Patents
Literature
46 results about "Log sequence number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
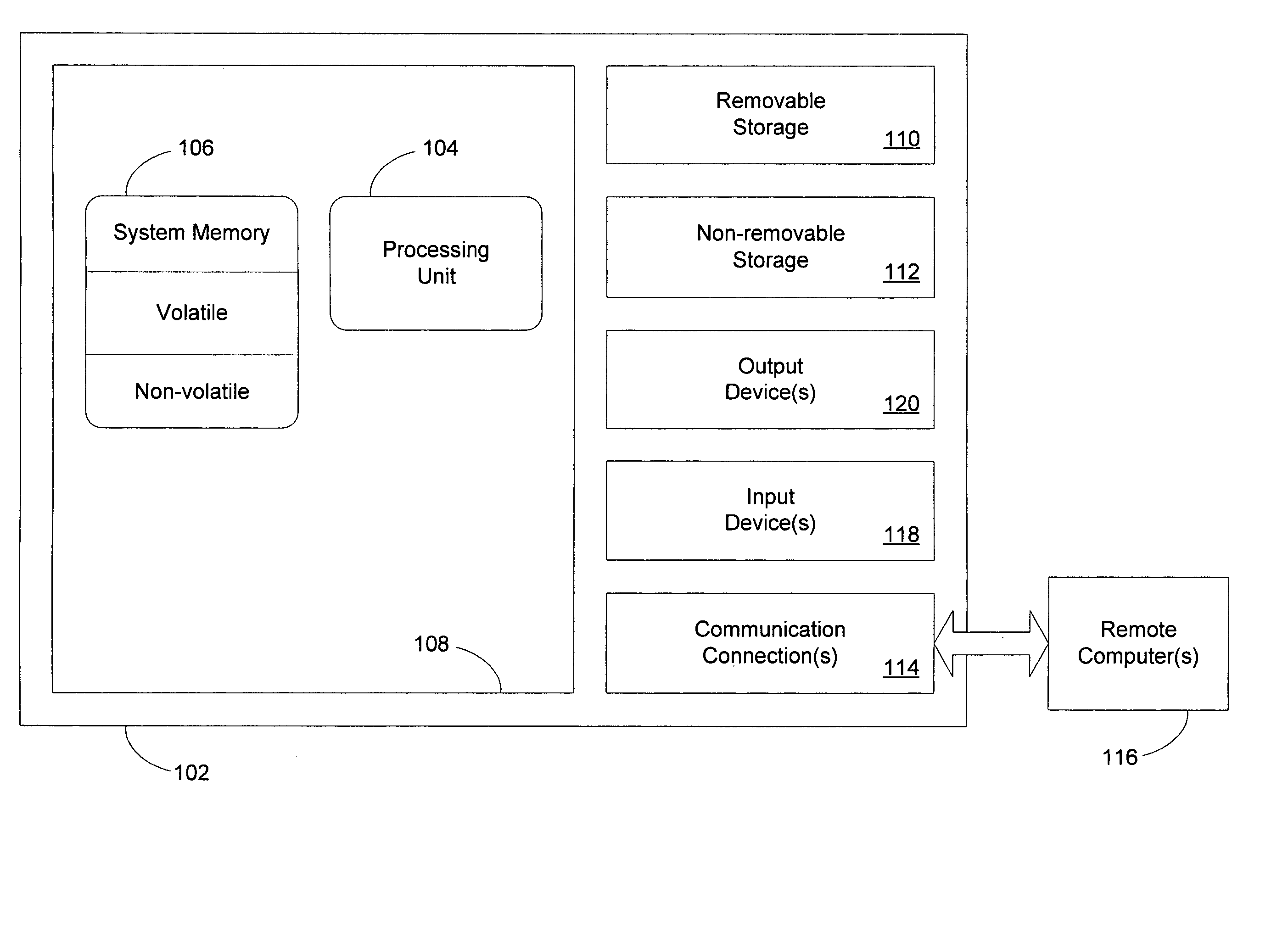
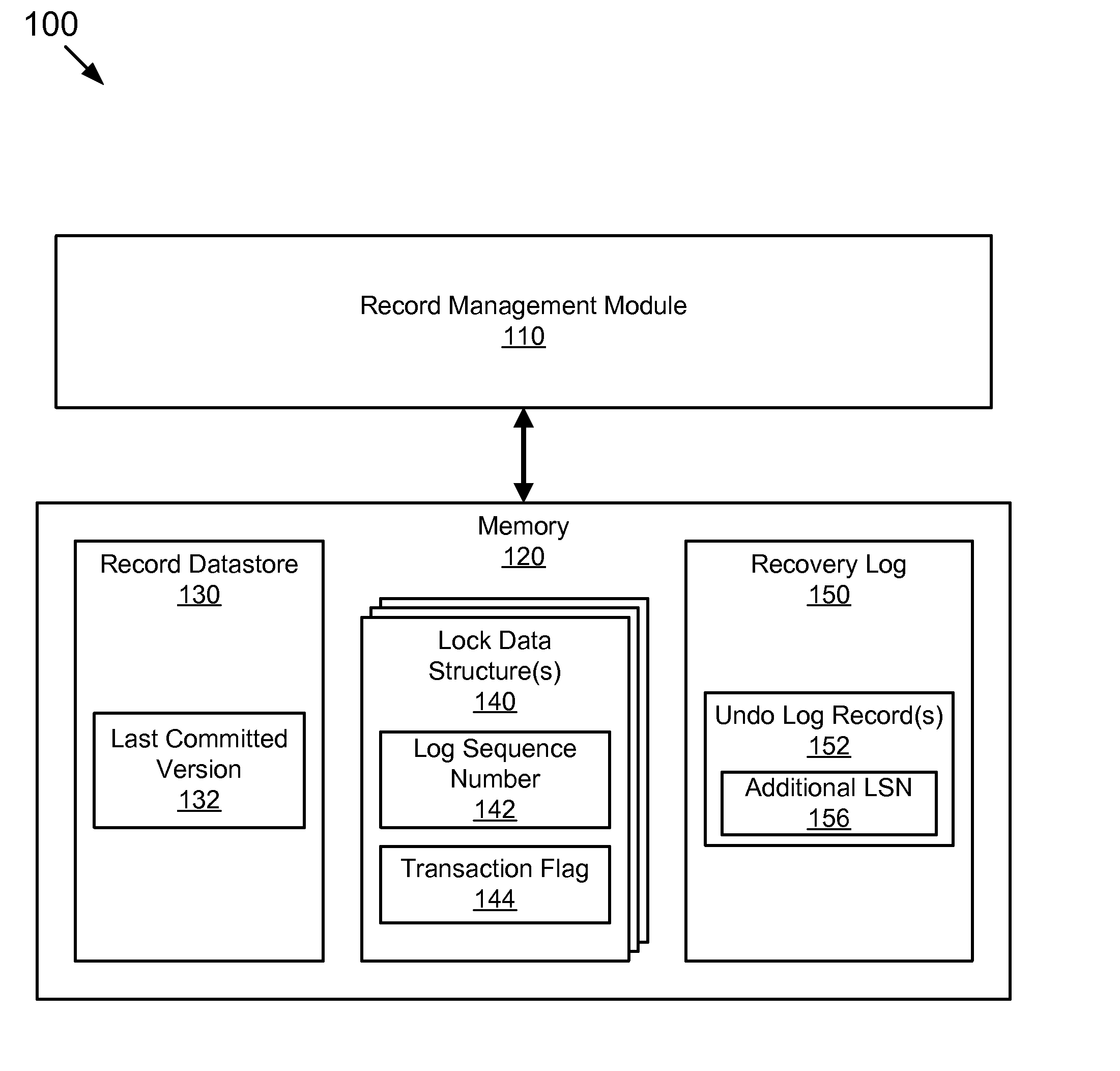
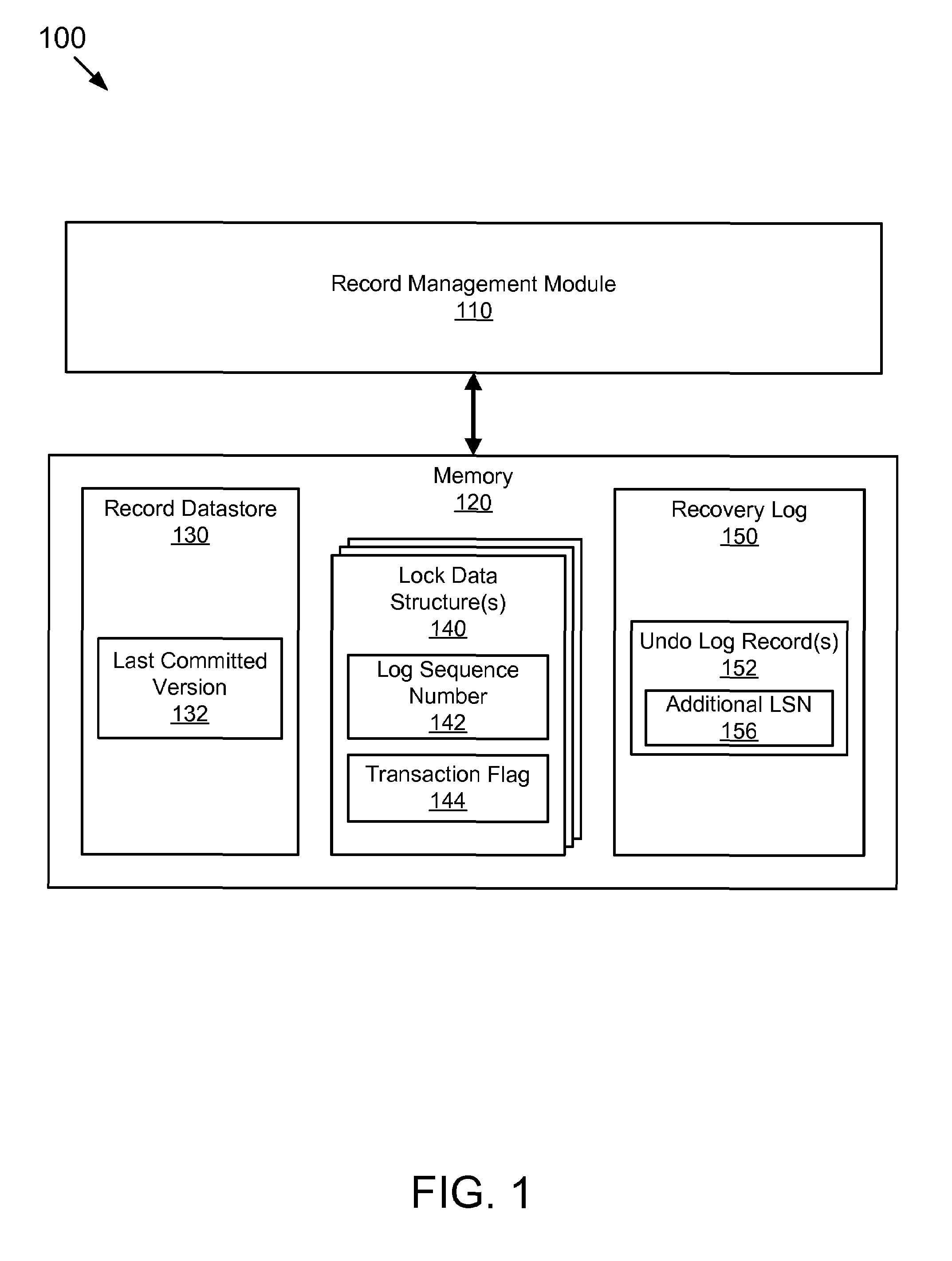
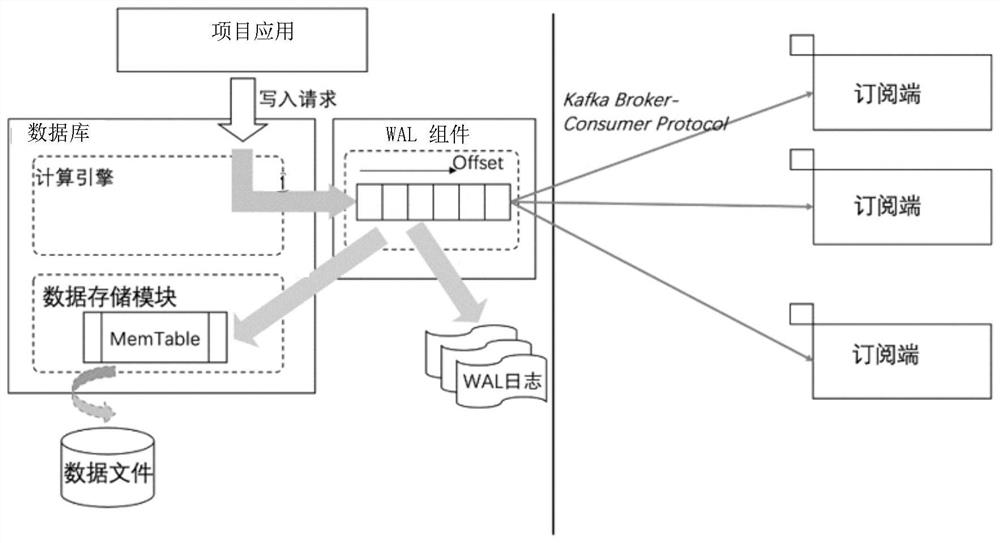
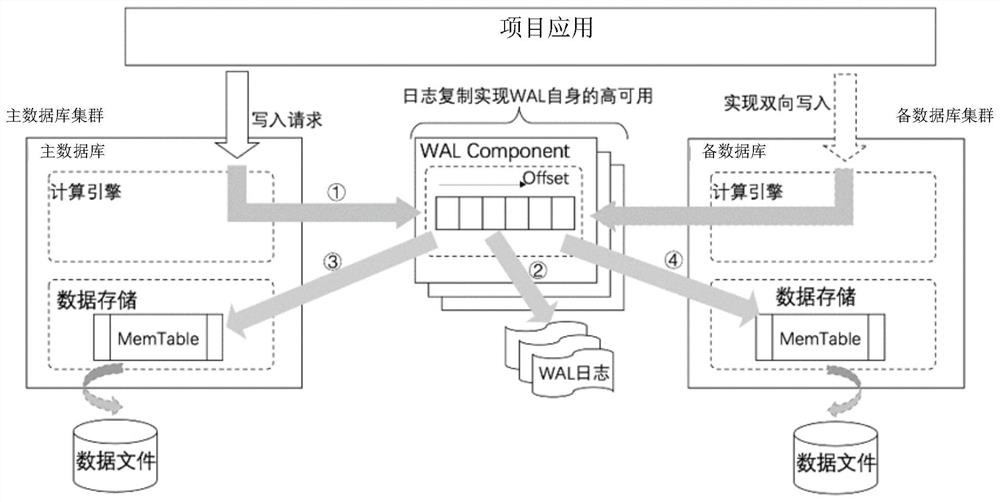
A log sequence number (LSN) represents the offset, in bytes, of a log record from the beginning of a database log file. It identifies the location within the log file of a specific log file record.
Lossless recovery for computer systems with remotely dependent data recovery
InactiveUS20050289414A1Well formedElectronic circuit testingRedundant hardware error correctionDistributed File SystemKernel level
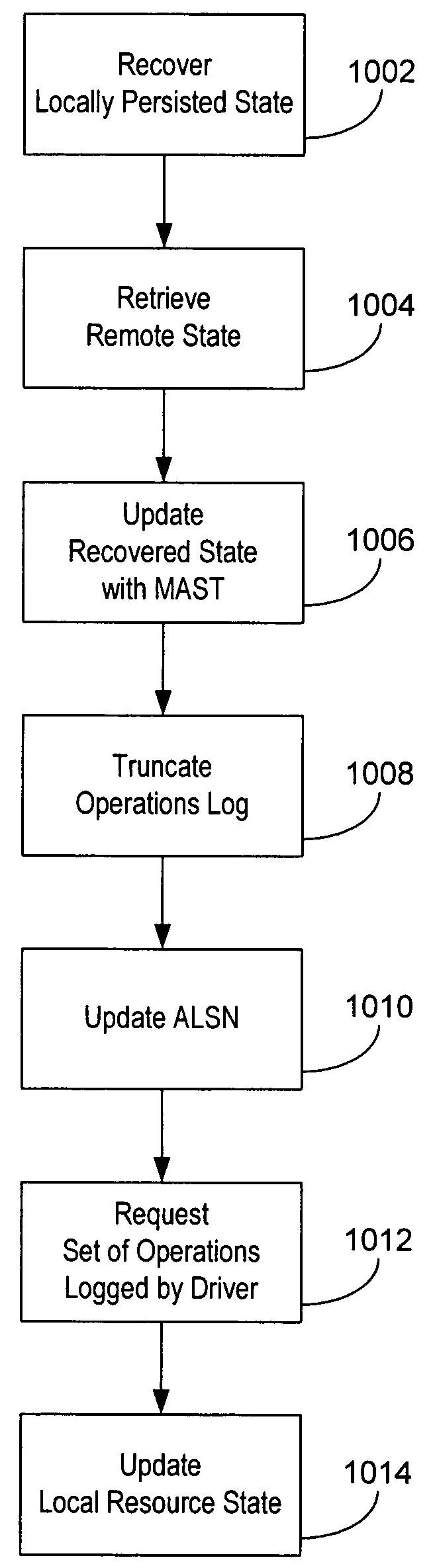
An architecture and implementation for losslessly restarting subsystems in a distributed file system is described. By partitioning functionality and logging appropriately across the kernel and user-level boundaries on a client, the user-level subsystem may be made losslessly restartable. Practical mechanisms for supporting state-based recovery in replicated state machines and like replica are described. In particular, each client daemon may include an operations log and an applied log sequence number. Each client driver may include a potentially different operations log. Each client daemon may be configured to request logged operations associated with log sequence numbers in one or more ranges specified by a specification that includes the applied log sequence number. The requested logged operations may reside in the operations log maintained by a client driver. Each client daemon may operate in accordance with user-level constraints and each client driver may operate in accordance with kernel-level constraints.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
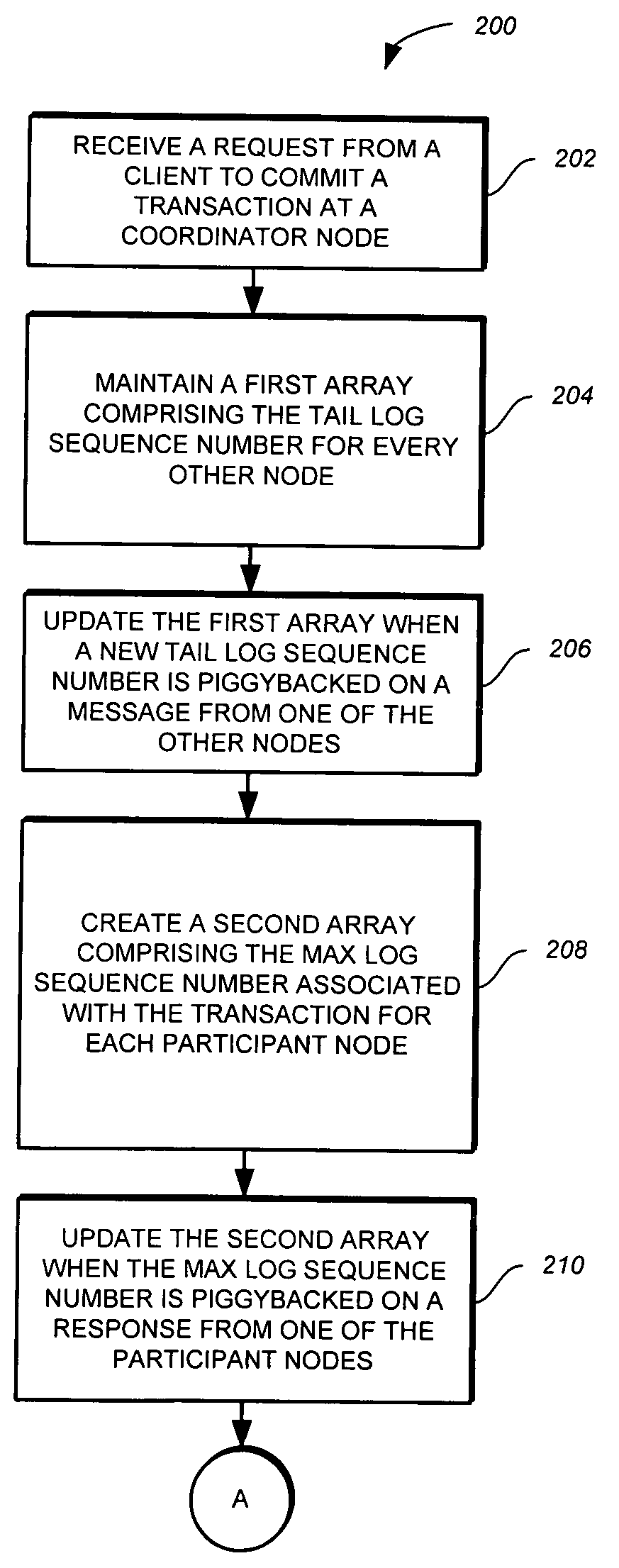
Commitment of transactions in a distributed system
ActiveUS20070143299A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsClient-sideDistributed computing
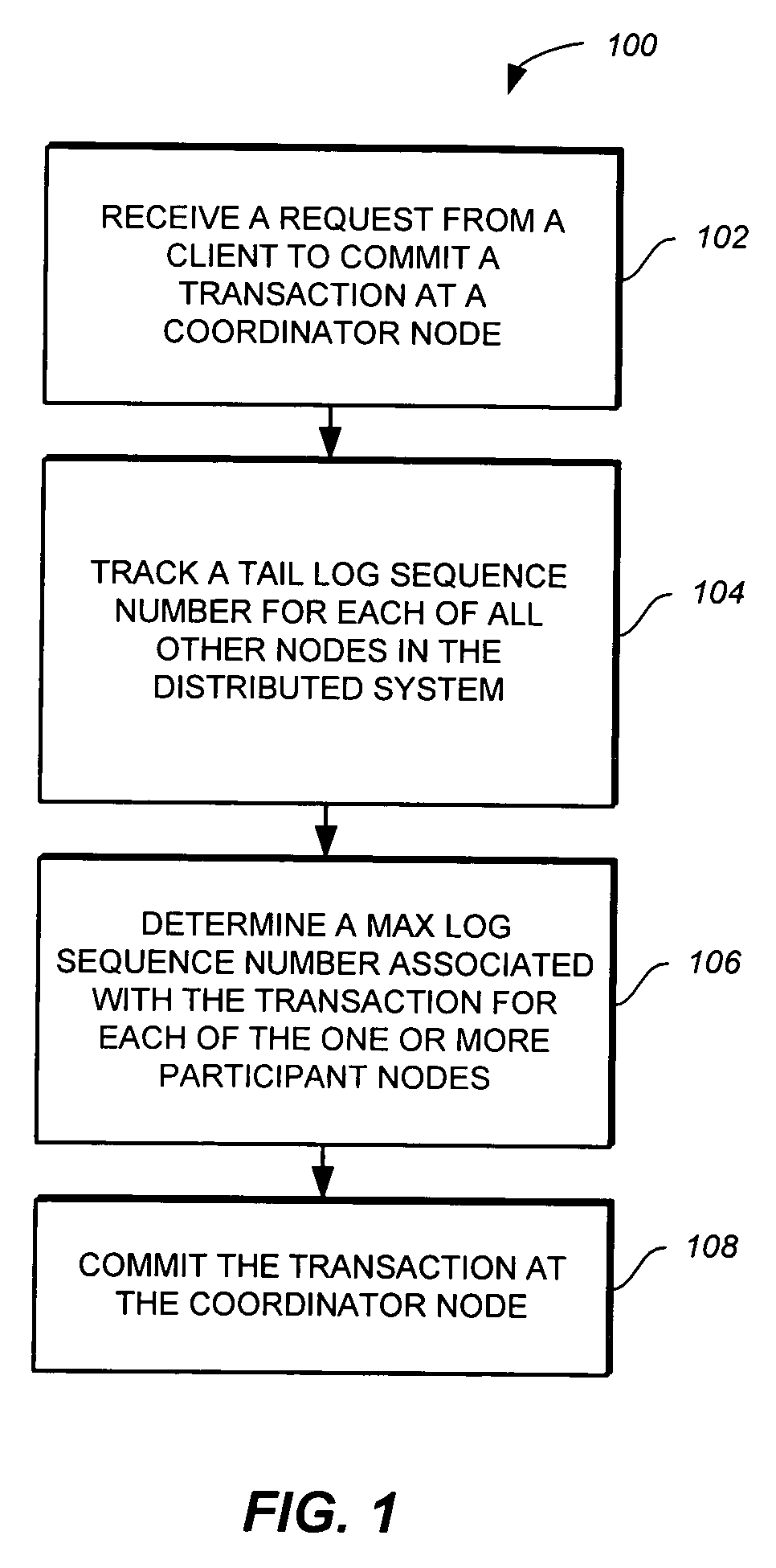
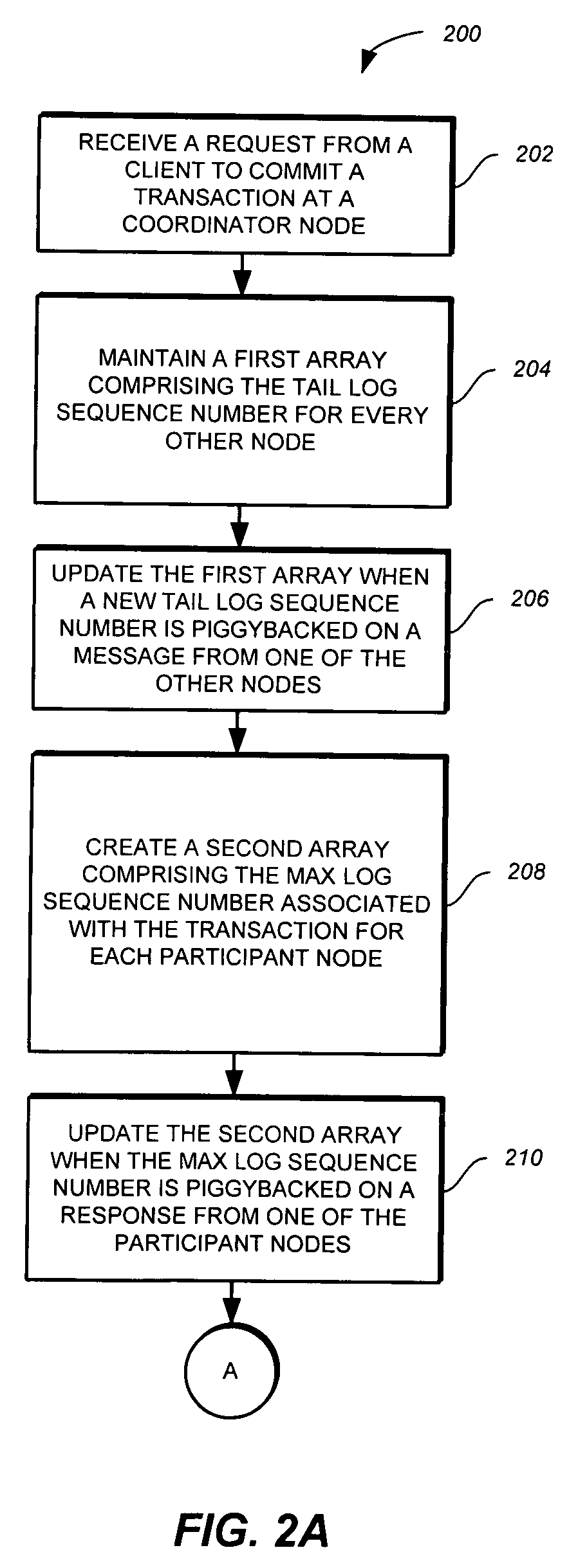
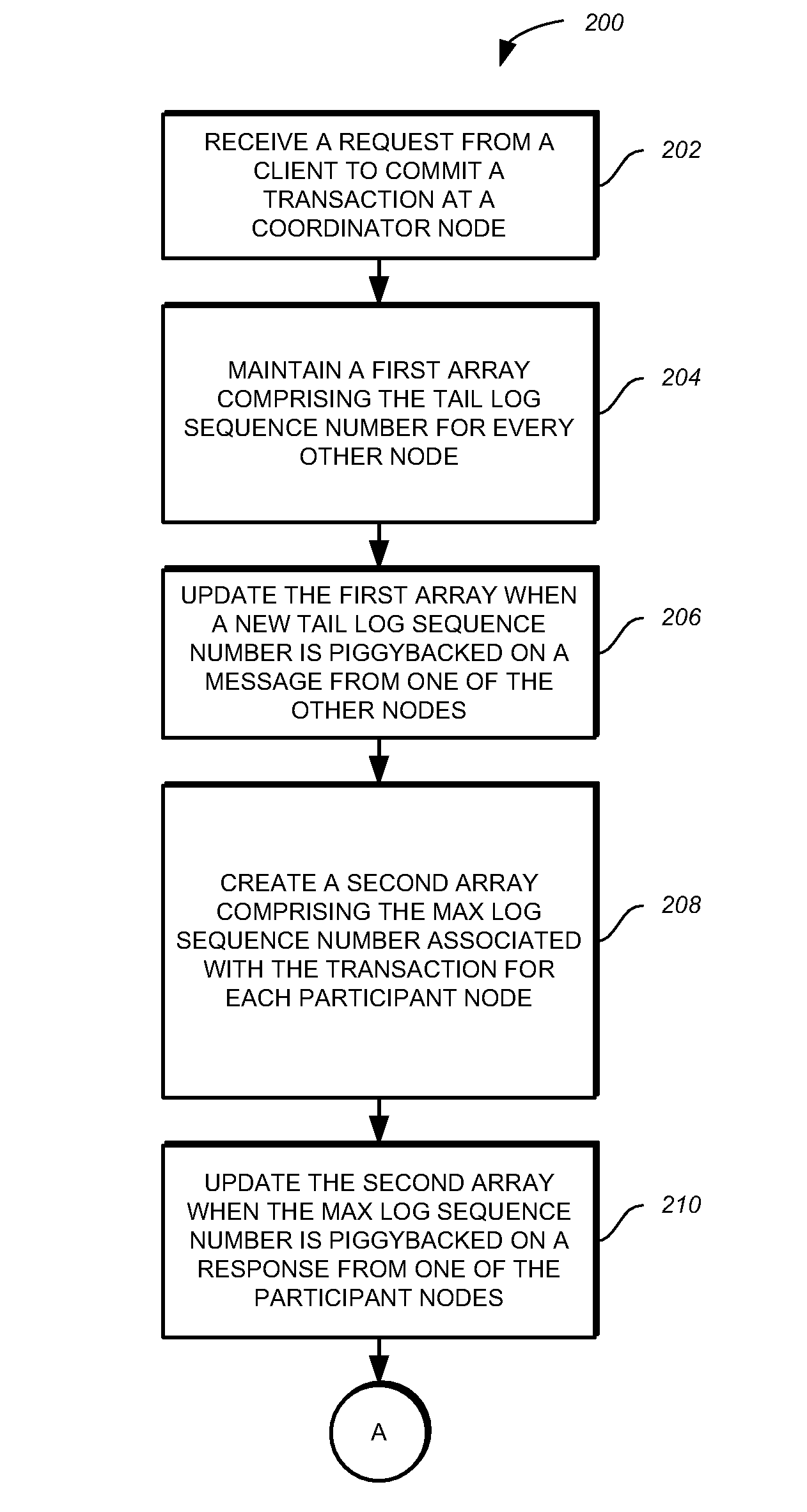
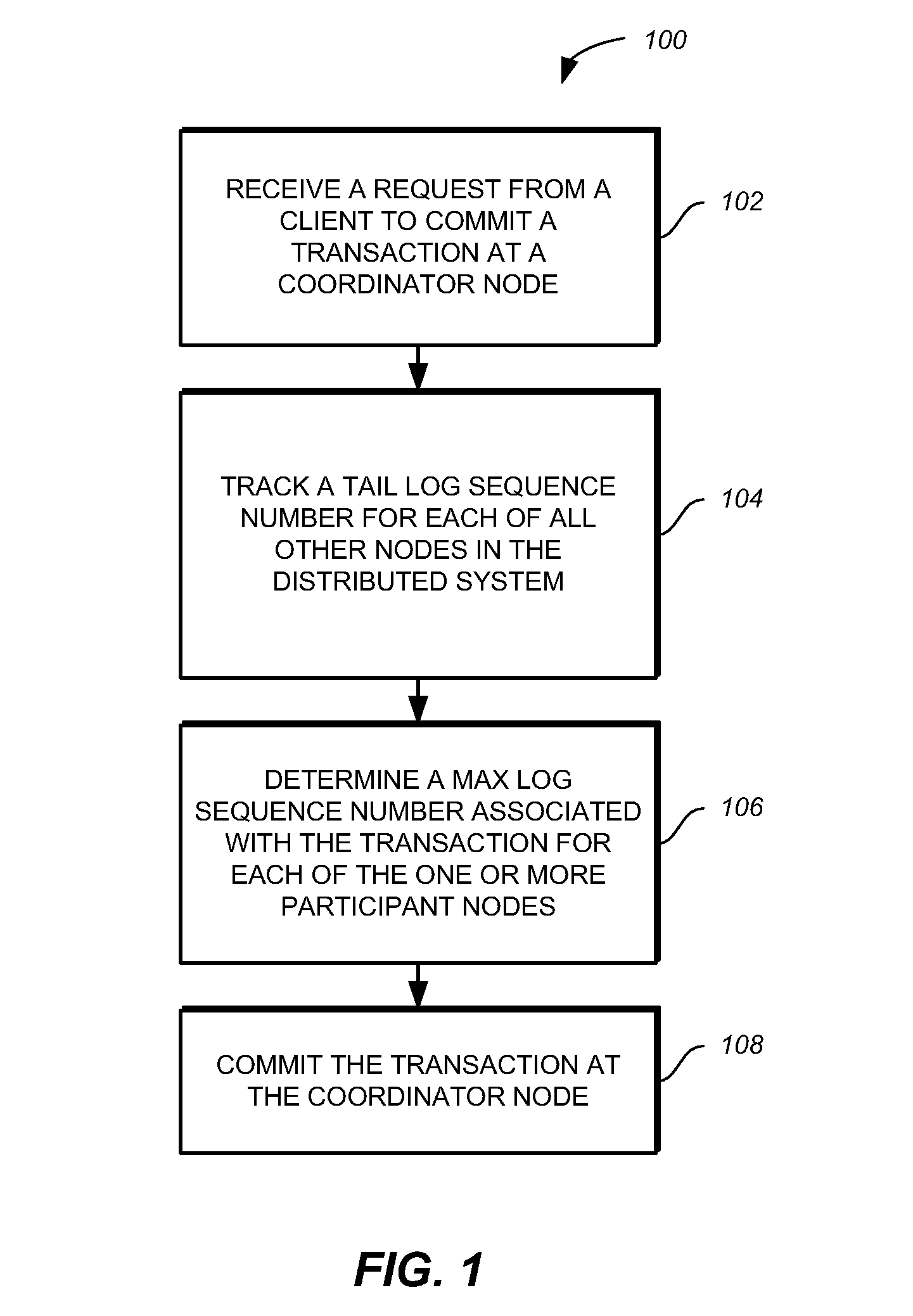
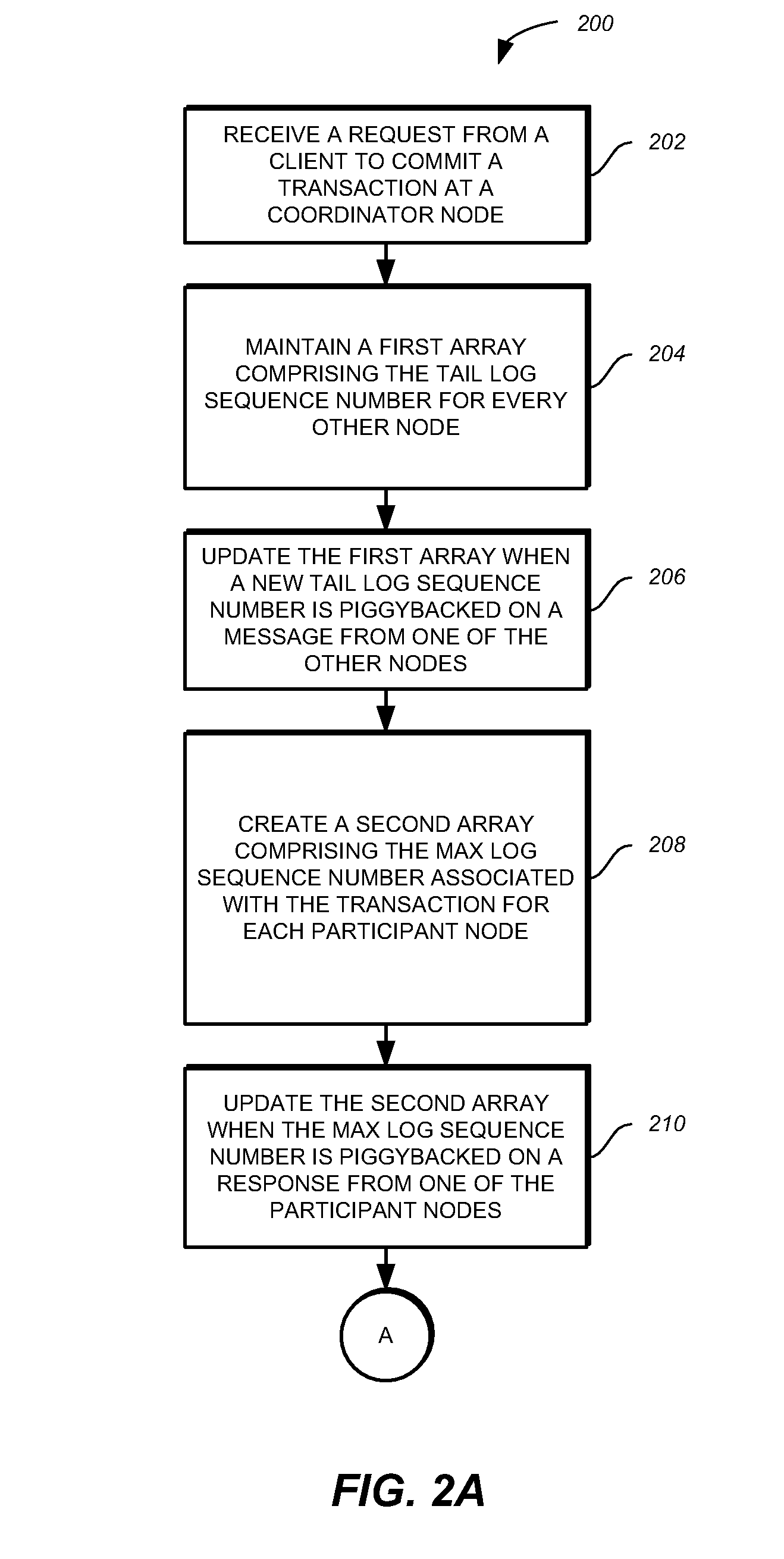
A method, computer program product, and system for committing transactions in a distributed system are provided. The method, computer program product, and system provide for receiving a request from a client to commit a transaction at a coordinator node in the distributed system, tracking a tail log sequence number for every other node in the distributed system, determining a max log sequence number associated with the transaction for each participant node in the distributed system, and committing the transaction at the coordinator node when the tail log sequence number for each participant node is greater than or equal to the max log sequence number associated with the transaction at the respective participant node.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Commitment of transactions in a distributed system
InactiveUS20080235245A1Special data processing applicationsTransaction processingClient-sideDistributed computing
A computer program product and system for committing transactions in a distributed system are provided. The method, computer program product, and system provide for receiving a request from a client to commit a transaction at a coordinator node in the distributed system, tracking a tail log sequence number for every other node in the distributed system, determining a max log sequence number associated with the transaction for each participant node in the distributed system, and committing the transaction at the coordinator node when the tail log sequence number for each participant node is greater than or equal to the max log sequence number associated with the transaction at the respective participant node.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
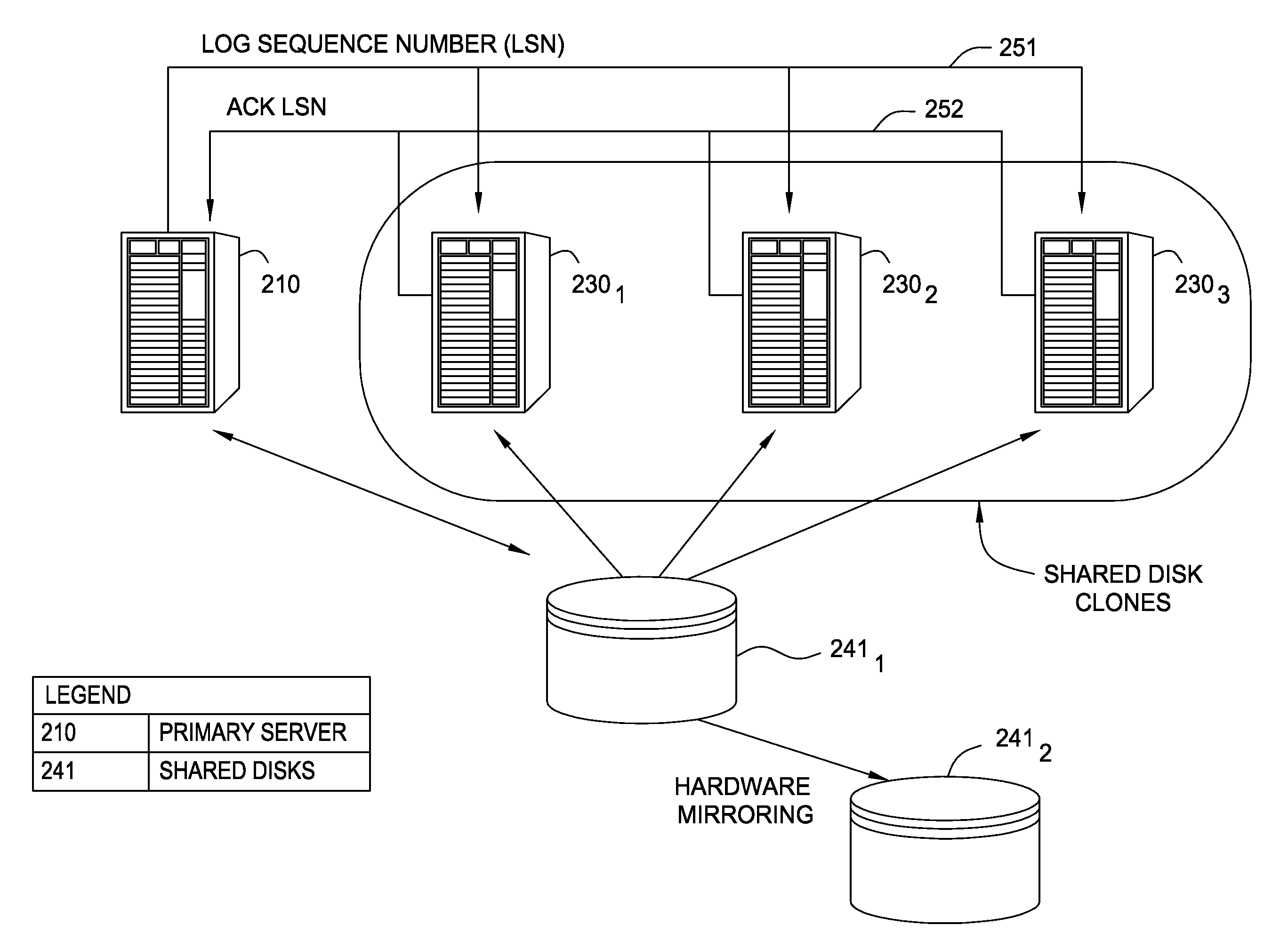
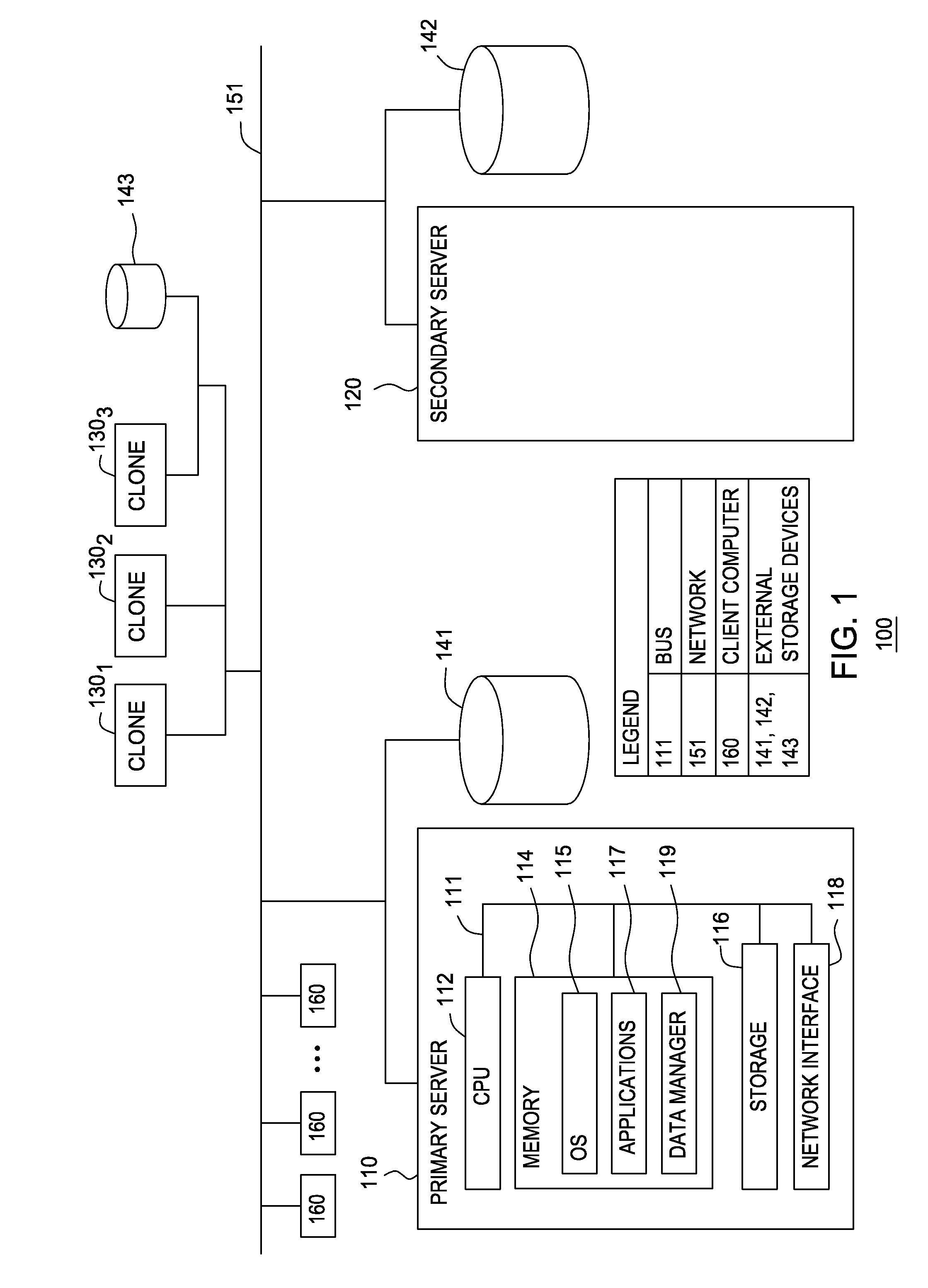
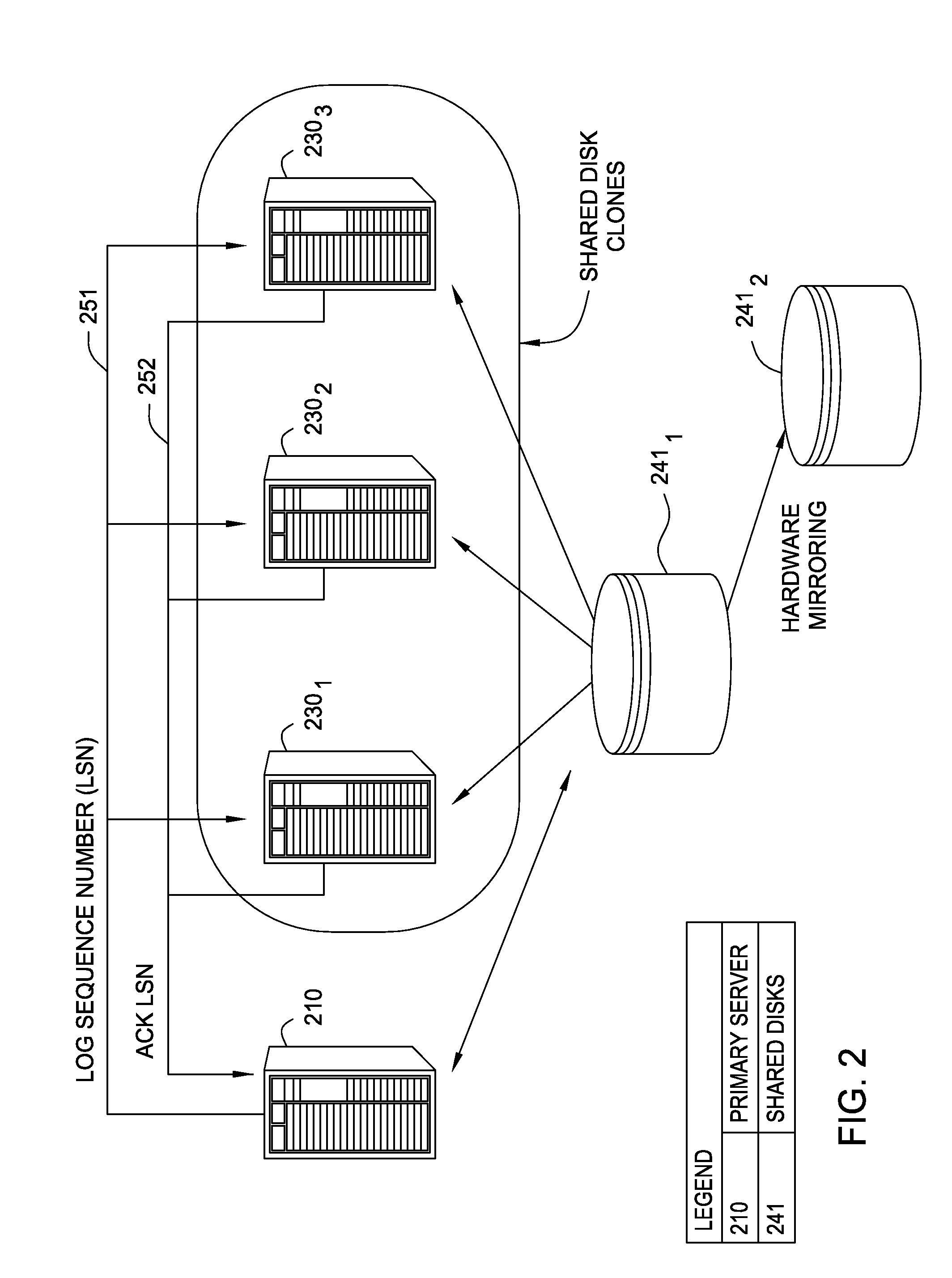
Shared disk clones
InactiveUS20080228835A1Data processing applicationsError detection/correctionData processing systemHigh availability
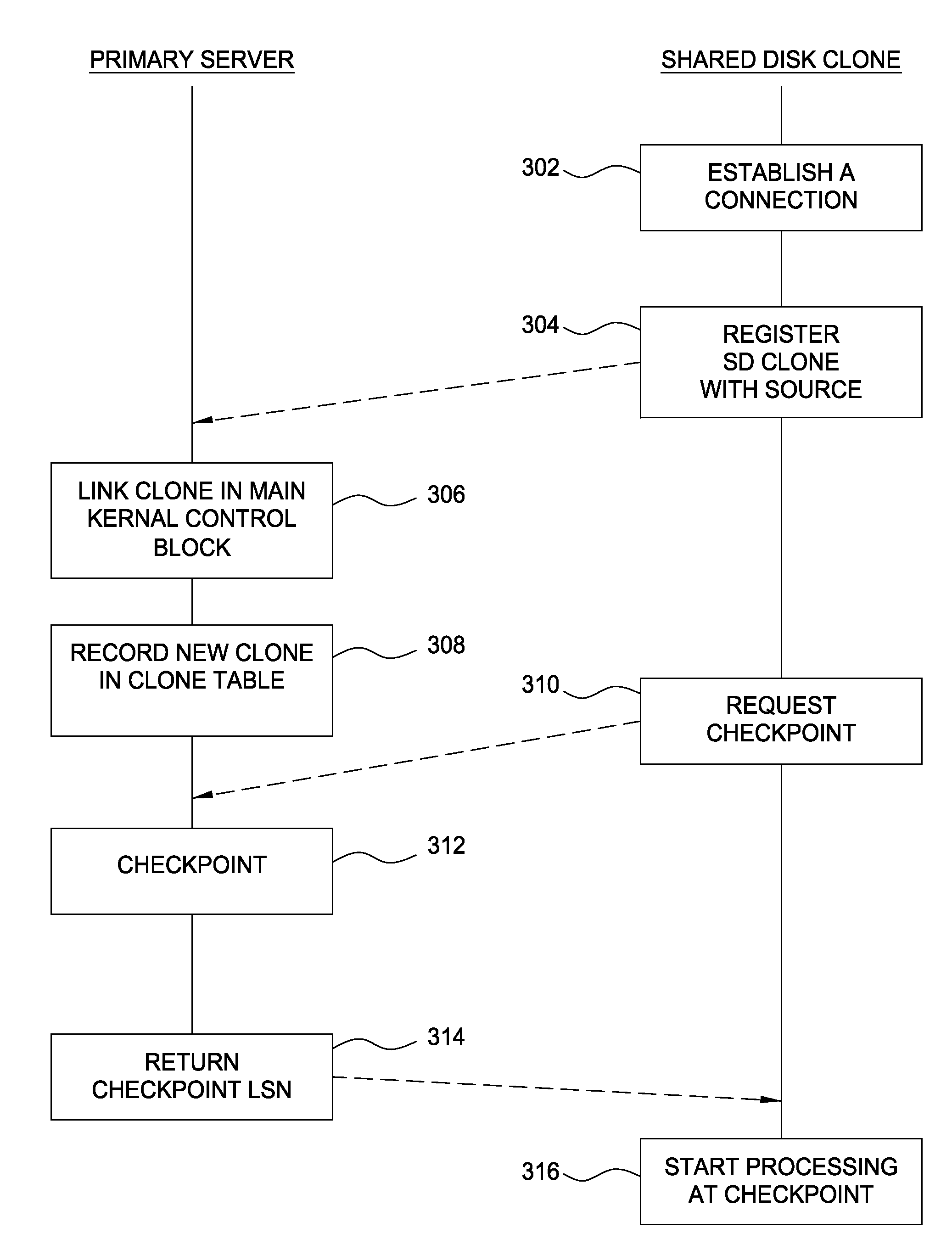
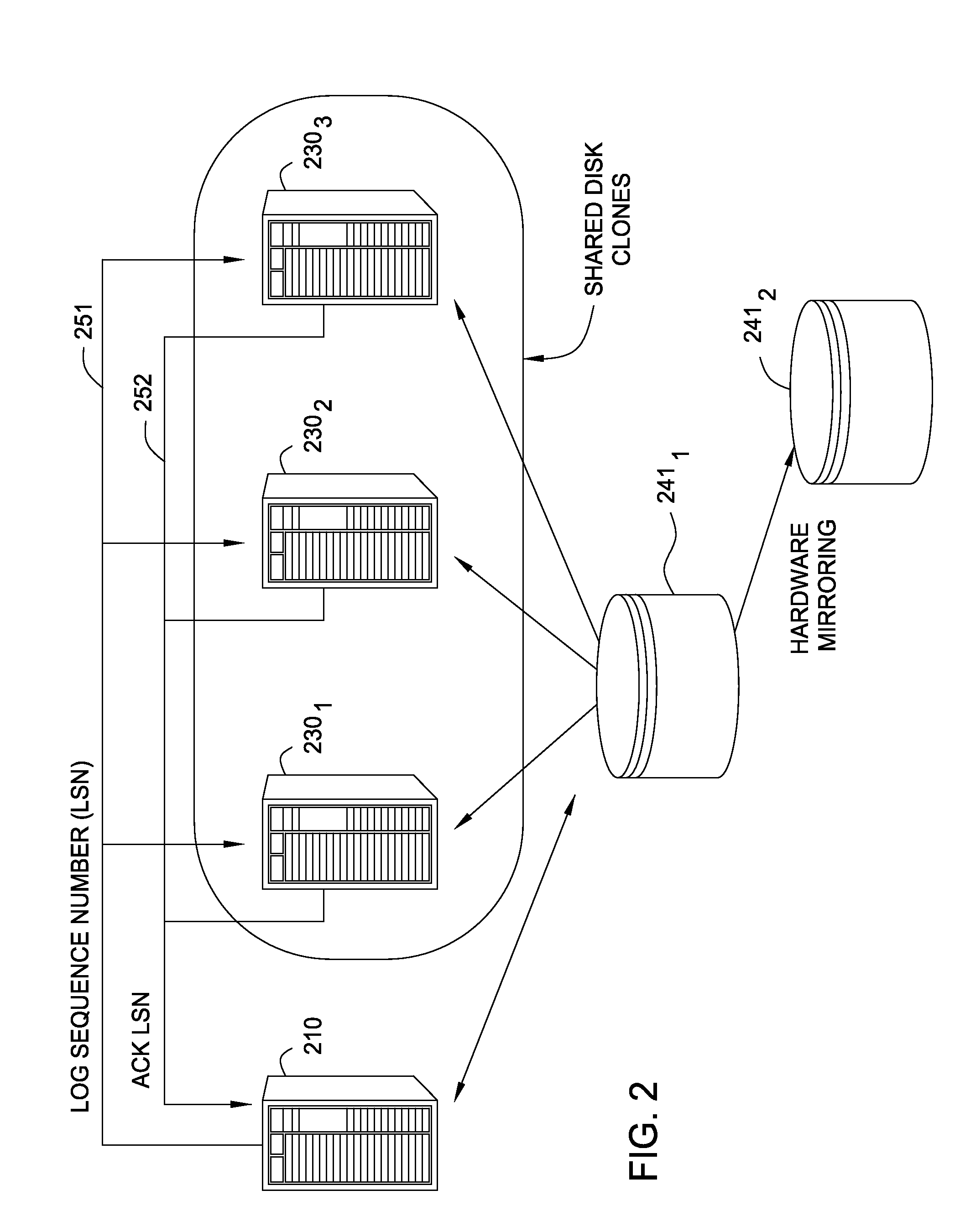
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to data processing systems and more particularly to high availability data processing systems. A primary server may share a storage device with one or more clone systems. Each clone generally replicates the state of the primary server, but relies on the same disk-based storage as the primary server. Thus, the clone systems may provide a shadow of the primary server, ready to take over should the primary server fail. The clone systems may access a log file that includes entries reflecting the actions performed by the primary system. The primary server may flush entries from a log buffer maintained on the primary server to a log file stored on the shared disk-based storage. The primary server may also send a log sequence number to the clone systems, and the clone systems periodically transmit a log sequence number back to the primary server indicating how far through the log file a clone system has progressed.
Owner:IBM CORP
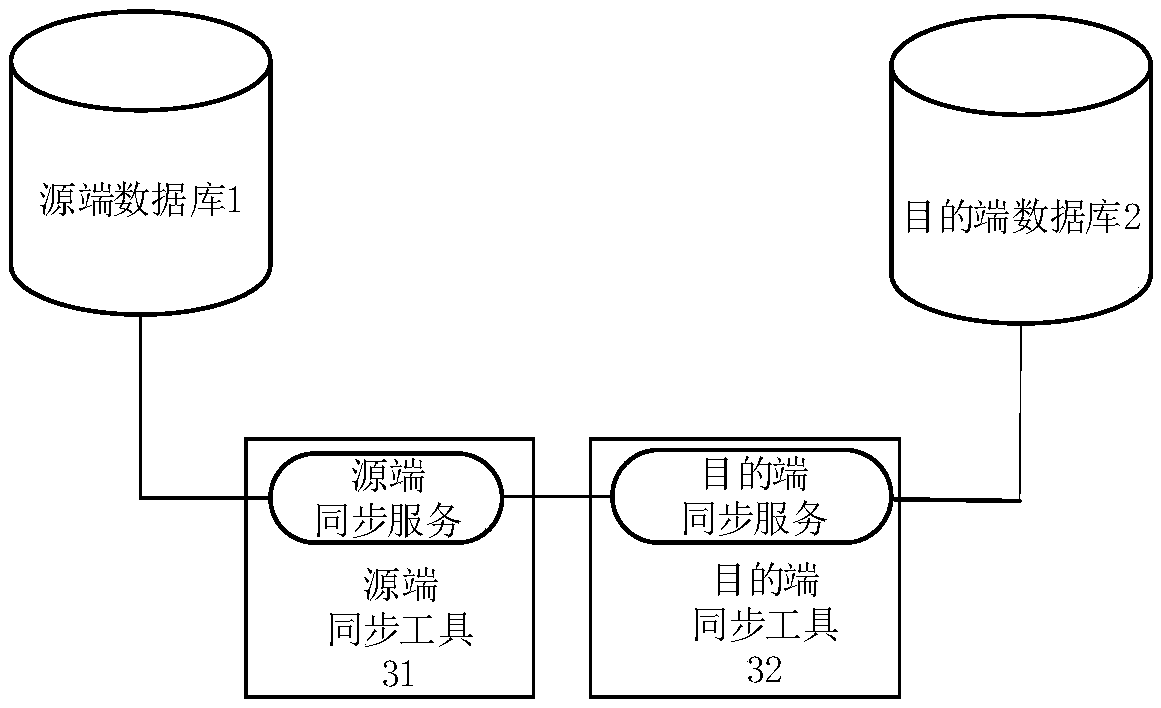
A data synchronization method and a data synchronization device
ActiveCN109241185AReduce data processingImprove synchronization efficiencyDatabase distribution/replicationData synchronizationCompletion time
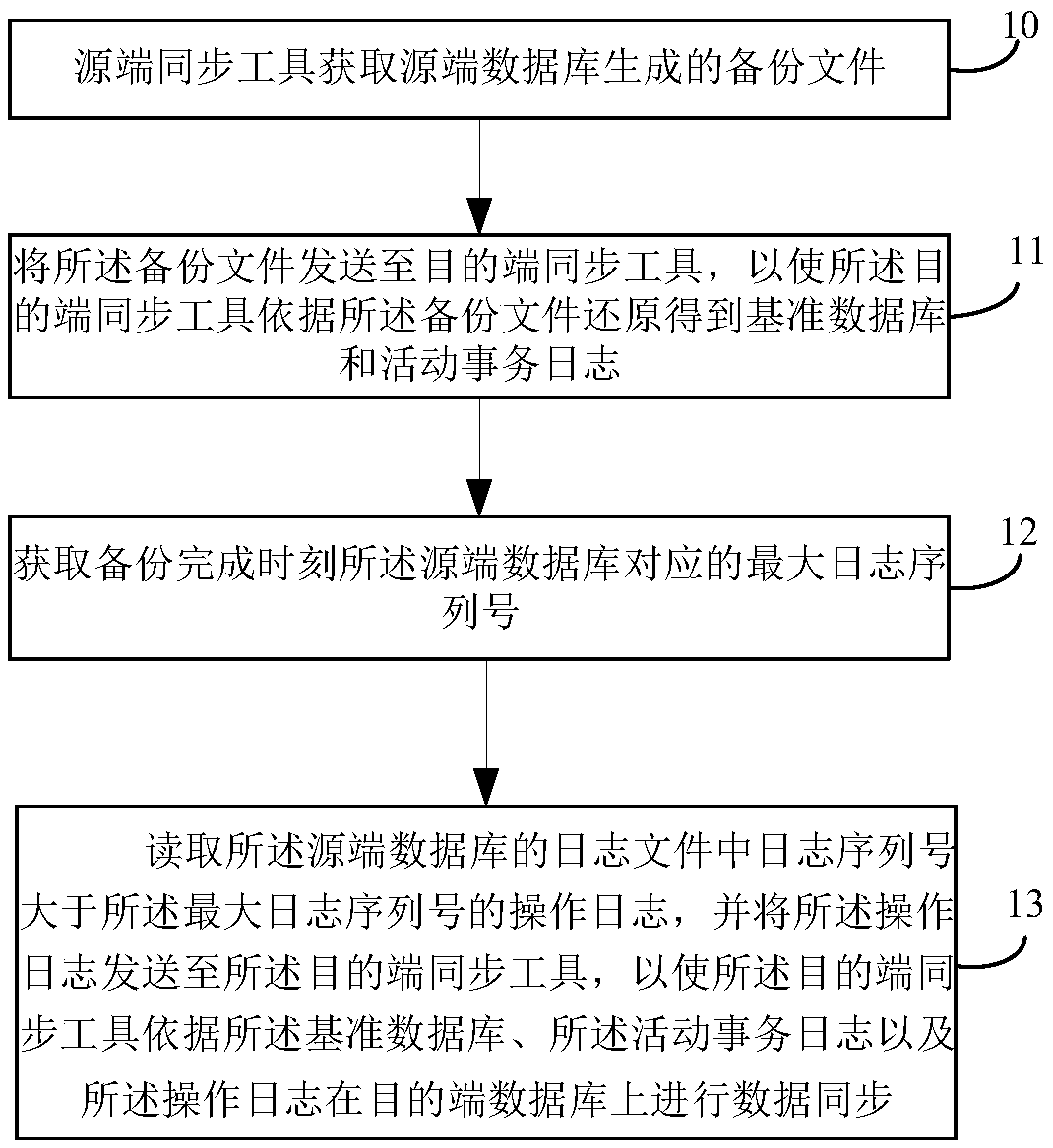
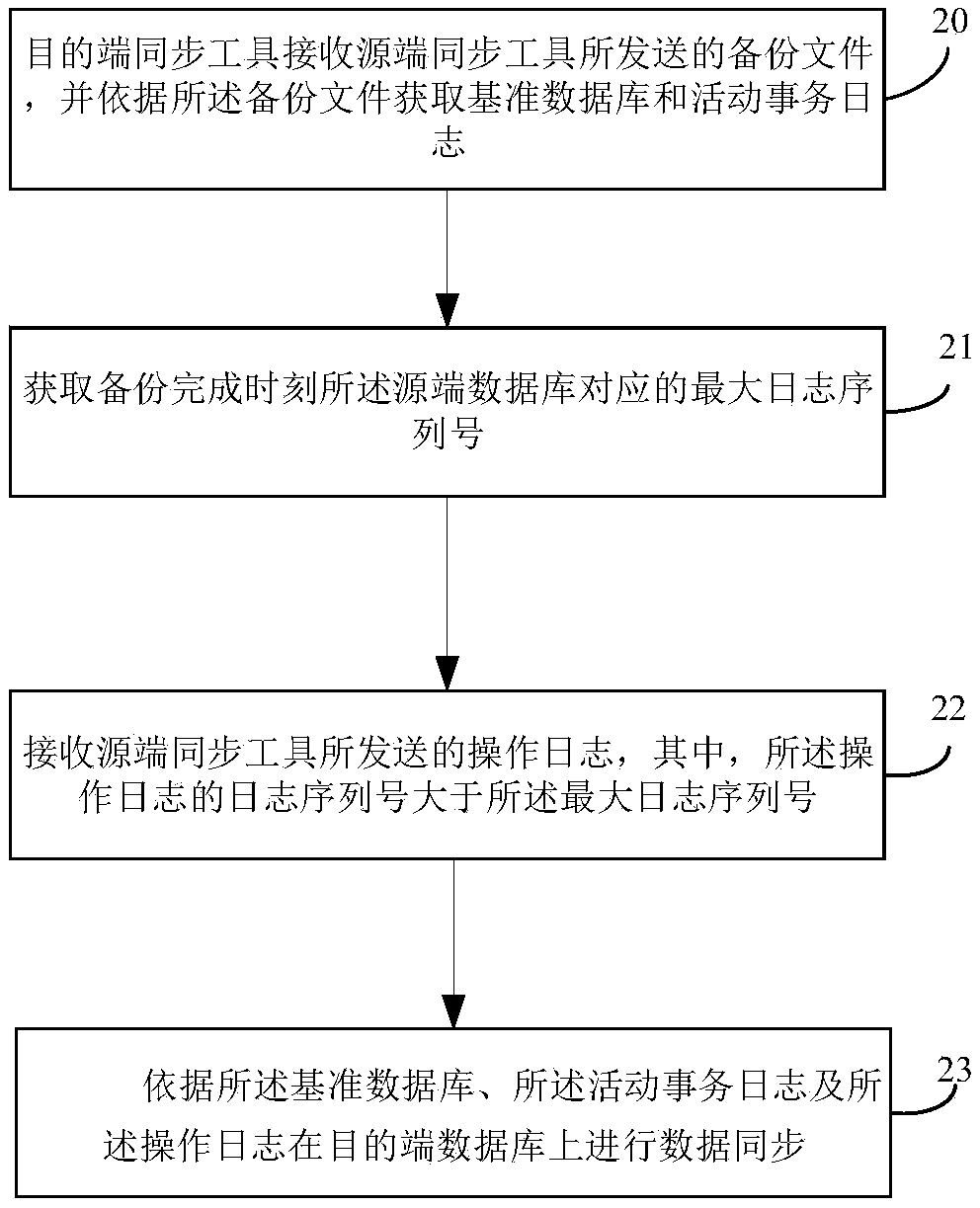
The invention relates to the technical field of database synchronization, and provides a data synchronization method and a data synchronization device. The data synchronization method comprises the following steps: obtaining a backup file generated by a source database by a source synchronization tool; Sending the backup file to the destination synchronization tool so that the destination synchronization tool can restore the reference database and the active transaction log according to the backup file; Obtaining the maximum log sequence number corresponding to the source database at the backup completion time; reading the operation log whose log sequence number is larger than the maximum log sequence number in the log file of the source database, and sending the operation log to the destination synchronization tool, so that the destination synchronization tool synchronizes data on the destination database according to the reference database, the active transaction log and the operation log. The data synchronization method of the invention does not need to perform a rollback operation on the active transaction, and the data processing amount is reduced. At the same time, there isno need to limit the transaction commit time and the backup start time, which can effectively improve the efficiency of synchronization.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
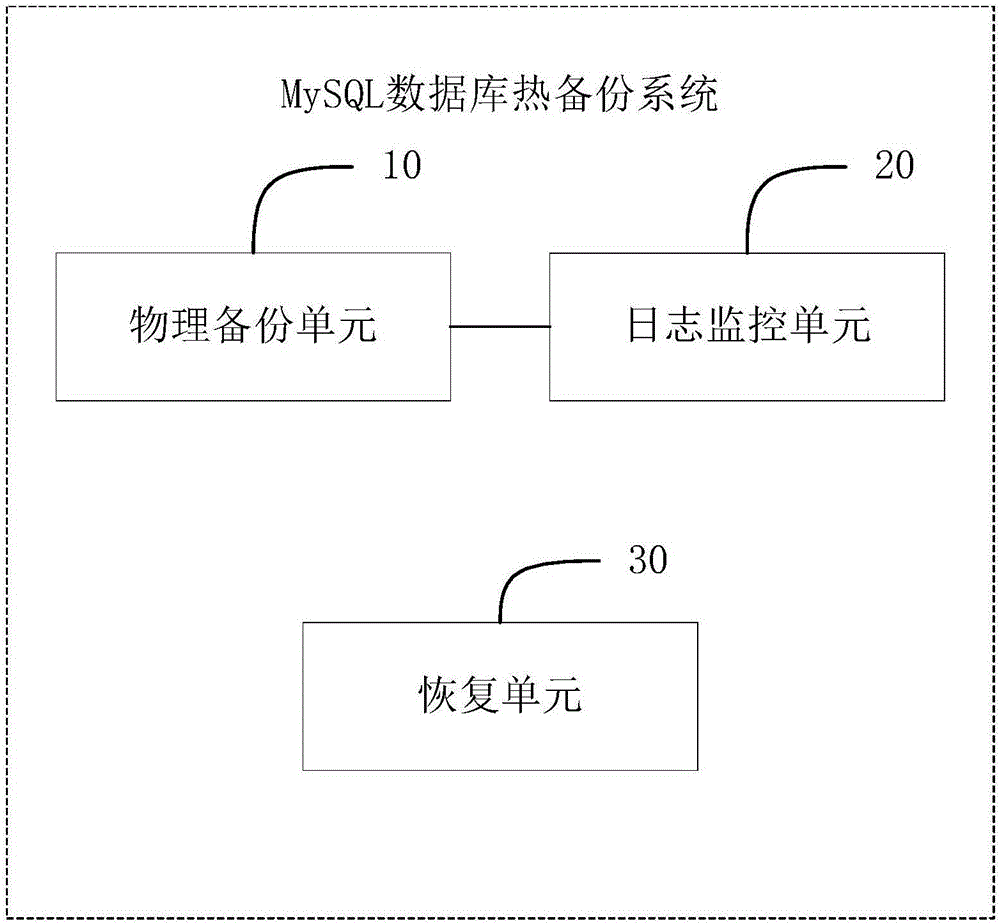
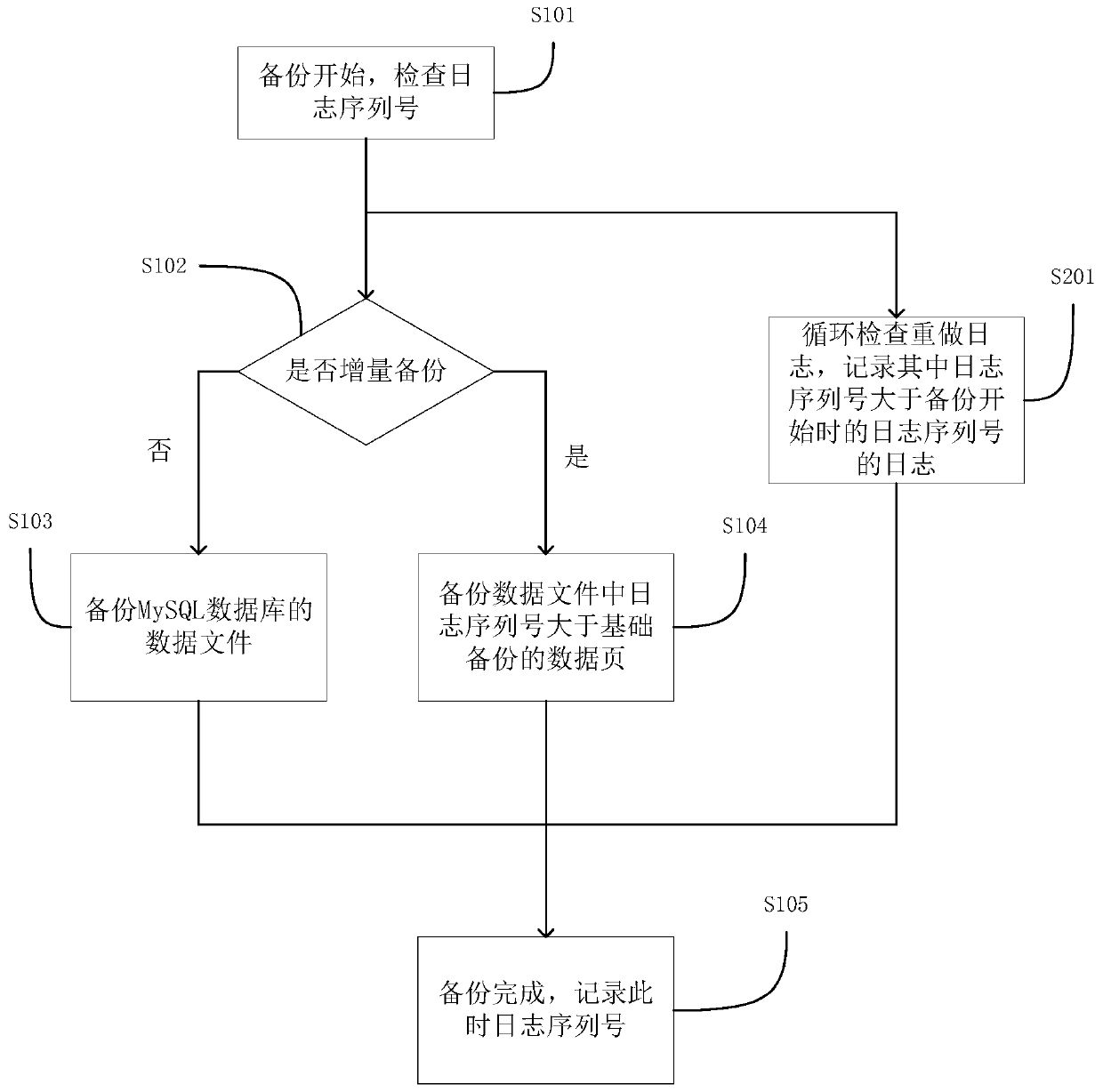
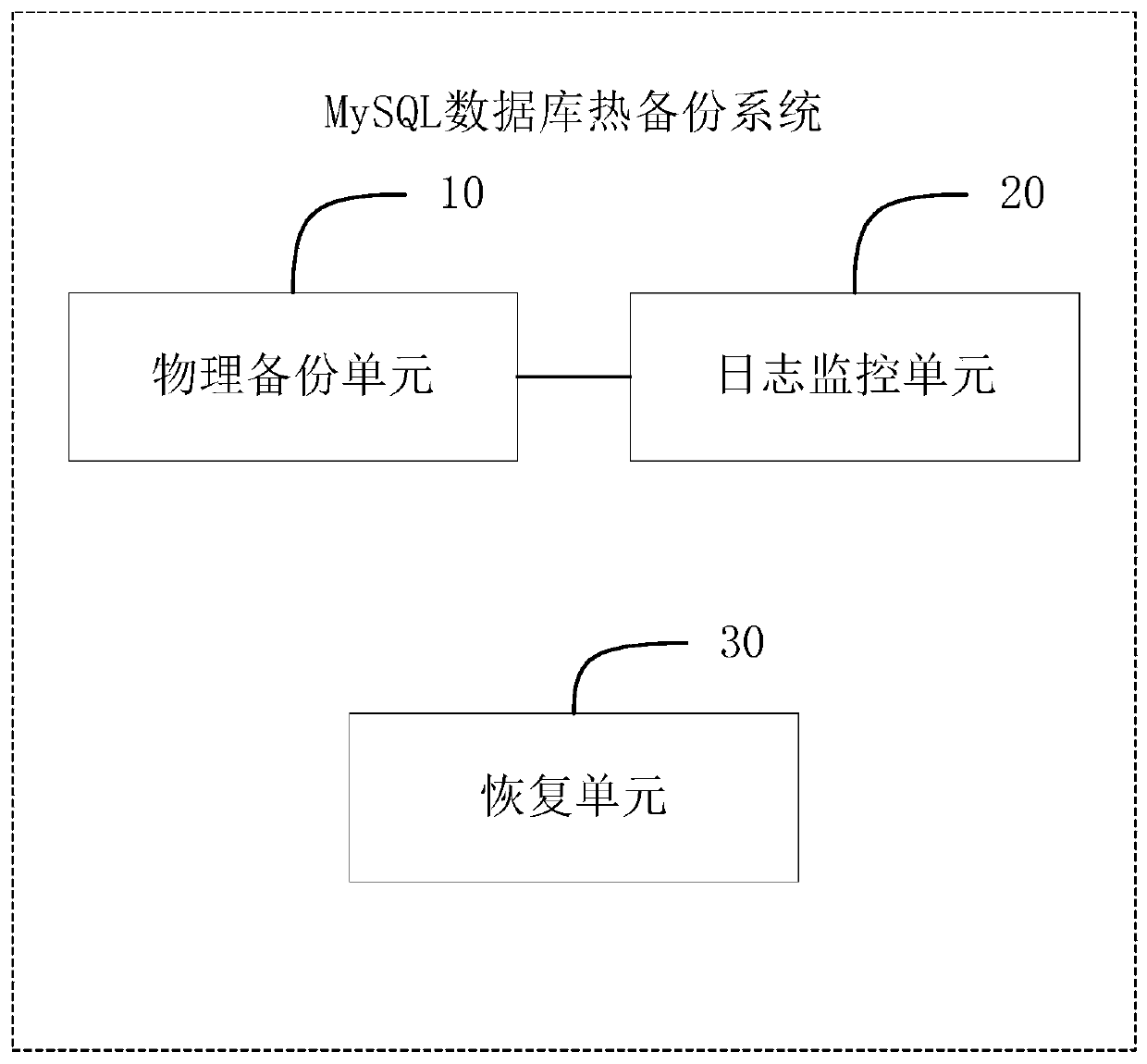
Hot backup method and system for MySQL database
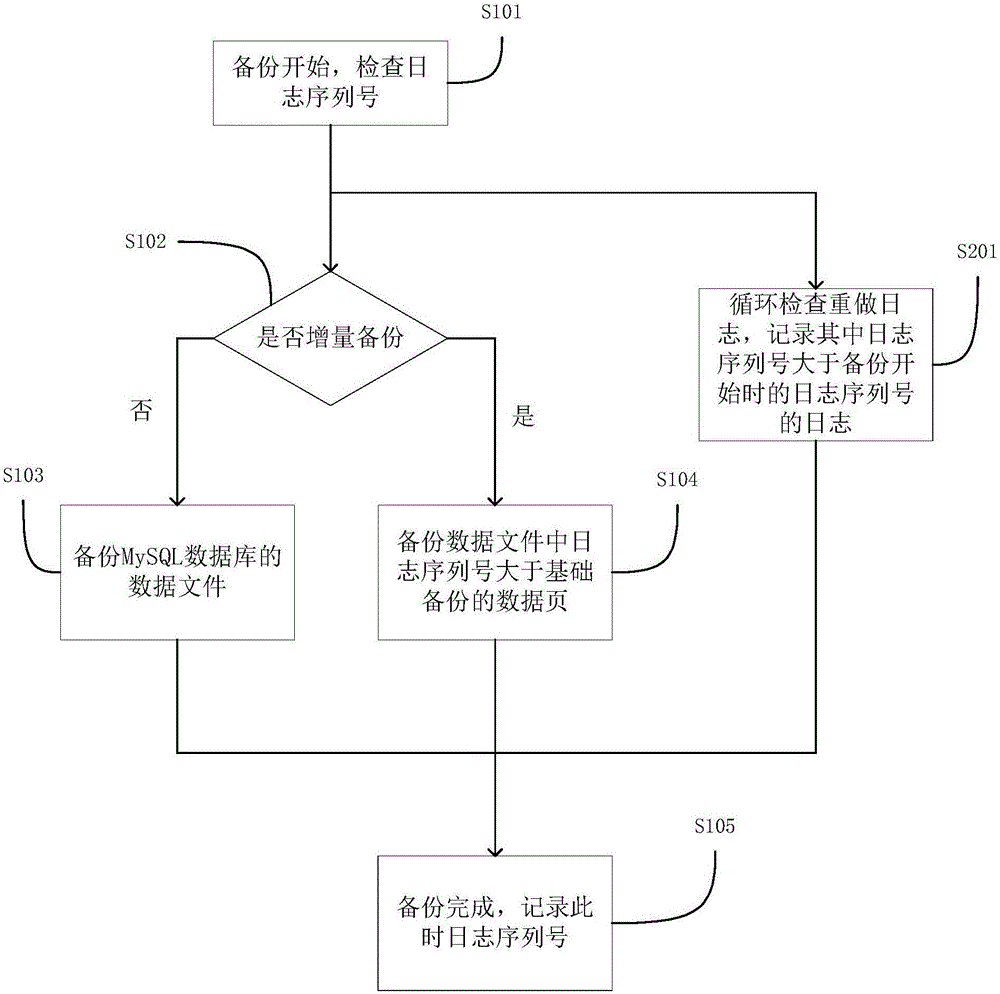
ActiveCN106354583AReduce the impactPhysical backup is fastRedundant operation error correctionData fileDatabase services
The invention relates to the technical field of backup and recovery of databases, in particular to a hot backup method for a MySQL database. The hot backup method includes the steps: firstly checking a log sequence number of the MySQL database when backup begins, and then performing backup for data files of the MySQL database; simultaneously and circularly checking redo logs of the MySQL database in the backup process of the data files, performing backup for modification of the data files in the backup process, recoding logs into a file when log sequence numbers in redo logs are larger than log sequence numbers beginning backup, and storing the file to a shared storage device; recording a log sequence number after backup is finished to prepare for next backup. The invention further provides a hot backup system for the MySQL database. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme is rapid in backup and recovery and overcomes the shortcoming that running MySQL database must be stopped before backup, and MySQL database services are less affected.
Owner:广州鼎甲计算机科技有限公司
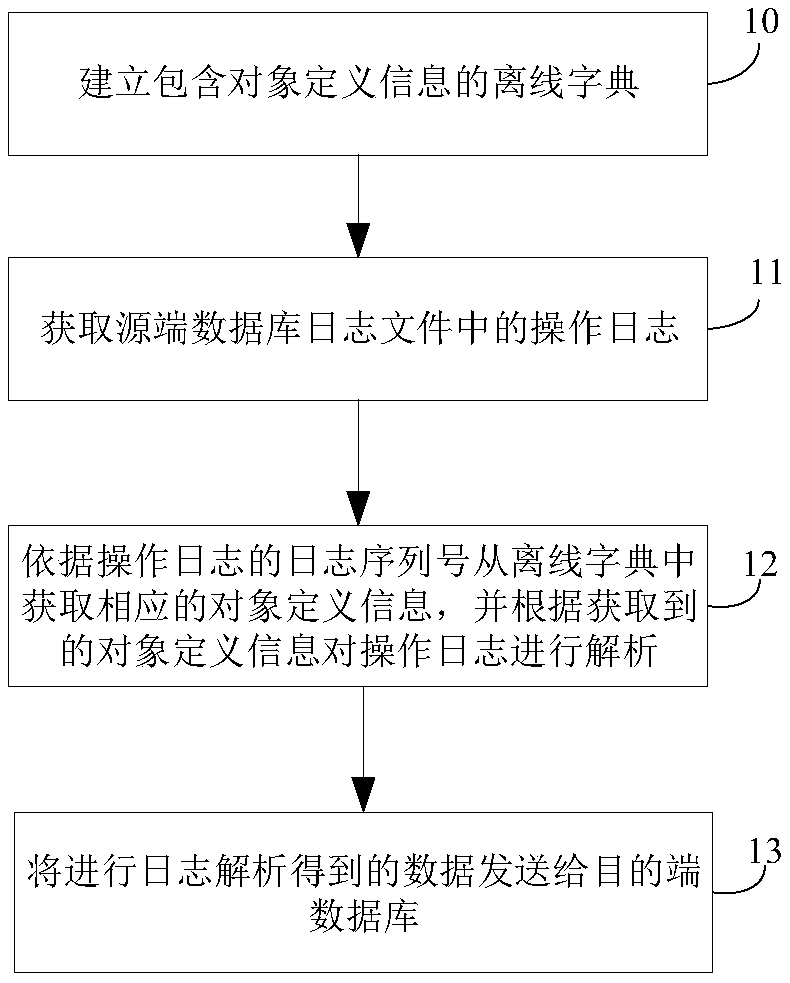
A data synchronization method and a device for data synchronization
ActiveCN109189852AGuaranteed correctnessConditions that affect performanceDatabase distribution/replicationData synchronizationObject definition
The invention relates to the technical field of database synchronization, which provides a data synchronization method and a device for data synchronization. The data synchronization method includes establishing an offline dictionary containing object definition information; obtaining the operation log from the source database log file; obtaining the corresponding object definition information from the offline dictionary according to the log sequence number of the operation log, and parsing the operation log according to the obtained object definition information; sending the log parsed data to the destination database. The data synchronization method of the invention can establish complementary analysis with the operation log containing only local key information in the prior art by accessing the offline dictionary, which not only ensures the correctness of the definition information of the object in the operation log, but also avoids the situation that the database is accessed in real time and the performance of the database is affected.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE +1
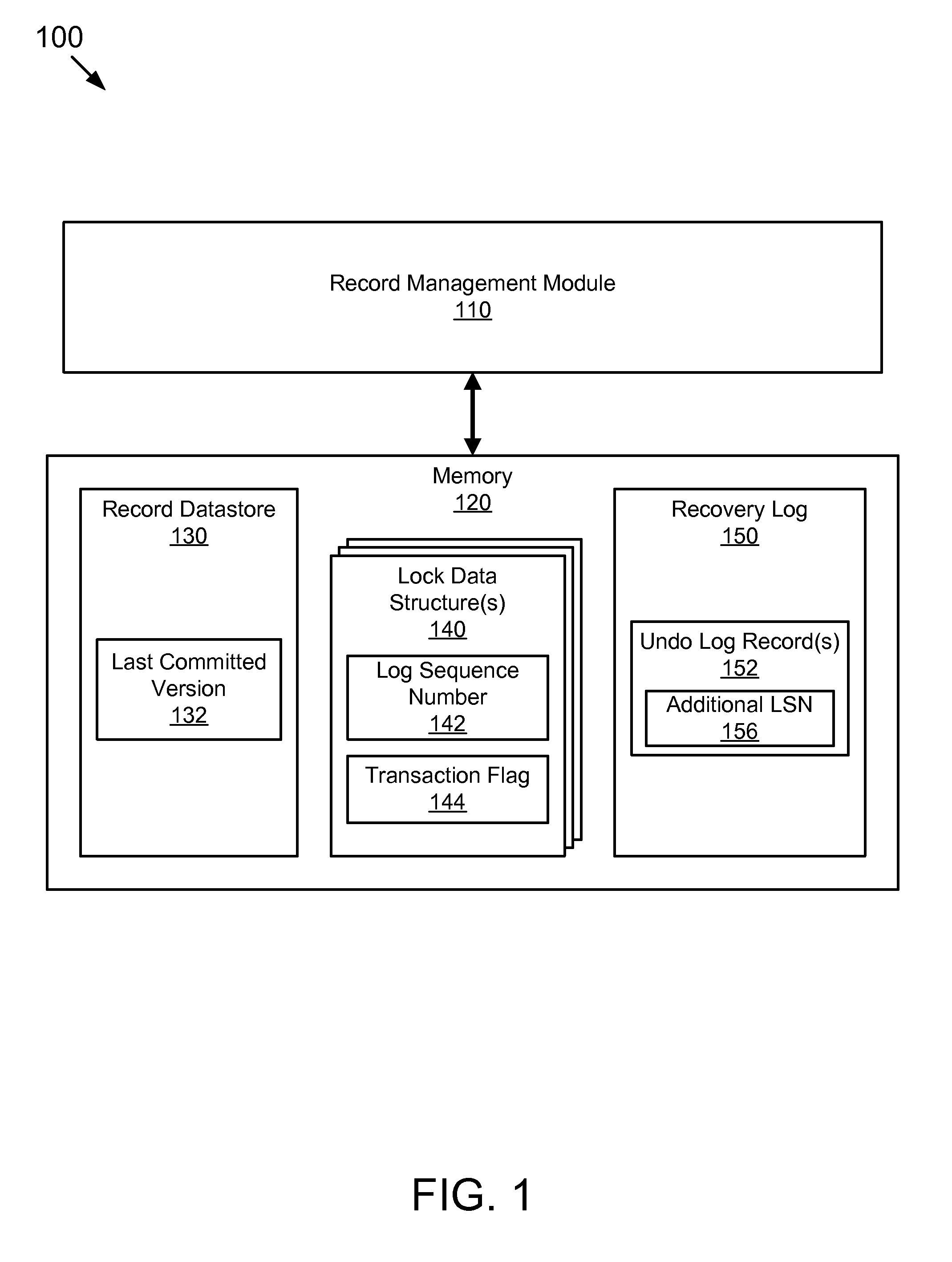
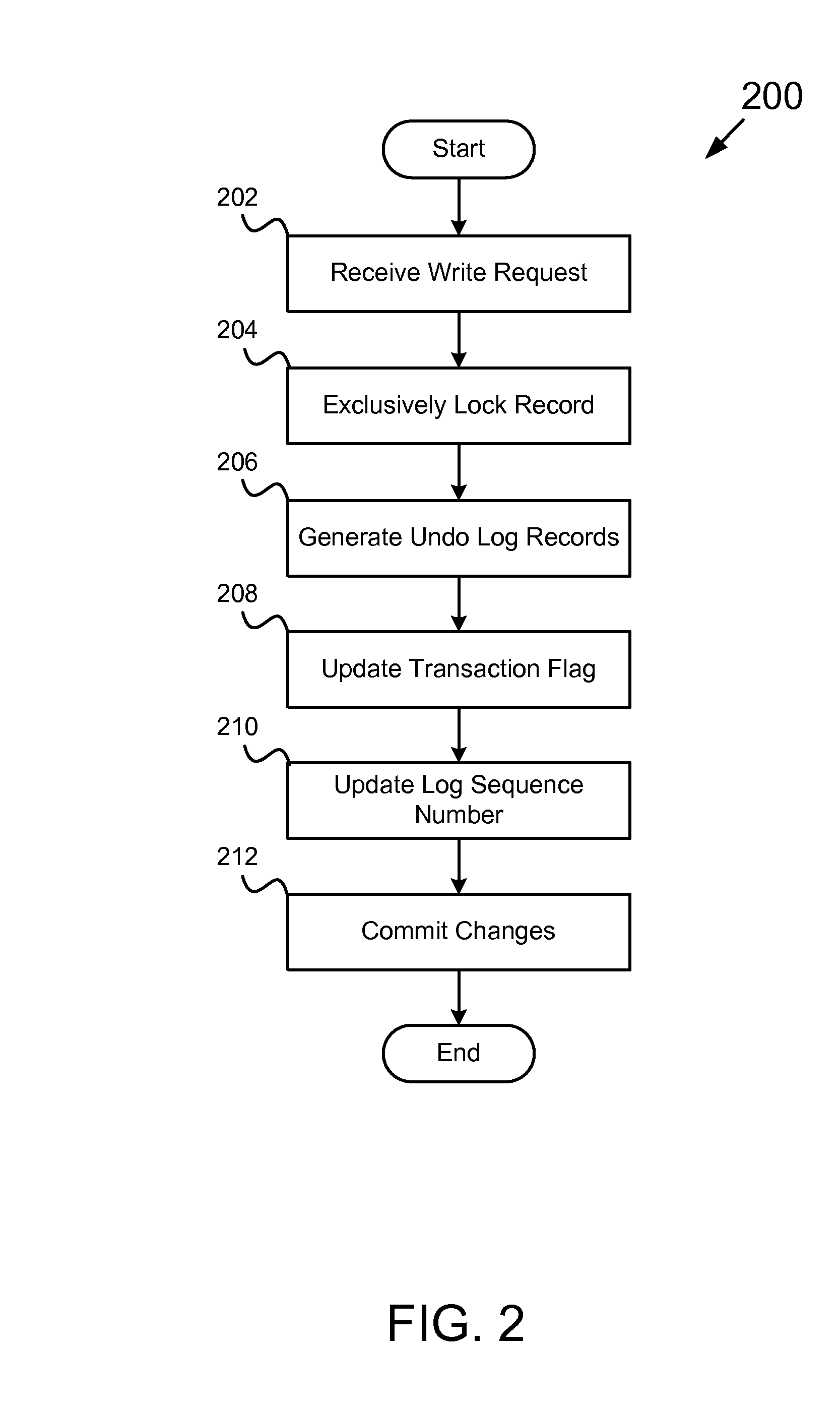
Computer program product for conducting a lock free read
ActiveUS20080077591A1Level of isolation can be increasedAvoid deadlockData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData storingData store
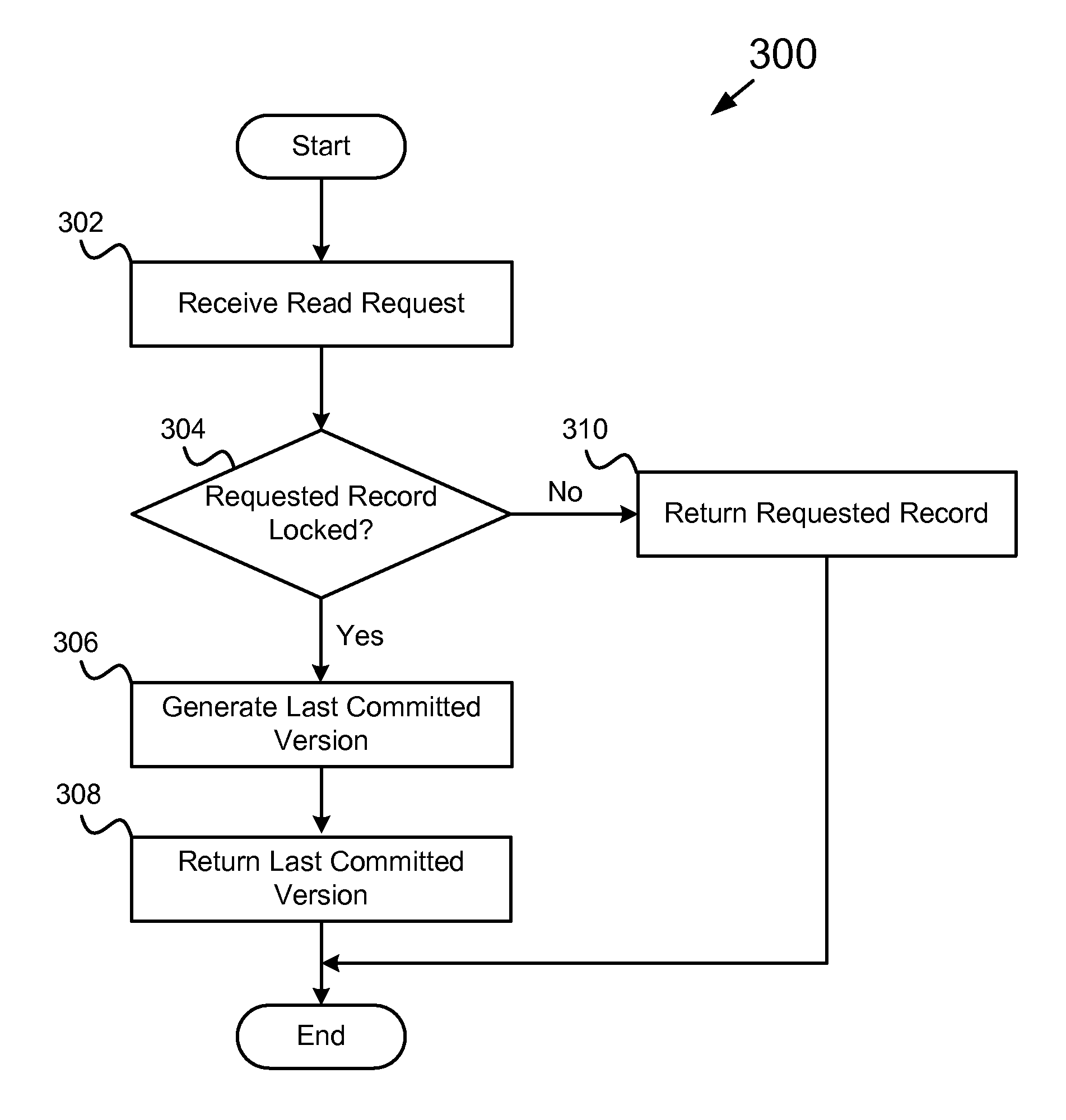
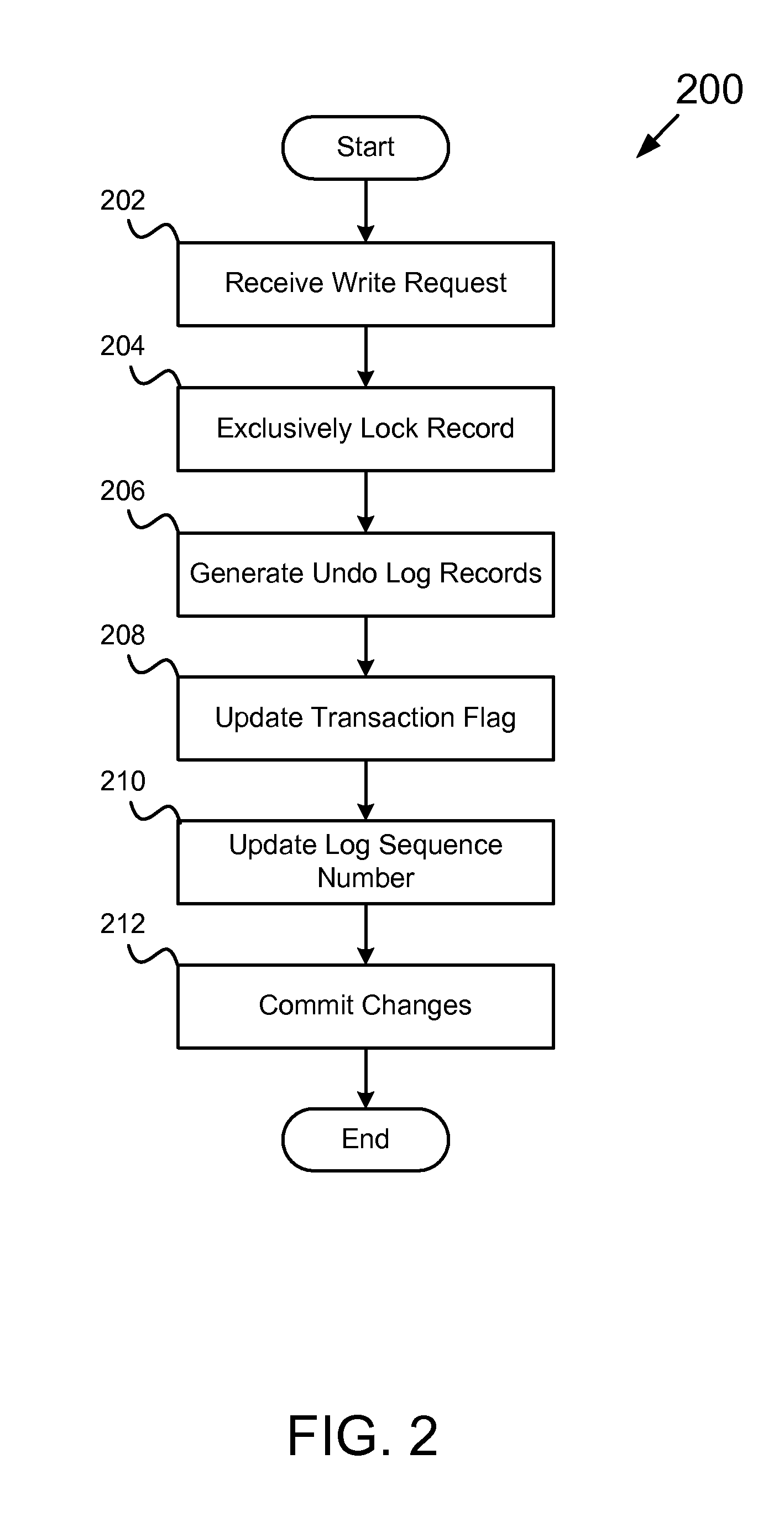
The present invention expounds upon the ANSI “read committed” isolation level by allowing readers to read committed data without waiting for a concurrent writer to the data to finish. The method returns a last committed version of the data as it existed prior to changes made by the concurrent writer. Only two versions of any data record are required to be stored in the record data store, the last committed version and the current version. The last committed version may be generated from an undo log record. Locating the appropriate undo log record may be accomplished by storing a log sequence number in a lock data structure associated with the requested data record. A transaction flag may also stored in the lock data structure to facilitate generating the last committed version. The method may also utilize one or more locks to detect a concurrent writer to the requested data.
Owner:SAP AG
A method for ensuring consistency of replication transactions and a corresponding replication device
ActiveCN109189608ADelete in timeSmall scaleDatabase distribution/replicationRedundant operation error correctionTransaction logDatabase
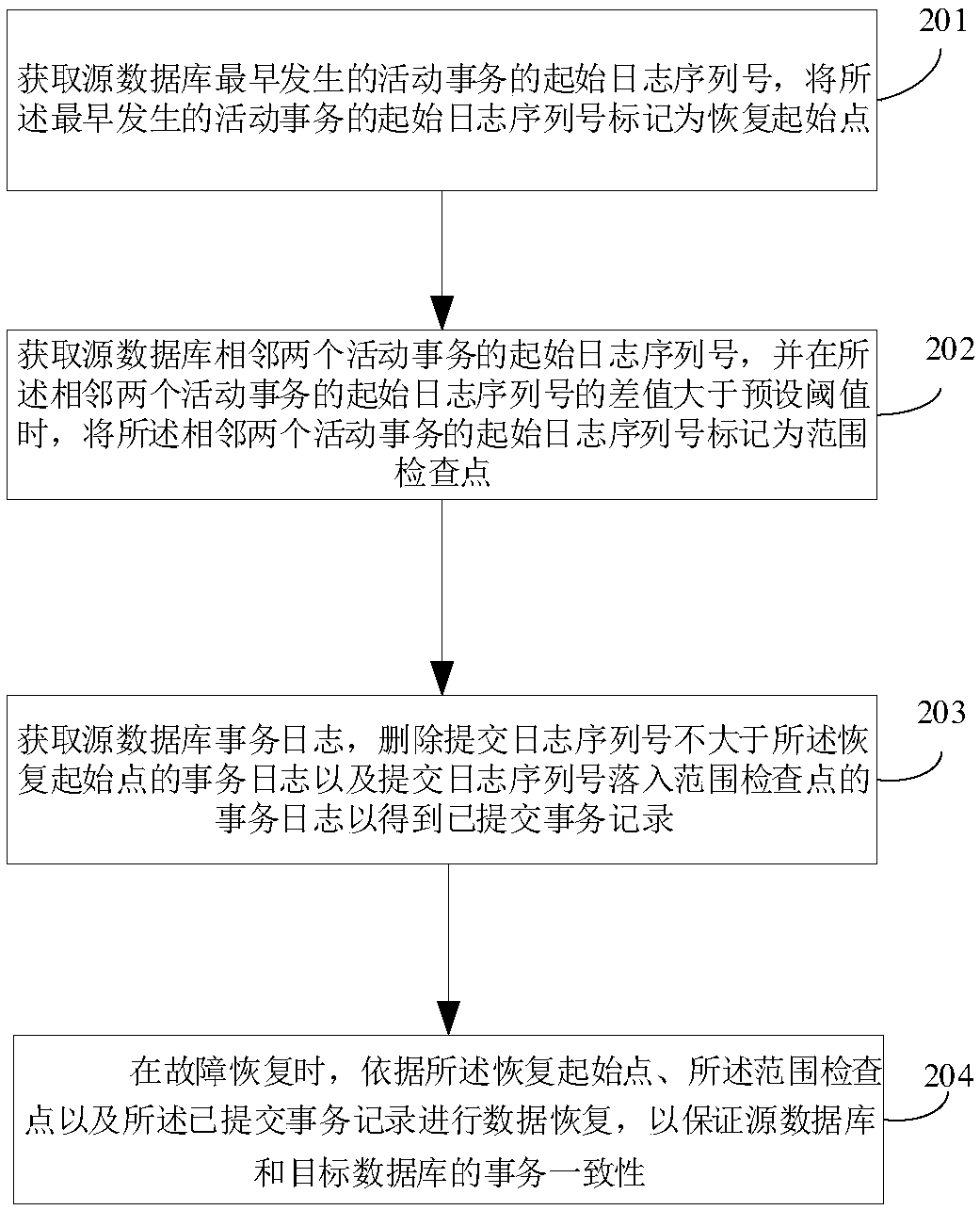
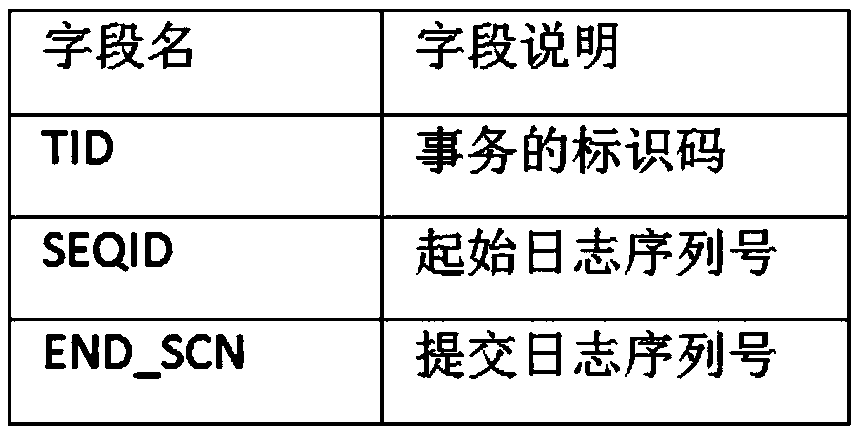
The invention provides a method for ensuring the consistency of replication transactions and a corresponding replication device. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the starting log sequence number of the earliest active transaction in the source database; marking the starting log sequence number of the earliest active transaction as the recovery starting point; obtaining the starting log sequence number of the earliest active transaction in the source database; obtaining the starting log sequence numbers of two adjacent active transactions of the source database, and marking the starting log sequence numbers of the two adjacent active transactions as a range checkpoint when the difference between the starting log sequence numbers of the two adjacent active transactions isgreater than a preset threshold value; obtaining the transaction log of the source database, deleting the transaction log whose log submitting sequence number is not greater than the recovery startingpoint and the transaction log whose log submitting sequence number falls into the checkpoint of the range; performing data recovery based on the recovery start point, range checkpoint, and submittedtransaction records. The invention adopts the range checkpoint mechanism to compress the submitted transaction table, which can effectively reduce the scale of the submitted transaction table.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
Lossless recovery for computer systems with remotely dependent data recovery
InactiveUS7360111B2Electronic circuit testingRedundant hardware error correctionDistributed File SystemComputerized system
An architecture and implementation for losslessly restarting subsystems in a distributed file system is described. By partitioning functionality and logging appropriately across the kernel and user-level boundaries on a client, the user-level subsystem may be made losslessly restartable. Practical mechanisms for supporting state-based recovery in replicated state machines and like replica are described. In particular, each client daemon may include an operations log and an applied log sequence number. Each client driver may include a potentially different operations log. Each client daemon may be configured to request logged operations associated with log sequence numbers in one or more ranges specified by a specification that includes the applied log sequence number. The requested logged operations may reside in the operations log maintained by a client driver. Each client daemon may operate in accordance with user-level constraints and each client driver may operate in accordance with kernel-level constraints.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Data storage method, device and equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110543386AImplement data storageImprove robustnessRedundant operation error correctionSerial codeDatabase clustering
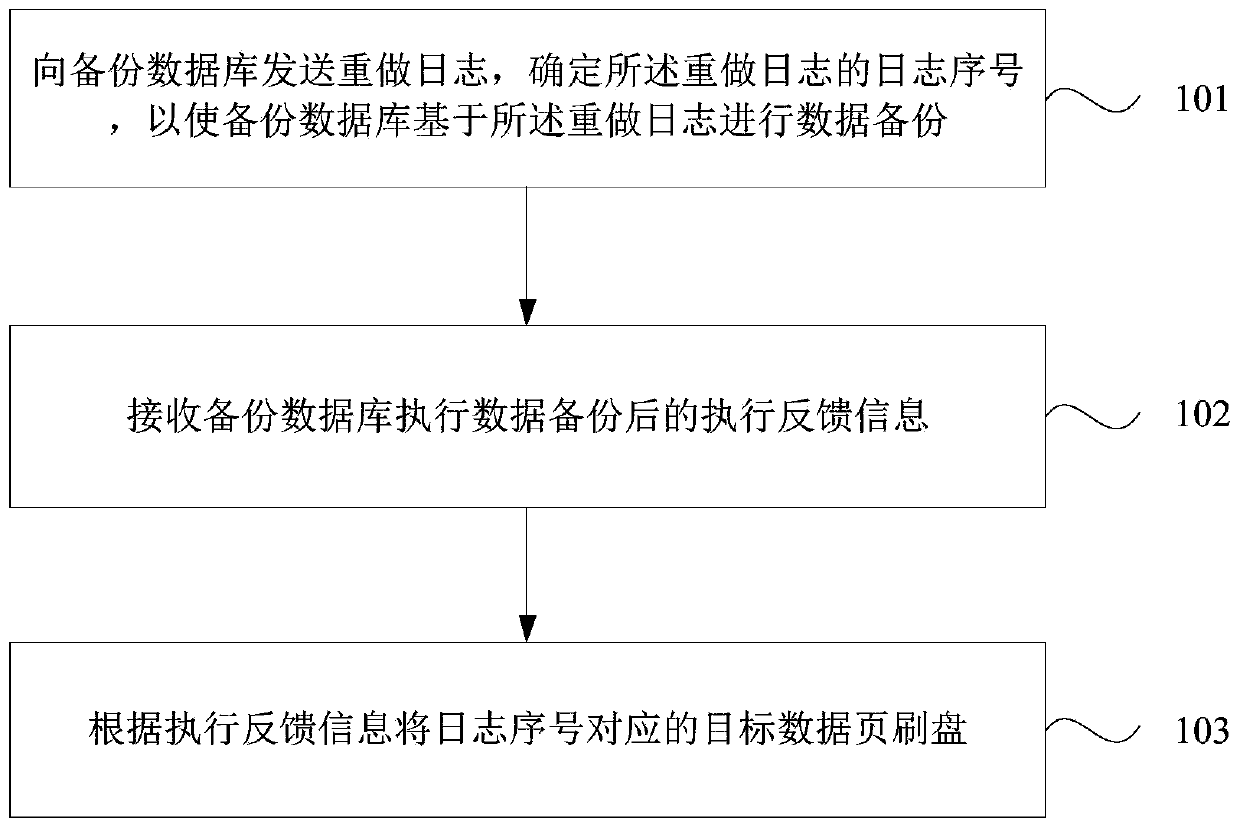
The invention discloses a data storage method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: sending a redo log to a backup database, and determining a log serial number of the redo log, so that the backup database performs data backup based on the redo log; receiving execution feedback information after the backup database executes data backup; and refreshing the target data page corresponding to the log sequence number according to the execution feedback information. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, after the backup database backs up the data according to the redo log, the main database writes the data page corresponding to the redo log, so that the data storage consistency of the main database and the backup database in the read-write separation database cluster is kept, the database storage safety is improved, and the robustness of the read-write separation database cluster can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI DAMENG DATABASE
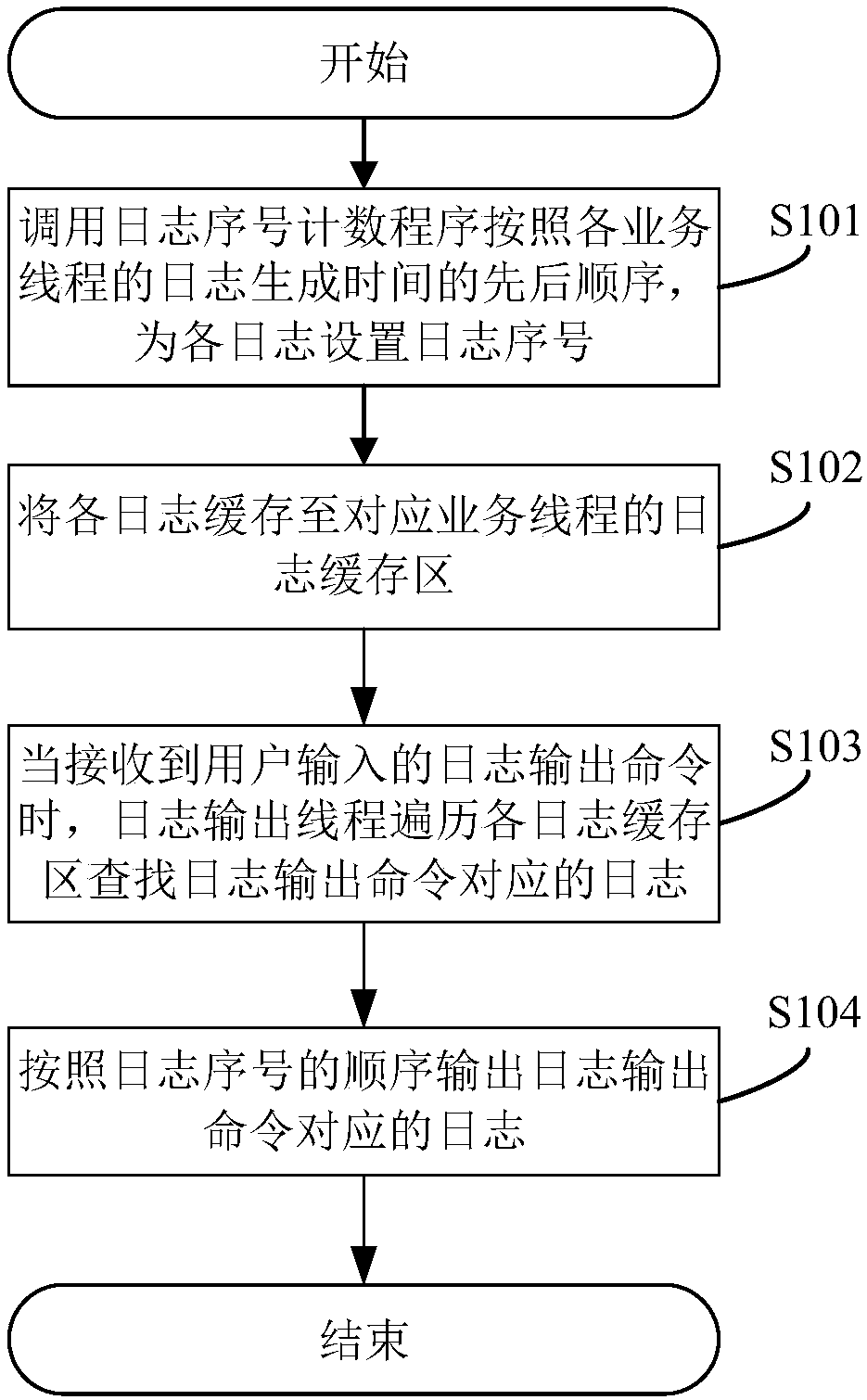
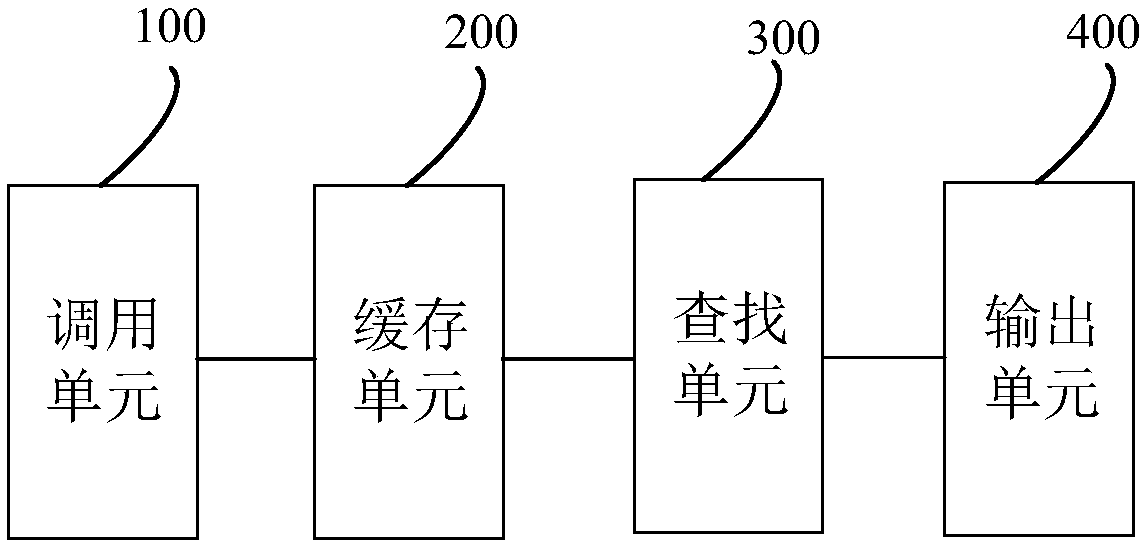
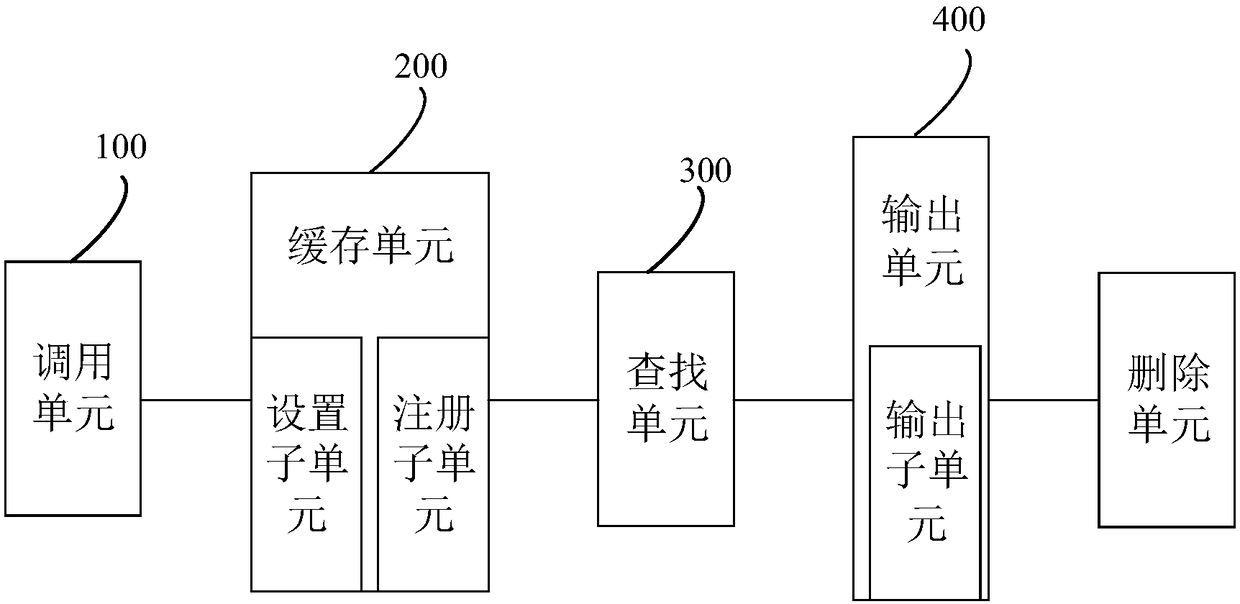
Multi-thread log output method and device
InactiveCN108205476AEasy to detectAchieve isolationProgram synchronisationInterprogram communicationUser inputOutput device
The invention discloses a multi-thread log output method. The method comprises the steps that a log sequence number counting program is called to set log sequence numbers for all logs according to thesequential order of log generation time of all service threads; all the logs are cached into log cache regions corresponding to the service threads; when a log output command input by a user is received, a log output thread is utilized to traverse all the log cache regions to find logs corresponding to the log output command; and the logs corresponding to the log output command are output according to the order of the log sequence numbers. According to the method, by presetting the log cache regions, isolation of output logs is realized; by calling the log sequence number counting program toset the log sequence numbers for all the logs, it is convenient to review the calling order of all the service threads; and by utilizing the log output thread to perform asynchronous order-placing output on the logs, the influence of log output on a system is lowered to the minimum. The invention meanwhile provides a multi-thread log output device, equipment and a computer readable storage medium.The multi-thread log output device, the equipment and the computer readable storage medium also have the advantages.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
DB2 database data synchronous update method and device
ActiveCN109271452AEnsure consistencyReduce adverse effectsDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationData synchronizationResult set
The embodiment of the invention provides a DB2 database data synchronous update method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a data detailed address storage column is created accordingto a table to be synchronously updated; an S lock on the table to be synchronously updated is obtained; the current log sequence number LSN of the DB2 database at the source end is used as a startingLSN of the table to be synchronously updated; and the S lock is released; Obtaining a result set of a table to be updated synchronously, sending the result set to a database at a target end for storage, and obtaining a current LSN of a DB2 database at a source end as an end LSN of the table to be updated synchronously; Receiving the initialization data sent by the synchronous update service of the source end, inserting the ROWID into the data detailed address storage column in the database of the target end, and initializing the data of the table to be synchronized update; Start the Data Real-time Synchronous Update Service and send the changes of the source DB2 database to the target database for data synchronous updates. The embodiments of the invention can avoid the adverse influence of the S lock on the table to be synchronously updated for a long time on the premise of ensuring the consistency of the database data at the target end.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
Data synchronization method and system
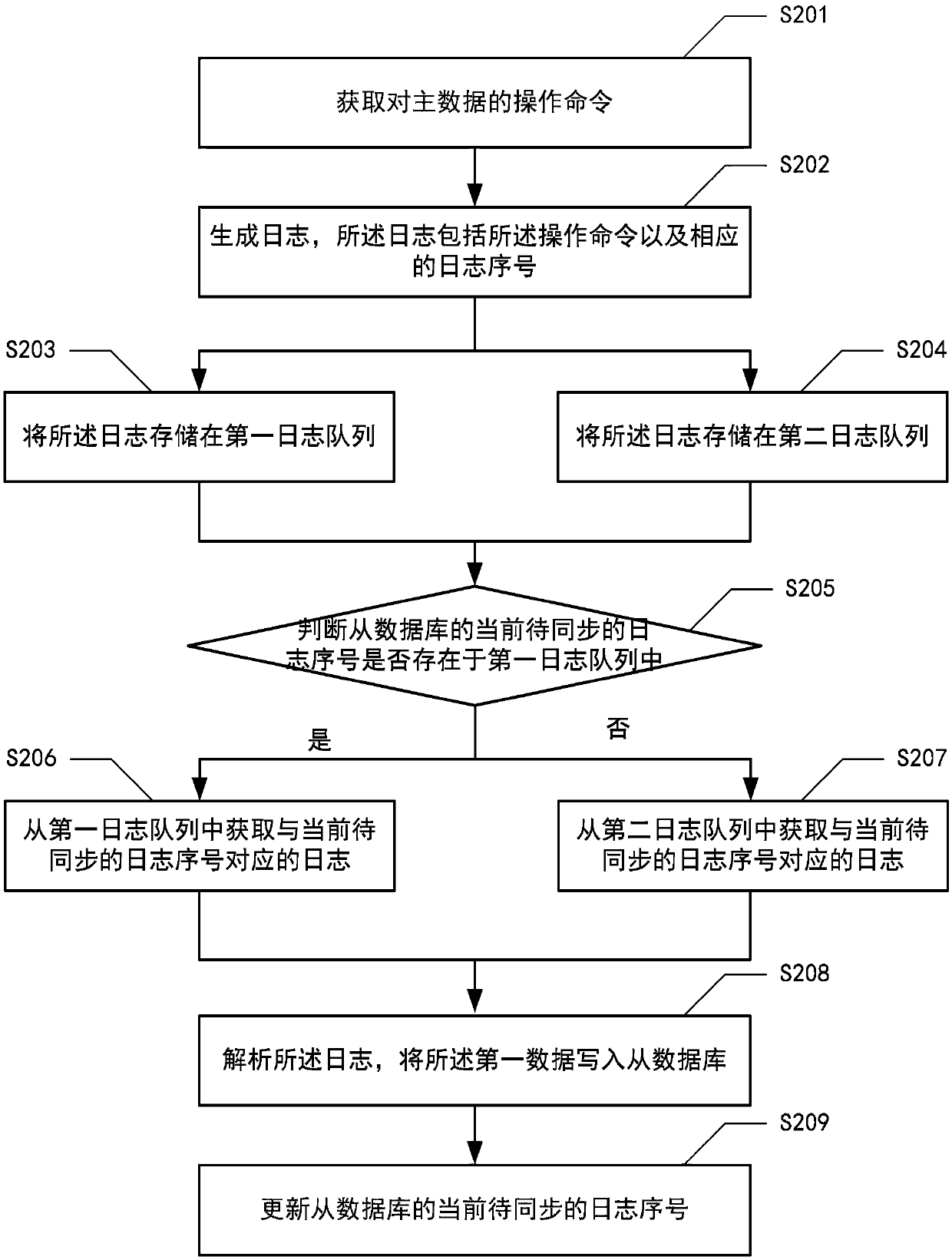
PendingCN110019062AAvoid synchronizationReduce sync timeDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationDatabase schema
The invention provides a data synchronization method, which is applied to a database system with a master database and a slave database architecture, and comprises the following steps of: obtaining anoperation command for the master database; generating a log, wherein the log comprises the write operation command and a corresponding log serial number; storing the log in a first log queue; obtaining a corresponding log from the first log queue according to a current to-be-synchronized log sequence number of a slave database, wherein the slave database sequentially realizes data synchronizationwith the master database according to the sequence of the log serial numbers, and the current to-be-synchronized log serial number is used for indicating the next log to be synchronized of the slavedatabase; and analyzing the obtained log, and executing an operation command corresponding to the log on the slave database.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Log grooming in a multi-log environment
InactiveUS7085782B2Reduce the possibilityLess effortData processing applicationsStructured data retrievalData miningSerial code
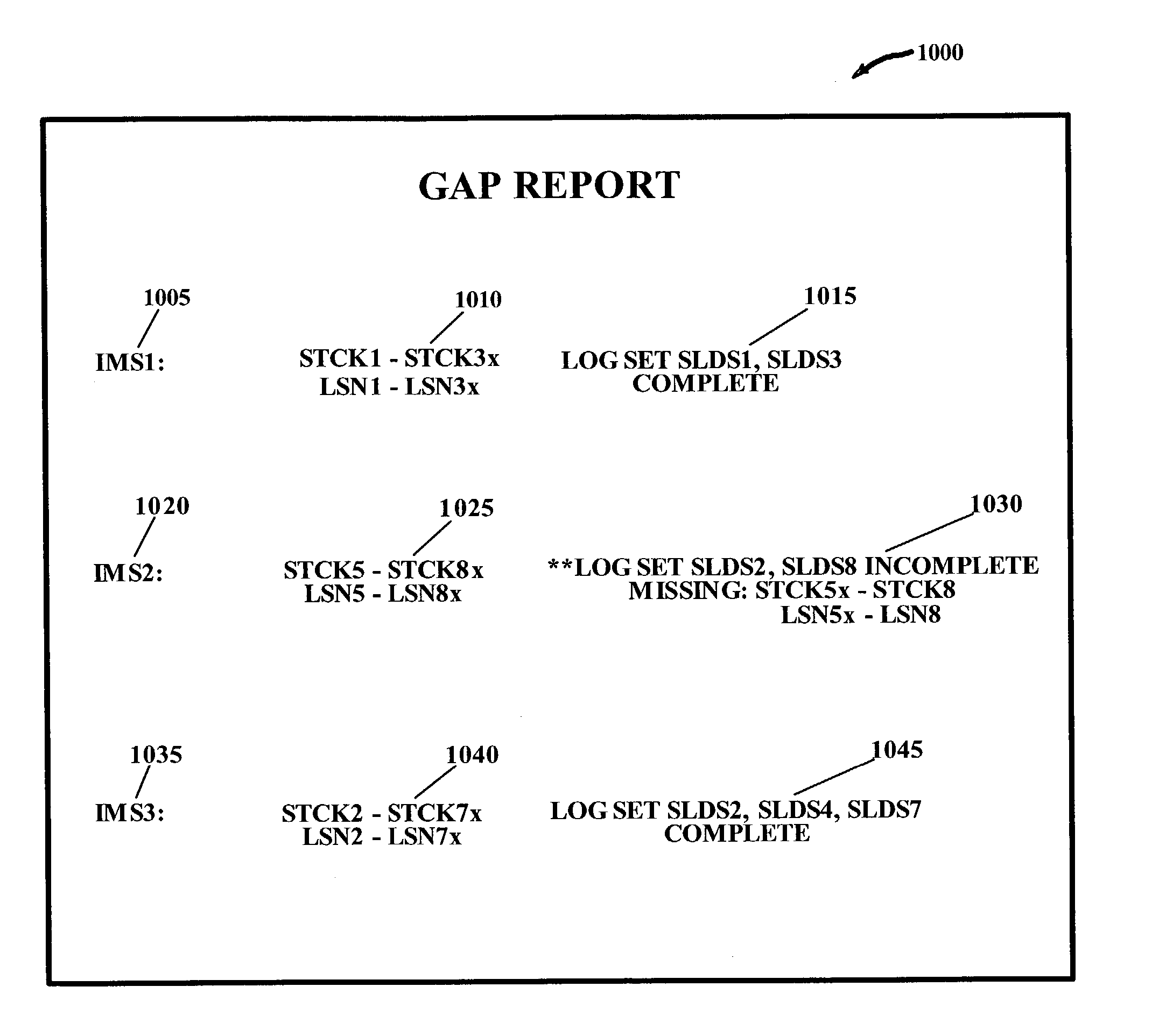
A log list comprising log identifiers is received, wherein the log list delineates a set of logs to be groomed. A log sequence number and a time-stamp are extracted from the first log record of each log in the set of logs. A system ID is extracted from a log record of each log in the set of logs. An appended log list is created wherein the system ID, time-stamp and log sequence number comprise appended information that is logically appended to each of respective ones of the log identifiers. The appended log list is sorted utilizing at least a portion of the appended information, the result comprising a sorted appended log list. An actual log sequence number is extracted from the last log record of each log in the set of logs. Each of the actual log sequence numbers is compared to a corresponding predicted log sequence number, wherein the corresponding predicted log sequence number is computed utilizing the sorted appended log list. A report is generated wherein range information reflecting all discrepancies between the actual log sequence numbers and the corresponding predicted log sequence numbers are disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Computer program product for conducting a lock free read
ActiveUS7548919B2Facilitates safely modifyingFacilitates returning last committed versionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData storingData store
The present invention expounds upon the ANSI “read committed” isolation level by allowing readers to read committed data without waiting for a concurrent writer to the data to finish. The method returns a last committed version of the data as it existed prior to changes made by the concurrent writer. Only two versions of any data record are required to be stored in the record data store, the last committed version and the current version. The last committed version may be generated from an undo log record. Locating the appropriate undo log record may be accomplished by storing a log sequence number in a lock data structure associated with the requested data record. A transaction flag may also stored in the lock data structure to facilitate generating the last committed version. The method may also utilize one or more locks to detect a concurrent writer to the requested data.
Owner:SAP AG
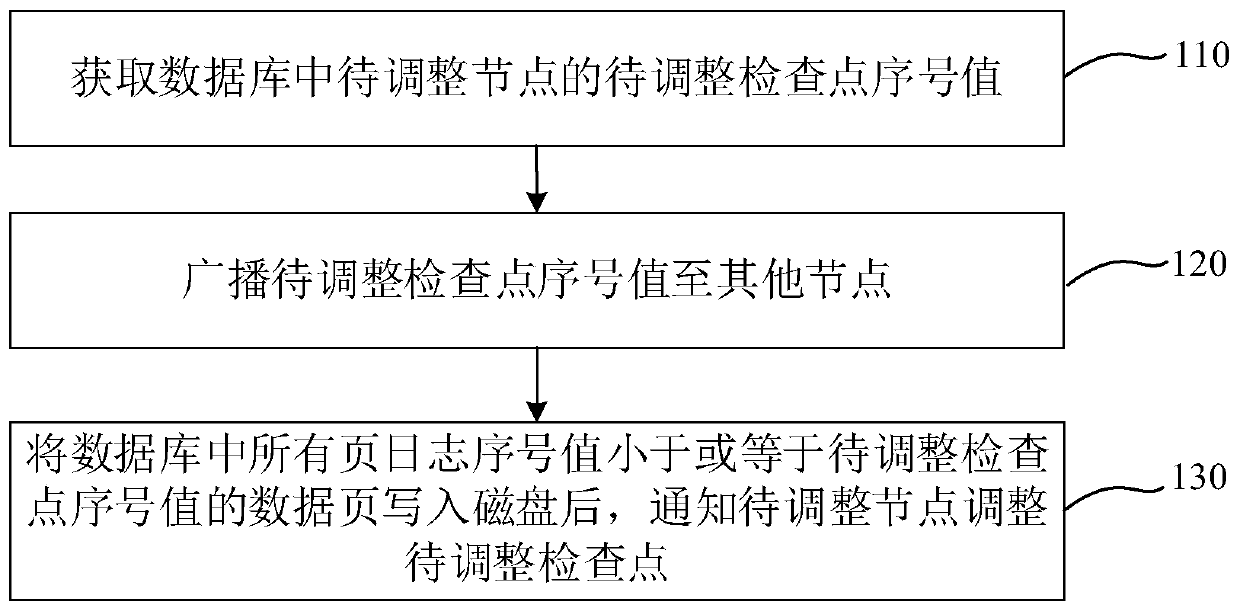
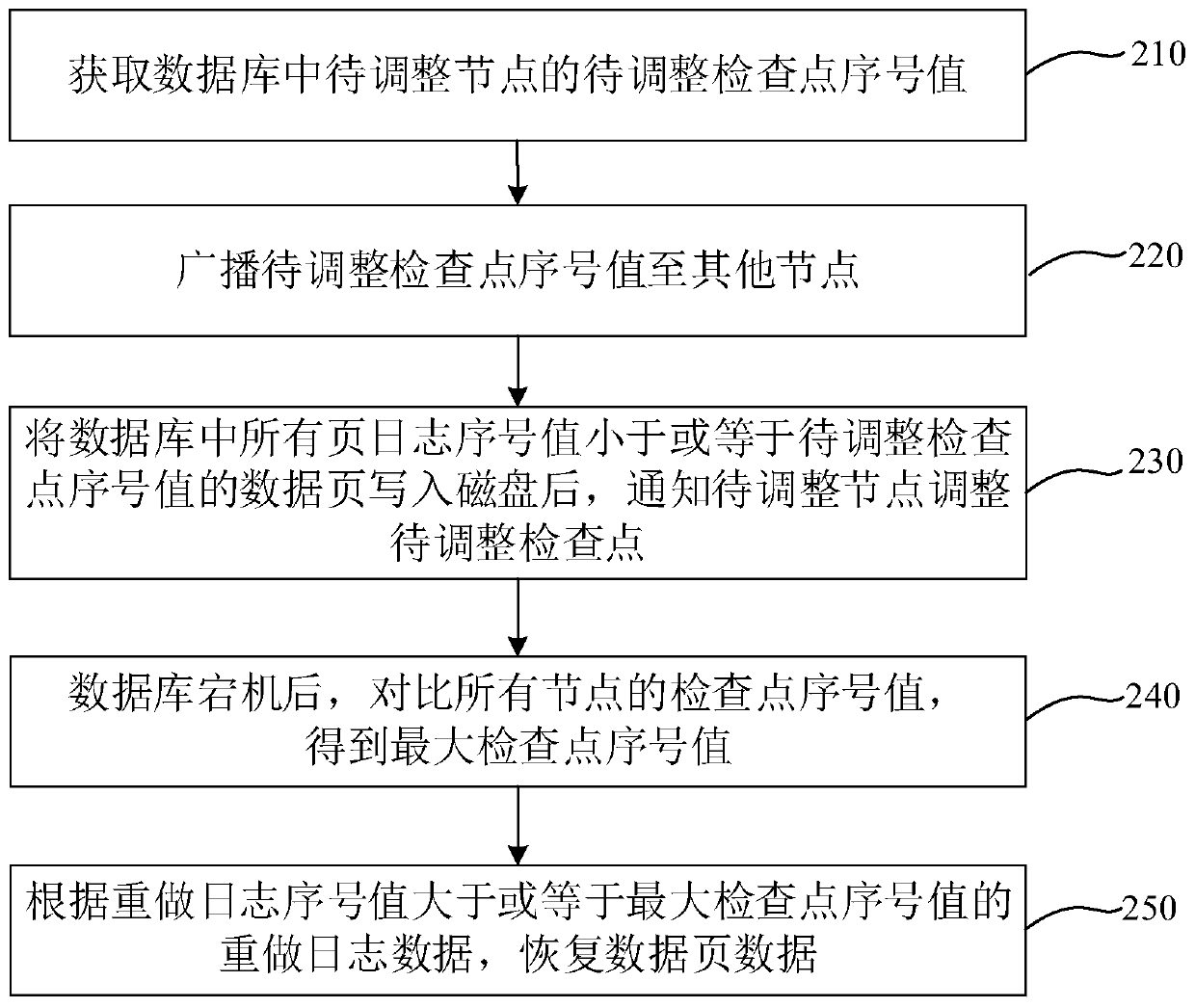
Data processing method and device for shared storage database, equipment and medium
ActiveCN111046024AEffective preservationWill not cause lossDatabase updatingEnergy efficient computingCheck pointEngineering
The invention discloses a data processing method and device for a shared storage database, equipment and a medium. The method comprises the steps: acquiring a to-be-adjusted check point serial numbervalue of a to-be-adjusted check point in a database, wherein the database at least comprises two nodes, and the to-be-adjusted check point serial number value is the adjusted check point serial numbervalue of the to-be-adjusted check point; broadcasting the serial number value of the check point to be adjusted to other nodes; writing all data pages of which the page log serial number values are smaller than or equal to the to-be-adjusted check point serial number value in a database into a disk; and notifying the to-be-adjusted node of adjusting the to-be-adjusted check point, the page log serial number value being a record serial number value generated when each node modifies the data page, and the redo log being used for recording an operation of modifying the data page by the corresponding node. According to the method, the data can be effectively stored, the problem of page breakage in the existing shared storage database cluster environment is solved, and the reliability and effectiveness of data storage are realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI DAMENG DATABASE
Automatically restoring data replication consistency without service interruption during parallel apply
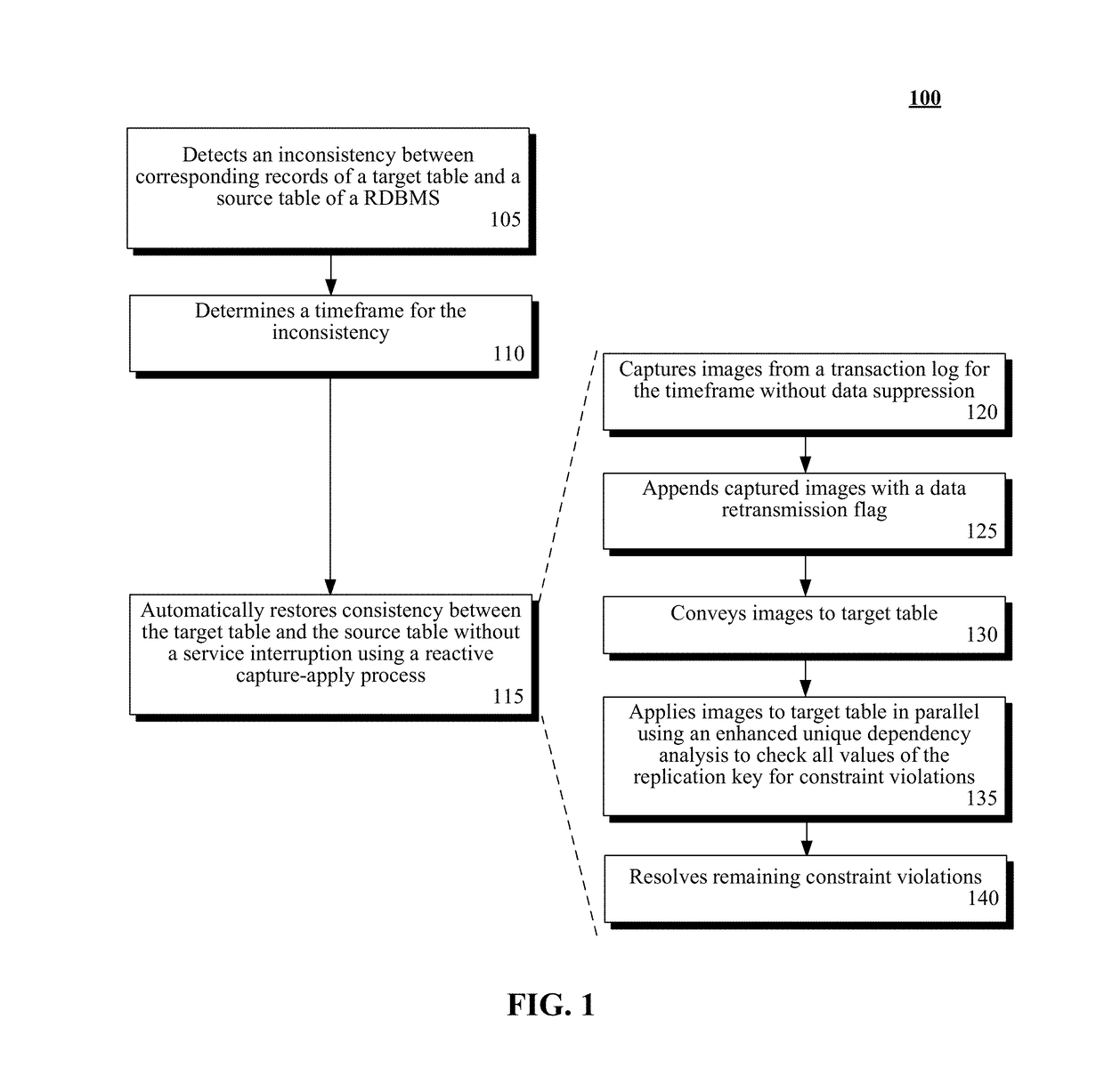
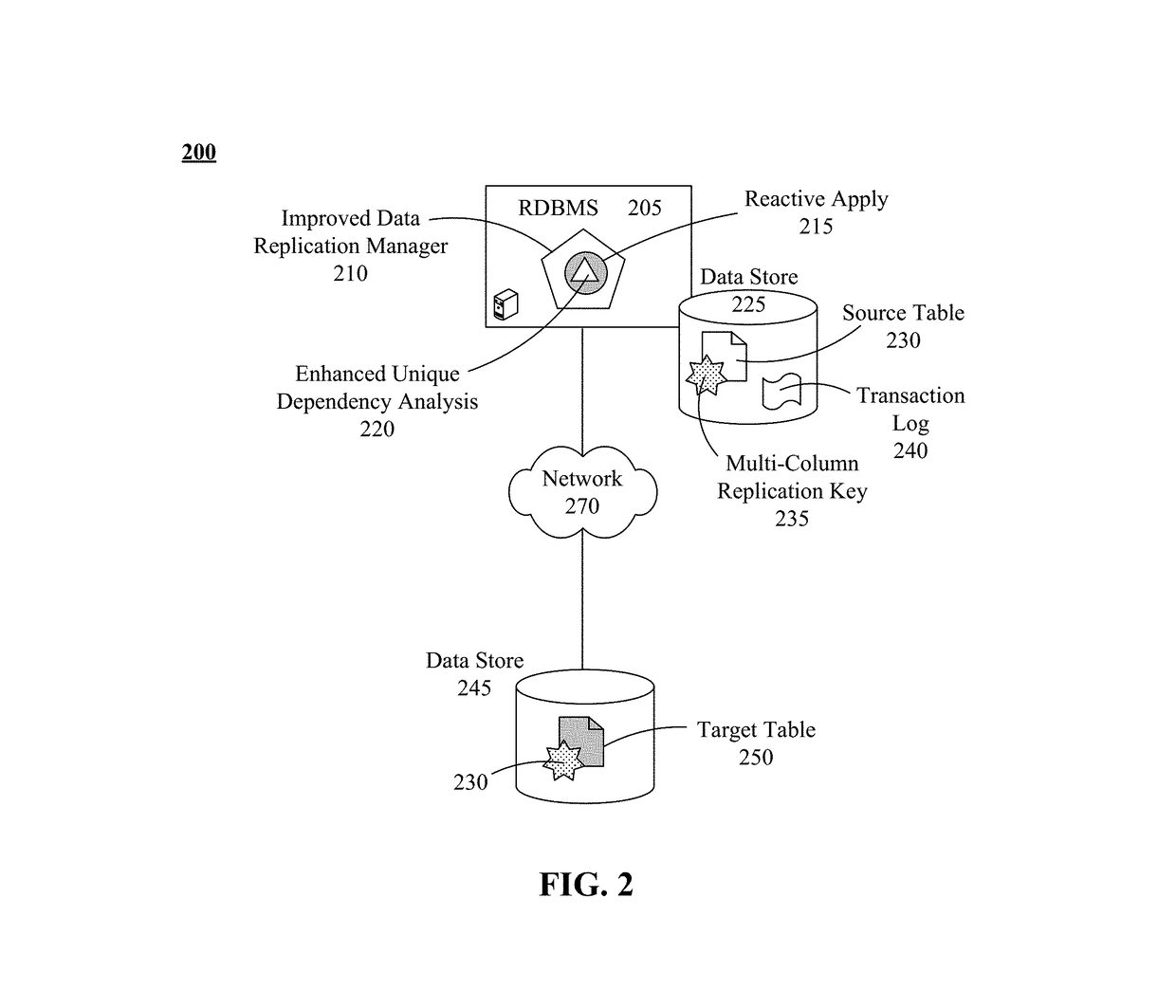
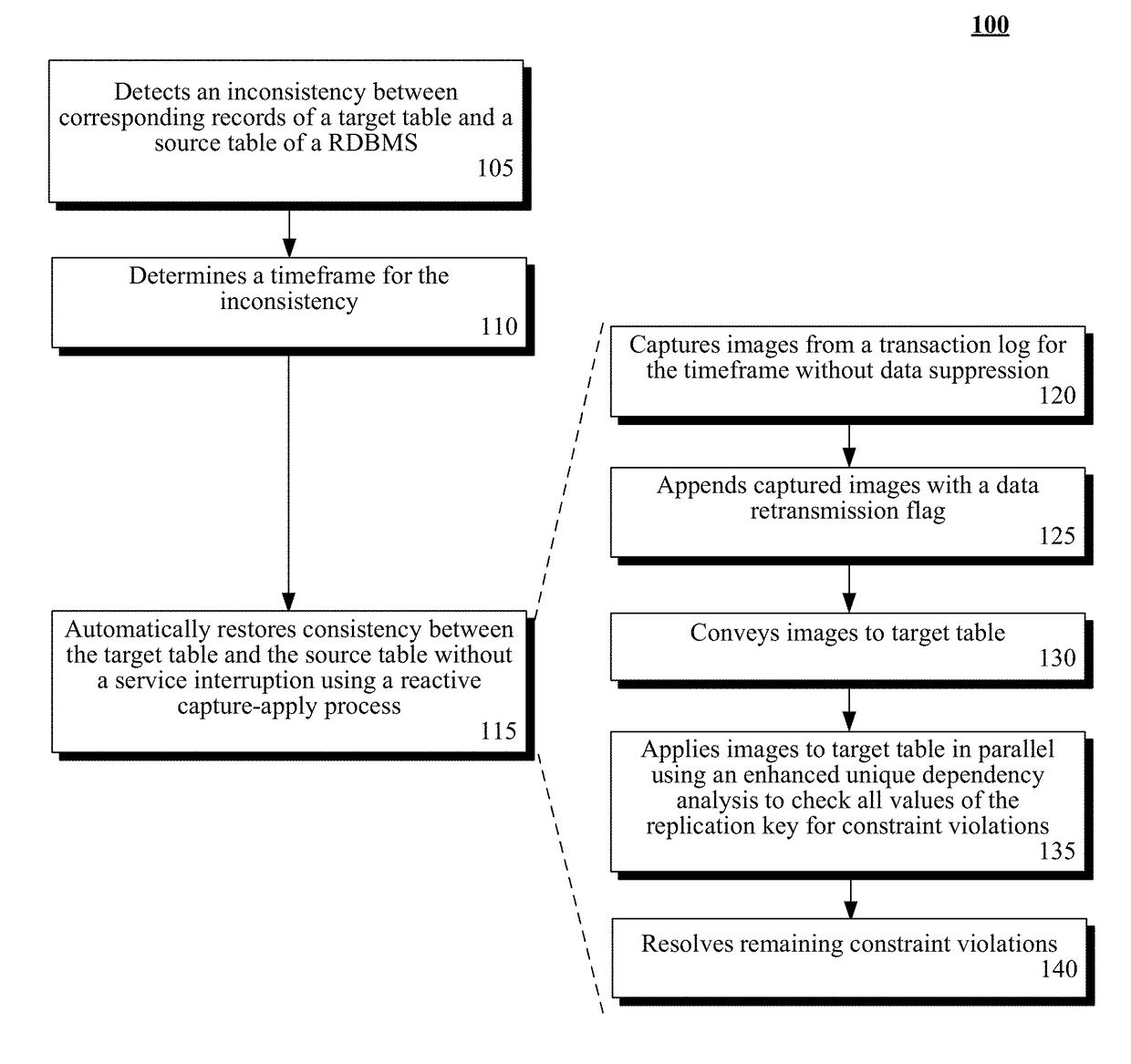
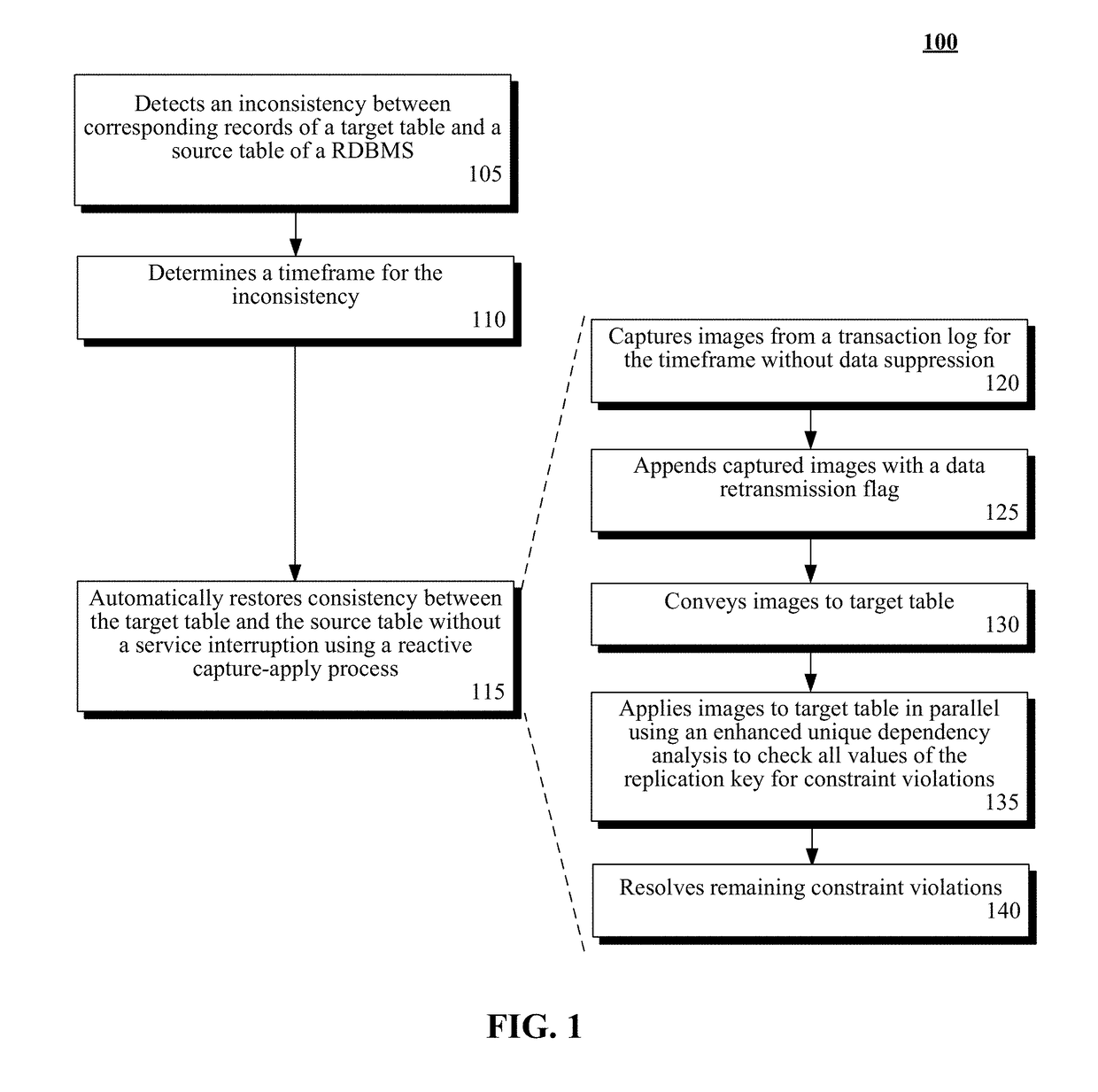
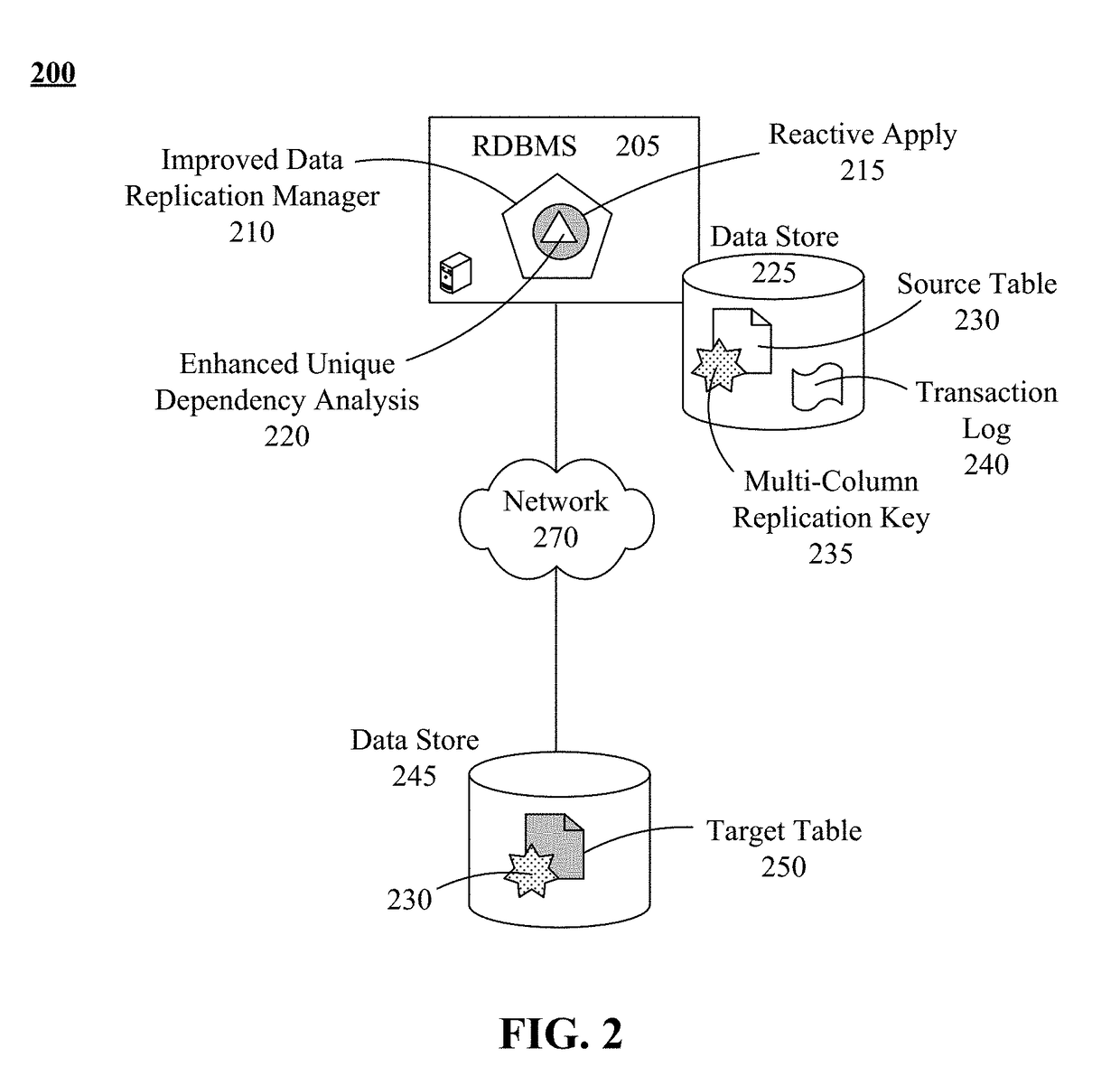
A data replication method can begin with the detection of an inconsistency between records of a target table and corresponding records of a source table of a relational database management system (RDBMS) performing a parallel apply replication by an improved data replication manager. The target table can be a copy of the source table, both of which include multiple unique constraints and indexes. A timeframe that encompasses the records of the target table having the inconsistency can be determined. The timeframe can utilize a commit timestamp or a log sequence number. Consistency between the target table and the source table can be automatically restored for the determined timeframe through use of a reactive-apply process. Data suppression for updates is automatically restored once the copy is consistent. Transactions performed upon the target table by the reactive-apply process can be performed in parallel. Service at the source table and the target table can be uninterrupted.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
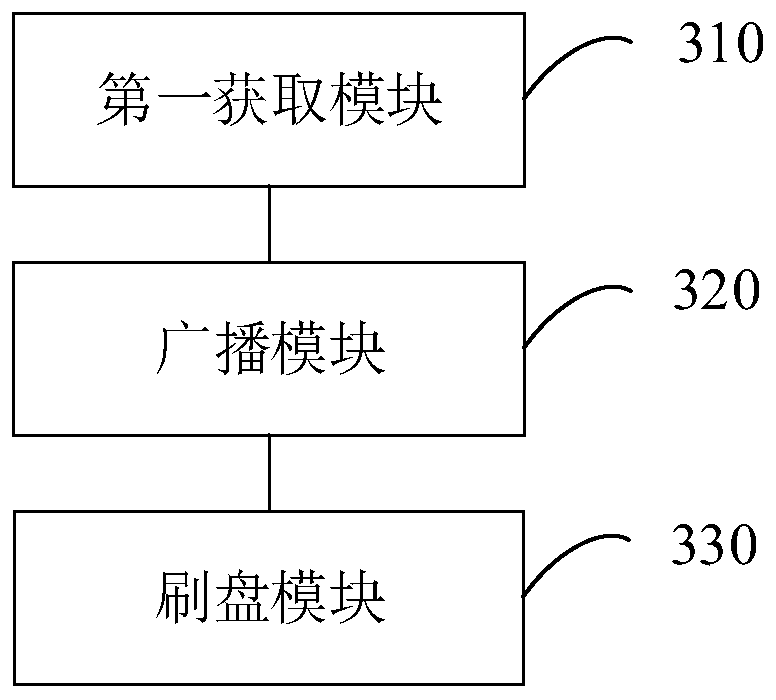
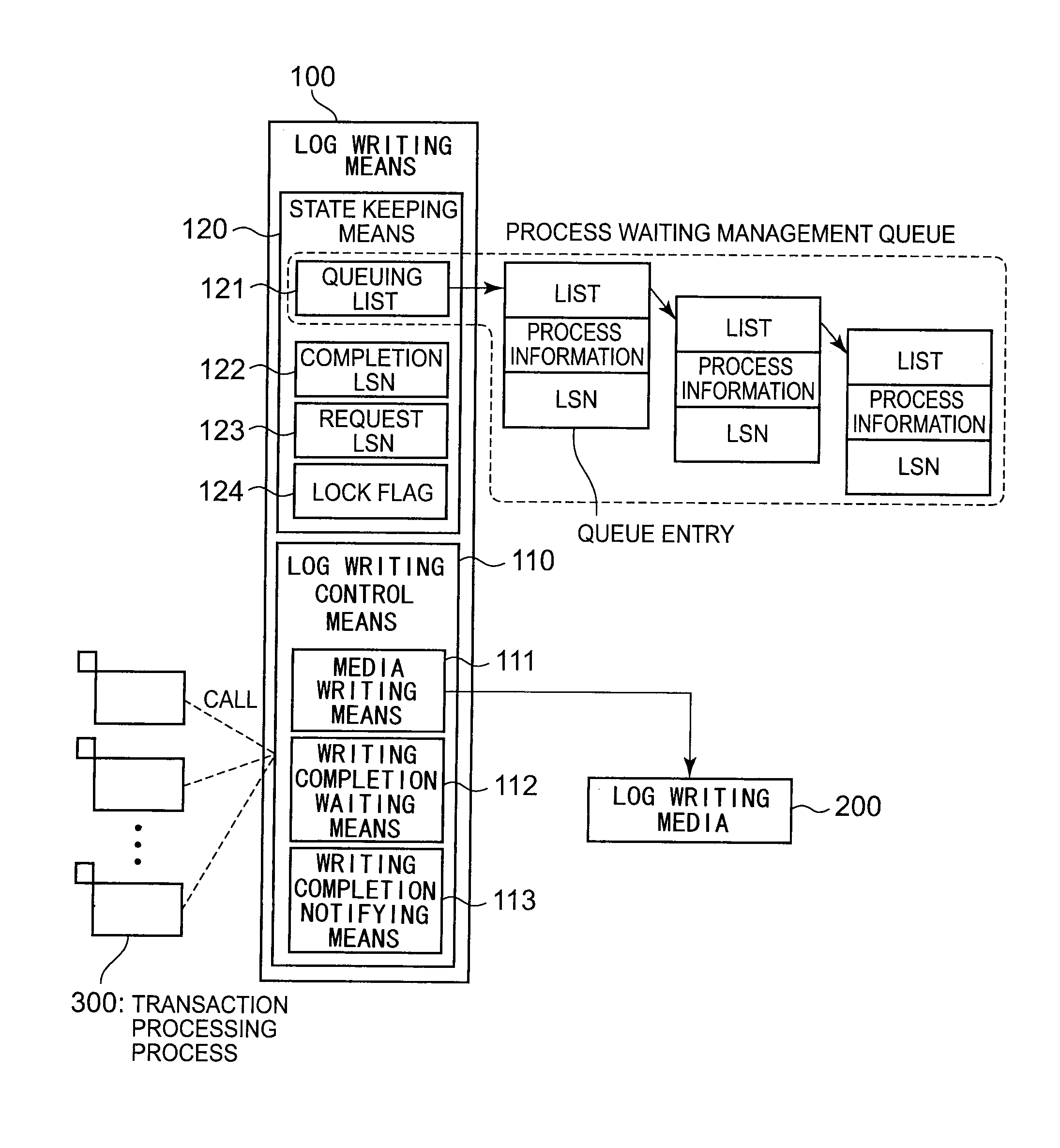
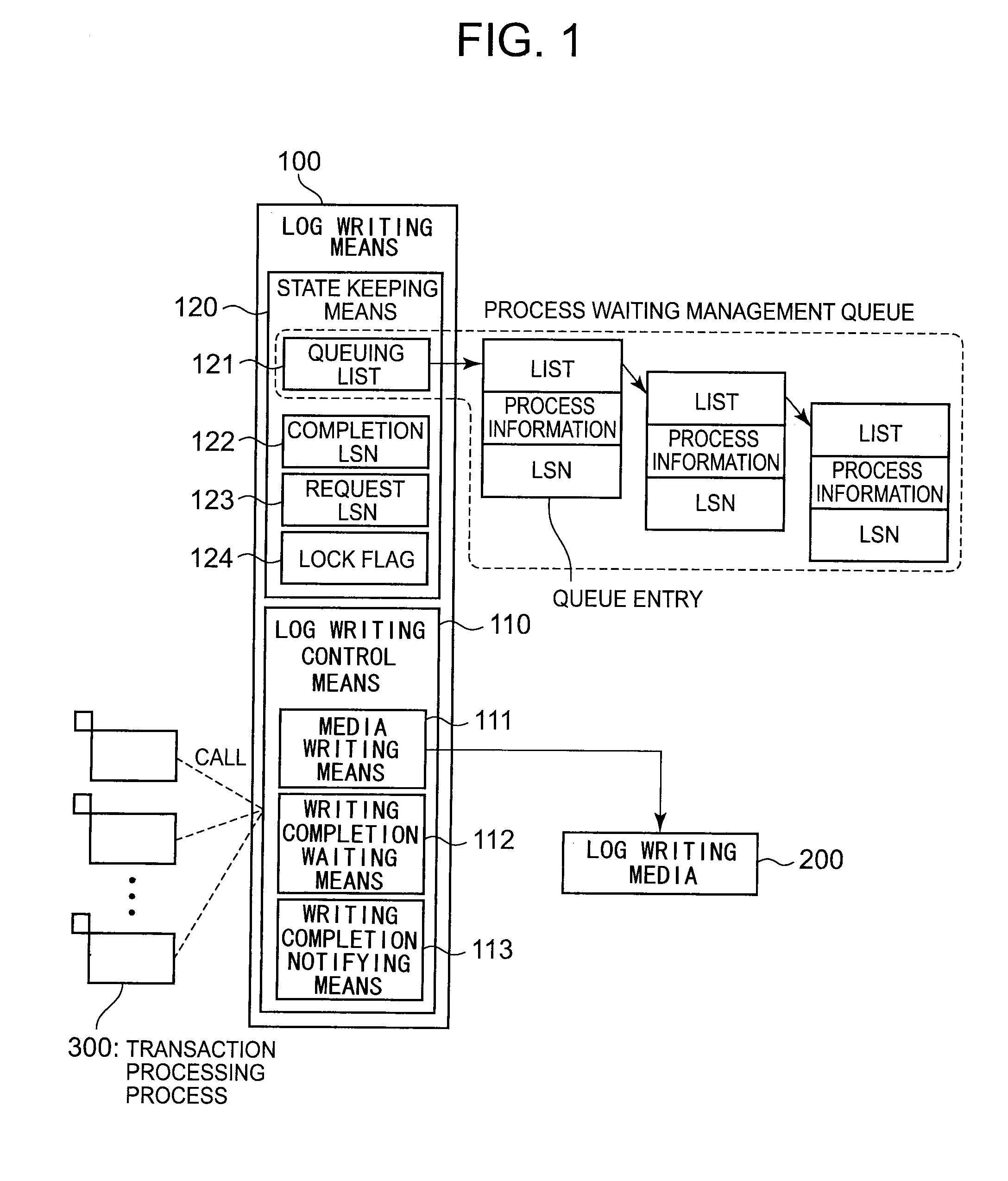
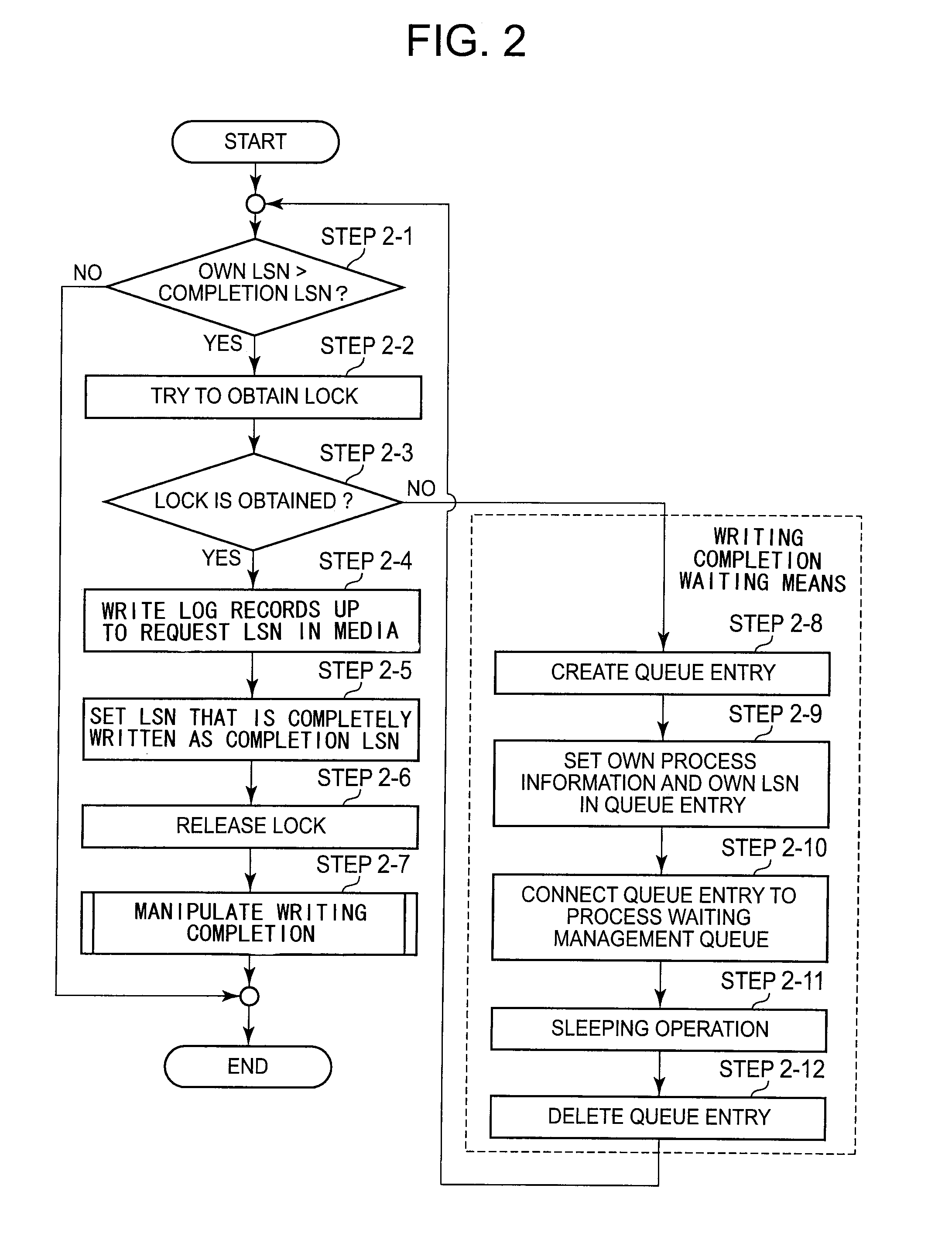
Log record writing system, device, method, and program
InactiveUS20140108839A1Write efficientlyLow efficiencyPower supply for data processingSpecial data processing applicationsSleep stateProcess information
A log record writing system includes a log writing media 1, a log writing control unit 2 which manages writing operation of a log record according to a log sequence number which is sequentially increased and writes the log record in the log writing media, and a queue storing unit 3 which stores a queue used so as to select a process which is an object for the waking-up operation among the processes which are waiting for completion of writing the log record in a sleeping state, and keeps the entries, which are elements of the queue, including process information and log sequence operation of the log record is performed by the other process, the log writing control unit 2 stores the queue entry that sets the log sequence number and the first process information and puts the first process to be in a sleeping state, and when the log record is completely written, the log writing control unit 2 compares the log sequence number included in an entry stored in the queue with a log sequence number of the log record which is completely written to extract all processes which completely write the log record and wakes up the processes.
Owner:NEC CORP
Automatically restoring data replication consistency without service interruption during parallel apply
A data replication method can begin with the detection of an inconsistency between records of a target table and corresponding records of a source table of a relational database management system (RDBMS) performing a parallel apply replication by an improved data replication manager. The target table can be a copy of the source table, both of which include multiple unique constraints and indexes. A timeframe that encompasses the records of the target table having the inconsistency can be determined. The timeframe can utilize a commit timestamp or a log sequence number. Consistency between the target table and the source table can be automatically restored for the determined timeframe through use of a reactive-apply process. Data suppression for updates is automatically restored once the copy is consistent. Transactions performed upon the target table by the reactive-apply process can be performed in parallel. Service at the source table and the target table can be uninterrupted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Shared disk clones
InactiveUS7680795B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData processing systemHigh availability
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to data processing systems and more particularly to high availability data processing systems. A primary server may share a storage device with one or more clone systems. Each clone generally replicates the state of the primary server, but relies on the same disk-based storage as the primary server. Thus, the clone systems may provide a shadow of the primary server, ready to take over should the primary server fail. The clone systems may access a log file that includes entries reflecting the actions performed by the primary system. The primary server may flush entries from a log buffer maintained on the primary server to a log file stored on the shared disk-based storage. The primary server may also send a log sequence number to the clone systems, and the clone systems periodically transmit a log sequence number back to the primary server indicating how far through the log file a clone system has progressed.
Owner:IBM CORP
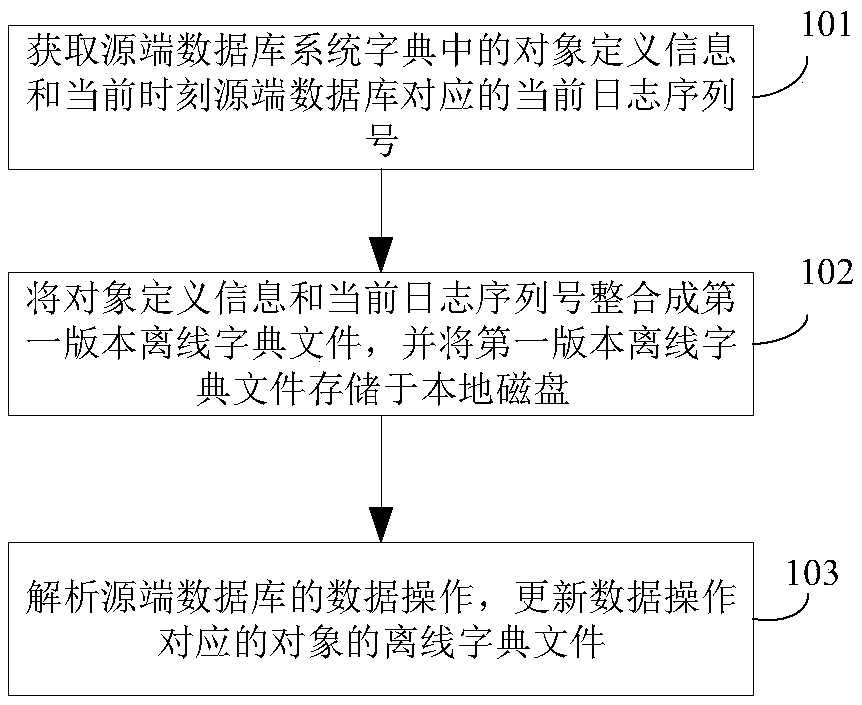
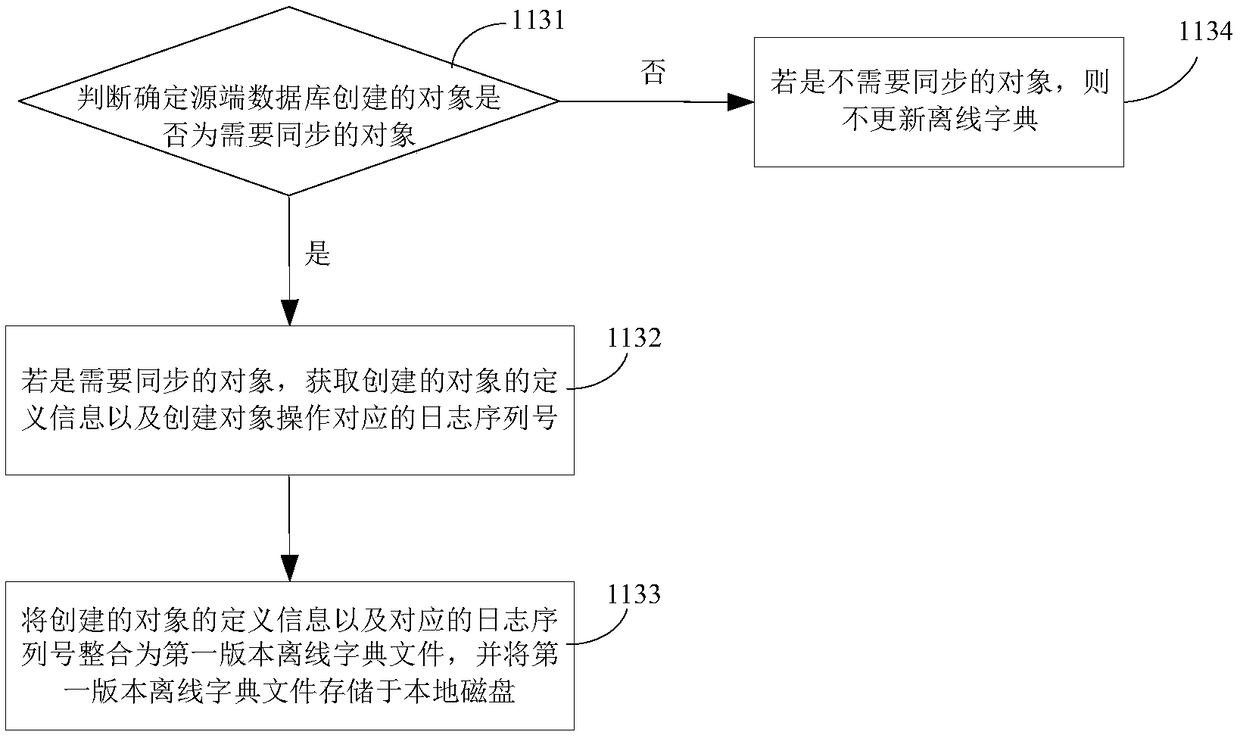
Data synchronization method and data synchronization system based on log analysis
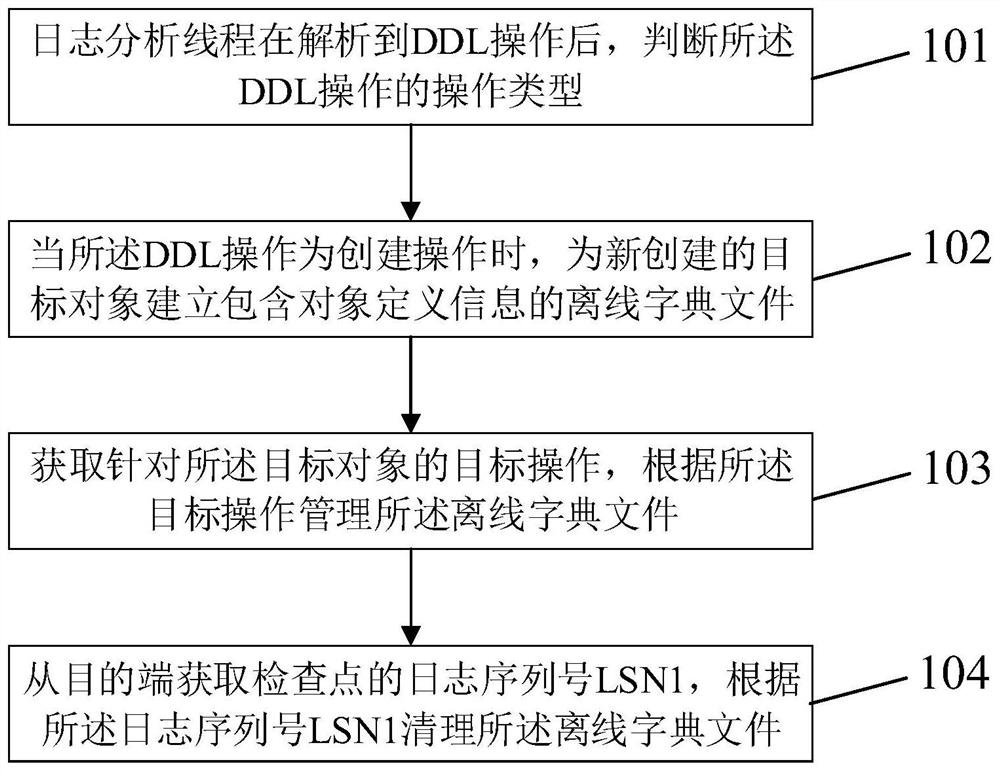
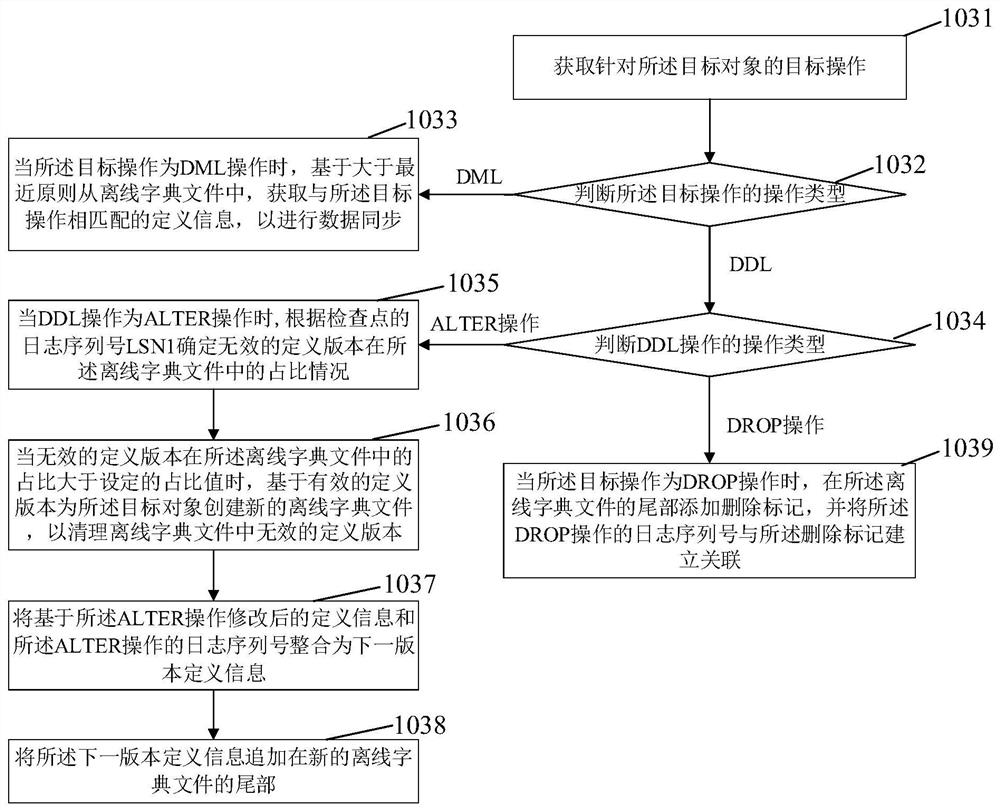
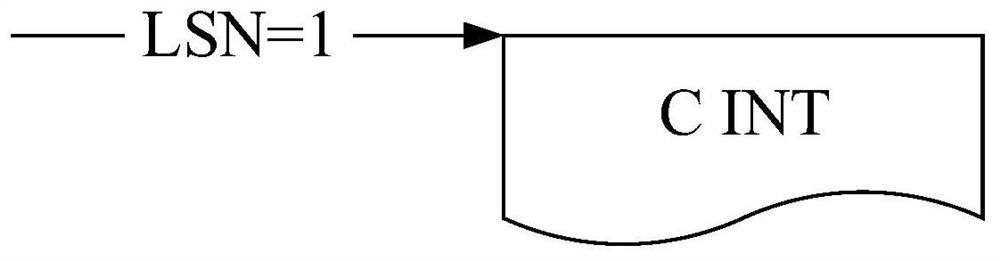
PendingCN111930828ALittle impact on performanceAvoid slowing downDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationData synchronizationObject definition
The invention discloses a data synchronization method and system based on log analysis. The method comprises steps of judging the operation type of a DDL operation after a log analysis thread analyzesthe DDL operation; when the DDL operation is a creation operation, establishing an offline dictionary file containing object definition information for a newly created target object; obtaining a target operation for the target object, and managing the offline dictionary file according to the target operation; and obtaining a log sequence number LSN1 of a check point from a destination end, and cleaning the offline dictionary file according to the log sequence number LSN1. According to the method, the offline dictionary file is managed and updated in time according to the actual operation of the source end database, so excessive versions of definition information in the dictionary file are avoided, the disk space is released in time, and the speed of slowing down the log synchronization service restart process is avoided.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
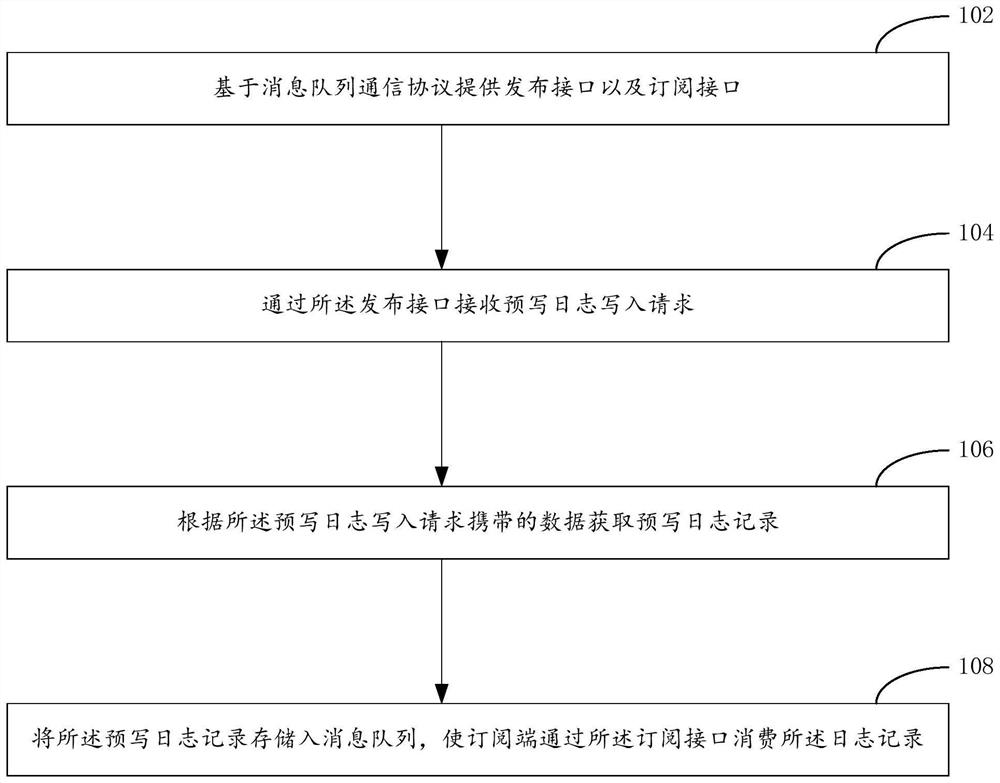
Method, device and system for processing pre-writing log
PendingCN114579532AGuaranteed functionReduce redundant storageInterprogram communicationDatabase distribution/replicationMessage queueEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a method, a device and a system for processing a pre-written log. The method for processing the pre-written log comprises the following steps: providing a publishing interface and a subscription interface based on a message queue communication protocol; receiving a pre-writing log writing request through the publishing interface; obtaining a pre-writing log record according to data carried by the pre-writing log writing request; storing the pre-written log record into a message queue, so that a subscription end consumes the log record through the subscription interface; wherein the log sequence number in the pre-writing log record is determined based on the corresponding rule between the message offset and the log sequence number, the message offset is the message offset of the pre-writing log record in the message queue, and the log sequence number is used for enabling the subscription end to write the pre-writing log record in the message queue based on the corresponding rule between the message offset and the log sequence number. And determining a message offset corresponding to the pre-write log record needing to be played back.
Owner:ALIBABA (CHINA) CO LTD
Systems and methods to optimize multi-version support in indexes
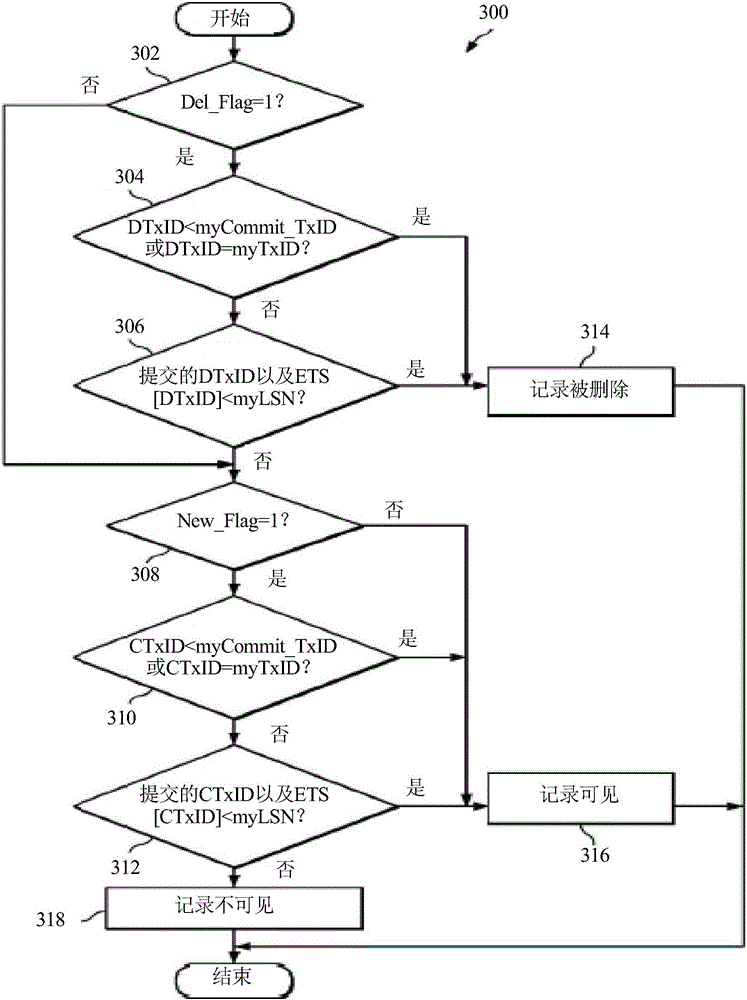
ActiveCN106462592AEasy to implementEffective Visibility DetectionDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemData treatment
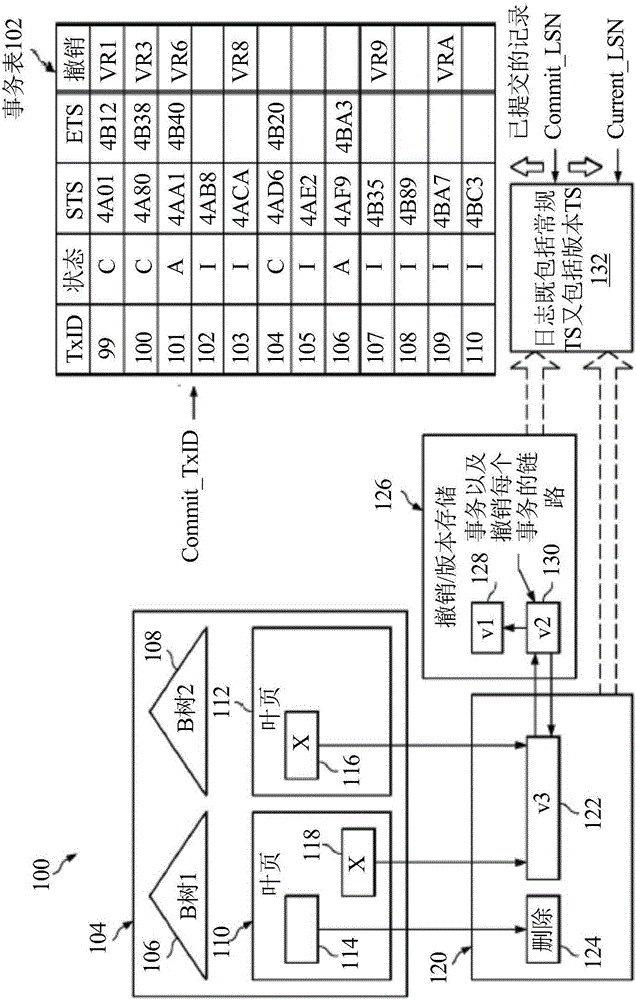
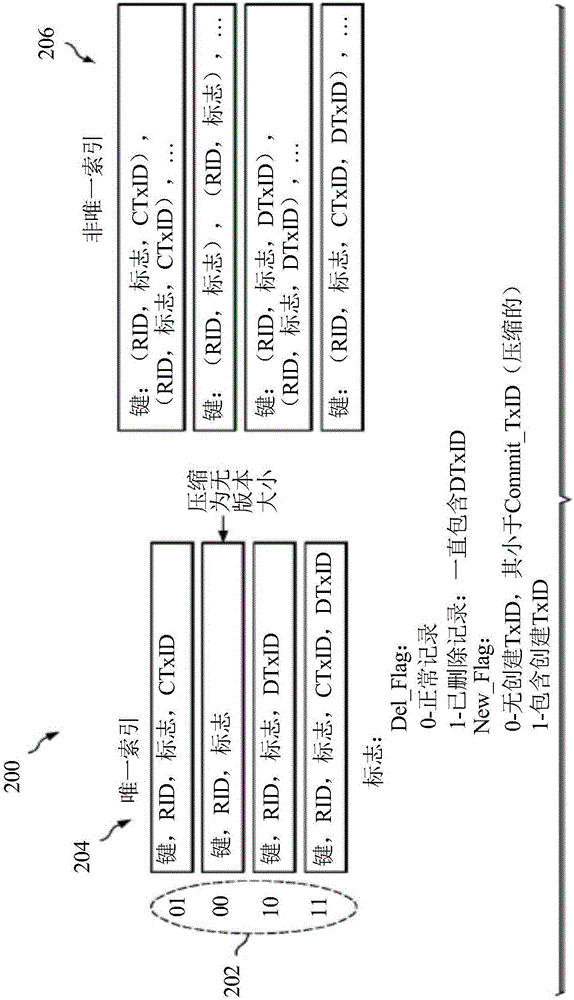
System and method embodiments are provided for multi-version support in indexes in a database. The embodiments enable substantially optimized multi-version support in index and avoid backfill of commit log sequence number (LSN) for a transaction identifier (TxID). In an embodiment, a method in a data processing system for managing a database includes determining with the data processing system whether a record is deleted according to a delete indicator in an index leaf page record corresponding to the record; and determining with the data processing system, when the record is not deleted, whether the record is visible according to a new record indicator in the index leaf page record and according to a comparison of a system commit TxID at the transaction start with a record commit TxID obtained from the index leaf page record.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
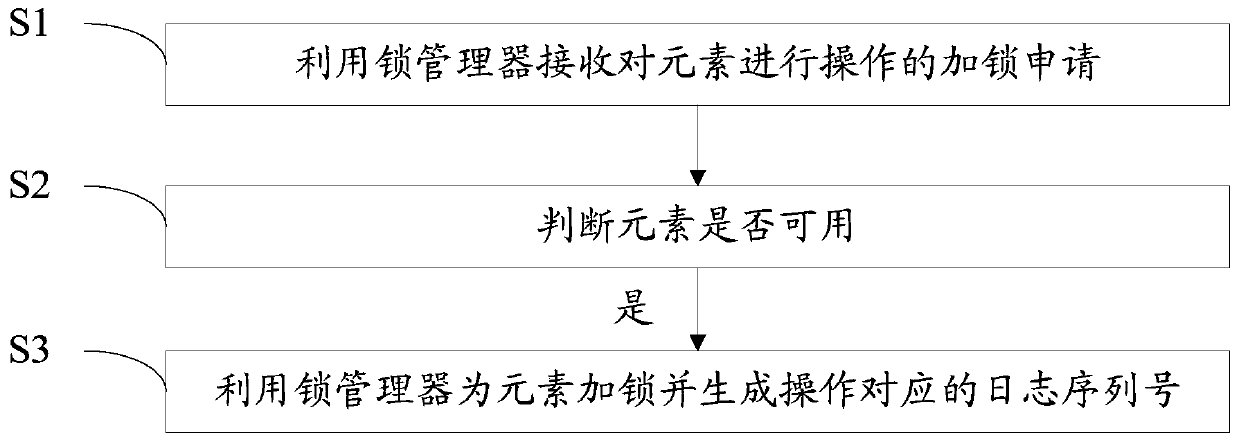
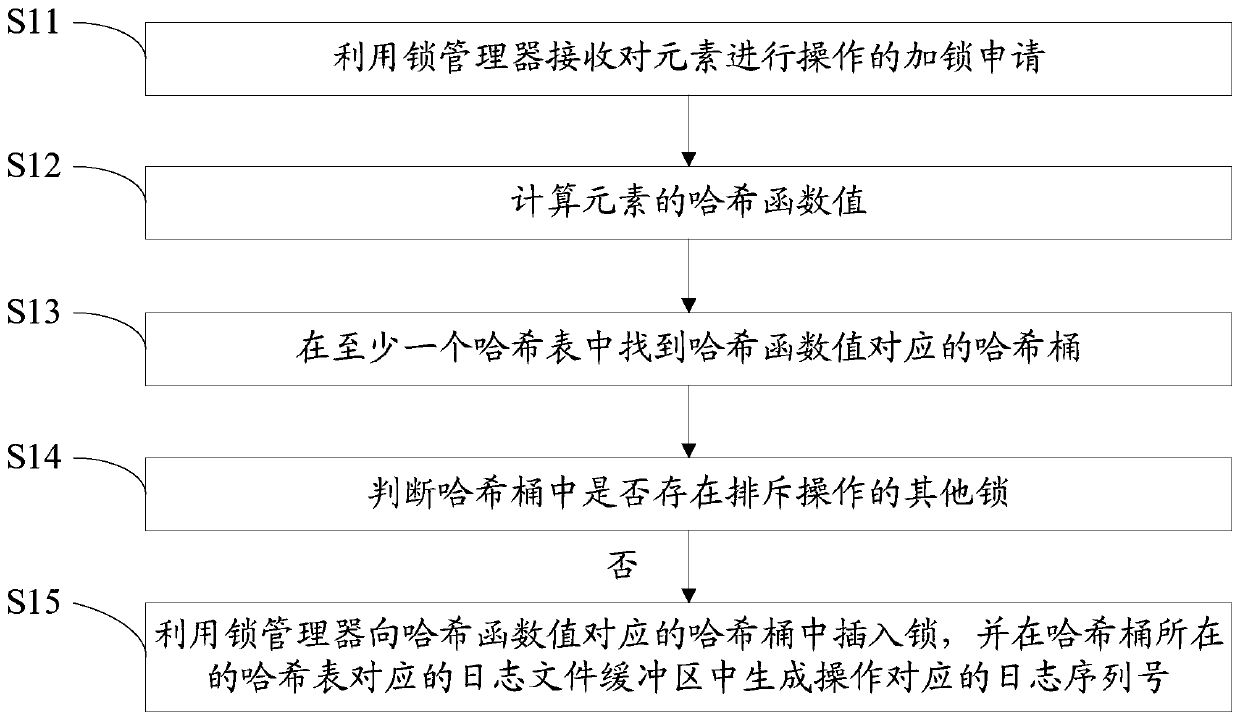
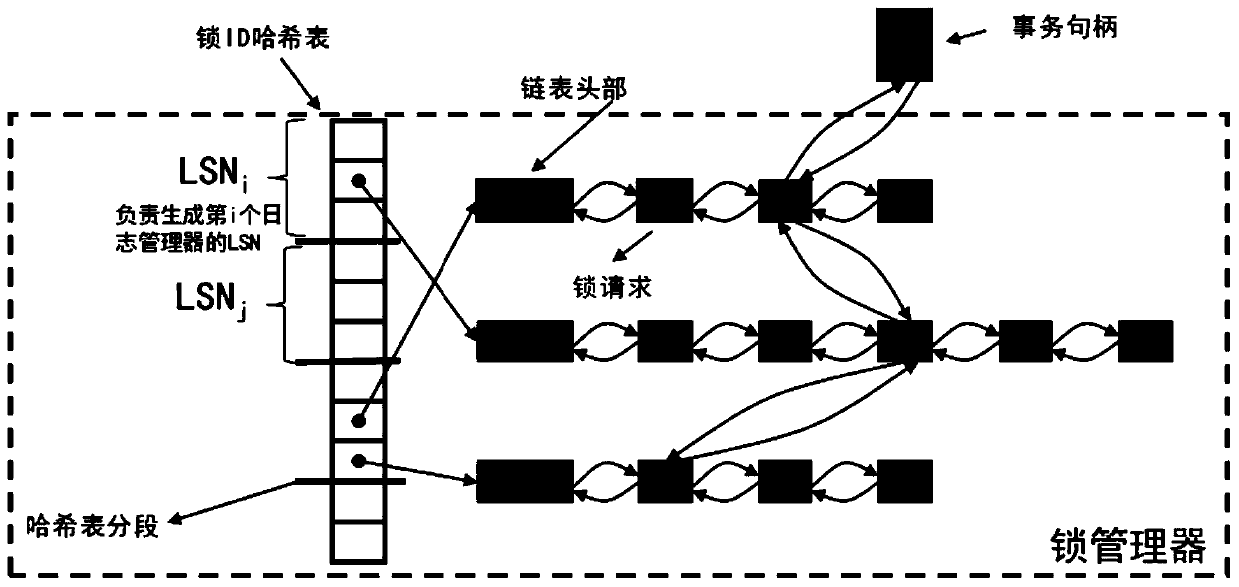
Log sequence number generation method and device and readable storage medium
PendingCN109791541AImprove performanceReduce contention operationsHardware monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsLock managerComputer engineering
The present application discloses a log sequence number generation method, which comprises: using a lock manager to receive a locking application for operating an element; determining whether an element is available; and if the element is available, using the lock manager to lock the element and generate a log sequence number corresponding to the operation. The present application also discloses alog sequence number generation device and a readable storage medium.
Owner:袁振南 +1
Priority-based two-way synchronization method and priority-based two-way synchronization system
ActiveCN112559473ASpeed upProgram synchronisationDatabase distribution/replicationDistributed computingSynchronization system
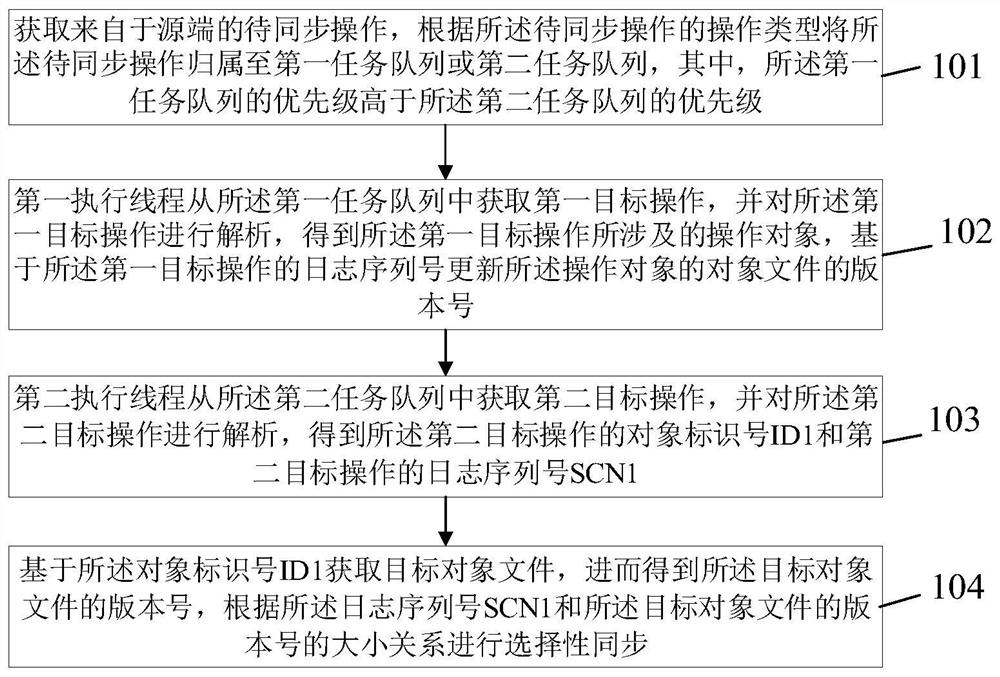
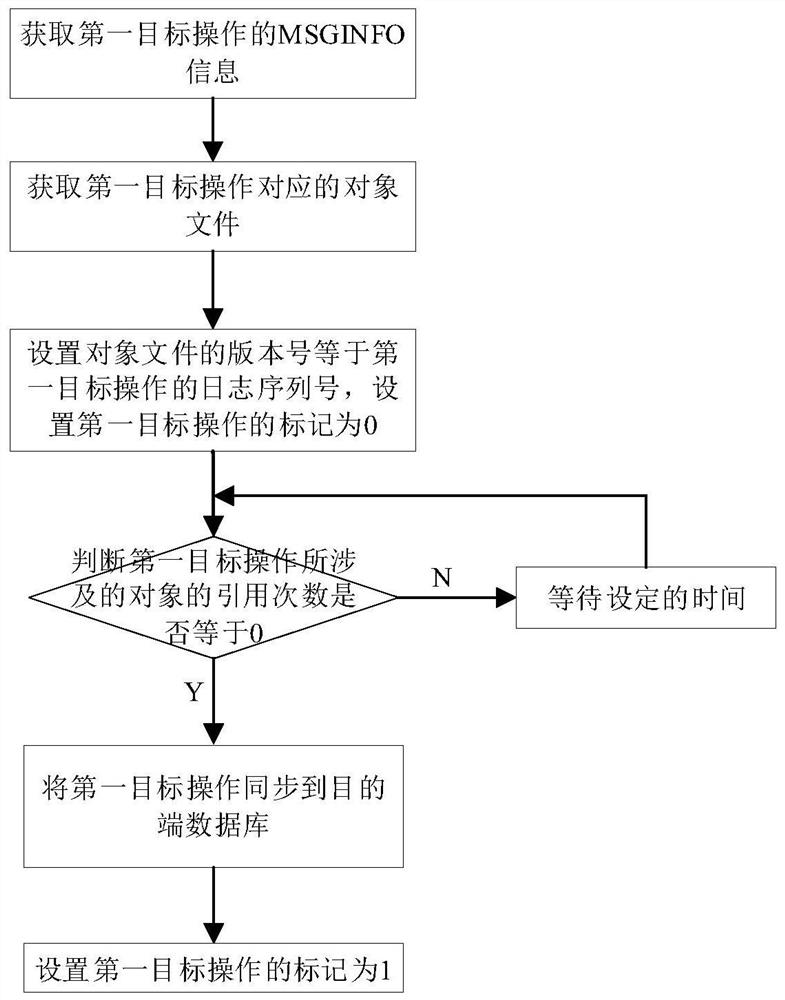
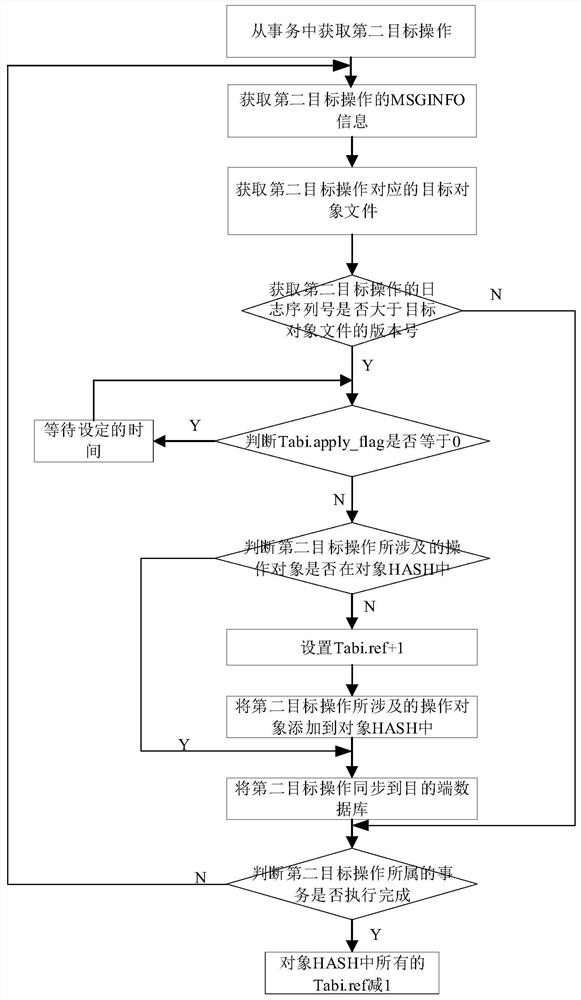
The invention discloses a priority-based two-way synchronization method and synchronization system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-synchronized operation from a source end, andenabling the to-be-synchronized operation to belong to a first task queue or a second task queue according to the operation type of the to-be-synchronized operation; enabling the first execution thread to obtain a first target operation from the first task queue, analyze the first target operation to obtain an operation object involved in the first target operation, and update a version number ofan object file of the operation object based on a log serial number of the first target operation; enabling the second execution thread to obtain a second target operation from the second task queue and analyze the second target operation to obtain an object identification number ID1 of the second target operation and a log sequence number SCN1 of the second target operation; and obtaining the version number of the target object file based on the object identification number ID1, and performing selective synchronization according to the size relationship between the log sequence number SCN1 and the version number of the target object file.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
Log reading method based on log analysis synchronization and synchronization system
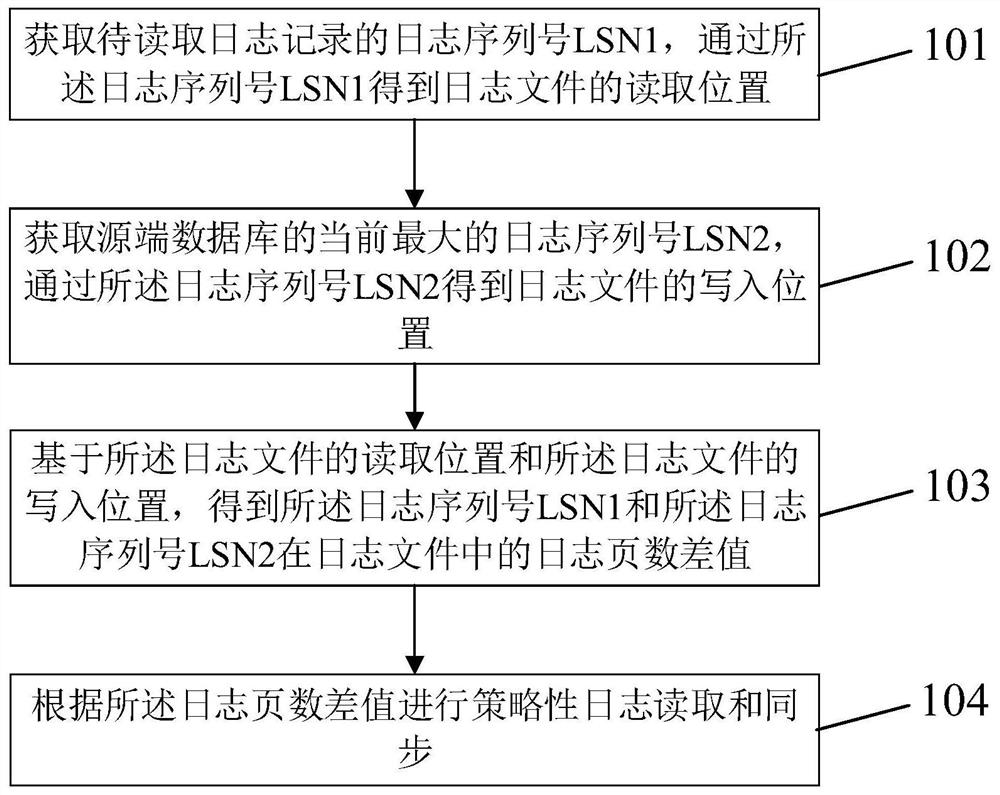
PendingCN111858502AAvoid reading and writing conflictsDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationAlgorithmSynchronization system
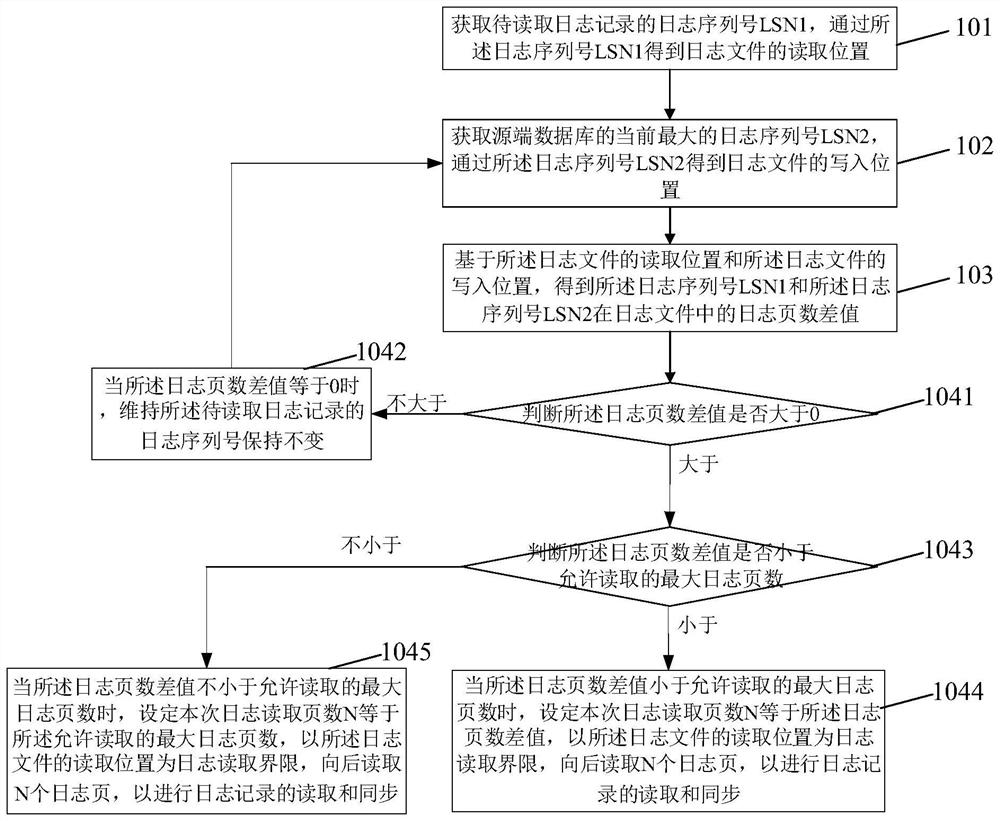
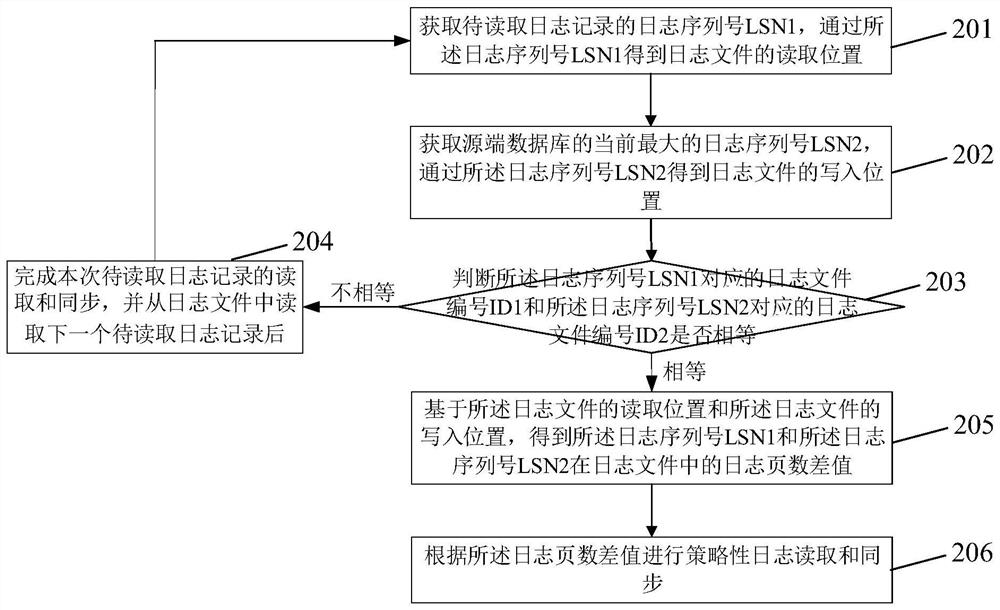
The invention discloses a log reading method based on log analysis synchronization and a synchronization system, and the method comprises the steps of obtaining a log sequence number LSN1 of a to-be-read log record, and obtaining the reading position of a log file through the log sequence number LSN1; obtaining the current maximum log sequence number LSN2 of the source end database, and obtainingthe writing position of the log file through the log sequence number LSN2; obtaining a log page number difference value of the log serial number LSN1 and the log serial number LSN2 in the log file based on the reading position of the log file and the writing position of the log file; and performing strategic log reading and synchronization according to the log page number difference. According tothe invention, by calculating the distance between the log sequence number of the log record to be read and the current maximum log sequence number in the database system, the number of log pages readwhen the log file is read can be dynamically adjusted, strategic log reading and synchronization are carried out, and log reading and writing conflicts are prevented.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
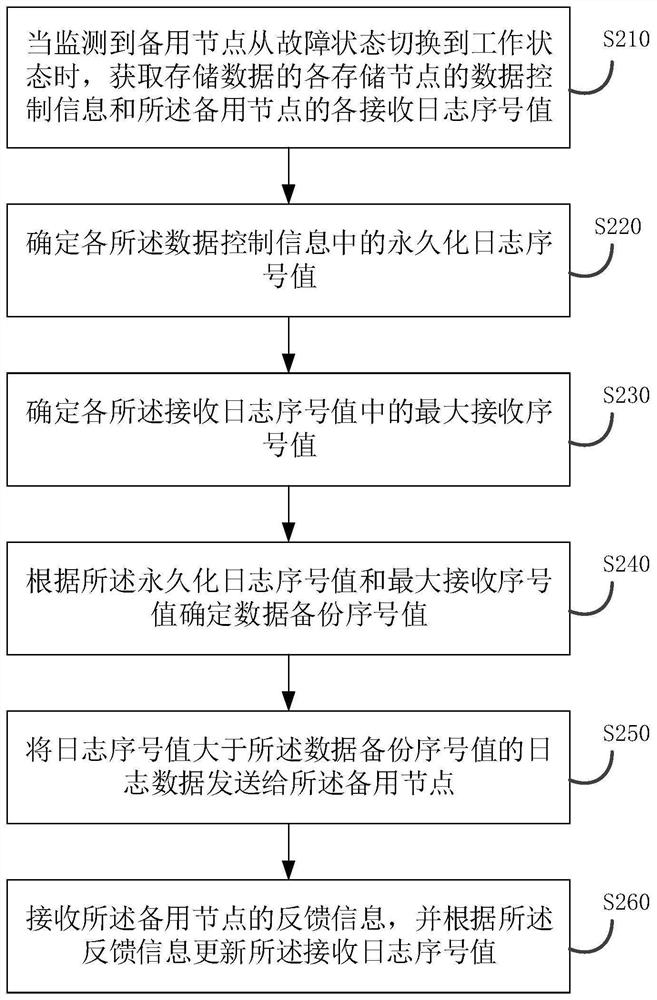
Data backup method, device and apparatus and storage medium
PendingCN111858171AImprove recovery efficiencyReduce system riskDatabase distribution/replicationRedundant operation error correctionData controlComputer network
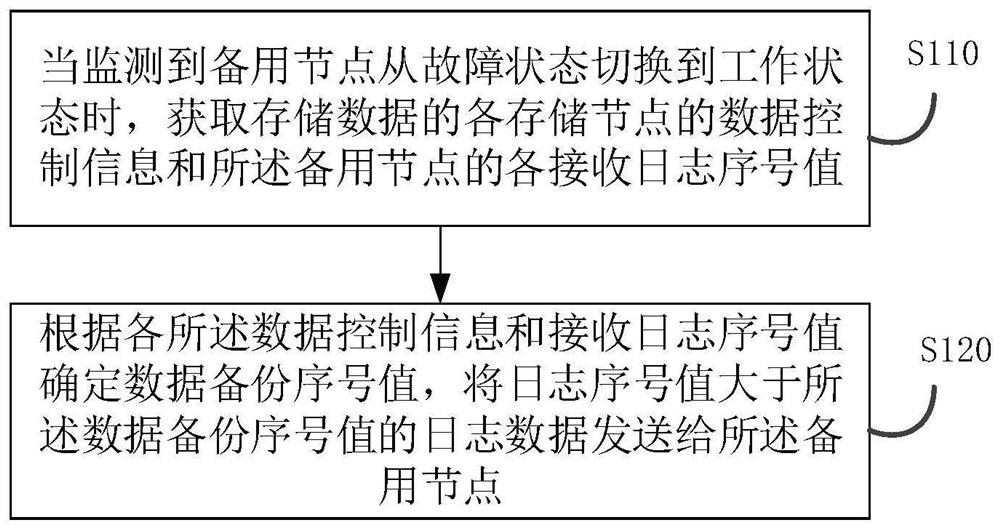
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data backup method, device and apparatus and a storage medium, and the method comprises: obtaining the data control information of each storage node for storing data and each receiving log serial number value of the standby node when a condition that the standby node is switched from a fault state to a working state is monitored; and determining a data backup serial number value according to each piece of data control information and the received log serial number value, and sending the log data of which the log serial number value is greater than the data backup serial number value to a standby node. The problem of resource loss caused by the fact that all data and control information generated in the period from failure of the standby node to recovery of normal work are all sent to the standby node during data backup is solved. The log data sent to the standby node is determined according to the data backup serial number value, the effect that stored permanent data do not need to be transmitted and backed up again is achieved, network consumption in the system and system risks in the recovery period of the standby node are reduced, andthe recovery efficiency of the standby node is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI DAMENG DATABASE
A kind of hot backup method and system of mysql database
ActiveCN106354583BPhysical backup is fastFast backupRedundant operation error correctionData fileSerial code
Owner:广州鼎甲计算机科技有限公司
DB2 database data synchronous updating method and equipment
ActiveCN109271452BEnsure consistencyReduce adverse effectsDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationData synchronizationEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention provide a DB2 database data synchronization update method and device. The method includes: creating a data detailed address storage column according to the table to be updated to be synchronized, an S lock on the table to be updated to be synchronized, acquiring the current log sequence number LSN of the source DB2 database as the starting LSN of the table to be updated to be synchronized, and releasing the S lock; Obtain the result set of the table to be synchronized and updated, send the result set to the target database for storage, and obtain the current LSN of the source DB2 database as the end LSN of the table to be synchronized and updated; receive the initialization data sent by the source synchronization update service, on the target The database inserts ROWID into the data detailed address storage column, initializes the data of the table to be updated synchronously; starts the real-time data synchronization update service, and sends the changes of the source DB2 database to the target database for data synchronization update. Various embodiments of the present invention can avoid the adverse effects caused by the S lock on the table to be synchronously updated for a long time under the premise of ensuring the data consistency of the target database.
Owner:WUHAN DAMENG DATABASE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com