Biologically induced composite artificial esophagus
A compound and biological technology, applied in the field of artificial esophagus, can solve problems such as digestive dysfunction, esophageal defect, and long time, and achieve the effect of good flexibility, reduced impact, and strong support force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1: Cross grid type bio-induced composite artificial esophagus of the present invention
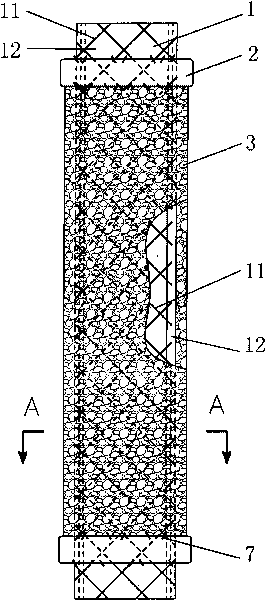
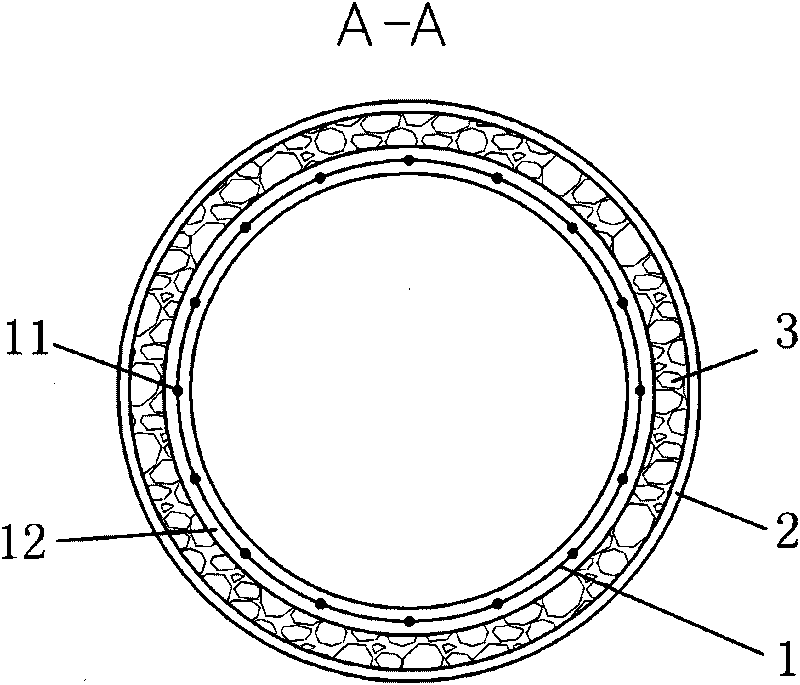
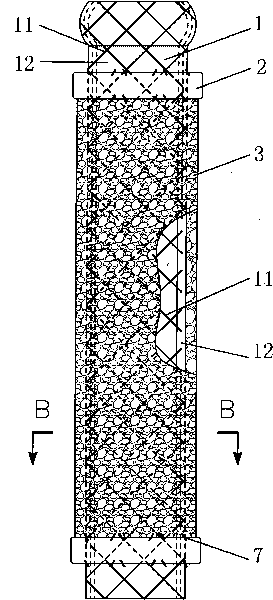
[0084] Use nickel-titanium shape memory alloy (Nitinol alloy) wires with a recovery temperature of 15°C and a diameter of 0.25 mm to weave the support frame 11 of the support tube in the mold, and then carry out heat treatment in the mold to make it reticular above the recovery temperature The structure is cylindrical and tubular, and after polishing and cleaning, the support frame 11 of the present invention is obtained.
[0085] In the medical silicone coating equipment, the support tube 11 is installed in a special mold, and the support frame 11 is coated according to the general process of medical silicone (if the artificial esophagus with the anti-reflux device is manufactured, the anti-reflux device can also be manufactured at the same time ,refer to Figure 5 ), to get support tube 1.
[0086] A braided polyester ring is used as the connector 2, and the connector 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Example 2: Bio-induced composite artificial esophagus of the present invention coated with polylactide-ethylene glycol-caprolactone copolymer containing transforming growth factor
[0092] Support tube 1 is prepared according to Example 1.
[0093] A braided polyester ring is used as the connector 2, and the connector 2 is sutured and fixed on the end of the support tube 1 with a surgical suture 7, and the distance from the end is 10 mm. Cleaned, sterilized, and awaiting application of the absorbable coating3.
[0094] Dissolve absorbable biomaterials (such as polylactide-ethylene glycol-caprolactone copolymer) and growth factors (such as transforming growth factor TGFα, PDGF, etc.) in a suitable volatile solvent (such as acetone) to form a suspension Liquid, made into a uniform coating solution with a concentration of 0.01 to 10%, and set aside.
[0095] First, pour the prepared coating solution into the syringe, adjust the power of the ultrasonic generator to 0.1-5w...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3: Bio-induced composite artificial esophagus of the present invention containing polylactide-ethylene glycol copolymer coating of bioglass
[0098] Support tube 1 is prepared according to Example 1.
[0099] A braided polyester ring is used as the connector 2, and the connector 2 is sutured and fixed on the end of the support tube 1 with a surgical suture 7, and the distance from the end is 10 mm. Cleaned, sterilized, and awaiting application of the absorbable coating3.
[0100] Dissolve absorbable biomaterials (such as polylactide-ethylene glycol copolymer) and bioactive glass in a suitable volatile solvent (such as double-distilled water + acetone), and disperse by ultrasonic to form a suspension or emulsion, and formulate A uniform coating solution with a concentration of 0.01% to 10%, which is ready for use.
[0101] Inject the coating solution into the ultrasonic atomization spraying device, rotate the support tube body 1 while spraying the liquid con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com