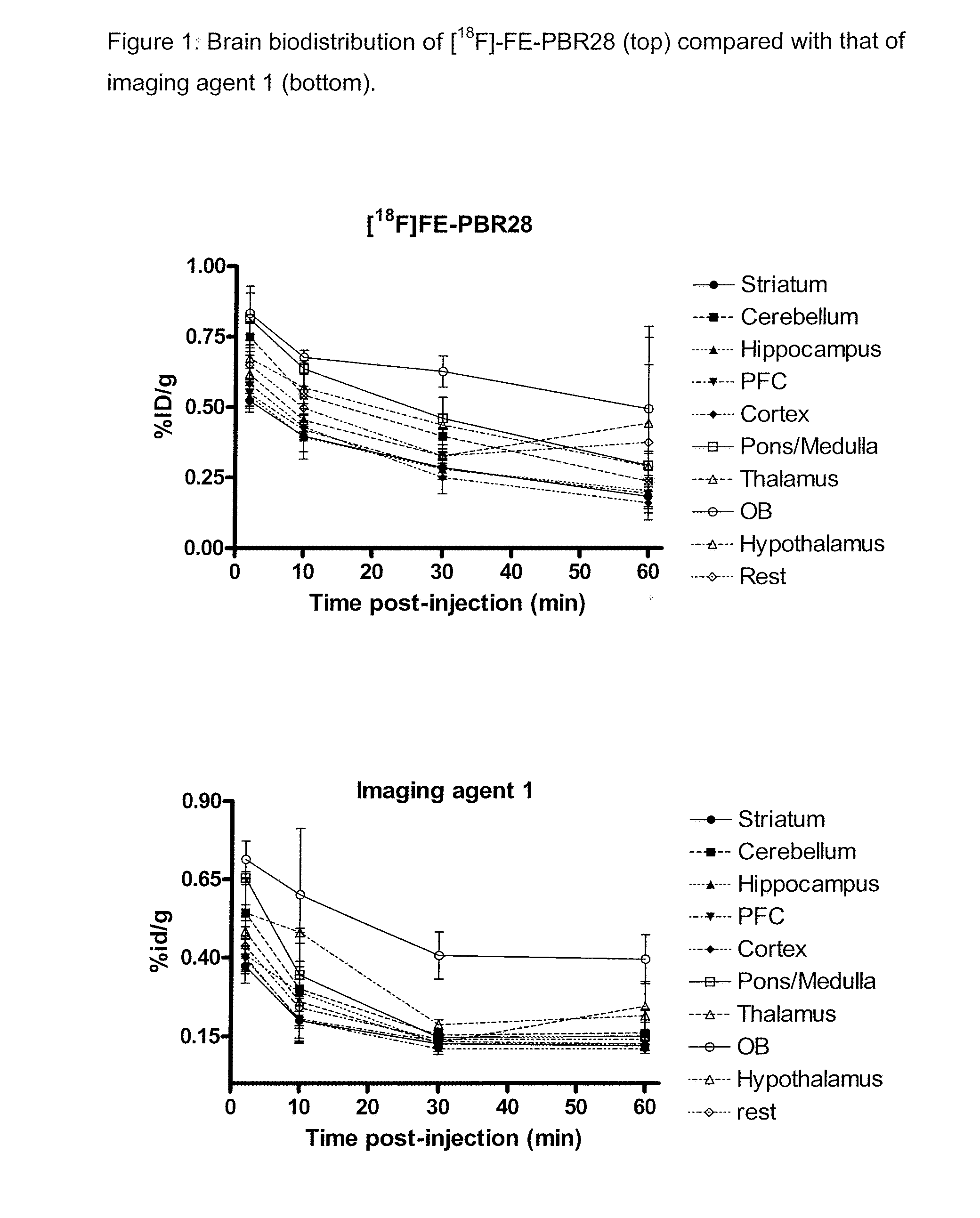
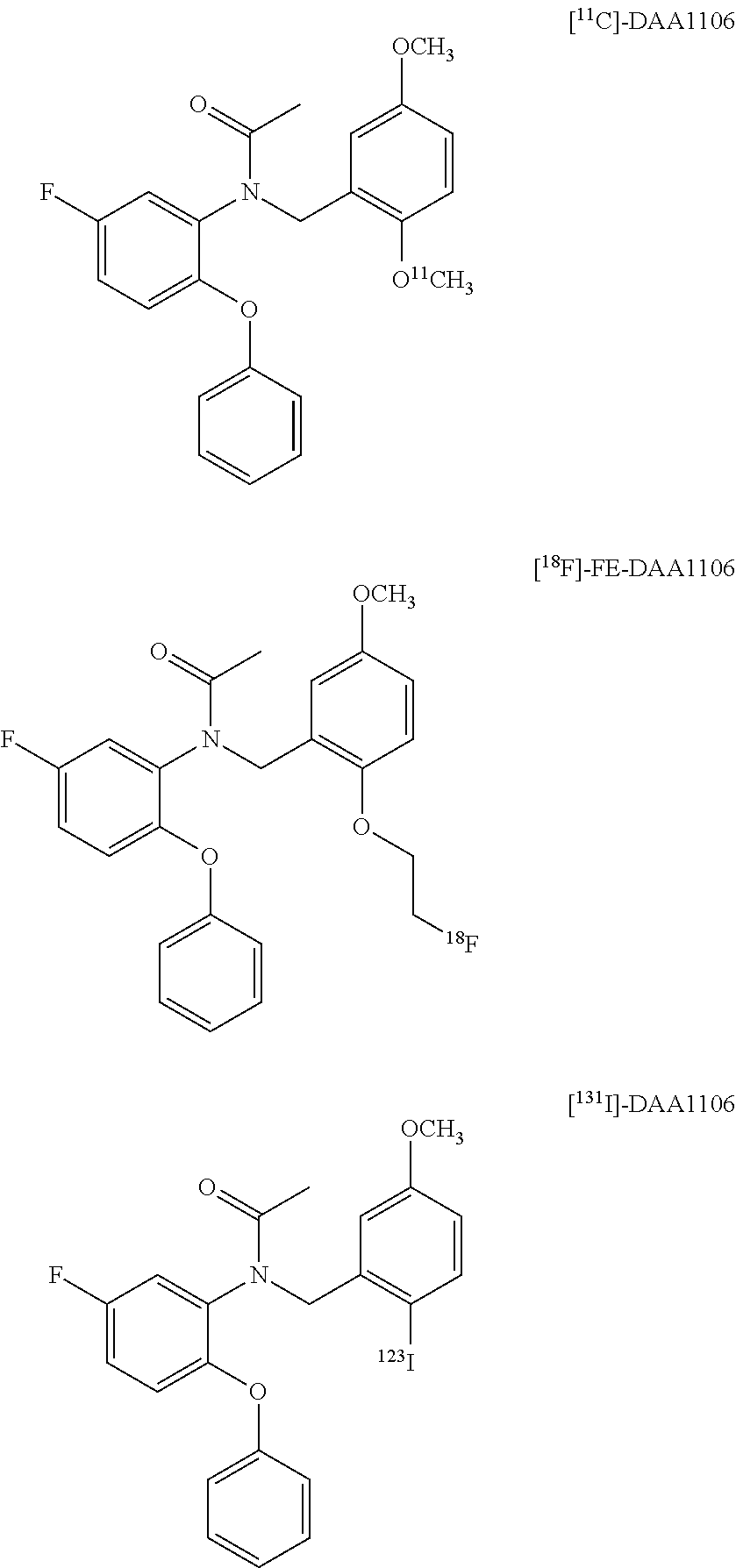
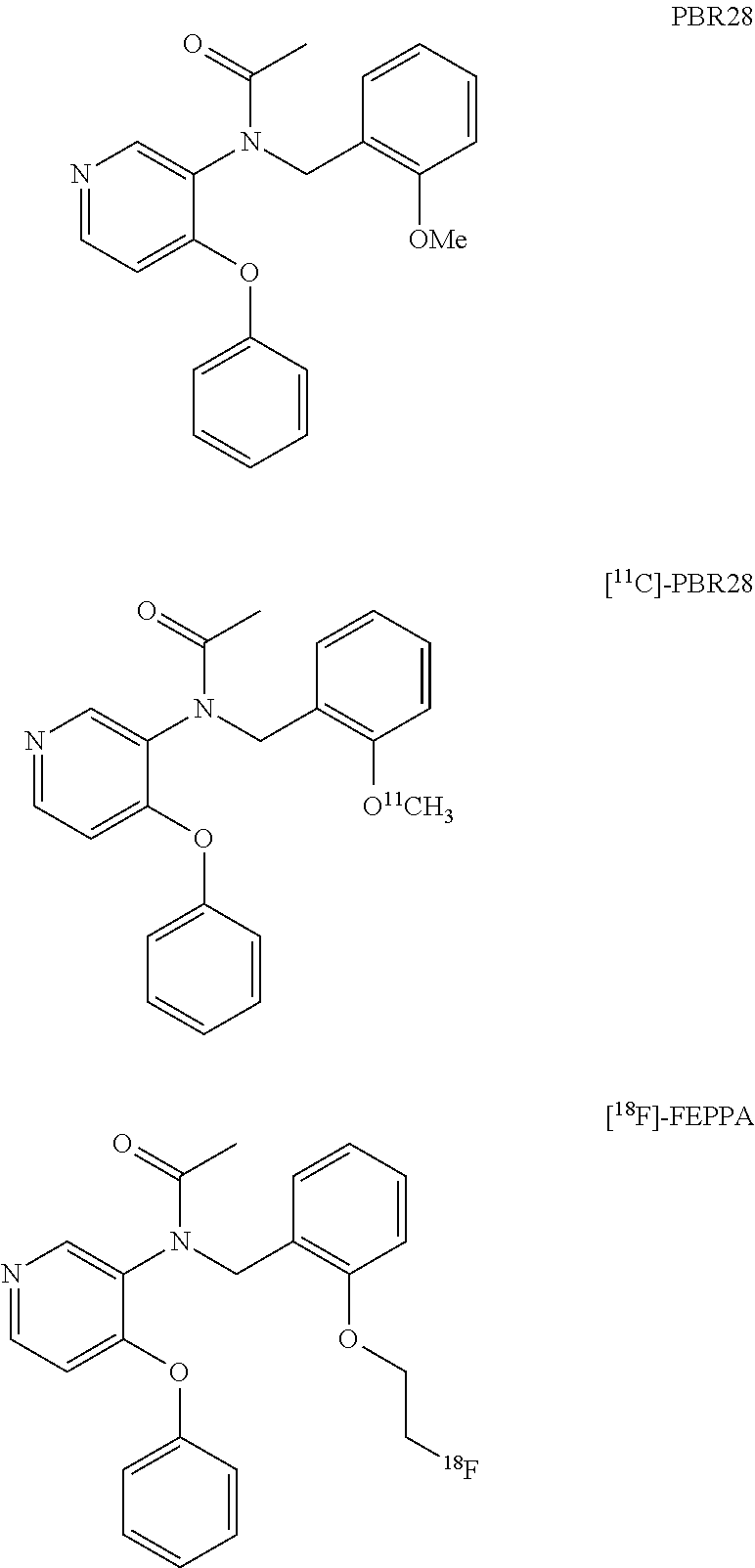
The present invention relates to an [18F]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, a synthesis thereof, and a method for evaluating biological results using the same. In the present invention, a fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer was prepared by introducing [18F]fluoroiodomethane, in which a prosthetic group diiodomethane is labeled with fluorine-18, into PBR28-OH through two stages, or substituting fluorine-18 using a triazolium triflate precursor in one stage at high yield. It was confirmed that, as a result of comparison and evaluation with exiting known [11C]PBR28 in view of in vitro binding affinity, fat affinity, and pharmacodynamic characteristics in a brain neuroinflammation model, the fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer had similar binding affinity and fat affinity to [11C]PBR28. Further, it was confirmed from the PET image comparison and evaluation in the brain neuroinflammation model that the fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer exhibited excellent selective / specific absorption in the inflammatory region more quickly and had high stability at the brain neuroinflammation site. According to the present invention, with respect to the synthesis of the novel fluoromethyl group-introduced fluorine-18 labeled radiotracer for PET targeting brain neuroinflammation and the diagnosis of brain neuroinflammation diseases, fluorine-18 having a relatively longer half-life than [11C]PBR28 was capable of being excellently labeled through the minimum structural change, and its excellent selective and specific imaging and pharmacodynamic advantages were verified, and thus a useful radiotracer for PET targeting brain neuroinflammation can be expected.
Owner:BIO IMAGING KOREA
Pet visualization of amyloid-associated neuroinflammation in the brain
InactiveUS20100055036A1High sensitivityMinimal interferenceNervous disorderOrganic chemistryMammalAmyloid
The present invention relate to a method for monitoring a response to a therapy on a mammal having a neurodegenerative or neuroinflammatory disorder. According to a preferred embodiment, the method comprising the steps of:a) imaging the mammal using a radio-labeled peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand;b) administrating in the mammal at least one anti-amyloid or anti-neuroinflammatory agent;c) imaging the mammal of step b) using a radio-labeled peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand; andd) detecting the level of CNS neuroinflammation by the signals from the radio-labeled peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI
Tricyclic oxazepines as in vivo imaging compounds
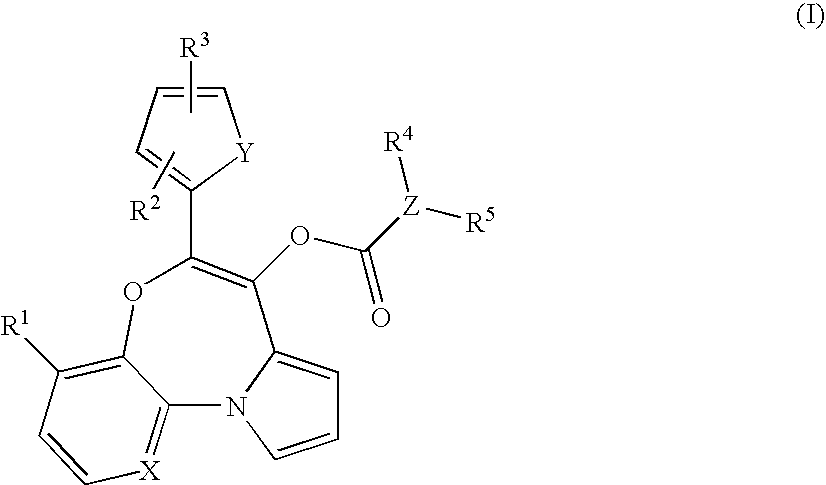
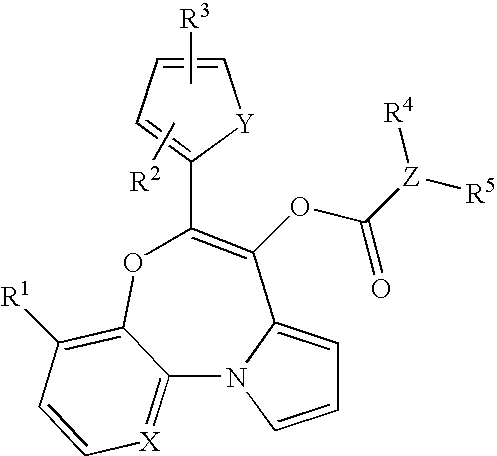
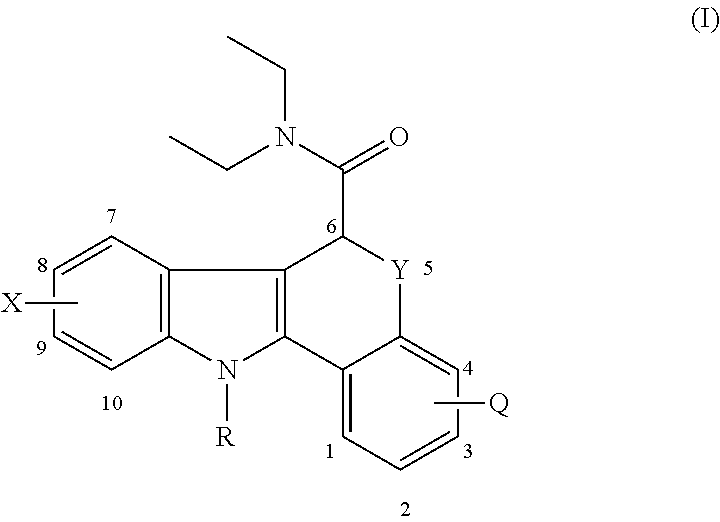
Novel compounds of formula (I): suitable for use as in vivo imaging agents are provided as well as precursors suitable for the preparation of said compounds. The present invention also provides pharmaceuticals comprising the compounds and kits for the preparation of the pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, use of the compounds for imaging peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in a subject is provided, in particular for imaging pathological conditions in which PBR are upregulated, e.g. Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease, neuropathic pain, arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis and cancer.
Owner:ARSTAD ERIK +2
18F-Labeled Phenoxyphenyl Nu-benzyl Alkanamid Derivatives for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging of Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptor
The present invention provides novel 18F-labeled phenoxyphenyl N-benzyl alkanamid derivative compounds that are suitable for use as an in vivo imaging agent. A pharmaceutical comprising the compound and a kit for the preparation of the pharmaceutical are also provided. Methods of use and use of claims for novel 18F-labeled phenoxyphenyl N-benzyl alkanamid derivative compounds are provided as well.
Owner:LANGSTROM BENGT +1
DAA-pyridine as peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand for diagnostic imaging and pharmaceutical treatment
This invention relates to novel compounds suitable for labelling or already labelled by 18F, methods of preparing such a compound, compositions comprising such compounds, kits comprising such compounds or compositions and uses of such compounds, compositions or kits for therapy and diagnostic imaging by positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA OY
Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor associated proteins, cloning, expression and methods of use
InactiveUS20060106202A1Increasing and decreasing and expressionIncrease and decrease functionFungiNervous disorderCDNA libraryHybrid system
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor: a tool for detection, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cancer
InactiveUS7267977B2Inhibit bindingReduce functionBacteriaGenetic material ingredientsSubcellular localizationPeripheral-Type Benzodiazepine Receptor
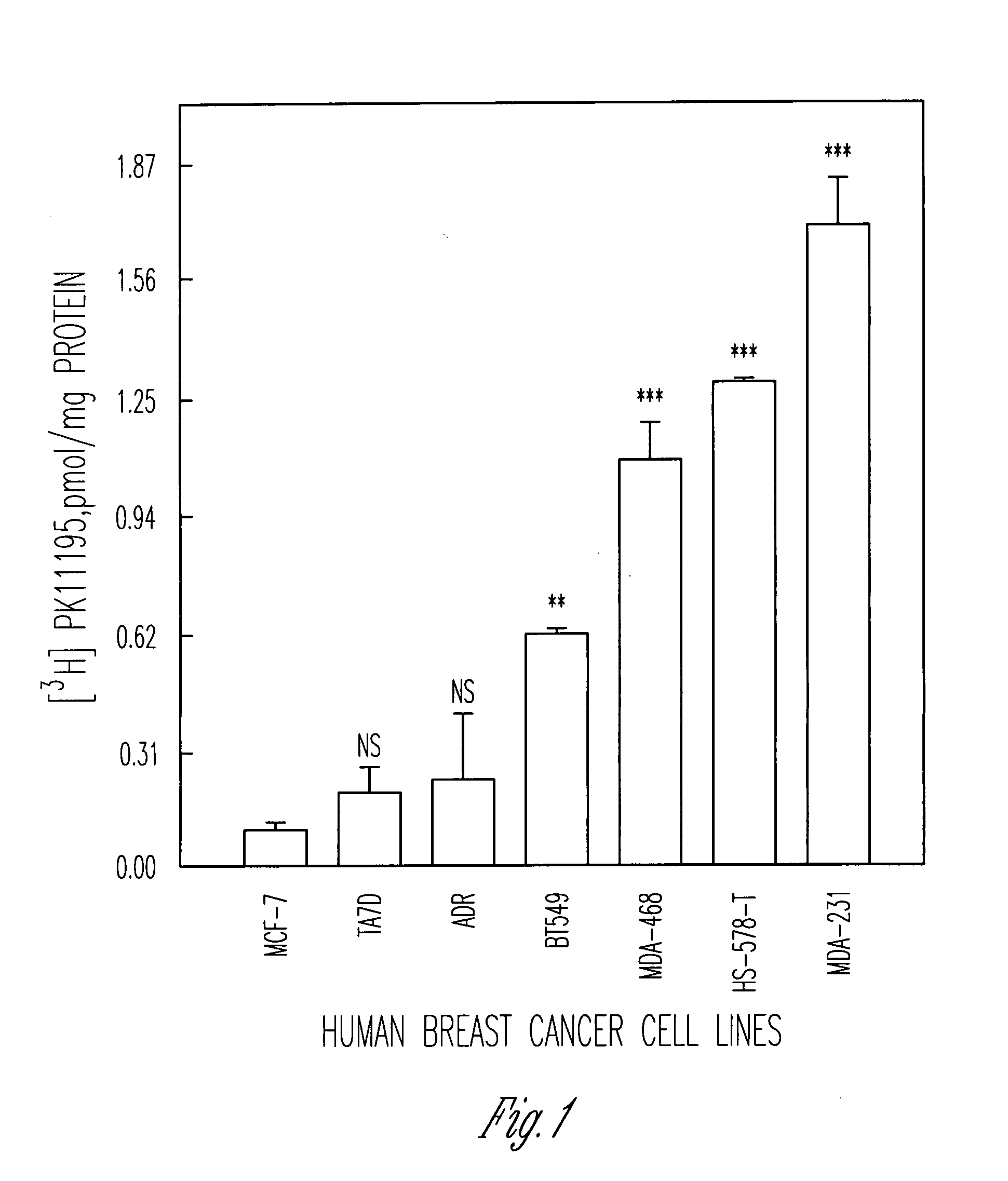
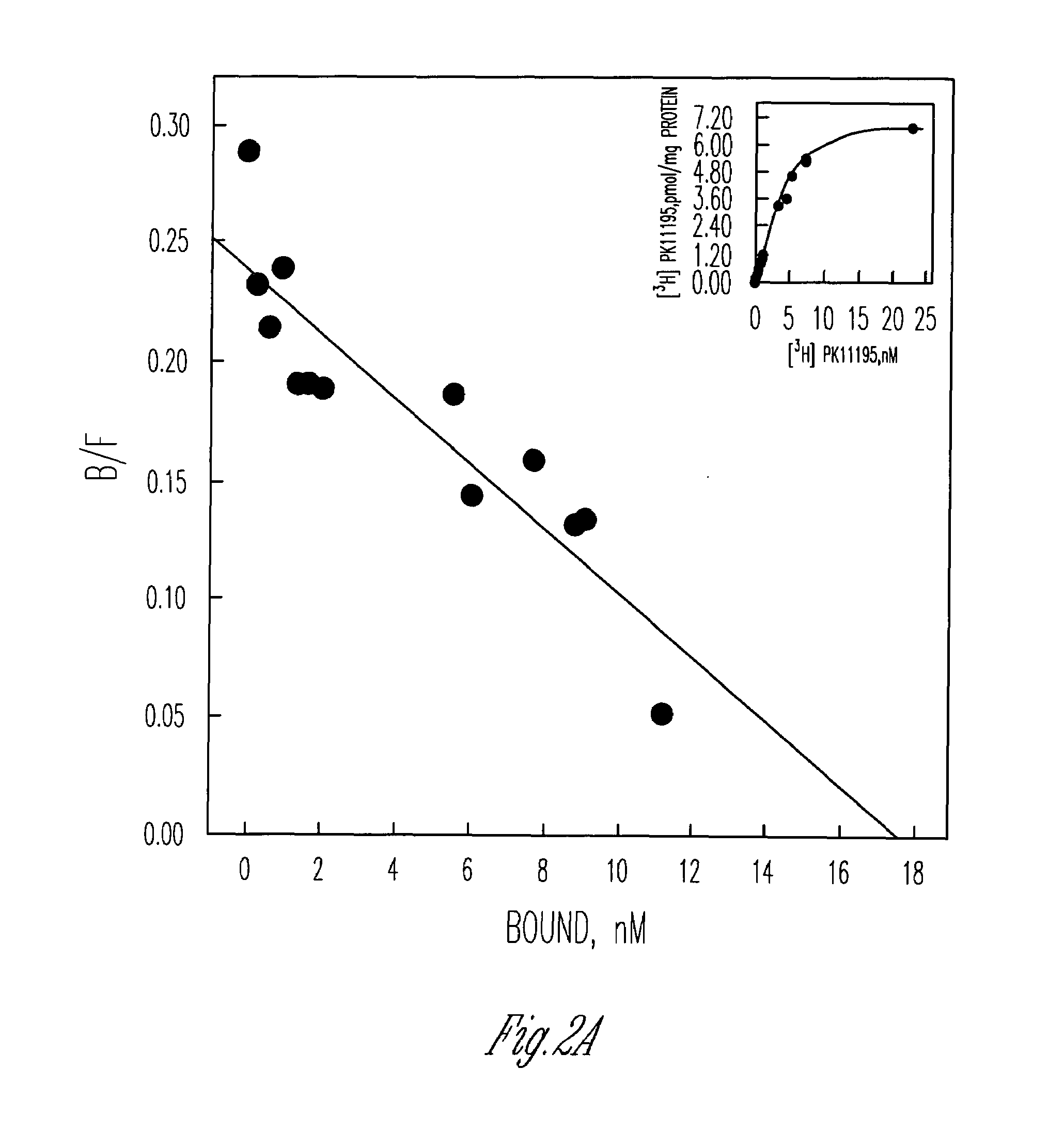
The expression and subcellular localization of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors (PBR) is shown in this application to correlate with the metastatic potential of cells, and increased cell proliferation. Inhibition of PBR expression, function or stability results in a decrease in cell proliferation. Compositions and methods for regulating and / or monitoring PBR and its expression are useful for the detection, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumors, in particular, breast cancer.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Imaging neuroinflammation
InactiveUS20110190618A1Maintain good propertiesImprove bindingOrganic chemistrySurgeryImaging agentBenzodiazepine receptor ligand
The present invention concerns in vivo imaging and in particular in vivo imaging of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (PBR). A tetracyclic indole in vivo imaging agent is provided that binds with high affinity to PBR, has good uptake into the brain following administration, and which preferentially binds to tissues expressing higher levels of PBR. The present invention also provides a precursor compound useful in the synthesis of the in vivo imaging agent of the invention, as well as a method for synthesis of said in vivo imaging agent comprising use of said precursor compound, and a kit for carrying out said method. A cassette for the automated synthesis of the in vivo imaging agent is also provided. In addition, the invention provides a radiopharmaceutical composition comprising the in vivo imaging agent of the invention, as well as methods for the use of said in vivo imaging agent.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Daa-pyridine as peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand for diagnostic imaging and pharmaceutical treatment
InactiveUS20110200535A1Good water solubilityImprove bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderLabellingPyridine
This invention relates to novel compounds suitable for labelling or already labelled by 18F, methods of preparing such a compound, compositions comprising such compounds, kits comprising such compounds or compositions and uses of such compounds, compositions or kits for therapy and diagnostic imaging by positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:PIRAMAL IMAGING
Imidazo-pyrimidines and triazolo-pyrimidines: benzodiazepine receptor ligands
Compounds of Formula Iare provided, as are methods for their preparation. The variables Z1, Z2, Z3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8 and Ar in the above formula are defined herein. Such compounds may be used to modulate ligand binding to GABAA receptors in vivo or in vitro, and are particularly useful in the treatment of a variety of central nervous system (CNS) disorders in humans, domesticated companion animals and livestock animals. Compounds provided herein may be administered alone or in combination with one or more other CNS agents to potentiate the effects of the other CNS agent(s). Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating such disorders are provided, as are methods for using such ligands for detecting GABAA receptors (e.g., receptor localization studies).
Owner:NEUROGEN
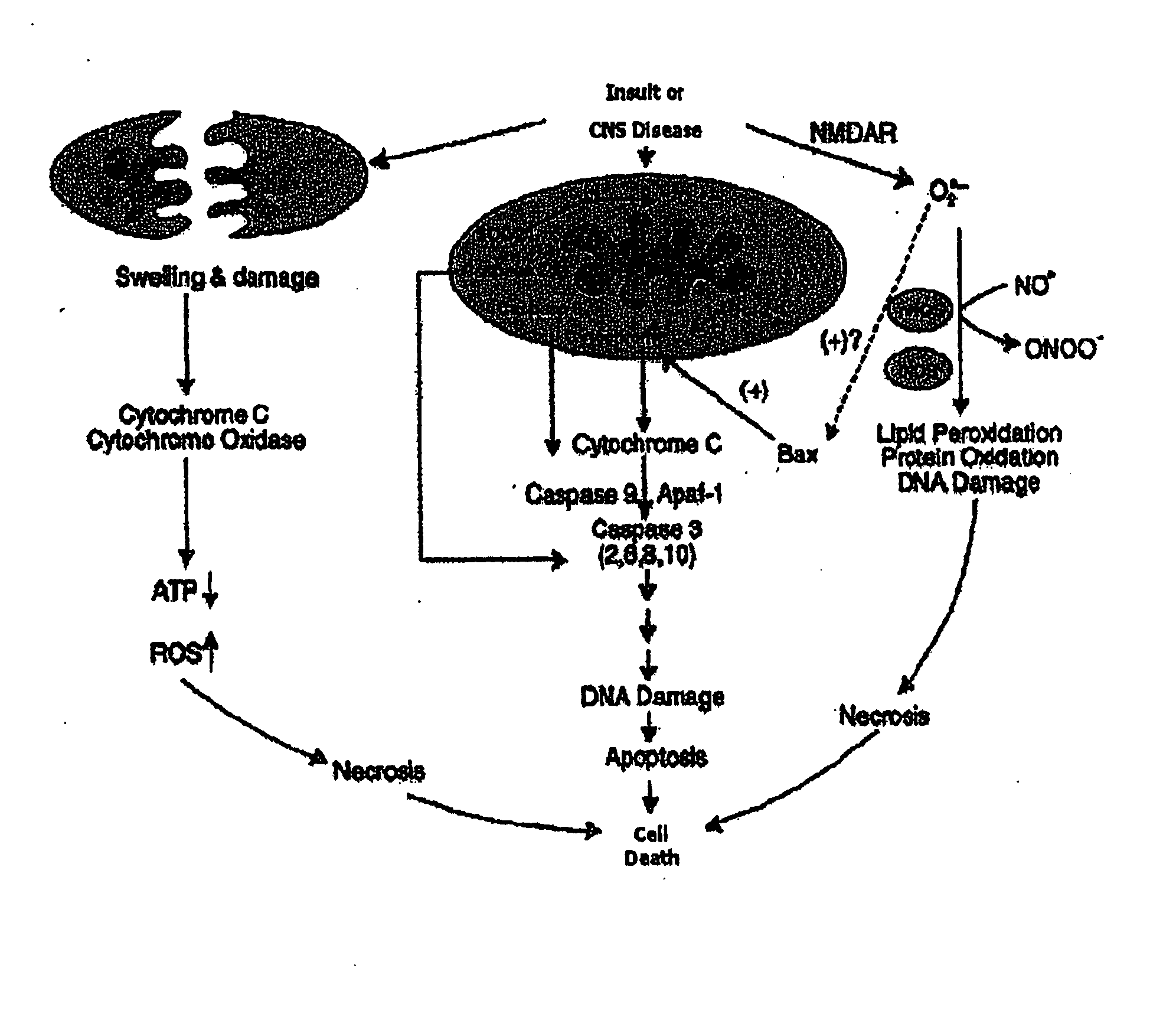
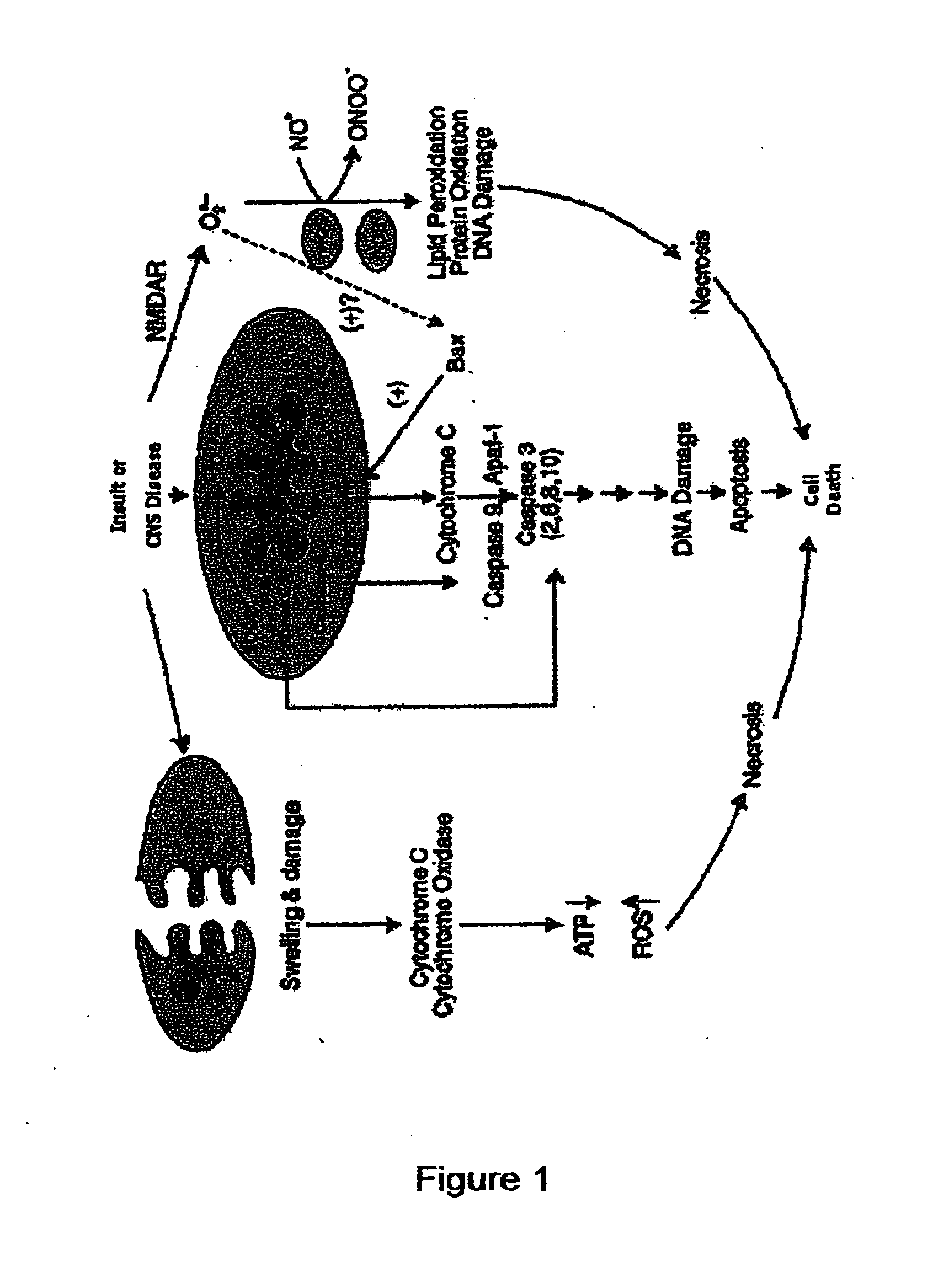
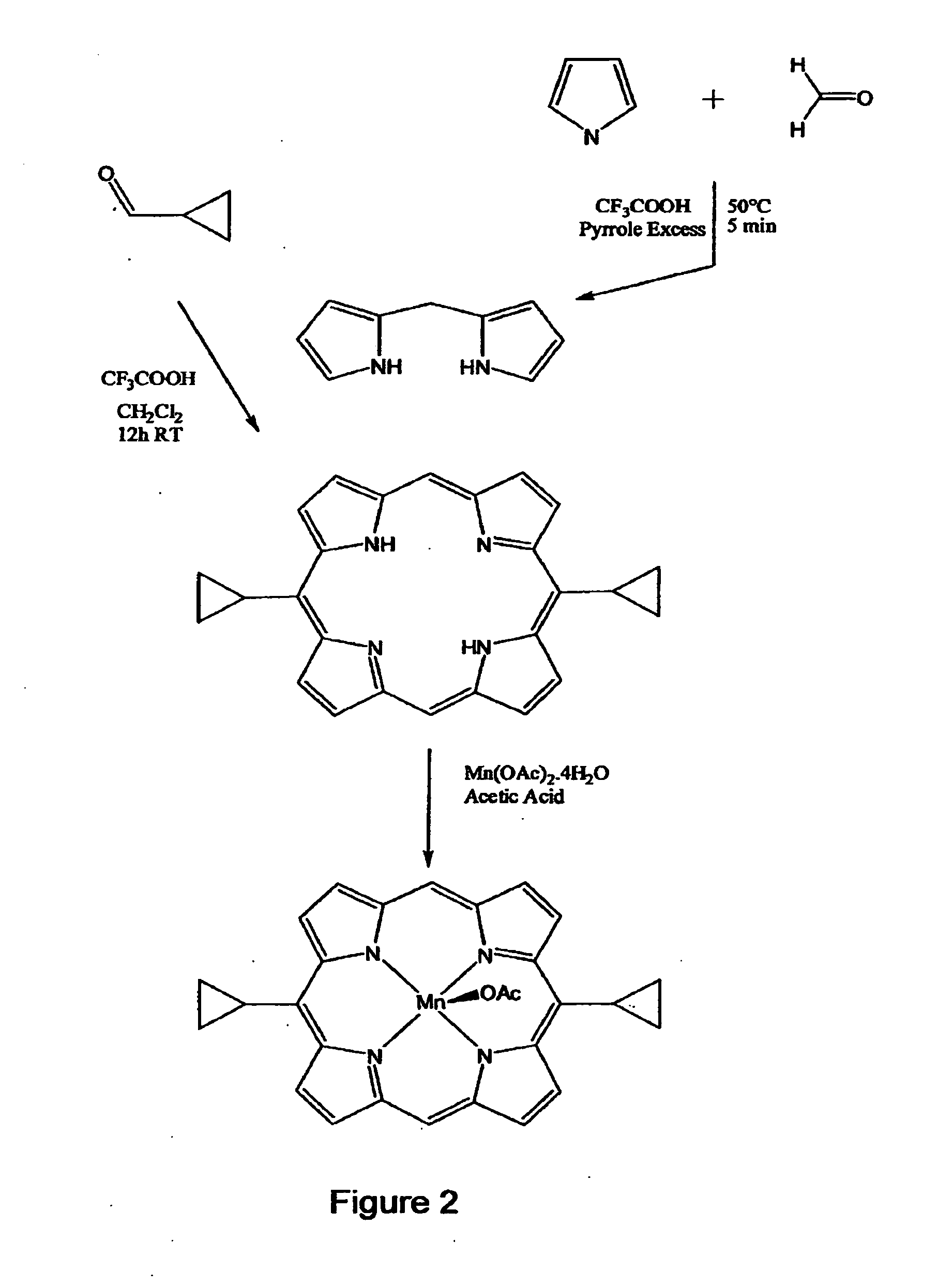
Anti-apoptotic benzodiazepine receptor ligand inhibitors
InactiveUS20100120738A1Inhibit delay prevent bindingSufficient stability and solubility and oral bioavailabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRadiation induced apoptosisDrug overdose
The present invention provides low molecular weight porphyrin compositions for inhibiting, preventing or delaying the binding of a ligand of a mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising these porphyrin compositions and their use in the treatment of conditions involving the mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor or interactions between the receptor and the mitochondrial permeability transition pore e.g., drug overdose or apoptosis including neural degeneration and radiation-induced apoptosis.
Owner:MALFROY CAMINE BERNARD +1
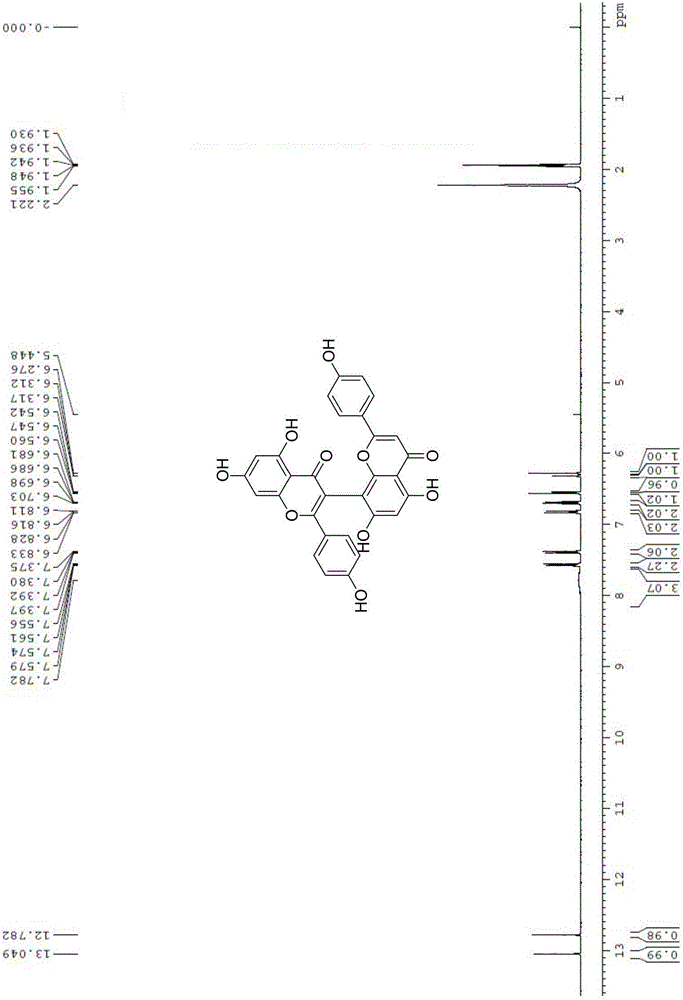
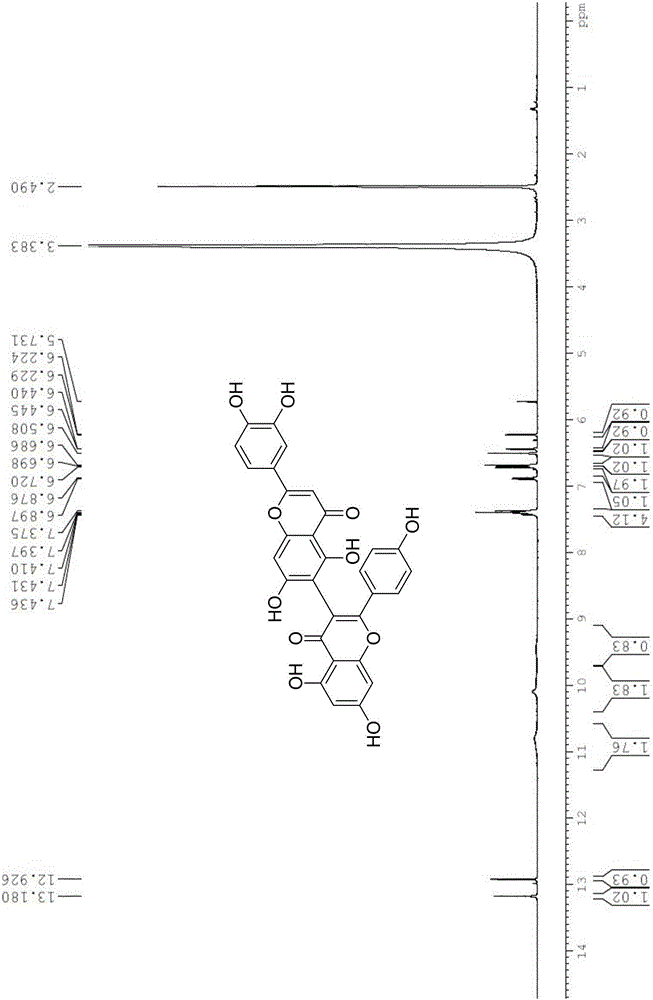
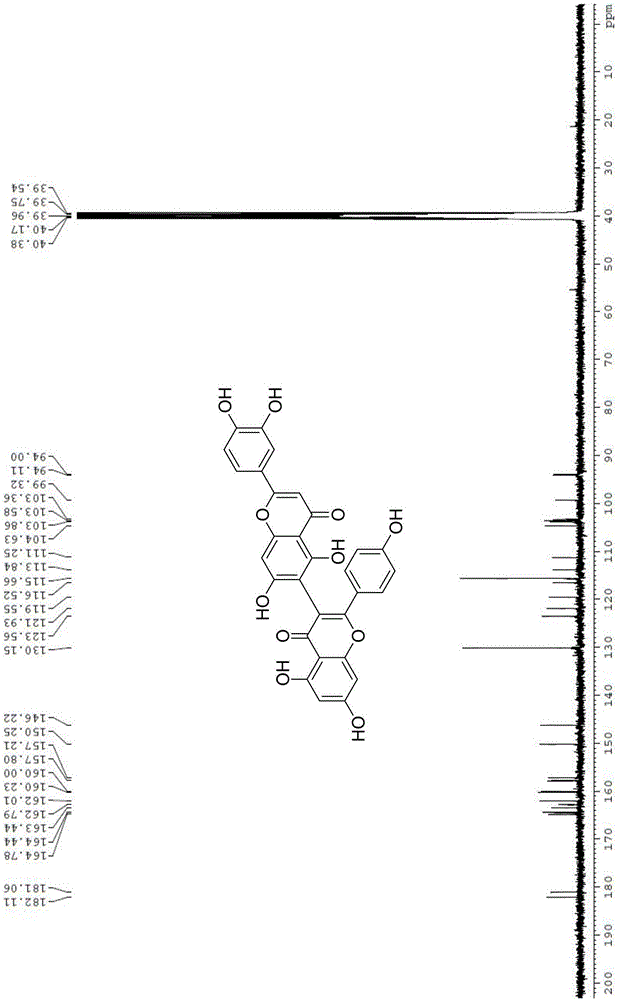
Preparation method of natural biflavones such as I3,II8-Biapgienin and Ridiculuflavone A
ActiveCN106518827AAddressing Limitations of Activity StudiesFull synthesisOrganic chemistryEstrogen receptorDrug development
The present invention belongs to the field of new compound preparation methods and medicine research, and particularly relates to a preparation method of natural biflavones such as I3,II8-Biapgienin and Ridiculuflavone A. According to the present invention, the two compounds such as I3,II8-Biapgienin and Ridiculuflavone A are firstly synthesized, wherein I3,II8-Biapgienin has good anti-depression activity, good anti-tumor activity, good anti-oxidation activity, good anti-inflammatory activity and good anti-liver injury activity, further has inhibition activity on estrogen receptors, benzodiazepine receptors and CYP, and has broad prospects in the fields of drug development and application.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of treating or preventing central nervous system disorders with compounds having selectivity for the alpha 3 subunit of the benzodiazepine receptor
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Method of treating or preventing central nervous system disorders with compounds having selectivity for the alpha 3 subunit of the benzodiazepine receptor
InactiveUS20050032863A1Easy to detectHigh selectivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The present invention relates to the use of 1-ar(alk)ylimidazolin-2-ones which contain a disubstituted amine radical in the 4-position for the treatment or prevention of central nervous system disorders including depression, anxiety, movement disorders, and especially dystonia, and psychotic disorders, and especially schizophrenia and psychotic symptoms associated to other mental disorders.
Owner:ARZNEIMITTELWERK DRESDEN GMBH
Carbazole compounds for in vivo imaging
ActiveUS20160214936A1Improve bindingOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersRadioactive tracerCarbazole
The present invention concerns in vivo imaging and in particular in vivo imaging of translocator protein (TSPO, formerly known as the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor). An indole-based in vivo imaging agent is provided that overcomes problems relating to known TSPO-binding radiotracers. The present invention also provides a precursor compound useful in the synthesis of the in vivo imaging agent of the invention, as well as a method for synthesis of said precursor compound. Other aspects of the invention include a method for the synthesis of the in vivo imaging agent of the invention comprising use of the precursor compound of the invention, a kit for carrying out said method, and a cassette for carrying out an automated version of said method. In addition, the invention provides a radiopharmaceutical composition comprising the in vivo imaging agent of the invention, as well as methods for the use of said in vivo imaging agent.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Carbazole compounds for in vivo imaging
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
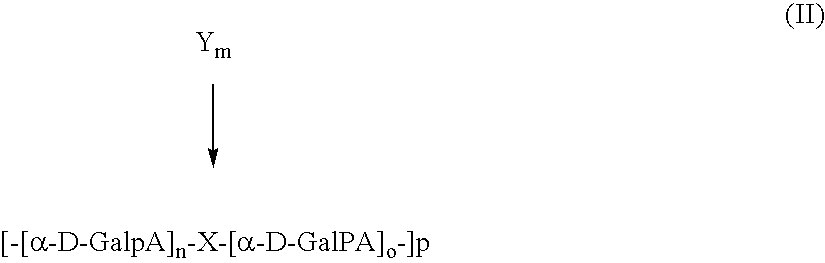

![[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same [18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/968fa248-169b-432d-ae39-6511ddb8404d/HDA0000939678010000011.PNG)
![[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same [18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/968fa248-169b-432d-ae39-6511ddb8404d/HDA0000939678010000012.PNG)
![[18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same [18f]fluoromethyl group-introduced radiotracer for positron emission tomography for targeting brain neuroinflammation, synthesis thereof, and method for evaluating biological results using same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/968fa248-169b-432d-ae39-6511ddb8404d/HDA0000939678010000021.PNG)