Application of OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene of rice in improvement of plant disease resistance
A transcription factor and disease resistance technology, applied in the application field of rice OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene in improving plant disease resistance, can solve problems such as difficult research, slow process, and lack of resistance sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Isolation and Cloning of OsWRKY28 Gene
[0025] Using rice variety 9311 (He Guangming et al. Studies on the aggregation of rice anti-aging IPT gene and bacterial blight resistance gene Xa23. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2004, 31(8)) as material, inoculated D. Strong pathogenic strain RH-9 of Rhizoctonia solani (Li Aihong et al. Chitinase activity and sheath blight resistance of transgenic lines and different rice varieties. Acta Crops Sinica, 2003, 29(4)) . Inoculate the mycelial block of Rhizoctonia solani on the PDA medium, culture in the dark at 25°C for 3 days, use the tip of a Gilson 10mL pipette (D10mL, Gilson Company) as a hole puncher, and place on the outer edge of the mycelial culture Take mycelium agar strips (diameter 1.8mm, length 3mm), and use tweezers to insert the mycelium agar strips into the inner side of the third leaf sheath from top to bottom of the stem, so that the leaf sheaths maintain the original phimosis state. After 24 hours, the rice le...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2 Expression profile analysis of OsWRKY28 gene
[0028]Using the rice variety 9311 as the material, use the same method as in Example 1 to inoculate Rhizoctonia solani strain RH-9 on tillering stage (10-week-old) rice, and insert blank agar strips into the mock control group (mock), respectively before inoculation. (0h) and 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h, 72h after inoculation, the rice leaf sheaths were cut and stored in liquid nitrogen. 3-week-old rice seedlings were sprayed with 2 mM salicylic acid (SA, prepared with pH 6.5 double-distilled water) and 100 μM jasmonic acid (JA, prepared with 0.1% (v / v) ethanol solution), and the simulated control group were respectively sprayed. The solvent components in these two solutions were sprayed, and all solutions were added with 0.05% (v / v) Tween20 to increase the adhesion of the leaf surface, respectively before spraying (0h) and after spraying 0.5h, 1h, 3h, Cut off rice leaves at 6h, 9h, 12h, and 24h, and store them in liquid n...
Embodiment 3
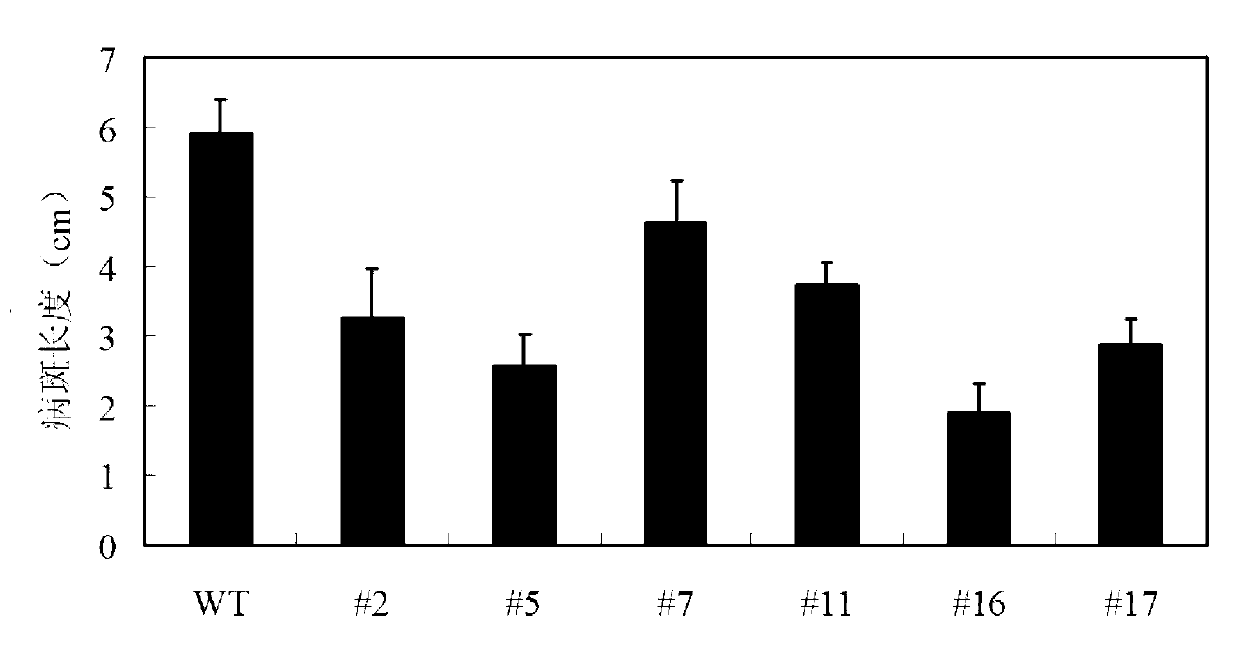
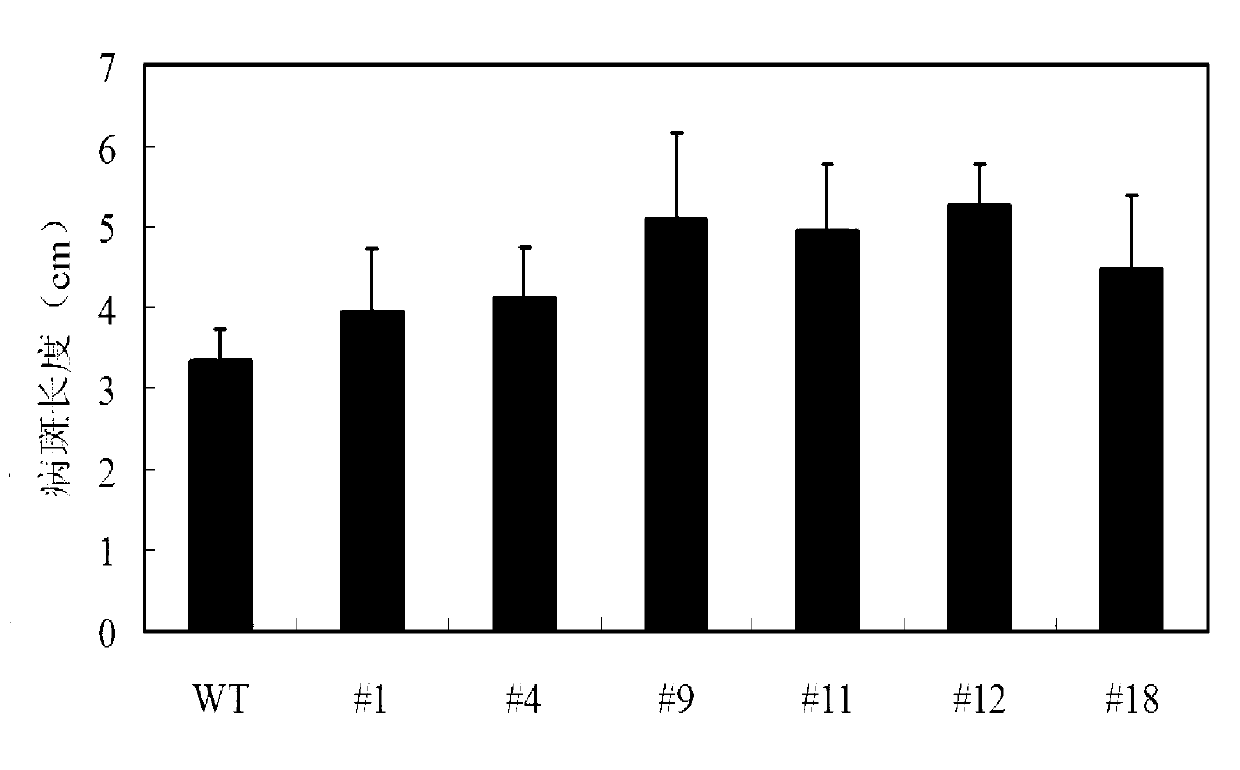
[0029] Example 3 Production and disease resistance identification of transgenic rice overexpressed with OsWRKY28 gene
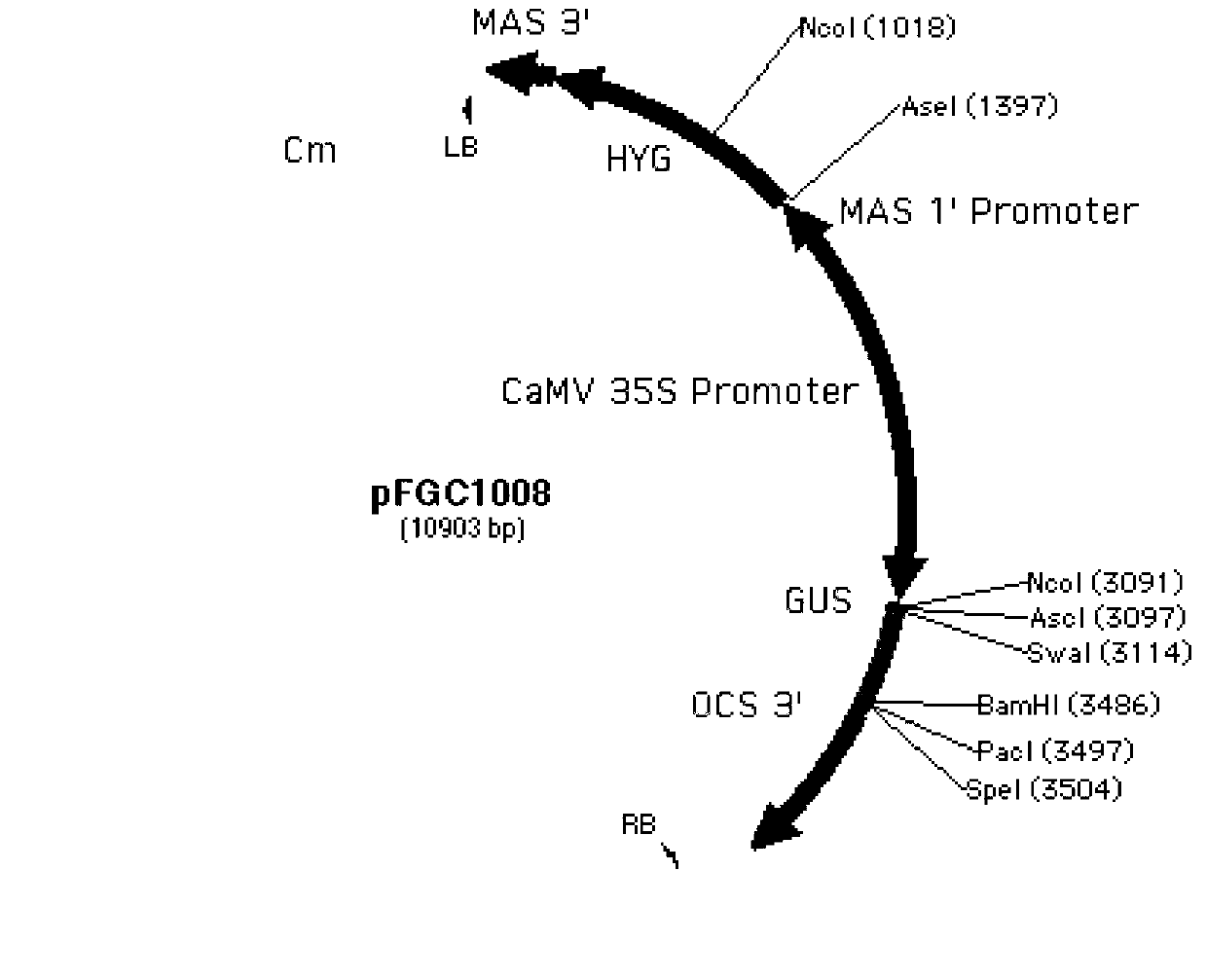
[0030] The plasmid pGEM-OsWRKY28 obtained in Example 1 was double digested with AscI and BamHI, the full-length coding frame sequence of the OsWRKY28 gene was isolated and purified, and the sequence was connected to Figure 4 The shown plant expression vector pFGC1008 (Kerschen et al. Effectiveness of RNA interference in transgenic plants. FEBS letters. 2004, 566 (1)) between the AscI and BamHI restriction sites, the detailed steps of recombination are restricted by TaKaRa company Endonuclease and T4 ligase manual standard operation, transfer the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli DH5α, screen positive clones by enzyme digestion and confirm by sequencing, and name the correct recombinant plasmid pRSE-OsWRKY28, which is the overexpression of the OsWRKY28 gene carrier. The plasmid was transformed into Agrobacterium strain LBA4404 (Hiei et al. Efficient ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com