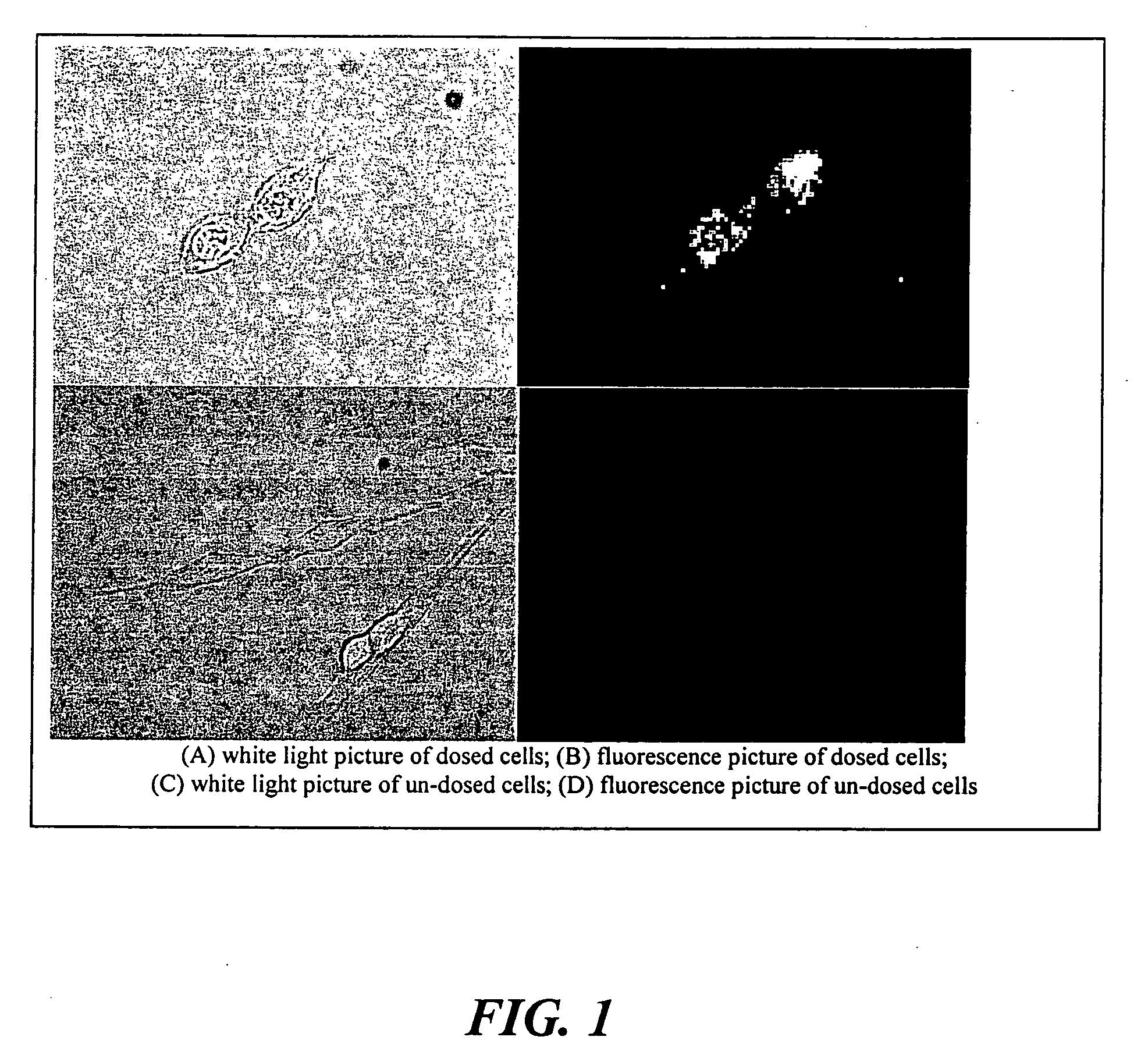
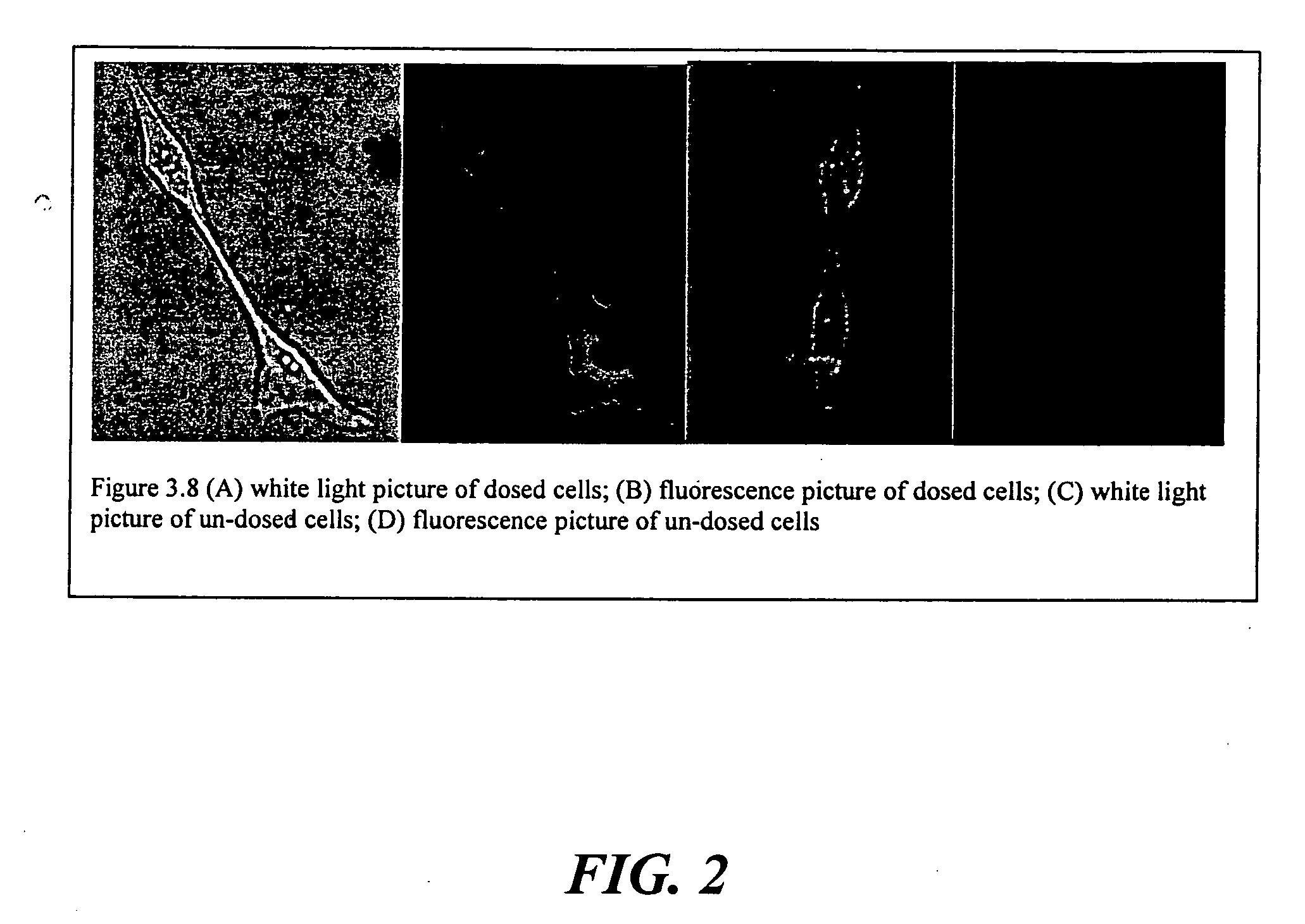
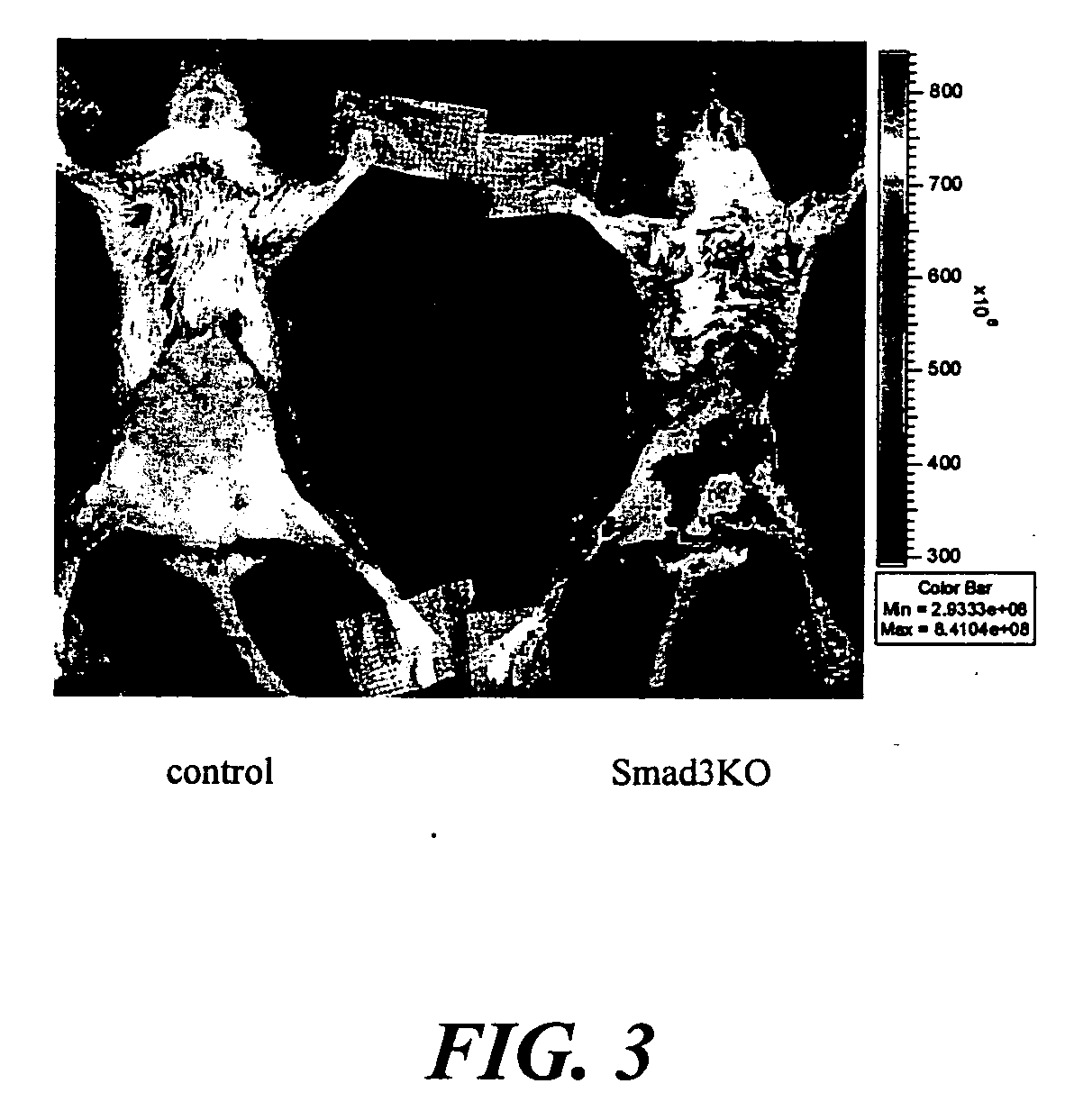
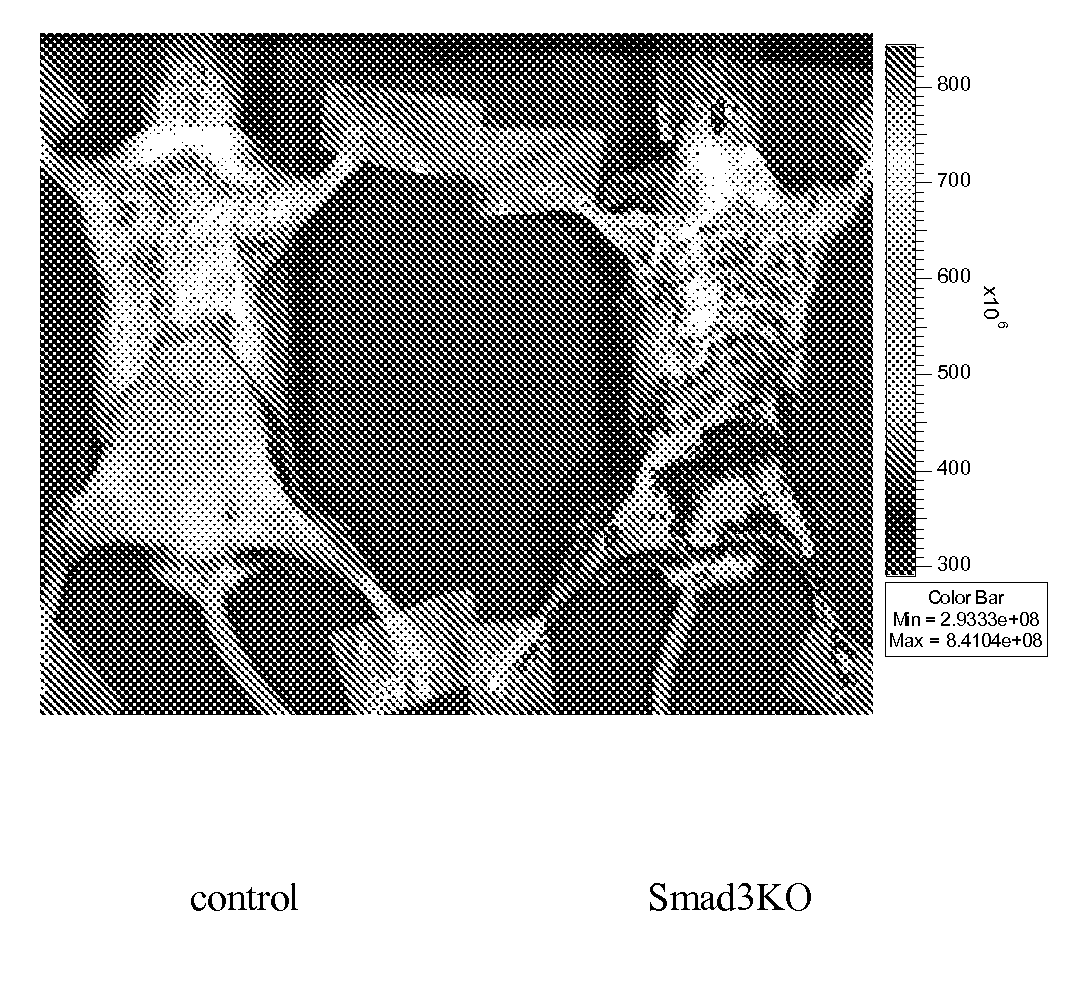
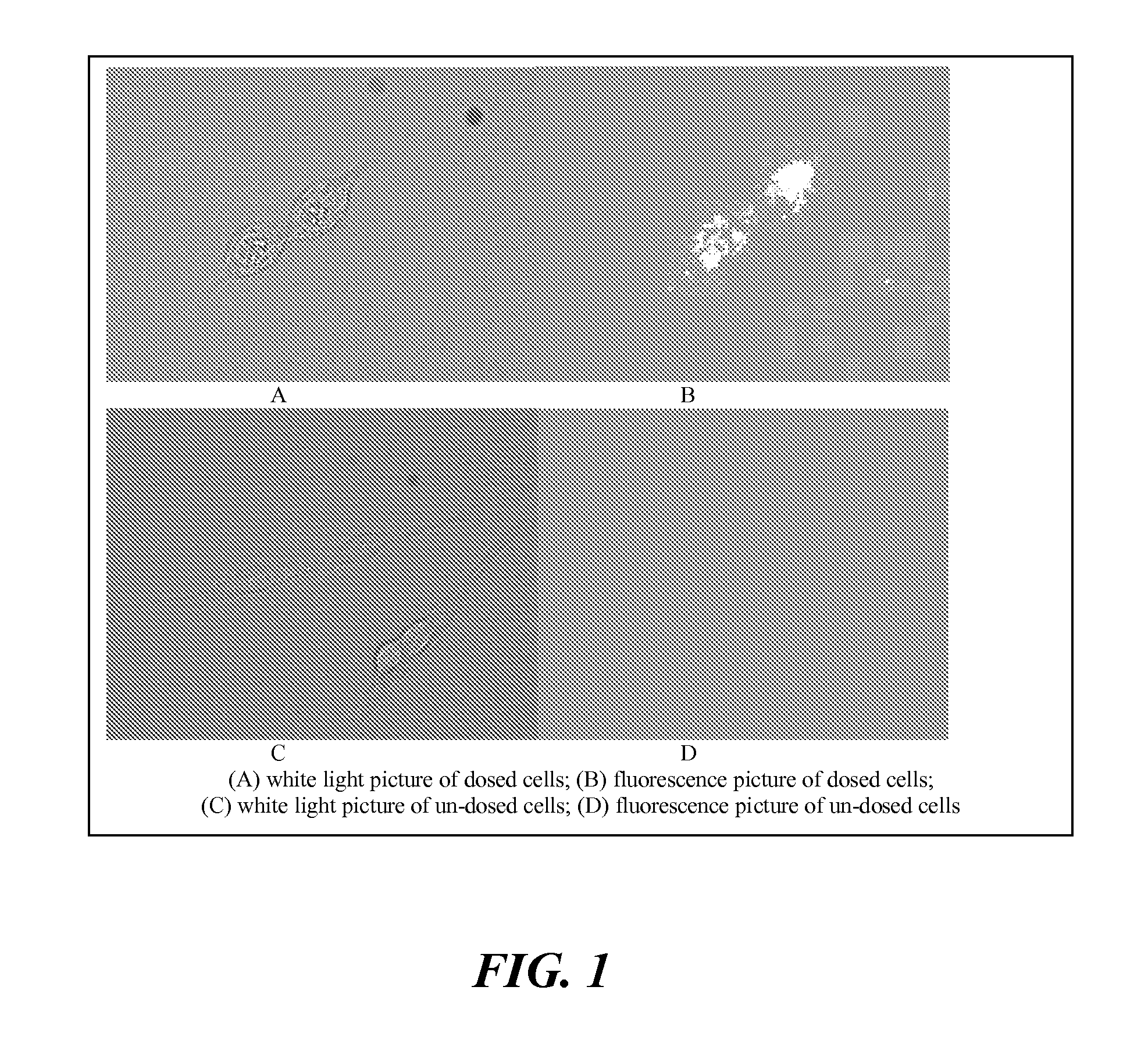
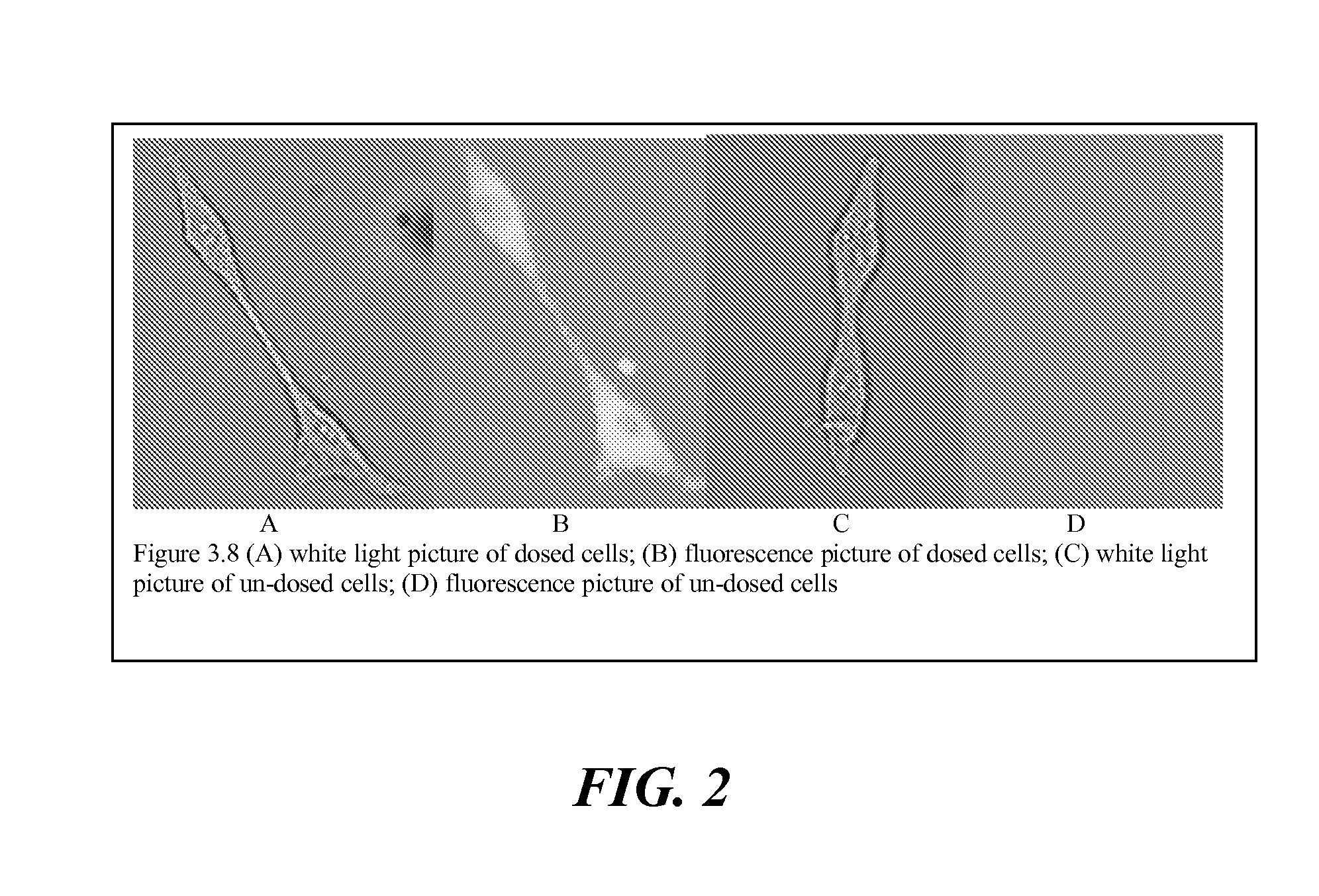
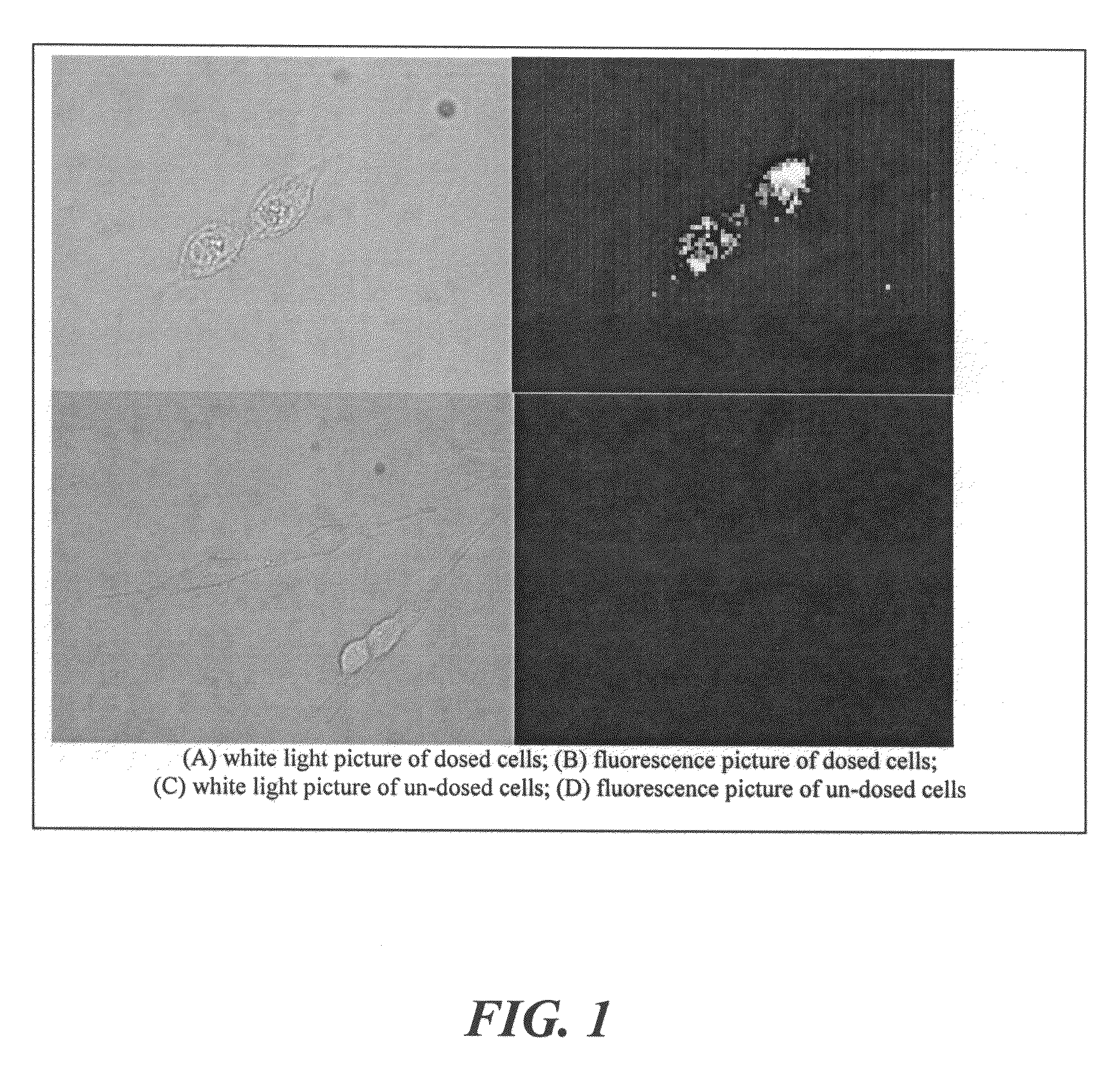
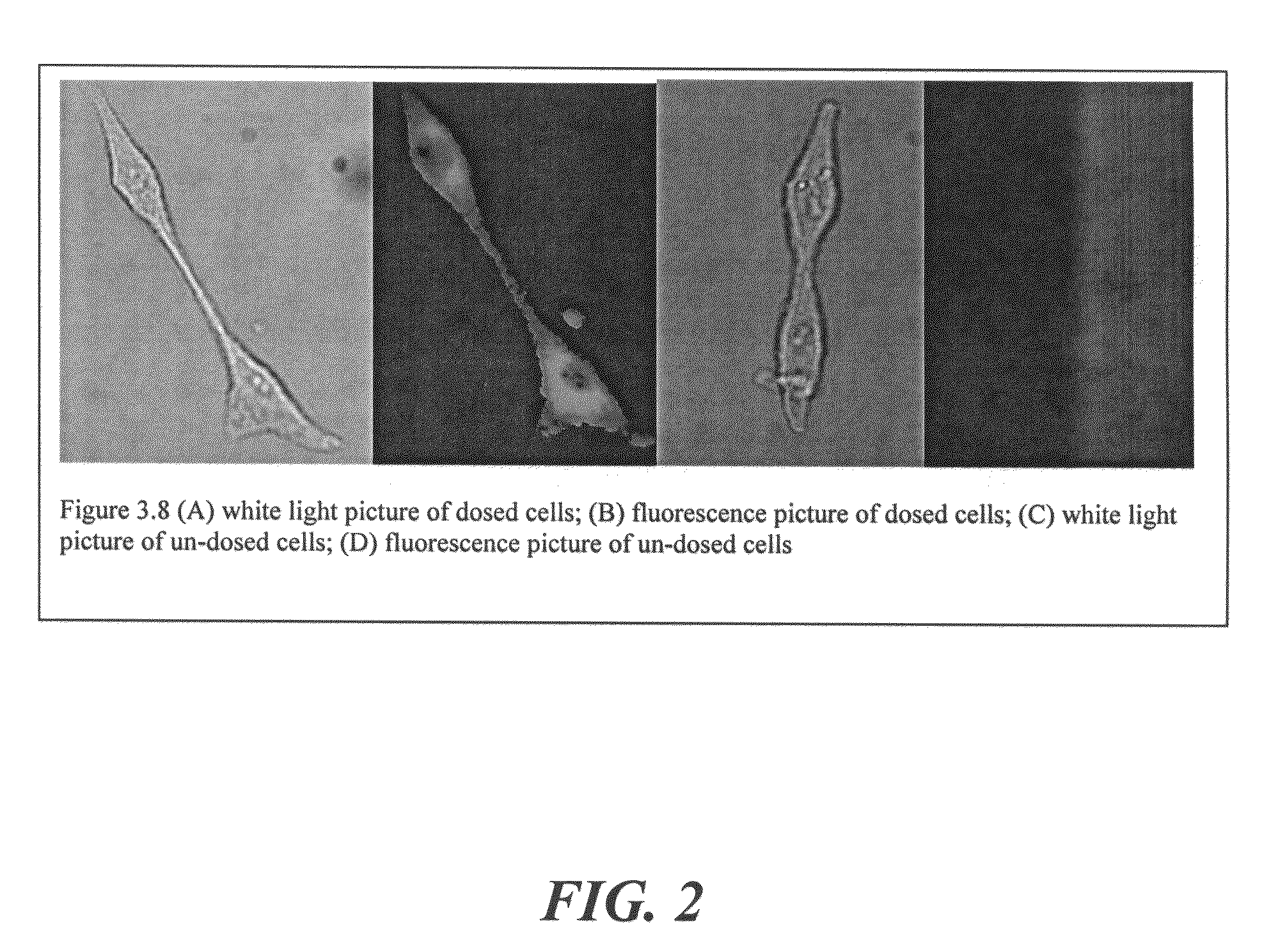
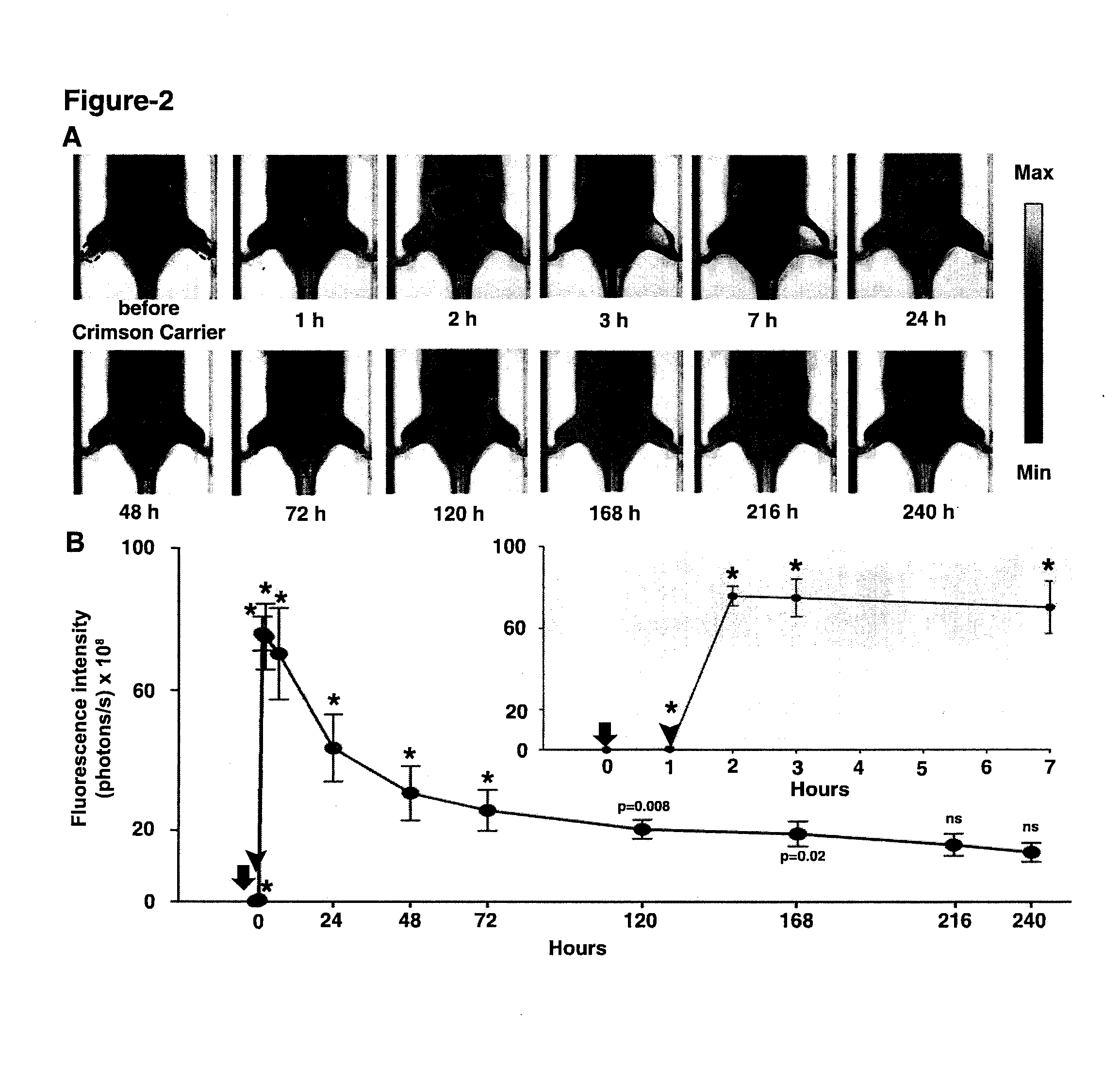
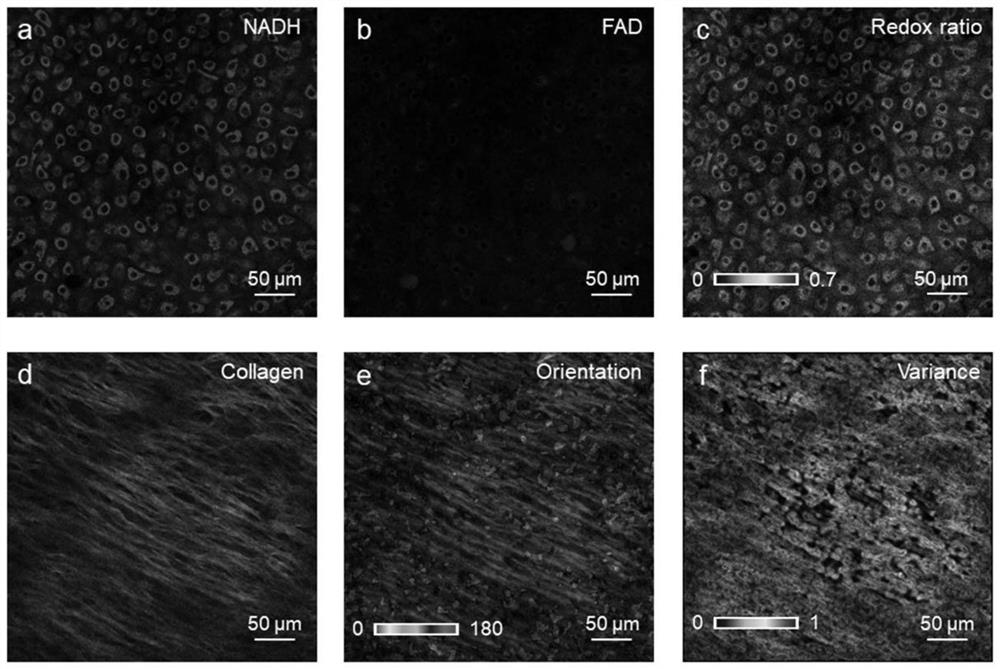
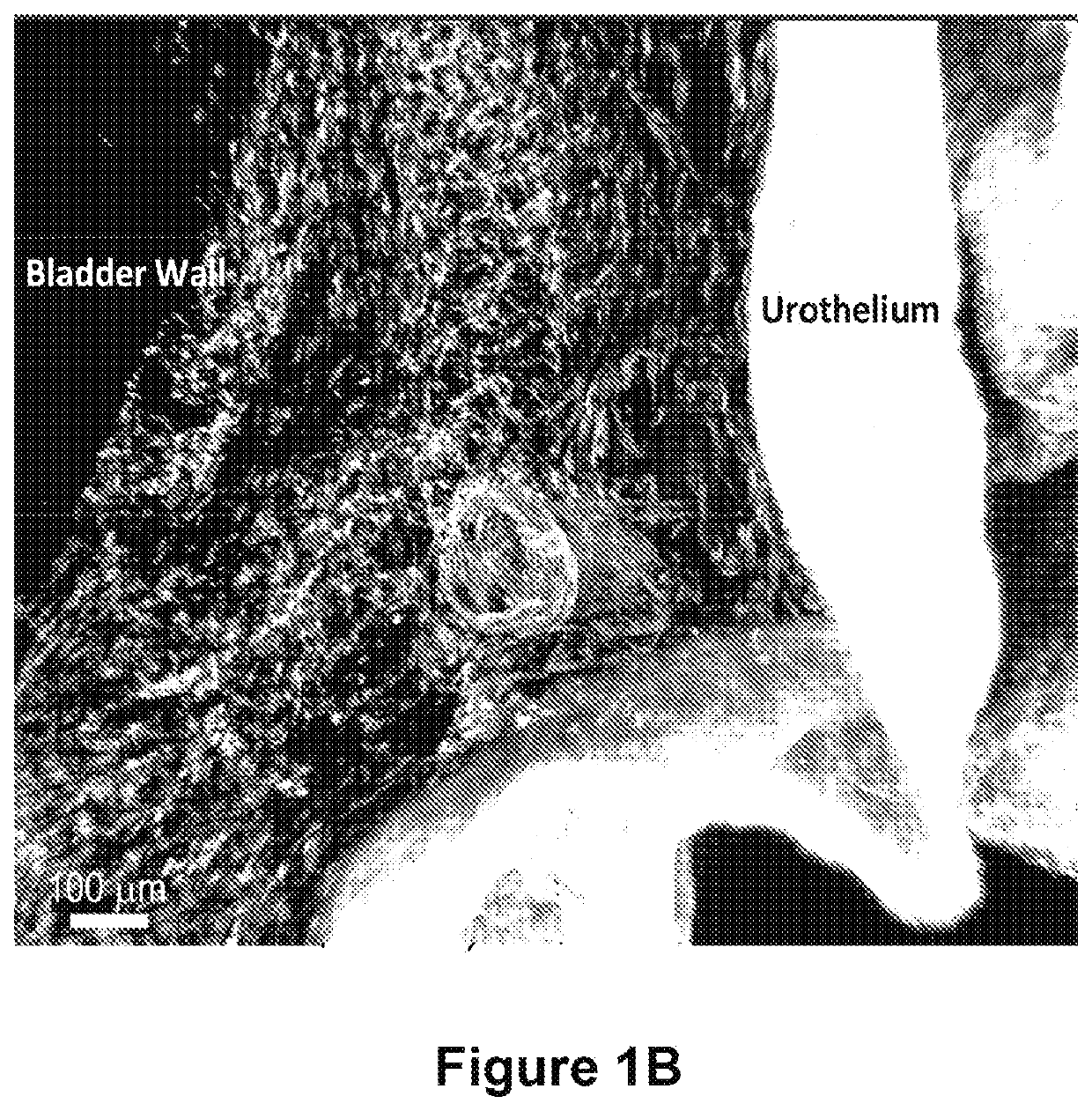
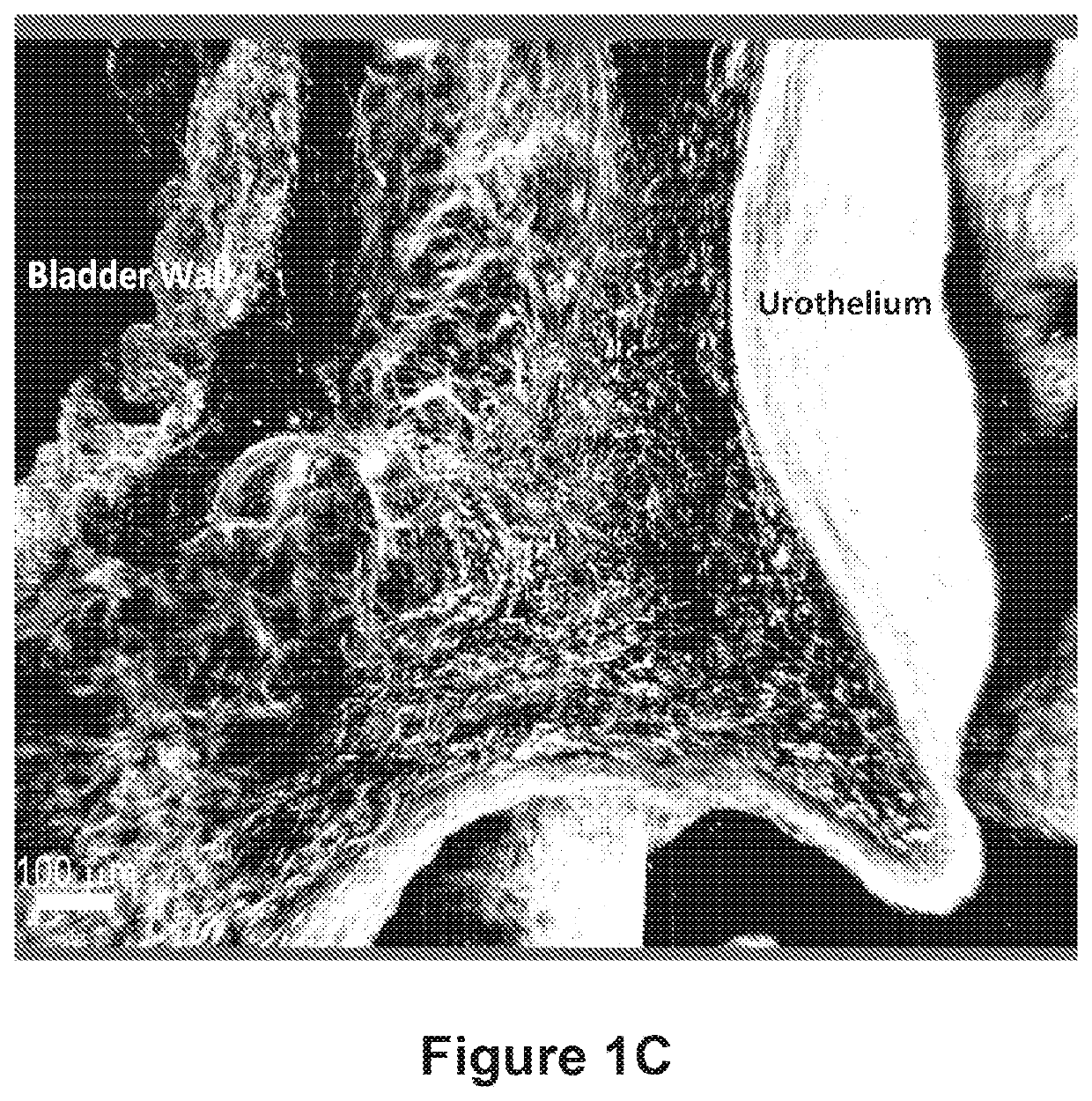
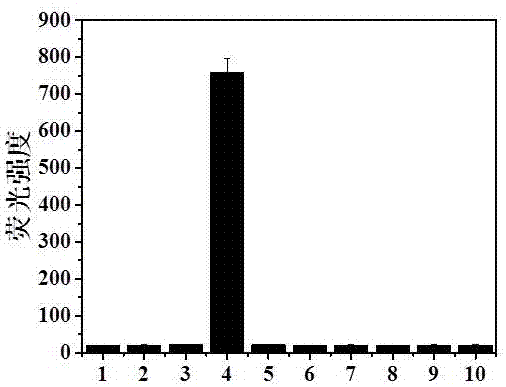
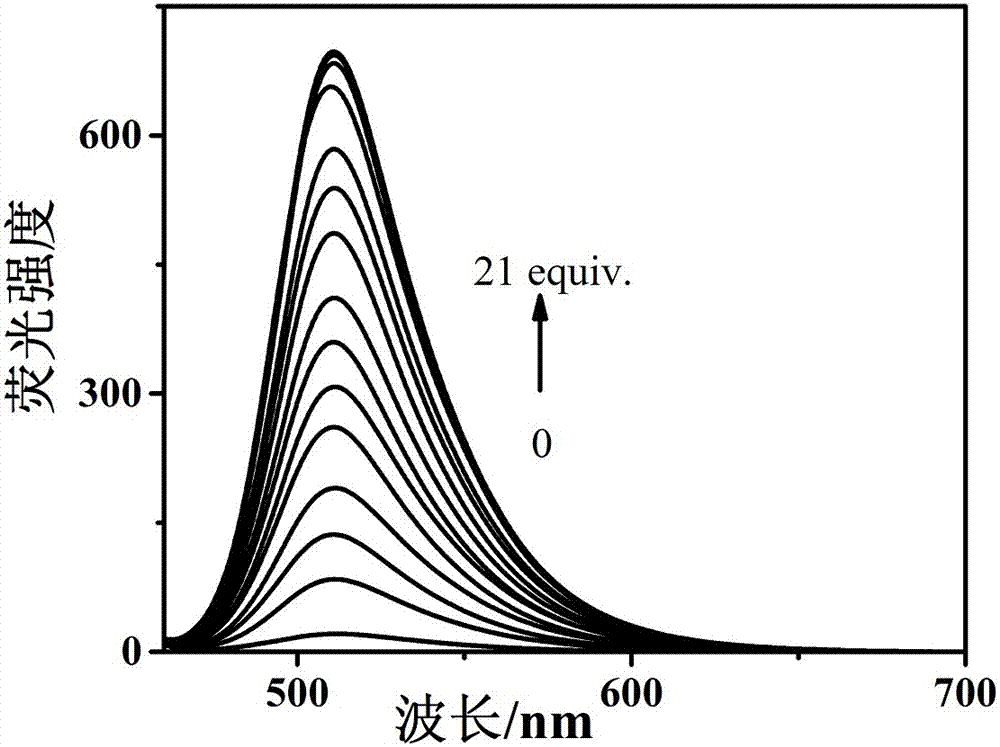
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Deep tissue imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Targeted, NIR imaging agents for therapy efficacy monitoring, deep tissue disease demarcation and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20060147379A1Maximize signal-to-background ratioUseful in therapyCompounds screening/testingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseCellular respiration
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Agents for therapy efficacy monitoring and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20080031823A1Limited applicationImprove clinical efficacyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideCellular respirationFunctional imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Targeted, NIR imaging agents for therapy efficacy monitoring, deep tissue disease demarcation and deep tissue imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Deep tissue X-ray excitation multispectral tomography system and method
ActiveCN105640582AGreat penetration depthMeet imaging requirementsComputerised tomographsTomographyX-rayWavelength
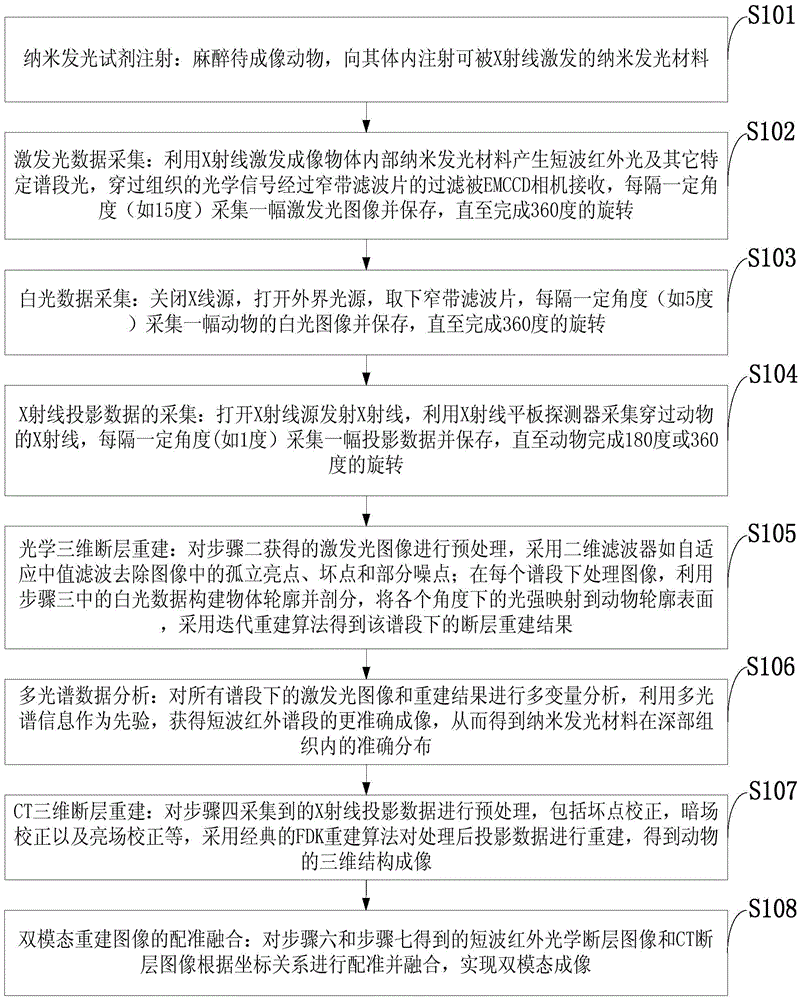
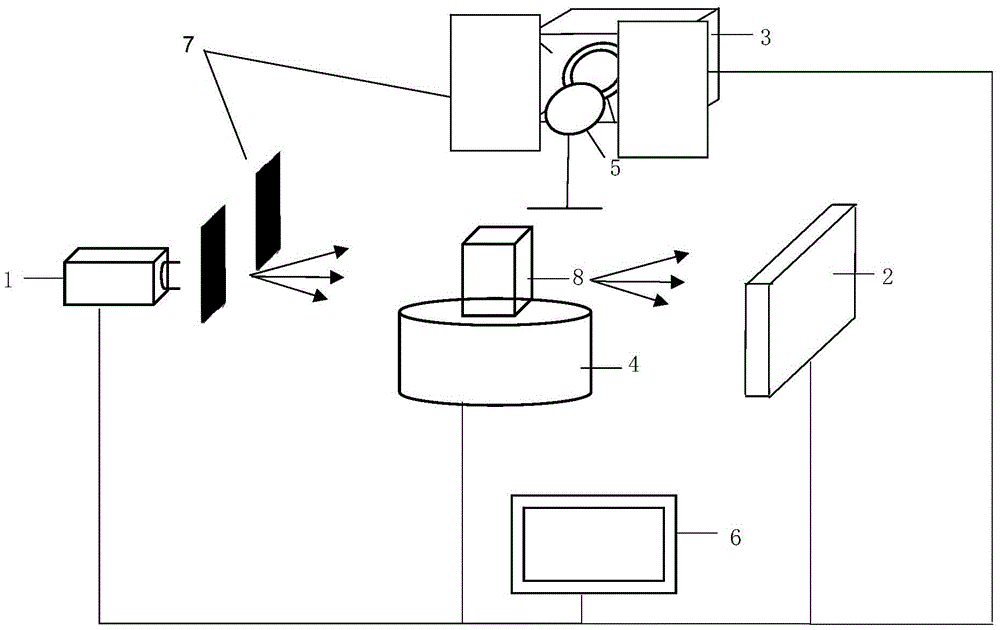
The invention discloses a deep tissue X-ray excitation multispectral tomography system and method. The system comprises an X-ray source, an X-ray flat panel detector, an EMCCD camera, an electric control rotary table, a narrow-band filter, a lead plate, a computer and an animal to be imaged; nano-luminescence materials are excited through an X ray, short-wave infrared light with the specific spectra sections, particularly high penetration depth is emitted, photons penetrate through tissue to reach the surface of an imaged object, the light of different wave length spectra sections is received by an EMCCD camera by being filtered by the narrow-band filter, and an obtained image and a rebuilt result under each spectra section are obtained; multivariate analysis is adopted for carrying out treatment and analysis on multispectral images and rebuilt results, accurate distribution of the nano-luminescence materials in the object is obtained and combined with CT tomography results, and finally a deep tissue multispectral tomography image is obtained. The imaging depth of X-ray excitation multispectral tomography can be effectively improved, and deep tissue imaging of small living animals is achieved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method of deep tissue imaging using multi-photon excitation of a fluorophore
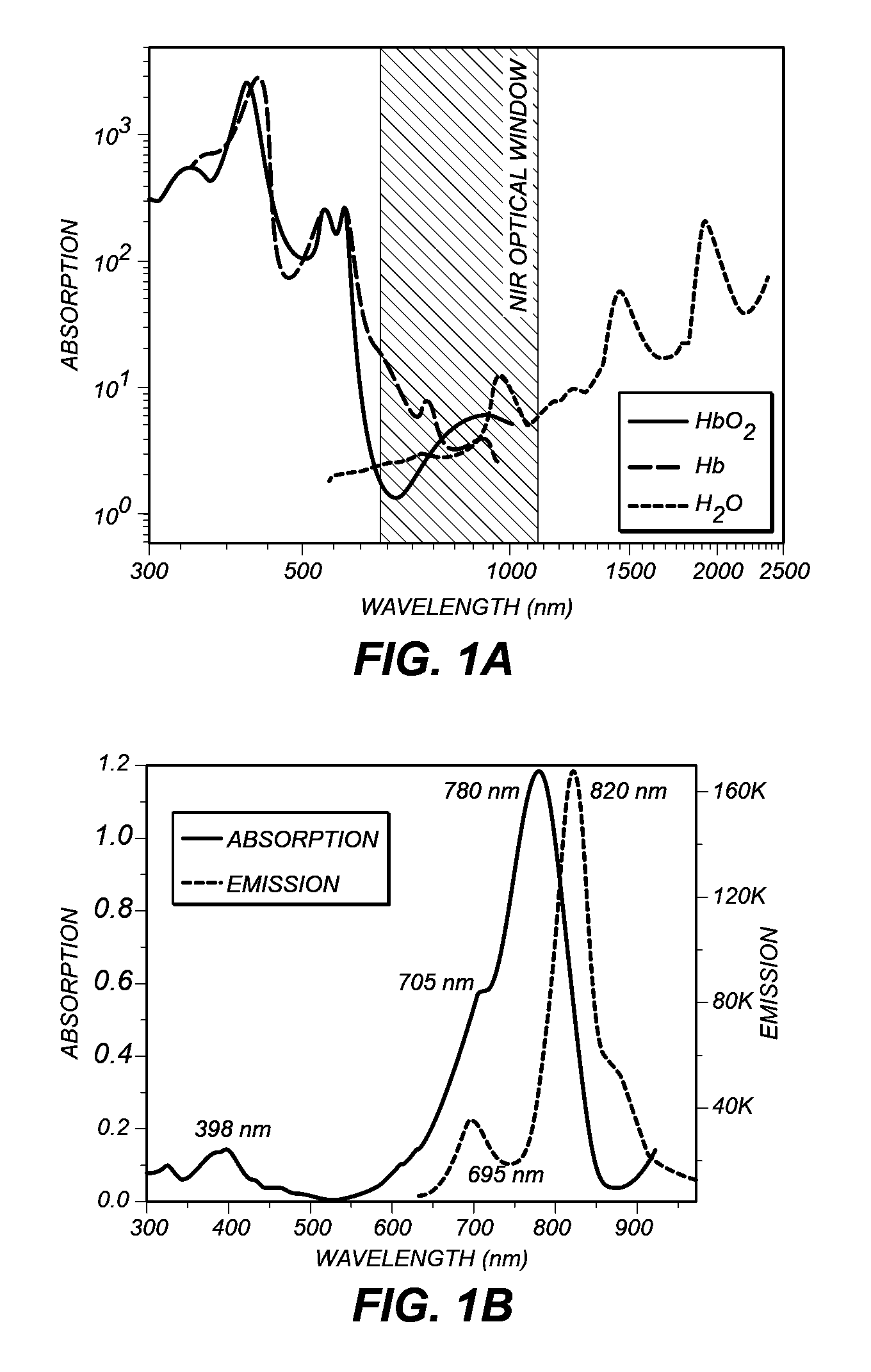
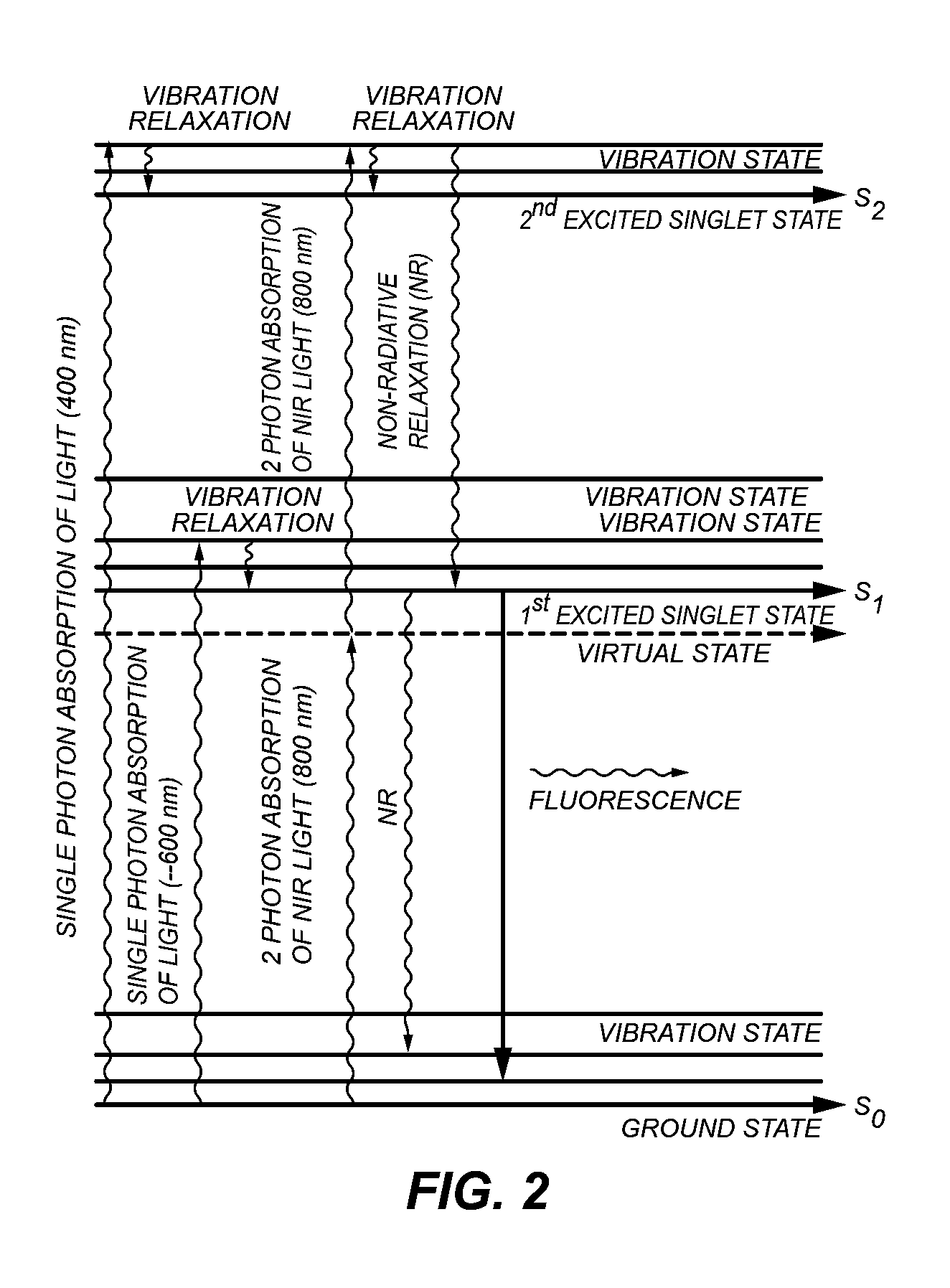
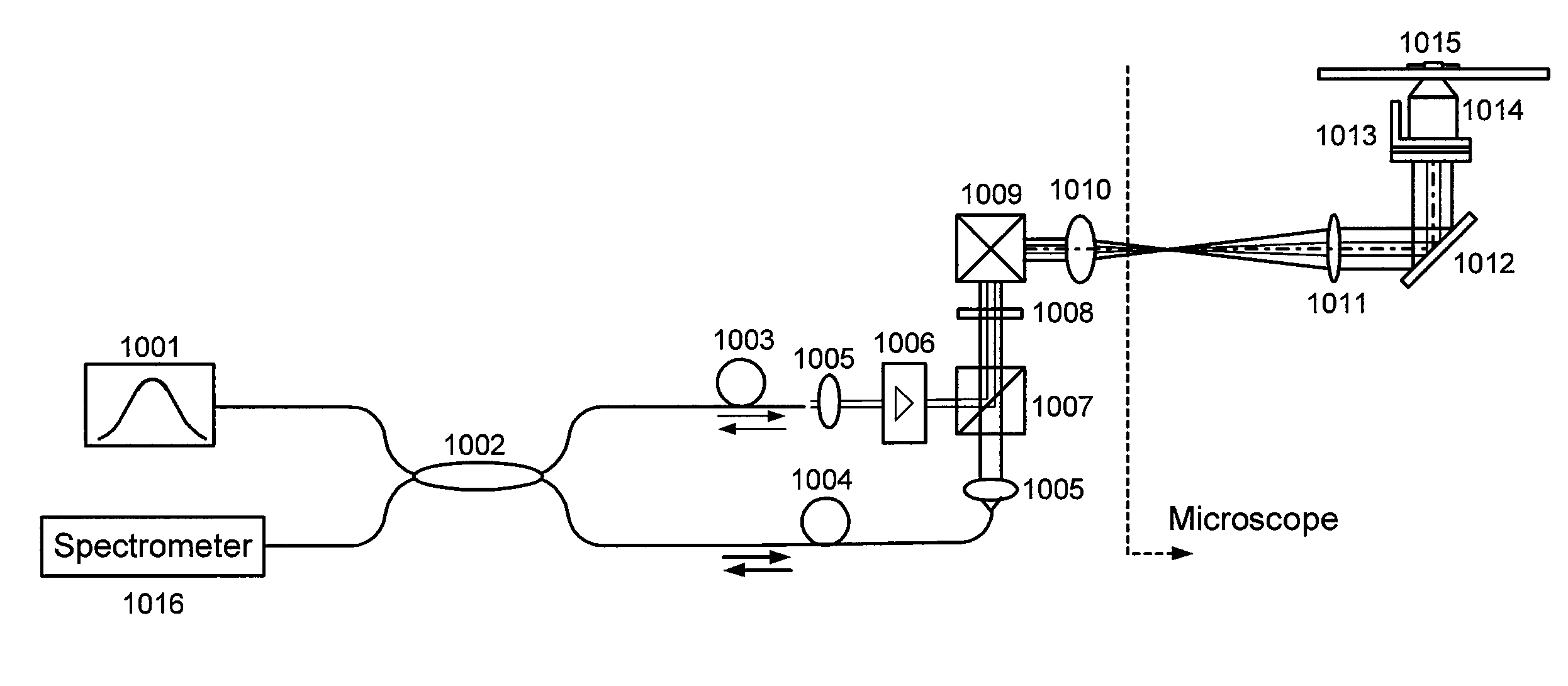
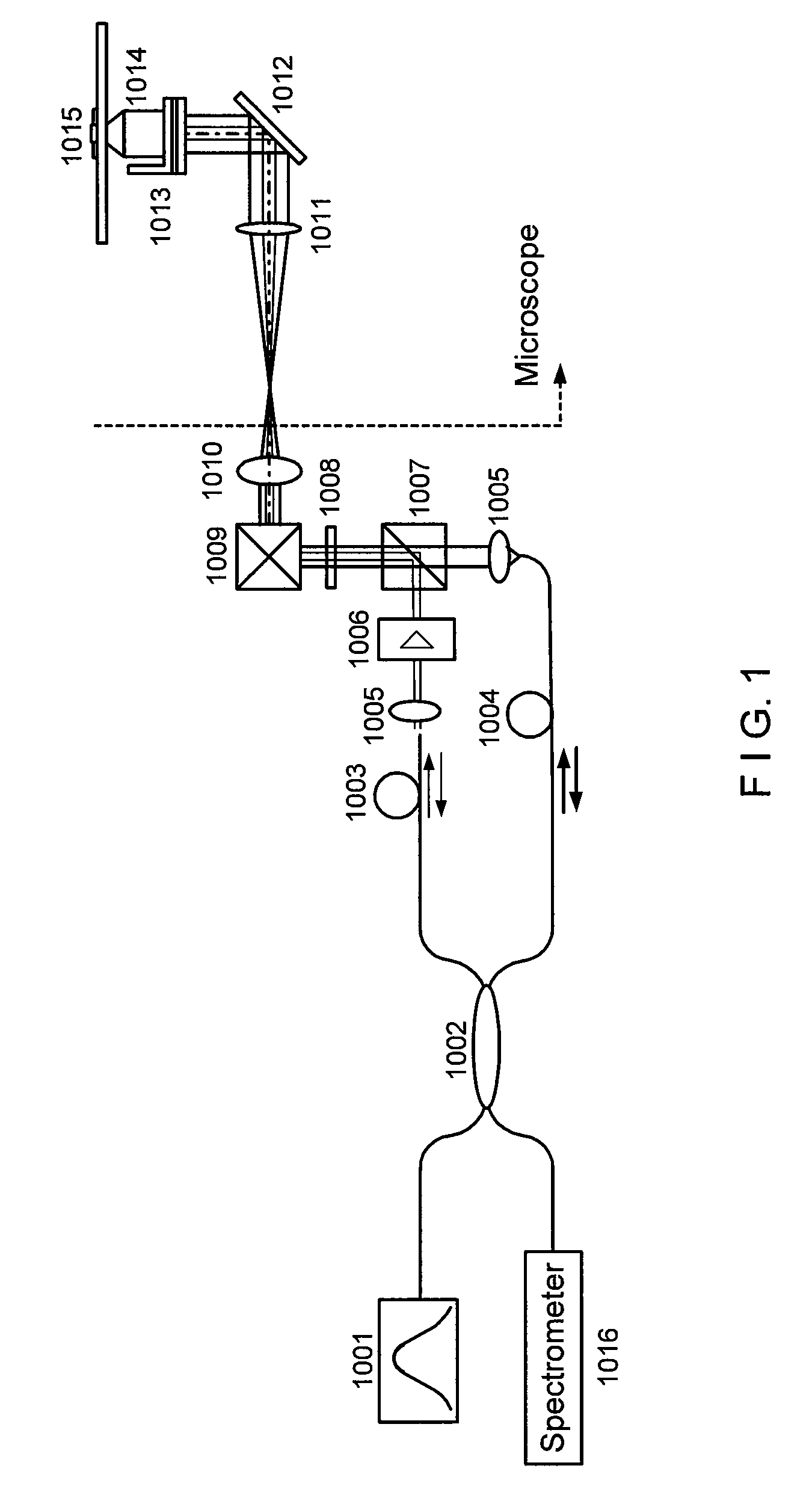
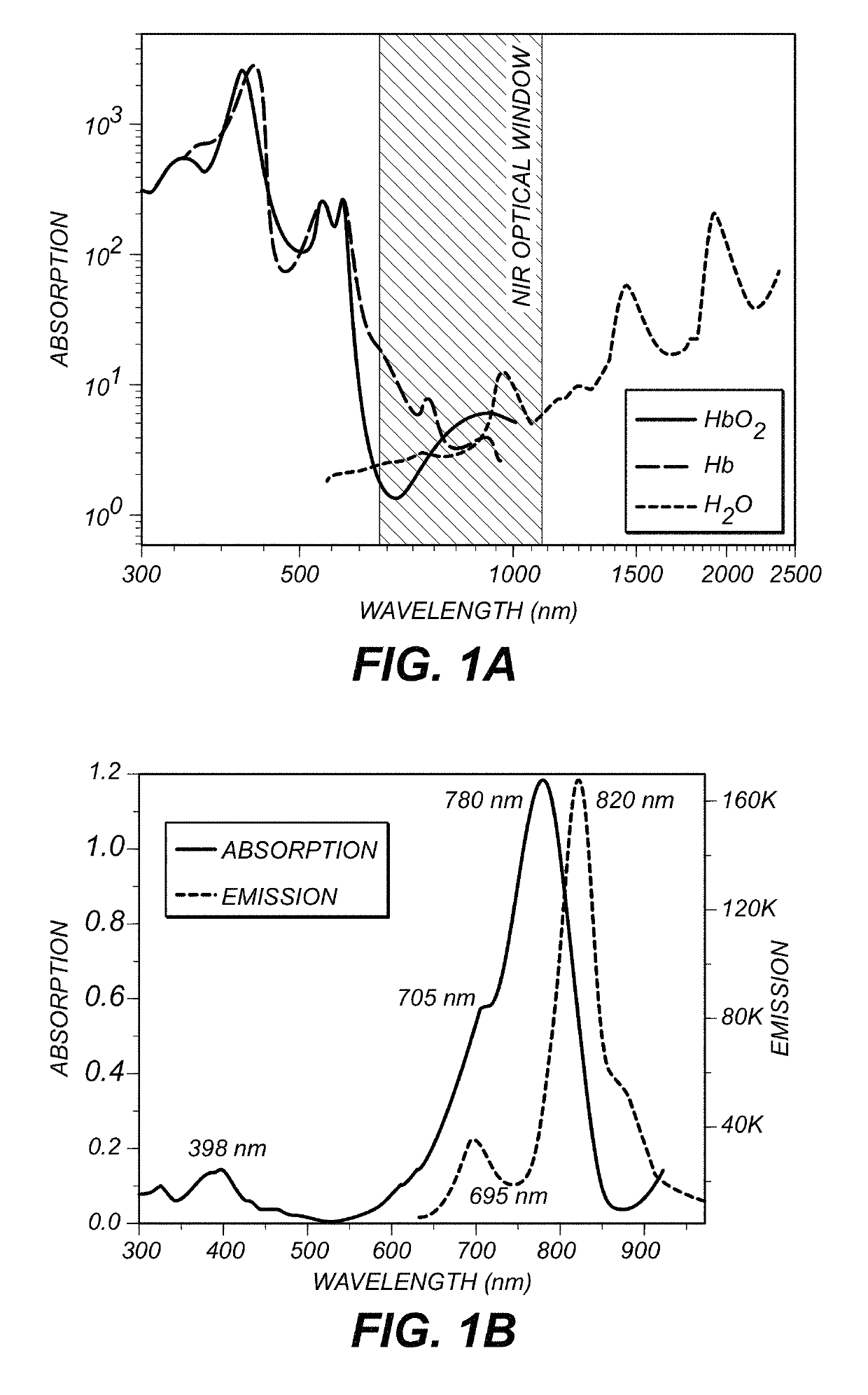
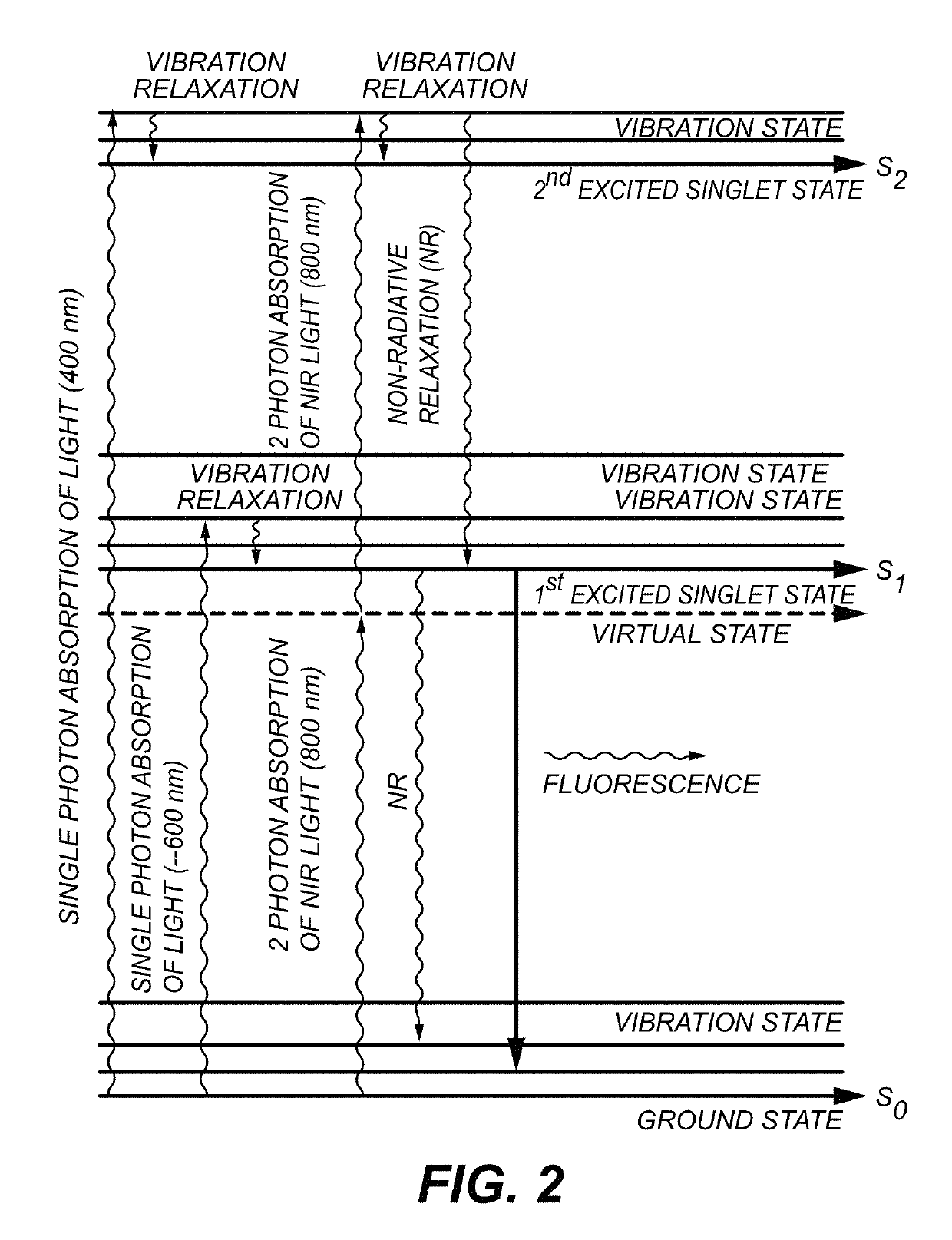
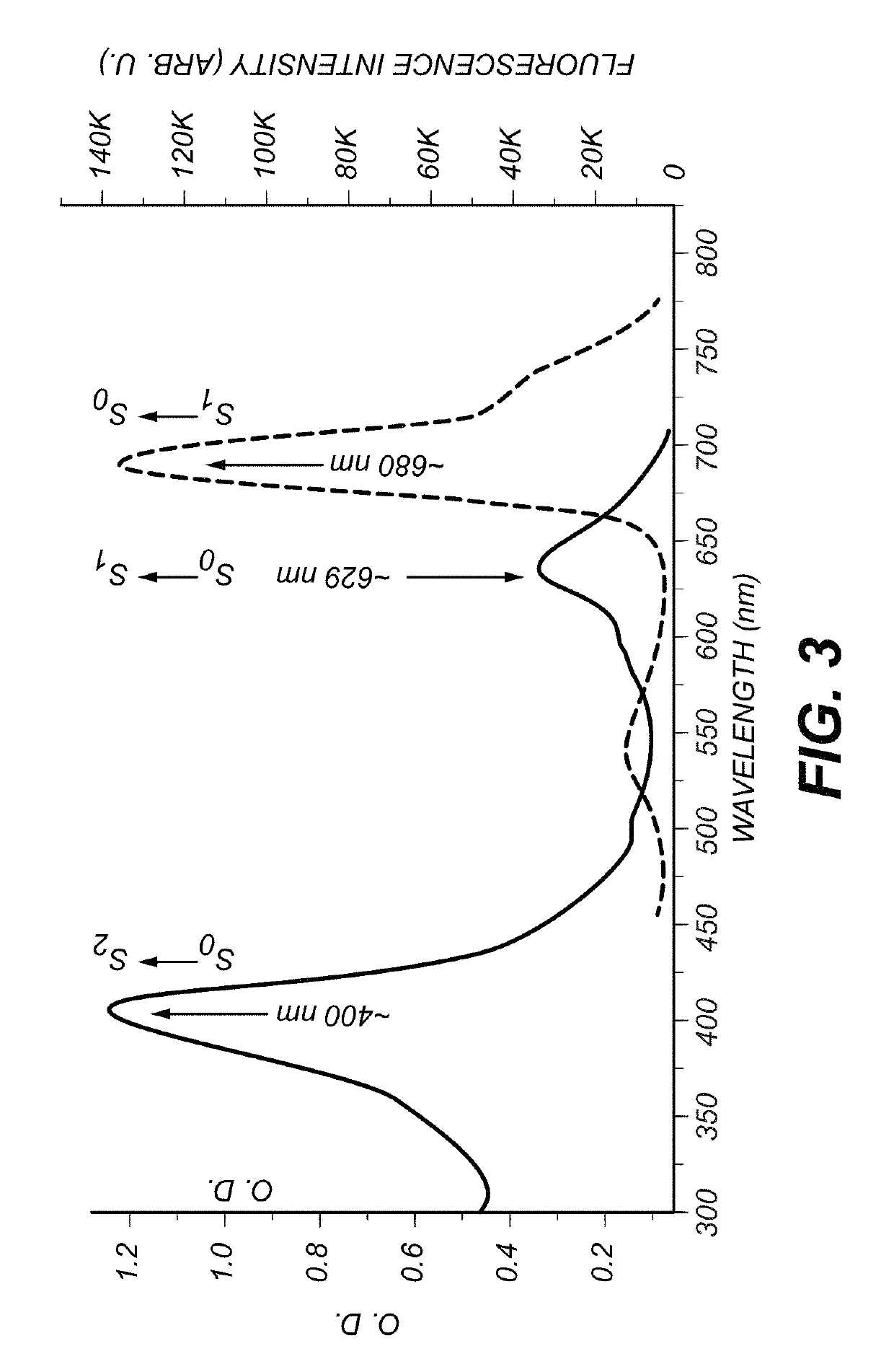
A method is provided for deep tissue imaging using multi-photon excitation of a fluorescent agent. The fluorescent agent is irradiated with an ultrafast laser to produce an excited singlet state (Sn) which subsequently undergoes non-radiative relaxation to a first singlet state (S1). The S1 state undergoes fluorescence to the ground state S0 to produce an emission wavelength. Both the excitation and emission wavelengths are within the near infrared optical window, thereby permitting deep tissue penetration for both the incoming and outgoing signals.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT R
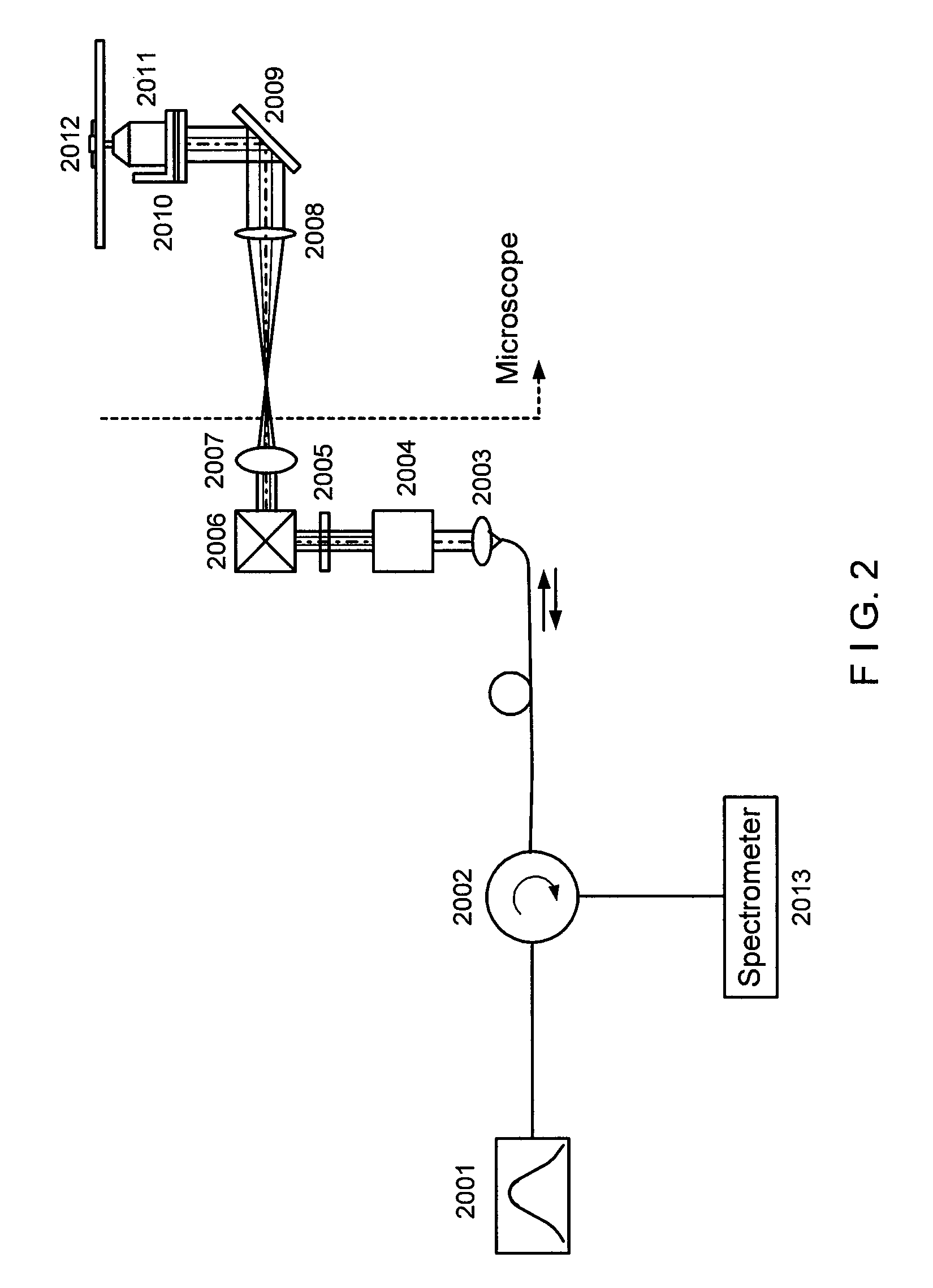
Systems, methods and computer-accessible medium for providing spectral-domain optical coherence phase microscopy for cell and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20090219544A1Facilitate high-resolution imagingFacilitate high-sensitive measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectral domainElectromagnetic radiation
Exemplary arrangement, apparatus, method and computer accessible can be provided. For example, using the exemplary arrangement, apparatus and method, it is possible to configured to propagate at least one electro-magnetic radiation. Indeed, it is possible to receive, using at least one first arrangement, a first portion of the at least one electro-magnetic radiation directed to a sample and a second portion of the least one electro-magnetic radiation directed to a reference, the first arrangement can be structured to at least partially reflect and at least partially allow to transmit the first and second portions. In addition, it is possible to receive, using a second arrangement, (i) a third portion of the electro-magnetic radiation associated with at least one of the transmitted first portion or the reflected first portion from the sample and (ii) a fourth portion of the electro-magnetic radiation associated with at least one of the second transmitted portion of the least one electro-magnetic radiation or the reflected second portion from the reference. The third and fourth portions can travel at least partially along substantially the same path toward the second arrangement, Further, the second arrangement can be configured to receive the reflected first and second portion(s) which interfere with one another, and generate at least one signal which includes information associated with at least one fluctuation in an uncommon path of the first and second portions prior to a receipt thereof by the at least one first arrangement. In addition or alternatively, the second arrangement can be configured to determine information regarding a spectrally resolved interference associated with the third and fourth portions.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Agents for therapy efficacy monitoring and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS8188116B2Improve clinical efficacyHighly expressed in leukemiaUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideCellular respirationMolecular imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Optical imaging agent
InactiveUS8343463B2High molecular weightEliminate needUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSenses disorderAbnormal tissue growthBlood pool
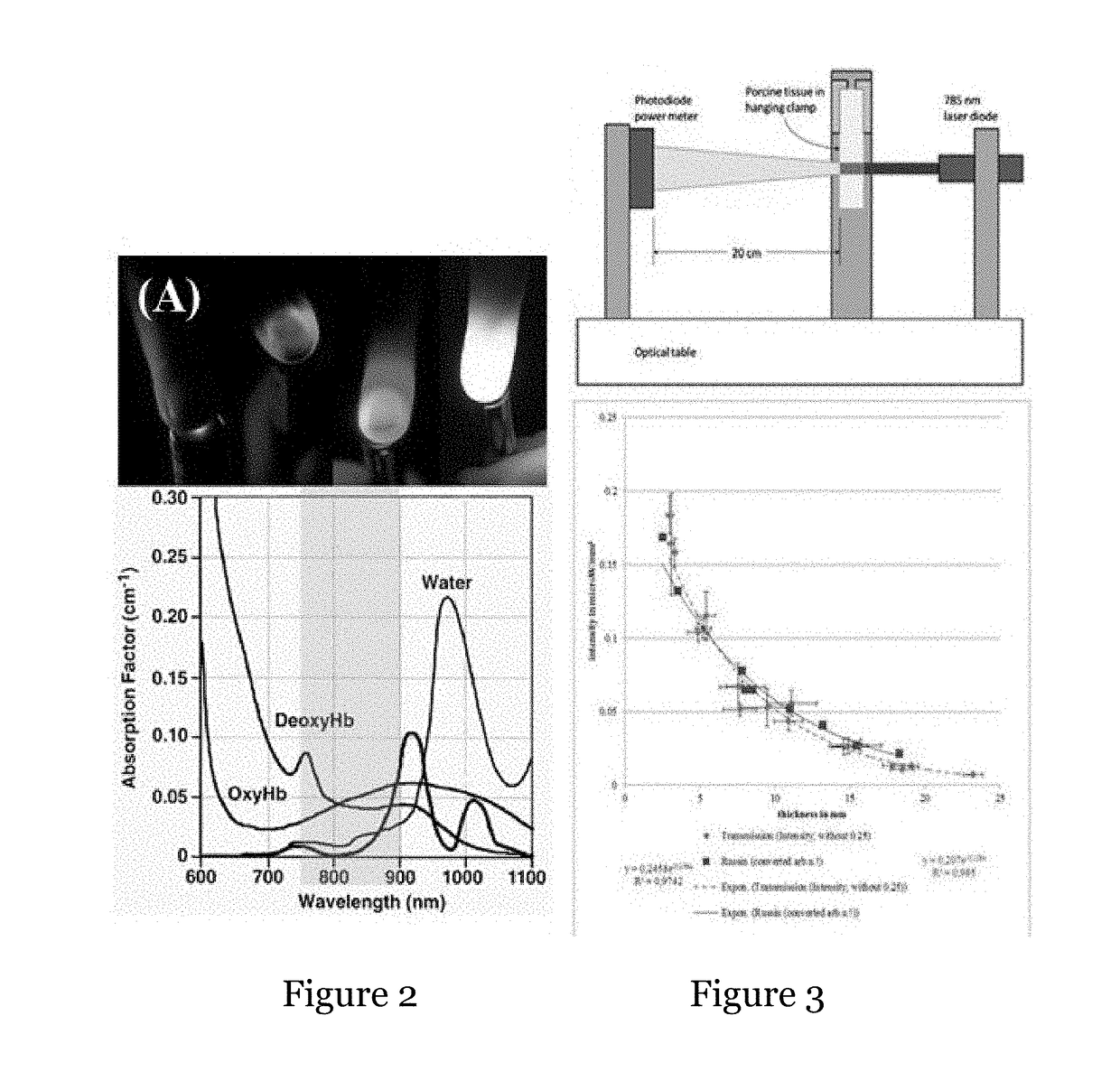
The near-infrared wavelengths (700 nm-900 nm) are a suitable optical window for light penetration and deep tissue imaging. The present invention provides a near-infrared fluorescent blood pool contrast agent. The agent is of use to detect and quantify pathological capillary leak in live animals, e.g., serially imaging of traumatized tissue (muscle) as well as tumors.
Owner:INVICRO
High speed deep tissue imaging system using multiplexed scanned temporal focusing
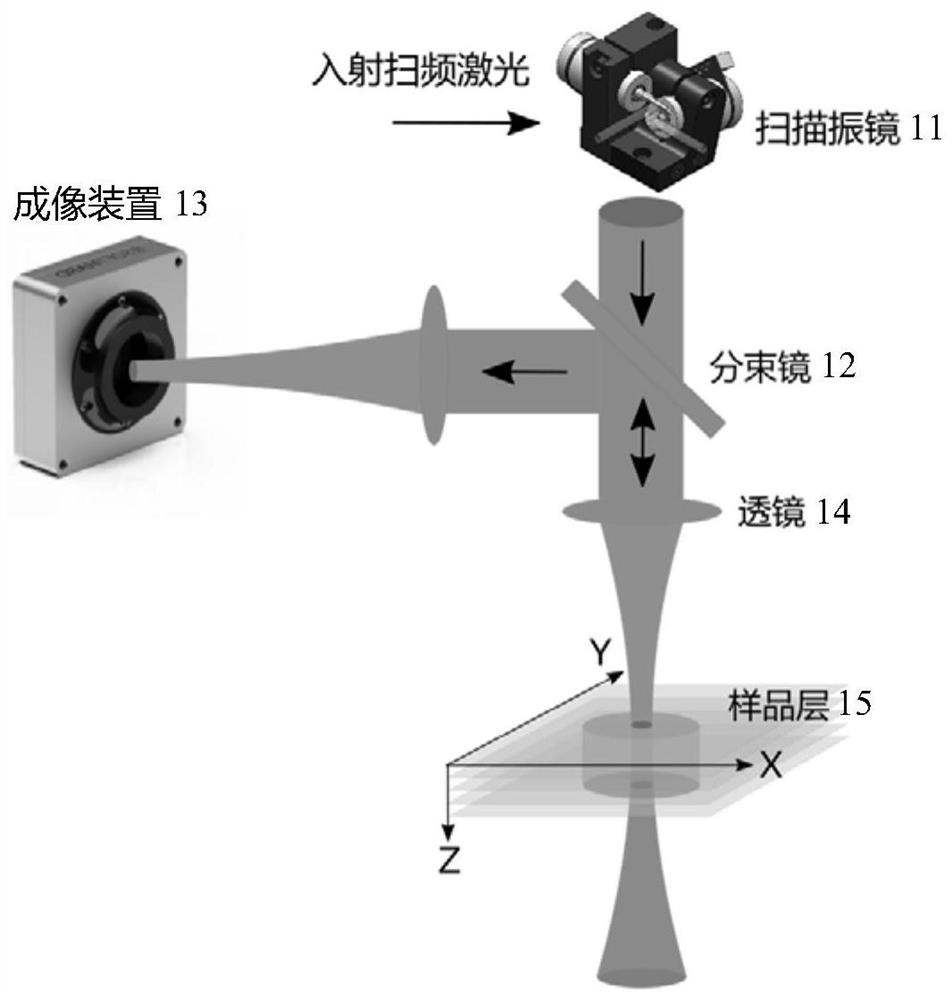
A tissue imaging system includes a laser module for outputting a laser pulse, an optical delay module configured to split a laser pulse received from the laser module into a plurality of time-delayedsub-pulses, a telescope for delivering the sub-pulses from the optical delay module to a target volume and a photodetector configured to collect photons generated within the target volume in responseto excitation of the target volume by the first and second sub-pulses. The system may further include a spatial multiplexing module configured to receive the temporally multiplexed laser pulse from the optical delay module and splitting the temporally multiplexed laser pulse into a plurality of sub-beams including a first sub-beam and a second sub-beam, wherein the first sub-beam and the second sub-beam are spatially separated with respect to a first image plane formed at a first depth within the target volume and with respect to a second image plane formed at a second depth within the targetvolume.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA +1
Optical imaging agent
InactiveUS20110027191A1High molecular weightUse of procedureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSenses disorderBlood poolLight penetration
The near-infrared wavelengths (700 nm-900 nm) are a suitable optical window for light penetration and deep tissue imaging. The present invention provides a near-infrared fluorescent blood pool contrast agent. The agent is of use to detect and quantify pathological capillary leak in live animals, e.g., serially imaging of traumatized tissue (muscle) as well as tumors.
Owner:INVICRO
Non-reactive mitochondrial tracking fluorescent probe containing C12 lalkyl chain, and applications thereof
InactiveCN109293632AGood two-photon propertiesOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceMembrane potentialDeep tissue imaging
The invention discloses a non-reactive mitochondrial tracking fluorescent probe containing a C12 lalkyl chain, and applications of the probe in labeling or displaying of the distribution of mitochondria in cells, and in mitochondrial autophagy observation, wherein the fluorescent probe is a carbazole pyridine salt compound having a structure represented by a formula (I). According to the present invention, the probe can stain mitochondria in normal living cells, and especially can be fixed on mitochondria when the mitochondrial membrane potential is reduced or disappears, such that the resultsshow that the probe can track the dynamic changes of mitochondria; the probe further has good two-photon properties, and can be used for deep tissue imaging; and the probe has low toxicity, can real-timely track the dynamic process of mitochondrial autophagy, and has broad application prospect in the field of fluorescent biomarkers.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
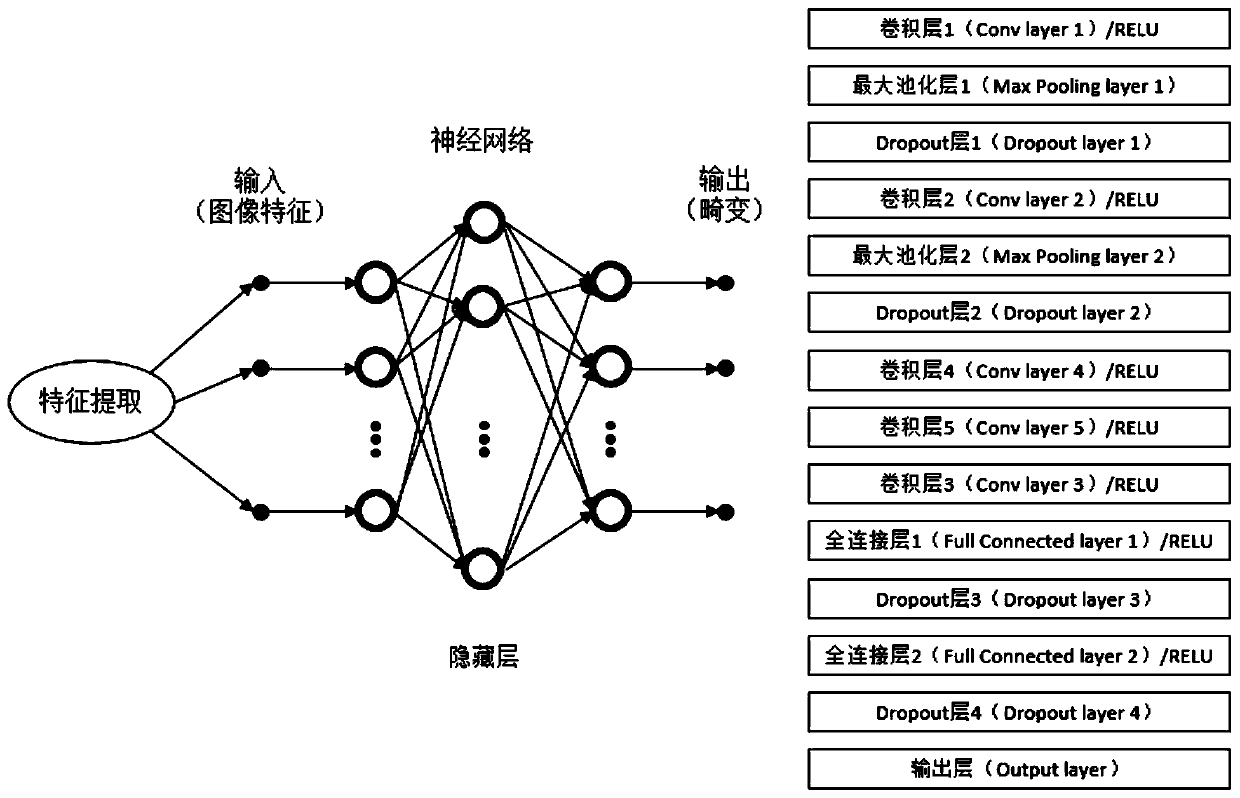
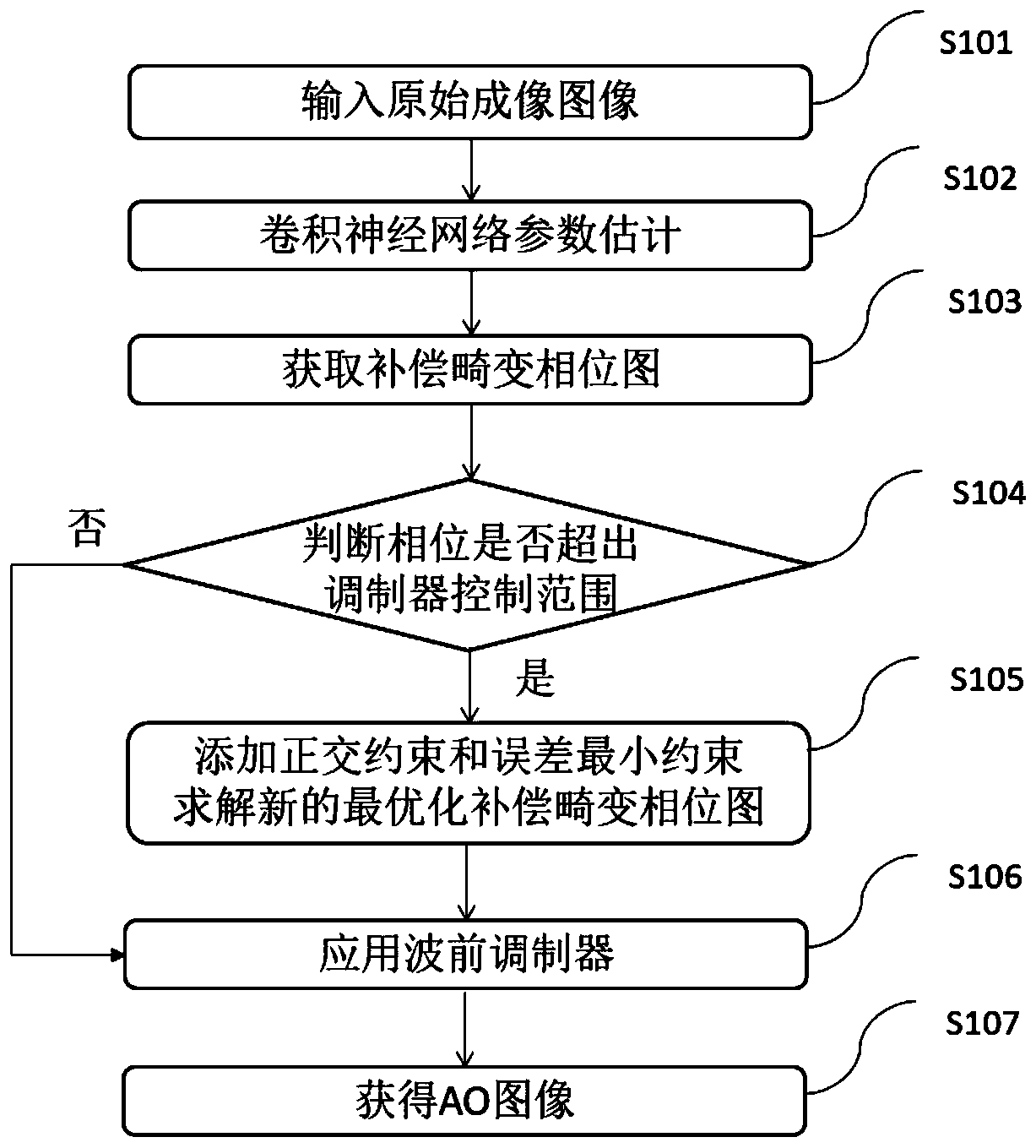
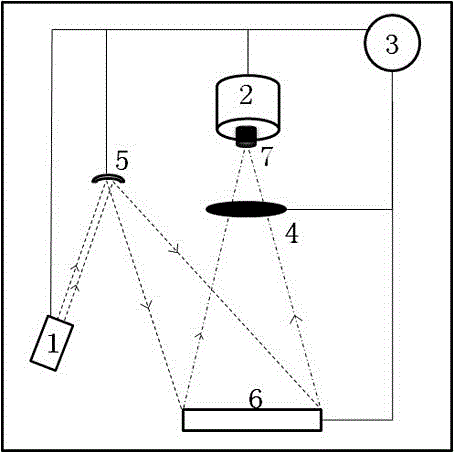
Optimized self-adaptive microscopic imaging method and device based on machine learning
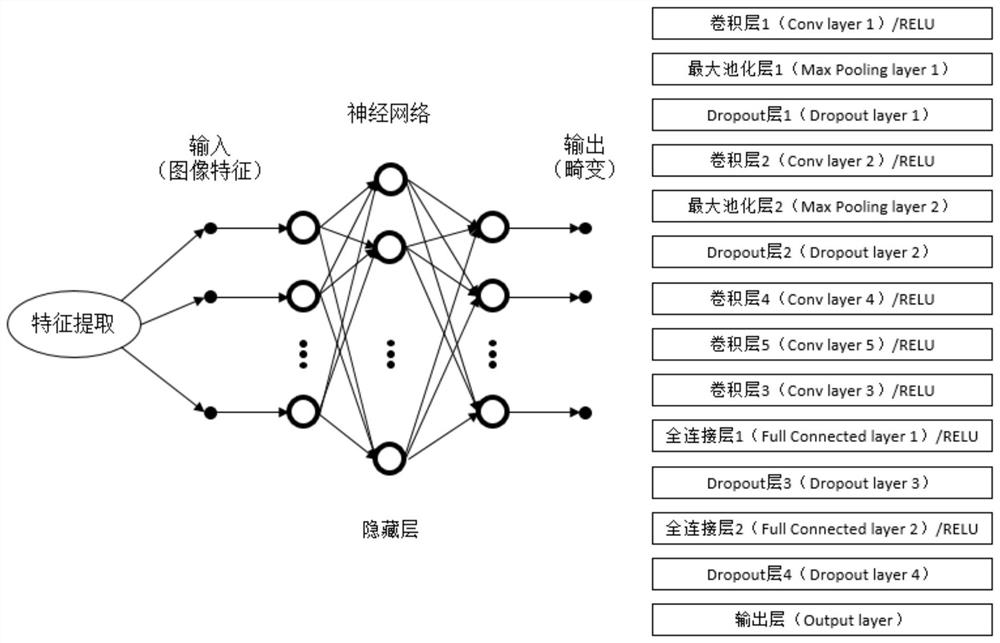
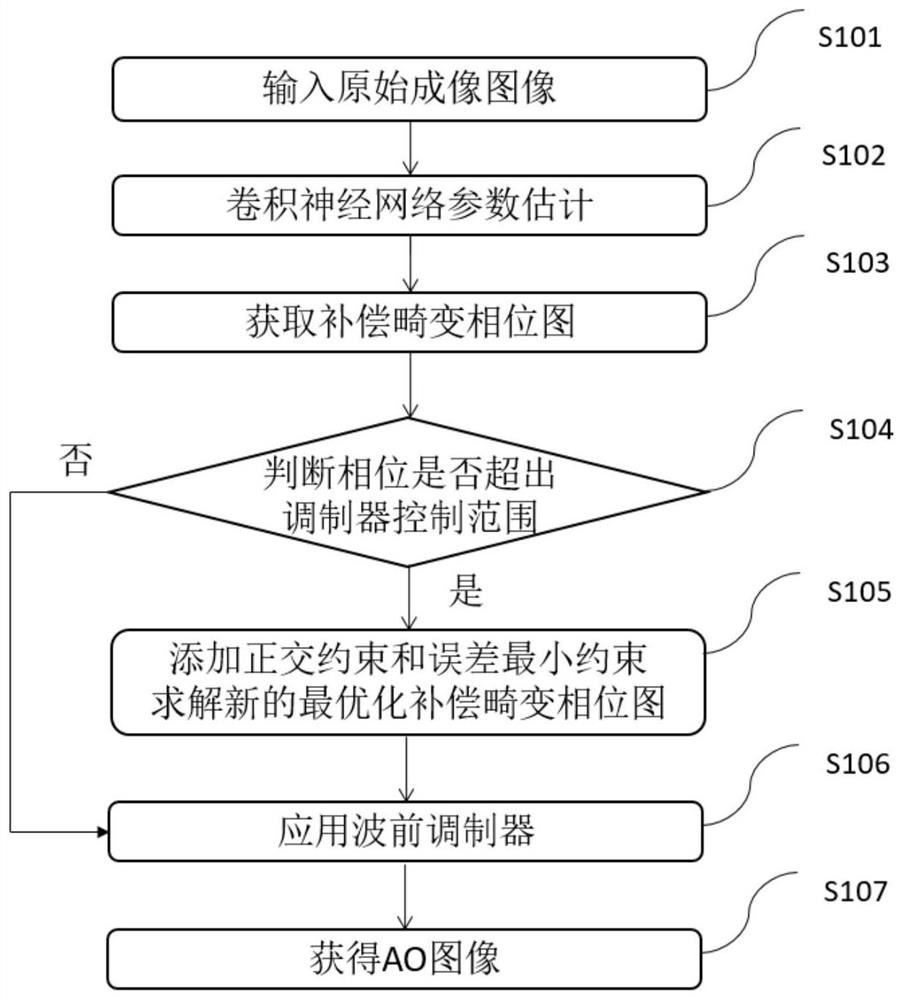
ActiveCN110309910AAddressing Insufficient Scope of WorkImage Quality RestorationImage enhancementNeural architecturesImaging qualityPhysical model
The invention discloses an optimized self-adaptive microscopic imaging method and device based on machine learning, and the method comprises the following steps: employing ultra-short pulse laser to collect image data through a point scanning method; constructing a convolutional neural network, and inputting image data to the physical model to obtain a simulation result training network; applyingthe training network obtained through training to an adaptive method to optimize an imaging result and eliminate image distortion and acquiring the optimal phase compensation of system and sample distortion correction through a model fitting method. The method can obtain an imaging result with high optimization performance, high image quality and high imaging speed, has the advantages of high speed, high image quality, good expandability and the like, realizes high-speed wavefront distortion compensation based on machine learning, and has a great application prospect in rapid deep tissue imaging of bioscience.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Broadband spectrum fluorescent imaging equipment
PendingCN106841155AImplementing Dynamic Parallel RecordingAvoid timeFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam expanderSmall animal
The invention discloses broadband spectrum fluorescent imaging equipment which is mainly composed of an excitation light source, an imaging camera, a controller, an optical fiber unit, a focusing objective lens, a beam expander, an objective table and the like. The excitation light source, the imaging camera, the optical fiber unit, the focusing objective lens, the beam expander, and the objective table can be controlled by the controller. The fluorescent imaging wavelength coverage of the broadband spectrum fluorescent imaging equipment is 400-1700nm, can perform fluorescent imaging on a to-be-imaged object to obtain a fluorescent imaging picture, and particularly can efficiently and rapidly perform nondestructive deep tissue imaging on a living small animal without damage.
Owner:苏州影睿光学科技有限公司
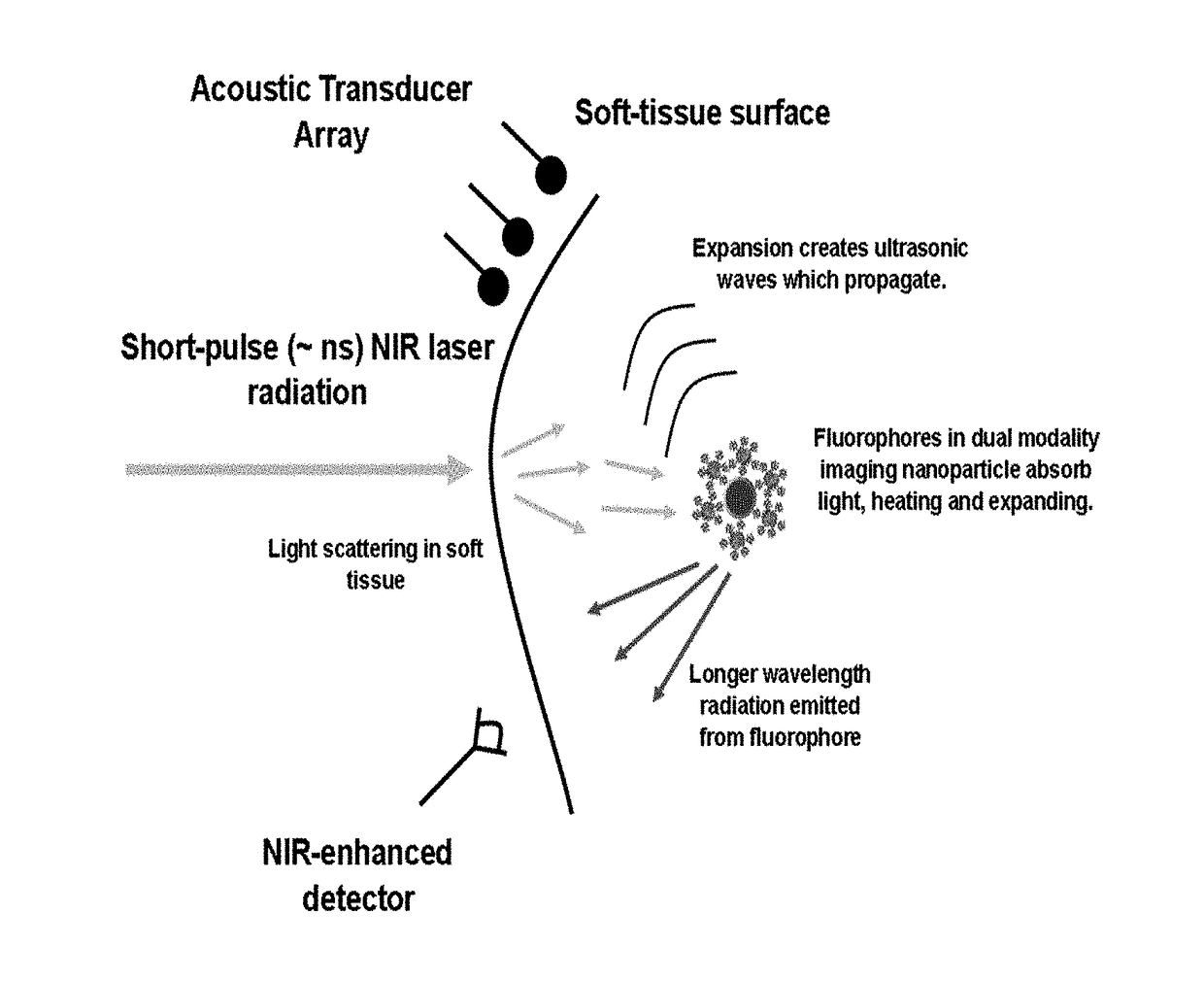
Handheld device and multimodal contrast agent for early detection of human disease
InactiveUS20180064347A1Deeper imagingUse diagnosisEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsDiagnostic recording/measuringMRI contrast agentHand held
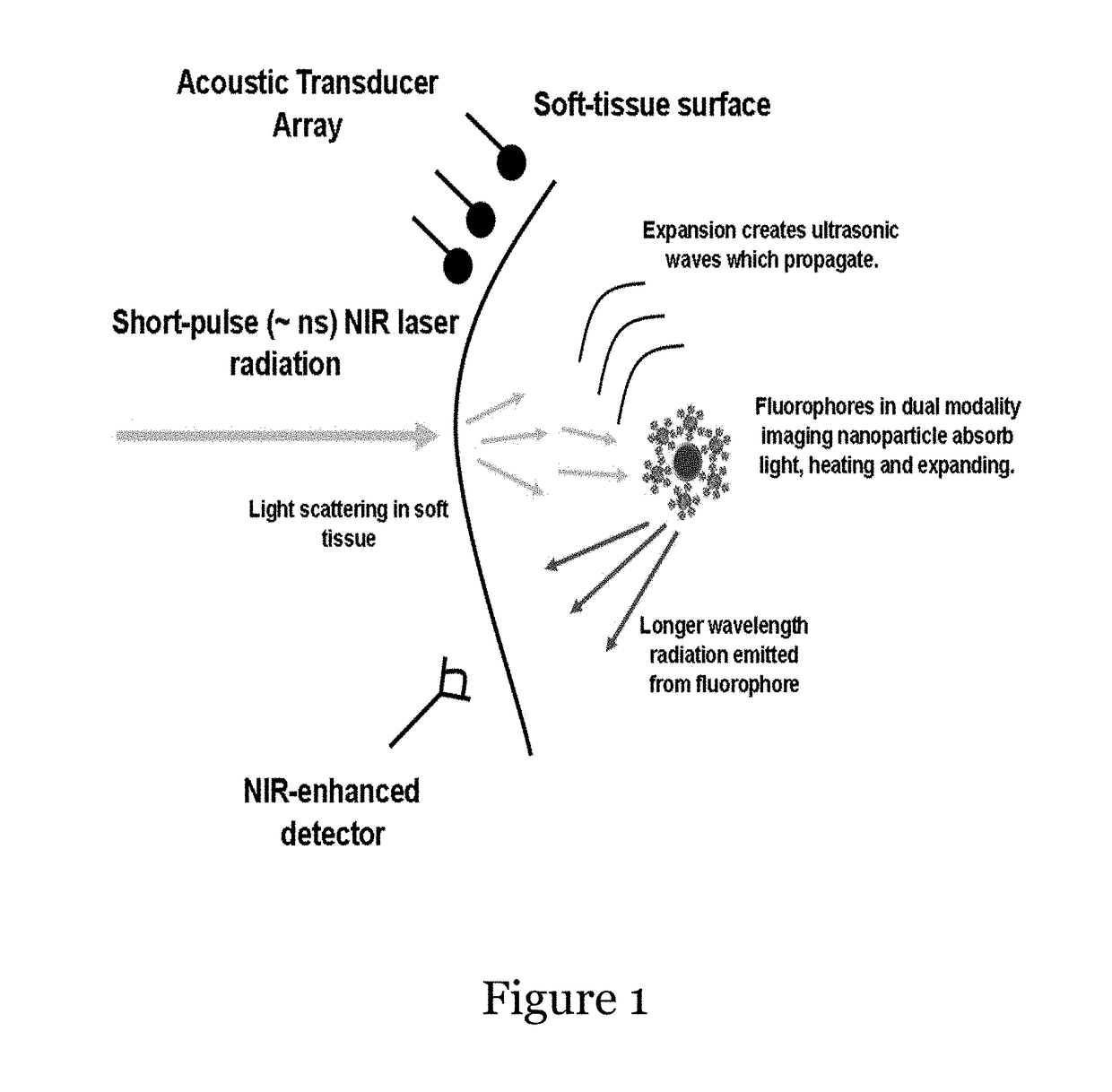
Systems comprising a combination of the handheld imaging system with a nanoparticle multimodal contrast agent are disclosed. The imaging system exploits the advantages of both near-infrared emission and the photoacoustic effect by employing calcium phosphosilicate nanocolloid that encapsulates NIR and CT / MRI contrast agents for enhanced deep tissue imaging as well as a portable NIR / PA system using a tunable pulsed laser, CCD imaging technology and acoustic transducer arrays. Methods for using the system, for example in rapid diagnosis of trauma such as that inflicted on a battlefield, are provided.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Multi-photon ultra-deep tissue imaging equipment based on coherent detection and detection imaging method thereof
PendingCN113390827AFast imagingAdd depthPhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionRapid imagingLaser light
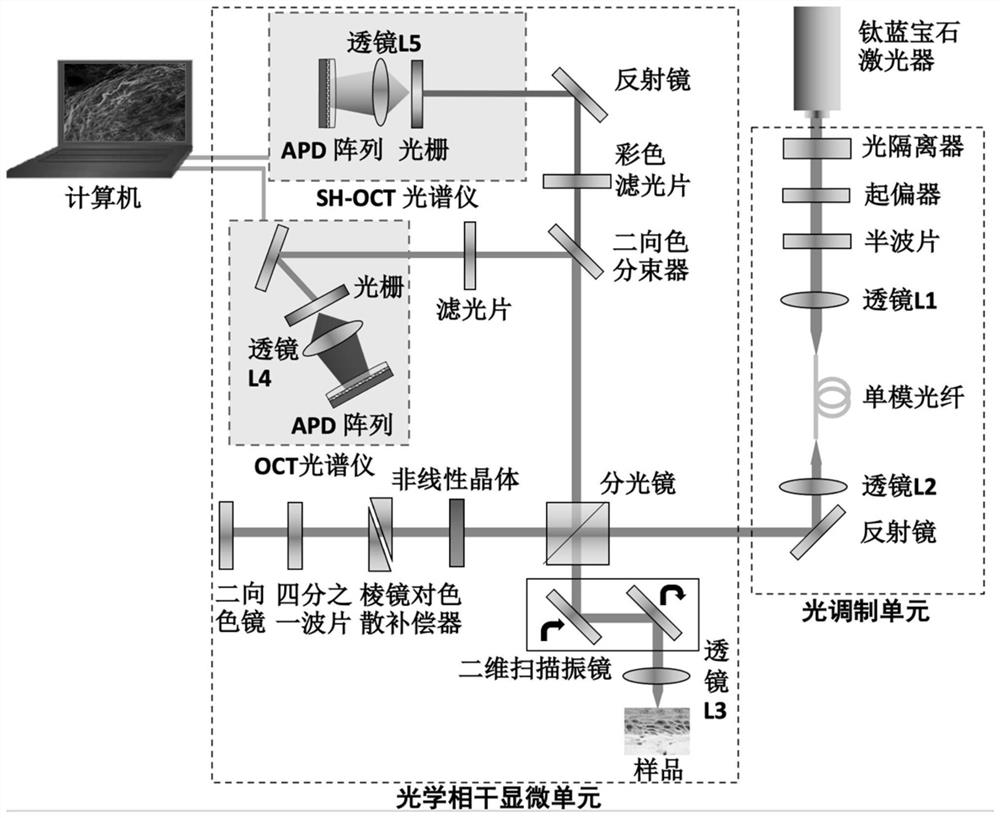
The invention discloses multi-photon ultra-deep tissue imaging equipment based on coherent detection and a detection imaging method thereof. A multi-photon imaging technology is combined with an optical coherence tomography technology to realize ultra-deep and high-molecular specific imaging of a detected sample. The equipment comprises an ultrashort pulse femtosecond laser light source, a light modulation unit and an optical coherence microscopic unit. The light modulation unit modulates input laser to generate continuous spectrum laser. The optical coherence microscopic unit is used for conducting coherent detection on a biological sample. The system can detect OCT and SH-OCT signals of a tissue at the same time and obtain the specific structure of the tissue and the molecular micro-environment information of the surrounding environment of the tissue, and can quantitatively characterize the structure and function of the tissue through an image analysis method. The equipment can reflect the ultra-deep structure and functional information of the tissue, has the advantages of ultra depth, strong molecular specificity recognition capability, high temporal-spatial resolution, rapid imaging and the like, and provides the tissue structure and function information and the molecular specificity information at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method and product of mulberry silk capable of fluorescing under irradiation of near-infrared light
ActiveCN110367209AStable in natureHigh biosecurityMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Nanoparticle
The invention discloses a preparation method of mulberry silk capable of fluorescing under irradiation of near-infrared light, including the steps of (1), preparing upconversion nanoparticles, performing surface modification with concanavalin to obtain modified upconversion nanoparticles; (2), uniformly dispersing the upconversion nanoparticles in water to prepare aqueous solution of upconversionnanoparticles; (3), picking mature mulberry leaves, soaking the mulberry leaves in the aqueous solution of upconversion nanoparticles, draining water and then drying in air naturally; (4), feeding silkworms the processed mulberry leaves until the silkworms spin and make cocoons when the silkworms grow to the designed stage; (5), collecting silk so as to obtain the mulberry silk capable of fluorescing under irradiation of near-infrared light. According to the preparation method, the upconversion nanoparticles applied to preparation is capable of fluorescing under irradiation of near-infrared light having higher penetrating power, and accordingly has better application in imaging of deep tissue. Besides, the upconversion nanoparticles have much stable property, higher bio-security, higher signal to noise ratio and wider application range.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
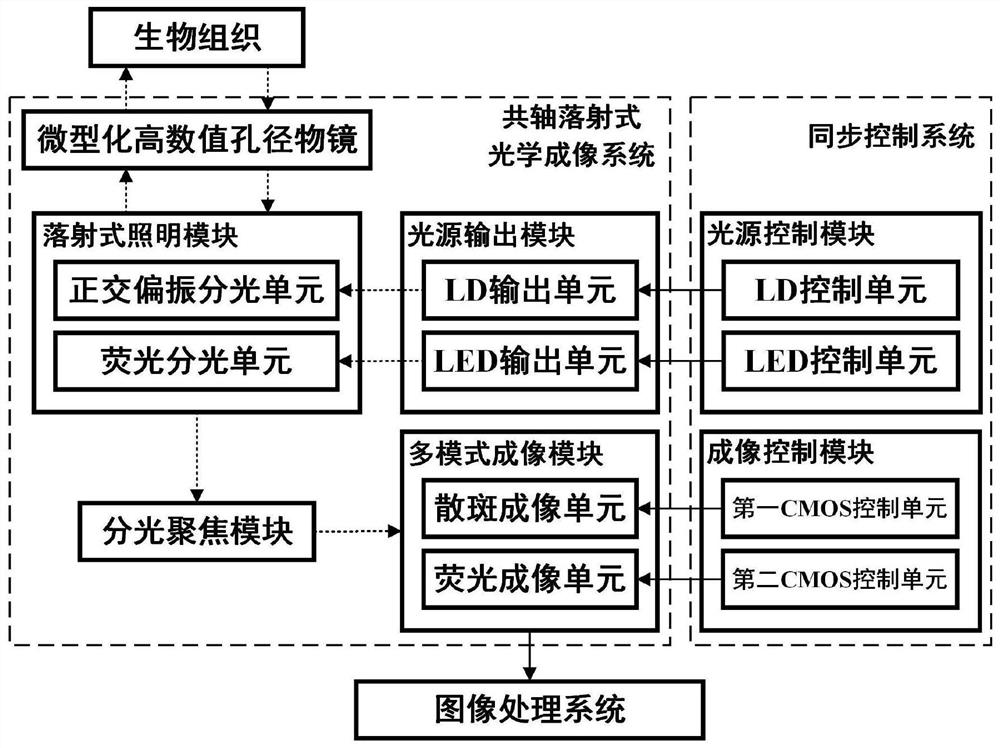
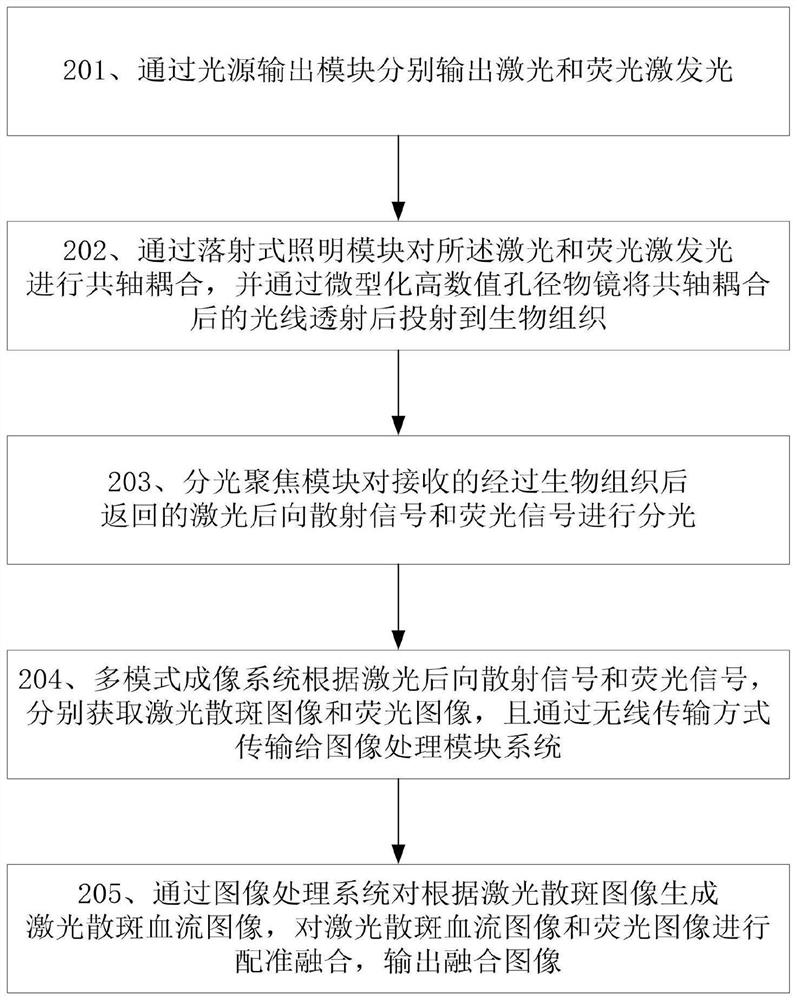
Multi-mode optical microscopic imaging device and microscopic imaging method
PendingCN112603268AImaging RealizationHigh resolutionMedical imagingCatheterMicroscopic imageDeep tissue imaging
The invention provides a multi-mode optical microscopic imaging device and a microscopic imaging method. The device comprises a coaxial incident optical imaging system and an image processing system, and the coaxial incident optical imaging system comprises a light source output module, an incident illumination module, a miniaturized high numerical aperture objective lens, a light splitting focusing module and a multi-mode imaging module. The method can be applied to an experimental animal in a waking free activity state, and high-resolution and stable blood flow change distribution and nerve activity distribution in the free behavior process of the experimental animal can be obtained at the same time; multiple imaging modes in the same view field area can be fused by adopting a registration fusion technology; based on the implantable miniaturized objective lens, superficial or deep tissue imaging of an experimental animal can be realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH INST (CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP THE NO 717 INST)
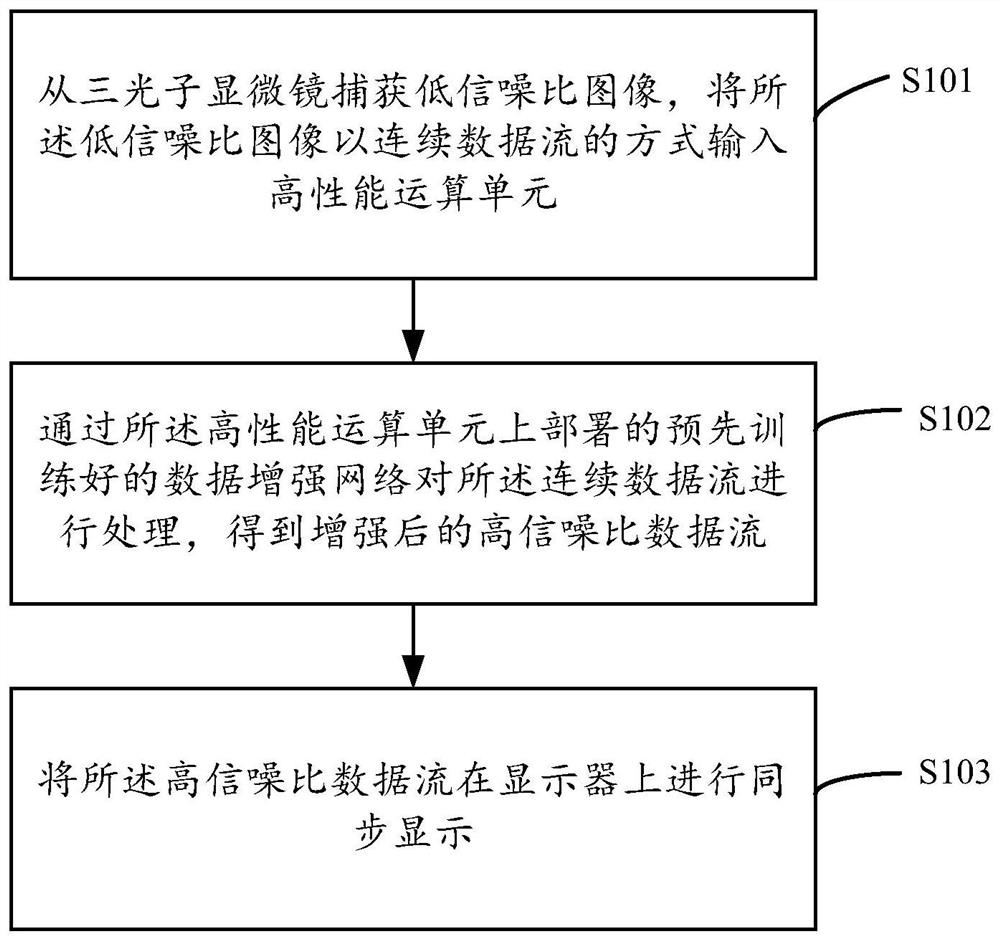
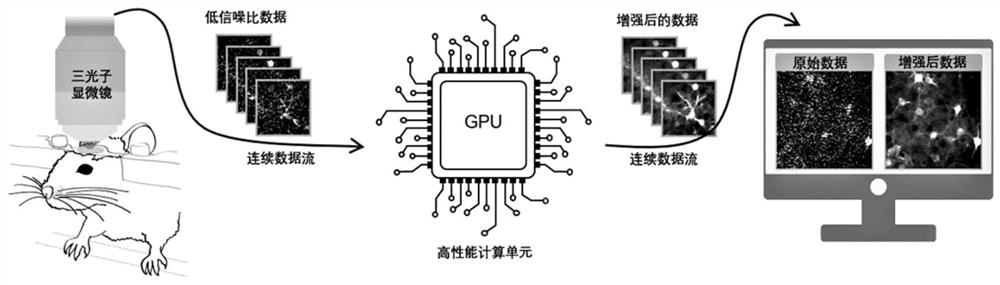
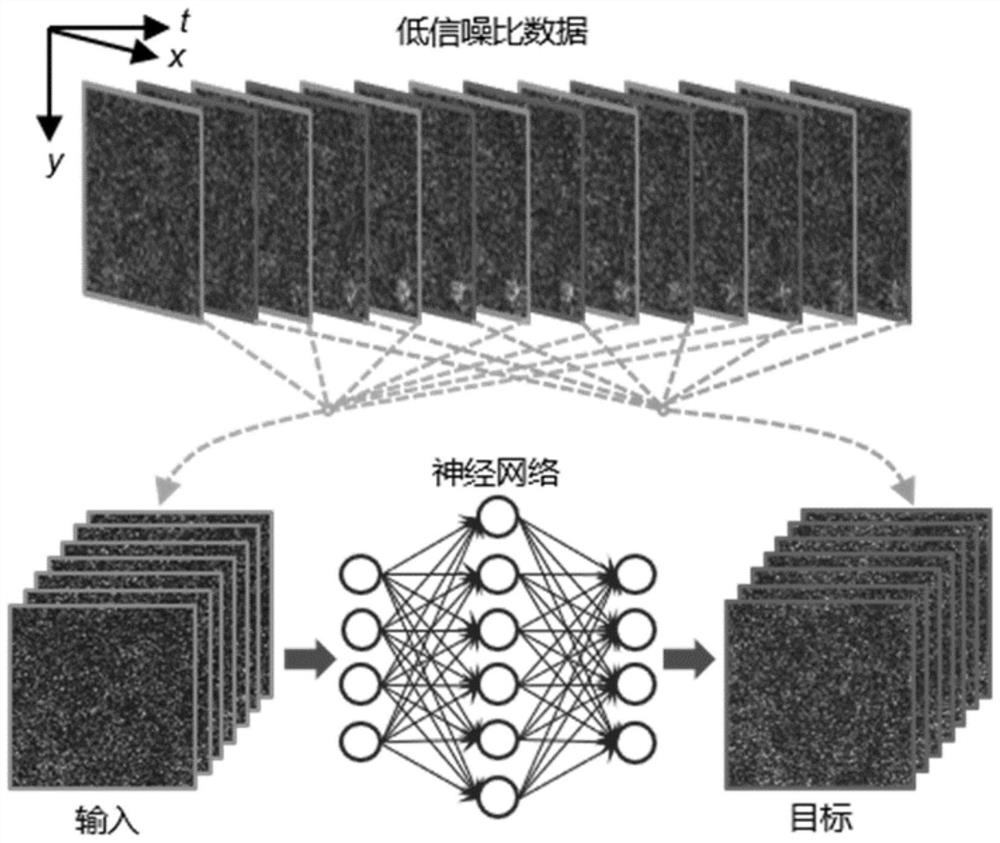
Three-photon deep tissue imaging method and device
PendingCN114119415AImprove image signal-to-noise ratioImplement embeddingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareData stream
The invention discloses a three-photon deep tissue imaging method and device, and the method comprises the steps: capturing a low-signal-to-noise-ratio image from a three-photon microscope, and inputting the low-signal-to-noise-ratio image into a high-performance operation unit in a continuous data flow manner; processing the continuous data stream through a pre-trained data enhancement network deployed on the high-performance arithmetic unit to obtain an enhanced data stream with a high signal-to-noise ratio; and synchronously displaying the high signal-to-noise ratio data stream on a display. On the premise that the imaging temporal-spatial resolution is not affected, the three-photon deep tissue imaging signal-to-noise ratio is improved, the algorithm is embedded into a microscopic hardware device, and real-time denoising is achieved.
Owner:杭州涿溪脑与智能研究所
A kind of preparation method and product of fluorescent mulberry silk under near-infrared light
ActiveCN110367209BStable in natureHigh biosecurityMaterial nanotechnologyAnimal feeding stuffNanoparticleDeep tissue imaging
The invention discloses a method for preparing mulberry silk that fluoresces under near-infrared light, comprising: (1) preparing upconversion nanoparticles, and performing surface modification with concanavalin to obtain the modified upconversion nanoparticles; 2) Uniformly disperse the up-conversion nanoparticles in water, and prepare an aqueous solution with a concentration of up-conversion nanoparticles; (3) Extract mature mulberry leaves, immerse the mulberry leaves in the nano-particle aqueous solution system, drain the water and dry naturally (4) After the silkworm grows to the set time, the silkworm is fed with treated mulberry leaves until the silkworm spins and cocoons; (5) Collects silk to obtain fluorescent mulberry silk under near-infrared light. The present invention selects up-conversion nanoparticles capable of emitting fluorescence under the irradiation of near-infrared light with stronger penetrating power, and has better application for deep tissue imaging. Moreover, the properties of the upconversion nanoparticles are more stable, the biological safety is higher, the signal-to-noise ratio is stronger, and the scope of application is wider.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
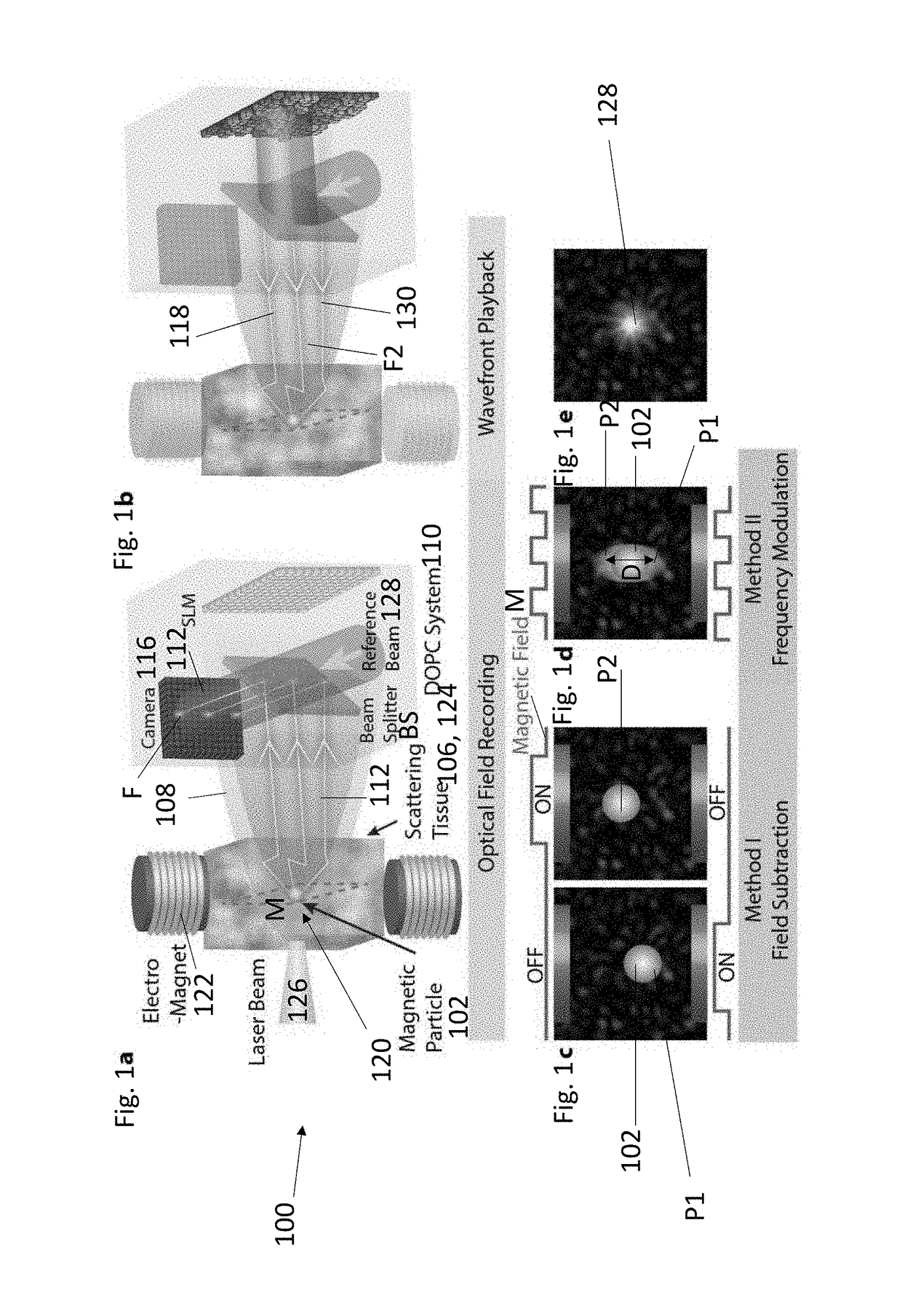
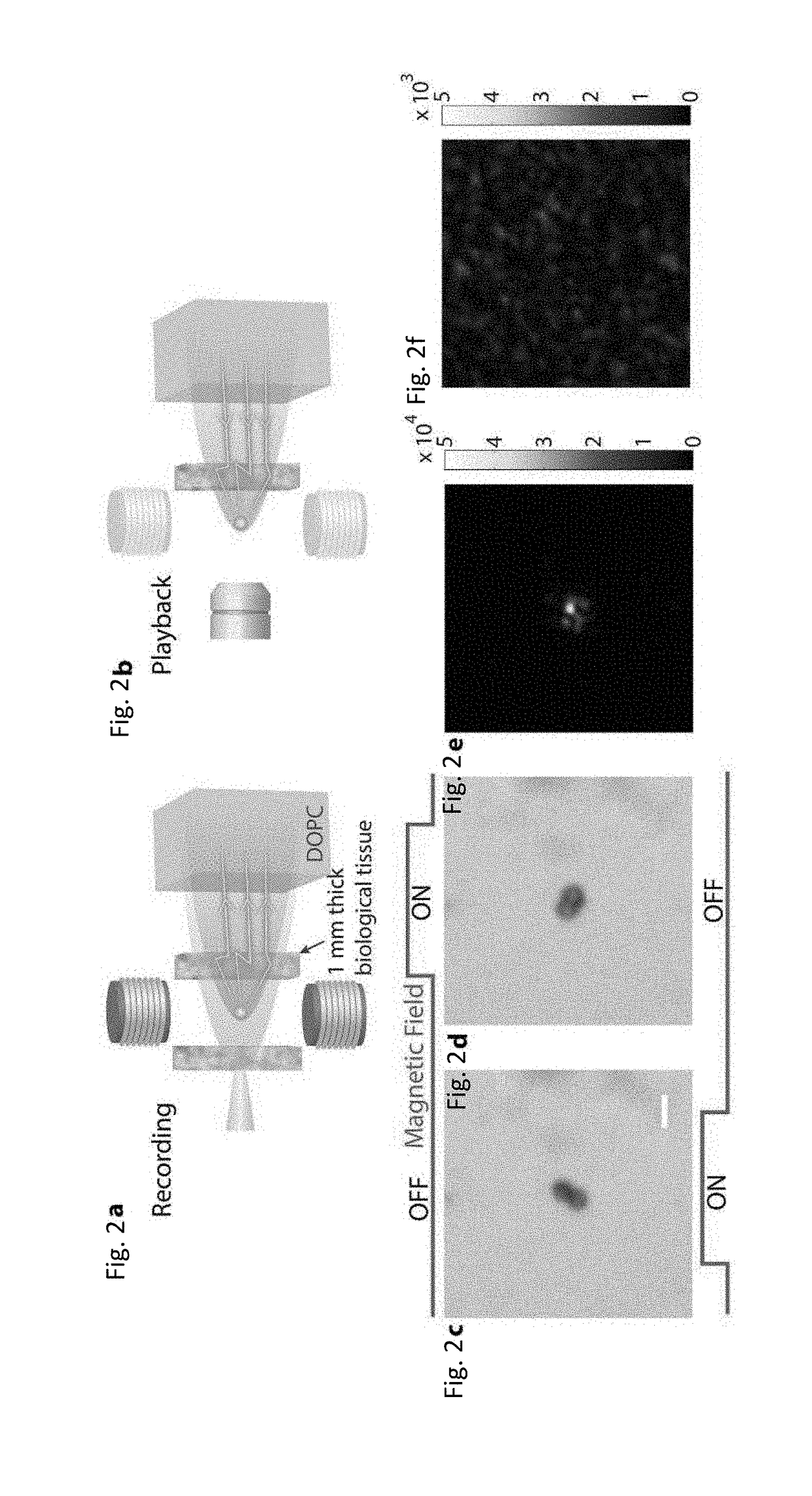
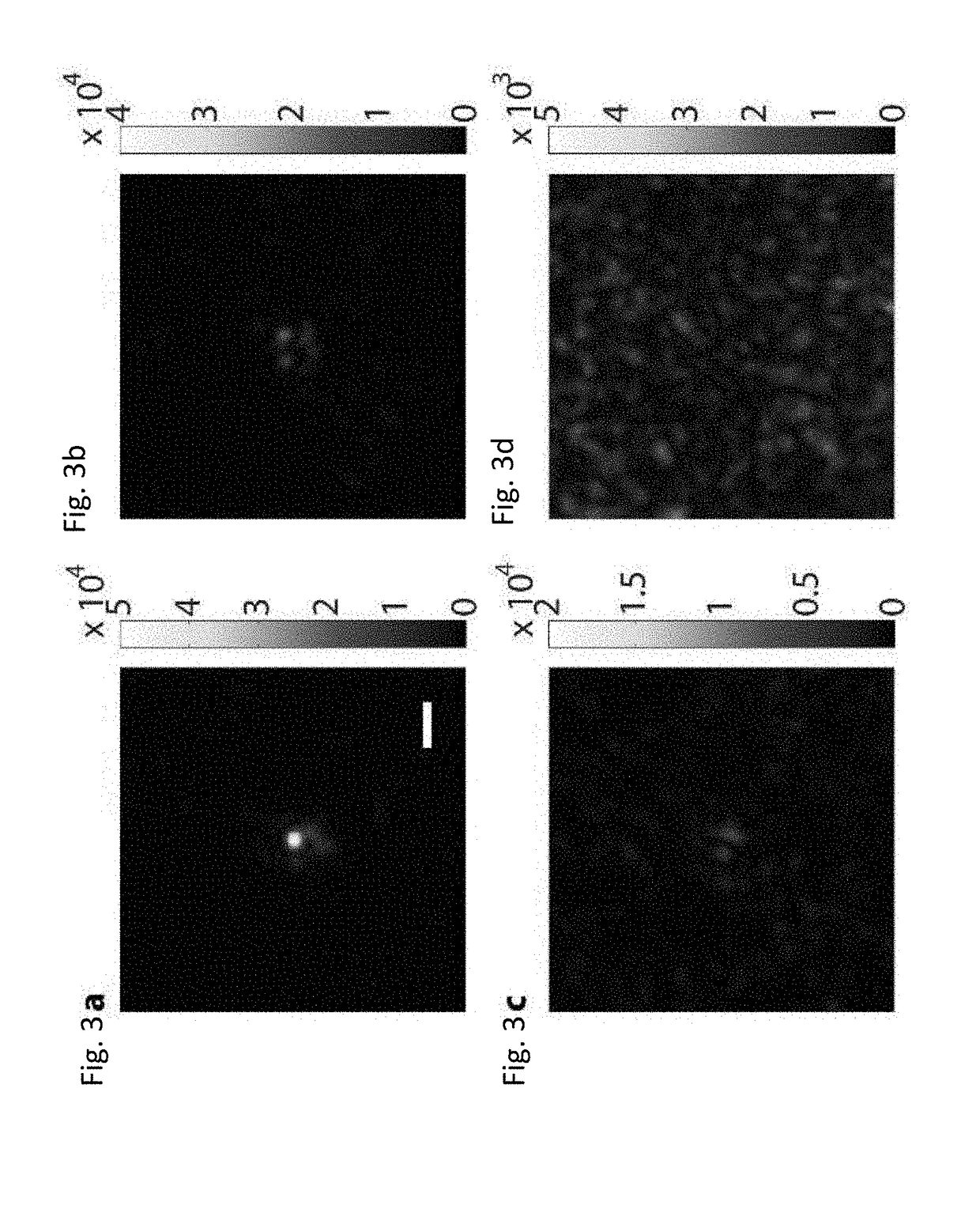
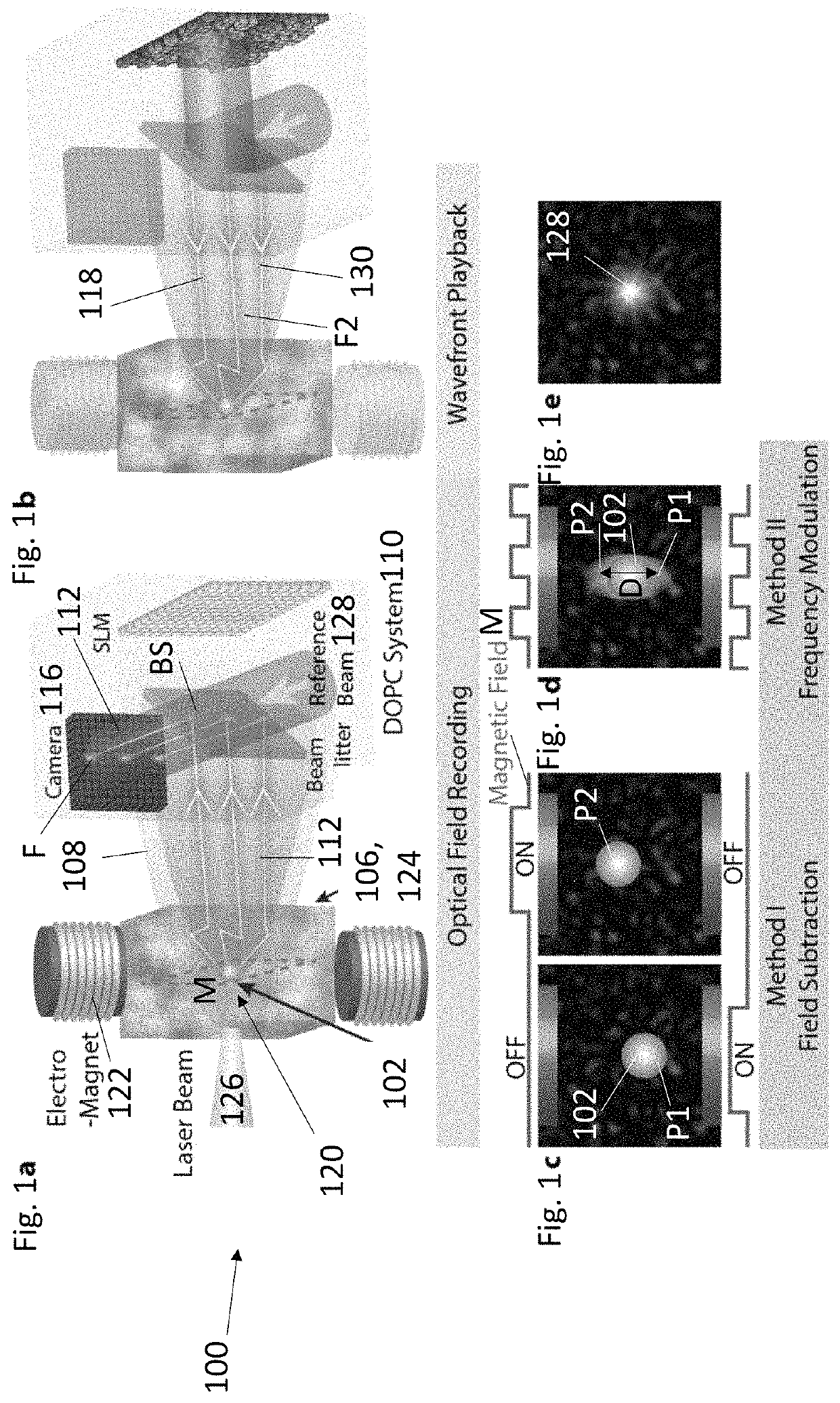
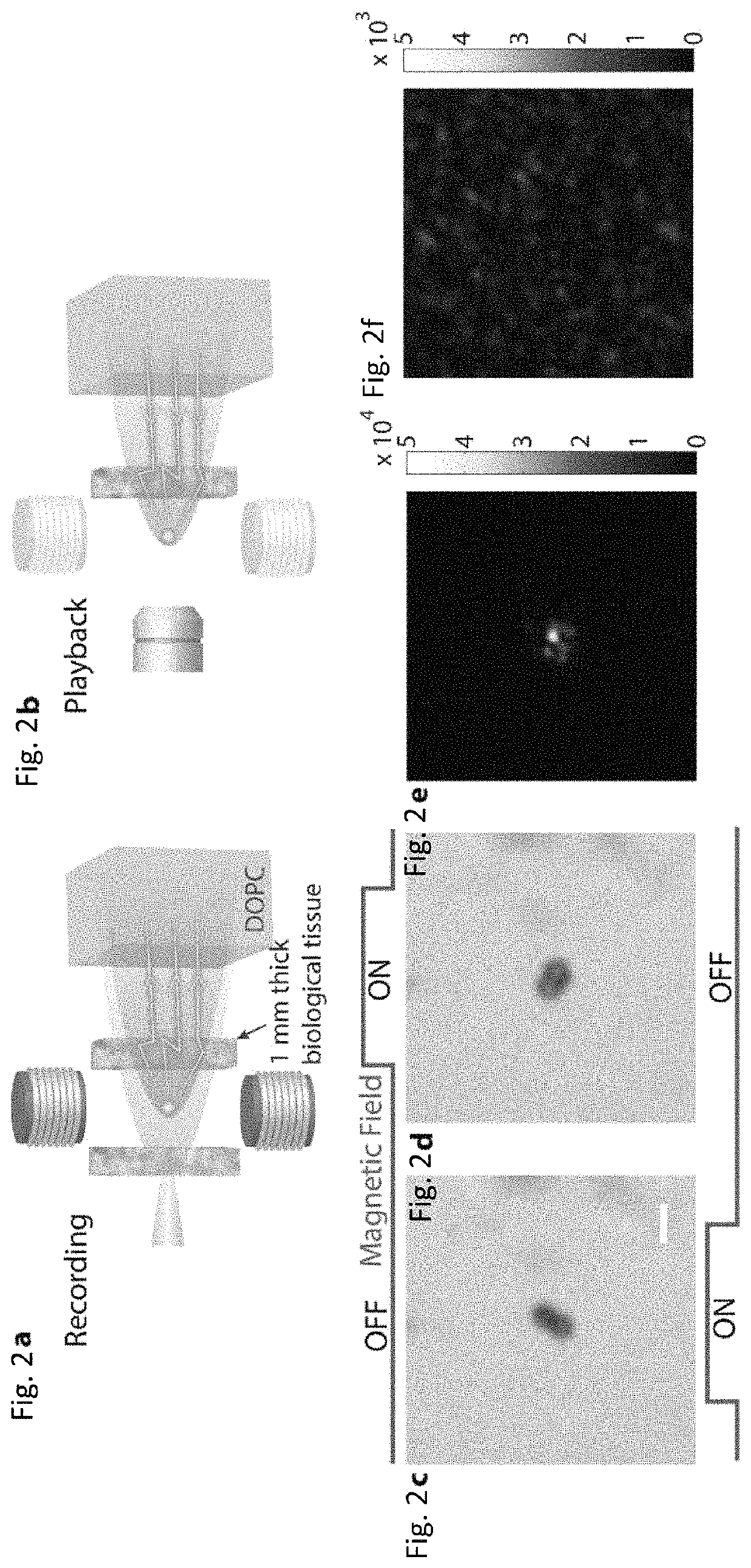
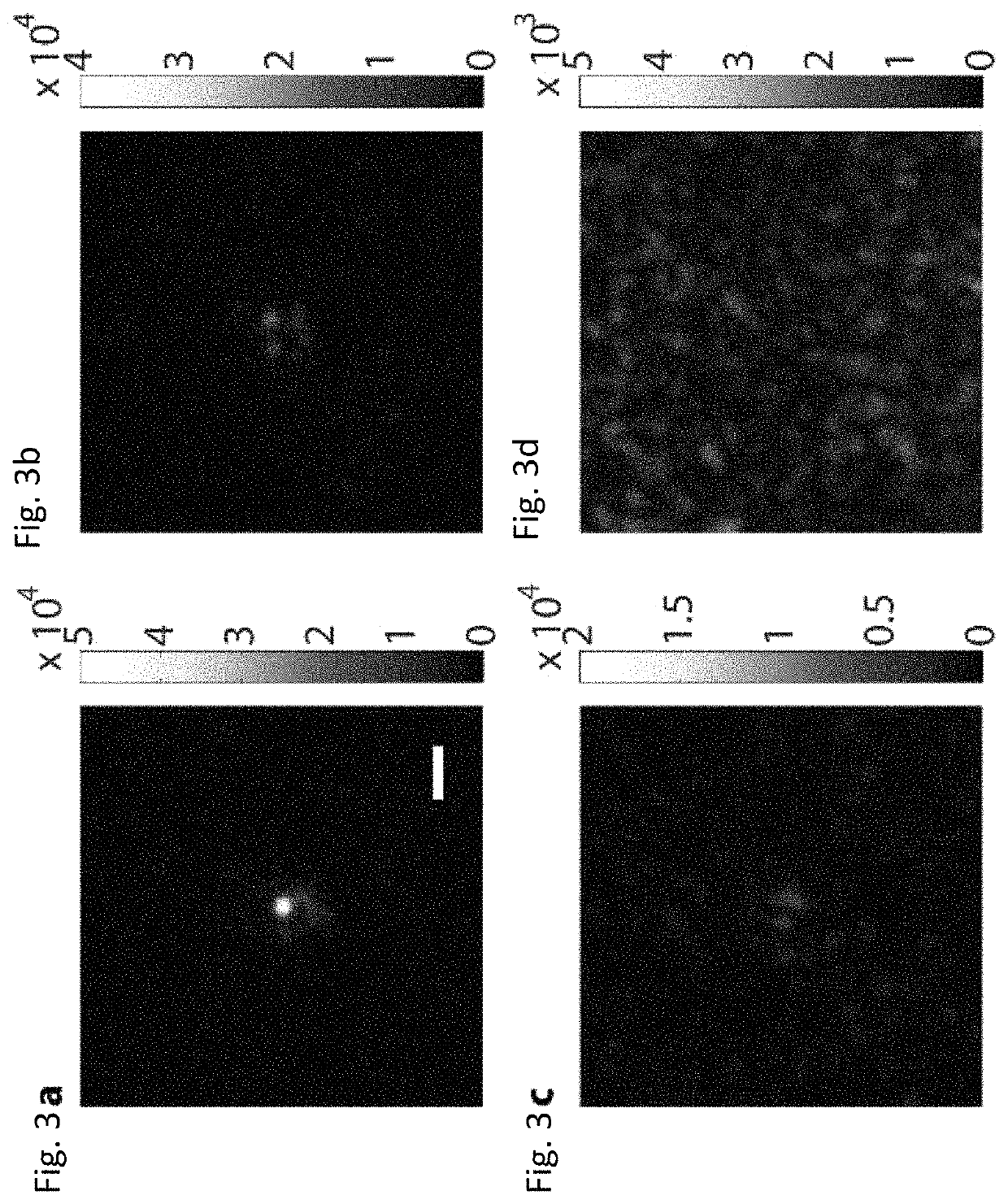
Focusing light inside scattering media with magnetic particle guided wavefront shaping
ActiveUS20190064736A1Scattering properties measurementsActive addressable light modulatorPhotodynamic therapyWavefront
A magnetic field controlled guidestar for focusing light deep inside scattering media using optical phase conjugation. Compared with the optical and ultrasonic field, the magnetic field has an exceptional penetration depth. The magnetic particle guidestar has a high light-tagging efficiency, good biocompatibility, and a small diameter which enables a sharp and bright focusing deep inside biological tissue. This new method can benefit a wide range of biomedical applications including deep-tissue imaging, neural modulation, and targeted photothermal and photodynamic therapies.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Fluorescence identification dye based on nile blue matrix and preparing method and application thereof
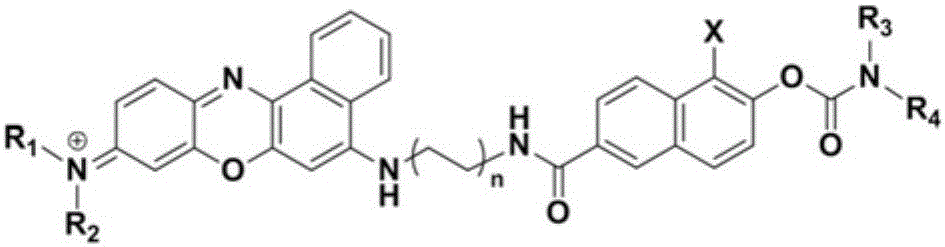
ActiveCN105802273ALow biological toxicityReduce phototoxicityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSolubilityCancer cell
The invention discloses a fluorescence identification dye based on a nile blue matrix and a preparing method and application thereof. The fluorescence identification dye has a structure as shown in the general formula I, wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are C1-8 alkyl group, C1-6 alkyl sulfonic acid group and C1-6 alkyl carboxylic acid group respectively, X is halogen, and n is an integer from 1 to 4. The fluorescence identification dye can achieve targeted identification of enzyme KIAA1363 in a specific mode, has excellent tissue permeability, light stability and water solubility, low biotoxicity, excellent near infrared fluorescence property, high sensitivity and low background interference degree, and is suitable for biological sample detection. The fluorescence identification dye conducts identification and distinguishing of cancer cells and tissues and non-cancer cells and tissues by means of KIAA1363 expression difference, and the effect of distinguishing in-vitro cancer cell and tissue samples from non-cancer cell and tissue samples is remarkable especially. The fluorescence identification dye can be applied to deep issue imaging and mouse living imaging, and has high application value in imaging assistance and boundary determination during early diagnosis of cancer and operative treatment of cancer.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
A deep tissue x-ray excited multi-spectral tomography system and method
ActiveCN105640582BGreat penetration depthMeeting Deep Tissue Imaging RequirementsComputerised tomographsTomographyX-rayElectric control
The invention discloses a deep tissue X-ray excitation multispectral tomography system and method. The system comprises an X-ray source, an X-ray flat panel detector, an EMCCD camera, an electric control rotary table, a narrow-band filter, a lead plate, a computer and an animal to be imaged; nano-luminescence materials are excited through an X ray, short-wave infrared light with the specific spectra sections, particularly high penetration depth is emitted, photons penetrate through tissue to reach the surface of an imaged object, the light of different wave length spectra sections is received by an EMCCD camera by being filtered by the narrow-band filter, and an obtained image and a rebuilt result under each spectra section are obtained; multivariate analysis is adopted for carrying out treatment and analysis on multispectral images and rebuilt results, accurate distribution of the nano-luminescence materials in the object is obtained and combined with CT tomography results, and finally a deep tissue multispectral tomography image is obtained. The imaging depth of X-ray excitation multispectral tomography can be effectively improved, and deep tissue imaging of small living animals is achieved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for clearing a biological sample
The disclosure provides improved materials and methods for optically clearing biological tissue that is subsequently used for deep tissue imaging analysis. Also provided is a description of a microscopic image acquisition methodology in which imagery of intact tissues are acquired to rapidly acquire microscopy data on a whole-organ scale to maximize cost effectiveness for biological microscopy and minimize time spent performing such analysis.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Preparation and application of a hydrogen peroxide fluorescent probe compound
InactiveCN106632436BInnovative designGood choiceGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzaldehydeNitrogen
The invention relates to a hydrogen peroxide fluorescence probe compound as well as preparation and application thereof. The hydrogen peroxide fluorescence probe compound has a structure of a formula I. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking imidazole as a catalyst, and carrying out a reaction 2,4-dihydroxy benzaldehyde and cyclohexenone under nitrogen protection so as to produce a product II; carrying out a reaction the product II and 4-bromobenzyl borate, taking anhydrous potassium carbonate as a catalyst, performing return flow agitation in acetonitrile, so as to obtain the final product probe I. The probe compound has excellent selectivity and sensitivity on hydrogen peroxide, is low in detection limit, does not have toxicity to cells, can be applied to detection and imaging of the hydrogen peroxide in cells and can also be applied to deep tissue imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Focusing light inside scattering media with magnetic particle guided wavefront shaping
ActiveUS11156960B2Scattering properties measurementsActive addressable light modulatorBiocompatibilityDeep tissue imaging
A magnetic field controlled guidestar for focusing light deep inside scattering media using optical phase conjugation. Compared with the optical and ultrasonic field, the magnetic field has an exceptional penetration depth. The magnetic particle guidestar has a high light-tagging efficiency, good biocompatibility, and a small diameter which enables a sharp and bright focusing deep inside biological tissue. This new method can benefit a wide range of biomedical applications including deep-tissue imaging, neural modulation, and targeted photothermal and photodynamic therapies.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Method of deep tissue imaging using multi-photon excitation of a fluorophore
ActiveUS10420471B2Diagnostics using lightLuminescence/biological staining preparationFluorophoreLength wave
A method is provided for deep tissue imaging using multi-photon excitation of a fluorescent agent. The fluorescent agent is irradiated with an ultrafast laser to produce an excited singlet state (Sn) which subsequently undergoes non-radiative relaxation to a first singlet state (S1). The S1 state undergoes fluorescence to the ground state S0 to produce an emission wavelength. Both the excitation and emission wavelengths are within the near infrared optical window, thereby permitting deep tissue penetration for both the incoming and outgoing signals.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT R
An optical coherence tomography method
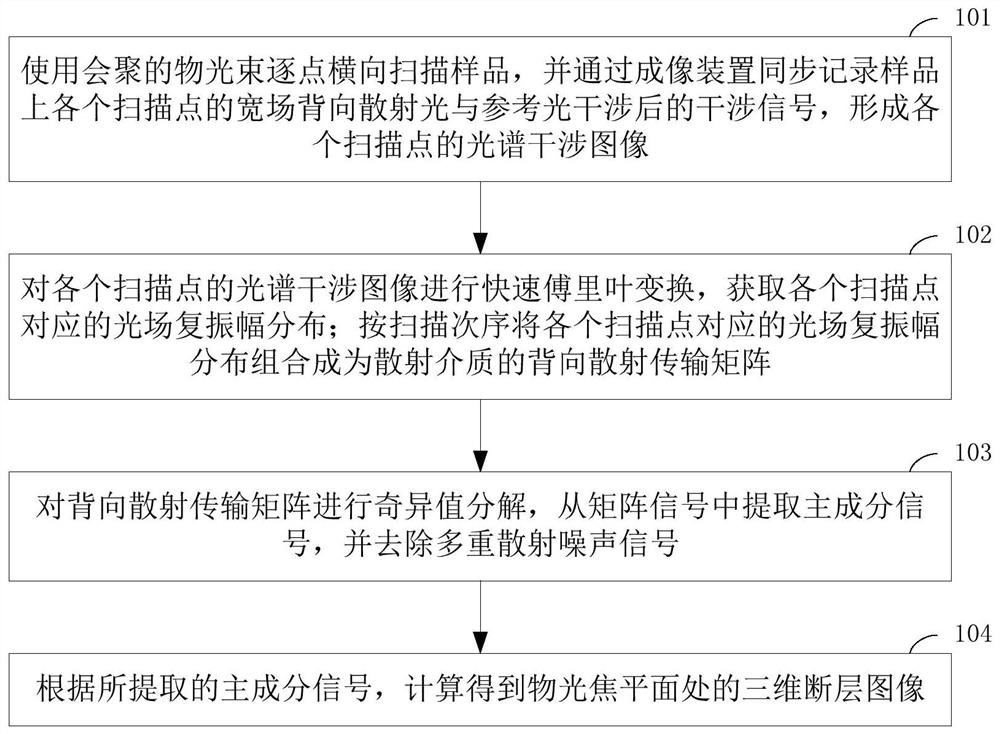
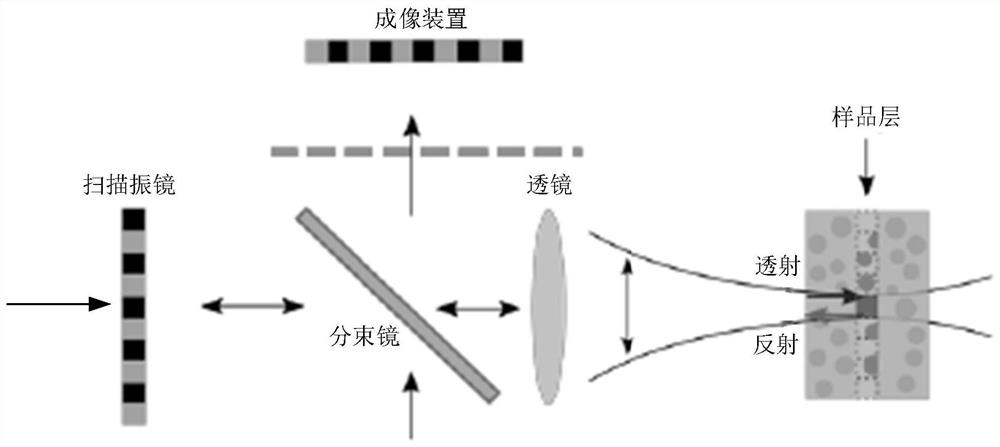
ActiveCN110881947BEasy accessImprove imaging depthDiagnostic signal processingPhase-affecting property measurementsSingular value decompositionFast Fourier transform
The invention provides an optical coherence tomography imaging method. The method includes: using a converged object beam to scan the sample point by point, and synchronously recording the interference signal of the wide-field backscattered light of each scanning point on the sample after interference with the reference light by an imaging device, so as to form a spectral interference image of each scanning point ; Perform fast Fourier transform on the spectral interference image of each scanning point to obtain the complex amplitude distribution of the light field corresponding to each scanning point; combine the complex amplitude distribution of the light field corresponding to each scanning point in the scanning order to form the back transmission of the scattering medium matrix; perform singular value decomposition on the back transmission matrix, extract the principal component signal from the matrix signal, and remove the multiple scattering noise signal; according to the extracted principal component signal, calculate the three-dimensional tomographic image at the focal plane of the object light. By applying the present invention, deep tissue imaging can be realized, and the imaging depth and imaging speed can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Optimal Adaptive Microscopic Imaging Method and Device Based on Machine Learning
ActiveCN110309910BAddressing Insufficient Scope of WorkImage Quality RestorationImage enhancementNeural architecturesMicro imagingImaging quality
The invention discloses a machine learning-based optimized self-adaptive microscopic imaging method and device, wherein the method includes the following steps: using ultrashort pulse laser to collect image data through a point scanning method; constructing a convolutional neural network to input The simulation results obtained from the image data to the physical model train the network; apply the trained training network to the adaptive method, optimize the imaging result, and eliminate image distortion, and use the model fitting method to find the optimal phase of the system and sample distortion correction compensate. This method can obtain imaging results with high optimization performance, high image quality, and high imaging speed, and has the advantages of high speed, high image quality, and good scalability, and realizes high-speed wavefront distortion compensation based on machine learning. It has great application prospects in deep tissue imaging.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Near-infrared light response photosensitizer compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
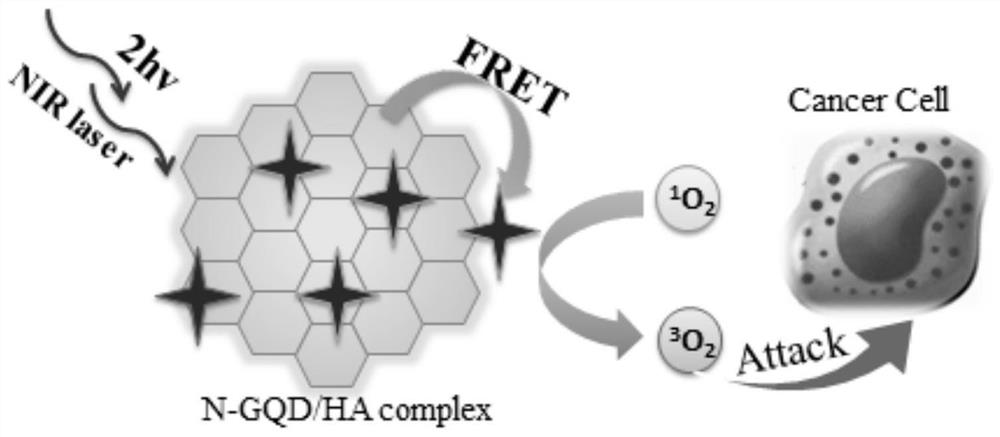
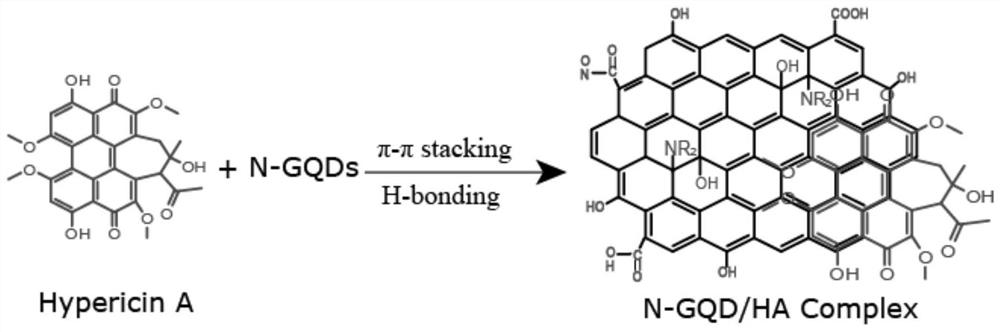
InactiveCN114028566AImprove stabilityEfficient killingPhotodynamic therapyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCell culture mediaSinglet oxygen
The invention relates to a near-infrared light response photosensitizer compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The near-infrared light response photosensitizer compound comprises graphene quantum dots and a photosensitizer loaded on the graphene quantum dots. The graphene quantum dots have high two-photon absorption cross section and deep tissue imaging capacity, fluorescence emitted by the graphene quantum dots is matched with the absorption wavelength of the photosensitizer under excitation of near-infrared light, the photosensitizer is excited through fluorescence resonance energy transfer, high-yield singlet oxygen is generated, and tumor cells are effectively killed. On the other hand, the oxygen-containing functional groups at the edges of the graphene quantum dots are very easy to dissolve in water and have good biocompatibility, so that after the graphene quantum dots and an aromatic photosensitizer form a compound, the stability of the photosensitizer in physiological environments such as an aqueous solution, PBS and even a cell culture medium is greatly improved, and the curative effect of tumor photodynamic therapy is promoted; the application and development of the graphene quantum dots in the field of biomedicine can be further promoted.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
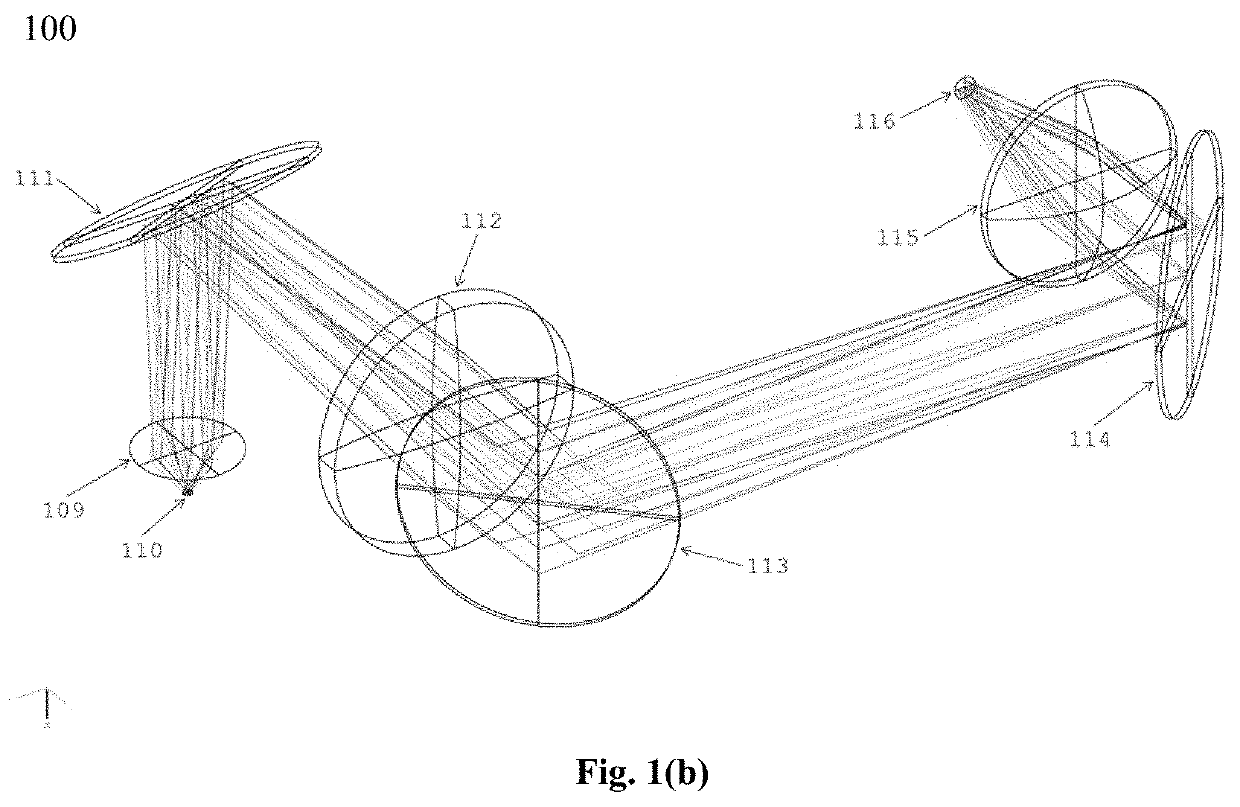
Large-angle optical raster scanning system for deep tissue imaging
ActiveUS11333870B2Reduce the number of pixelsReduce signal strengthMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLarge fovOphthalmology
The field of view (FOV) of a nonlinear optical microscope (NLOM) is expected to be large enough for employing high-speed raster scanning on a mesoscale volumetric biological sample. Concurrently, three-dimensional (3D) visualization of fine sub-micron biological structures requires high enough lateral and axial resolutions, enforcing a high numerical aperture (NA) objective lens to be employed, thereby limiting the FOV of an NLOM. The invention is directed to a laser scanning NLOM, or to a large-angle optical raster scanning system, for deep biological tissue imaging with a large FOV of more than one square millimeter, up to 1.6×1.6 mm2, while simultaneously maintaining a sub-femtoliter effective 3D resolution by means of a high-NA and low magnification objective lens and further maintaining a high acquisition speed with synchronized sampling, limited by the repetition rate of a high repetition rate pulsed laser source, thereby exceeding Nyquist Criterion for resolving micro-optical resolution throughout a horizontal FOV of more than one millimeter.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com